⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-29 更新
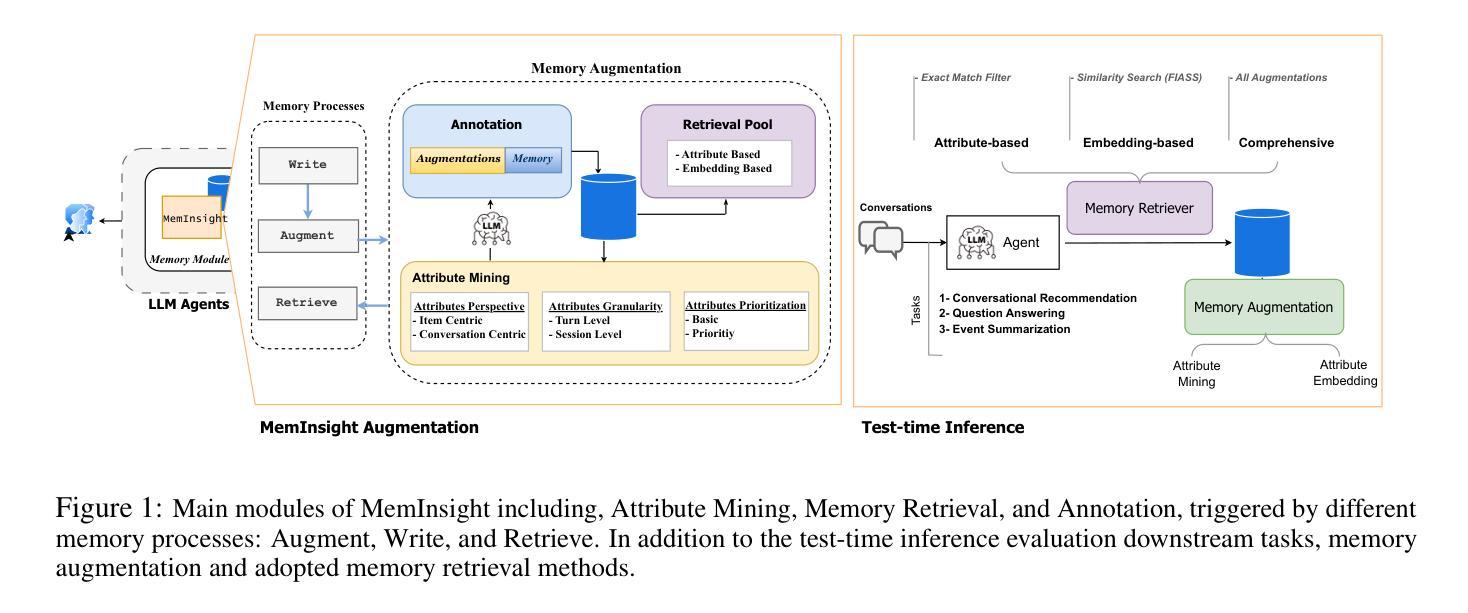
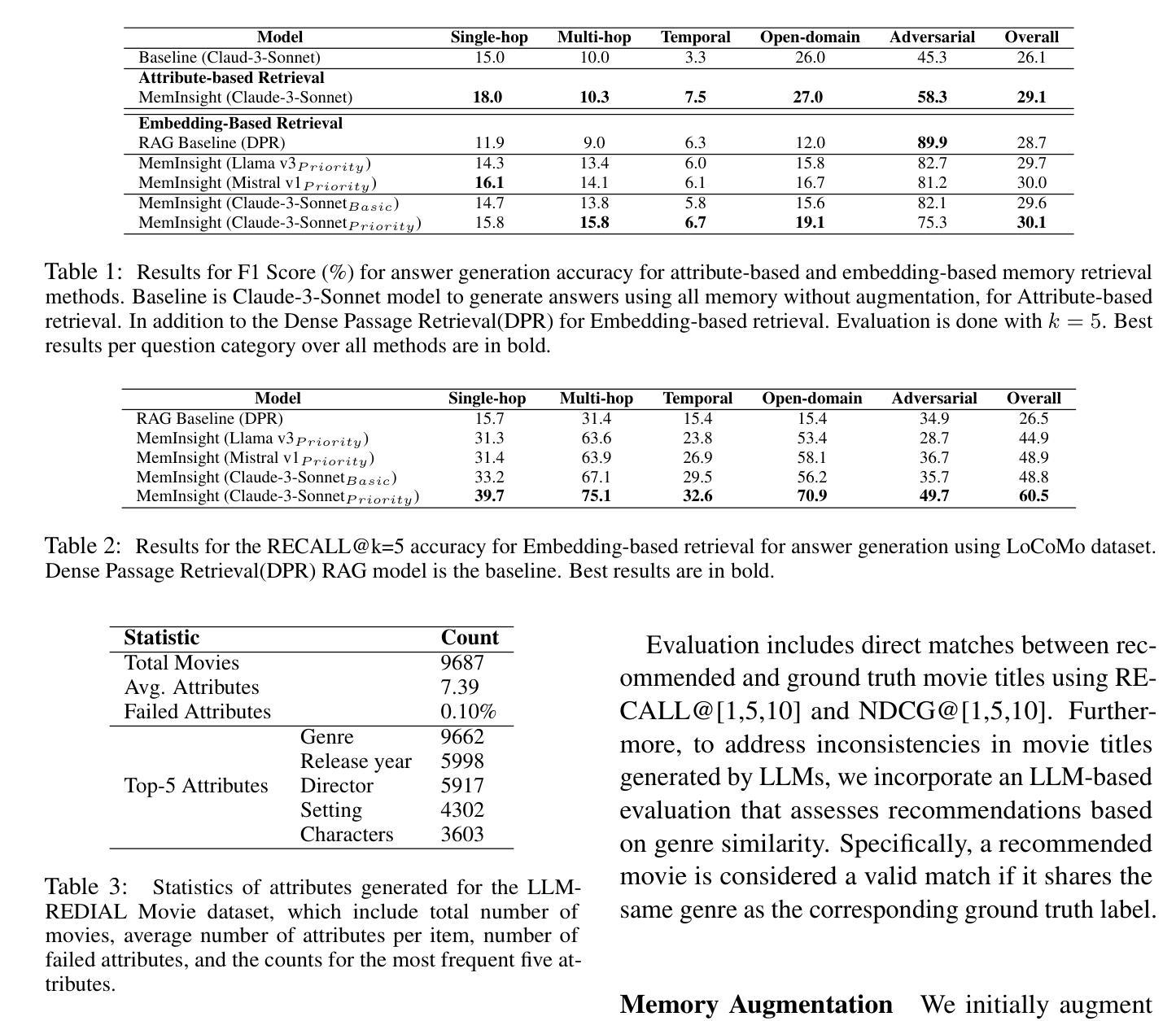
MemInsight: Autonomous Memory Augmentation for LLM Agents
Authors:Rana Salama, Jason Cai, Michelle Yuan, Anna Currey, Monica Sunkara, Yi Zhang, Yassine Benajiba
Large language model (LLM) agents have evolved to intelligently process information, make decisions, and interact with users or tools. A key capability is the integration of long-term memory capabilities, enabling these agents to draw upon historical interactions and knowledge. However, the growing memory size and need for semantic structuring pose significant challenges. In this work, we propose an autonomous memory augmentation approach, MemInsight, to enhance semantic data representation and retrieval mechanisms. By leveraging autonomous augmentation to historical interactions, LLM agents are shown to deliver more accurate and contextualized responses. We empirically validate the efficacy of our proposed approach in three task scenarios; conversational recommendation, question answering and event summarization. On the LLM-REDIAL dataset, MemInsight boosts persuasiveness of recommendations by up to 14%. Moreover, it outperforms a RAG baseline by 34% in recall for LoCoMo retrieval. Our empirical results show the potential of MemInsight to enhance the contextual performance of LLM agents across multiple tasks.
大型语言模型(LLM)代理已经进化到可以智能地处理信息、做出决策和与用户或工具进行交互。一个关键功能是整合长期记忆能力,使这些代理能够利用历史交互和知识。然而,不断增长的内存大小和语义结构的需求构成了重大挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种自主记忆增强方法MemInsight,以增强语义数据表示和检索机制。通过利用对历史交互的自主增强,LLM代理可以提供更准确和情境化的响应。我们通过三种任务场景:对话推荐、问答和事件摘要,实证验证了我们的方法的有效性。在LLM-REDIAL数据集上,MemInsight提高了推荐的说服力,提高了高达14%。此外,它在LoCoMo检索的召回率方面优于RAG基线34%。我们的实证结果表明,MemInsight在多个任务上提高LLM代理的上下文性能潜力巨大。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)智能处理信息、决策以及与用户或工具交互的能力不断增强。集成长期记忆功能是关键之一,使得这些智能模型能够利用历史交互和知识。然而,随着记忆规模的扩大和语义结构的需求增长,也带来了挑战。本研究提出了一种自主记忆增强方法MemInsight,以提高语义数据表示和检索机制。通过利用自主增强对历史交互数据,LLM智能模型能够提供更准确、更贴合语境的响应。实证验证显示,在对话推荐、问答和事件摘要三个任务场景中,MemInsight方法均有效。在LLM-REDIAL数据集上,MemInsight提升了推荐的合理性达14%。在LoCoMo检索的召回率方面,MemInsight相较于RAG基线提高了34%。实证结果表明MemInsight在多个任务中提升LLM智能模型的语境性能潜力巨大。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)能够智能处理信息、做出决策并与用户或工具进行交互。
- LLM的关键能力之一是集成长期记忆功能,可依赖历史交互和知识。
- 随着记忆规模扩大和语义结构需求增长,LLM面临挑战。
- 提出了自主记忆增强方法MemInsight,用于提高语义数据表示和检索。
- MemInsight通过利用自主增强历史交互数据,增强了LLM的准确性及语境适应性。
- 在对话推荐、问答和事件摘要等任务场景中,MemInsight表现出良好的性能。
点此查看论文截图


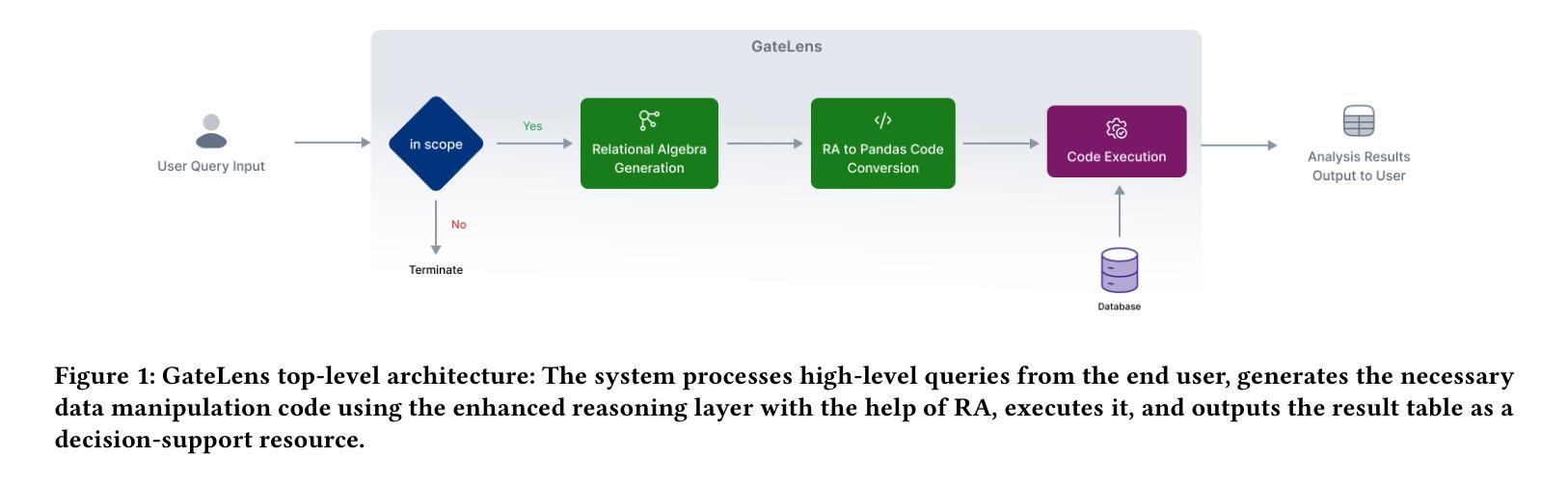
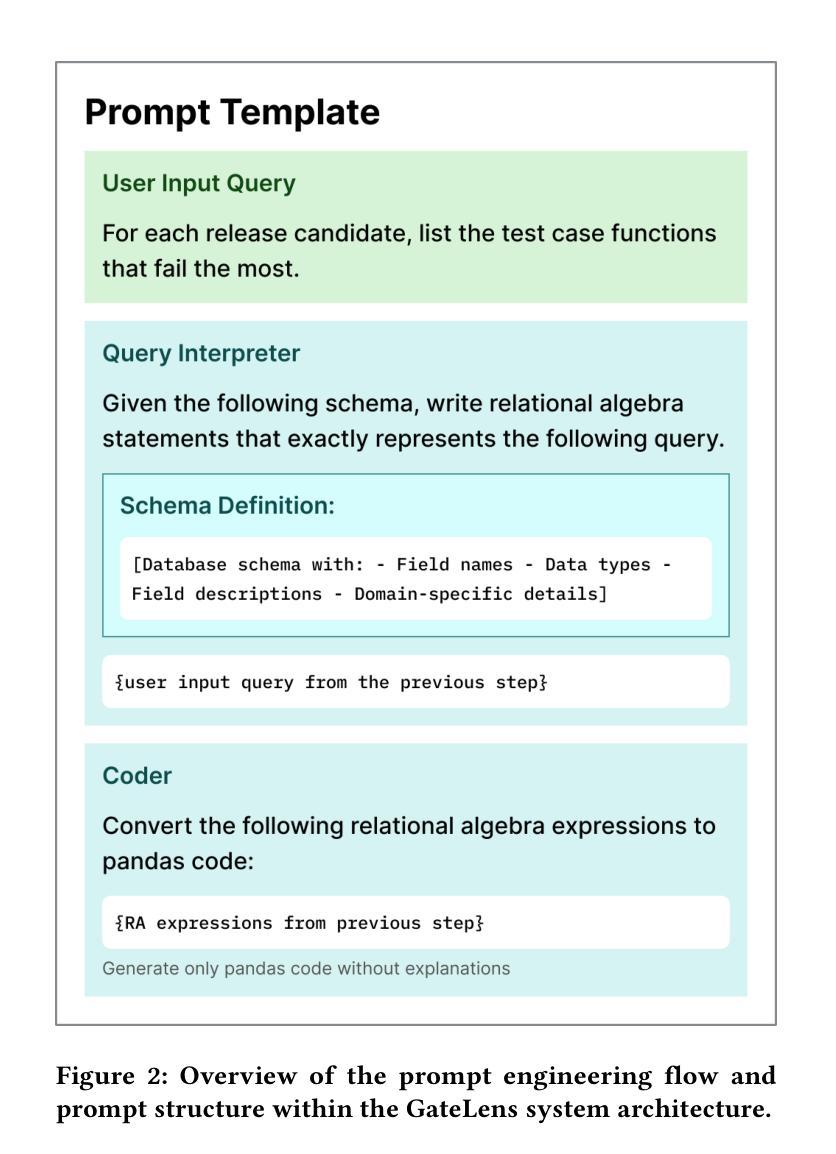
GateLens: A Reasoning-Enhanced LLM Agent for Automotive Software Release Analytics
Authors:Arsham Gholamzadeh Khoee, Shuai Wang, Yinan Yu, Robert Feldt, Dhasarathy Parthasarathy
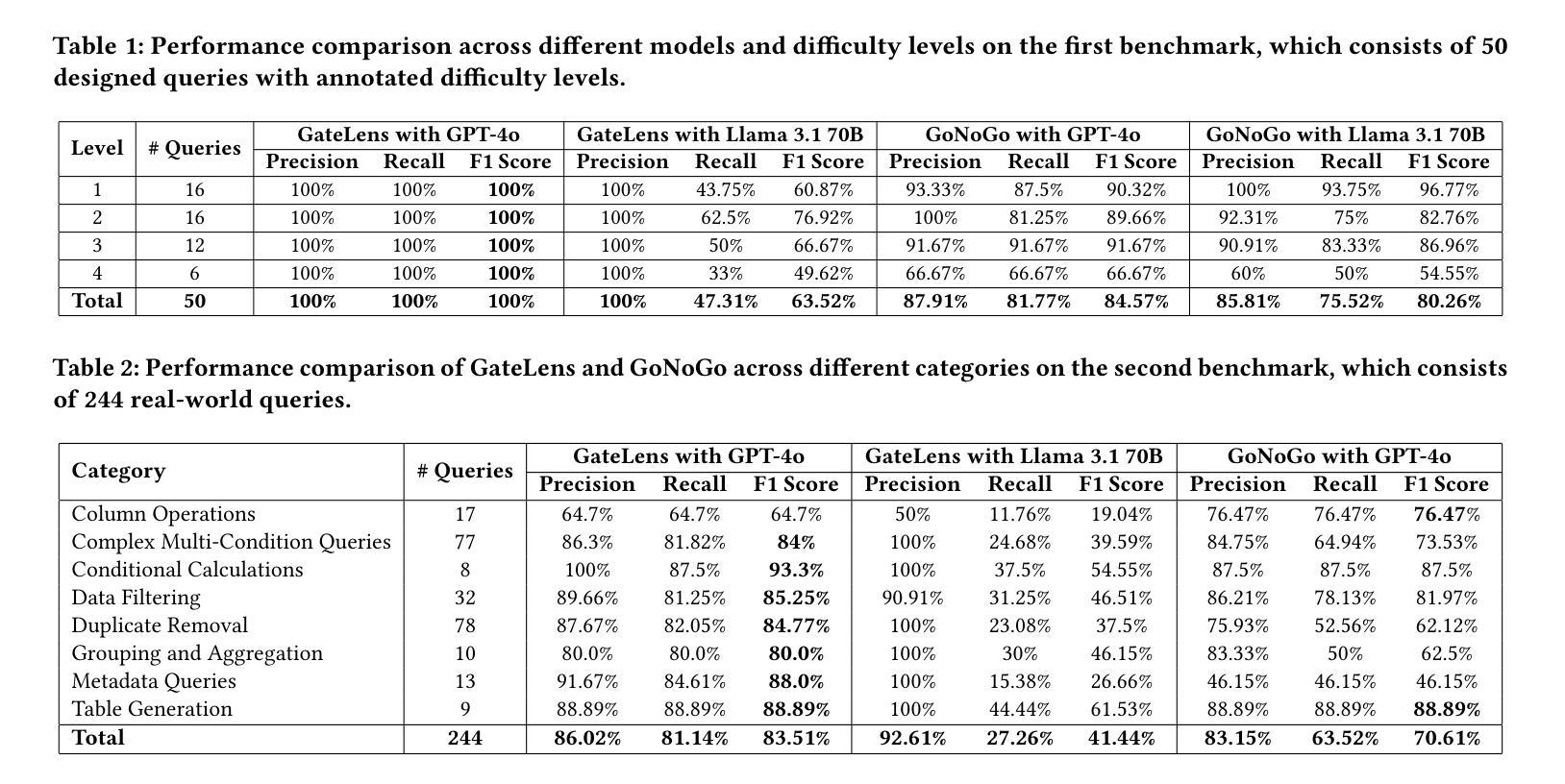
Ensuring the reliability and effectiveness of software release decisions is critical, particularly in safety-critical domains like automotive systems. Precise analysis of release validation data, often presented in tabular form, plays a pivotal role in this process. However, traditional methods that rely on manual analysis of extensive test datasets and validation metrics are prone to delays and high costs. Large Language Models (LLMs) offer a promising alternative but face challenges in analytical reasoning, contextual understanding, handling out-of-scope queries, and processing structured test data consistently; limitations that hinder their direct application in safety-critical scenarios. This paper introduces GateLens, an LLM-based tool for analyzing tabular data in the automotive domain. GateLens translates natural language queries into Relational Algebra (RA) expressions and then generates optimized Python code. It outperforms the baseline system on benchmarking datasets, achieving higher F1 scores and handling complex and ambiguous queries with greater robustness. Ablation studies confirm the critical role of the RA module, with performance dropping sharply when omitted. Industrial evaluations reveal that GateLens reduces analysis time by over 80% while maintaining high accuracy and reliability. As demonstrated by presented results, GateLens achieved high performance without relying on few-shot examples, showcasing strong generalization across various query types from diverse company roles. Insights from deploying GateLens with a partner automotive company offer practical guidance for integrating AI into critical workflows such as release validation. Results show that by automating test result analysis, GateLens enables faster, more informed, and dependable release decisions, and can thus advance software scalability and reliability in automotive systems.
确保软件发布决策的可信度和有效性至关重要,特别是在汽车系统这样的安全关键领域。以表格形式呈现的软件发布验证数据的精确分析在此过程中起着至关重要的作用。然而,传统的方法依赖于对大量测试数据集和验证指标的手动分析,容易出现延迟和成本高昂的问题。大型语言模型(LLM)提供了有前景的替代方案,但在分析推理、上下文理解、处理超出范围查询和一致处理结构化测试数据方面面临挑战;这些局限性阻碍了其在安全关键场景中的直接应用。本文介绍了GateLens,一个基于LLM的汽车领域表格数据分析工具。GateLens将自然语言查询翻译成关系代数(RA)表达式,然后生成优化的Python代码。它在基准测试数据集上的表现优于基线系统,实现了更高的F1分数,并更稳健地处理复杂和模糊查询。消融研究证实了RA模块的关键作用,在省略该模块时性能急剧下降。工业评估表明,GateLens在保持高准确性和可靠性的同时,将分析时间减少了80%以上。如结果所示,GateLens在高性能的同时不需要依赖少量示例,展示了在各种查询类型中的强大泛化能力,这些查询类型来自各种公司角色。通过与合作伙伴汽车公司部署GateLens所获得的见解为将人工智能集成到关键工作流程(如发布验证)提供了实际指导。结果表明,通过自动化测试结果分析,GateLens能够做出更快、更明智、更可靠的发布决策,从而可以提高汽车系统的软件可扩展性和可靠性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一款名为GateLens的基于大语言模型的工具,用于汽车领域的表格数据分析。该工具将自然语言查询转化为关系代数表达式,并生成优化的Python代码。与传统的手动分析方法相比,GateLens能够更高效地进行测试数据分析,显著减少时间成本,并提高准确性和可靠性。它对各种类型查询的强泛化能力得到了验证。通过将GateLens与一家汽车合作伙伴公司集成,实践表明它能够自动化测试结果分析,为软件发布决策提供更快、更有根据的支持,有助于提升汽车系统的软件可扩展性和可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- 汽车系统中软件发布的决策需要确保可靠性和有效性。
- 传统的手动数据分析方式在处理大量测试数据集时存在延迟和成本高昂的问题。
- 大语言模型(LLMs)在表格数据分析中具有潜力,但需要克服挑战如解析推理、上下文理解、处理超出范围查询和结构化数据处理等问题。
- GateLens工具引入了一种基于大语言模型的方法来分析汽车领域的表格数据,通过自然语言查询转化为关系代数表达式并生成Python代码。
- GateLens在基准测试数据集上的性能优于基准系统,具有处理复杂和模糊查询的高稳健性。
- 工业评估显示,GateLens将分析时间减少了超过80%,同时保持了高准确性和可靠性。
- GateLens具备在不依赖少量示例的情况下进行泛化的能力,对多种查询类型具有良好的适应能力。
点此查看论文截图

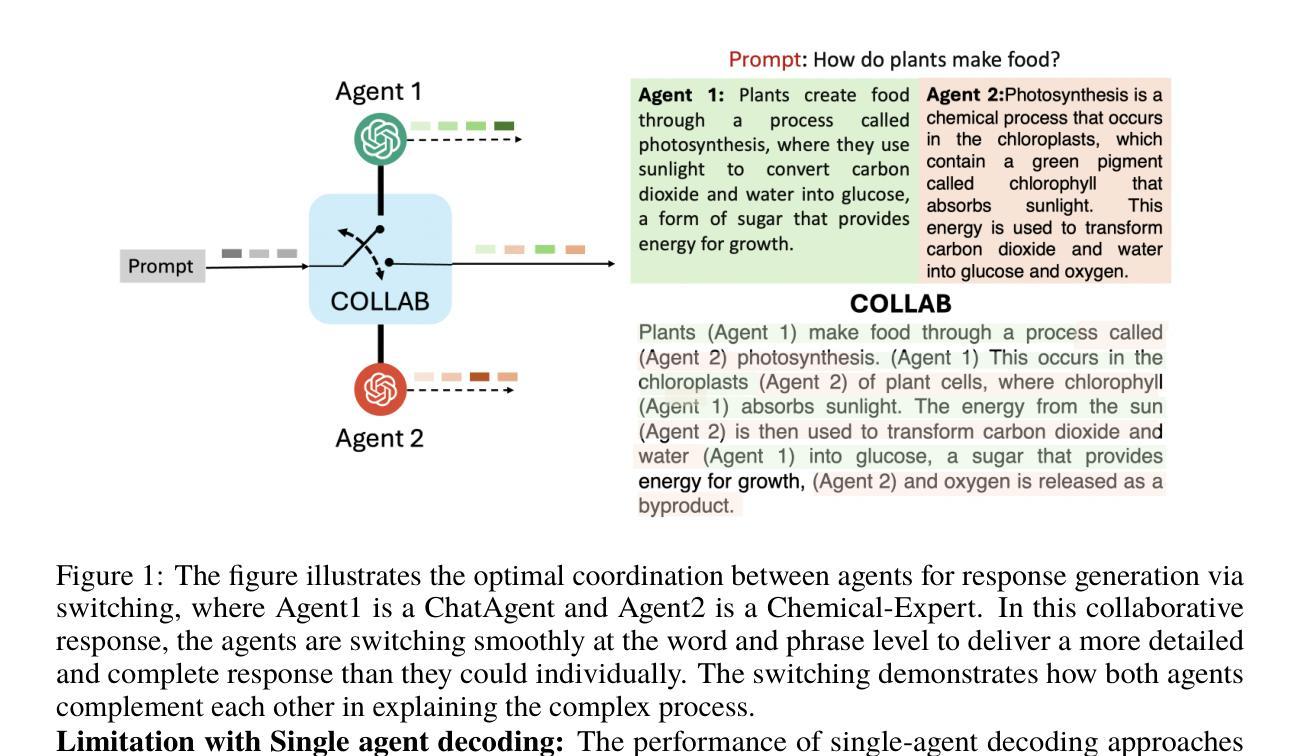
Collab: Controlled Decoding using Mixture of Agents for LLM Alignment
Authors:Souradip Chakraborty, Sujay Bhatt, Udari Madhushani Sehwag, Soumya Suvra Ghosal, Jiahao Qiu, Mengdi Wang, Dinesh Manocha, Furong Huang, Alec Koppel, Sumitra Ganesh
Alignment of Large Language models (LLMs) is crucial for safe and trustworthy deployment in applications. Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) has emerged as an effective technique to align LLMs to human preferences and broader utilities, but it requires updating billions of model parameters, which is computationally expensive. Controlled Decoding, by contrast, provides a mechanism for aligning a model at inference time without retraining. However, single-agent decoding approaches often struggle to adapt to diverse tasks due to the complexity and variability inherent in these tasks. To strengthen the test-time performance w.r.t the target task, we propose a mixture of agent-based decoding strategies leveraging the existing off-the-shelf aligned LLM policies. Treating each prior policy as an agent in the spirit of mixture of agent collaboration, we develop a decoding method that allows for inference-time alignment through a token-level selection strategy among multiple agents. For each token, the most suitable LLM is dynamically chosen from a pool of models based on a long-term utility metric. This policy-switching mechanism ensures optimal model selection at each step, enabling efficient collaboration and alignment among LLMs during decoding. Theoretical analysis of our proposed algorithm establishes optimal performance with respect to the target task represented via a target reward for the given off-the-shelf models. We conduct comprehensive empirical evaluations with open-source aligned models on diverse tasks and preferences, which demonstrates the merits of this approach over single-agent decoding baselines. Notably, Collab surpasses the current SoTA decoding strategy, achieving an improvement of up to 1.56x in average reward and 71.89% in GPT-4 based win-tie rate.
大型语言模型(LLM)的对齐对于其在应用中的安全和可信部署至关重要。强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)作为一种有效的技术,能够对齐LLM以符合人类偏好和更广泛的实用性,但需要更新数十亿的模型参数,这在计算上是非常昂贵的。相比之下,受控解码提供了一种在推理时不对模型进行再训练的对齐机制。然而,由于任务的复杂性和可变性,单智能体解码方法往往难以适应多样化的任务。为了加强针对目标任务的测试时性能,我们提出了一种基于智能体的解码策略混合方法,利用现有的即用型对齐LLM策略。我们将每个先前策略视为智能体,在智能体协作的混合精神下,开发了一种解码方法,该方法允许通过标记级选择策略在多个智能体之间进行推理时对齐。对于每个标记,从模型中动态选择最合适的LLM,这是基于长期效用指标的。这种策略切换机制确保了每一步的最优模型选择,使得LLM在解码过程中能够进行有效的协作和对齐。我们提出算法的理论分析建立了针对给定即用型模型的目标奖励表示的目标任务的优化性能。我们使用开源对齐模型在多样化任务和偏好上进行了全面的实证评估,证明了该方法相对于单智能体解码基线方法的优点。值得注意的是,Collab超越了当前的最新解码策略,在平均奖励上提高了1.56倍,在GPT-4基础上的胜率提高了71.89%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)的对齐对于其在应用中的安全可信部署至关重要。强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)是一种有效的对齐技术,但需要更新数十亿的模型参数,计算成本高。相比之下,受控解码提供了一种在推理时间对齐模型的机制,无需重新训练。然而,单代理解码方法由于任务的复杂性和可变性,往往难以适应多样化的任务。为了加强针对目标任务的测试性能,我们提出了基于代理的解码策略混合物,利用现有的即插即用对齐LLM策略。我们将每个先前策略视为代理,开发了一种解码方法,通过标记级别的选择策略在多个代理之间进行推理时间对齐。对于每个标记,从模型池中动态选择最合适的LLM,基于长期效用指标。这种策略切换机制确保了每一步的最优模型选择,使得在解码过程中LLM之间的协作和对齐更加高效。我们进行了全面的实证评估,使用开源对齐模型在多样化任务和偏好上验证了该方法优于单代理解码基线。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的对齐对于其在应用中的表现至关重要。
- 强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)是一种有效的LLM对齐技术,但计算成本高。
- 受控解码提供了一种在推理时间对齐模型的机制,无需重新训练。
- 单代理解码方法难以适应多样化任务,因为任务的复杂性和可变性。
- 我们提出了基于代理的解码策略混合物,利用即插即用对齐LLM策略。
- 对于每个标记,该方法从模型池中动态选择最合适的LLM。
点此查看论文截图

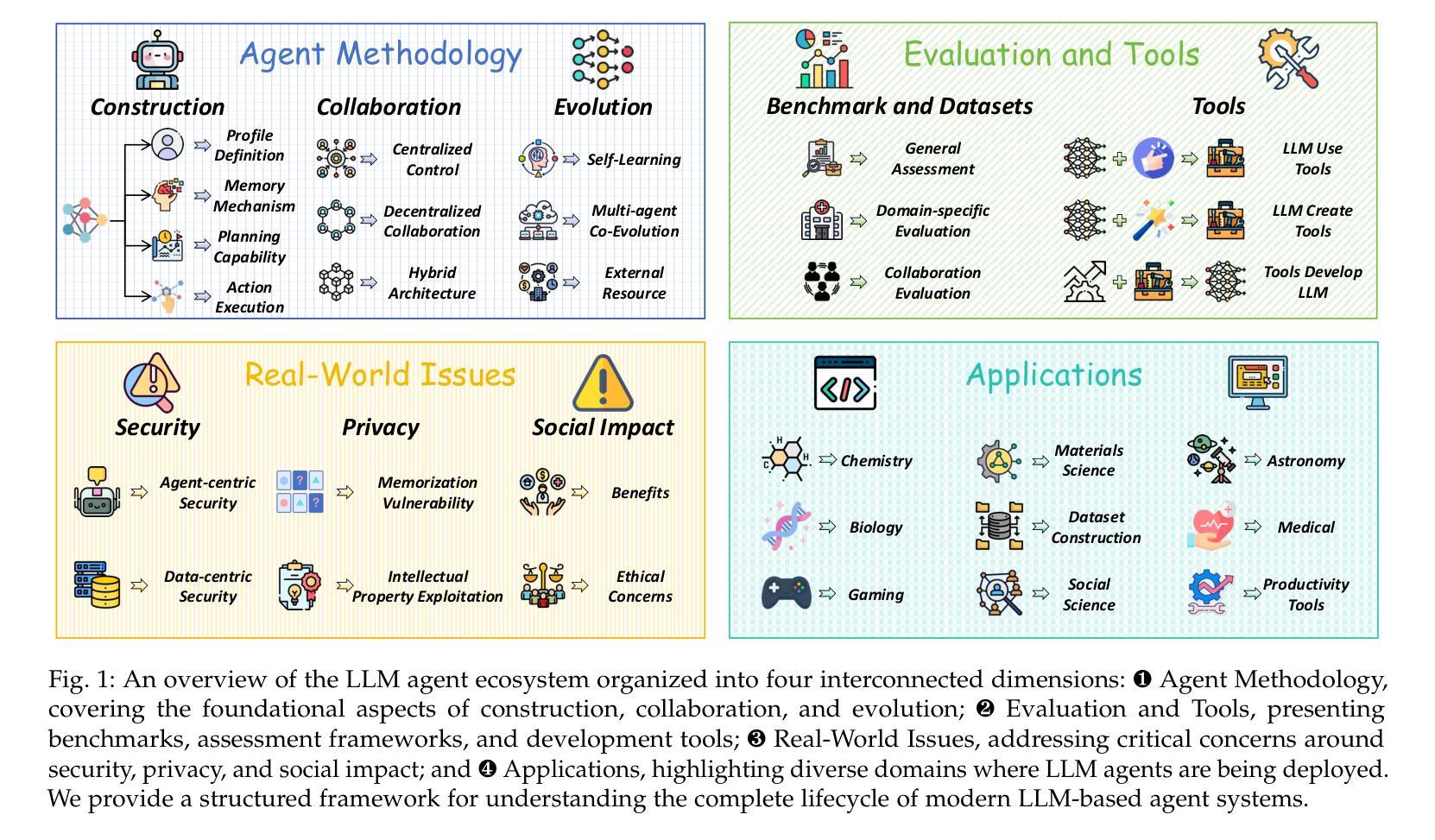
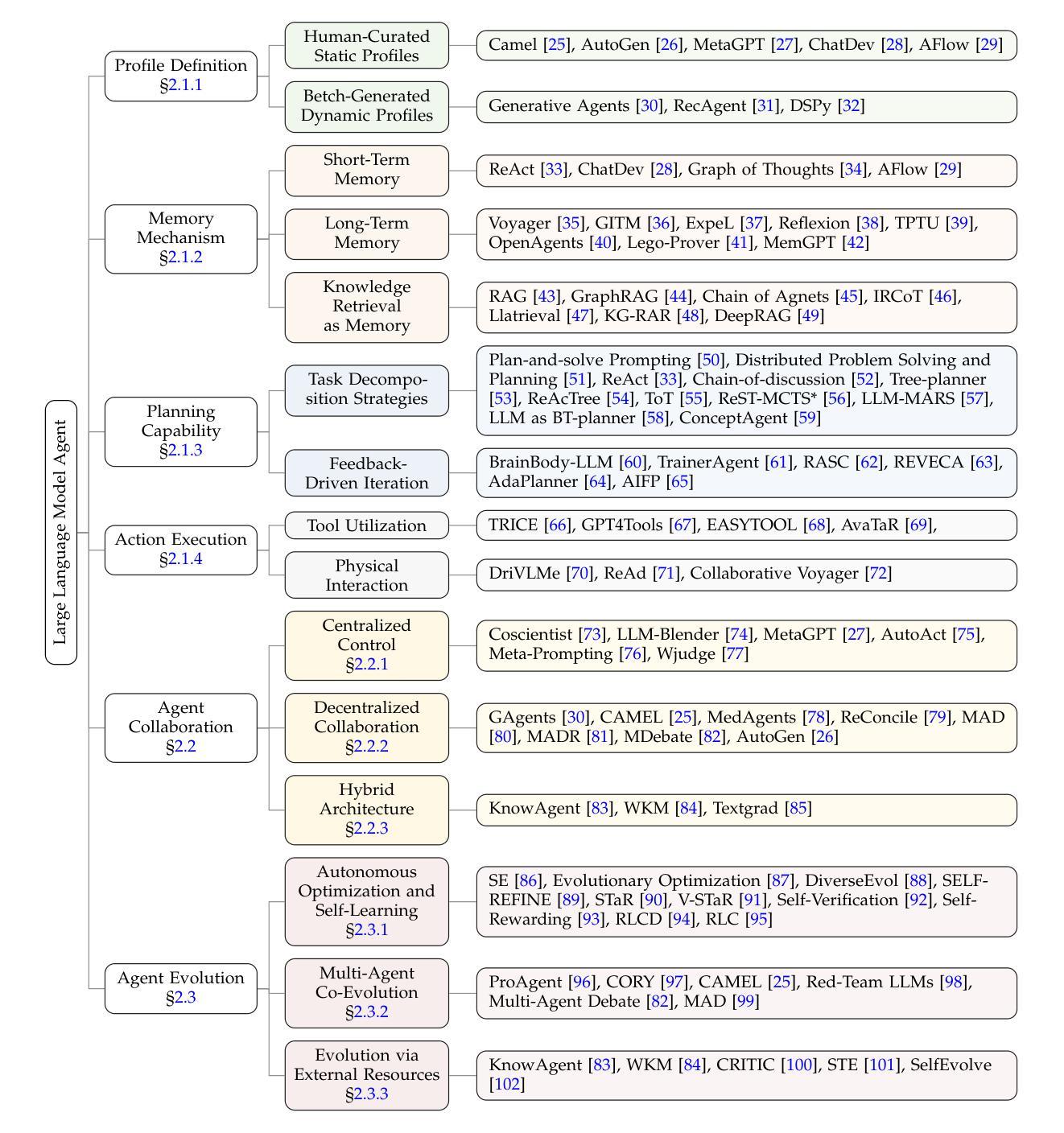
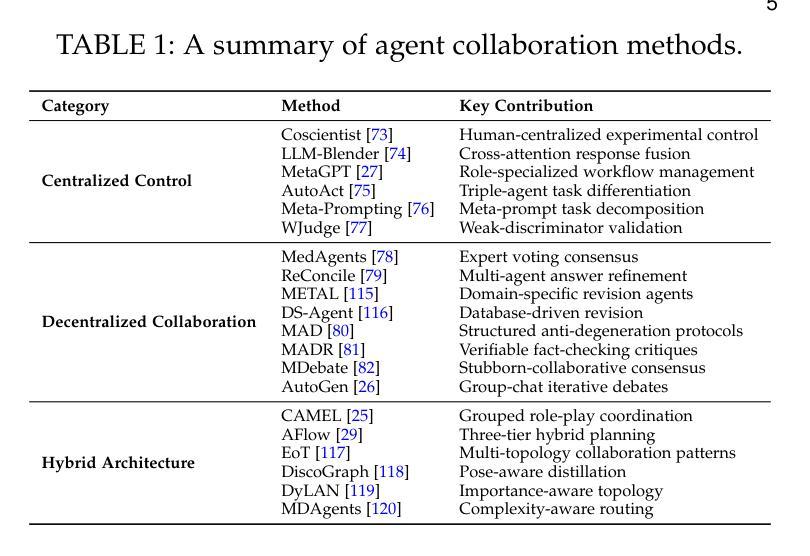
Large Language Model Agent: A Survey on Methodology, Applications and Challenges
Authors:Junyu Luo, Weizhi Zhang, Ye Yuan, Yusheng Zhao, Junwei Yang, Yiyang Gu, Bohan Wu, Binqi Chen, Ziyue Qiao, Qingqing Long, Rongcheng Tu, Xiao Luo, Wei Ju, Zhiping Xiao, Yifan Wang, Meng Xiao, Chenwu Liu, Jingyang Yuan, Shichang Zhang, Yiqiao Jin, Fan Zhang, Xian Wu, Hanqing Zhao, Dacheng Tao, Philip S. Yu, Ming Zhang
The era of intelligent agents is upon us, driven by revolutionary advancements in large language models. Large Language Model (LLM) agents, with goal-driven behaviors and dynamic adaptation capabilities, potentially represent a critical pathway toward artificial general intelligence. This survey systematically deconstructs LLM agent systems through a methodology-centered taxonomy, linking architectural foundations, collaboration mechanisms, and evolutionary pathways. We unify fragmented research threads by revealing fundamental connections between agent design principles and their emergent behaviors in complex environments. Our work provides a unified architectural perspective, examining how agents are constructed, how they collaborate, and how they evolve over time, while also addressing evaluation methodologies, tool applications, practical challenges, and diverse application domains. By surveying the latest developments in this rapidly evolving field, we offer researchers a structured taxonomy for understanding LLM agents and identify promising directions for future research. The collection is available at https://github.com/luo-junyu/Awesome-Agent-Papers.
智能代理的时代已经来临,这得益于大型语言模型的革命性进步。大型语言模型(LLM)代理具有目标驱动行为和动态适应能力,可能代表实现通用人工智能的关键途径。本文系统地通过以方法论为中心的分类法对LLM代理系统进行解构,联系架构基础、协作机制和进化路径。我们揭示了代理设计原则与其在复杂环境中出现的基本联系,从而统一了碎片化的研究线索。我们的工作提供了一个统一的架构视角,考察了代理的构造方式、协作方式以及随时间推移的进化过程,同时解决了评估方法、工具应用、实际挑战和各种应用领域的问题。通过对这一快速演变领域的最新发展进行调查,我们为研究人员提供了理解LLM代理的结构化分类,并指出了未来研究的有前途的方向。该合集可通过以下网址获取:https://github.com/luo-junyu/Awesome-Agent-Papers 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 329 papers surveyed, resources are at https://github.com/luo-junyu/Awesome-Agent-Papers
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)代理驱动的行为和目标驱动的智能代理时代来临,代理具有动态适应能力和进化行为的特点,这是通往人工智能通用化道路的关键一环。本文通过方法论中心的分类法对LLM代理系统进行系统解构,链接架构基础、协作机制和进化路径。我们的工作提供了一个统一的架构视角,研究代理的构造、协作和进化过程,同时探讨了评估方法、工具应用、实际挑战和多样化的应用域。通过调查这一快速演变领域的最新发展,我们为研究人员提供了理解LLM代理的结构化分类,并指出了未来研究的有希望方向。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)代理的智能代理时代来临。
- LLM代理具有动态适应能力和进化行为的特点。
- LLM代理在通往人工智能通用化道路上扮演关键角色。
- 系统解构LLM代理的分类方法涵盖架构基础、协作机制和进化路径。
- 提供了一个统一的架构视角,以理解代理的构造、协作和进化过程。
- 讨论了评估方法、工具应用、实际挑战和多样化的应用域等问题。
点此查看论文截图

CA+: Cognition Augmented Counselor Agent Framework for Long-term Dynamic Client Engagement
Authors:Yuanrong Tang, Yu Kang, Yifan Wang, Tianhong Wang, Chen Zhong, Jiangtao Gong
Current AI counseling systems struggle with maintaining effective long-term client engagement. Through formative research with counselors and a systematic literature review, we identified five key design considerations for AI counseling interactions. Based on these insights, we propose CA+, a Cognition Augmented counselor framework enhancing contextual understanding through three components: (1) Therapy Strategies Module: Implements hierarchical Goals-Session-Action planning with bidirectional adaptation based on client feedback; (2) Communication Form Module: Orchestrates parallel guidance and empathy pathways for balanced therapeutic progress and emotional resonance; (3) Information Management: Utilizes client profile and therapeutic knowledge databases for dynamic, context-aware interventions. A three-day longitudinal study with 24 clients demonstrates CA+’s significant improvements in client engagement, perceived empathy, and overall satisfaction compared to a baseline system. Besides, two licensed counselors confirm its high professionalism. Our research demonstrates the potential for enhancing LLM engagement in psychological counseling dialogues through cognitive theory, which may inspire further innovations in computational interaction in the future.
当前的人工智能咨询系统难以维持长期有效的客户参与度。通过咨询师的格式研究及系统文献回顾,我们确定了人工智能咨询互动的五个关键设计考量因素。基于这些见解,我们提出了CA+,这是一个认知辅助咨询师框架,通过三个组件增强上下文理解:(1)治疗策略模块:实现基于客户反馈的层次化目标-会话-行动计划的双向适应;(2)沟通形式模块:为平衡的治疗进展和情感共鸣协调并行指导和共情途径;(3)信息管理:利用客户档案和治疗知识数据库进行动态、基于上下文干预。一项为期三天、涉及24名客户的纵向研究表明,与基准系统相比,CA+在客户参与度、感知的同理心和整体满意度方面都有显著改善。此外,两名持证咨询师也证实了其高度的专业性。我们的研究展示了通过认知理论提高心理咨询服务对话中大型语言模型参与度的潜力,这可能为未来计算交互的进一步创新提供灵感。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于对当前AI咨询系统在长期客户参与度方面的挑战,本研究通过咨询师调研和文献综述,提出了AI咨询交互设计的五个关键考量因素。据此,提出增强认知能力的辅导员框架CA+,它通过以下三个模块强化情境理解:疗法策略模块实施基于分级目标的会话与行动规划,并根据客户反馈进行双向调整;沟通形式模块协调指导与同理心路径,实现均衡治疗进展和情感共鸣;信息管理模块利用客户资料和疗愈知识数据库进行动态、情境感知干预。为期三天的纵向研究显示,相较于基础系统,CA+在客户参与度、感知同理心和整体满意度方面表现出显著改进。此外,两名持证咨询师亦证实其高度的专业性。本研究展示了认知理论在提升心理咨询对话中的大型语言模型参与度方面的潜力,为计算交互的未来创新提供了启示。
Key Takeaways
- 当前AI咨询系统在长期客户参与度上存在问题。
- 通过咨询师调研和文献综述,确定了AI咨询交互设计的五个关键考量因素。
- 提出了CA+框架,包含疗法策略模块、沟通形式模块以及信息管理模块。
- CA+显著提高了客户参与度、感知同理心和整体满意度。
- CA+得到两名持证咨询师的认可和高度的专业性评价。
- 本研究展示了认知理论在增强心理咨询对话中的大型语言模型参与度方面的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

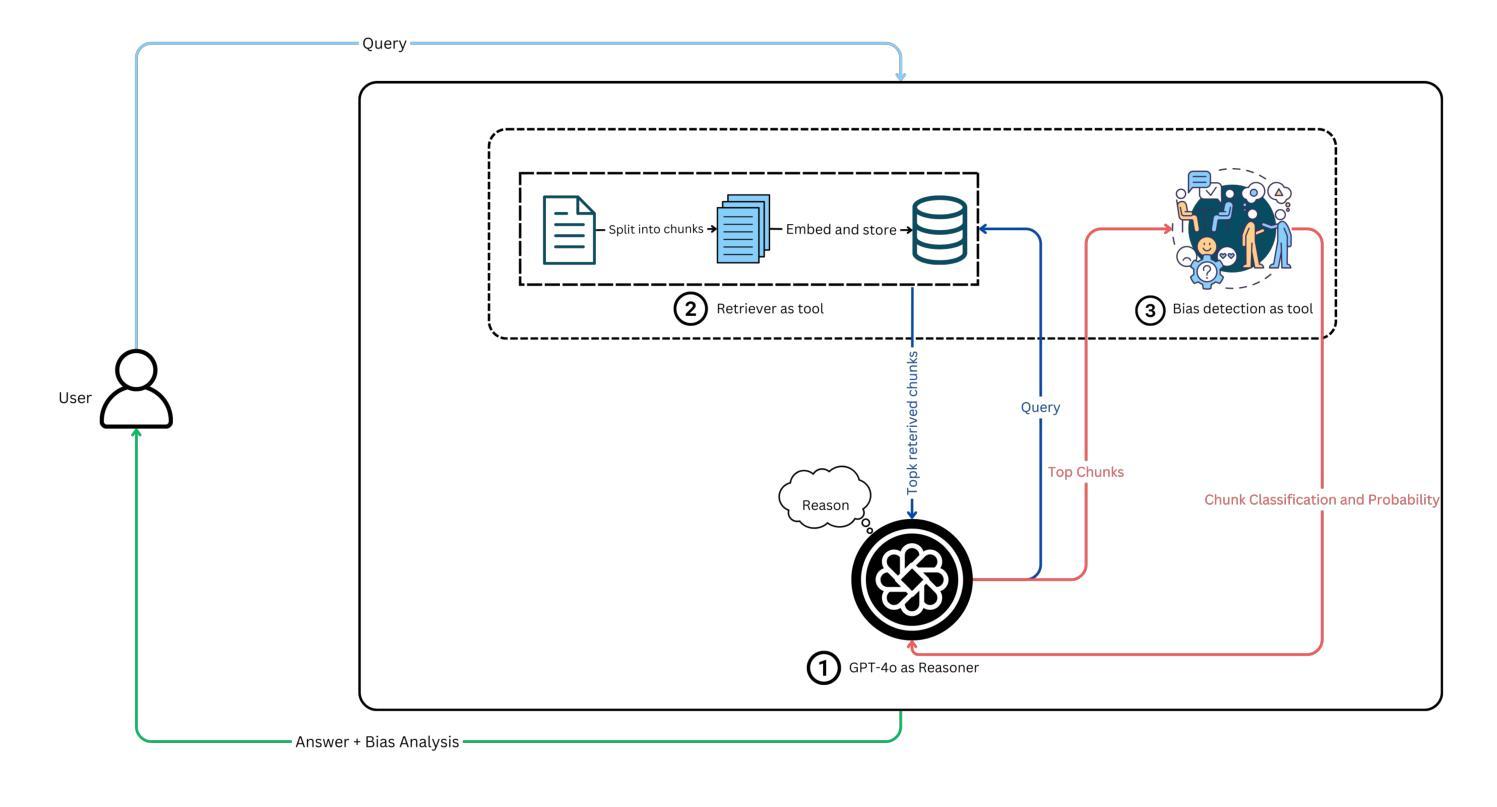
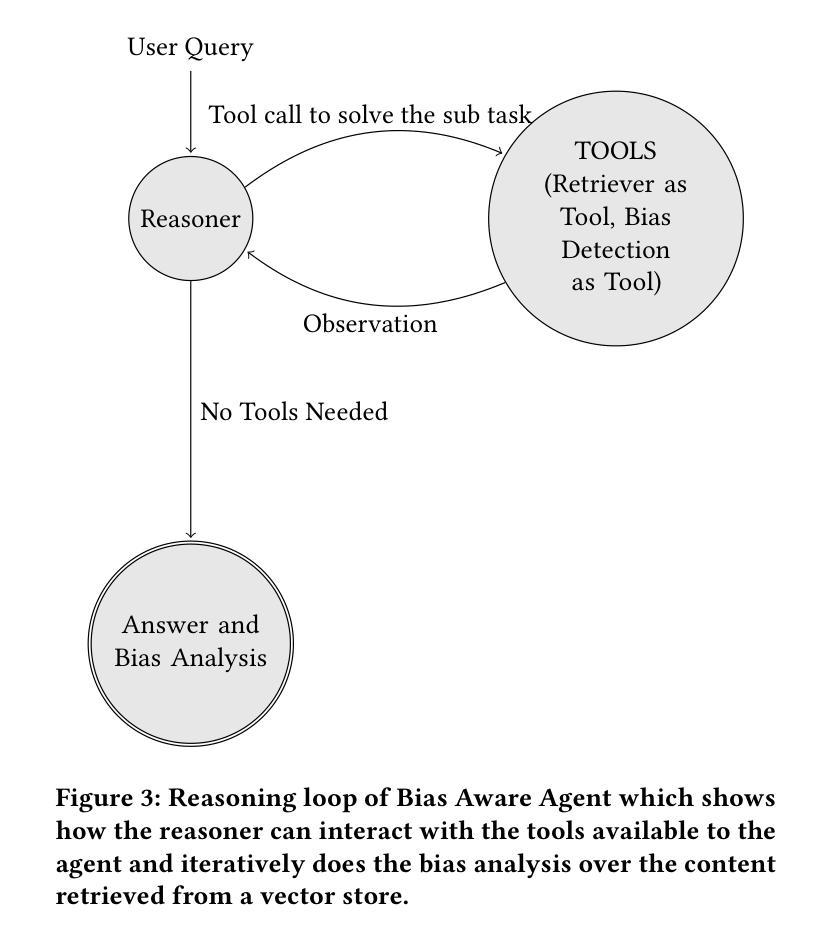
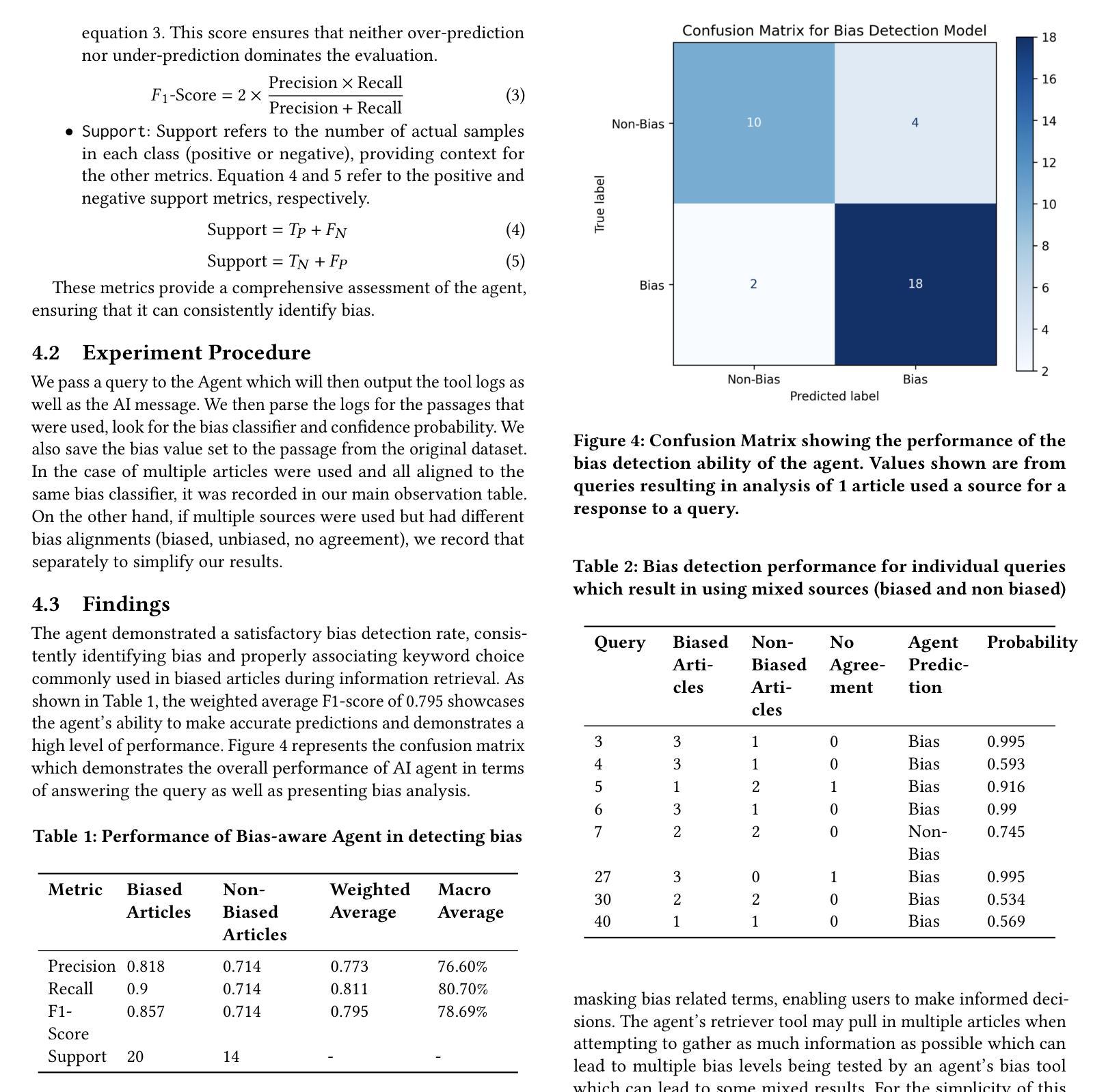
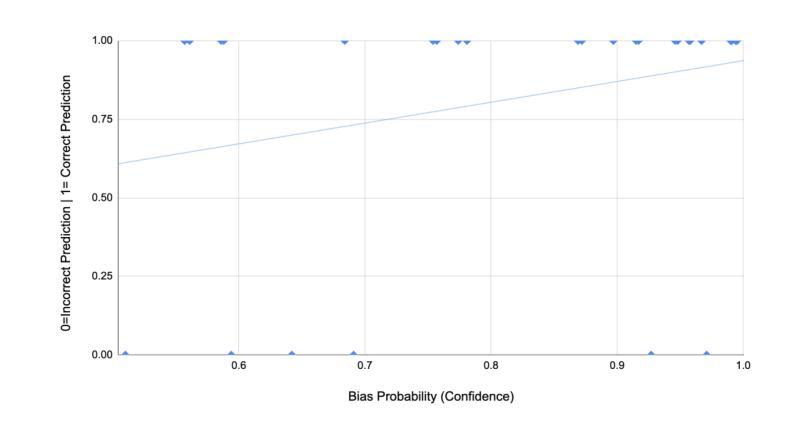
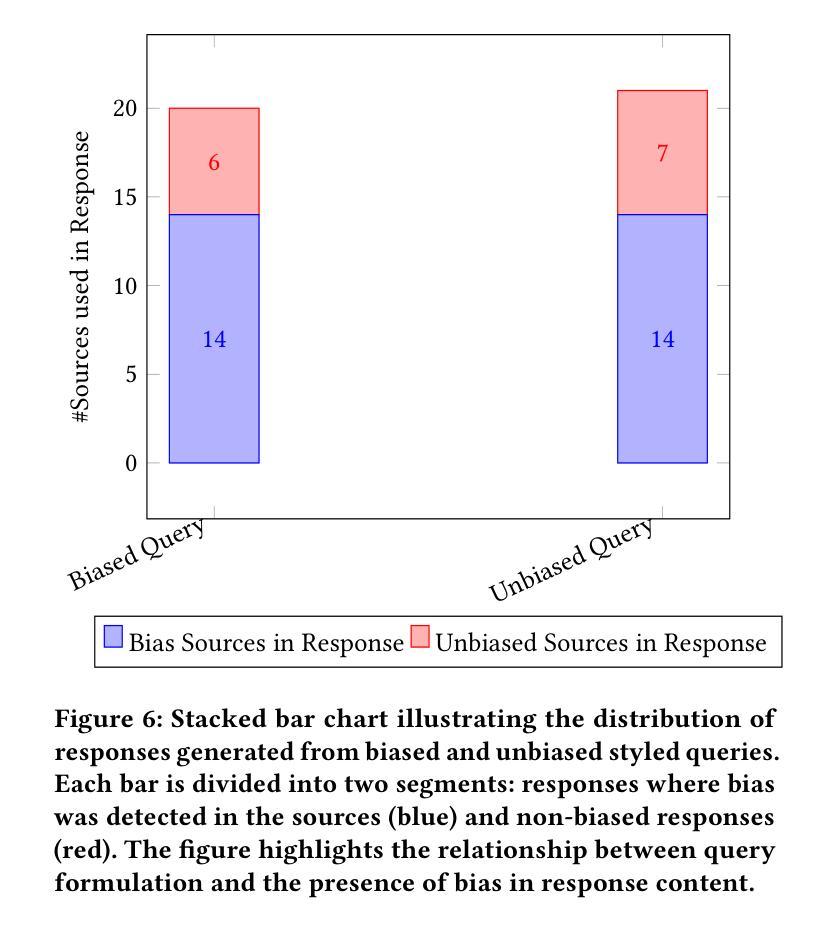
Bias-Aware Agent: Enhancing Fairness in AI-Driven Knowledge Retrieval
Authors:Karanbir Singh, William Ngu
Advancements in retrieving accessible information have evolved faster in the last few years compared to the decades since the internet’s creation. Search engines, like Google, have been the number one way to find relevant data. They have always relied on the user’s abilities to find the best information in its billions of links and sources at everybody’s fingertips. The advent of large language models (LLMs) has completely transformed the field of information retrieval. The LLMs excel not only at retrieving relevant knowledge but also at summarizing it effectively, making information more accessible and consumable for users. On top of it, the rise of AI Agents has introduced another aspect to information retrieval i.e. dynamic information retrieval which enables the integration of real-time data such as weather forecasts, and financial data with the knowledge base to curate context-aware knowledge. However, despite these advancements the agents remain susceptible to issues of bias and fairness, challenges deeply rooted within the knowledge base and training of LLMs. This study introduces a novel approach to bias-aware knowledge retrieval by leveraging agentic framework and the innovative use of bias detectors as tools to identify and highlight inherent biases in the retrieved content. By empowering users with transparency and awareness, this approach aims to foster more equitable information systems and promote the development of responsible AI.
近年来,与互联网创建以来的几十年相比,获取可访问信息的进步发展得更快。搜索引擎(如谷歌)一直是查找相关数据的第一种方式。它们一直依赖于用户的能力,在每个人触手可及的上亿链接和来源中找到最佳信息。大型语言模型(LLM)的出现彻底改变了信息检索领域。LLM不仅擅长检索相关知识,而且还擅长有效地对其进行总结,使用户更容易访问和消耗信息。此外,AI代理的兴起为信息检索引入了另一个方面,即动态信息检索,它能够实现实时数据与知识库的集成,以创建上下文感知知识。然而,尽管有这些进展,代理仍容易受到偏见和公平性问题的影响,这些问题是深深植根于知识库和LLM训练中的挑战。本研究通过利用代理框架和偏见检测器的创新使用,介绍了一种新型的偏见感知知识检索方法,以识别和突出检索内容中的固有偏见。通过增强用户的透明度和意识,这种方法旨在促进更公平的信息系统的发展,并推动负责任的AI的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着互联网的发展,信息检索技术不断进步,尤其是近年的进步速度远超过去几十年。搜索引擎如谷歌仍是获取信息的主要途径,但大型语言模型(LLM)的出现彻底改变了信息检索领域。LLM不仅能高效检索相关知识,还能进行有效总结,使用户更容易获取和消化信息。此外,AI代理的兴起为信息检索带来了动态获取信息的能力,能整合实时数据与知识库以形成语境知识。然而,尽管有这些进步,代理仍面临偏见和公平性问题,这是深深根植于知识库和LLM训练中的挑战。本研究通过利用代理框架和偏见检测工具来识别和强调检索内容中的固有偏见,从而引入了一种新型的偏见感知知识检索方法。通过增强用户的透明度和意识,这种方法旨在促进更公平的信息系统,推动负责任的人工智能的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 信息检索技术在近年来取得了显著进步,尤其是大型语言模型(LLM)的应用彻底改变了该领域。
- LLM不仅能检索相关知识,还能进行有效总结,提高信息的可用性和可消费性。
- AI代理的兴起带来了动态信息检索的能力,整合了实时数据与知识库以生成语境知识。
- 尽管有技术进步,但代理在信息检索中仍面临偏见和公平性问题。
- 偏见感知知识检索方法利用代理框架和偏见检测工具来识别和强调检索内容中的偏见。
- 增强用户对信息透明度和意识的做法有助于促进更公平的信息系统的发展。
点此查看论文截图


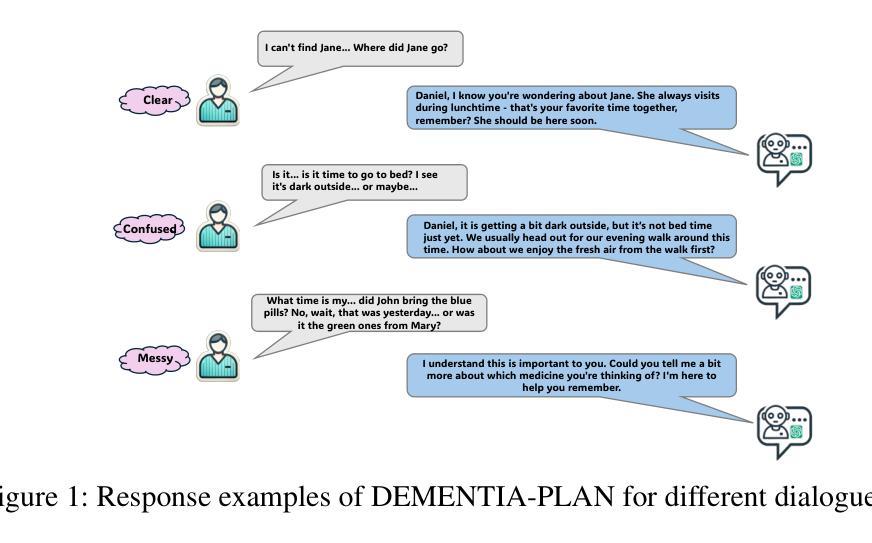
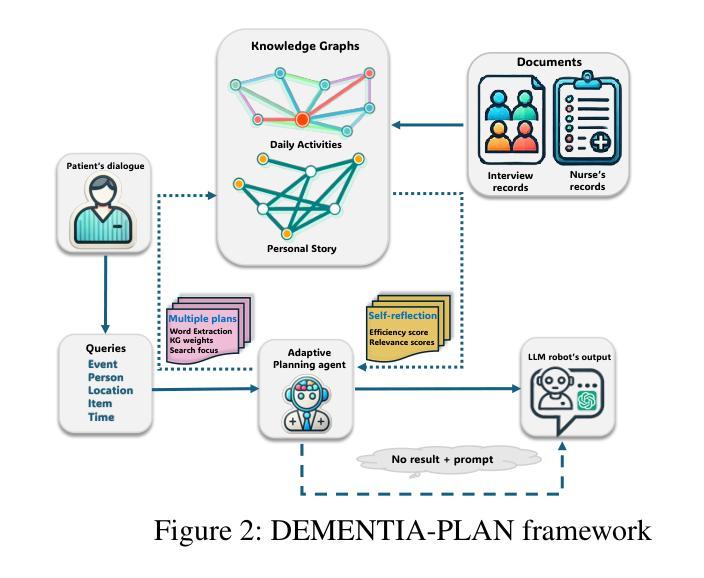
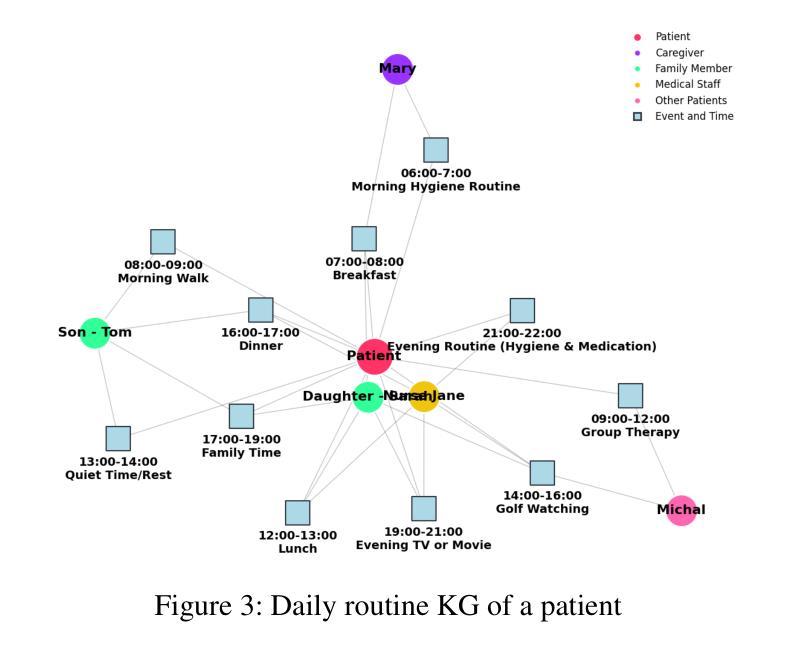
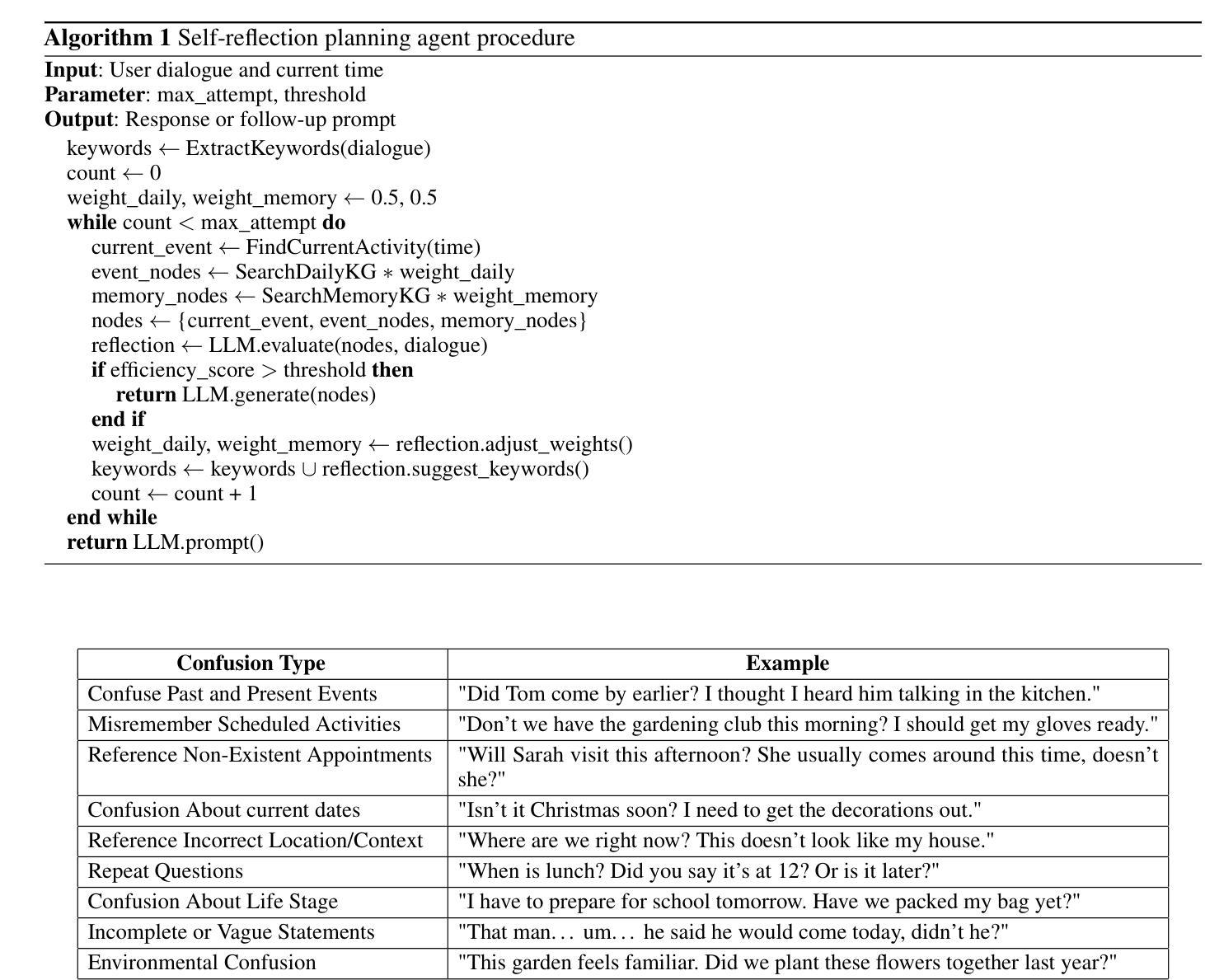
DEMENTIA-PLAN: An Agent-Based Framework for Multi-Knowledge Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation in Dementia Care
Authors:Yutong Song, Chenhan Lyu, Pengfei Zhang, Sabine Brunswicker, Nikil Dutt, Amir Rahmani
Mild-stage dementia patients primarily experience two critical symptoms: severe memory loss and emotional instability. To address these challenges, we propose DEMENTIA-PLAN, an innovative retrieval-augmented generation framework that leverages large language models to enhance conversational support. Our model employs a multiple knowledge graph architecture, integrating various dimensional knowledge representations including daily routine graphs and life memory graphs. Through this multi-graph architecture, DEMENTIA-PLAN comprehensively addresses both immediate care needs and facilitates deeper emotional resonance through personal memories, helping stabilize patient mood while providing reliable memory support. Our notable innovation is the self-reflection planning agent, which systematically coordinates knowledge retrieval and semantic integration across multiple knowledge graphs, while scoring retrieved content from daily routine and life memory graphs to dynamically adjust their retrieval weights for optimized response generation. DEMENTIA-PLAN represents a significant advancement in the clinical application of large language models for dementia care, bridging the gap between AI tools and caregivers interventions.
轻度痴呆症患者主要经历两种关键症状:严重的记忆丧失和情感不稳定。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了DEMENTIA-PLAN,这是一种创新的检索增强生成框架,利用大型语言模型来增强对话支持。我们的模型采用多知识图谱架构,整合了包括日常例行公事图谱和生活记忆图谱在内的各种维度知识表示。通过这种多图架构,DEMENTIA-PLAN全面满足了即时护理需求,并通过个人记忆促进更深层次的情感共鸣,有助于稳定患者情绪,同时提供可靠的记忆支持。我们显著的创新点是自我反思规划代理,它系统地协调知识检索和跨多个知识图谱的语义集成,同时从日常例行公事和生活记忆图谱中评分检索内容,以动态调整其检索权重,从而实现优化的响应生成。DEMENTIA-PLAN在痴呆症护理中大型语言模型的临床应用方面代表了重大进展,架起了人工智能工具和护理干预之间的桥梁。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025 Workshop on Knowledge Graphs for Personalized Public Health
Summary
DEMENTIA-PLAN是一个针对轻度阶段痴呆症患者记忆和情感问题的创新框架。它利用大型语言模型提供增强的会话支持,并借助多重知识图谱,整合日常习惯和个人记忆图谱,全面满足即时护理需求并促进情感共鸣。其创新点在于自我反思规划代理,能够系统地协调知识检索和语义整合,动态调整检索权重以生成优化响应。DEMENTIA-PLAN是大型语言模型在痴呆症护理临床应用中的重大进展,缩小了人工智能工具和护理干预之间的差距。
Key Takeaways
- DEMENTIA-PLAN旨在解决轻度阶段痴呆症患者的主要症状:严重记忆丧失和情感不稳定。
- 该框架利用大型语言模型增强会话支持。
- DEMENTIA-PLAN采用多重知识图谱架构,包括日常习惯和个人记忆图谱。
- 通过该架构,DEMENTIA-PLAN满足患者的即时护理需求并促进情感共鸣。
- 自我反思规划代理是DEMENTIA-PLAN的创新点,能协调知识检索和语义整合。
- DEMENTIA-PLAN动态调整检索权重以生成优化响应。
点此查看论文截图

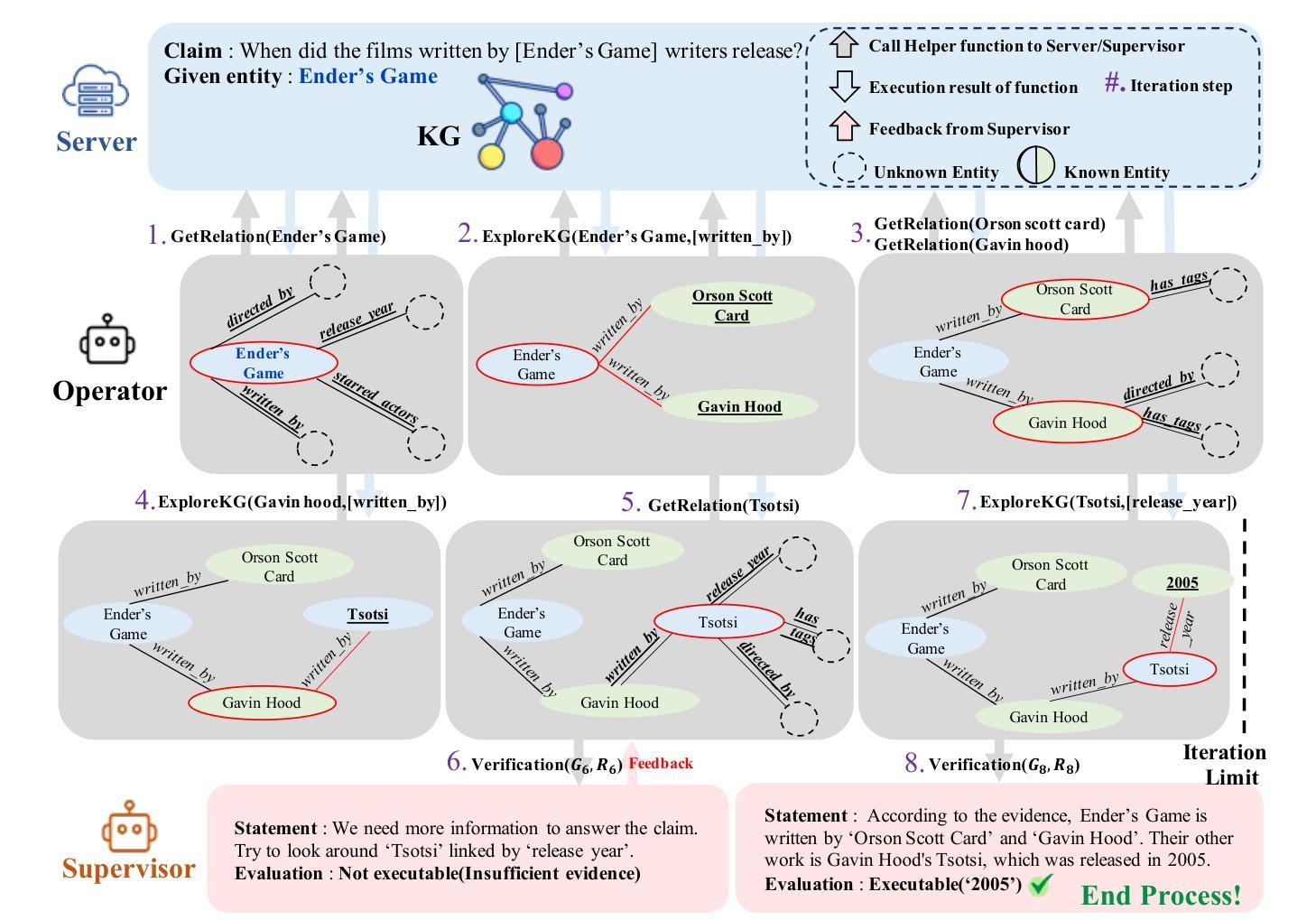
R2-KG: General-Purpose Dual-Agent Framework for Reliable Reasoning on Knowledge Graphs
Authors:Sumin Jo, Junseong Choi, Jiho Kim, Edward Choi
Recent studies have combined Large Language Models (LLMs) with Knowledge Graphs (KGs) to enhance reasoning, improving inference accuracy without additional training while mitigating hallucination. However, existing frameworks are often rigid, struggling to adapt to KG or task changes. They also rely heavily on powerful LLMs for reliable (i.e., trustworthy) reasoning. To address this, We introduce R2-KG, a plug-and-play, dual-agent framework that separates reasoning into two roles: an Operator (a low-capacity LLM) that gathers evidence and a Supervisor (a high-capacity LLM) that makes final judgments. This design is cost-efficient for LLM inference while still maintaining strong reasoning accuracy. Additionally, R2-KG employs an Abstention mechanism, generating answers only when sufficient evidence is collected from KG, which significantly enhances reliability. Experiments across multiple KG-based reasoning tasks show that R2-KG consistently outperforms baselines in both accuracy and reliability, regardless of the inherent capability of LLMs used as the Operator. Further experiments reveal that the single-agent version of R2-KG, equipped with a strict self-consistency strategy, achieves significantly higher-than-baseline reliability while reducing inference cost. However, it also leads to a higher abstention rate in complex KGs. Our findings establish R2-KG as a flexible and cost-effective solution for KG-based reasoning. It reduces reliance on high-capacity LLMs while ensuring trustworthy inference. The code is available at https://github.com/ekrxjwh2009/R2-KG/.
最近的研究结合了大型语言模型(LLM)和知识图谱(KG),以提高推理能力,可以在不进行额外训练的情况下提高推理准确性,同时减轻虚构现象。然而,现有的框架通常很僵化,难以适应知识图谱或任务的变化。它们也严重依赖于功能强大的LLM进行可靠(即值得信赖)的推理。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了R2-KG,这是一个即插即用的双代理框架,将推理分为两个角色:一个负责收集证据的Operator(低容量LLM)和一个负责做出最终判断的Supervisor(高容量LLM)。这种设计在LLM推理方面是成本效益高的,同时仍能保持强大的推理准确性。此外,R2-KG采用了一种弃权机制,仅在从知识图谱收集到足够证据时才生成答案,这显著提高了可靠性。在多个基于知识图谱的推理任务上的实验表明,R2-KG在准确性和可靠性方面始终优于基线,无论使用的Operator的固有能力如何。进一步的实验表明,配备有严格自我一致性策略的R2-KG的单代理版本在降低推理成本的同时,实现了高于基线的可靠性。然而,这在复杂的知识图谱中也导致了更高的弃权率。我们的研究结果表明,R2-KG是一个灵活且经济实惠的解决基于知识图谱的推理问题的方案。它能减少了对高性能LLM的依赖,同时确保可信的推理。代码可在https://github.com/ekrxjwh2009/R2-KG/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于知识图谱(KG)的大型语言模型(LLM)结合技术能增强推理能力,提高推理准确性,并缓解虚构现象。然而,现有框架适应性差,严重依赖高性能LLM进行可靠推理。为解决这一问题,我们推出R2-KG,一个双代理框架,将推理分为两个角色:收集证据的操作者(低容量LLM)和做出最终判断的监督者(高容量LLM)。这种设计成本效益高且推理准确性强。此外,R2-KG采用拒绝机制,仅在从知识图谱收集到足够证据时才生成答案,显著提高可靠性。实验表明,无论使用的操作者LLM能力如何,R2-KG在多任务知识图谱推理中都表现出色。仅装备严格自我一致性策略的单一代理版本R2-KG,虽然降低了推理成本,但在复杂知识图谱中的拒绝率更高。研究结果表明R2-KG是一个灵活且经济的解决知识图谱推理的方案。
Key Takeaways
- R2-KG结合了大型语言模型与知识图谱,增强推理能力并提高准确性。
- R2-KG采用双代理框架设计,分离推理角色以提高成本效益和灵活性。
- R2-KG采用拒绝机制,确保只有在有足够证据时才会生成答案,从而提高可靠性。
- R2-KG在多个知识图谱推理任务中表现优异,无论LLM操作者的能力如何。
- 仅装备严格自我一致性策略的单一代理版本R2-KG在复杂知识图谱中的拒绝率较高。
点此查看论文截图

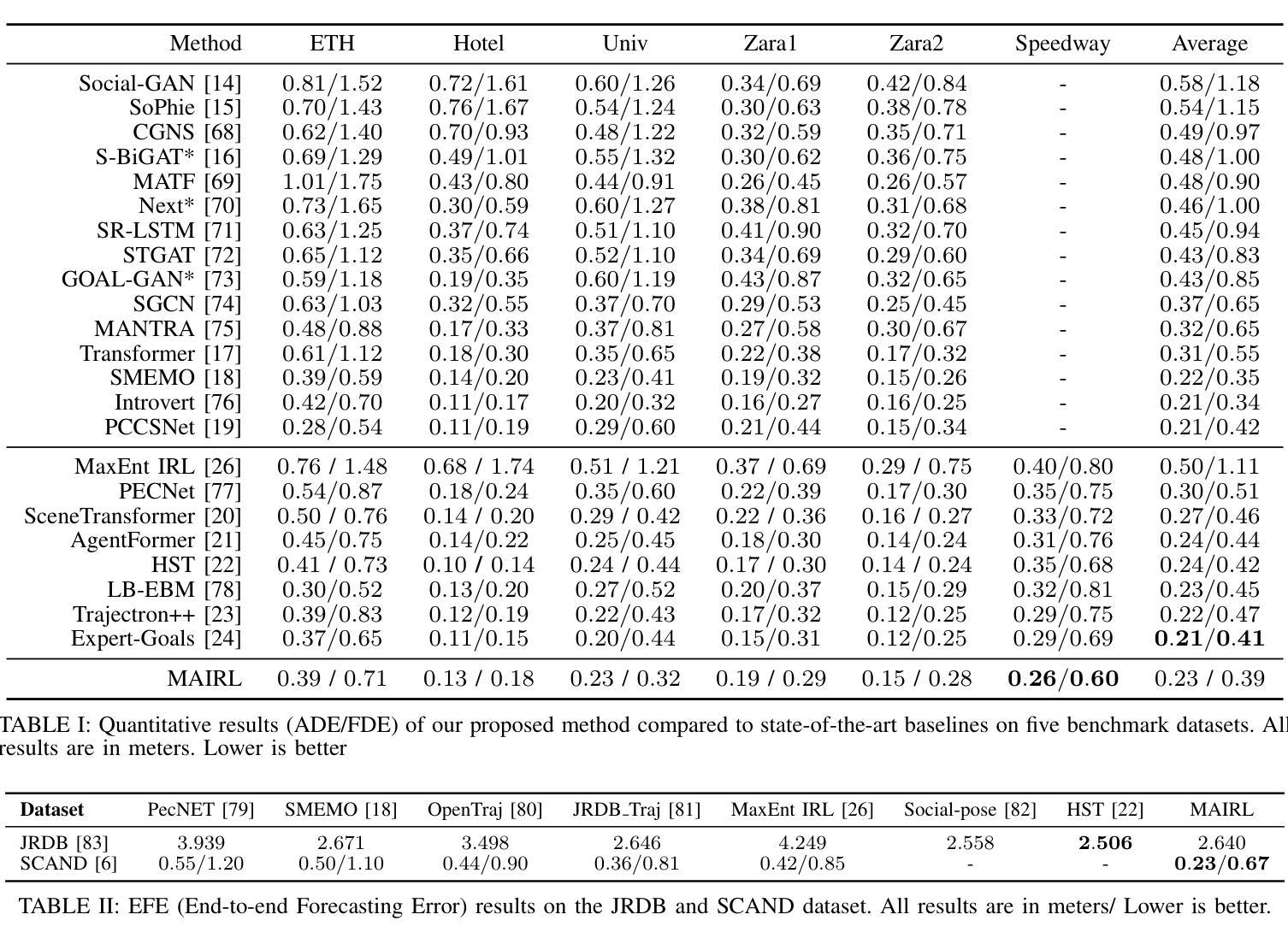
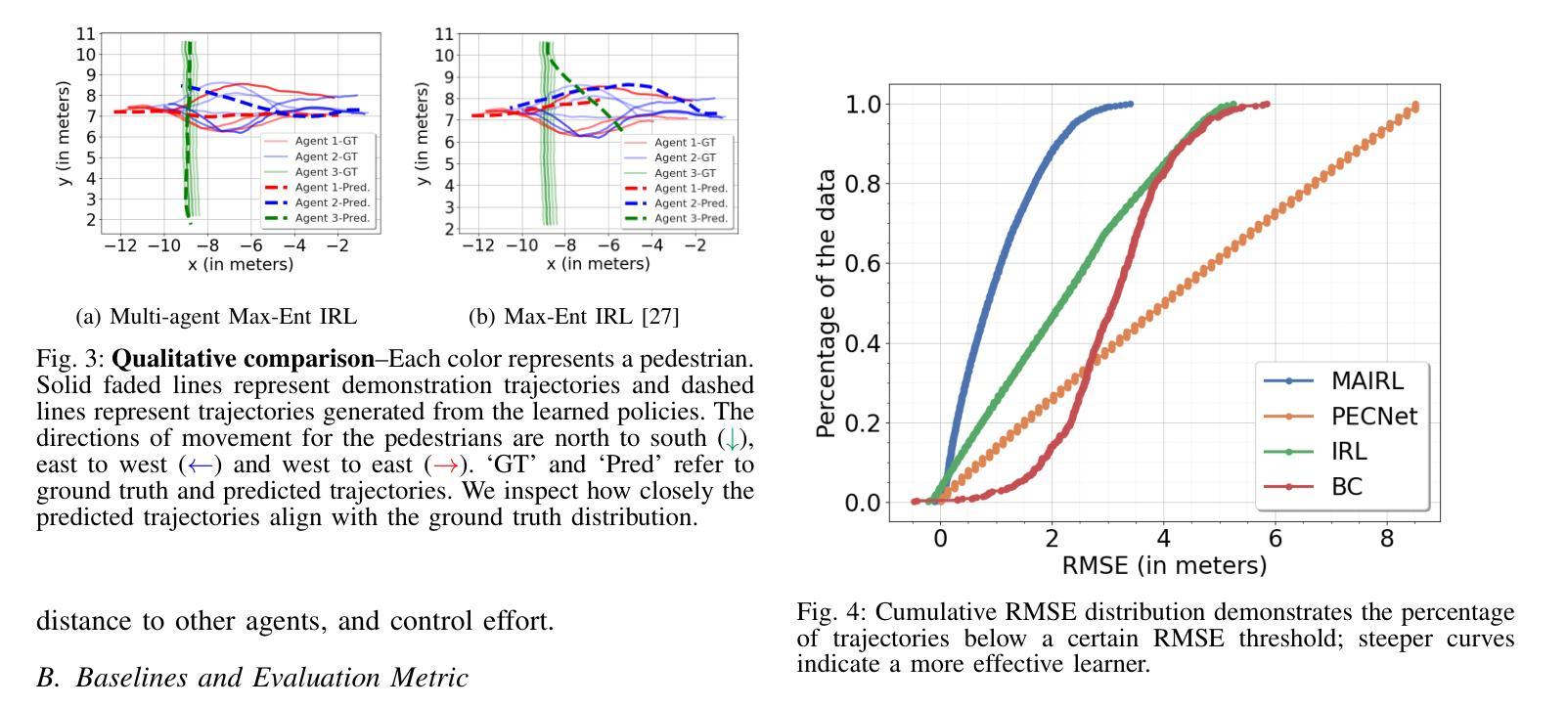
Multi-Agent Inverse Reinforcement Learning in Real World Unstructured Pedestrian Crowds
Authors:Rohan Chandra, Haresh Karnan, Negar Mehr, Peter Stone, Joydeep Biswas
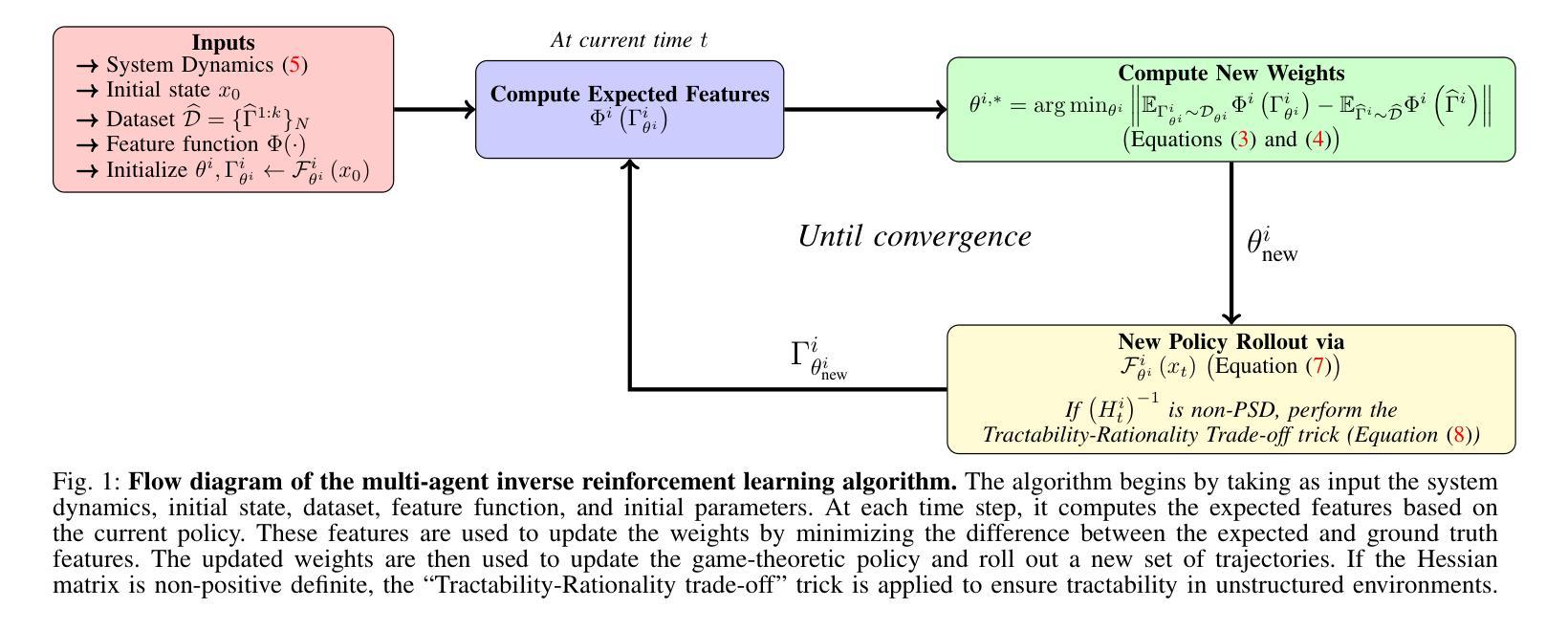
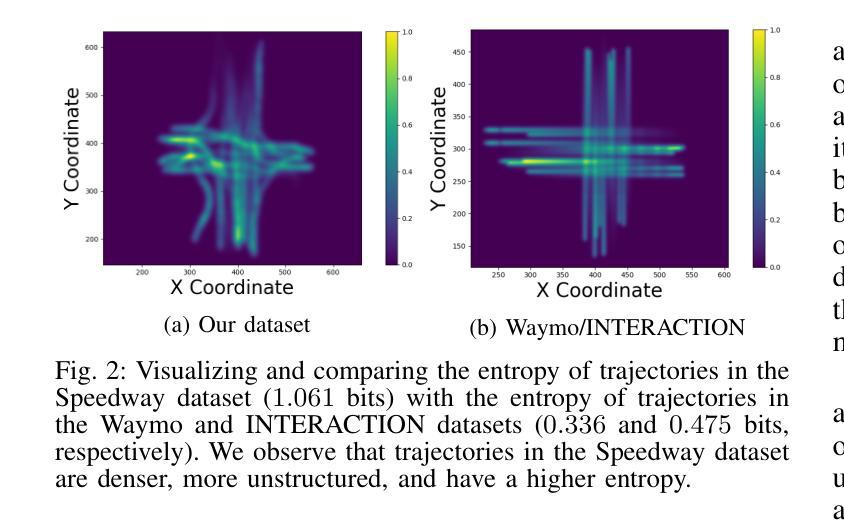
Social robot navigation in crowded public spaces such as university campuses, restaurants, grocery stores, and hospitals, is an increasingly important area of research. One of the core strategies for achieving this goal is to understand humans’ intent–underlying psychological factors that govern their motion–by learning their reward functions, typically via inverse reinforcement learning (IRL). Despite significant progress in IRL, learning reward functions of multiple agents simultaneously in dense unstructured pedestrian crowds has remained intractable due to the nature of the tightly coupled social interactions that occur in these scenarios \textit{e.g.} passing, intersections, swerving, weaving, etc. In this paper, we present a new multi-agent maximum entropy inverse reinforcement learning algorithm for real world unstructured pedestrian crowds. Key to our approach is a simple, but effective, mathematical trick which we name the so-called tractability-rationality trade-off trick that achieves tractability at the cost of a slight reduction in accuracy. We compare our approach to the classical single-agent MaxEnt IRL as well as state-of-the-art trajectory prediction methods on several datasets including the ETH, UCY, SCAND, JRDB, and a new dataset, called Speedway, collected at a busy intersection on a University campus focusing on dense, complex agent interactions. Our key findings show that, on the dense Speedway dataset, our approach ranks 1st among top 7 baselines with >2X improvement over single-agent IRL, and is competitive with state-of-the-art large transformer-based encoder-decoder models on sparser datasets such as ETH/UCY (ranks 3rd among top 7 baselines).
社会机器人在拥挤的公共空间(如大学校园、餐馆、杂货店和医院)的导航是研究领域的热点之一。实现这一目标的核心策略之一是理解人类的意图——通过逆向强化学习(IRL)学习他们的奖励函数,即控制他们运动的潜在心理因素。尽管在IRL方面取得了重大进展,但由于在这种场景中发生的紧密耦合的社会互动的性质(例如,超越、交叉、转弯、绕行等),在密集的非结构化人群中同时学习多个代理的奖励功能仍然是一个棘手的问题。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的多代理最大熵逆向强化学习算法,用于现实世界中的非结构化人群。我们方法的关键是一个简单有效的数学技巧,我们称之为所谓的可管理性-理性权衡技巧,以轻微的准确性降低为代价实现了可管理性。我们将我们的方法与经典的单一代理MaxEnt IRL以及几个数据集上的最新轨迹预测方法进行了比较,包括ETH、UCY、SCAND、JRDB以及一个新的数据集Speedway,该数据集是在一所大学校园内繁忙的十字路口收集的,专注于密集复杂的代理交互。我们的主要研究发现,在密集的Speedway数据集上,我们的方法在七个基线中排名第一,相比单一代理IRL有2倍以上的改进;而在较稀疏的数据集如ETH/UCY上,它与最新的大型基于变压器的编码器-解码器模型具有竞争力,在七个基线中位列第三。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
社会机器人导航在拥挤的公共空间如大学校园、餐馆、杂货店和医院等是一个日益重要的研究领域。其核心策略之一是理解人类的意图,即通过逆向强化学习来了解他们的奖励函数。尽管在单代理的逆向强化学习上取得显著进展,但由于复杂的社会互动性质,多代理同时学习的奖励函数仍然困难重重。本文提出了一种新的多代理最大熵逆向强化学习算法,用于现实世界中的非结构化行人群体。算法的关键在于一个简单有效的数学技巧——所谓的“可处理性合理性权衡技巧”,以实现处理的可处理性,但可能牺牲了部分准确性。本文还对多个数据集进行了评估,并在校园繁忙十字路口收集的密集复杂代理交互的新数据集“Speedway”上取得了最佳排名。我们的方法优于单代理最大熵逆强化学习,并且在稀疏数据集上表现良好。
Key Takeaways
- 社会机器人导航在拥挤公共空间是一个重要的研究领域。
- 核心策略是理解人类意图,通过逆向强化学习了解奖励函数。
- 多代理同时学习的奖励函数因复杂社会互动性质而具有挑战性。
- 提出了一种新的多代理最大熵逆向强化学习算法,用于非结构化行人群体。
- 算法采用“可处理性合理性权衡技巧”,实现处理的可处理性可能牺牲部分准确性。
- 在校园繁忙十字路口的密集数据集上取得了最佳排名,优于单代理最大熵逆强化学习。
点此查看论文截图


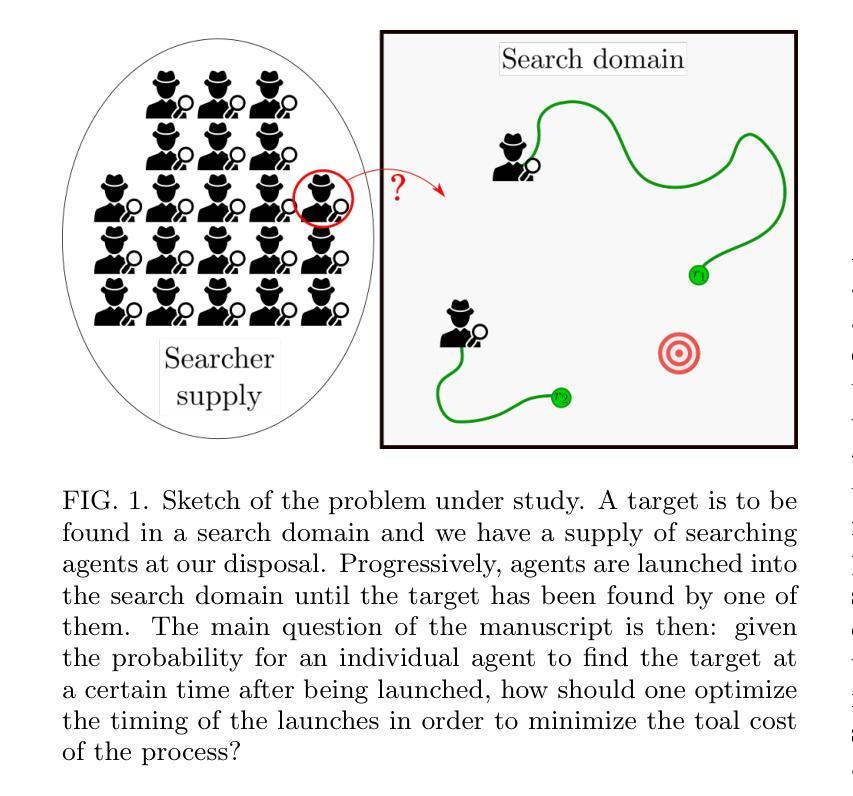
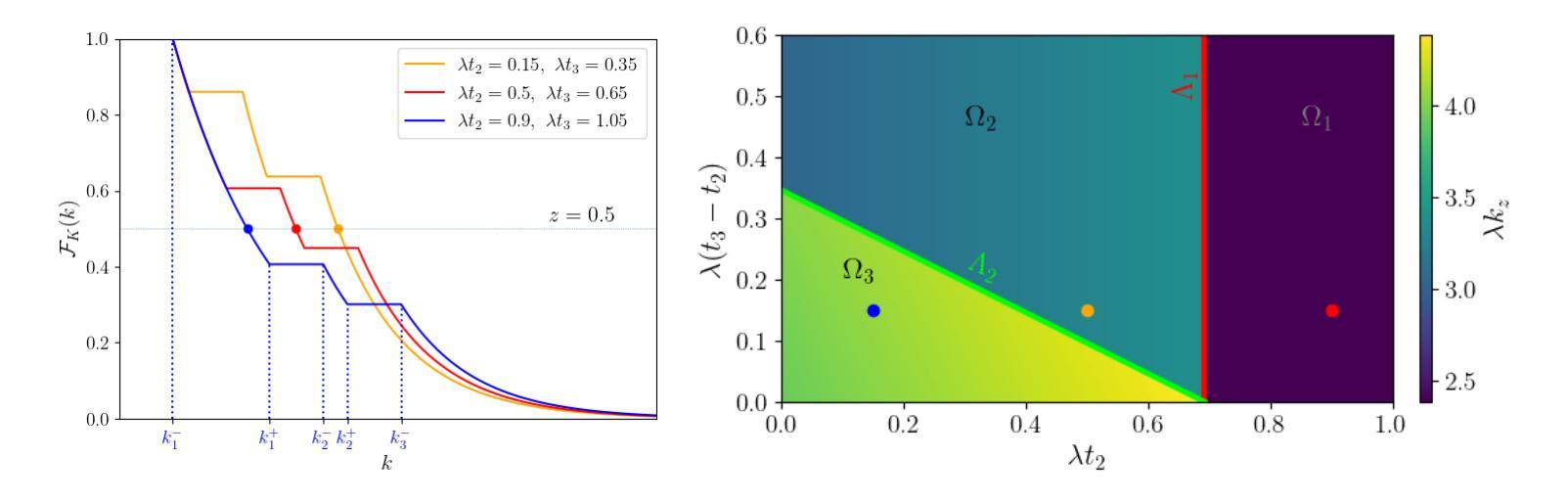
Optimal number of agents in a collective search, and when to launch them
Authors:Hugues Meyer, Heiko Rieger
Search processes often involve multiple agents that collectively search a randomly located target. While increasing the number of agents usually decreases the time at which the first agent finds the target, it also requires resources to create and sustain more agents. In this manuscript, we raise the question of the optimal timing for launching multiple agents in a search in order to reach the best compromise between minimizing the overall search time and minimizing the costs associated with launching and sustaining agents. After introducing a general formalism for independent agents in which we allow them to be launched at arbitrary times, we investigate by means of analytical calculations and numerical optimization the optimal launch strategies to optimize the quantiles of the search cost and its mean. Finally, we compare our results with the case of stochastic resetting and study the conditions under which it is preferable to launch new searchers rather than resetting the first one to its initial position.
在搜索过程中,通常会涉及多个代理共同搜索随机位置的目标。虽然增加代理的数量通常会减少第一个代理找到目标的时间,但它也需要资源来创建和维持更多的代理。在本手稿中,我们提出了关于何时启动多个代理进行搜索的问题,以便在最小化总体搜索时间和减少启动和维持代理的成本之间取得最佳平衡。在引入独立代理的一般形式化方法后,我们允许它们在任意时间启动,通过解析计算和数值优化来研究最优启动策略,以优化搜索成本的分位数和平均值。最后,我们将结果与随机重置的情况进行比较,并研究在何种情况下启动新的搜索器比将第一个重置为其初始位置更为可取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了多代理搜索过程中的最优启动时间问题,旨在平衡减少总体搜索时间与降低启动和维持代理所需的成本。文章通过理论分析和数值优化,研究了独立代理的最优启动策略,优化了搜索成本的分位数和均值。此外,文章还将结果与随机重置的情况进行了比较,分析了启动新搜索器与将第一个搜索器重置到初始位置的情况的优劣条件。
Key Takeaways
- 多代理搜索中,增加代理数量可缩短首个代理找到目标的时间,但需投入更多资源创建和维持代理。
- 文章提出了独立代理的一般形式化描述,允许其在任意时间启动。
- 通过理论分析和数值优化,研究了最优启动策略以优化搜索成本的分位数和均值。
- 文章比较了不同条件下的搜索策略,包括随机重置与启动新搜索器的情况。
- 文章揭示了最优启动时间的权衡问题,即在减少搜索时间与降低资源消耗之间寻求最佳平衡。
- 通过研究独立代理的最优启动策略,为实际搜索任务提供了理论指导。
点此查看论文截图

LQG Risk-Sensitive Single-Agent and Major-Minor Mean-Field Game Systems: A Variational Framework
Authors:Hanchao Liu, Dena Firoozi, Michèle Breton
We develop a variational approach to address risk-sensitive optimal control problems with an exponential-of-integral cost functional in a general linear-quadratic-Gaussian (LQG) single-agent setup, offering new insights into such problems. Our analysis leads to the derivation of a nonlinear necessary and sufficient condition of optimality, expressed in terms of martingale processes. Subject to specific conditions, we find an equivalent risk-neutral measure, under which a linear state feedback form can be obtained for the optimal control. It is then shown that the obtained feedback control is consistent with the imposed condition and remains optimal under the original measure. Building upon this development, we (i) propose a variational framework for general LQG risk-sensitive mean-field games (MFGs) and (ii) advance the LQG risk-sensitive MFG theory by incorporating a major agent in the framework. The major agent interacts with a large number of minor agents, and unlike the minor agents, its influence on the system remains significant even with an increasing number of minor agents. We derive the Markovian closed-loop best-response strategies of agents in the limiting case where the number of agents goes to infinity. We establish that the set of obtained best-response strategies yields a Nash equilibrium in the limiting case and an $\varepsilon$-Nash equilibrium in the finite-player case.
我们针对一般线性二次高斯(LQG)单智能体设置下的具有指数积分成本函数的风险敏感最优控制问题,开发了一种变分方法,为这类问题提供了新的见解。我们的分析导致推导出了一种非线性最优的必要和充分条件,用随机过程来表达。在特定条件下,我们找到了一个等效的风险中性度量,在该度量下可以获得线性状态反馈形式的最优控制。然后证明了所获得的反馈控制符合施加的条件,并且在原始度量下仍然是最优的。在此基础上,(i)我们为一般的LQG风险敏感平均场博弈(MFGs)提出了一个变分框架;(ii)通过将主要智能体纳入框架,推进了LQG风险敏感MFG理论的发展。主要智能体与大量次要智能体相互作用,与次要智能体不同,即使随着次要智能体数量的增加,其对系统的影响仍然显著。我们推导出在智能体数量趋于无穷大的情况下,智能体的马尔可夫闭环最佳响应策略。我们证明了所获得的最佳响应策略集合在极限情况下构成一个纳什均衡,在有限玩家的情况下构成一个ε-纳什均衡。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:针对具有指数积分成本函数的线性二次高斯(LQG)单智能体风险敏感最优控制问题,我们开发了一种变分方法,为这些问题提供了新的见解。我们的分析推导出了基于马尔可夫过程的非线性必要充分最优条件。在满足特定条件下,我们找到了一个等效的风险中性度量,在该度量下可以获得线性状态反馈形式的最佳控制。然后证明了所获得的反馈控制与施加条件一致,并且在原始度量下仍然是最优的。在此基础上,我们为一般LQG风险敏感均值场博弈(MFGs)提出了变分框架,并通过引入主要智能体来发展LQG风险敏感MFG理论。主要智能体与大量次要智能体相互作用,与次要智能体不同,其对系统的影响即使在次要智能体数量增加的情况下仍然具有重要意义。我们推导出了在智能体数量趋于无穷大时的马尔可夫闭环最佳响应策略。我们证明了所获得的最佳响应策略集合在极限情况下构成纳什均衡,在有限玩家情况下构成ε-纳什均衡。
Key Takeaways:
- 开发了针对风险敏感最优控制问题的变分方法,适用于具有特定成本函数的线性二次高斯(LQG)单智能体设置。
- 推导出了基于马尔可夫过程的非线性最优条件。
- 在特定条件下找到了风险中性度量,并在此度量下获得了线性状态反馈形式的最佳控制。
- 扩展了LQG风险敏感MFG理论,引入了主要智能体与次要智能体的区别。
- 主要智能体的影响在智能体数量增加时仍显著。
- 推导出了智能体数量趋于无穷大时的最佳响应策略。
点此查看论文截图