⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-29 更新
MotionDiff: Training-free Zero-shot Interactive Motion Editing via Flow-assisted Multi-view Diffusion
Authors:Yikun Ma, Yiqing Li, Jiawei Wu, Xing Luo, Zhi Jin
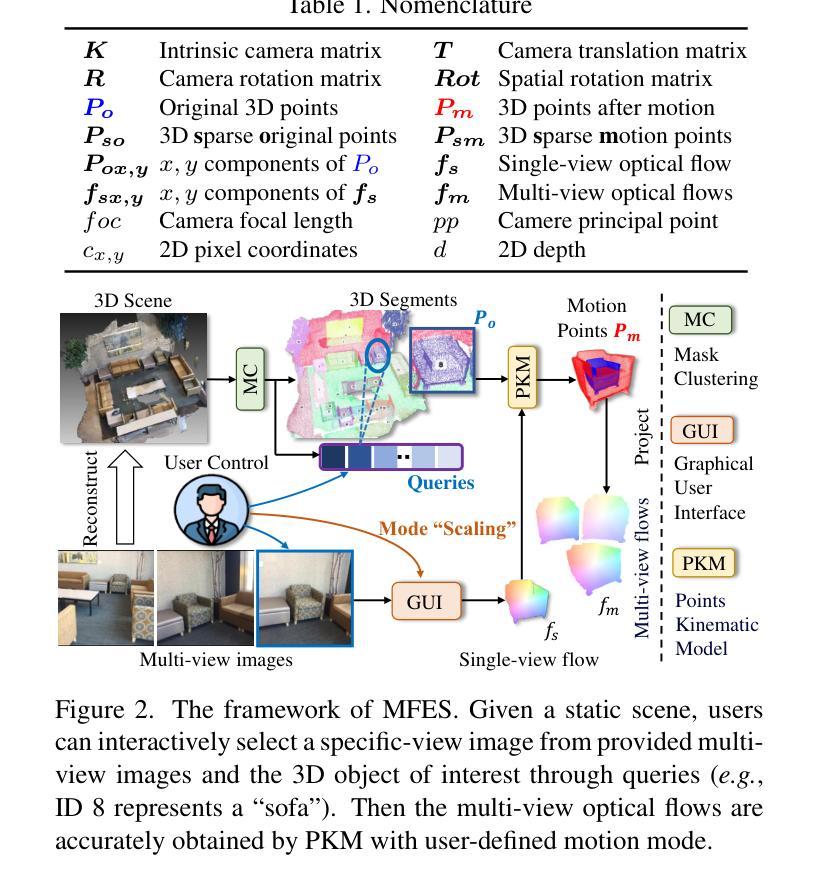
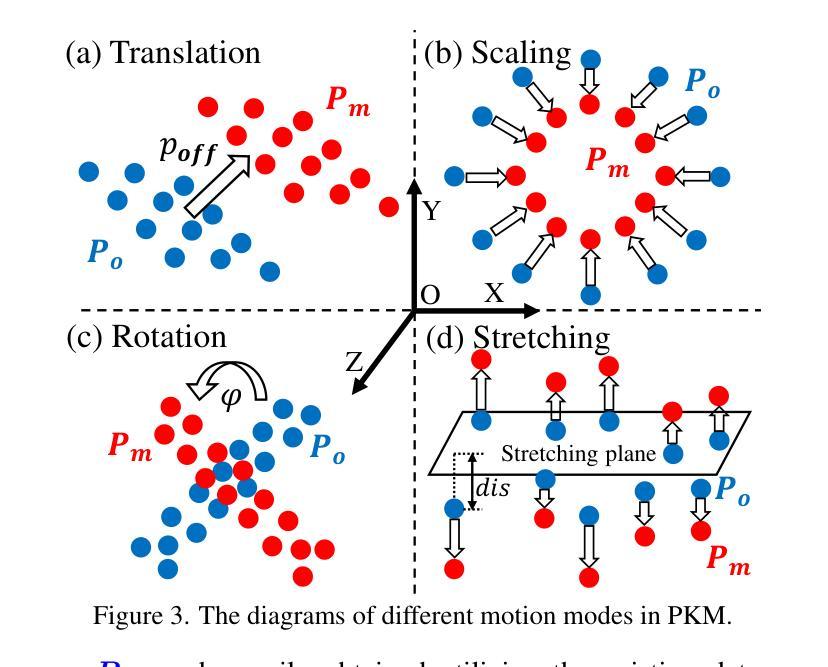
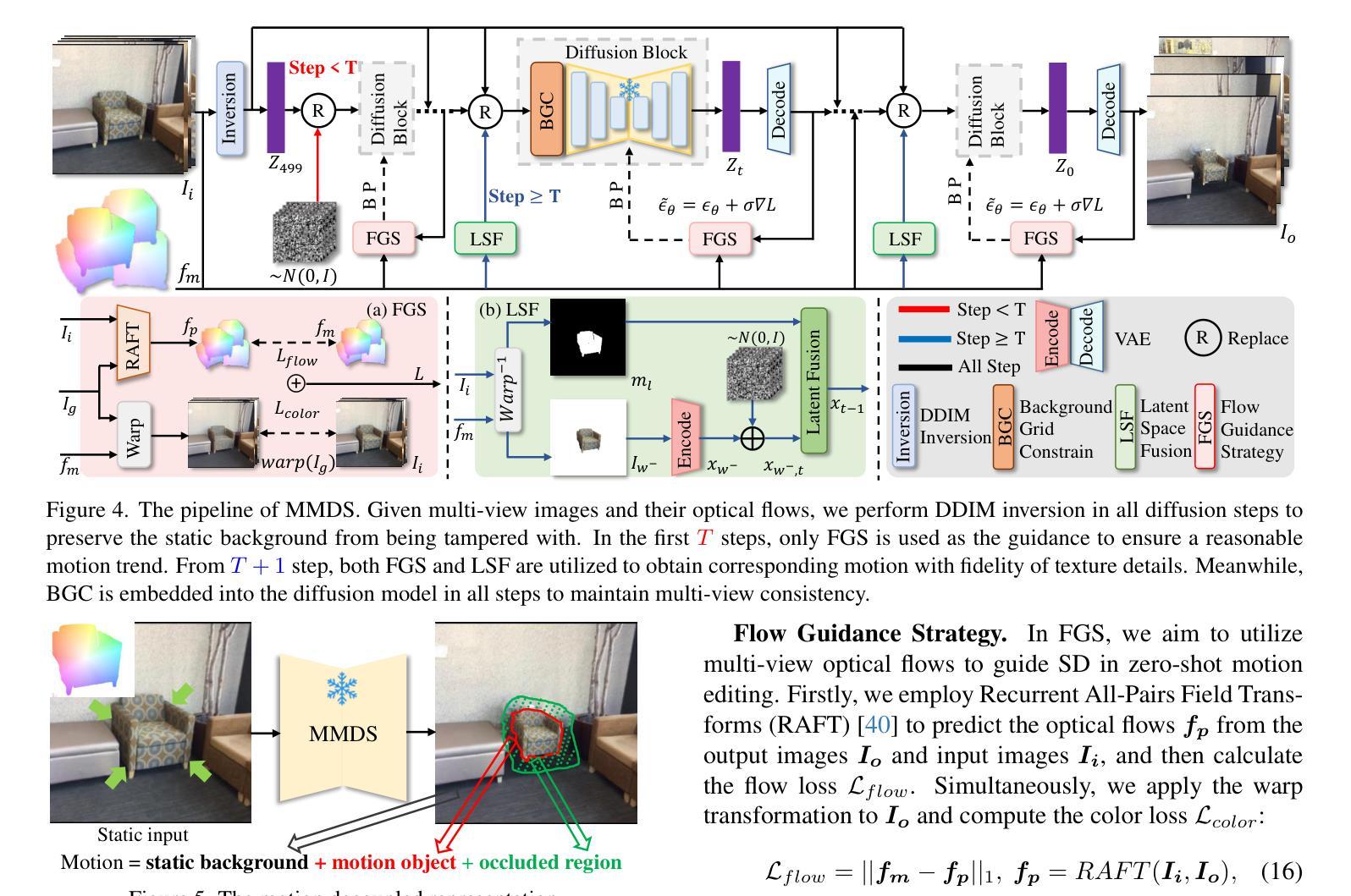
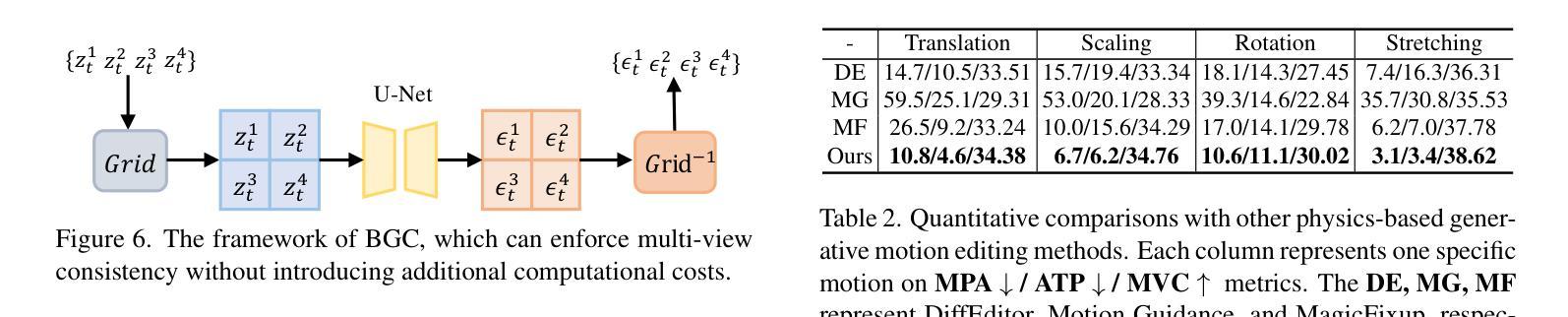
Generative models have made remarkable advancements and are capable of producing high-quality content. However, performing controllable editing with generative models remains challenging, due to their inherent uncertainty in outputs. This challenge is praticularly pronounced in motion editing, which involves the processing of spatial information. While some physics-based generative methods have attempted to implement motion editing, they typically operate on single-view images with simple motions, such as translation and dragging. These methods struggle to handle complex rotation and stretching motions and ensure multi-view consistency, often necessitating resource-intensive retraining. To address these challenges, we propose MotionDiff, a training-free zero-shot diffusion method that leverages optical flow for complex multi-view motion editing. Specifically, given a static scene, users can interactively select objects of interest to add motion priors. The proposed Point Kinematic Model (PKM) then estimates corresponding multi-view optical flows during the Multi-view Flow Estimation Stage (MFES). Subsequently, these optical flows are utilized to generate multi-view motion results through decoupled motion representation in the Multi-view Motion Diffusion Stage (MMDS). Extensive experiments demonstrate that MotionDiff outperforms other physics-based generative motion editing methods in achieving high-quality multi-view consistent motion results. Notably, MotionDiff does not require retraining, enabling users to conveniently adapt it for various down-stream tasks.
生成模型已经取得了显著的进步,并能够产生高质量的内容。然而,由于生成模型在输出方面存在固有的不确定性,因此对其进行可控编辑仍然是一个挑战。这一挑战在运动编辑中尤为突出,运动编辑涉及空间信息的处理。虽然一些基于物理的生成方法已经尝试实现运动编辑,但它们通常仅在具有简单运动的单视图图像上运行,例如平移和拖动。这些方法在处理复杂的旋转和拉伸运动以及确保多视图一致性方面表现吃力,通常需要资源密集型的重新训练。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了MotionDiff,这是一种无需训练即可使用的零样本扩散方法,它利用光流进行复杂的多视图运动编辑。具体来说,给定一个静态场景,用户可以交互式地选择感兴趣的对象来添加运动先验。然后,所提出的点运动学模型(PKM)在多重视图流估计阶段(MFES)估计相应的多视图光流。随后,这些光流在多视图运动扩散阶段(MMDS)通过解耦运动表示来生成多视图运动结果。大量实验表明,MotionDiff在其他基于物理的生成运动编辑方法中表现出色,能够实现高质量的多视图一致运动结果。值得注意的是,MotionDiff不需要重新训练,使用户能够轻松地将其适应于各种下游任务。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了生成模型在运动编辑方面的挑战,并提出了MotionDiff,一种无需训练、利用光学流进行复杂多视角运动编辑的方法。通过PKM模型估计多视角光学流,MotionDiff可在无需重训的情况下生成高质量的多视角运动结果。MotionDiff在达到高效性能的同时避免了资源密集的重训需求,使其适应多种下游任务。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型在运动编辑方面存在挑战,特别是处理复杂运动和确保多视角一致性方面。
- 当前物理基础的生成方法主要处理简单运动,难以处理复杂旋转和拉伸运动。
- MotionDiff是一种无需训练的零镜头扩散方法,利用光学流进行复杂的多视角运动编辑。
- 用户可以通过MotionDiff交互选择对象并添加运动先验。
- PKM模型在MFES阶段估计多视角光学流,为后续的运动编辑提供基础。
- 在MMDS阶段,MotionDiff通过解耦运动表示生成多视角运动结果。
点此查看论文截图

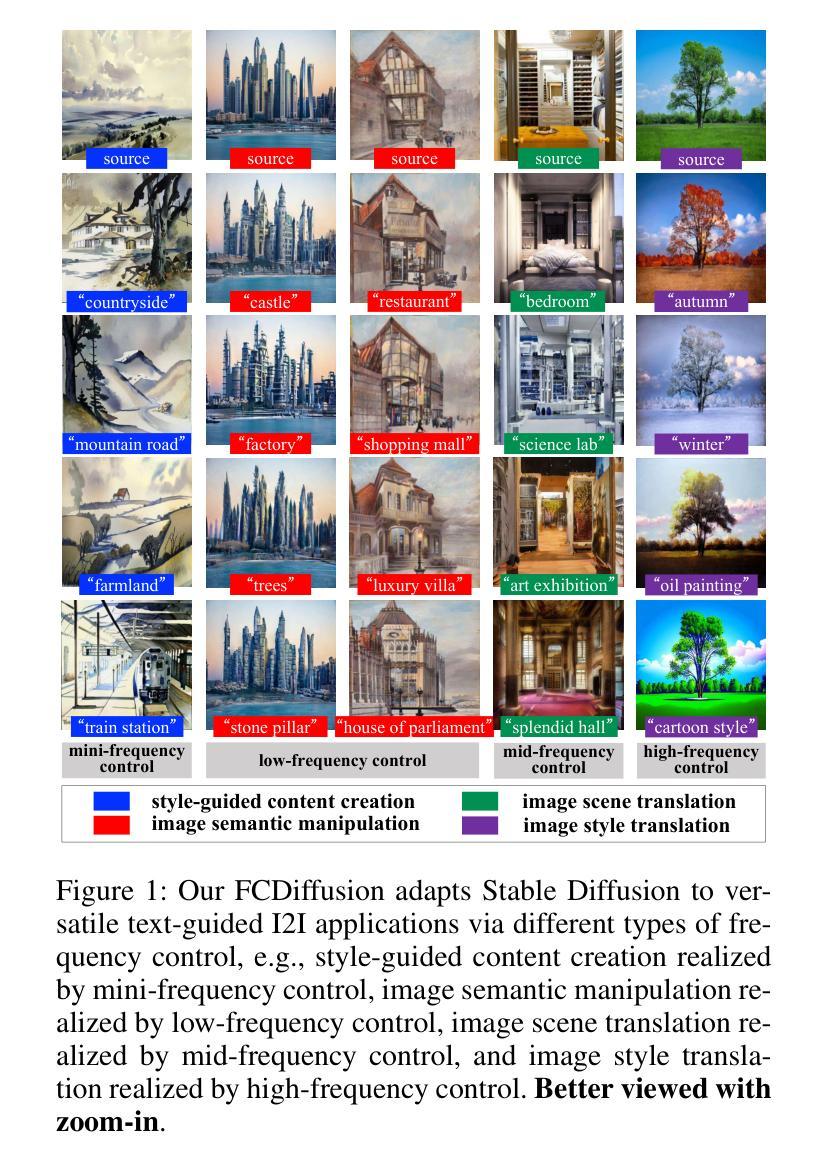
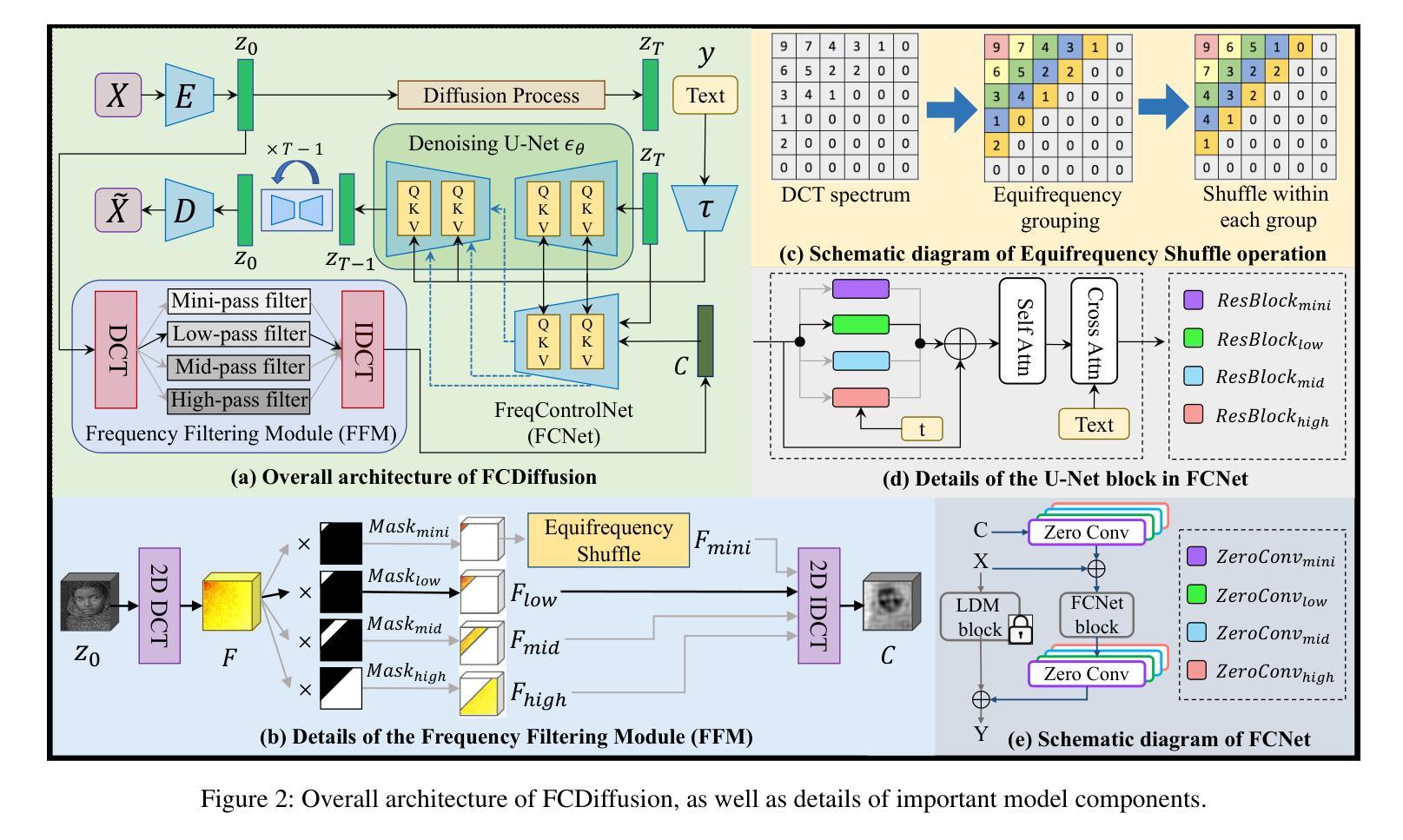
Frequency-Controlled Diffusion Model for Versatile Text-Guided Image-to-Image Translation
Authors:Xiang Gao, Zhengbo Xu, Junhan Zhao, Jiaying Liu
Recently, large-scale text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models have emerged as a powerful tool for image-to-image translation (I2I), allowing open-domain image translation via user-provided text prompts. This paper proposes frequency-controlled diffusion model (FCDiffusion), an end-to-end diffusion-based framework that contributes a novel solution to text-guided I2I from a frequency-domain perspective. At the heart of our framework is a feature-space frequency-domain filtering module based on Discrete Cosine Transform, which filters the latent features of the source image in the DCT domain, yielding filtered image features bearing different DCT spectral bands as different control signals to the pre-trained Latent Diffusion Model. We reveal that control signals of different DCT spectral bands bridge the source image and the T2I generated image in different correlations (e.g., style, structure, layout, contour, etc.), and thus enable versatile I2I applications emphasizing different I2I correlations, including style-guided content creation, image semantic manipulation, image scene translation, and image style translation. Different from related approaches, FCDiffusion establishes a unified text-guided I2I framework suitable for diverse image translation tasks simply by switching among different frequency control branches at inference time. The effectiveness and superiority of our method for text-guided I2I are demonstrated with extensive experiments both qualitatively and quantitatively. Our project is publicly available at: https://xianggao1102.github.io/FCDiffusion/.
最近,大规模的文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型作为图像到图像翻译(I2I)的强大工具而出现,允许通过用户提供的文本提示进行开放域图像翻译。本文提出了频率控制扩散模型(FCDiffusion),这是一个基于端到端扩散的框架,从频域角度为文本引导I2I提供了一种新型解决方案。我们框架的核心是一个基于离散余弦变换的特征空间频域滤波模块,该模块过滤源图像在DCT域的潜在特征,产生带有不同DCT频谱带的滤波图像特征,作为不同的控制信号传递给预训练的潜在扩散模型。我们发现不同DCT频谱带的控制信号在不同相关性(例如风格、结构、布局、轮廓等)上搭建了源图像和T2I生成图像之间的桥梁,从而实现了强调不同I2I相关性的通用I2I应用程序,包括风格引导的内容创建、图像语义操作、图像场景翻译和图像风格翻译。不同于相关的方法,FCDiffusion建立了一个统一的文本引导I2I框架,通过简单地切换不同频控分支即可适用于多种图像翻译任务。我们的方法在文本引导I2I上的有效性和优越性已通过定性和定量实验得到证明。我们的项目在:https://xianggao1102.github.io/FCDiffusion/ 公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Proceedings of the 38th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2024)
Summary
文本介绍了一种基于频率控制的扩散模型(FCDiffusion),该模型为文本引导的图像到图像翻译(I2I)提供了全新的解决方案。该模型通过离散余弦变换(DCT)领域的特征空间频率域过滤模块,过滤源图像的潜在特征,并将其作为控制信号输入到预训练的潜在扩散模型中。不同DCT光谱带的控制信号可实现不同的图像翻译相关性,如风格、结构、布局、轮廓等。该方法通过切换不同的频率控制分支,适用于多种图像翻译任务。
Key Takeaways
- FCDiffusion是一个基于扩散模型的端到端框架,用于文本引导的图像到图像翻译(I2I)。
- 该框架通过离散余弦变换(DCT)领域的特征空间频率域过滤模块,实现了对源图像潜在特征的过滤。
- 过滤后的图像特征作为不同的控制信号输入到预训练的潜在扩散模型中,实现了对图像翻译的不同相关性的控制。
- FCDiffusion可以通过切换不同的频率控制分支,适用于多种图像翻译任务。
- 该方法实现了对图像风格、结构、布局、轮廓等不同方面的控制,为图像翻译提供了更多可能性。
- FCDiffusion的有效性及优越性已通过广泛的实验得到了验证。
点此查看论文截图