⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-29 更新
Video-R1: Reinforcing Video Reasoning in MLLMs
Authors:Kaituo Feng, Kaixiong Gong, Bohao Li, Zonghao Guo, Yibing Wang, Tianshuo Peng, Benyou Wang, Xiangyu Yue
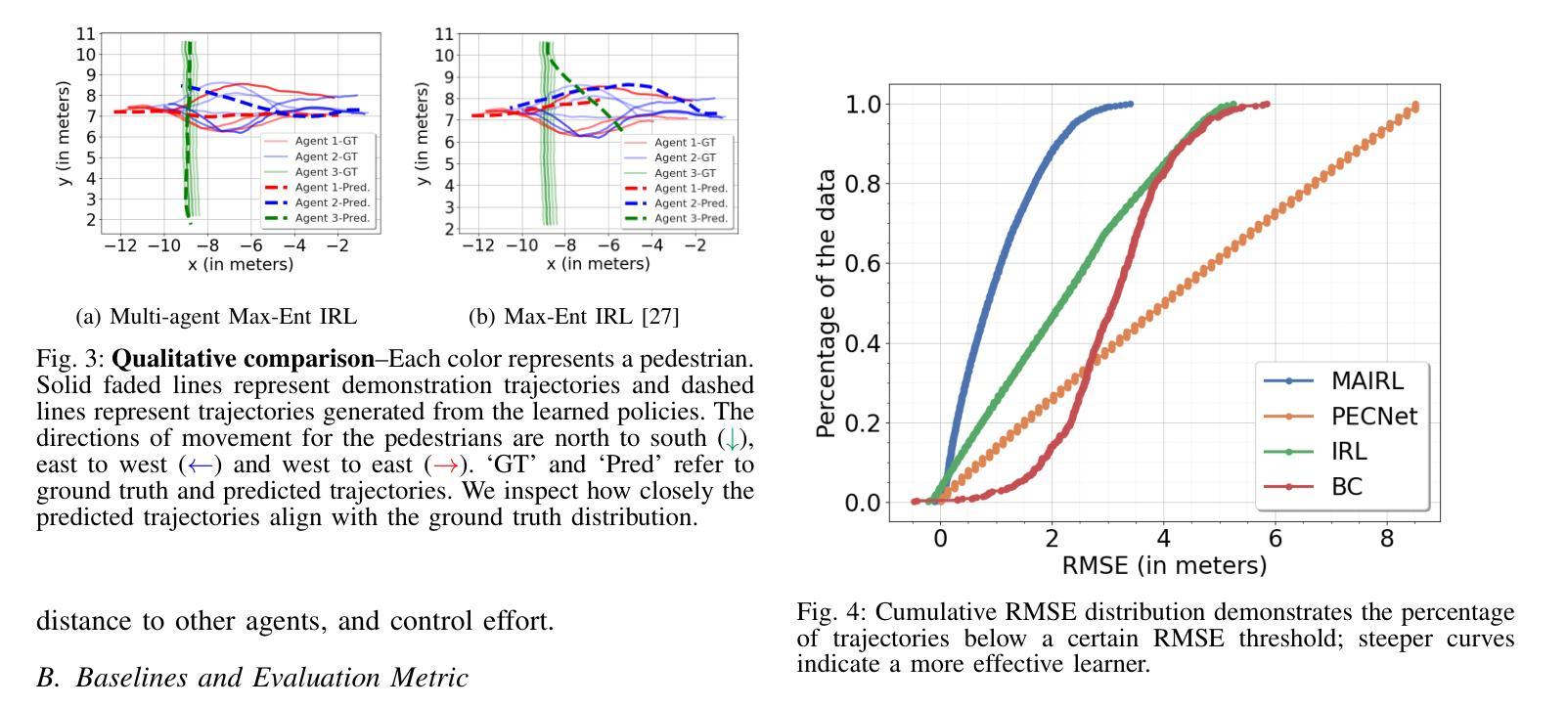
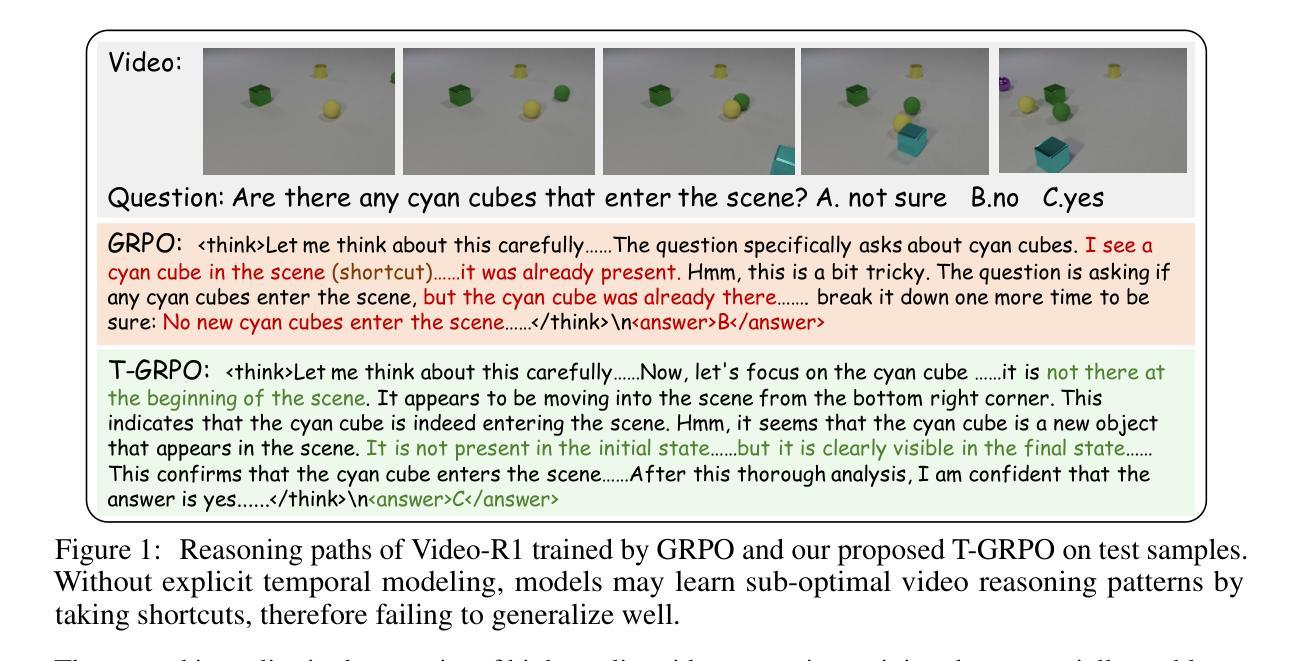
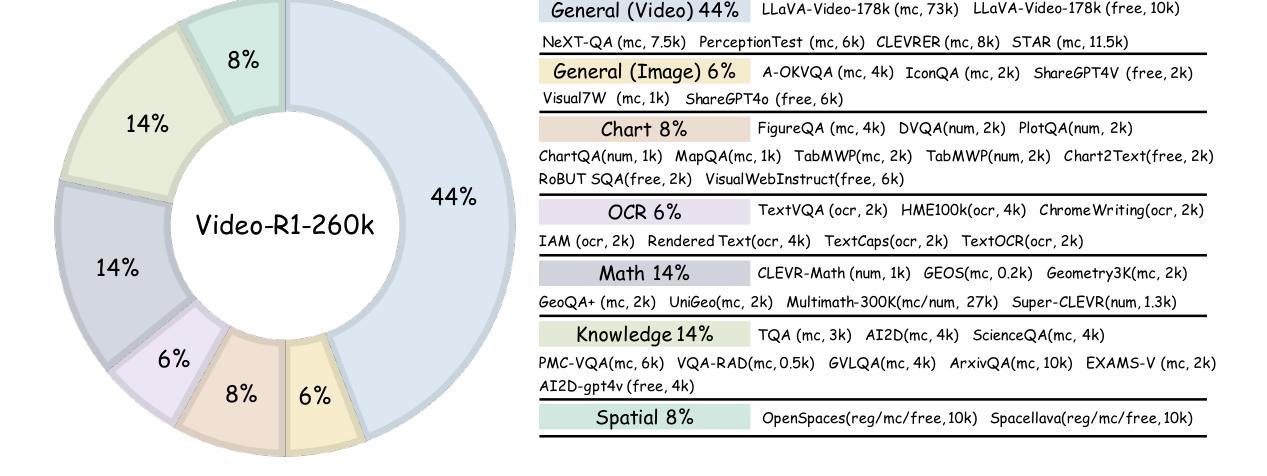
Inspired by DeepSeek-R1’s success in eliciting reasoning abilities through rule-based reinforcement learning (RL), we introduce Video-R1 as the first attempt to systematically explore the R1 paradigm for eliciting video reasoning within multimodal large language models (MLLMs). However, directly applying RL training with the GRPO algorithm to video reasoning presents two primary challenges: (i) a lack of temporal modeling for video reasoning, and (ii) the scarcity of high-quality video-reasoning data. To address these issues, we first propose the T-GRPO algorithm, which encourages models to utilize temporal information in videos for reasoning. Additionally, instead of relying solely on video data, we incorporate high-quality image-reasoning data into the training process. We have constructed two datasets: Video-R1-COT-165k for SFT cold start and Video-R1-260k for RL training, both comprising image and video data. Experimental results demonstrate that Video-R1 achieves significant improvements on video reasoning benchmarks such as VideoMMMU and VSI-Bench, as well as on general video benchmarks including MVBench and TempCompass, etc. Notably, Video-R1-7B attains a 35.8% accuracy on video spatial reasoning benchmark VSI-bench, surpassing the commercial proprietary model GPT-4o. All codes, models, data are released.
受DeepSeek-R1通过基于规则的强化学习(RL)激发推理能力成功的启发,我们推出Video-R1,作为首次系统性探索在多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)中进行视频推理的R1范式。然而,直接使用基于GRPO算法的RL训练进行视频推理面临两个主要挑战:(i)视频推理缺乏时间建模;(ii)高质量视频推理数据稀缺。为解决这些问题,我们首先提出T-GRPO算法,该算法鼓励模型在推理时利用视频中的时间信息。此外,我们不是仅依赖视频数据,而是将高质量图像推理数据纳入训练过程。我们构建了两个数据集:用于SFT冷启动的Video-R1-COT-165k和用于RL训练的视频R1-260k,两者都包含图像和视频数据。实验结果表明,Video-R1在视频推理基准测试(如VideoMMMU和VSI-Bench)以及通用视频基准测试(包括MVBench和TempCompass等)上取得了显著改进。值得注意的是,Video-R1-7B在视频空间推理基准VSI-bench上达到了35.8%的准确率,超过了商业专有模型GPT-4o。所有代码、模型、数据均已发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://github.com/tulerfeng/Video-R1
Summary
基于DeepSeek-R1通过基于规则的强化学习(RL)激发推理能力的成功,我们推出Video-R1,首次尝试在多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)中系统地探索R1范式以激发视频推理能力。针对直接应用RL训练和GRPO算法进行视频推理所面临的两个主要挑战,我们提出了T-GRPO算法,鼓励模型利用视频中的时间信息进行推理;同时,我们不只是依赖视频数据,还结合了高质量图像推理数据来训练过程。实验结果表明,Video-R1在视频推理基准测试(如VideoMMMU和VSI-Bench)以及通用视频基准测试(如MVBench和TempCompass等)上取得了显著改进。特别是Video-R1-7B在VSI-bench视频空间推理基准测试上的准确率达到了35.8%,超过了商业专有模型GPT-4o。所有代码、模型和数据均已发布。
Key Takeaways
- Video-R1是首个尝试在多模态大型语言模型中系统地探索R1范式以激发视频推理能力的项目。
- 直接应用RL训练和GRPO算法进行视频推理面临两个主要挑战:缺乏视频推理的时间建模和高质量视频推理数据的稀缺性。
- 为解决这些问题,提出了T-GRPO算法,鼓励模型利用视频中的时间信息进行推理。
- 除了视频数据外,还结合了高质量图像推理数据来进行训练。
- Video-R1在多个视频推理基准测试上取得了显著改进。
- Video-R1-7B在VSI-bench上的准确率达到了35.8%,超过了GPT-4o。
点此查看论文截图

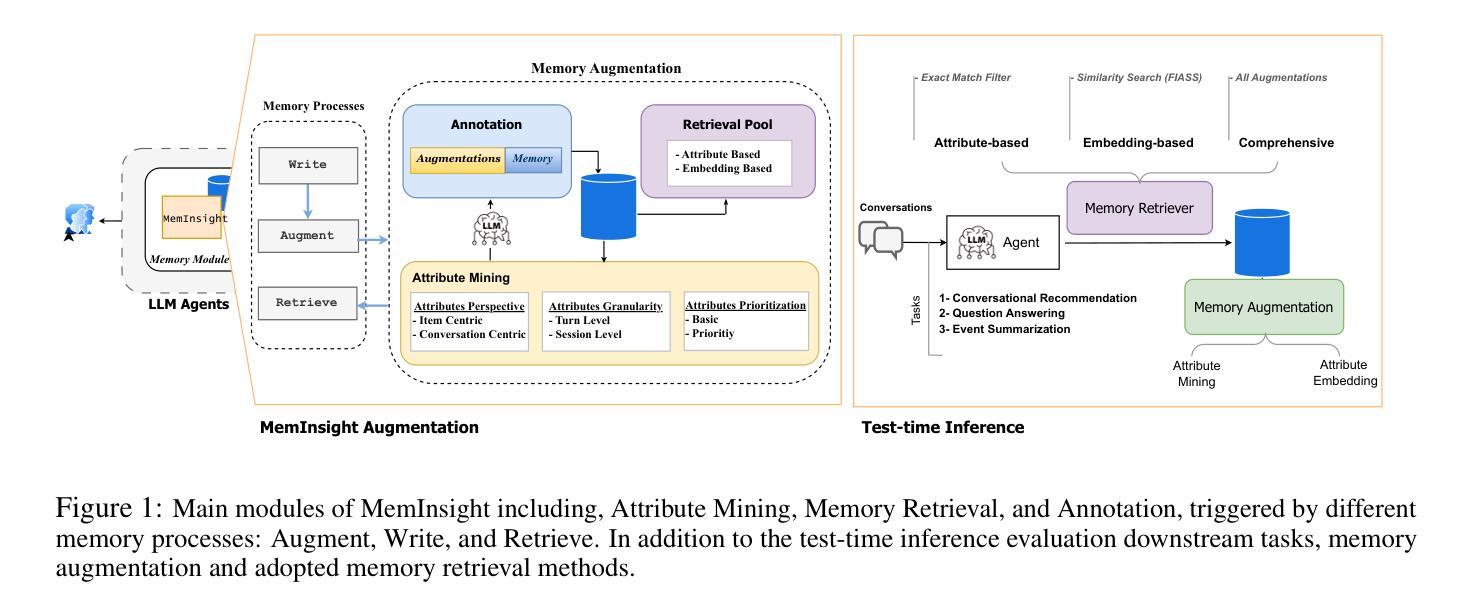
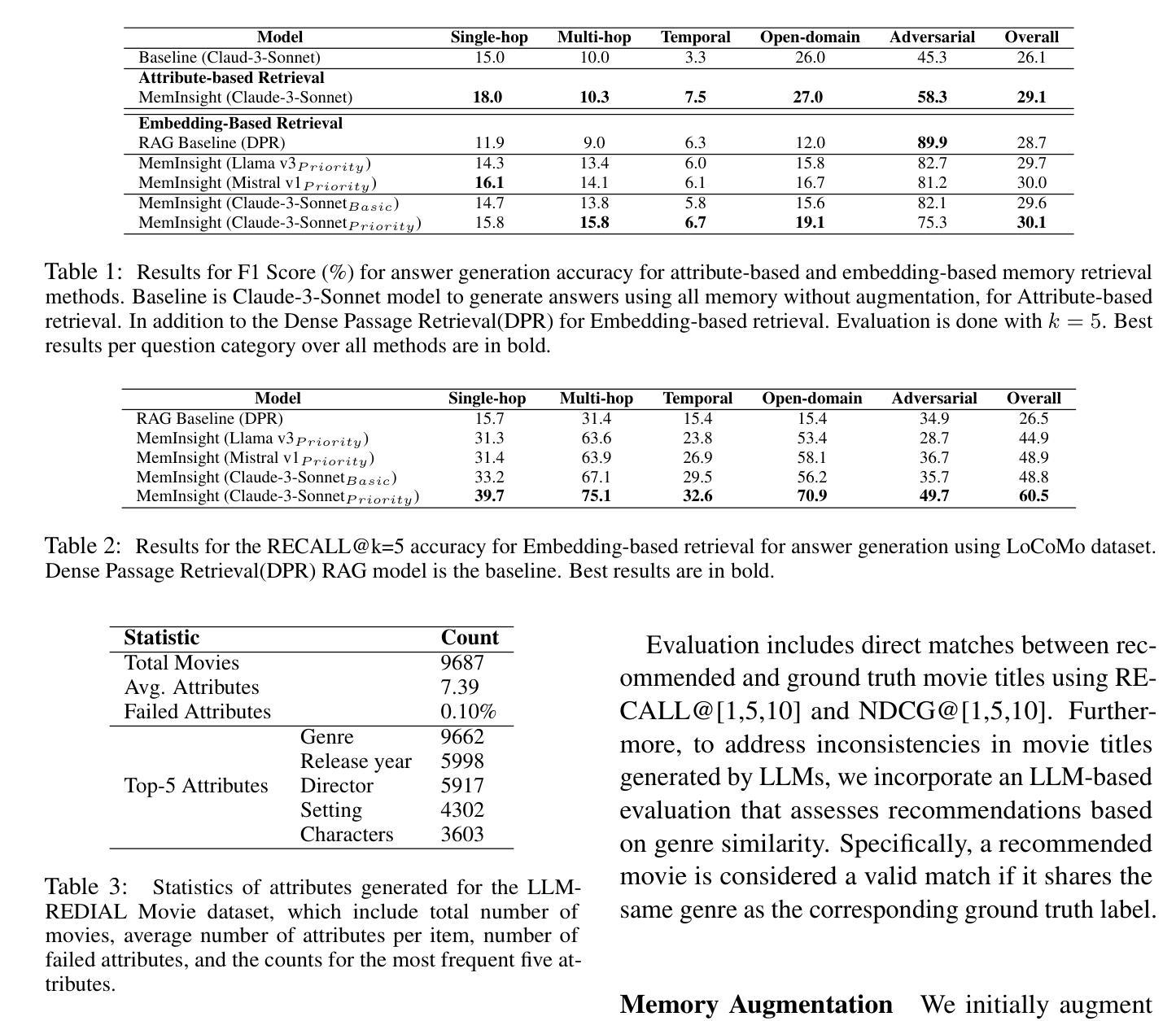
MemInsight: Autonomous Memory Augmentation for LLM Agents
Authors:Rana Salama, Jason Cai, Michelle Yuan, Anna Currey, Monica Sunkara, Yi Zhang, Yassine Benajiba
Large language model (LLM) agents have evolved to intelligently process information, make decisions, and interact with users or tools. A key capability is the integration of long-term memory capabilities, enabling these agents to draw upon historical interactions and knowledge. However, the growing memory size and need for semantic structuring pose significant challenges. In this work, we propose an autonomous memory augmentation approach, MemInsight, to enhance semantic data representation and retrieval mechanisms. By leveraging autonomous augmentation to historical interactions, LLM agents are shown to deliver more accurate and contextualized responses. We empirically validate the efficacy of our proposed approach in three task scenarios; conversational recommendation, question answering and event summarization. On the LLM-REDIAL dataset, MemInsight boosts persuasiveness of recommendations by up to 14%. Moreover, it outperforms a RAG baseline by 34% in recall for LoCoMo retrieval. Our empirical results show the potential of MemInsight to enhance the contextual performance of LLM agents across multiple tasks.
大型语言模型(LLM)代理已经进化到可以智能地处理信息、做出决策以及与用户或工具进行交互。一个关键的能力是融合了长期记忆能力,使这些代理能够利用历史互动和知识。然而,不断增长的内存需求和语义结构的需求构成了重大挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种自主记忆增强方法MemInsight,以增强语义数据表示和检索机制。通过利用对历史互动的自主增强,LLM代理能够提供更准确和情境化的回应。我们通过三项任务场景实证验证了所提出方法的有效性,分别是会话推荐、问题回答和事件摘要。在LLM-REDIAL数据集上,MemInsight将推荐的说服力提高了14%。此外,在LoCoMo检索的召回率方面,它超越了RAG基线34%。我们的实证结果表明,MemInsight在多个任务上增强LLM代理的上下文性能方面具有潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LLM智能代理通过整合长期记忆能力处理信息、做出决策和与用户或工具互动。然而,随着记忆规模的扩大和语义结构的需求增加,带来了挑战。本研究提出一种自主记忆增强方法MemInsight,改进语义数据表示和检索机制。通过利用自主增强对历史互动的利用,LLM代理能提供更准确和情境化的回应。在对话推荐、问答和事件摘要三个任务场景中,MemInsight方法均得到实证验证。在LLM-REDIAL数据集上,MemInsight将推荐的说服力提高了14%。在LoCoMo检索的召回率方面,它比RAG基线高出34%。实证结果表明,MemInsight在多个任务上增强了LLM代理的上下文性能。
Key Takeaways
- LLM智能代理具备长期记忆能力,能处理信息、做出决策和互动。
- 记忆规模的扩大和语义结构需求增加带来挑战。
- 提出自主记忆增强方法MemInsight,改进语义数据表示和检索。
- MemInsight利用自主增强对历史互动的利用,提高LLM代理回应的准确性和情境化。
- 在对话推荐、问答和事件摘要等任务场景中,MemInsight方法表现优异。
- 在LLM-REDIAL数据集上,MemInsight提高了推荐的说服力。
点此查看论文截图


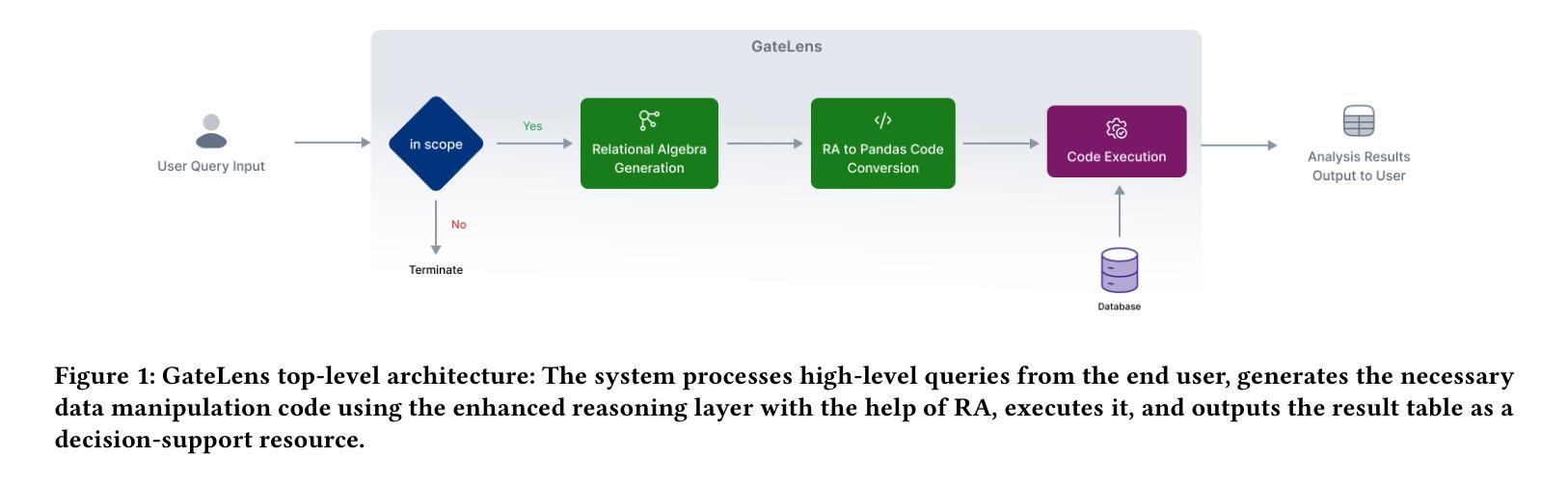
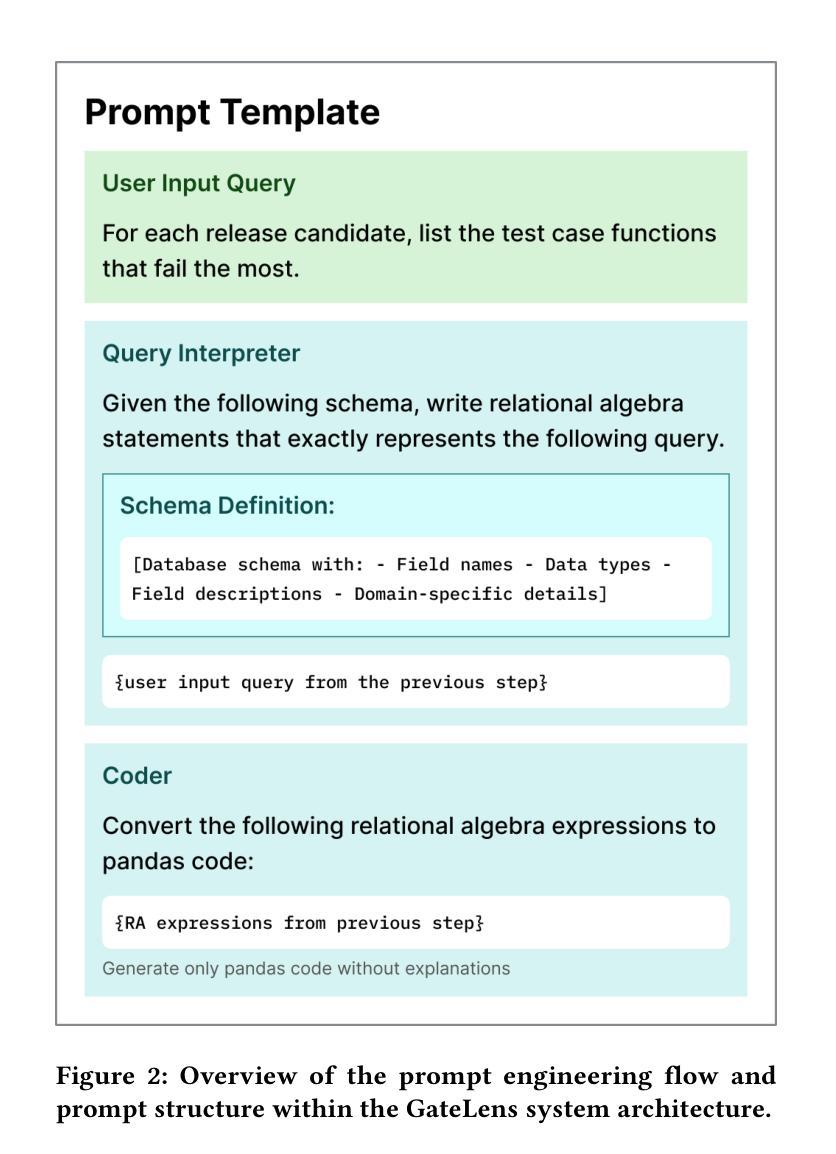
GateLens: A Reasoning-Enhanced LLM Agent for Automotive Software Release Analytics
Authors:Arsham Gholamzadeh Khoee, Shuai Wang, Yinan Yu, Robert Feldt, Dhasarathy Parthasarathy
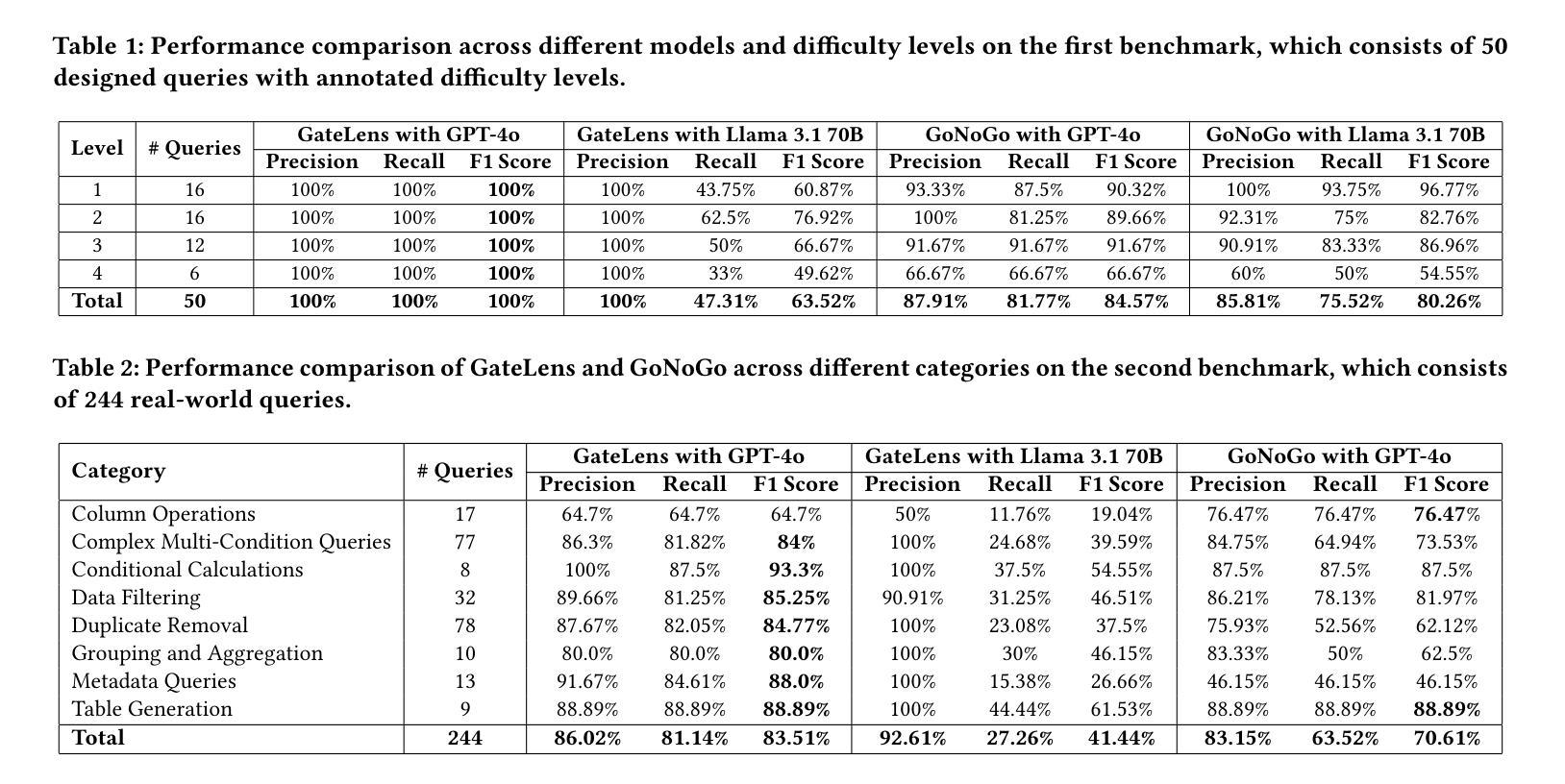
Ensuring the reliability and effectiveness of software release decisions is critical, particularly in safety-critical domains like automotive systems. Precise analysis of release validation data, often presented in tabular form, plays a pivotal role in this process. However, traditional methods that rely on manual analysis of extensive test datasets and validation metrics are prone to delays and high costs. Large Language Models (LLMs) offer a promising alternative but face challenges in analytical reasoning, contextual understanding, handling out-of-scope queries, and processing structured test data consistently; limitations that hinder their direct application in safety-critical scenarios. This paper introduces GateLens, an LLM-based tool for analyzing tabular data in the automotive domain. GateLens translates natural language queries into Relational Algebra (RA) expressions and then generates optimized Python code. It outperforms the baseline system on benchmarking datasets, achieving higher F1 scores and handling complex and ambiguous queries with greater robustness. Ablation studies confirm the critical role of the RA module, with performance dropping sharply when omitted. Industrial evaluations reveal that GateLens reduces analysis time by over 80% while maintaining high accuracy and reliability. As demonstrated by presented results, GateLens achieved high performance without relying on few-shot examples, showcasing strong generalization across various query types from diverse company roles. Insights from deploying GateLens with a partner automotive company offer practical guidance for integrating AI into critical workflows such as release validation. Results show that by automating test result analysis, GateLens enables faster, more informed, and dependable release decisions, and can thus advance software scalability and reliability in automotive systems.
确保软件发布决策的可信度和有效性至关重要,特别是在汽车系统这样的安全关键领域。以表格形式呈现的软件发布验证数据的精确分析在此过程中起着至关重要的作用。然而,传统的方法依赖于对大量测试数据集和验证指标的手动分析,容易出现延迟和成本高昂的问题。大型语言模型(LLM)提供了有前景的替代方案,但在分析推理、上下文理解、处理超出范围查询和处理结构化测试数据一致性方面面临挑战;这些局限性阻碍了它们在安全关键场景中的直接应用。本文介绍了GateLens,一个基于LLM的汽车领域表格数据分析工具。GateLens将自然语言查询翻译成关系代数(RA)表达式,然后生成优化的Python代码。它在基准数据集上的表现优于基准系统,实现了更高的F1分数,并更稳健地处理复杂和模糊查询。消融研究证实了RA模块的关键作用,在省略该模块后性能急剧下降。工业评估表明,GateLens在保持高准确性和可靠性的同时,将分析时间减少了80%以上。结果表明,GateLens在不依赖少量示例的情况下实现了高性能,展示了在各种查询类型中从各种公司角色中强大的泛化能力。通过与合作伙伴汽车公司部署GateLens所获得的见解为将人工智能集成到关键工作流程(如发布验证)中提供了实际指导。结果表明,通过自动化测试结果分析,GateLens能够做出更快、更明智、更可靠的发布决策,从而提高汽车系统软件的可扩展性和可靠性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
软件发布决策在安全性关键领域如汽车系统中的作用至关重要。精确分析以表格形式呈现的发版验证数据在这一过程中起着至关重要的作用。然而,传统方法依赖于对大量测试数据集和验证指标的手动分析,容易出现延误和成本高昂。本论文介绍了一种基于大型语言模型(LLM)的工具——GateLens,用于汽车领域的表格数据分析。GateLens将自然语言查询翻译成关系代数(RA)表达式,并生成优化的Python代码。与基准系统相比,它在基准数据集上的表现更优,实现更高的F1分数并处理复杂和模糊查询的鲁棒性更强。工业评估显示,GateLens减少了超过80%的分析时间,同时保持了高准确性和可靠性。通过展示结果,证明GateLens在不依赖少数示例的情况下实现了高性能,展示了在不同查询类型和各种公司角色中的强大通用性。与合作伙伴汽车公司共同部署GateLens的经验提供了将人工智能集成到关键工作流程(如发布验证)的实际指导。结果表明,通过自动化测试结果分析,GateLens有助于更快、更明智、更可靠的发布决策,从而促进汽车系统中软件的可扩展性和可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- 软件发布决策在安全性关键领域的重要性。
- 传统方法在软件发布验证数据分析中的局限性。
- LLM在软件数据分析中的应用潜力及其挑战。
- GateLens工具引入:基于LLM进行汽车领域表格数据分析的方法。
- GateLens通过RA模块将自然语言查询转化为Python代码的能力及其性能优势。
- GateLens在工业环境中的性能评估和效益:减少了分析时间并提高了准确性和可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

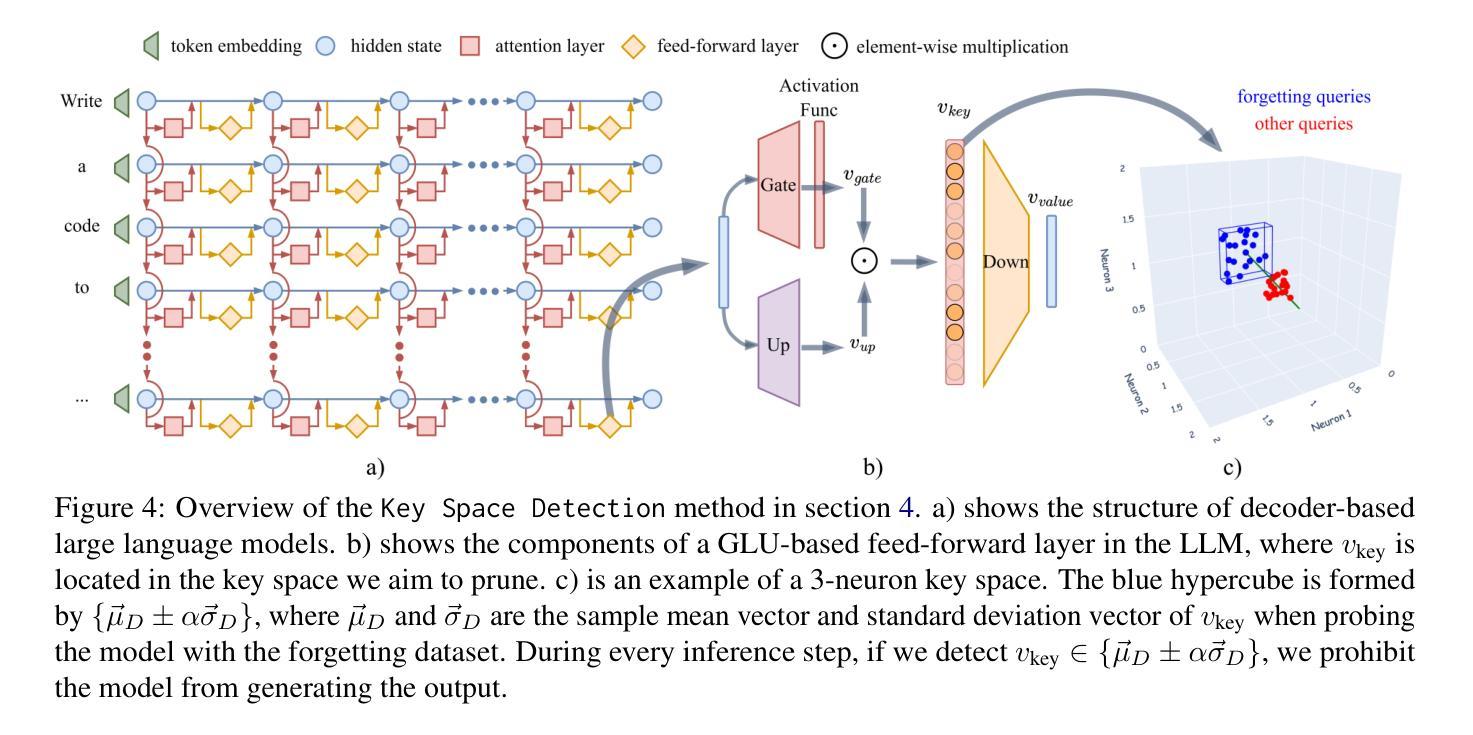
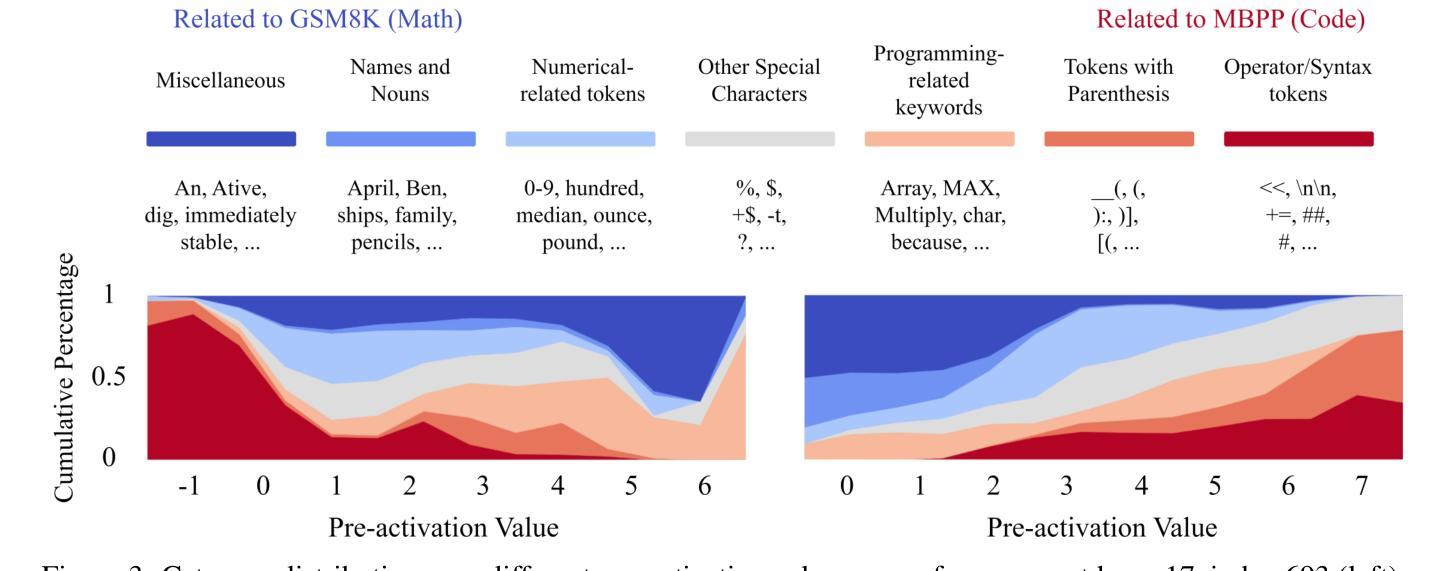
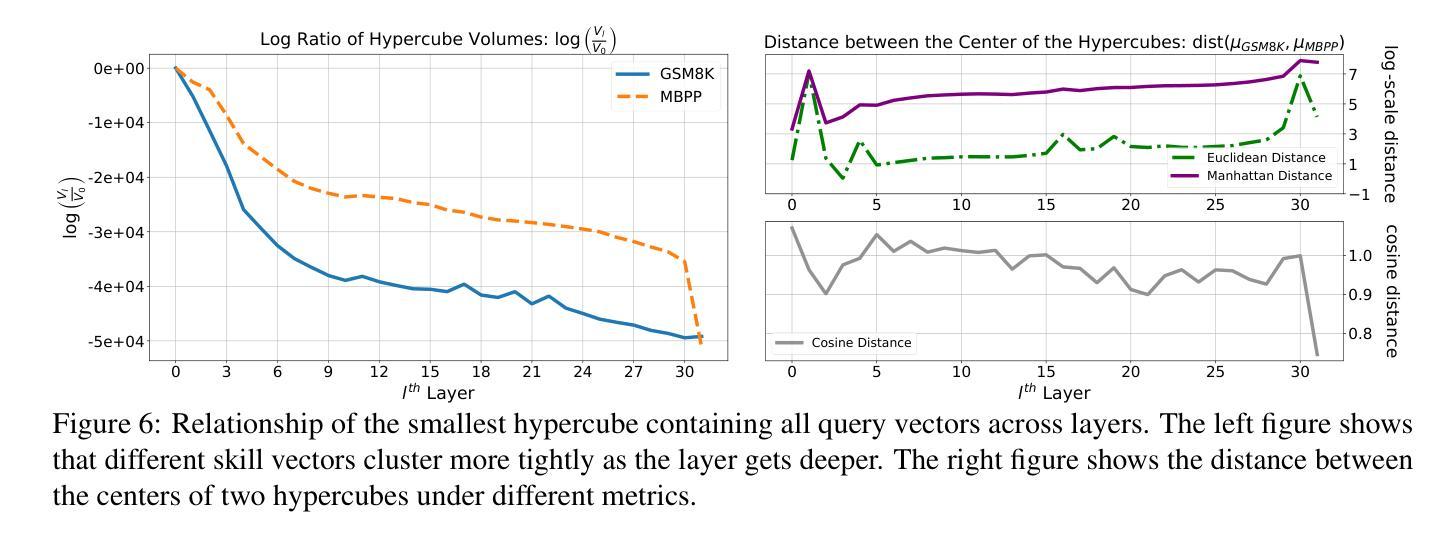
Effective Skill Unlearning through Intervention and Abstention
Authors:Yongce Li, Chung-En Sun, Tsui-Wei Weng
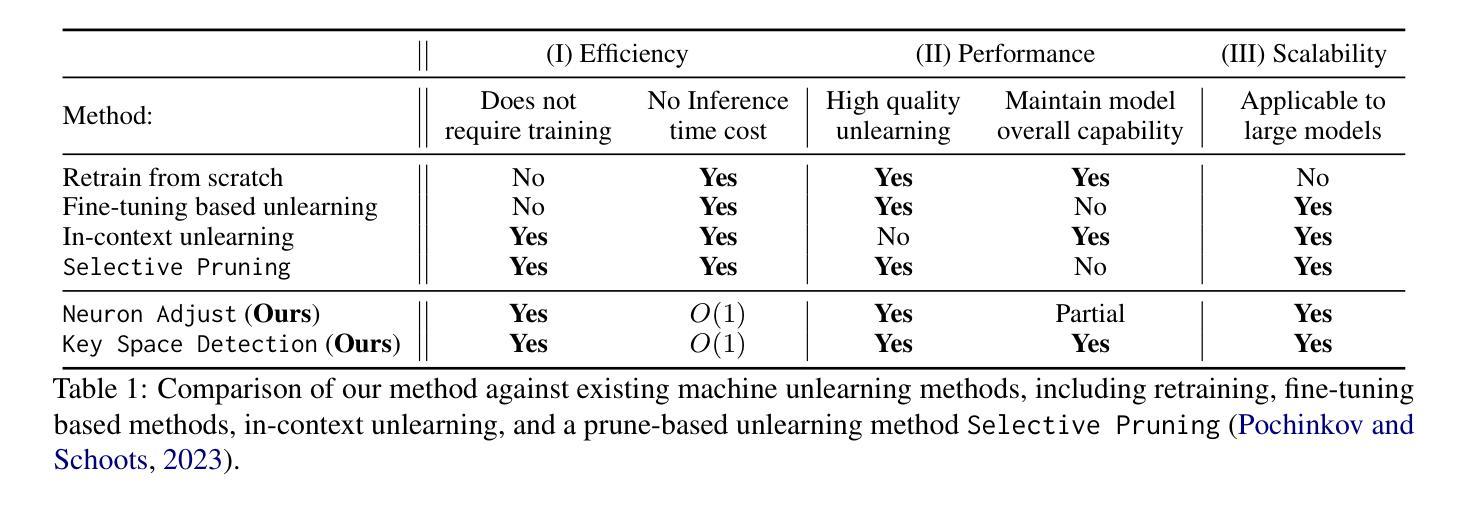
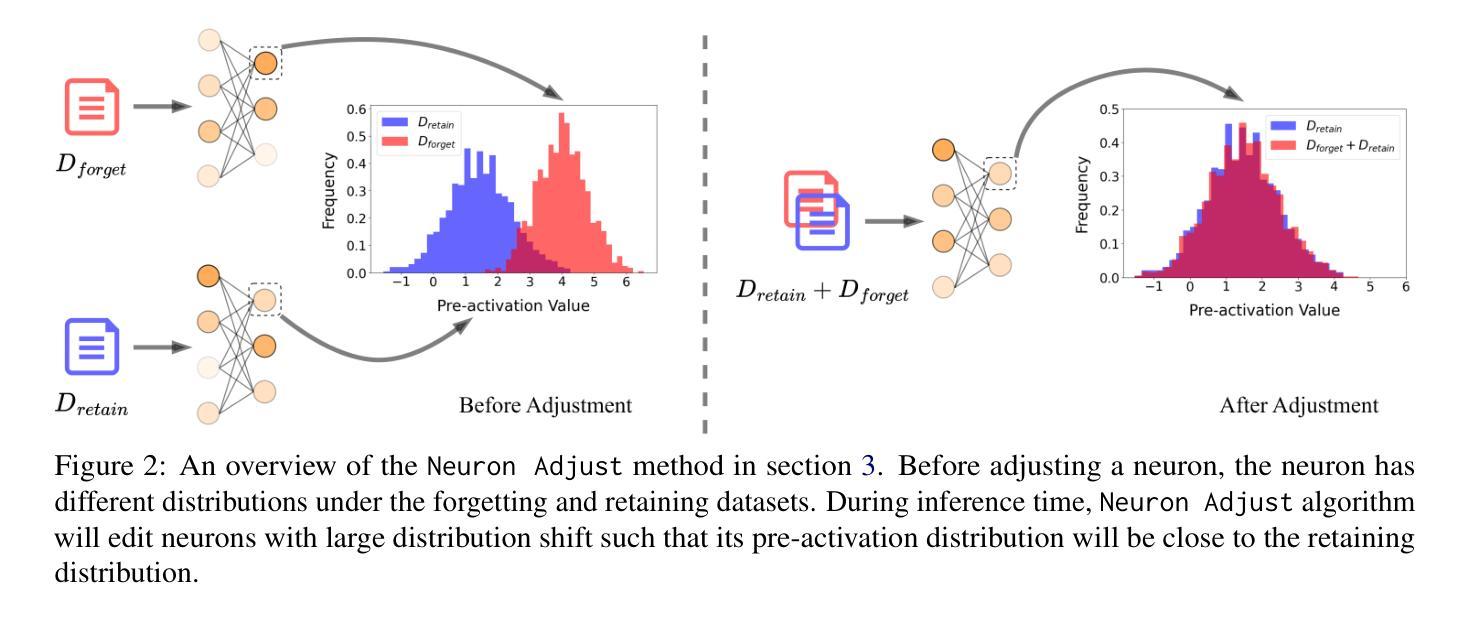
Large language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable skills across various domains. Understanding the mechanisms behind their abilities and implementing controls over them is becoming increasingly important for developing better models. In this paper, we focus on skill unlearning in LLMs, specifically unlearning a particular skill while retaining their overall capabilities. We introduce two lightweight, training-free machine skill unlearning techniques for LLMs. First, we observe that the pre-activation distribution of neurons in each Feed-Forward Layer (FFL) differs when the model demonstrates different skills. Additionally, we find that queries triggering the same skill cluster within the FFL key space and can be separated from other queries using a hypercube. Based on these observations, we propose two lightweight, training-free skill unlearning methods via \textit{intervention} and \textit{abstention} respectively: \texttt{Neuron Adjust} and \texttt{Key Space Detection}. We evaluate our methods on unlearning math-solving, Python-coding, and comprehension skills across seven different languages. The results demonstrate their strong unlearning capabilities for the designated skills. Specifically, \texttt{Key Space Detection} achieves over 80% relative performance drop on the forgetting skill and less than 10% relative performance drop on other skills and the model’s general knowledge (MMLU) for most unlearning tasks. Our code is available at https://github.com/Trustworthy-ML-Lab/effective_skill_unlearning
大型语言模型(LLM)在各种领域表现出了卓越的技能。了解它们能力背后的机制并对它们进行控制,对于开发更好的模型来说变得越来越重要。本文中,我们关注LLM中的技能遗忘,特别是遗忘特定技能的同时保持其整体能力。我们为LLM引入两种轻量级的、无需训练的技能遗忘技术。首先,我们观察到每个前馈层(FFL)的神经元预激活分布在不同技能展示时存在差异。此外,我们发现触发相同技能的查询会在FFL密钥空间内聚簇,可以使用超立方体将其与其他查询分开。基于这些观察,我们分别通过“干预”和“弃权”提出了两种轻量级的、无需训练的技能遗忘方法:神经元调整和密钥空间检测。我们在七种不同语言上对数学求解、Python编码和理解技能的遗忘进行了评估。结果表明它们在指定技能上的遗忘能力很强。具体来说,密钥空间检测在遗忘技能上实现了超过80%的相对性能下降,而在其他技能和模型的一般知识(MMLU)上,对于大多数遗忘任务,相对性能下降不到10%。我们的代码位于https://github.com/Trustworthy-ML-Lab/effective_skill_unlearning。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to NAACL 2025 main conference
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的技能忘却研究已经引起关注。本文提出两种轻量级的、无需训练的语言模型技能忘却技术,分别为“神经元调整”和“关键空间检测”。这两种方法基于神经元的预激活分布和关键空间内的查询聚类观察,可以在不训练的情况下实现特定技能的忘却,同时保留模型的整体能力。在多种语言和技能上的实验结果表明,这些方法在忘却指定技能方面表现出强大的能力。
Key Takeaways
- LLM的技能忘却对于开发更好的模型至关重要。
- 本文介绍两种轻量级的、无需训练的技能忘却技术:神经元调整和关键空间检测。
- 神经元预激活分布和关键空间内的查询聚类是技能忘却的关键。
- 神经元调整通过干预方式实现技能忘却。
- 关键空间检测通过识别并隔离特定技能相关查询来实现技能忘却。
- 在多种语言和技能上的实验验证了这两种方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

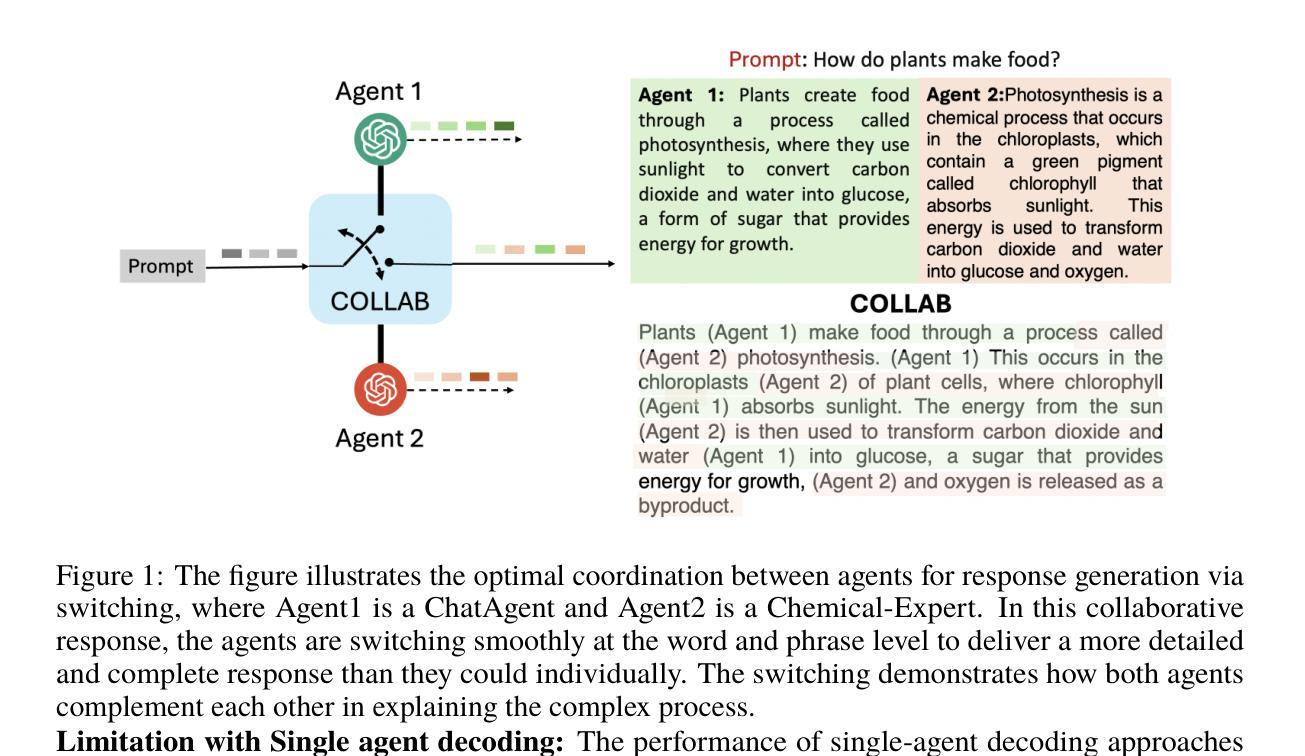
Collab: Controlled Decoding using Mixture of Agents for LLM Alignment
Authors:Souradip Chakraborty, Sujay Bhatt, Udari Madhushani Sehwag, Soumya Suvra Ghosal, Jiahao Qiu, Mengdi Wang, Dinesh Manocha, Furong Huang, Alec Koppel, Sumitra Ganesh
Alignment of Large Language models (LLMs) is crucial for safe and trustworthy deployment in applications. Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) has emerged as an effective technique to align LLMs to human preferences and broader utilities, but it requires updating billions of model parameters, which is computationally expensive. Controlled Decoding, by contrast, provides a mechanism for aligning a model at inference time without retraining. However, single-agent decoding approaches often struggle to adapt to diverse tasks due to the complexity and variability inherent in these tasks. To strengthen the test-time performance w.r.t the target task, we propose a mixture of agent-based decoding strategies leveraging the existing off-the-shelf aligned LLM policies. Treating each prior policy as an agent in the spirit of mixture of agent collaboration, we develop a decoding method that allows for inference-time alignment through a token-level selection strategy among multiple agents. For each token, the most suitable LLM is dynamically chosen from a pool of models based on a long-term utility metric. This policy-switching mechanism ensures optimal model selection at each step, enabling efficient collaboration and alignment among LLMs during decoding. Theoretical analysis of our proposed algorithm establishes optimal performance with respect to the target task represented via a target reward for the given off-the-shelf models. We conduct comprehensive empirical evaluations with open-source aligned models on diverse tasks and preferences, which demonstrates the merits of this approach over single-agent decoding baselines. Notably, Collab surpasses the current SoTA decoding strategy, achieving an improvement of up to 1.56x in average reward and 71.89% in GPT-4 based win-tie rate.
大型语言模型(LLM)的对齐对于其在应用中的安全和可信部署至关重要。强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)作为一种有效的技术,能够将LLM与人类偏好和更广泛的实用性对齐,但更新数十亿模型参数的需求带来了巨大的计算成本。相比之下,受控解码提供了一种在推理时对齐模型而无需重新训练机制。然而,由于任务的复杂性和固有变化性,单一智能体解码方法往往难以适应多样化的任务。为了加强针对目标任务的测试性能,我们提出了一种基于智能体的解码策略混合方法,利用现有的现成的对齐LLM策略。将每个先前策略视为智能体,在智能体协作混合的精神下,我们开发了一种解码方法,它允许通过标记级别的选择策略在不同的智能体之间进行推理时对齐。对于每个标记,会从模型中动态选择最合适的LLM,选择依据是长期效用指标。这种策略切换机制确保了每一步的最优模型选择,使得LLM在解码过程中能够进行有效的协作和对齐。我们提出算法的理论分析证明了对于给定现成的模型,通过目标奖励表示的目标任务的性能最优。我们在多样化的任务和偏好上对开源对齐模型进行了全面的实证评估,证明了该方法相对于单一智能体解码基线方法的优势。值得注意的是,Collab超越了当前的最新解码策略,平均奖励提高了1.56倍,GPT-4的胜率提高了71.89%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR 2025
摘要
大语言模型(LLM)的对齐对于其在应用中的安全和可信部署至关重要。强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)是一种有效的对齐技术,但需要更新数十亿的模型参数,计算成本高。相比之下,受控解码提供了一种在推理阶段对齐模型而无需重新训练的方法。然而,单代理解码方法往往难以适应多样化的任务。为了强化其在目标任务的测试性能,我们提出了一种基于代理的解码策略混合方法,利用现有的对齐LLM策略。我们将每个先前策略视为一种代理,开发了一种解码方法,允许在多个代理之间进行令牌级别的选择策略,从而在推理阶段进行对齐。对于每个令牌,从模型池中动态选择最合适的LLM,基于长期效用指标。这种策略切换机制确保了每步的最优模型选择,使得LLM在解码过程中的协作和对齐更加高效。我们通过对现有模型进行理论分析和在多样化任务和偏好上的实证评估,证明了该方法优于单代理解码基线。特别地,“Collab”策略超越了当前最佳解码策略,平均奖励提高了1.56倍,GPT-4的胜率提高了71.89%。
关键见解
- LLM的对齐对于其在实际应用中的安全和可靠部署至关重要。
- 强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)是一种有效的LLM对齐技术,但计算成本较高。
- 受控解码是一种在推理阶段对齐LLM而无需重新训练的方法。
- 单代理解码方法在面对多样化任务时可能难以适应。
- 提出了一种基于代理的解码策略混合方法,利用现有的对齐LLM策略。
- 对每个令牌,该方法从模型池中动态选择最合适的LLM。
- “Collab”策略在多样化任务上表现优异,超越了当前最佳解码策略。
点此查看论文截图

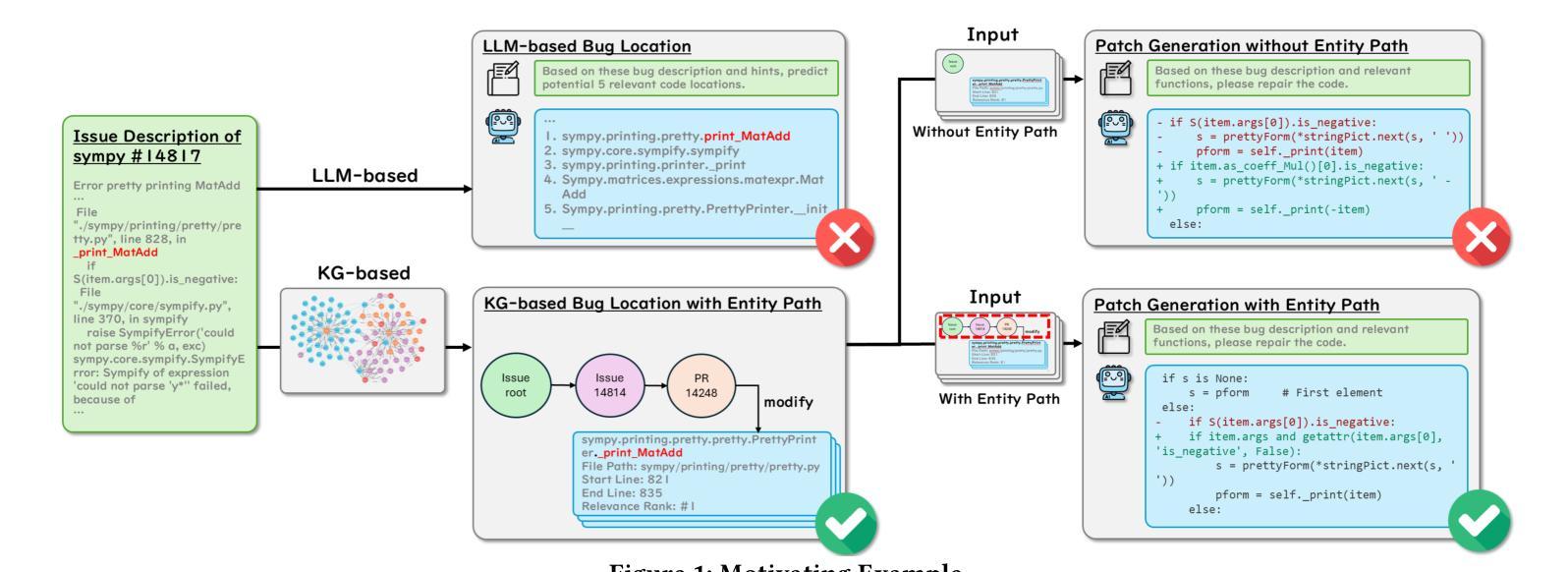
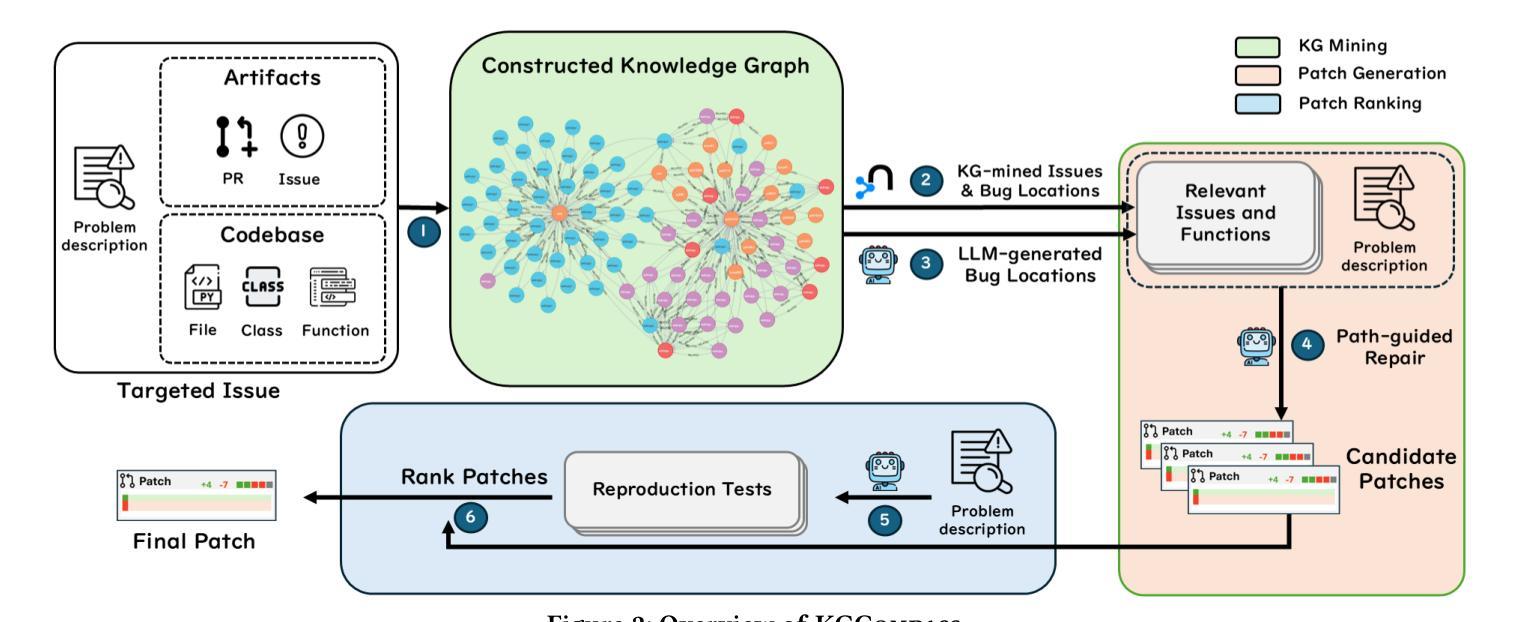
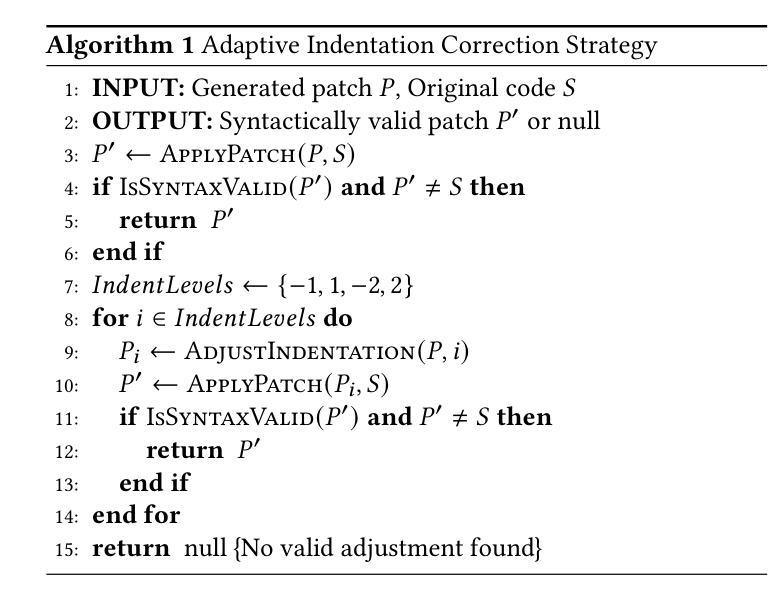
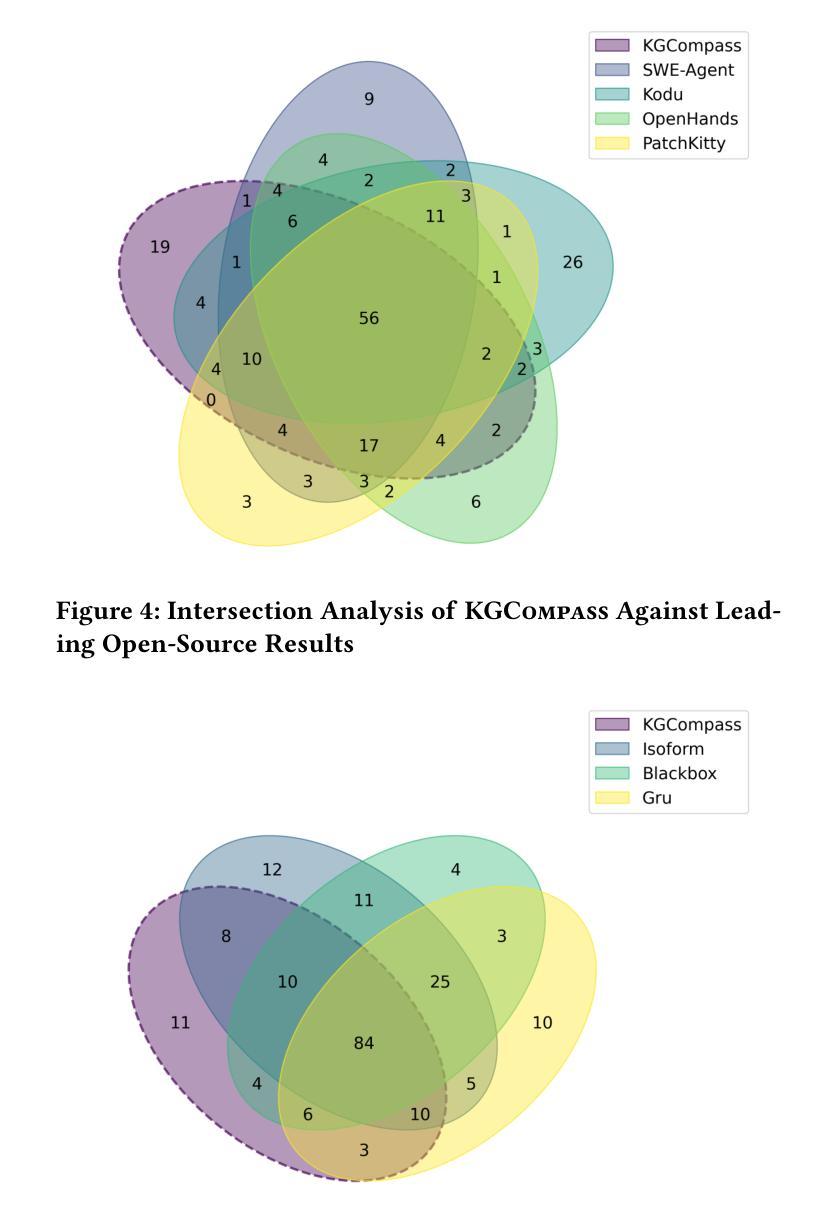
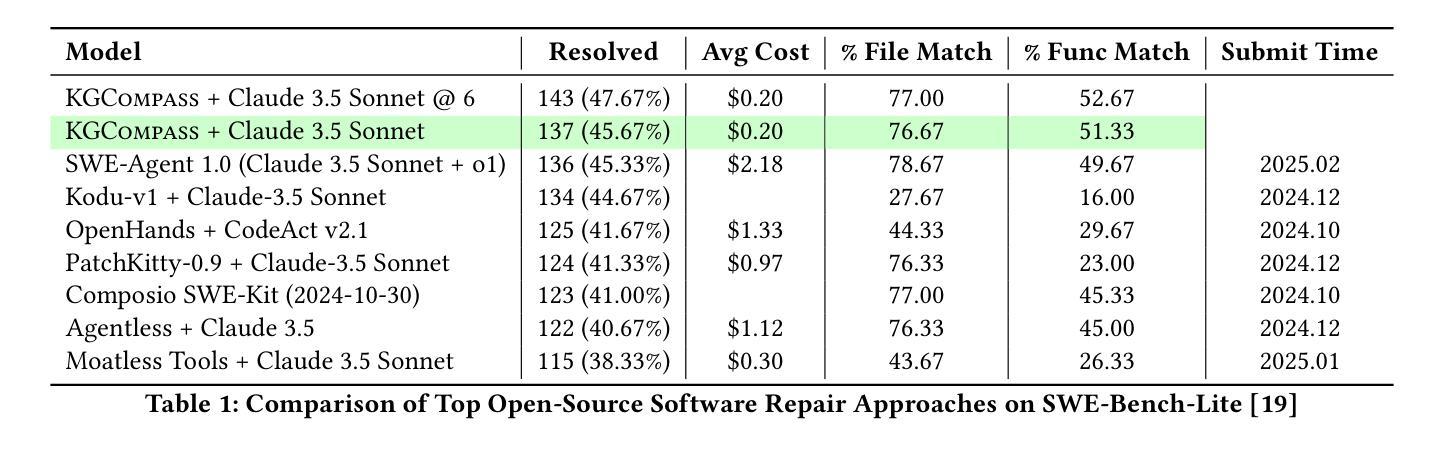
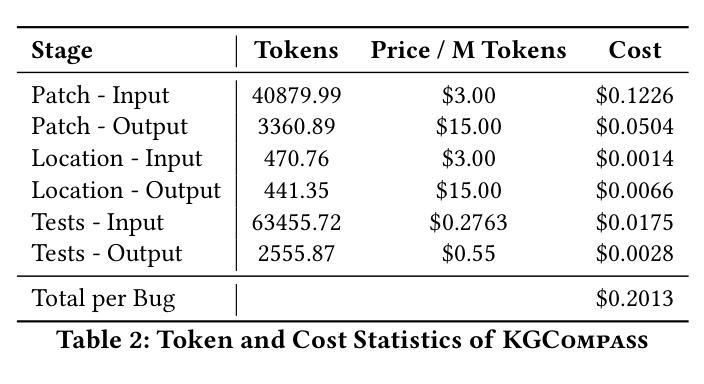
Enhancing Repository-Level Software Repair via Repository-Aware Knowledge Graphs
Authors:Boyang Yang, Haoye Tian, Jiadong Ren, Shunfu Jin, Yang Liu, Feng Liu, Bach Le
Repository-level software repair faces challenges in bridging semantic gaps between issue descriptions and code patches. Existing approaches, which mostly depend on large language models (LLMs), suffer from semantic ambiguities, limited structural context understanding, and insufficient reasoning capability. To address these limitations, we propose KGCompass with two innovations: (1) a novel repository-aware knowledge graph (KG) that accurately links repository artifacts (issues and pull requests) and codebase entities (files, classes, and functions), allowing us to effectively narrow down the vast search space to only 20 most relevant functions with accurate candidate bug locations and contextual information, and (2) a path-guided repair mechanism that leverages KG-mined entity path, tracing through which allows us to augment LLMs with relevant contextual information to generate precise patches along with their explanations. Experimental results in the SWE-Bench-Lite demonstrate that KGCompass achieves state-of-the-art repair performance (45.67%) and function-level localization accuracy (51.33%) across open-source approaches, costing only $0.20 per repair. Our analysis reveals that among successfully localized bugs, 69.7% require multi-hop traversals through the knowledge graph, without which LLM-based approaches struggle to accurately locate bugs. The knowledge graph built in KGCompass is language agnostic and can be incrementally updated, making it a practical solution for real-world development environments.
软件仓库级修复面临着缩小问题描述和代码补丁之间语义差距的挑战。现有方法大多依赖于大型语言模型(LLM),存在语义模糊、结构上下文理解有限和推理能力不足的问题。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了KGCompass,其中包含两项创新:(1)一种新型仓库感知知识图谱(KG),能够准确链接仓库工件(问题和拉取请求)和代码库实体(文件、类和函数),从而有效地将庞大的搜索空间缩小到仅20个最相关的函数,并准确提供候选错误位置和上下文信息;(2)一种路径引导修复机制,它利用知识图谱挖掘的实体路径,通过跟踪相关上下文信息来增强LLM的能力,生成精确的补丁及其解释。在SWE-Bench-Lite的实验结果表明,KGCompass在开源方法中实现了最先进的修复性能(45.67%)和功能级别的定位精度(51.33%),每次修复成本仅为0.2美元。我们的分析表明,在成功定位的漏洞中,有69.7%需要通过知识图谱进行多跳遍历,没有这些知识图谱的帮助,基于LLM的方法很难准确定位漏洞。KGCompass中构建的知识图谱与语言无关,可以增量更新,使其成为适用于真实开发环境的实用解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了针对软件修复过程中语义鸿沟问题的KGCompass方案。该方案通过构建知识图谱和路径引导修复机制,实现了对代码库中问题描述与代码补丁之间语义差异的准确理解和衔接。知识图谱可缩小大规模搜索空间并精准定位到代码功能实体,从而提高软件修复的准确率和效率。此外,该方案基于知识图谱挖掘的实体路径指导修复机制,增强了大型语言模型的上下文理解能力,生成精准的代码补丁及其解释。实验结果表明,KGCompass在SWE-Bench-Lite数据集上取得了领先的修复性能和函数定位精度,且成本较低。分析显示,成功定位的问题中有相当一部分需要跨多个节点在知识图谱中进行遍历,这对于单纯依赖大型语言模型的方案来说是一项挑战。KGCompass构建的知识图谱具有语言无关性和可增量更新的特点,适用于实际开发环境。
Key Takeaways
- KGCompass解决了软件修复中语义鸿沟的问题,通过构建知识图谱和路径引导修复机制提高了软件修复的准确率和效率。
- 知识图谱能够缩小搜索空间并精准定位到代码功能实体,增强大型语言模型的上下文理解能力。
- KGCompass在SWE-Bench-Lite数据集上实现了领先的修复性能和函数定位精度,成本较低。
- 成功定位的问题中有相当一部分需要跨多个节点在知识图谱中进行遍历,单纯依赖大型语言模型的方案难以解决。
- KGCompass构建的知识图谱具有语言无关性和可增量更新的特点。
- KGCompass方案包括两个创新点:构建仓库感知的知识图谱和利用知识图谱进行路径引导修复机制。
点此查看论文截图

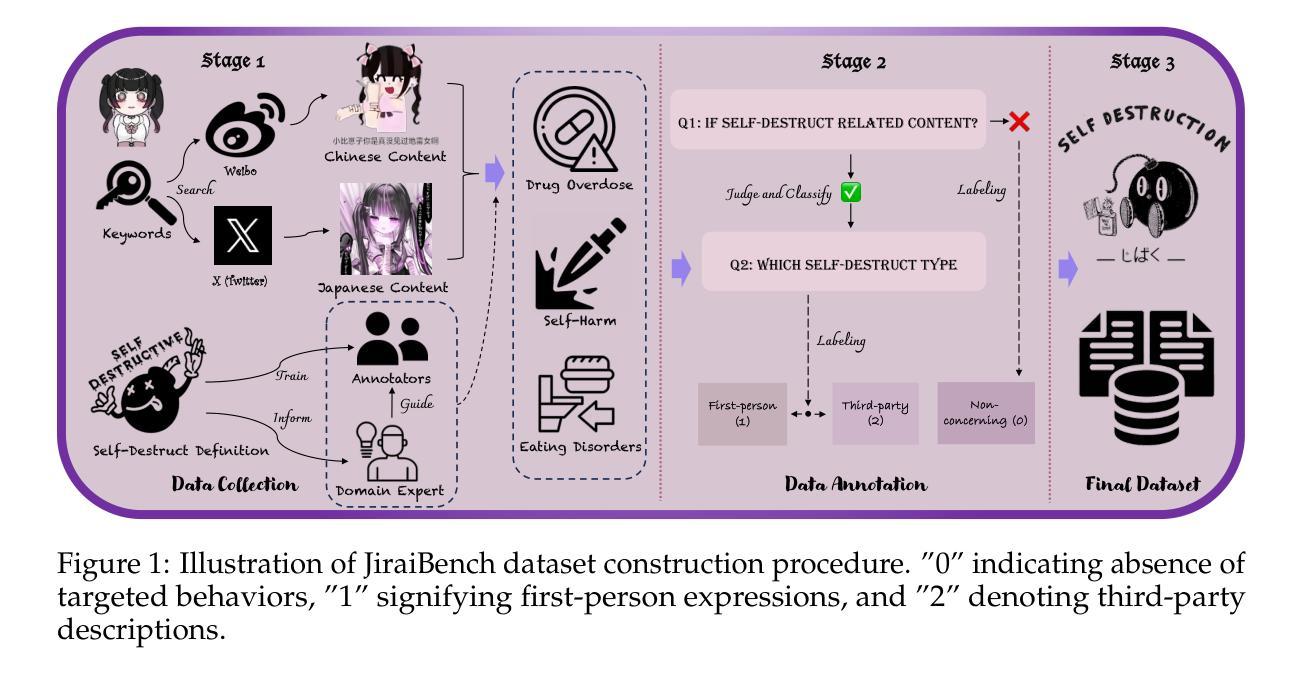
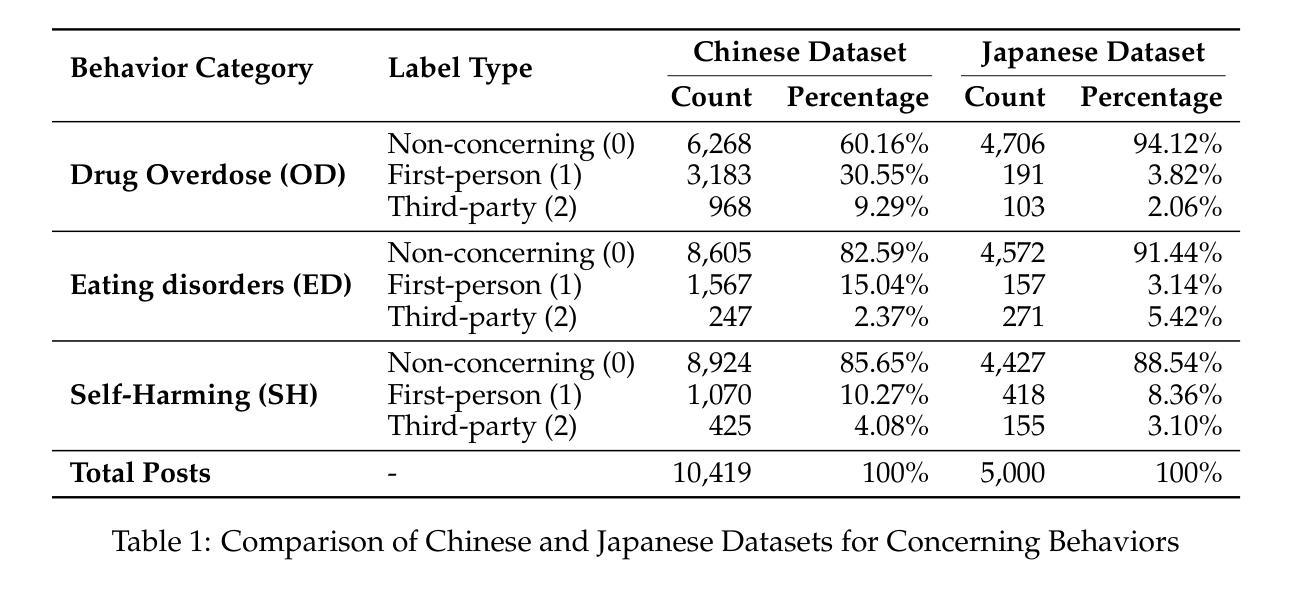
JiraiBench: A Bilingual Benchmark for Evaluating Large Language Models’ Detection of Human Self-Destructive Behavior Content in Jirai Community
Authors:Yunze Xiao, Tingyu He, Lionel Z. Wang, Yiming Ma, Xingyu Song, Xiaohang Xu, Irene Li, Ka Chung Ng
This paper introduces JiraiBench, the first bilingual benchmark for evaluating large language models’ effectiveness in detecting self-destructive content across Chinese and Japanese social media communities. Focusing on the transnational “Jirai” (landmine) online subculture that encompasses multiple forms of self-destructive behaviors including drug overdose, eating disorders, and self-harm, we present a comprehensive evaluation framework incorporating both linguistic and cultural dimensions. Our dataset comprises 10,419 Chinese posts and 5,000 Japanese posts with multidimensional annotation along three behavioral categories, achieving substantial inter-annotator agreement. Experimental evaluations across four state-of-the-art models reveal significant performance variations based on instructional language, with Japanese prompts unexpectedly outperforming Chinese prompts when processing Chinese content. This emergent cross-cultural transfer suggests that cultural proximity can sometimes outweigh linguistic similarity in detection tasks. Cross-lingual transfer experiments with fine-tuned models further demonstrate the potential for knowledge transfer between these language systems without explicit target language training. These findings highlight the need for culturally-informed approaches to multilingual content moderation and provide empirical evidence for the importance of cultural context in developing more effective detection systems for vulnerable online communities.
本文介绍了JiraiBench,这是首个针对大型语言模型在中文和日文社交媒体社区中检测自我毁灭性内容效果的双语基准测试。我们以跨国界的“Jirai”(地雷)在线亚文化为焦点,该文化包含多种自我毁灭性行为,包括药物过量、饮食失调和自我伤害。我们提出了一个全面的评估框架,该框架结合了语言和文化的双重维度。我们的数据集包含10419个中文帖子和5000个日文帖子,这些帖子按照三种行为类别进行了多维注释,并实现了相当大的标注间一致性。对四种最先进模型的实验评估显示,不同语言的提示指导下的性能存在显著差异,在处理中文内容时,日语提示出乎意料地优于中文提示。这种跨文化的转移表明,文化相似性有时不如文化接近度在检测任务中的重要性大。经过精细调整的模型的语言转移实验进一步证明了在这些语言系统之间进行知识转移而不进行明确的目标语言训练的潜力。这些发现强调了跨文化内容审查的需要,并为开发针对脆弱在线社区的更有效的检测系统提供了重要的文化背景的实证证据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 1 figures
Summary
本文介绍了JiraiBench,首个针对中文和日语社交媒体社区中自我破坏性内容检测效果评估的双语基准测试。文章聚焦于跨国“Jirai”(地雷)在线亚文化,涵盖多种自我破坏性行为,如药物过量、饮食失调和自我伤害。文章提出了一个综合评估框架,该框架结合了语言和文化的维度。数据集包含10,419篇中文帖子和5,000篇日语帖子,按三个行为类别进行多维度注释,实现了显著的标注间一致性。实验评估表明,基于指令语言的性能存在显著差异,在处理中文内容时,日语提示出人意料地优于中文提示。这种跨文化的转移表明,在某些检测任务中,文化接近度有时会超过语言相似性。对精细调整过的模型进行跨语言转移实验,进一步证明了在不同语言系统之间进行知识转移而不进行明确的目标语言训练的潜力。这些发现强调了跨文化方法在多元语言内容管理中的重要性,并为开发针对脆弱在线社区的更有效检测系统提供了实证证据。
Key Takeaways
- 文章介绍了JiraiBench,它是首个针对自我破坏性内容检测的双语基准测试。
- 测试涵盖中文和日语社交媒体上的“Jirai”在线亚文化内容,包括多种自我破坏性行为的评估。
- 评估框架结合了语言和文化的维度。
- 数据集包含大量中文和日语帖子,标注一致性强。
- 实验显示,不同语言的指令会影响模型性能,有时日语提示在中文内容检测中表现更好。
- 跨语言实验表明不同语言系统间的知识转移潜力。
点此查看论文截图

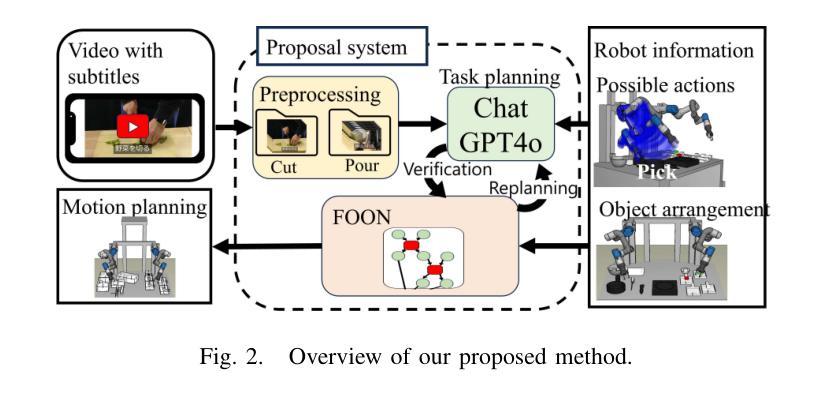
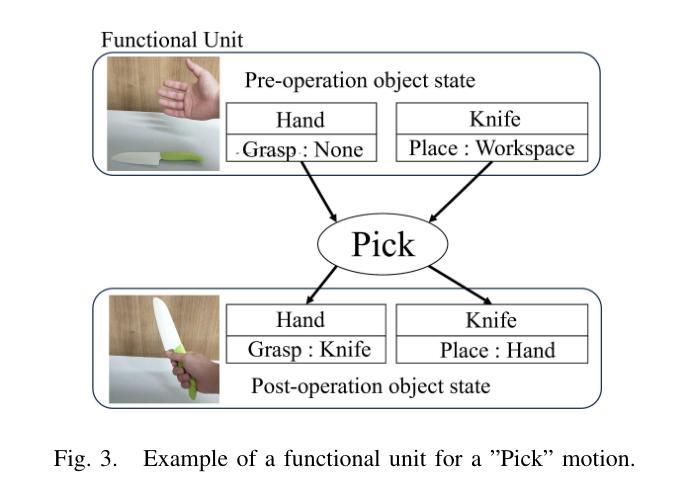
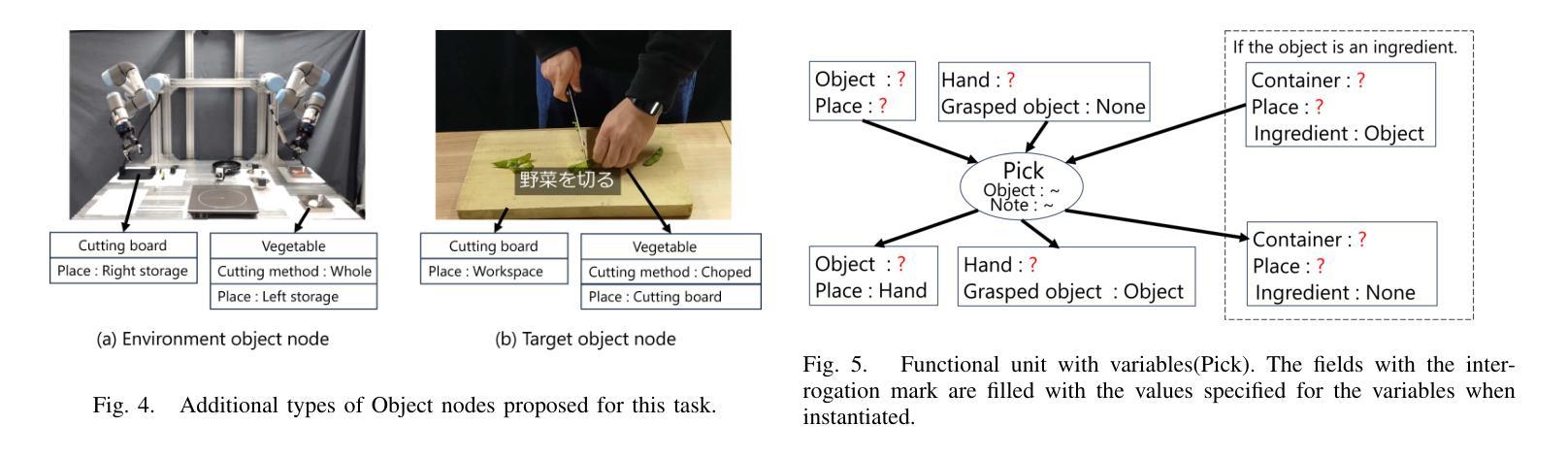
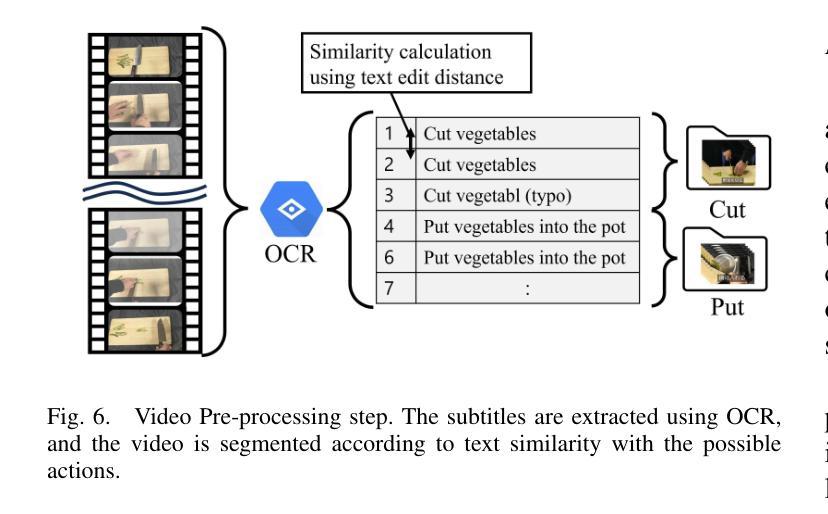
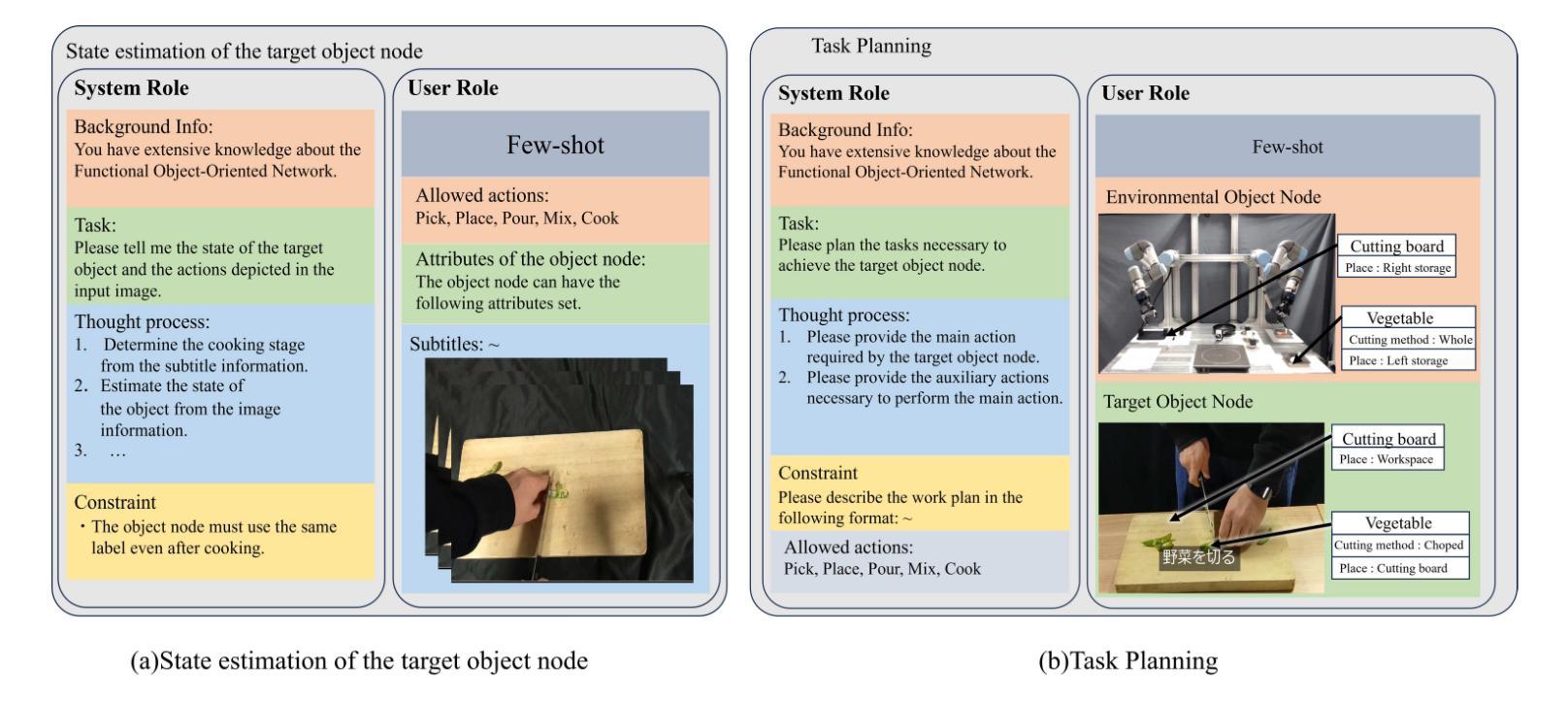
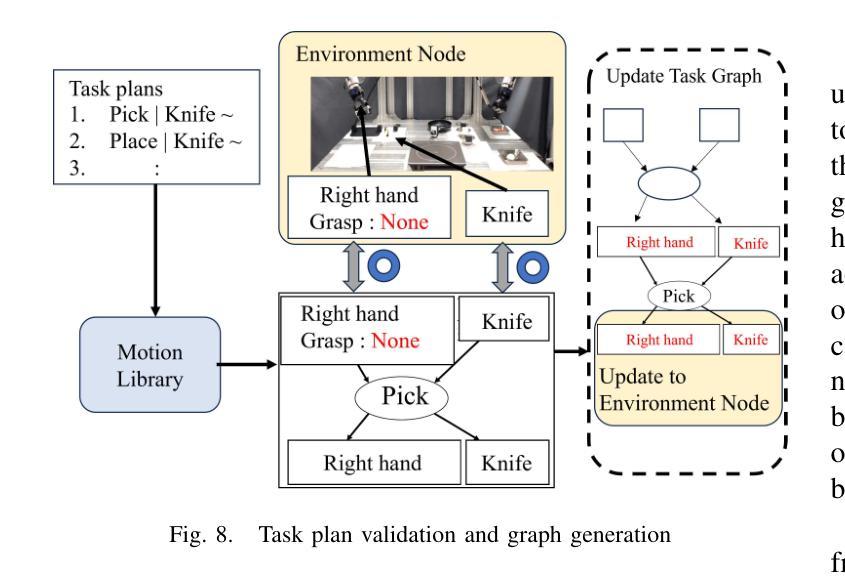
Cooking Task Planning using LLM and Verified by Graph Network
Authors:Ryunosuke Takebayashi, Vitor Hideyo Isume, Takuya Kiyokawa, Weiwei Wan, Kensuke Harada
Cooking tasks remain a challenging problem for robotics due to their complexity. Videos of people cooking are a valuable source of information for such task, but introduces a lot of variability in terms of how to translate this data to a robotic environment. This research aims to streamline this process, focusing on the task plan generation step, by using a Large Language Model (LLM)-based Task and Motion Planning (TAMP) framework to autonomously generate cooking task plans from videos with subtitles, and execute them. Conventional LLM-based task planning methods are not well-suited for interpreting the cooking video data due to uncertainty in the videos, and the risk of hallucination in its output. To address both of these problems, we explore using LLMs in combination with Functional Object-Oriented Networks (FOON), to validate the plan and provide feedback in case of failure. This combination can generate task sequences with manipulation motions that are logically correct and executable by a robot. We compare the execution of the generated plans for 5 cooking recipes from our approach against the plans generated by a few-shot LLM-only approach for a dual-arm robot setup. It could successfully execute 4 of the plans generated by our approach, whereas only 1 of the plans generated by solely using the LLM could be executed.
烹饪任务仍然是机器人技术面临的挑战,因为这些任务的复杂性。人们烹饪的视频是这类任务的重要信息来源,但如何将这类数据转化为机器人环境存在很大的变数。本研究旨在简化这一过程,重点关注任务计划生成步骤,通过使用基于大型语言模型(LLM)的任务和动作规划(TAMP)框架,自主地从带字幕的视频生成烹饪任务计划,并执行它们。由于视频中的不确定性以及输出的虚构风险,传统的基于LLM的任务规划方法并不适合解释烹饪视频数据。为了解决这两个问题,我们探索将LLM与面向功能对象的网络(FOON)相结合,以验证计划并在失败时提供反馈。这种结合可以生成逻辑正确且机器人可执行的带有操作动作的任务序列。我们将从我们的方法生成的5个烹饪食谱的任务执行与仅使用LLM生成的任务计划进行比较,用于双机械臂机器人设置。我们的方法生成的任务计划中有四个可以成功执行,而仅使用LLM生成的任务计划中只有一个可以执行。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了利用大型语言模型(LLM)和任务与动作规划(TAMP)框架,从带有字幕的烹饪视频自主生成任务计划并执行的问题。针对烹饪视频数据的不确定性及输出可能出现的幻觉风险,结合功能面向对象网络(FOON)进行验证和反馈。该组合能生成逻辑正确、机器人可执行的带操作动作的任务序列。对比实验显示,对于双机械臂机器人设置,使用此方法生成的计划成功执行了四项烹饪食谱,而仅使用LLM的计划仅成功执行一项。
Key Takeaways
- 烹饪任务仍然是机器人技术面临的挑战之一,而视频中的烹饪过程是一个有价值的信息来源。
- 使用大型语言模型(LLM)进行任务规划对于烹饪视频数据的解读存在不确定性及输出幻觉的风险。
- 本文结合了大型语言模型和基于功能面向对象网络(FOON)的方法来解决上述问题。
- 通过组合大型语言模型和FOON网络,能够生成逻辑正确且机器人可执行的带操作动作的任务序列。
- 对比实验表明,对于双机械臂机器人设置,使用结合大型语言模型和FOON的方法生成的计划执行成功率更高。
- 本文旨在通过自动化生成任务计划来简化从烹饪视频到机器人环境的翻译过程。
点此查看论文截图

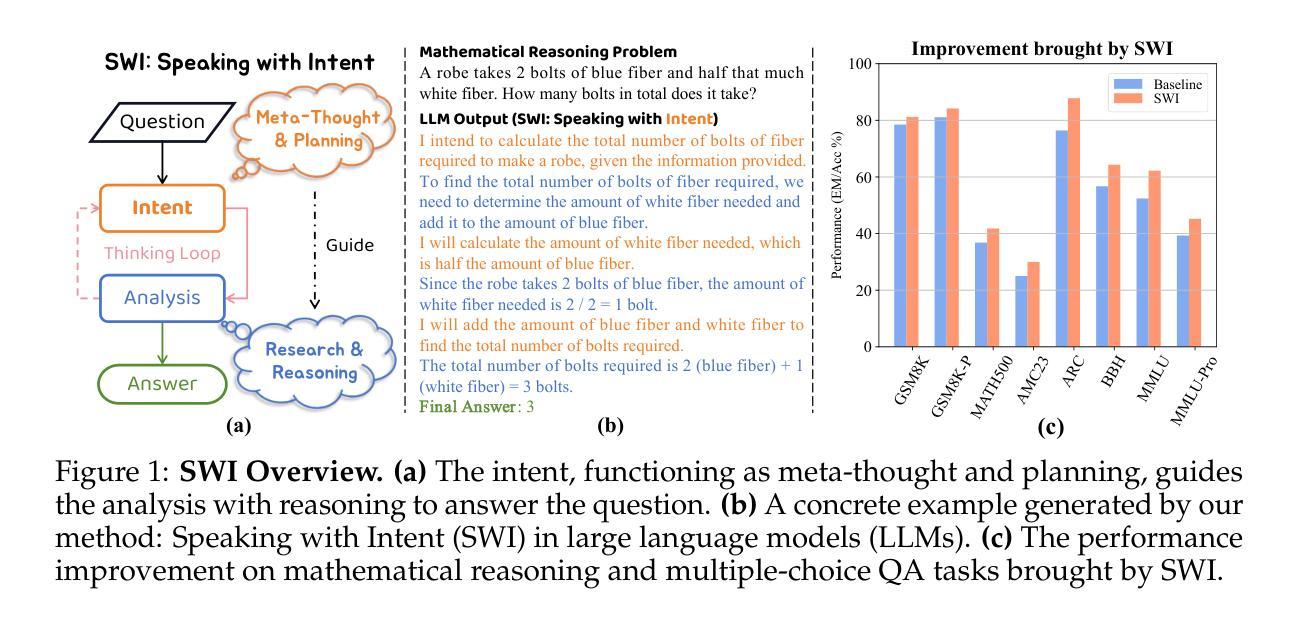
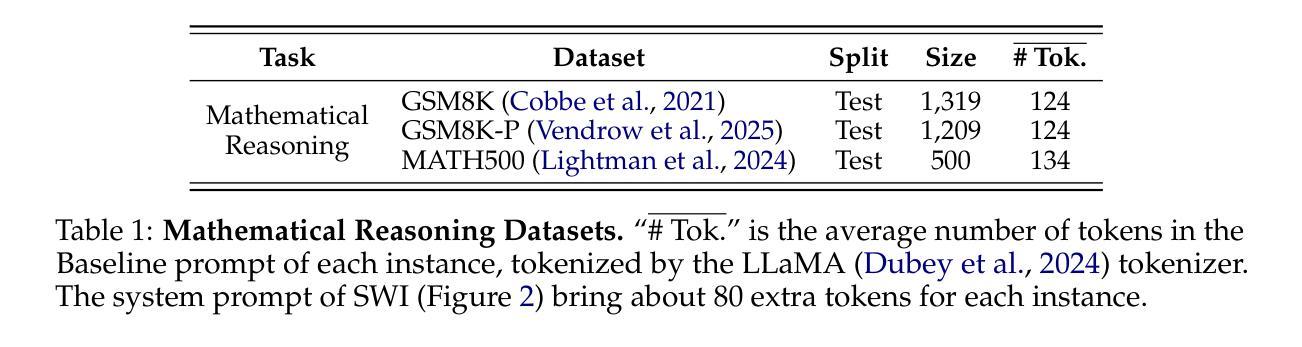
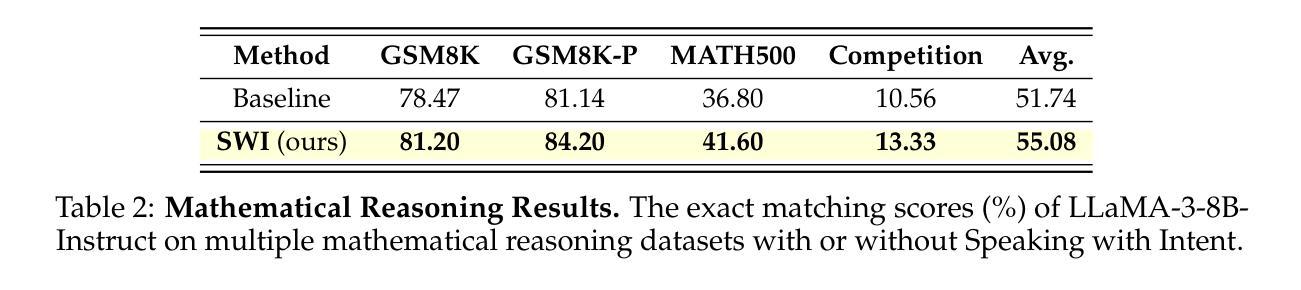
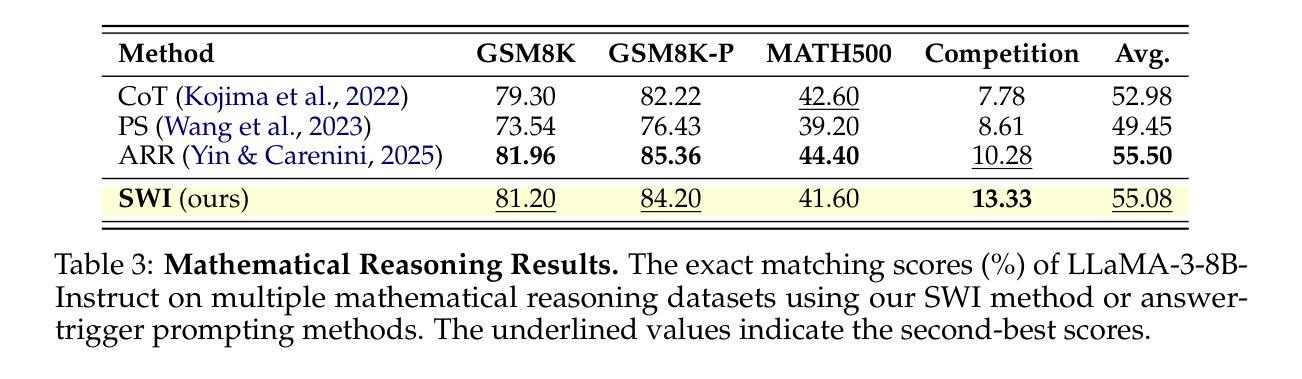
SWI: Speaking with Intent in Large Language Models
Authors:Yuwei Yin, EunJeong Hwang, Giuseppe Carenini
Intent, typically clearly formulated and planned, functions as a cognitive framework for reasoning and problem-solving. This paper introduces the concept of Speaking with Intent (SWI) in large language models (LLMs), where the explicitly generated intent encapsulates the model’s underlying intention and provides high-level planning to guide subsequent analysis and communication. By emulating deliberate and purposeful thoughts in the human mind, SWI is hypothesized to enhance the reasoning capabilities and generation quality of LLMs. Extensive experiments on mathematical reasoning benchmarks consistently demonstrate the superiority of Speaking with Intent over Baseline (i.e., generation without explicit intent). Moreover, SWI outperforms answer-trigger prompting methods Chain-of-Thought and Plan-and-Solve and maintains competitive performance with the strong method ARR (Analyzing, Retrieving, and Reasoning). Additionally, the effectiveness and generalizability of SWI are solidified on reasoning-intensive question answering (QA) and text summarization benchmarks, where SWI brings consistent improvement to the Baseline generation. In text summarization, SWI-generated summaries exhibit greater accuracy, conciseness, and factual correctness, with fewer hallucinations. Furthermore, human evaluations verify the coherence, effectiveness, and interpretability of the intent produced by SWI. This proof-of-concept study creates a novel avenue for enhancing LLMs’ reasoning abilities with cognitive notions.
意图通常被明确制定和计划,作为推理和解决问题的认知框架。本文介绍了大型语言模型(LLM)中的“有意表达”(SWI)的概念,其中明确生成的意图涵盖了模型的基本意图,并为随后的分析和通信提供了高级规划。通过模拟人类心智中的有意识和有目的的思考,假设SWI可以提高LLM的推理能力和生成质量。在数学推理基准测试的大量实验中,与基线(即无明确意图的生成)相比,“有意表达”始终表现出卓越的性能。而且,在推理密集的问题回答和文本摘要基准测试中,与“思维链”和“计划并解决”的触发提示方法相比,尽管在某些方面性能与强大的ARR(分析、检索和推理)方法相当,但SWI的有效性也更为突出。此外,它在基线生成的基础上带来了持续的改进。在文本摘要中,由SWI生成的摘要展现出更高的准确性、简洁性和事实正确性,减少了幻觉现象的出现。此外,人类评估验证了由SWI产生的意图的连贯性、有效性和可解释性。这项概念验证研究为利用认知概念提高LLM的推理能力开辟了一条新的途径。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages. Code: https://github.com/YuweiYin/SWI
Summary:
本文介绍了在大语言模型(LLM)中引入“带意图的说话”(Speaking with Intent,简称SWI)的概念。通过明确生成的意图,模拟人类的深思熟虑和目的性思考,提高模型的推理能力和生成质量。实验证明,相较于基线生成方法(无明确意图的生成方式),带意图的说话在数学推理和文本总结等方面表现出优越性。同时,人类评估也验证了其生成的意图的连贯性、有效性和可解释性。本文开创了一条利用认知概念增强LLM推理能力的新途径。
Key Takeaways:
- 引入“带意图的说话”(Speaking with Intent,简称SWI)概念,作为大语言模型(LLM)中的认知框架,用于提高模型的推理能力和生成质量。
- 通过模拟人类的深思熟虑和目的性思考,明确生成的意图有助于增强模型的推理能力。
- 实验证明,相较于基线生成方法,带意图的说话在数学推理方面表现出优越性。
- 带意图的说话在文本总结方面表现优秀,能提高准确性、简洁性和事实正确性,减少虚构内容。
- 人类评估验证了带意图的说话生成的连贯性、有效性和可解释性。
- 带意图的说话在多种任务上表现出竞争力,包括与强大的ARR方法相比保持竞争力。
点此查看论文截图


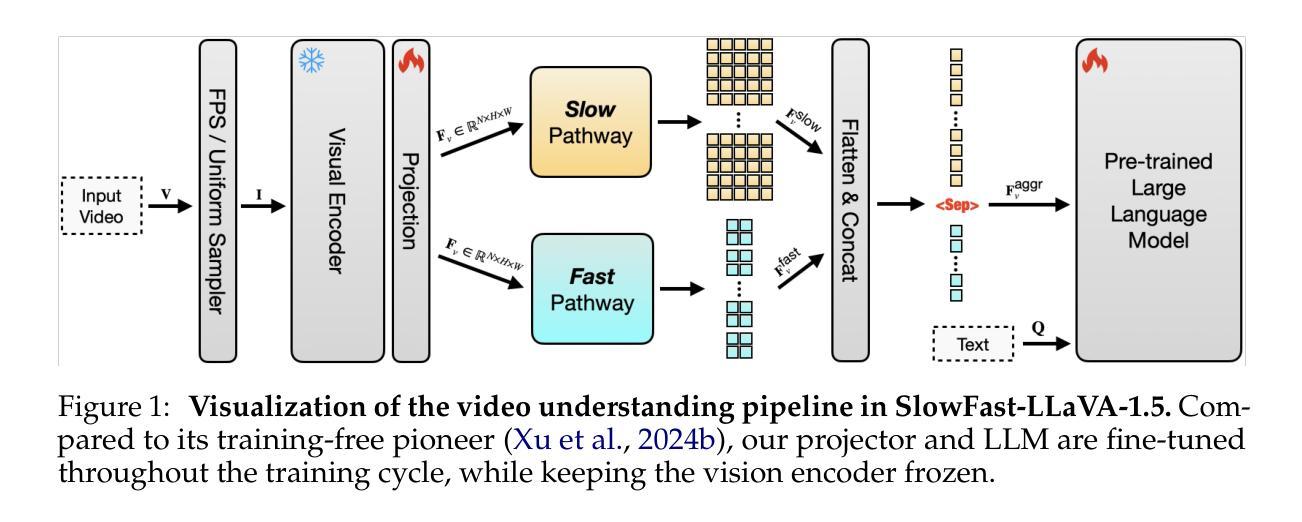
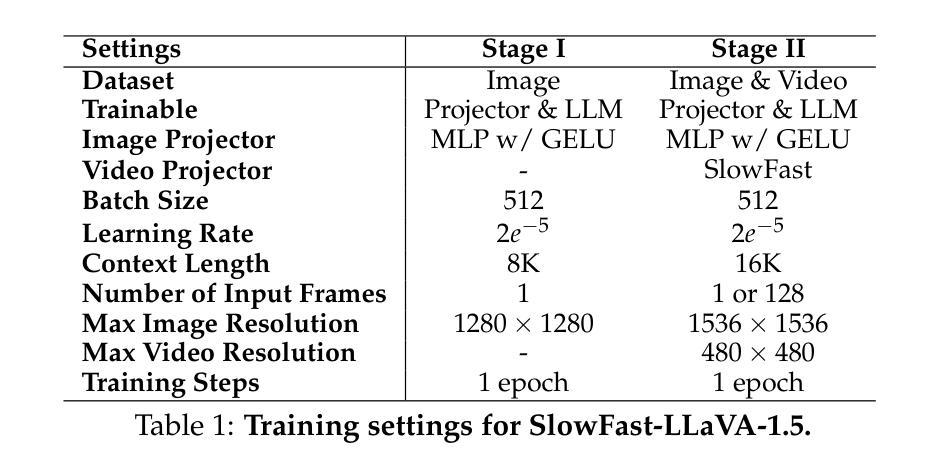
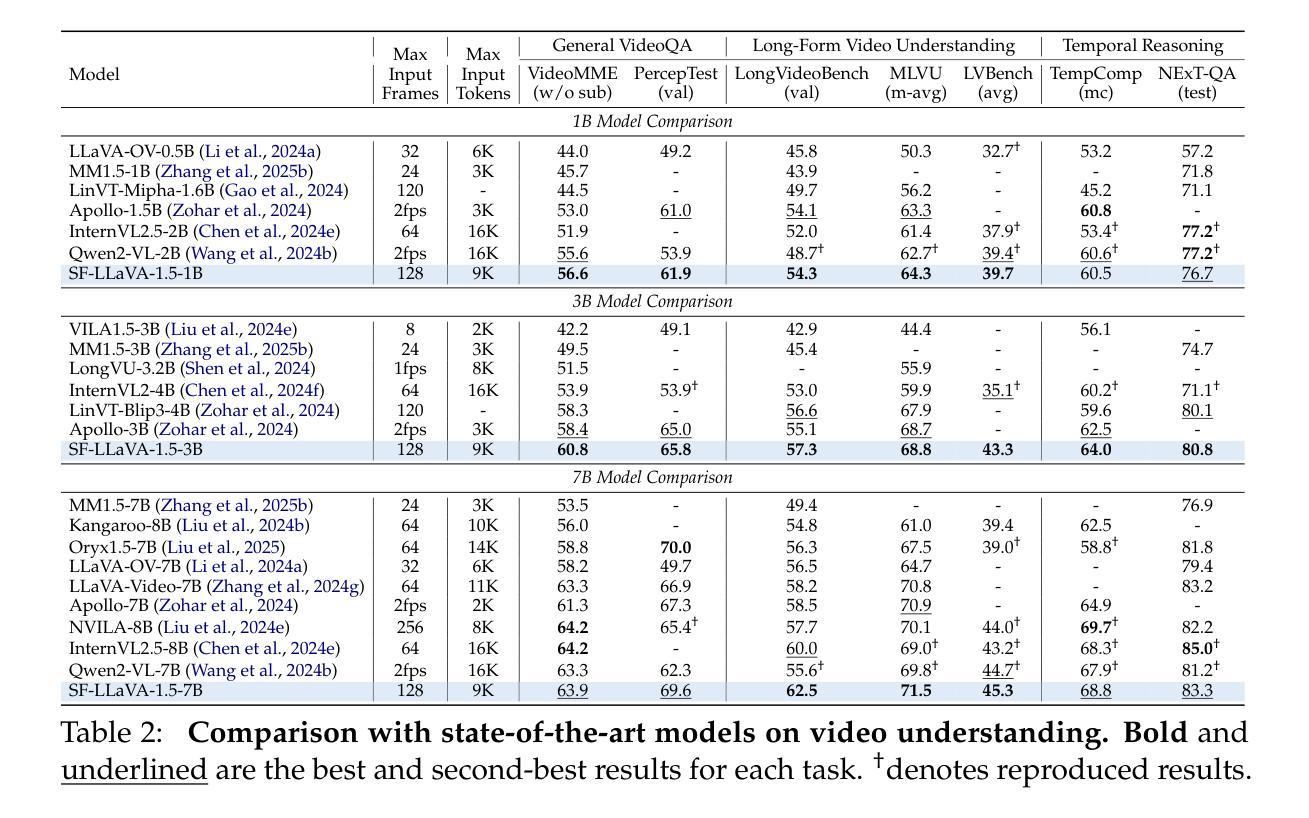
SlowFast-LLaVA-1.5: A Family of Token-Efficient Video Large Language Models for Long-Form Video Understanding
Authors:Mingze Xu, Mingfei Gao, Shiyu Li, Jiasen Lu, Zhe Gan, Zhengfeng Lai, Meng Cao, Kai Kang, Yinfei Yang, Afshin Dehghan
We introduce SlowFast-LLaVA-1.5 (abbreviated as SF-LLaVA-1.5), a family of video large language models (LLMs) offering a token-efficient solution for long-form video understanding. We incorporate the two-stream SlowFast mechanism into a streamlined training pipeline, and perform joint video-image training on a carefully curated data mixture of only publicly available datasets. Our primary focus is on highly efficient model scales (1B and 3B), demonstrating that even relatively small Video LLMs can achieve state-of-the-art performance on video understanding, meeting the demand for mobile-friendly models. Experimental results demonstrate that SF-LLaVA-1.5 achieves superior performance on a wide range of video and image tasks, with robust results at all model sizes (ranging from 1B to 7B). Notably, SF-LLaVA-1.5 achieves state-of-the-art results in long-form video understanding (e.g., LongVideoBench and MLVU) and excels at small scales across various video benchmarks.
我们介绍了SlowFast-LLaVA-1.5(简称SF-LLaVA-1.5),这是一款视频大型语言模型(LLM)系列,为长视频理解提供了一种标记有效的解决方案。我们将双流SlowFast机制纳入简化的训练管道,并在仅公开数据集精心挑选的数据混合上进行联合视频图像训练。我们的主要焦点是高效模型规模(1B和3B),证明即使相对较小的视频LLM也可以在视频理解方面实现最先进的性能,满足对移动友好型模型的需求。实验结果表明,SF-LLaVA-1.5在广泛的视频和图像任务上表现卓越,在各种模型规模(从1B到7B)上均表现出稳健的结果。值得注意的是,SF-LLaVA-1.5在长视频理解(例如LongVideoBench和MLVU)方面达到了最新水平,并在各种视频基准测试中表现出色,尤其在小规模测试中表现尤为突出。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical report
Summary
SF-LLaVA-1.5系列视频大型语言模型(LLM)采用高效的token解决方案,用于长格式视频理解。该模型结合了两流SlowFast机制,并在精心挑选的公开数据集上进行联合视频图像训练。研究重点是小规模模型(规模为1B和3B),即使相对较小的视频LLM也能在视频理解方面实现最先进的性能,满足对移动友好型模型的需求。实验结果表明,SF-LLaVA-1.5在各种视频和图像任务上表现优异,在各种模型规模下均表现稳健,特别是在长格式视频理解方面达到业界领先。
Key Takeaways
- SF-LLaVA-1.5是一个用于长格式视频理解的新型视频大型语言模型家族。
- 结合了两流SlowFast机制以提高模型的效率和性能。
- 模型在精心挑选的公开数据集上进行训练,强调高度效率模型规模(尤其是1B和3B)。
- 实验结果表明SF-LLaVA-1.5在各种视频和图像任务上表现优异,性能稳健。
- 模型在长格式视频理解方面达到业界领先水平。
- SF-LLaVA-1.5适用于移动应用,满足移动友好型模型的需求。
点此查看论文截图

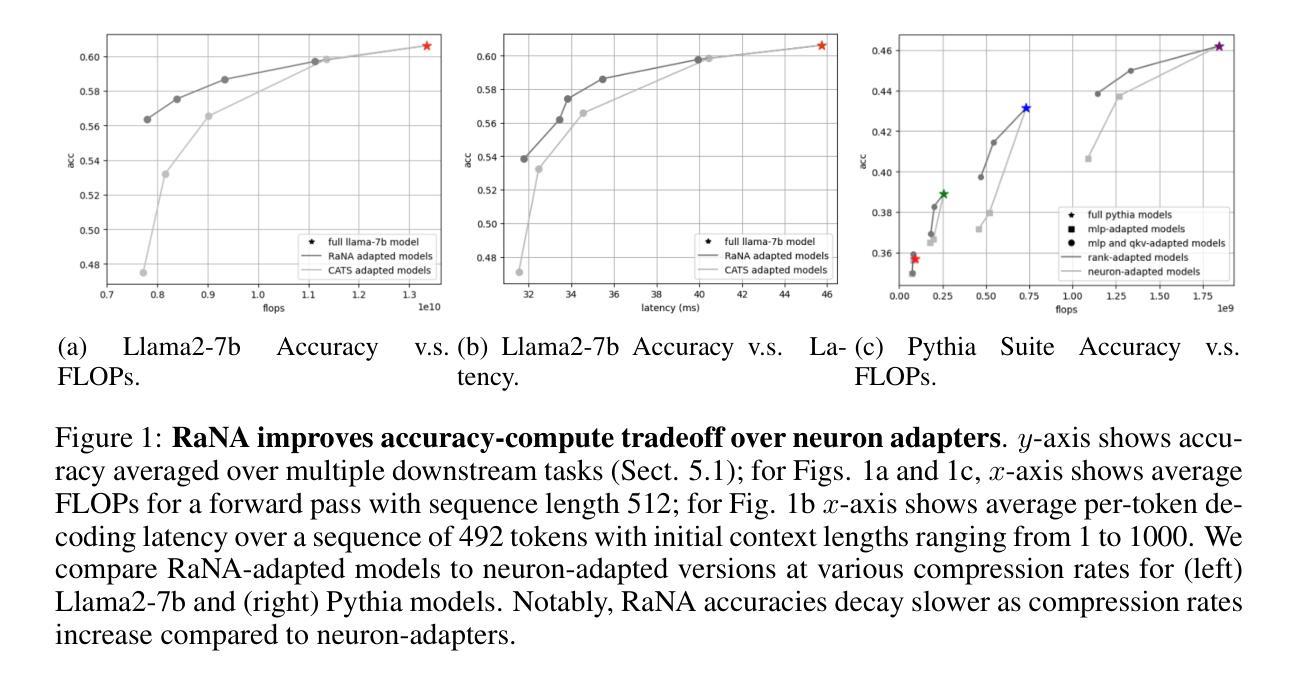
Adaptive Rank Allocation: Speeding Up Modern Transformers with RaNA Adapters
Authors:Roberto Garcia, Jerry Liu, Daniel Sorvisto, Sabri Eyuboglu
Large Language Models (LLMs) are computationally intensive, particularly during inference. Neuron-adaptive techniques, which selectively activate neurons in Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) layers, offer some speedups but suffer from limitations in modern Transformers. These include reliance on sparse activations, incompatibility with attention layers, and the use of costly neuron masking techniques. To address these issues, we propose the Adaptive Rank Allocation framework and introduce the Rank and Neuron Allocator (RaNA) adapter. RaNA adapters leverage rank adapters, which operate on linear layers by applying both low-rank matrix decompositions and adaptive masking to efficiently allocate compute without depending on activation sparsity. This enables RaNA to be generally applied to MLPs and linear components of attention modules, while eliminating the need for expensive maskers found in neuron-adaptive methods. Notably, when compared to neuron adapters, RaNA improves perplexity by up to 7 points and increases accuracy by up to 8 percentage-points when reducing FLOPs by $\sim$44% in state-of-the-art Transformer architectures. These results position RaNA as a robust solution for improving inference efficiency in modern Transformer architectures.
大型语言模型(LLM)计算密集,特别是在推理阶段。神经元自适应技术通过选择性激活多层感知器(MLP)层中的神经元提供了一些加速,但在现代Transformer中受到一些限制。这些限制包括依赖于稀疏激活、与注意力层不兼容以及使用昂贵的神经元掩蔽技术。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了自适应排名分配框架,并引入了Rank和神经元分配器(RaNA)适配器。RaNA适配器利用排名适配器,该排名适配器通过应用低阶矩阵分解和自适应掩蔽来操作线性层,从而有效地分配计算资源,而无需依赖激活稀疏性。这使得RaNA能够广泛应用于MLP和注意力模块的线性组件,同时消除了神经元自适应方法中发现的昂贵掩蔽器的需求。值得注意的是,与神经元适配器相比,RaNA在减少约44%的浮点运算量(FLOPs)的情况下,困惑度降低了最多7个点,准确率提高了最多8个百分点。这些结果使RaNA成为提高现代Transformer架构推理效率的一种稳健解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 5 figures. ICLR 2025
Summary
基于LLM的大型语言模型计算密集,特别是在推理阶段。神经适应技术通过在多层感知器(MLP)层中选择性激活神经元提供了一些加速,但在现代Transformer中仍存在依赖稀疏激活、不兼容注意力层以及使用昂贵的神经元掩码技术等问题。为解决这些问题,我们提出了自适应排名分配框架,并引入了名为RaNA的适配器。RaNA适配器利用排名适配器,通过在线性层上应用低秩矩阵分解和自适应掩码进行有效计算分配,不依赖于激活稀疏性。这使得RaNA可广泛应用于MLP和注意力模块的线性组件,同时消除了神经元自适应方法中发现的昂贵掩蔽器需求。在减少浮点运算量约44%的情况下,RaNA与神经元适配器相比,在最先进的Transformer架构中降低了困惑度达7点,并提高了准确性达8个百分点。这些结果确立了RaNA在提高现代Transformer架构推理效率方面的稳健解决方案地位。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在推理阶段计算密集。
- 神经适应技术在多层感知器(MLP)层中选择性激活神经元以提供加速,但在现代Transformer中有局限性。
- RaNA框架通过结合低秩矩阵分解和自适应掩码,在线性层上进行计算分配。
- RaNA适用于MLP和注意力模块的线性组件,无需昂贵的掩蔽器。
- RaNA在减少计算成本的同时,提高了模型的准确性和困惑度。
- 与神经元适配器相比,RaNA在减少浮点运算量约44%的情况下表现出优越性。
点此查看论文截图

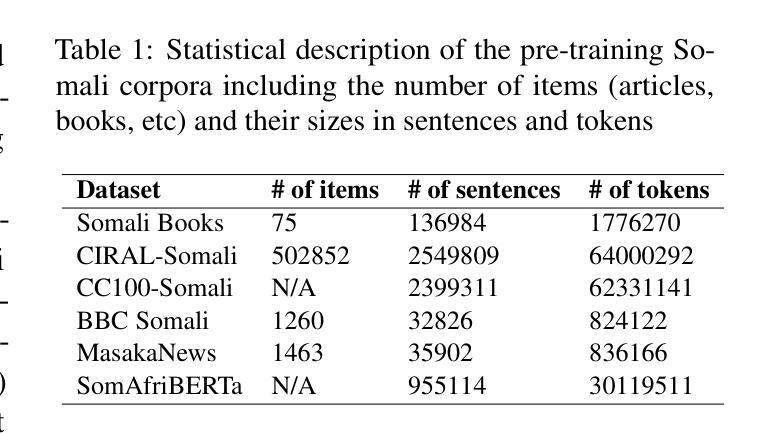
Detection of Somali-written Fake News and Toxic Messages on the Social Media Using Transformer-based Language Models
Authors:Muhidin A. Mohamed, Shuab D. Ahmed, Yahye A. Isse, Hanad M. Mohamed, Fuad M. Hassan, Houssein A. Assowe
The fact that everyone with a social media account can create and share content, and the increasing public reliance on social media platforms as a news and information source bring about significant challenges such as misinformation, fake news, harmful content, etc. Although human content moderation may be useful to an extent and used by these platforms to flag posted materials, the use of AI models provides a more sustainable, scalable, and effective way to mitigate these harmful contents. However, low-resourced languages such as the Somali language face limitations in AI automation, including scarce annotated training datasets and lack of language models tailored to their unique linguistic characteristics. This paper presents part of our ongoing research work to bridge some of these gaps for the Somali language. In particular, we created two human-annotated social-media-sourced Somali datasets for two downstream applications, fake news & toxicity classification, and developed a transformer-based monolingual Somali language model (named SomBERTa) – the first of its kind to the best of our knowledge. SomBERTa is then fine-tuned and evaluated on toxic content, fake news and news topic classification datasets. Comparative evaluation analysis of the proposed model against related multilingual models (e.g., AfriBERTa, AfroXLMR, etc) demonstrated that SomBERTa consistently outperformed these comparators in both fake news and toxic content classification tasks while achieving the best average accuracy (87.99%) across all tasks. This research contributes to Somali NLP by offering a foundational language model and a replicable framework for other low-resource languages, promoting digital and AI inclusivity and linguistic diversity.
拥有社交媒体账户的用户都可以创建和分享内容,且公众对社交媒体平台的新闻和信息来源的依赖程度不断增加,这带来了重大挑战,例如假消息、错误信息、有害内容等。虽然在一定程度上人类内容审核对这些平台标记发布材料是有用的,但人工智能模型的使用提供了一种更可持续、可扩展和有效的缓解这些有害内容的方法。然而,对于索马里语等低资源语言来说,人工智能自动化面临着挑战,包括训练数据集标注稀缺以及缺乏针对其独特语言特性量身定制的语言模型。这篇论文展示了我们正在进行的研究工作的一部分,旨在缩小这些差距并为索马里语提供支持。特别是,我们创建了两个基于社交媒体来源的索马里数据集,用于两个下游应用——假新闻和有毒内容分类。并且我们开发了一种基于变换器的单语种索马里语言模型(名为SomBERTa)——据我们所知,这是该领域首创。随后对SomBERTa进行微调并在有毒内容、假新闻和新闻主题分类数据集上进行评估。对所提出的模型与相关多语种模型(如AfriBERTa、AfroXLMR等)的比较评估分析表明,在假新闻和有毒内容分类任务中,SomBERTa均优于这些比较模型,并在所有任务中取得了最佳平均准确率(87.99%)。这项研究为索马里NLP领域提供了基础语言模型和可复制框架,对于其他低资源语言也具有借鉴意义,推动了数字人工智能包容性和语言多样性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
社交媒体账号的普及以及公众对社交媒体平台作为新闻和信息来源的依赖,带来了诸如错误信息、虚假新闻、有害内容等挑战。人工智能模型的使用为解决这些问题提供了更可持续、可扩展和有效的方法,但低资源语言如索马里语在人工智能自动化方面面临挑战,包括训练数据集稀少和缺乏针对其独特语言特性的语言模型。本文展示了我们正在进行的部分研究工作,旨在缩小这些差距并为索马里语构建语言模型。我们创建了两个由社交媒体源提供的人类注释索马里数据集,用于两个下游应用——虚假新闻和毒性分类,并开发了一种基于转换器的单语索马里语言模型(名为SomBERTa)。SomBERTa经过微调并在有毒内容、虚假新闻和新闻主题分类数据集上进行评估。与相关多语种模型的比较分析表明,SomBERTa在虚假新闻和有毒内容分类任务中表现更佳,并在所有任务中取得最佳平均准确率(87.99%)。该研究为索马里自然语言处理提供了基础语言模型和可复制的框架,对其他低资源语言具有借鉴意义,促进了数字与人工智能的包容性和语言多样性。
关键见解
- 社交媒体内容的创建和分享带来了错误信息、虚假新闻、有害内容等挑战。
- AI模型在解决社交媒体内容问题方面表现出更可持续、可扩展和有效的优势。
- 低资源语言如索马里语在AI自动化方面面临数据稀少和语言模型缺乏的挑战。
- 本文为索马里语创建了两个社交媒体来源的注释数据集,用于虚假新闻和毒性分类。
- 开发了基于转换器的单语索马里语言模型SomBERTa,这是针对索马里语的首次尝试。
- SomBERTa在虚假新闻和有毒内容分类任务上表现优异,平均准确率达87.99%。
点此查看论文截图

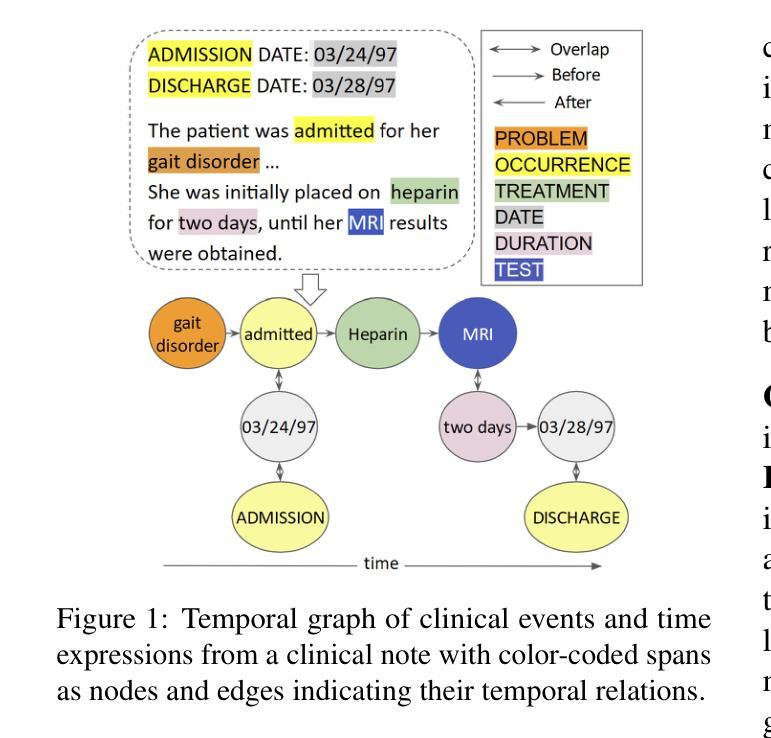
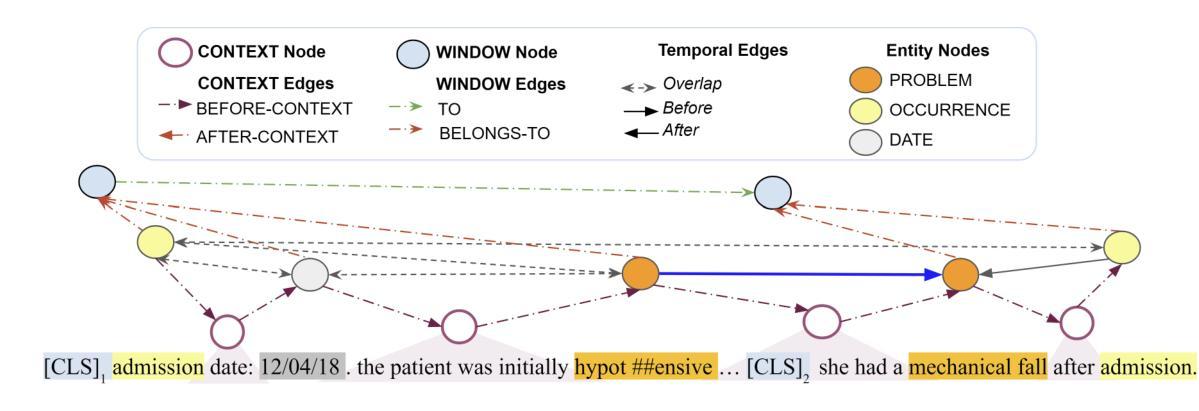
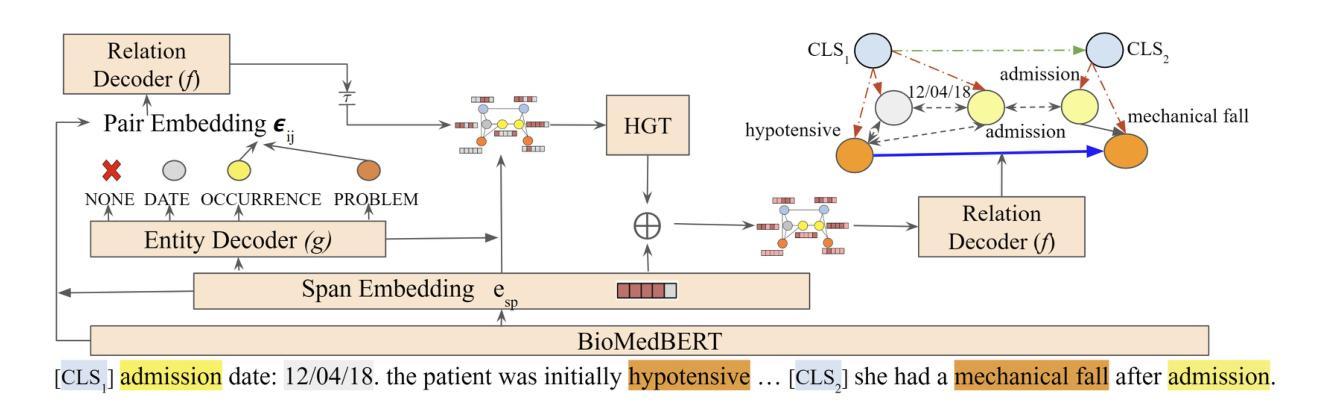
Temporal Relation Extraction in Clinical Texts: A Span-based Graph Transformer Approach
Authors:Rochana Chaturvedi, Peyman Baghershahi, Sourav Medya, Barbara Di Eugenio
Temporal information extraction from unstructured text is essential for contextualizing events and deriving actionable insights, particularly in the medical domain. We address the task of extracting clinical events and their temporal relations using the well-studied I2B2 2012 Temporal Relations Challenge corpus. This task is inherently challenging due to complex clinical language, long documents, and sparse annotations. We introduce GRAPHTREX, a novel method integrating span-based entity-relation extraction, clinical large pre-trained language models (LPLMs), and Heterogeneous Graph Transformers (HGT) to capture local and global dependencies. Our HGT component facilitates information propagation across the document through innovative global landmarks that bridge distant entities. Our method improves the state-of-the-art with 5.5% improvement in the tempeval $F_1$ score over the previous best and up to 8.9% improvement on long-range relations, which presents a formidable challenge. This work not only advances temporal information extraction but also lays the groundwork for improved diagnostic and prognostic models through enhanced temporal reasoning.
从非结构化文本中提取时间信息是上下文情境化事件和获取可操作洞察的关键,特别是在医疗领域。我们利用经过深入研究的I2B2 2012时间关系挑战语料库,解决提取临床事件及其时间关系的任务。由于复杂的临床语言、长文档和稀疏的注释,此任务本质上具有挑战性。我们引入了GRAPHTREX,这是一种集成基于范围实体关系提取、临床大型预训练语言模型(LPLMs)和异质图变换器(HGT)的新方法,以捕获局部和全局依赖关系。我们的HGT组件通过创新的全局地标,促进跨越文档的信息传播,从而连接遥远的实体。我们的方法在现有技术的基础上改进了5.5%,特别是在处理长程关系时,改进幅度高达8.9%,这是一个相当大的挑战。这项工作不仅推动了时间信息的提取发展,而且通过增强时间推理为改进诊断和预后模型奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Introducing a novel method for joint extraction of medical events and temporal relations from free-text, leveraging clinical LPLMs and Heterogeneous Graph Transformers, achieving a 5.5% improvement over the previous state-of-the-art and up to 8.9% on long-range relations
Summary
临床文本中的时序信息提取对于事件上下文化和获取可操作的见解至关重要,特别是在医疗领域。研究使用I2B2 2012时序关系挑战语料库,提出一种新方法GRAPHTREX,整合基于范围的实体关系提取、临床大型预训练语言模型和异质图转换器,以捕捉局部和全局依赖关系。该方法通过创新的全球地标,促进了跨越文档的信息传播,并改善了状态最优的5.5%的tempeval F1分数,并在长距离关系上提高了8.9%,这构成了一个巨大的挑战。这项工作不仅推动了时序信息提取的进步,而且通过增强时序推理为改进诊断和预后模型奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 时序信息提取对于理解临床事件的上下文和获取见解至关重要。
- I2B2 2012 Temporal Relations Challenge语料库被用于研究。
- GRAPHTREX方法结合了多种技术:基于范围的实体关系提取、临床大型预训练语言模型和异质图转换器。
- HGT组件通过全球地标促进了文档中的信息传播。
- GRAPHTREX方法改善了现有技术的tempeval F1分数,并且在处理长距离关系方面取得了显著进步。
- 该研究不仅推动了时序信息提取的发展,而且为改进诊断和预后模型打下了基础。
点此查看论文截图

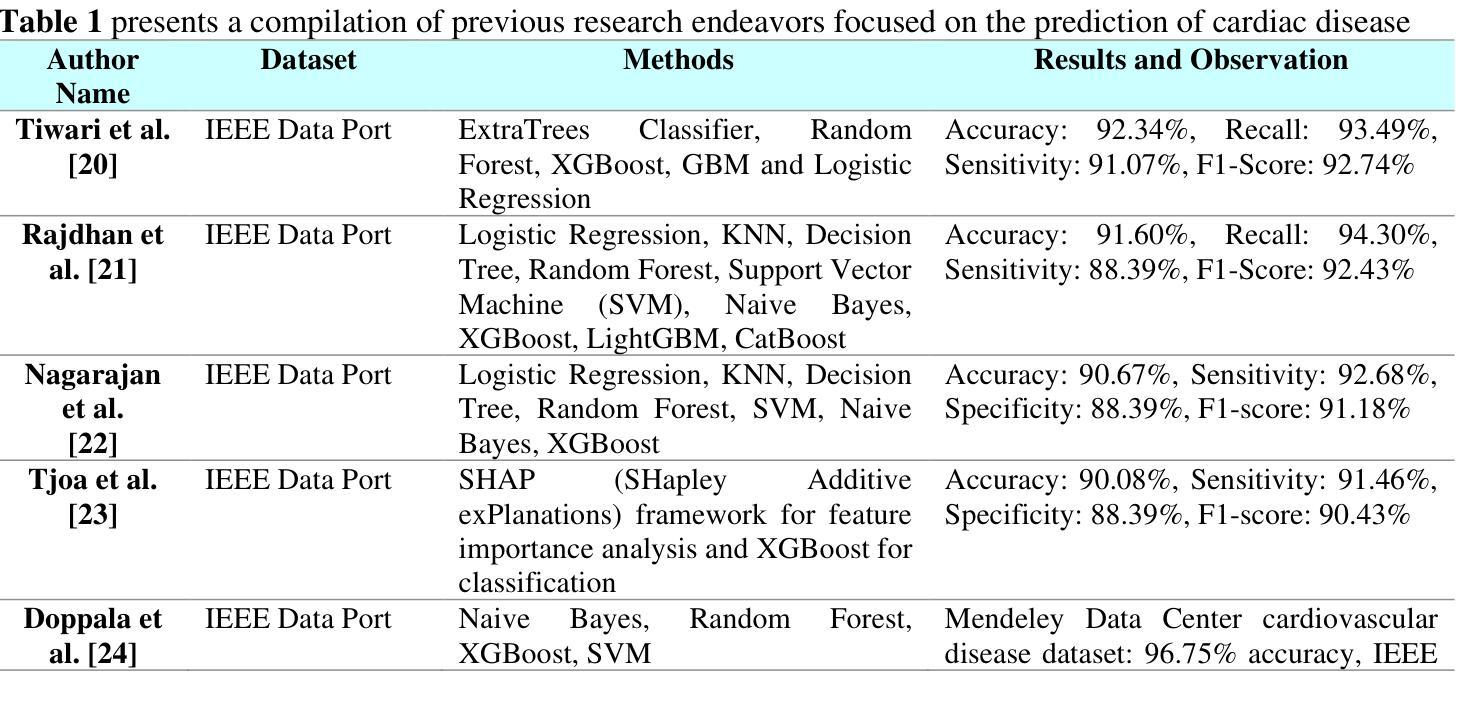
CardioTabNet: A Novel Hybrid Transformer Model for Heart Disease Prediction using Tabular Medical Data
Authors:Md. Shaheenur Islam Sumon, Md. Sakib Bin Islam, Md. Sohanur Rahman, Md. Sakib Abrar Hossain, Amith Khandakar, Anwarul Hasan, M Murugappan, Muhammad E. H. Chowdhury
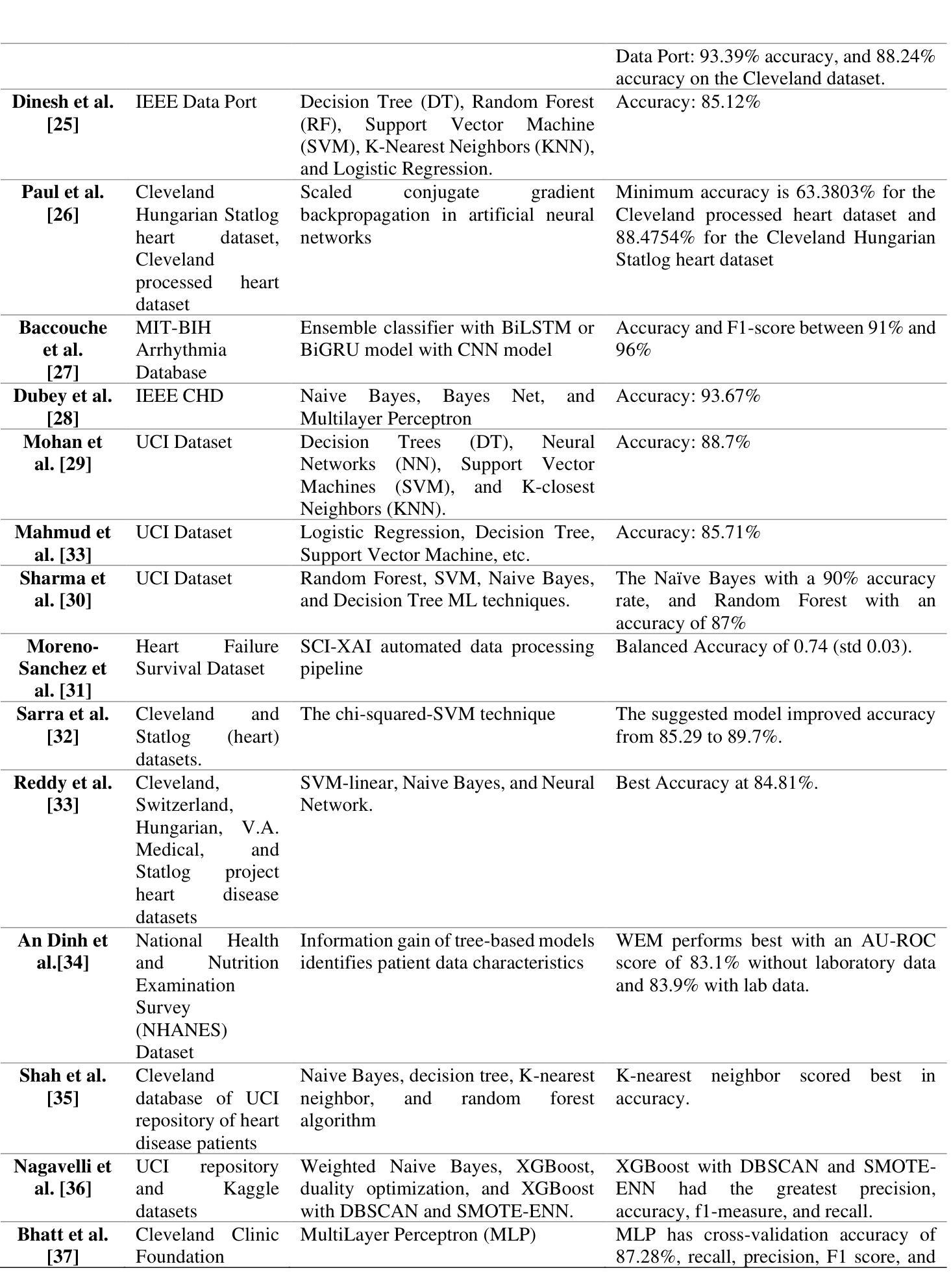
The early detection and prediction of cardiovascular diseases are crucial for reducing the severe morbidity and mortality associated with these conditions worldwide. A multi-headed self-attention mechanism, widely used in natural language processing (NLP), is operated by Transformers to understand feature interactions in feature spaces. However, the relationships between various features within biological systems remain ambiguous in these spaces, highlighting the necessity of early detection and prediction of cardiovascular diseases to reduce the severe morbidity and mortality with these conditions worldwide. We handle this issue with CardioTabNet, which exploits the strength of tab transformer to extract feature space which carries strong understanding of clinical cardiovascular data and its feature ranking. As a result, performance of downstream classical models significantly showed outstanding result. Our study utilizes the open-source dataset for heart disease prediction with 1190 instances and 11 features. In total, 11 features are divided into numerical (age, resting blood pressure, cholesterol, maximum heart rate, old peak, weight, and fasting blood sugar) and categorical (resting ECG, exercise angina, and ST slope). Tab transformer was used to extract important features and ranked them using random forest (RF) feature ranking algorithm. Ten machine-learning models were used to predict heart disease using selected features. After extracting high-quality features, the top downstream model (a hyper-tuned ExtraTree classifier) achieved an average accuracy rate of 94.1% and an average Area Under Curve (AUC) of 95.0%. Furthermore, a nomogram analysis was conducted to evaluate the model’s effectiveness in cardiovascular risk assessment. A benchmarking study was conducted using state-of-the-art models to evaluate our transformer-driven framework.
早期发现和预测心血管疾病对于减少这些疾病在全球范围内导致的严重发病率和死亡率至关重要。多头自注意力机制在自然语言处理(NLP)中广泛使用,并由Transformer进行操作以理解特征空间中的特征交互。然而,在这些空间中,生物系统内各种特征之间的关系仍然模糊,这再次强调了早期发现和预测心血管疾病以减少这些疾病在全球范围内导致的严重发病率和死亡率的必要性。我们通过CardioTabNet解决这个问题,它利用tab transformer的优势来提取对临床心血管数据有深刻理解的特征空间及其特征排名。因此,下游经典模型的表现显示出了出色的结果。我们的研究利用开放源代码数据集进行心脏病预测,包含1190个实例和11个特征。总共的11个特征分为数值型(年龄、静息血压、胆固醇、最大心率、旧峰值、体重和空腹血糖)和分类型(静息心电图、运动性心绞痛和ST斜率)。Tab transformer被用来提取重要特征,并使用随机森林(RF)特征排名算法进行排名。使用选定的特征,共采用了十种机器学习模型来预测心脏病。在提取高质量特征后,顶级下游模型(经过超参数调整的ExtraTree分类器)的平均准确率为94.1%,平均曲线下面积(AUC)为95.0%。此外,还进行了列线图分析,以评估模型在心血管风险评估中的有效性。使用最新模型进行了一项基准测试研究,以评估我们基于transformer的框架。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper is currently under review in the Health Information Science and Systems journal
Summary
心血管疾病早期检测和预测对于降低全球相关严重发病率和死亡率至关重要。本研究采用多头自注意力机制,通过CardioTabNet利用表转换器的优势提取特征空间,对心血管疾病数据进行深入理解并排名。研究使用开源数据集,采用十种机器学习模型预测心脏病,并利用随机森林算法对特征进行排名。最高性能模型达到平均准确率94.1%,平均AUC值95.0%。研究还通过标准对比研究和列线图分析评估了模型在心血管疾病风险评估中的有效性。本研究结果突出了基于表转换器的特征提取方法在心血管疾病预测中的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 早期检测和预测心血管疾病对于减少全球发病率和死亡率非常重要。
- 多头自注意力机制用于理解特征间的相互作用。
- CardioTabNet利用表转换器的优势提取特征空间并深入理解心血管临床数据。
- 研究使用开源数据集进行心脏病预测,涉及多种机器学习模型。
- 通过随机森林算法对特征进行排名,最高性能模型平均准确率94.1%,平均AUC值95.0%。
- 研究通过列线图分析和标准对比研究评估了模型的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

OmniScience: A Domain-Specialized LLM for Scientific Reasoning and Discovery
Authors:Vignesh Prabhakar, Md Amirul Islam, Adam Atanas, Yao-Ting Wang, Joah Han, Aastha Jhunjhunwala, Rucha Apte, Robert Clark, Kang Xu, Zihan Wang, Kai Liu
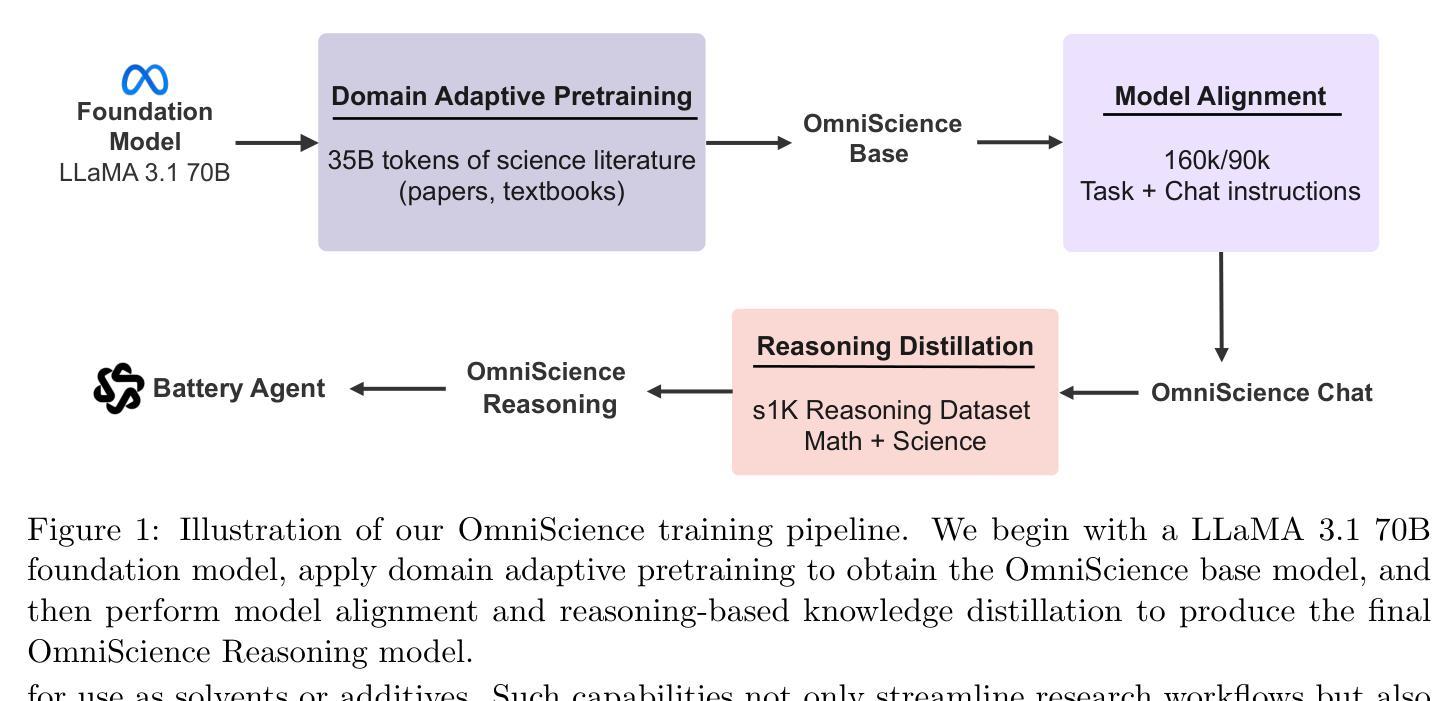
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable potential in advancing scientific knowledge and addressing complex challenges. In this work, we introduce OmniScience, a specialized large reasoning model for general science, developed through three key components: (1) domain adaptive pretraining on a carefully curated corpus of scientific literature, (2) instruction tuning on a specialized dataset to guide the model in following domain-specific tasks, and (3) reasoning-based knowledge distillation through fine-tuning to significantly enhance its ability to generate contextually relevant and logically sound responses. We demonstrate the versatility of OmniScience by developing a battery agent that efficiently ranks molecules as potential electrolyte solvents or additives. Comprehensive evaluations reveal that OmniScience is competitive with state-of-the-art large reasoning models on the GPQA Diamond and domain-specific battery benchmarks, while outperforming all public reasoning and non-reasoning models with similar parameter counts. We further demonstrate via ablation experiments that domain adaptive pretraining and reasoning-based knowledge distillation are critical to attain our performance levels, across benchmarks.
大型语言模型(LLM)在推进科学知识和应对复杂挑战方面显示出显著潜力。在这项工作中,我们介绍了OmniScience,这是一个针对通用科学的特殊大型推理模型,通过三个关键组件开发:(1)在精心筛选的科学文献语料库上进行领域自适应预训练,(2)在专门的数据集上进行指令调整,以指导模型执行特定领域的任务,(3)通过微调进行基于推理的知识蒸馏,以显著提高其生成语境相关和逻辑严谨响应的能力。我们通过开发电池代理来展示OmniScience的通用性,该代理可以有效地对分子进行排名,作为潜在的电解质溶剂或添加剂。综合评估表明,OmniScience在GPQA Diamond和特定领域的电池基准测试上具有竞争力,优于所有具有相似参数数量的公共推理和非推理模型。我们还通过消融实验进一步证明,领域自适应预训练和基于推理的知识蒸馏对于达到我们的性能水平至关重要,跨越各个基准测试。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
大型语言模型(LLMs)在推进科学知识及应对复杂挑战方面展现出显著潜力。本研究介绍了一款针对通用科学的特殊大型推理模型——OmniScience,其开发涉及三个关键部分:1)在精心筛选的科学文献语料库上进行领域自适应预训练;2)在专门数据集上进行指令调整,以指导模型执行特定领域任务;3)通过微调进行基于推理的知识蒸馏,以显著增强模型生成语境相关和逻辑严谨回应的能力。通过开发电池代理,我们展示了OmniScience的通用性,该代理能够高效地对分子进行潜在电解质溶剂或添加剂的排名。综合评估表明,OmniScience在GPQA Diamond和特定领域电池基准测试上,与最新大型推理模型具有竞争力,并在参数数量相似的所有公共推理和非推理模型中表现最佳。通过消融实验进一步证明,领域自适应预训练和基于推理的知识蒸馏对于达到我们的性能水平至关重要。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在推进科学知识和应对复杂挑战方面具有显著潜力。
- OmniScience是一款针对通用科学的特殊大型推理模型,包含领域自适应预训练、指令调整、和基于推理的知识蒸馏三个关键部分。
- OmniScience能够通过开发电池代理展示其通用性,该代理能够高效排名潜在电解质溶剂或添加剂。
- 综合评估显示,OmniScience在GPQA Diamond和特定领域电池基准测试中表现出竞争力。
- OmniScience在同类模型中表现最佳,尤其是在参数数量相似的情况下。
- 消融实验证明领域自适应预训练对于OmniScience的性能至关重要。
- 基于推理的知识蒸馏也是达到OmniScience高性能水平的关键因素。
点此查看论文截图

Modifying Large Language Model Post-Training for Diverse Creative Writing
Authors:John Joon Young Chung, Vishakh Padmakumar, Melissa Roemmele, Yuqian Sun, Max Kreminski
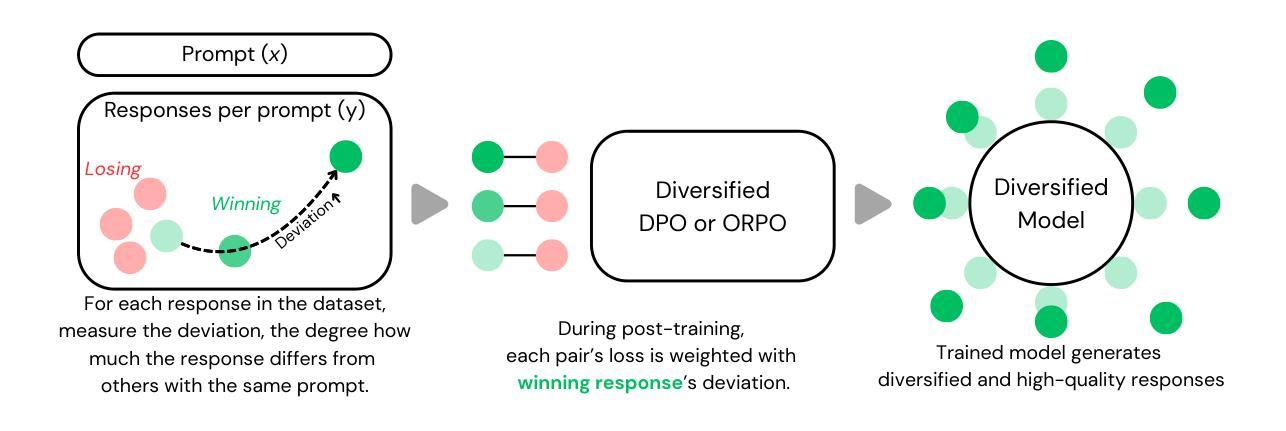
As creative writing tasks do not have singular correct answers, large language models (LLMs) trained to perform these tasks should be able to generate diverse valid outputs. However, LLM post-training often focuses on improving generation quality but neglects to facilitate output diversity. Hence, in creative writing generation, we investigate post-training approaches to promote both output diversity and quality. Our core idea is to include deviation – the degree of difference between a training sample and all other samples with the same prompt – in the training objective to facilitate learning from rare high-quality instances. By adopting our approach to direct preference optimization (DPO) and odds ratio preference optimization (ORPO), we demonstrate that we can promote the output diversity of trained models while minimally decreasing quality. Our best model with 8B parameters could achieve on-par diversity as a human-created dataset while having output quality similar to the best instruction-tuned models we examined, GPT-4o and DeepSeek-R1. We further validate our approaches with a human evaluation, an ablation, and a comparison to an existing diversification approach, DivPO.
由于创造性写作任务没有单一的正确答案,因此训练用于执行这些任务的大型语言模型(LLM)应该能够生成多样化的有效输出。然而,LLM的后期训练通常侧重于提高生成质量,却忽视了促进输出的多样性。因此,在创造性写作生成中,我们研究了促进输出多样性和质量的后期训练方法。我们的核心思想是将偏差纳入训练目标中,偏差是指一个训练样本与具有相同提示的所有其他样本之间的差异程度,以促进从罕见的高质量实例中学习。通过采用我们的直接偏好优化(DPO)和赔率比率偏好优化(ORPO)方法,我们证明了可以在不显著降低质量的情况下促进训练模型的输出多样性。我们最好的包含8亿参数的模型可以达到与人类创建数据集相当的多样性,同时其输出质量与我们所考察的最佳指令调整模型GPT-4o和DeepSeek-R1相似。我们通过人类评估、消除对比以及与现有的多样化方法DivPO的比较,进一步验证了我们的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大语言模型(LLM)在创作写作任务中能够生成多样的有效输出,但现有的训练后处理方式往往侧重于提高生成质量而忽略了输出多样性。为此,研究者提出在训练目标中加入偏差的方法,利用罕见的高质量实例促进学习。通过采用直接偏好优化(DPO)和赔率比率偏好优化(ORPO)的方法,能够在保持输出质量的同时提高模型的输出多样性。最佳模型的参数达到8B,其输出多样性与人类创建的数据集相当,输出质量也与最佳指令调整模型GPT-4o和DeepSeek-R1相似。经过人工评估、消去法和与现有多样化方法DivPO的比较,验证了该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在创作写作任务中可以生成多样的有效输出,但现有的训练后处理方式忽略了输出多样性。
- 研究者提出在训练目标中加入偏差的方法,利用罕见的高质量实例促进学习。
- 采用直接偏好优化(DPO)和赔率比率偏好优化(ORPO)的方法可以提高模型的输出多样性。
- 最佳模型的参数达到8B,其输出多样性与人类创建的数据集相当。
- 最佳模型的输出质量与最佳指令调整模型GPT-4o和DeepSeek-R1相似。
- 经过人工评估验证了该方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

LoRASculpt: Sculpting LoRA for Harmonizing General and Specialized Knowledge in Multimodal Large Language Models
Authors:Jian Liang, Wenke Huang, Guancheng Wan, Qu Yang, Mang Ye
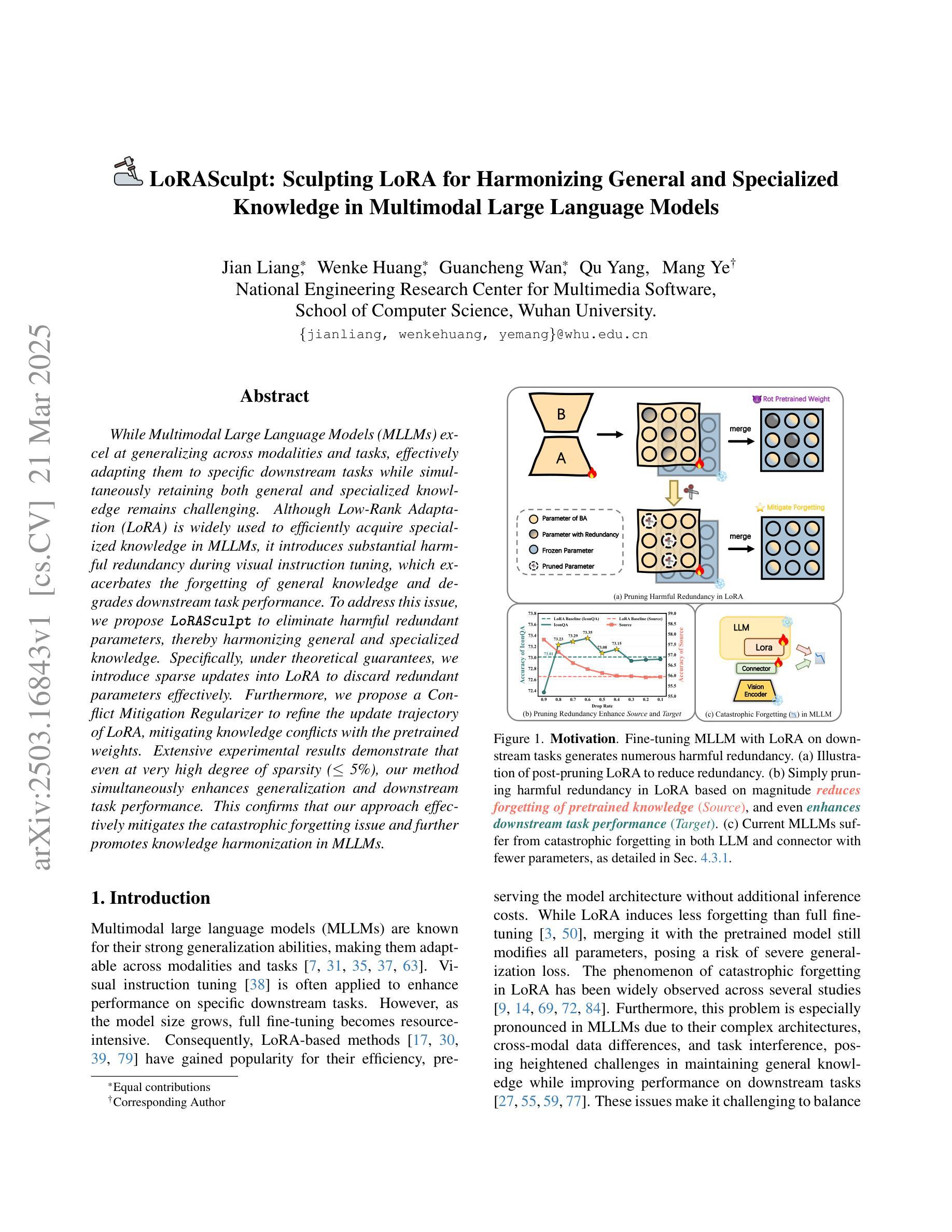
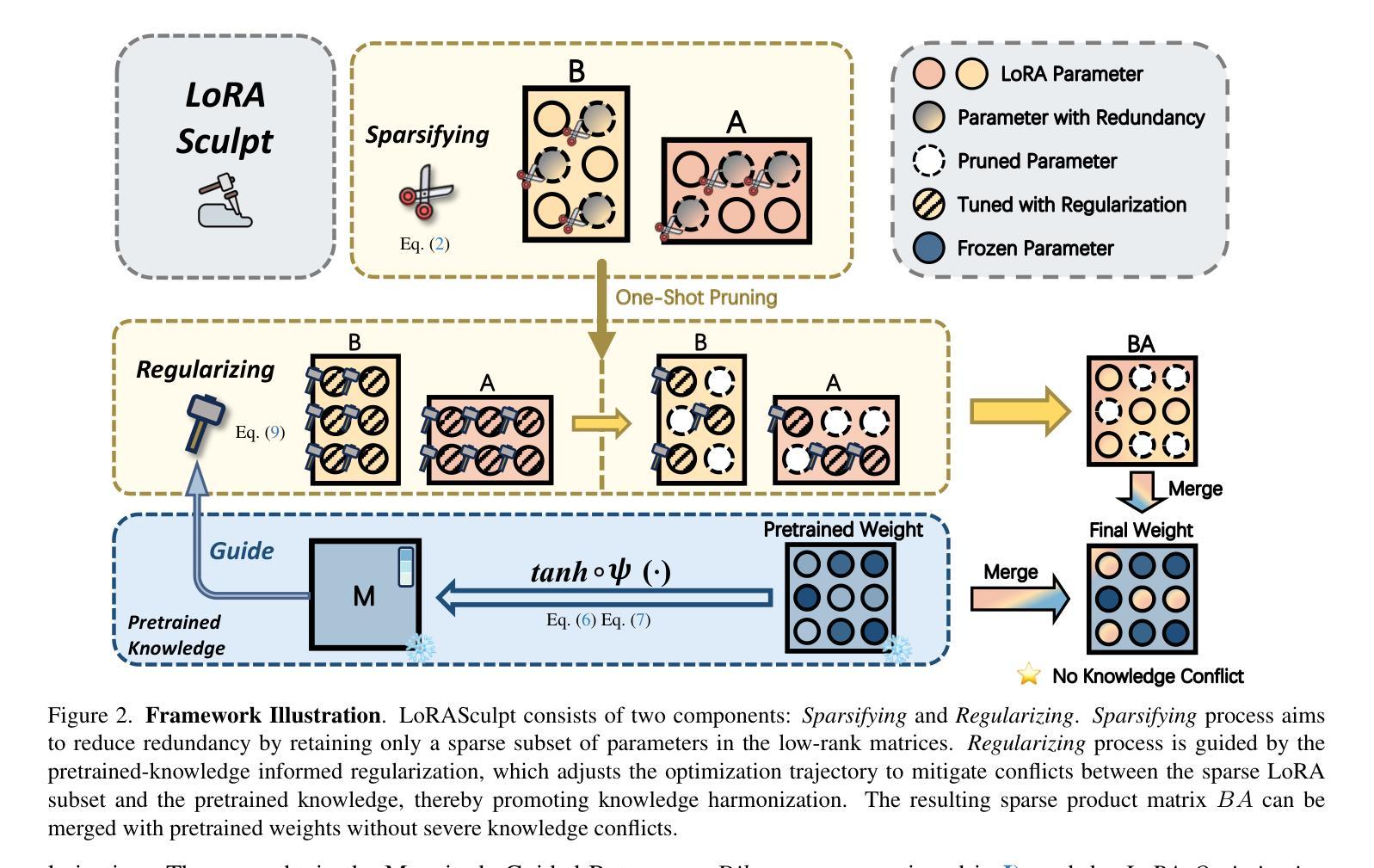
While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) excel at generalizing across modalities and tasks, effectively adapting them to specific downstream tasks while simultaneously retaining both general and specialized knowledge remains challenging. Although Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) is widely used to efficiently acquire specialized knowledge in MLLMs, it introduces substantial harmful redundancy during visual instruction tuning, which exacerbates the forgetting of general knowledge and degrades downstream task performance. To address this issue, we propose LoRASculpt to eliminate harmful redundant parameters, thereby harmonizing general and specialized knowledge. Specifically, under theoretical guarantees, we introduce sparse updates into LoRA to discard redundant parameters effectively. Furthermore, we propose a Conflict Mitigation Regularizer to refine the update trajectory of LoRA, mitigating knowledge conflicts with the pretrained weights. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that even at very high degree of sparsity ($\le$ 5%), our method simultaneously enhances generalization and downstream task performance. This confirms that our approach effectively mitigates the catastrophic forgetting issue and further promotes knowledge harmonization in MLLMs.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在跨模态和任务泛化方面表现出色,但如何有效地将它们适应特定的下游任务,同时保留一般和专业知识仍然具有挑战性。虽然低秩适应(LoRA)被广泛用于在MLLMs中高效地获取专业知识,但在视觉指令调整过程中会引入大量的有害冗余,这加剧了对一般知识的遗忘并降低了下游任务性能。为了解决这一问题,我们提出LoRASculpt来消除有害的冗余参数,从而协调一般知识和专业知识。具体地说,在理论保证下,我们将稀疏更新引入LoRA,以有效地丢弃冗余参数。此外,我们提出了一种冲突缓解正则化器,以优化LoRA的更新轨迹,缓解与预训练权重的知识冲突。大量的实验结果表明,即使在非常高的稀疏度(≤5%)下,我们的方法同时提高了泛化和下游任务性能。这证实了我们的方法有效地缓解了灾难性遗忘问题,并进一步促进了MLLMs中的知识协调。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025
摘要
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在跨模态和任务上的泛化能力出色,但在特定下游任务中有效适应并同时保留一般和专业知识仍然具有挑战性。虽然低秩适应(LoRA)广泛用于在MLLMs中高效获取专业知识,但在视觉指令调整时引入了大量有害冗余,这加剧了对一般知识的遗忘并降低了下游任务性能。为解决这一问题,我们提出LoRASculpt以消除有害冗余参数,从而协调一般知识和专业知识。具体而言,在理论保证下,我们将稀疏更新引入LoRA以有效地消除冗余参数。此外,我们还提出了一种冲突缓解正则化器,以优化LoRA的更新轨迹,缓解与预训练权重的知识冲突。大量实验结果表明,即使在非常高的稀疏度(≤5%)下,我们的方法同时提高了泛化和下游任务性能。这证实我们的方法有效地缓解了灾难性遗忘问题,并进一步促进了MLLMs中的知识协调。
要点
- MLLMs在跨模态和任务上的泛化能力强大,但适应特定下游任务时保留一般和专业知识具有挑战性。
- LoRA在获取专业知识时引入有害冗余,影响下游任务性能。
- LoRASculpt通过消除冗余参数解决这一问题,协调一般知识和专业知识。
- LoRASculpt使用稀疏更新有效消除冗余参数。
- 引入冲突缓解正则化器,优化更新轨迹,缓解与预训练权重的知识冲突。
- 实验结果表明,LoRASculpt在较高稀疏度下提高了泛化和下游任务性能。
- LoRASculpt有效缓解灾难性遗忘问题,促进MLLMs中的知识协调。
点此查看论文截图
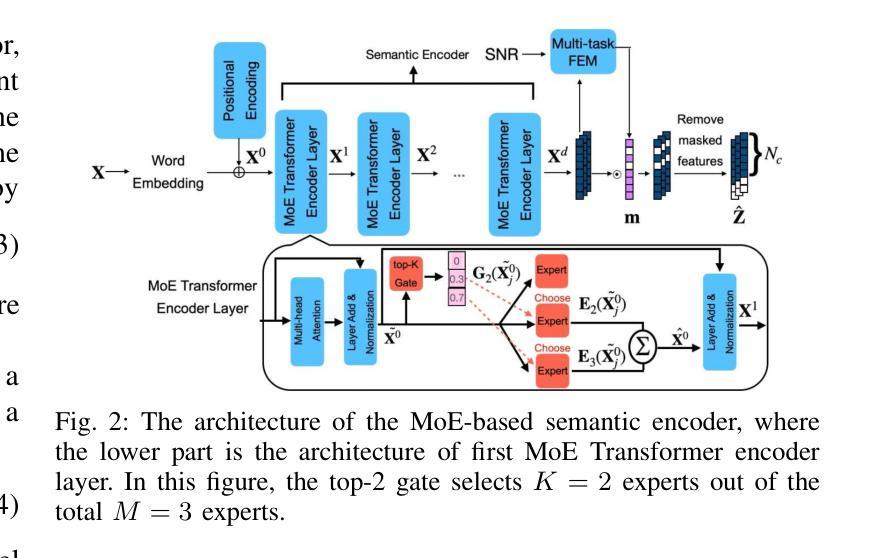
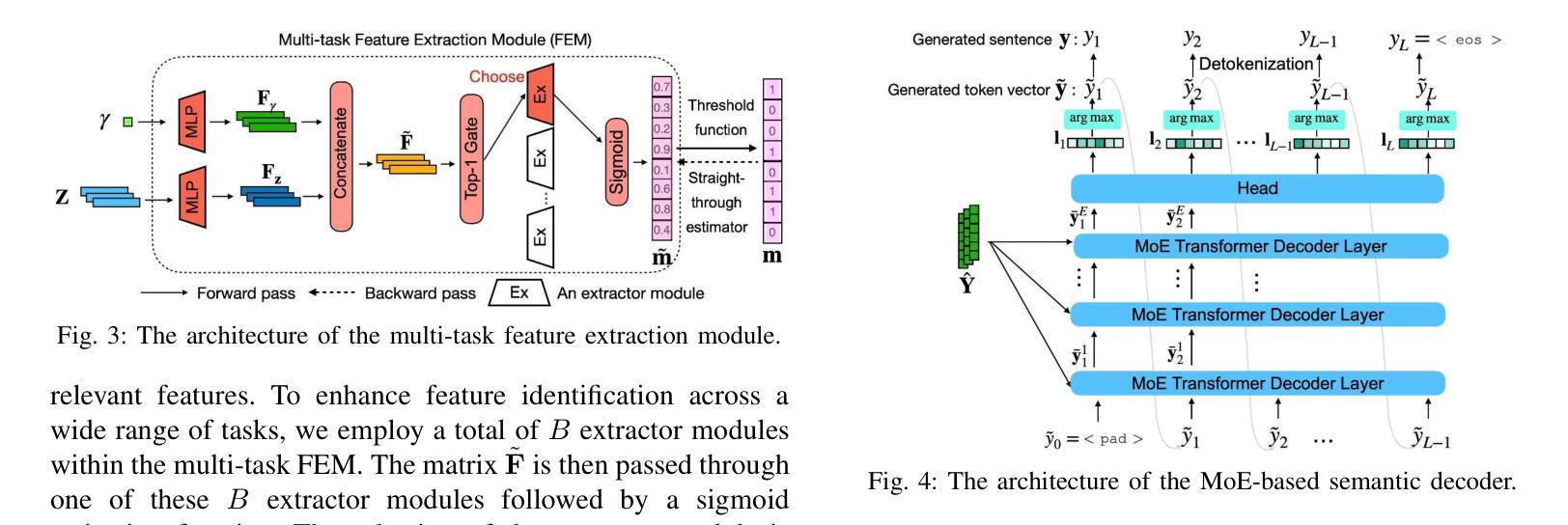
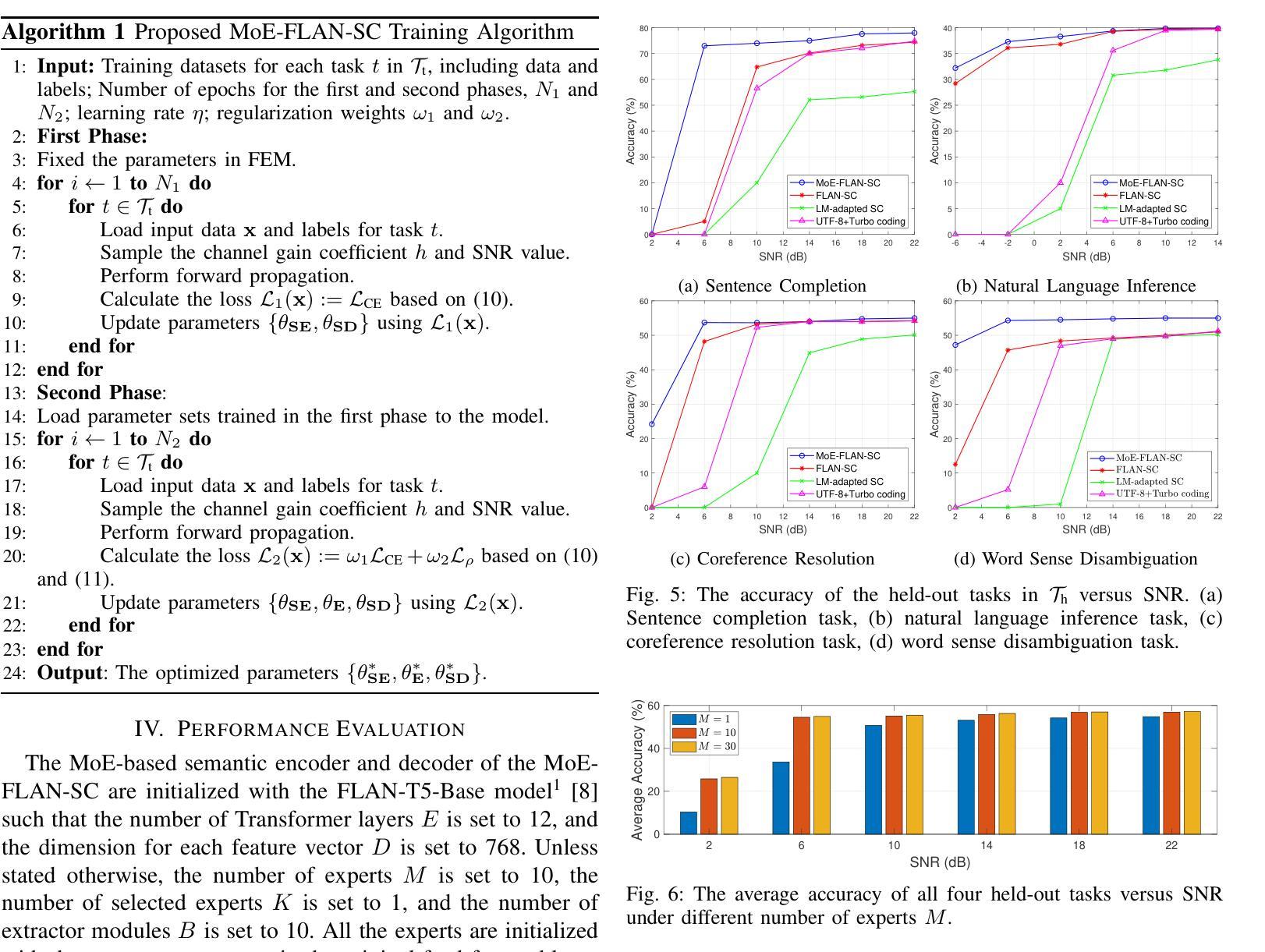
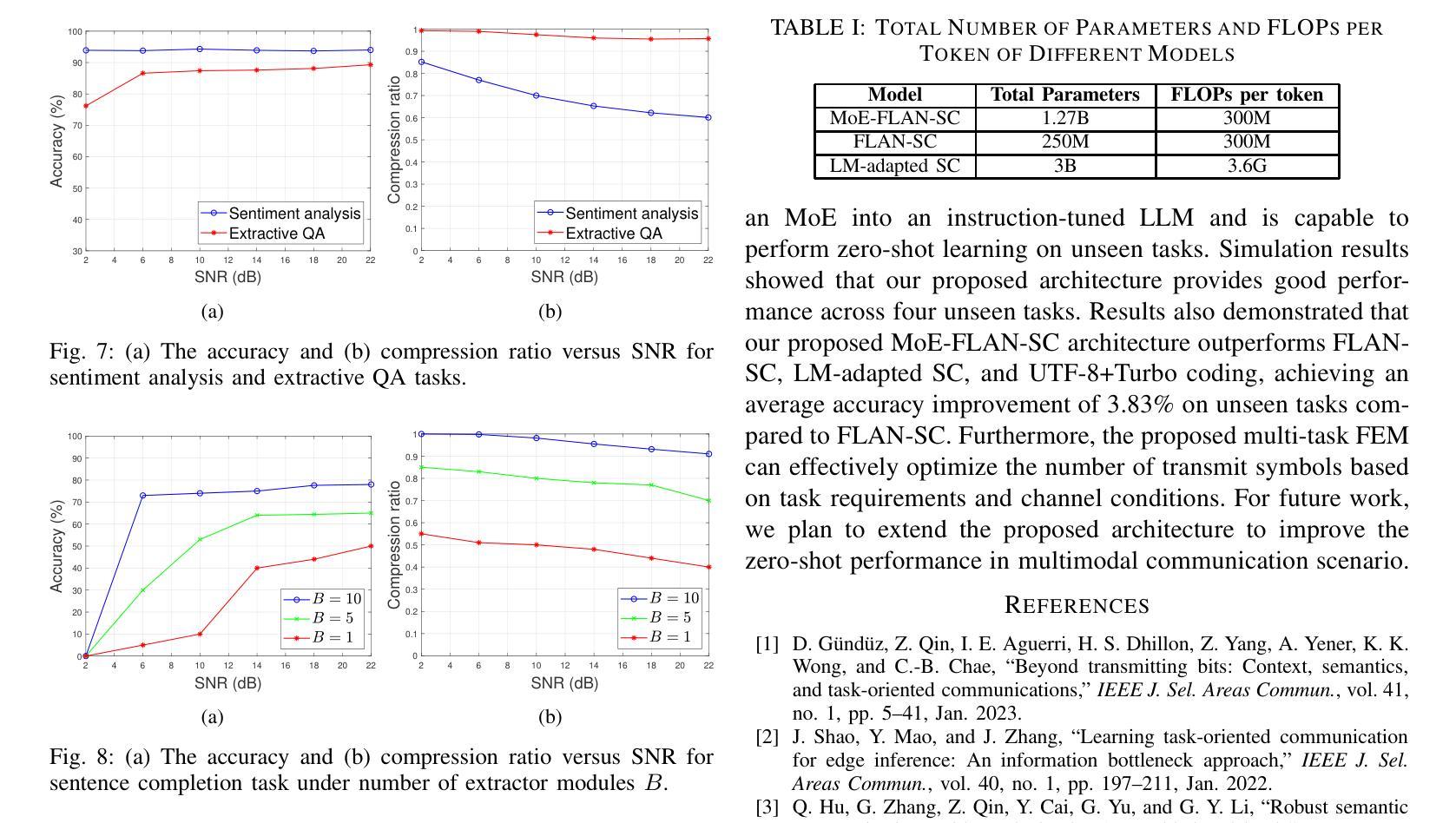
Leveraging MoE-based Large Language Model for Zero-Shot Multi-Task Semantic Communication
Authors:Sin-Yu Huang, Renjie Liao, Vincent W. S. Wong
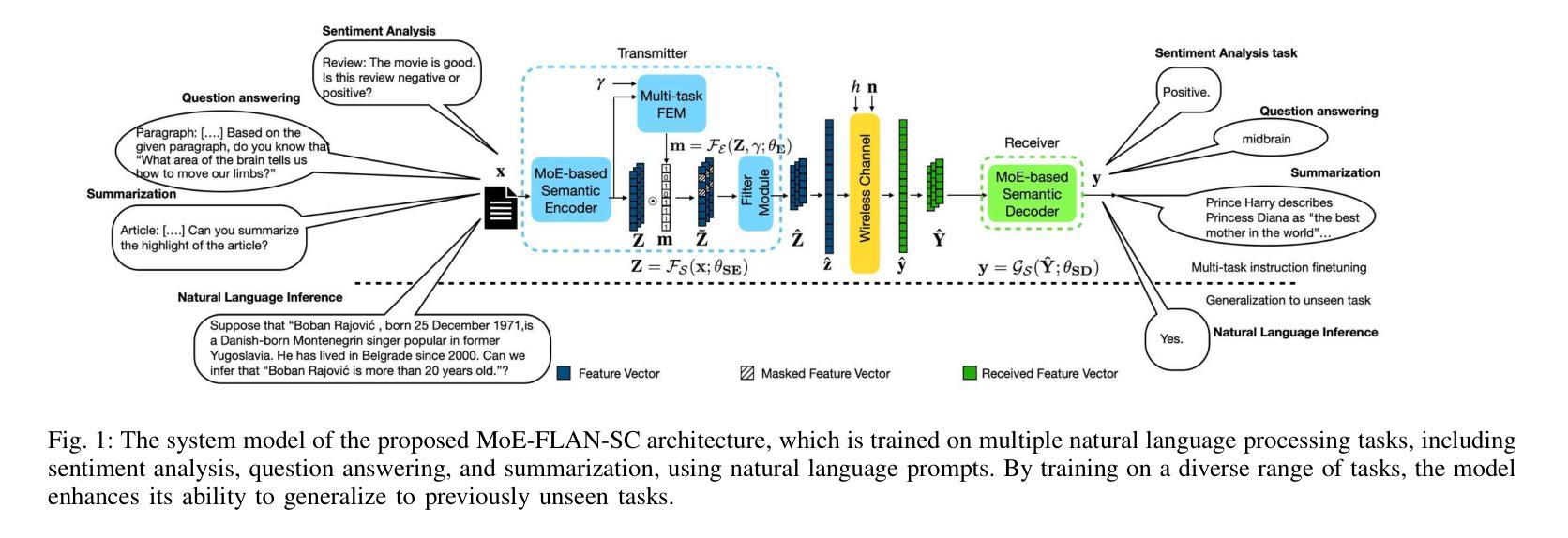
Multi-task semantic communication (SC) can reduce the computational resources in wireless systems since retraining is not required when switching between tasks. However, existing approaches typically rely on task-specific embeddings to identify the intended task, necessitating retraining the entire model when given a new task. Consequently, this drives the need for a multi-task SC system that can handle new tasks without additional training, known as zero-shot learning. Inspired by the superior zero-shot capabilities of large language models (LLMs), we leverage pre-trained instruction-tuned LLMs, referred to as fine-tuned language net (FLAN), to improve the generalization capability. We incorporate a mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture in the FLAN model and propose MoE-FLAN-SC architecture for multi-task SC systems. Our proposed MoE-FLAN-SC architecture can further improve the performance of FLAN-T5 model without increasing the computational cost. Moreover, we design a multi-task feature extraction module (FEM) which can adaptively extract relevant features across various tasks given the provided features and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Simulation results show that our proposed MoE-FLAN-SC architecture outperforms three state-of-the-art models in terms of the average accuracy on four different unseen tasks.
多任务语义通信(SC)能够节省无线系统中的计算资源,因为任务间切换时无需重新训练。然而,现有方法通常依赖于特定任务的嵌入来识别意图任务,当给定新任务时需要重新训练整个模型。因此,这引发了对能够处理新任务而无需额外训练的多任务SC系统的需求,这被称为零射击学习。受大型语言模型(LLM)卓越零射击能力的启发,我们利用预训练的指令调整LLM,称为精细调整语言网络(FLAN),以提高泛化能力。我们将混合专家(MoE)架构融入FLAN模型,并提出MoE-FLAN-SC架构用于多任务SC系统。我们提出的MoE-FLAN-SC架构可以进一步提高FLAN-T5模型的性能,同时不增加计算成本。此外,我们设计了一个多任务特征提取模块(FEM),该模块可以自适应地提取给定特征和信噪比(SNR)下各种任务的相关特征。仿真结果表明,我们提出的MoE-FLAN-SC架构在四个不同未见任务上的平均准确率优于三种最新模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), June 2025, Montreal, Canada
Summary
多任务语义通信(SC)能减少无线系统中的计算资源,因为任务切换时无需重新训练。然而,现有方法通常依赖任务特定嵌入来识别目标任务,当面临新任务时需要重新训练整个模型。因此,需要一种能处理新任务而无需额外训练的多任务SC系统,即零样本学习能力。受大型语言模型(LLM)出色零样本学习能力的启发,我们利用预训练的指令调整LLM(称为精细调整语言网络(FLAN))来提高泛化能力。我们将混合专家(MoE)架构融入FLAN模型,并提出MoE-FLAN-SC架构用于多任务SC系统。我们提出的MoE-FLAN-SC架构能在不增加计算成本的情况下提高FLAN-T5模型的性能。此外,我们设计了一个多任务特征提取模块(FEM),可以自适应地提取各种任务的相关特征,并考虑提供的特征和信噪比(SNR)。模拟结果表明,我们提出的MoE-FLAN-SC架构在四个不同未见任务上的平均准确率优于三种最新模型。
Key Takeaways
- 多任务语义通信(SC)能减少无线系统中的计算资源,且切换任务时无需重新训练。
- 现有方法依赖任务特定嵌入来识别目标任务,这在新任务处理时带来不便。
- 需要一种具有零样本学习能力的多任务SC系统来处理新任务而无需额外训练。
- 受LLM出色零样本学习能力的启发,结合预训练指令调整的LLM(FLAN)提升泛化能力。
- 融入混合专家(MoE)架构到FLAN模型中,提出MoE-FLAN-SC架构用于多任务SC系统,提高性能且计算成本不增。
- 设计多任务特征提取模块(FEM),能自适应提取不同任务的相关特征,并考虑信噪比(SNR)。
点此查看论文截图

X2I: Seamless Integration of Multimodal Understanding into Diffusion Transformer via Attention Distillation
Authors:Jian Ma, Qirong Peng, Xu Guo, Chen Chen, Haonan Lu, Zhenyu Yang
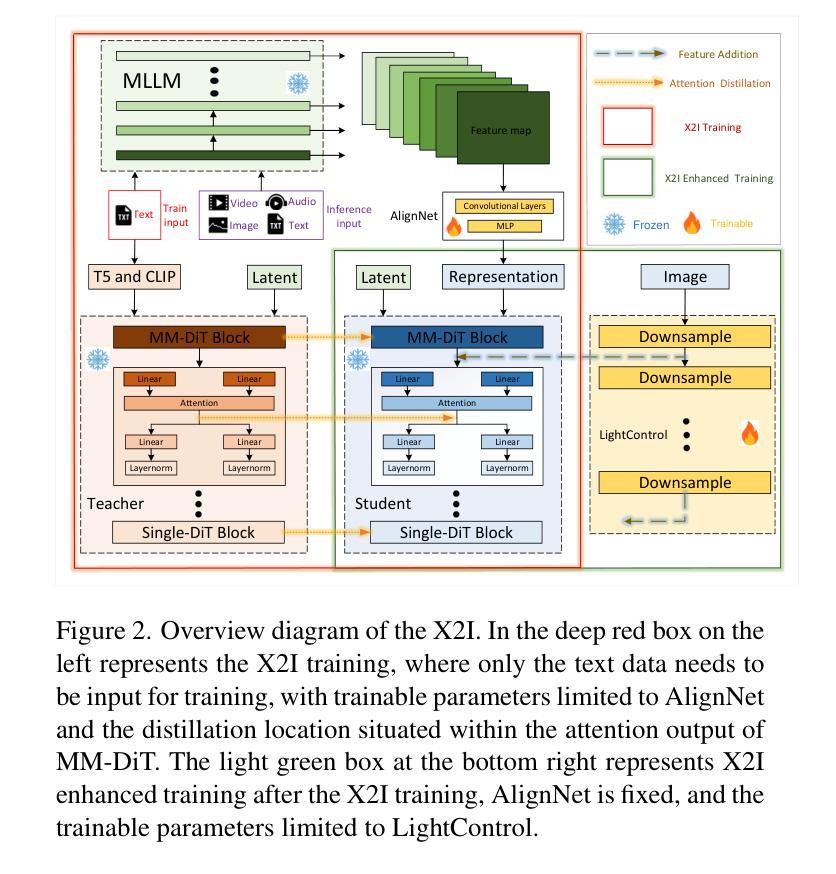
Text-to-image (T2I) models are well known for their ability to produce highly realistic images, while multimodal large language models (MLLMs) are renowned for their proficiency in understanding and integrating multiple modalities. However, currently there is no straightforward and efficient framework to transfer the multimodal comprehension abilities of MLLMs to T2I models to enable them to understand multimodal inputs. In this paper, we propose the X2I framework, which endows Diffusion Transformer (DiT) models with the capability to comprehend various modalities, including multilingual text, screenshot documents, images, videos, and audio. X2I is trained using merely 100K English corpus with 160 GPU hours. Building on the DiT teacher model, we adopt an innovative distillation method to extract the inference capabilities of the teacher model and design a lightweight AlignNet structure to serve as an intermediate bridge. Compared to the teacher model, X2I shows a decrease in performance degradation of less than 1% while gaining various multimodal understanding abilities, including multilingual to image, image to image, image-text to image, video to image, audio to image, and utilizing creative fusion to enhance imagery. Furthermore, it is applicable for LoRA training in the context of image-text to image generation, filling a void in the industry in this area. We further design a simple LightControl to enhance the fidelity of instructional image editing. Finally, extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness, efficiency, multifunctionality, and transferability of our X2I. The open-source code and checkpoints for X2I can be found at the following link: https://github.com/OPPO-Mente-Lab/X2I.
文本到图像(T2I)模型以其生成高度逼真的图像的能力而闻名,而多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)则以其在理解和融合多种模态方面的熟练程度而闻名。然而,目前尚没有简单有效的框架能够将MLLM的多模态理解能力转移到T2I模型上,以便使其能够理解多模态输入。在本文中,我们提出了X2I框架,该框架赋予了Diffusion Transformer(DiT)模型理解各种模态的能力,包括多语言文本、截图文档、图像、视频和音频。X2I仅使用100K英文语料库和160 GPU小时进行训练。基于DiT教师模型,我们采用了一种创新的知识蒸馏方法来提取教师模型的推理能力,并设计了一个轻量级的AlignNet结构作为中间桥梁。与教模型相比,X2I的性能下降程度不到1%,同时获得了多种多模态理解能力,包括多语言到图像、图像到图像、图像文本到图像、视频到图像、音频到图像,并利用创意融合增强图像。此外,它适用于图像文本到图像生成的LoRA训练,填补了行业空白。我们还设计了一个简单的LightControl来增强指令性图像编辑的保真度。最后,大量实验证明了我们的X2I的有效性、效率、多功能性和可转移性。X2I的开源代码和检查点可以在以下链接找到:https://github.com/OPPO-Mente-Lab/X2I。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://github.com/OPPO-Mente-Lab/X2I
Summary
本文提出了一个名为X2I的框架,它赋予Diffusion Transformer(DiT)模型理解多种模式的能力,包括多语言文本、截图文档、图像、视频和音频。该框架使用仅100K的英文语料库和160个GPU小时进行训练,通过创新的蒸馏方法和轻量级的AlignNet结构,实现了对多种模态的深入理解。与DiT教师模型相比,X2I在获得多种模态理解能力的同时,性能下降不到1%,并展示了在各种模态到图像转换任务中的有效性。此外,它适用于图像文本到图像生成的LoRA训练,填补了行业空白。并设计了一个简单的LightControl,以提高指导图像编辑的保真度。
Key Takeaways
- X2I框架成功将Diffusion Transformer模型扩展为多模态理解能力,涵盖多种输入模式,如多语言文本、截图、图像、视频和音频。
- 仅使用100K的英文语料库和160GPU小时的训练,实现了高效的模型训练。
- 通过创新的蒸馏方法和轻量级AlignNet结构,有效提取教师模型的推理能力。
- 与教师模型相比,X2I性能降低不到1%,在多种模态到图像转换任务中表现出优异的性能。
- 适用于图像文本到图像生成的LoRA训练,填补了行业内的空白。
- 设计了LightControl,提高了指导图像编辑的保真度。
- 进行了广泛的实验,证明了X2I的有效性、效率、多功能性和可迁移性。
点此查看论文截图


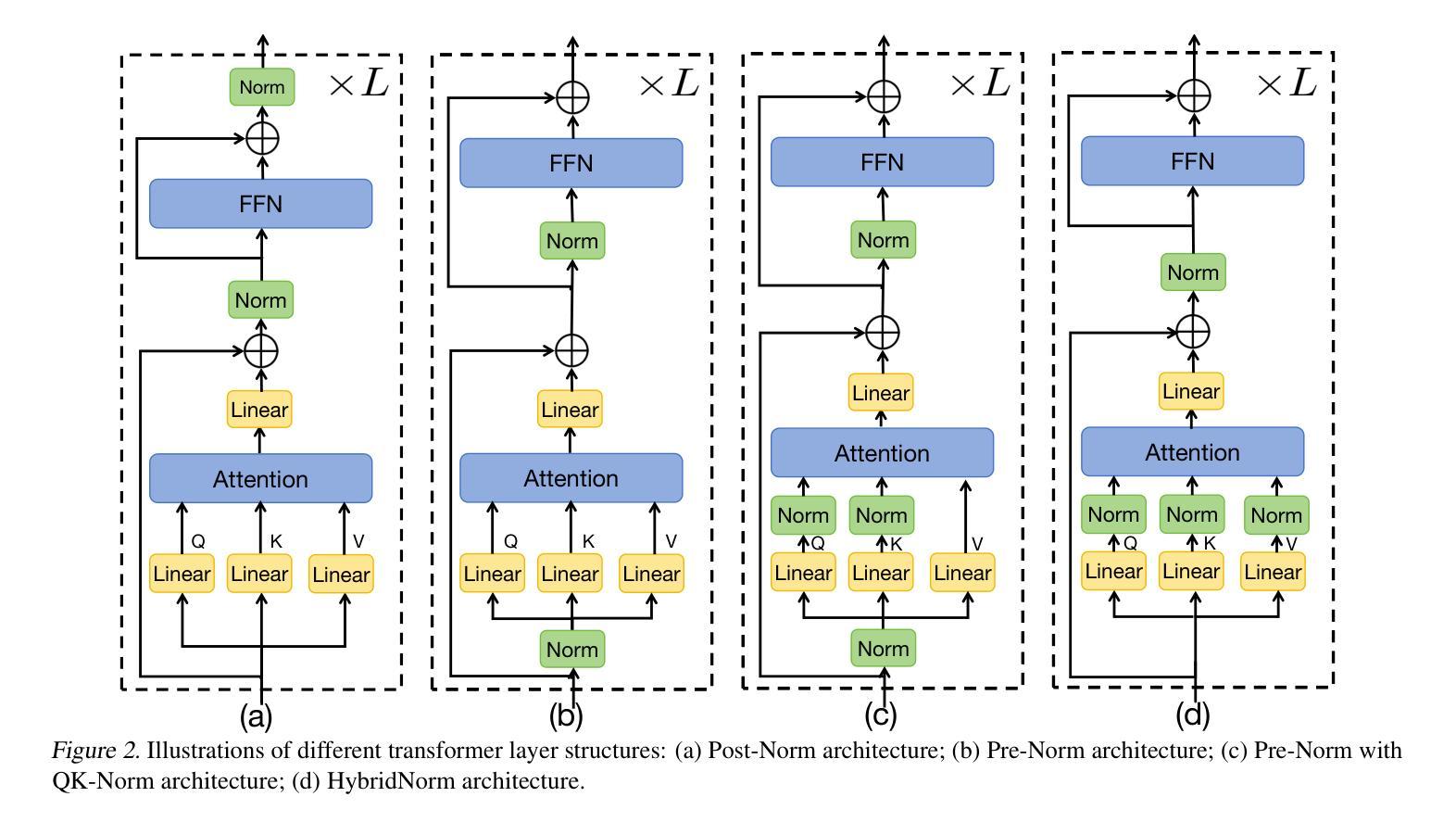
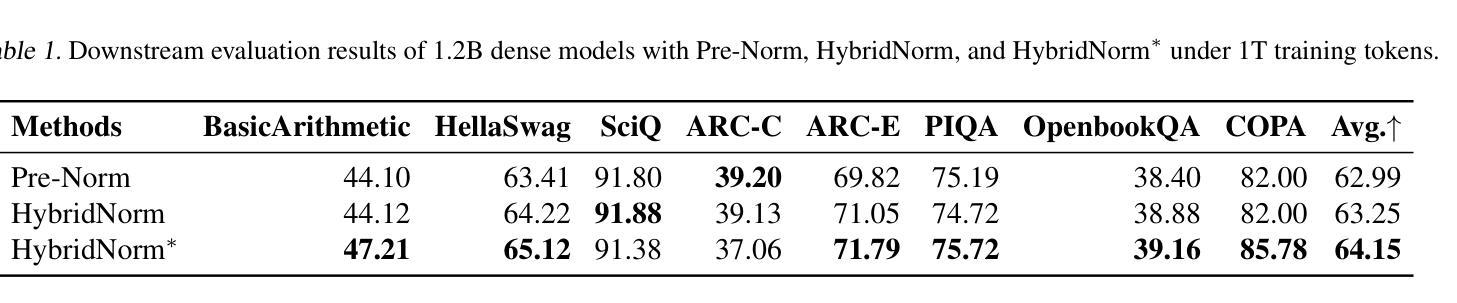
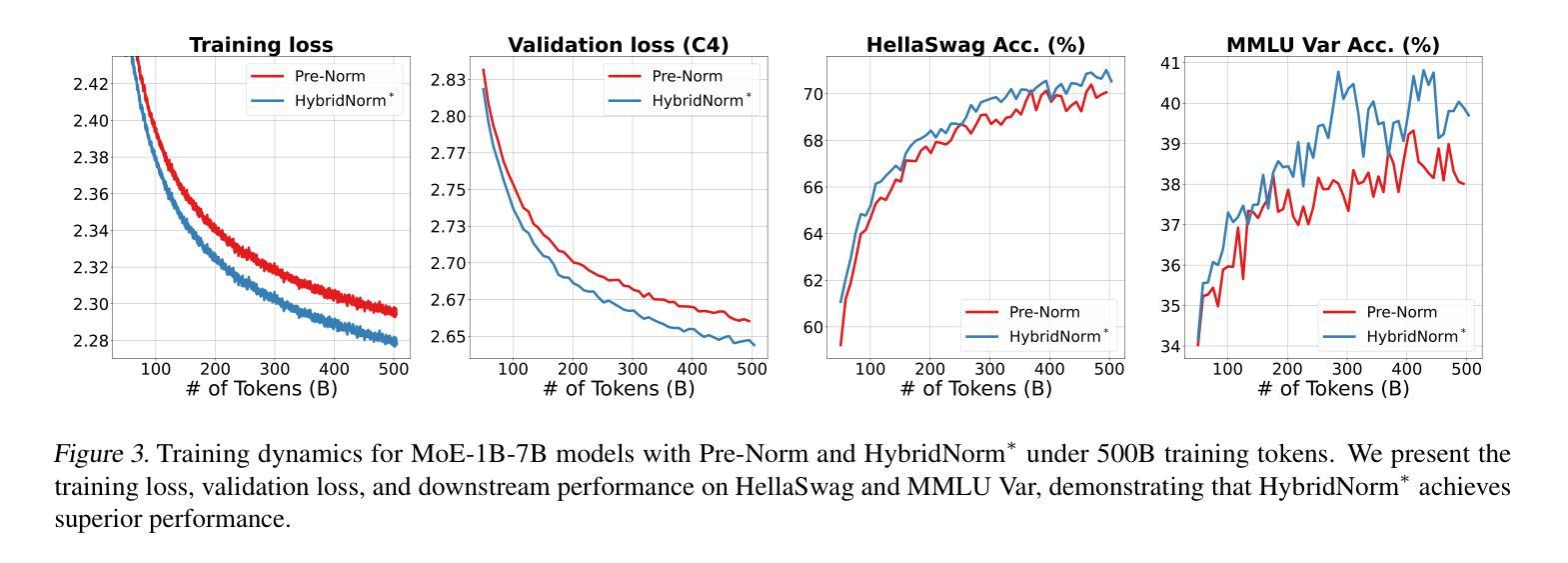
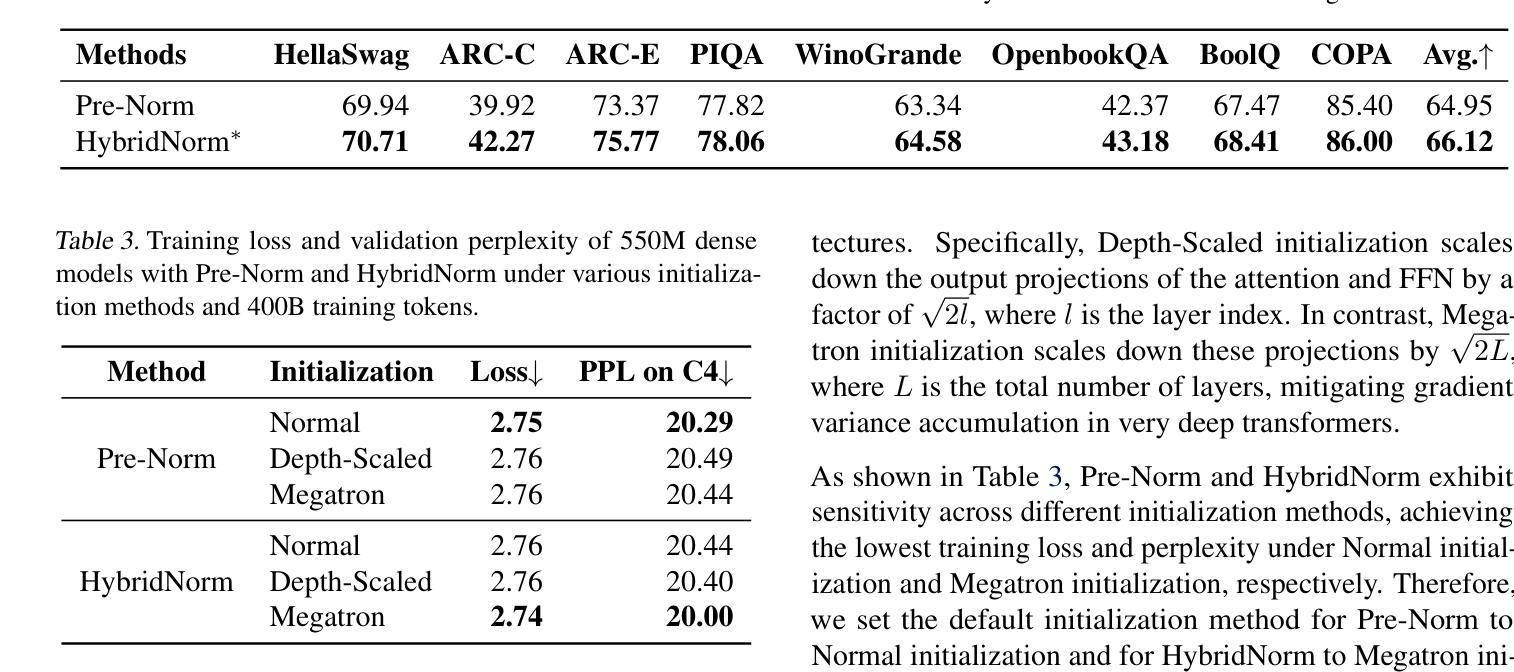
HybridNorm: Towards Stable and Efficient Transformer Training via Hybrid Normalization
Authors:Zhijian Zhuo, Yutao Zeng, Ya Wang, Sijun Zhang, Jian Yang, Xiaoqing Li, Xun Zhou, Jinwen Ma
Transformers have become the de facto architecture for a wide range of machine learning tasks, particularly in large language models (LLMs). Despite their remarkable performance, challenges remain in training deep transformer networks, especially regarding the location of layer normalization. While Pre-Norm structures facilitate easier training due to their more prominent identity path, they often yield suboptimal performance compared to Post-Norm. In this paper, we propose $\textbf{HybridNorm}$, a straightforward yet effective hybrid normalization strategy that integrates the advantages of both Pre-Norm and Post-Norm approaches. Specifically, HybridNorm employs QKV normalization within the attention mechanism and Post-Norm in the feed-forward network (FFN) of each transformer block. This design not only stabilizes training but also enhances performance, particularly in the context of LLMs. Comprehensive experiments in both dense and sparse architectures show that HybridNorm consistently outperforms both Pre-Norm and Post-Norm approaches, achieving state-of-the-art results across various benchmarks. These findings highlight the potential of HybridNorm as a more stable and effective technique for improving the training and performance of deep transformer models. Code is available at https://github.com/BryceZhuo/HybridNorm.
Transformer架构在众多机器学习任务中已成为实际应用的标配,特别是在大型语言模型(LLM)中。尽管其性能显著,但在训练深度Transformer网络时仍存在挑战,特别是关于层归一化的位置。虽然Pre-Norm结构由于其更突出的身份路径而易于训练,但它通常产生的性能不如Post-Norm。在本文中,我们提出了$\textbf{HybridNorm}$,这是一种简单有效的混合归一化策略,它结合了Pre-Norm和Post-Norm方法的优势。具体来说,HybridNorm在注意力机制中采用QKV归一化,并在每个Transformer块的前馈网络(FFN)中使用Post-Norm。这种设计不仅稳定训练,还提高了性能,特别是在大型语言模型的背景下。在密集和稀疏架构中的综合实验表明,HybridNorm始终优于Pre-Norm和Post-Norm方法,在各种基准测试中取得最新结果。这些发现突显了HybridNorm作为更稳定、更有效的技术,可以改善深度Transformer模型的训练和性能。代码可在https://github.com/BryceZhuo/HybridNorm获得。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出了HybridNorm,一种结合了Pre-Norm和Post-Norm优势的混合归一化策略。在注意力机制中采用QKV归一化,并在每个transformer块的feed-forward网络(FFN)中采用Post-Norm。这种方法既稳定训练,又提升性能,特别是在大型语言模型(LLMs)的背景下。综合实验表明,HybridNorm在多种基准测试中始终优于Pre-Norm和Post-Norm方法,取得了最先进的成果。HybridNorm具有潜力成为改进深度transformer模型训练和性能的更稳定、更有效的技术。
关键见解
- Transformers已成为多种机器学习任务的默认架构,特别是在大型语言模型(LLMs)中。
- 尽管Transformer表现出色,但在训练深度网络时仍面临挑战,其中之一是层归一化的位置问题。
- Pre-Norm结构因更突出的身份路径而易于训练,但相比Post-Norm,其性能往往不佳。
- HybridNorm结合了Pre-Norm和Post-Norm的优点,提出了一种新的混合归一化策略。
- HybridNorm在注意力机制中采用QKV归一化,并在feed-forward网络(FFN)中使用Post-Norm。
- 综合实验表明,HybridNorm在各种基准测试中表现卓越,不仅稳定训练,而且提高了性能。
- HybridNorm具有潜力成为改进深度transformer模型训练和性能的有效技术。
点此查看论文截图