⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-03-29 更新
Video-R1: Reinforcing Video Reasoning in MLLMs
Authors:Kaituo Feng, Kaixiong Gong, Bohao Li, Zonghao Guo, Yibing Wang, Tianshuo Peng, Benyou Wang, Xiangyu Yue
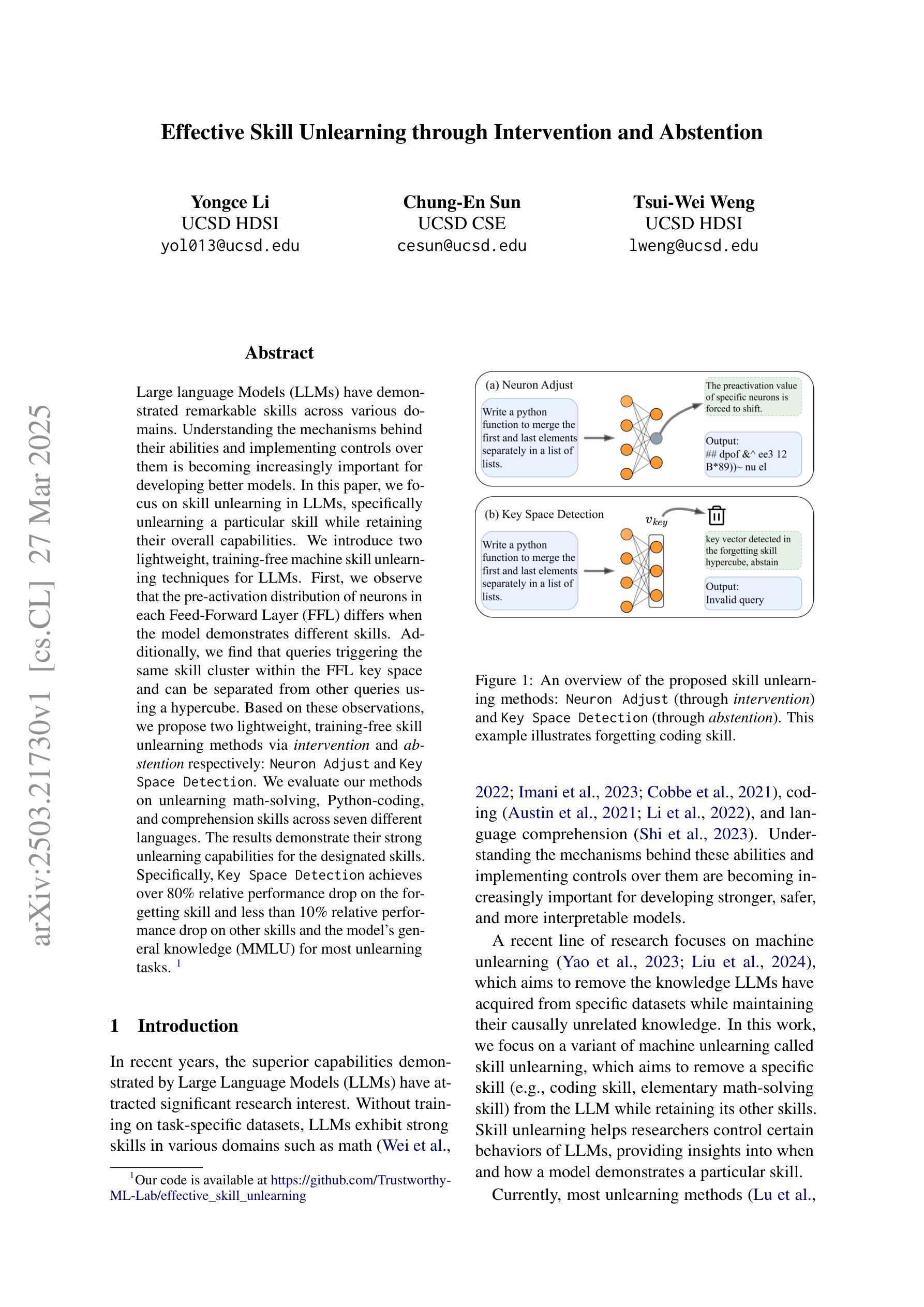
Inspired by DeepSeek-R1’s success in eliciting reasoning abilities through rule-based reinforcement learning (RL), we introduce Video-R1 as the first attempt to systematically explore the R1 paradigm for eliciting video reasoning within multimodal large language models (MLLMs). However, directly applying RL training with the GRPO algorithm to video reasoning presents two primary challenges: (i) a lack of temporal modeling for video reasoning, and (ii) the scarcity of high-quality video-reasoning data. To address these issues, we first propose the T-GRPO algorithm, which encourages models to utilize temporal information in videos for reasoning. Additionally, instead of relying solely on video data, we incorporate high-quality image-reasoning data into the training process. We have constructed two datasets: Video-R1-COT-165k for SFT cold start and Video-R1-260k for RL training, both comprising image and video data. Experimental results demonstrate that Video-R1 achieves significant improvements on video reasoning benchmarks such as VideoMMMU and VSI-Bench, as well as on general video benchmarks including MVBench and TempCompass, etc. Notably, Video-R1-7B attains a 35.8% accuracy on video spatial reasoning benchmark VSI-bench, surpassing the commercial proprietary model GPT-4o. All codes, models, data are released.
受DeepSeek-R1通过基于规则的强化学习(RL)激发推理能力的成功的启发,我们推出Video-R1,这是首次尝试在系统探索R1范式以激发多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)中的视频推理。然而,将GRPO算法直接应用于视频推理的强化学习训练面临两个主要挑战:(i)视频推理缺乏时间建模;(ii)高质量视频推理数据的稀缺。为了解决这些问题,我们首先提出T-GRPO算法,该算法鼓励模型利用视频中的时间信息进行推理。此外,我们不是仅依赖视频数据,而是将高质量图像推理数据纳入训练过程。我们构建了两个数据集:用于SFT冷启动的Video-R1-COT-165k和用于RL训练的视频R1-260k,两者都包含图像和视频数据。实验结果表明,Video-R1在视频推理基准测试(如VideoMMMU和VSI-Bench)以及通用视频基准测试(包括MVBench和TempCompass等)上取得了显著改进。值得注意的是,Video-R1-7B在视频空间推理基准测试VSI-bench上达到了35.8%的准确率,超过了商业专有模型GPT-4o。所有代码、模型、数据均已发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://github.com/tulerfeng/Video-R1
Summary
基于DeepSeek-R1通过规则强化学习(RL)激发推理能力的成功,我们首次尝试推出Video-R1,旨在系统探索R1范式在多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)中的视频推理应用。为应对视频推理中缺乏时间建模和高质量视频推理数据稀缺的问题,我们提出T-GRPO算法并整合图像推理数据。实验结果显示,Video-R1在视频推理基准测试VideoMMMU和VSI-Bench上表现显著,且在通用视频基准测试MVBench和TempCompass等上也有良好表现。我们发布代码、模型和全部数据集。
Key Takeaways
- Video-R1首次尝试系统探索R1范式在多模态大型语言模型中的视频推理应用。
- Video-R1面临的主要挑战包括缺乏视频推理的时间建模和高质量视频推理数据的稀缺性。
- 为解决这些问题,提出T-GRPO算法来鼓励模型利用视频中的时间信息进行推理。
- 结合高质量图像推理数据以增强模型训练效果。
- Video-R1在多个视频推理基准测试中表现优异,包括VideoMMMU和VSI-Bench等。
- Video-R1在通用视频基准测试上也有良好表现,如MVBench和TempCompass等。
点此查看论文截图

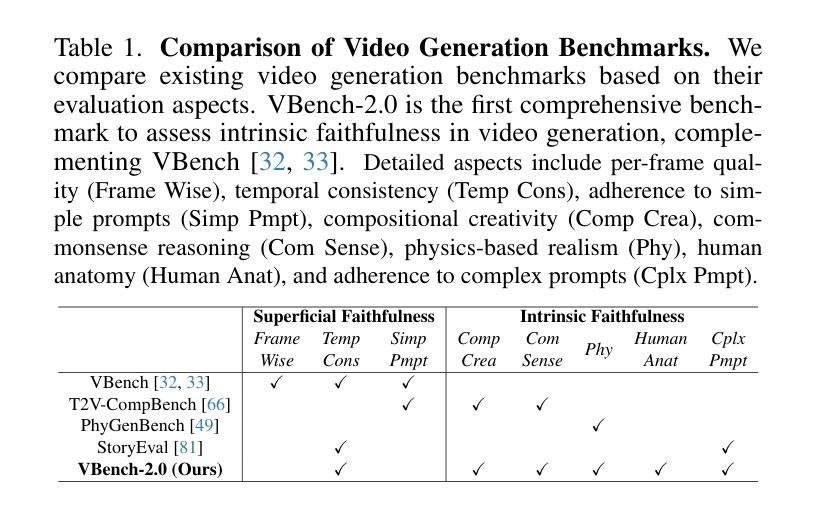
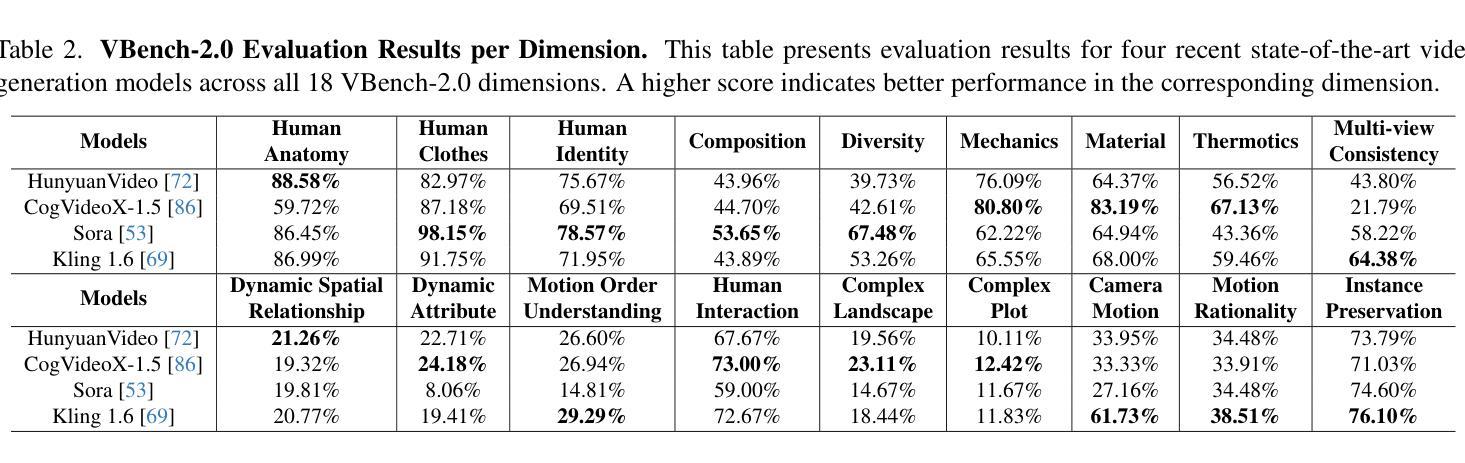
VBench-2.0: Advancing Video Generation Benchmark Suite for Intrinsic Faithfulness
Authors:Dian Zheng, Ziqi Huang, Hongbo Liu, Kai Zou, Yinan He, Fan Zhang, Yuanhan Zhang, Jingwen He, Wei-Shi Zheng, Yu Qiao, Ziwei Liu
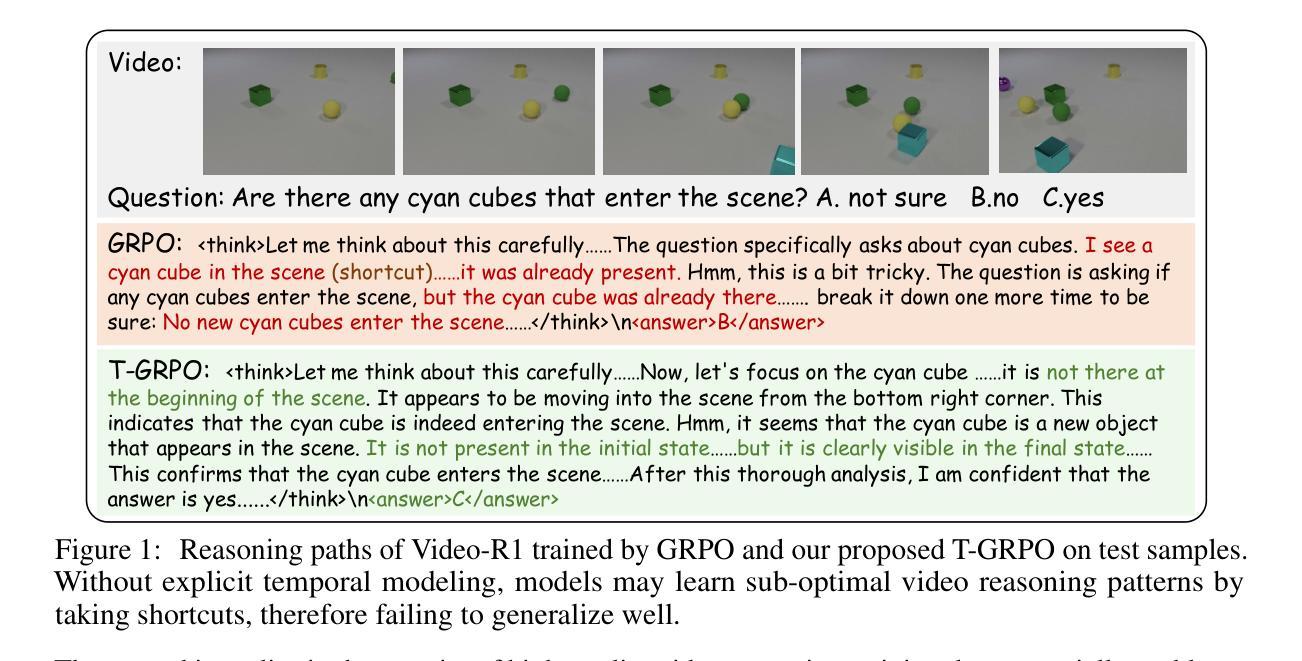
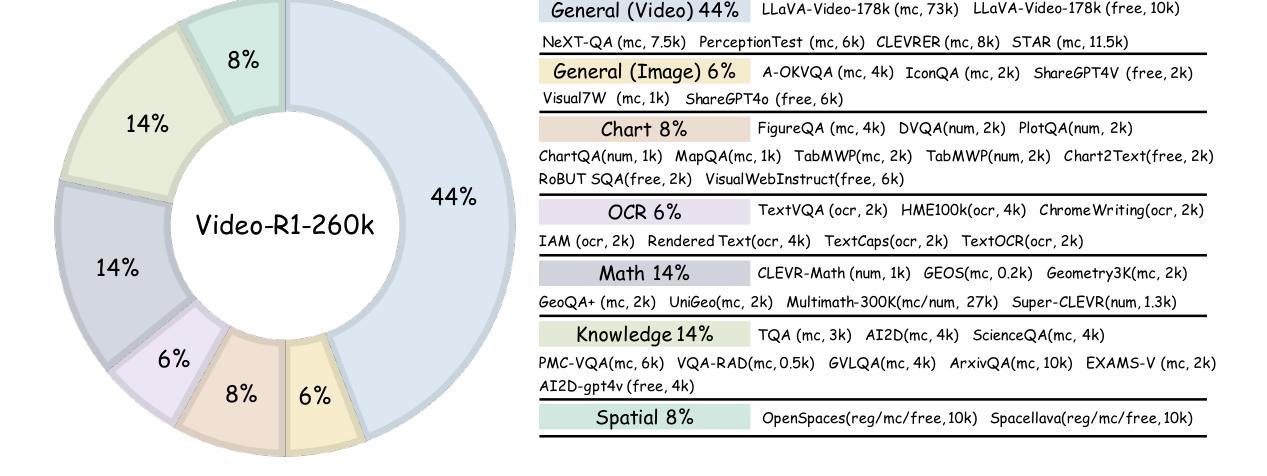
Video generation has advanced significantly, evolving from producing unrealistic outputs to generating videos that appear visually convincing and temporally coherent. To evaluate these video generative models, benchmarks such as VBench have been developed to assess their faithfulness, measuring factors like per-frame aesthetics, temporal consistency, and basic prompt adherence. However, these aspects mainly represent superficial faithfulness, which focus on whether the video appears visually convincing rather than whether it adheres to real-world principles. While recent models perform increasingly well on these metrics, they still struggle to generate videos that are not just visually plausible but fundamentally realistic. To achieve real “world models” through video generation, the next frontier lies in intrinsic faithfulness to ensure that generated videos adhere to physical laws, commonsense reasoning, anatomical correctness, and compositional integrity. Achieving this level of realism is essential for applications such as AI-assisted filmmaking and simulated world modeling. To bridge this gap, we introduce VBench-2.0, a next-generation benchmark designed to automatically evaluate video generative models for their intrinsic faithfulness. VBench-2.0 assesses five key dimensions: Human Fidelity, Controllability, Creativity, Physics, and Commonsense, each further broken down into fine-grained capabilities. Tailored for individual dimensions, our evaluation framework integrates generalists such as state-of-the-art VLMs and LLMs, and specialists, including anomaly detection methods proposed for video generation. We conduct extensive annotations to ensure alignment with human judgment. By pushing beyond superficial faithfulness toward intrinsic faithfulness, VBench-2.0 aims to set a new standard for the next generation of video generative models in pursuit of intrinsic faithfulness.
视频生成技术已经取得了显著的进步,从产生不现实的输出发展到生成在视觉上令人信服并且在时间上连贯的视频。为了评估这些视频生成模型的性能,已经开发出了像VBench这样的基准测试平台,来评估它们的忠实度,测量诸如每帧美学、时间一致性和基本提示遵循等因素。然而,这些方面主要代表了表面忠实度,重点在于视频在视觉上是否令人信服,而不是是否遵循现实世界的原则。尽管最近的模型在这些指标上的表现越来越好,但它们仍然难以生成不仅仅是视觉上可信、而是从根本上现实的视频。通过视频生成实现真正的“世界模型”,下一个前沿在于内在忠实度,以确保生成的视频遵循物理定律、常识推理、解剖正确性和构图完整性。实现这种程度的真实性对于AI辅助电影制作和模拟世界建模等应用至关重要。为了弥合这一差距,我们推出了VBench-2..下一代基准测试平台旨在自动评估视频生成模型的内在忠实度。VBench-2.评估五个关键维度:人类保真度、可控性、创造力、物理学和常识,每个维度都进一步细化为精细功能。我们的评估框架针对各个维度进行定制,集成了诸如最新技术中的大型视频模型和大型语言模型等通用模型以及针对视频生成的异常检测方法等专家系统。我们进行了广泛的注释以确保与人类判断一致。通过超越表面忠实度而追求内在忠实度,VBench-旨在树立视频生成模型的新一代标准,以追求内在忠实度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Equal contributions from first two authors. Project page: https://vchitect.github.io/VBench-2.0-project/ Code: https://github.com/Vchitect/VBench
摘要
视频生成技术已显著进步,从产生不真实的输出发展到能够生成视觉上令人信服且时间连贯的视频。为评估视频生成模型,已开发出诸如VBench等基准测试来评估其忠实度,主要衡量每帧美学、时间连贯性和基本提示遵循等因素。然而,这些方面主要代表表面忠实度,关注的是视频是否视觉上令人信服,而不是是否遵循现实世界的原则。尽管最近模型在这些指标上的表现越来越好,但它们仍然难以生成不仅是视觉上可信的,而且从根本上现实的视频。为实现通过视频生成的真实“世界模型”,下一个前沿在于内在忠实度,以确保生成的视频遵循物理定律、常识推理、解剖正确性和组成完整性。为了实现这一级别的现实主义,我们引入了VBench-2.0,这是一个旨在自动评估视频生成模型的内在忠实度的下一代基准测试。VBench-2.0评估了五个关键维度:人类保真度、可控性、创造力、物理学和常识,每个维度进一步细化为精细功能。我们的评估框架整合了通用人员(如最先进的视频语言模型和大型语言模型)和专家(包括针对视频生成提出的异常检测方法)。通过超越表面忠实度追求内在忠实度,VBench-2.0旨在为追求内在忠实度的下一代视频生成模型设定新标准。
关键见解
- 视频生成技术已取得显著进展,从产生不真实的输出到生成视觉上有说服力的视频。
- 现有基准测试如VBench主要衡量视频生成模型的表面忠实度。
- 内在忠实度是确保生成的视频遵循物理定律、常识推理等的关键因素。
- VBench-2.0是一个新的基准测试,旨在自动评估视频生成模型的内在忠实度。
- VBench-2.0评估了五个关键维度:人类保真度、可控性、创造力、物理学和常识。
- VBench-2.0结合了通用模型和针对特定任务的专家模型进行评估。
点此查看论文截图

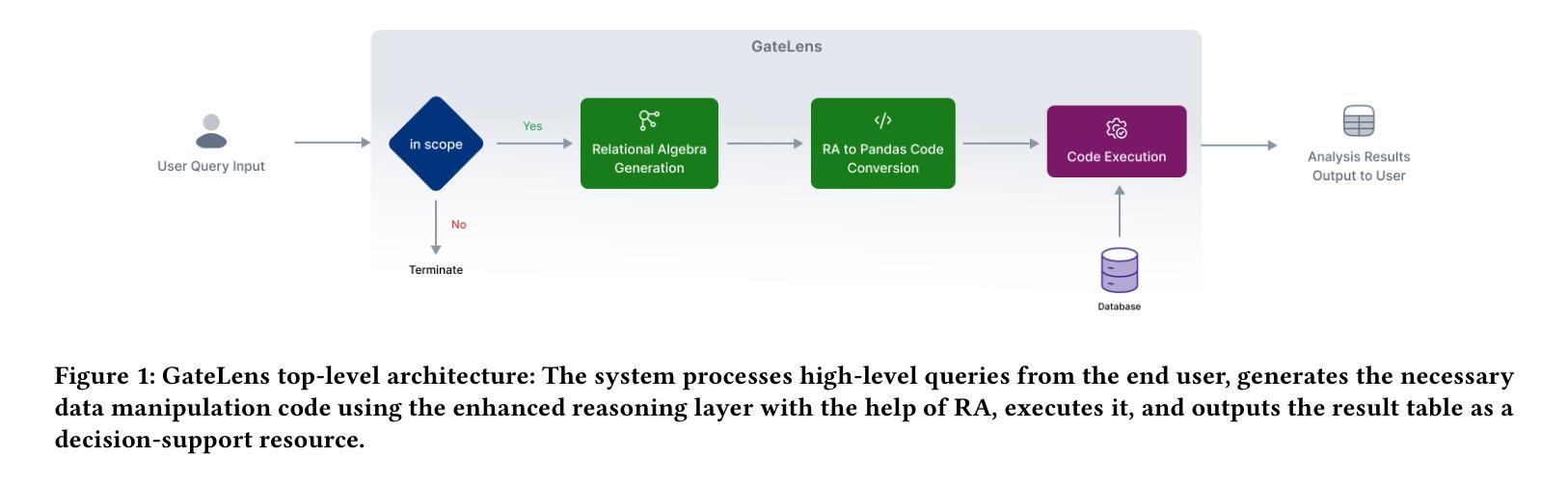
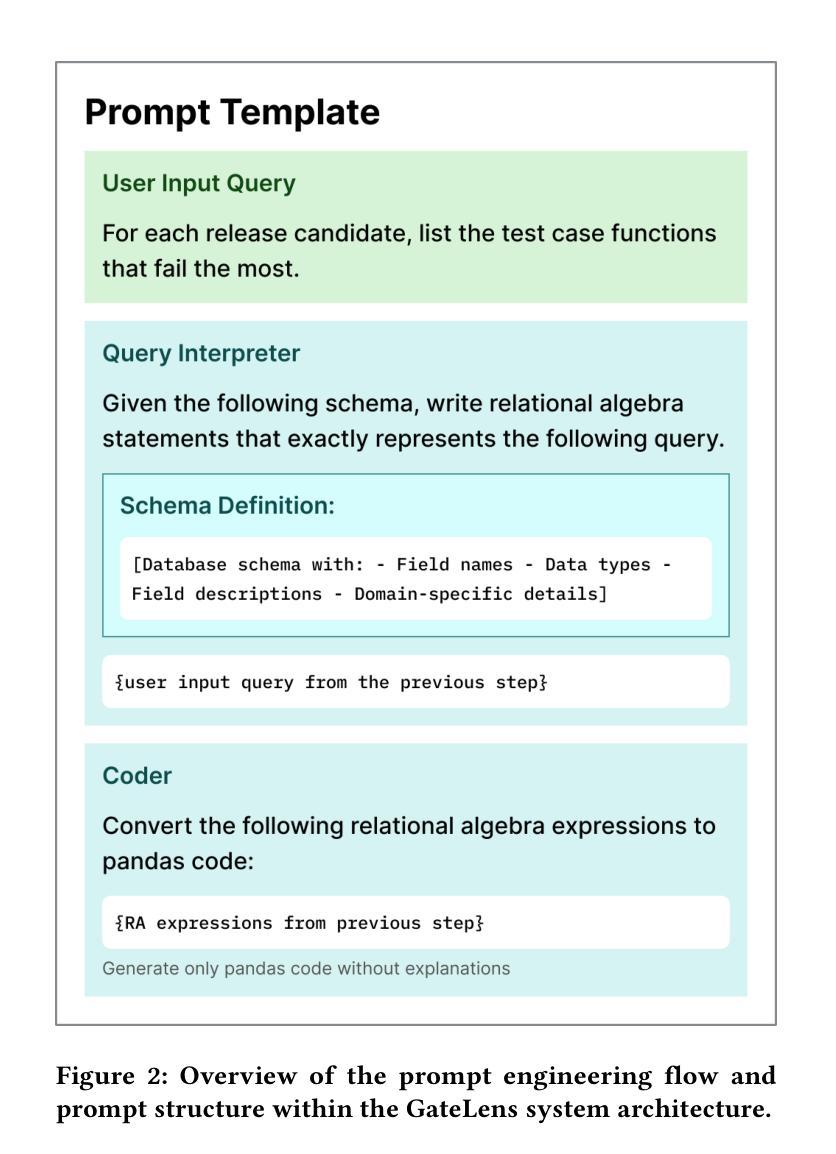
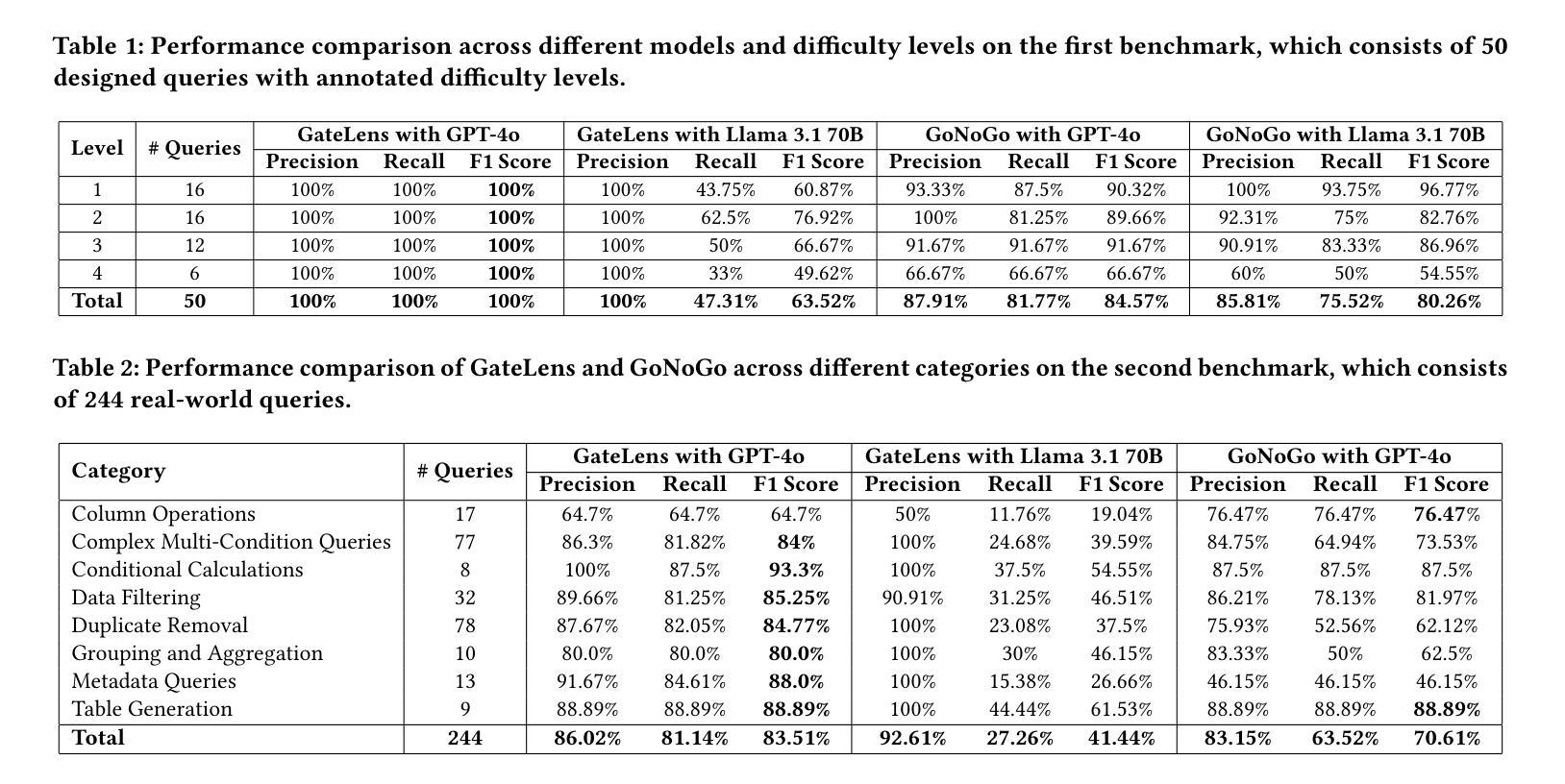
GateLens: A Reasoning-Enhanced LLM Agent for Automotive Software Release Analytics
Authors:Arsham Gholamzadeh Khoee, Shuai Wang, Yinan Yu, Robert Feldt, Dhasarathy Parthasarathy
Ensuring the reliability and effectiveness of software release decisions is critical, particularly in safety-critical domains like automotive systems. Precise analysis of release validation data, often presented in tabular form, plays a pivotal role in this process. However, traditional methods that rely on manual analysis of extensive test datasets and validation metrics are prone to delays and high costs. Large Language Models (LLMs) offer a promising alternative but face challenges in analytical reasoning, contextual understanding, handling out-of-scope queries, and processing structured test data consistently; limitations that hinder their direct application in safety-critical scenarios. This paper introduces GateLens, an LLM-based tool for analyzing tabular data in the automotive domain. GateLens translates natural language queries into Relational Algebra (RA) expressions and then generates optimized Python code. It outperforms the baseline system on benchmarking datasets, achieving higher F1 scores and handling complex and ambiguous queries with greater robustness. Ablation studies confirm the critical role of the RA module, with performance dropping sharply when omitted. Industrial evaluations reveal that GateLens reduces analysis time by over 80% while maintaining high accuracy and reliability. As demonstrated by presented results, GateLens achieved high performance without relying on few-shot examples, showcasing strong generalization across various query types from diverse company roles. Insights from deploying GateLens with a partner automotive company offer practical guidance for integrating AI into critical workflows such as release validation. Results show that by automating test result analysis, GateLens enables faster, more informed, and dependable release decisions, and can thus advance software scalability and reliability in automotive systems.
确保软件发布决策的可信度和有效性至关重要,特别是在汽车系统这样的安全关键领域。以表格形式呈现的发布验证数据的精确分析在此过程中起着至关重要的作用。然而,传统的方法依赖于对大量测试数据集和验证指标的手动分析,容易出现延迟和成本高昂的问题。大型语言模型(LLM)提供了有前景的替代方案,但在分析推理、上下文理解、处理超出范围查询和处理结构化测试数据方面面临挑战;这些局限性阻碍了它们在安全关键场景中的直接应用。本文介绍了GateLens,一个基于LLM的汽车领域表格数据分析工具。GateLens将自然语言查询翻译成关系代数(RA)表达式,然后生成优化的Python代码。它在基准数据集上超越了基准系统,实现了更高的F1分数,并能更稳健地处理复杂和模糊查询。消融研究证实了RA模块的关键作用,在省略该模块时性能急剧下降。工业评估表明,GateLens将分析时间减少了80%以上,同时保持了高准确性和可靠性。正如所展示的结果,GateLens在不依赖少量示例的情况下实现了高性能,展示了在各种查询类型中的强大泛化能力,这些查询类型来自各种公司角色。通过与合作伙伴汽车公司部署GateLens所获得的见解为将人工智能集成到关键工作流程(如发布验证)提供了实际指导。结果表明,通过自动化测试结果分析,GateLens能够做出更快、更可靠、更有根据的发布决策,从而可以提高汽车系统的软件可扩展性和可靠性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了一种名为GateLens的基于大语言模型的工具,用于分析汽车领域的表格数据。它能够将自然语言查询转化为关系代数表达式,并生成优化的Python代码。相较于传统方法,GateLens在处理汽车软件发布决策的数据分析时表现出更高的效率和准确性。它能够减少分析时间并维持高可靠性和精确度,推进了软件在汽车系统的可扩展性和可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- 汽车系统软件的发布决策需要确保可靠性和有效性。
- 传统方法在处理大量测试数据集和验证指标时存在延迟和成本高昂的问题。
- 大语言模型(LLMs)为软件分析提供了有前景的替代方案,但在汽车安全关键场景中直接应用时面临挑战。
- GateLens是一款基于LLM的工具,用于分析汽车领域的表格数据,可将自然语言查询转化为关系代数表达式并生成Python代码。
- GateLens在基准测试数据集上的性能优于基线系统,表现出更高的F1分数和处理复杂模糊查询的鲁棒性。
- 工业评估显示,GateLens减少了超过80%的分析时间,同时保持了高准确性和可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

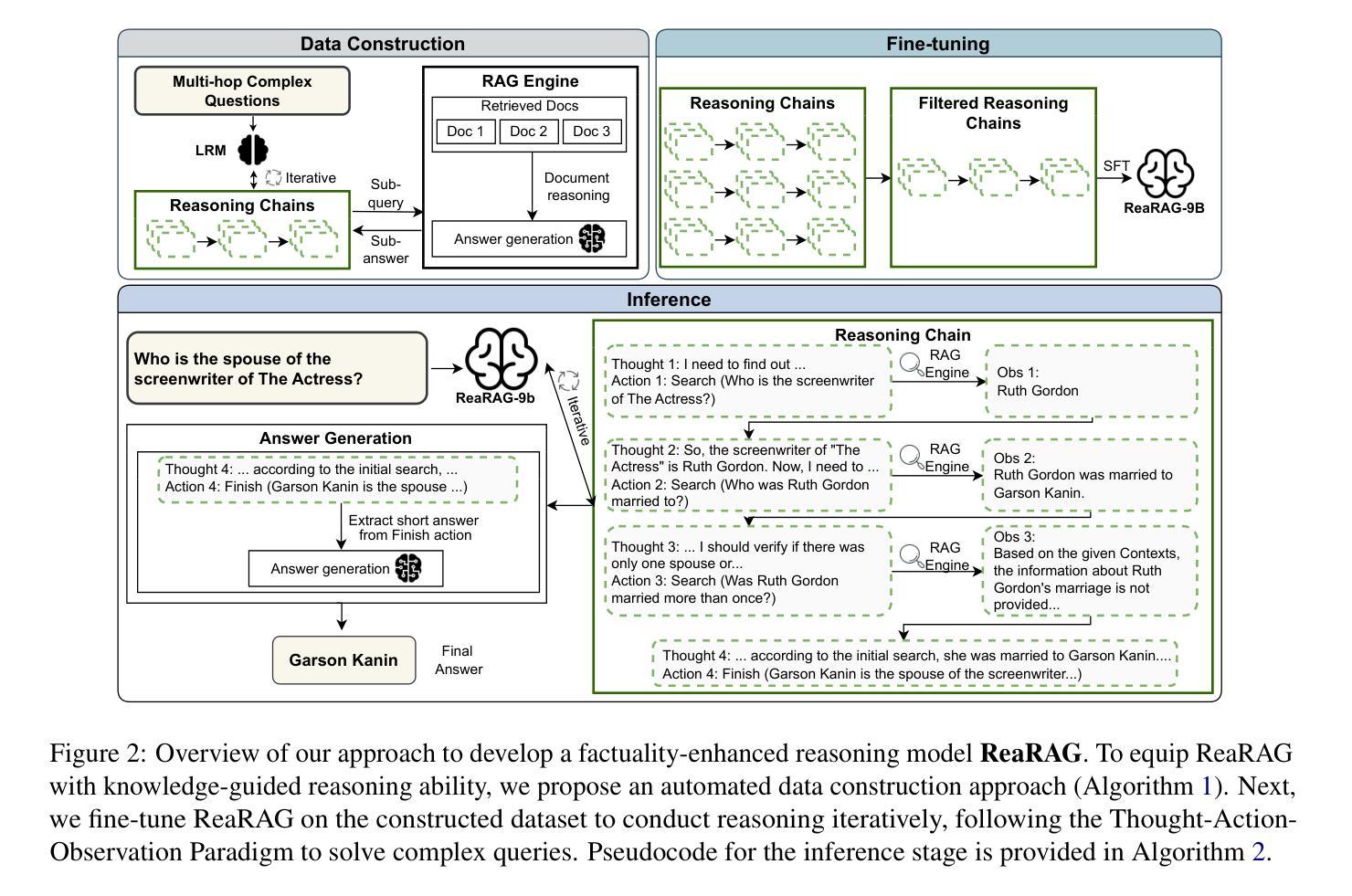
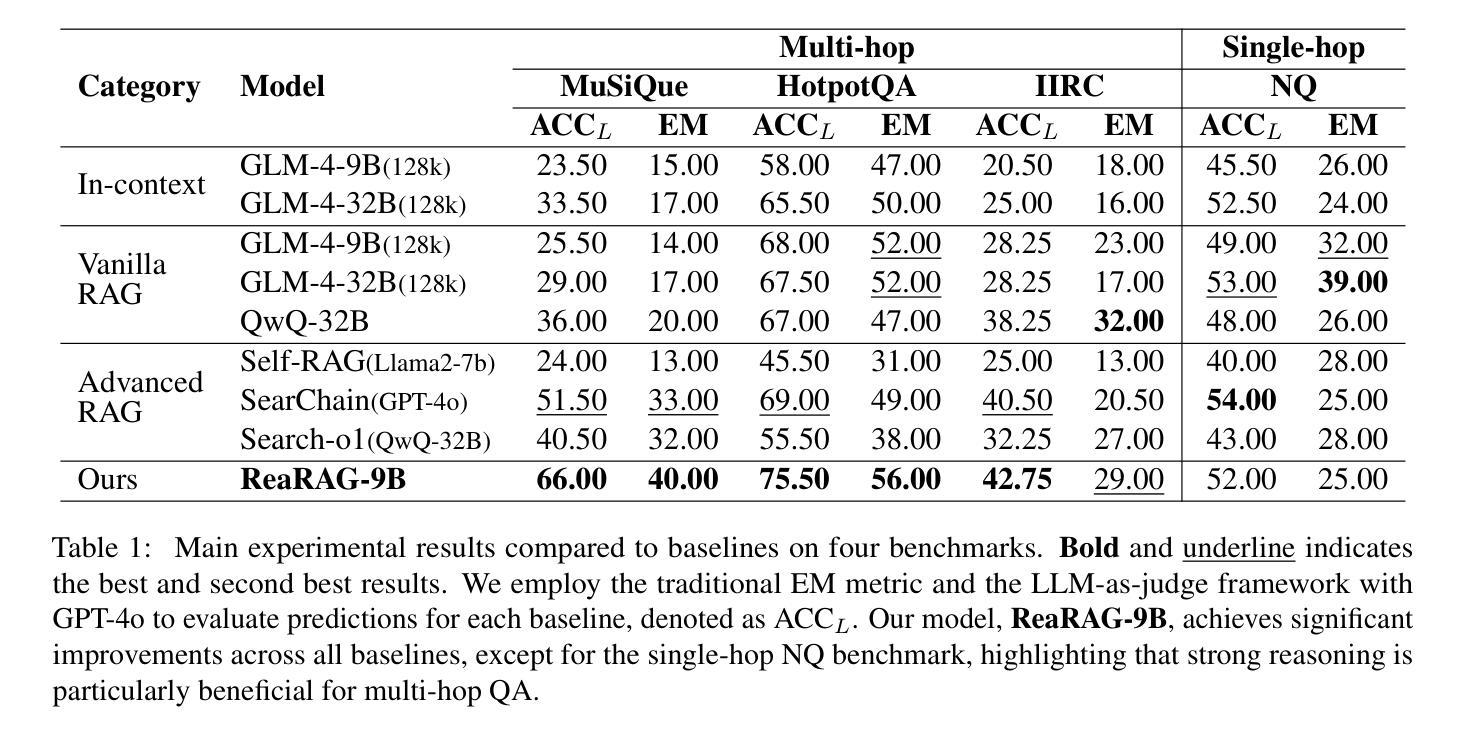
ReaRAG: Knowledge-guided Reasoning Enhances Factuality of Large Reasoning Models with Iterative Retrieval Augmented Generation
Authors:Zhicheng Lee, Shulin Cao, Jinxin Liu, Jiajie Zhang, Weichuan Liu, Xiaoyin Che, Lei Hou, Juanzi Li
Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) exhibit remarkable reasoning abilities but rely primarily on parametric knowledge, limiting factual accuracy. While recent works equip reinforcement learning (RL)-based LRMs with retrieval capabilities, they suffer from overthinking and lack robustness in reasoning, reducing their effectiveness in question answering (QA) tasks. To address this, we propose ReaRAG, a factuality-enhanced reasoning model that explores diverse queries without excessive iterations. Our solution includes a novel data construction framework with an upper bound on the reasoning chain length. Specifically, we first leverage an LRM to generate deliberate thinking, then select an action from a predefined action space (Search and Finish). For Search action, a query is executed against the RAG engine, where the result is returned as observation to guide reasoning steps later. This process iterates until a Finish action is chosen. Benefiting from ReaRAG’s strong reasoning capabilities, our approach outperforms existing baselines on multi-hop QA. Further analysis highlights its strong reflective ability to recognize errors and refine its reasoning trajectory. Our study enhances LRMs’ factuality while effectively integrating robust reasoning for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG).
大型推理模型(LRMs)展现出显著的推理能力,但主要依赖于参数知识,这限制了事实准确性。虽然最近的工作为基于强化学习(RL)的LRMs配备了检索能力,但它们在推理时过于深思熟虑,缺乏稳健性,降低了在问答(QA)任务中的有效性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了ReaRAG,这是一种增强事实性的推理模型,它可以在不进行过多迭代的情况下探索各种查询。我们的解决方案包括一个具有推理链长度上限的新型数据构建框架。具体来说,我们首先利用LRM进行深思熟虑的生成,然后从预定的动作空间中选择一个动作(搜索和完成)。对于搜索动作,会对RAG引擎执行一个查询,结果将作为观察结果返回,以指导后续的推理步骤。这个过程会迭代,直到选择一个完成动作。得益于ReaRAG的强大推理能力,我们的方法在多跳问答任务上的表现超过了现有基线。进一步的分析突出了其强大的反思能力,能够识别错误并优化其推理轨迹。我们的研究提高了LRMs的事实性,同时有效地结合了用于增强检索生成(RAG)的稳健推理。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型推理模型展现出卓越的推理能力,但主要依赖参数知识,影响事实准确性。最新结合强化学习与检索能力的工作虽提升了模型性能,但存在过度思考和缺乏稳健推理的问题,降低了在问答任务中的有效性。本研究提出ReaRAG模型,通过数据构建新框架和限制推理链长度,增强模型的事实性和推理能力。ReaRAG模型能生成深思熟虑的思考,从预设的动作空间中选择动作(搜索和完成)。搜索动作会查询RAG引擎,结果会引导后续的推理步骤。ReaRAG在多步问答任务上超越现有基线,展现出强大的纠错能力和优化推理轨迹的能力。本研究提高了大型推理模型的事实性,同时实现了检索增强生成式模型的稳健推理。
Key Takeaways
- 大型推理模型主要依赖参数知识,影响事实准确性。
- 强化学习与检索能力结合的工作存在过度思考和缺乏稳健推理的问题。
- ReaRAG模型通过数据构建新框架和限制推理链长度,增强事实性和推理能力。
- ReaRAG模型能生成深思熟虑的思考,并能从预设动作空间中选择动作(搜索和完成)。
- ReaRAG模型通过搜索动作查询RAG引擎,结果引导后续推理步骤。
- ReaRAG在多步问答任务上表现优越,具备强大的纠错和优化推理轨迹能力。
点此查看论文截图


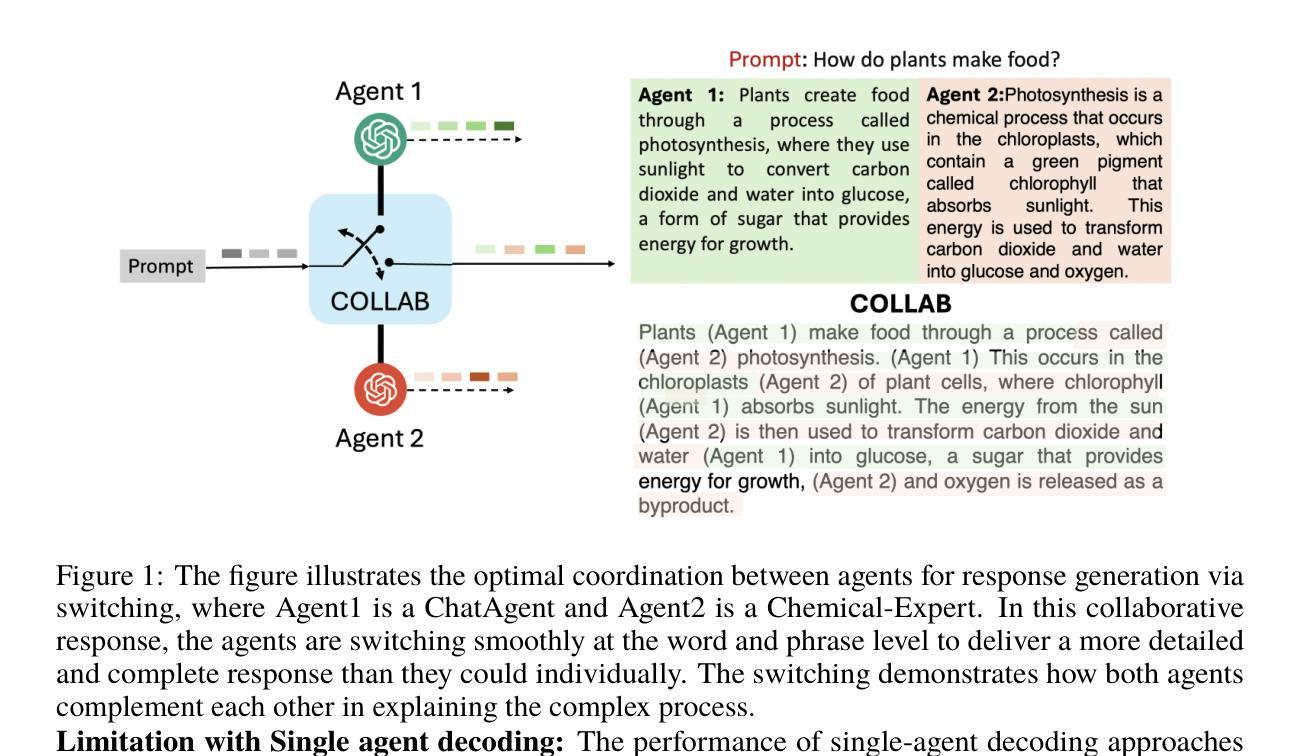
Collab: Controlled Decoding using Mixture of Agents for LLM Alignment
Authors:Souradip Chakraborty, Sujay Bhatt, Udari Madhushani Sehwag, Soumya Suvra Ghosal, Jiahao Qiu, Mengdi Wang, Dinesh Manocha, Furong Huang, Alec Koppel, Sumitra Ganesh
Alignment of Large Language models (LLMs) is crucial for safe and trustworthy deployment in applications. Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) has emerged as an effective technique to align LLMs to human preferences and broader utilities, but it requires updating billions of model parameters, which is computationally expensive. Controlled Decoding, by contrast, provides a mechanism for aligning a model at inference time without retraining. However, single-agent decoding approaches often struggle to adapt to diverse tasks due to the complexity and variability inherent in these tasks. To strengthen the test-time performance w.r.t the target task, we propose a mixture of agent-based decoding strategies leveraging the existing off-the-shelf aligned LLM policies. Treating each prior policy as an agent in the spirit of mixture of agent collaboration, we develop a decoding method that allows for inference-time alignment through a token-level selection strategy among multiple agents. For each token, the most suitable LLM is dynamically chosen from a pool of models based on a long-term utility metric. This policy-switching mechanism ensures optimal model selection at each step, enabling efficient collaboration and alignment among LLMs during decoding. Theoretical analysis of our proposed algorithm establishes optimal performance with respect to the target task represented via a target reward for the given off-the-shelf models. We conduct comprehensive empirical evaluations with open-source aligned models on diverse tasks and preferences, which demonstrates the merits of this approach over single-agent decoding baselines. Notably, Collab surpasses the current SoTA decoding strategy, achieving an improvement of up to 1.56x in average reward and 71.89% in GPT-4 based win-tie rate.
大型语言模型(LLM)的对齐对于其在应用中的安全和可信赖部署至关重要。强化学习通过人类反馈(RLHF)已经成为一种有效的技术,用于将LLM与人类偏好和更广泛的实用性对齐,但它需要更新数十亿的模型参数,这在计算上是昂贵的。相比之下,受控解码提供了一种在推理阶段对齐模型而无需重新训练机制。然而,由于任务的复杂性和可变性,单代理解码方法通常难以适应各种任务。为了增强针对目标任务的测试性能,我们提出了一种基于代理的解码策略混合方法,利用现有的即用型对齐LLM策略。将每个先前策略视为代理,在代理协作的混合精神下,我们开发了一种解码方法,该方法允许通过标记级别的选择策略在多个代理之间进行推理时的对齐。对于每个标记,最合适的LLM将基于长期效用指标从模型池中动态选择。这种策略切换机制确保了每一步的最优模型选择,使得LLM在解码过程中能够进行高效的协作和对齐。我们提出算法的理论分析证明了针对给定即用型模型通过目标奖励表示的目标任务的最优性能。我们使用开源对齐模型在多种任务和偏好上进行了全面的实证评估,证明了该方法相对于单代理解码基线方法的优势。值得注意的是,Collab超越了当前的最新解码策略,在平均奖励方面提高了1.56倍,在基于GPT-4的胜率中达到了71.89%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的对齐对于其在应用中的安全可信部署至关重要。强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)是一种有效的对齐技术,但需要更新数十亿的模型参数,计算成本高。相比之下,受控解码提供了一种在推理阶段对齐模型的机制,无需重新训练。然而,单智能体解码方法由于任务的复杂性和可变性,往往难以适应多样化的任务。为了强化针对目标任务的测试性能,本文提出了一种基于现有现成的对齐LLM策略的混合多智能体解码策略。我们开发了一种解码方法,允许在令牌级别上选择多个智能体之间的策略,从而实现在推理阶段的模型对齐。对于每个令牌,根据长期效用指标从模型池中动态选择最合适的LLM。该策略切换机制确保了每一步的最优模型选择,实现了LLM之间的有效协作和对齐。理论分析和实证评估均证明了该方法在目标任务上的优势。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的对齐对于其在实际应用中的部署至关重要。
- 强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)虽然是一种有效的LLM对齐技术,但需要大量的计算资源。
- 受控解码提供了一种在推理阶段对齐模型的替代方法,无需重新训练模型。
- 单智能体解码方法在应对多样化任务时面临困难,因为任务的复杂性和可变性。
- 本文提出了一种混合多智能体解码策略,该策略利用现有的对齐LLM策略,并在推理阶段通过令牌级别的选择实现模型对齐。
- 该策略切换机制确保了每一步的最优模型选择,提高了LLM之间的协作和对齐效率。
点此查看论文截图

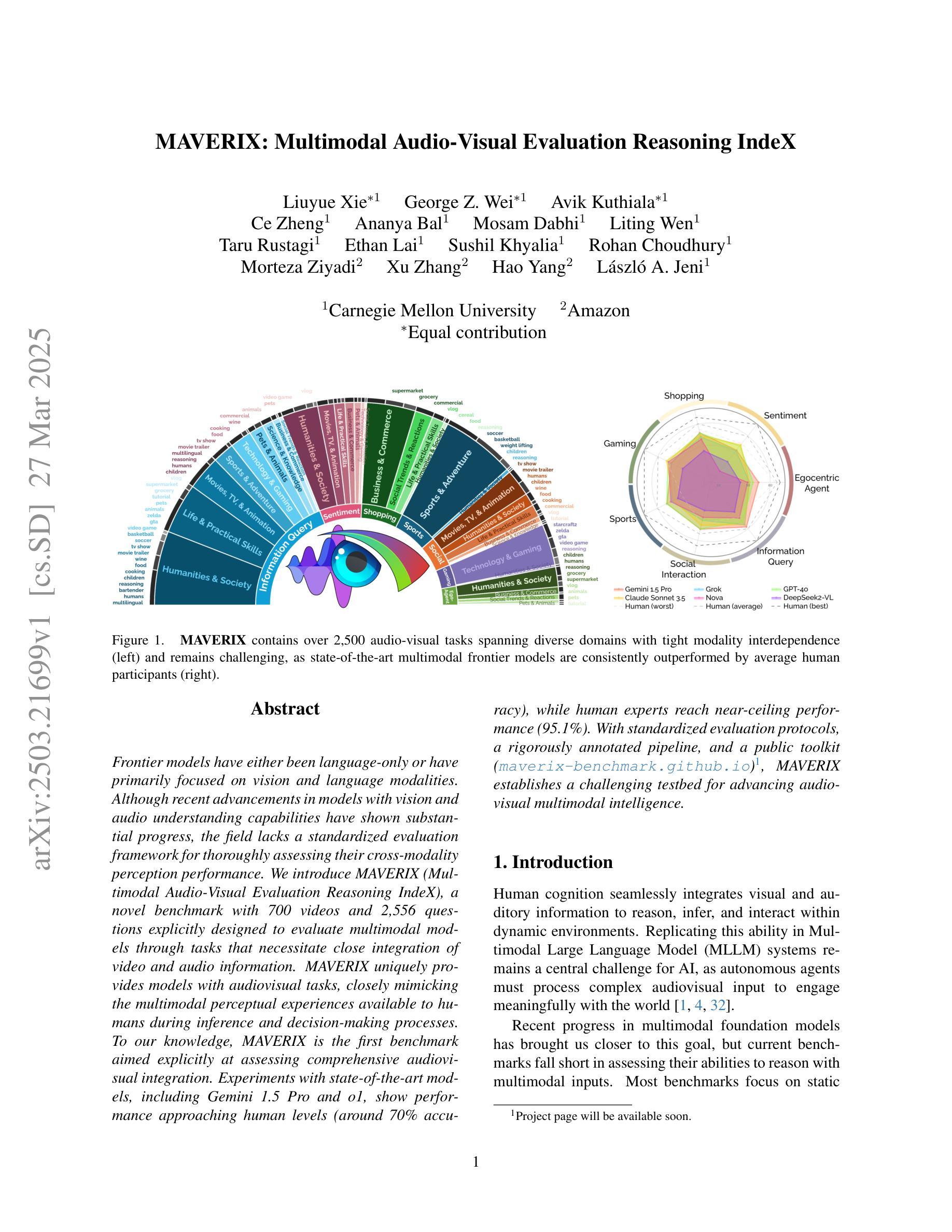
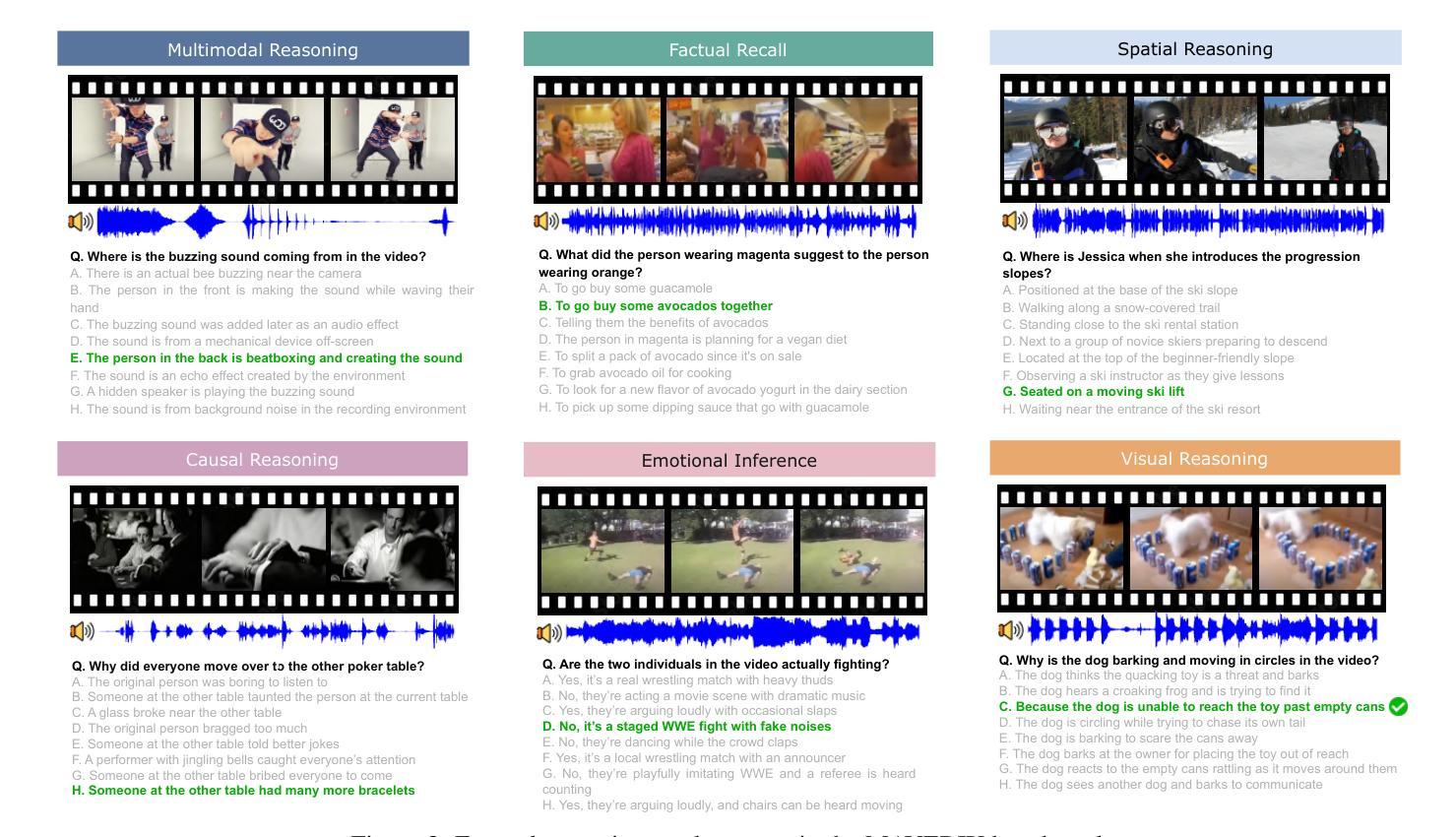
MAVERIX: Multimodal Audio-Visual Evaluation Reasoning IndeX
Authors:Liuyue Xie, George Z. Wei, Avik Kuthiala, Ce Zheng, Ananya Bal, Mosam Dabhi, Liting Wen, Taru Rustagi, Ethan Lai, Sushil Khyalia, Rohan Choudhury, Morteza Ziyadi, Xu Zhang, Hao Yang, László A. Jeni
Frontier models have either been language-only or have primarily focused on vision and language modalities. Although recent advancements in models with vision and audio understanding capabilities have shown substantial progress, the field lacks a standardized evaluation framework for thoroughly assessing their cross-modality perception performance. We introduce MAVERIX~(Multimodal Audio-Visual Evaluation Reasoning IndeX), a novel benchmark with 700 videos and 2,556 questions explicitly designed to evaluate multimodal models through tasks that necessitate close integration of video and audio information. MAVERIX uniquely provides models with audiovisual tasks, closely mimicking the multimodal perceptual experiences available to humans during inference and decision-making processes. To our knowledge, MAVERIX is the first benchmark aimed explicitly at assessing comprehensive audiovisual integration. Experiments with state-of-the-art models, including Gemini 1.5 Pro and o1, show performance approaching human levels (around 70% accuracy), while human experts reach near-ceiling performance (95.1%). With standardized evaluation protocols, a rigorously annotated pipeline, and a public toolkit, MAVERIX establishes a challenging testbed for advancing audiovisual multimodal intelligence.
前沿模型要么是单一语言模型,要么主要关注视觉和语言模态。尽管最近具有视觉和音频理解能力的模型的最新进展已经取得了重大进展,但该领域缺乏一个标准化的评估框架来全面评估它们的跨模态感知性能。我们引入了MAVERIX(多模态音频视觉评估推理指数),这是一个新的基准测试,包含700个视频和2556个明确设计的问题,旨在通过需要密切整合视频和音频信息的任务来评估多模态模型。MAVERIX独特地提供了视听任务,紧密模仿人类在推理和决策过程中的多模态感知体验。据我们所知,MAVERIX是第一个专门旨在评估全面视听整合能力的基准测试。使用最前沿的模型进行的实验,包括Gemini 1.5 Pro和o1,显示其性能接近人类水平(约70%的准确率),而人类专家则接近天花板性能(95.1%)。通过标准化的评估协议、严格的注释管道和公共工具包,MAVERIX为推进视听多模态智能提供了一个具有挑战性的测试平台。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态感知技术近年来取得了显著进展,特别是在视觉和音频理解方面。然而,缺乏一个标准化的评估框架来全面评估跨模态感知性能。为此,本文介绍了MAVERIX(多模态音频视觉评估推理指数),这是一个包含700个视频和2556个问题的新型基准测试,旨在通过需要紧密融合视频和音频信息的任务来评估多模态模型。MAVERIX独特地提供了视听任务,紧密模仿人类在推理和决策过程中的多模态感知体验。据我们所知,MAVERIX是第一个旨在明确评估全面视听整合能力的基准测试。使用最前沿的模型(如双子座 1.5 专业版和 o1)进行的实验表明,其性能接近人类水平(约70%准确率),而人类专家则达到了近上限性能(95.1%)。MAVERIX的建立为推进视听多模态智能提供了一个具有挑战性的测试平台,包括标准化的评估协议、严格的注释管道和公共工具包。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一种新型基准测试MAVERIX,旨在评估多模态模型的跨模态感知性能。
- MAVERIX包含700个视频和2556个问题,设计有视听任务,模拟人类的多媒体感知体验。
- 目前最前沿的模型在MAVERIX上的性能接近人类水平(约70%准确率)。
- 人类专家在MAVERIX上的表现接近上限(95.1%)。
- MAVERIX提供了标准化的评估协议、严格的注释管道和公共工具包。
- MAVERIX的建立为推进视听多模态智能的发展提供了一个具有挑战性的测试平台。
点此查看论文截图
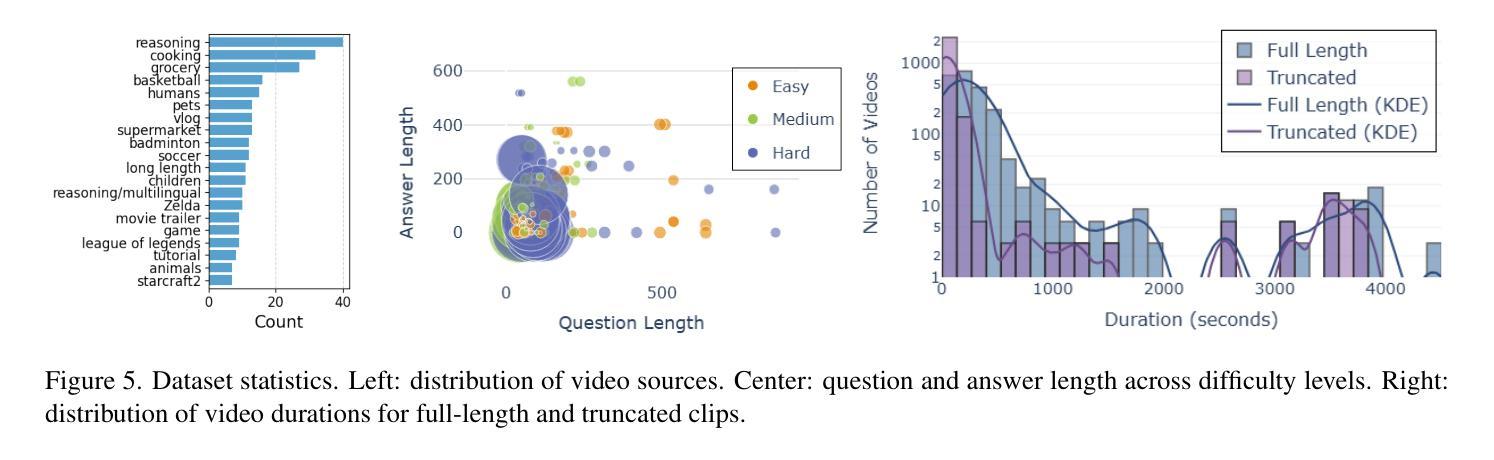
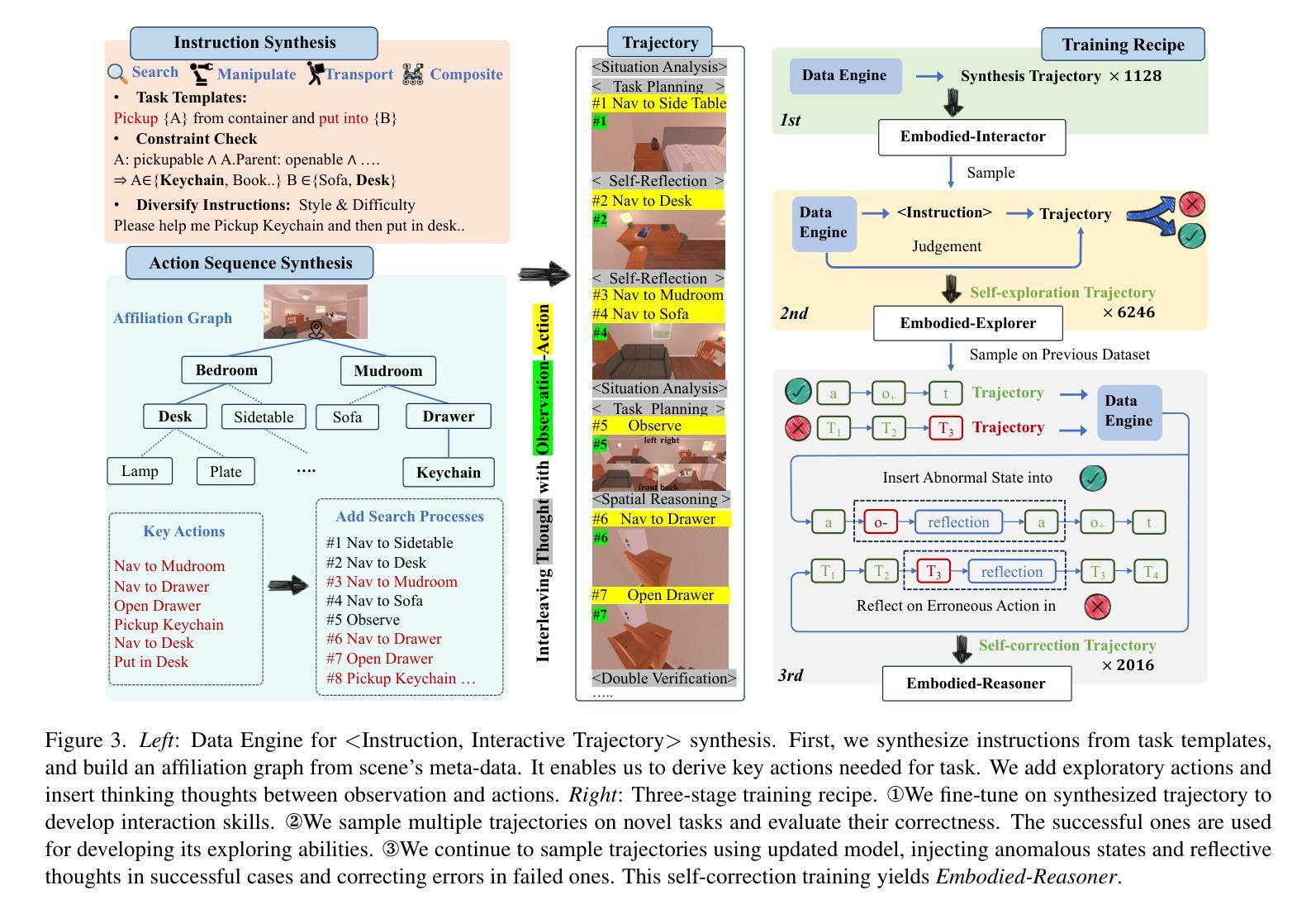
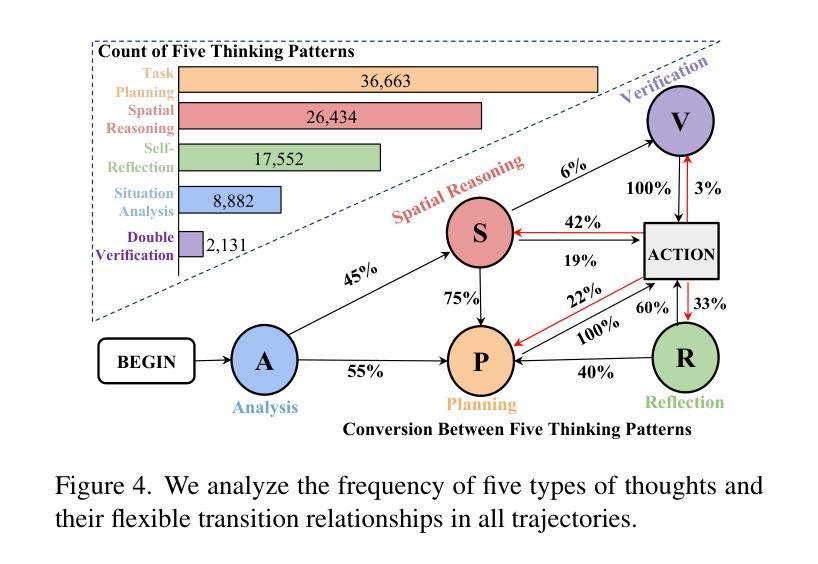
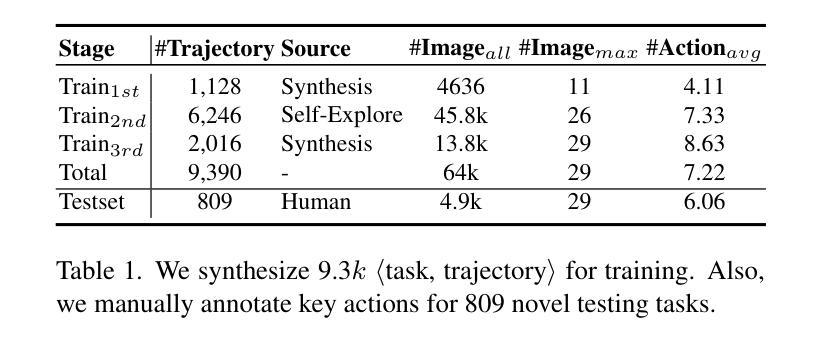
Embodied-Reasoner: Synergizing Visual Search, Reasoning, and Action for Embodied Interactive Tasks
Authors:Wenqi Zhang, Mengna Wang, Gangao Liu, Xu Huixin, Yiwei Jiang, Yongliang Shen, Guiyang Hou, Zhe Zheng, Hang Zhang, Xin Li, Weiming Lu, Peng Li, Yueting Zhuang
Recent advances in deep thinking models have demonstrated remarkable reasoning capabilities on mathematical and coding tasks. However, their effectiveness in embodied domains which require continuous interaction with environments through image action interleaved trajectories remains largely -unexplored. We present Embodied Reasoner, a model that extends o1 style reasoning to interactive embodied search tasks. Unlike mathematical reasoning that relies primarily on logical deduction, embodied scenarios demand spatial understanding, temporal reasoning, and ongoing self-reflection based on interaction history. To address these challenges, we synthesize 9.3k coherent Observation-Thought-Action trajectories containing 64k interactive images and 90k diverse thinking processes (analysis, spatial reasoning, reflection, planning, and verification). We develop a three-stage training pipeline that progressively enhances the model’s capabilities through imitation learning, self-exploration via rejection sampling, and self-correction through reflection tuning. The evaluation shows that our model significantly outperforms those advanced visual reasoning models, e.g., it exceeds OpenAI o1, o3-mini, and Claude-3.7 by +9%, 24%, and +13%. Analysis reveals our model exhibits fewer repeated searches and logical inconsistencies, with particular advantages in complex long-horizon tasks. Real-world environments also show our superiority while exhibiting fewer repeated searches and logical inconsistency cases.
近期深度思考模型在数学和编码任务上展现出卓越的推理能力。然而,它们在需要与环境持续交互的图像动作轨迹方面的实际应用领域中的效果仍然很大程度上未被探索。我们提出了Embodied Reasoner模型,该模型将一阶推理扩展到交互式实体搜索任务。与主要依赖于逻辑演绎的数学推理不同,实体场景需要空间理解、时间推理以及基于交互历史的持续自我反思。为了应对这些挑战,我们综合了9.3k个连贯的观察-思考-行动轨迹,包含6.4万张交互图像和9万多个多样化的思考过程(分析、空间推理、反思、规划和验证)。我们开发了一个分三阶段的训练管道,通过模仿学习、通过拒绝采样的自我探索以及通过反思调整的自我修正,逐步增强模型的能力。评估表明,我们的模型显著优于先进的视觉推理模型,例如,它比OpenAI的一阶、三阶小模型和Claude-3.7高出+9%、24%和+13%。分析显示,我们的模型在复杂的长期任务中具有较少的重复搜索和逻辑不一致性,具有特别的优势。在真实世界环境中的表现也证明了我们的优越性,表现出较少的重复搜索和逻辑不一致情况。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/zwq2018/embodied_reasoner Dataset: https://huggingface.co/datasets/zwq2018/embodied_reasoner
Summary
本文介绍了近期深度思考模型在体感领域(需要与环境连续互动的任务)中的表现,并提出了一个新的模型——Embodied Reasoner。该模型能应用于互动式体感搜索任务,并通过合成Observation-Thought-Action轨迹数据训练模型,使其在空间理解、时间推理和持续自我反思方面表现出卓越的能力。通过三个阶段的学习管道,模型能力逐步提升,并在复杂长周期任务中展现出显著优势。相较于其他先进的视觉推理模型,Embodied Reasoner表现出更高的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 深度思考模型在体感领域(需要与环境连续互动的任务)中的表现被提出并受到关注。
- Embodied Reasoner模型被引入,适用于互动式体感搜索任务。
- 模型通过合成Observation-Thought-Action轨迹数据进行训练,强调空间理解、时间推理和持续自我反思的重要性。
- 模型经过三个阶段的学习管道,包括模仿学习、自我探索和自我校正,逐步提升能力。
- 与其他视觉推理模型相比,Embodied Reasoner展现出更高的性能,特别是在复杂长周期任务中。
- 模型在实际环境中的表现也优于其他模型,具有较少的重复搜索和逻辑不一致情况。
点此查看论文截图


JiraiBench: A Bilingual Benchmark for Evaluating Large Language Models’ Detection of Human Self-Destructive Behavior Content in Jirai Community
Authors:Yunze Xiao, Tingyu He, Lionel Z. Wang, Yiming Ma, Xingyu Song, Xiaohang Xu, Irene Li, Ka Chung Ng
This paper introduces JiraiBench, the first bilingual benchmark for evaluating large language models’ effectiveness in detecting self-destructive content across Chinese and Japanese social media communities. Focusing on the transnational “Jirai” (landmine) online subculture that encompasses multiple forms of self-destructive behaviors including drug overdose, eating disorders, and self-harm, we present a comprehensive evaluation framework incorporating both linguistic and cultural dimensions. Our dataset comprises 10,419 Chinese posts and 5,000 Japanese posts with multidimensional annotation along three behavioral categories, achieving substantial inter-annotator agreement. Experimental evaluations across four state-of-the-art models reveal significant performance variations based on instructional language, with Japanese prompts unexpectedly outperforming Chinese prompts when processing Chinese content. This emergent cross-cultural transfer suggests that cultural proximity can sometimes outweigh linguistic similarity in detection tasks. Cross-lingual transfer experiments with fine-tuned models further demonstrate the potential for knowledge transfer between these language systems without explicit target language training. These findings highlight the need for culturally-informed approaches to multilingual content moderation and provide empirical evidence for the importance of cultural context in developing more effective detection systems for vulnerable online communities.
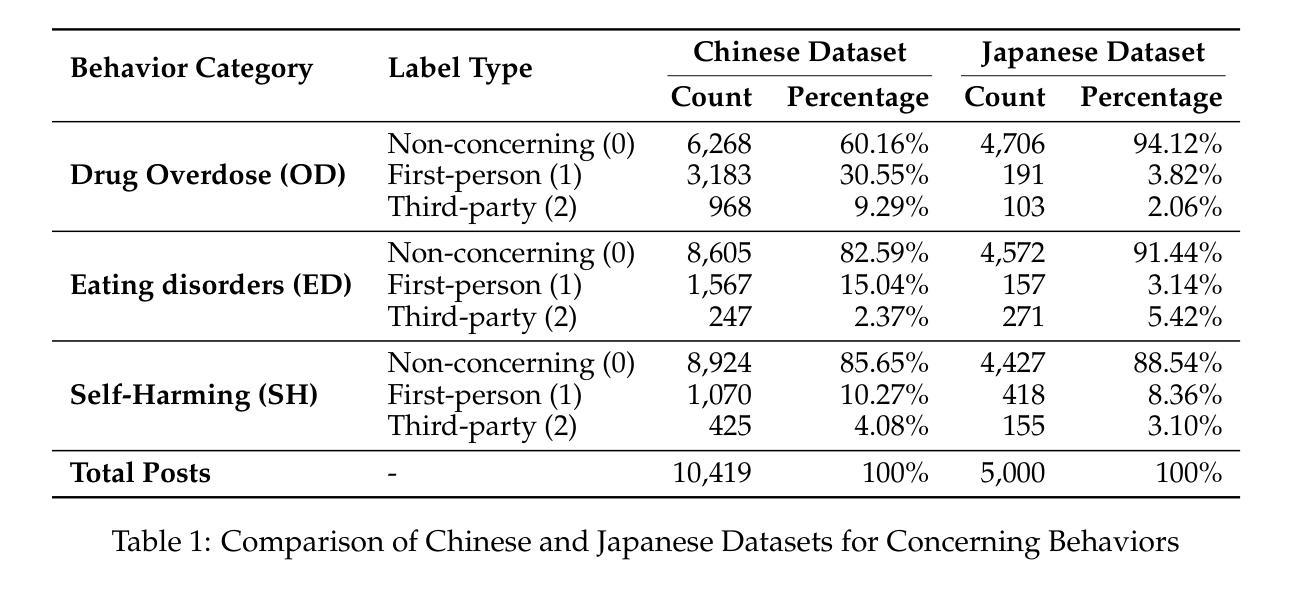
本文介绍了JiraiBench,它是首个双语基准测试,旨在评估大型语言模型在检测和识别中文和日语社交媒体社区中的自我破坏性内容方面的有效性。本文重点关注跨国界的“Jirai”(地雷)在线亚文化,这种文化包含多种形式的自我破坏性行为,包括过量服药、饮食失调和自我伤害等。我们提出了一个综合评估框架,其中包括语言和文化的双重维度。我们的数据集包含中国帖子十万四千一百九十九个和日本帖子五千个,涵盖了三个行为类别的多维度注释,实现了显著的分析师间一致性。在四种最新模型上的实验评估显示,根据指令性语言的不同,性能存在显著差异,其中在处理中文内容时,日语提示意外地优于中文提示。这种跨文化迁移的出现表明,在某些情况下,文化接近度可能会超过语言相似性在检测任务中的重要性。对微调模型的跨语言迁移实验进一步证明了在这些语言系统之间进行知识迁移的潜力,无需明确的目标语言训练。这些发现突显了文化背景下的跨语言方法对于多语言内容管理的必要性,并为开发针对脆弱在线社区的更有效检测系统在文化背景方面的重要性提供了实证证据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 1 figures
Summary
本文介绍了JiraiBench,首个针对大型语言模型在中文和日语社交媒体社区中检测自我毁灭内容效果的双语基准测试。文章以跨国“Jirai”(地雷)在线亚文化为背景,涵盖药物过量、饮食失调和自我伤害等多种自我毁灭行为,提出了一个综合评估框架,该框架融入了语言和文化的双重维度。数据集包含10,419条中文帖子和5,000条日语帖子,按三个行为类别进行多维度标注,并实现了显著的跨标注者一致性。实验评估结果显示,基于指示性语言的性能差异显著,且在处理中文内容时,日语提示出乎意料地优于中文提示。这种跨文化转移的出现表明,在某些检测任务中,文化接近性有时可能比语言相似性更重要。对精细调整过的模型进行跨语言转移实验,进一步证明了在这些语言系统之间进行知识转移而不进行明确的目标语言培训的潜力。这些发现强调了在多元语言内容管理中考虑文化因素的重要性,并为开发针对脆弱在线社区的更有效检测系统提供了实证证据。
Key Takeaways
- JiraiBench是首个针对大型语言模型的双语基准测试,旨在评估其在中文和日语社交媒体中检测自我毁灭内容的效果。
- 评估框架综合考虑了语言和文化的双重维度,反映了跨国在线亚文化“Jirai”的特点。
- 数据集包含中文和日语的社交媒体帖子,并进行了多维度的标注。
- 实验结果显示,在处理某些任务时,文化接近性比语言相似性更重要。
- 不同语言的提示对模型性能有显著影响,日语提示在处理中文内容时表现出意外的优势。
- 跨语言转移实验证明了不同语言系统间的知识转移潜力,无需明确的目标语言培训。
点此查看论文截图

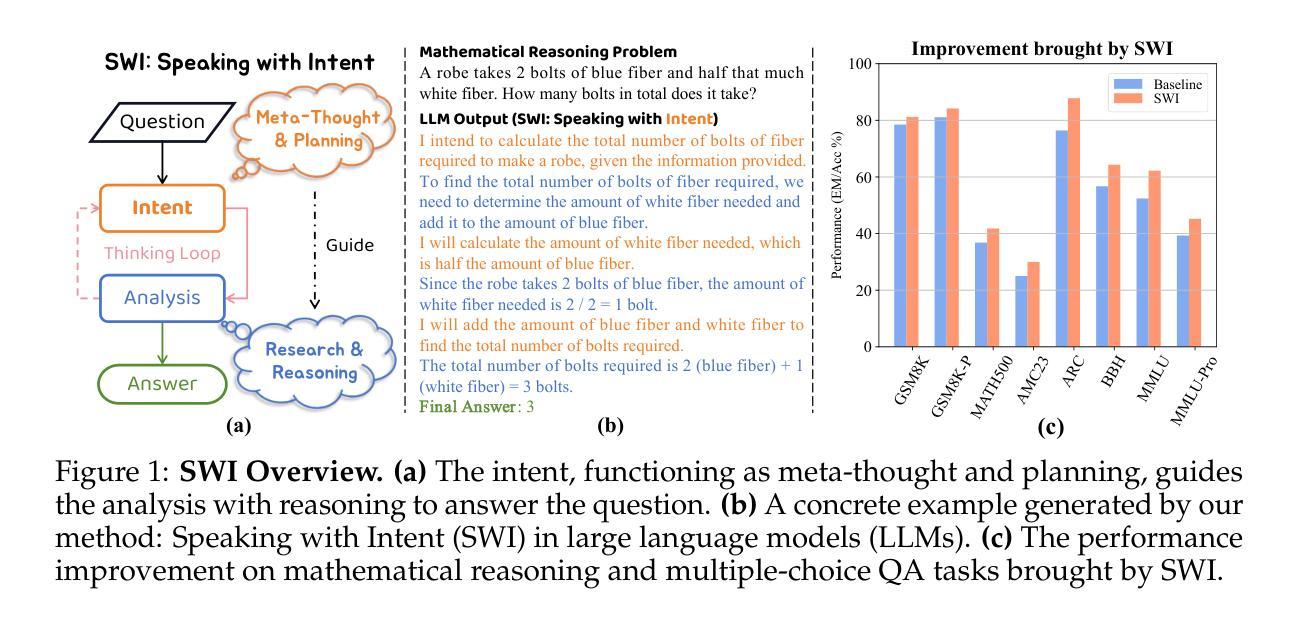
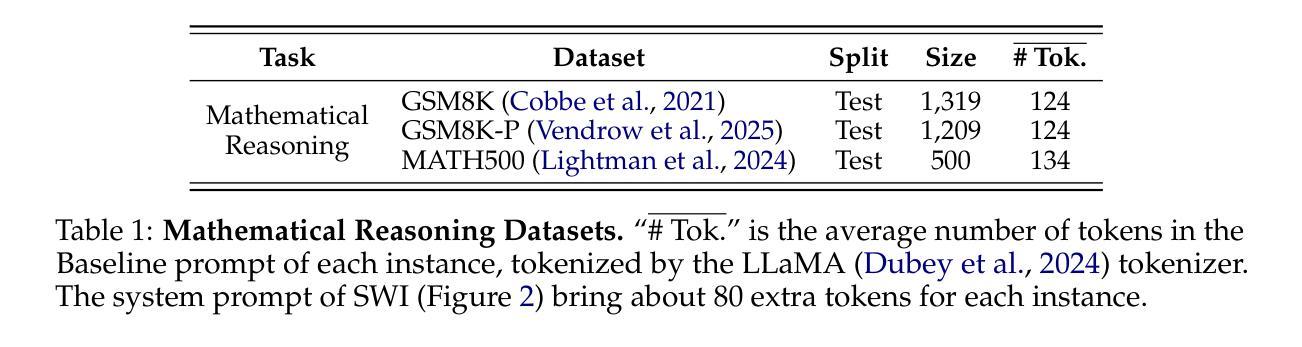
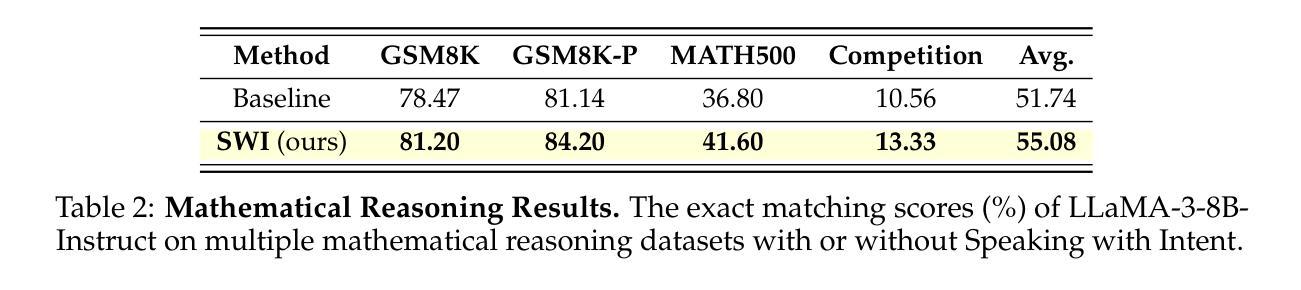
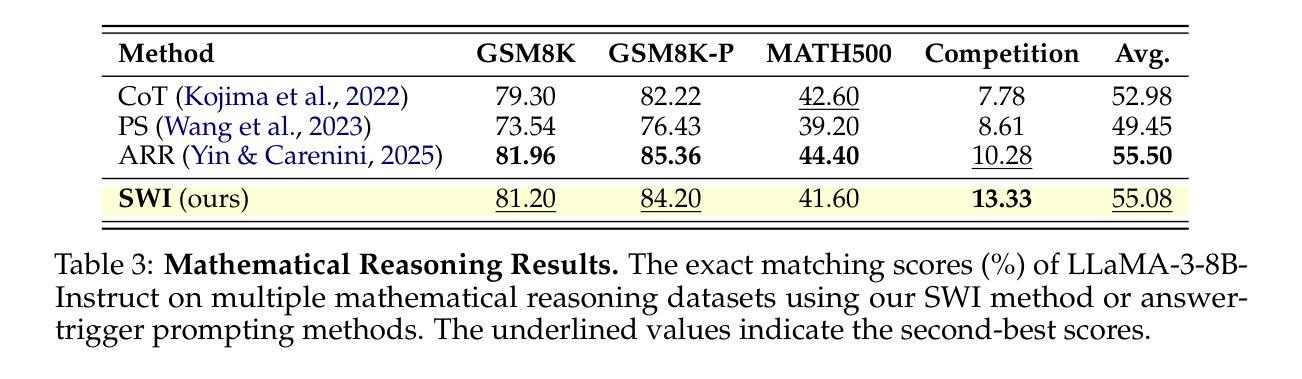
SWI: Speaking with Intent in Large Language Models
Authors:Yuwei Yin, EunJeong Hwang, Giuseppe Carenini
Intent, typically clearly formulated and planned, functions as a cognitive framework for reasoning and problem-solving. This paper introduces the concept of Speaking with Intent (SWI) in large language models (LLMs), where the explicitly generated intent encapsulates the model’s underlying intention and provides high-level planning to guide subsequent analysis and communication. By emulating deliberate and purposeful thoughts in the human mind, SWI is hypothesized to enhance the reasoning capabilities and generation quality of LLMs. Extensive experiments on mathematical reasoning benchmarks consistently demonstrate the superiority of Speaking with Intent over Baseline (i.e., generation without explicit intent). Moreover, SWI outperforms answer-trigger prompting methods Chain-of-Thought and Plan-and-Solve and maintains competitive performance with the strong method ARR (Analyzing, Retrieving, and Reasoning). Additionally, the effectiveness and generalizability of SWI are solidified on reasoning-intensive question answering (QA) and text summarization benchmarks, where SWI brings consistent improvement to the Baseline generation. In text summarization, SWI-generated summaries exhibit greater accuracy, conciseness, and factual correctness, with fewer hallucinations. Furthermore, human evaluations verify the coherence, effectiveness, and interpretability of the intent produced by SWI. This proof-of-concept study creates a novel avenue for enhancing LLMs’ reasoning abilities with cognitive notions.
意图通常被明确制定和计划,作为推理和解决问题的认知框架。本文介绍了大型语言模型(LLM)中的“带有意图的表述”(Speaking with Intent,简称SWI)这一概念,其中明确生成的意图包含了模型的基本意图,并为随后的分析和通信提供了高级规划。通过模拟人类思维中的深思熟虑和目的性思考,假设SWI可以提高LLM的推理能力和生成质量。在数学推理基准测试的大量实验中,带有意图的表述始终表现出优于基准线(即无明确意图的生成)。此外,SWI的表现优于答案触发提示方法Chain-of-Thought和Plan-and-Solve,并与强大的方法ARR(分析、检索和推理)保持竞争力。另外,在需要大量推理的问答和文本摘要基准测试中,SWI的有效性泛化性得到了巩固,它为基准线生成带来了持续的改进。在文本摘要中,由SWI生成的摘要表现出更高的准确性、简洁性和事实正确性,幻觉更少。此外,人类评估验证了由SWI产生的意图的连贯性、有效性和可解释性。这项概念验证研究为利用认知概念增强LLM的推理能力开辟了一条新途径。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages. Code: https://github.com/YuweiYin/SWI
Summary:
意图通常被明确地制定和计划,作为推理和解决问题的认知框架。本文介绍了大型语言模型(LLM)中的“带意图表达(SWI)”的概念,显式生成的意图涵盖了模型的基本意图,并提供高级规划来指导后续分析和通信。通过模拟人类思维的深思熟虑和目的性,假设SWI可以提高LLM的推理能力和生成质量。在数学推理基准测试上的广泛实验表明,与无明确意图的基线生成相比,带意图表达具有优越性。此外,在文本摘要基准测试上,带意图表达也带来了持续的改进。人类评估验证了由带意图表达产生的意图的连贯性、有效性和可解释性。这项概念验证研究为利用认知概念增强LLM的推理能力开辟了一条新途径。
Key Takeaways:
- 论文提出了大型语言模型中的带意图表达(SWI)概念,旨在增强模型的推理能力和生成质量。
- 通过模拟人类思维的深思熟虑和目的性,假设并验证了带意图表达对于提升模型性能的重要性。
- 与基线生成相比,带意图表达在数学推理上表现优越。
- 带意图表达在数学推理和文本摘要方面的实验证明了其有效性和通用性。
- 在文本摘要任务中,带意图表达生成的摘要更准确、简洁、符合事实且减少了虚构情况的出现。
- 人类评估显示带意图表达的意图具有良好的连贯性、有效性和可解释性。
点此查看论文截图


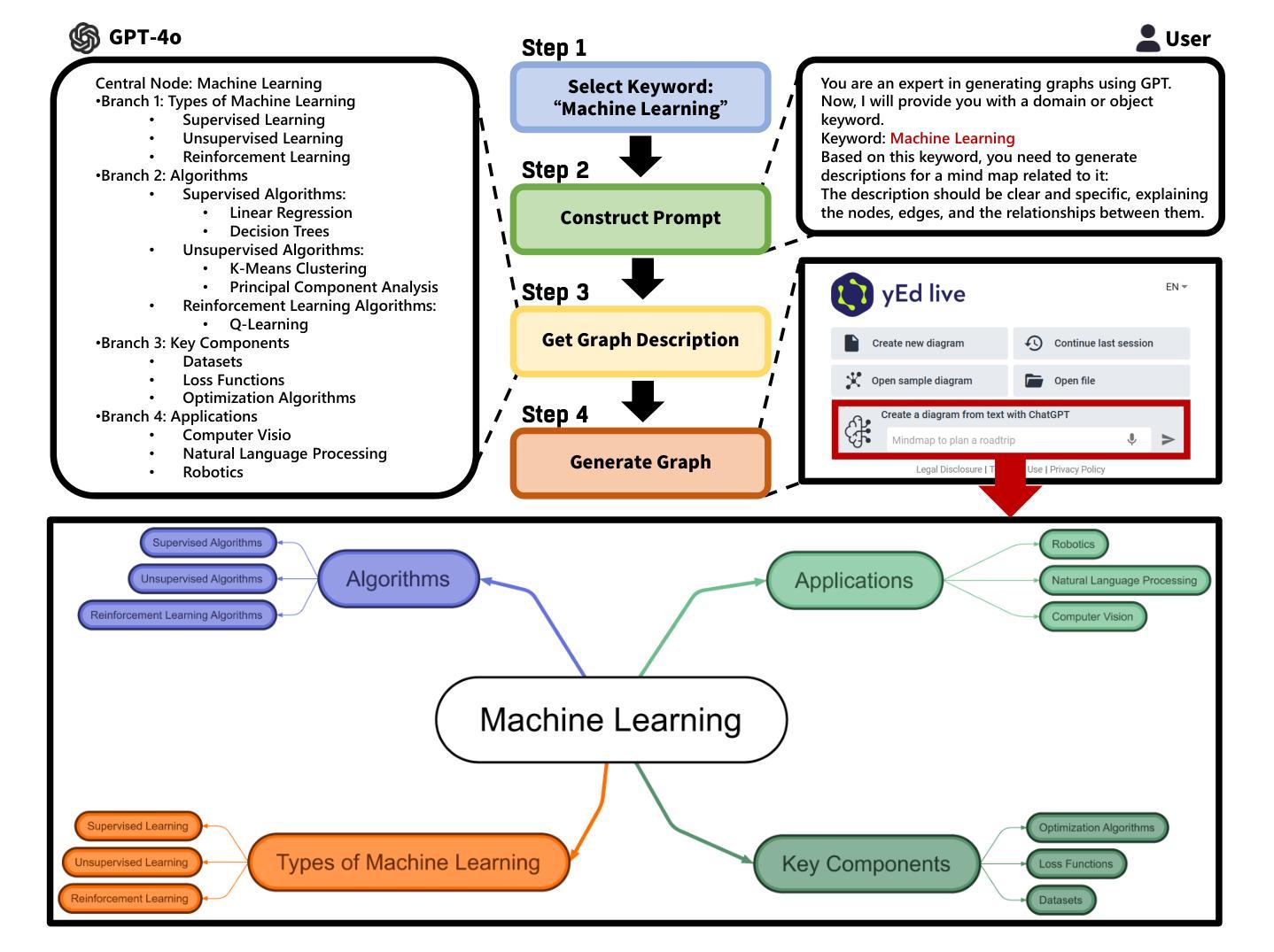
Graph-to-Vision: Multi-graph Understanding and Reasoning using Vision-Language Models
Authors:Ruizhou Li, Haiyun Jiang
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), as the dominant paradigm for graph-structured learning, have long faced dual challenges of exponentially escalating computational complexity and inadequate cross-scenario generalization capability. With the rapid advancement of multimodal learning, Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated exceptional cross-modal relational reasoning capabilities and generalization capacities, thereby opening up novel pathways for overcoming the inherent limitations of conventional graph learning paradigms. However, current research predominantly concentrates on investigating the single-graph reasoning capabilities of VLMs, which fundamentally fails to address the critical requirement for coordinated reasoning across multiple heterogeneous graph data in real-world application scenarios. To address these limitations, we propose the first multi-graph joint reasoning benchmark for VLMs. Our benchmark encompasses four graph categories: knowledge graphs, flowcharts, mind maps, and route maps,with each graph group accompanied by three progressively challenging instruction-response pairs. Leveraging this benchmark, we conducted comprehensive capability assessments of state-of-the-art VLMs and performed fine-tuning on open-source models. This study not only addresses the underexplored evaluation gap in multi-graph reasoning for VLMs but also empirically validates their generalization superiority in graph-structured learning.
图神经网络(GNNs)作为图结构学习的主流范式,长期以来一直面临着计算复杂度指数级上升和跨场景泛化能力不足的双重挑战。随着多模态学习的快速发展,视觉语言模型(VLMs)表现出了卓越的多模态关系推理能力和泛化能力,从而开辟了克服传统图学习范式固有局限性的新途径。然而,当前的研究主要集中在调查VLMs的单图推理能力上,这从根本上未能满足现实世界应用场景中跨多个异构图数据的协同推理的迫切需求。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了首个针对VLMs的多图联合推理基准测试。我们的基准测试包含四种类型的图:知识图谱、流程图、思维导图和路线图,每种类型的图都配备了三组逐步挑战性的指令-响应对。利用这一基准测试,我们对最先进的VLMs进行了全面的能力评估,并对开源模型进行了微调。这项研究不仅解决了VLMs在图推理方面的评估缺口,而且从实证上验证了它们在图结构学习中的泛化优势。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Graph神经网络(GNNs)面临计算复杂性急剧上升和跨场景泛化能力不足的双重挑战。随着多模态学习(Multimodal Learning)的快速发展,视觉语言模型(VLMs)展现出强大的跨模态关系推理和泛化能力,为克服传统图学习范式的局限性提供了新途径。然而,当前研究主要关注VLMs的单图推理能力,未能满足现实应用中多异构图数据的协同推理需求。为解决此问题,我们首次提出多图联合推理基准测试(Multi-Graph Joint Reasoning Benchmark),涵盖知识图谱、流程图、思维导图和路线图四类图。通过这一基准测试,我们对最先进的VLMs进行了全面的能力评估,并对开源模型进行了微调。这不仅填补了VLMs在多图推理方面的评估空白,而且实证了其在图结构学习中的泛化优势。
Key Takeaways
- Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) 面临计算复杂性和泛化能力的挑战。
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)在多模态学习中展现出强大的跨模态关系推理和泛化能力。
- 当前研究主要关注VLMs的单图推理能力,缺乏多异构图数据的协同推理研究。
- 首次提出多图联合推理基准测试,包括知识图谱、流程图、思维导图和路线图四类。
- 通过基准测试,对VLMs进行了全面的能力评估。
- 实证了VLMs在图结构学习中的泛化优势。
点此查看论文截图

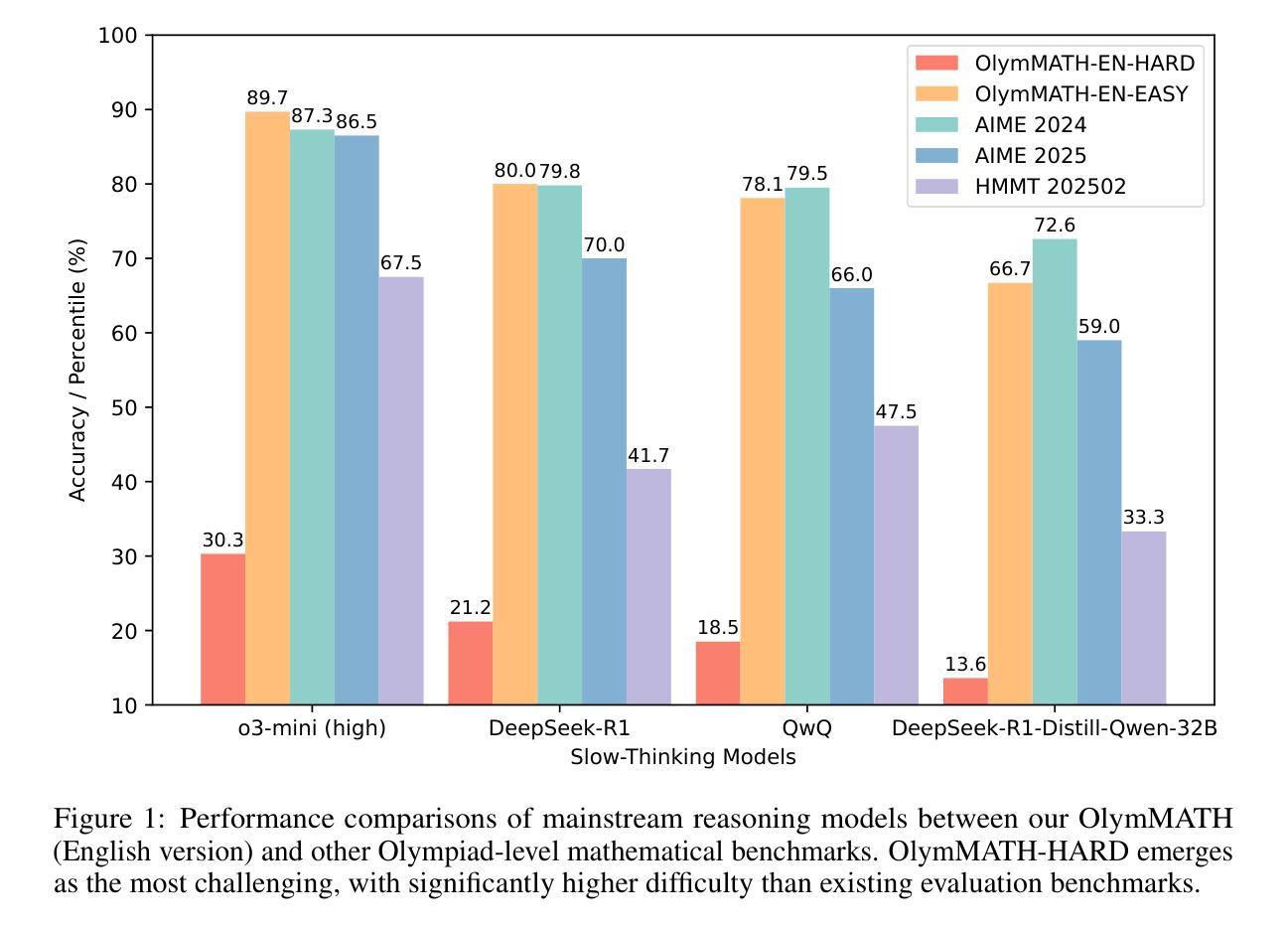
Challenging the Boundaries of Reasoning: An Olympiad-Level Math Benchmark for Large Language Models
Authors:Haoxiang Sun, Yingqian Min, Zhipeng Chen, Wayne Xin Zhao, Zheng Liu, Zhongyuan Wang, Lei Fang, Ji-Rong Wen
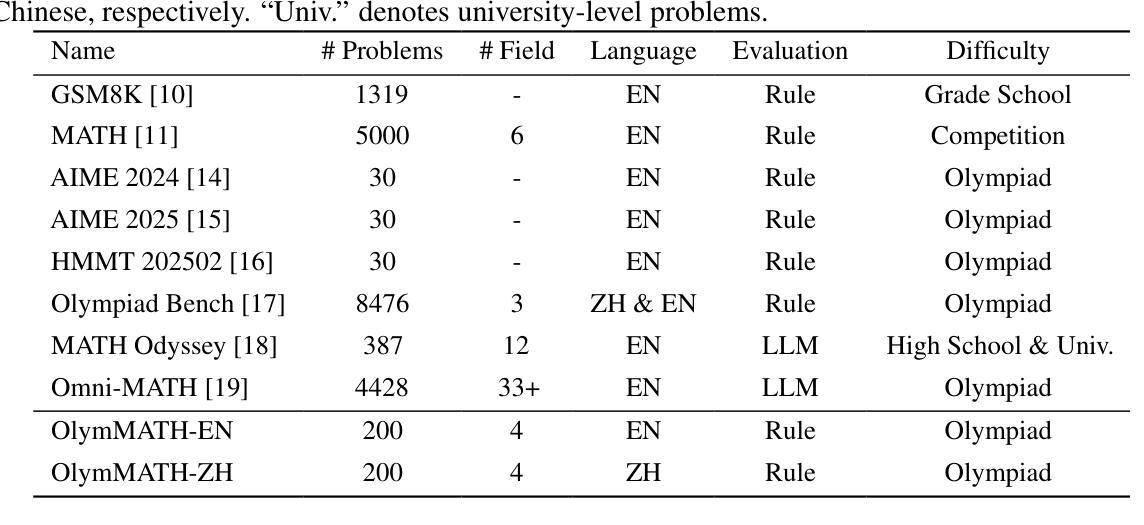
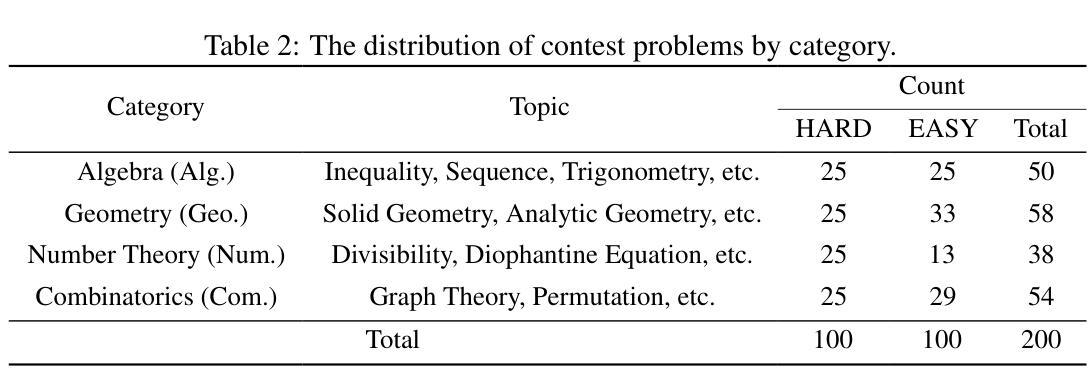
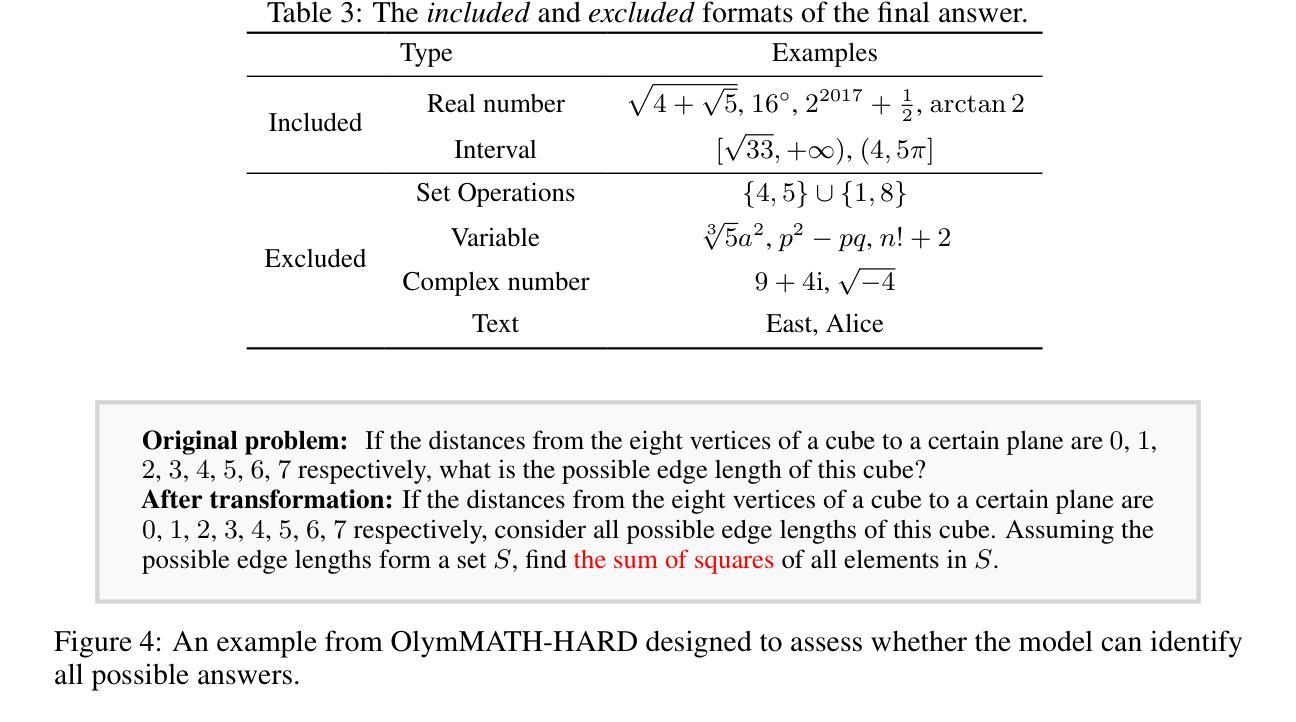
In recent years, the rapid development of large reasoning models has resulted in the saturation of existing benchmarks for evaluating mathematical reasoning, highlighting the urgent need for more challenging and rigorous evaluation frameworks. To address this gap, we introduce OlymMATH, a novel Olympiad-level mathematical benchmark, designed to rigorously test the complex reasoning capabilities of LLMs. OlymMATH features 200 meticulously curated problems, each manually verified and available in parallel English and Chinese versions. The problems are systematically organized into two distinct difficulty tiers: (1) AIME-level problems (easy) that establish a baseline for mathematical reasoning assessment, and (2) significantly more challenging problems (hard) designed to push the boundaries of current state-of-the-art models. In our benchmark, these problems span four core mathematical fields, each including a verifiable numerical solution to enable objective, rule-based evaluation. Empirical results underscore the significant challenge presented by OlymMATH, with state-of-the-art models including DeepSeek-R1 and OpenAI’s o3-mini demonstrating notably limited accuracy on the hard subset. Furthermore, the benchmark facilitates comprehensive bilingual assessment of mathematical reasoning abilities-a critical dimension that remains largely unaddressed in mainstream mathematical reasoning benchmarks. We release the OlymMATH benchmark at the STILL project: https://github.com/RUCAIBox/Slow_Thinking_with_LLMs.
近年来,大型推理模型的快速发展导致现有数学推理评估基准测试趋于饱和,这凸显了对更具挑战性和严格的评估框架的迫切需求。为了弥补这一空白,我们推出了OlymMATH,这是一个新的奥林匹克级别的数学基准测试,旨在严格测试大型语言模型的复杂推理能力。OlymMATH包含200个精心挑选的问题,每个问题都经过手动验证,并有英文和中文的平行版本。这些问题被系统地分为两个难度等级:一是AIME级别的问题(简单),为数学推理评估建立基准线;二是更具挑战性的问题(困难),旨在挑战当前最前沿模型的极限。在我们的基准测试中,这些问题涉及四个核心数学领域,每个领域都包括可验证的数值解决方案,以实现客观、基于规则的评估。经验结果突显了OlymMATH的巨大挑战,最先进的模型包括DeepSeek-R1和OpenAI的o3-mini在困难子集上显示出明显的准确性限制。此外,该基准测试还可以全面评估双语数学推理能力——这是主流数学推理基准测试中尚未涉及的关键维度。我们在STILL项目的网址上发布了OlymMATH基准测试:https://github.com/RUCAIBox/Slow_Thinking_with_LLMs。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report on Slow Thinking with LLMs: Evaluation Benchmark
Summary
该文本介绍了近期大型推理模型快速发展导致现有评估基准测试饱和的问题,并指出需要更具挑战性和严格性的评估框架。为此,作者提出了一种新型的奥赛级数学基准测试——OlymMATH,旨在严格测试大型语言模型的复杂推理能力。该基准测试包含200个精心策划的问题,分为两个难度等级,涵盖四个核心数学领域,每个问题都有可验证的数值解,以便进行客观、基于规则的评价。实证结果表明,OlymMATH具有显著挑战性,目前最先进的模型在该基准测试上的准确率较低。此外,该基准测试还便于对主流数学推理基准测试尚未涵盖的重要双语评估维度进行数学推理能力评估。
Key Takeaways
- 大型推理模型的快速发展导致现有数学推理评估基准测试的饱和。
- 推出新型奥赛级数学基准测试OlymMATH,用以严格测试大型语言模型的推理能力。
- OlymMATH包含200个手工验证的问题,分为两个难度等级。
- 涵盖四个核心数学领域,每个问题都有可验证的数值解。
- OlymMATH具有显著挑战性,目前最先进的模型在该基准测试上的准确率较低。
- OlymMATH便于进行双语评估,这是主流数学推理基准测试尚未充分涵盖的重要维度。
- OlymMATH基准测试已在STILL项目上发表:https://github.com/RUCAIBox/Slow_Thinking_with_LLMs。
点此查看论文截图


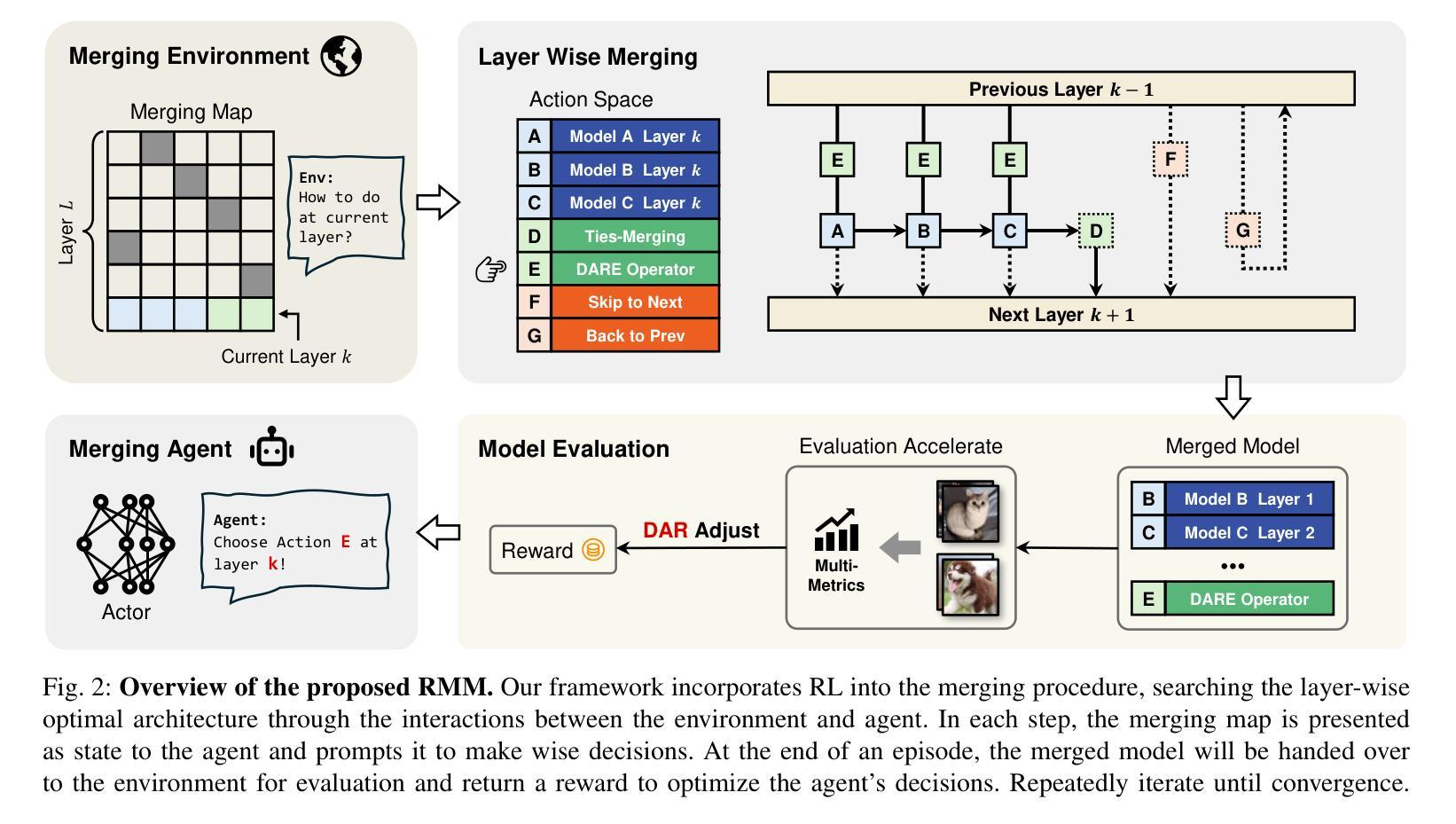
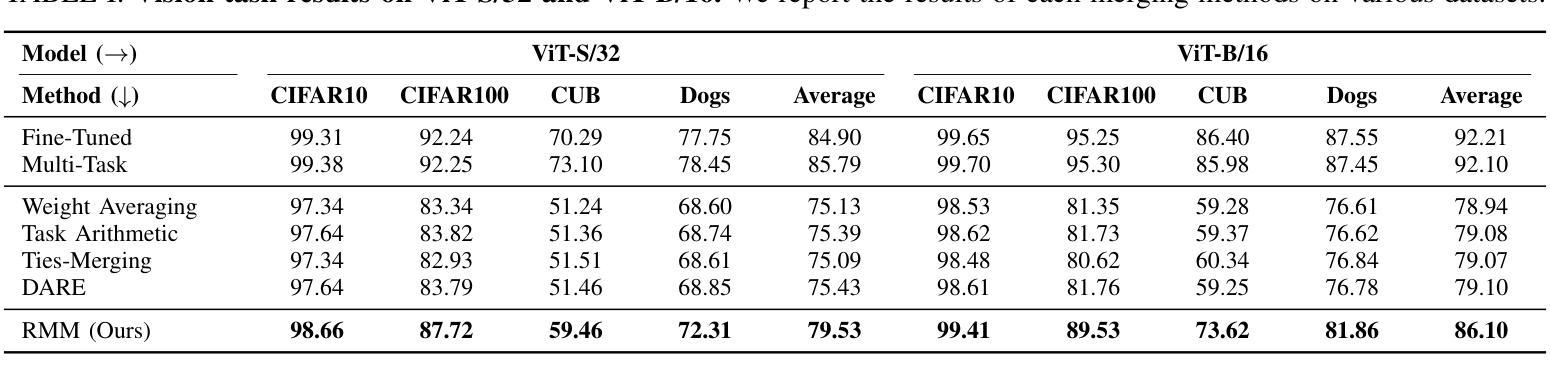
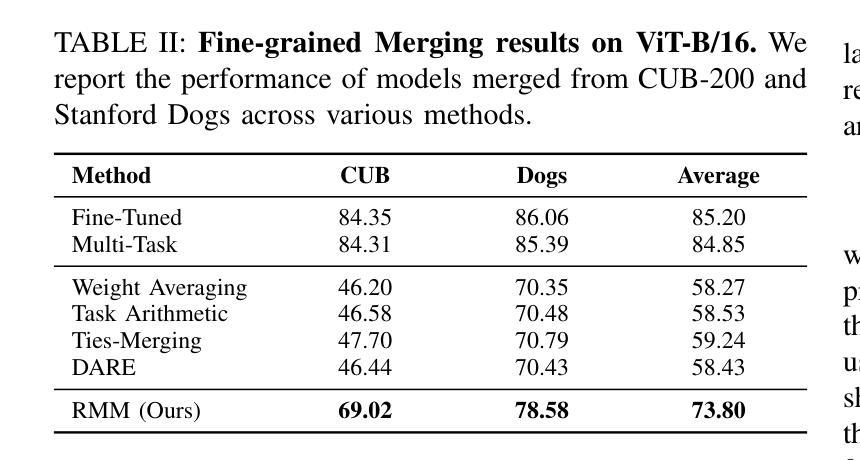
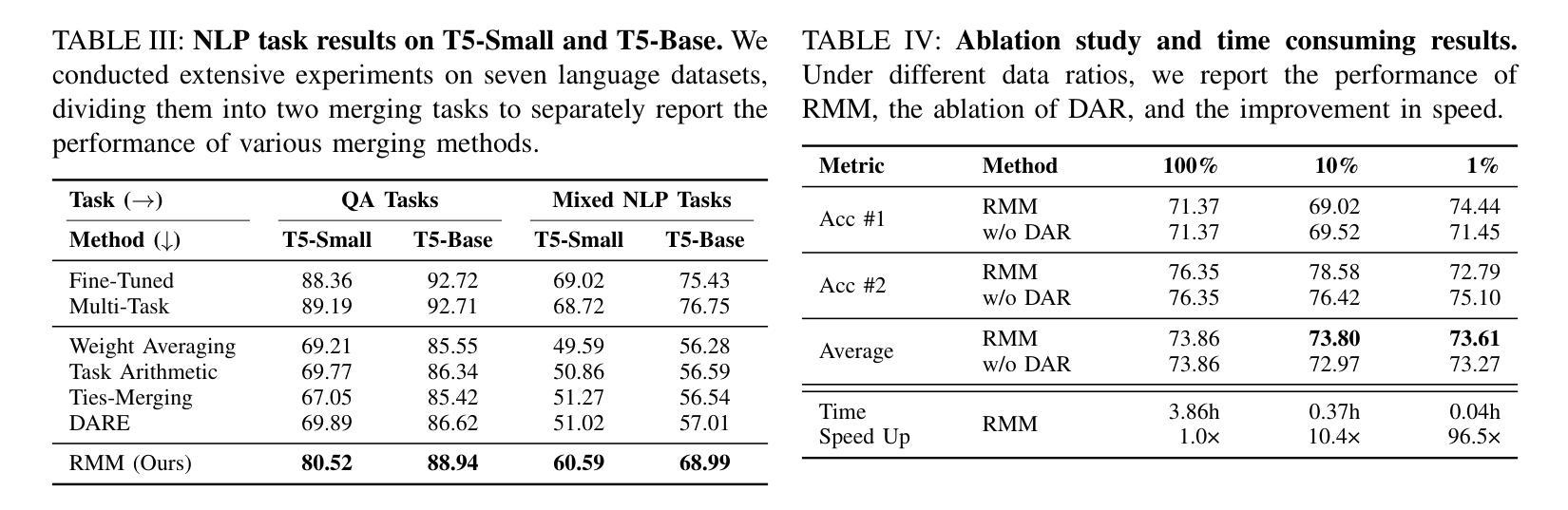
Reinforced Model Merging
Authors:Jiaqi Han, Jingwen Ye, Shunyu Liu, Haofei Zhang, Jie Song, Zunlei Feng, Mingli Song
The success of large language models has garnered widespread attention for model merging techniques, especially training-free methods which combine model capabilities within the parameter space. However, two challenges remain: (1) uniform treatment of all parameters leads to performance degradation; (2) search-based algorithms are often inefficient. In this paper, we present an innovative framework termed Reinforced Model Merging (RMM), which encompasses an environment and agent tailored for merging tasks. These components interact to execute layer-wise merging actions, aiming to search the optimal merging architecture. Notably, RMM operates without any gradient computations on the original models, rendering it feasible for edge devices. Furthermore, by utilizing data subsets during the evaluation process, we addressed the bottleneck in the reward feedback phase, thereby accelerating RMM by up to 100 times. Extensive experiments demonstrate that RMM achieves state-of-the-art performance across various vision and NLP datasets and effectively overcomes the limitations of the existing baseline methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/WuDiHJQ/Reinforced-Model-Merging.
大型语言模型的成功引发了人们对模型合并技术的广泛关注,尤其是无需训练的参数空间内模型能力组合方法。然而,仍存在两个挑战:(1)对所有参数进行统一处理会导致性能下降;(2)基于搜索的算法通常效率不高。在本文中,我们提出了一种名为强化模型合并(RMM)的创新框架,它包含一个针对合并任务量身定制的环境和代理。这些组件相互作用执行逐层合并操作,旨在搜索最佳的合并架构。值得注意的是,RMM在原始模型上没有任何梯度计算,使其适用于边缘设备。此外,通过在评估过程中使用数据子集,我们解决了奖励反馈阶段的瓶颈问题,从而使RMM的加速速度提高高达100倍。大量实验表明,RMM在不同类型的视觉和自然语言处理数据集上达到了最先进的性能,并有效地克服了现有基准方法的局限性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/WuDiHJQ/Reinforced-Model-Merging上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文提出了一种名为Reinforced Model Merging(RMM)的创新框架,旨在解决大型语言模型合并过程中的两个主要问题:参数处理不均导致性能下降以及搜索算法效率低下。RMM框架通过定制的环境和代理执行层级的合并动作,旨在搜索最佳的合并架构。其特点是无需对原始模型进行梯度计算,适合在边缘设备上运行。此外,通过评估过程中的数据子集使用,解决了奖励反馈阶段的瓶颈问题,使RMM加速达百倍。实验表明,RMM在多种视觉和NLP数据集上实现最佳性能,并成功克服现有基线方法的局限性。
Key Takeaways
- Reinforced Model Merging(RMM)框架旨在解决大型语言模型合并中的挑战,如性能降效和搜索算法效率低下。
- RMM通过定制的环境和代理进行层级的模型合并,旨在找到最佳的合并架构。
- RMM在合并过程中不需要对原始模型进行梯度计算,适合在边缘设备上运行。
- 使用数据子集进行评估,解决了奖励反馈阶段的瓶颈,极大加速了RMM的运行速度。
- 实验证明,RMM在多种视觉和NLP数据集上达到最佳性能。
- RMM成功克服了现有基线方法的局限性。
点此查看论文截图

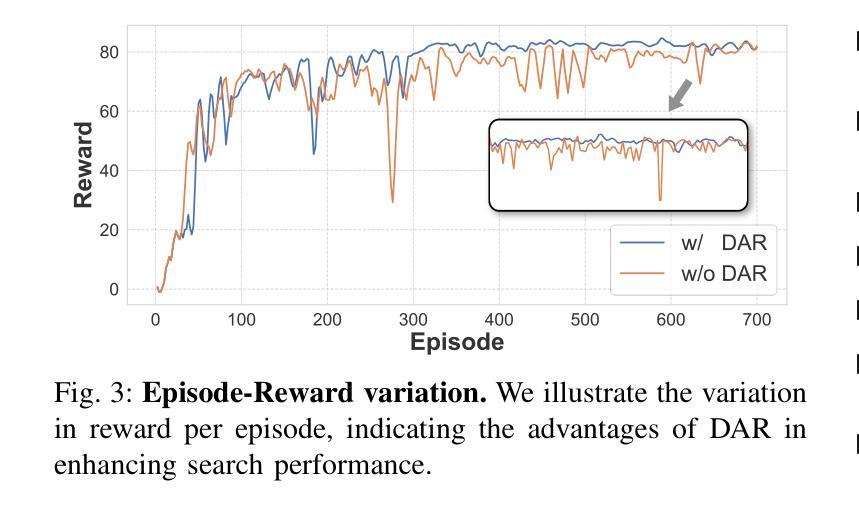
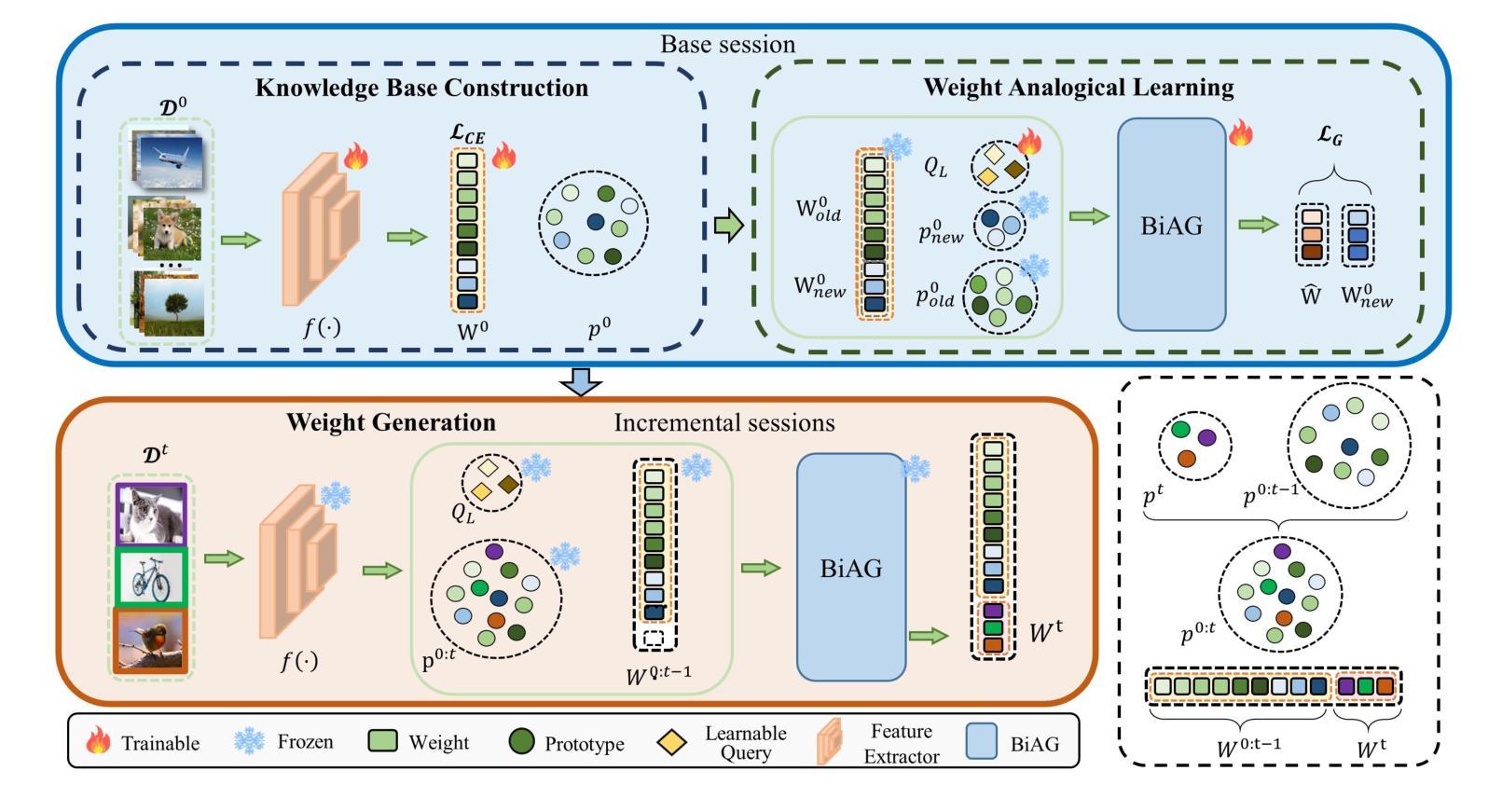
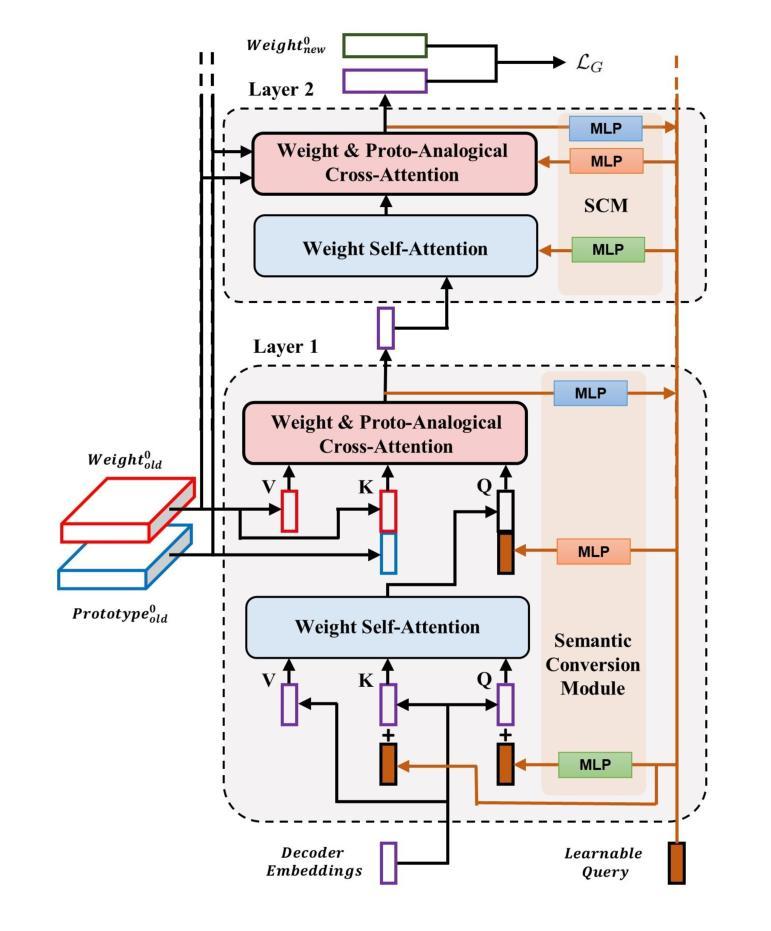
Learn by Reasoning: Analogical Weight Generation for Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning
Authors:Jizhou Han, Chenhao Ding, Yuhang He, Songlin Dong, Qiang Wang, Xinyuan Gao, Yihong Gong
Few-shot class-incremental Learning (FSCIL) enables models to learn new classes from limited data while retaining performance on previously learned classes. Traditional FSCIL methods often require fine-tuning parameters with limited new class data and suffer from a separation between learning new classes and utilizing old knowledge. Inspired by the analogical learning mechanisms of the human brain, we propose a novel analogical generative method. Our approach includes the Brain-Inspired Analogical Generator (BiAG), which derives new class weights from existing classes without parameter fine-tuning during incremental stages. BiAG consists of three components: Weight Self-Attention Module (WSA), Weight & Prototype Analogical Attention Module (WPAA), and Semantic Conversion Module (SCM). SCM uses Neural Collapse theory for semantic conversion, WSA supplements new class weights, and WPAA computes analogies to generate new class weights. Experiments on miniImageNet, CUB-200, and CIFAR-100 datasets demonstrate that our method achieves higher final and average accuracy compared to SOTA methods.
少量样本类增量学习(FSCIL)使模型能够在有限的样本中学习新类别,同时保留先前学习类别的性能。传统的FSCIL方法通常需要利用有限的样本数据对参数进行微调,并且存在学习新类别和利用旧知识之间的分离问题。受人类大脑类比学习机制的启发,我们提出了一种新型的类比生成方法。我们的方法包括基于大脑启发的类比生成器(BiAG),能够在增量阶段从现有类别中推导出新类别的权重,无需对参数进行微调。BiAG包含三个组件:权重自关注模块(WSA)、权重与原型类比关注模块(WPAA)和语义转换模块(SCM)。SCM利用神经崩溃理论进行语义转换,WSA补充新类别权重,WPAA计算类比以生成新类别权重。在miniImageNet、CUB-200和CIFAR-100数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法相较于最新方法取得了更高的最终和平均准确率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
少量类别增量学习(FSCIL)使得模型能够在有限的数据中学习新类别,同时保留对先前学习类别的性能。受人类大脑类比学习机制的启发,我们提出了一种新型的类比生成方法,包括Brain-Inspired Analogical Generator(BiAG)。BiAG通过权重自注意力模块(WSA)、权重与原型类比注意力模块(WPAA)和语义转换模块(SCM)三个组件,从现有类别中推导出新类别的权重,无需在增量阶段微调参数。实验表明,在miniImageNet、CUB-200和CIFAR-100数据集上,我们的方法相较于当前最先进的方法,最终的平均准确率更高。
Key Takeaways
- FSCIL允许模型在有限数据中学习新类别,同时保持对旧类别的性能。
- 提出的Brain-Inspired Analogical Generator(BiAG)方法能够从现有类别中推导出新类别的权重。
- BiAG包含三个组件:Weight Self-Attention Module(WSA)、Weight & Prototype Analogical Attention Module(WPAA)和Semantic Conversion Module(SCM)。
- WSA为新课程提供权重补充,WPAA计算类比以生成新课程权重。
- 语义转换模块使用神经崩溃理论进行语义转换。
点此查看论文截图

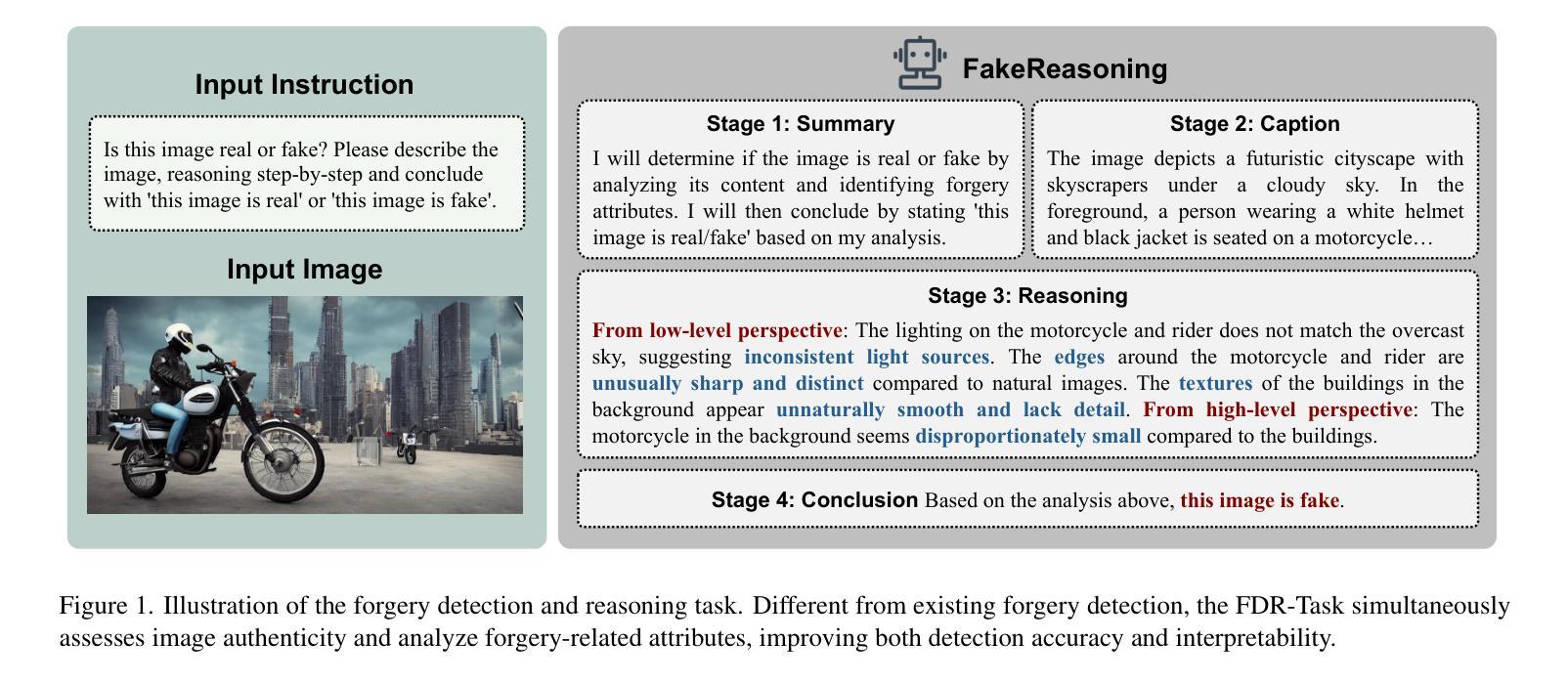
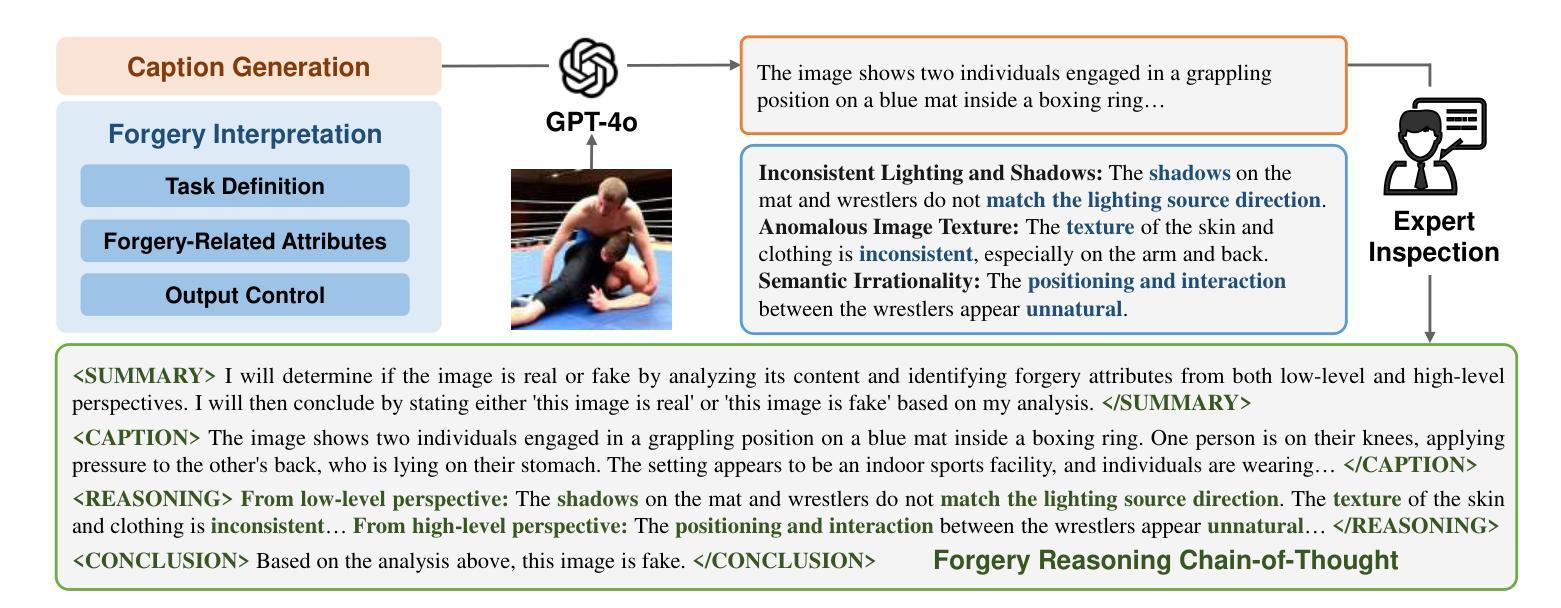
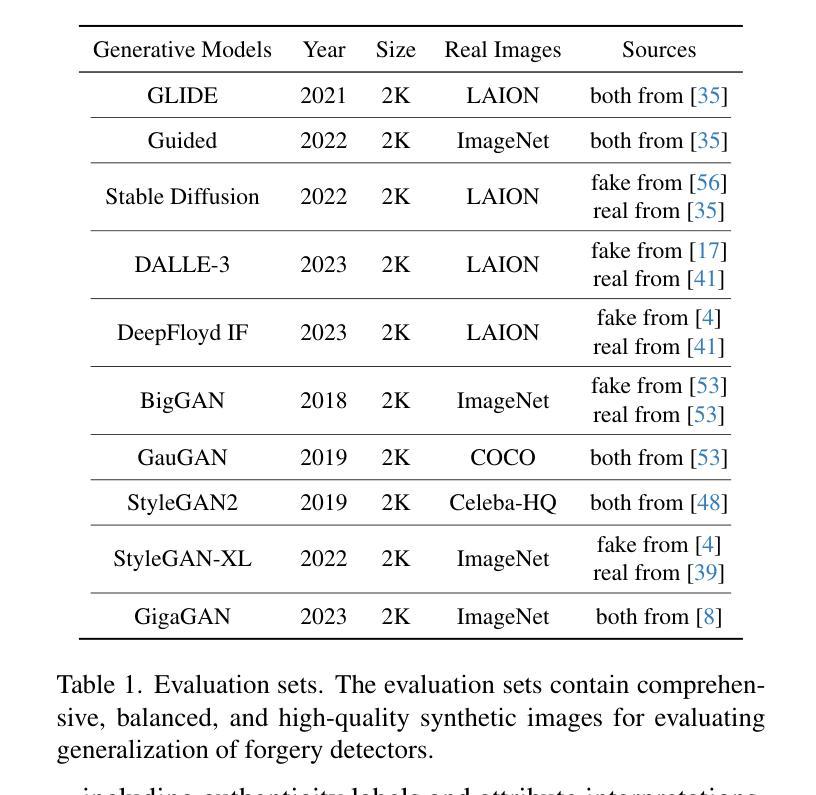
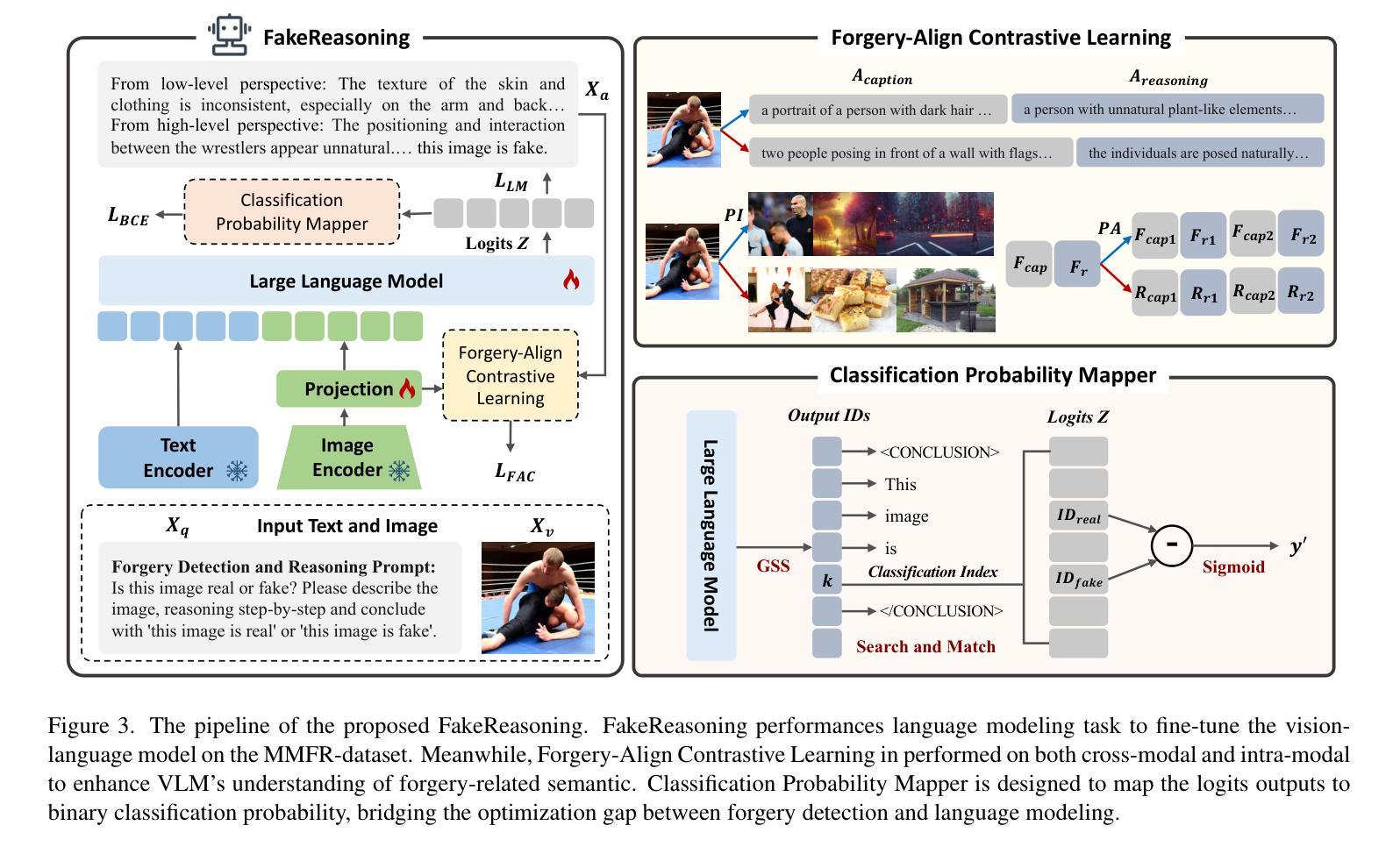
FakeReasoning: Towards Generalizable Forgery Detection and Reasoning
Authors:Yueying Gao, Dongliang Chang, Bingyao Yu, Haotian Qin, Lei Chen, Kongming Liang, Zhanyu Ma
Accurate and interpretable detection of AI-generated images is essential for mitigating risks associated with AI misuse. However, the substantial domain gap among generative models makes it challenging to develop a generalizable forgery detection model. Moreover, since every pixel in an AI-generated image is synthesized, traditional saliency-based forgery explanation methods are not well suited for this task. To address these challenges, we propose modeling AI-generated image detection and explanation as a Forgery Detection and Reasoning task (FDR-Task), leveraging vision-language models (VLMs) to provide accurate detection through structured and reliable reasoning over forgery attributes. To facilitate this task, we introduce the Multi-Modal Forgery Reasoning dataset (MMFR-Dataset), a large-scale dataset containing 100K images across 10 generative models, with 10 types of forgery reasoning annotations, enabling comprehensive evaluation of FDR-Task. Additionally, we propose FakeReasoning, a forgery detection and reasoning framework with two key components. First, Forgery-Aligned Contrastive Learning enhances VLMs’ understanding of forgery-related semantics through both cross-modal and intra-modal contrastive learning between images and forgery attribute reasoning. Second, a Classification Probability Mapper bridges the optimization gap between forgery detection and language modeling by mapping the output logits of VLMs to calibrated binary classification probabilities. Experiments across multiple generative models demonstrate that FakeReasoning not only achieves robust generalization but also outperforms state-of-the-art methods on both detection and reasoning tasks.
准确且可解释的AI生成图像检测对于缓解与AI误用相关的风险至关重要。然而,生成模型之间的巨大领域差距使得开发可通用的伪造检测模型具有挑战性。此外,由于AI生成的图像中的每个像素都是合成的,因此传统的基于显著性的伪造解释方法并不适合此任务。为了应对这些挑战,我们将AI生成图像的检测和解释建模为伪造检测与推理任务(FDR-Task),利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)通过结构化且可靠的推理提供准确的检测。为了促进此任务,我们引入了多模态伪造推理数据集(MMFR-Dataset),这是一个包含跨越十个生成模型的十万张图像的大规模数据集,带有十种伪造推理注释类型,可全面评估FDR任务。此外,我们提出了FakeReasoning这一伪造检测与推理框架,该框架包含两个关键组件。首先,伪造对齐对比学习通过图像和伪造属性推理之间的跨模态和模态内对比学习增强VLMs对伪造相关语义的理解。其次,分类概率映射器通过映射VLMs的输出逻辑值到校准的二元分类概率来缩小伪造检测和语言建模之间的优化差距。在多个生成模型上的实验表明,FakeReasoning不仅实现了稳健的泛化能力,而且在检测和推理任务上的表现均优于现有先进技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文针对人工智能生成图像的检测与解释难题,提出了一个全新的任务——伪造检测与推理任务(FDR-Task)。为了应对不同生成模型间的领域差距,利用跨模态和模态内的对比学习增强视觉语言模型(VLMs)对伪造相关语义的理解。同时,引入大型多模态伪造推理数据集MMFR-Dataset,包含10万个跨越10种生成模型的图像和10种伪造推理注释。实验证明,FakeReasoning框架在检测与推理任务上实现了稳健的泛化性能,并优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- AI生成图像的检测与解释对缓解AI误用风险至关重要。
- 现有方法难以应对不同生成模型间的领域差距,因此需要一种更具泛化能力的伪造检测模型。
- 传统基于显著性的伪造解释方法不适用于AI生成图像的检测与解释任务。
- 提出FDR-Task(伪造检测与推理任务),将AI生成图像的检测与解释建模为一项新的任务。
- 引入大型多模态伪造推理数据集MMFR-Dataset,包含多种生成模型的图像和多种伪造推理注释。
- FakeReasoning框架包括两个关键组件:Forgery-Aligned Contrastive Learning和Classification Probability Mapper。前者通过跨模态和模态内的对比学习增强VLMs对伪造语义的理解,后者缩小了优化差距,映射VLMs的输出逻辑到校准的二元分类概率。
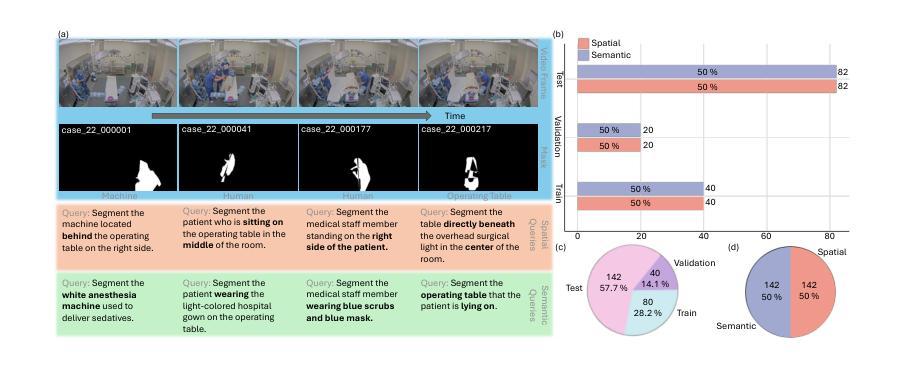
点此查看论文截图

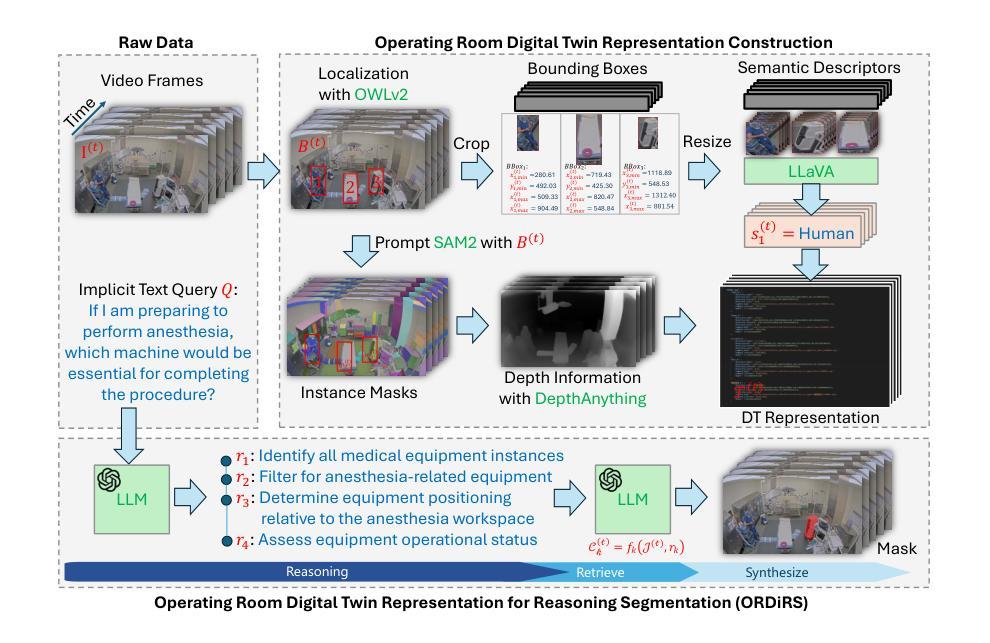
Operating Room Workflow Analysis via Reasoning Segmentation over Digital Twins
Authors:Yiqing Shen, Chenjia Li, Bohan Liu, Cheng-Yi Li, Tito Porras, Mathias Unberath
Analyzing operating room (OR) workflows to derive quantitative insights into OR efficiency is important for hospitals to maximize patient care and financial sustainability. Prior work on OR-level workflow analysis has relied on end-to-end deep neural networks. While these approaches work well in constrained settings, they are limited to the conditions specified at development time and do not offer the flexibility necessary to accommodate the OR workflow analysis needs of various OR scenarios (e.g., large academic center vs. rural provider) without data collection, annotation, and retraining. Reasoning segmentation (RS) based on foundation models offers this flexibility by enabling automated analysis of OR workflows from OR video feeds given only an implicit text query related to the objects of interest. Due to the reliance on large language model (LLM) fine-tuning, current RS approaches struggle with reasoning about semantic/spatial relationships and show limited generalization to OR video due to variations in visual characteristics and domain-specific terminology. To address these limitations, we first propose a novel digital twin (DT) representation that preserves both semantic and spatial relationships between the various OR components. Then, building on this foundation, we propose ORDiRS (Operating Room Digital twin representation for Reasoning Segmentation), an LLM-tuning-free RS framework that reformulates RS into a “reason-retrieval-synthesize” paradigm. Finally, we present ORDiRS-Agent, an LLM-based agent that decomposes OR workflow analysis queries into manageable RS sub-queries and generates responses by combining detailed textual explanations with supporting visual evidence from RS. Experimental results on both an in-house and a public OR dataset demonstrate that our ORDiRS achieves a cIoU improvement of 6.12%-9.74% compared to the existing state-of-the-arts.
分析手术室(OR)的工作流程以得出关于手术室效率的定量见解,对于医院最大限度地改善患者护理和财务可持续性至关重要。先前关于手术室级别的工作流分析依赖于端到端的深度神经网络。虽然这些方法在受控环境中效果很好,但它们仅限于开发时指定的条件,并不提供适应各种手术室情景(例如大型学术中心与乡村医疗机构)所需的灵活性,而无需进行数据采集、标注和重新训练。基于基础模型的推理分割(RS)通过仅与感兴趣的对象相关的隐含文本查询自动分析手术室工作流,从而提供了这种灵活性。由于依赖于大型语言模型(LLM)的微调,当前的RS方法在处理语义/空间关系方面存在困难,并且在面对手术室视频的视觉特征和领域特定术语的变体时,其泛化能力有限。为了解决这些局限性,我们首先提出了一种新颖的数字孪生(DT)表示法,该表示法可以保留手术室各组件之间的语义和空间关系。然后,在此基础上,我们提出了ORDiRS(手术室数字孪生推理分割),这是一种无需LLM调整的RS框架,它将RS重新制定为“推理-检索-合成”的模式。最后,我们展示了基于LLM的ORDiRS-Agent,它将手术室工作流程分析查询分解为可管理的RS子查询,并通过结合详细的文本解释和来自RS的支持视觉证据来生成响应。在内部和公共手术室数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的ORDiRS与现有最新技术相比,cIoU提高了6.12%-9.74%。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
手术室(OR)工作流的分析对于医院提升病患照护及财务可持续性至关重要。之前的OR级别工作流分析大多依赖深度神经网络。虽然这些方法在受限环境下效果良好,但它们难以适应不同OR场景的需求。为此,研究提出了一种基于数字双胞胎(DT)的手术室工作流分析框架,无需调整大型语言模型(LLM),该框架将推理分割重新构建为“推理-检索-合成”的模式。在此基础上,进一步开发了名为ORDiRS-Agent的LLM基础代理,该代理可将复杂的OR工作流分析查询分解为可管理的子查询,并通过结合详细的文本解释和来自推理检索的视觉证据来生成响应。实验结果表明,与现有技术相比,我们的ORDiRS在完全集成的交并比(cIoU)上提高了6.12%-9.74%。
关键见解
- 分析手术室工作流对于医院的运营效率至关重要。
- 现有的深度神经网络方法虽然有效,但缺乏适应不同手术室场景变化的灵活性。
- 提出了一种新型的数字双胞胎表示法,能够保留手术室组件间的语义和空间关系。
- 介绍了一种无需调整大型语言模型的推理分割框架——ORDiRS。
- ORDiRS框架重新定义了“推理-检索-合成”的模式以改进分析。
- 开发了ORDiRS-Agent,能有效分解复杂查询并生成详细的解释和视觉证据支持的响应。
点此查看论文截图

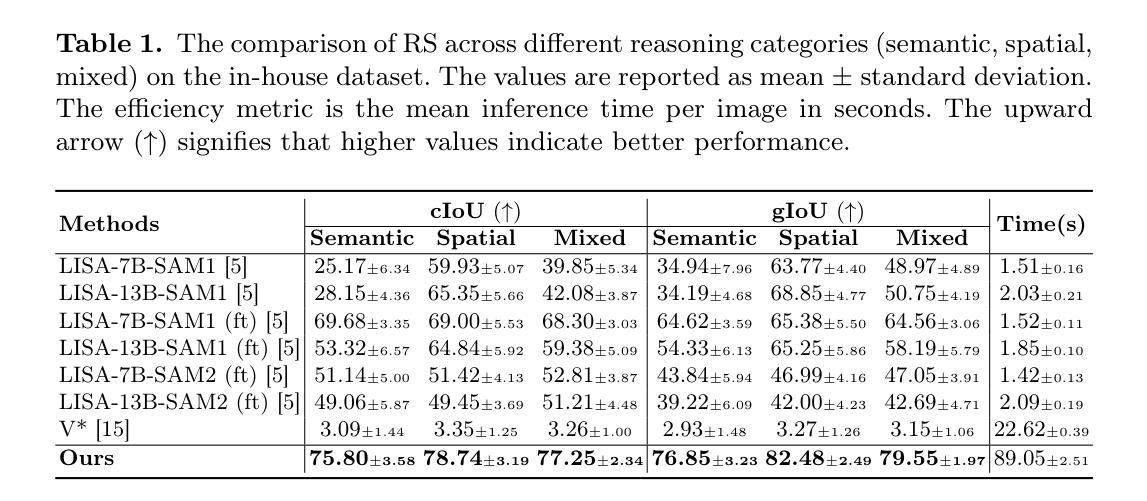
Generating Synthetic Data with Formal Privacy Guarantees: State of the Art and the Road Ahead
Authors:Viktor Schlegel, Anil A Bharath, Zilong Zhao, Kevin Yee
Privacy-preserving synthetic data offers a promising solution to harness segregated data in high-stakes domains where information is compartmentalized for regulatory, privacy, or institutional reasons. This survey provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the landscape of privacy-preserving synthetic data, presenting the theoretical foundations of generative models and differential privacy followed by a review of state-of-the-art methods across tabular data, images, and text. Our synthesis of evaluation approaches highlights the fundamental trade-off between utility for down-stream tasks and privacy guarantees, while identifying critical research gaps: the lack of realistic benchmarks representing specialized domains and insufficient empirical evaluations required to contextualise formal guarantees. Through empirical analysis of four leading methods on five real-world datasets from specialized domains, we demonstrate significant performance degradation under realistic privacy constraints ($\epsilon \leq 4$), revealing a substantial gap between results reported on general domain benchmarks and performance on domain-specific data. %Our findings highlight key challenges including unaccounted privacy leakage, insufficient empirical verification of formal guarantees, and a critical deficit of realistic benchmarks. These challenges underscore the need for robust evaluation frameworks, standardized benchmarks for specialized domains, and improved techniques to address the unique requirements of privacy-sensitive fields such that this technology can deliver on its considerable potential.
隐私保护合成数据为在监管、隐私或制度原因下信息细分的高风险领域利用分散数据提供了有前景的解决方案。这篇综述提供了一个全面的框架,用于了解隐私保护合成数据的景观,介绍了生成模型和差分隐私的理论基础,并回顾了表格数据、图像和文本的最先进方法。我们对评估方法的综合突出了下游任务的实用性与隐私保证之间的基本权衡,同时识别了关键的研究空白:缺乏代表专业领域和缺乏实证评估的现实基准测试,无法将正式保证置于特定情境中。通过对四种领先方法在五个专业领域真实数据集上的实证分析,我们在现实的隐私约束(ε≤4)下表现出显著的性能下降,这揭示了与一般基准测试上的报告结果相比在特定领域数据上性能上存在显著差距。我们的研究揭示了重要挑战,包括未考虑的隐私泄露、正式保证的实证验证不足以及缺乏真实基准测试的关键缺陷。这些挑战强调了建立稳健的评估框架、针对特定领域的标准化基准和改进技术的必要性,以便实现隐私敏感领域的独特需求,从而使这项技术发挥其巨大的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages + references + Appendix. Preprint
Summary
隐私保护合成数据在解决高风险领域中的分立数据问题方面展现出巨大潜力,特别是在信息因监管、隐私或机构原因而被隔离的情况下。本文提供了理解隐私保护合成数据景观的综合框架,介绍了生成模型和差分隐私的理论基础,并评述了跨表格数据、图像和文本的最新方法。本文的评价方法合成揭示了下游任务的实用性与隐私保证之间的基本权衡,并确定了研究空白,包括缺乏代表专业领域的现实基准测试以及缺乏将形式保证置于情境中的实证评估。通过对四种领先方法在五个专业领域的真实数据集上的实证分析,我们在现实的隐私约束下显示了显著的性能下降(ε≤4),揭示了通用领域基准测试报告的结果与特定领域数据性能之间的巨大差距。
Key Takeaways
- 隐私保护合成数据在高风险领域解决分立数据问题方面具有巨大潜力。
- 文章提供了理解隐私保护合成数据景观的综合框架,包括生成模型和差分隐私的理论基础。
- 现有方法在特定领域的真实数据集上表现出性能下降,在现实的隐私约束下效果不佳。
- 综述了最新的表格数据、图像和文本处理方法。
- 揭示了下游任务实用性与隐私保证之间的权衡关系。
- 研究存在多个关键挑战,包括未考虑的隐私泄露、实证验证的缺乏以及针对特定领域的现实基准测试的不足。
点此查看论文截图

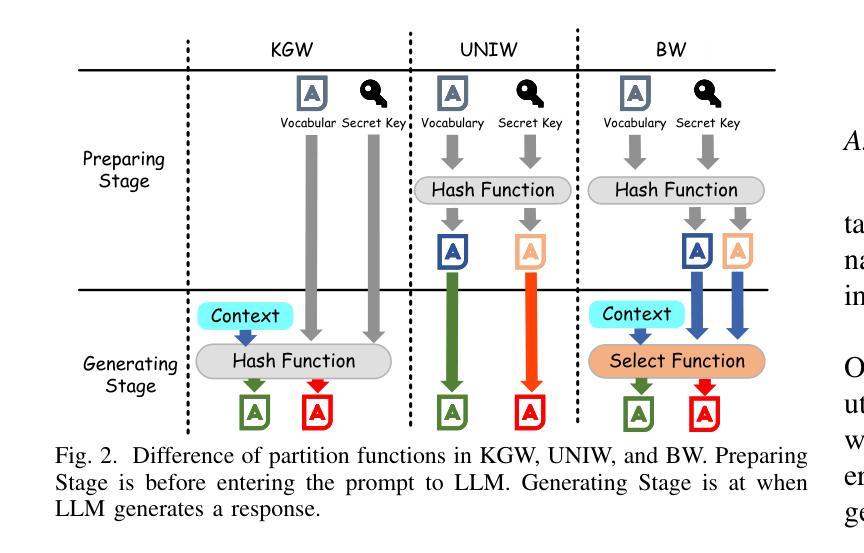
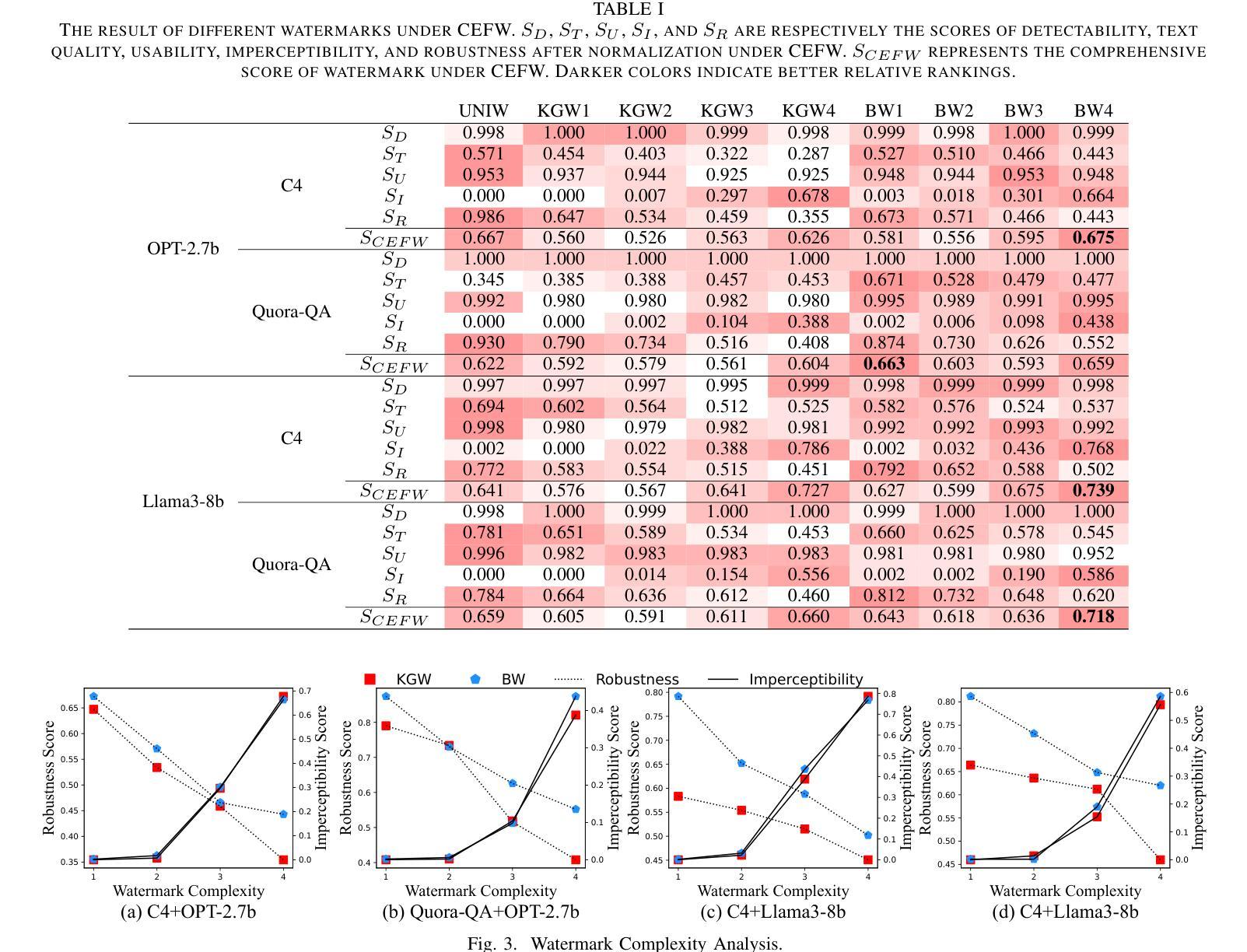
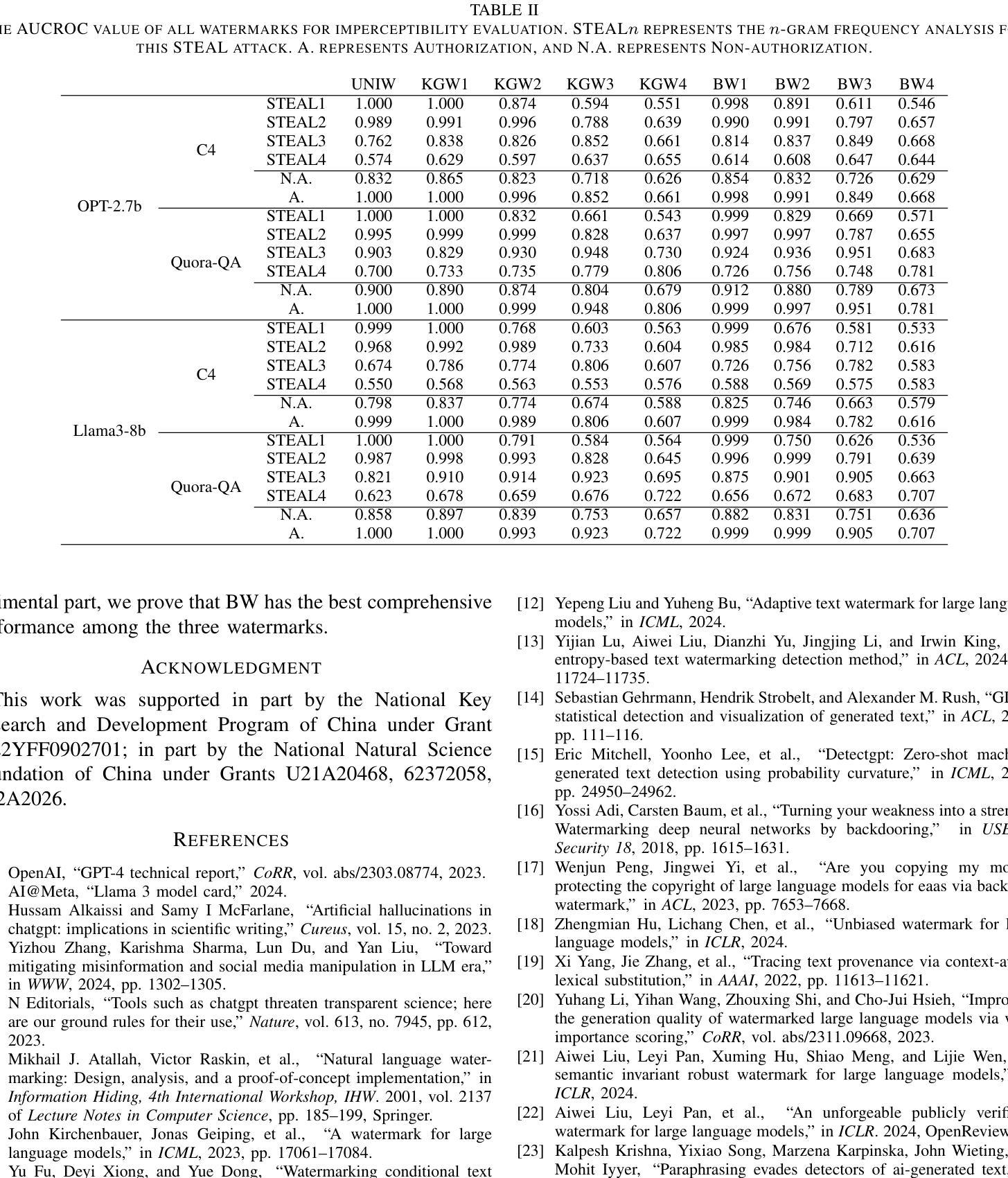
CEFW: A Comprehensive Evaluation Framework for Watermark in Large Language Models
Authors:Shuhao Zhang, Bo Cheng, Jiale Han, Yuli Chen, Zhixuan Wu, Changbao Li, Pingli Gu
Text watermarking provides an effective solution for identifying synthetic text generated by large language models. However, existing techniques often focus on satisfying specific criteria while ignoring other key aspects, lacking a unified evaluation. To fill this gap, we propose the Comprehensive Evaluation Framework for Watermark (CEFW), a unified framework that comprehensively evaluates watermarking methods across five key dimensions: ease of detection, fidelity of text quality, minimal embedding cost, robustness to adversarial attacks, and imperceptibility to prevent imitation or forgery. By assessing watermarks according to all these key criteria, CEFW offers a thorough evaluation of their practicality and effectiveness. Moreover, we introduce a simple and effective watermarking method called Balanced Watermark (BW), which guarantees robustness and imperceptibility through balancing the way watermark information is added. Extensive experiments show that BW outperforms existing methods in overall performance across all evaluation dimensions. We release our code to the community for future research. https://github.com/DrankXs/BalancedWatermark.
文本水印为识别大型语言模型生成的合成文本提供了有效的解决方案。然而,现有技术往往只关注满足特定标准而忽视其他关键方面,缺乏统一的评估体系。为了填补这一空白,我们提出了水印综合评估框架(CEFW),这是一个全面评估水印方法的统一框架,涵盖了五个关键维度:检测便捷性、文本质量保真度、最小嵌入成本、对抗攻击的鲁棒性以及防止模仿或伪造的不可察觉性。通过这些关键标准来评估水印,CEFW提供了对其实用性和有效性的全面评估。此外,我们引入了一种简单有效的水印方法——平衡水印(BW),它通过平衡水印信息添加的方式,保证了鲁棒性和不可察觉性。大量实验表明,BW在所有评估维度上的总体性能优于现有方法。我们向社区发布我们的代码以供未来研究使用。相关链接:https://github.com/DrankXs/BalancedWatermark。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本水印为识别大型语言模型生成的合成文本提供了有效的解决方案。针对现有技术缺乏统一评估的问题,提出了综合水印评价框架(CEFW),从五个关键维度全面评估水印方法:检测便捷性、文本质量保真度、嵌入成本最小化、对抗攻击的鲁棒性,以及防止模仿或伪造的不可察觉性。CEFW为水印的实际效果和实用性提供了全面的评估。此外,还提出了一种简单有效的水印方法——平衡水印(BW),通过平衡添加水印信息的方式,保证了其鲁棒性和不可察觉性。实验表明,BW在所有的评估维度上整体性能优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 文本水印是识别大型语言模型生成的合成文本的有效解决方案。
- 当前技术缺乏统一的水印评价框架,导致难以全面评估水印方法的性能。
- 综合水印评价框架(CEFW)从五个关键维度全面评估水印方法:检测便捷性、文本质量保真度等。
- CEFW能全面评估水印的实际效果和实用性。
- 提出了一种新的简单有效的水印方法——平衡水印(BW)。
- 平衡水印通过平衡添加水印信息的方式,保证了其鲁棒性和不可察觉性。
点此查看论文截图

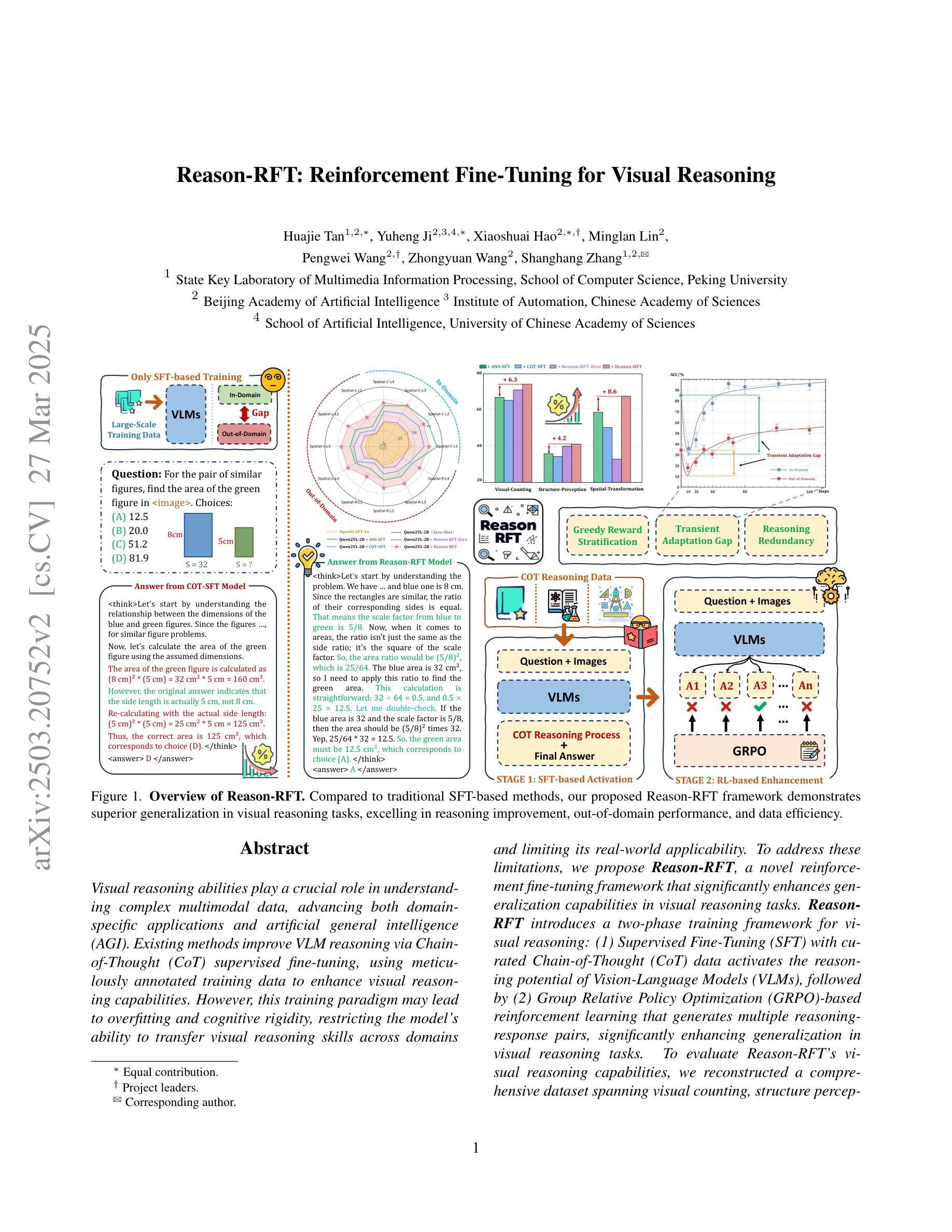
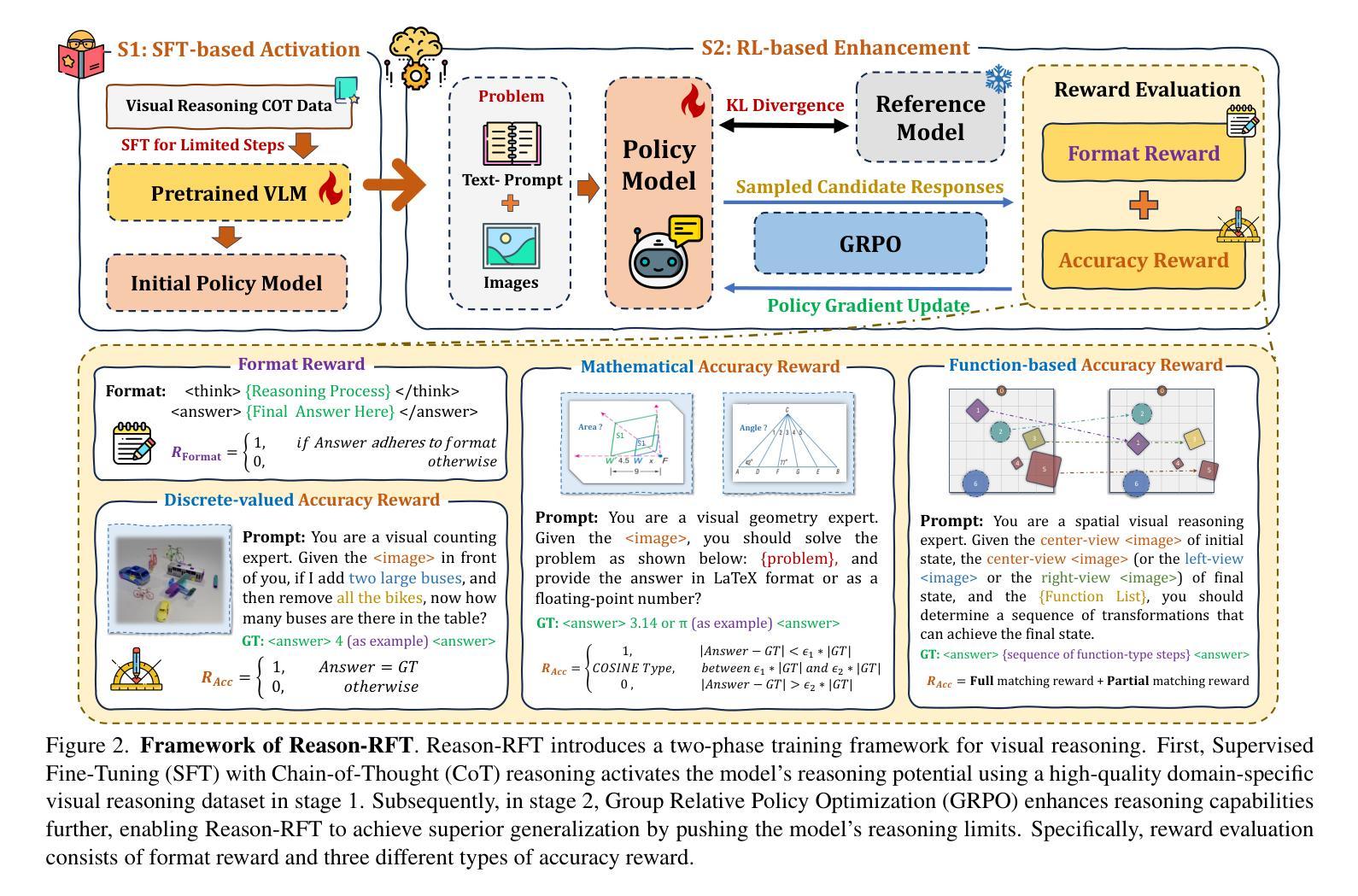
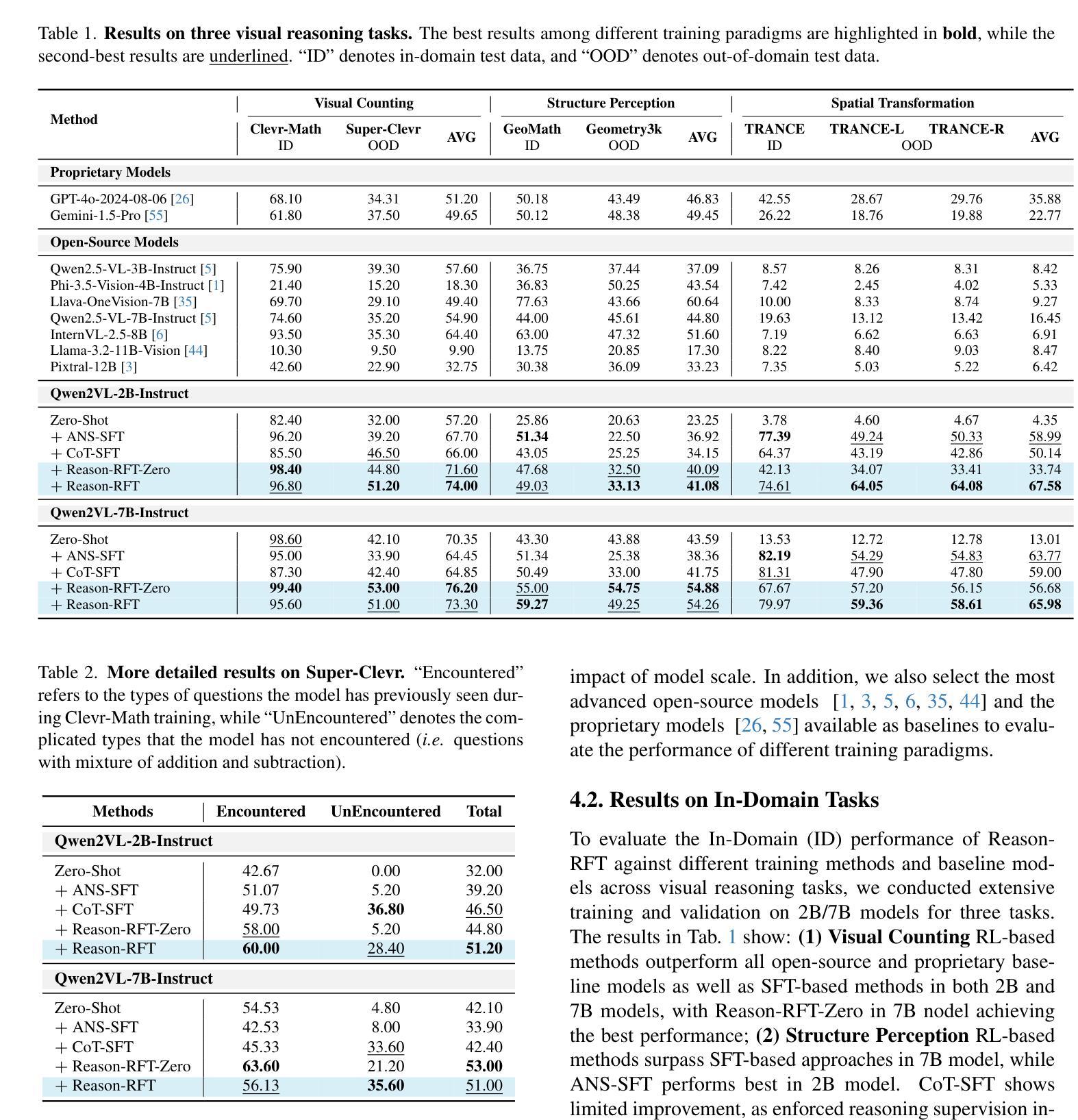
Reason-RFT: Reinforcement Fine-Tuning for Visual Reasoning
Authors:Huajie Tan, Yuheng Ji, Xiaoshuai Hao, Minglan Lin, Pengwei Wang, Zhongyuan Wang, Shanghang Zhang
Visual reasoning abilities play a crucial role in understanding complex multimodal data, advancing both domain-specific applications and artificial general intelligence (AGI). Existing methods improve VLM reasoning via Chain-of-Thought (CoT) supervised fine-tuning, using meticulously annotated training data to enhance visual reasoning capabilities. However, this training paradigm may lead to overfitting and cognitive rigidity, restricting the model’s ability to transfer visual reasoning skills across domains and limiting its real-world applicability. To address these limitations, we propose Reason-RFT, a novel reinforcement fine-tuning framework that significantly enhances generalization capabilities in visual reasoning tasks. Reason-RFT introduces a two-phase training framework for visual reasoning: (1) Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) with curated Chain-of-Thought (CoT) data activates the reasoning potential of Vision-Language Models (VLMs), followed by (2) Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO)-based reinforcement learning that generates multiple reasoning-response pairs, significantly enhancing generalization in visual reasoning tasks. To evaluate Reason-RFT’s visual reasoning capabilities, we reconstructed a comprehensive dataset spanning visual counting, structure perception, and spatial transformation. Experimental results demonstrate Reasoning-RFT’s three key advantages: (1) Performance Enhancement: achieving state-of-the-art results across multiple tasks, outperforming most mainstream open-source and proprietary models; (2) Generalization Superiority: consistently maintaining robust performance across diverse tasks and domains, outperforming alternative training paradigms; (3) Data Efficiency: excelling in few-shot learning scenarios while surpassing full-dataset SFT baselines. Project website: https://tanhuajie.github.io/ReasonRFT
视觉推理能力在理解复杂的多模态数据、推动特定领域应用和通用人工智能(AGI)发展方面发挥着至关重要的作用。现有方法通过思维链(CoT)监督微调(SFT)提升视觉推理能力,使用精心标注的训练数据增强视觉推理能力。然而,这种训练模式可能会导致过度拟合和认知僵化,限制模型在不同领域转移视觉推理技能的能力,并限制其在现实世界中的应用性。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了Reason-RFT,这是一种新的强化微调框架,能显著提高视觉推理任务的泛化能力。Reason-RFT引入了视觉推理的两阶段训练框架:首先使用精选的思维链(CoT)数据进行监督微调(SFT),激活视觉语言模型(VLM)的推理潜力,然后基于群体相对策略优化(GRPO)的强化学习生成多个推理响应对,显著增强视觉推理任务的泛化能力。为了评估Reason-RFT的视觉推理能力,我们重建了一个综合数据集,涵盖了视觉计数、结构感知和空间转换。实验结果表明,Reasoning-RFT具有三大优势:(1)性能提升:在多任务上取得最先进的成果,超越大多数主流开源和专有模型;(2)泛化优势:在不同任务和领域上始终保持良好的性能,超越其他训练模式;(3)数据效率:在少量学习场景中表现出色,超越全数据集的SFT基准。项目网站:https://tanhuajie.github.io/ReasonRFT
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 35 pages, 22 figures
Summary
视觉推理能力在处理复杂多模态数据、推动领域特定应用和通用人工智能(AGI)发展方面发挥着重要作用。现有方法通过链式思维(CoT)监督微调提升视觉推理能力,但需应对过拟合和认知僵化问题,限制了模型跨域转移视觉推理技能的能力及其在现实世界中的应用范围。为应对这些局限性,本文提出Reason-RFT框架,该框架包括两个阶段:首先使用精选的链式思维(CoT)数据激活视觉语言模型(VLM)的推理潜力,然后采用基于群体相对策略优化(GRPO)的强化学习生成多个推理响应对,从而显著提高视觉推理任务的泛化能力。实验结果表明,Reasoning-RFT具有三大优势:性能提升、泛化优势和数据效率。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉推理在处理复杂多模态数据和推动人工智能领域发展上扮演重要角色。
- 当前方法通过链式思维(CoT)监督微调提升视觉推理能力,但存在过拟合和认知僵化问题。
- Reason-RFT框架旨在解决上述问题,包括监督微调(SFT)和基于群体相对策略优化(GRPO)的强化学习两个阶段。
- 实验表明Reasoning-RFT在视觉推理任务上表现优越,具有性能提升、泛化优势和数据效率三大优点。
- 该框架在多种任务上实现最佳结果,并优于主流开源和专有模型。
- Reason-RFT框架能够保持跨不同任务和领域的稳健性能,并优于其他训练范式。
点此查看论文截图
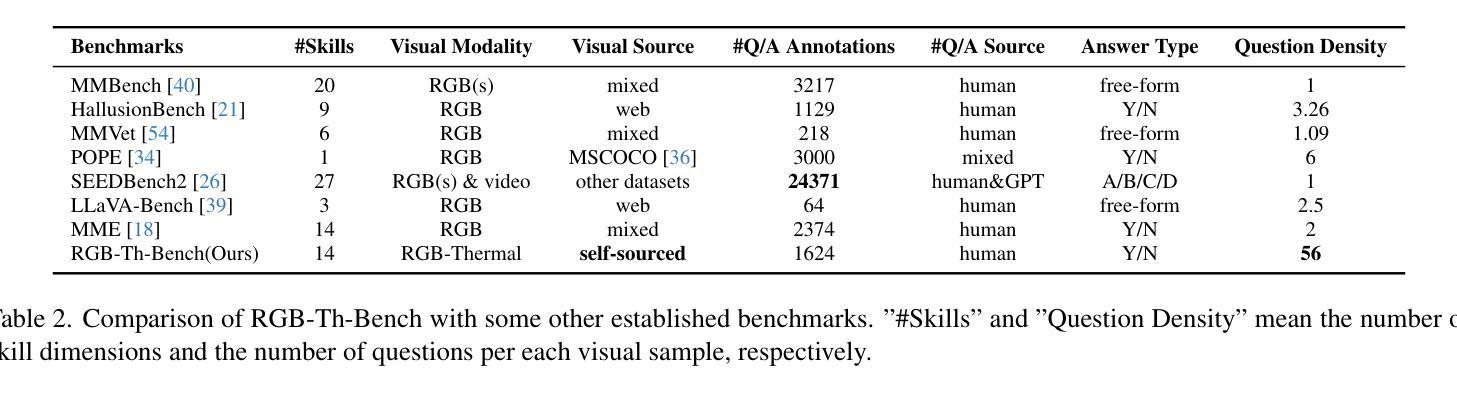
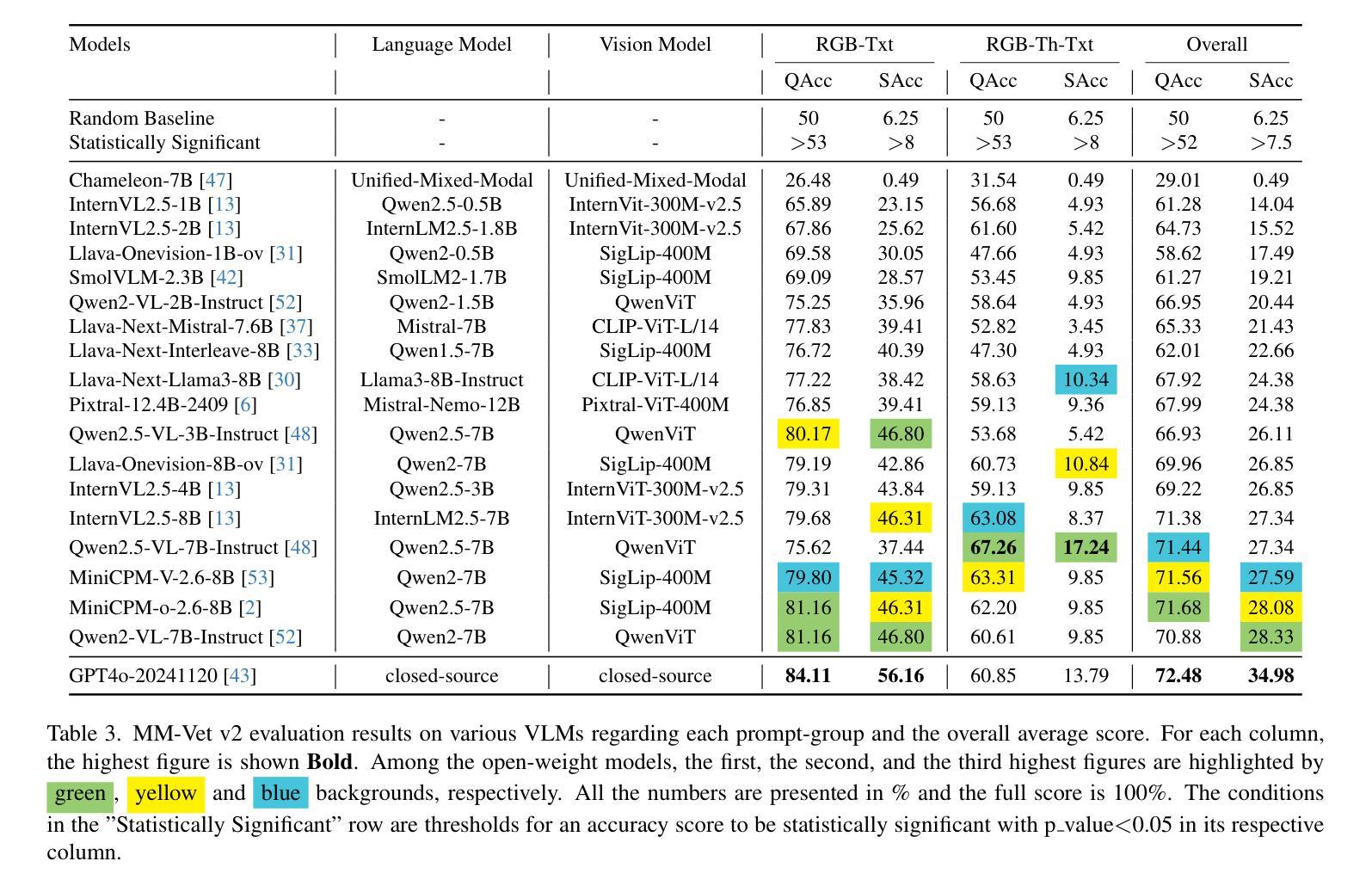
RGB-Th-Bench: A Dense benchmark for Visual-Thermal Understanding of Vision Language Models
Authors:Mehdi Moshtaghi, Siavash H. Khajavi, Joni Pajarinen
We introduce RGB-Th-Bench, the first benchmark designed to evaluate the ability of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to comprehend RGB-Thermal image pairs. While VLMs have demonstrated remarkable progress in visual reasoning and multimodal understanding, their evaluation has been predominantly limited to RGB-based benchmarks, leaving a critical gap in assessing their capabilities in infrared vision tasks. Existing visible-infrared datasets are either task-specific or lack high-quality annotations necessary for rigorous model evaluation. To address these limitations, RGB-Th-Bench provides a comprehensive evaluation framework covering 14 distinct skill dimensions, with a total of 1,600+ expert-annotated Yes/No questions. The benchmark employs two accuracy metrics: a standard question-level accuracy and a stricter skill-level accuracy, which evaluates model robustness across multiple questions within each skill dimension. This design ensures a thorough assessment of model performance, including resilience to adversarial and hallucinated responses. We conduct extensive evaluations on 19 state-of-the-art VLMs, revealing significant performance gaps in RGB-Thermal understanding. Our results show that even the strongest models struggle with thermal image comprehension, with performance heavily constrained by their RGB-based capabilities. Additionally, the lack of large-scale application-specific and expert-annotated thermal-caption-pair datasets in pre-training is an important reason of the observed performance gap. RGB-Th-Bench highlights the urgent need for further advancements in multimodal learning to bridge the gap between visible and thermal image understanding. The dataset is available through this link, and the evaluation code will also be made publicly available.
我们推出RGB-Th-Bench,这是首个专门用于评估视觉语言模型(VLMs)理解RGB-热成像图像对能力的基准测试。尽管VLMs在视觉推理和多模态理解方面取得了显著的进步,但其评估主要局限于基于RGB的基准测试,在评估红外视觉任务的能力方面存在关键差距。现有的可见光-红外数据集是特定任务的,或者缺乏进行严格模型评估所需的高质量注释。为了解决这些局限性,RGB-Th-Bench提供了一个全面的评估框架,涵盖14个不同的技能维度,总共有1600多个专家注释的是非问题。该基准测试采用两项准确度指标:标准的问答准确度和严格的技能准确度,后者评估模型在各个技能维度内跨多个问题的稳健性。这种设计确保了全面评估模型性能,包括对抗性和幻觉响应的韧性。我们对19个最先进VLM进行了广泛评估,发现RGB-热理解方面的性能差距很大。我们的结果表明,即使是最强大的模型在热成像理解方面也面临困难,其性能严重受到基于RGB的能力的限制。此外,缺乏大规模特定应用和专家注释的热成像字幕对数据集进行预训练是观察到性能差距的重要原因。RGB-Th-Bench强调了在多模态学习方面进一步发展的迫切需求,以缩小可见光和热成像理解之间的差距。数据集可通过此链接获取,评估代码也将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
推出首个针对视觉语言模型(VLMs)的RGB-Th-Bench基准测试平台,用于评估模型理解RGB-Thermal图像对的能力。现有基准测试主要局限于RGB基准测试,缺乏评估红外视觉任务能力的工具。RGB-Th-Bench提供全面的评估框架,涵盖14个不同的技能维度,共有1,600多个专家标注的是非问题。采用两种准确度指标进行评估,确保全面评估模型性能,包括对抗性和虚构响应的抵抗力。对19个最先进的VLMs进行了广泛评估,发现RGB-Thermal理解的性能差距显著。最强模型在热图像理解方面仍有困难,性能受RGB能力限制。呼吁进一步改进多模态学习,以缩小可见与热图像理解之间的差距。数据集可通过链接获取,评估代码也将公开发布。
Key Takeaways:
- RGB-Th-Bench是首个评估视觉语言模型(VLMs)理解RGB-Thermal图像对能力的基准测试平台。
- 现有基准测试主要局限于RGB图像,缺乏评估模型在红外视觉任务中能力的工具。
- RGB-Th-Bench提供全面的评估框架,涵盖多种技能维度和准确度指标,确保全面评估模型性能。
- 最先进的VLMs在RGB-Thermal理解方面存在显著性能差距,最强模型在热图像理解方面仍有困难。
- 模型性能受RGB能力限制,表明多模态学习的改进是迫切需要的。
- 缺乏大规模应用特定的和专家标注的热图像数据集是性能差距的重要原因。
点此查看论文截图


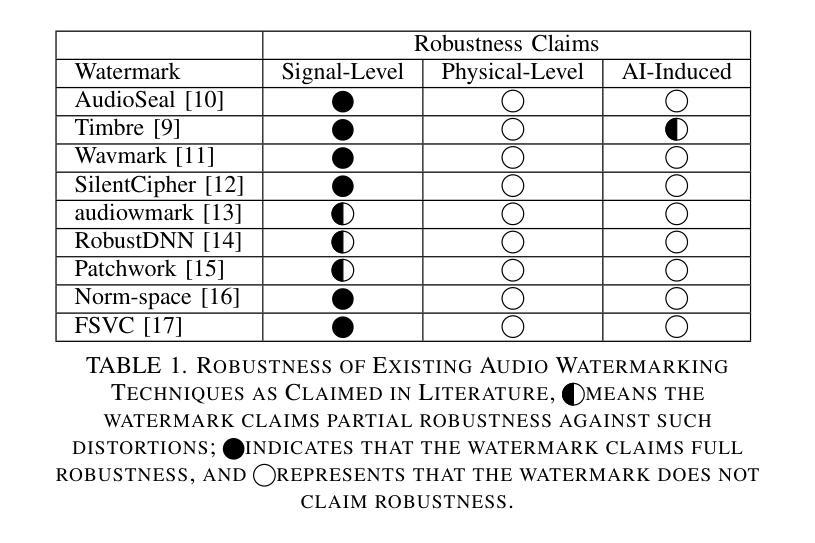
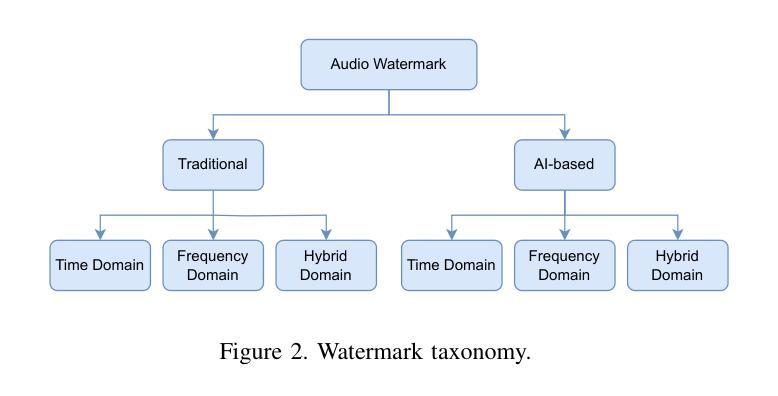
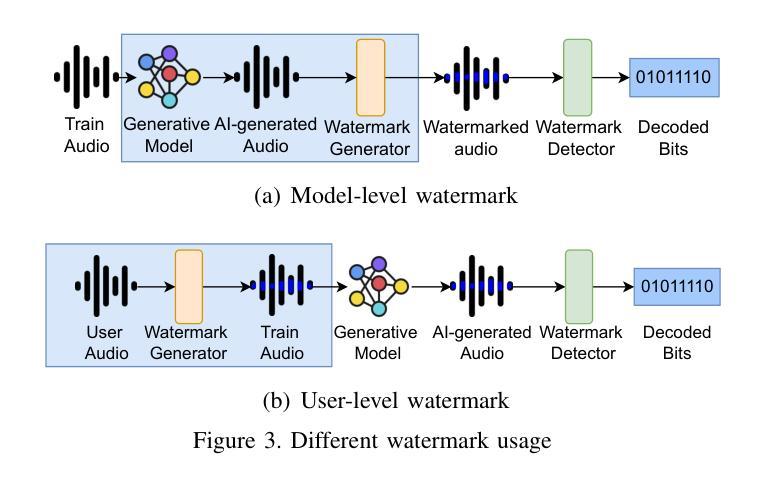
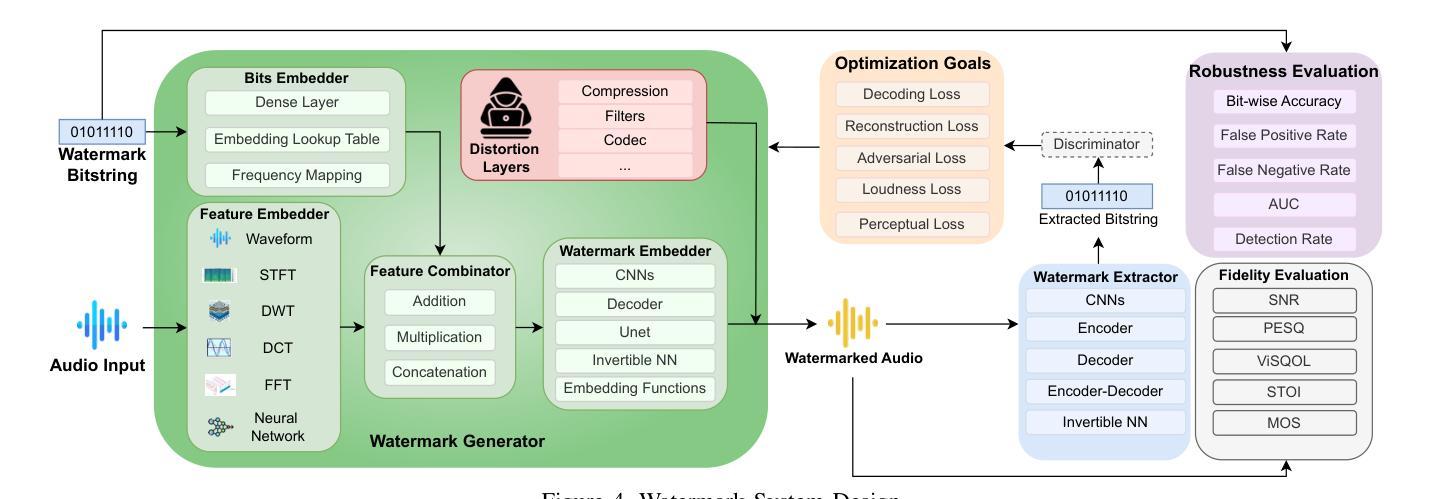
SoK: How Robust is Audio Watermarking in Generative AI models?
Authors:Yizhu Wen, Ashwin Innuganti, Aaron Bien Ramos, Hanqing Guo, Qiben Yan
Audio watermarking is increasingly used to verify the provenance of AI-generated content, enabling applications such as detecting AI-generated speech, protecting music IP, and defending against voice cloning. To be effective, audio watermarks must resist removal attacks that distort signals to evade detection. While many schemes claim robustness, these claims are typically tested in isolation and against a limited set of attacks. A systematic evaluation against diverse removal attacks is lacking, hindering practical deployment. In this paper, we investigate whether recent watermarking schemes that claim robustness can withstand a broad range of removal attacks. First, we introduce a taxonomy covering 22 audio watermarking schemes. Next, we summarize their underlying technologies and potential vulnerabilities. We then present a large-scale empirical study to assess their robustness. To support this, we build an evaluation framework encompassing 22 types of removal attacks (109 configurations) including signal-level, physical-level, and AI-induced distortions. We reproduce 9 watermarking schemes using open-source code, identify 8 new highly effective attacks, and highlight 11 key findings that expose the fundamental limitations of these methods across 3 public datasets. Our results reveal that none of the surveyed schemes can withstand all tested distortions. This evaluation offers a comprehensive view of how current watermarking methods perform under real-world threats. Our demo and code are available at https://sokaudiowm.github.io/.
音频水印技术越来越多地用于验证人工智能生成内容的出处,支持检测人工智能生成的语音、保护音乐知识产权和防范声音克隆等应用。要有效发挥作用,音频水印必须抵抗能够扭曲信号以逃避检测的去除攻击。尽管许多方案都声称具有稳健性,但这些声称通常是在孤立的情况下和有限的攻击集上进行测试的。缺乏针对多种去除攻击的系统评估,阻碍了实际部署。在本文中,我们调查了最近声称具有稳健性的水印方案是否能够承受广泛的去除攻击。首先,我们介绍了涵盖22种音频水印方案的分类。接下来,我们总结了其基础技术和潜在漏洞。然后,我们进行了一项大规模实证研究来评估其稳健性。为此,我们建立了一个评估框架,包括22种类型的去除攻击(109种配置),包括信号级、物理级和人工智能引起的失真。我们使用开源代码重新制作了9种水印方案,识别了8种新的高度有效的攻击,并强调了11个关键发现,揭示了这些方法在3个公共数据集上的根本局限性。我们的结果表明,所调查的方案中没有哪一种能够承受所有测试的失真。这一评估提供了当前水印方法在现实世界威胁下的全面视图。我们的演示和代码可在[https://sokaudiowm.github.io/]上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇论文探讨了音频水印技术在验证AI生成内容方面的应用,包括检测AI生成的语音、保护音乐知识产权和防范声音克隆。为了有效应对各种移除攻击,文章对不同的音频水印方案进行了系统的评估,发现目前的水印方案普遍存在漏洞,无法应对所有测试中的失真。该评估为当前水印方法在真实威胁下的表现提供了全面的视角。
Key Takeaways
- 音频水印技术用于验证AI生成内容的来源,如检测AI生成的语音、保护音乐知识产权和防范声音克隆。
- 目前的水印方案缺乏对各种移除攻击的全面评估,限制了其实践应用。
- 文章引入了一个包含22种音频水印方案的分类,并概述了它们的基础技术和潜在漏洞。
- 通过大规模实证研究评估了水印方案的稳健性,建立了包含22种类型(共109种配置)的移除攻击评估框架。
- 研究人员复现了9种水印方案并发现了8种新的高效攻击方式。
- 调查结果揭示了这些方法的根本局限性,即没有一种方案能够抵御所有测试的失真。
点此查看论文截图