⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-04 更新
Data Synthesis with Diverse Styles for Face Recognition via 3DMM-Guided Diffusion
Authors:Yuxi Mi, Zhizhou Zhong, Yuge Huang, Qiuyang Yuan, Xuan Zhao, Jianqing Xu, Shouhong Ding, ShaoMing Wang, Rizen Guo, Shuigeng Zhou
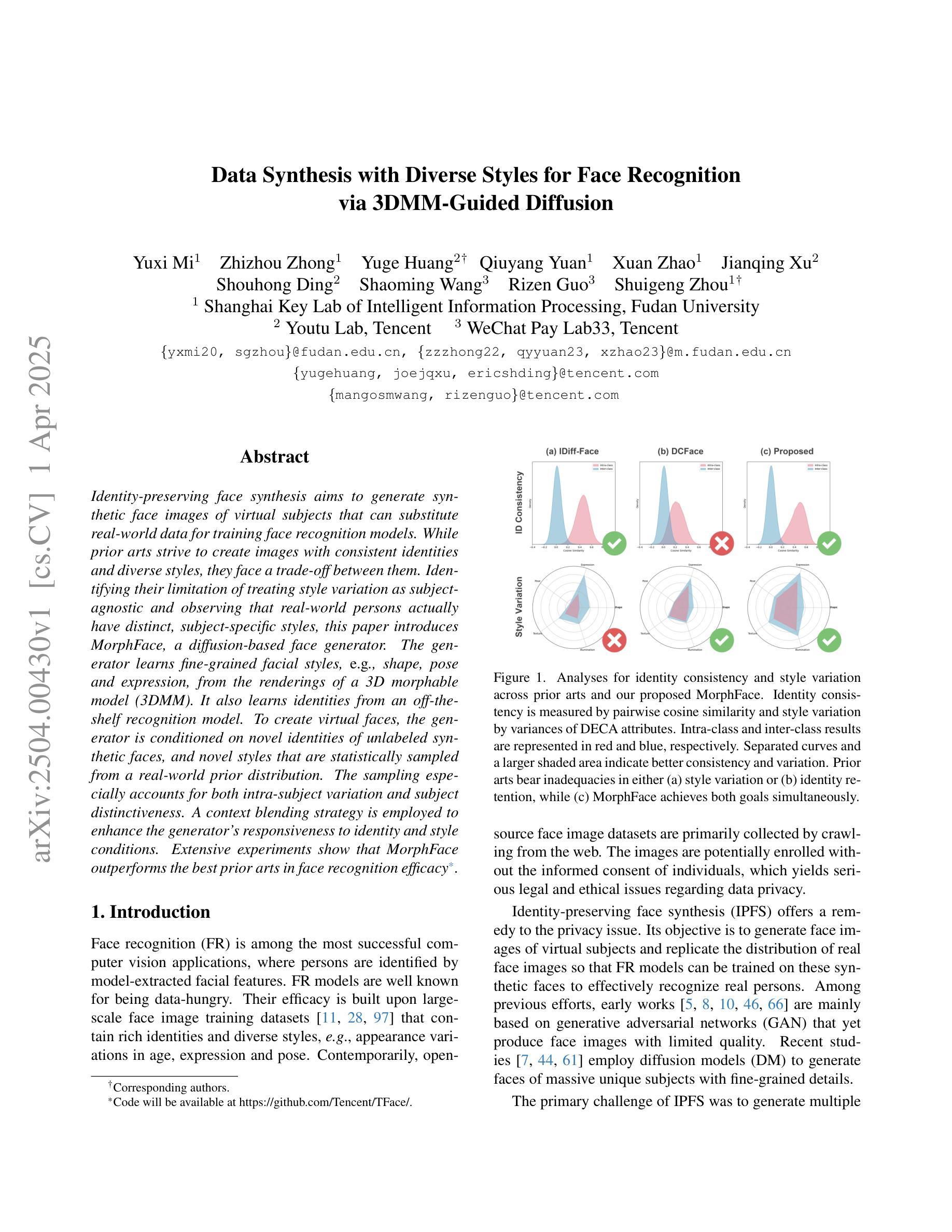
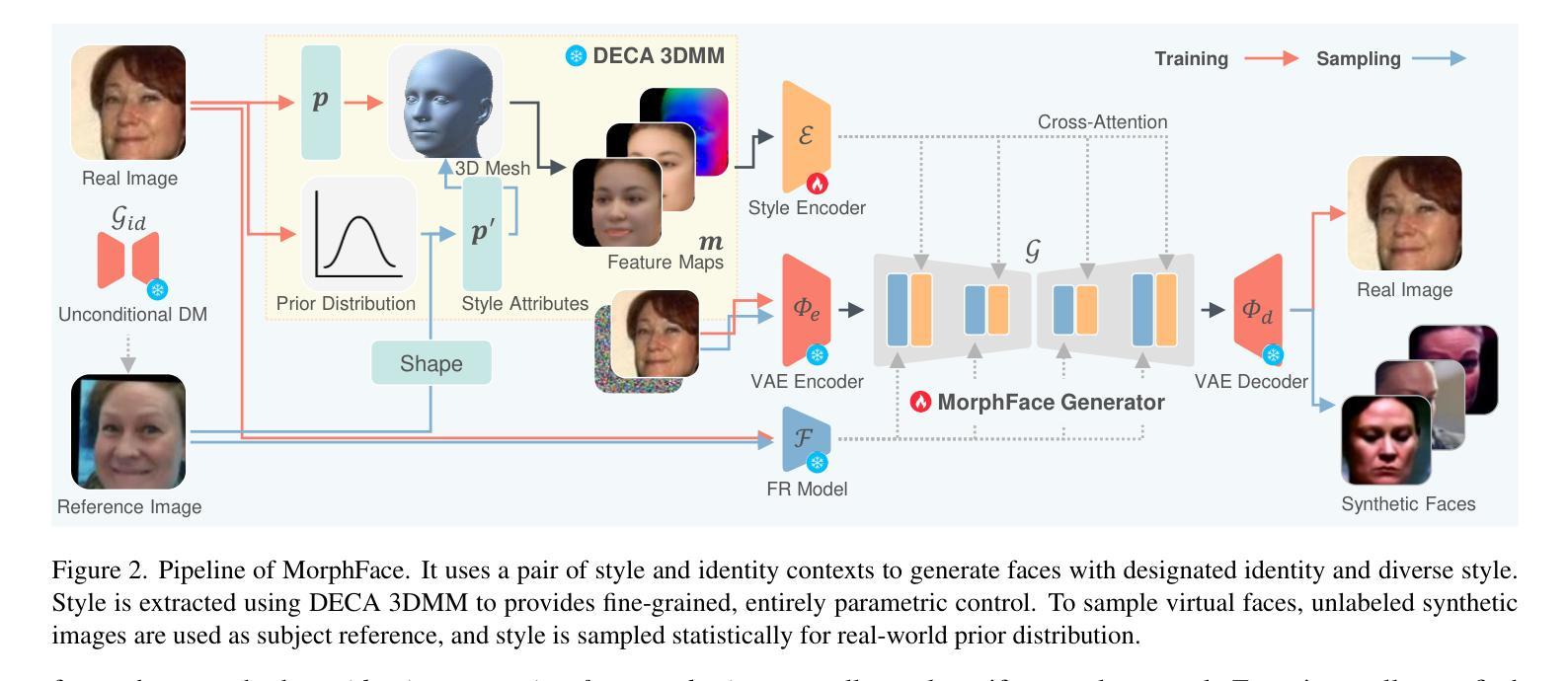
Identity-preserving face synthesis aims to generate synthetic face images of virtual subjects that can substitute real-world data for training face recognition models. While prior arts strive to create images with consistent identities and diverse styles, they face a trade-off between them. Identifying their limitation of treating style variation as subject-agnostic and observing that real-world persons actually have distinct, subject-specific styles, this paper introduces MorphFace, a diffusion-based face generator. The generator learns fine-grained facial styles, e.g., shape, pose and expression, from the renderings of a 3D morphable model (3DMM). It also learns identities from an off-the-shelf recognition model. To create virtual faces, the generator is conditioned on novel identities of unlabeled synthetic faces, and novel styles that are statistically sampled from a real-world prior distribution. The sampling especially accounts for both intra-subject variation and subject distinctiveness. A context blending strategy is employed to enhance the generator’s responsiveness to identity and style conditions. Extensive experiments show that MorphFace outperforms the best prior arts in face recognition efficacy.
身份保留面部合成旨在生成虚拟主体的合成面部图像,这些图像可以替代真实世界数据来训练人脸识别模型。虽然先前技术致力于创建具有一致身份和多种风格的图像,但它们面临两者之间的权衡。本文识别出将风格变化视为与主题无关而导致的局限,并观察到现实世界中的个人实际上具有独特、与主题相关的风格。因此,本文引入了MorphFace,这是一种基于扩散的面部生成器。该生成器从3D可变形模型(3DMM)的渲染中学习精细的面部风格,例如形状、姿势和表情。它还从一个现成的识别模型中学习身份。为了创建虚拟面部,该生成器受到无标签合成面部的全新身份和从现实世界先验分布统计采样得到的新型风格的制约。采样特别考虑了主体内变化和主体差异性。采用上下文融合策略,以提高生成器对身份和风格条件的响应能力。大量实验表明,MorphFace在人脸识别效率方面优于最佳先前技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
基于扩散模型的脸部生成器MorphFace,旨在生成能够替代真实世界数据进行面部识别模型训练的身份保留面部合成图像。它学习了精细的面部风格,如形状、姿势和表情,并能够从三维可变形模型(3DMM)的渲染中学习身份。该生成器能够创建虚拟面部,并响应身份和风格条件的需求。实验表明,MorphFace在面部识别效果上优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 身份保留面部合成旨在生成可替代真实世界数据的虚拟面部图像,用于训练面部识别模型。
- MorphFace是一种基于扩散的面部生成器,能够学习精细的面部风格,如形状、姿势和表情。
- 该生成器从三维可变形模型(3DMM)的渲染中学习身份特征。
- 生成器通过条件控制生成具有新型身份和风格的虚拟面部。
- 该生成器采用上下文融合策略,以提高对身份和风格条件的响应能力。
- 实验结果显示,MorphFace在面部识别效果上超越了现有技术。
点此查看论文截图
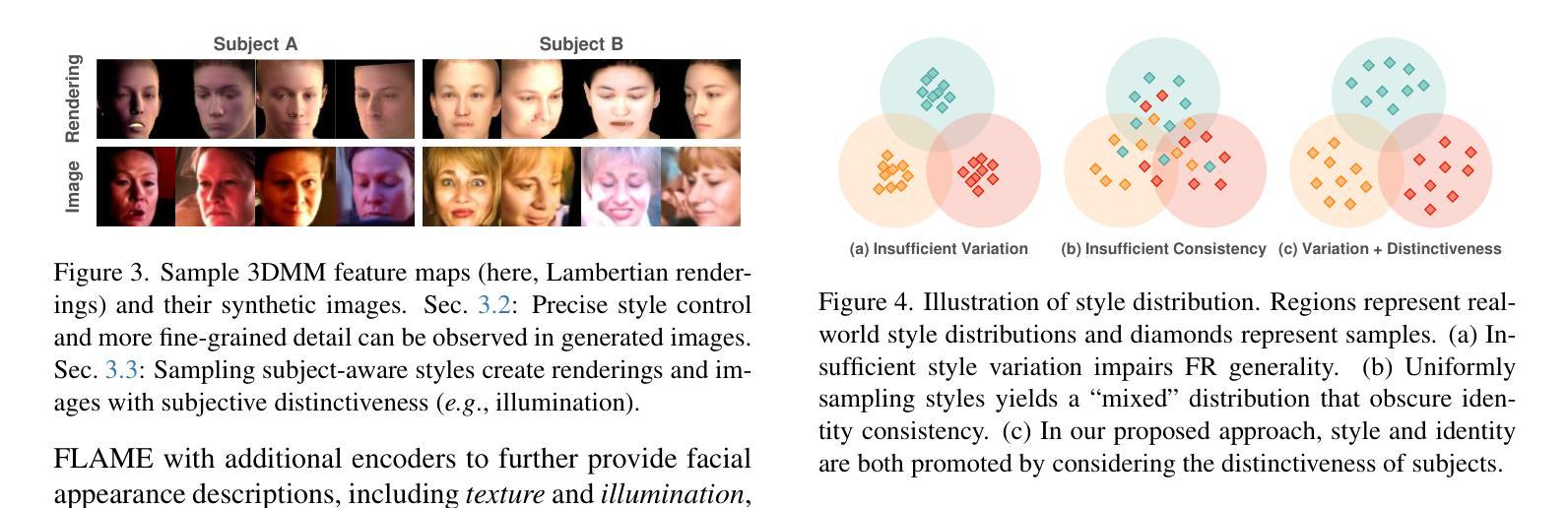
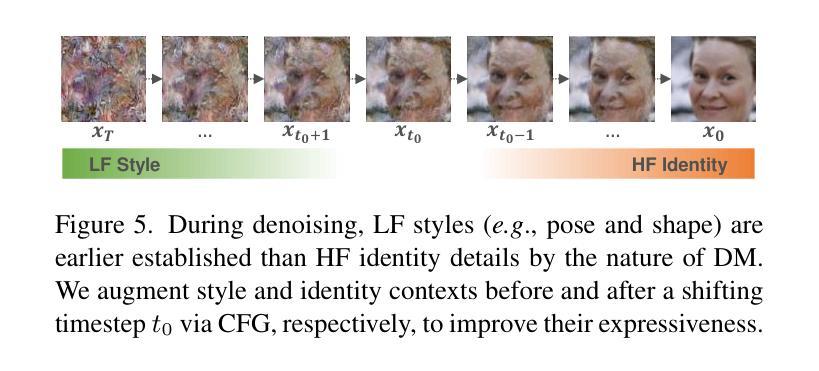

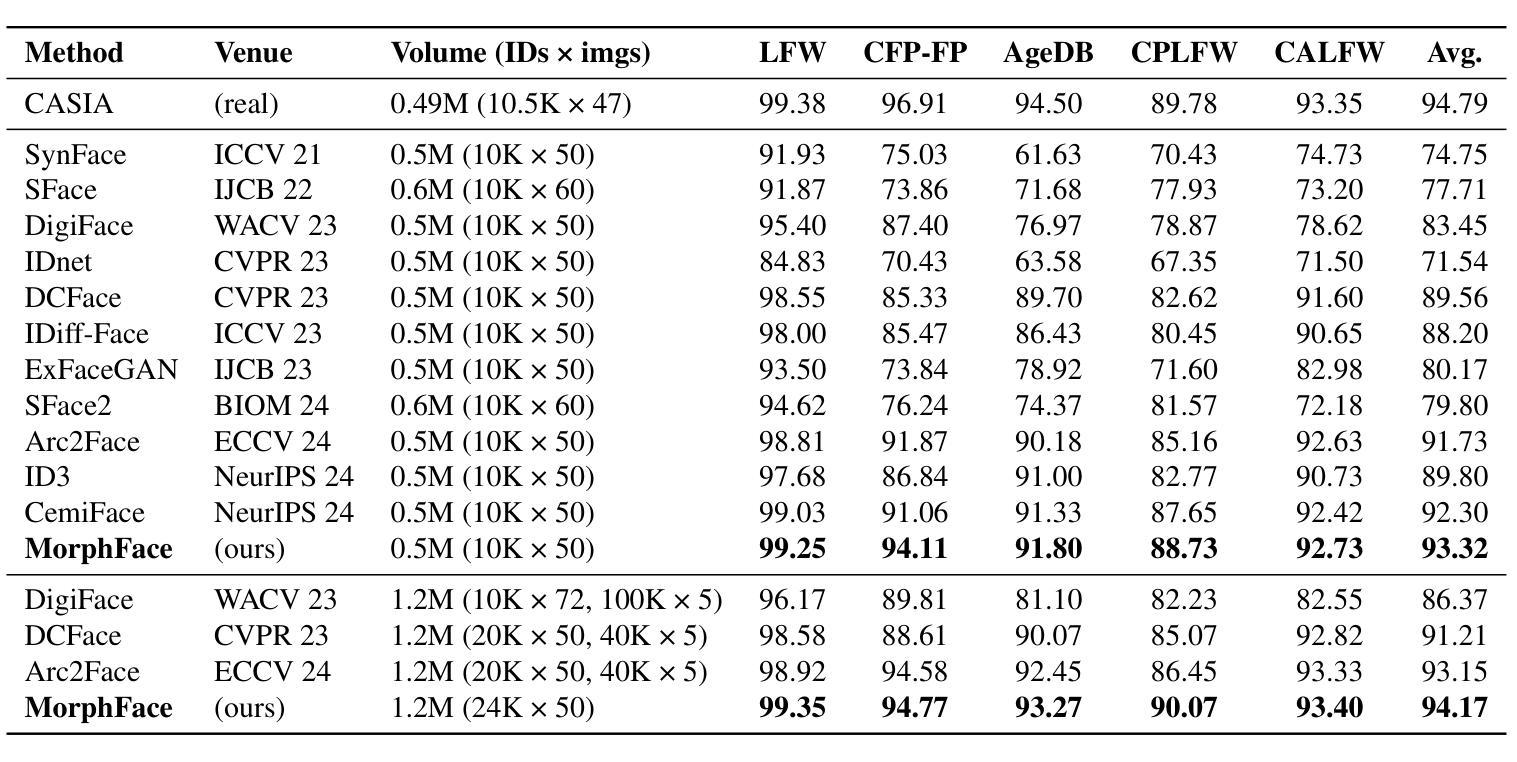
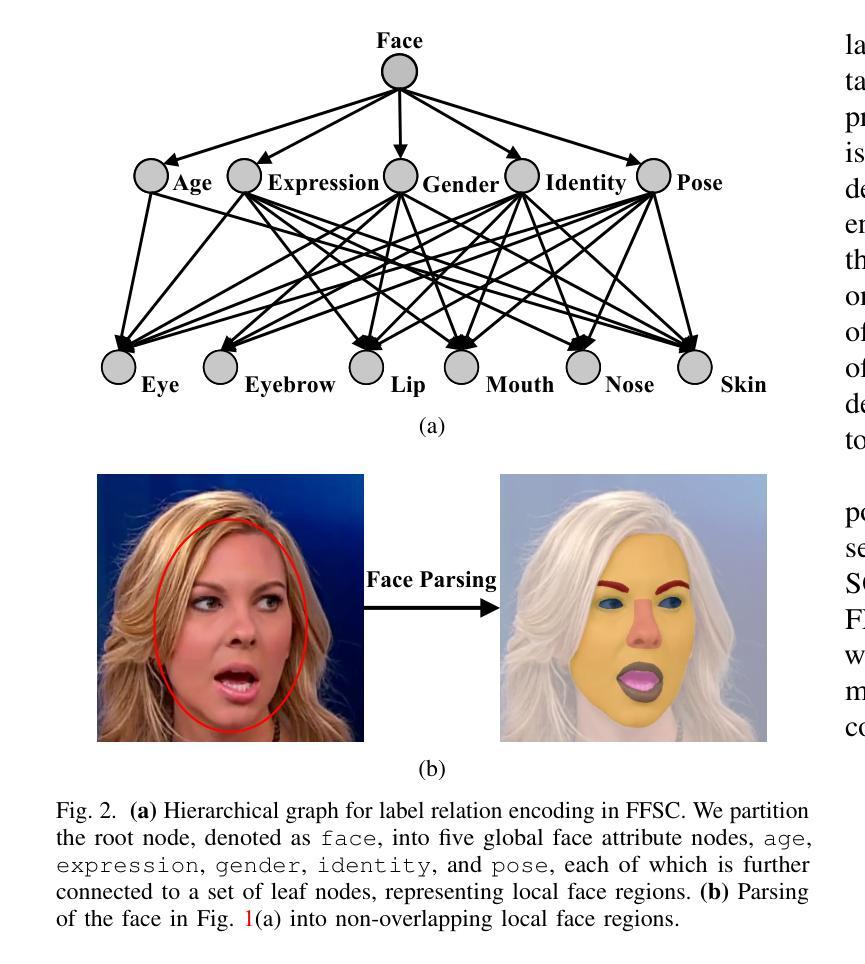
Semantic Contextualization of Face Forgery: A New Definition, Dataset, and Detection Method
Authors:Mian Zou, Baosheng Yu, Yibing Zhan, Siwei Lyu, Kede Ma
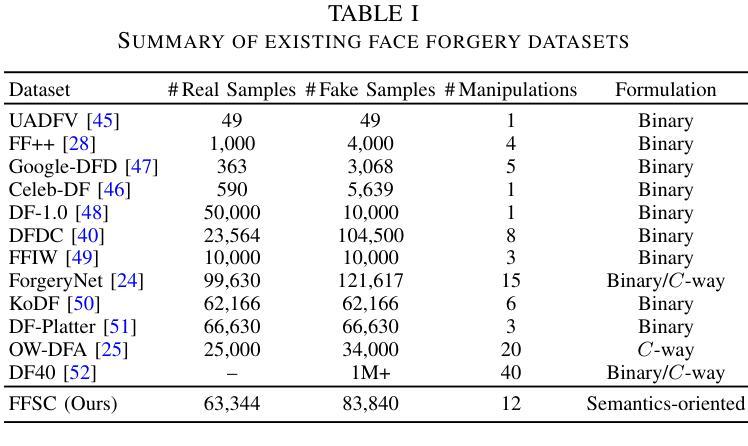
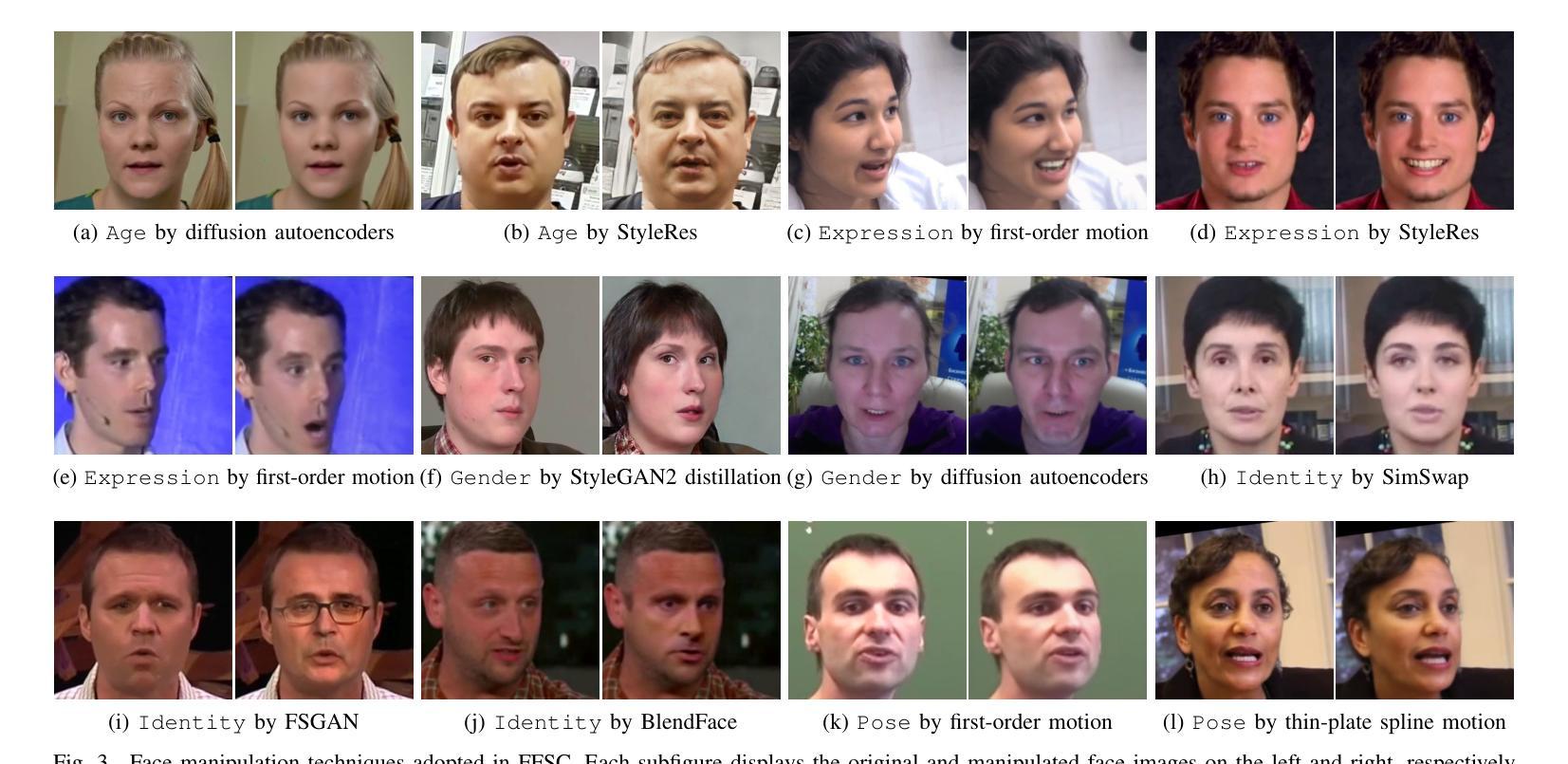
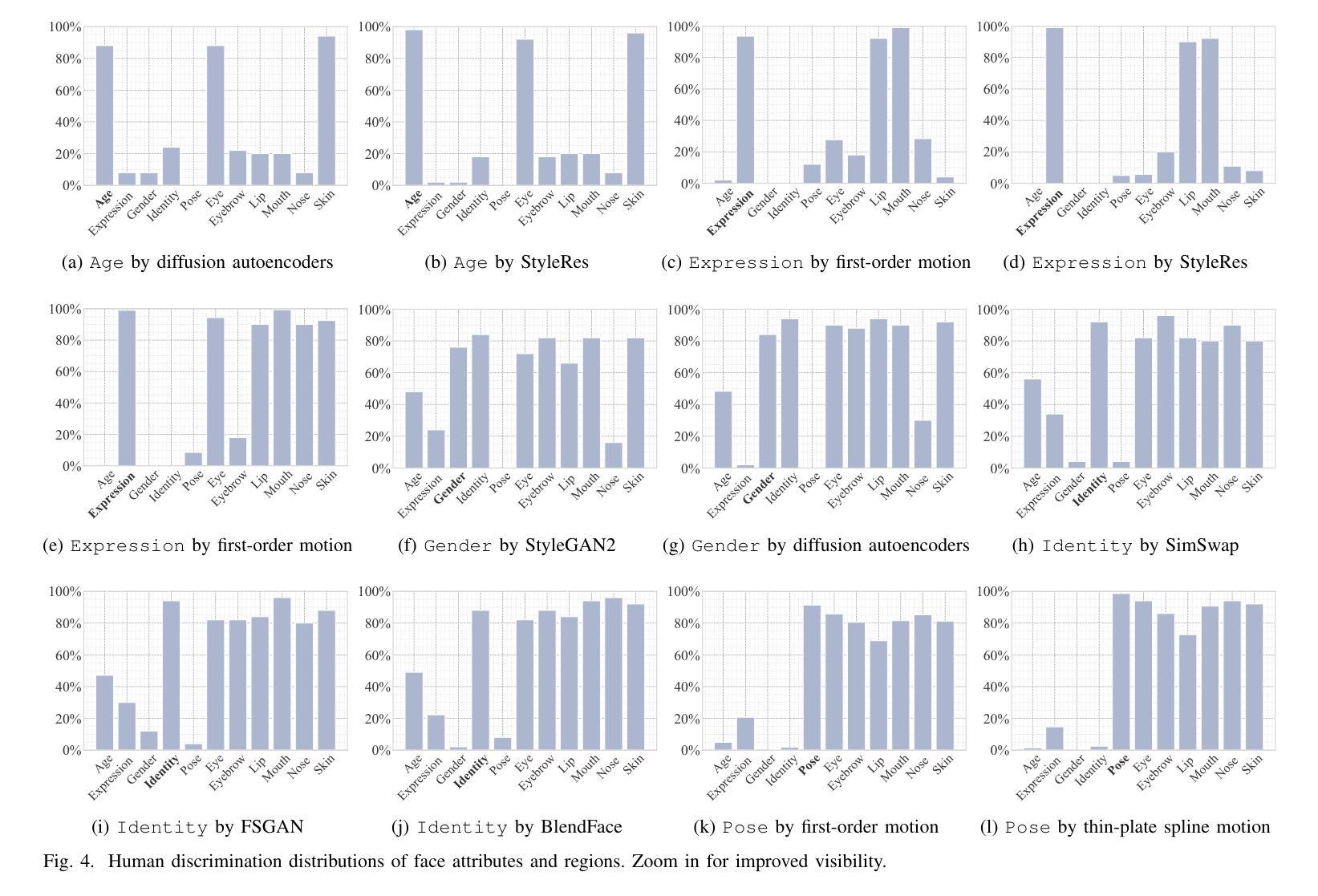
In recent years, deep learning has greatly streamlined the process of manipulating photographic face images. Aware of the potential dangers, researchers have developed various tools to spot these counterfeits. Yet, none asks the fundamental question: \textit{What digital manipulations make a real photographic face image fake, while others do not?} In this paper, we put face forgery in a semantic context and define that \textit{computational methods that alter semantic face attributes to exceed human discrimination thresholds are sources of face forgery}. Following our definition, we construct a large face forgery image dataset, where each image is associated with a set of labels organized in a hierarchical graph. Our dataset enables two new testing protocols to probe the generalizability of face forgery detectors. Moreover, we propose a semantics-oriented face forgery detection method that captures label relations and prioritizes the primary task (\ie, real or fake face detection). We show that the proposed dataset successfully exposes the weaknesses of current detectors as the test set and consistently improves their generalizability as the training set. Additionally, we demonstrate the superiority of our semantics-oriented method over traditional binary and multi-class classification-based detectors.
近年来,深度学习极大地简化了操作照相面部图像的过程。虽然研究人员已经开发出了各种检测假冒照片的工具并意识到潜在的危险,但很少有人从根本上提问:哪些数字操作会使真实的照片面部图像变得虚假,而其他操作则不会?在本文中,我们将面部伪造置于语义背景下,并定义改变语义面部属性超出人类辨别阈值的计算方法是面部伪造的来源。根据我们的定义,我们构建了一个大型面部伪造图像数据集,每个图像都与一组标签相关联,并按层次结构组织。我们的数据集使两种新的测试协议成为可能,以检验面部伪造检测器的泛化能力。此外,我们提出了一种面向语义的面部伪造检测方法,该方法可以捕获标签关系并优先考虑主要任务(即检测真实或虚假的面部)。我们展示所提出的数据集作为测试集成功暴露了当前检测器的弱点,并且作为训练集时始终提高了它们的泛化能力。此外,我们还证明了与基于传统二元分类和多类分类的检测器相比,我们的面向语义的方法具有优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人脸识别伪造问题近期备受关注。本研究首次关注问题的核心——何种数字操作会令真实人脸图像显得虚假。为此,研究团队定义了语义人脸属性改变超出人类辨识阈值的计算方法是造成人脸伪造的原因。他们构建了一个大型人脸伪造图像数据集,并提出了语义导向的人脸伪造检测方法。研究结果显示,新方法优于传统的二元分类和多类分类检测器。
Key Takeaways
- 研究关注数字操作如何影响真实人脸图像的真实性。
- 定义了语义人脸属性改变超出人类辨识阈值的计算方法是造成人脸伪造的原因。
- 构建了一个大型人脸伪造图像数据集,包括带有层次结构标签的图像。
- 提出新的测试协议以评估人脸伪造检测器的通用性。
- 提出了语义导向的人脸伪造检测方法,能捕捉标签关系并优先完成主要任务(即检测真实或虚假人脸)。
- 研究发现,所构建的数据集能暴露当前检测器的弱点,并在训练集上提高其通用性。
点此查看论文截图