⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-04 更新
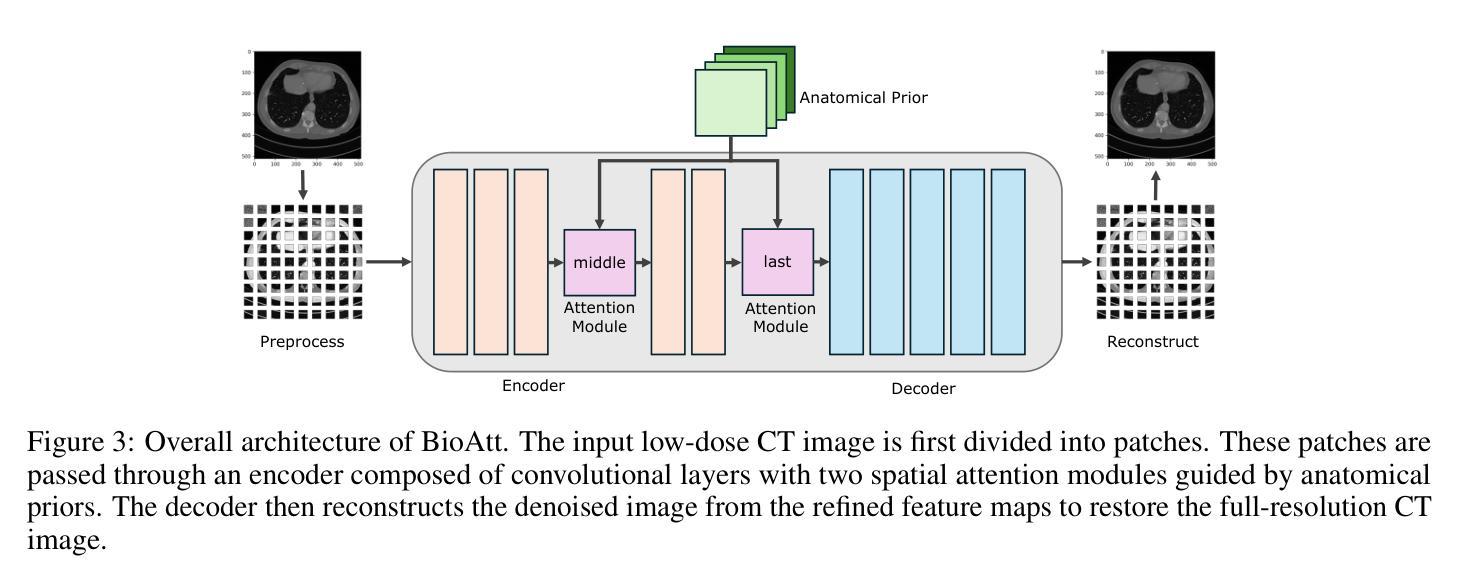
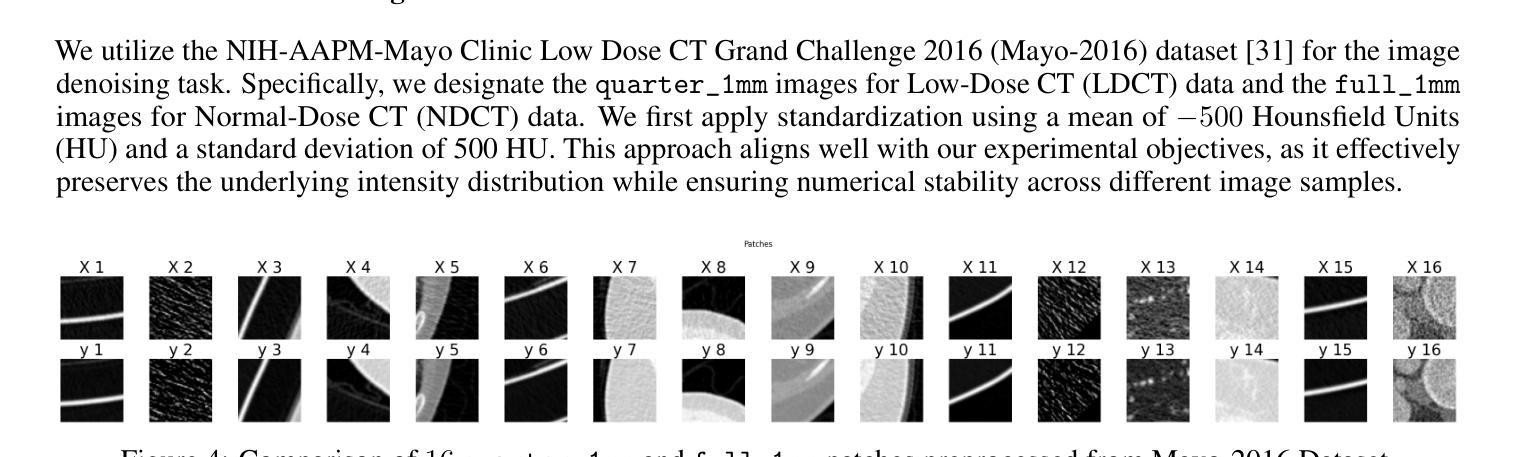
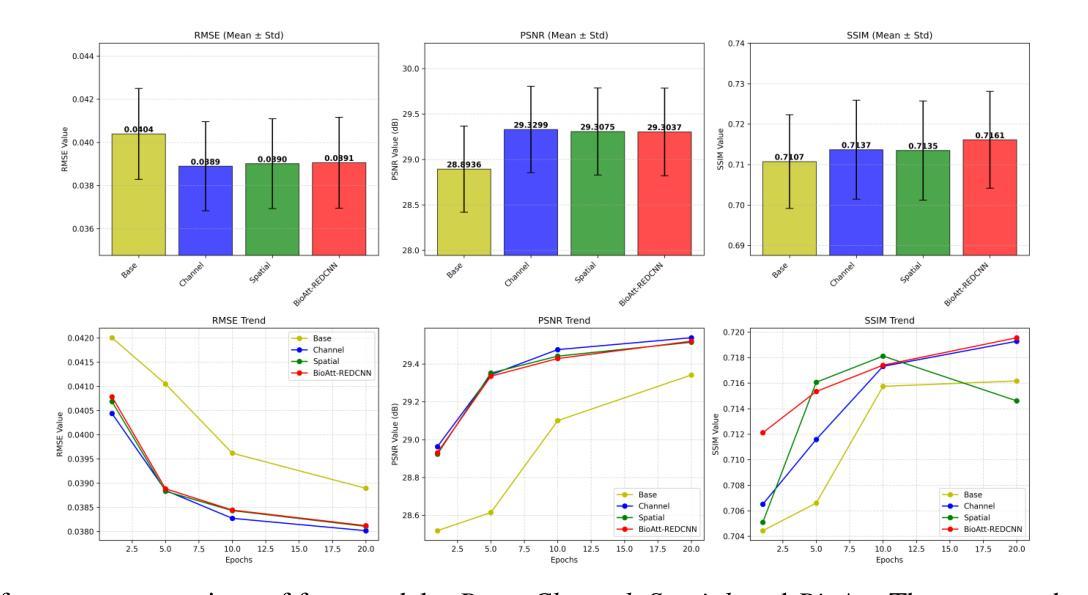
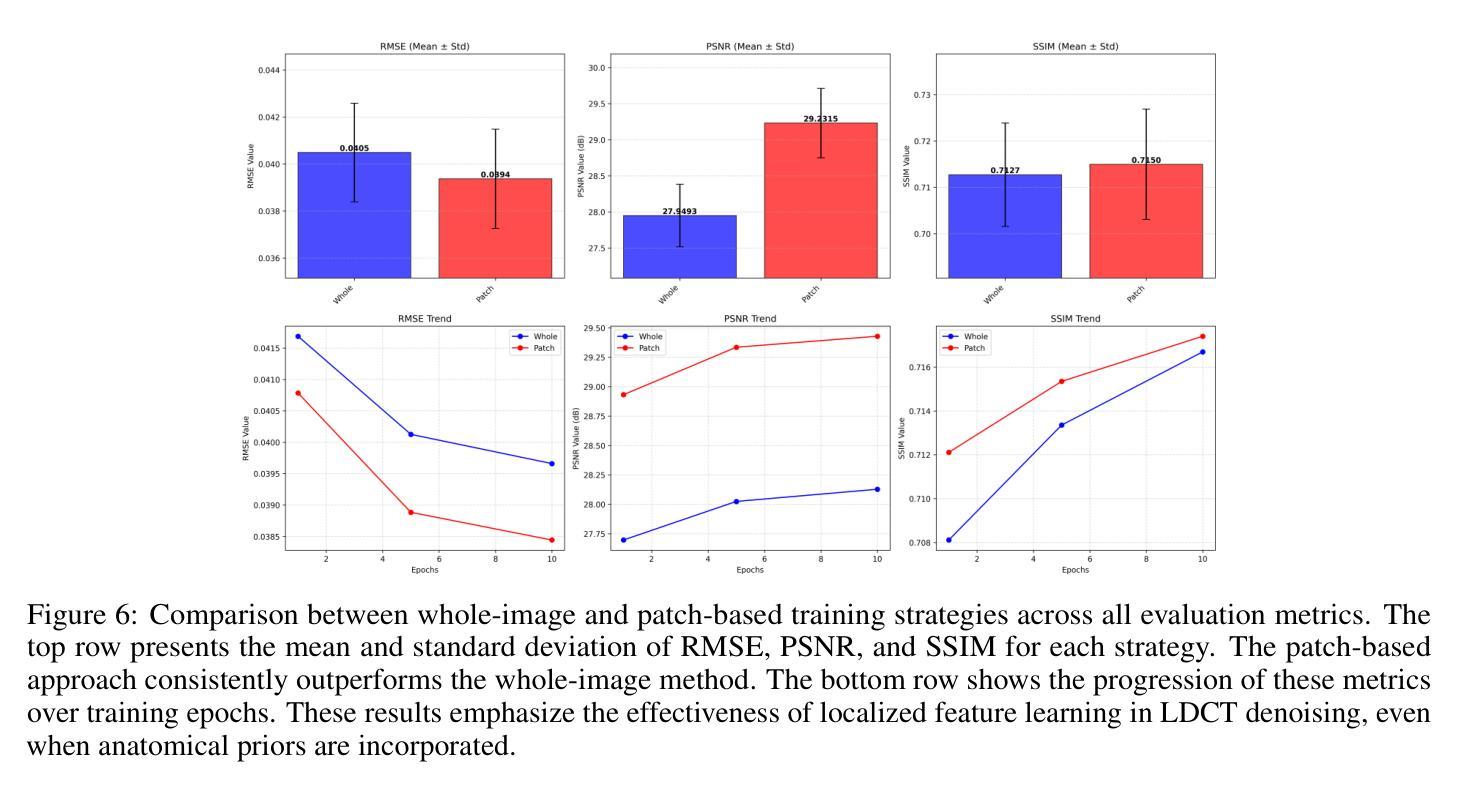
BioAtt: Anatomical Prior Driven Low-Dose CT Denoising
Authors:Namhun Kim, UiHyun Cho
Deep-learning-based denoising methods have significantly improved Low-Dose CT (LDCT) image quality. However, existing models often over-smooth important anatomical details due to their purely data-driven attention mechanisms. To address this challenge, we propose a novel LDCT denoising framework, BioAtt. The key innovation lies in attending anatomical prior distributions extracted from the pretrained vision-language model BiomedCLIP. These priors guide the denoising model to focus on anatomically relevant regions to suppress noise while preserving clinically relevant structures. We highlight three main contributions: BioAtt outperforms baseline and attention-based models in SSIM, PSNR, and RMSE across multiple anatomical regions. The framework introduces a new architectural paradigm by embedding anatomic priors directly into spatial attention. Finally, BioAtt attention maps provide visual confirmation that the improvements stem from anatomical guidance rather than increased model complexity.
基于深度学习的降噪方法已经显著提高了低剂量CT(LDCT)图像的质量。然而,现有模型由于其纯粹的数据驱动注意力机制,往往会过度平滑重要的解剖细节。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种新型的LDCT降噪框架BioAtt。关键创新之处在于关注由预训练的视觉语言模型BiomedCLIP提取的解剖先验分布。这些先验知识引导降噪模型关注解剖相关的区域,以抑制噪声的同时保留临床上相关的结构。我们强调三个主要贡献:BioAtt在多个解剖区域的SSIM、PSNR和RMSE方面优于基准模型和基于注意力的模型。该框架通过直接将解剖先验嵌入空间注意力,引入了一种新的架构范式。最后,BioAtt的注意力图视觉确认改进源于解剖指导而非模型复杂度的增加。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages
Summary
深度学习在医学图像去噪方面取得显著进展,特别是在低剂量CT(LDCT)图像去噪中。然而,现有模型因过于依赖数据驱动而忽视了解剖学细节。为此,我们提出了一种新的LDCT去噪框架BioAtt,通过引入解剖学先验信息提高去噪效果,并优化结构相似性指标(SSIM)、峰值信噪比(PSNR)和均方根误差(RMSE)。新架构的范式化以及通过视觉确认的解剖学指导改进提升了模型性能。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在去噪领域取得显著进展,特别是在LDCT图像去噪中。
- 现有模型过度依赖数据驱动,容易忽视解剖学细节,导致过度平滑现象。
- BioAtt框架引入解剖学先验信息作为核心创新点,通过结合预训练的视觉语言模型BiomedCLIP提取先验分布信息。
- BioAtt框架在多个解剖学区域的表现优于基准模型和基于注意力的模型,提高了SSIM、PSNR和RMSE等指标。
- BioAtt引入了一种新架构范式,通过直接将解剖学先验嵌入空间注意力机制中。
点此查看论文截图

KTaO3(001) Preparation Methods in Vacuum: Effects on Surface Stoichiometry, Crystallography, and in-gap States
Authors:Andrea M. Lucero Manzano, Esteban D. Cantero, Emanuel A. Martínez, F. Y. Bruno, Esteban A. Sánchez, Oscar Grizzi
KTaO3 single crystals with different orientations are used as substrates for the epitaxial growth of thin films and/or as hosts for two-dimensional electron gases. Due to the polar nature of the KTaO3(001) surface, one can expect difficulties and challenges to arise in its preparation. Maintaining good insulating characteristics without adding undesirable in-gap electronic states, obtaining good crystalline order up to the top surface layer, a sufficiently flat surface, and complete cleanliness of the surface (without water, C or OH contaminants), are in general difficult conditions to accomplish simultaneously. Cleaving in vacuum is likely the best option for obtaining a clean surface. However, since KTaO3 is cubic and lacks a well-defined cleavage plane, this method is notsuitable for sample growth or reproducible device fabrication. Here, we systematically evaluate the effect of typical preparation methods applied on the surfaces of KTaO3(001) single crystals. In particular, we used annealing in vacuum at different temperatures, light sputtering with Ar+ ions at low energy (500 eV) followed by annealing, heavy Ar+ ion bombardment and annealing, and grazing Ar+ ion bombardment under continuous azimuthal rotation combined with both annealing in vacuum and in O2 atmosphere. Possible side effects after each treatment are evaluated by a combination of techniques, including low-energy ion scattering at forward angles, Auger electron spectroscopy, low-energy electron energy loss, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, low-energy electron diffraction, and time of flightsecondary ion mass spectrometry. Advantages and shortcomings of each preparation method are discussed in detail.
具有不同取向的KTaO3单晶被用作外延生长薄膜的基片或二维电子气体的宿主。由于KTaO3(001)表面的极性特性,其制备过程中可能会遇到困难和挑战。在保持优良的绝缘性能而不增加不必要的带内电子态的同时,还需要保持良好的晶体有序性至顶层表面、表面平坦性和清洁度(无水分、碳或羟基污染物)。一般来说,同时实现这些条件是非常困难的。真空下的劈裂可能是获得清洁表面的最佳方法。然而,由于KTaO3是立方的并且缺乏明确的劈裂平面,这种方法不适用于样品生长或可重复的器件制造。在这里,我们系统地评估了典型的制备方法对KTaO3(001)单晶表面的影响。特别是我们通过真空退火处理不同温度下的样品、低能量(500 eV)的氩离子溅射后结合退火处理、重氩离子轰击和退火处理以及连续方位旋转下的倾斜氩离子轰击结合真空和氧气环境下的退火处理等方法。通过低能离子前向散射、俄歇电子光谱、低能电子能量损失、X射线光电子光谱、低能电子衍射以及飞行时间二次离子质谱等技术组合来评估每种处理后的可能副作用。每种制备方法的优缺点都进行了详细讨论。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 28 pages, 8 figures
Summary
本文研究了不同预处理方法对KTaO3(001)单晶表面性能的影响,探讨了各种预处理方法的优缺点,包括真空退火、低能离子轰击等处理方法。文章通过一系列技术手段对处理后的表面进行评估,讨论了各种方法的优势和局限性。
Key Takeaways
- KTaO3单晶因其极性表面特性,在制备过程中面临诸多挑战。
- 文中评估了多种表面处理方法对KTaO3(001)单晶的影响。
- 真空退火是获得干净表面的可能方法,但由于KTaO3的立方结构,该方法不适用于样品生长和可重复的器件制造。
- 低能离子轰击和退火等处理方法被用于改善KTaO3的表面性能。
- 各种处理技术对表面的可能影响通过一系列技术手段进行评估。
- 文章详细讨论了各种预处理方法的优势和局限性。
点此查看论文截图



STPNet: Scale-aware Text Prompt Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Dandan Shan, Zihan Li, Yunxiang Li, Qingde Li, Jie Tian, Qingqi Hong
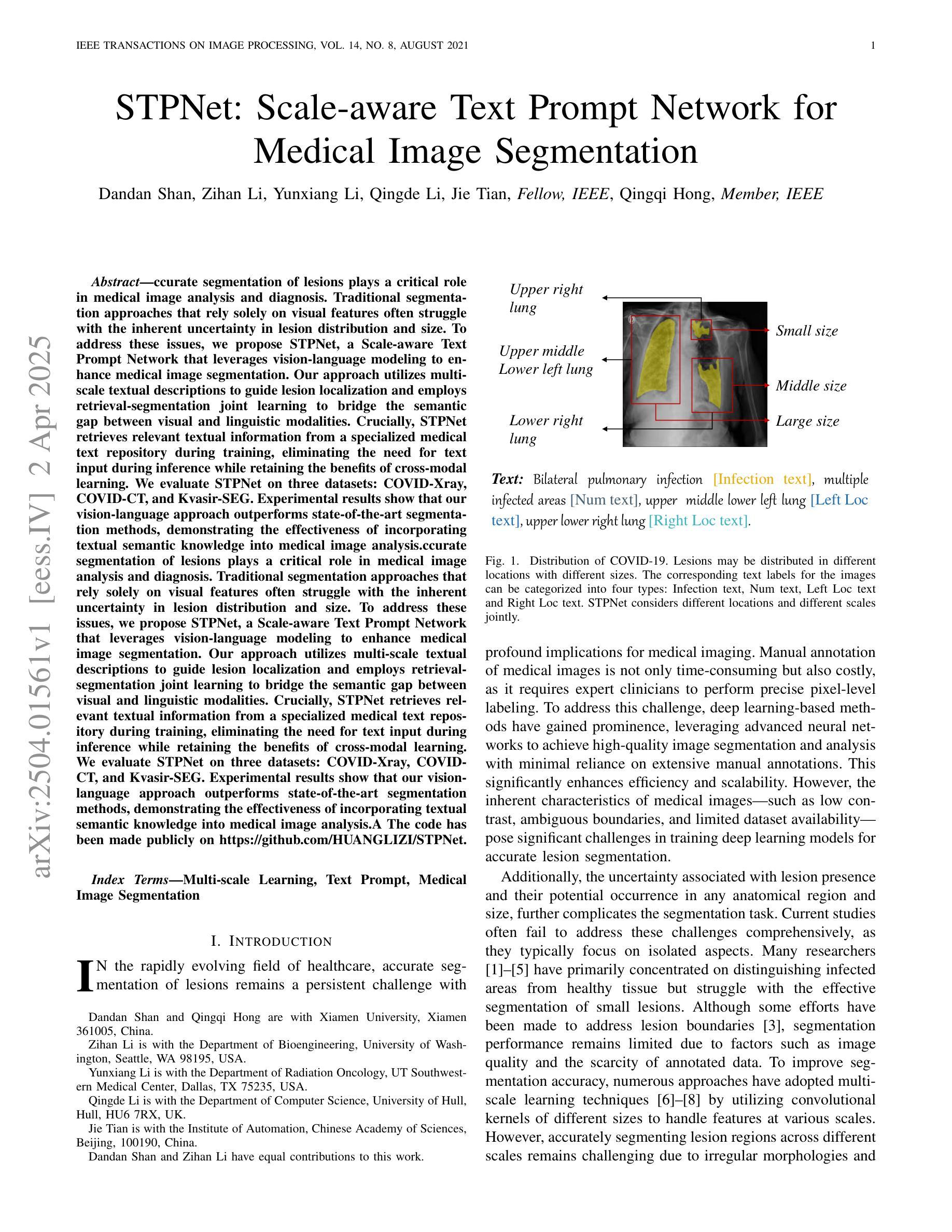
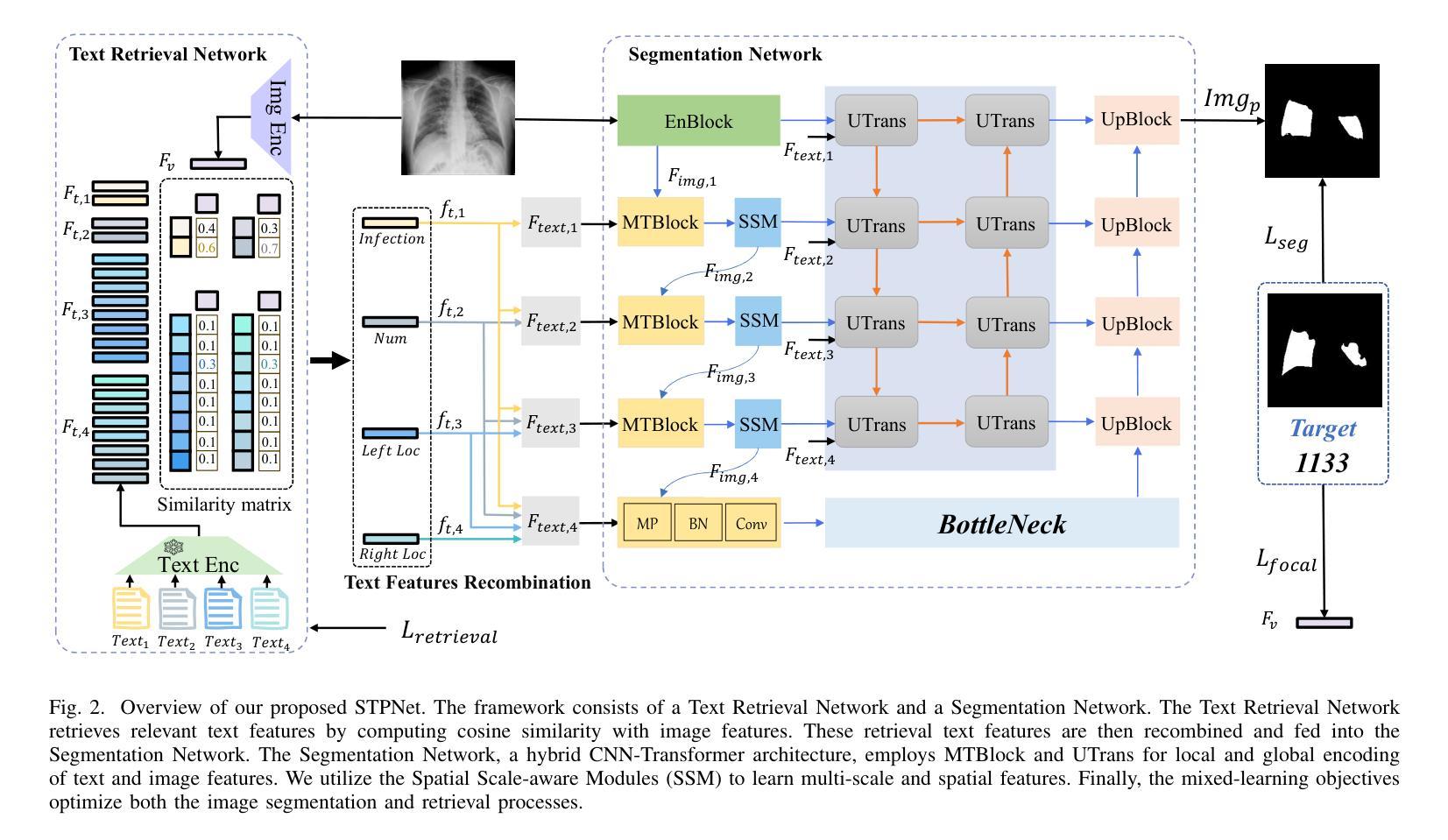
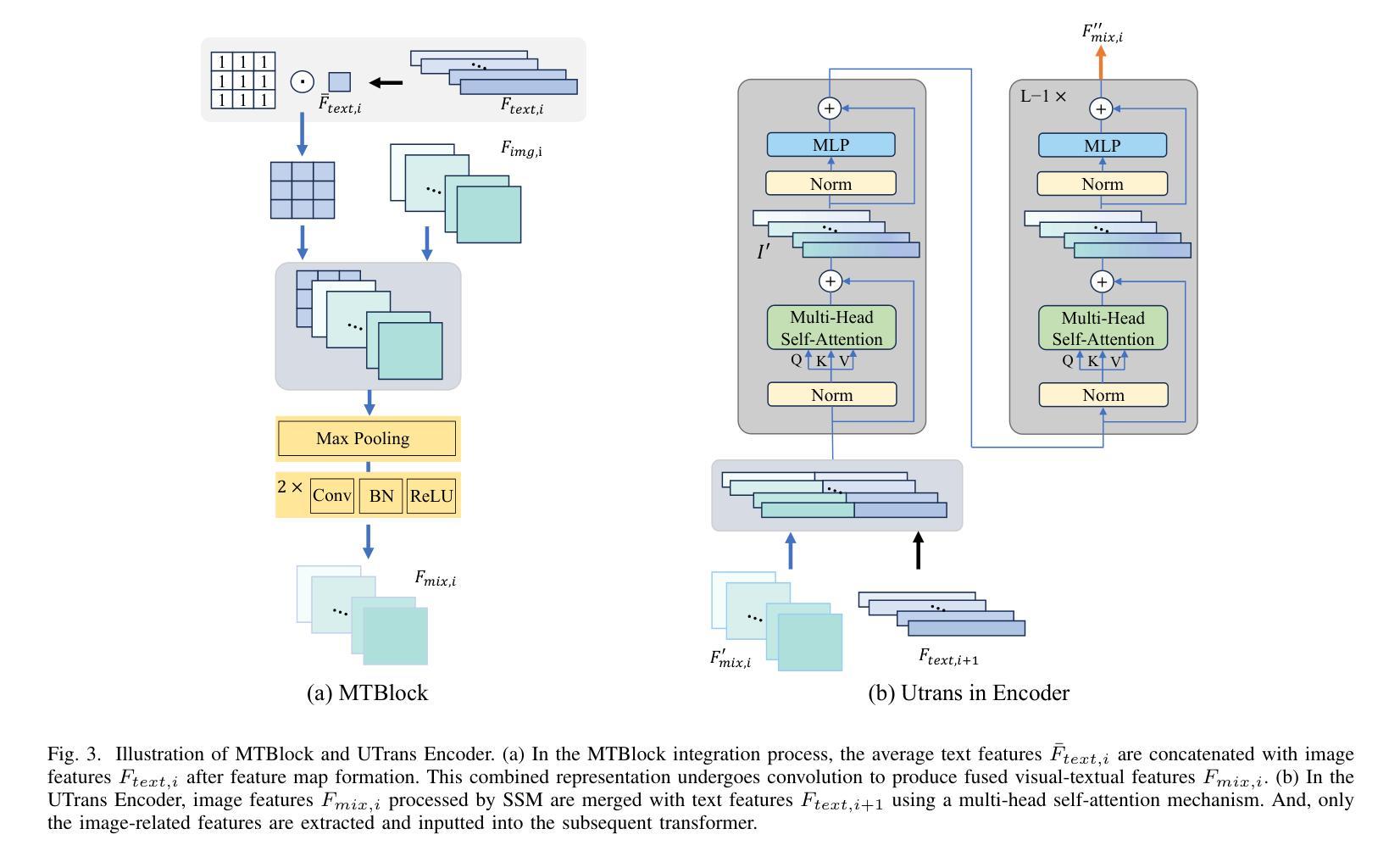
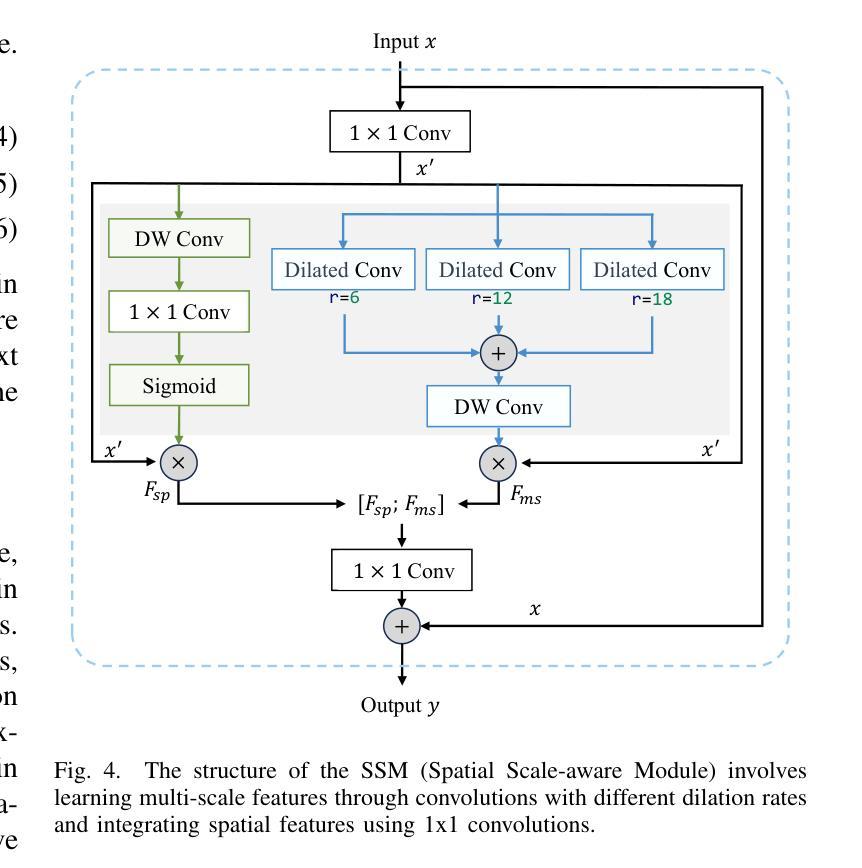
Accurate segmentation of lesions plays a critical role in medical image analysis and diagnosis. Traditional segmentation approaches that rely solely on visual features often struggle with the inherent uncertainty in lesion distribution and size. To address these issues, we propose STPNet, a Scale-aware Text Prompt Network that leverages vision-language modeling to enhance medical image segmentation. Our approach utilizes multi-scale textual descriptions to guide lesion localization and employs retrieval-segmentation joint learning to bridge the semantic gap between visual and linguistic modalities. Crucially, STPNet retrieves relevant textual information from a specialized medical text repository during training, eliminating the need for text input during inference while retaining the benefits of cross-modal learning. We evaluate STPNet on three datasets: COVID-Xray, COVID-CT, and Kvasir-SEG. Experimental results show that our vision-language approach outperforms state-of-the-art segmentation methods, demonstrating the effectiveness of incorporating textual semantic knowledge into medical image analysis. The code has been made publicly on https://github.com/HUANGLIZI/STPNet.
在医学图像分析和诊断中,精确地分割病灶起着至关重要的作用。传统的仅依赖于视觉特征的分割方法往往难以应对病灶分布和大小的不确定性。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了STPNet,这是一个利用视觉语言建模增强医学图像分割的规模感知文本提示网络。我们的方法利用多尺度文本描述来引导病灶定位,并采用检索分割联合学习来弥合视觉和语言模态之间的语义鸿沟。重要的是,STPNet在训练过程中从专门的医学文本存储库中检索相关的文本信息,从而在推理过程中不需要文本输入,同时保留跨模态学习的优势。我们在三个数据集上评估了STPNet:COVID-Xray、COVID-CT和Kvasir-SEG。实验结果表明,我们的视觉语言方法优于最先进的分割方法,证明了将文本语义知识融入医学图像分析中的有效性。代码已公开在https://github.com/HUANGLIZI/STPNet。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分析中,病灶准确分割对诊断至关重要。传统方法常因病灶分布和大小的不确定性而面临挑战。STPNet是一个尺度感知文本提示网络,采用跨视觉语言建模增强医学图像分割。它利用多尺度文本描述引导病灶定位,并通过检索分割联合学习来弥合视觉和语言模态之间的语义鸿沟。STPNet在训练时从专业医学文本库中检索相关文本信息,推理时无需文本输入,仍能保留跨模态学习的优势。在三个数据集上的实验表明,STPNet的视语言方法优于最先进的分割方法,证明了将文本语义知识融入医学图像分析的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分析中,STPNet网络模型利用视觉语言建模提高医学图像分割的准确性。
- STPNet采用多尺度文本描述,以增强模型对病灶的定位能力。
- 通过检索分割联合学习,STPNet能够弥合视觉和语言模态之间的语义鸿沟。
- STPNet从专业医学文本库中检索相关文本信息,以提升模型的性能。
- 在多个数据集上的实验证明STPNet的视语言方法优于传统方法。
- STPNet提高了医学图像分析的效率和准确性,具有实际应用价值。
点此查看论文截图
Semi-Supervised Biomedical Image Segmentation via Diffusion Models and Teacher-Student Co-Training
Authors:Luca Ciampi, Gabriele Lagani, Giuseppe Amato, Fabrizio Falchi
Supervised deep learning for semantic segmentation has achieved excellent results in accurately identifying anatomical and pathological structures in medical images. However, it often requires large annotated training datasets, which limits its scalability in clinical settings. To address this challenge, semi-supervised learning is a well-established approach that leverages both labeled and unlabeled data. In this paper, we introduce a novel semi-supervised teacher-student framework for biomedical image segmentation, inspired by the recent success of generative models. Our approach leverages denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPMs) to generate segmentation masks by progressively refining noisy inputs conditioned on the corresponding images. The teacher model is first trained in an unsupervised manner using a cycle-consistency constraint based on noise-corrupted image reconstruction, enabling it to generate informative semantic masks. Subsequently, the teacher is integrated into a co-training process with a twin-student network. The student learns from ground-truth labels when available and from teacher-generated pseudo-labels otherwise, while the teacher continuously improves its pseudo-labeling capabilities. Finally, to further enhance performance, we introduce a multi-round pseudo-label generation strategy that iteratively improves the pseudo-labeling process. We evaluate our approach on multiple biomedical imaging benchmarks, spanning multiple imaging modalities and segmentation tasks. Experimental results show that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art semi-supervised techniques, highlighting its effectiveness in scenarios with limited annotated data. The code to replicate our experiments can be found at https://github.com/ciampluca/diffusion_semi_supervised_biomedical_image_segmentation
基于深度学习的语义分割在准确识别医学图像中的解剖和病理结构方面取得了卓越成果。然而,这通常需要大量已标注的训练数据集,这在临床环境中限制了其可扩展性。为了应对这一挑战,半监督学习是一种既利用标记数据又利用未标记数据的成熟方法。在本文中,我们介绍了一种受生成模型最新成功启发的生物医学图像分割新型半监督师徒框架。我们的方法利用去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)逐步细化基于相应图像的噪声输入来生成分割掩膜。首先,使用基于噪声损坏图像重建的循环一致性约束以无监督方式训练教师模型,使其能够生成信息丰富的语义掩膜。随后,教师被整合到一个与学生网络协同训练的过程中。当学生可从可用的真实标签中学习时,则从其生成伪标签中学习,同时教师不断提高其伪标签生成能力。最后,为了进一步提高性能,我们引入了一种多轮伪标签生成策略,该策略通过迭代改进伪标签生成过程。我们在多个生物医学成像基准测试上对提出的方法进行了评估,涉及多种成像方式和分割任务。实验结果表明,我们的方法始终优于最新的半监督技术,在标注数据有限的情况下表现出了有效性。我们实验的代码可在 https://github.com/ciampluca/diffusion_semi_supervised_biomedical_image_segmentation 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习监督法对于医学图像中的解剖结构和病理结构的识别取得了优异成果。然而,它通常需要大量的标注训练数据集,这在临床环境中限制了其可扩展性。为解决此挑战,半监督学习法利用标注和非标注数据,成为一种有效的方法。本文介绍了一种受生成模型启发的新型半监督教师-学生框架,用于生物医学图像分割。该框架利用去噪扩散概率模型(DDPMs)逐步优化噪声输入,生成基于对应图像的分割掩膜。首先,以循环一致性约束训练教师模型,通过噪声干扰图像重建生成信息丰富的语义掩膜。随后,教师模型与双学生网络共同训练。学生模型在有可用真实标签时学习,否则从教师生成的伪标签中学习,同时教师不断提高其伪标签生成能力。最后,引入多轮伪标签生成策略,以迭代改进伪标签过程。在多个生物医学成像基准测试上的实验结果表明,该方法优于最新的半监督技术,在标注数据有限的情况下尤为有效。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在医学图像分割中表现优秀,但需求大量标注数据。
- 半监督学习法利用标注和非标注数据,解决标注数据需求问题。
- 引入新型教师-学生框架,利用去噪扩散概率模型(DDPMs)生成分割掩膜。
- 教师模型通过循环一致性约束进行训练,生成语义掩膜。
- 教师和学生模型共同训练,学生模型可从教师生成的伪标签中学习。
- 引入多轮伪标签生成策略提高性能。
- 在多个生物医学成像基准测试上,该方法表现优越。
点此查看论文截图

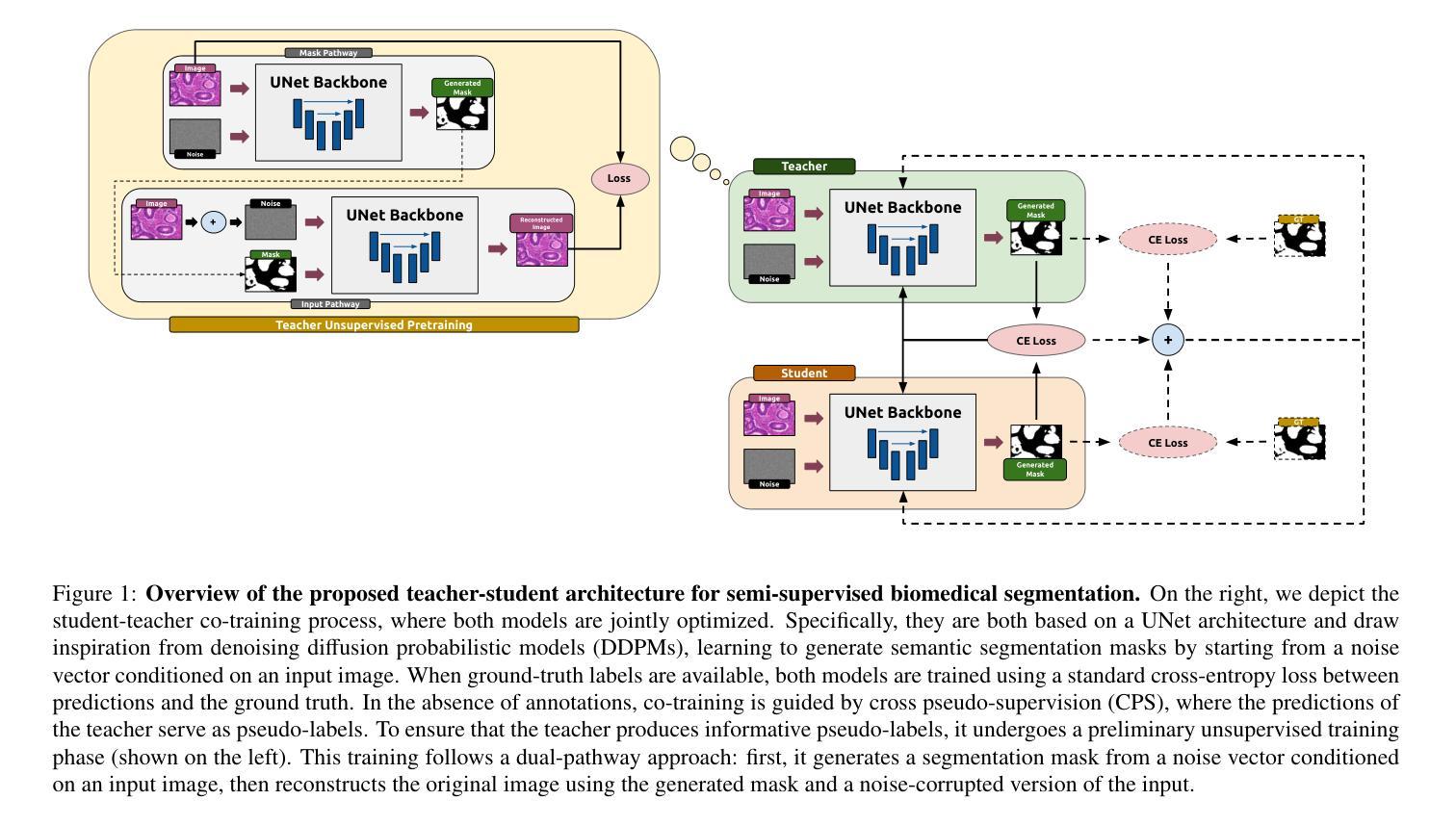
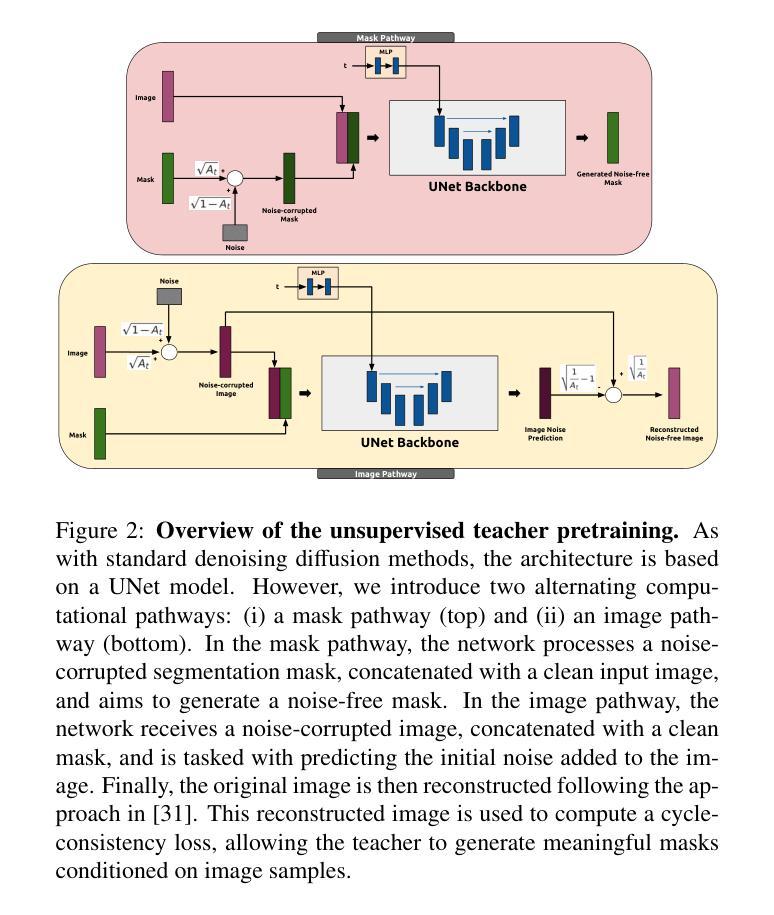
FUSION: Frequency-guided Underwater Spatial Image recOnstructioN
Authors:Jaskaran Singh Walia, Shravan Venkatraman, Pavithra LK
Underwater images suffer from severe degradations, including color distortions, reduced visibility, and loss of structural details due to wavelength-dependent attenuation and scattering. Existing enhancement methods primarily focus on spatial-domain processing, neglecting the frequency domain’s potential to capture global color distributions and long-range dependencies. To address these limitations, we propose FUSION, a dual-domain deep learning framework that jointly leverages spatial and frequency domain information. FUSION independently processes each RGB channel through multi-scale convolutional kernels and adaptive attention mechanisms in the spatial domain, while simultaneously extracting global structural information via FFT-based frequency attention. A Frequency Guided Fusion module integrates complementary features from both domains, followed by inter-channel fusion and adaptive channel recalibration to ensure balanced color distributions. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets (UIEB, EUVP, SUIM-E) demonstrate that FUSION achieves state-of-the-art performance, consistently outperforming existing methods in reconstruction fidelity (highest PSNR of 23.717 dB and SSIM of 0.883 on UIEB), perceptual quality (lowest LPIPS of 0.112 on UIEB), and visual enhancement metrics (best UIQM of 3.414 on UIEB), while requiring significantly fewer parameters (0.28M) and lower computational complexity, demonstrating its suitability for real-time underwater imaging applications.
水下图像受到严重的退化影响,包括色彩失真、能见度降低以及由于波长相关衰减和散射导致的结构细节损失。现有的增强方法主要关注空间域处理,忽视了频率域在捕捉全局颜色分布和长距离依赖方面的潜力。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了FUSION,这是一个双域深度学习框架,能够联合利用空间和频率域信息。FUSION通过空间域中的多尺度卷积核和自适应注意力机制独立处理每个RGB通道,同时利用基于FFT的频率注意力提取全局结构信息。频率引导融合模块整合了来自两个域的特征,然后进行跨通道融合和自适应通道再校准,以确保颜色分布平衡。在基准数据集(UIEB、EUVP、SUIM-E)上的大量实验表明,FUSION达到了最先进的性能,在重建保真度、感知质量和视觉增强指标方面均优于现有方法(在UIEB上,PSNR最高达23.717 dB,SSIM为0.883;在感知质量方面,UIEB上的LPIPS最低,为0.112;在UIEB上获得最佳UIQM为3.414),同时所需参数大大减少(仅0.28M)且计算复杂度较低,显示出其适用于实时水下成像应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为FUSION的深度学习框架,该框架结合了空间域和频域信息,旨在解决水下图像色彩失真、能见度降低和结构细节丢失的问题。FUSION通过多尺度卷积核和自适应注意力机制独立处理每个RGB通道的空间域信息,同时利用FFT基于频域的注意力机制提取全局结构信息。实验结果表明,FUSION在基准数据集上的性能达到领先水平,在重建保真度、感知质量和视觉增强指标方面均优于现有方法,且参数较少、计算复杂度较低,适合用于实时水下成像应用。
Key Takeaways
- 水下图像存在严重的失真问题,包括色彩失真、能见度降低和结构细节丢失。
- 现有增强方法主要关注空间域处理,忽略了频域信息在捕捉全局颜色分布和远程依赖方面的潜力。
- FUSION框架结合了空间域和频域信息,通过多尺度卷积核和自适应注意力机制处理RGB通道的空间域信息。
- FUSION利用FFT-based频率注意力机制提取全局结构信息。
- FUSION通过频率引导融合模块整合两个域的特征,然后进行跨通道融合和自适应通道校准以确保颜色分布的平衡。
- 实验结果表明,FUSION在多个基准数据集上达到最佳性能,优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

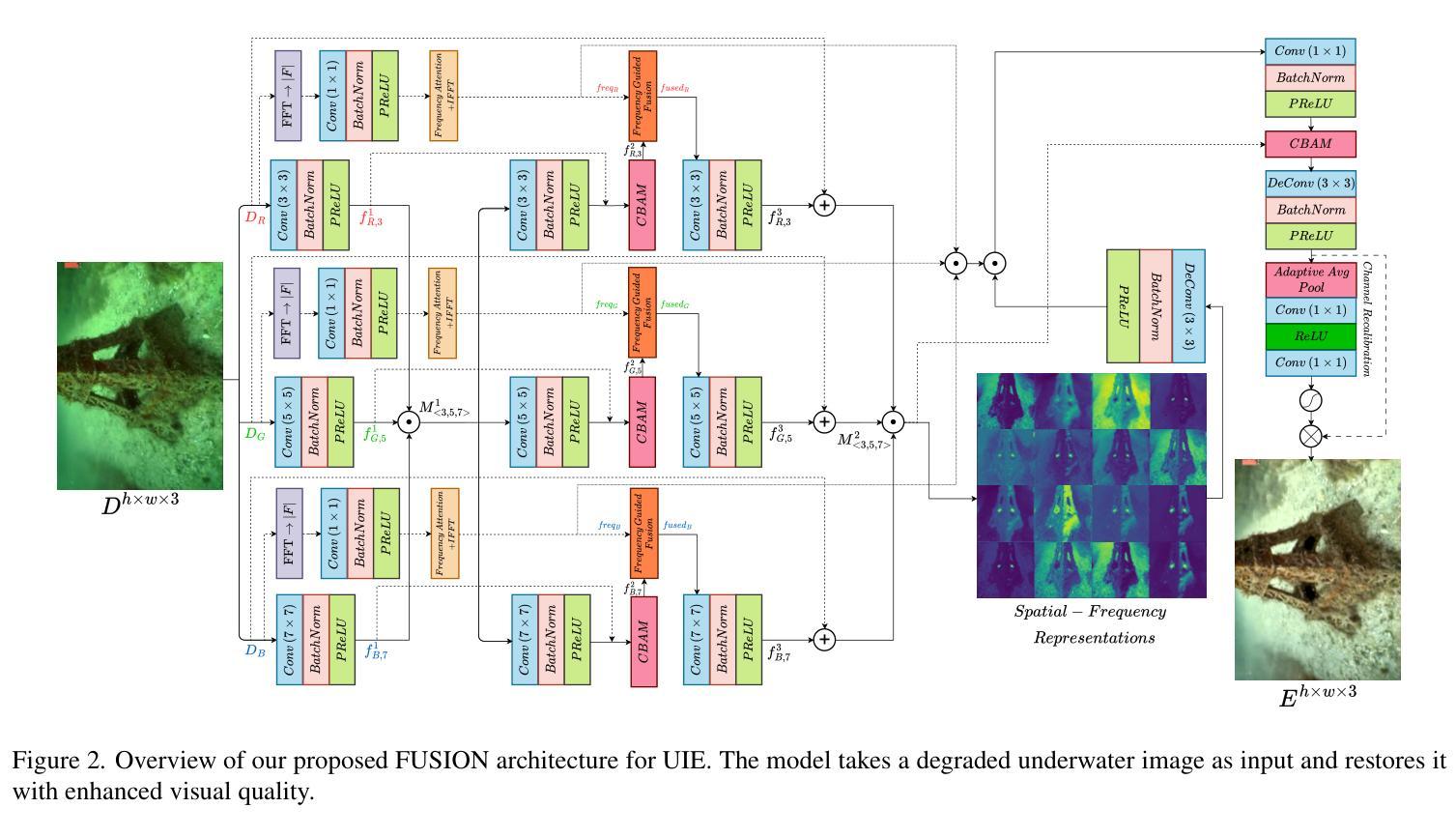
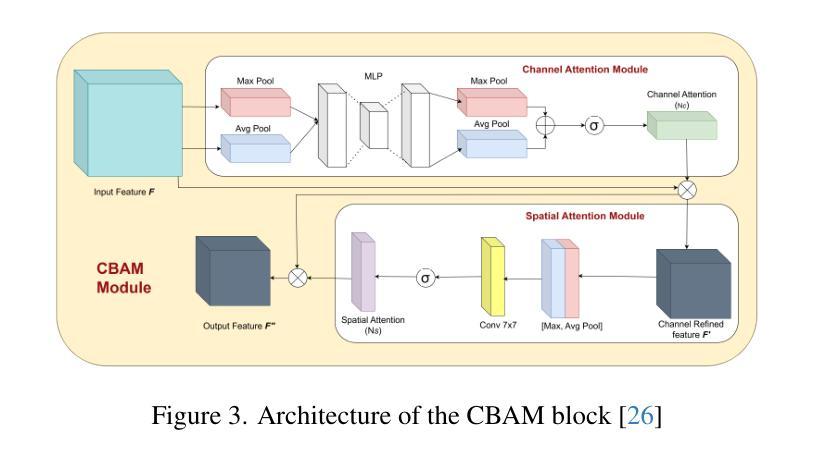
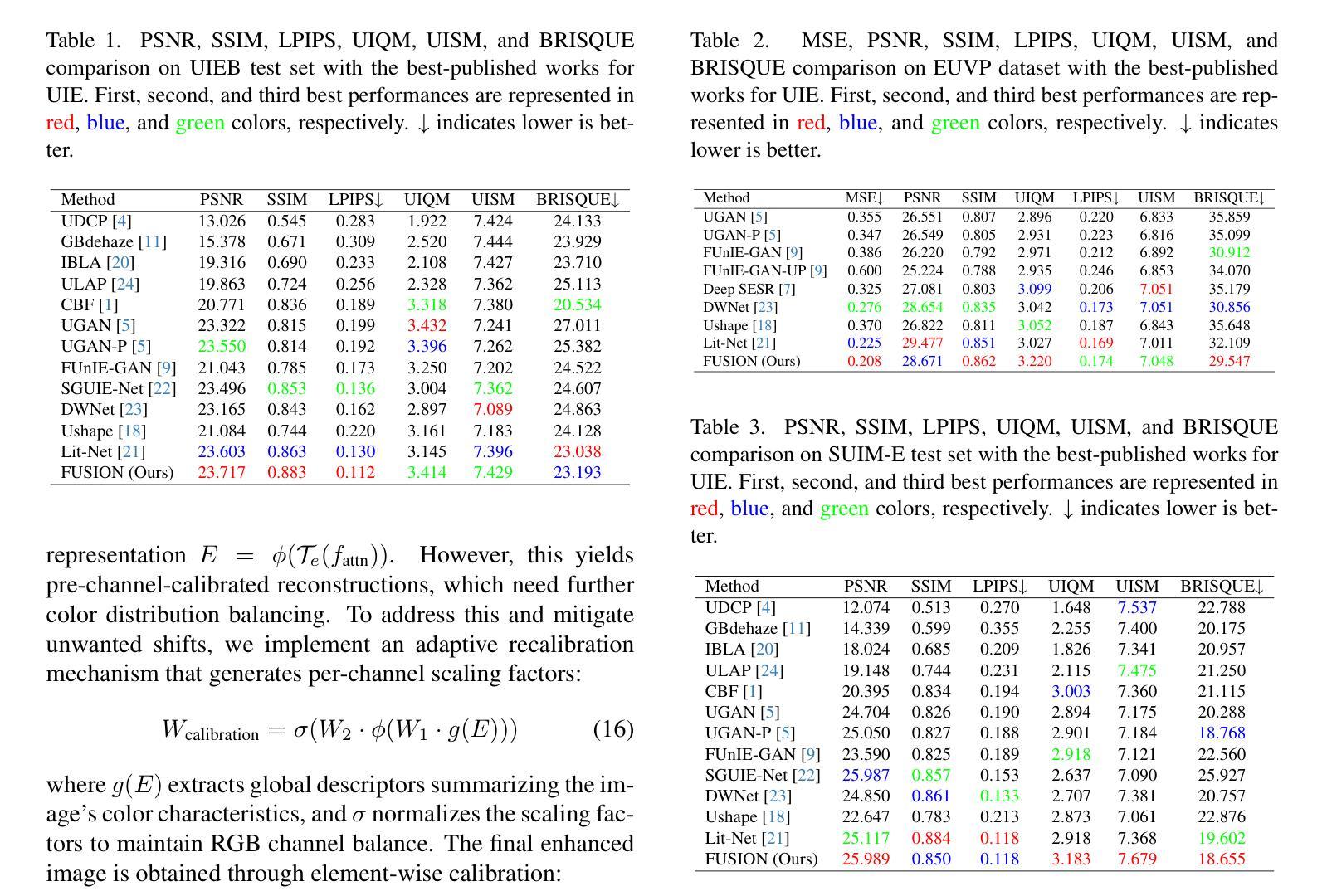
An Integrated AI-Enabled System Using One Class Twin Cross Learning (OCT-X) for Early Gastric Cancer Detection
Authors:Xian-Xian Liu, Yuanyuan Wei, Mingkun Xu, Yongze Guo, Hongwei Zhang, Huicong Dong, Qun Song, Qi Zhao, Wei Luo, Feng Tien, Juntao Gao, Simon Fong
Early detection of gastric cancer, a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, remains hampered by the limitations of current diagnostic technologies, leading to high rates of misdiagnosis and missed diagnoses. To address these challenges, we propose an integrated system that synergizes advanced hardware and software technologies to balance speed-accuracy. Our study introduces the One Class Twin Cross Learning (OCT-X) algorithm. Leveraging a novel fast double-threshold grid search strategy (FDT-GS) and a patch-based deep fully convolutional network, OCT-X maximizes diagnostic accuracy through real-time data processing and seamless lesion surveillance. The hardware component includes an all-in-one point-of-care testing (POCT) device with high-resolution imaging sensors, real-time data processing, and wireless connectivity, facilitated by the NI CompactDAQ and LabVIEW software. Our integrated system achieved an unprecedented diagnostic accuracy of 99.70%, significantly outperforming existing models by up to 4.47%, and demonstrated a 10% improvement in multirate adaptability. These findings underscore the potential of OCT-X as well as the integrated system in clinical diagnostics, offering a path toward more accurate, efficient, and less invasive early gastric cancer detection. Future research will explore broader applications, further advancing oncological diagnostics. Code is available at https://github.com/liu37972/Multirate-Location-on-OCT-X-Learning.git.
胃癌是全球癌症相关死亡的主要原因之一,其早期检测仍受到当前诊断技术局限的阻碍,导致误诊和漏诊率较高。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种协同先进硬件和软件技术的集成系统,以平衡速度和准确性。本研究介绍了单类双交叉学习(OCT-X)算法。该算法利用新型快速双阈值网格搜索策略(FDT-GS)和基于补丁的深度全卷积网络,通过实时数据处理和无缝病变监测,最大限度地提高诊断准确性。硬件组件包括具有高清成像传感器、实时数据处理和无线连接的一体化即时检测(POCT)设备,由NI CompactDAQ和LabVIEW软件提供支持。我们的集成系统达到了前所未有的99.70%的诊断准确率,比现有模型高出4.47%,并且在多速率适应性方面提高了10%。这些发现强调了OCT-X及其在临床诊断中的集成系统的潜力,为更准确、高效和非侵入性的早期胃癌检测提供了途径。未来的研究将探索更广泛的应用,并进一步推动肿瘤诊断的发展。代码可访问https://github.com/liu37972/Multirate-Location-on-OCT-X-Learning.git获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 26 pages, 4 figures, 6 tables
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对胃癌早期诊断的集成系统,该系统结合了先进的软硬件技术,实现了快速准确的数据处理和无缝病灶监测。研究中提出的One Class Twin Cross Learning(OCT-X)算法,借助新型快速双阈值网格搜索策略(FDT-GS)和基于补丁的深度全卷积网络,最大化了诊断准确性。此外,系统的硬件部分包括一个集高分辨率成像传感器、实时数据处理和无线连接于一体的便携式现场检测(POCT)设备,软件部分采用NI CompactDAQ和LabVIEW。该集成系统诊断准确率高达99.70%,较现有模型提高了4.47%,并在多速率适应性方面提高了10%。这显示了OCT-X及其在胃癌临床诊断中应用的潜力,为更准确、高效和非侵入性的早期胃癌检测提供了新的途径。
Key Takeaways
- 当前胃癌诊断技术存在挑战,导致高误诊率。
- 提出了一个集成系统,结合先进软硬件技术,提高诊断速度和准确性。
- 引入OCT-X算法,通过FDT-GS和深度全卷积网络最大化诊断准确性。
- 硬件包括高分辨率成像传感器、实时数据处理和无线连接的POCT设备。
- 诊断准确率高达99.7%,较现有模型显著提高,并增强了多速率适应性。
- OCT-X系统在临床诊断和治疗中有广泛应用潜力。
- 未来的研究将探索更广泛的应用,并进一步推动肿瘤学诊断的进步。
点此查看论文截图

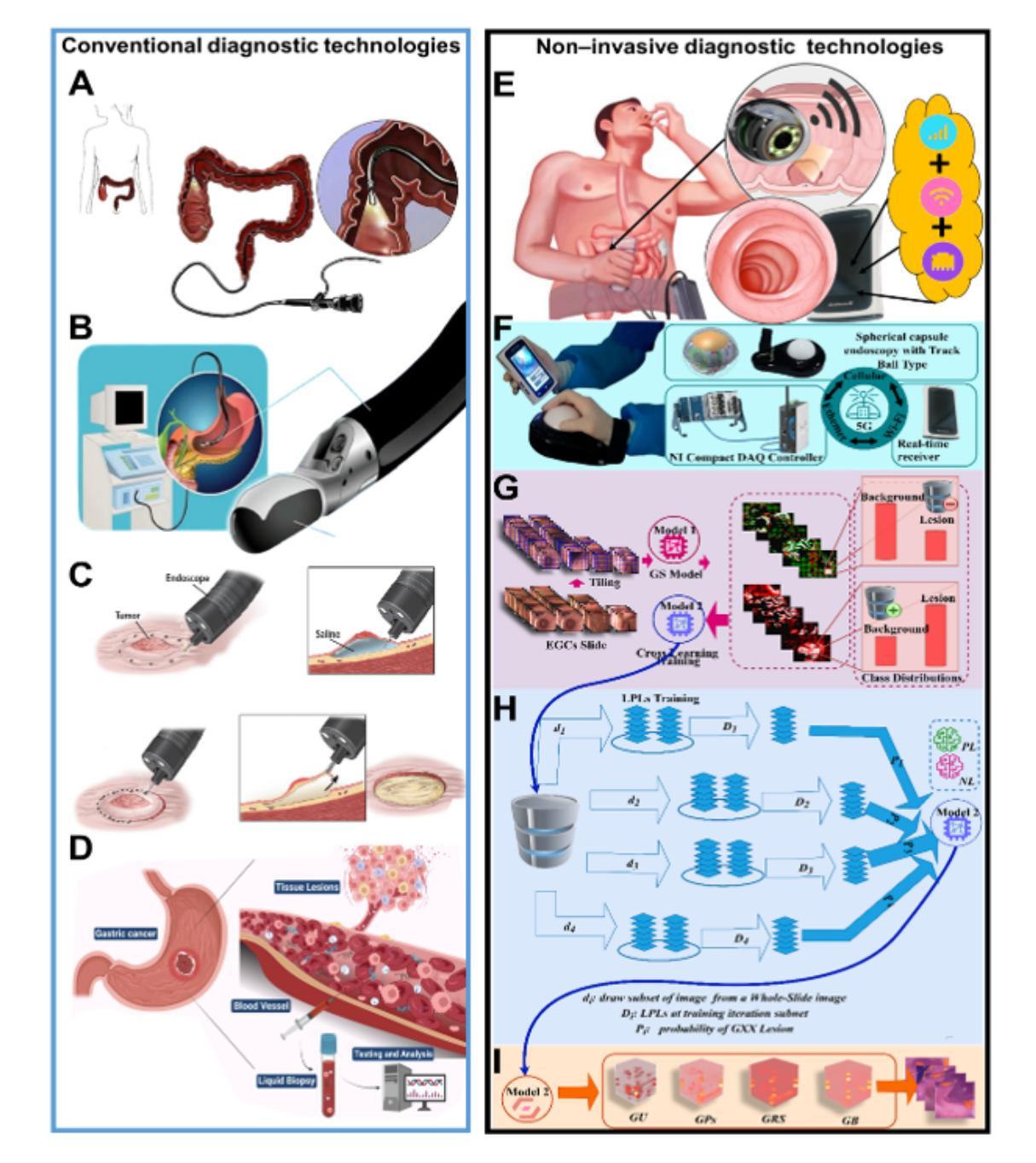
GKAN: Explainable Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease Using Graph Neural Network with Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks
Authors:Tianqi Ding, Dawei Xiang, Keith E Schubert, Liang Dong
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that poses significant diagnostic challenges due to its complex etiology. Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) have shown promise in modeling brain connectivity for AD diagnosis, yet their reliance on linear transformations limits their ability to capture intricate nonlinear patterns in neuroimaging data. To address this, we propose GCN-KAN, a novel single-modal framework that integrates Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KAN) into GCNs to enhance both diagnostic accuracy and interpretability. Leveraging structural MRI data, our model employs learnable spline-based transformations to better represent brain region interactions. Evaluated on the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) dataset, GCN-KAN outperforms traditional GCNs by 4-8% in classification accuracy while providing interpretable insights into key brain regions associated with AD. This approach offers a robust and explainable tool for early AD diagnosis.
阿尔茨海默病(AD)是一种进展性的神经退行性疾病,由于其复杂的病因,给诊断带来了重大挑战。图卷积网络(GCNs)在AD诊断的脑连接建模中显示出潜力,但它们对线性转换的依赖限制了捕捉神经成像数据中复杂非线性模式的能力。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了GCN-KAN,这是一种新型的单模态框架,它将Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KAN)集成到GCNs中,以提高诊断准确性和可解释性。我们的模型利用结构MRI数据,采用可学习的基于样条的转换来更好地表示脑区相互作用。在阿尔茨海默病神经影像学倡议(ADNI)数据集上评估,GCN-KAN的分类精度比传统GCNs高出4-8%,同时提供了关于与AD相关的关键脑区的可解释见解。这种方法为早期AD诊断提供了稳健和可解释的工具。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 4 figures, under review of The Southwest Data Science Conference (SDSC 2025)
Summary
针对阿尔茨海默病(AD)诊断的挑战,提出一种结合图卷积网络(GCN)和柯尔莫哥洛夫-阿诺尔德网络(KAN)的新型单模态框架GCN-KAN。该框架利用结构磁共振成像数据,通过采用可学习的基于样条的转换,更好地表示脑区交互作用,提高诊断准确性和解释性。在阿尔茨海默病神经影像学倡议(ADNI)数据集上评估,GCN-KAN在分类准确性上比传统GCN高出4-8%,同时提供对AD相关关键脑区的解释性见解。此框架为早期AD诊断提供了稳健和可解释的工具。
Key Takeaways
- Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) 是一种具有复杂病因的渐进性神经退行性疾病,存在重大诊断挑战。
- 图卷积网络(GCN)在AD诊断的脑连接建模中显示出潜力,但其对线性转换的依赖限制了捕捉神经成像数据中复杂非线性模式的能力。
- 提出一种新型单模态框架GCN-KAN,集成了Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks(KAN)以增强GCNs的诊断准确性和解释性。
- GCN-KAN利用结构磁共振成像数据,采用可学习的基于样条的转换,更好地表示脑区交互。
- 在ADNI数据集上评估,GCN-KAN在分类准确性上优于传统GCN方法,提高了4-8%。
- GCN-KAN提供了对与AD相关的关键脑区的解释性见解。
点此查看论文截图

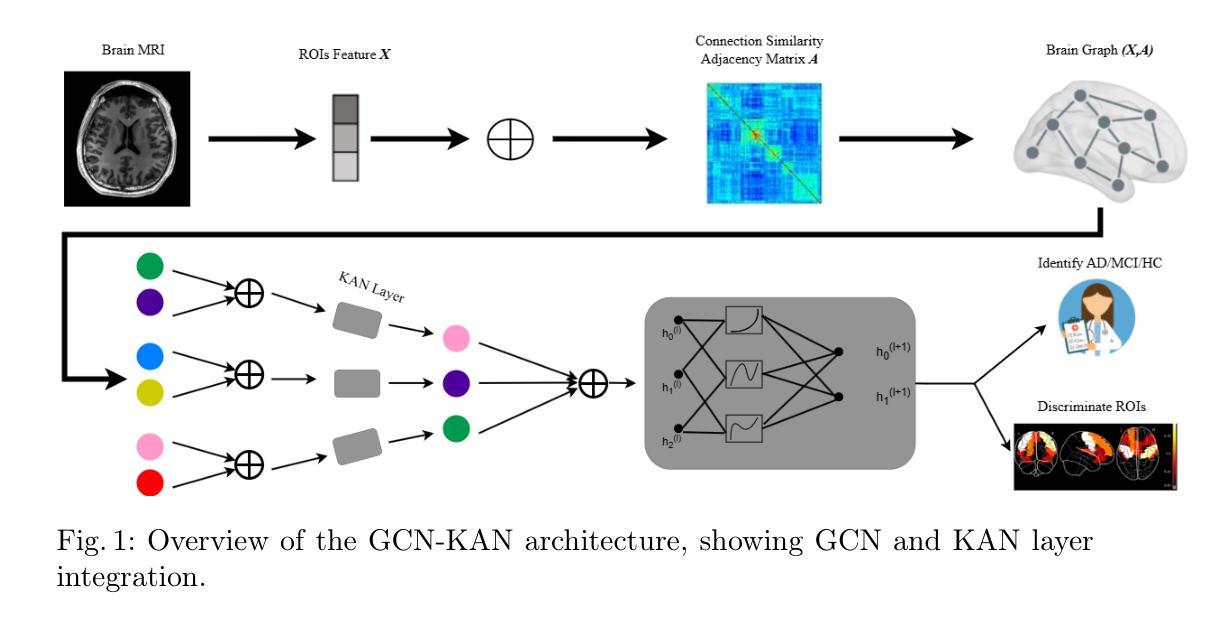
Graph Classification and Radiomics Signature for Identification of Tuberculous Meningitis
Authors:Snigdha Agarwal, Ganaraja V H, Neelam Sinha, Abhilasha Indoria, Netravathi M, Jitender Saini
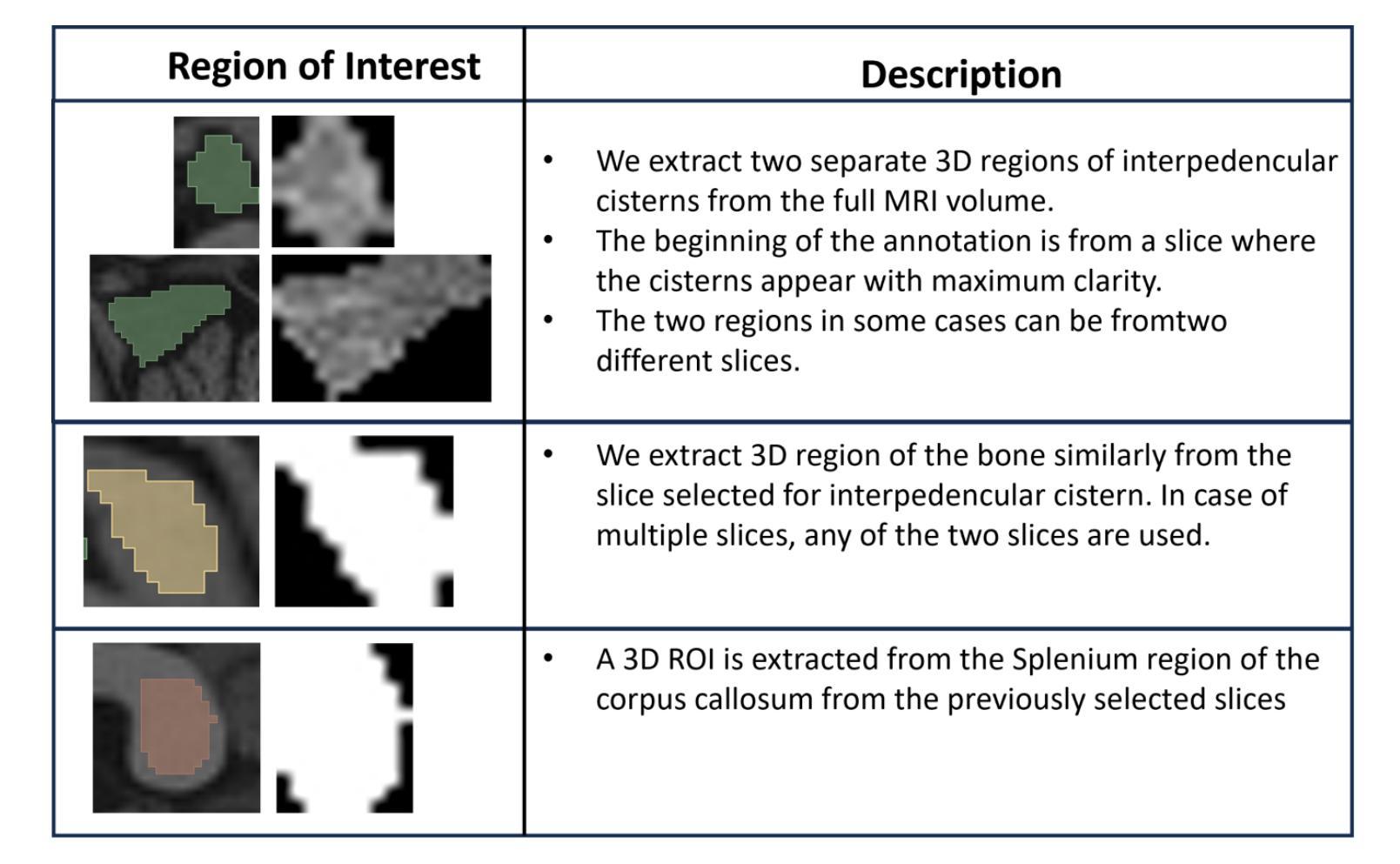
Introduction: Tuberculous meningitis (TBM) is a serious brain infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, characterized by inflammation of the meninges covering the brain and spinal cord. Diagnosis often requires invasive lumbar puncture (LP) and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis. Objectives: This study aims to classify TBM patients using T1-weighted (T1w) non-contrast Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans. We hypothesize that specific brain regions, such as the interpeduncular cisterns, bone, and corpus callosum, contain visual markers that can non-invasively distinguish TBM patients from healthy controls. We propose a novel Pixel-array Graphs Classifier (PAG-Classifier) that leverages spatial relationships between neighbouring 3D pixels in a graph-based framework to extract significant features through eigen decomposition. These features are then used to train machine learning classifiers for effective patient classification. We validate our approach using a radiomics-based methodology, classifying TBM patients based on relevant radiomics features. Results: We utilized an internal dataset consisting of 52 scans, 32 from confirmed TBM patients based on mycobacteria detection in CSF, and 20 from healthy individuals. We achieved a 5-fold cross-validated average F1 score of 85.71% for cistern regions with our PAG-Classifier and 92.85% with the radiomics features classifier, surpassing current state-of-the-art benchmarks by 15% and 22%, respectively. However, bone and corpus callosum regions showed poor classification effectiveness, with average F1 scores below 50%. Conclusion: Our study suggests that algorithms like the PAG-Classifier serve as effective tools for non-invasive TBM analysis, particularly by targeting the interpeduncular cistern. Findings indicate that the bone and corpus callosum regions lack distinctive patterns for differentiation.
引言:结核性脑膜炎(TBM)是由结核分枝杆菌引起的一种严重的大脑感染,表现为大脑和脊髓的脑膜发炎。诊断通常需要侵入性的腰椎穿刺(LP)和脑脊液(CSF)分析。目标:本研究旨在利用T1加权(T1w)非对比磁共振成像(MRI)扫描对TBM患者进行分类。我们假设特定的脑区,如脚间池、骨骼和胼胝体,存在视觉标记,可以无创地区分TBM患者和健康对照。我们提出了一种新型的像素阵列图分类器(PAG-Classifier),它利用基于图的框架中相邻3D像素之间的空间关系,通过特征分解提取重要特征。然后,这些特征被用来训练机器学习分类器,以实现有效的患者分类。我们使用基于放射组学的方法验证了我们的方法,根据相关的放射学特征对TBM患者进行分类。结果:我们使用了内部数据集,包括52次扫描,其中32次来自经脑脊液中分枝杆菌检测确认的TBM患者,20次来自健康个体。使用我们的PAG-Classifier,在池区实现了平均F1分数为85.71%的5倍交叉验证,使用放射学特征分类器达到了92.85%,分别比当前最新技术高出15%和22%。然而,骨骼和胼胝体区域的分类效果较差,平均F1分数低于50%。结论:我们的研究表明,像PAG-Classifier这样的算法是结核性脑膜炎无创分析的有效工具,尤其是通过脚间池进行的分析。研究结果表明,骨骼和胼胝体区域缺乏明显的模式来进行区分。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 6 figures, 3 tables
Summary
本文旨在利用T1加权非对比磁共振成像(MRI)扫描对结核性脑膜炎(TBM)患者进行分类。研究提出了一种新的Pixel-array Graphs Classifier(PAG-Classifier),通过图框架中的邻接三维像素的空间关系提取特征,并通过特征分解进行训练机器学习分类器,以有效地对患者进行分类。使用基于放射学的方法对TBM患者进行分类验证时,结果显示在某些区域,如脑桥小脑蚓部区域的平均F1分数达到85.71%,而放射学特征分类器的平均F1分数为92.85%。但骨和胼胝体区域分类效果不佳,平均F1得分低于50%。总体而言,该研究建议,像PAG-Classifier这样的算法可以作为非侵入性TBM分析的有效工具。
Key Takeaways
- TBM是一种由结核分枝杆菌引起的严重脑部感染,通常表现为脑膜和脊髓的炎症。
- 研究使用T1加权MRI扫描对TBM患者进行分类,提出了一种新的Pixel-array Graphs Classifier(PAG-Classifier)。
- PAG-Classifier通过利用邻接三维像素的空间关系提取特征,并用于训练机器学习分类器。
- 在脑桥小脑蚓部区域,PAG-Classifier的平均F1分数达到85.71%,放射学特征分类器的平均F1分数为92.85%,超过了当前的最佳水平。
- 骨和胼胝体区域在分类中的表现较差,平均F1得分低于50%。
- 该研究证明了像PAG-Classifier这样的算法可以作为非侵入性TBM分析的有效工具。
点此查看论文截图

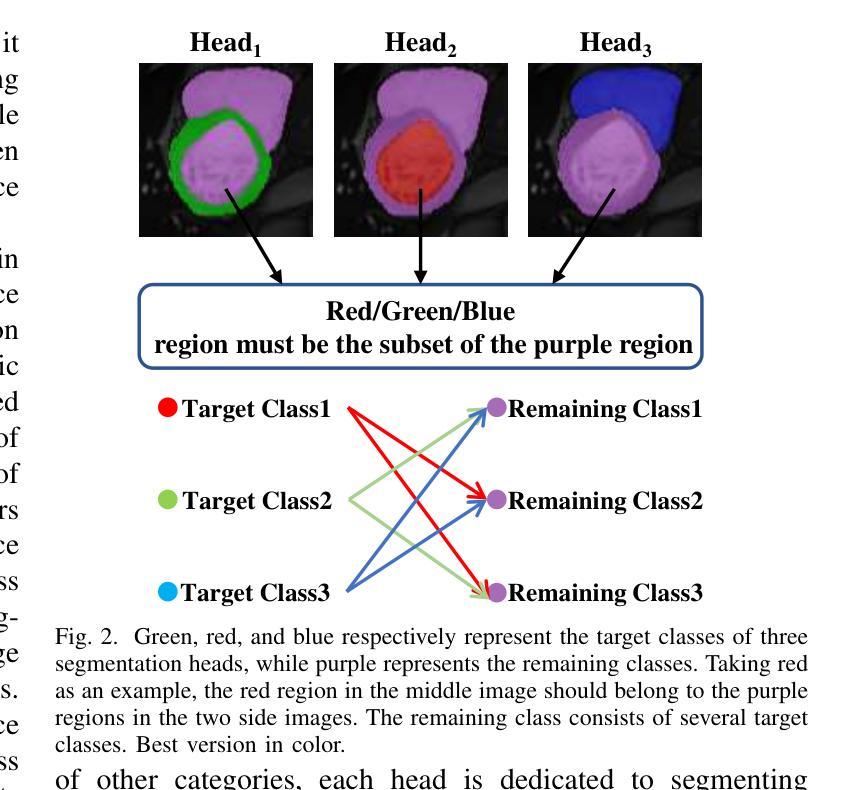
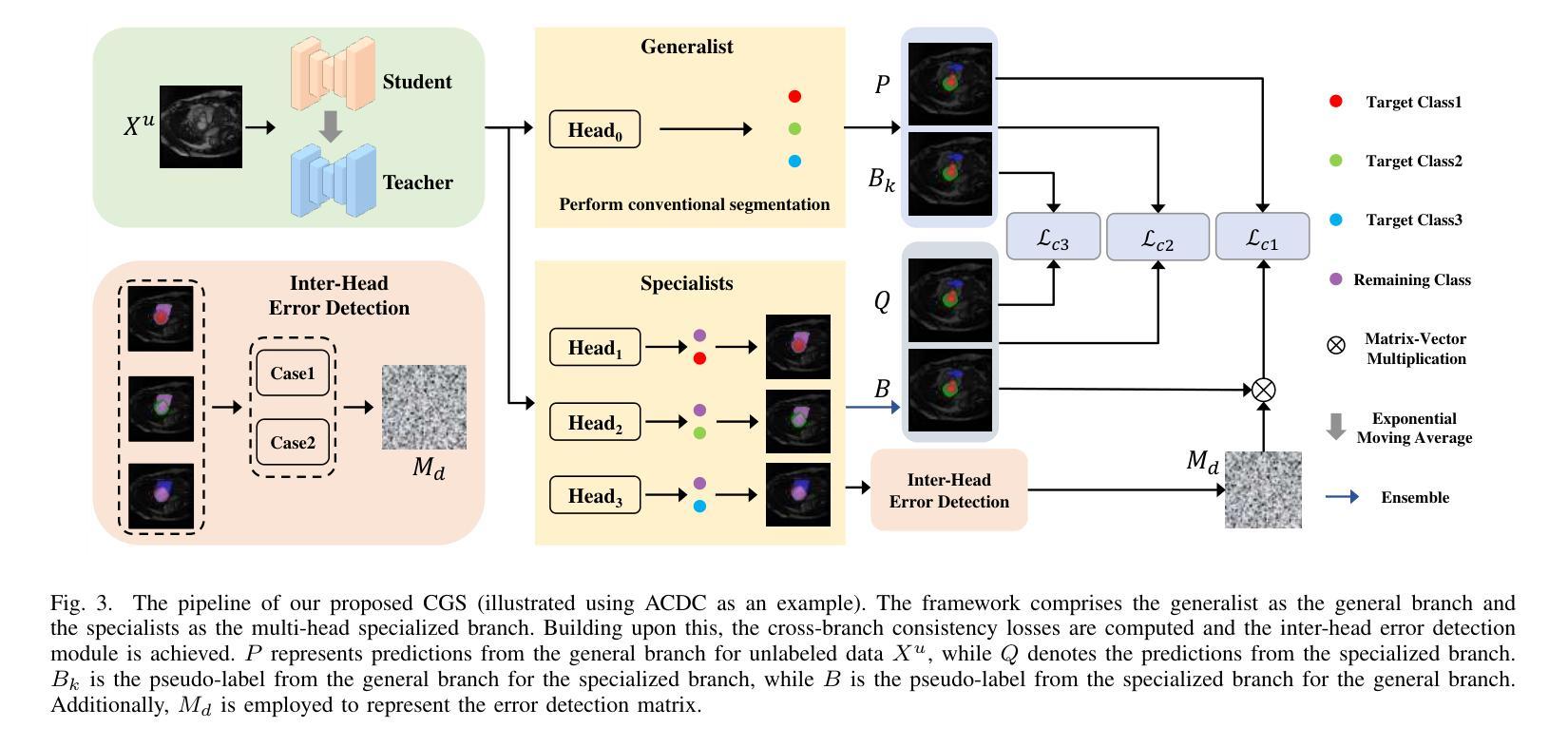
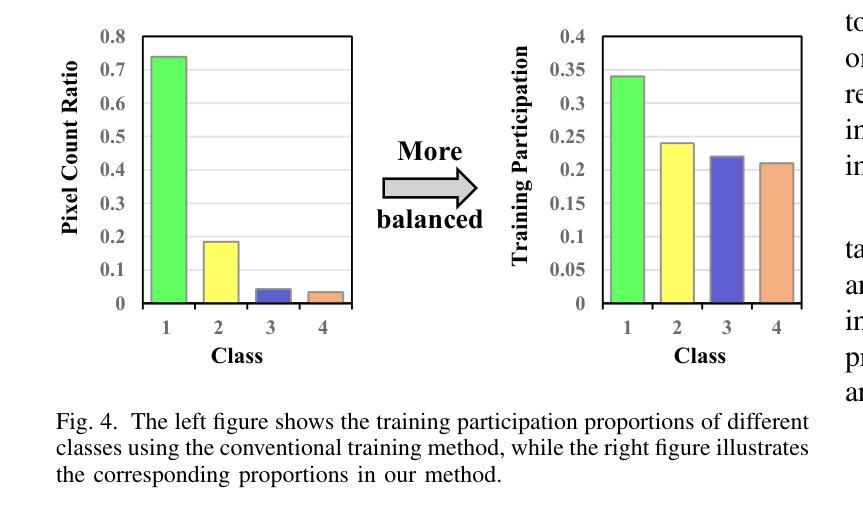
Balancing Multi-Target Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation with Collaborative Generalist and Specialists
Authors:You Wang, Zekun Li, Lei Qi, Qian Yu, Yinghuan Shi, Yang Gao
Despite the promising performance achieved by current semi-supervised models in segmenting individual medical targets, many of these models suffer a notable decrease in performance when tasked with the simultaneous segmentation of multiple targets. A vital factor could be attributed to the imbalanced scales among different targets: during simultaneously segmenting multiple targets, large targets dominate the loss, leading to small targets being misclassified as larger ones. To this end, we propose a novel method, which consists of a Collaborative Generalist and several Specialists, termed CGS. It is centered around the idea of employing a specialist for each target class, thus avoiding the dominance of larger targets. The generalist performs conventional multi-target segmentation, while each specialist is dedicated to distinguishing a specific target class from the remaining target classes and the background. Based on a theoretical insight, we demonstrate that CGS can achieve a more balanced training. Moreover, we develop cross-consistency losses to foster collaborative learning between the generalist and the specialists. Lastly, regarding their intrinsic relation that the target class of any specialized head should belong to the remaining classes of the other heads, we introduce an inter-head error detection module to further enhance the quality of pseudo-labels. Experimental results on three popular benchmarks showcase its superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods.
尽管当前半监督模型在分割单个医学目标方面取得了令人鼓舞的表现,但它们在同时分割多个目标时,性能显著下降。一个重要的因素可能是由于不同目标之间的尺度不平衡:在同时分割多个目标时,大目标会主导损失,导致小目标被误分类为大目标。为此,我们提出了一种新方法,它由通用专家(Generalist)和多个专业专家(Specialists)组成,称为CGS。它围绕为每个目标类别雇佣一个专业专家的理念,从而避免大目标的主导。通用专家执行常规的多目标分割,而每个专业专家致力于将其特定的目标类别与其余目标类别和背景区分开。基于理论洞察,我们证明CGS可以实现更平衡的训练。此外,我们开发了交叉一致性损失,以促进通用专家和专业专家之间的协作学习。最后,鉴于专业头部目标类别与其他头部的剩余类别之间存在内在联系,我们引入了跨头部误差检测模块,以进一步提高伪标签的质量。在三个流行基准测试上的实验结果表明,与最先进的方法相比,其性能卓越。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为CGS的新型半监督医学图像分割方法,通过引入通用专家(generalist)和多个针对特定目标的专家(specialist)来解决同时分割多个目标时性能下降的问题。该方法通过为每个目标类别分配一个专家,避免了大目标的主导作用,实现了更平衡的训练,并在三个流行基准测试上表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 当前半监督模型在同时分割多个医学目标时性能下降的问题。
- 问题原因是不同目标之间的尺度失衡,大目标在同时分割多个目标时占据主导,导致小目标被误分类。
- 提出的CGS方法包括一个通用专家(进行常规多目标分割)和多个针对特定目标的专家(专注于将特定目标类别与其余类别和背景区分开)。
- CGS方法通过引入交叉一致性损失(cross-consistency losses)促进了通用专家与专家之间的协作学习。
- CGS方法引入了跨头误差检测模块(inter-head error detection module),以提高伪标签的质量。
- 实验结果表明,CGS方法在三个流行基准测试上的性能优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

SCFANet: Style Distribution Constraint Feature Alignment Network For Pathological Staining Translation
Authors:Zetong Chen, Yuzhuo Chen, Hai Zhong, Xu Qiao
Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining serves as a valuable technique for detecting specific antigens or proteins through antibody-mediated visualization. However, the IHC staining process is both time-consuming and costly. To address these limitations, the application of deep learning models for direct translation of cost-effective Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) stained images into IHC stained images has emerged as an efficient solution. Nevertheless, the conversion from H&E to IHC images presents significant challenges, primarily due to alignment discrepancies between image pairs and the inherent diversity in IHC staining style patterns. To overcome these challenges, we propose the Style Distribution Constraint Feature Alignment Network (SCFANet), which incorporates two innovative modules: the Style Distribution Constrainer (SDC) and Feature Alignment Learning (FAL). The SDC ensures consistency between the generated and target images’ style distributions while integrating cycle consistency loss to maintain structural consistency. To mitigate the complexity of direct image-to-image translation, the FAL module decomposes the end-to-end translation task into two subtasks: image reconstruction and feature alignment. Furthermore, we ensure pathological consistency between generated and target images by maintaining pathological pattern consistency and Optical Density (OD) uniformity. Extensive experiments conducted on the Breast Cancer Immunohistochemical (BCI) dataset demonstrate that our SCFANet model outperforms existing methods, achieving precise transformation of H&E-stained images into their IHC-stained counterparts. The proposed approach not only addresses the technical challenges in H&E to IHC image translation but also provides a robust framework for accurate and efficient stain conversion in pathological analysis.
免疫组织化学(IHC)染色作为一种通过抗体介导的可视化检测特定抗原或蛋白质的有价值的技术。然而,IHC染色过程既耗时又成本高昂。为了解决这些局限性,应用深度学习模型将经济实惠的苏木精-伊红(H&E)染色图像直接翻译为IHC染色图像已成为一种高效的解决方案。然而,从H&E到IHC图像的转换存在重大挑战,主要是因为图像对之间的对齐差异和IHC染色风格模式的固有多样性。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了风格分布约束特征对齐网络(SCFANet),它包含两个创新模块:风格分布约束器(SDC)和特征对齐学习(FAL)。SDC确保生成图像和目标图像之间风格分布的一致性,同时结合循环一致性损失以保持结构一致性。为了减轻直接图像到图像翻译的复杂性,FAL模块将端到端的翻译任务分解为两个子任务:图像重建和特征对齐。此外,我们通过保持病理模式的一致性和光学密度(OD)的均匀性,确保生成图像和目标图像之间的病理一致性。在乳腺癌免疫组织化学(BCI)数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,我们的SCFANet模型优于现有方法,实现了H&E染色图像向IHC染色图像的精确转换。所提出的方法不仅解决了H&E到IHC图像转换中的技术挑战,而且为病理分析中的准确和高效染色转换提供了稳健的框架。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于免疫组化染色在病理学分析中的重要性,但其耗时长、成本高的缺点,研究人员通过深度学习模型实现基于H&E染料的图像转换为IHC染色图像的直接转换。提出了SCFANet模型包含SDC和FAL两个创新模块,能够在确保风格分布和结构一致性的基础上,完成从H&E到IHC的图像转换,且在乳腺癌免疫组化数据集上的表现优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 免疫组化染色是检测特定抗原或蛋白质的重要技术,但其过程耗时且成本较高。
- 深度学习模型被应用于将H&E染色图像直接转换为IHC染色图像,以解决这一问题。
- 从H&E到IHC的图像转换面临挑战,如图像对齐和IHC染色风格的多样性。
- SCFANet模型通过SDC和FAL两个模块克服这些挑战,实现风格分布和结构的一致性。
- SCFANet在乳腺癌免疫组化数据集上的表现优于现有方法,实现了精确的H&E染色图像向IHC染色图像的转换。
点此查看论文截图

Hybrid Global-Local Representation with Augmented Spatial Guidance for Zero-Shot Referring Image Segmentation
Authors:Ting Liu, Siyuan Li
Recent advances in zero-shot referring image segmentation (RIS), driven by models such as the Segment Anything Model (SAM) and CLIP, have made substantial progress in aligning visual and textual information. Despite these successes, the extraction of precise and high-quality mask region representations remains a critical challenge, limiting the full potential of RIS tasks. In this paper, we introduce a training-free, hybrid global-local feature extraction approach that integrates detailed mask-specific features with contextual information from the surrounding area, enhancing mask region representation. To further strengthen alignment between mask regions and referring expressions, we propose a spatial guidance augmentation strategy that improves spatial coherence, which is essential for accurately localizing described areas. By incorporating multiple spatial cues, this approach facilitates more robust and precise referring segmentation. Extensive experiments on standard RIS benchmarks demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing zero-shot RIS models, achieving substantial performance gains. We believe our approach advances RIS tasks and establishes a versatile framework for region-text alignment, offering broader implications for cross-modal understanding and interaction. Code is available at https://github.com/fhgyuanshen/HybridGL .
近期,零样本图像分割(Zero-Shot Referring Image Segmentation,简称RIS)领域在Segment Anything Model(SAM)和CLIP等模型的推动下取得了重大进展,其在视觉和文本信息的对齐方面取得了实质性进步。然而,提取精确高质量的掩膜区域表示仍然是一个关键挑战,限制了RIS任务的全潜力。在本文中,我们提出了一种无训练、混合全局-局部特征提取方法,该方法将详细的掩膜特定特征与周围区域的上文信息相结合,增强了掩膜区域表示。为了进一步加强对掩膜区域和参照表达式之间的对齐,我们提出了一种空间引导增强策略,该策略提高了空间连贯性,对于准确定位描述区域至关重要。通过融入多种空间线索,该方法实现了更稳健和精确的参照分割。在标准的RIS基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法显著优于现有的零样本RIS模型,实现了实质性的性能提升。我们相信,我们的方法推动了RIS任务的发展,并建立了用于区域文本对齐的通用框架,为跨模态理解和交互提供了更广泛的启示。代码已发布在https://github.com/fhgyuanshen/HybridGL上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted to CVPR2025
Summary
近期,零样本指代图像分割(RIS)领域在Segment Anything Model(SAM)和CLIP等模型的推动下取得了显著进展,但在生成精确高质量掩膜区域表示方面仍存在挑战。本文提出了一种无需训练的混合全局局部特征提取方法,该方法结合了掩膜特定特征与周围区域的上下文信息,改进了掩膜区域表示。为进一步强化掩膜区域和指代表达式之间的对齐,本文提出了空间引导增强策略,提高了空间连贯性,有助于准确定位描述区域。通过融入多种空间线索,该方法实现了更稳健精确的指代分割。在标准RIS基准测试上的实验表明,该方法显著优于现有零样本RIS模型,实现了性能的大幅提升。
Key Takeaways
- Segment Anything Model (SAM) 和 CLIP 等模型推动了零样本指代图像分割(RIS)的进步。
- 精确和高质量的掩膜区域表示仍是 RIS 任务的关键挑战。
- 提出了一种无需训练的混合全局局部特征提取方法,结合了掩膜特定特征和上下文信息。
- 提出了空间引导增强策略,以强化掩膜区域和指代表达式之间的对齐,提高空间连贯性。
- 通过融入多种空间线索,实现了更稳健和精确的指代分割。
- 在标准RIS基准测试上,该方法显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图
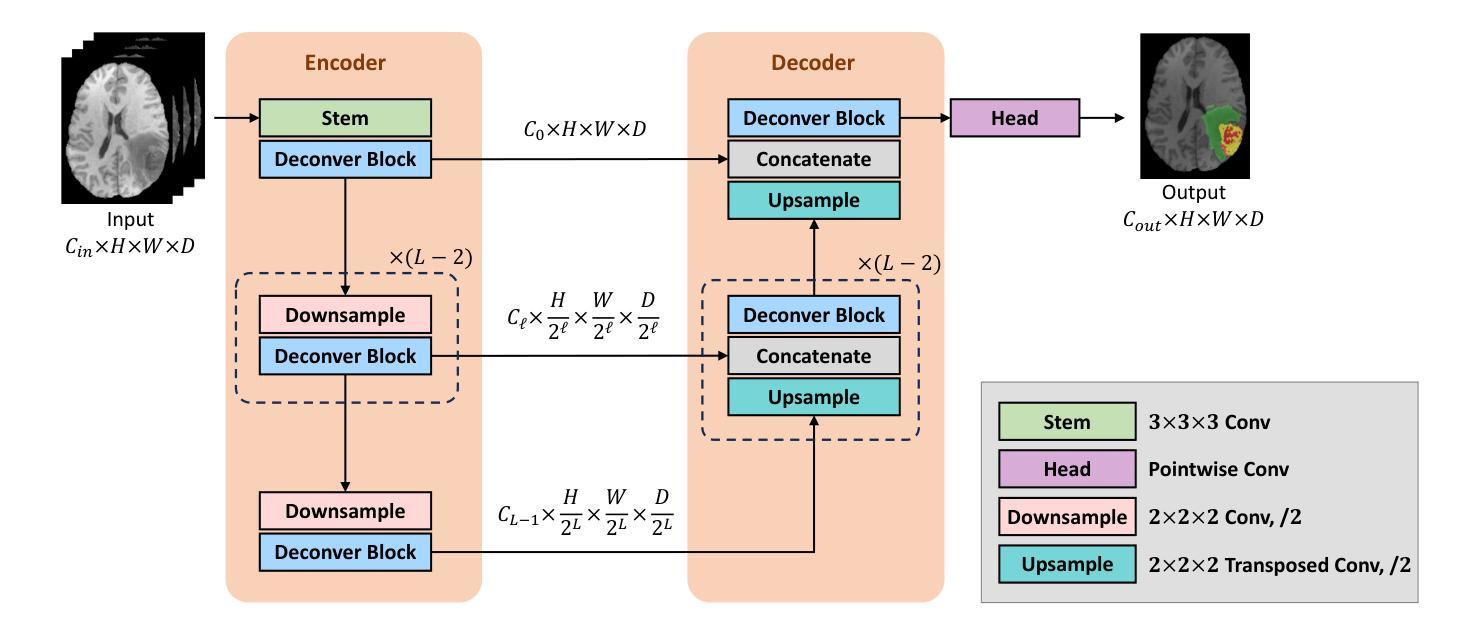
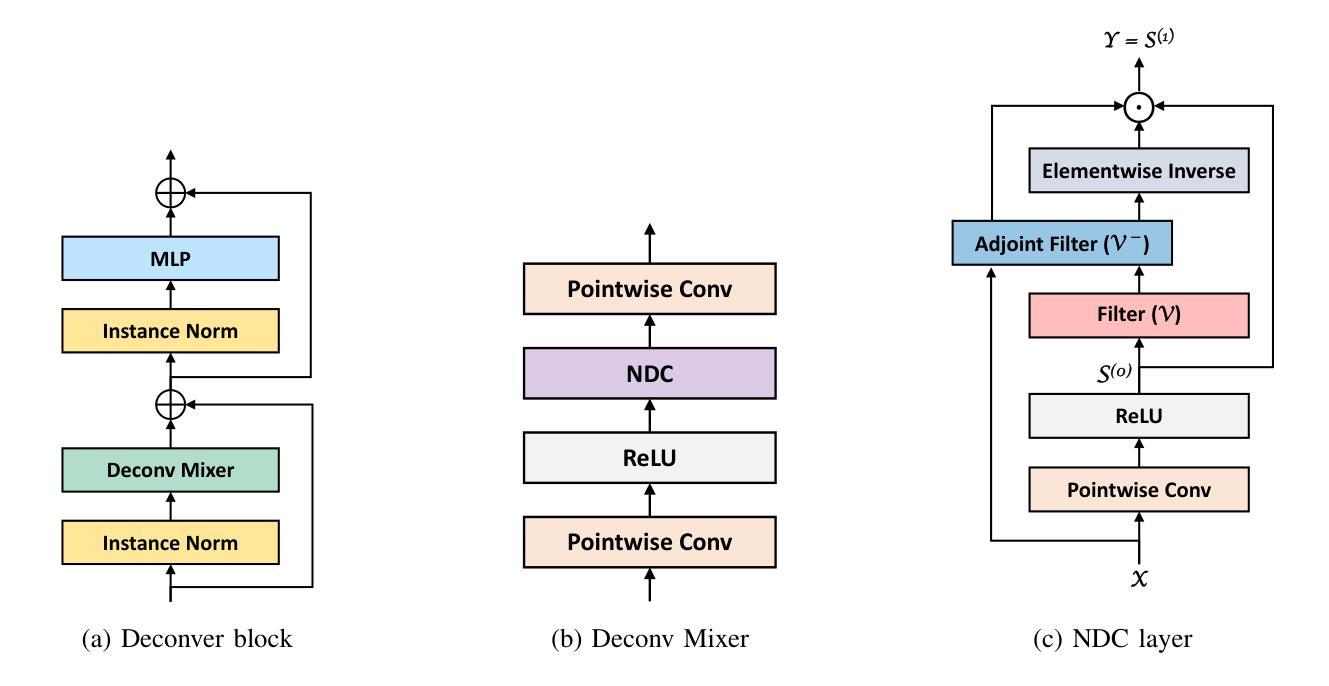
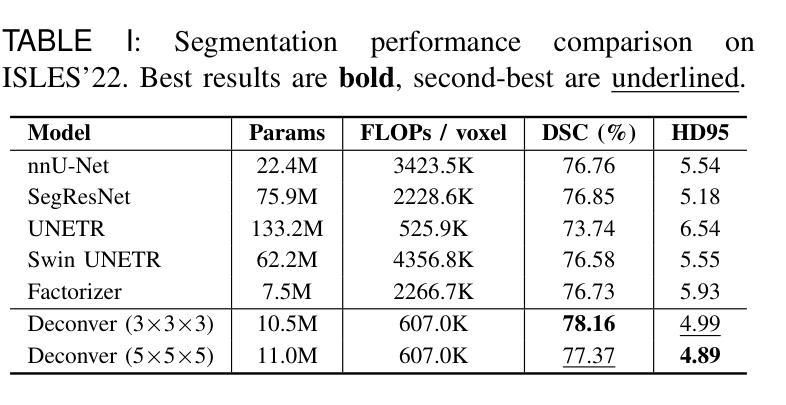
Deconver: A Deconvolutional Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Pooya Ashtari, Shahryar Noei, Fateme Nateghi Haredasht, Jonathan H. Chen, Giuseppe Jurman, Aleksandra Pizurica, Sabine Van Huffel
While convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformers (ViTs) have advanced medical image segmentation, they face inherent limitations such as local receptive fields in CNNs and high computational complexity in ViTs. This paper introduces Deconver, a novel network that integrates traditional deconvolution techniques from image restoration as a core learnable component within a U-shaped architecture. Deconver replaces computationally expensive attention mechanisms with efficient nonnegative deconvolution (NDC) operations, enabling the restoration of high-frequency details while suppressing artifacts. Key innovations include a backpropagation-friendly NDC layer based on a provably monotonic update rule and a parameter-efficient design. Evaluated across four datasets (ISLES’22, BraTS’23, GlaS, FIVES) covering both 2D and 3D segmentation tasks, Deconver achieves state-of-the-art performance in Dice scores and Hausdorff distance while reducing computational costs (FLOPs) by up to 90% compared to leading baselines. By bridging traditional image restoration with deep learning, this work offers a practical solution for high-precision segmentation in resource-constrained clinical workflows. The project is available at https://github.com/pashtari/deconver.
尽管卷积神经网络(CNNs)和视觉变压器(ViTs)已经推动了医学图像分割的发展,但它们仍面临固有的局限性,例如CNN的局部感受野和ViT的高计算复杂度。本文介绍了一种名为Deconver的新型网络,它将图像恢复中的传统反卷积技术集成到一个U形架构中的核心可学习组件。Deconver用高效的非负反卷积(NDC)操作取代了计算昂贵的注意力机制,能够在恢复高频细节的同时抑制伪影。主要创新包括基于可证明的单调更新规则的反向传播友好的NDC层以及参数高效的设计。在涵盖2D和3D分割任务的四个数据集(ISLES’22、BraTS’23、GlaS、FIVES)上进行了评估,Deconver在Dice得分和Hausdorff距离方面达到了最先进的性能,与领先的基线相比,计算成本(FLOPs)降低了高达90%。通过桥接传统图像恢复和深度学习,这项工作为资源受限的临床工作流程中的高精度分割提供了实用解决方案。该项目可在https://github.com/pashtari/deconver获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 6 figures, 5 tables
Summary
本文提出了一种名为Deconver的新型网络,该网络将传统图像恢复中的反卷积技术作为核心学习组件,集成到U形架构中。它使用高效的非负反卷积(NDC)操作替代了计算成本高昂的注意力机制,能够在恢复高频细节的同时抑制伪影。在多个数据集上评估,Deconver在Dice得分和Hausdorff距离方面达到了最新技术水平,并降低了高达90%的计算成本。该研究为资源受限的临床工作流程提供了高精度分割的实用解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- Deconver网络结合了传统图像恢复中的反卷积技术,解决了CNN和ViT在医学图像分割中的局限性。
- Deconver使用非负反卷积(NDC)操作替代了计算成本高昂的注意力机制。
- NDC操作基于可证明的单调更新规则,便于反向传播。
- Deconver实现了高效的参数设计。
- 在四个数据集上评估,Deconver在Dice得分和Hausdorff距离方面达到了最新技术水平。
- Deconver降低了高达90%的计算成本,适用于资源受限的环境。
点此查看论文截图

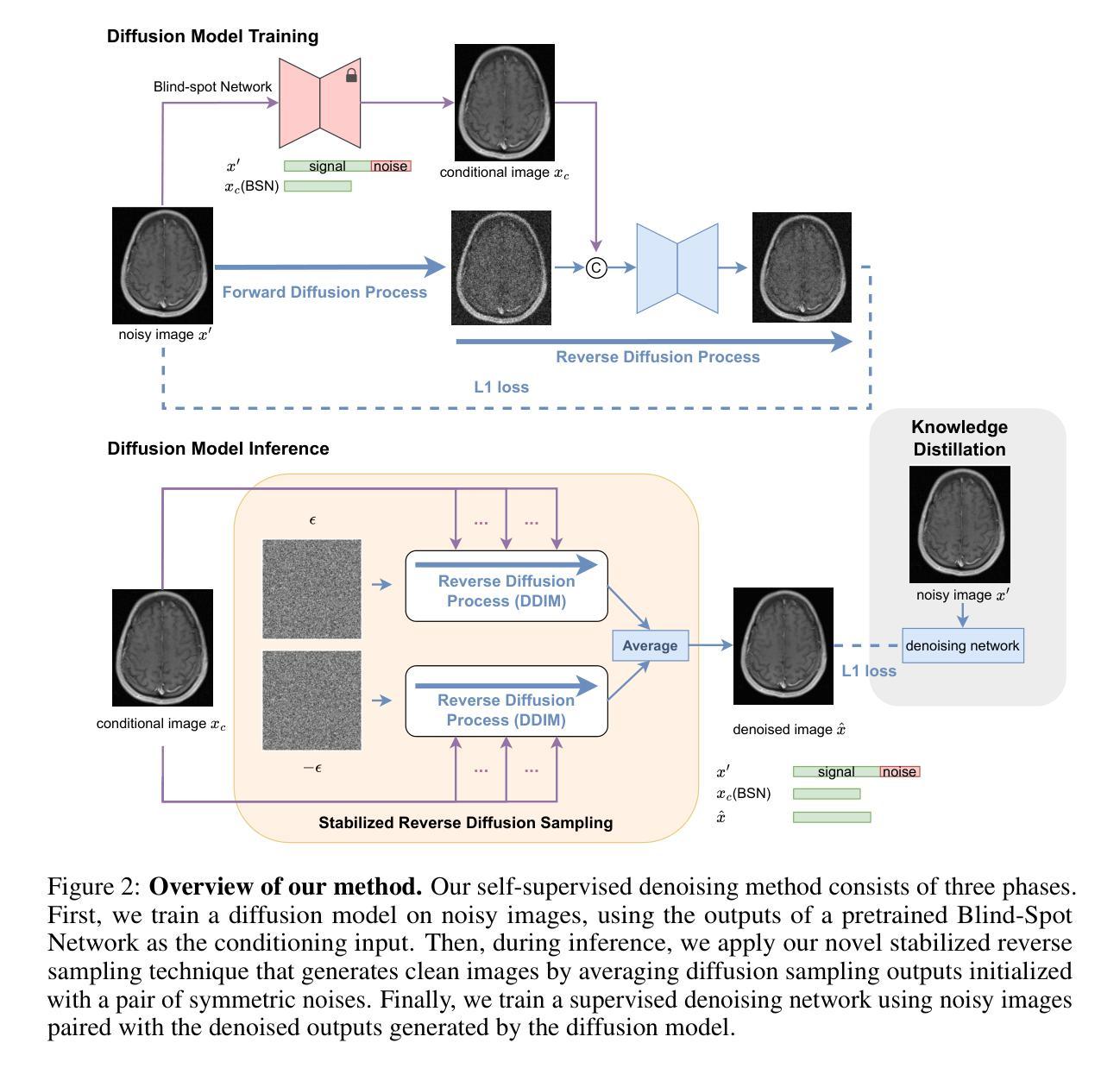
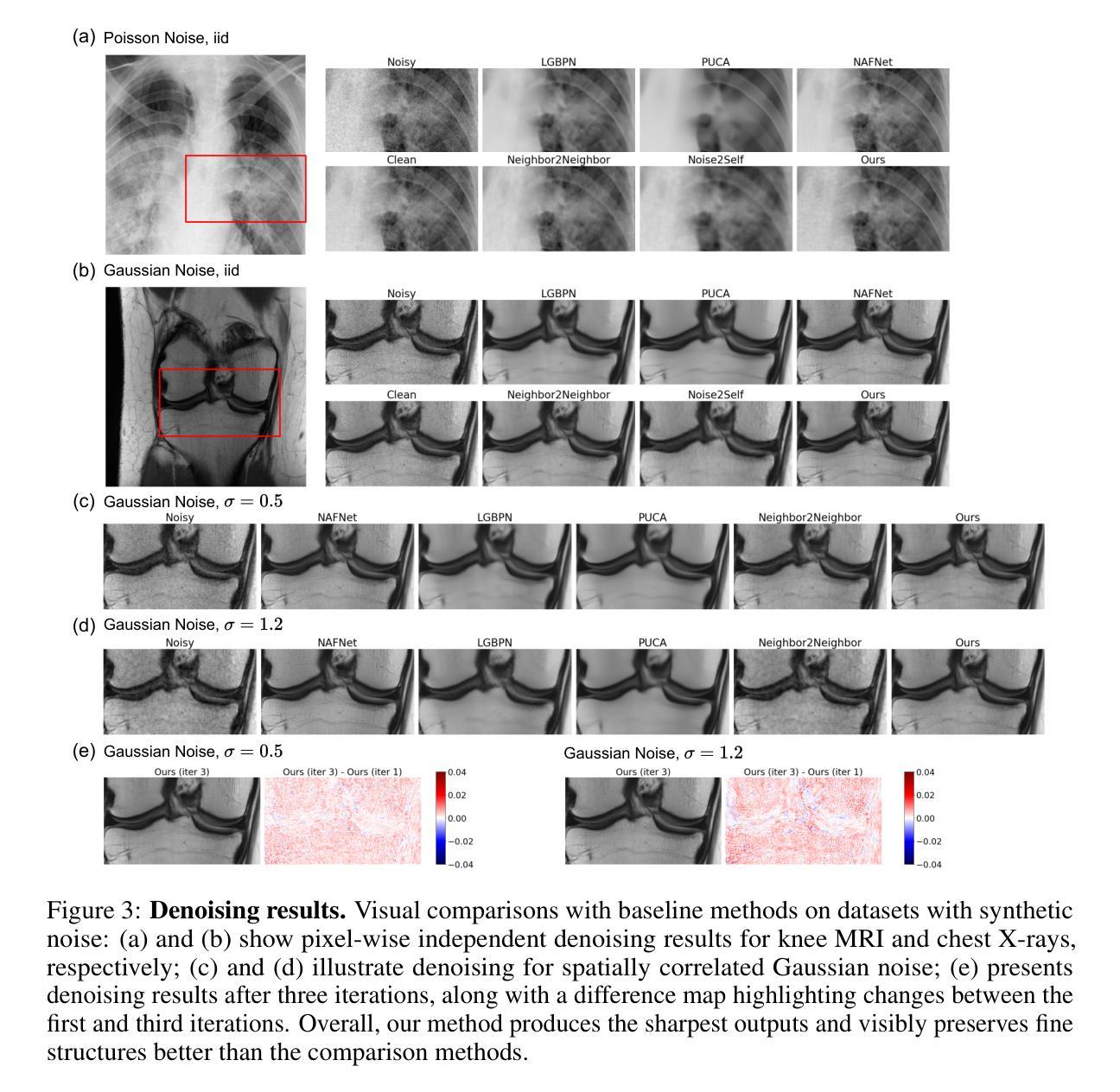
DiffDenoise: Self-Supervised Medical Image Denoising with Conditional Diffusion Models
Authors:Basar Demir, Yikang Liu, Xiao Chen, Eric Z. Chen, Lin Zhao, Boris Mailhe, Terrence Chen, Shanhui Sun
Many self-supervised denoising approaches have been proposed in recent years. However, these methods tend to overly smooth images, resulting in the loss of fine structures that are essential for medical applications. In this paper, we propose DiffDenoise, a powerful self-supervised denoising approach tailored for medical images, designed to preserve high-frequency details. Our approach comprises three stages. First, we train a diffusion model on noisy images, using the outputs of a pretrained Blind-Spot Network as conditioning inputs. Next, we introduce a novel stabilized reverse sampling technique, which generates clean images by averaging diffusion sampling outputs initialized with a pair of symmetric noises. Finally, we train a supervised denoising network using noisy images paired with the denoised outputs generated by the diffusion model. Our results demonstrate that DiffDenoise outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in both synthetic and real-world medical image denoising tasks. We provide both a theoretical foundation and practical insights, demonstrating the method’s effectiveness across various medical imaging modalities and anatomical structures.
近年来已经提出了许多自监督降噪方法。然而,这些方法往往过度平滑图像,导致丢失对医疗应用至关重要的精细结构。在本文中,我们提出了DiffDenoise,这是一种针对医学图像设计的强大自监督降噪方法,旨在保留高频细节。我们的方法分为三个步骤。首先,我们在噪声图像上训练扩散模型,使用预训练的盲点网络的输出来作为条件输入。接下来,我们引入了一种新颖的稳定反向采样技术,该技术通过平均使用一对对称噪声初始化的扩散采样输出来生成干净图像。最后,我们使用与扩散模型生成的降噪输出配对的噪声图像来训练一个监督降噪网络。我们的结果表明,无论是在合成还是在真实世界的医学图像降噪任务中,DiffDenoise都优于现有的最先进方法。我们既提供了理论基础,也提供了实践见解,证明了该方法在各种医学成像模式和解剖结构中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出一种针对医学图像的强大自监督去噪方法——DiffDenoise,旨在保留高频细节。该方法包括三个阶段:首先,使用预训练的盲点网络输出作为条件输入,对噪声图像进行扩散模型训练;接着,引入一种新颖的稳定逆向采样技术,通过平均扩散采样输出并初始化为一对对称噪声来生成干净图像;最后,使用与扩散模型生成的去噪输出配对的噪声图像,训练一个监督去噪网络。实验结果表明,DiffDenoise在合成和真实世界医学图像去噪任务中均优于现有最先进的方法,并提供了理论框架和实践见解,证明该方法在不同医学成像模态和解剖结构中的有效性。
关键见解
- DiffDenoise是一种针对医学图像设计的自监督去噪方法,旨在保留高频细节,解决现有方法过度平滑图像的问题。
- 方法包括三个阶段:扩散模型训练、稳定逆向采样技术、监督去噪网络训练。
- 使用预训练的盲点网络输出作为条件输入,对噪声图像进行扩散模型训练。
- 引入新颖的稳定逆向采样技术,通过平均扩散采样输出并初始化为对称噪声对来生成干净图像。
- DiffDenoise在合成和真实世界医学图像去噪任务中表现优异。
- 提供理论框架和实践见解,证明该方法的有效性。
- DiffDenoise方法适用于各种医学成像模态和解剖结构。
点此查看论文截图

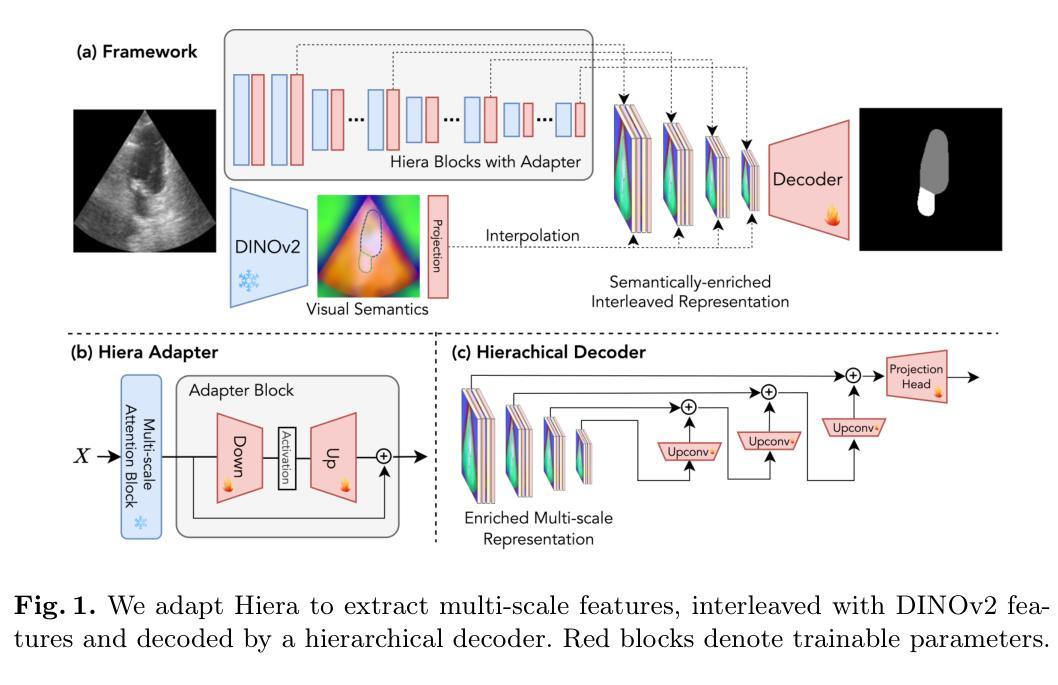
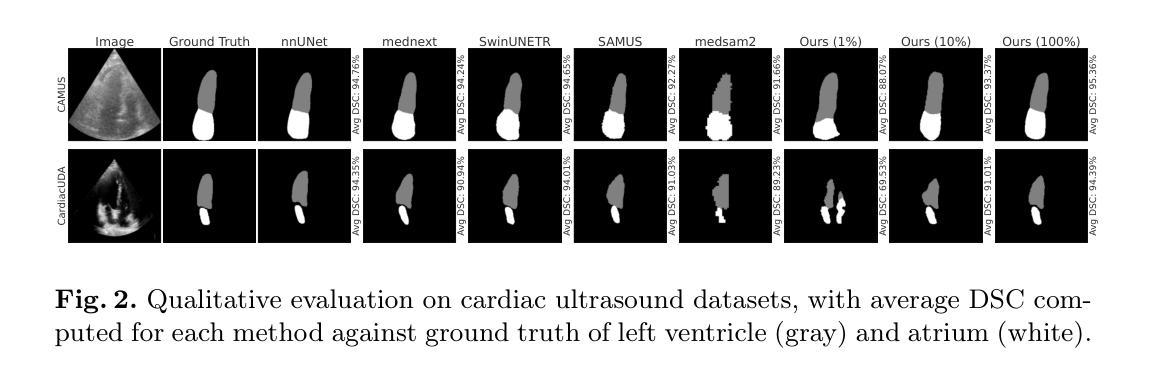
Adapting Vision Foundation Models for Real-time Ultrasound Image Segmentation
Authors:Xiaoran Zhang, Eric Z. Chen, Lin Zhao, Xiao Chen, Yikang Liu, Boris Maihe, James S. Duncan, Terrence Chen, Shanhui Sun
We propose a novel approach that adapts hierarchical vision foundation models for real-time ultrasound image segmentation. Existing ultrasound segmentation methods often struggle with adaptability to new tasks, relying on costly manual annotations, while real-time approaches generally fail to match state-of-the-art performance. To overcome these limitations, we introduce an adaptive framework that leverages the vision foundation model Hiera to extract multi-scale features, interleaved with DINOv2 representations to enhance visual expressiveness. These enriched features are then decoded to produce precise and robust segmentation. We conduct extensive evaluations on six public datasets and one in-house dataset, covering both cardiac and thyroid ultrasound segmentation. Experiments show that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods across multiple datasets and excels with limited supervision, surpassing nnUNet by over 20% on average in the 1% and 10% data settings. Our method achieves $\sim$77 FPS inference speed with TensorRT on a single GPU, enabling real-time clinical applications.
我们提出了一种新型方法,该方法将层次化的视觉基础模型应用于实时超声图像分割。现有的超声分割方法往往难以适应新任务,并依赖于昂贵的手动标注,而实时方法通常无法达到最新技术的性能水平。为了克服这些局限性,我们引入了一个自适应框架,该框架利用视觉基础模型Hiera提取多尺度特征,并与DINOv2表示交替使用,以增强视觉表现力。这些丰富的特征随后被解码以产生精确且稳定的分割。我们在六个公开数据集和一个内部数据集上进行了广泛评估,涵盖了心脏和甲状腺超声分割。实验表明,我们的方法在多数据集上优于最新技术的方法,并在有限监督下表现出色,在1%和10%的数据设置下平均超出nnUNet超过20%。我们的方法在单个GPU上使用TensorRT达到了约77 FPS的推理速度,可实现实时临床应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型方法,采用分层视觉基础模型进行实时超声图像分割。该方法克服了现有超声分割方法对新任务适应性差、依赖昂贵手动标注的局限性,以及实时方法难以达到最新性能的不足。通过引入自适应框架,利用视觉基础模型Hiera提取多尺度特征,并与DINOv2表示进行交替,提高视觉表现力。经过广泛评估,该方法在多数据集上表现优于最新方法,并在有限监督下表现尤为出色,在1%和10%数据集设置上平均超过nnUNet超过20%。该方法在单个GPU上使用TensorRT达到约77 FPS的推理速度,适用于实时临床应用。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种新型超声图像分割方法,采用分层视觉基础模型。
- 引入自适应框架,结合Hiera和DINOv2技术,提高图像分割精度和鲁棒性。
- 方法在多数据集上表现优异,特别是在有限监督下。
- 与现有方法相比,新方法在多个数据集上的性能平均提高超过20%。
- 方法实现实时推理,适用于临床应用的实时需求。
- 使用TensorRT在单个GPU上实现约77 FPS的推理速度。
- 该方法能够处理心脏和甲状腺的超声图像分割。
点此查看论文截图

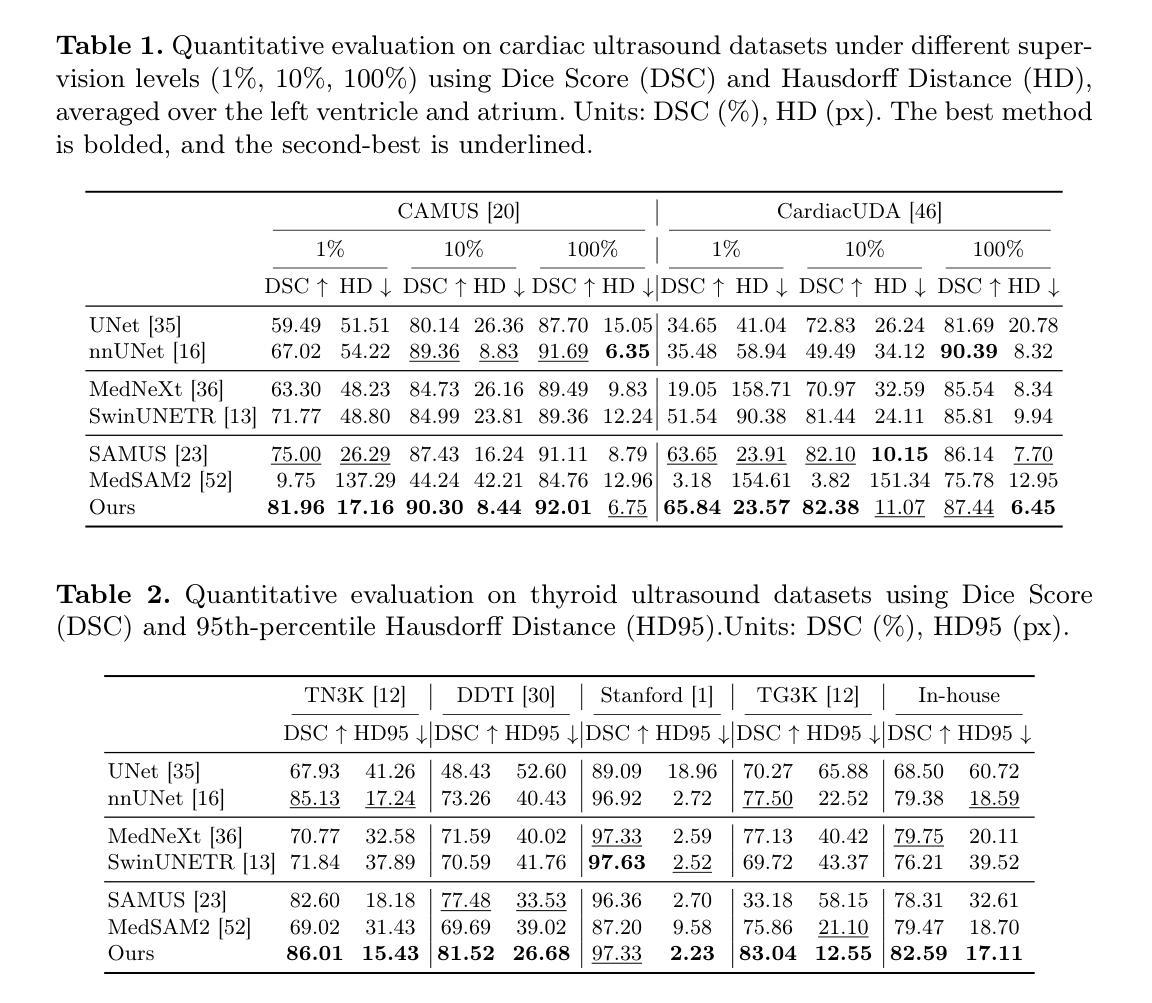
IMPACT: A Generic Semantic Loss for Multimodal Medical Image Registration
Authors:Valentin Boussot, Cédric Hémon, Jean-Claude Nunes, Jason Downling, Simon Rouzé, Caroline Lafond, Anaïs Barateau, Jean-Louis Dillenseger
Image registration is fundamental in medical imaging, enabling precise alignment of anatomical structures for diagnosis, treatment planning, image-guided treatment or longitudinal monitoring. This work introduces IMPACT (Image Metric with Pretrained model-Agnostic Comparison for Transmodality registration), a generic semantic similarity metric designed for seamless integration into diverse image registration frameworks (such as Elastix and Voxelmorph). It compares deep learning-based features extracted from medical images without requiring task-specific training, ensuring broad applicability across various modalities. By leveraging the features of the large-scale pretrained TotalSegmentator models and the ability to integrate Segment Anything Model (SAM) and other large-scale segmentation networks, this approach offers significant advantages. It provides robust, scalable, and efficient solutions for multimodal image registration. The IMPACT loss was evaluated on five challenging registration tasks involving thoracic CT/CBCT, and pelvic MR/CT datasets. Quantitative metrics, such as Target Registration Error and Dice Similarity Coefficient, demonstrated significant improvements in anatomical alignment compared to baseline methods. Qualitative analyses further confirmed the increased robustness of the proposed metric in the face of noise, artifacts, and modality variations. IMPACT’s versatility and efficiency make it a valuable tool for advancing registration performance in clinical and research applications, addressing critical challenges in multimodal medical imaging.
医学影像中的图像配准是基本且至关重要的技术,它能够实现解剖结构的精确对齐,为诊断、治疗计划、图像引导治疗或纵向监测提供支持。本文介绍了IMPACT(用于跨模态配准的预训练模型无关比较的图像度量指标),这是一种通用语义相似性度量指标,旨在无缝集成到多种图像配准框架(如Elastix和Voxelmorph)中。它比较医学图像中提取的深度学习特征,无需特定任务的训练,确保在不同模态之间具有广泛的应用性。通过利用大规模预训练TotalSegmentator模型的特征以及集成Segment Anything Model(SAM)和其他大规模分割网络的能力,此方法具有显著优势。它为多模态图像配准提供了稳健、可扩展和高效的解决方案。IMPACT损失在五个具有挑战性的配准任务上进行了评估,涉及胸部CT/CBCT和盆腔MR/CT数据集。目标注册误差和Dice相似系数等定量指标证明,与基准方法相比,其在解剖结构对齐方面实现了显著改善。定性分析进一步证实了所提出的度量指标在应对噪声、伪影和模态变化时的增强稳健性。IMPACT的通用性和效率使其成为推动临床和研究应用中配准性能提高的宝贵工具,解决了多模态医学影像中的关键挑战。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI). This is a preprint version and has not been peer-reviewed
Summary
本摘要提出了一种新型的图像配准方法IMPACT,它通过利用大规模预训练模型的特性,无需特定任务训练即可从医学图像中提取深度特征,为多种图像配准框架提供了无缝集成。IMPACT在跨模态图像配准中表现出稳健、可扩展和高效的解决方案,并在五个具有挑战性的注册任务中进行了评估,包括胸部CT/CBCT和盆腔MR/CT数据集。与基线方法相比,定量指标(如目标注册误差和Dice相似系数)证明了其在解剖学对齐方面的显著改善。此外,定性分析进一步证实了该度量在面对噪声、伪影和模态变化时的稳健性。它为临床和研究应用中注册性能的提升提供了有价值的工具。
Key Takeaways
- IMPACT是一种为无缝集成到多种图像配准框架而设计的通用语义相似性度量方法。
- 它利用大规模预训练模型的特性,可从医学图像中提取深度特征,无需特定任务训练。
- IMPACT具有稳健、可扩展和高效的解决方案,适用于跨模态图像配准。
- 在五个挑战性的注册任务中评估了IMPACT,包括使用胸部CT/CBCT和盆腔MR/CT数据集的任务。
- 与基线方法相比,IMPACT在解剖学对齐方面表现出显著改善,定量指标证明了这一点。
- 定性分析证实了IMPACT在面对噪声、伪影和模态变化时的稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

Learned Image Compression and Restoration for Digital Pathology
Authors:SeonYeong Lee, EonSeung Seong, DongEon Lee, SiYeoul Lee, Yubin Cho, Chunsu Park, Seonho Kim, MinKyung Seo, YoungSin Ko, MinWoo Kim
Digital pathology images play a crucial role in medical diagnostics, but their ultra-high resolution and large file sizes pose significant challenges for storage, transmission, and real-time visualization. To address these issues, we propose CLERIC, a novel deep learning-based image compression framework designed specifically for whole slide images (WSIs). CLERIC integrates a learnable lifting scheme and advanced convolutional techniques to enhance compression efficiency while preserving critical pathological details. Our framework employs a lifting-scheme transform in the analysis stage to decompose images into low- and high-frequency components, enabling more structured latent representations. These components are processed through parallel encoders incorporating Deformable Residual Blocks (DRB) and Recurrent Residual Blocks (R2B) to improve feature extraction and spatial adaptability. The synthesis stage applies an inverse lifting transform for effective image reconstruction, ensuring high-fidelity restoration of fine-grained tissue structures. We evaluate CLERIC on a digital pathology image dataset and compare its performance against state-of-the-art learned image compression (LIC) models. Experimental results demonstrate that CLERIC achieves superior rate-distortion (RD) performance, significantly reducing storage requirements while maintaining high diagnostic image quality. Our study highlights the potential of deep learning-based compression in digital pathology, facilitating efficient data management and long-term storage while ensuring seamless integration into clinical workflows and AI-assisted diagnostic systems. Code and models are available at: https://github.com/pnu-amilab/CLERIC.
数字病理图像在医学诊断中起着至关重要的作用,但其超高的分辨率和庞大的文件大小给存储、传输和实时可视化带来了重大挑战。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了CLERIC,这是一个基于深度学习专为全幻灯片图像(WSI)设计的图像压缩框架。CLERIC集成了一种可学习的提升方案和先进的卷积技术,以提高压缩效率的同时保留关键的病理细节。我们的框架在分析阶段采用提升方案变换,将图像分解为低频和高频成分,以实现更结构化的潜在表示。这些成分通过包含可变形残差块(DRB)和循环残差块(R2B)的并行编码器进行处理,以改善特征提取和空间适应性。合成阶段应用逆向提升变换进行有效的图像重建,确保精细纹理组织结构的高保真恢复。我们在数字病理图像数据集上评估了CLERIC的性能,并将其与最先进的学习图像压缩(LIC)模型进行了比较。实验结果表明,CLERIC在速率失真(RD)性能上表现优越,在保持高诊断图像质量的同时显著减少了存储需求。我们的研究突出了基于深度学习的压缩在数字病理学中的潜力,有助于高效的数据管理和长期存储,同时确保无缝集成到临床工作流程和人工智能辅助诊断系统中。代码和模型可在:https://github.com/pnu-amilab/CLERIC获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于深度学习的图像压缩框架CLERIC,专为全幻灯片图像(WSIs)设计,旨在解决数字病理图像在医疗诊断中的超高分辨率和大文件尺寸带来的存储、传输和实时可视化挑战。CLERIC采用可学习的提升方案和先进的卷积技术,提高压缩效率的同时保留关键的病理细节。
Key Takeaways
- 数字病理图像在医疗诊断中至关重要,但其超高分辨率和大文件尺寸带来存储、传输和实时可视化挑战。
- CLERIC是一个基于深度学习的图像压缩框架,专为全幻灯片图像(WSIs)设计。
- CLERIC采用可学习的提升方案,将图像分解为低频和高频成分,实现更结构化的潜在表示。
- 框架中的并行编码器采用可变残余块和循环残余块,改进特征提取和空间适应性。
- CLERIC在合成阶段应用逆向提升变换,实现有效的图像重建,确保细粒度组织结构的高保真恢复。
- 在数字病理图像数据集上评估CLERIC,与最先进的图像压缩模型相比,实现了优越的速率失真性能。
点此查看论文截图

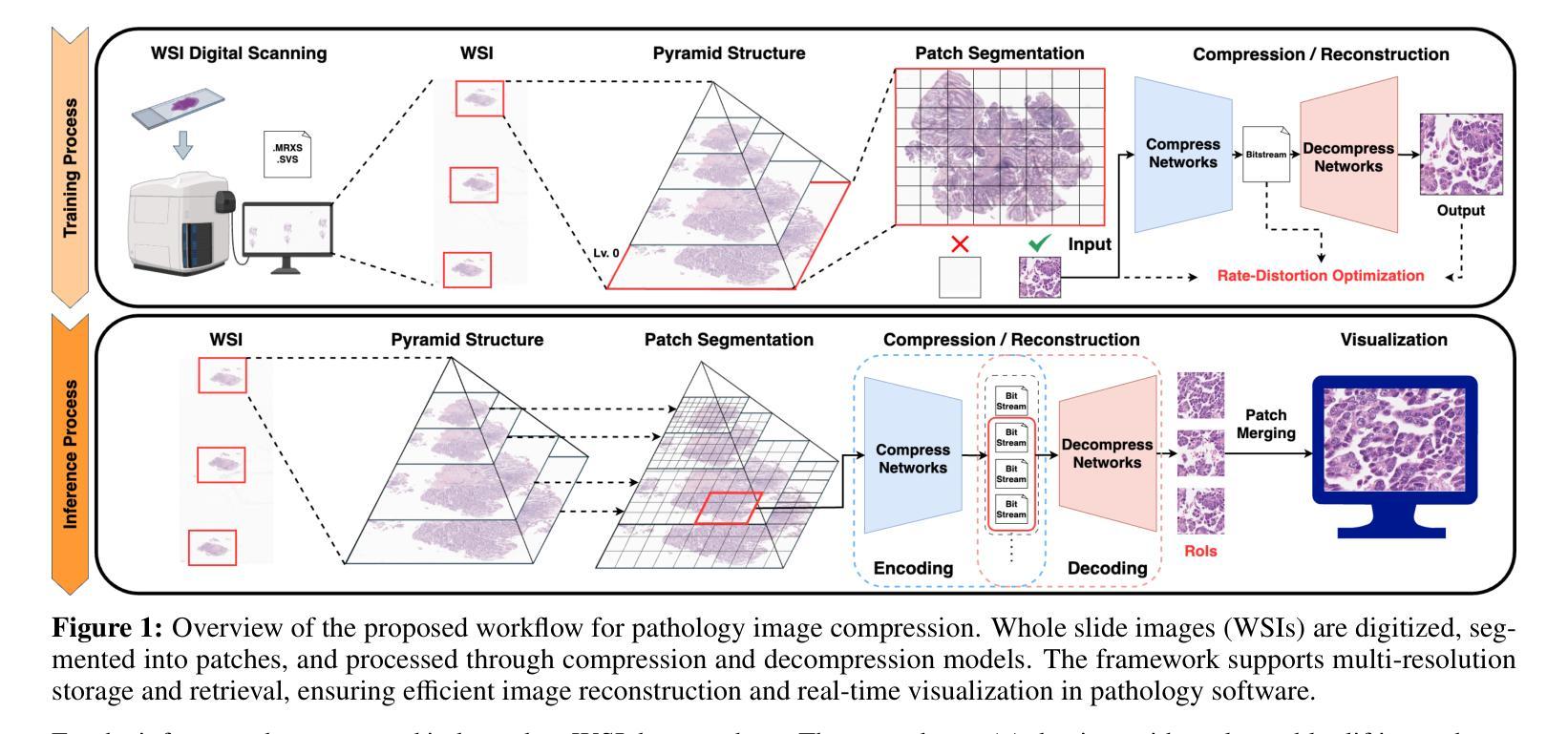
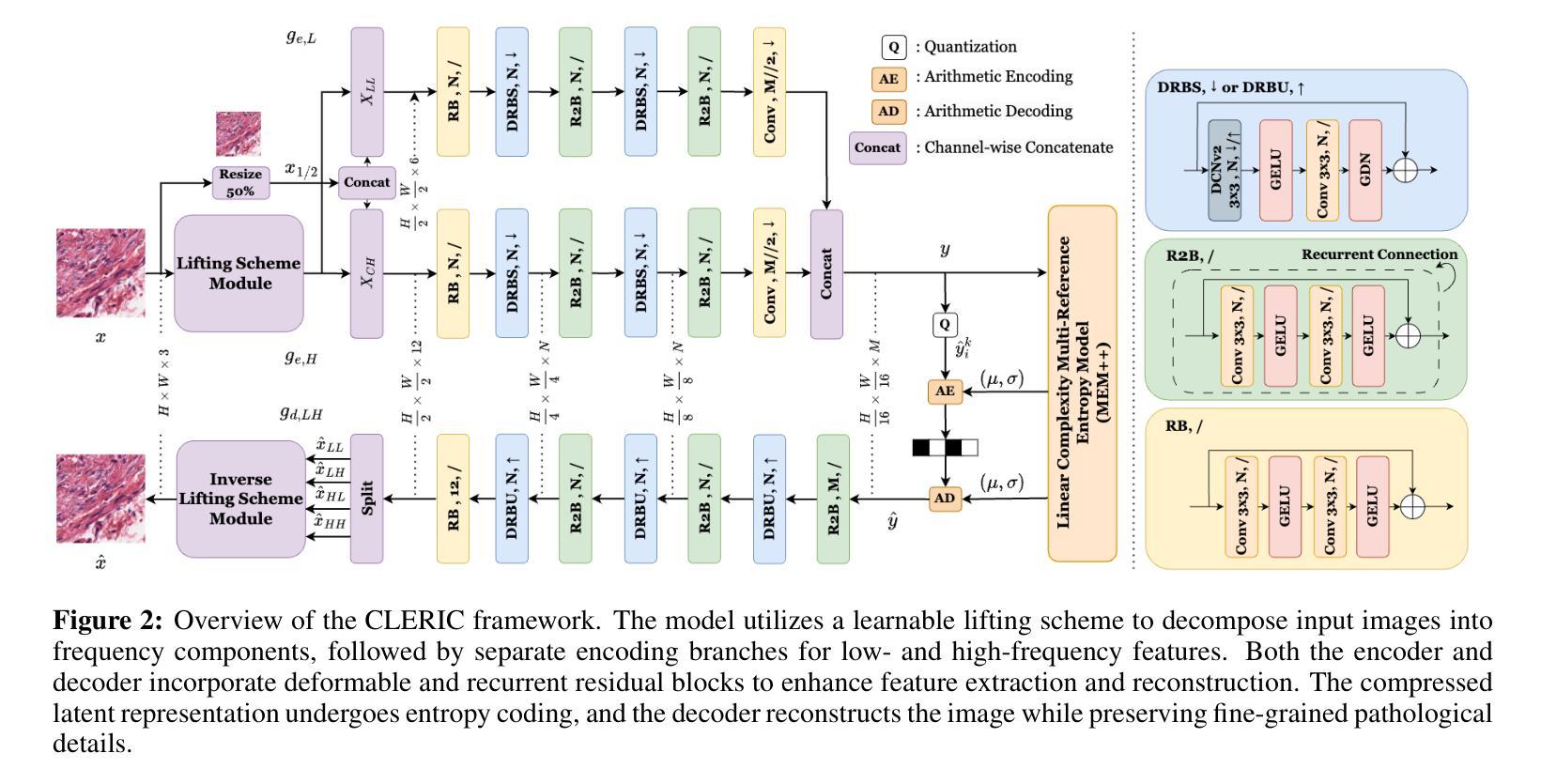
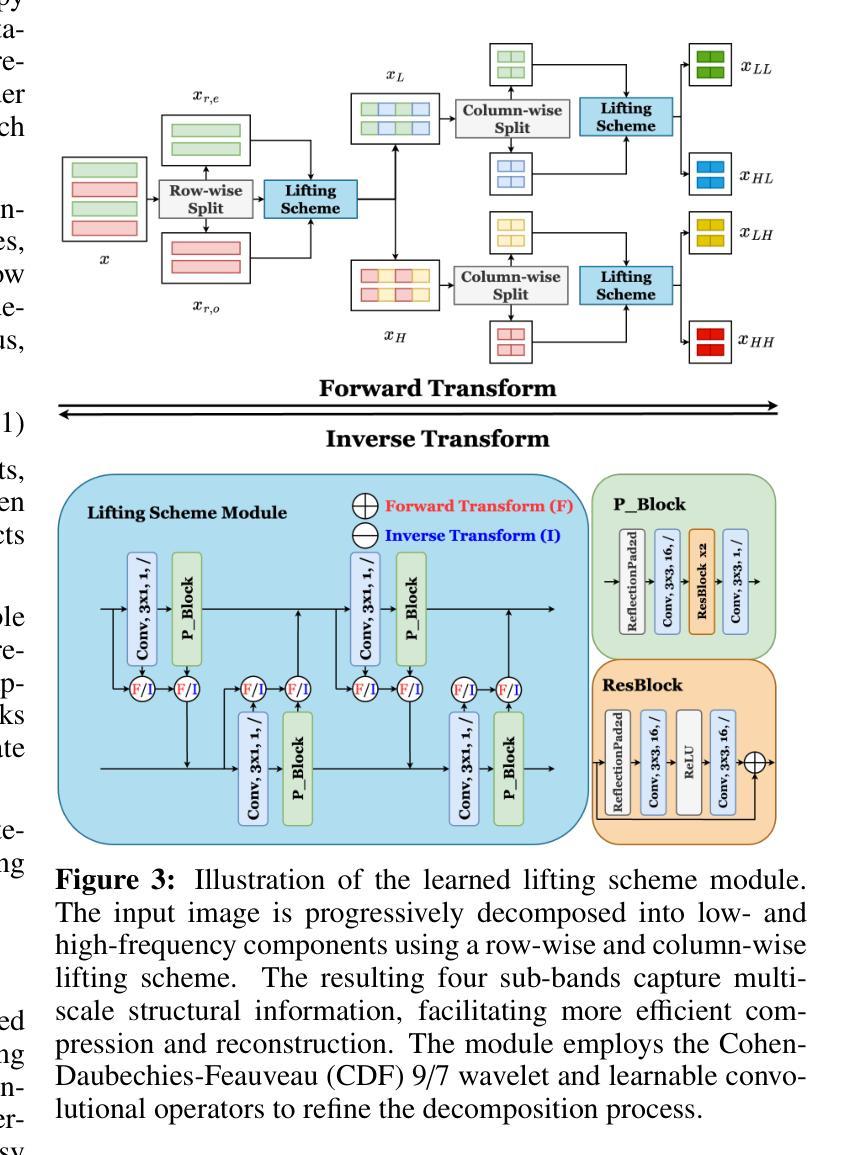
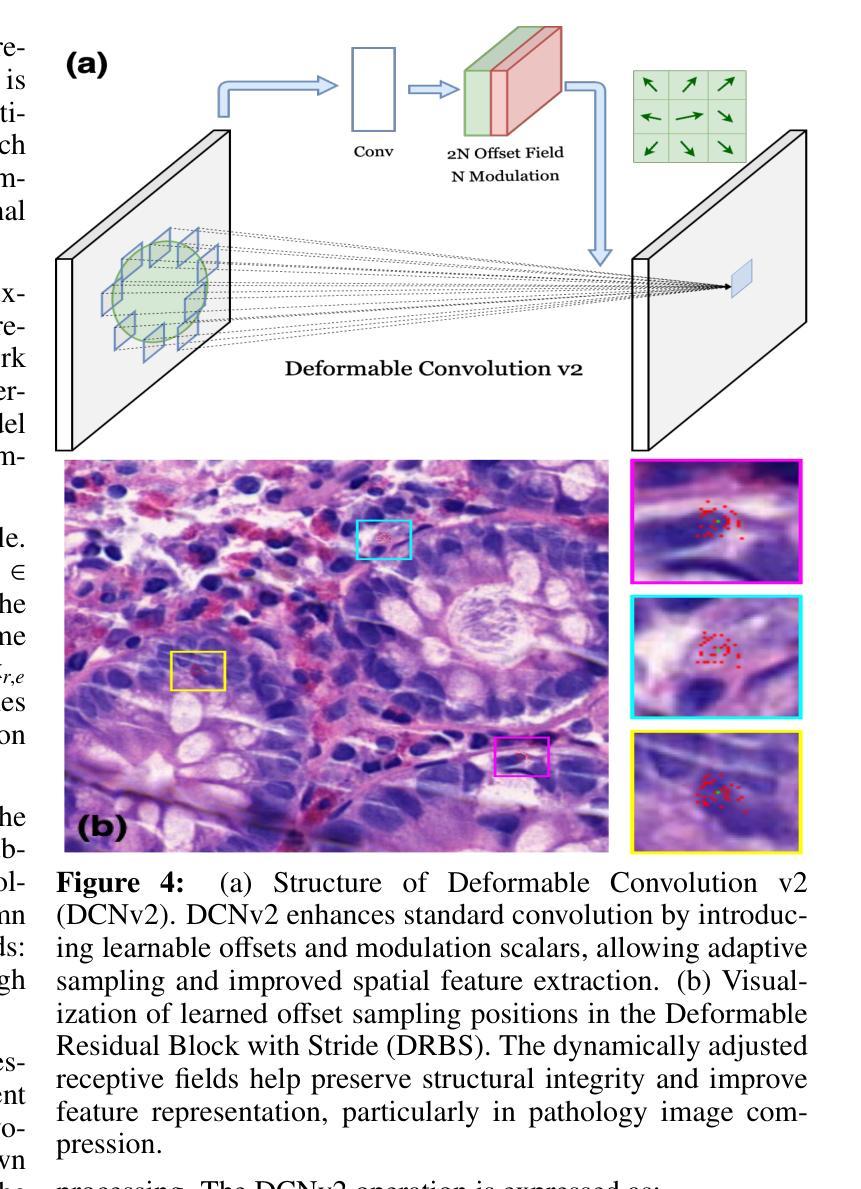
WaveFormer: A 3D Transformer with Wavelet-Driven Feature Representation for Efficient Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Md Mahfuz Al Hasan, Mahdi Zaman, Abdul Jawad, Alberto Santamaria-Pang, Ho Hin Lee, Ivan Tarapov, Kyle See, Md Shah Imran, Antika Roy, Yaser Pourmohammadi Fallah, Navid Asadizanjani, Reza Forghani
Transformer-based architectures have advanced medical image analysis by effectively modeling long-range dependencies, yet they often struggle in 3D settings due to substantial memory overhead and insufficient capture of fine-grained local features. We address these limitations with WaveFormer, a novel 3D-transformer that: i) leverages the fundamental frequency-domain properties of features for contextual representation, and ii) is inspired by the top-down mechanism of the human visual recognition system, making it a biologically motivated architecture. By employing discrete wavelet transformations (DWT) at multiple scales, WaveFormer preserves both global context and high-frequency details while replacing heavy upsampling layers with efficient wavelet-based summarization and reconstruction. This significantly reduces the number of parameters, which is critical for real-world deployment where computational resources and training times are constrained. Furthermore, the model is generic and easily adaptable to diverse applications. Evaluations on BraTS2023, FLARE2021, and KiTS2023 demonstrate performance on par with state-of-the-art methods while offering substantially lower computational complexity.
基于Transformer的架构通过有效地建模长程依赖关系,已经推动了医学图像分析的发展。然而,它们在3D环境中往往面临巨大的内存开销和精细局部特征捕捉不足的问题。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了WaveFormer,这是一种新型的3D transformer,它:(i)利用特征的基频域属性进行上下文表示;(ii)受到人类视觉识别系统的自上而下机制的启发,是一种具有生物动机的架构。通过采用多尺度的离散小波变换(DWT),WaveFormer在保留全局上下文和高频细节的同时,用高效的小波总结与重建替代复杂的上采样层。这显著减少了参数数量,对于计算资源和训练时间受限的现实世界部署环境而言至关重要。此外,该模型具有通用性,可轻松适应多种应用。在BraTS2023、FLARE2021和KiTS2023上的评估结果表明,其性能与最新方法相当,同时计算复杂度大大降低。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
波前网络(WaveFormer)是一种新型三维变压器(3D-transformer),通过利用特征的频域属性进行上下文表示,并结合人类视觉识别系统的自上而下机制,解决了当前三维设置中变压器架构面临的一些局限性。WaveFormer采用多尺度离散小波变换(DWT),保留了全局上下文和高频细节,用高效的基于小波总结与重建替换了大量的上采样层,显著减少了参数数量。该模型具有通用性,易于适应多种应用,并在BraTS2023、FLARE2021和KiTS2023上的评估显示,其性能与最先进的方法相当,但计算复杂度大幅降低。
Key Takeaways
- WaveFormer是一种针对医学图像分析的三维变压器架构。
- 它利用特征的频域属性进行上下文表示,这是其独特之处。
- 该模型受到人类视觉识别系统自上而下机制的启发。
- 通过使用离散小波变换(DWT),WaveFormer能够同时保留全局上下文和高频细节。
- WaveFormer通过高效的基于小波的方法减少计算复杂性。
- 该模型具有通用性,可以很容易地适应不同的医学图像分析应用。
点此查看论文截图

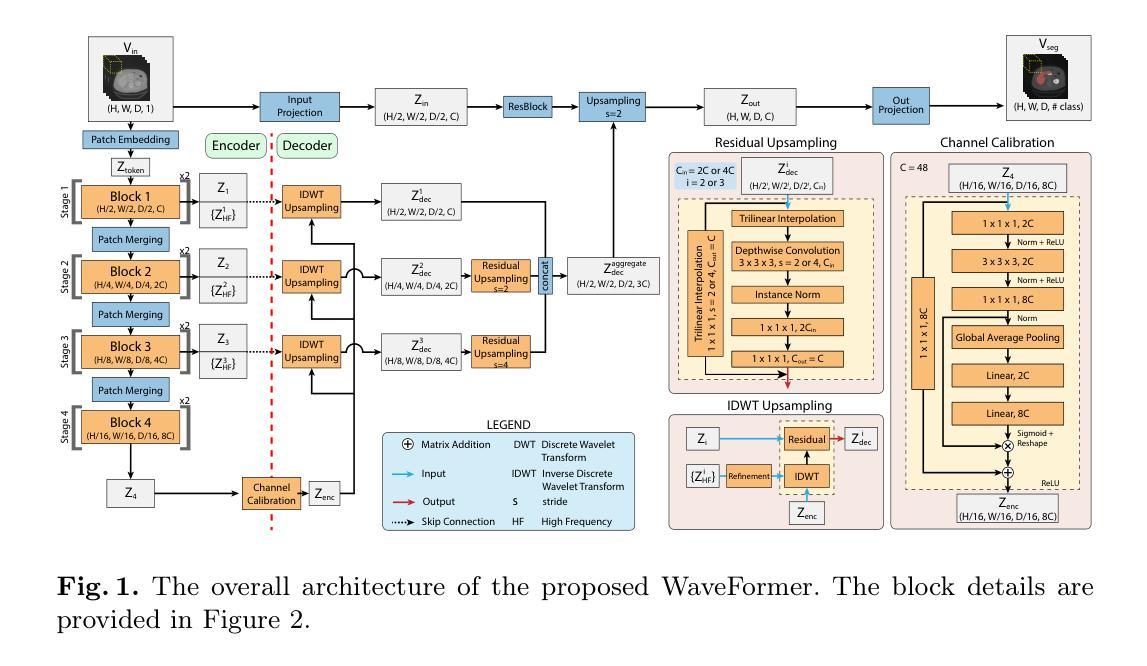
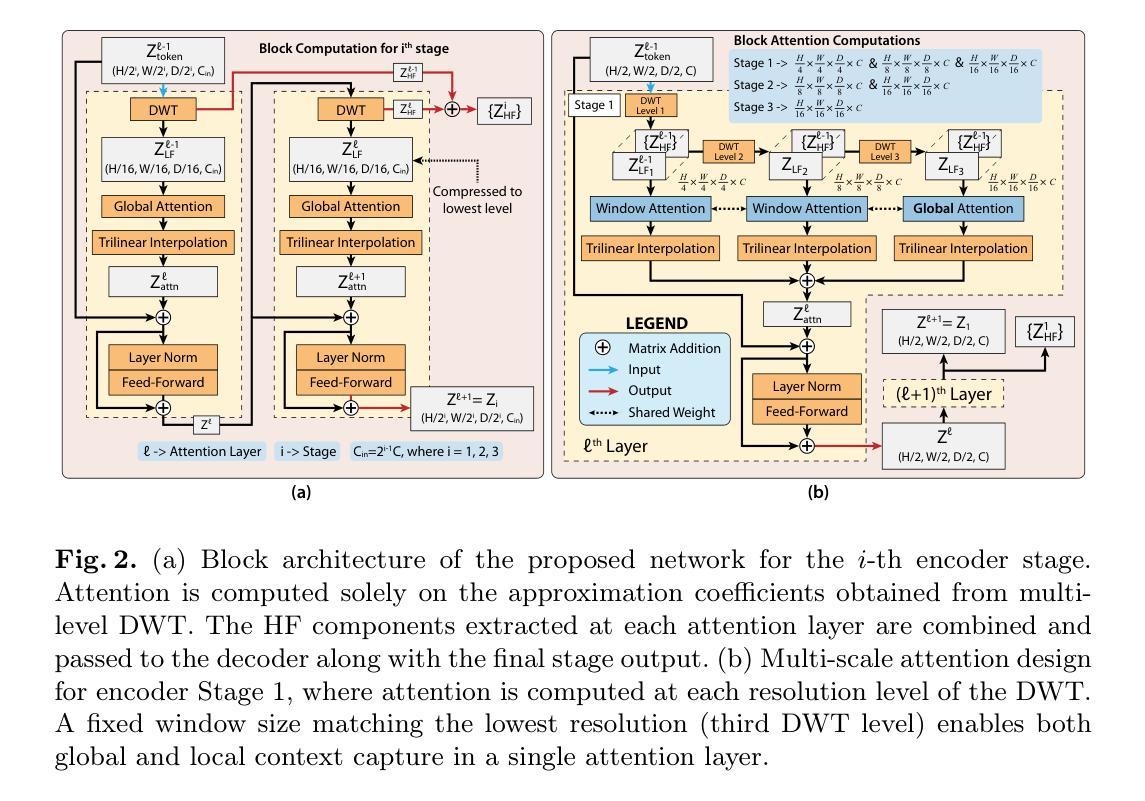
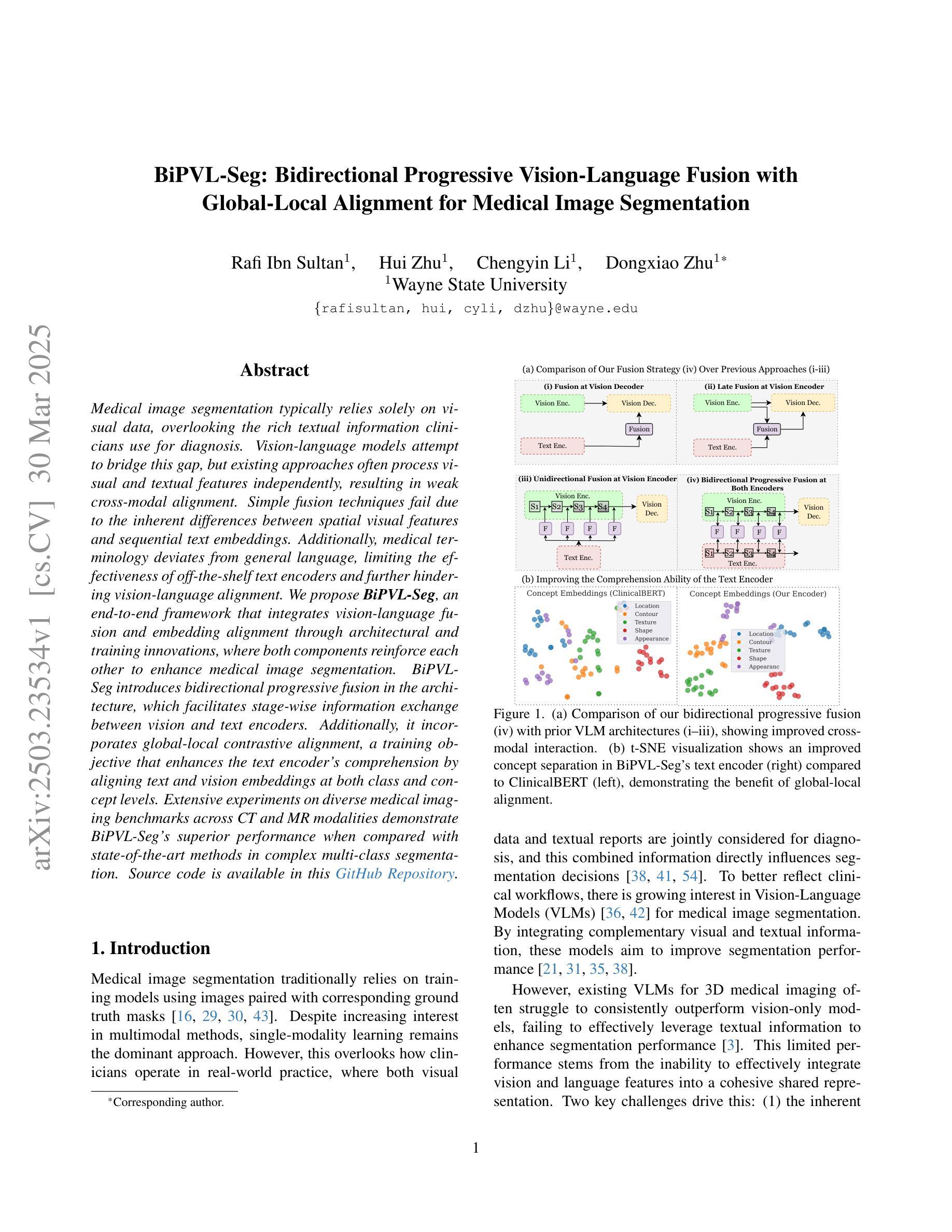
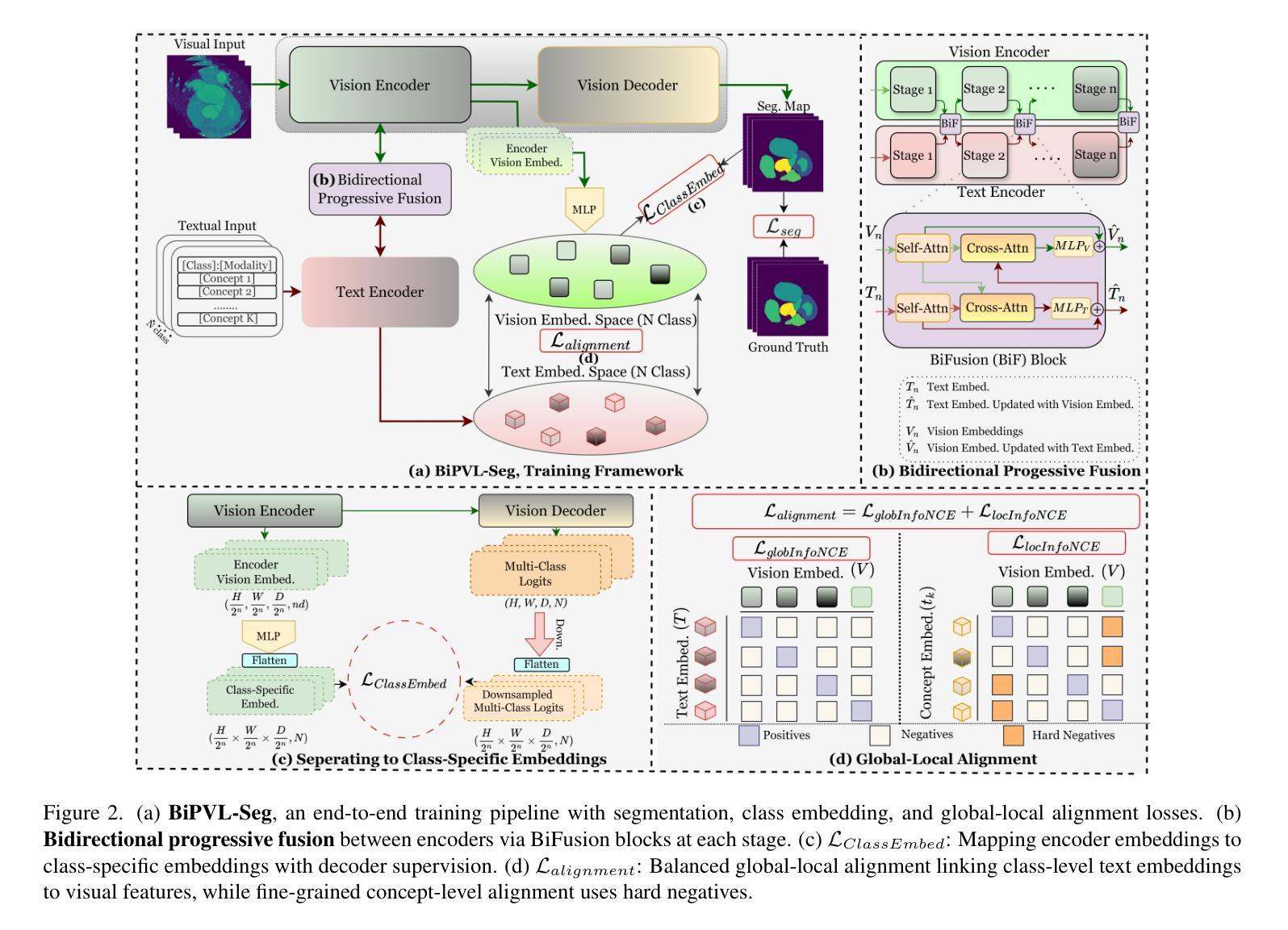
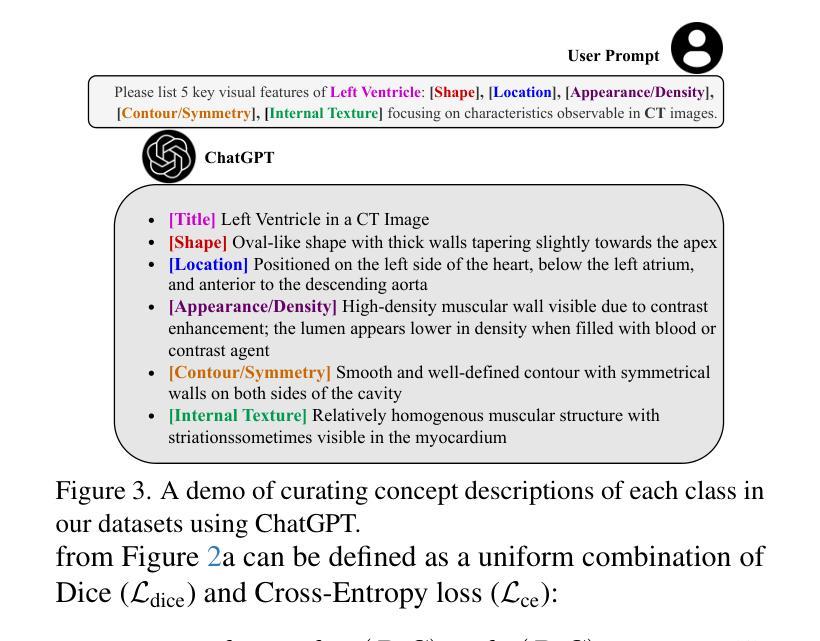
BiPVL-Seg: Bidirectional Progressive Vision-Language Fusion with Global-Local Alignment for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Rafi Ibn Sultan, Hui Zhu, Chengyin Li, Dongxiao Zhu
Medical image segmentation typically relies solely on visual data, overlooking the rich textual information clinicians use for diagnosis. Vision-language models attempt to bridge this gap, but existing approaches often process visual and textual features independently, resulting in weak cross-modal alignment. Simple fusion techniques fail due to the inherent differences between spatial visual features and sequential text embeddings. Additionally, medical terminology deviates from general language, limiting the effectiveness of off-the-shelf text encoders and further hindering vision-language alignment. We propose BiPVL-Seg, an end-to-end framework that integrates vision-language fusion and embedding alignment through architectural and training innovations, where both components reinforce each other to enhance medical image segmentation. BiPVL-Seg introduces bidirectional progressive fusion in the architecture, which facilitates stage-wise information exchange between vision and text encoders. Additionally, it incorporates global-local contrastive alignment, a training objective that enhances the text encoder’s comprehension by aligning text and vision embeddings at both class and concept levels. Extensive experiments on diverse medical imaging benchmarks across CT and MR modalities demonstrate BiPVL-Seg’s superior performance when compared with state-of-the-art methods in complex multi-class segmentation. Source code is available in this GitHub repository.
医学图像分割通常仅依赖于视觉数据,忽略了临床医生用于诊断的丰富文本信息。视听语言模型试图弥合这一鸿沟,但现有方法通常独立处理视觉和文本特征,导致跨模态对齐效果不佳。由于空间视觉特征和顺序文本嵌入之间的固有差异,简单的融合技术会失败。此外,医学术语与通用语言有偏差,限制了现成的文本编码器的有效性,并进一步阻碍了视听语言对齐。我们提出了BiPVL-Seg,这是一个端到端的框架,通过架构和训练创新,将视听语言融合和嵌入对齐相结合,两个组件相互增强,以提高医学图像分割的效果。BiPVL-Seg在架构中引入了双向渐进融合,便于视听编码器之间分阶段的信息交换。此外,它结合了全局局部对比对齐,这是一个训练目标,通过对齐文本和视觉嵌入的类别和概念级别,提高文本编码器的理解能力。在CT和MR模态的多种医学成像基准测试上的广泛实验表明,与最新方法相比,BiPVL-Seg在复杂的多类分割中具有卓越的性能。源代码可在GitHub仓库中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分割常仅依赖视觉数据,忽略了临床医生用于诊断的丰富文本信息。本研究提出BiPVL-Seg框架,通过架构和训练创新实现视觉语言融合和嵌入对齐,提升医学图像分割效果。该框架引入双向渐进融合,促进视觉和文本编码器之间的阶段性信息交流。同时采用全局局部对比对齐训练目标,提高文本编码器对医学术语的理解,实现文本与视觉嵌入的类别和概念级别对齐。在多种医学影像基准测试上的实验表明,BiPVL-Seg在复杂多类分割中的性能优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割常依赖视觉数据而忽视临床文本信息。
- BiPVL-Seg框架通过视觉与语言的融合与嵌入对齐提升医学图像分割效果。
- BiPVL-Seg引入双向渐进融合促进视觉和文本编码器的信息交流。
- 全局局部对比对齐训练目标用于提高文本编码器对医学术语的理解。
- BiPVL-Seg在多样医学影像基准测试中表现优异。
- BiPVL-Seg可实现文本与视觉嵌入的类别和概念级别对齐。
点此查看论文截图
Federated Self-Supervised Learning for One-Shot Cross-Modal and Cross-Imaging Technique Segmentation
Authors:Siladittya Manna, Suresh Das, Sayantari Ghosh, Saumik Bhattacharya
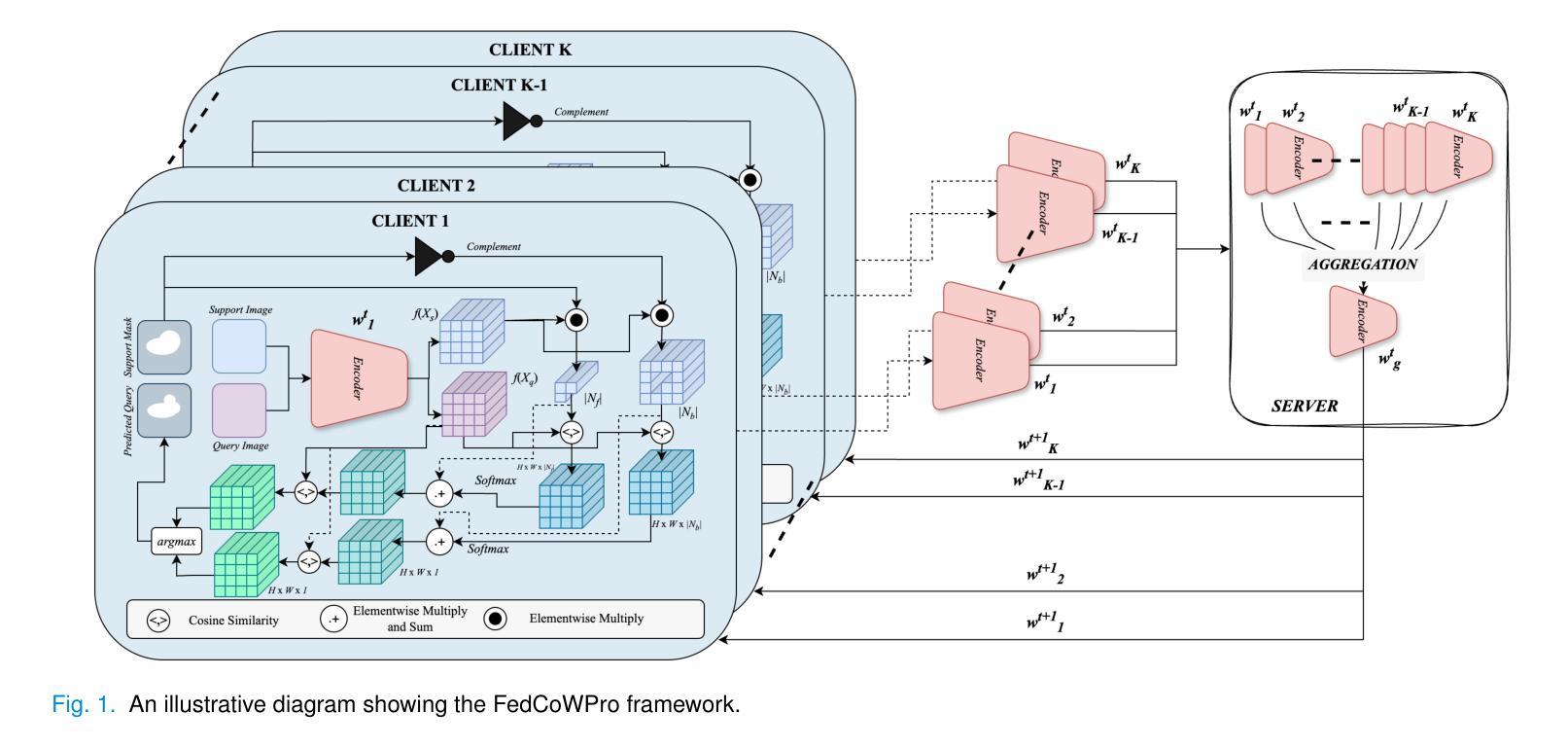
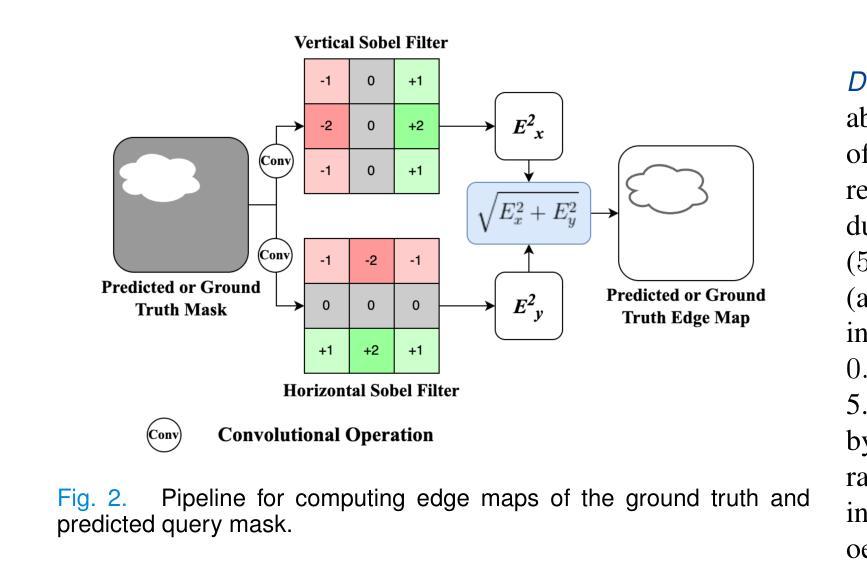
Decentralized federated learning enables learning of data representations from multiple sources without compromising the privacy of the clients. In applications like medical image segmentation, where obtaining a large annotated dataset from a single source is a distressing problem, federated self-supervised learning can provide some solace. In this work, we push the limits further by exploring a federated self-supervised one-shot segmentation task representing a more data-scarce scenario. We adopt a pre-existing self-supervised few-shot segmentation framework CoWPro and adapt it to the federated learning scenario. To the best of our knowledge, this work is the first to attempt a self-supervised few-shot segmentation task in the federated learning domain. Moreover, we consider the clients to be constituted of data from different modalities and imaging techniques like MR or CT, which makes the problem even harder. Additionally, we reinforce and improve the baseline CoWPro method using a fused dice loss which shows considerable improvement in performance over the baseline CoWPro. Finally, we evaluate this novel framework on a completely unseen held-out part of the local client dataset. We observe that the proposed framework can achieve performance at par or better than the FedAvg version of the CoWPro framework on the held-out validation dataset.
分布式联邦学习能够从多个源学习数据表示,而不损害客户端的隐私。在医学图像分割等应用中,从单一来源获取大量标注数据集是一个令人头疼的问题,联邦自监督学习可以提供一些慰藉。在这项工作中,我们通过探索联邦自监督一次分割任务,进一步拓展了界限,这代表了一个数据更稀缺的场景。我们采用预先存在的自监督少镜头分割框架CoWPro,并将其适应于联邦学习场景。据我们所知,这是首次尝试在联邦学习领域进行自监督少镜头分割任务。而且,我们认为客户端由不同模态和数据成像技术(如MR或CT)构成的数据组成,这使得问题变得更加困难。此外,我们使用融合Dice损失来加强和改进基线CoWPro方法,与基线CoWPro相比,它在性能上显示出显著改进。最后,我们在本地客户端数据集的完全未见过的保留部分上评估了这种新型框架。我们发现,在保留的验证数据集上,所提出的框架的性能可以达到或超过CoWPro框架的FedAvg版本。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
联邦化自我监督的一站式分割任务在医学图像分割中的应用实现了数据稀缺场景下的学习。该研究采用现有的自我监督少样本分割框架CoWPro,并适应联邦学习场景。这是首次尝试在联邦学习领域进行自监督的少量样本分割任务,解决了从多个来源获取大量标注数据的问题。该研究还融合了不同模态和成像技术的数据,如MR或CT,提高了基线CoWPro方法使用融合Dice损失的改进版性能,并在本地客户端数据集的未见部分进行了评估。评估结果显示,该框架的性能可与CoWPro的FedAvg版本相当或更好。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦化自我监督学习用于医学图像分割,能在数据稀缺场景下学习数据表示。
- 采用并改进了现有的自我监督少样本分割框架CoWPro,适应联邦学习场景。
- 此研究是首次在联邦学习领域尝试自监督的少量样本分割任务。
- 研究考虑了不同模态和成像技术的数据,如MR或CT。
- 使用了融合Dice损失的改进版CoWPro方法,提高了性能。
- 在本地客户端数据集的未见部分进行了评估。
点此查看论文截图

Evolutionary Prompt Optimization Discovers Emergent Multimodal Reasoning Strategies in Vision-Language Models
Authors:Sid Bharthulwar, John Rho, Katrina Brown
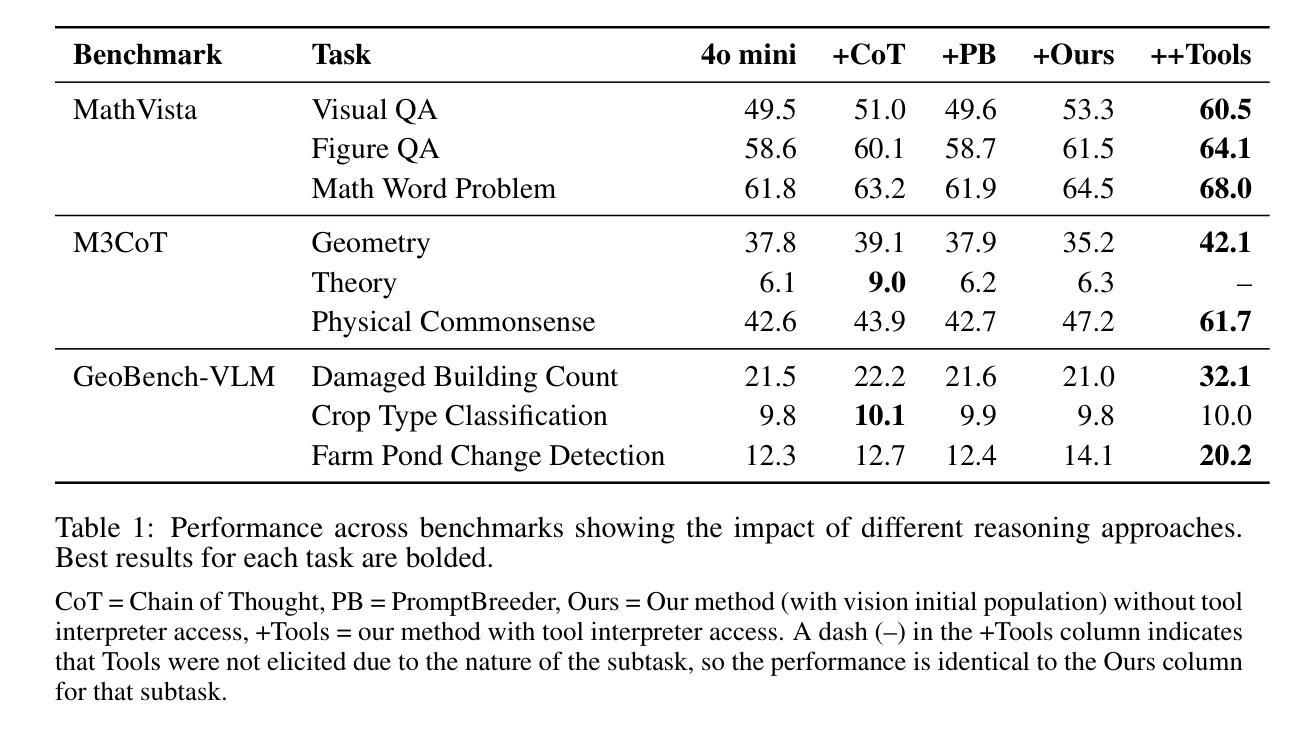
We present a framework for optimizing prompts in vision-language models to elicit multimodal reasoning without model retraining. Using an evolutionary algorithm to guide prompt updates downstream of visual tasks, our approach improves upon baseline prompt-updating algorithms, which lack evolution-style “survival of the fittest” iteration. Crucially, we find this approach enables the language model to independently discover progressive problem-solving techniques across several evolution generations. For example, the model reasons that to “break down” visually complex spatial tasks, making a tool call to a Python interpreter to perform tasks (such as cropping, image segmentation, or saturation changes) would improve performance significantly. Our experimentation shows that explicitly evoking this “tool calling” call, via system-level XML $…\texttt{
我们提出了一种优化视觉语言模型提示的框架,以激发多模态推理而无需重新训练模型。我们使用进化算法来指导视觉任务下游的提示更新,我们的方法改进了基线提示更新算法,后者缺乏进化式的“适者生存”迭代。关键的是,我们发现这种方法使语言模型能够在多个进化世代中独立地发现渐进的问题解决技术。例如,模型推理出为了“分解”视觉上复杂的空间任务,调用Python解释器执行一些任务(如裁剪、图像分割或饱和度更改)将显著提高性能。我们的实验表明,通过系统级别的XML `$…\texttt{
} … \texttt{ }…$ 标签显式调用这种“工具调用”,可以有效地标记同一语言模型的Python解释器访问,以生成相关程序,从而产生高级多模态功能。此功能可以转化为系统级别的提示,在推理时间时提高性能,我们的实验表明,在某些视觉任务上相对改进了高达约50%。下游性能是在MathVista、M3CoT和GeoBench-VLM数据集的任务中进行训练和评估的。重要的是,我们的方法表明,进化提示优化指导语言模型进行自我推理发现,从而导致任务之间的零样本泛化能力提高。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at ICLR 2025 Workshop on Reasoning and Planning for LLMs
Summary
优化视觉语言模型提示框架,促进多模态推理,无需模型重训。利用进化算法引导视觉任务下游的提示更新,改进基础提示更新算法。模型独立发现跨多代进化的渐进问题解决技术。例如,模型推理出利用Python解释器执行裁剪、图像分割或饱和度更改等任务能显著提高性能。通过系统级别的XML标签明确调用Python解释器访问功能,将其融入系统级别的提示中,可在推理时间提高性能表现,实验结果显该功能在某些视觉任务中提高相对性能达约50%。训练和评估范围包括MathVista、M3CoT和GeoBench-VLM数据集的任务。方法显示进化提示优化可引导语言模型进行自我推理发现,提高跨任务的零样本泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 框架使用进化算法优化视觉语言模型的提示,以促进多模态推理。
- 与基础提示更新算法相比,进化算法能更好地改进性能。
- 模型能够独立发现渐进问题解决技术,通过多代进化改善性能。
- 通过系统级XML标签明确调用Python等解释器执行特定任务可以提高性能。
- 将这些功能融入系统级提示中,在推理时间提高性能表现。
- 实验结果显示在某些视觉任务中性能提高达约50%。
- 训练和评估涵盖MathVista、M3CoT和GeoBench-VLM数据集的任务。
点此查看论文截图