⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-04 更新
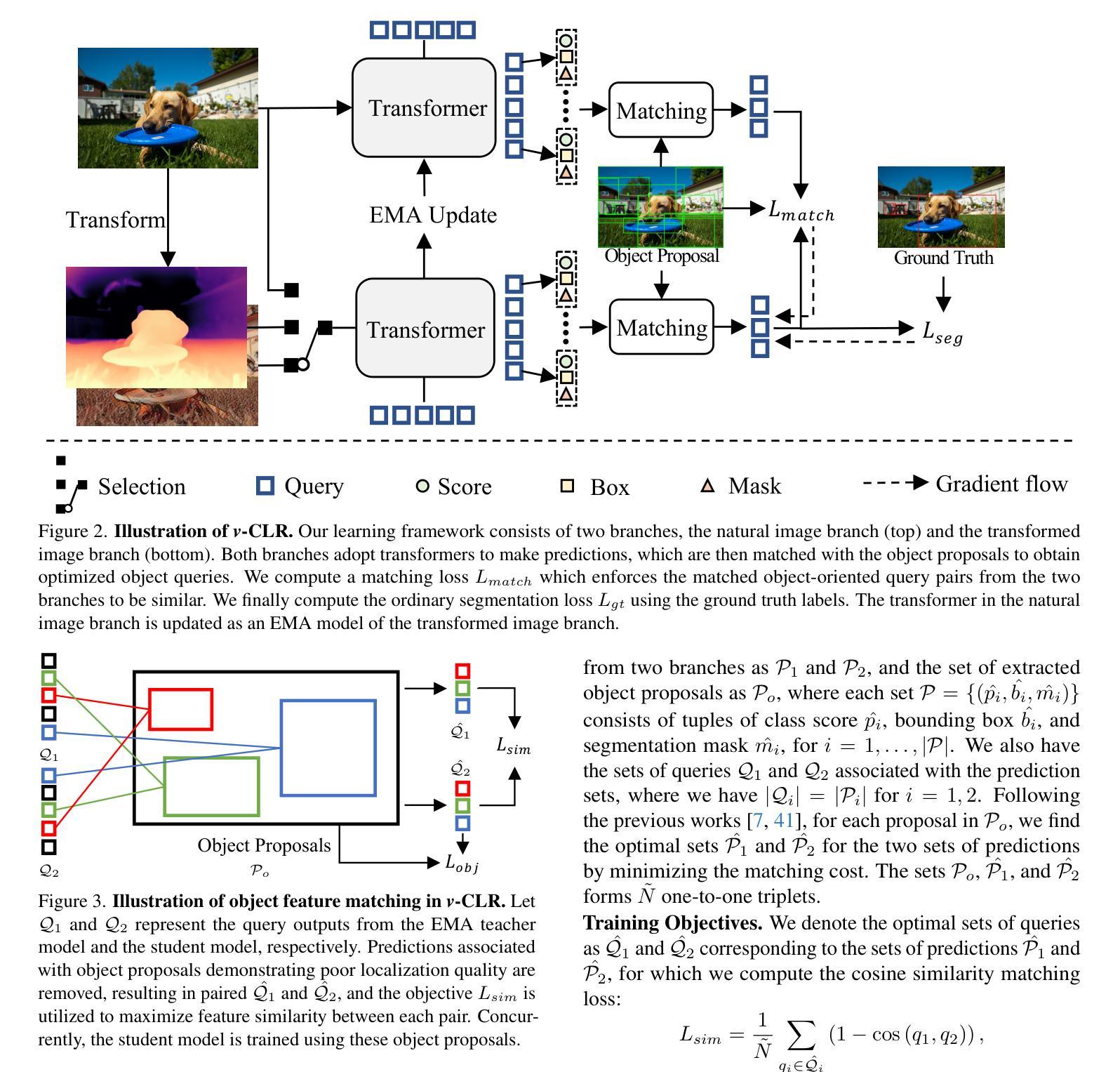
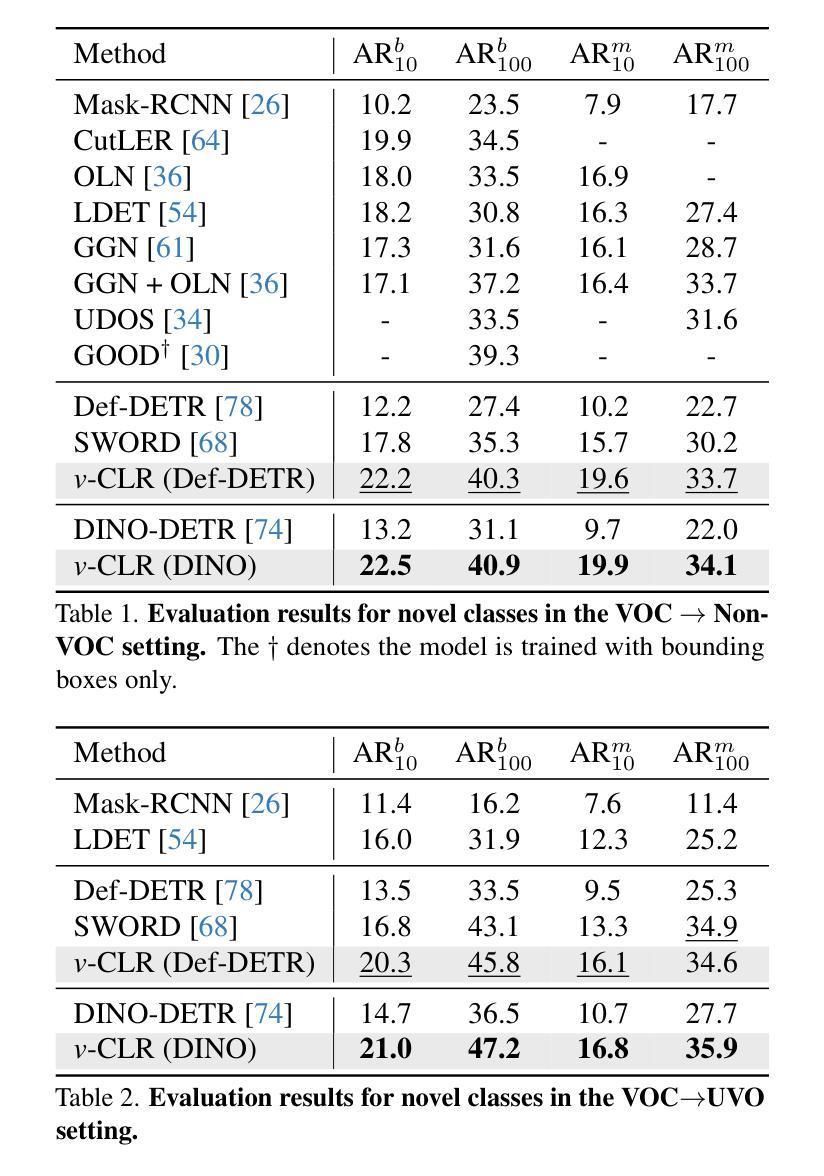
v-CLR: View-Consistent Learning for Open-World Instance Segmentation
Authors:Chang-Bin Zhang, Jinhong Ni, Yujie Zhong, Kai Han
In this paper, we address the challenging problem of open-world instance segmentation. Existing works have shown that vanilla visual networks are biased toward learning appearance information, \eg texture, to recognize objects. This implicit bias causes the model to fail in detecting novel objects with unseen textures in the open-world setting. To address this challenge, we propose a learning framework, called view-Consistent LeaRning (v-CLR), which aims to enforce the model to learn appearance-invariant representations for robust instance segmentation. In v-CLR, we first introduce additional views for each image, where the texture undergoes significant alterations while preserving the image’s underlying structure. We then encourage the model to learn the appearance-invariant representation by enforcing the consistency between object features across different views, for which we obtain class-agnostic object proposals using off-the-shelf unsupervised models that possess strong object-awareness. These proposals enable cross-view object feature matching, greatly reducing the appearance dependency while enhancing the object-awareness. We thoroughly evaluate our method on public benchmarks under both cross-class and cross-dataset settings, achieving state-of-the-art performance. Project page: https://visual-ai.github.io/vclr
本文解决了开放世界实例分割的挑战性问题。现有工作表明,普通视觉网络在学习识别物体时偏向于外观信息,例如纹理。这种隐性偏见导致模型在开放世界环境中检测具有未见纹理的新物体时失败。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了一种学习框架,称为视图一致性学习(v-CLR),旨在强制模型学习鲁棒的外观不变表示来进行稳健的实例分割。在v-CLR中,我们首先为每张图像引入额外的视图,其中纹理经历了显著的变化,同时保留了图像的基本结构。然后,我们通过强制不同视图之间对象特征的一致性,鼓励模型学习外观不变表示。为此,我们使用现成的具有强烈对象意识的非监督模型获得类无关的对象提案。这些提案实现了跨视图对象特征匹配,大大降低了外观依赖性,同时增强了对象意识。我们在公共基准测试上彻底评估了我们的方法,在跨类和跨数据集设置下均实现了最先进的性能。项目页面:https://visual-ai.github.io/vclr
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025, Project page: https://visual-ai.github.io/vclr, Code: https://github.com/Visual-AI/vCLR
Summary
本文解决开放世界实例分割的挑战性问题。现有视觉网络倾向于学习外观信息(如纹理)来识别物体,导致模型在检测开放世界中未见纹理的新物体时失败。为此,本文提出一种学习框架——视图一致性学习(v-CLR),旨在强制模型学习鲁棒的、对外观变化的表示,以实现稳健的实例分割。v-CLR通过引入图像的不同视图,在保持图像底层结构的同时,使纹理发生显著变化。然后,通过在不同视图间保持对象特征的一致性,鼓励模型学习外观不变的表示。利用通用的无监督模型生成类无关的对象提案,这些提案具有强烈的对象意识,能够实现跨视图的对象特征匹配,从而极大地减少了外观依赖性,提高了对象意识。在公共基准测试上的评估结果表明,该方法在跨类和跨数据集设置下均达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 本文解决开放世界实例分割中的挑战,指出现有视觉网络倾向于学习外观信息,导致在新环境下识别失败。
- 提出一种名为v-CLR的学习框架,通过引入不同视图来学习外观不变的表示,以提高模型的鲁棒性。
- v-CLR在保持图像底层结构的同时,使纹理发生显著变化。
- 利用无监督模型生成类无关的对象提案,实现跨视图的对象特征匹配。
- 该方法减少了外观依赖性,提高了对象意识。
- 在公共基准测试上的评估结果表明,v-CLR在跨类和跨数据集设置下均达到了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

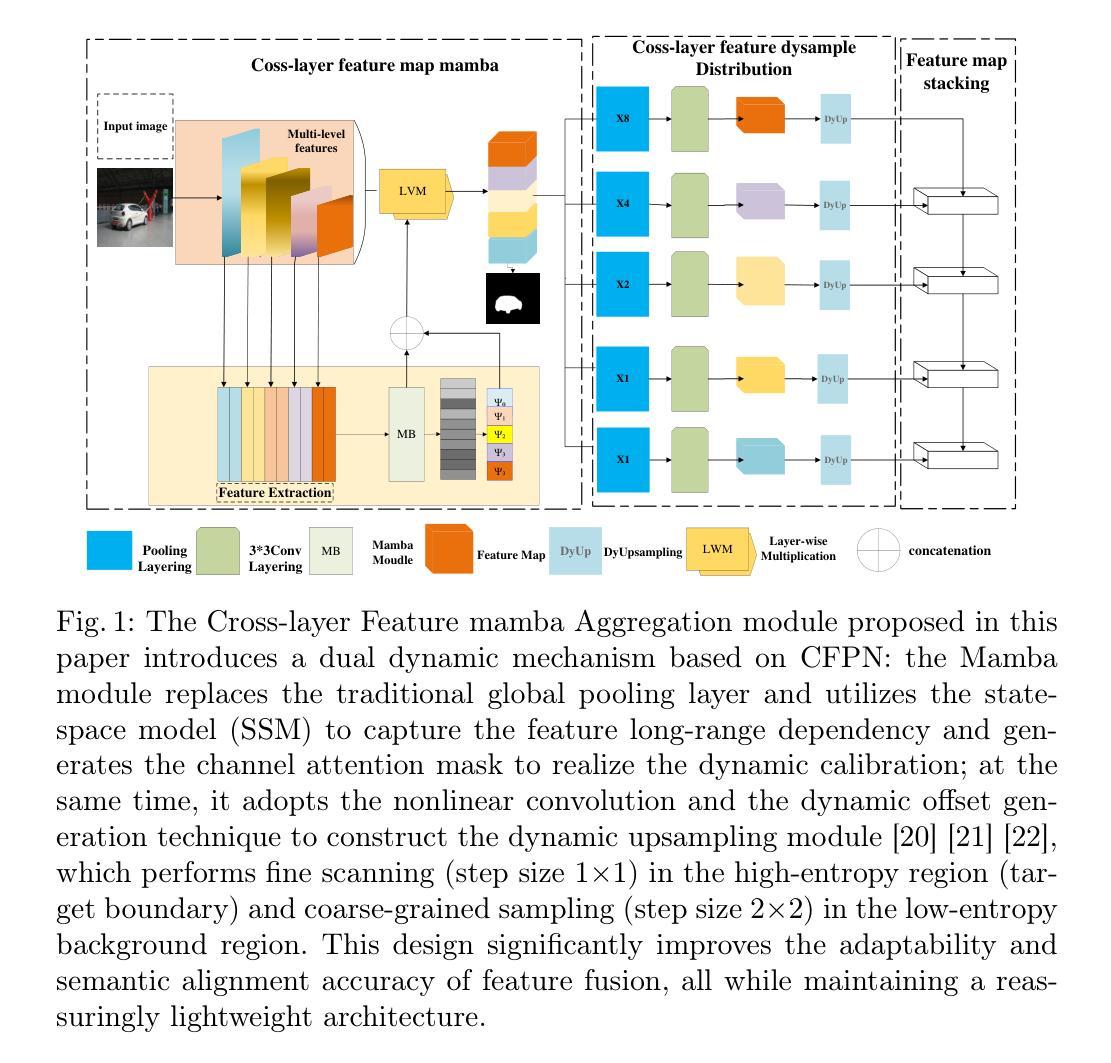
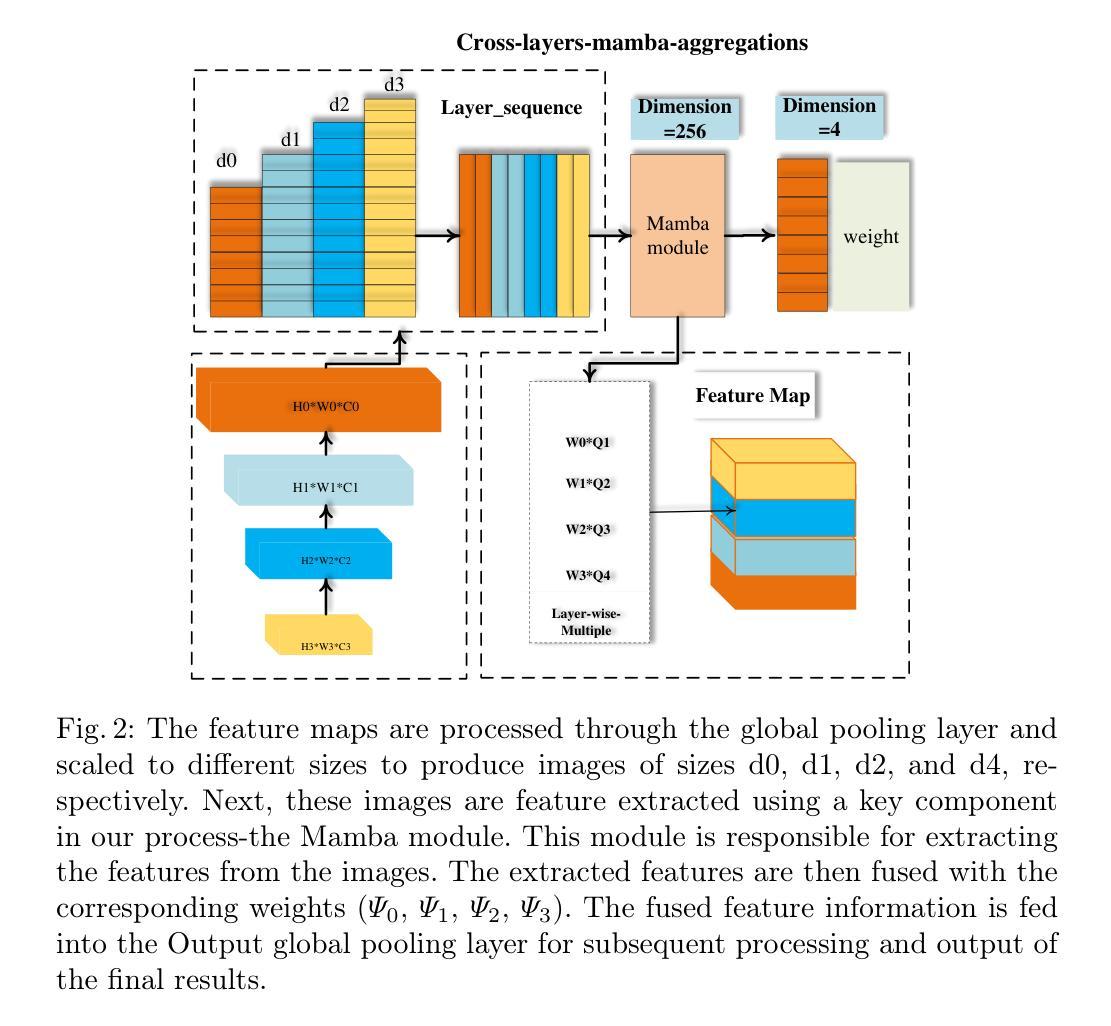
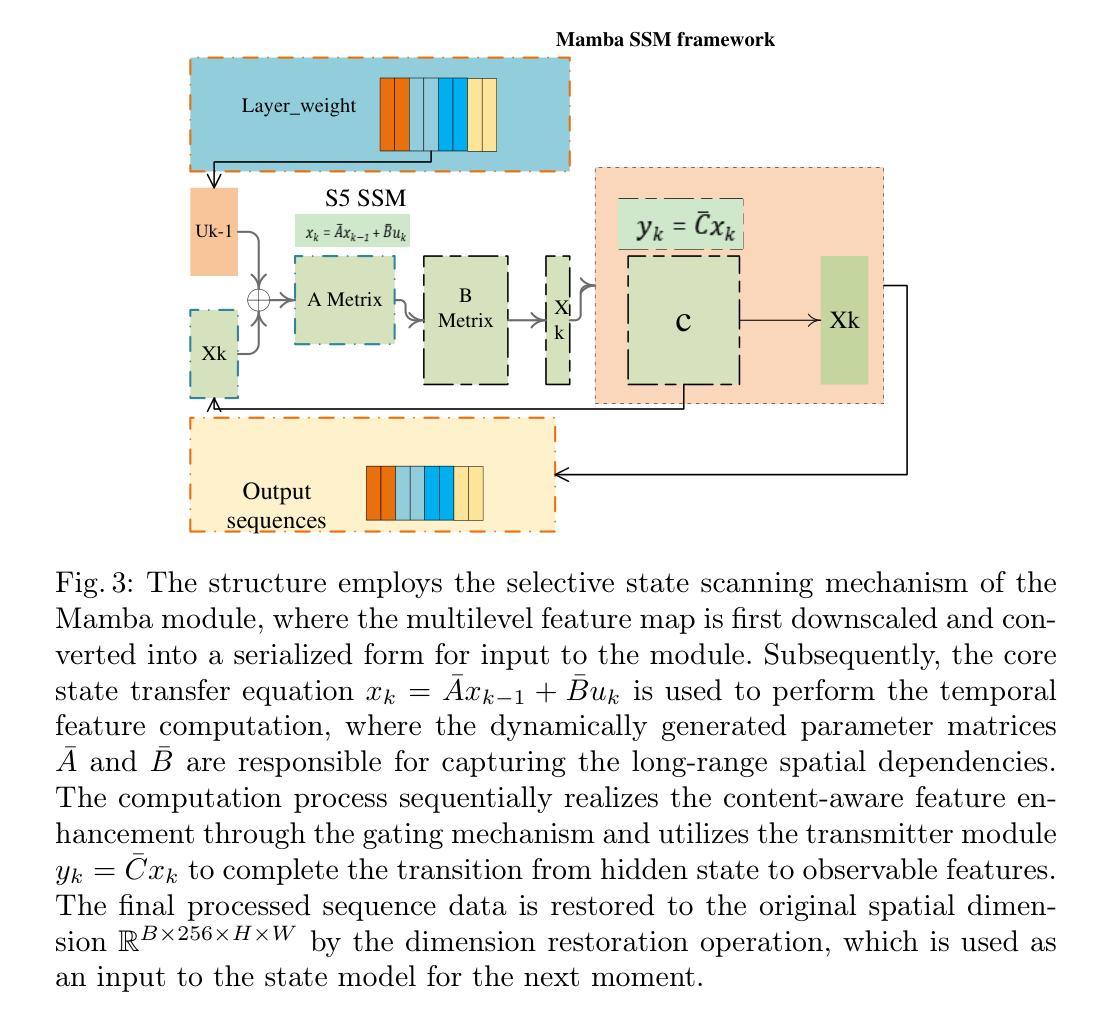
CFMD: Dynamic Cross-layer Feature Fusion for Salient Object Detection
Authors:Jin Lian, Zhongyu Wan, Ming Gao, JunFeng Chen
Cross-layer feature pyramid networks (CFPNs) have achieved notable progress in multi-scale feature fusion and boundary detail preservation for salient object detection. However, traditional CFPNs still suffer from two core limitations: (1) a computational bottleneck caused by complex feature weighting operations, and (2) degraded boundary accuracy due to feature blurring in the upsampling process. To address these challenges, we propose CFMD, a novel cross-layer feature pyramid network that introduces two key innovations. First, we design a context-aware feature aggregation module (CFLMA), which incorporates the state-of-the-art Mamba architecture to construct a dynamic weight distribution mechanism. This module adaptively adjusts feature importance based on image context, significantly improving both representation efficiency and generalization. Second, we introduce an adaptive dynamic upsampling unit (CFLMD) that preserves spatial details during resolution recovery. By adjusting the upsampling range dynamically and initializing with a bilinear strategy, the module effectively reduces feature overlap and maintains fine-grained boundary structures. Extensive experiments on three standard benchmarks using three mainstream backbone networks demonstrate that CFMD achieves substantial improvements in pixel-level accuracy and boundary segmentation quality, especially in complex scenes. The results validate the effectiveness of CFMD in jointly enhancing computational efficiency and segmentation performance, highlighting its strong potential in salient object detection tasks.
跨层特征金字塔网络(CFPNs)在显著目标检测的尺度特征融合和边界细节保留方面取得了显著的进展。然而,传统的CFPNs仍然存在两个核心局限性:(1)由于复杂的特征加权操作导致的计算瓶颈;(2)由于上采样过程中的特征模糊而导致的边界精度下降。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了CFMD,这是一种新型跨层特征金字塔网络,它引入了两个关键创新点。首先,我们设计了上下文感知特征聚合模块(CFLMA),它结合了最先进的Mamba架构来构建动态权重分布机制。该模块根据图像上下文自适应地调整特征重要性,显著提高了表征效率和泛化能力。其次,我们引入了一个自适应动态上采样单元(CFLMD),在分辨率恢复过程中保留空间细节。通过动态调整上采样范围并使用双线性策略进行初始化,该模块有效地减少了特征重叠并保持精细的边界结构。在三个标准基准测试上对三种主流骨干网络的大量实验表明,CFMD在像素级精度和边界分割质量方面取得了显著提高,尤其是在复杂场景中。结果验证了CFMD在提高计算效率和分割性能方面的有效性,突显了其在显著目标检测任务中的强大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
CFMD网络解决了传统特征金字塔网络在计算瓶颈和边界精度下降的问题。通过引入上下文感知特征聚合模块和自适应动态上采样单元,CFMD网络提高了多尺度特征融合和边界细节保留的效果,显著提升了显著性目标检测的像素级精度和边界分割质量。
Key Takeaways:
- CFMD网络针对传统特征金字塔网络的两个核心问题进行了改进:计算瓶颈和边界精度下降。
- CFMD网络引入了上下文感知特征聚合模块(CFLMA),结合Mamba架构构建动态权重分布机制,自适应调整特征重要性。
- CFMD网络通过自适应动态上采样单元(CFLMD)在分辨率恢复过程中保留空间细节,有效减少特征重叠并保持精细的边界结构。
- CFMD网络在三个标准基准测试上的实验结果表明,其像素级精度和边界分割质量有显著提高,尤其在复杂场景中表现更优秀。
- CFMD网络联合提高了计算效率和分割性能,凸显了其在显著性目标检测任务中的强大潜力。
- 实验结果验证了CFMD网络的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

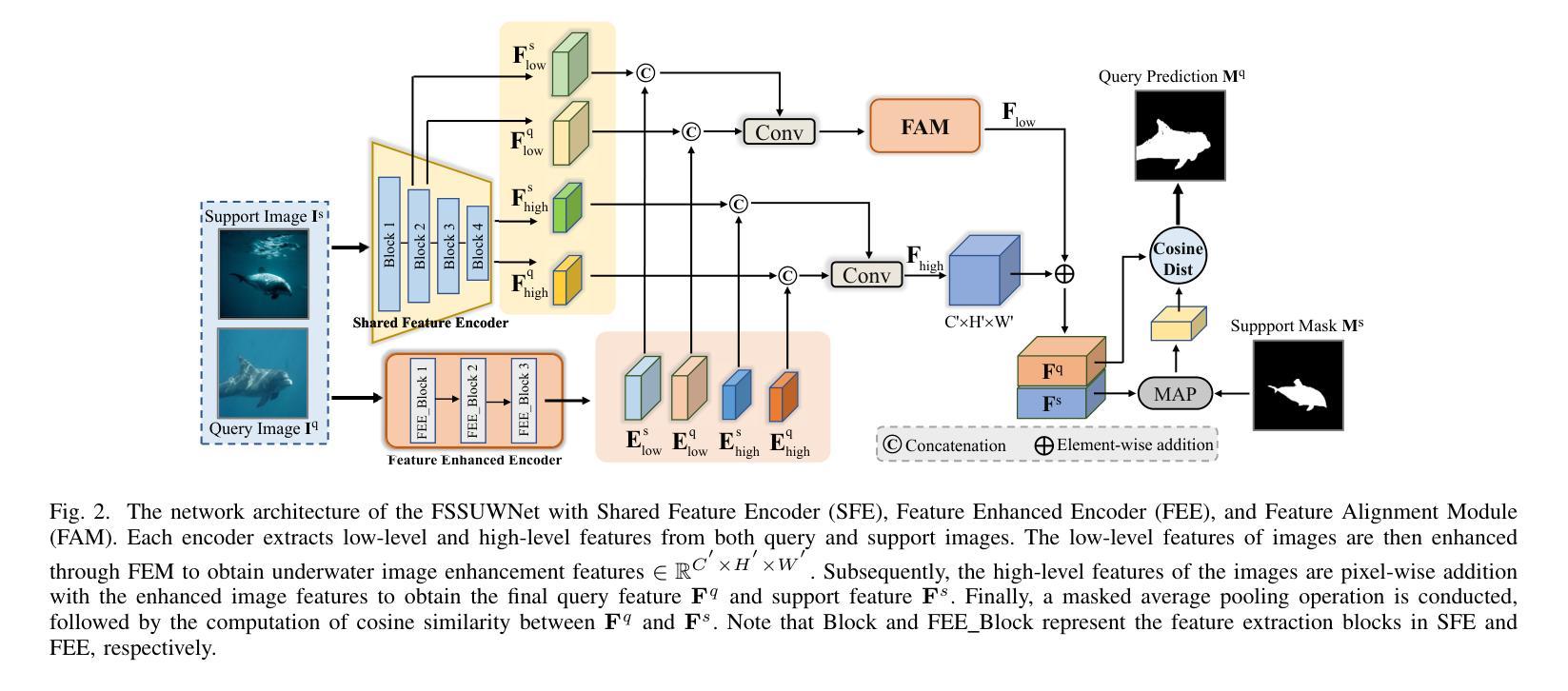
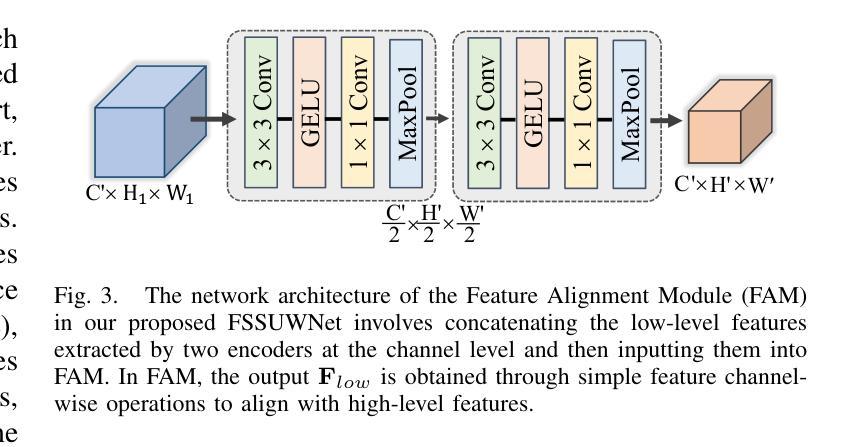
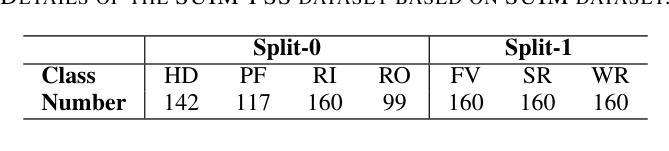
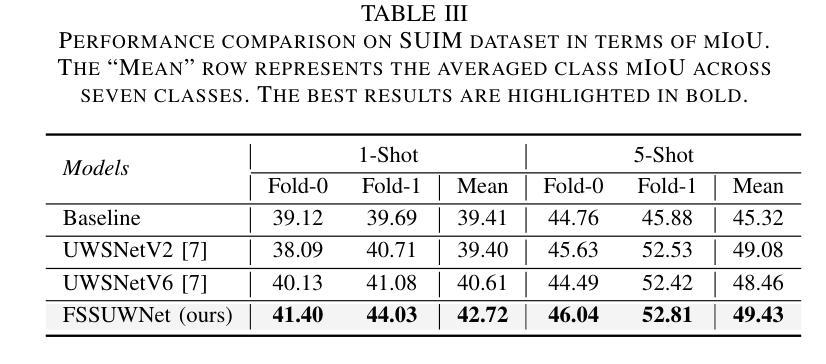
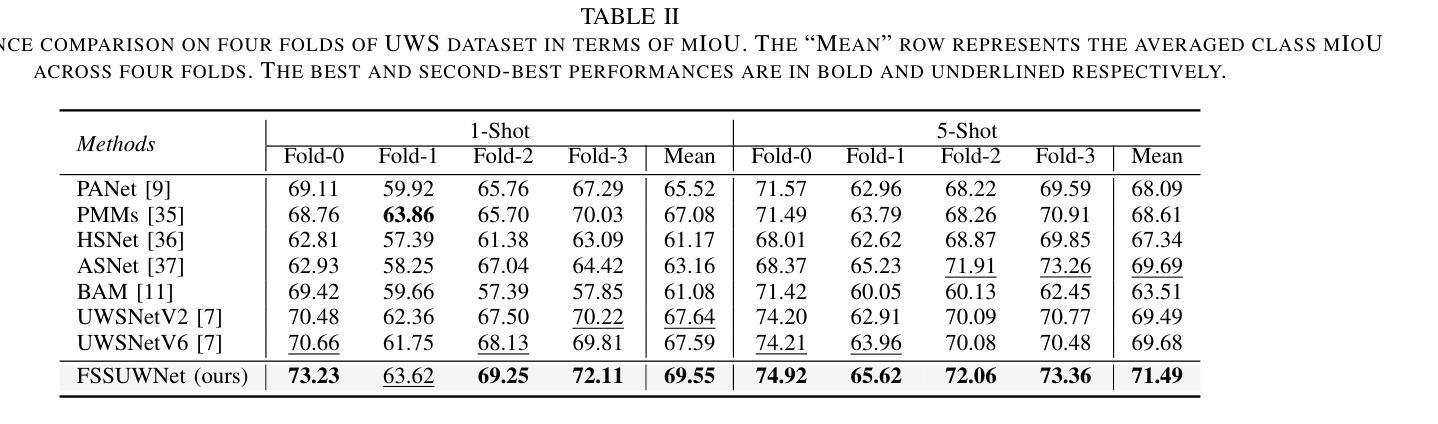
FSSUWNet: Mitigating the Fragility of Pre-trained Models with Feature Enhancement for Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation in Underwater Images
Authors:Zhuohao Li, Zhicheng Huang, Wenchao Liu, Zhuxing Zhang, Jianming Miao
Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation (FSS), which focuses on segmenting new classes in images using only a limited number of annotated examples, has recently progressed in data-scarce domains. However, in this work, we show that the existing FSS methods often struggle to generalize to underwater environments. Specifically, the prior features extracted by pre-trained models used as feature extractors are fragile due to the unique challenges of underwater images. To address this, we propose FSSUWNet, a tailored FSS framework for underwater images with feature enhancement. FSSUWNet exploits the integration of complementary features, emphasizing both low-level and high-level image characteristics. In addition to employing a pre-trained model as the primary encoder, we propose an auxiliary encoder called Feature Enhanced Encoder which extracts complementary features to better adapt to underwater scene characteristics. Furthermore, a simple and effective Feature Alignment Module aims to provide global prior knowledge and align low-level features with high-level features in dimensions. Given the scarcity of underwater images, we introduce a cross-validation dataset version based on the Segmentation of Underwater Imagery dataset. Extensive experiments on public underwater segmentation datasets demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance. For example, our method outperforms the previous best method by 2.8% and 2.6% in terms of the mean Intersection over Union metric for 1-shot and 5-shot scenarios in the datasets, respectively. Our implementation is available at https://github.com/lizhh268/FSSUWNet.
少量语义分割(FSS)技术专注于使用有限的标注样本对图像中的新类别进行分割,最近在数据稀缺领域取得了进展。然而,在这项工作中,我们展示了现有的FSS方法往往难以推广到水下环境。具体来说,由于水下图像的独特挑战,预训练模型提取的先验特征是脆弱的。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了FSSUWNet,这是一个针对水下图像进行特征增强的FSS框架。FSSUWNet利用互补特征的集成,强调图像的低级和高级特征。除了使用预训练模型作为主编码器外,我们还提出了一个名为特征增强编码器的辅助编码器,以提取互补特征,更好地适应水下场景特征。此外,简单有效的特征对齐模块旨在提供全局先验知识,并对低级特征与高级特征进行维度对齐。鉴于水下图像的稀缺性,我们基于水下图像分割数据集引入了一个交叉验证数据集版本。在公开的水下分割数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法达到了最新性能水平。例如,我们的方法在数据集的单样本和五样本场景下的平均交并比指标上分别比之前的最佳方法高出2.8%和2.6%。我们的实现可在https://github.com/lizhh268/FSSUWNet找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
水下环境对于现有少样本语义分割(FSS)方法来说是一大挑战。为应对这一难题,提出一种针对水下图像的FSS框架——FSSUWNet,通过特征增强来应对水下环境的独特挑战。FSSUWNet集成了主要编码器和辅助编码器提取的互补特征,同时强调低级别和高级别图像特性。另外,还引入了一个特征对齐模块,旨在提供全局先验知识并在维度上对齐低级别与高级别特征。在公开的水下分割数据集上进行的大量实验表明,该方法取得了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- FSS在水下环境面临挑战,现有方法难以推广。
- FSSUWNet是一个针对水下图像的FSS框架,具备特征增强功能。
- FSSUWNet集成了主要编码器和辅助编码器提取的互补特征,适应水下场景特性。
- 特征对齐模块提供全局先验知识,对齐低级别和高级别特征。
- 引入基于水下图像集的交叉验证数据集版本。
- 在公开的水下分割数据集上,FSSUWNet取得了最先进的性能表现。
点此查看论文截图

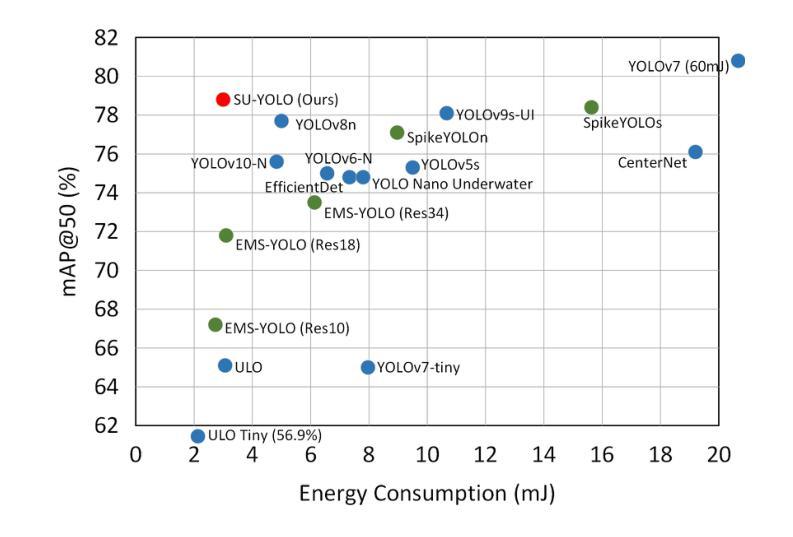
SU-YOLO: Spiking Neural Network for Efficient Underwater Object Detection
Authors:Chenyang Li, Wenxuan Liu, Guoqiang Gong, Xiaobo Ding, Xian Zhong
Underwater object detection is critical for oceanic research and industrial safety inspections. However, the complex optical environment and the limited resources of underwater equipment pose significant challenges to achieving high accuracy and low power consumption. To address these issues, we propose Spiking Underwater YOLO (SU-YOLO), a Spiking Neural Network (SNN) model. Leveraging the lightweight and energy-efficient properties of SNNs, SU-YOLO incorporates a novel spike-based underwater image denoising method based solely on integer addition, which enhances the quality of feature maps with minimal computational overhead. In addition, we introduce Separated Batch Normalization (SeBN), a technique that normalizes feature maps independently across multiple time steps and is optimized for integration with residual structures to capture the temporal dynamics of SNNs more effectively. The redesigned spiking residual blocks integrate the Cross Stage Partial Network (CSPNet) with the YOLO architecture to mitigate spike degradation and enhance the model’s feature extraction capabilities. Experimental results on URPC2019 underwater dataset demonstrate that SU-YOLO achieves mAP of 78.8% with 6.97M parameters and an energy consumption of 2.98 mJ, surpassing mainstream SNN models in both detection accuracy and computational efficiency. These results underscore the potential of SNNs for engineering applications. The code is available in https://github.com/lwxfight/snn-underwater.
水下目标检测对于海洋研究和工业安全检查至关重要。然而,复杂的光学环境和水下设备的有限资源给实现高精度和低功耗带来了重大挑战。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了Spiking Underwater YOLO(SU-YOLO),这是一种脉冲神经网络(SNN)模型。SU-YOLO利用SNNs的轻量级和节能特性,结合了一种基于脉冲的新型水下图像去噪方法,该方法仅使用整数加法,可在几乎不增加计算开销的情况下提高特征图的质量。此外,我们引入了分离批归一化(SeBN)技术,该技术能够独立地对多个时间步长的特征图进行归一化,并针对与残差结构的集成进行优化,以更有效地捕捉SNNs的时空动态。重新设计的脉冲残差块将跨阶段部分网络(CSPNet)与YOLO架构相结合,减轻了脉冲退化现象,提高了模型的特征提取能力。在URPC2019水下数据集上的实验结果表明,SU-YOLO达到了78.8%的mAP,具有6.97M的参数和2.98mJ的能耗,在检测精度和计算效率方面都超越了主流的SNN模型。这些结果凸显了SNN在工程应用中的潜力。代码可在https://github.com/lwxfight/snn-underwater中获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为Spiking Underwater YOLO(SU-YOLO)的脉冲神经网络模型,用于水下目标检测。该模型结合脉冲神经网络的轻量级和能效优势,采用基于整数添加的脉冲水下图像去噪方法,提高特征映射质量且计算开销小。同时引入分离批归一化(SeBN)技术,独立地对多个时间步长的特征映射进行归一化,与残差结构结合,更有效地捕捉SNN的时空动态。实验结果表明,SU-YOLO在URPC2019水下数据集上达到78.8%的mAP,参数仅6.97M,能耗为2.98 mJ,在检测精度和计算效率上均超越主流SNN模型,凸显了SNN在工程应用中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 水下目标检测面临复杂光学环境和设备资源限制的挑战。
- 提出Spiking Underwater YOLO(SU-YOLO)模型,结合脉冲神经网络的优点。
- 采用基于整数添加的脉冲水下图像去噪方法,提高特征映射质量。
- 引入分离批归一化(SeBN)技术,有效捕捉SNN的时空动态。
- 融合Cross Stage Partial Network(CSPNet)和YOLO架构,增强特征提取能力。
- 在URPC2019水下数据集上实现高检测精度和计算效率。
点此查看论文截图

Improving underwater semantic segmentation with underwater image quality attention and muti-scale aggregation attention
Authors:Xin Zuo, Jiaran Jiang, Jifeng Shen, Wankou Yang
Underwater image understanding is crucial for both submarine navigation and seabed exploration. However, the low illumination in underwater environments degrades the imaging quality, which in turn seriously deteriorates the performance of underwater semantic segmentation, particularly for outlining the object region boundaries. To tackle this issue, we present UnderWater SegFormer (UWSegFormer), a transformer-based framework for semantic segmentation of low-quality underwater images. Firstly, we propose the Underwater Image Quality Attention (UIQA) module. This module enhances the representation of highquality semantic information in underwater image feature channels through a channel self-attention mechanism. In order to address the issue of loss of imaging details due to the underwater environment, the Multi-scale Aggregation Attention(MAA) module is proposed. This module aggregates sets of semantic features at different scales by extracting discriminative information from high-level features,thus compensating for the semantic loss of detail in underwater objects. Finally, during training, we introduce Edge Learning Loss (ELL) in order to enhance the model’s learning of underwater object edges and improve the model’s prediction accuracy. Experiments conducted on the SUIM and DUT-USEG (DUT) datasets have demonstrated that the proposed method has advantages in terms of segmentation completeness, boundary clarity, and subjective perceptual details when compared to SOTA methods. In addition, the proposed method achieves the highest mIoU of 82.12 and 71.41 on the SUIM and DUT datasets, respectively. Code will be available at https://github.com/SAWRJJ/UWSegFormer.
水下图像理解对于潜艇导航和海底探索都至关重要。然而,水下环境的低照明条件会降低图像质量,进而严重损害水下语义分割的性能,特别是在描绘物体区域边界时。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了UnderWater SegFormer(UWSegFormer),这是一个基于变压器的框架,用于对低质量的水下图像进行语义分割。首先,我们提出了水下图像质量注意力(UIQA)模块。该模块通过通道自注意力机制,增强水下图像特征通道中高质量语义信息的表示。为了解决水下环境导致的成像细节丢失问题,我们提出了多尺度聚合注意力(MAA)模块。该模块通过从高级特征中提取判别信息来聚合不同尺度的语义特征集,从而弥补水下物体语义细节的损失。最后,在训练过程中,我们引入了边缘学习损失(ELL),以提高模型对水下物体边缘的学习能力,提高模型的预测精度。在SUIM和DUT-USEG(DUT)数据集上进行的实验表明,与最新方法相比,所提方法在分割完整性、边界清晰度和主观感知细节方面具优势。此外,所提方法在SUIM和DUT数据集上分别达到了最高的mIoU值,分别为82.12和71.41。代码将发布在https://github.com/SAWRJJ/UWSegFormer。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Pattern Analysis and Applications
Summary
针对水下图像质量低影响语义分割的问题,提出了基于Transformer的UnderWater SegFormer框架。通过UIQA模块增强高质量语义信息表示,通过MAA模块补偿水下物体细节语义损失,引入Edge Learning Loss提高模型对水下物体边缘的学习能力。实验证明,该方法在分割完整性、边界清晰度和主观感知细节方面优于现有方法,并在SUIM和DUT数据集上达到最高mIoU值。
Key Takeaways
- 水下图像理解对潜艇导航和海底探索至关重要。
- 低照明环境导致水下图像质量下降,影响语义分割性能,特别是在描绘物体区域边界方面。
- 提出的UnderWater SegFormer是一个基于Transformer的框架,用于对低质量水下图像进行语义分割。
- UIQA模块增强水下图像特征通道的高质量语义信息表示。
- MAA模块通过聚合不同尺度的语义特征来补偿水下物体细节语义的损失。
- 引入Edge Learning Loss以提高模型对水下物体边缘的学习能力,提高预测准确性。
点此查看论文截图

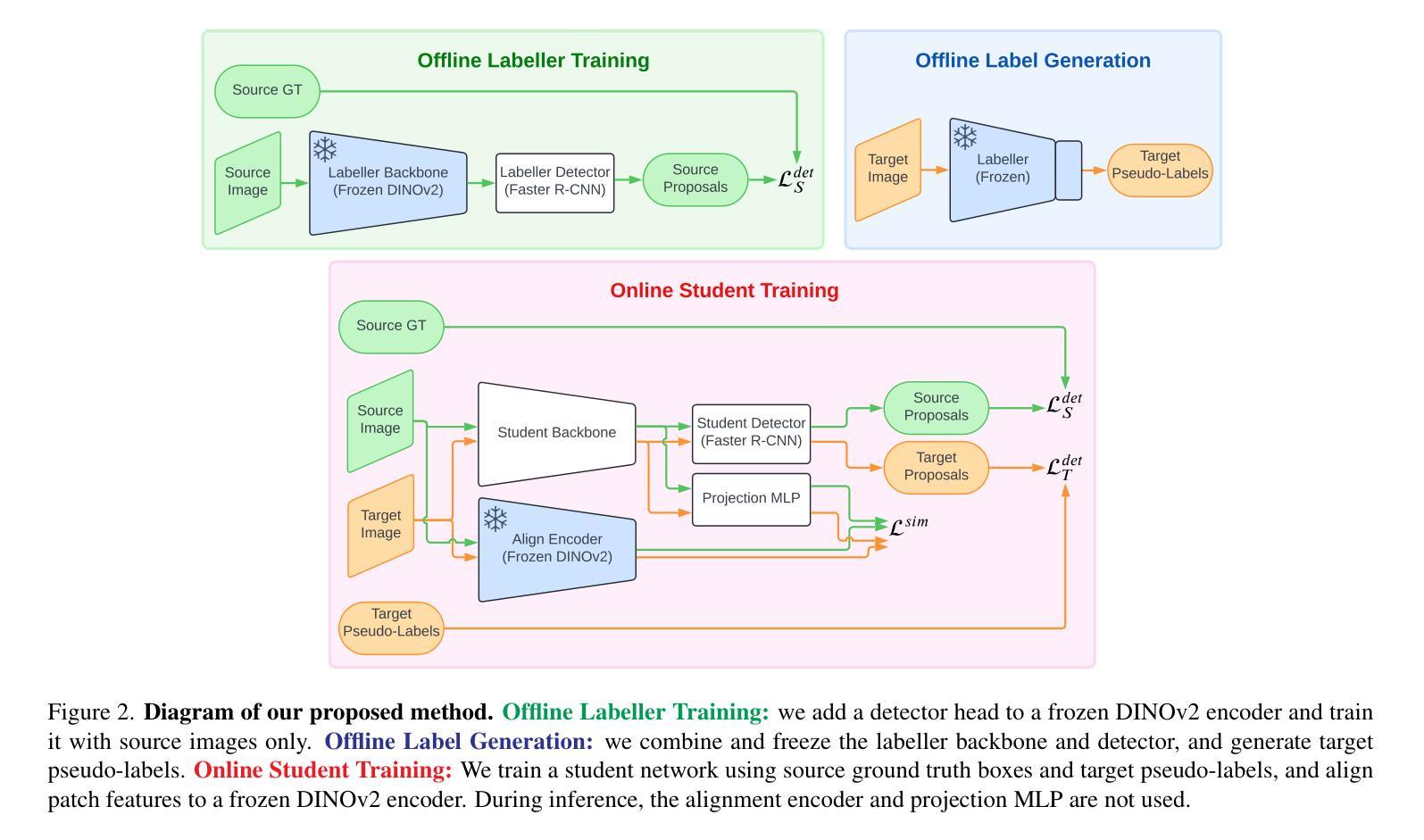
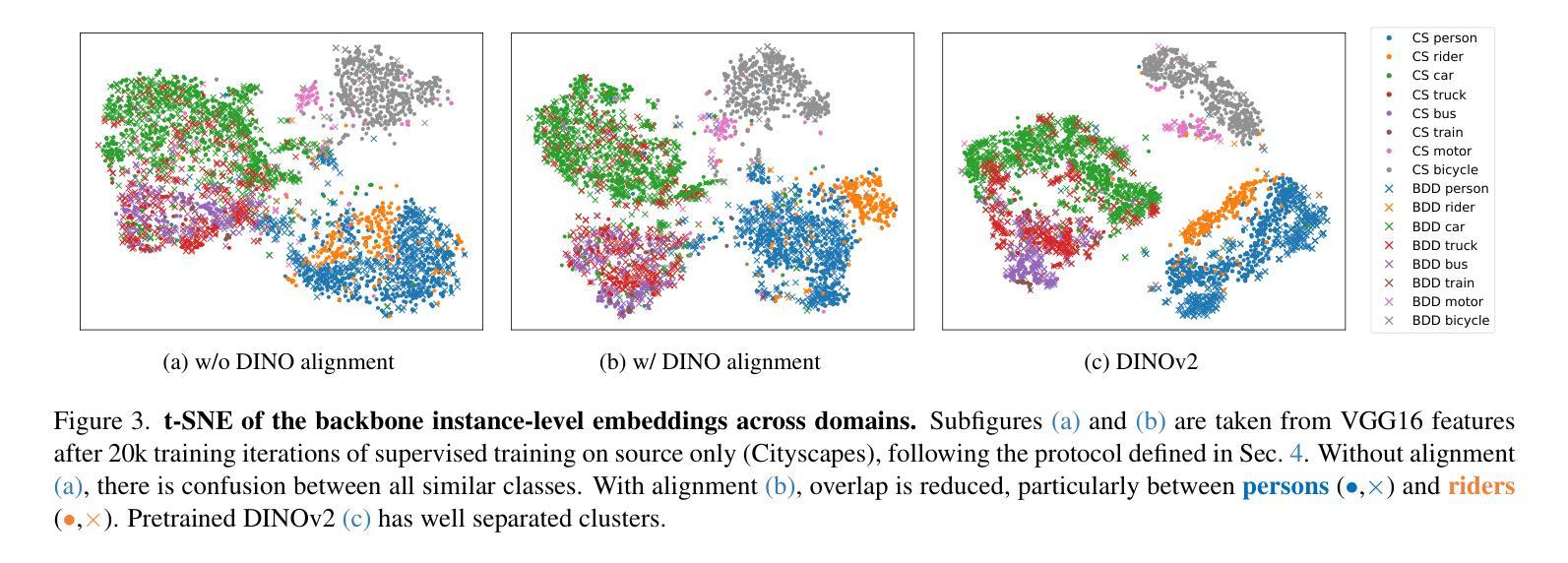
Large Self-Supervised Models Bridge the Gap in Domain Adaptive Object Detection
Authors:Marc-Antoine Lavoie, Anas Mahmoud, Steven L. Waslander
The current state-of-the-art methods in domain adaptive object detection (DAOD) use Mean Teacher self-labelling, where a teacher model, directly derived as an exponential moving average of the student model, is used to generate labels on the target domain which are then used to improve both models in a positive loop. This couples learning and generating labels on the target domain, and other recent works also leverage the generated labels to add additional domain alignment losses. We believe this coupling is brittle and excessively constrained: there is no guarantee that a student trained only on source data can generate accurate target domain labels and initiate the positive feedback loop, and much better target domain labels can likely be generated by using a large pretrained network that has been exposed to much more data. Vision foundational models are exactly such models, and they have shown impressive task generalization capabilities even when frozen. We want to leverage these models for DAOD and introduce DINO Teacher, which consists of two components. First, we train a new labeller on source data only using a large frozen DINOv2 backbone and show it generates more accurate labels than Mean Teacher. Next, we align the student’s source and target image patch features with those from a DINO encoder, driving source and target representations closer to the generalizable DINO representation. We obtain state-of-the-art performance on multiple DAOD datasets. Code available at https://github.com/TRAILab/DINO_Teacher
当前最先进的领域自适应目标检测(DAOD)方法采用Mean Teacher自标注技术。其中,教师模型被直接用作学生模型的指数移动平均模型,在目标域上生成标签,并用于在正向循环中改进这两个模型。这种技术将学习和在目标域上生成标签相结合,其他近期的研究也利用生成的标签来增加额外的域对齐损失。我们认为这种结合方式脆弱且受到过度约束:没有保证仅通过源数据训练的学生模型能够在目标域上生成准确的标签并启动正向反馈循环;通过使用已接触到更多数据的大型预训练网络,很可能会生成更好的目标域标签。视觉基础模型正是这样的模型,即使在冻结状态下,它们也表现出了令人印象深刻的任务泛化能力。我们希望利用这些模型进行DAOD,并引入DINO Teacher,它包含两个组件。首先,我们仅使用源数据训练一个新的标注器,采用大型冻结的DINOv2骨干网,并证明其生成的标签比Mean Teacher更准确。接下来,我们将学生模型的源图像和目标图像补丁特征与DINO编码器的特征进行对齐,使源和目标表示更接近可泛化的DINO表示。我们在多个DAOD数据集上获得了最先进的性能。代码可访问:https://github.com/TRAILab/DINO_Teacher 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages (8 main), 5 figures, accepted at CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了在自适应目标检测领域的新方法,提出使用DINO Teacher代替传统的Mean Teacher自标注技术。DINO Teacher利用大型预训练模型生成更准确的目标域标签,并通过与学生模型的源图像和目标图像块特征对齐,拉近源和目标表示的差距,实现跨领域自适应性能的提升。此研究获得多个自适应目标检测数据集的最佳表现。
Key Takeaways
- 当前自适应目标检测的主流方法使用Mean Teacher自标注技术,通过教师模型生成目标域标签来改善学生和教师模型。
- 本文认为这种方法的耦合性强且过于受限,因为仅依赖源数据训练的学生模型可能无法生成准确的目标域标签。
- 大型预训练模型(如Vision foundational models)在任务泛化方面表现出色,本文旨在利用这类模型进行自适应目标检测。
- 引入DINO Teacher,其包含两个组成部分:一是使用大型冻结的DINOv2骨干网在源数据上训练新的标注器,生成更准确的标签;二是通过与学生模型的源图像和目标图像块特征对齐,拉近源和目标表示的差距。
- DINO Teacher在多个自适应目标检测数据集上获得最佳性能。
- 研究者提供了代码实现,可供公众访问。
点此查看论文截图

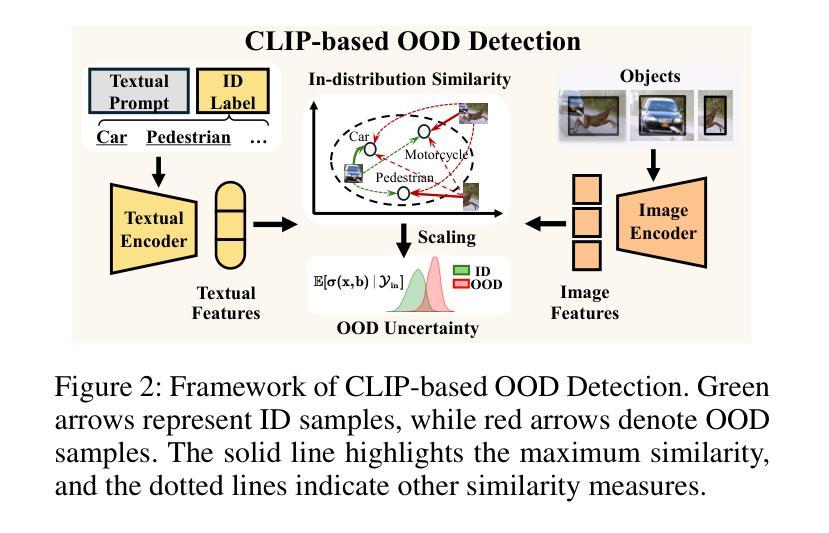
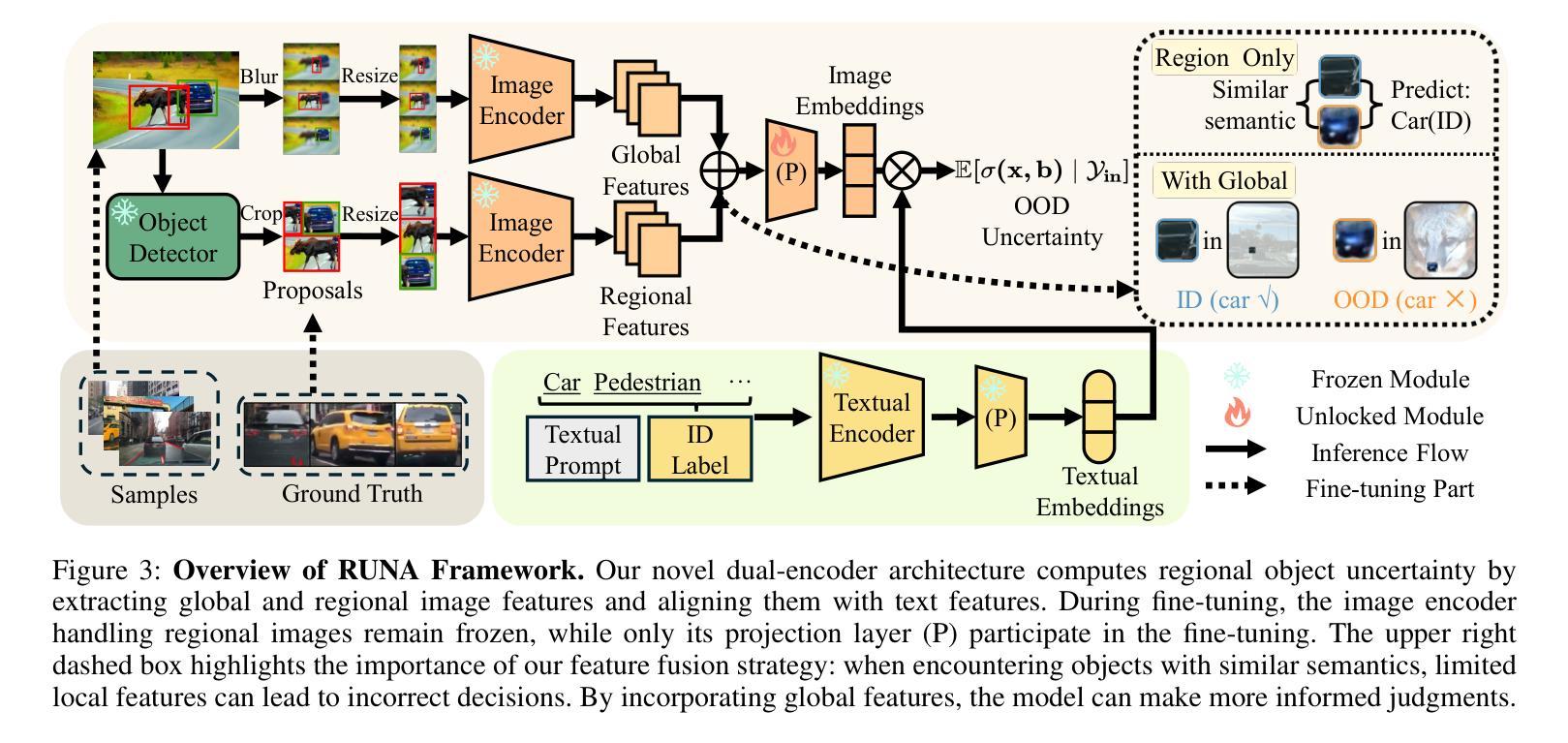
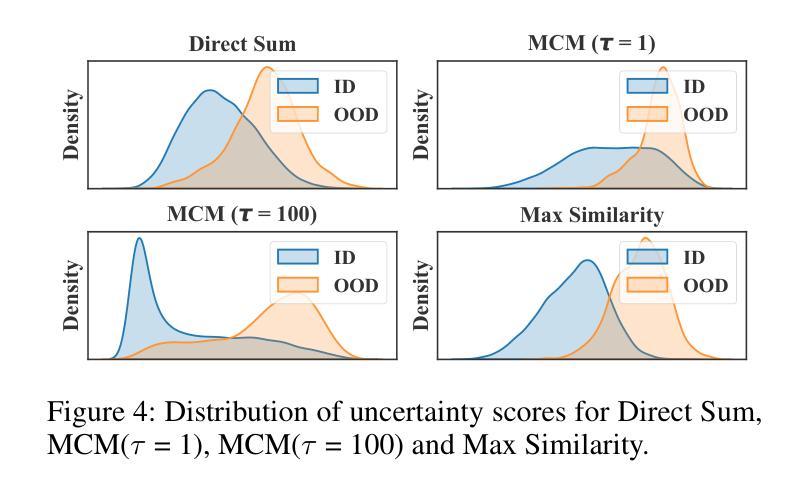
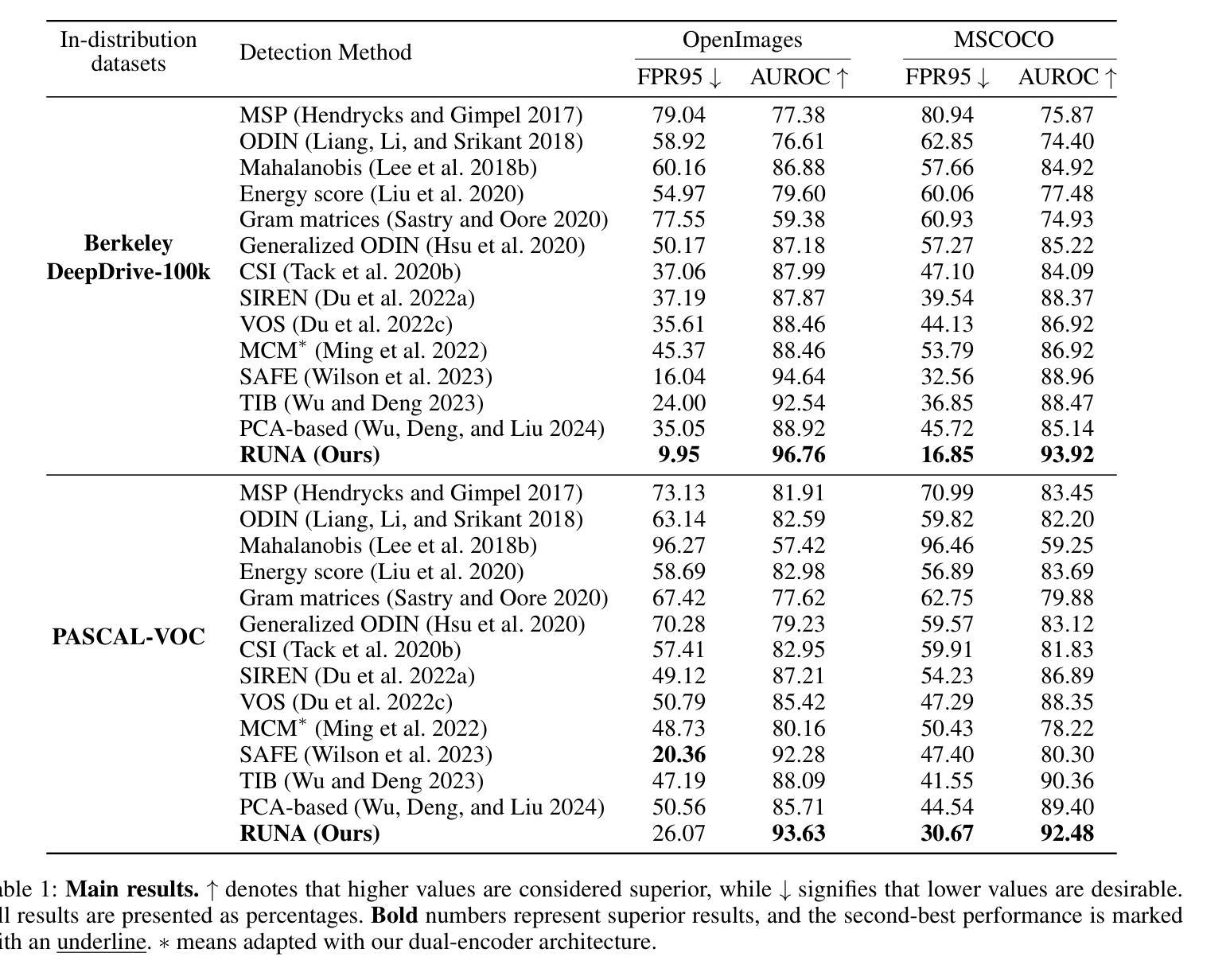
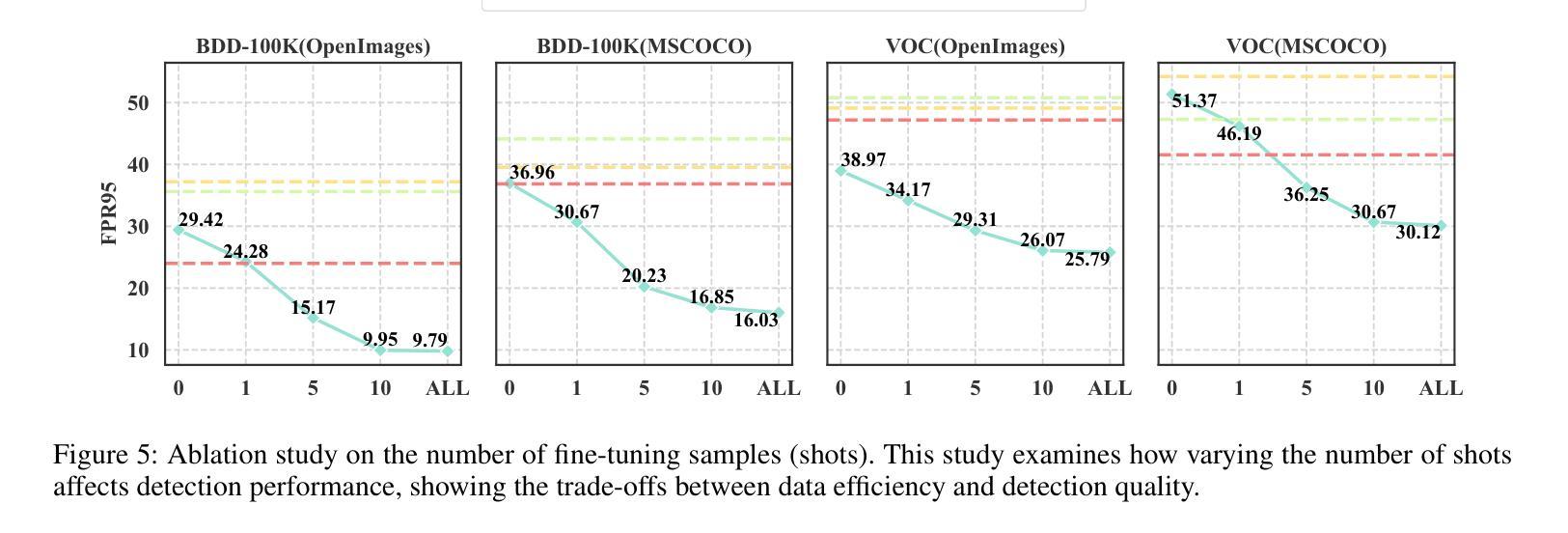
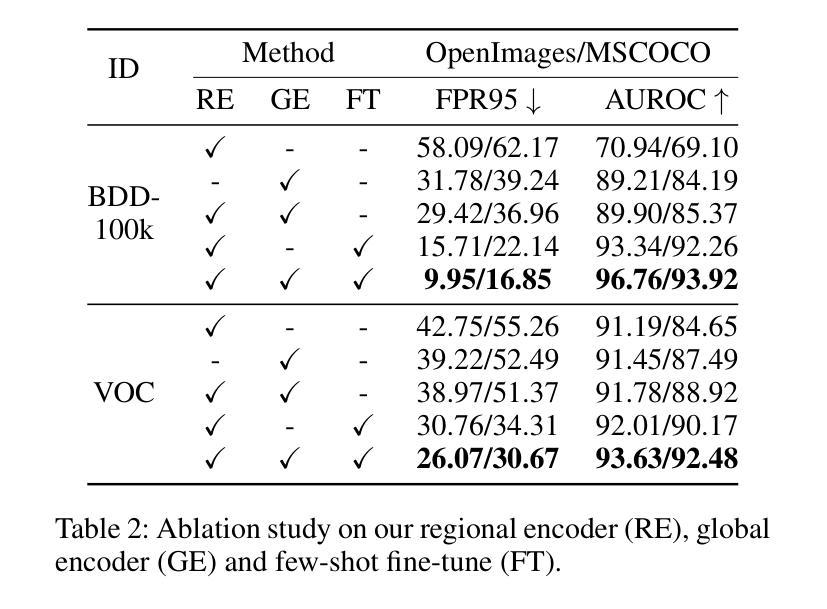
RUNA: Object-level Out-of-Distribution Detection via Regional Uncertainty Alignment of Multimodal Representations
Authors:Bin Zhang, Jinggang Chen, Xiaoyang Qu, Guokuan Li, Kai Lu, Jiguang Wan, Jing Xiao, Jianzong Wang
Enabling object detectors to recognize out-of-distribution (OOD) objects is vital for building reliable systems. A primary obstacle stems from the fact that models frequently do not receive supervisory signals from unfamiliar data, leading to overly confident predictions regarding OOD objects. Despite previous progress that estimates OOD uncertainty based on the detection model and in-distribution (ID) samples, we explore using pre-trained vision-language representations for object-level OOD detection. We first discuss the limitations of applying image-level CLIP-based OOD detection methods to object-level scenarios. Building upon these insights, we propose RUNA, a novel framework that leverages a dual encoder architecture to capture rich contextual information and employs a regional uncertainty alignment mechanism to distinguish ID from OOD objects effectively. We introduce a few-shot fine-tuning approach that aligns region-level semantic representations to further improve the model’s capability to discriminate between similar objects. Our experiments show that RUNA substantially surpasses state-of-the-art methods in object-level OOD detection, particularly in challenging scenarios with diverse and complex object instances.
实现对象检测器对离群分布(OOD)对象的识别对于构建可靠系统至关重要。主要的障碍在于模型经常无法从未知数据中获取监督信号,导致对OOD对象的预测过于自信。尽管先前的工作已经基于检测模型和内部分布(ID)样本估计了OOD不确定性,但我们在对象级别的OOD检测中探索了使用预训练的视觉语言表示。我们首先讨论了将基于图像级别的CLIP的OOD检测方法应用于对象级别场景的局限性。基于这些见解,我们提出了RUNA这一新型框架,它采用双编码器架构来捕获丰富的上下文信息,并采用了区域不确定性对齐机制来有效地区分ID和OOD对象。我们引入了一种小样本微调方法,通过调整区域级别的语义表示来进一步提高模型区分相似对象的能力。实验表明,RUNA在对象级别的OOD检测方面显著超越了现有先进技术,特别是在具有多样化和复杂对象实例的具有挑战性的场景中。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 5 figures
Summary
对象检测器识别出分布外(OOD)对象的能力对于构建可靠系统至关重要。本文探讨了将预训练的视觉语言表示应用于对象级别的OOD检测。针对图像级别的CLIP基OOD检测方法在对象级别场景中的应用局限性,我们提出了RUNA框架,该框架采用双编码器架构捕捉丰富的上下文信息,并利用区域不确定性对齐机制有效区分ID和OOD对象。通过引入少量样本微调方法,进一步提高了模型区分相似对象的能力。实验表明,RUNA在对象级别的OOD检测中显著超越了现有方法,特别是在具有多样性和复杂性对象实例的挑战场景中。
Key Takeaways
- 对象检测器识别分布外(OOD)对象的重要性。
- 模型在面对不熟悉数据时缺乏监督信号,导致对OOD对象的预测过于自信,这是主要障碍之一。
- 借助预训练的视觉语言表示进行对象级别的OOD检测是一种新探索。
- RUNA框架采用双编码器架构和区域不确定性对齐机制来区分ID和OOD对象。
- RUNA框架通过引入少量样本微调方法来提高模型区分相似对象的能力。
- 实验显示RUNA在对象级别的OOD检测中表现优越,尤其是处理多样性和复杂性对象实例的挑战场景。
- 该研究为构建更可靠的对象检测器提供了新的思路和方法。
点此查看论文截图

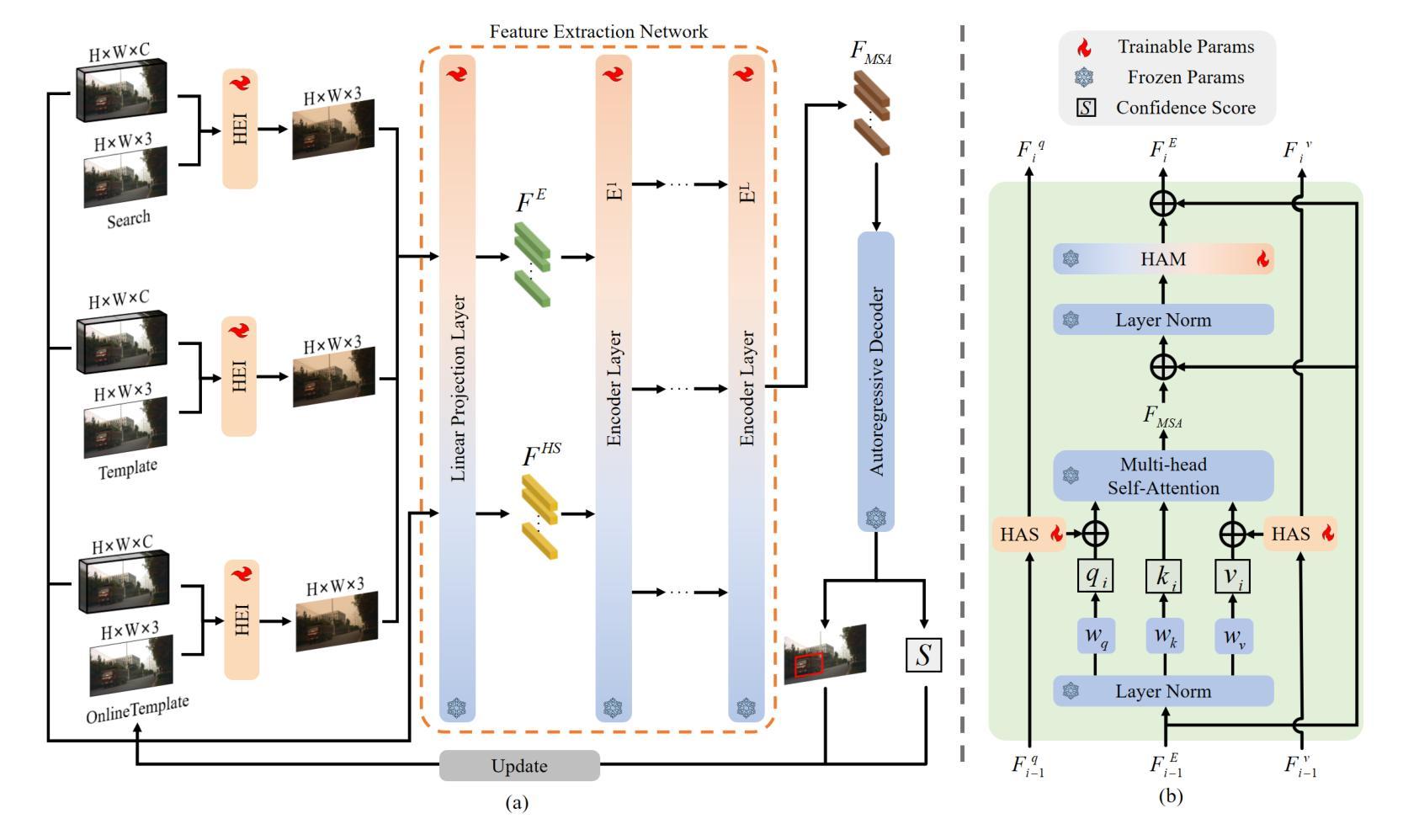
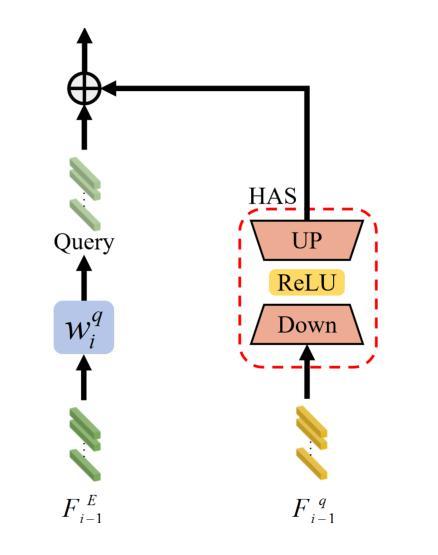
Hyperspectral Adapter for Object Tracking based on Hyperspectral Video
Authors:Long Gao, Yunhe Zhang, Langkun Chen, Yan Jiang, Weiying Xie, Yunsong Li
Object tracking based on hyperspectral video attracts increasing attention to the rich material and motion information in the hyperspectral videos. The prevailing hyperspectral methods adapt pretrained RGB-based object tracking networks for hyperspectral tasks by fine-tuning the entire network on hyperspectral datasets, which achieves impressive results in challenging scenarios. However, the performance of hyperspectral trackers is limited by the loss of spectral information during the transformation, and fine-tuning the entire pretrained network is inefficient for practical applications. To address the issues, a new hyperspectral object tracking method, hyperspectral adapter for tracking (HyA-T), is proposed in this work. The hyperspectral adapter for the self-attention (HAS) and the hyperspectral adapter for the multilayer perceptron (HAM) are proposed to generate the adaption information and to transfer the multi-head self-attention (MSA) module and the multilayer perceptron (MLP) in pretrained network for the hyperspectral object tracking task by augmenting the adaption information into the calculation of the MSA and MLP. Additionally, the hyperspectral enhancement of input (HEI) is proposed to augment the original spectral information into the input of the tracking network. The proposed methods extract spectral information directly from the hyperspectral images, which prevent the loss of the spectral information. Moreover, only the parameters in the proposed methods are fine-tuned, which is more efficient than the existing methods. Extensive experiments were conducted on four datasets with various spectral bands, verifing the effectiveness of the proposed methods. The HyA-T achieves state-of-the-art performance on all the datasets.
基于高光谱视频的物体跟踪吸引了人们对高光谱视频中丰富的材料和运动信息的关注。目前流行的高光谱方法通过在高光谱数据集上微调整个网络,将预训练的基于RGB的物体跟踪网络适应于高光谱任务,这在具有挑战性的场景中取得了令人印象深刻的结果。然而,高光谱跟踪器的性能受到转换过程中光谱信息损失的限制,并且微调整个预训练网络对于实际应用是不高效的。为了解决这些问题,本文提出了一种新的高光谱物体跟踪方法,即用于跟踪的高光谱适配器(HyA-T)。提出了用于自注意力机制的高光谱适配器(HAS)和用于多层感知器的高光谱适配器(HAM),以生成适应信息,并将多头自注意力(MSA)模块和多层感知器(MLP)转移到高光谱物体跟踪任务中,通过将适应信息增加到MSA和MLP的计算中。此外,还提出了高光谱增强输入(HEI)的方法,将原始光谱信息增强到跟踪网络的输入中。所提出的方法直接从高光谱图像中提取光谱信息,防止了光谱信息的损失。而且,只有所提出的方法中的参数进行了微调,这比现有方法更有效率。在四个具有不同光谱波段的数据库上进行了大量实验,验证了所提出方法的有效性。HyA-T在所有数据集上均达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注基于高光谱视频的物体跟踪技术。现有的高光谱方法通过微调整个网络在高光谱数据集上进行RGB基础物体跟踪网络的预训练,虽然在具有挑战性的场景中表现惊人,但仍面临信息转换中的光谱信息损失以及实际应用中的效率低下的问题。为解决这些问题,本文提出了一种新的高光谱物体跟踪方法——高光谱适配器跟踪(HyA-T)。该方法包括高光谱自注意力适配器(HAS)和高光谱多层感知器适配器(HAM),旨在生成适应信息并将多头自注意力模块和多层感知器转移到高光谱物体跟踪任务中。同时提出了高光谱增强输入(HEI),以将原始光谱信息添加到跟踪网络的输入中。该方法直接从高光谱图像中提取光谱信息,避免了信息损失,并且仅微调该方法的参数,使得其在效率和效果上都超越了现有方法。经过四个数据集上的广泛实验验证了该方法的有效性。HyA-T在所有数据集上达到了最先进的表现。
Key Takeaways
- 高光谱视频物体跟踪重视丰富的材料和运动信息。
- 现有方法通过微调整个预训练网络以适应高光谱任务,虽效果良好但存在效率和信息损失问题。
- 新方法HyA-T包括HAS、HAM和HEI,旨在解决信息损失和提高效率问题。
- HAS和HAM生成适应信息并转移预训练网络中的特定模块到高光谱物体跟踪任务。
- HEI将原始光谱信息添加到跟踪网络输入中。
- 方法直接从高光谱图像提取信息,避免了信息损失。
- 仅微调新方法参数,提高了效率。
点此查看论文截图

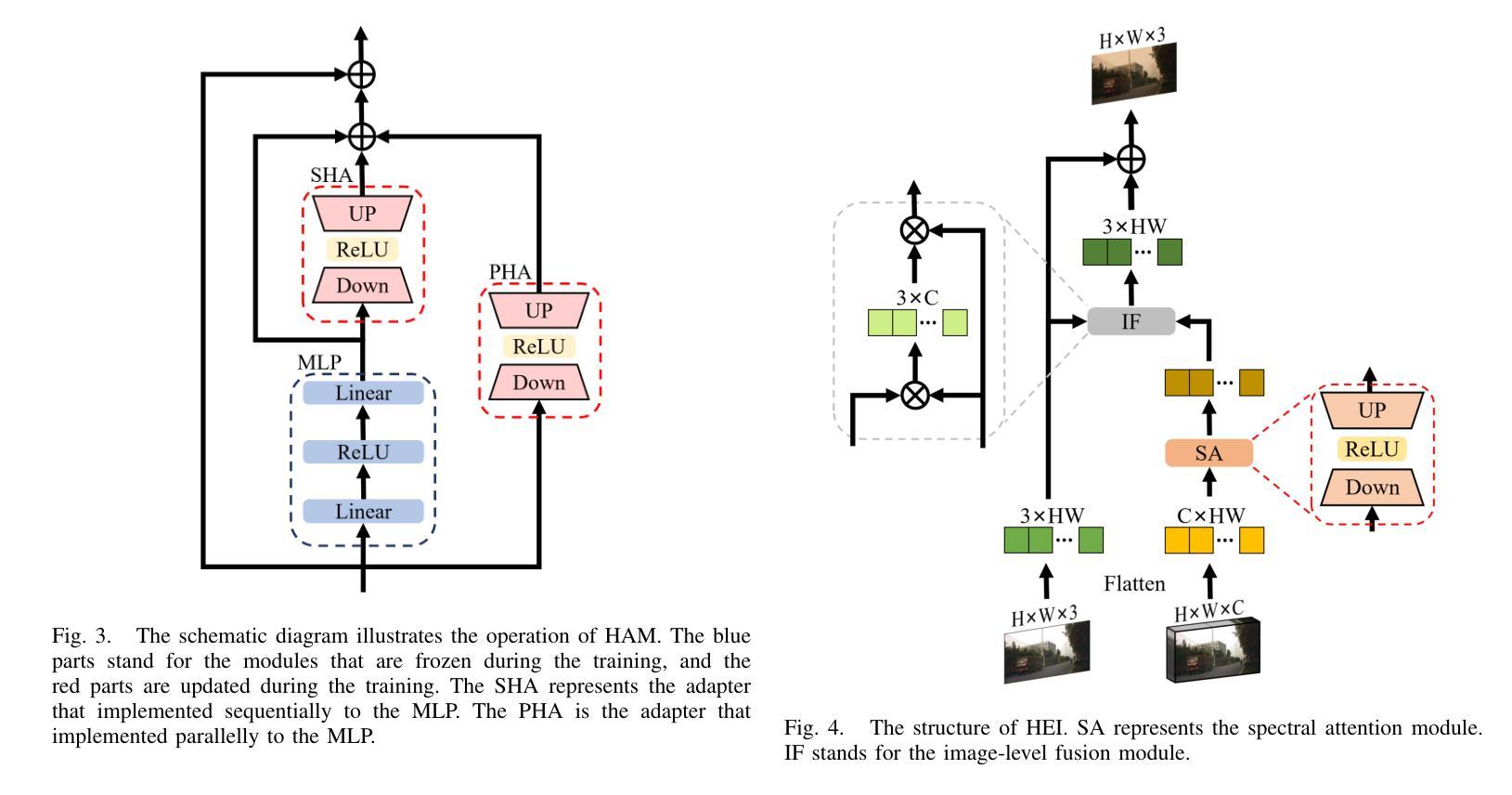
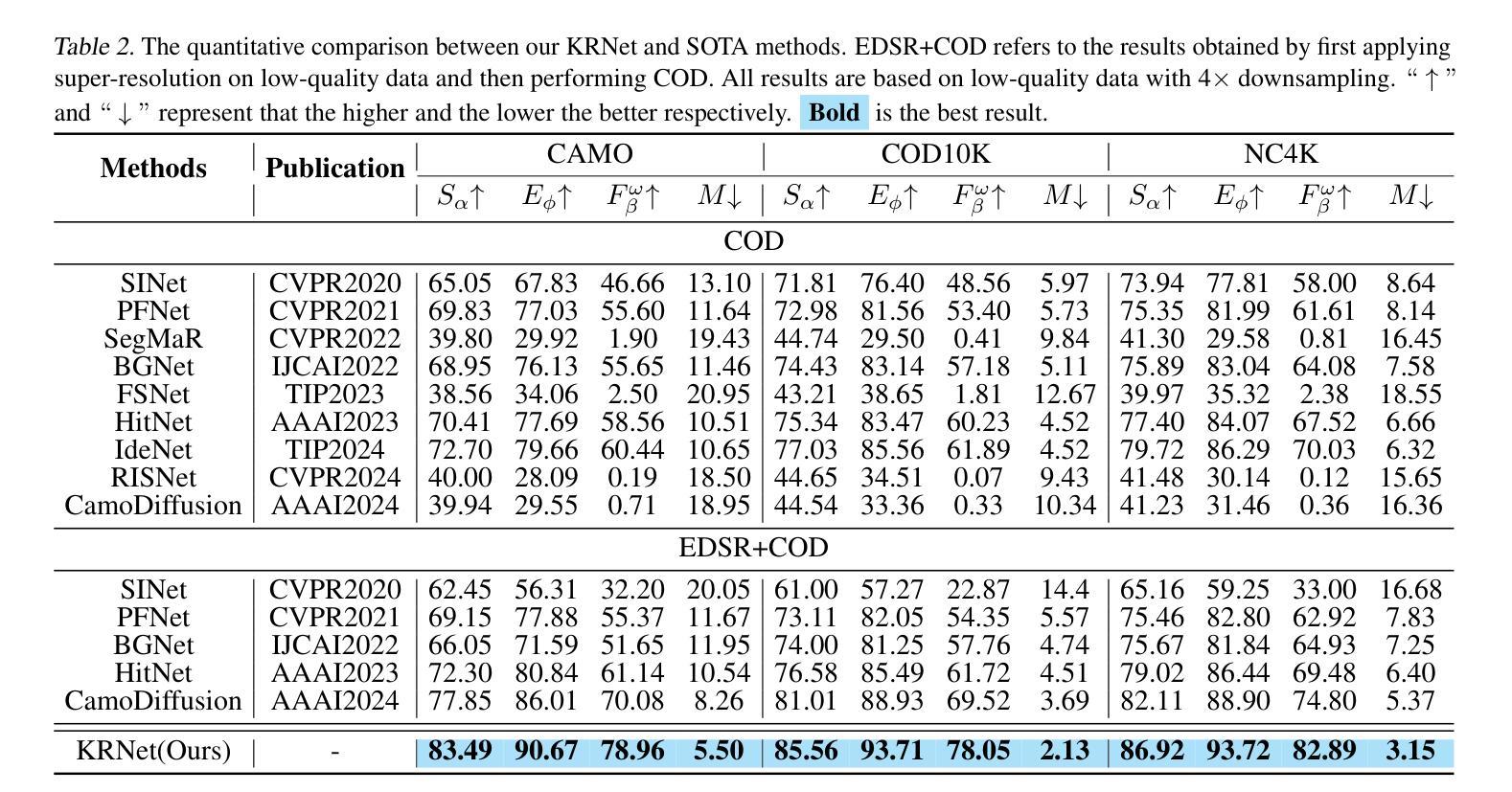
Knowledge Rectification for Camouflaged Object Detection: Unlocking Insights from Low-Quality Data
Authors:Juwei Guan, Xiaolin Fang, Donghyun Kim, Haotian Gong, Tongxin Zhu, Zhen Ling, Ming Yang
Low-quality data often suffer from insufficient image details, introducing an extra implicit aspect of camouflage that complicates camouflaged object detection (COD). Existing COD methods focus primarily on high-quality data, overlooking the challenges posed by low-quality data, which leads to significant performance degradation. Therefore, we propose KRNet, the first framework explicitly designed for COD on low-quality data. KRNet presents a Leader-Follower framework where the Leader extracts dual gold-standard distributions: conditional and hybrid, from high-quality data to drive the Follower in rectifying knowledge learned from low-quality data. The framework further benefits from a cross-consistency strategy that improves the rectification of these distributions and a time-dependent conditional encoder that enriches the distribution diversity. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that KRNet outperforms state-of-the-art COD methods and super-resolution-assisted COD approaches, proving its effectiveness in tackling the challenges of low-quality data in COD.
低质量数据通常存在图像细节不足的问题,引入了一种额外的隐性伪装方面,这增加了对隐蔽目标检测(COD)的复杂性。现有的COD方法主要关注高质量数据,忽视了低质量数据带来的挑战,这导致了性能的大幅下降。因此,我们提出了KRNet,这是第一个专为低质量数据进行COD设计的框架。KRNet采用领导者-追随者框架,其中领导者从高质量数据中提取双金标准分布:条件分布和混合分布,以驱动追随者纠正从低质量数据中学习的知识。该框架还受益于交叉一致性策略,提高了这些分布的校正效果,以及时间相关的条件编码器,丰富了分布的多样性。在基准数据集上的大量实验表明,KRNet优于最先进的COD方法和超分辨率辅助的COD方法,证明了其在解决COD中低质量数据挑战方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要针对低质量数据在隐蔽目标检测中的挑战,提出了KRNet框架。该框架通过领导者(Leader)从高质量数据中提取两种黄金标准分布(条件分布和混合分布),驱动跟随者(Follower)纠正从低质量数据中学习的知识。此外,还采用了跨一致性策略和时间依赖条件编码器,以提高分布的修正和丰富分布多样性。实验证明,KRNet在低质量数据的隐蔽目标检测方面优于最新的技术方法和超分辨率辅助隐蔽目标检测法。
Key Takeaways
- 低质量数据因其图像细节不足而具有隐蔽性,增加了隐蔽目标检测的复杂性。
- 当前隐蔽目标检测方法主要关注高质量数据,忽视了低质量数据的挑战,导致性能下降。
- KRNet是首个专为低质量数据隐蔽目标检测设计的框架。
- KRNet采用领导者-跟随者框架,领导者从高质量数据中提取两种黄金标准分布来指导跟随者纠正从低质量数据中学习的知识。
- 采用跨一致性策略改善分布的修正过程。
- 时间依赖条件编码器丰富分布多样性,进一步提高检测性能。
点此查看论文截图

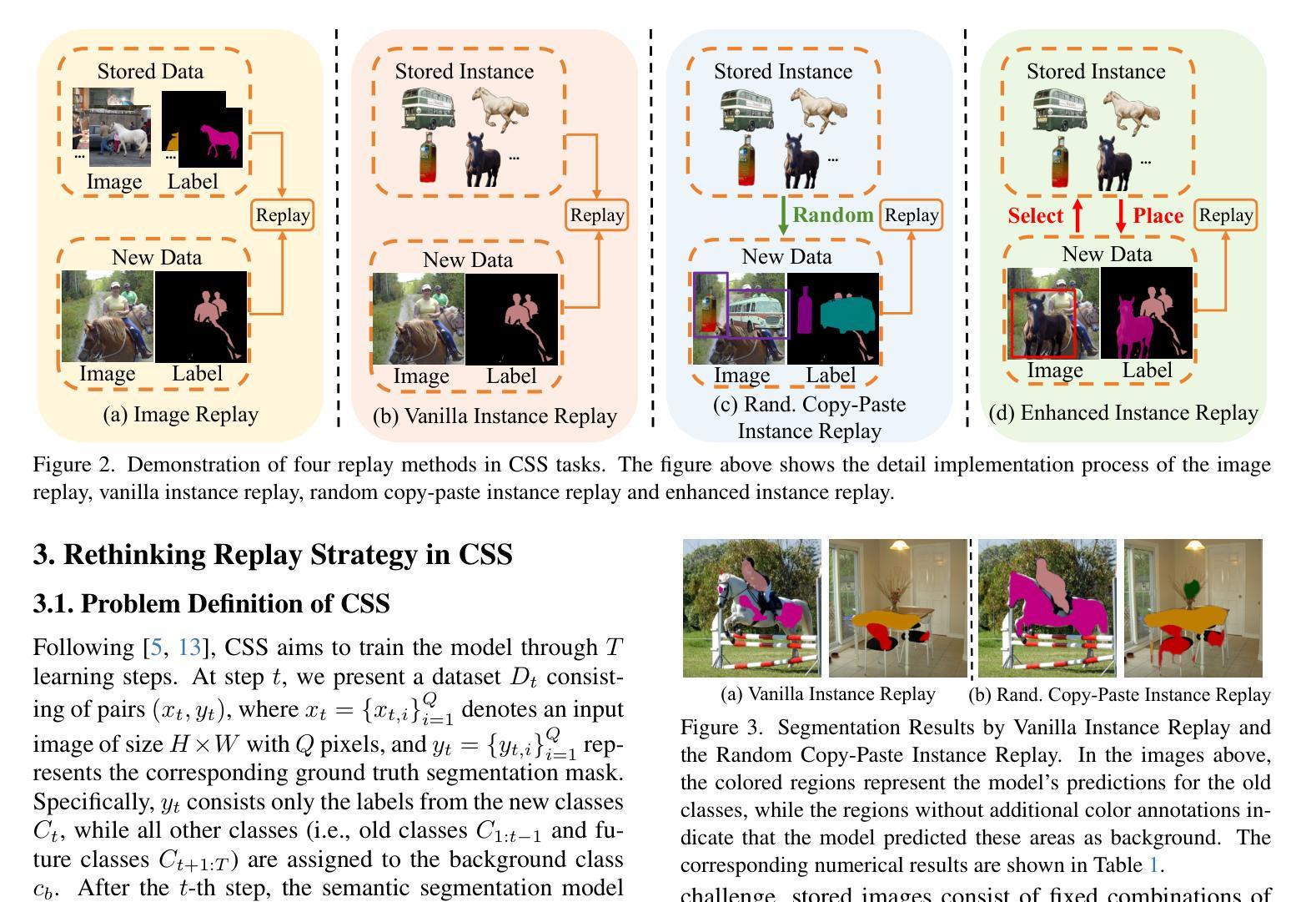
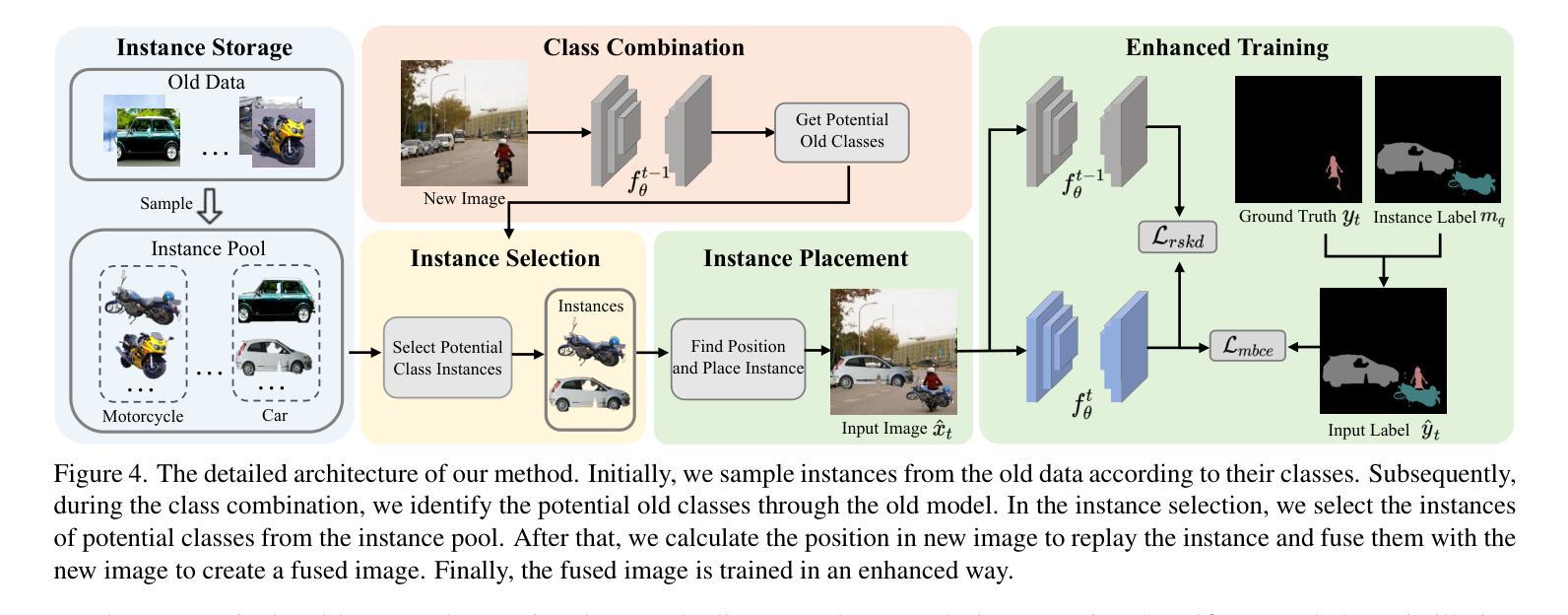
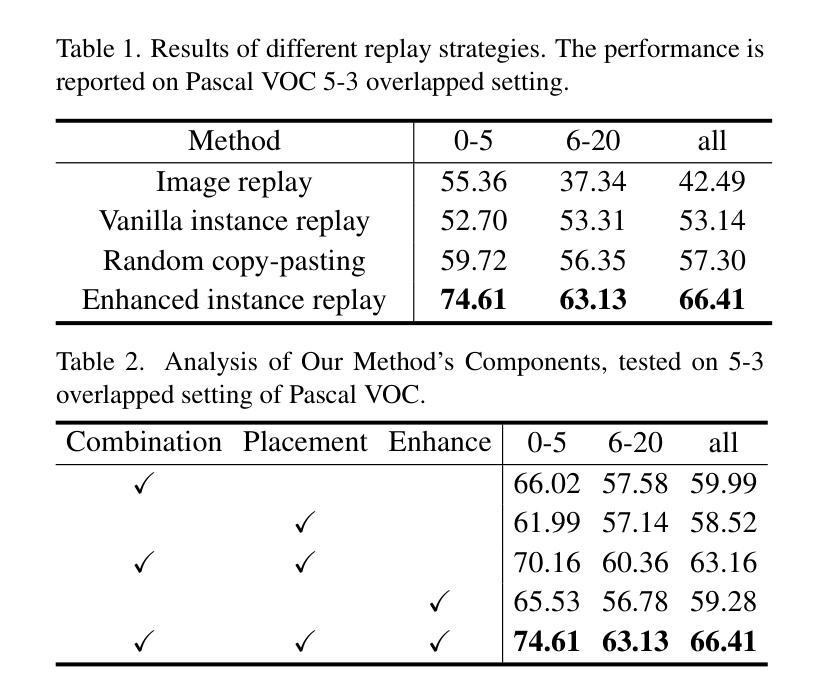
Beyond Background Shift: Rethinking Instance Replay in Continual Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Hongmei Yin, Tingliang Feng, Fan Lyu, Fanhua Shang, Hongying Liu, Wei Feng, Liang Wan
In this work, we focus on continual semantic segmentation (CSS), where segmentation networks are required to continuously learn new classes without erasing knowledge of previously learned ones. Although storing images of old classes and directly incorporating them into the training of new models has proven effective in mitigating catastrophic forgetting in classification tasks, this strategy presents notable limitations in CSS. Specifically, the stored and new images with partial category annotations leads to confusion between unannotated categories and the background, complicating model fitting. To tackle this issue, this paper proposes a novel Enhanced Instance Replay (EIR) method, which not only preserves knowledge of old classes while simultaneously eliminating background confusion by instance storage of old classes, but also mitigates background shifts in the new images by integrating stored instances with new images. By effectively resolving background shifts in both stored and new images, EIR alleviates catastrophic forgetting in the CSS task, thereby enhancing the model’s capacity for CSS. Experimental results validate the efficacy of our approach, which significantly outperforms state-of-the-art CSS methods.
在这项工作中,我们主要关注持续语义分割(CSS),这需要分割网络能够在不断学习新类别的同时,不会遗忘之前已经学过的知识。虽然存储旧类别的图像并将其直接纳入新模型的训练中被证明可以有效缓解分类任务中的灾难性遗忘问题,但这种策略在CSS中却存在明显的局限性。具体来说,带有部分类别注释的存储和新图像会导致未标注类别与背景之间的混淆,使模型拟合复杂化。为了解决这个问题,本文提出了一种新型的增强实例回放(EIR)方法,它不仅通过存储旧类的实例来保留对旧类的知识,同时消除背景混淆,而且还通过整合存储的实例与新图像来缓解新图像中的背景变化。通过有效解决存储和新图像中的背景变化问题,EIR减轻了CSS任务中的灾难性遗忘问题,从而增强了模型进行CSS的能力。实验结果验证了我们的方法的有效性,该方法显著优于最先进的CSS方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文关注持续语义分割(CSS)问题,其中要求分割网络能够连续学习新类别,同时不遗忘已学知识。针对分类任务中通过存储旧类别图像并直接将其纳入新模型训练来减轻灾难性遗忘的策略在CSS中的局限性,论文提出了一种新型的增强实例回放(EIR)方法。EIR不仅通过实例存储旧类别来保留对旧知识的了解,同时消除背景混淆,还通过整合存储的实例与新图像来减轻新图像中的背景偏移。实验结果表明,EIR方法在CSS任务上有效缓解灾难性遗忘,显著优于现有CSS方法。
Key Takeaways
- 论文关注持续语义分割(CSS)问题,要求模型在连续学习中能够识别新类别并保留对旧知识的了解。
- 存储旧类别图像并直接用于新模型训练的策略在CSS中存在局限性,会引起类别和背景之间的混淆。
- 提出的增强实例回放(EIR)方法通过实例存储旧类别,以消除背景混淆并保留对旧知识的了解。
- EIR方法还通过整合存储的实例与新图像,减轻新图像中的背景偏移问题。
- EIR方法有效缓解CSS任务中的灾难性遗忘问题。
- 实验结果表明,EIR方法在CSS任务上的表现显著优于现有的方法。
- EIR方法为持续语义分割提供了一个有效的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

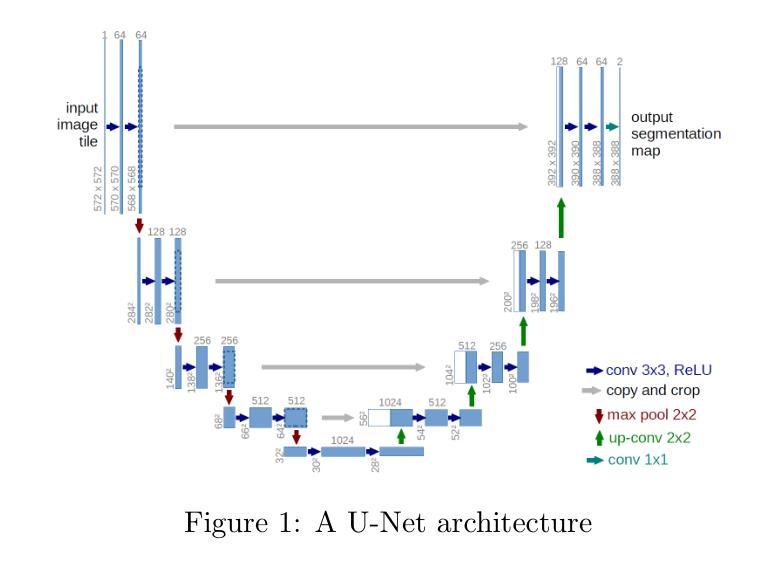
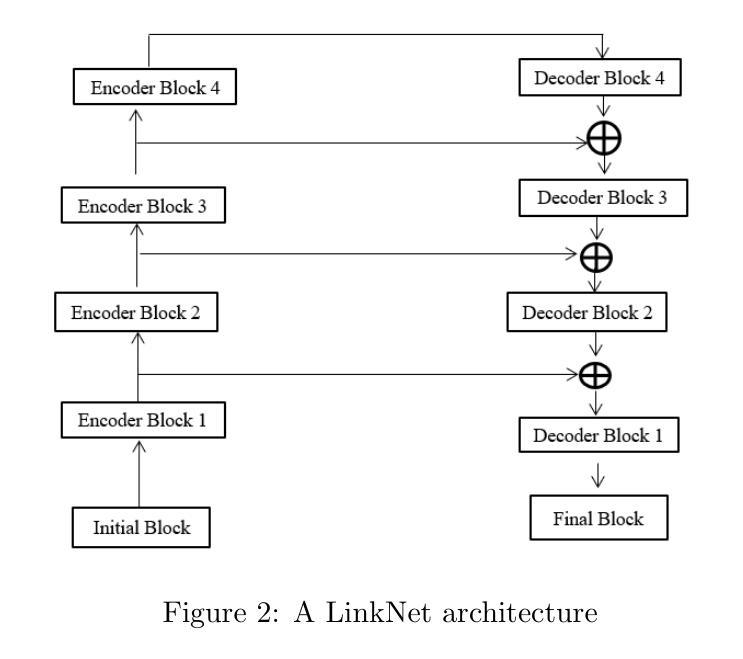
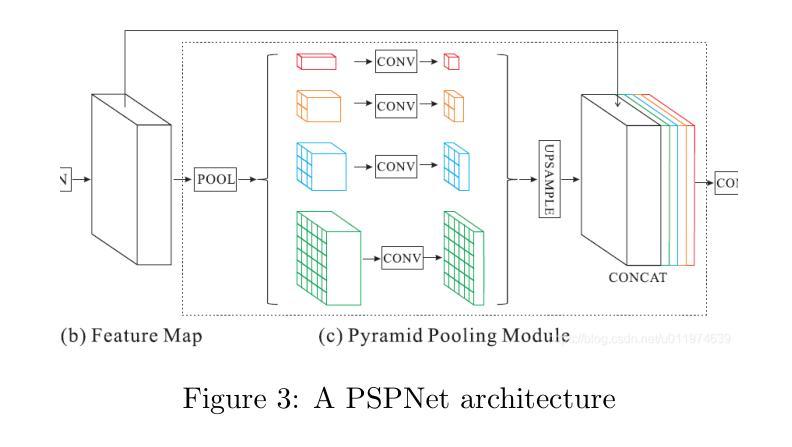
Semantic segmentation for building houses from wooden cubes
Authors:Ivan Beleacov
Automated construction is one of the most promising areas that can improve efficiency, reduce costs and minimize errors in the process of building construction. In this paper, a comparative analysis of three neural network models for semantic segmentation, U-Net(light), LinkNet and PSPNet, is performed. Two specialized datasets with images of houses built from wooden cubes were created for the experiments. The first dataset contains 4 classes (background, foundation, walls, roof ) and is designed for basic model evaluation, while the second dataset includes 44 classes where each cube is labeled as a separate object. The models were trained with the same hyperparameters and their accuracy was evaluated using MeanIoU and F1 Score metrics. According to the results obtained, U-Net(light) showed the best performance with 78% MeanIoU and 87% F1 Score on the first dataset and 17% and 25% respectively on the second dataset. The poor results on the second dataset are due to the limited amount of data, the complexity of the partitioning and the imbalance of classes, making it difficult to accurately select individual cubes. In addition, overtraining was observed in all experiments, manifested by high accuracy on the training dataset and its significant decrease on the validation dataset. The present work is the basis for the development of algorithms for automatic generation of staged building plans, which can be further scaled to design complete buildings. Future research is planned to extend the datasets and apply methods to combat overfitting (L1/L2 regularization, Early Stopping). The next stage of work will be the development of algorithms for automatic generation of a step-by-step plan for building houses from cubes using manipulators. Index Terms-Deep Learning, Computer vision, CNN, Semantic segmentation, Construction materials.
自动化建造是一个能够提高建造效率、降低成本并减少错误的领域之一。本文比较分析了三种用于语义分割的神经网络模型,即U-Net(轻量级)、LinkNet和PSPNet。为了实验,创建了两组包含由木方块建造的房屋的图片数据集。第一组数据集包含四类(背景、地基、墙壁、屋顶),用于基础模型评估;而第二组数据集则包含44类,其中每个木方块都被标记为一个单独的对象。这些模型采用相同的超参数进行训练,并使用MeanIoU和F1分数指标对其准确性进行评估。根据结果,U-Net(轻量级)表现最佳,在第一组数据集上达到78%的MeanIoU和87%的F1分数,而在第二组数据集上分别为17%和25%。第二组数据的结果不佳是由于数据量有限、分区复杂以及类别不平衡,导致难以准确选择单个木方块。此外,所有实验中均观察到过拟合现象,表现为训练集上的准确性很高,而在验证集上的准确性却大幅下降。目前的工作是开发用于自动生成分阶段建筑计划的算法的基础,这些算法可以进一步扩展以设计完整的建筑物。未来的研究计划是扩展数据集并应用方法来对抗过拟合(L1/L2正则化、早期停止)。下一阶段的工作将是开发算法,以自动生成使用操纵器从木方块建造房屋的逐步计划。关键词:深度学习、计算机视觉、卷积神经网络、语义分割、建筑材料。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 6 figures, 2 tables
Summary
本文比较分析了三种神经网络模型(U-Net(light)、LinkNet和PSPNet)在语义分割方面的表现,应用于自动化建筑领域。实验采用包含木制立方体建造房屋图像的两个专用数据集,结果U-Net(light)表现最佳。这为开发用于自动生成分阶段建筑计划的算法奠定了基础,未来研究将扩展数据集并应用方法对抗过拟合问题。
Key Takeaways
- 自动化建筑领域具有提高效率、降低成本和减少错误的潜力。
- 三种神经网络模型(U-Net(light)、LinkNet和PSPNet)在语义分割方面进行比较分析。
- 采用包含木制立方体建造房屋图像的两个专用数据集进行实验。
- U-Net(light)在实验中表现最佳,在基本数据集上达到78%的MeanIoU和87%的F1分数。
- 第二数据集的较差结果是由于数据量有限、分区复杂以及类别不平衡所导致的。
- 所有实验中观察到过拟合现象,未来研究计划包括扩展数据集并应用方法对抗过拟合(如L1/L2正则化、早期停止)。
点此查看论文截图

A Deep Learning Framework for Boundary-Aware Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Tai An, Weiqiang Huang, Da Xu, Qingyuan He, Jiacheng Hu, Yujia Lou
As a fundamental task in computer vision, semantic segmentation is widely applied in fields such as autonomous driving, remote sensing image analysis, and medical image processing. In recent years, Transformer-based segmentation methods have demonstrated strong performance in global feature modeling. However, they still struggle with blurred target boundaries and insufficient recognition of small targets. To address these issues, this study proposes a Mask2Former-based semantic segmentation algorithm incorporating a boundary enhancement feature bridging module (BEFBM). The goal is to improve target boundary accuracy and segmentation consistency. Built upon the Mask2Former framework, this method constructs a boundary-aware feature map and introduces a feature bridging mechanism. This enables effective cross-scale feature fusion, enhancing the model’s ability to focus on target boundaries. Experiments on the Cityscapes dataset demonstrate that, compared to mainstream segmentation methods, the proposed approach achieves significant improvements in metrics such as mIOU, mDICE, and mRecall. It also exhibits superior boundary retention in complex scenes. Visual analysis further confirms the model’s advantages in fine-grained regions. Future research will focus on optimizing computational efficiency and exploring its potential in other high-precision segmentation tasks.
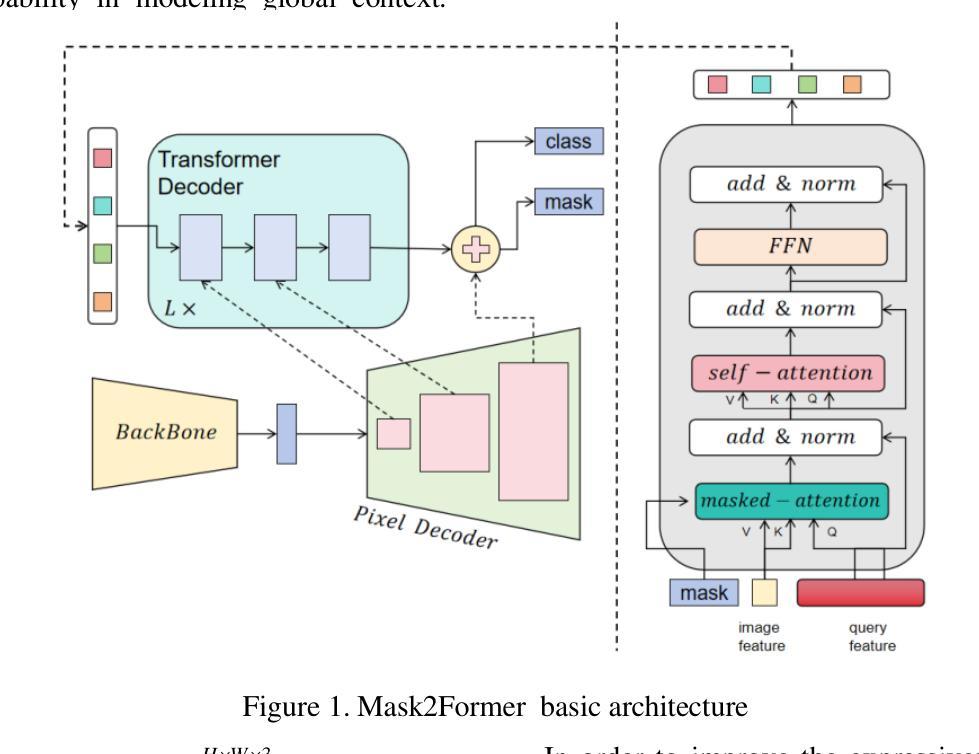
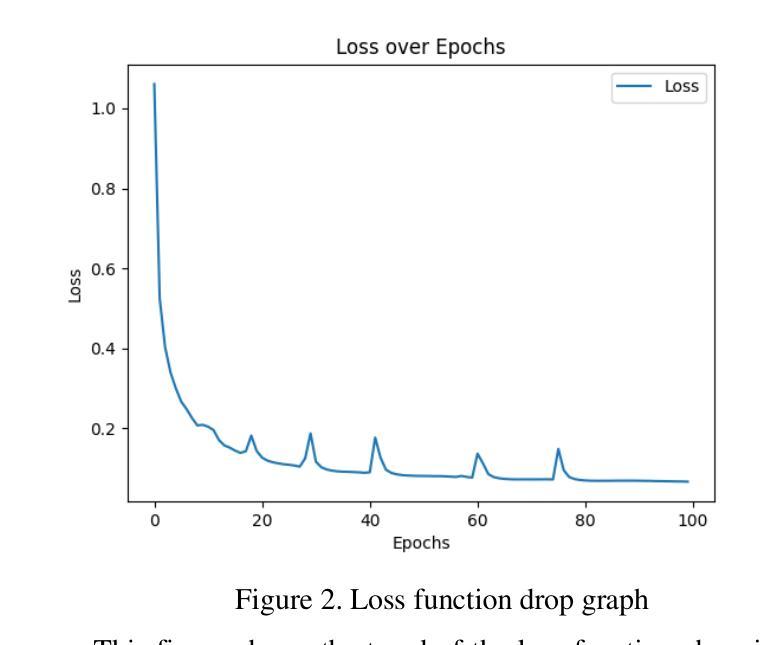
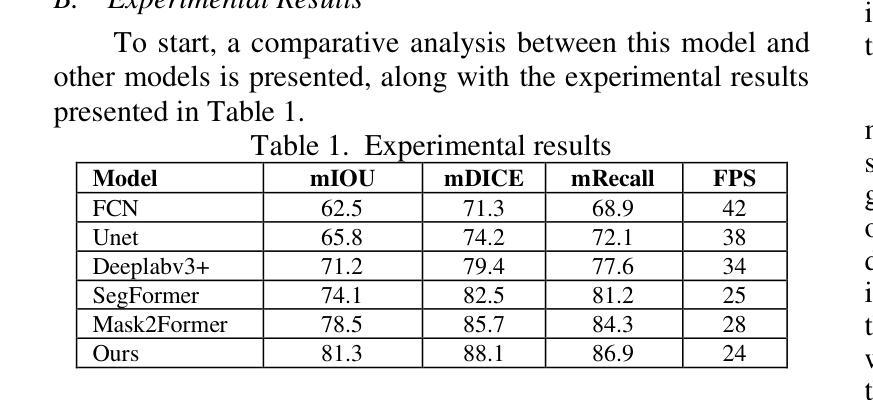
语义分割是计算机视觉中的一项基本任务,广泛应用于自动驾驶、遥感图像分析和医学图像处理等领域。近年来,基于Transformer的分割方法在全局特征建模方面表现出强大的性能。然而,它们仍然面临目标边界模糊以及小目标识别不足的问题。为了解决这些问题,本研究提出了一种基于Mask2Former的语义分割算法,该算法融入了一个边界增强特征桥接模块(BEFBM),旨在提高目标边界的准确性和分割的一致性。该方法基于Mask2Former框架,构建了一个边界感知特征图,并引入了一种特征桥接机制,能够实现有效的跨尺度特征融合,增强模型对目标边界的关注度。在城市景观数据集上的实验表明,与主流分割方法相比,该方法在mIOU、mDICE和mRecall等指标上取得了显著的改进,并且在复杂场景中表现出优越的边界保持能力。可视化分析进一步证实了该模型在细节区域的优势。未来的研究将重点关注计算效率的优化,并探索其在其他高精度分割任务中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Transformer的语义分割方法已广泛应用于自动驾驶、遥感图像分析和医疗图像处理等领域。为解决目标边界模糊和小目标识别不足的问题,本研究提出一种基于Mask2Former的语义分割算法,融入边界增强特征桥接模块(BEFBM),旨在提高目标边界精度和分割一致性。实验证明,该方法在Cityscapes数据集上较主流分割方法有明显提升,尤其在mIOU、mDICE和mRecall等指标上表现优异,复杂场景下的边界保留能力也更强。
Key Takeaways
- 语义分割是计算机视觉中的基础任务,广泛应用于多个领域。
- 基于Transformer的分割方法已展现出色的全局特征建模能力。
- 边界增强特征桥接模块(BEFBM)被引入以解决目标边界模糊和小目标识别问题。
- Mask2Former框架被用来构建边界感知特征图,并引入特征桥接机制,实现跨尺度特征融合。
- 在Cityscapes数据集上的实验证明,该方法在多个指标上较主流分割方法有显著提升。
- 该方法在复杂场景下的边界保留能力较强。
点此查看论文截图

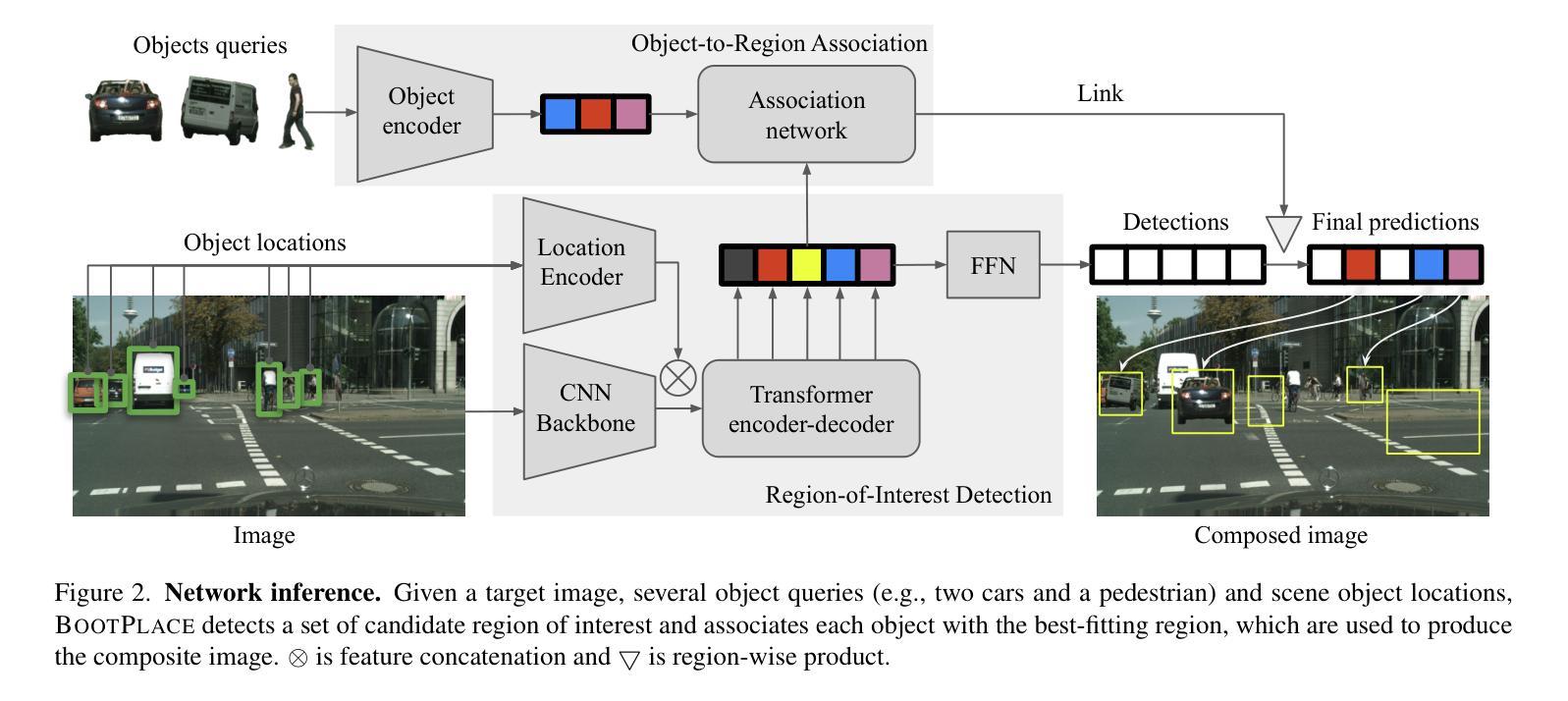
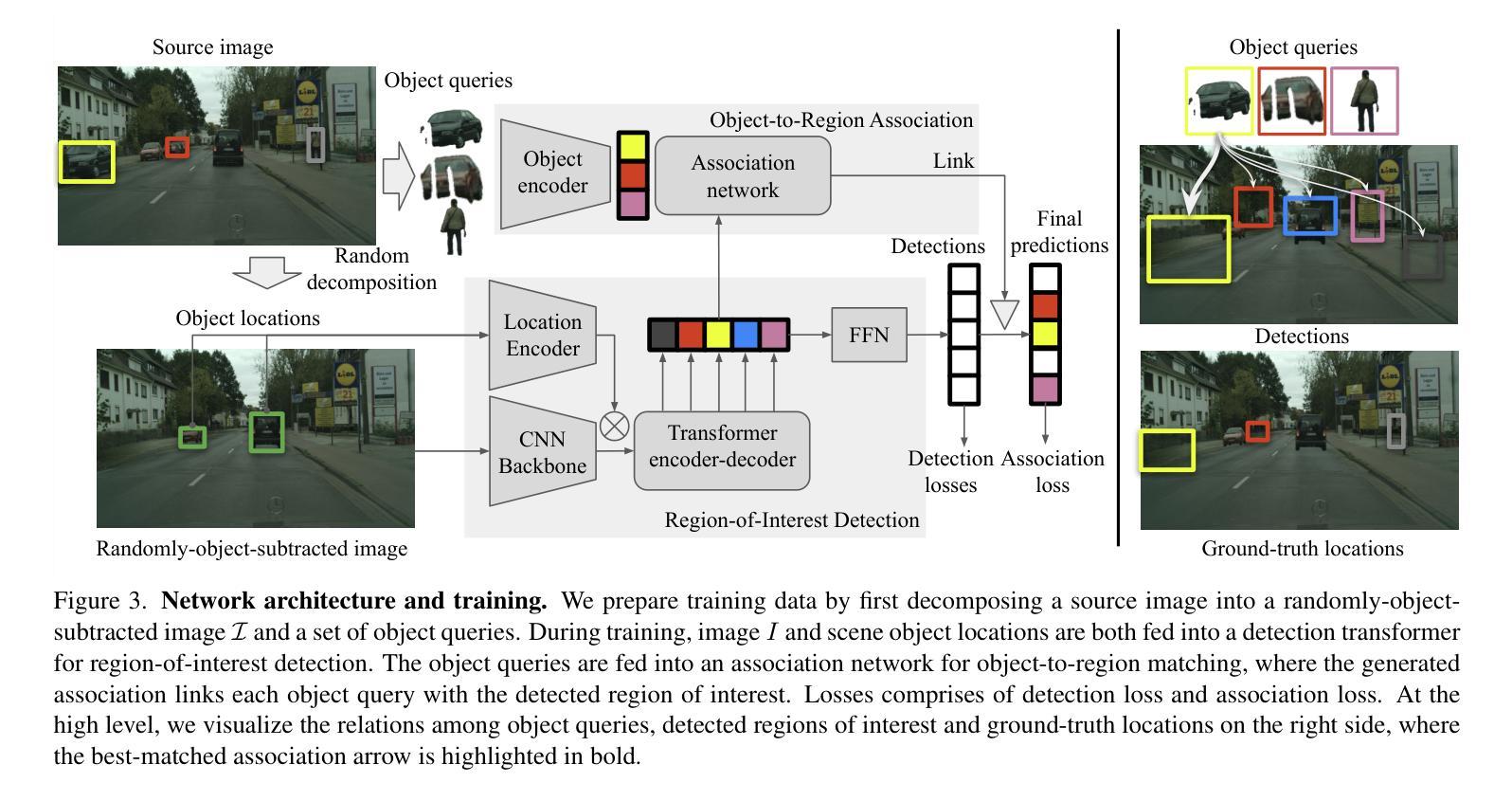
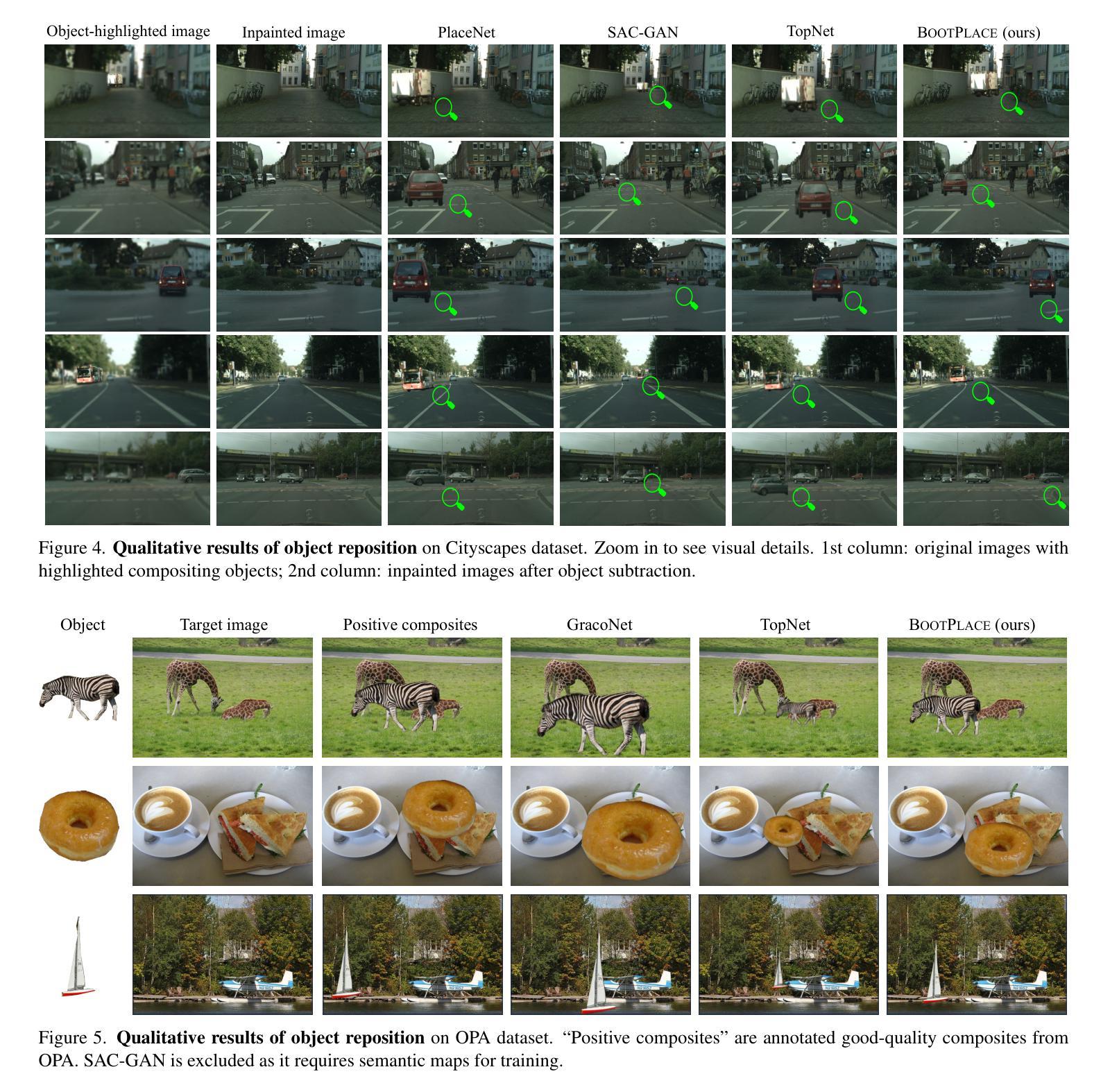
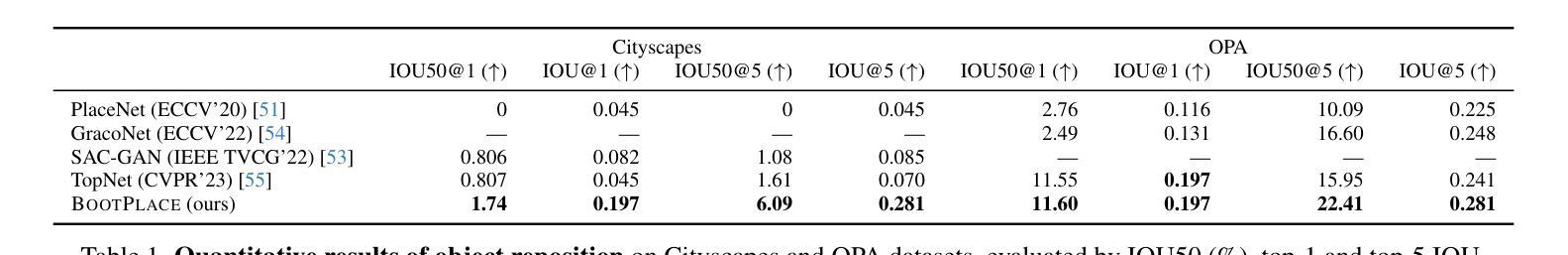
BOOTPLACE: Bootstrapped Object Placement with Detection Transformers
Authors:Hang Zhou, Xinxin Zuo, Rui Ma, Li Cheng
In this paper, we tackle the copy-paste image-to-image composition problem with a focus on object placement learning. Prior methods have leveraged generative models to reduce the reliance for dense supervision. However, this often limits their capacity to model complex data distributions. Alternatively, transformer networks with a sparse contrastive loss have been explored, but their over-relaxed regularization often leads to imprecise object placement. We introduce BOOTPLACE, a novel paradigm that formulates object placement as a placement-by-detection problem. Our approach begins by identifying suitable regions of interest for object placement. This is achieved by training a specialized detection transformer on object-subtracted backgrounds, enhanced with multi-object supervisions. It then semantically associates each target compositing object with detected regions based on their complementary characteristics. Through a boostrapped training approach applied to randomly object-subtracted images, our model enforces meaningful placements through extensive paired data augmentation. Experimental results on established benchmarks demonstrate BOOTPLACE’s superior performance in object repositioning, markedly surpassing state-of-the-art baselines on Cityscapes and OPA datasets with notable improvements in IOU scores. Additional ablation studies further showcase the compositionality and generalizability of our approach, supported by user study evaluations.
本文着重解决图像复制粘贴的图像组合问题,重点关注对象放置学习。先前的方法已经利用生成模型来减少对密集监督的依赖,但这往往限制了它们对复杂数据分布的建模能力。虽然也探索了带有稀疏对比损失的转换器网络,但它们过于宽松的规则化常常导致对象放置不准确。我们引入了BOOTPLACE,这是一种将对象放置制定为检测定位问题的新型范式。我们的方法首先识别适合对象放置的兴趣区域。这是在减去背景对象的图像上训练专用检测转换器实现的,并用多目标监督增强。然后,它根据目标复合对象的补充特征,将这些目标与检测到的区域进行语义关联。通过对随机减去对象的图像应用引导训练法,我们的模型通过大量的配对数据增强来执行有意义的放置。在基准测试上的实验结果表明,BOOTPLACE在对象重新定位方面表现出卓越性能,在Cityscapes和OPA数据集上显著超越了最新基线技术,并在IOU得分上取得了显著的改进。额外的消融研究进一步展示了我们的方法的组合性和通用性,并得到用户研究评估的支持。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Project page: https://ryanhangzhou.github.io/bootplace/ , code: https://github.com/RyanHangZhou/BOOTPLACE
Summary
本文解决复制粘贴图像组合问题,重点关注对象放置学习。引入BOOTPLACE方法,将对象放置问题转化为检测问题。通过训练特定检测器在移除对象的背景上识别合适的感兴趣区域,实现目标合成对象的语义关联。采用随机移除对象的图像进行引导训练,通过广泛的数据增强实现有意义放置。在Cityscapes和OPA数据集上的实验结果表明,BOOTPLACE在对象重新定位方面表现出卓越性能,显著优于现有技术基线,并得到了用户研究的支持。
Key Takeaways
以下是文本的主要观点与见解:
- 本文主要解决复制粘贴图像组合问题,侧重于对象放置学习。
- 引入了一种新型方法BOOTPLACE,将对象放置问题转化为检测问题。
- 通过训练特定检测器识别感兴趣区域,实现目标合成对象的语义关联。
- 采用随机移除对象的图像进行引导训练,增强模型对有意义放置的理解。
- 在Cityscapes和OPA数据集上的实验验证了BOOTPLACE在对象重新定位方面的卓越性能。
- BOOTPLACE显著优于现有技术基线,提高了IOU分数。
点此查看论文截图

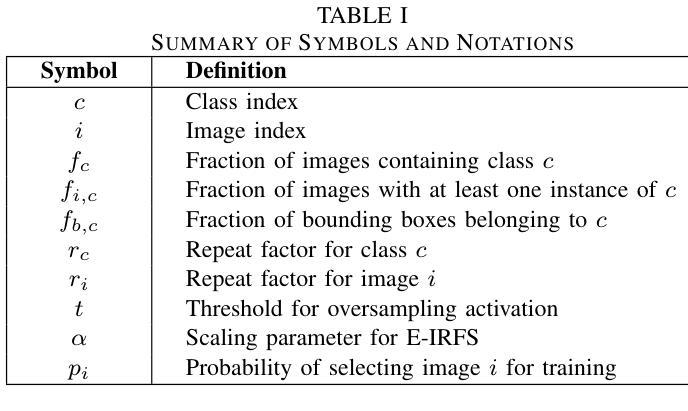
Exponentially Weighted Instance-Aware Repeat Factor Sampling for Long-Tailed Object Detection Model Training in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Surveillance Scenarios
Authors:Taufiq Ahmed, Abhishek Kumar, Constantino Álvarez Casado, Anlan Zhang, Tuomo Hänninen, Lauri Loven, Miguel Bordallo López, Sasu Tarkoma
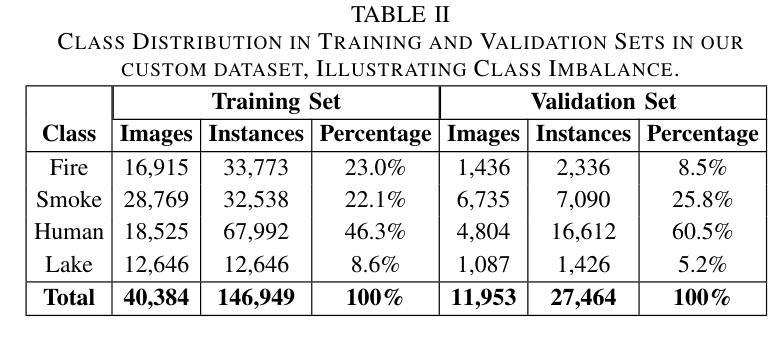
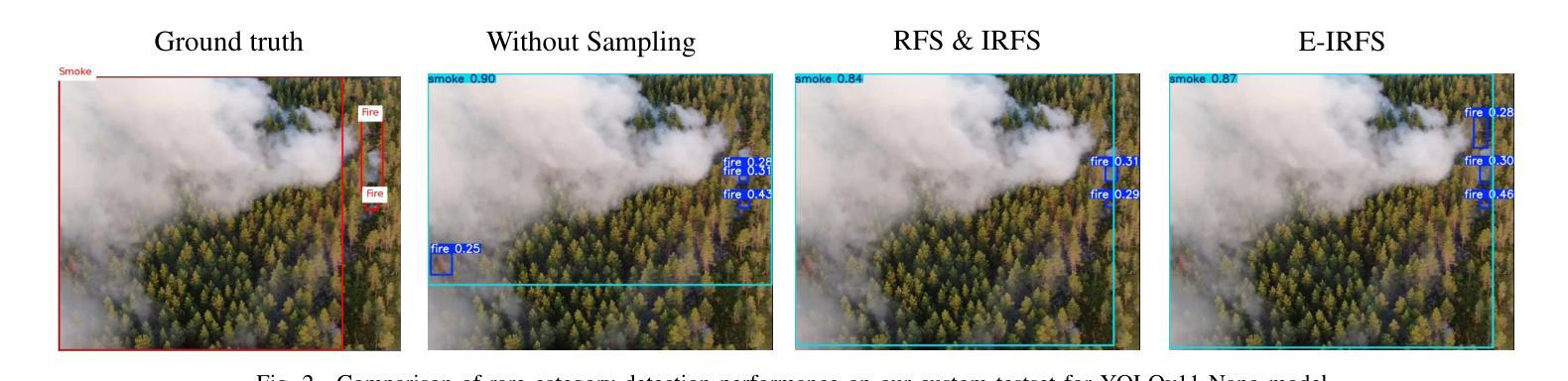
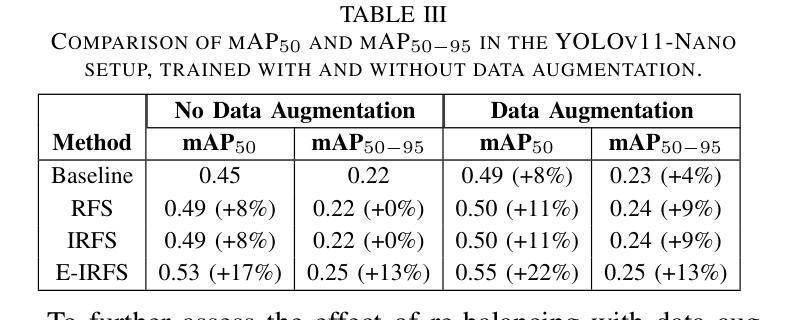
Object detection models often struggle with class imbalance, where rare categories appear significantly less frequently than common ones. Existing sampling-based rebalancing strategies, such as Repeat Factor Sampling (RFS) and Instance-Aware Repeat Factor Sampling (IRFS), mitigate this issue by adjusting sample frequencies based on image and instance counts. However, these methods are based on linear adjustments, which limit their effectiveness in long-tailed distributions. This work introduces Exponentially Weighted Instance-Aware Repeat Factor Sampling (E-IRFS), an extension of IRFS that applies exponential scaling to better differentiate between rare and frequent classes. E-IRFS adjusts sampling probabilities using an exponential function applied to the geometric mean of image and instance frequencies, ensuring a more adaptive rebalancing strategy. We evaluate E-IRFS on a dataset derived from the Fireman-UAV-RGBT Dataset and four additional public datasets, using YOLOv11 object detection models to identify fire, smoke, people and lakes in emergency scenarios. The results show that E-IRFS improves detection performance by 22% over the baseline and outperforms RFS and IRFS, particularly for rare categories. The analysis also highlights that E-IRFS has a stronger effect on lightweight models with limited capacity, as these models rely more on data sampling strategies to address class imbalance. The findings demonstrate that E-IRFS improves rare object detection in resource-constrained environments, making it a suitable solution for real-time applications such as UAV-based emergency monitoring.
对象检测模型经常面临类别不平衡的问题,其中稀有类别的出现频率远远低于常见类别。现有的基于采样的再平衡策略,如重复因子采样(RFS)和实例感知重复因子采样(IRFS),通过根据图像和实例计数调整样本频率来缓解这个问题。然而,这些方法基于线性调整,在长尾分布中限制了其有效性。本文引入了加权实例感知重复因子采样(E-IRFS),这是IRFS的扩展,应用指数缩放来更好地区分稀有类别和常见类别。E-IRFS使用应用于图像和实例频率几何均值的指数函数来调整采样概率,确保更自适应的再平衡策略。我们在从消防无人机RGBT数据集派生的数据集和四套公开数据集上评估了E-IRFS,使用YOLOv11目标检测模型来识别紧急场景中的火灾、烟雾、人员和湖泊。结果表明,E-IRFS在基线基础上提高了22%的检测性能,并且在稀有类别上优于RFS和IRFS。分析还表明,E-IRFS对容量有限的轻量级模型影响更大,因为这些模型更依赖数据采样策略来解决类别不平衡问题。研究结果表明,E-IRFS改进了在资源受限环境中稀有对象的检测,使其成为适用于实时应用(如无人机应急监测)的合适解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
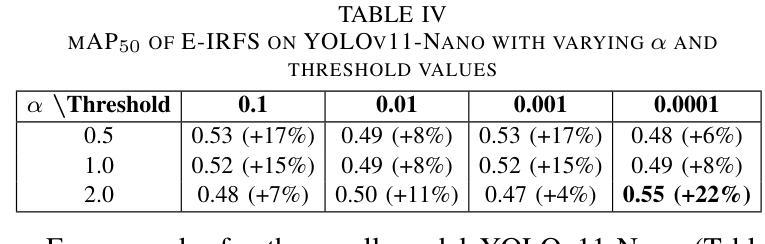
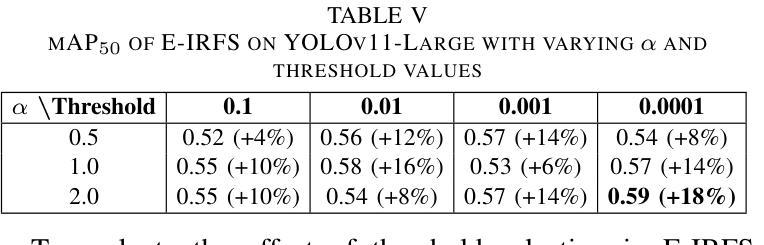
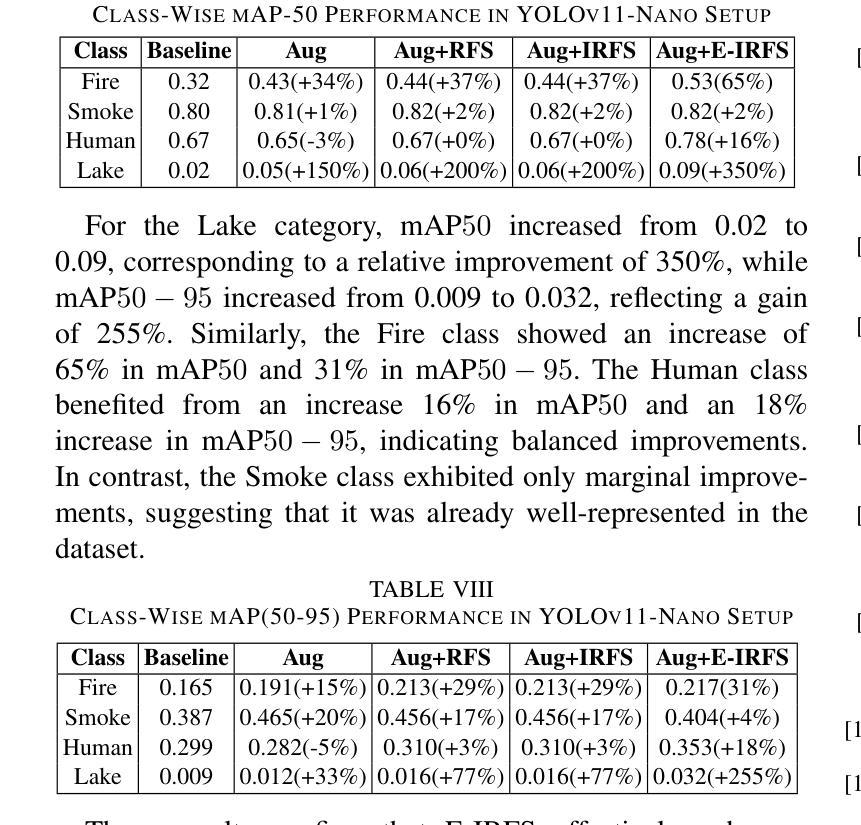
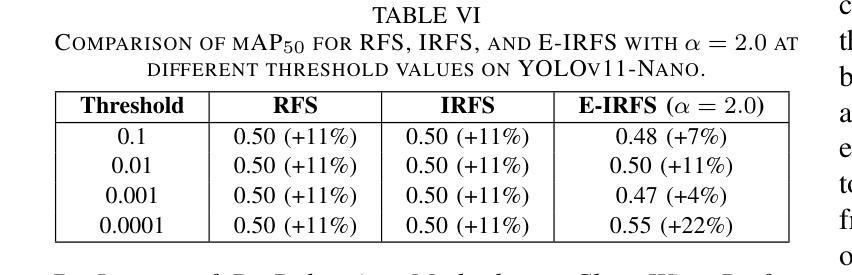
PDF 6 pages, 2 figures, 9 tables, 6 formulas, conference paper
Summary:该文本介绍了一种解决目标检测模型中类别不平衡问题的方法——指数加权实例感知重复因子采样(E-IRFS)。E-IRFS通过应用指数缩放来调整样本概率,更好地区分稀有类和常见类。在紧急场景下的数据集测试中,E-IRFS提高了目标检测性能,特别是在识别火情、烟雾、人员和湖泊等稀有类别时表现更佳。分析显示,E-IRFS对容量有限的轻量级模型效果更强,适用于资源受限环境中的实时应用。
Key Takeaways:
- 目标检测模型面临类别不平衡问题,稀有类别的出现频率远低于常见类别。
- 现有采样重平衡策略如RFS和IRFS通过调整样本频率来解决此问题。
- E-IRFS是IRFS的扩展,应用指数缩放以更好地区分稀有和常见类别。
- E-IRFS通过调整采样概率,使用图像和实例频率的几何平均值进行指数函数应用。
- E-IRFS在多个数据集上的评估表明,与基准方法相比,它提高了目标检测性能22%。
- E-IRFS在识别稀有类别时表现优异,特别是在紧急场景下的数据集测试中。
- 分析显示,E-IRFS对轻量级模型的影响更大,这些模型更依赖于数据采样策略来解决类别不平衡问题。
点此查看论文截图

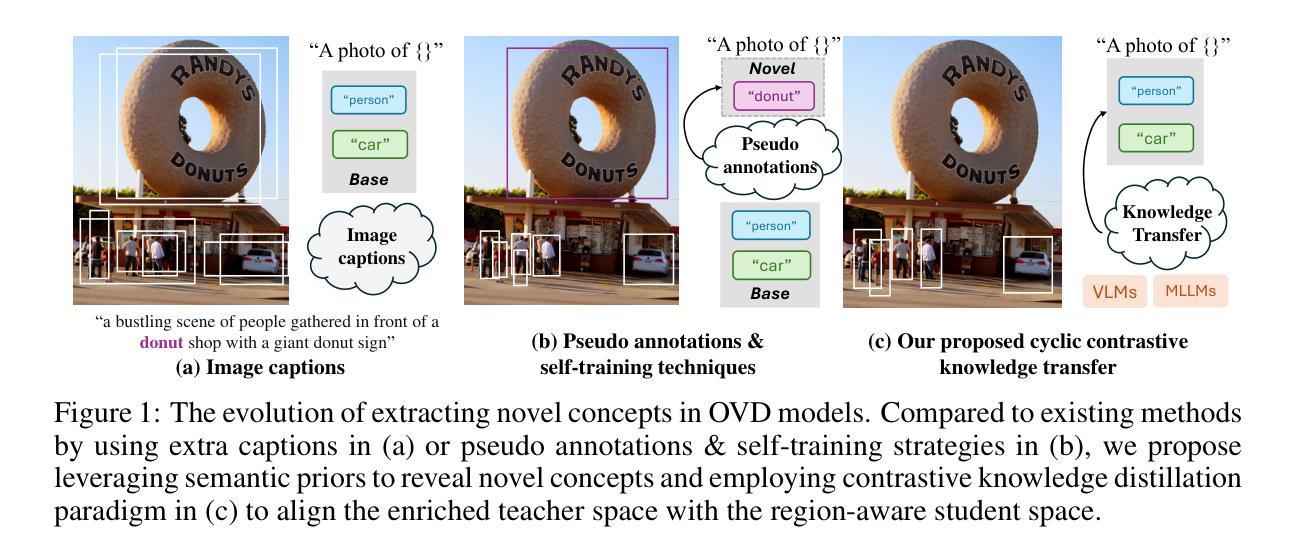
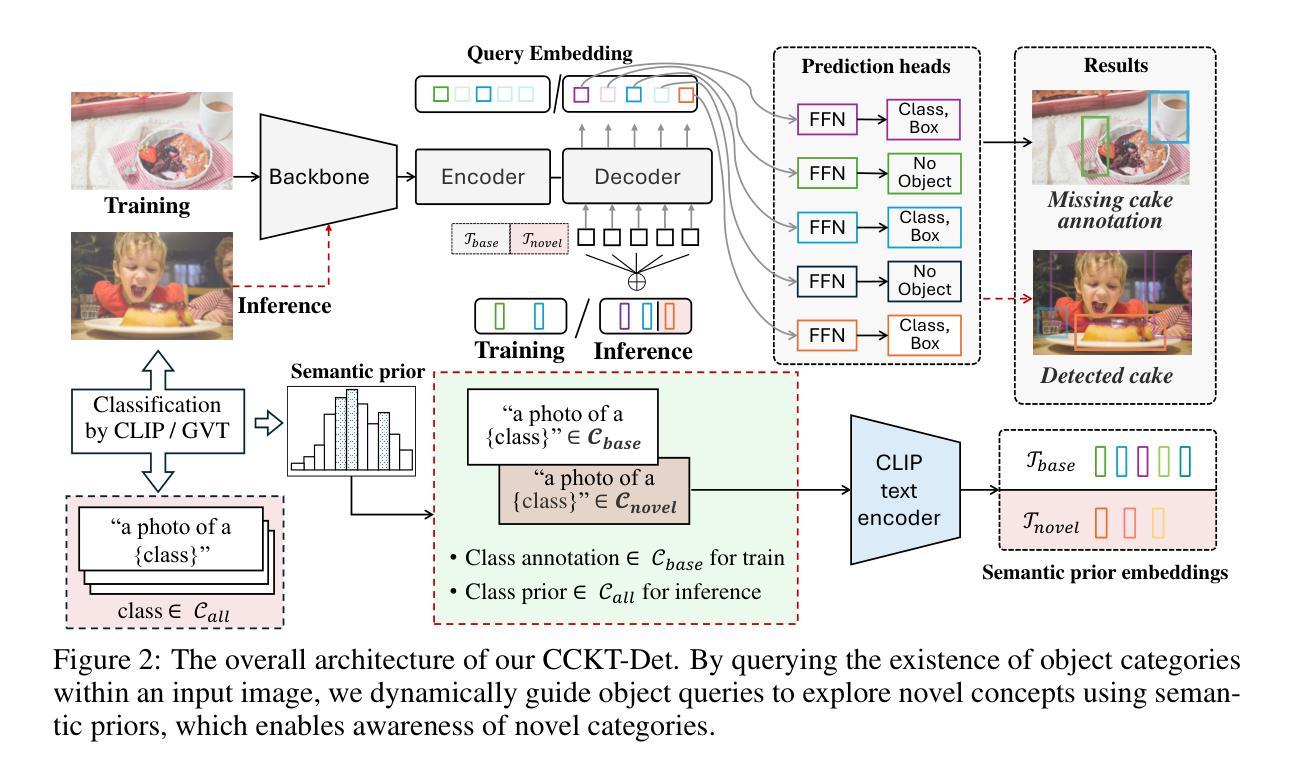
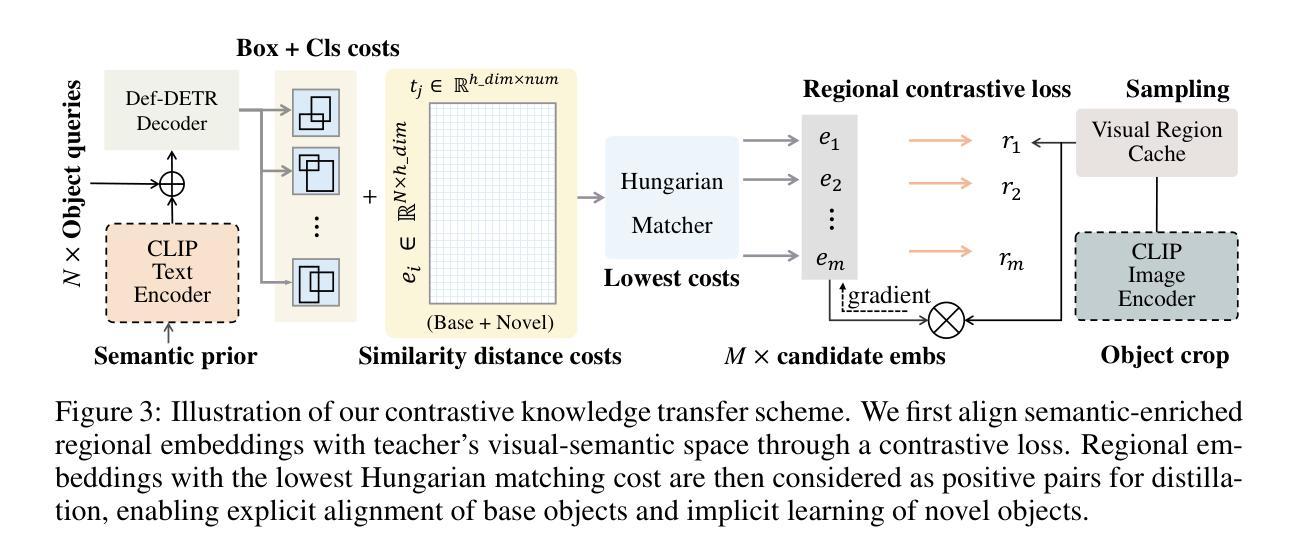
Cyclic Contrastive Knowledge Transfer for Open-Vocabulary Object Detection
Authors:Chuhan Zhang, Chaoyang Zhu, Pingcheng Dong, Long Chen, Dong Zhang
In pursuit of detecting unstinted objects that extend beyond predefined categories, prior arts of open-vocabulary object detection (OVD) typically resort to pretrained vision-language models (VLMs) for base-to-novel category generalization. However, to mitigate the misalignment between upstream image-text pretraining and downstream region-level perception, additional supervisions are indispensable, eg, image-text pairs or pseudo annotations generated via self-training strategies. In this work, we propose CCKT-Det trained without any extra supervision. The proposed framework constructs a cyclic and dynamic knowledge transfer from language queries and visual region features extracted from VLMs, which forces the detector to closely align with the visual-semantic space of VLMs. Specifically, 1) we prefilter and inject semantic priors to guide the learning of queries, and 2) introduce a regional contrastive loss to improve the awareness of queries on novel objects. CCKT-Det can consistently improve performance as the scale of VLMs increases, all while requiring the detector at a moderate level of computation overhead. Comprehensive experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves performance gain of +2.9% and +10.2% AP50 over previous state-of-the-arts on the challenging COCO benchmark, both without and with a stronger teacher model.
在追求检测不受限制的、超出预定类别的物体时,开放词汇表对象检测(OVD)的现有技术通常会借助预训练的视觉语言模型(VLMs)来实现基础到新颖类别的推广。然而,为了减轻上游图像文本预训练和下游区域级别感知之间的不一致性,额外的监督是必不可少的,例如通过自训练策略生成的图像文本对或伪注释。在这项工作中,我们提出了无需任何额外监督的CCKT-Det。所提出的框架构建了从语言查询和从VLMs提取的视觉区域特征之间的循环和动态知识转移,这迫使检测器紧密地对应于VLMs的视觉语义空间。具体来说,1)我们优先过滤并注入语义先验来指导查询学习,2)引入区域对比损失来提高查询对新物体的意识。随着VLMs规模的增加,CCKT-Det可以持续提高性能,同时只需适度增加检测器的计算开销。综合实验结果表明,我们的方法在具有挑战性的COCO基准测试上,相较于之前的最优方法,实现了+2.9%和+10.2%的AP50性能提升,无论是否使用更强的教师模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 5 figures, Published as a conference paper at ICLR 2025
Summary:为提高开放词汇表对象检测的准确率,先前技术主要借助预训练的跨媒体模型(VLMs)进行基础到新颖类别推广。本研究提出无需额外监督的CCKT-Det框架,通过构建循环动态知识转移机制,从语言查询和视觉区域特征中学习。通过预筛选和注入语义先验来引导查询学习,引入区域对比损失提高查询对新颖对象的感知能力。实验结果显示,该方法在COCO基准测试中性能提升显著。
Key Takeaways:
- 开放词汇表对象检测(OVD)面临从语言到视觉的跨媒体对齐挑战。
- 现有方法依赖预训练的视觉语言模型(VLMs)进行类别推广。
- CCKT-Det框架通过循环动态知识转移提高检测性能,无需额外监督。
4.CCKT-Det利用语义先验引导查询学习,提高查询对新颖对象的感知能力。 - 通过引入区域对比损失来强化模型的辨别能力。
- 随着VLM规模的扩大,CCKT-Det的性能可持续提升。
点此查看论文截图

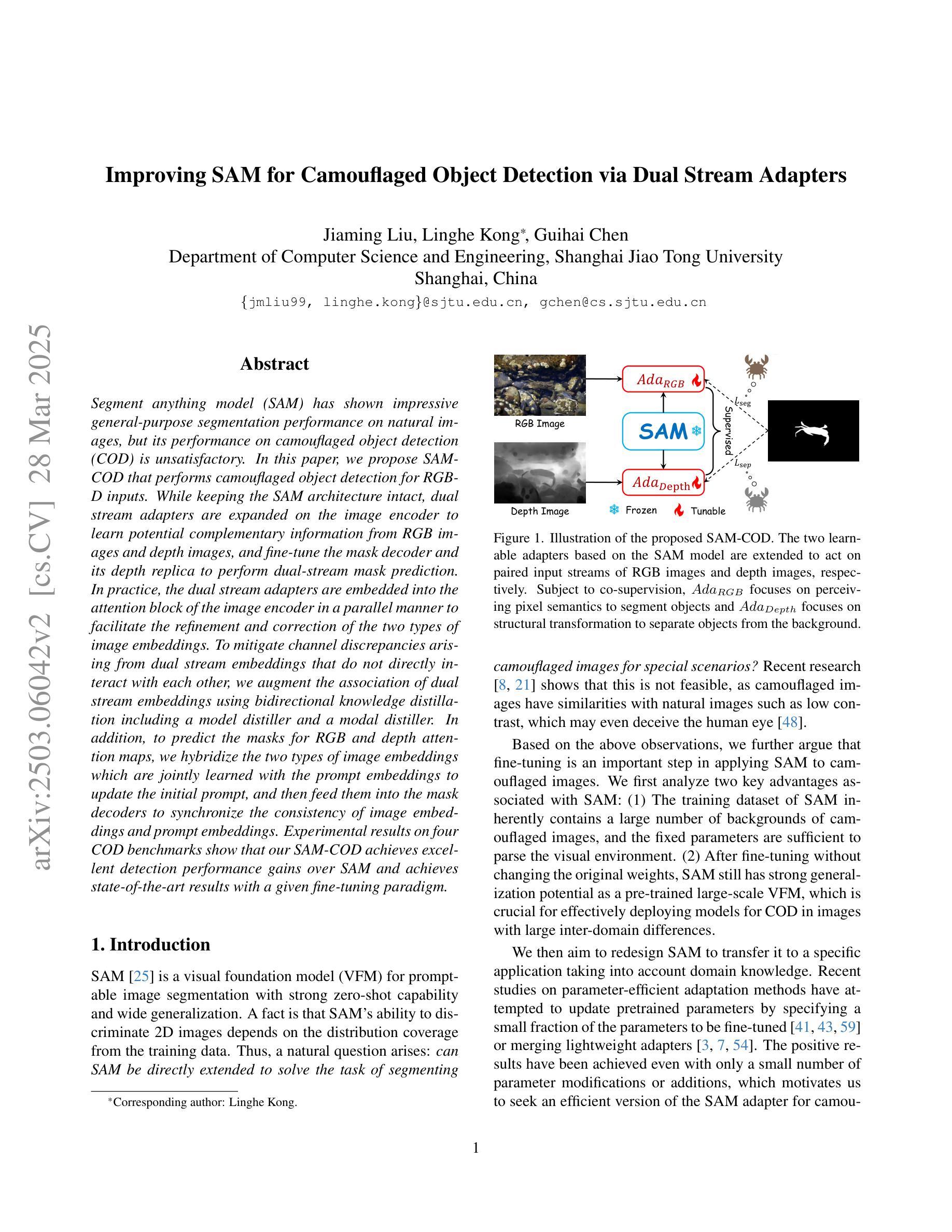
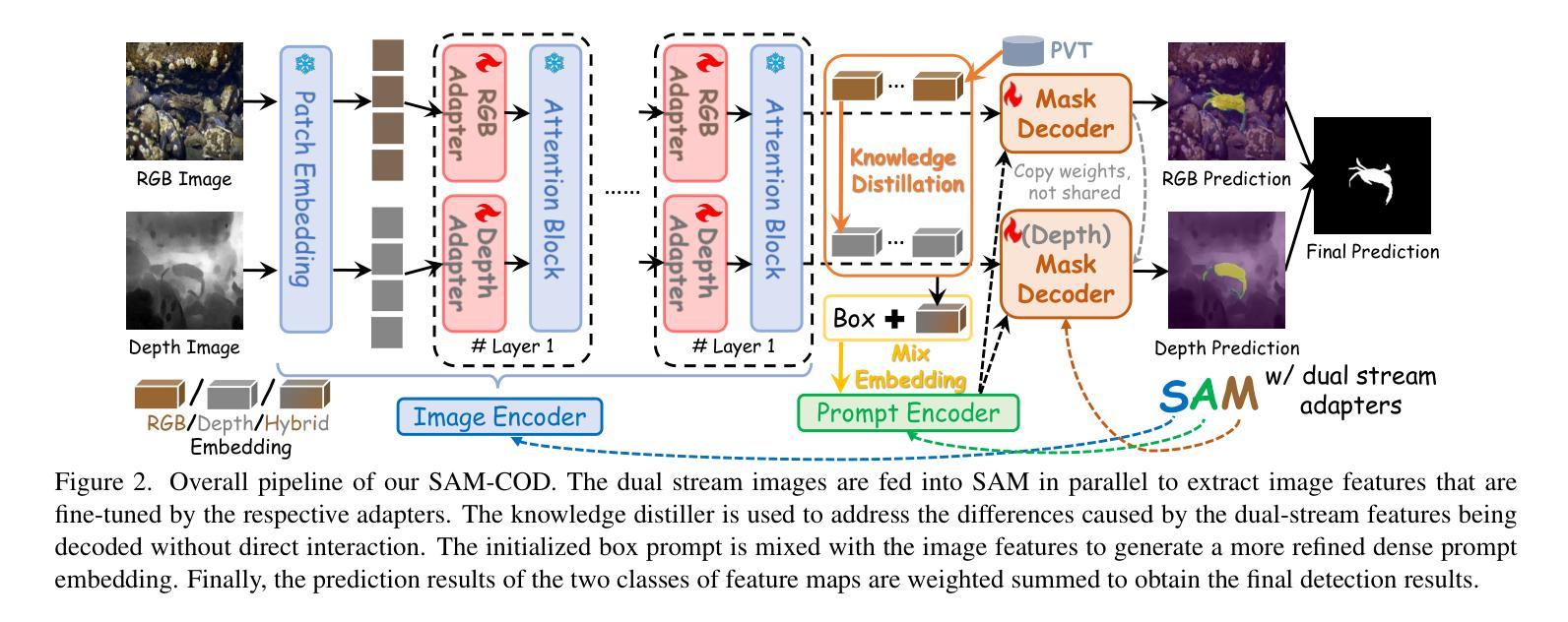
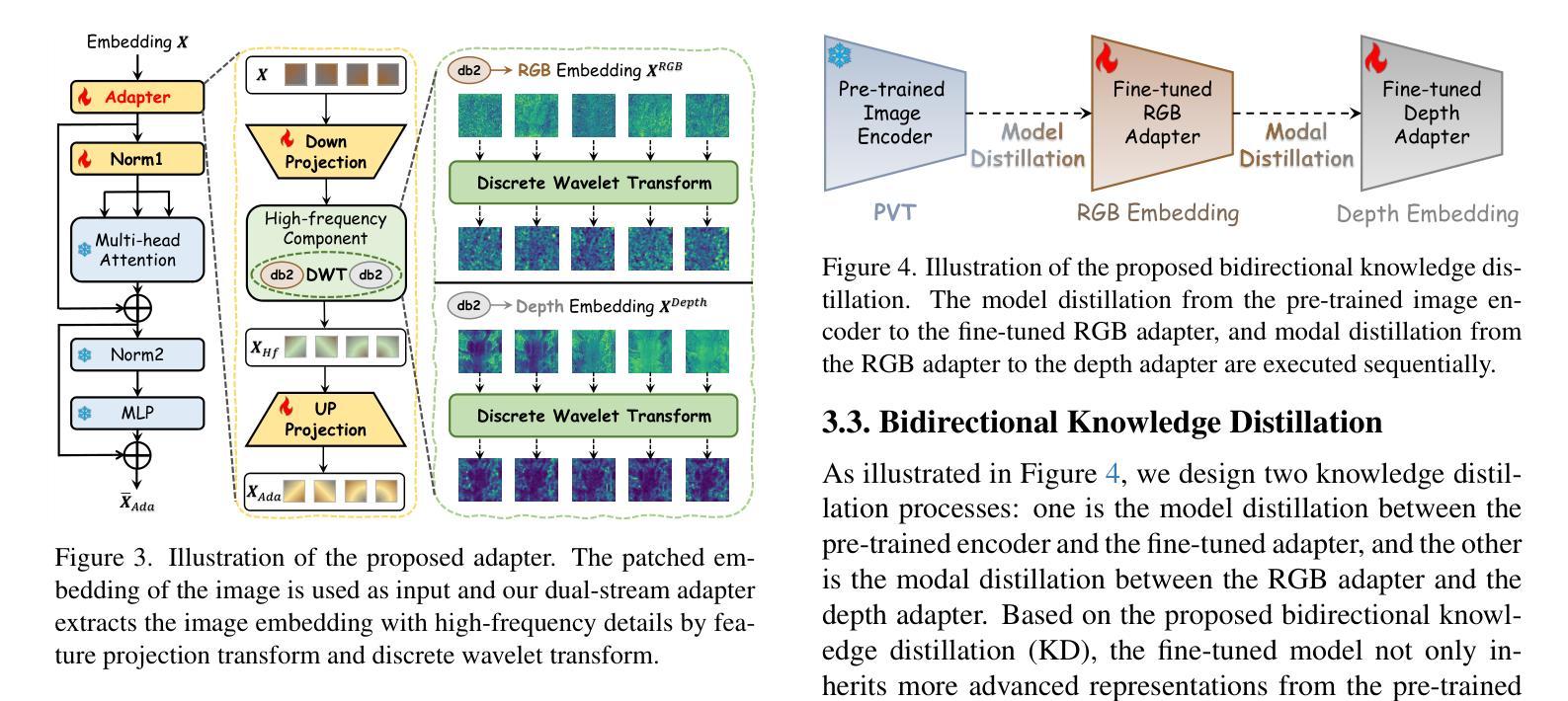
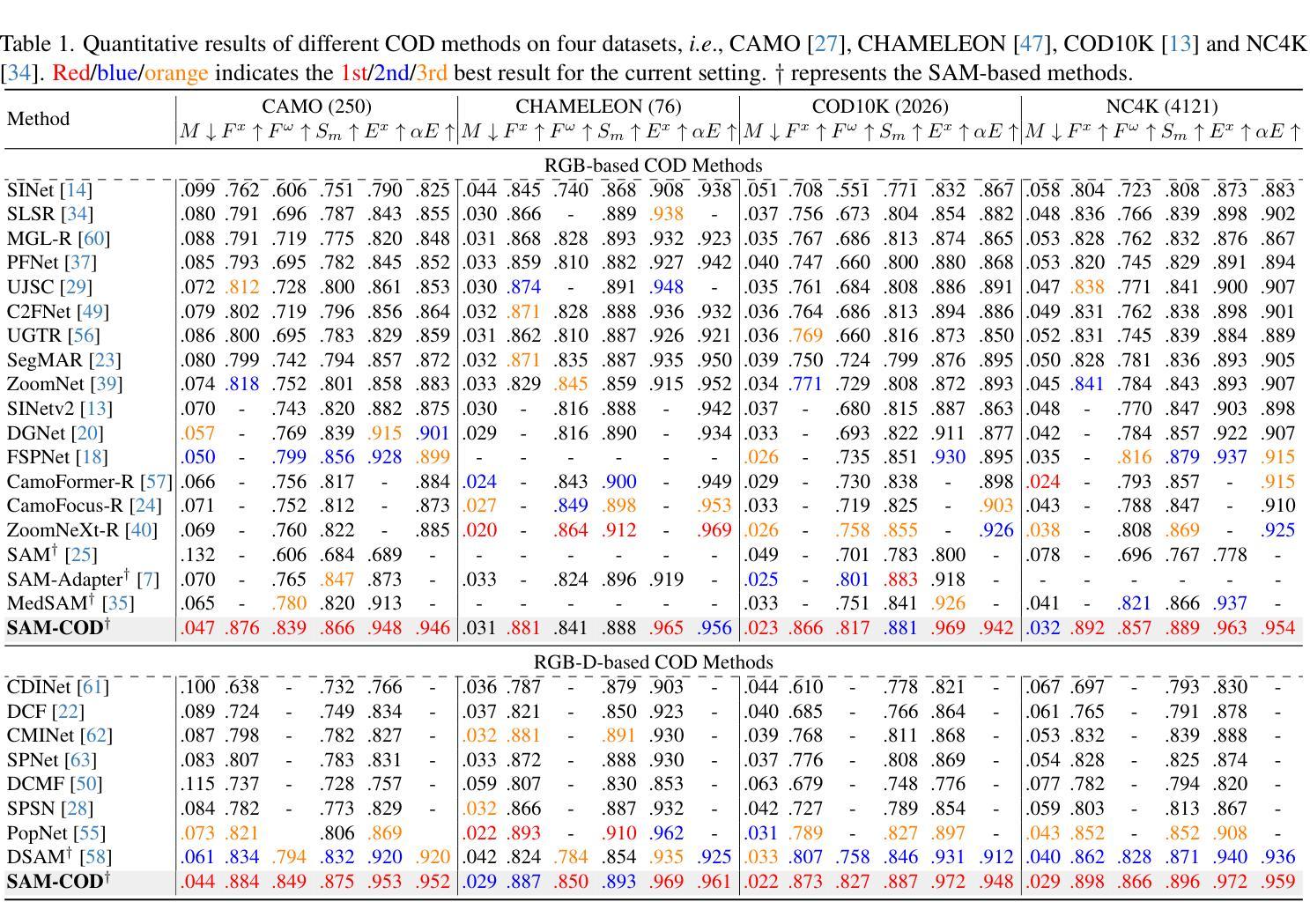
Improving SAM for Camouflaged Object Detection via Dual Stream Adapters
Authors:Jiaming Liu, Linghe Kong, Guihai Chen
Segment anything model (SAM) has shown impressive general-purpose segmentation performance on natural images, but its performance on camouflaged object detection (COD) is unsatisfactory. In this paper, we propose SAM-COD that performs camouflaged object detection for RGB-D inputs. While keeping the SAM architecture intact, dual stream adapters are expanded on the image encoder to learn potential complementary information from RGB images and depth images, and fine-tune the mask decoder and its depth replica to perform dual-stream mask prediction. In practice, the dual stream adapters are embedded into the attention block of the image encoder in a parallel manner to facilitate the refinement and correction of the two types of image embeddings. To mitigate channel discrepancies arising from dual stream embeddings that do not directly interact with each other, we augment the association of dual stream embeddings using bidirectional knowledge distillation including a model distiller and a modal distiller. In addition, to predict the masks for RGB and depth attention maps, we hybridize the two types of image embeddings which are jointly learned with the prompt embeddings to update the initial prompt, and then feed them into the mask decoders to synchronize the consistency of image embeddings and prompt embeddings. Experimental results on four COD benchmarks show that our SAM-COD achieves excellent detection performance gains over SAM and achieves state-of-the-art results with a given fine-tuning paradigm.
分段任何模型(SAM)在自然图像上的通用分割性能令人印象深刻,但在伪装目标检测(COD)方面的表现却不令人满意。在本文中,我们提出了SAM-COD,该模型针对RGB-D输入执行伪装目标检测。在保持SAM架构完整性的同时,在图像编码器上扩展了双流适配器,以从RGB图像和深度图像中学习潜在的互补信息,并微调掩膜解码器及其深度副本以执行双流掩膜预测。在实践中,双流适配器以并行方式嵌入到图像编码器的注意力块中,以促进两种图像嵌入的细化和校正。为了减轻由于双流嵌入不直接相互交互而产生的通道差异,我们使用双向知识蒸馏增强双流嵌入的关联,包括模型蒸馏器和模态蒸馏器。此外,为了预测RGB和深度注意力图的掩膜,我们混合了两种类型的图像嵌入,这些嵌入与提示嵌入一起联合学习以更新初始提示,然后将其输入到掩膜解码器中,以同步图像嵌入和提示嵌入的一致性。在四个COD基准测试上的实验结果表明,我们的SAM-COD在SAM上实现了出色的检测性能提升,并在给定的微调范式下达到了最先进的成果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:SAM模型在自然图像分割方面表现出色,但在伪装目标检测(COD)上的表现不佳。本文提出SAM-COD模型,该模型在RGB-D输入上执行伪装目标检测。通过扩展SAM架构,引入双流适配器学习RGB图像和深度图像之间的潜在互补信息,并微调掩膜解码器及其深度副本以执行双流掩膜预测。实践中,采用双向知识蒸馏技术关联双流嵌入信息以提高准确性,同时使用两种不同的掩膜编码器生成RGB和深度注意力图。实验结果证明,SAM-COD在伪装目标检测方面取得了显著的性能提升,并达到了给定微调模式的最佳状态。
Key Takeaways:
- SAM模型在自然图像分割上表现良好,但在伪装目标检测(COD)上的性能不佳。
- 提出SAM-COD模型以改进在COD上的性能。
- 通过扩展SAM架构并引入双流适配器学习RGB和深度图像的互补信息。
- 采用双向知识蒸馏技术关联双流嵌入信息,以提高检测的准确性。
- 双流适配器嵌入到图像编码器的注意力块中,以优化和校正两种类型的图像嵌入信息。
- 使用两种掩膜编码器生成RGB和深度注意力图以进行掩膜预测。
点此查看论文截图
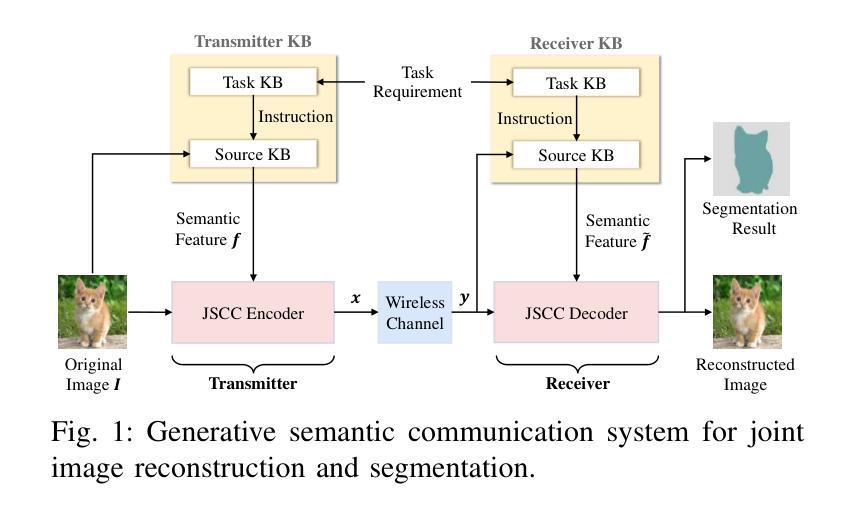
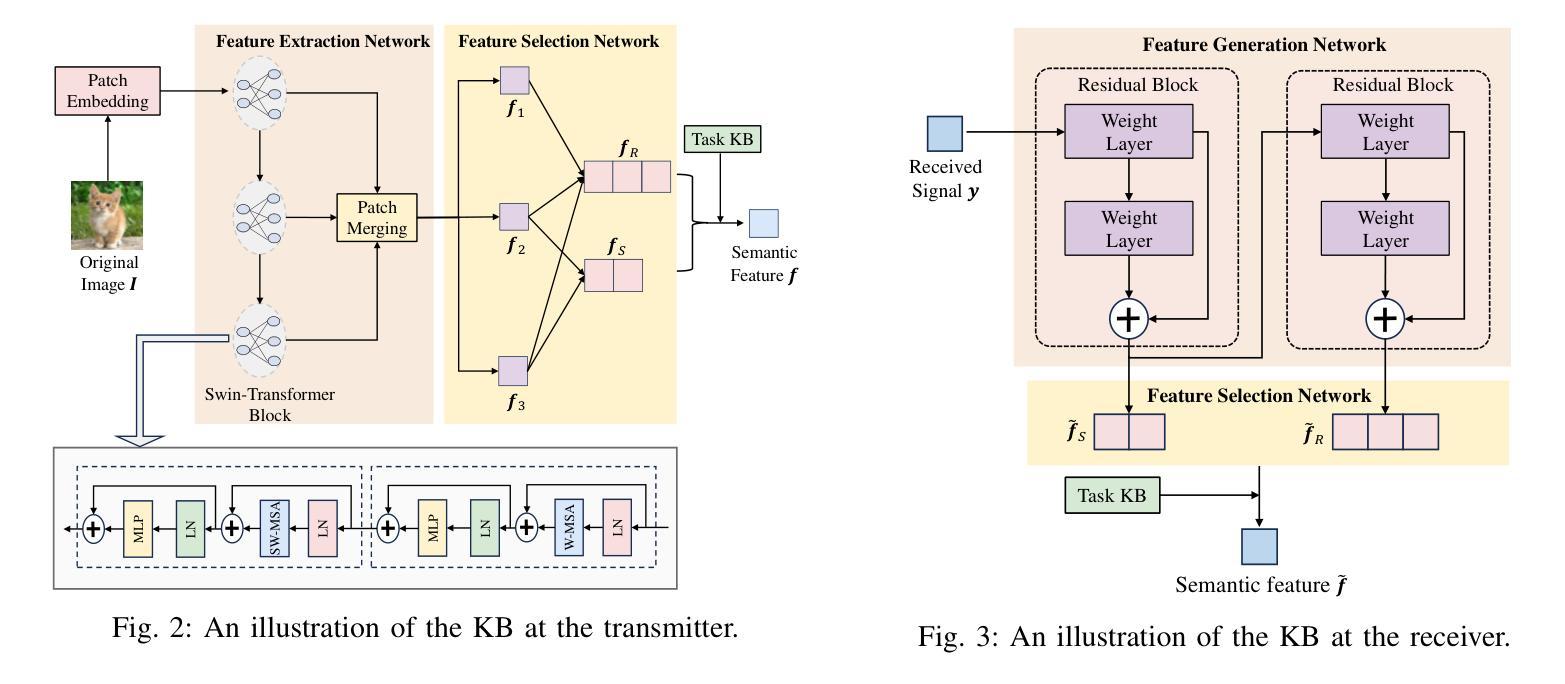
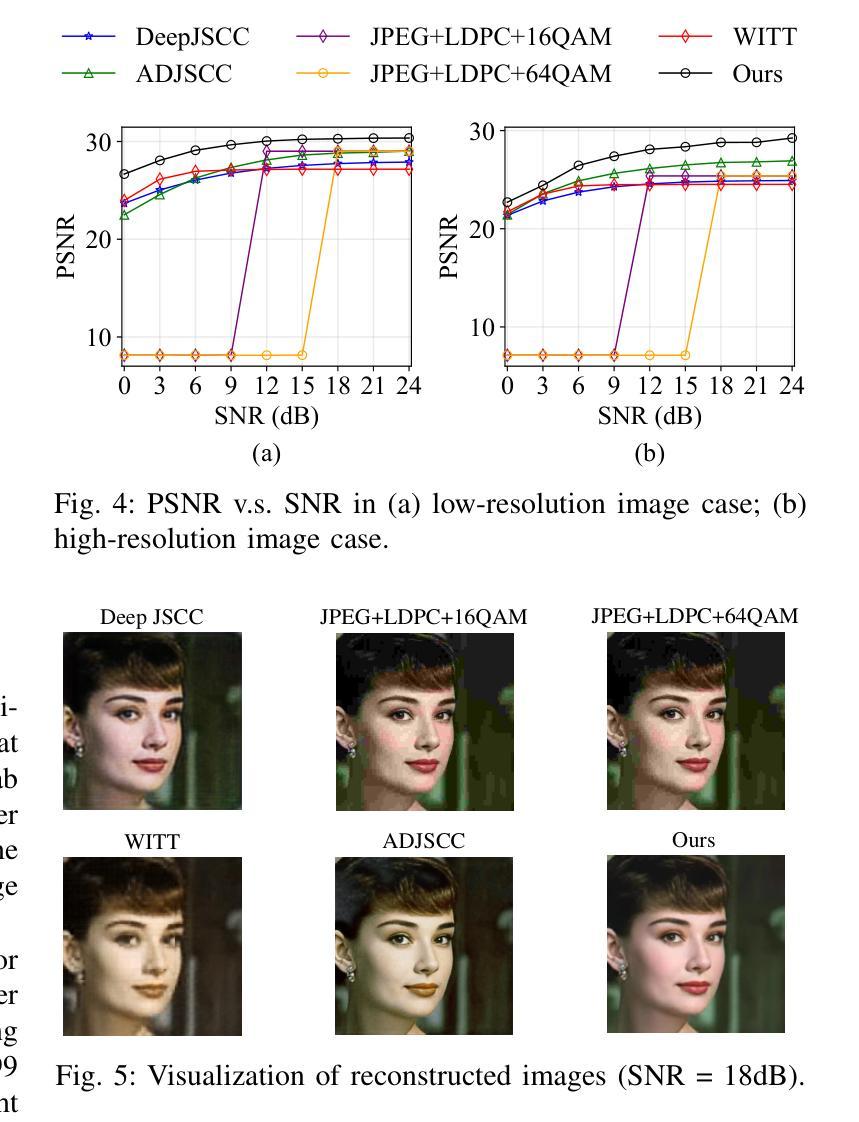
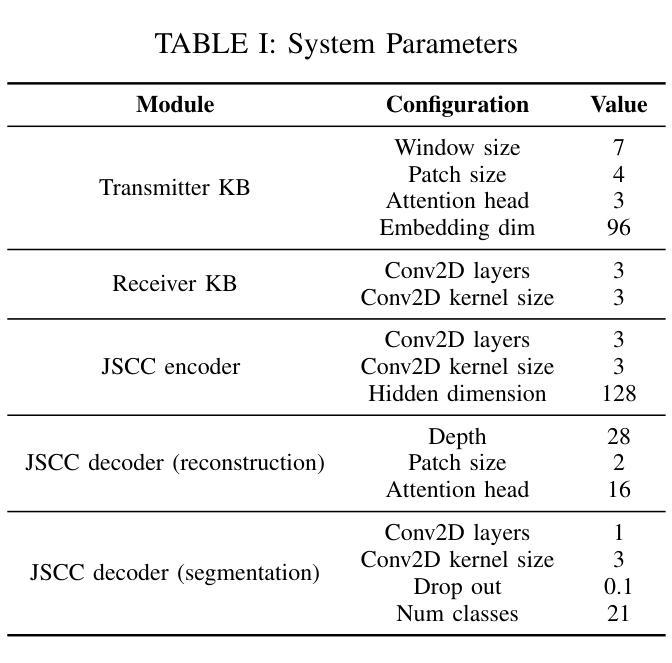
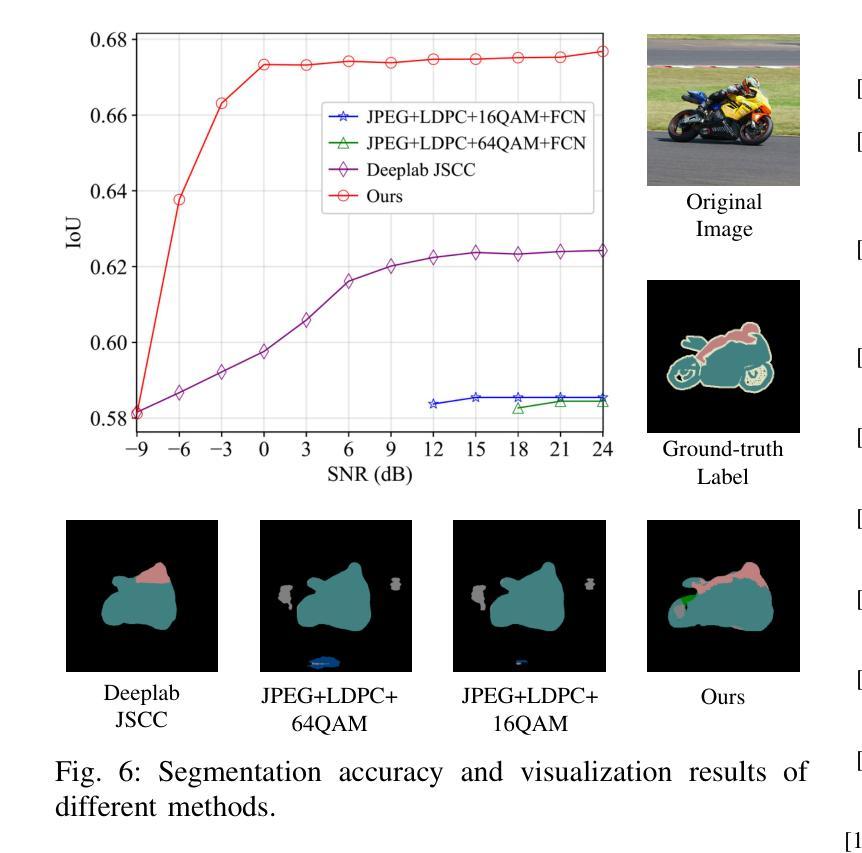
Generative Semantic Communication for Joint Image Transmission and Segmentation
Authors:Weiwen Yuan, Jinke Ren, Chongjie Wang, Ruichen Zhang, Jun Wei, Dong In Kim, Shuguang Cui
Semantic communication has emerged as a promising technology for enhancing communication efficiency. However, most existing research emphasizes single-task reconstruction, neglecting model adaptability and generalization across multi-task systems. In this paper, we propose a novel generative semantic communication system that supports both image reconstruction and segmentation tasks. Our approach builds upon semantic knowledge bases (KBs) at both the transmitter and receiver, with each semantic KB comprising a source KB and a task KB. The source KB at the transmitter leverages a hierarchical Swin-Transformer, a generative AI scheme, to extract multi-level features from the input image. Concurrently, the counterpart source KB at the receiver utilizes hierarchical residual blocks to generate task-specific knowledge. Furthermore, the task KBs adopt a semantic similarity model to map different task requirements into pre-defined task instructions, thereby facilitating the feature selection of the source KBs. Additionally, we develop a unified residual block-based joint source and channel (JSCC) encoder and two task-specific JSCC decoders to achieve the two image tasks. In particular, a generative diffusion model is adopted to construct the JSCC decoder for the image reconstruction task. Experimental results show that our multi-task generative semantic communication system outperforms previous single-task communication systems in terms of peak signal-to-noise ratio and segmentation accuracy.
语义通信作为一种提高通信效率的有前景的技术已经崭露头角。然而,现有的大多数研究强调单一任务的重建,忽视了模型在多任务系统中的适应性和泛化能力。在本文中,我们提出了一种支持图像重建和分割任务的新型生成式语义通信系统。我们的方法建立在发射器和接收器双方的语义知识库(KBs)之上,每个语义知识库都由源知识库和任务知识库组成。发射器的源知识库利用分层Swin-Transformer(一种生成式人工智能方案)从输入图像中提取多层次特征。同时,接收器的对应源知识库利用分层残差块生成特定任务的知识。此外,任务知识库采用语义相似性模型,将不同的任务要求映射到预定义的任务指令中,从而促进了源知识库的特征选择。此外,我们开发了一种基于统一残差块的联合源信道(JSCC)编码器,以及两个针对特定任务的JSCC解码器,以实现两个图像任务。特别是,采用生成扩散模型构建图像重建任务的JSCC解码器。实验结果表明,我们的多任务生成语义通信系统相较于之前的单任务通信系统,在峰值信噪比和分割准确度方面表现出更优的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted by the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops and is scheduled for publication
Summary
本文提出一种支持图像重建和分割任务的多任务生成语义通信系统。该系统基于发送器和接收器端的语义知识库,利用分层Swin-Transformer和生成AI方案提取输入图像的多层次特征,并通过任务特定的知识库实现任务映射和特征选择。实验结果表明,该系统在峰值信噪比和分割精度方面优于单一任务的通信系统。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种多任务生成语义通信系统,支持图像重建和分割任务。
- 系统基于语义知识库,包括源知识库和任务知识库。
- 发送端的源知识库利用分层Swin-Transformer提取多层次特征,生成AI方案用于处理。
- 接收端的源知识库利用层次残差块生成任务特定知识。
- 任务知识库采用语义相似性模型将不同任务要求映射到预定义的任务指令中。
- 开发了基于统一残差块的联合源和信道编码器以及两个任务特定的解码器。
点此查看论文截图

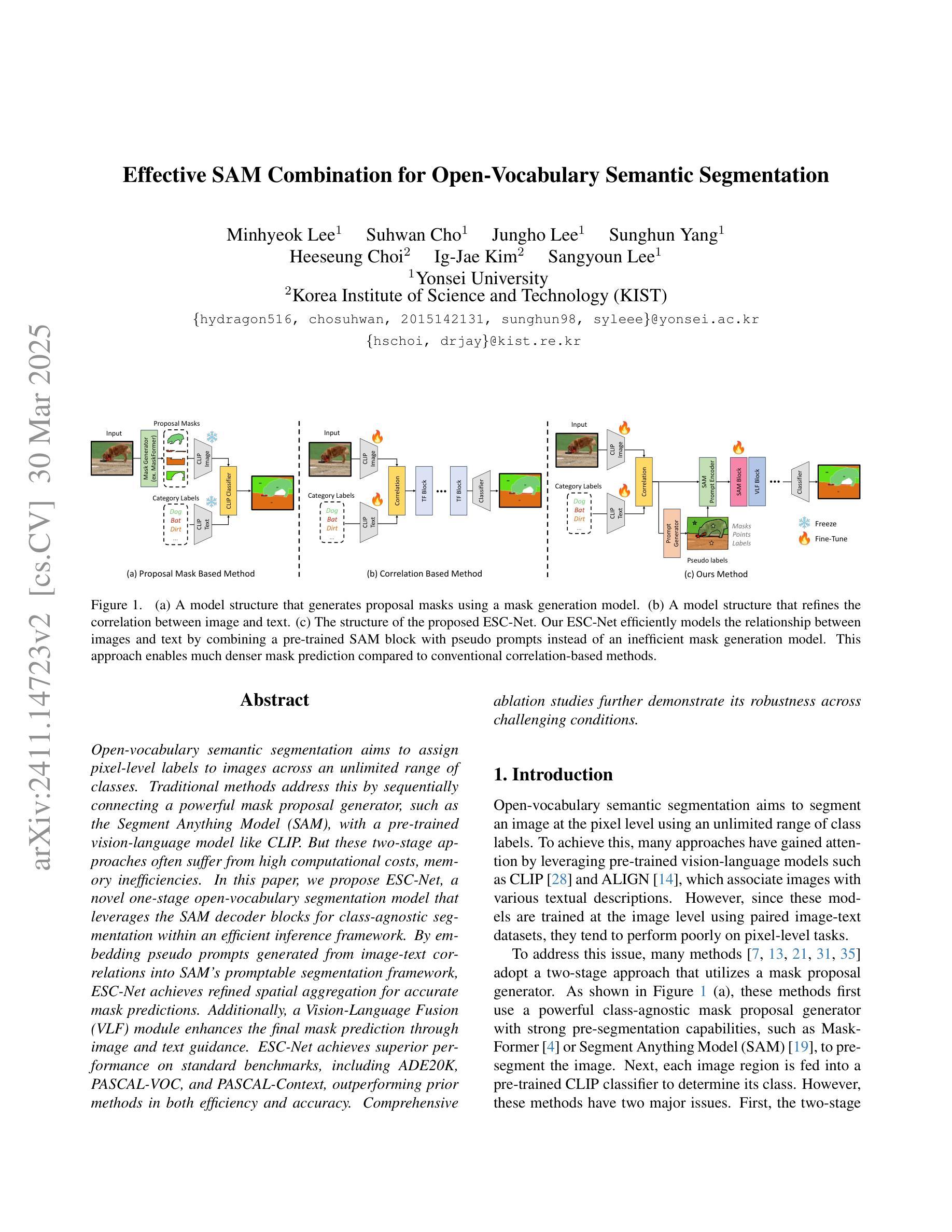
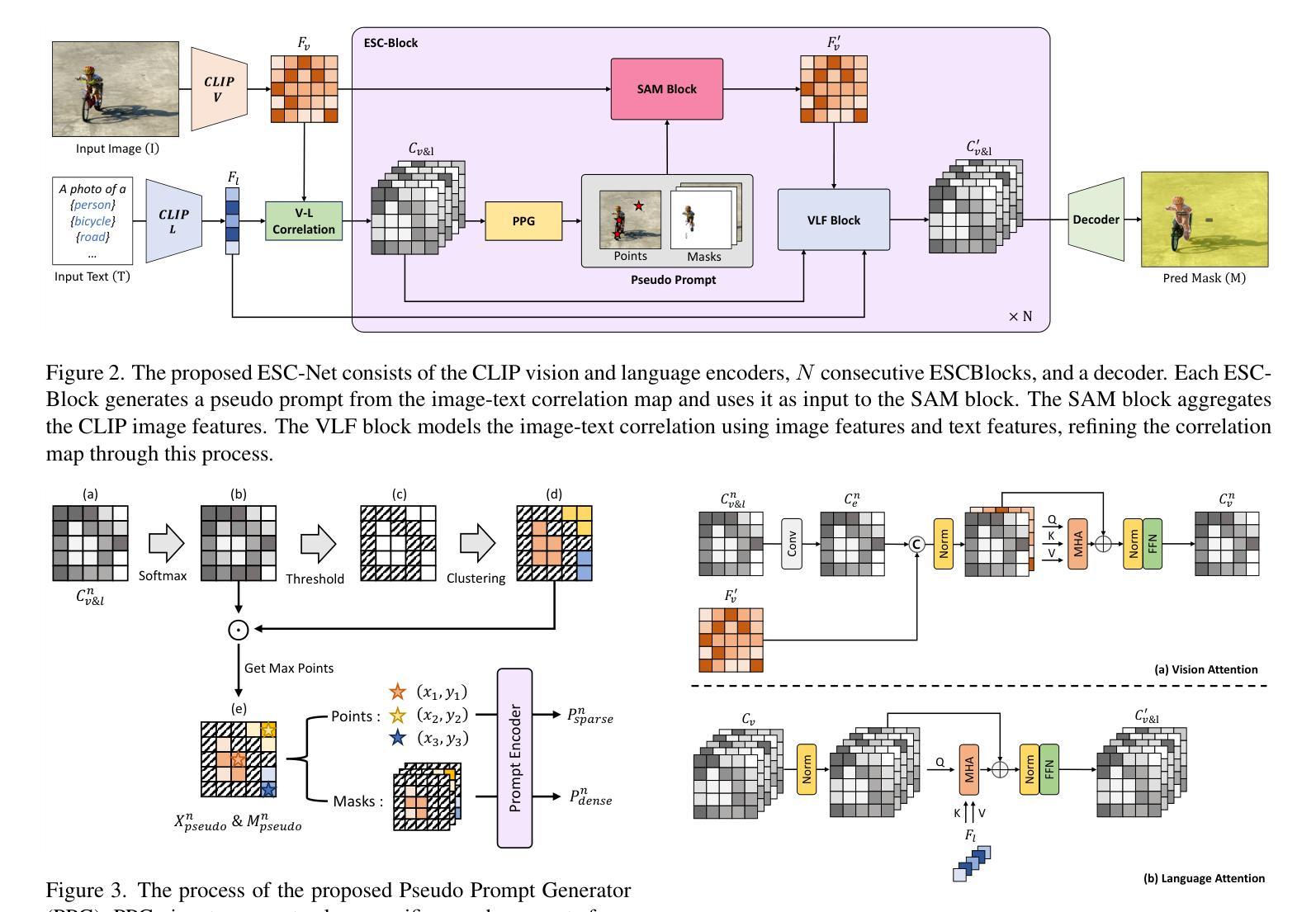
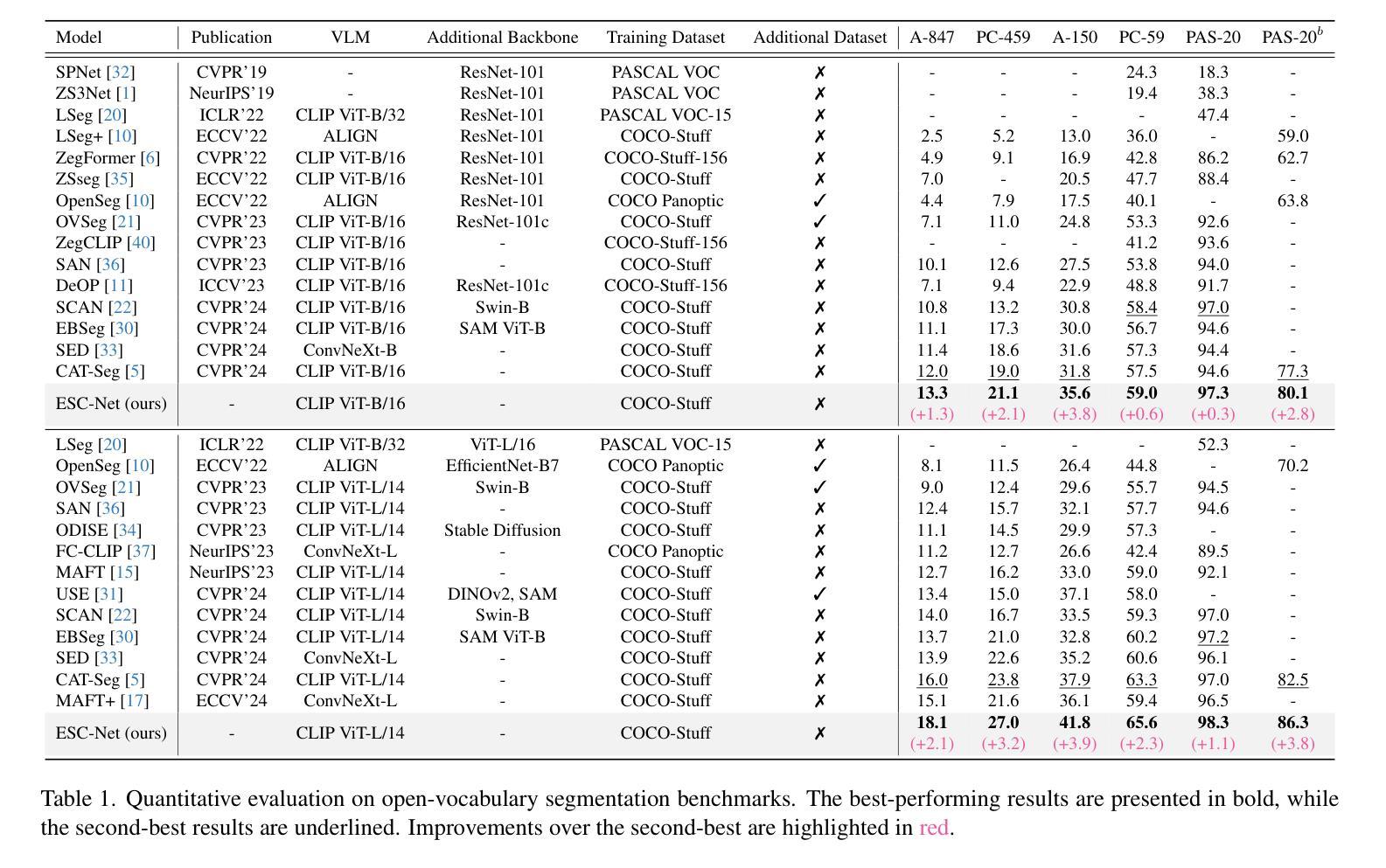
Effective SAM Combination for Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Minhyeok Lee, Suhwan Cho, Jungho Lee, Sunghun Yang, Heeseung Choi, Ig-Jae Kim, Sangyoun Lee
Open-vocabulary semantic segmentation aims to assign pixel-level labels to images across an unlimited range of classes. Traditional methods address this by sequentially connecting a powerful mask proposal generator, such as the Segment Anything Model (SAM), with a pre-trained vision-language model like CLIP. But these two-stage approaches often suffer from high computational costs, memory inefficiencies. In this paper, we propose ESC-Net, a novel one-stage open-vocabulary segmentation model that leverages the SAM decoder blocks for class-agnostic segmentation within an efficient inference framework. By embedding pseudo prompts generated from image-text correlations into SAM’s promptable segmentation framework, ESC-Net achieves refined spatial aggregation for accurate mask predictions. ESC-Net achieves superior performance on standard benchmarks, including ADE20K, PASCAL-VOC, and PASCAL-Context, outperforming prior methods in both efficiency and accuracy. Comprehensive ablation studies further demonstrate its robustness across challenging conditions.
开放词汇语义分割旨在给无限类别的图像分配像素级标签。传统方法通过按顺序连接强大的掩膜提案生成器(如Segment Anything Model (SAM))和预训练的视觉语言模型(如CLIP)来解决这个问题。但这些两阶段方法通常面临高计算成本和内存效率低的问题。在本文中,我们提出了ESC-Net,这是一种新型的一阶段开放词汇分割模型,它利用SAM解码器块在有效的推理框架内进行类别无关的分割。通过将由图像文本相关性生成的伪提示嵌入到SAM的可提示分割框架中,ESC-Net实现了精细的空间聚合,以获得准确的掩膜预测。ESC-Net在包括ADE20K、PASCAL-VOC和PASCAL-Context在内的标准基准测试上表现出卓越的性能,在效率和准确性方面均优于以前的方法。全面的消融研究进一步证明了其在各种挑战条件下的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary:
本文提出了一种新型的开放词汇语义分割模型ESC-Net,该模型采用单阶段设计,利用SAM解码器块进行类无关分割,并通过嵌入伪提示实现精确掩膜预测。ESC-Net在ADE20K、PASCAL-VOC和PASCAL-Context等标准数据集上表现优异,相较于之前的方法在效率和准确性上都有显著提升。
Key Takeaways:
- 开放词汇语义分割旨在给图像中的每个像素分配标签,涉及无限类别。
- 传统方法通常采用两阶段方法,结合掩膜提案生成器和预训练的语言视觉模型,但存在计算成本高和内存效率低的问题。
- ESC-Net是一个新型单阶段开放词汇分割模型,利用SAM解码器块进行类无关分割。
- ESC-Net通过将图像文本相关性生成的伪提示嵌入SAM的提示分割框架,实现了精确掩膜预测。
- ESC-Net在多个标准数据集上表现优异,证明其高效和准确。
- 综合消融研究进一步展示了ESC-Net在挑战条件下的稳健性。
- ESC-Net的设计为解决开放词汇语义分割问题提供了一种有效的新途径。
点此查看论文截图
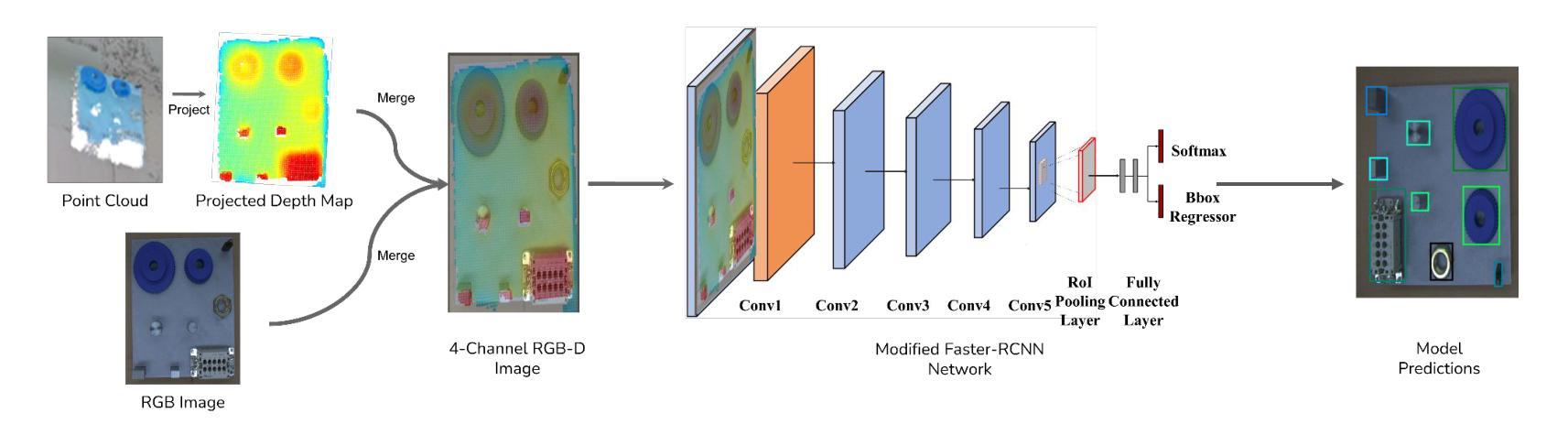
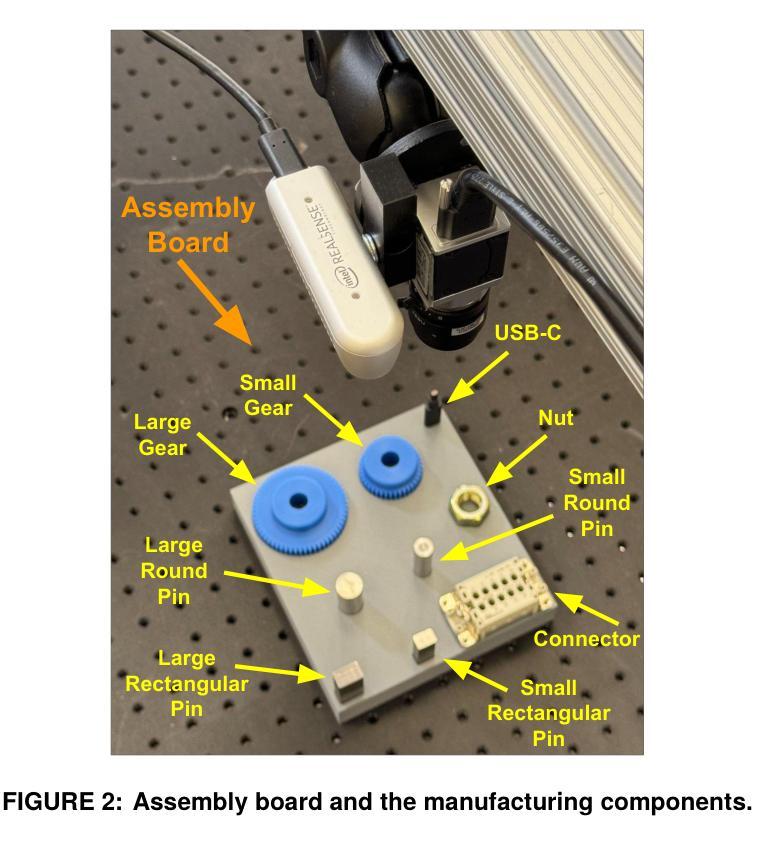
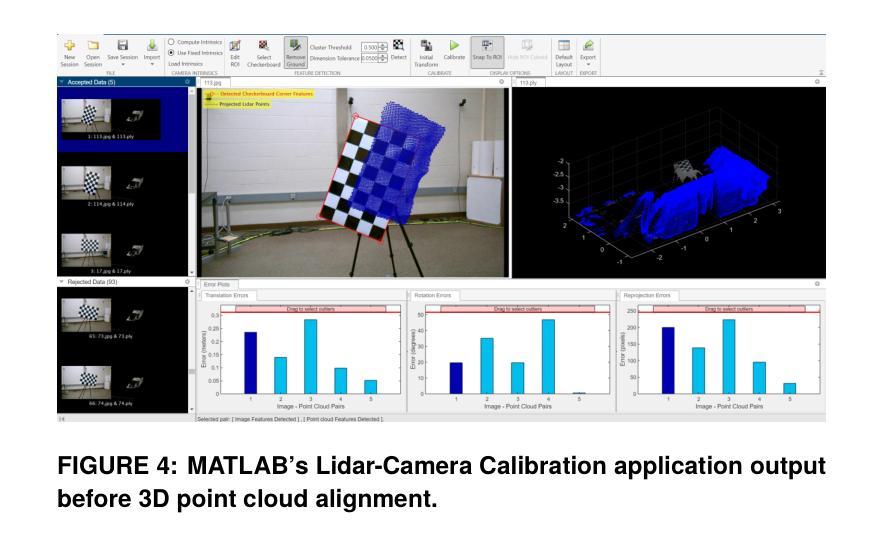
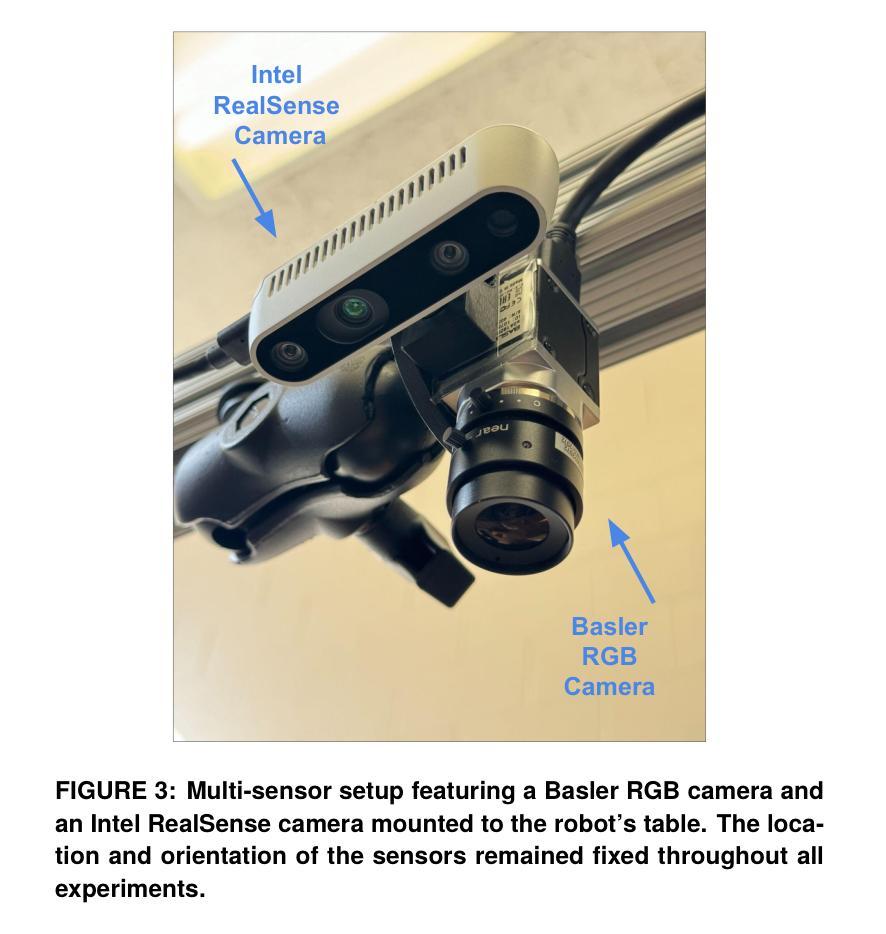
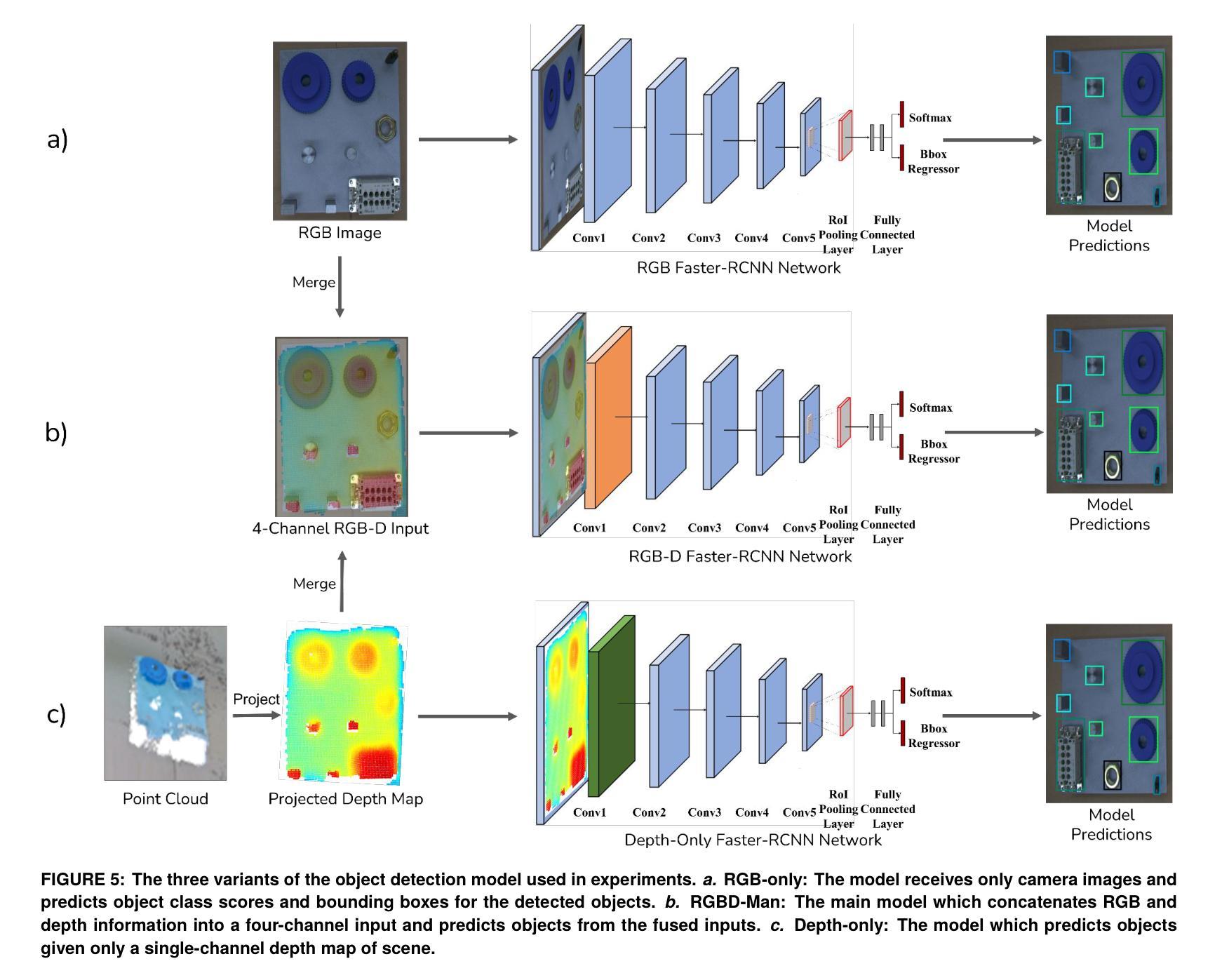
Multimodal Object Detection using Depth and Image Data for Manufacturing Parts
Authors:Nazanin Mahjourian, Vinh Nguyen
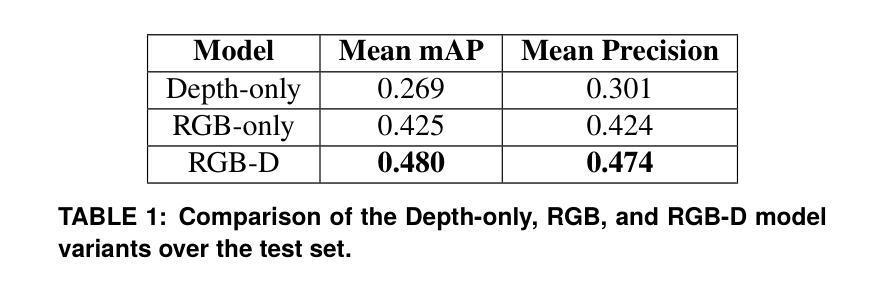
Manufacturing requires reliable object detection methods for precise picking and handling of diverse types of manufacturing parts and components. Traditional object detection methods utilize either only 2D images from cameras or 3D data from lidars or similar 3D sensors. However, each of these sensors have weaknesses and limitations. Cameras do not have depth perception and 3D sensors typically do not carry color information. These weaknesses can undermine the reliability and robustness of industrial manufacturing systems. To address these challenges, this work proposes a multi-sensor system combining an red-green-blue (RGB) camera and a 3D point cloud sensor. The two sensors are calibrated for precise alignment of the multimodal data captured from the two hardware devices. A novel multimodal object detection method is developed to process both RGB and depth data. This object detector is based on the Faster R-CNN baseline that was originally designed to process only camera images. The results show that the multimodal model significantly outperforms the depth-only and RGB-only baselines on established object detection metrics. More specifically, the multimodal model improves mAP by 13% and raises Mean Precision by 11.8% in comparison to the RGB-only baseline. Compared to the depth-only baseline, it improves mAP by 78% and raises Mean Precision by 57%. Hence, this method facilitates more reliable and robust object detection in service to smart manufacturing applications.
制造需要可靠的物体检测方法,以便对各种类型的制造零部件进行精确挑选和处理。传统的物体检测方法要么只使用相机的二维图像,要么使用激光雷达或类似的三维传感器的三维数据。然而,每种传感器都有其弱点和局限性。相机没有深度感知能力,而三维传感器通常不携带颜色信息。这些弱点可能会破坏工业制造系统的可靠性和稳健性。为了应对这些挑战,这项工作提出了一种多传感器系统,该系统结合了红绿蓝(RGB)相机和三维点云传感器。两个传感器经过校准,以精确对齐从两个硬件设备捕获的多模态数据。开发了一种新型的多模态物体检测方法,可同时处理RGB和深度数据。该物体检测器基于Faster R-CNN基线构建,后者最初是为仅处理相机图像而设计的。结果表明,多模态模型在既定的物体检测指标上显著优于仅使用深度和仅使用RGB的基线。具体来说,与仅使用RGB的基线相比,多模态模型提高了13%的mAP并提高了11.8%的平均精度。与仅使用深度的基线相比,它提高了78%的mAP并提高了57%的平均精度。因此,该方法有助于更可靠和稳健的物体检测,为智能制造应用提供服务。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
在制造过程中,可靠的目标检测方法是精确拾取和处理各种制造零部件的关键。传统方法主要依赖2D图像或3D数据,但存在局限性。为应对挑战,本文提出一种融合RGB相机和3D点云传感器的多传感器系统。两者校准可实现多模式数据的精确对齐。开发的新型多模式目标检测法可处理RGB和深度数据,基于Faster R-CNN基线技术构建,原本仅用于处理相机图像。结果显示,多模式模型在目标检测指标上显著优于仅使用深度或RGB数据的模型,mAP提高13%,平均精度提高11.8%。与仅使用深度数据的基线相比,mAP提高78%,平均精度提高57%。因此,此方法有助于更可靠、更稳健的目标检测,服务于智能制造应用。
要点提炼
- 制造中目标检测的可靠性对于精确拾取和处理零部件至关重要。
- 传统方法依赖单一传感器(如相机或3D传感器),存在局限性。
- 本文提出融合RGB相机和3D点云传感器的多传感器系统,以克服单一传感器的局限性。
- 通过校准两种传感器,可实现多模式数据的精确对齐。
- 新型多模式目标检测法结合RGB和深度数据,基于Faster R-CNN基线技术构建。
- 多模式模型在目标检测方面表现优于仅使用深度或RGB数据的模型。
点此查看论文截图

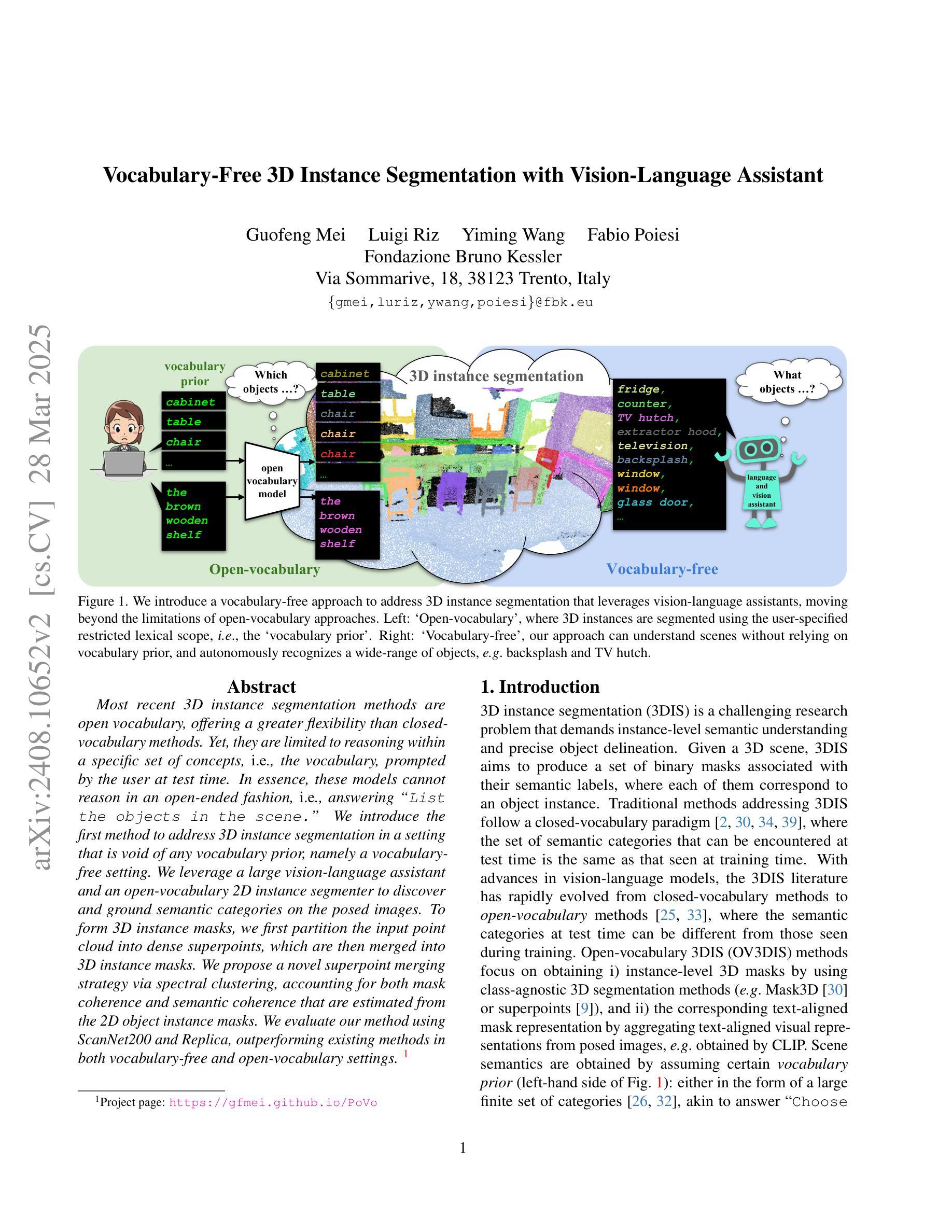
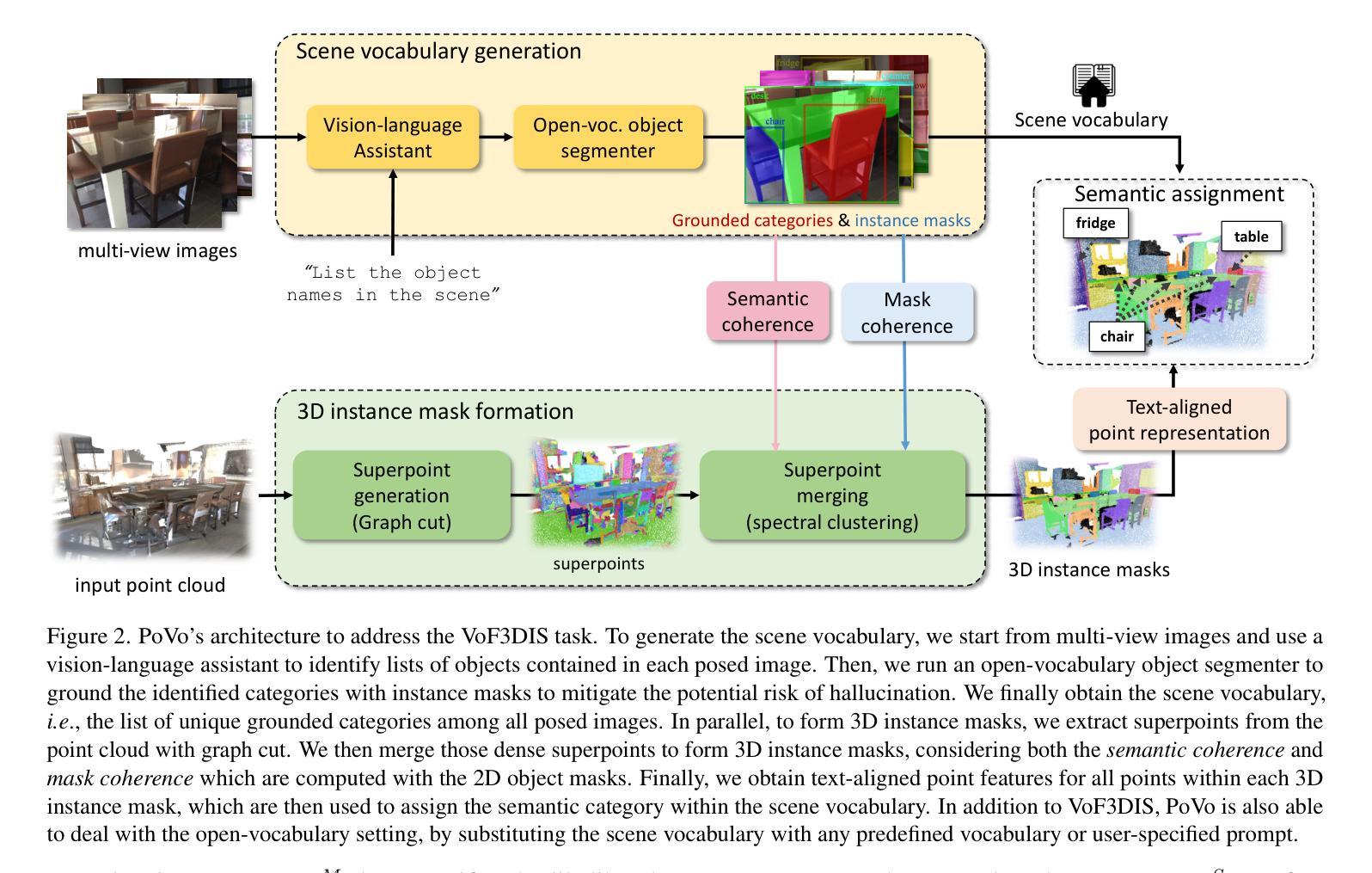
Vocabulary-Free 3D Instance Segmentation with Vision and Language Assistant
Authors:Guofeng Mei, Luigi Riz, Yiming Wang, Fabio Poiesi
Most recent 3D instance segmentation methods are open vocabulary, offering a greater flexibility than closed-vocabulary methods. Yet, they are limited to reasoning within a specific set of concepts, \ie the vocabulary, prompted by the user at test time. In essence, these models cannot reason in an open-ended fashion, i.e., answering “List the objects in the scene.’’. We introduce the first method to address 3D instance segmentation in a setting that is void of any vocabulary prior, namely a vocabulary-free setting. We leverage a large vision-language assistant and an open-vocabulary 2D instance segmenter to discover and ground semantic categories on the posed images. To form 3D instance mask, we first partition the input point cloud into dense superpoints, which are then merged into 3D instance masks. We propose a novel superpoint merging strategy via spectral clustering, accounting for both mask coherence and semantic coherence that are estimated from the 2D object instance masks. We evaluate our method using ScanNet200 and Replica, outperforming existing methods in both vocabulary-free and open-vocabulary settings. Code will be made available. Project page: https://gfmei.github.io/PoVo
最新的三维实例分割方法属于开放词汇方法,相比于封闭词汇方法提供了更大的灵活性。然而,它们受限于在特定概念集(即词汇)内的推理,这些词汇由用户在测试时提供。本质上,这些模型无法进行开放式推理,即回答“列出场景中的物体”。我们首次引入了一种解决无词汇先验设置下的三维实例分割问题的方法,即无词汇设置。我们利用大型视觉语言助理和一个开放词汇的二维实例分割器来发现和定位姿态图像上的语义类别。为了形成三维实例掩膜,我们首先输入点云分割成密集的超点,然后将这些超点合并为三维实例掩膜。我们提出了一种新的超点合并策略,通过谱聚类法,考虑了掩膜的一致性和从二维目标实例掩膜中估计出的语义一致性。我们在ScanNet200和Replica数据集上评估了我们的方法,在无词汇和开放词汇设置中均优于现有方法。代码将公开提供。项目页面:链接地址。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by 3DV
Summary
最新3D实例分割方法采用开放词汇表,较封闭词汇表方法更灵活。然而,它们受限于在特定概念集(即词汇表)内的推理,这些词汇表在测试时由用户提示。本质上,这些方法无法以开放式方式进行推理,即回答“列出场景中的物体”。我们首次提出解决在没有任何词汇先验条件下的三维实例分割问题的方法,即无词汇设置。我们利用大型视觉语言助理和开放词汇的二维实例分割器来发现和定位图像上的语义类别。为了形成三维实例掩膜,我们首先对输入的点云进行密集超点划分,然后将这些超点合并为三维实例掩膜。我们提出了一种新的超点合并策略,通过谱聚类考虑掩膜的一致性和语义一致性,这些一致性是根据二维对象实例掩膜估计的。我们在ScanNet200和Replica上评估了我们的方法,在无词汇表和开放词汇表设置中均优于现有方法。代码将公开提供。项目页面:https://gfmei.github.io/PoVo。
Key Takeaways
- 最新3D实例分割方法具有开放词汇特性,提供更大灵活性。
- 当前方法受限于在特定概念集(词汇表)内的推理。
- 提出一种无词汇设置下的三维实例分割方法。
- 利用视觉语言助理和开放词汇的二维实例分割器来识别和定位语义类别。
- 通过谱聚类实现超点合并策略,考虑掩膜的一致性和语义一致性。
- 在ScanNet200和Replica上的性能超越了现有方法,特别是在无词汇表和开放词汇表设置中。
点此查看论文截图