⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-04 更新
TimeSearch: Hierarchical Video Search with Spotlight and Reflection for Human-like Long Video Understanding
Authors:Junwen Pan, Rui Zhang, Xin Wan, Yuan Zhang, Ming Lu, Qi She
Large video-language models (LVLMs) have shown remarkable performance across various video-language tasks. However, they encounter significant challenges when processing long videos because of the large number of video frames involved. Downsampling long videos in either space or time can lead to visual hallucinations, making it difficult to accurately interpret long videos. Motivated by human hierarchical temporal search strategies, we propose \textbf{TimeSearch}, a novel framework enabling LVLMs to understand long videos in a human-like manner. TimeSearch integrates two human-like primitives into a unified autoregressive LVLM: 1) \textbf{Spotlight} efficiently identifies relevant temporal events through a Temporal-Augmented Frame Representation (TAFR), explicitly binding visual features with timestamps; 2) \textbf{Reflection} evaluates the correctness of the identified events, leveraging the inherent temporal self-reflection capabilities of LVLMs. TimeSearch progressively explores key events and prioritizes temporal search based on reflection confidence. Extensive experiments on challenging long-video benchmarks confirm that TimeSearch substantially surpasses previous state-of-the-art, improving the accuracy from 41.8% to 51.5% on the LVBench. Additionally, experiments on temporal grounding demonstrate that appropriate TAFR is adequate to effectively stimulate the surprising temporal grounding ability of LVLMs in a simpler yet versatile manner, which improves mIoU on Charades-STA by 11.8%. The code will be released.
大型视频语言模型(LVLMs)在各种视频语言任务中表现出了显著的性能。然而,在处理长视频时,由于涉及大量的视频帧,它们面临着巨大的挑战。在空间或时间上对长视频进行降采样可能会导致视觉错觉,使得准确解释长视频变得困难。受人类分层时序搜索策略的启发,我们提出了TimeSearch这一新型框架,使LVLMs能够以人类相似的方式理解长视频。TimeSearch将两个类似人类的原始元素整合到一个统一的自回归LVLM中:1)Spotlight通过时序增强帧表示(TAFR)有效地识别出相关的时序事件,显式地将视觉特征与时间戳绑定;2)Reflection利用LVLMs的固有时序自我反思能力,评估识别事件的正确性。TimeSearch逐步探索关键事件,并基于反思置信度优先进行时序搜索。在具有挑战性的长视频基准测试上的广泛实验证实,TimeSearch显著超越了之前的最先进水平,在LVBench上将准确率从41.8%提高到51.5%。此外,在时序定位实验上表明,适当的TAFR足以以更简单但多功能的方式有效激发LVLMs的时序定位能力,将Charades-STA上的mIoU提高了11.8%。代码将会发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为TimeSearch的新型框架,旨在使大型视频语言模型(LVLMs)以人类的方式理解长视频。该框架集成了两个类似人类的原始要素:Spotlight能高效识别相关的时间事件,通过时间增强帧表示(TAFR)显式绑定视觉特征和时间戳;Reflection则评估所识别事件的正确性,利用LVLMs的固有自我反思能力。TimeSearch渐进地探索关键事件并根据反射置信度优先进行时间搜索。实验表明,TimeSearch在具有挑战性的长视频基准测试中大幅超越了现有技术,在LVBench上的准确率从41.8%提高到51.5%。同时,在时序定位实验中,适当的TAFR能有效激发LVLMs的时序定位能力,提高了Charades-STA的mIoU值达11.8%。该框架将公开代码。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视频语言模型(LVLMs)在处理长视频时面临挑战,需解决视觉幻觉问题。
- TimeSearch框架模拟人类层次化的时间搜索策略,帮助LVLMs理解长视频。
- Spotlight能高效识别相关的时间事件,通过时间增强帧表示(TAFR)结合视觉特征和时间戳。
- Reflection利用LVLMs的固有自我反思能力评估事件正确性。
- TimeSearch渐进地探索关键事件,基于反射置信度优先进行时间搜索。
- TimeSearch在LVBench上的准确率显著提高,达到51.5%,超越现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

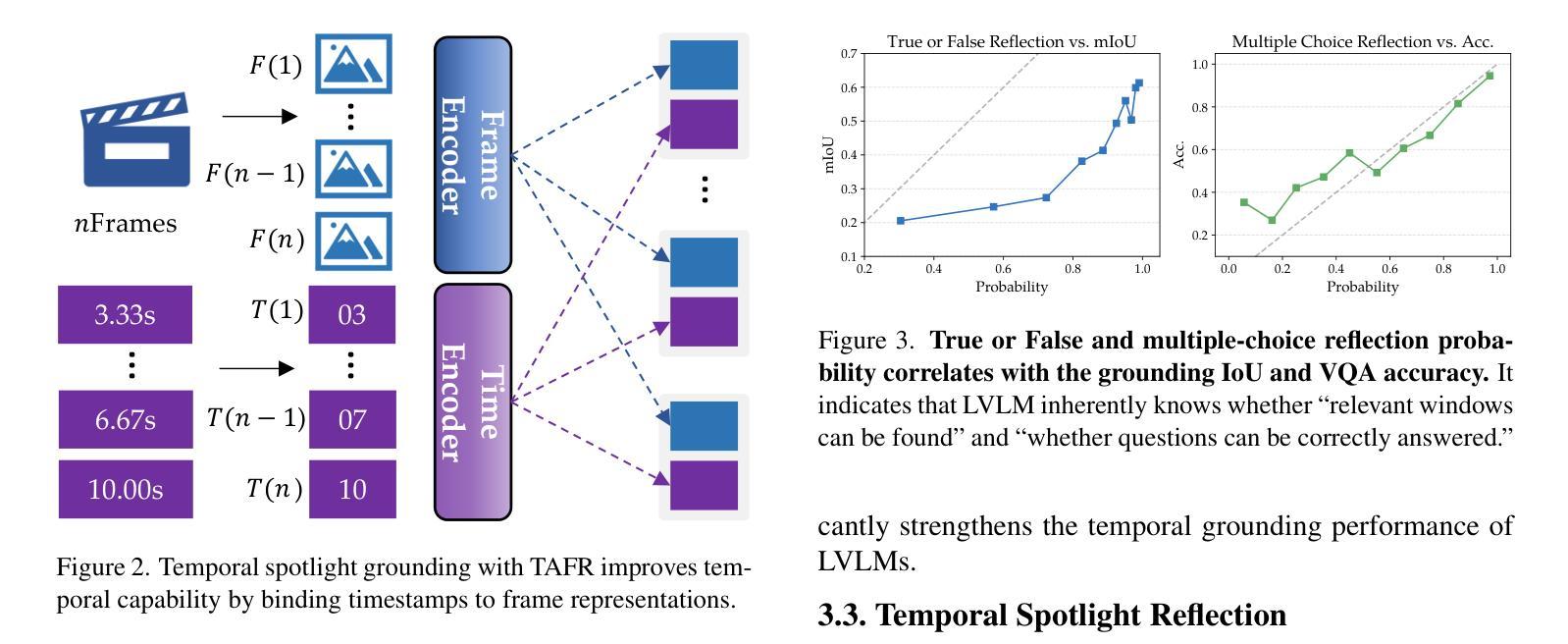


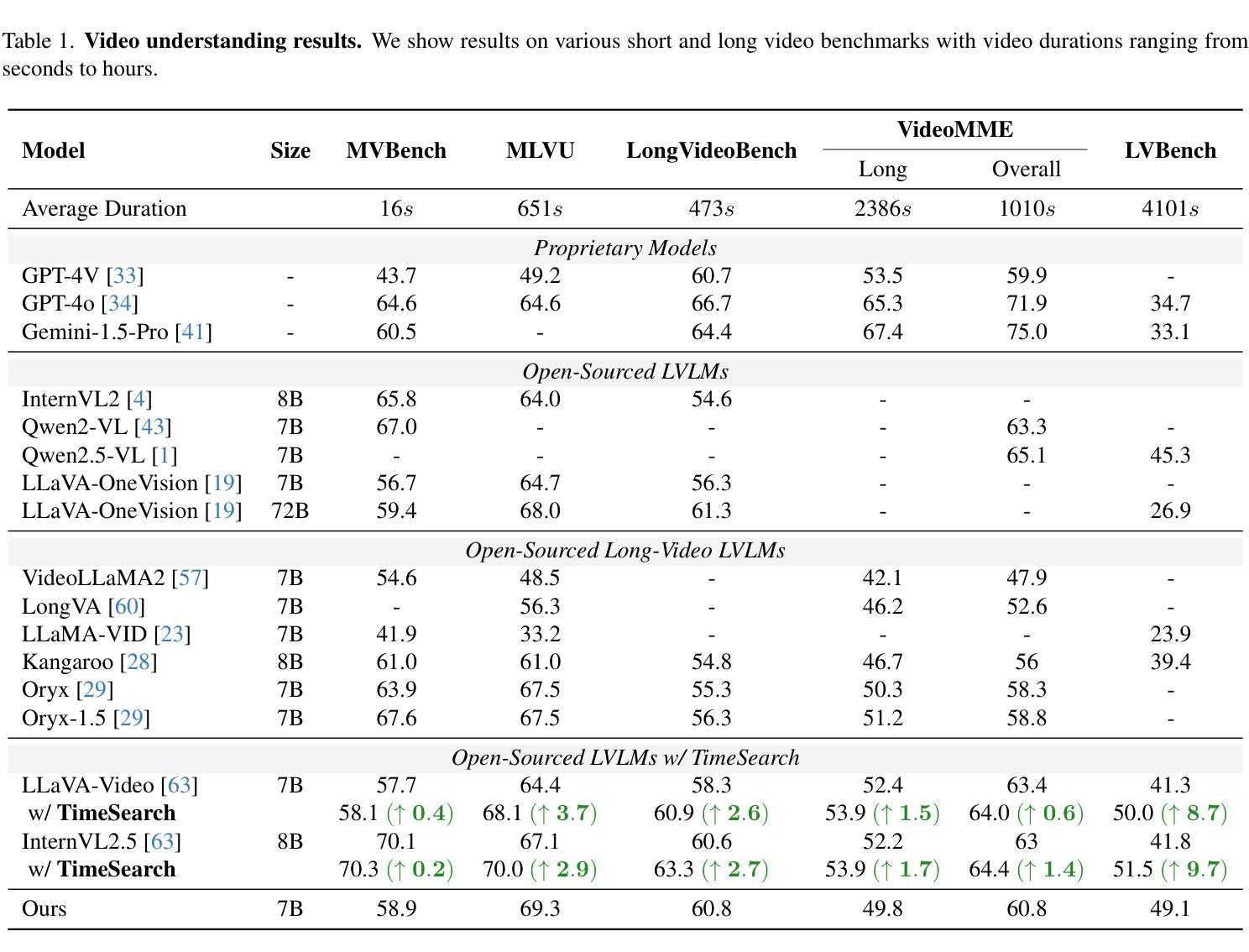
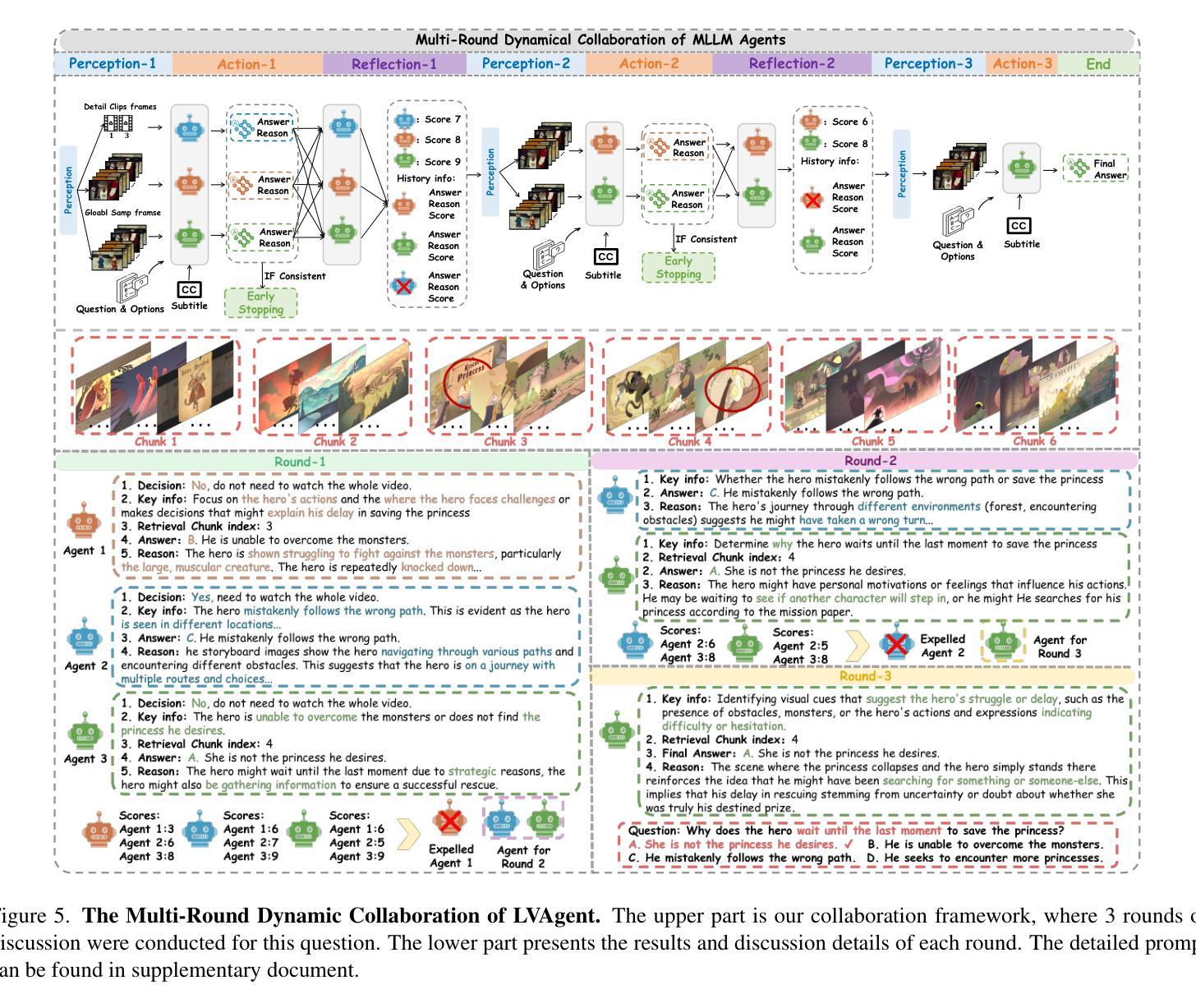
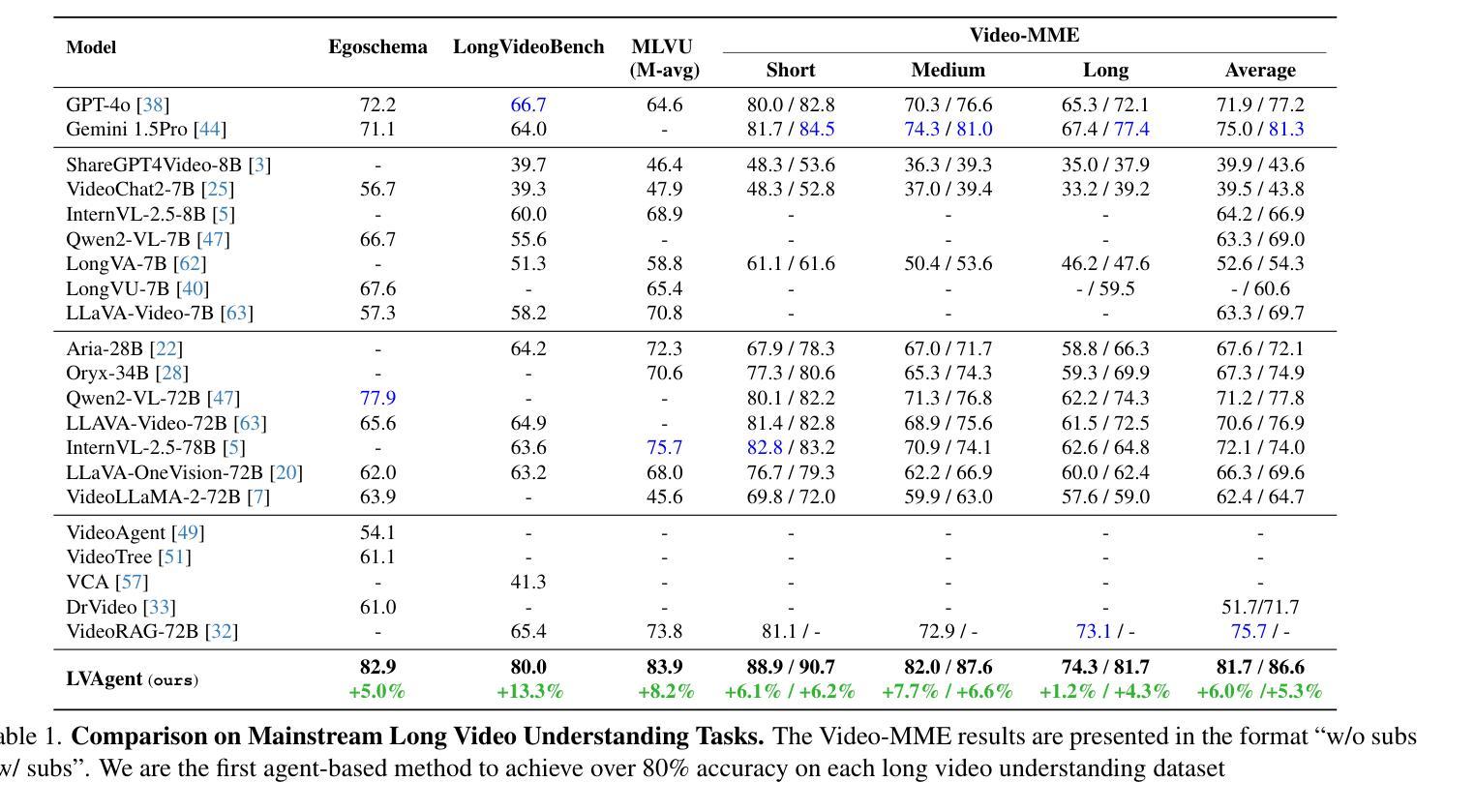
LVAgent: Long Video Understanding by Multi-Round Dynamical Collaboration of MLLM Agents
Authors:Boyu Chen, Zhengrong Yue, Siran Chen, Zikang Wang, Yang Liu, Peng Li, Yali Wang
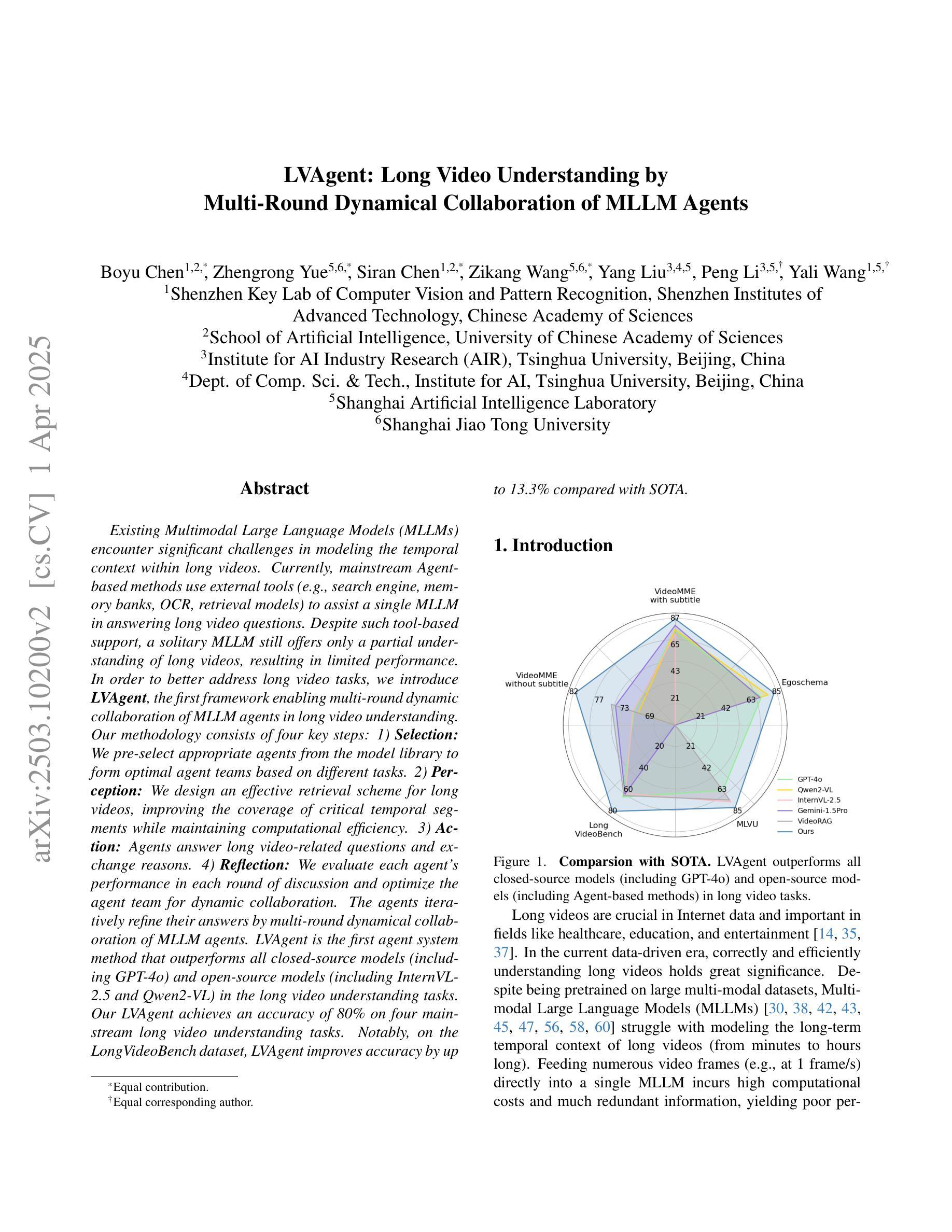
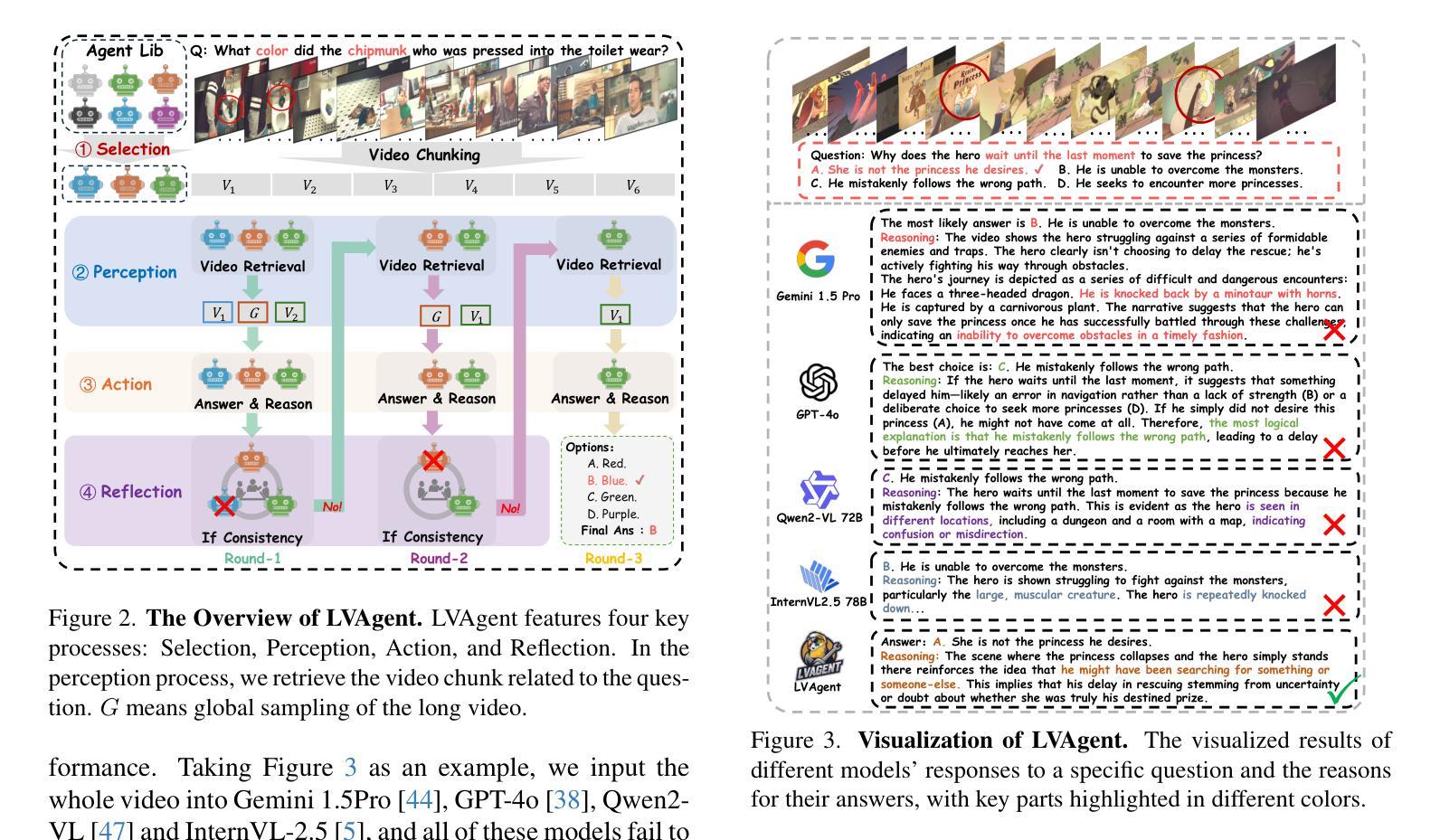
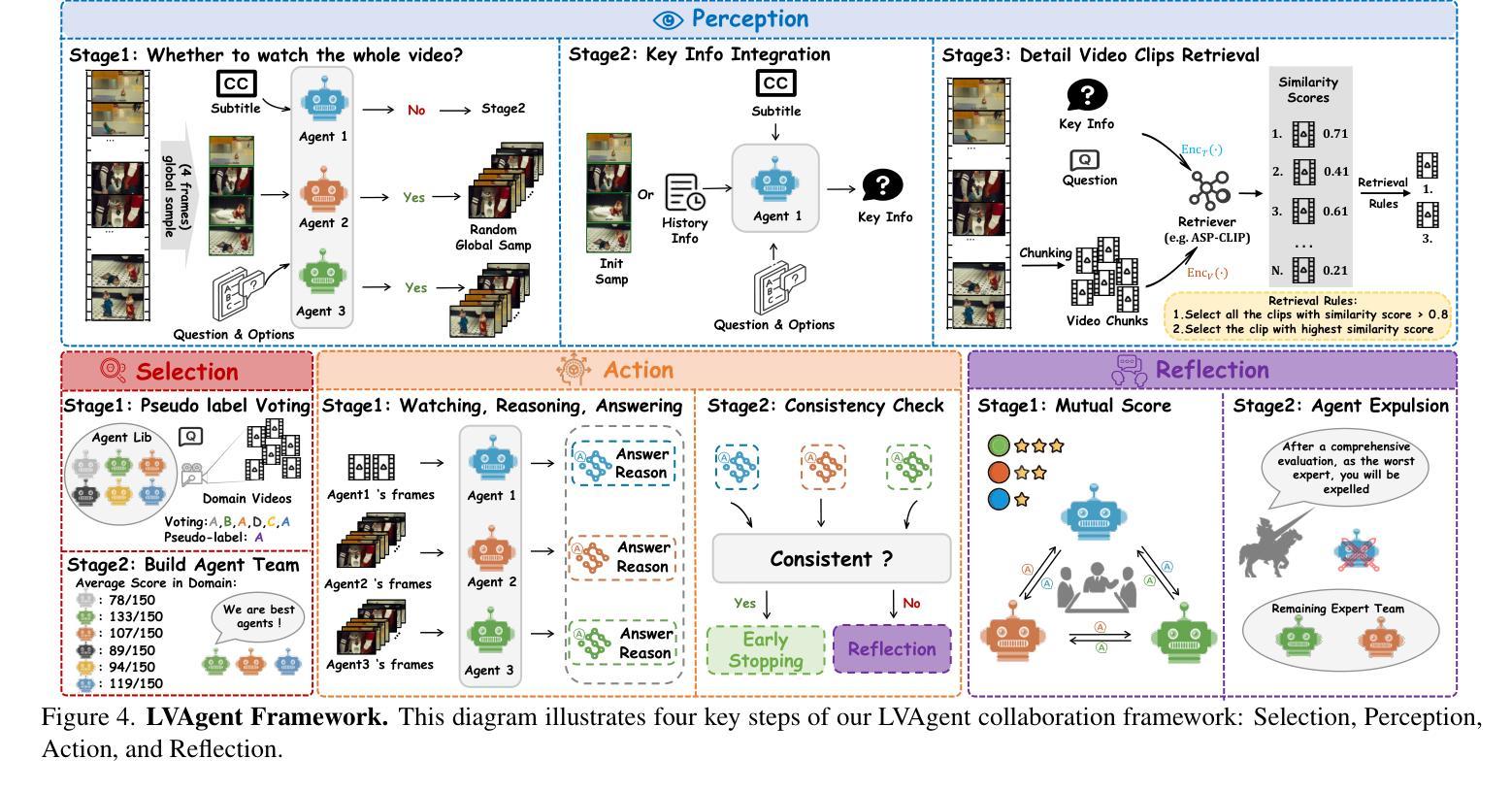
Existing Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) encounter significant challenges in modeling the temporal context within long videos. Currently, mainstream Agent-based methods use external tools (e.g., search engine, memory banks, OCR, retrieval models) to assist a single MLLM in answering long video questions. Despite such tool-based support, a solitary MLLM still offers only a partial understanding of long videos, resulting in limited performance. In order to better address long video tasks, we introduce LVAgent, the first framework enabling multi-round dynamic collaboration of MLLM agents in long video understanding. Our methodology consists of four key steps: 1. Selection: We pre-select appropriate agents from the model library to form optimal agent teams based on different tasks. 2. Perception: We design an effective retrieval scheme for long videos, improving the coverage of critical temporal segments while maintaining computational efficiency. 3. Action: Agents answer long video-related questions and exchange reasons. 4. Reflection: We evaluate the performance of each agent in each round of discussion and optimize the agent team for dynamic collaboration. The agents iteratively refine their answers by multi-round dynamical collaboration of MLLM agents. LVAgent is the first agent system method that outperforms all closed-source models (including GPT-4o) and open-source models (including InternVL-2.5 and Qwen2-VL) in the long video understanding tasks. Our LVAgent achieves an accuracy of 80% on four mainstream long video understanding tasks. Notably, on the LongVideoBench dataset, LVAgent improves accuracy by up to 13.3% compared with SOTA.
现有的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在建模长视频中的时间上下文时面临重大挑战。目前,主流的基于代理的方法使用外部工具(如搜索引擎、记忆库、OCR、检索模型)来辅助单个MLLM回答长视频问题。尽管有基于工具的支持,单个MLLM对长视频的理解仍然有限,导致性能受限。为了更好地解决长视频任务,我们引入了LVAgent,这是第一个使多轮动态协作的MLLM代理实现长视频理解的框架。我们的方法包括以下四个关键步骤:1.选择:我们从模型库中预先选择合适的代理,根据不同的任务形成最优代理团队。2.感知:我们为长视频设计了一种有效的检索方案,提高了关键时间段的覆盖率,同时保持了计算效率。3.行动:代理回答与长视频相关的问题并交流理由。4.反思:我们评估每个代理在每轮讨论中的表现,优化代理团队的动态协作。通过MLLM代理的多轮动态协作,代理能够逐步改进他们的答案。LVAgent是第一个在长视频理解任务中优于所有封闭源模型(包括GPT-4o)和开源模型(包括InternVL-2.5和Qwen2-VL)的代理系统方法。我们的LVAgent在四个主流的长视频理解任务上达到了80%的准确率。值得注意的是,在LongVideoBench数据集上,LVAgent与当前最佳技术相比,准确率提高了高达13.3%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对长视频理解的挑战,提出了一种多轮动态协作的多模态大型语言模型框架LVAgent。LVAgent通过选择适当的模型代理团队,设计有效的视频检索方案,进行代理间的问答交流并对性能进行评估和优化,实现了对长视频的多轮动态理解。LVAgent在主流长视频理解任务上取得了超过现有模型和方法的性能,准确率达到80%,并且在LongVideoBench数据集上提高了最高达13.3%的准确率。
Key Takeaways
- 长视频理解面临挑战,现有单一多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)难以完全理解。
- LVAgent框架通过多轮动态协作的MLLM代理团队解决长视频理解问题。
- LVAgent包含四个关键步骤:选择、感知、行动和反思。
- LVAgent通过有效的视频检索方案提高关键时间段的覆盖率并保持计算效率。
- 代理通过问答交流并不断优化协作,实现答案的迭代完善。
- LVAgent在主流长视频理解任务上实现80%的准确率。
点此查看论文截图
ALLVB: All-in-One Long Video Understanding Benchmark
Authors:Xichen Tan, Yuanjing Luo, Yunfan Ye, Fang Liu, Zhiping Cai
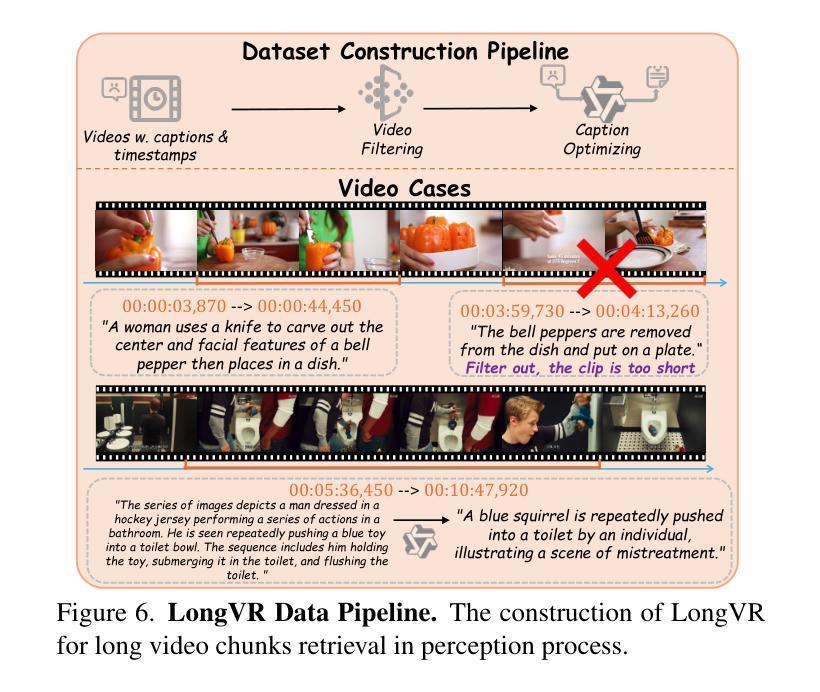
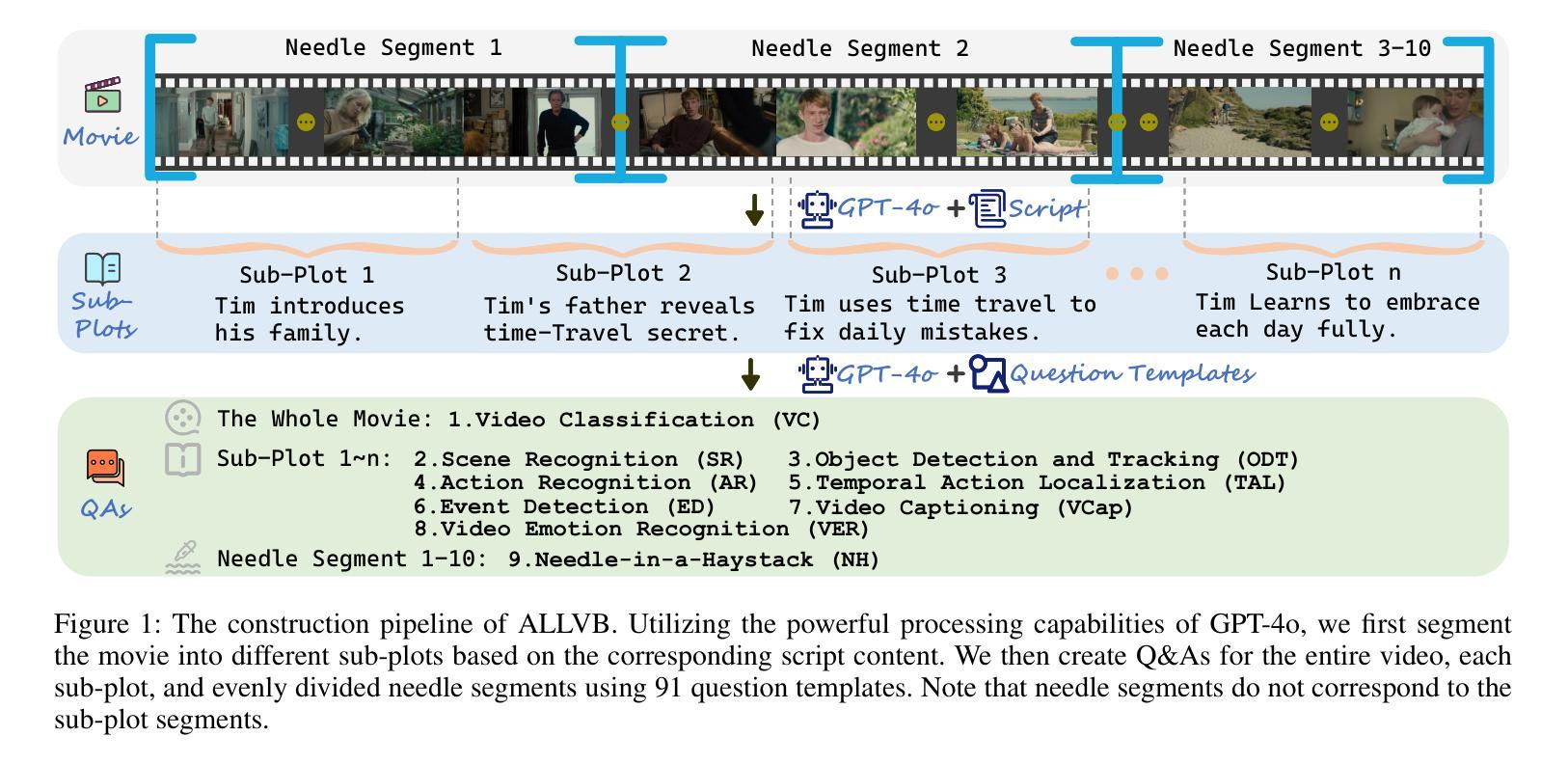
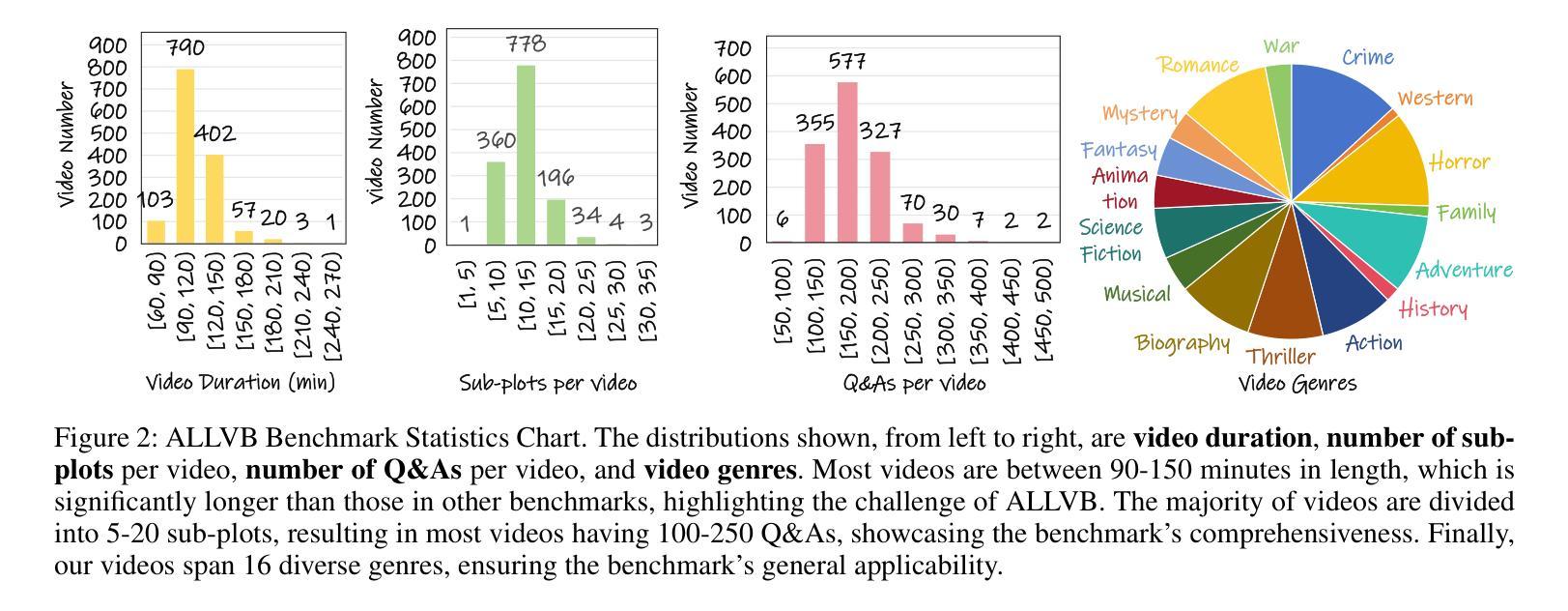
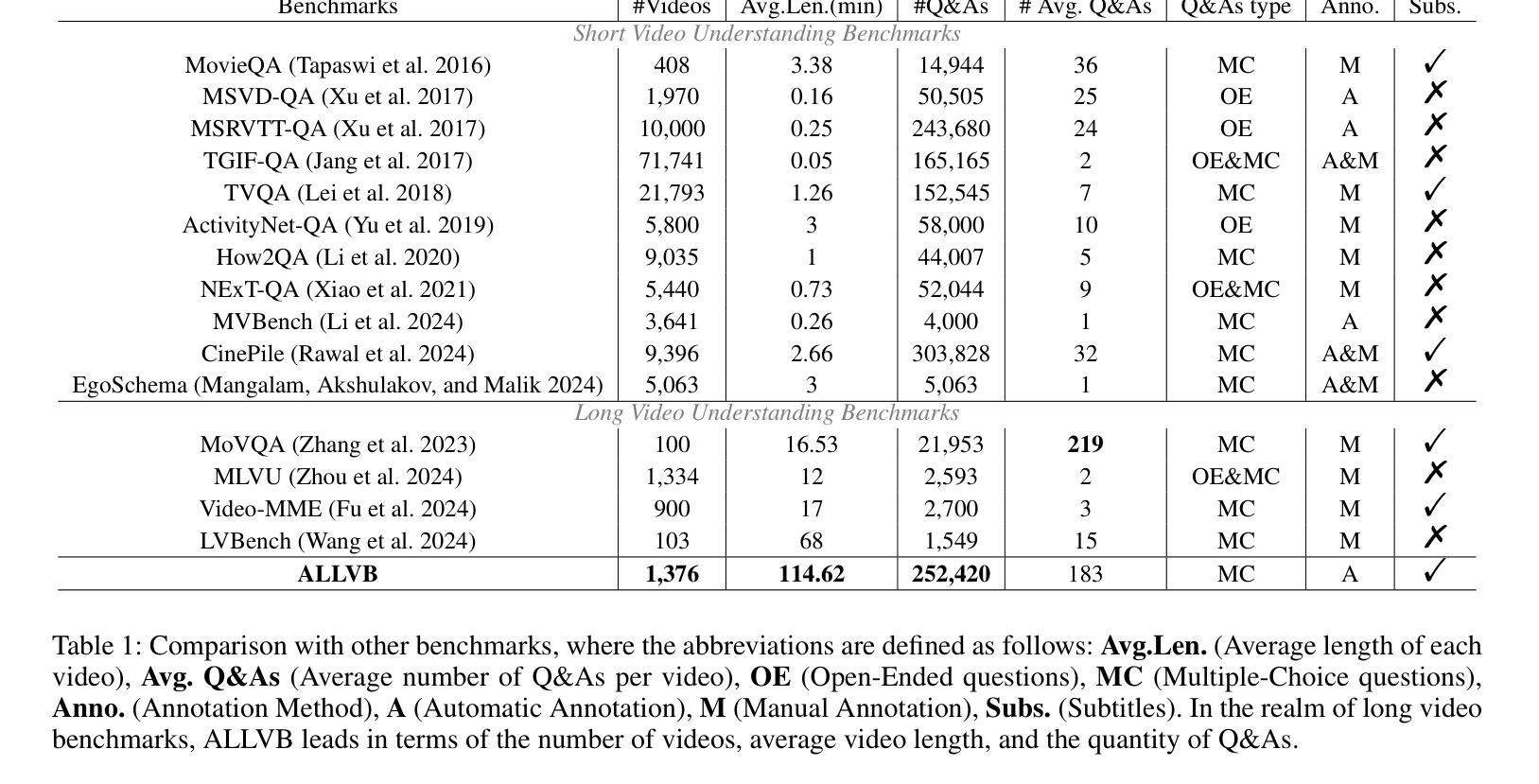
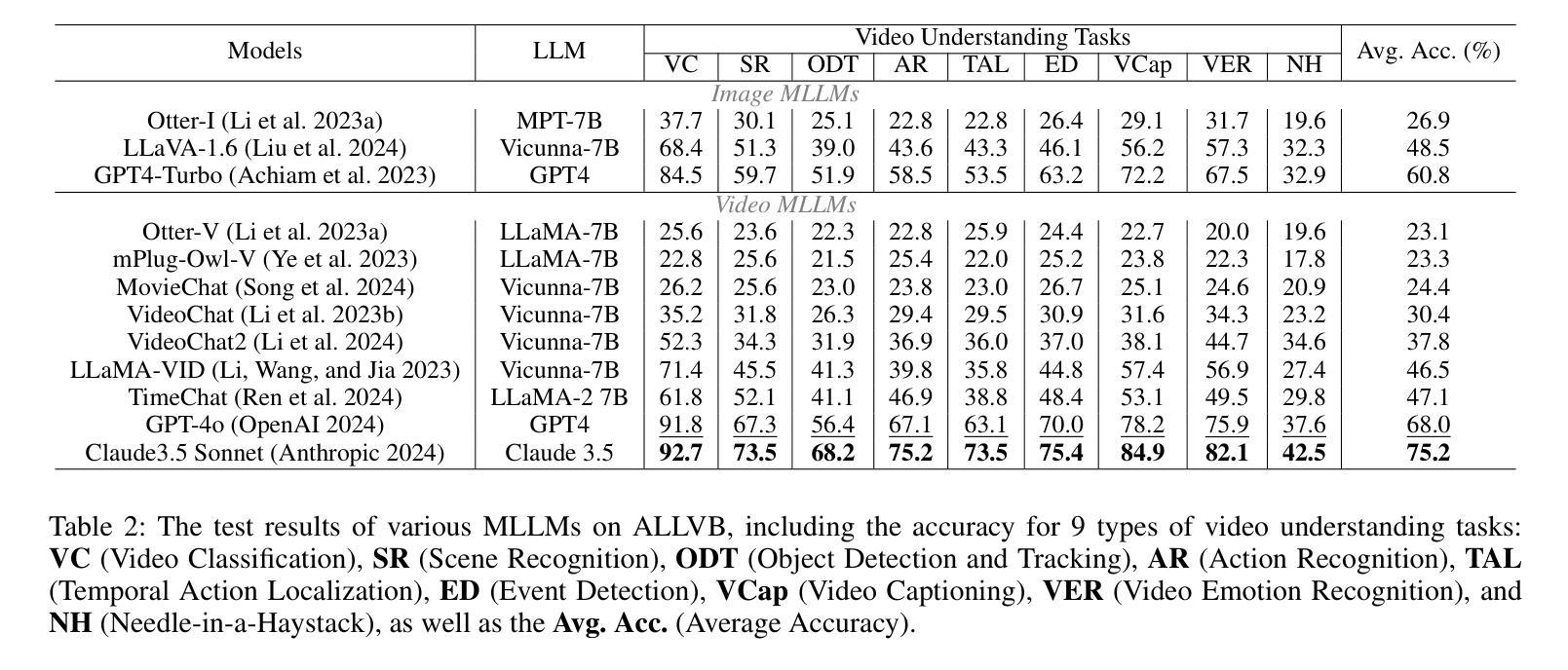
From image to video understanding, the capabilities of Multi-modal LLMs (MLLMs) are increasingly powerful. However, most existing video understanding benchmarks are relatively short, which makes them inadequate for effectively evaluating the long-sequence modeling capabilities of MLLMs. This highlights the urgent need for a comprehensive and integrated long video understanding benchmark to assess the ability of MLLMs thoroughly. To this end, we propose ALLVB (ALL-in-One Long Video Understanding Benchmark). ALLVB’s main contributions include: 1) It integrates 9 major video understanding tasks. These tasks are converted into video QA formats, allowing a single benchmark to evaluate 9 different video understanding capabilities of MLLMs, highlighting the versatility, comprehensiveness, and challenging nature of ALLVB. 2) A fully automated annotation pipeline using GPT-4o is designed, requiring only human quality control, which facilitates the maintenance and expansion of the benchmark. 3) It contains 1,376 videos across 16 categories, averaging nearly 2 hours each, with a total of 252k QAs. To the best of our knowledge, it is the largest long video understanding benchmark in terms of the number of videos, average duration, and number of QAs. We have tested various mainstream MLLMs on ALLVB, and the results indicate that even the most advanced commercial models have significant room for improvement. This reflects the benchmark’s challenging nature and demonstrates the substantial potential for development in long video understanding.
从图像到视频理解,多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的能力越来越强大。然而,大多数现有的视频理解基准测试相对较短,这使得它们无法有效地评估MLLMs的长序列建模能力。这凸显了全面综合的长视频理解基准测试的迫切需求,以全面评估MLLMs的能力。为此,我们提出了ALLVB(ALL-in-One长视频理解基准测试)。ALLVB的主要贡献包括:1)它集成了9大视频理解任务。这些任务转化为视频问答格式,允许单个基准测试评估MLLMs的9种不同视频理解能力,凸显ALLVB的通用性、全面性和挑战性。2)设计了一个使用GPT-4o的完全自动化的注释管道,只需要人工质量控制,这有助于基准测试的维护和扩展。3)包含16个类别的1376个视频,平均每个视频近2小时,总共有25.2万个问答。据我们所知,它是从视频数量、平均时长和问答数量方面来看,规模最大的长视频理解基准测试。我们在ALLVB上测试了各种主流MLLMs,结果表明,即使是最先进的商业模型也有很大的改进空间。这反映了基准测试的挑战性,并展示了长视频理解领域巨大的发展潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025
摘要
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在从图像到视频理解方面的能力越来越强大。然而,现有的视频理解基准测试大多相对较短,无法有效评估MLLMs的长序列建模能力。因此,迫切需要一个综合一体化的长视频理解基准测试,以全面评估MLLMs的能力。为此,我们提出了ALLVB(ALL-in-One长视频理解基准测试)。ALLVB的主要贡献包括:1)它整合了9大视频理解任务,将这些任务转化为视频问答格式,使一个基准测试能够评估MLLMs的9种不同视频理解能力,凸显了ALLVB的通用性、全面性和挑战性。2)设计了一个使用GPT-4o的完全自动化注释管道,只需要人工质量控制,便于基准测试的维护和扩展。3)包含1,376个视频,涵盖16个类别,平均时长近2小时,共有252k个问答。据我们所知,它是从视频数量、平均时长和问答数量方面来看,规模最大的长视频理解基准测试。我们在ALLVB上测试了各种主流MLLMs,结果显示,即使是最先进的商业模型也有很大的改进空间。这反映了该基准测试的挑战性,并展示了长视频理解领域的巨大发展潜力。
关键见解
- ALLVB基准测试集成了9大视频理解任务,全面评估MLLMs的能力。
- 视频理解任务被转化为视频问答格式,凸显其通用性和挑战性。
- 借助GPT-4o,设计了全自动化注释管道,简化了基准测试的维护。
- ALLVB包含大量长视频和丰富的问答,是规模最大的视频理解基准测试。
- 现有MLLMs在ALLVB上的表现仍有显著提升空间,表明该基准测试具有挑战性。
- 测试结果揭示了长视频理解领域的巨大发展潜力。
点此查看论文截图

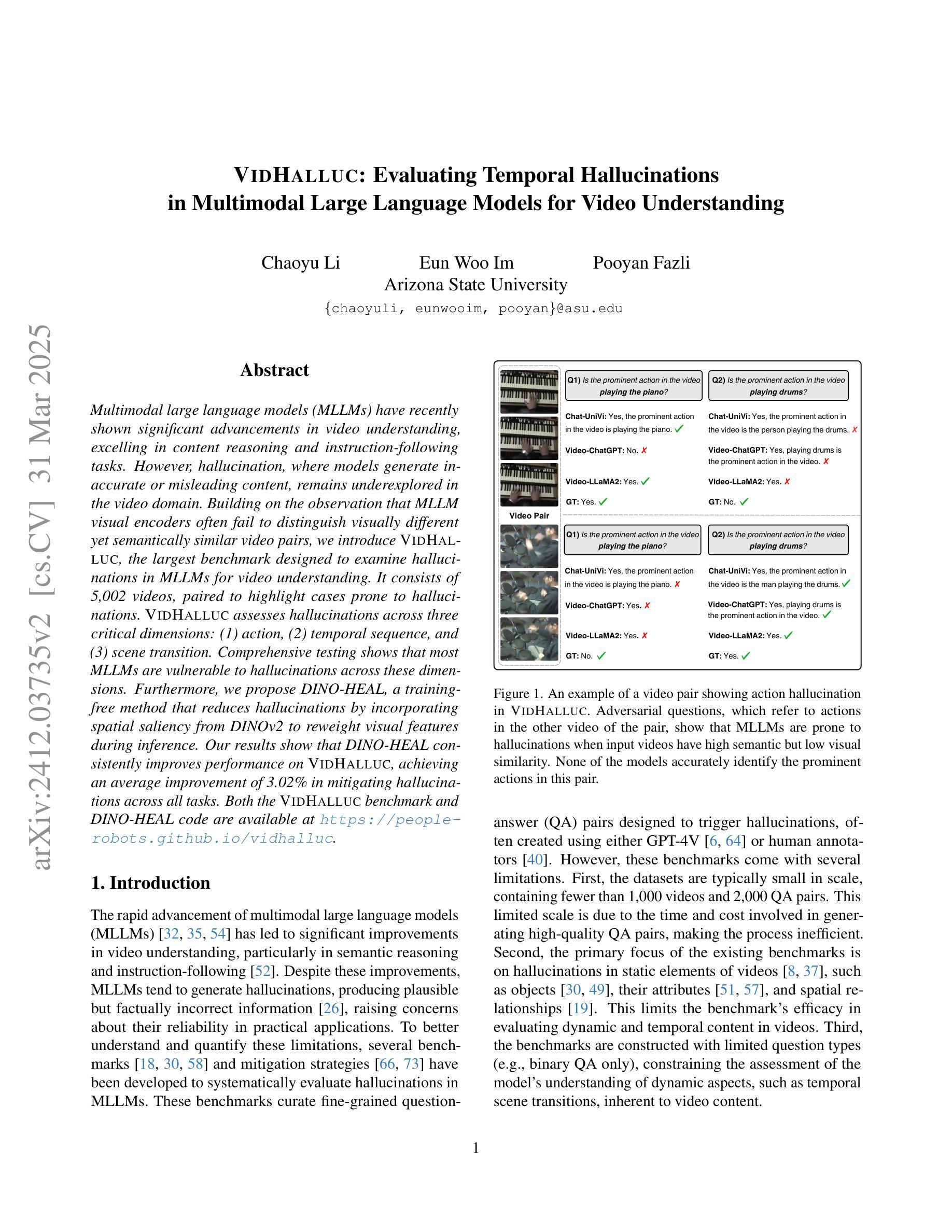
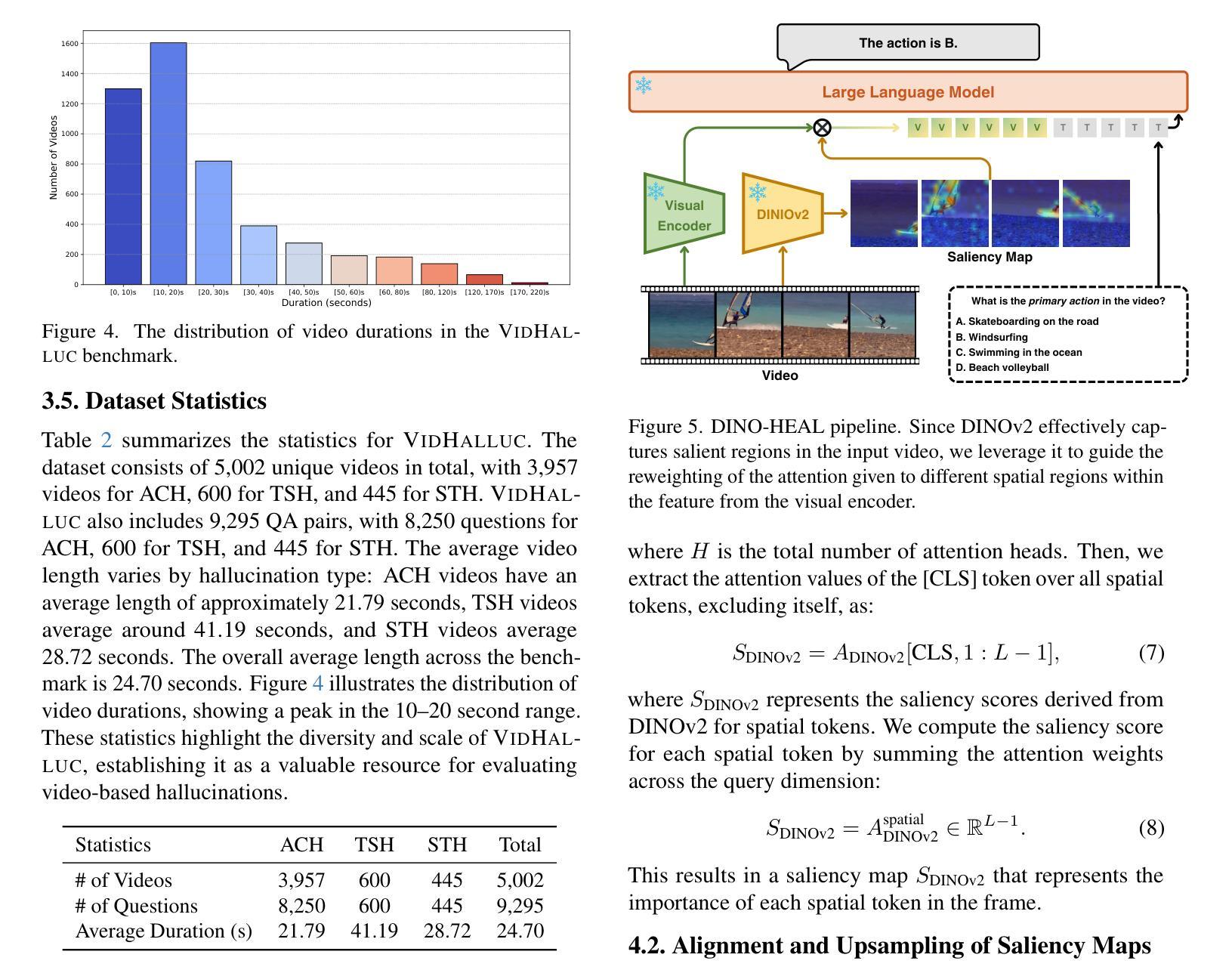
VidHalluc: Evaluating Temporal Hallucinations in Multimodal Large Language Models for Video Understanding
Authors:Chaoyu Li, Eun Woo Im, Pooyan Fazli
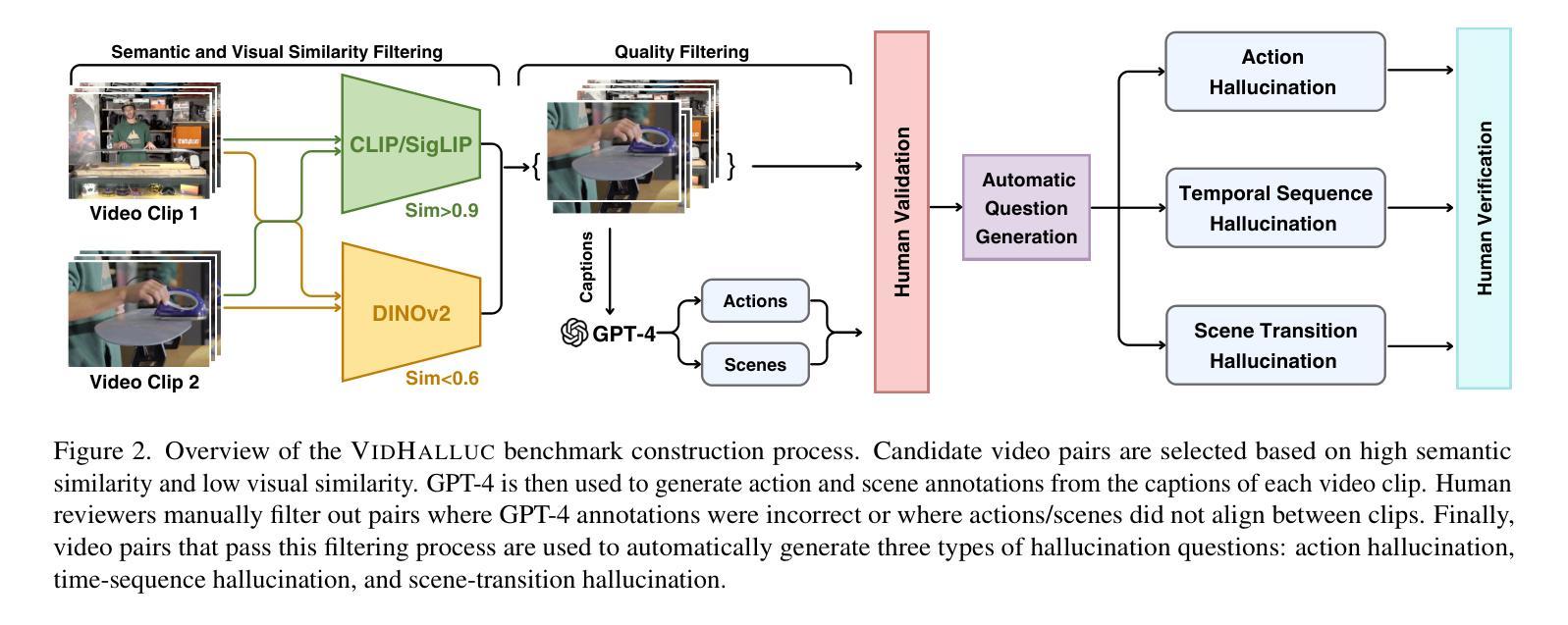
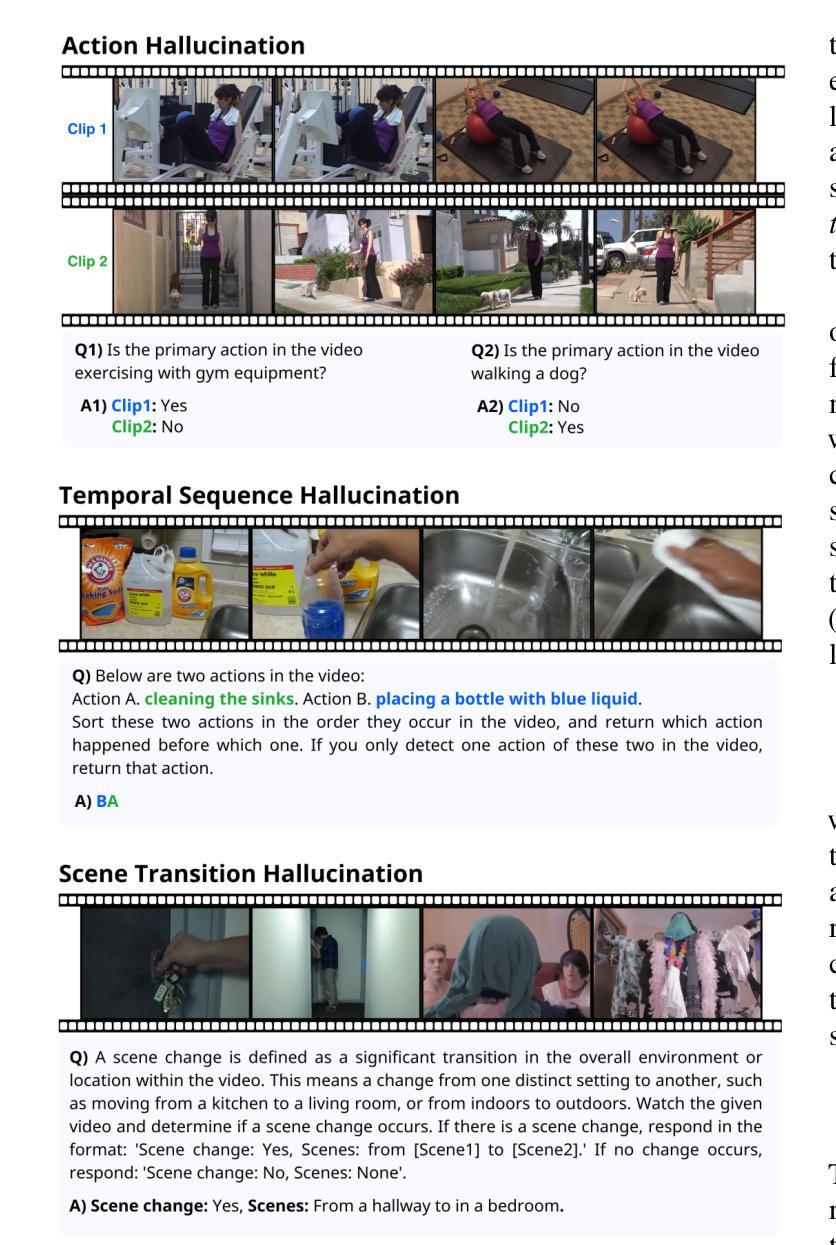
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have recently shown significant advancements in video understanding, excelling in content reasoning and instruction-following tasks. However, hallucination, where models generate inaccurate or misleading content, remains underexplored in the video domain. Building on the observation that MLLM visual encoders often fail to distinguish visually different yet semantically similar video pairs, we introduce VidHalluc, the largest benchmark designed to examine hallucinations in MLLMs for video understanding. It consists of 5,002 videos, paired to highlight cases prone to hallucinations. VidHalluc assesses hallucinations across three critical dimensions: (1) action, (2) temporal sequence, and (3) scene transition. Comprehensive testing shows that most MLLMs are vulnerable to hallucinations across these dimensions. Furthermore, we propose DINO-HEAL, a training-free method that reduces hallucinations by incorporating spatial saliency from DINOv2 to reweight visual features during inference. Our results show that DINO-HEAL consistently improves performance on VidHalluc, achieving an average improvement of 3.02% in mitigating hallucinations across all tasks. Both the VidHalluc benchmark and DINO-HEAL code are available at https://people-robots.github.io/vidhalluc.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视频理解方面最近取得了重大进展,尤其在内容推理和指令跟随任务方面表现出色。然而,关于模型生成不准确或误导性内容的幻觉(hallucination)在视频领域仍然被忽视。基于观察到MLLM视觉编码器往往无法区分视觉上不同但语义上相似的视频对这一现象,我们引入了VidHalluc,这是专门为视频理解的MLLMs检查幻觉而设计的大型基准测试。它包含5002个视频,配对以突出容易出现幻觉的情况。VidHalluc从三个方面评估幻觉:(1)动作,(2)时间顺序,(3)场景过渡。全面的测试表明,大多数MLLMs在这些方面都容易受到幻觉的影响。此外,我们提出了DINO-HEAL,这是一种无需训练的方法,通过结合DINOv2的空间显著性来在推理过程中重新加权视觉特征,从而减少幻觉。我们的结果表明,DINO-HEAL在VidHalluc上的表现持续提高,在所有任务中平均提高了3.02%的幻觉缓解效果。VidHalluc基准测试和DINO-HEAL代码均可在https://people-robots.github.io/vidhalluc获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视频理解方面取得了显著进展,擅长内容推理和指令执行任务。然而,关于模型生成不准确或误导性内容的“幻觉”现象在视频领域尚未得到充分探索。针对MLLM视觉编码器难以区分视觉不同但语义相似的视频对的问题,我们引入了VidHalluc基准测试,这是专为检查视频理解中MLLMs的幻觉现象而设计的最大基准测试。它包括5002个视频,配对以突出容易出现幻觉的情况。VidHalluc评估幻觉的三个关键维度:动作、时间顺序和场景过渡。综合测试表明,大多数MLLMs在这些维度上都容易受幻觉影响。此外,我们提出了无需训练的DINO-HEAL方法,通过结合DINOv2的空间显著性在推理时重新加权视觉特征,以减少幻觉。结果表明,DINO-HEAL在VidHalluc上持续提高性能,在所有任务中平均减少了3.02%的幻觉。VidHalluc基准测试和DINO-HEAL代码均可在[链接]找到。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视频理解方面存在幻觉问题,尤其是视觉编码器的区分能力不足。
- VidHalluc基准测试是专为评估MLLMs在视频理解中的幻觉现象而设计的最大基准测试,包括动作、时间顺序和场景过渡三个关键维度的评估。
- 综合测试表明大多数MLLMs容易受幻觉影响。
- DINO-HEAL方法通过结合空间显著性在推理时重新加权视觉特征,能有效减少幻觉现象。此方法无需训练即可实施。
- DINO-HEAL在VidHalluc基准测试上提高了性能,所有任务平均减少幻觉的效果为3.02%。
点此查看论文截图