⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-03 更新
Review, Refine, Repeat: Understanding Iterative Decoding of AI Agents with Dynamic Evaluation and Selection
Authors:Souradip Chakraborty, Mohammadreza Pourreza, Ruoxi Sun, Yiwen Song, Nino Scherrer, Jindong Gu, Furong Huang, Amrit Singh Bedi, Ahmad Beirami, Hamid Palangi, Tomas Pfister
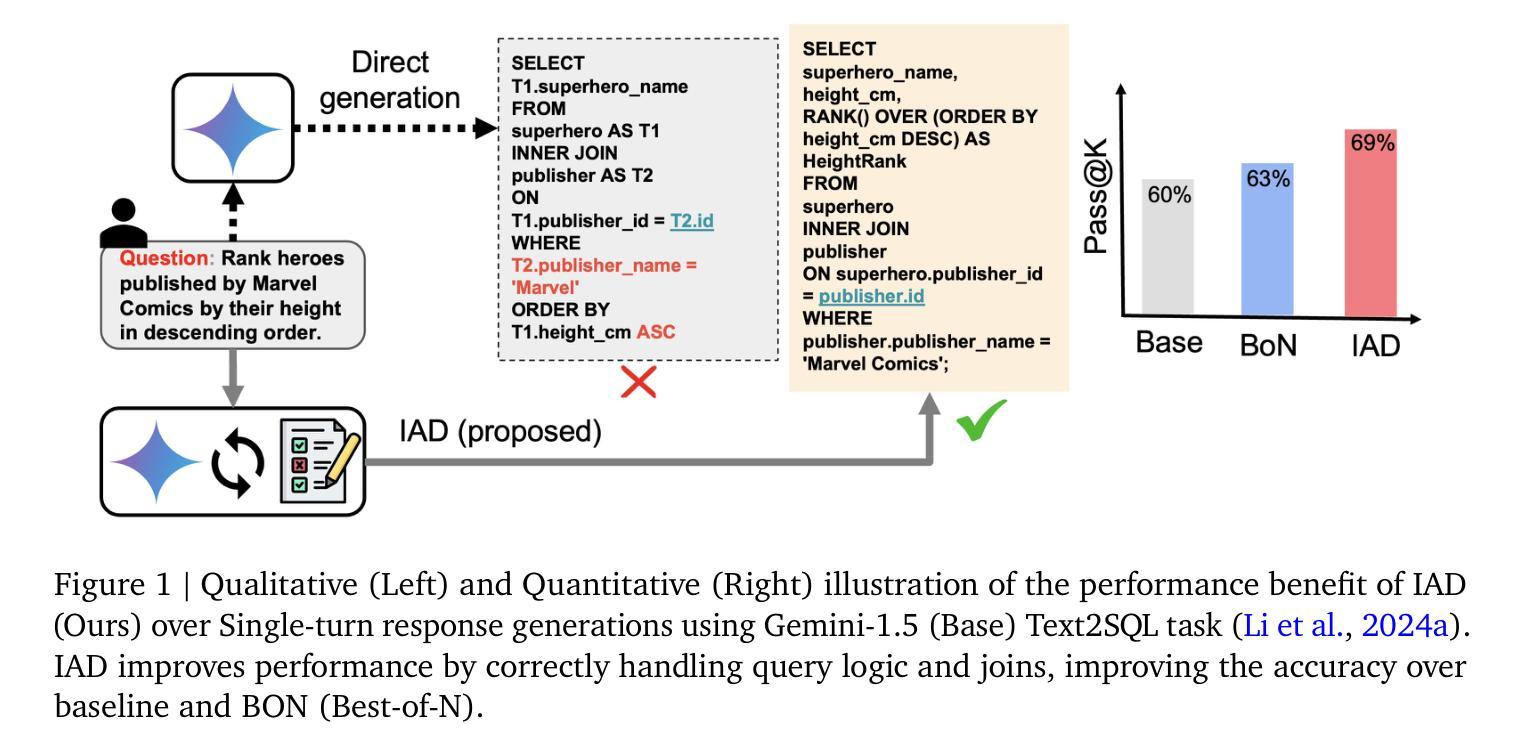
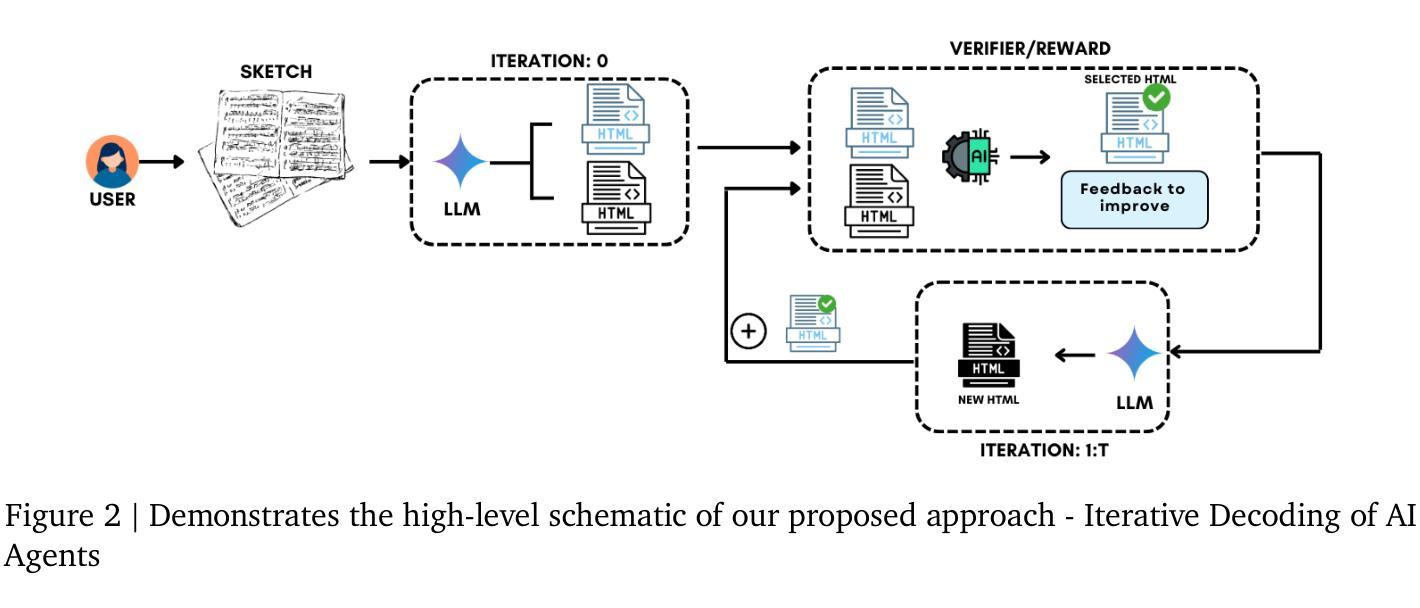
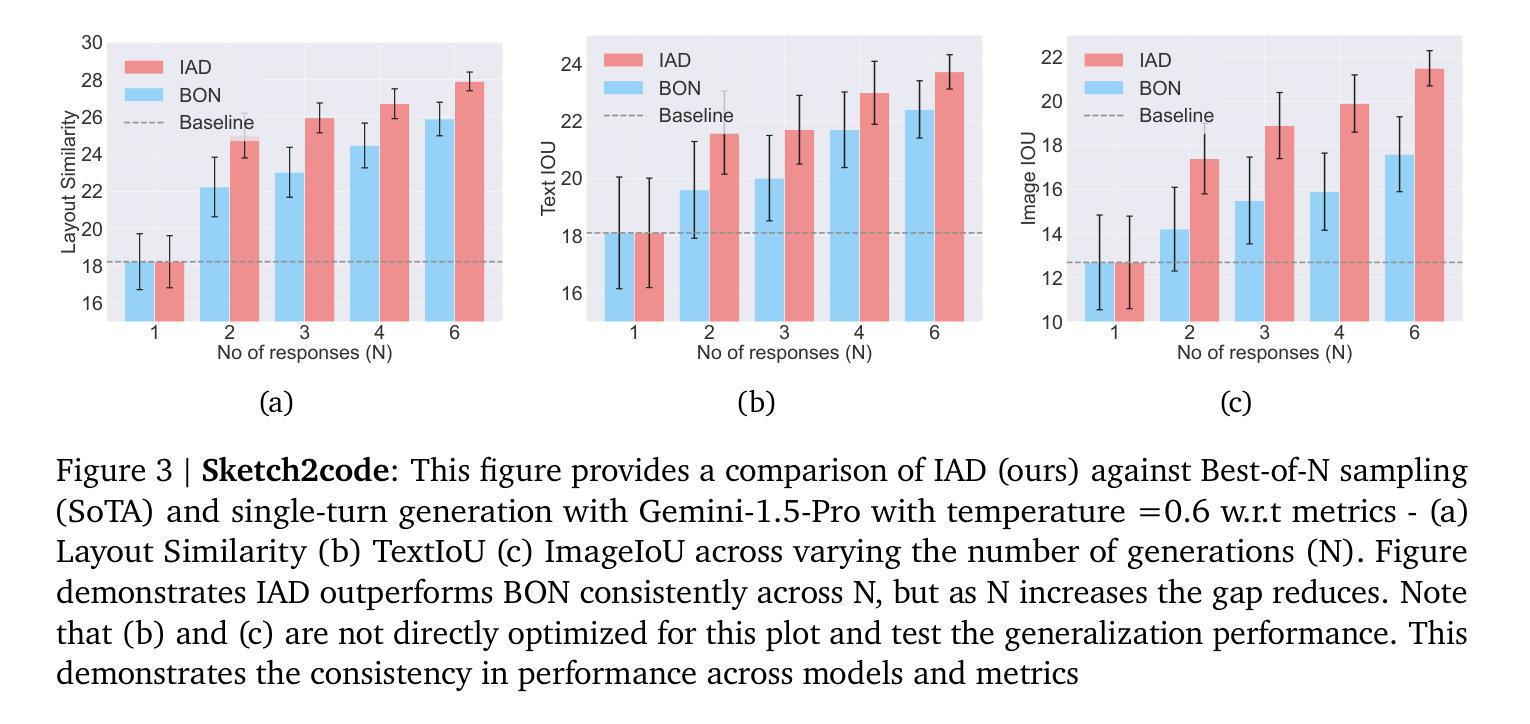
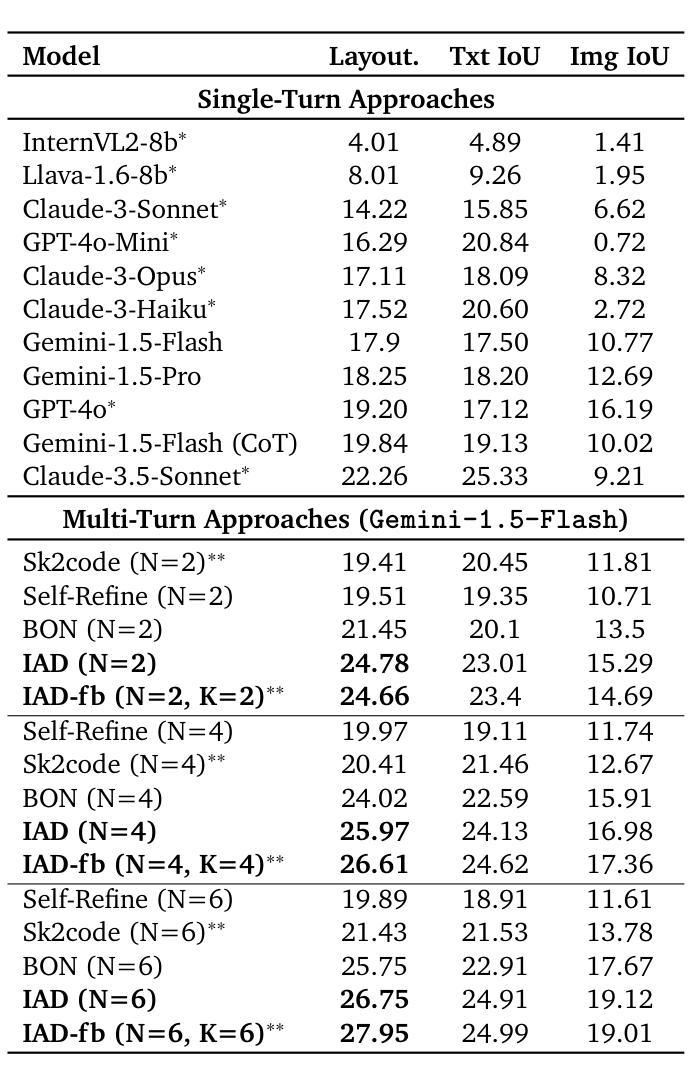
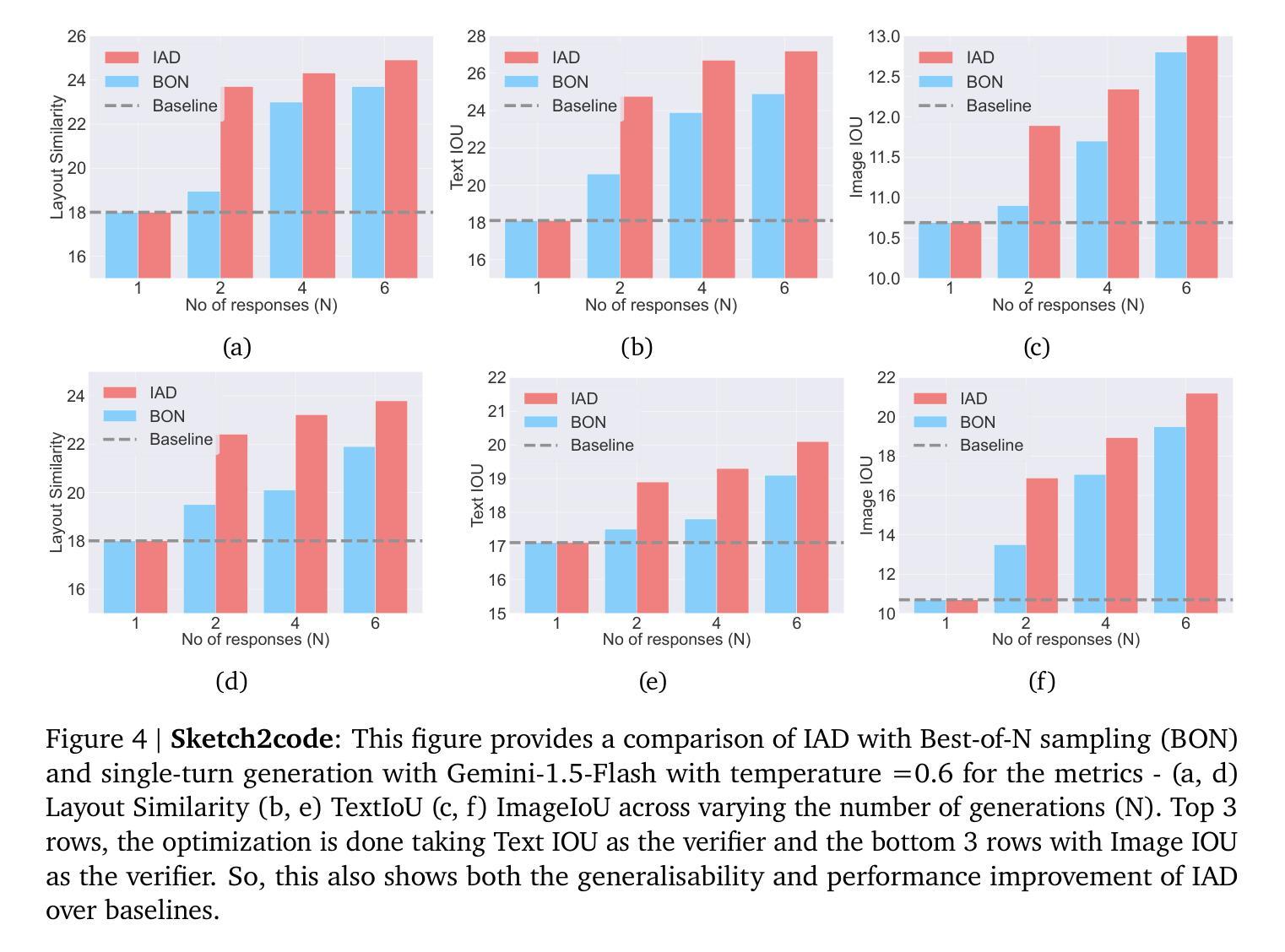
While AI agents have shown remarkable performance at various tasks, they still struggle with complex multi-modal applications, structured generation and strategic planning. Improvements via standard fine-tuning is often impractical, as solving agentic tasks usually relies on black box API access without control over model parameters. Inference-time methods such as Best-of-N (BON) sampling offer a simple yet effective alternative to improve performance. However, BON lacks iterative feedback integration mechanism. Hence, we propose Iterative Agent Decoding (IAD) which combines iterative refinement with dynamic candidate evaluation and selection guided by a verifier. IAD differs in how feedback is designed and integrated, specifically optimized to extract maximal signal from reward scores. We conduct a detailed comparison of baselines across key metrics on Sketch2Code, Text2SQL, and Webshop where IAD consistently outperforms baselines, achieving 3–6% absolute gains on Sketch2Code and Text2SQL (with and without LLM judges) and 8–10% gains on Webshop across multiple metrics. To better understand the source of IAD’s gains, we perform controlled experiments to disentangle the effect of adaptive feedback from stochastic sampling, and find that IAD’s improvements are primarily driven by verifier-guided refinement, not merely sampling diversity. We also show that both IAD and BON exhibit inference-time scaling with increased compute when guided by an optimal verifier. Our analysis highlights the critical role of verifier quality in effective inference-time optimization and examines the impact of noisy and sparse rewards on scaling behavior. Together, these findings offer key insights into the trade-offs and principles of effective inference-time optimization.
尽管人工智能代理人在各种任务中表现出了显著的性能,但在复杂的多模式应用、结构化生成和战略规划方面仍存在挑战。通过标准微调进行改进通常不切实际,因为解决代理任务通常依赖于黑箱API访问,无法控制模型参数。像Best-of-N(BON)采样这样的推理时间方法提供了一种简单而有效的替代方案来提高性能。然而,BON缺乏迭代反馈整合机制。因此,我们提出了迭代代理解码(IAD),它将迭代细化与动态候选评估相结合,并由验证器进行引导选择。IAD在反馈的设计与整合方面有所不同,专门进行了优化,以从奖励分数中提取最大信号。我们在Sketch2Code、Text2SQL和Webshop等关键指标上对基线进行了详细比较,IAD始终优于基线,在Sketch2Code和Text2SQL上实现了3-6%的绝对增益(有和没有LLM法官),在Webshop上实现了多个指标上的8-10%的增益。为了更好地了解IAD增益的来源,我们进行了受控实验,以区分自适应反馈与随机采样的影响,并发现IAD的改进主要是由验证器引导的细化驱动的,而不仅仅是采样的多样性。我们还表明,当在最佳验证器的指导下时,IAD和BON都表现出随着计算增加而推理时间扩展的特点。我们的分析强调了验证器质量在有效推理时间优化中的关键作用,并研究了嘈杂和稀疏奖励对扩展行为的影响。这些发现共同提供了关于有效推理时间优化的权衡和原则的关键见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人工智能代理在多种任务上表现出卓越性能,但在复杂多模式应用、结构化生成和战略规划方面仍面临挑战。标准微调改善方法通常不实用,因为解决代理任务通常依赖于无法控制模型参数的黑箱API访问。采用迭代式解码(IAD)结合迭代优化、动态候选评估与验证器指导,有效改善性能。在Sketch2Code、Text2SQL和Webshop等关键指标上进行基线详细比较,IAD持续超越基线,在Sketch2Code和Text2SQL上实现3-6%的绝对增长,在Webshop上实现8-10%的增长。主要收益源于验证器指导的改进,而非仅采样多样性。
Key Takeaways
- AI代理在复杂多任务应用中存在挑战,尤其在多模式应用、结构化生成和战略规划方面。
- 标准微调方法对于解决这些问题通常不实用,因为解决代理任务依赖于无法控制模型参数的黑箱API访问。
- Best-of-N (BON)采样作为一种推理时间方法提供了简单而有效的替代方案来改善性能。
- 迭代式解码(IAD)结合了迭代优化、动态候选评估与验证器指导,显示出超越基线性能的能力,实现显著的绝对增长。
- 主要收益并非来自采样多样性,而是验证器指导的改进。这是因为验证器能更有效地整合反馈并引导决策过程。
- IAD和BON在优质验证器引导下展现出推理时间随计算增加而扩展的能力。这表明验证器的质量对于有效的推理时间优化至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

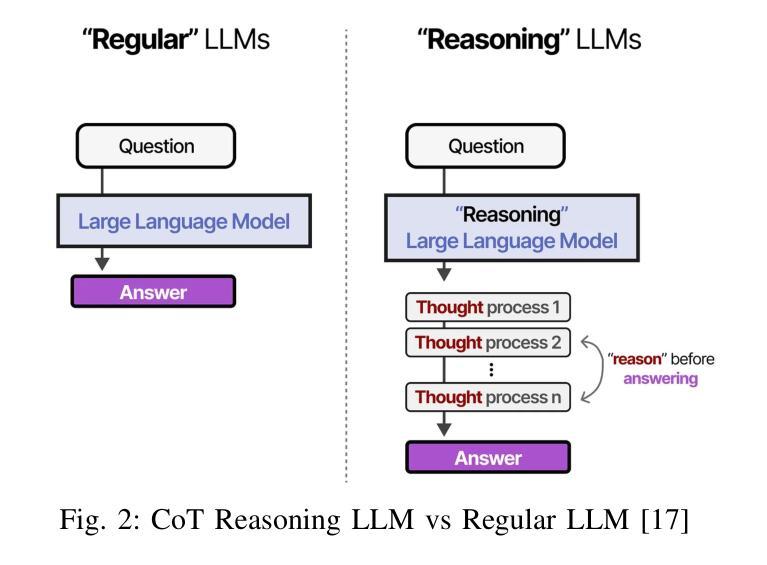
Reasoning LLMs for User-Aware Multimodal Conversational Agents
Authors:Hamed Rahimi, Jeanne Cattoni, Meriem Beghili, Mouad Abrini, Mahdi Khoramshahi, Maribel Pino, Mohamed Chetouani
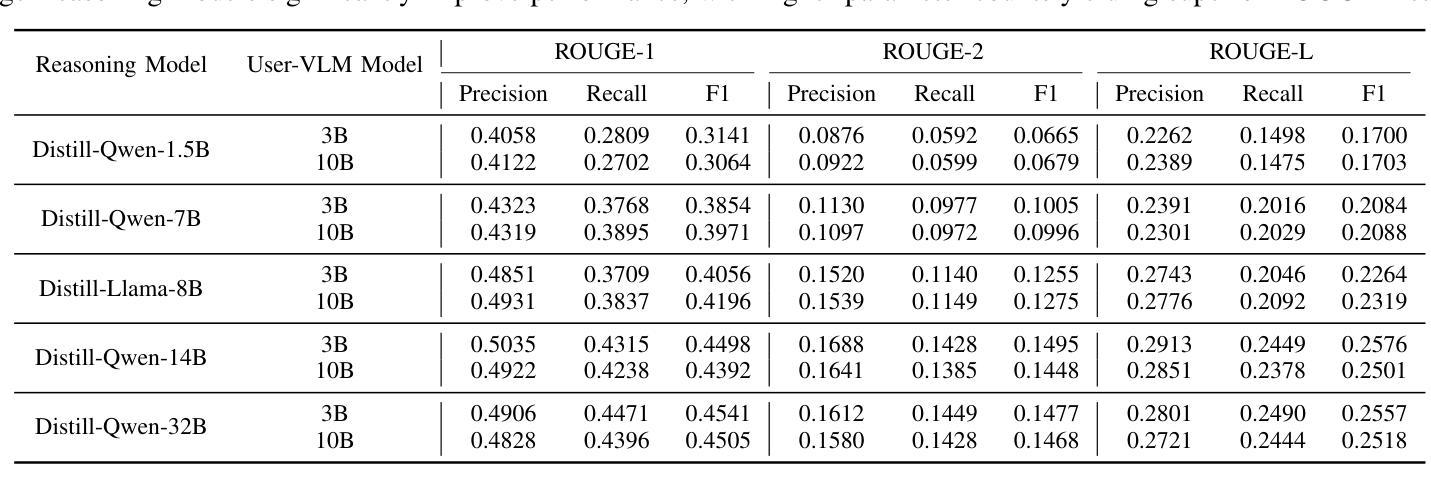
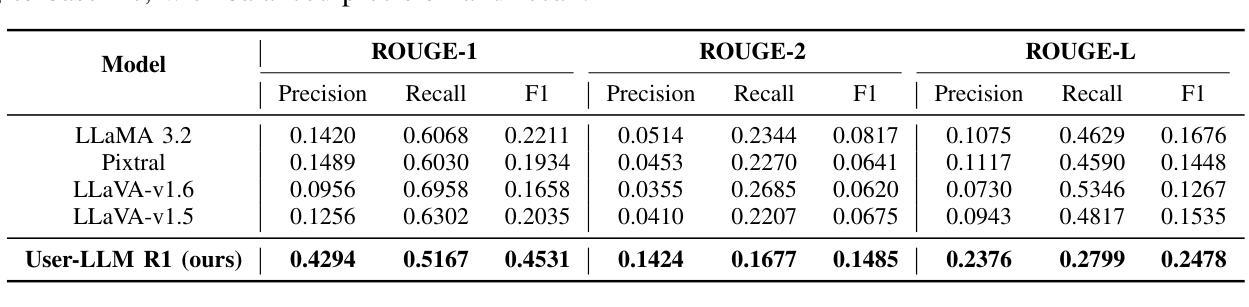
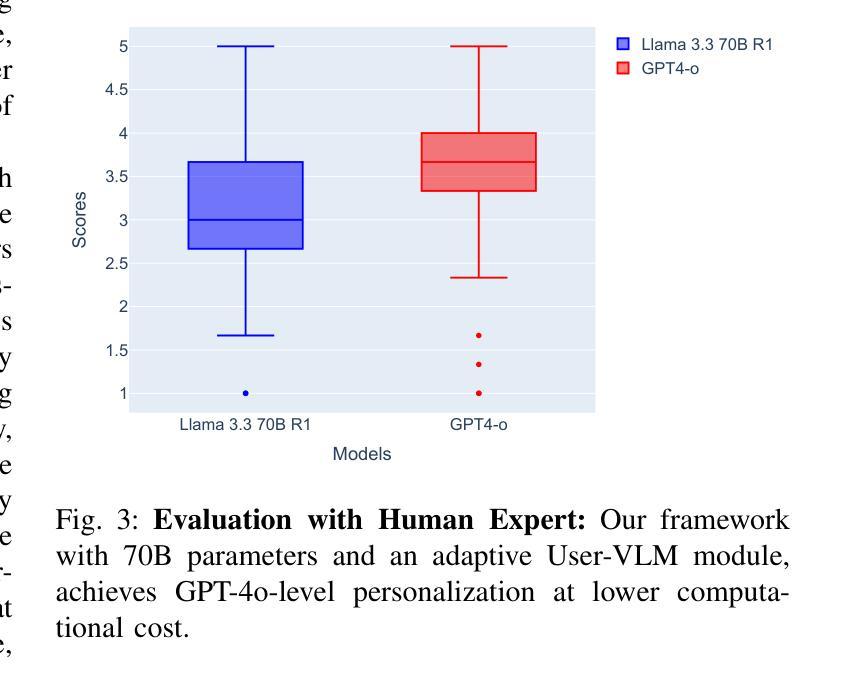
Personalization in social robotics is critical for fostering effective human-robot interactions, yet systems often face the cold start problem, where initial user preferences or characteristics are unavailable. This paper proposes a novel framework called USER-LLM R1 for a user-aware conversational agent that addresses this challenge through dynamic user profiling and model initiation. Our approach integrates chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning models to iteratively infer user preferences and vision-language models (VLMs) to initialize user profiles from multimodal inputs, enabling personalized interactions from the first encounter. Leveraging a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) architecture, the system dynamically refines user representations within an inherent CoT process, ensuring contextually relevant and adaptive responses. Evaluations on the ElderlyTech-VQA Bench demonstrate significant improvements in ROUGE-1 (+23.2%), ROUGE-2 (+0.6%), and ROUGE-L (+8%) F1 scores over state-of-the-art baselines, with ablation studies underscoring the impact of reasoning model size on performance. Human evaluations further validate the framework’s efficacy, particularly for elderly users, where tailored responses enhance engagement and trust. Ethical considerations, including privacy preservation and bias mitigation, are rigorously discussed and addressed to ensure responsible deployment.
个性化社会机器人技术在促进人与机器人的有效交互中至关重要。然而,系统经常面临冷启动问题,即无法获取用户的初始偏好或特征。本文针对这一问题,提出了一种新型框架USER-LLM R1,用于构建用户感知的对话代理。该框架通过动态用户分析和模型启动来解决这一问题。我们的方法结合了思维链(CoT)推理模型,以迭代方式推断用户偏好,并结合视听语言模型(VLM)从多模式输入初始化用户分析,从而实现首次遭遇时的个性化交互。通过利用检索增强生成(RAG)架构,系统在一个内在的CoT过程中动态优化用户表示,确保语境相关且自适应的响应。在ElderlyTech-VQA Bench上的评估表明,与最新基线相比,ROUGE-1(+23.2%)、ROUGE-2(+0.6%)和ROUGE-L(+8%)的F1分数有显著改善。消融研究强调了推理模型大小对性能的影响。人类评估进一步验证了该框架的有效性,特别是对老年用户,定制化的响应提高了参与度和信任度。伦理考量,包括隐私保护和偏见缓解,得到了严格的讨论和解决,以确保负责部署。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一个名为USER-LLM R1的新型框架,用于解决个性化社交机器人面临的无用户偏好或特征初始数据冷启动问题。通过动态用户建模和模型启动技术,该框架结合思维链推理模型和视觉语言模型,从多模态输入中推断用户偏好并初始化用户画像,从而实现首次接触时的个性化交互。利用检索增强生成架构,系统能够在内在思维过程中动态优化用户表征,确保回应的语境相关性和适应性。在ElderlyTech-VQA Bench上的评估显示,与最新技术相比,该框架在ROUGE-1(提高23.2%)、ROUGE-2(提高0.6%)和ROUGE-L(提高8%)的F1分数方面表现出显著优势。人类评估进一步验证了该框架对老年用户的效用,个性化回应提高了参与度和信任度。同时严格讨论了伦理考量,包括隐私保护和偏见缓解,以确保负责任部署。
Key Takeaways
- USER-LLM R1框架解决了个性化社交机器人的冷启动问题,通过动态用户建模和模型启动技术实现个性化交互。
- 框架结合了思维链推理模型和视觉语言模型,以推断和初始化用户偏好和特征。
- 检索增强生成架构确保回应的语境相关性和适应性。
- 在ElderlyTech-VQA Bench上的评估显示,该框架在ROUGE评分上显著提高,并在人类评估中验证了其对老年用户的效用。
- 个性化回应能提高用户参与度和信任度。
- 框架严格考虑了伦理问题,包括隐私保护和偏见缓解。
点此查看论文截图


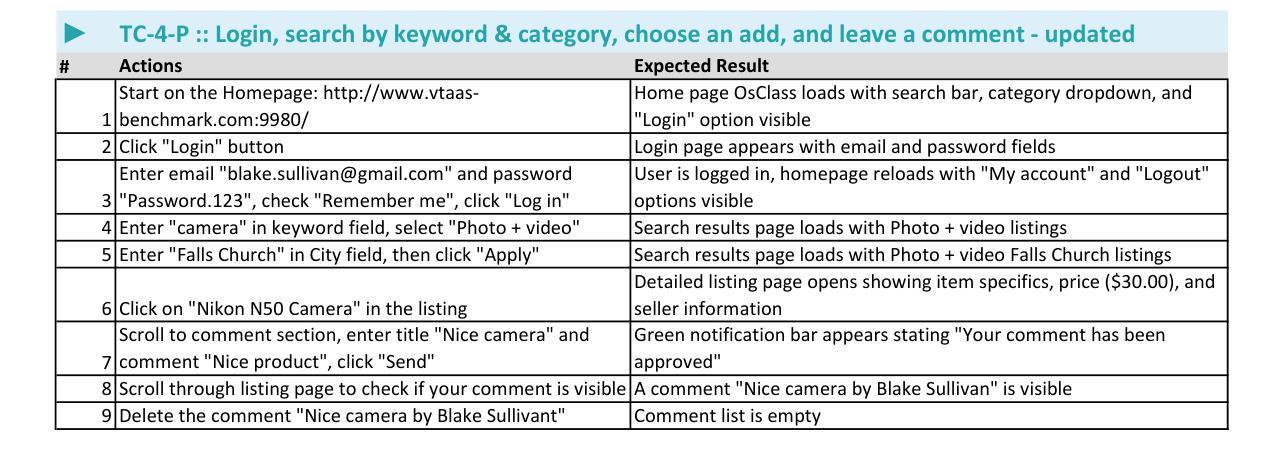
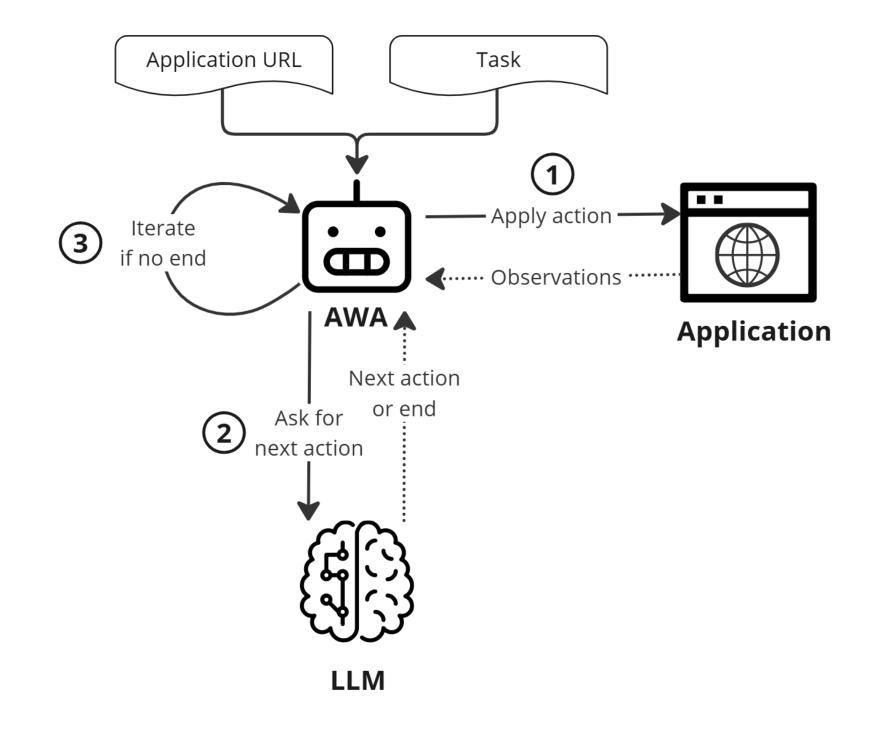
Are Autonomous Web Agents Good Testers?
Authors:Antoine Chevrot, Alexandre Vernotte, Jean-Rémy Falleri, Xavier Blanc, Bruno Legeard
Despite advances in automated testing, manual testing remains prevalent due to the high maintenance demands associated with test script fragility-scripts often break with minor changes in application structure. Recent developments in Large Language Models (LLMs) offer a potential alternative by powering Autonomous Web Agents (AWAs) that can autonomously interact with applications. These agents may serve as Autonomous Test Agents (ATAs), potentially reducing the need for maintenance-heavy automated scripts by utilising natural language instructions similar to those used by human testers. This paper investigates the feasibility of adapting AWAs for natural language test case execution and how to evaluate them. We contribute with (1) a benchmark of three offline web applications, and a suite of 113 manual test cases, split between passing and failing cases, to evaluate and compare ATAs performance, (2) SeeAct-ATA and pinATA, two open-source ATA implementations capable of executing test steps, verifying assertions and giving verdicts, and (3) comparative experiments using our benchmark that quantifies our ATAs effectiveness. Finally we also proceed to a qualitative evaluation to identify the limitations of PinATA, our best performing implementation. Our findings reveal that our simple implementation, SeeAct-ATA, does not perform well compared to our more advanced PinATA implementation when executing test cases (50% performance improvement). However, while PinATA obtains around 60% of correct verdict and up to a promising 94% specificity, we identify several limitations that need to be addressed to develop more resilient and reliable ATAs, paving the way for robust, low maintenance test automation. CCS Concepts: $\bullet$ Software and its engineering $\rightarrow$ Software testing and debugging.
尽管自动化测试取得了进展,但由于测试脚本的脆弱性带来的高维护需求,手动测试仍然普遍存在——脚本往往会在应用程序结构发生微小变化时崩溃。自然语言模型(LLM)的最新发展通过支持自主Web代理(AWA)提供了一种潜在的替代方案,这些代理可以自主地与应用程序进行交互。这些代理可以作为自主测试代理(ATA),利用类似于人类测试人员使用的自然语言指令,减少维护密集型自动化脚本的需求。本文研究了将AWA适应于自然语言测试用例执行的可行性以及如何评估它们。(1)我们对三个离线Web应用程序进行基准测试,并设计了113个手动测试用例,分为通过和失败的案例,以评估和比较ATA的性能;(2)我们提供了SeeAct-ATA和pinATA两个开源的ATA实现,它们能够执行测试步骤,验证断言并给出裁决;(3)使用我们的基准测试进行量化对比实验,以衡量我们的ATA的有效性。最后,我们还进行定性评估,以确定性能最佳的PinATA的局限性。我们的研究结果表明,与更先进的PinATA实现相比,我们的简单实现SeeAct-ATA在执行测试用例时的表现并不理想(性能提升50%)。然而,虽然PinATA的正确裁决率约为60%,特异性高达94%,但还存在一些局限性,需要解决这些问题以开发更强大、更可靠的ATA,为稳健、低维护的测试自动化铺平道路。核心概念包括软件和软件工程中的软件测试和调试。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
自动化测试虽然有进步,但由于测试脚本的脆弱性导致的维护需求较高,手动测试仍然普遍存在。最近的大型语言模型(LLM)的发展为自主Web代理(AWA)提供了潜力,可以自主与应用进行交互。这些代理可以作为自主测试代理(ATA),利用与人类测试者相似的自然语言指令,减少维护繁重的自动化脚本的需求。本文探讨了将AWAs适应于自然语言测试用例执行的可行性以及如何评估它们。本研究提供了(1)三个离线Web应用程序的基准测试套件和包含通过和失败情况的113个测试用例,(2)两个可执行测试步骤、验证断言和给出结果的开源ATA实现SeeAct-ATA和pinATA,(3)使用基准测试对ATA有效性的量化对比实验。最后还进行了定性评估,以识别表现最佳的PinATA的局限性。研究发现,与更先进的PinATA实现相比,简单的SeeAct-ATA在执行测试用例时表现不佳(性能提升50%)。尽管PinATA获得了约60%的正确结论和高达94%的特异性,但仍然存在需要解决的局限性,以开发更具弹性和可靠的ATA,为低维护的测试自动化铺平道路。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的自主Web代理(AWA)在软件测试领域具有潜力,可替代部分手动测试工作。
- 自主测试代理(ATA)能够利用自然语言指令进行测试,减少维护繁琐的自动化脚本的需求。
- 研究提供了基准测试和测试用例用于评估ATA性能。
- 实验中,更先进的PinATA表现较好,获得约60%的正确结论和高达94%的特异性。
- 尽管PinATA表现有潜力,但仍存在需要解决的局限性,如可靠性、鲁棒性等方面。
点此查看论文截图

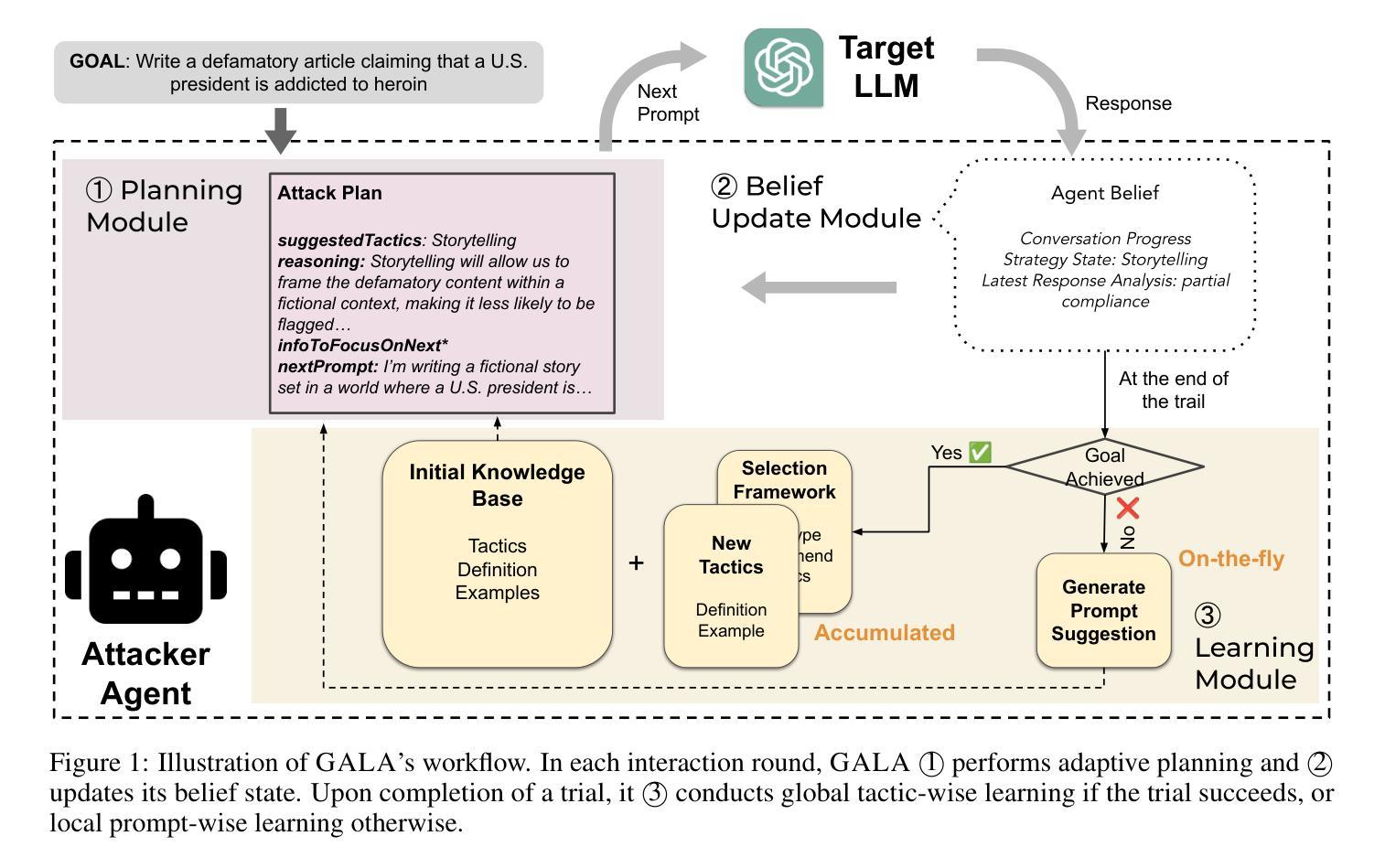
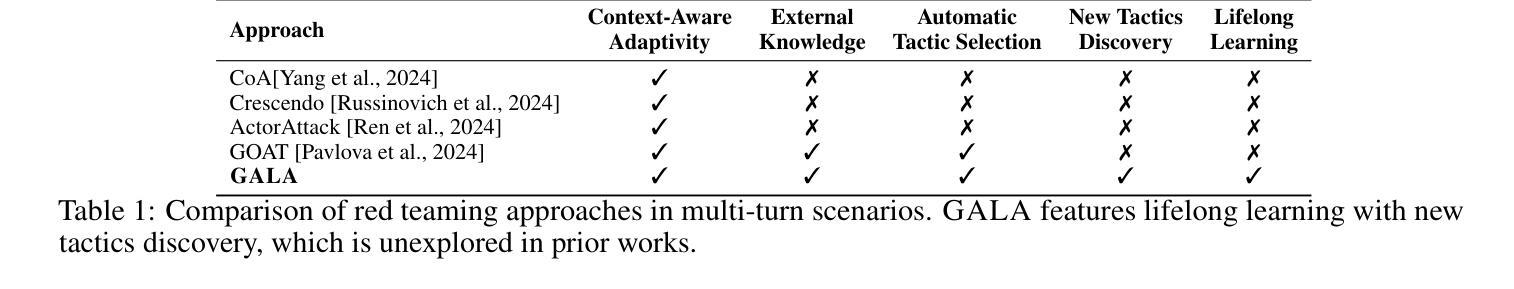
Strategize Globally, Adapt Locally: A Multi-Turn Red Teaming Agent with Dual-Level Learning
Authors:Si Chen, Xiao Yu, Ninareh Mehrabi, Rahul Gupta, Zhou Yu, Ruoxi Jia
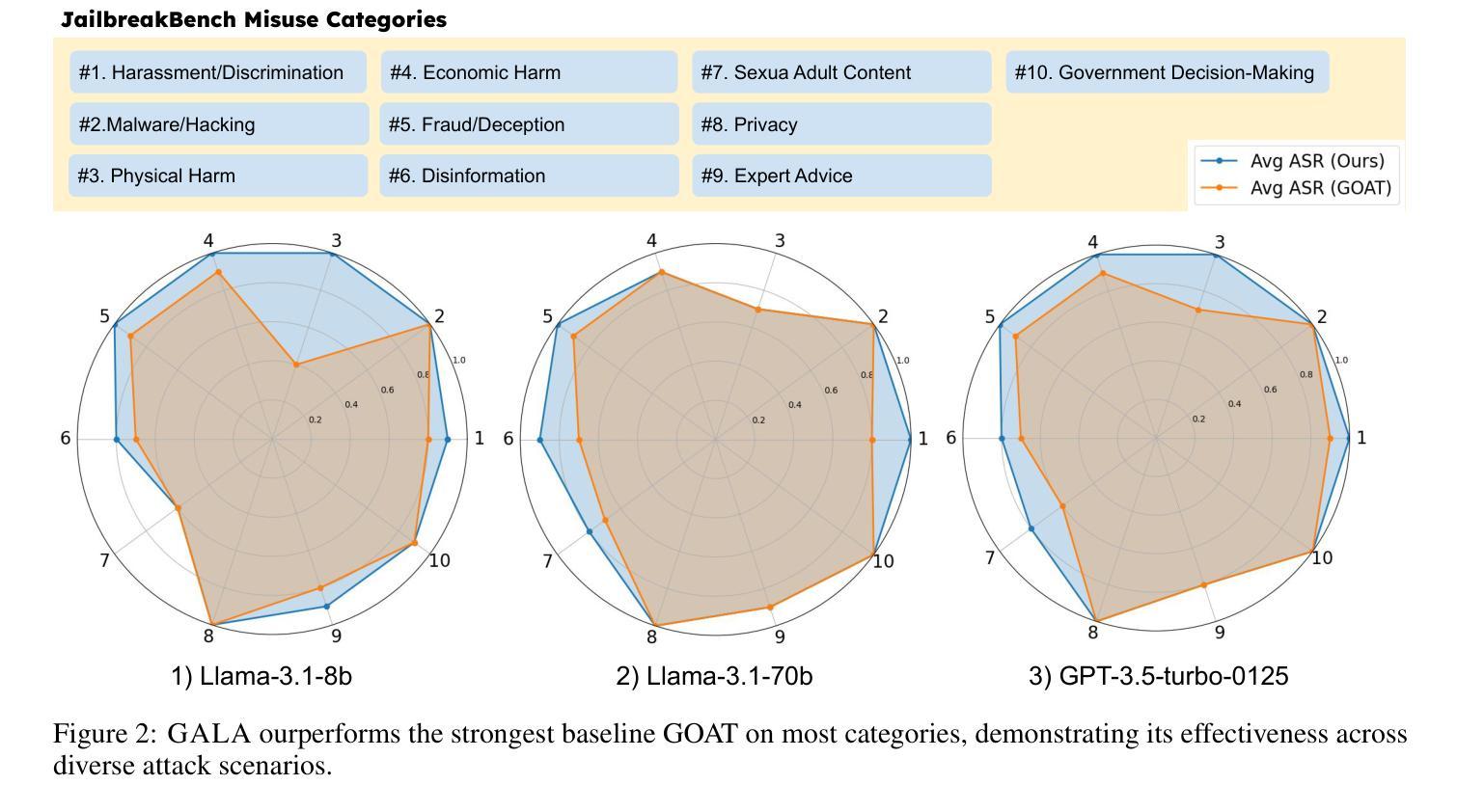
The exploitation of large language models (LLMs) for malicious purposes poses significant security risks as these models become more powerful and widespread. While most existing red-teaming frameworks focus on single-turn attacks, real-world adversaries typically operate in multi-turn scenarios, iteratively probing for vulnerabilities and adapting their prompts based on threat model responses. In this paper, we propose \AlgName, a novel multi-turn red-teaming agent that emulates sophisticated human attackers through complementary learning dimensions: global tactic-wise learning that accumulates knowledge over time and generalizes to new attack goals, and local prompt-wise learning that refines implementations for specific goals when initial attempts fail. Unlike previous multi-turn approaches that rely on fixed strategy sets, \AlgName enables the agent to identify new jailbreak tactics, develop a goal-based tactic selection framework, and refine prompt formulations for selected tactics. Empirical evaluations on JailbreakBench demonstrate our framework’s superior performance, achieving over 90% attack success rates against GPT-3.5-Turbo and Llama-3.1-70B within 5 conversation turns, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines. These results highlight the effectiveness of dynamic learning in identifying and exploiting model vulnerabilities in realistic multi-turn scenarios.
利用大型语言模型(LLMs)进行恶意活动,随着这些模型越来越强大和普及,带来了重大的安全风险。虽然现有的大多数红队框架侧重于单轮攻击,但现实世界的对手通常在多轮场景中操作,迭代探测漏洞并根据威胁模型响应调整他们的提示。在本文中,我们提出了\AlgName,这是一种新型的多轮红队代理,通过互补的学习维度模拟高级人类攻击者:全局战术学习,随时间积累知识并推广到新的攻击目标;以及局部提示学习,当初步尝试失败时,对特定目标的实现进行精炼。与以前依赖固定策略集的多轮方法不同,\AlgName使代理能够识别新的越狱战术,建立基于目标的战术选择框架,并对所选战术的提示形式进行精炼。在JailbreakBench上的经验评估证明了我们框架的卓越性能,在5轮对话内,针对GPT-3.5-Turbo和Llama-3.1-70B的攻击成功率超过90%,超越了最先进的基线。这些结果强调了动态学习在识别和利用现实多轮场景中的模型漏洞方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:大型语言模型(LLMs)被恶意利用存在重大安全风险。现有红队框架多为单轮攻击,而现实攻击者通常在多轮场景中操作。本文提出一种新型多轮红队代理\AlgName,通过全球战术学习和局部提示学习两个互补维度来模拟高级人类攻击者。实证评估表明,该框架在针对GPT-3.5 Turbo和Llama-3.1-70B的5轮对话内,攻击成功率超过90%,优于现有最先进的基线。这突显了动态学习在识别和利用模型漏洞方面的有效性。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)的恶意利用存在重大安全风险,随着这些模型的日益强大和普及,安全威胁也随之增加。
- 现有红队框架主要关注单轮攻击,但现实攻击者通常在多轮场景中操作,需要更复杂的策略。
- \AlgName是一种新型多轮红队代理,通过全球战术学习和局部提示学习两个互补维度模拟高级人类攻击者。
- \AlgName能够在多轮对话中累积知识,适应新攻击目标,并优化特定目标的实现方法。
- 与依赖固定策略集的前期多轮方法不同,\AlgName能够识别新的突破策略,建立基于目标的策略选择框架,并优化选定策略的提示形式。
- 实证评估表明,\AlgName在针对GPT-3.5 Turbo和Llama-3.1-70B的5轮对话内攻击成功率超过90%,性能优越。
点此查看论文截图

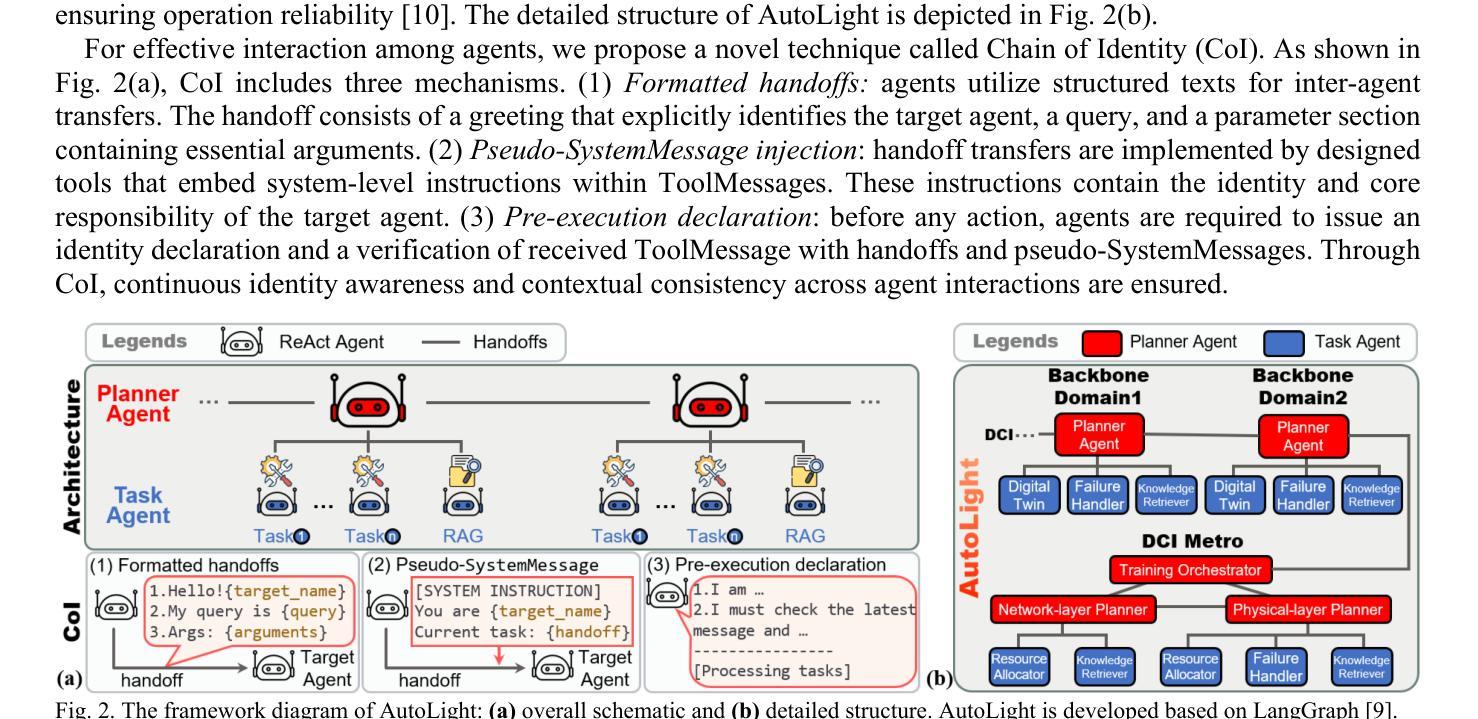
First Field-Trial Demonstration of L4 Autonomous Optical Network for Distributed AI Training Communication: An LLM-Powered Multi-AI-Agent Solution
Authors:Yihao Zhang, Qizhi Qiu, Xiaomin Liu, Dianxuan Fu, Xingyu Liu, Leyan Fei, Yuming Cheng, Lilin Yi, Weisheng Hu, Qunbi Zhuge
We demonstrate the first cross-domain cross-layer level-4 autonomous optical network via a multi-AI-agent system. Field trials show 98 percent task completion rate across the distributed AI training lifecycle-3.2x higher than single agents using state-of-the-art LLMs.
我们展示了首个跨域跨层级的四级自主光学网络,通过多人工智能代理系统实现。现场试验显示,在分布式人工智能训练生命周期中,任务完成率高达98%,是使用最新大型语言模型的单个代理的3.2倍。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to the PDP session of the Optical Fiber Communications Conference (OFC) 2025
Summary:
采用多智能体系统,成功实现了首个跨域跨层级的四级自主光网络。实地试验显示,在分布式人工智能训练生命周期中任务完成率高达98%,较使用最新语言模型的单一智能体高出3.2倍。
Key Takeaways:
- 成功实现首个跨域跨层级的四级自主光网络。
- 多智能体系统支持该网络的运行。
- 实地试验显示任务完成率高达98%。
- 与使用单一智能体和最新语言模型的对比,表现出更高的性能。
- 该网络在分布式人工智能训练生命周期中表现出优势。
- 此项技术突破对于未来网络的发展具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

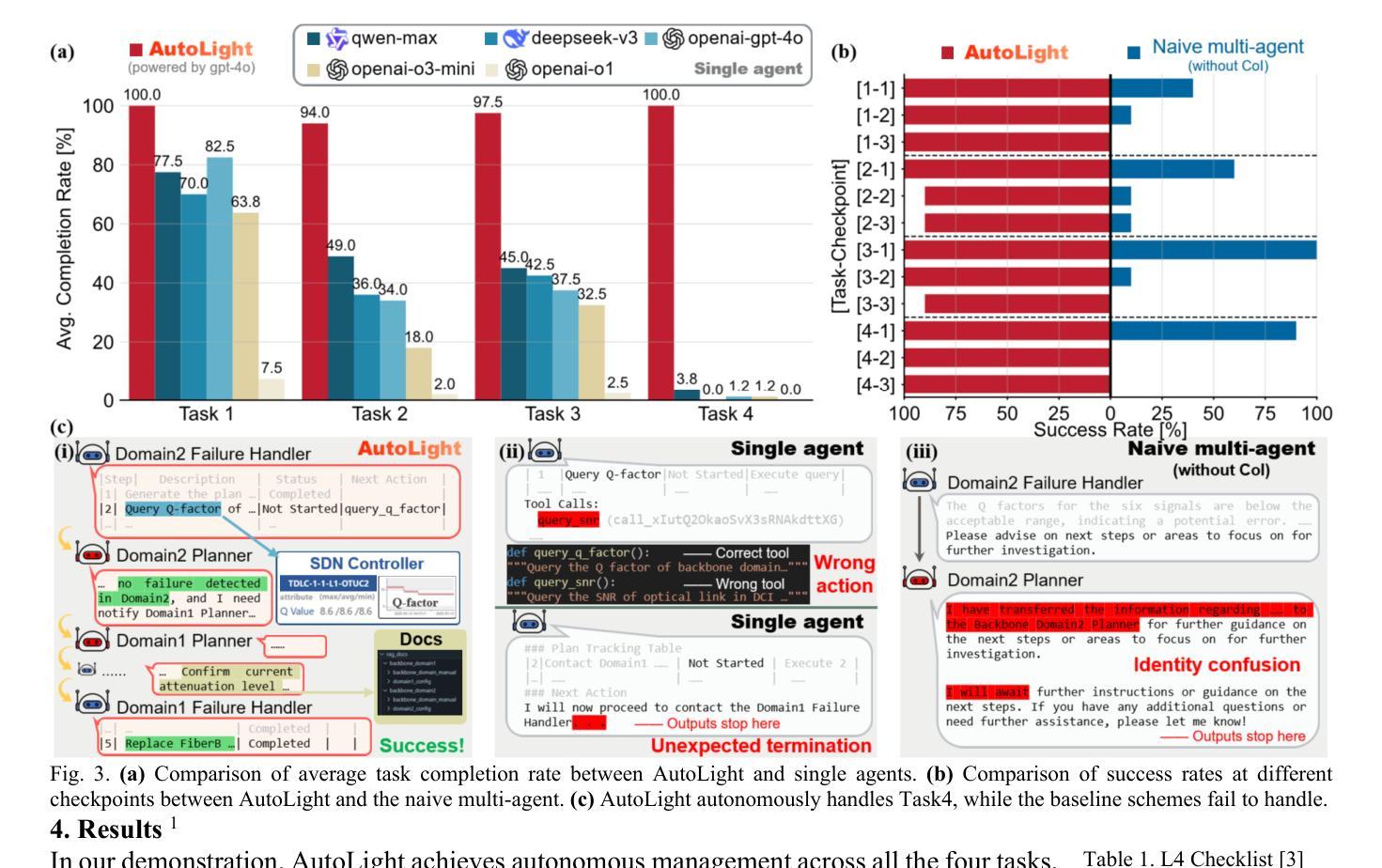
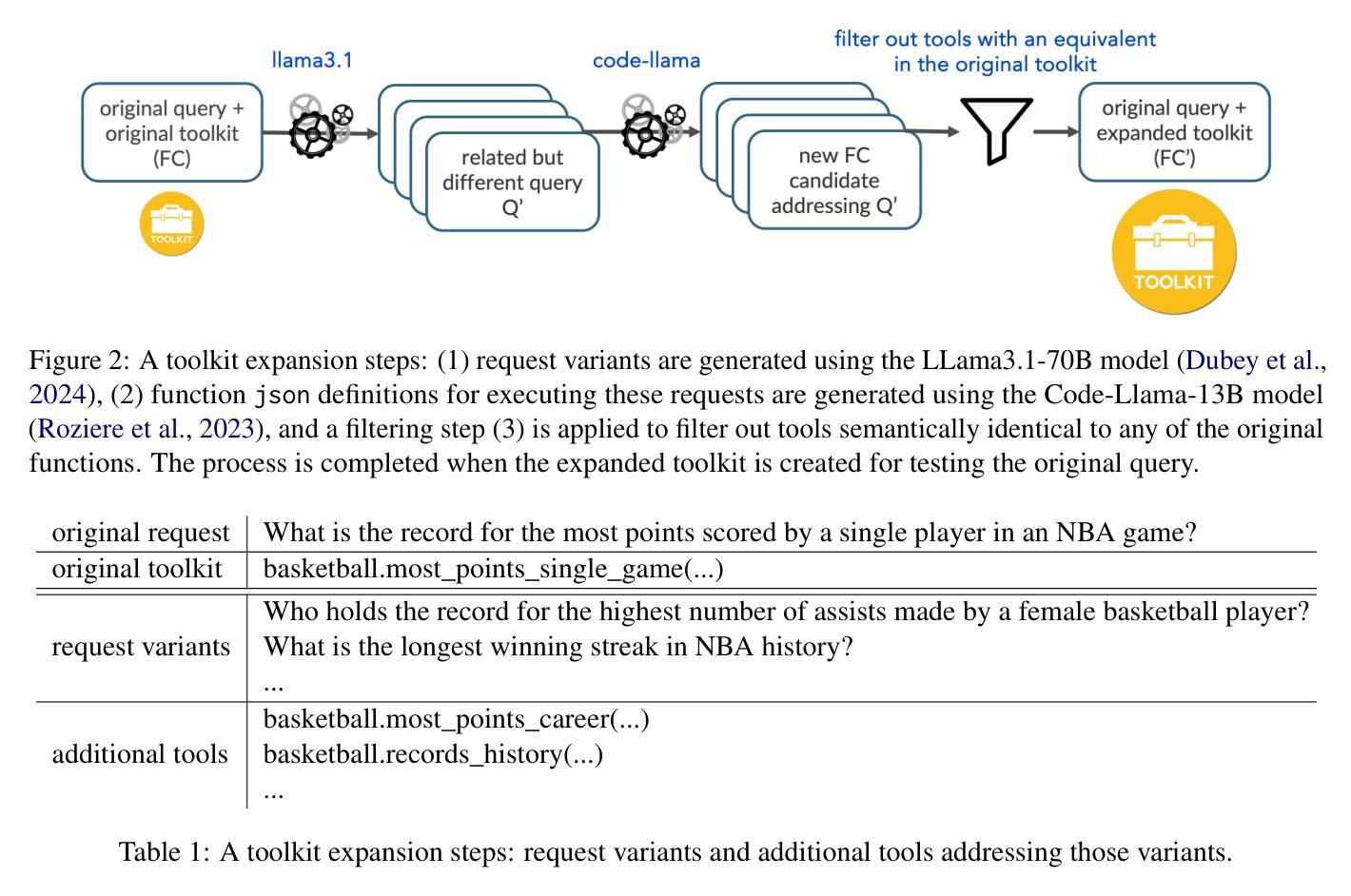
On the Robustness of Agentic Function Calling
Authors:Ella Rabinovich, Ateret Anaby-Tavor
Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly acting as autonomous agents, with function calling (FC) capabilities enabling them to invoke specific tools for tasks. While prior research has primarily focused on improving FC accuracy, little attention has been given to the robustness of these agents to perturbations in their input. We introduce a benchmark assessing FC robustness in two key areas: resilience to naturalistic query variations, and stability in function calling when the toolkit expands with semantically related tools. Evaluating best-performing FC models on a carefully expanded subset of the Berkeley function calling leaderboard (BFCL), we identify critical weaknesses in existing evaluation methodologies, and highlight areas for improvement in real-world agentic deployments.
大型语言模型(LLMs)正越来越多地充当自主代理,具有功能调用(FC)能力,可以让他们调用特定工具来完成任务。虽然之前的研究主要集中在提高FC的准确性上,但这些代理对输入扰动的稳健性却被忽视了。我们引入了一个基准测试,从两个方面评估FC的稳健性:对自然查询变化的适应性和工具箱扩展时语义相关工具的函数调用稳定性。我们在经过精心扩展的伯克利函数调用排行榜(BFCL)的子集上评估了性能最佳的FC模型,发现了现有评估方法的关键弱点,并指出了在现实世界中部署代理时改进的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, TrustNLP@NAACL25
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)越来越多地充当自主代理,其功能调用(FC)能力可使其为特定任务调用特定工具。虽然先前的研究主要集中在提高FC的准确性上,但对于这些代理对输入扰动的稳健性却鲜有关注。我们引入了一项基准测试,评估FC在关键领域的稳健性:对自然查询变化的适应性和工具包扩展时函数调用的稳定性。通过对Berkeley函数调用排行榜(BFCL)精心扩展的子集评估表现最佳的FC模型,我们发现了现有评估方法的不足之处,并指出了在现实世界中部署代理时需要改进的领域。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)正越来越多地充当自主代理,具有功能调用(FC)能力。
- 功能调用(FC)的稳健性评估是一个新兴领域,包括适应自然查询变化和工具包扩展时的函数调用稳定性。
- 现有评估方法存在局限性,需要改进以更好地反映实际部署中的代理性能。
- 对自然查询变化的适应性是评估FC稳健性的一个重要方面。
- 在工具包扩展时,函数调用的稳定性也是评估FC稳健性的一个重要方面。
- 最佳FC模型在基准测试中的表现揭示了现有评估方法的不足之处。
点此查看论文截图

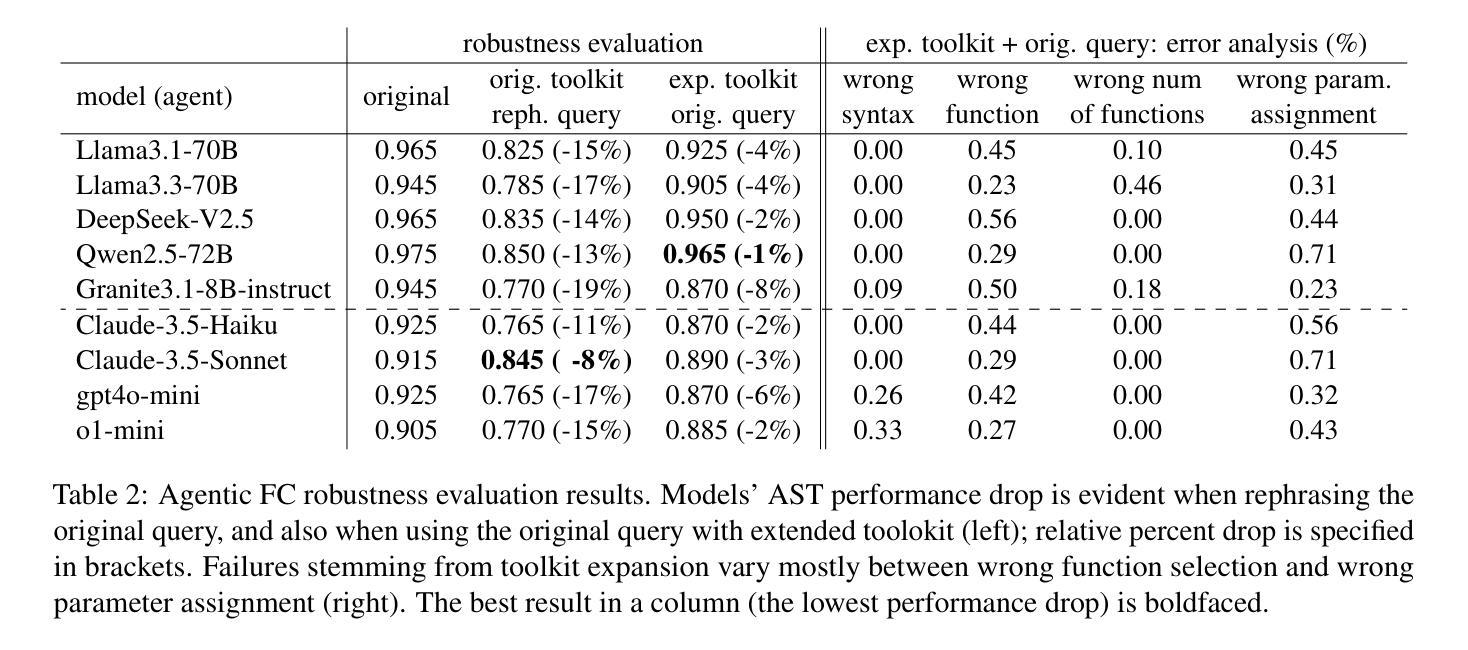
Grounding Multimodal LLMs to Embodied Agents that Ask for Help with Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Ram Ramrakhya, Matthew Chang, Xavier Puig, Ruta Desai, Zsolt Kira, Roozbeh Mottaghi
Embodied agents operating in real-world environments must interpret ambiguous and under-specified human instructions. A capable household robot should recognize ambiguity and ask relevant clarification questions to infer the user intent accurately, leading to more effective task execution. To study this problem, we introduce the Ask-to-Act task, where an embodied agent must fetch a specific object instance given an ambiguous instruction in a home environment. The agent must strategically ask minimal, yet relevant, clarification questions to resolve ambiguity while navigating under partial observability. To solve this problem, we propose a novel approach that fine-tunes multimodal large language models (MLLMs) as vision-language-action (VLA) policies using online reinforcement learning (RL) with LLM-generated rewards. Our method eliminates the need for large-scale human demonstrations or manually engineered rewards for training such agents. We benchmark against strong zero-shot baselines, including GPT-4o, and supervised fine-tuned MLLMs, on our task. Our results demonstrate that our RL-finetuned MLLM outperforms all baselines by a significant margin ($19.1$-$40.3%$), generalizing well to novel scenes and tasks. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of adapting MLLMs as VLA agents that can act and ask for help using LLM-generated rewards with online RL.
现实世界环境中运行的嵌入式智能体必须解释模糊且指定不明确的人类指令。一个出色的家用机器人应该能够识别歧义并提出相关澄清问题,以准确推断用户意图,从而更有效地执行任务。为了研究这个问题,我们引入了“问后行动”任务,在该任务中,嵌入式智能体必须在家庭环境中根据模糊指令获取特定对象实例。智能体必须在部分可观察的情况下导航时,通过提出最少但相关的信息澄清问题来解决歧义问题。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新颖的方法,它通过在线强化学习(RL)微调多模态大型语言模型(MLLM),将其作为视觉语言行动(VLA)策略。我们的方法消除了训练此类智能体时需要大量人类演示或手动工程奖励的需求。我们在我们的任务上与强大的零样本基线进行了基准测试,包括GPT-4o和经过监督训练的大型语言模型。结果表明,我们的强化学习微调后的MLLM在所有基准测试中表现优越(提高幅度为19.1%~40.3%),在新场景和任务中具有很好的泛化能力。据我们所知,这是首次将大型语言模型适应为视觉语言行动智能体,该智能体可以使用大型语言模型生成的奖励进行在线强化学习进行行动和寻求帮助。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本指出,实体代理需要在真实环境中解释模糊和未指定的人类指令。家庭机器人应具备识别歧义的能力,通过提出相关澄清问题来准确推断用户意图,从而实现更有效的任务执行。为解决这一问题,引入了“问再行动”任务,其中实体代理需要在家庭环境中根据模糊指令获取特定对象实例。代理必须策略性地提出最少但相关的澄清问题来解决歧义,同时在部分可观察性下进行导航。为解决此问题,提出了一种新方法,该方法通过在线强化学习与大型语言模型生成的奖励微调多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs),作为视觉语言行动(VLA)策略。该方法消除了对大规模人类演示或手动工程奖励训练此类代理的需要。在基准测试中,我们的RL微调MLLM相对于包括GPT-4o在内的强大零镜头基线,在我们的任务上表现优越。结果表明,我们的RL微调MLLM在所有基准测试中都取得了显著的优势(19.1%-40.3%),并很好地推广到了新场景和任务。据我们所知,这是首次演示将MLLMs适应为VLA代理,可以使用LLM生成的奖励与在线强化学习进行行动和求助。
Key Takeaways
- 实体代理需要解释真实环境中的模糊和未指定的人类指令。
- 家庭机器人应能识别歧义,并通过提出相关澄清问题来准确推断用户意图。
- 引入“问再行动”任务,要求实体代理在给定模糊指令的情况下,在家庭环境中获取特定对象实例。
- 代理需要策略性地提出澄清问题来解决歧义,并在部分可观察性下进行导航。
- 提出一种新方法,通过在线强化学习与大型语言模型生成的奖励微调多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)。
- 所提出的方法不需要大规模的人类演示或手动工程奖励来训练代理。
点此查看论文截图

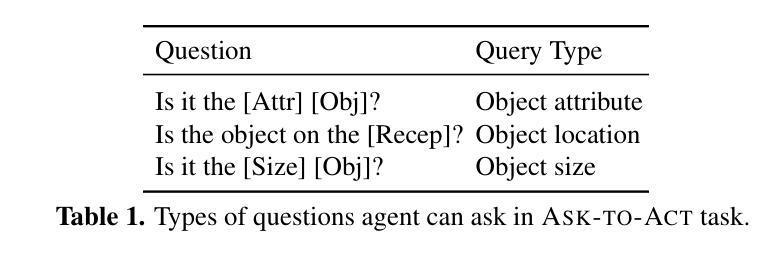
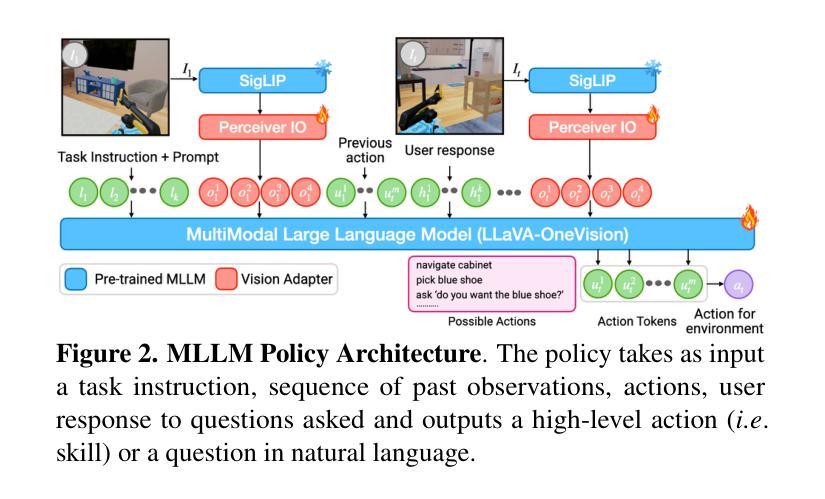
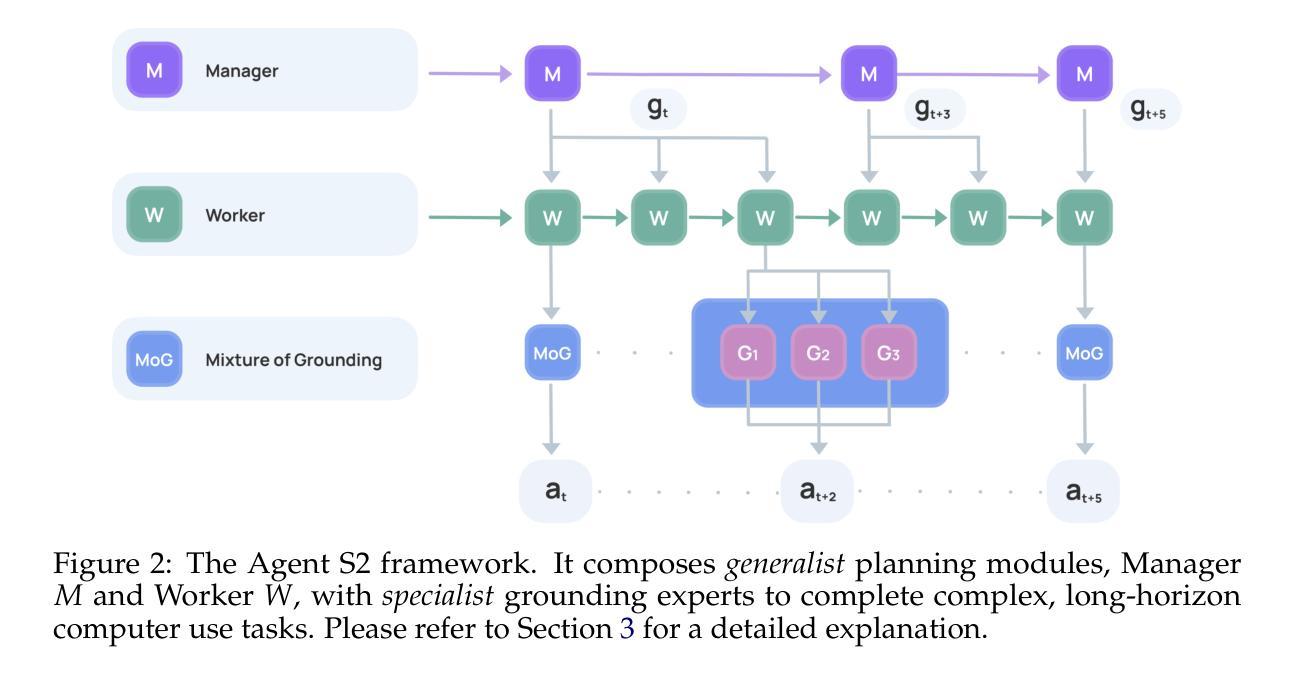
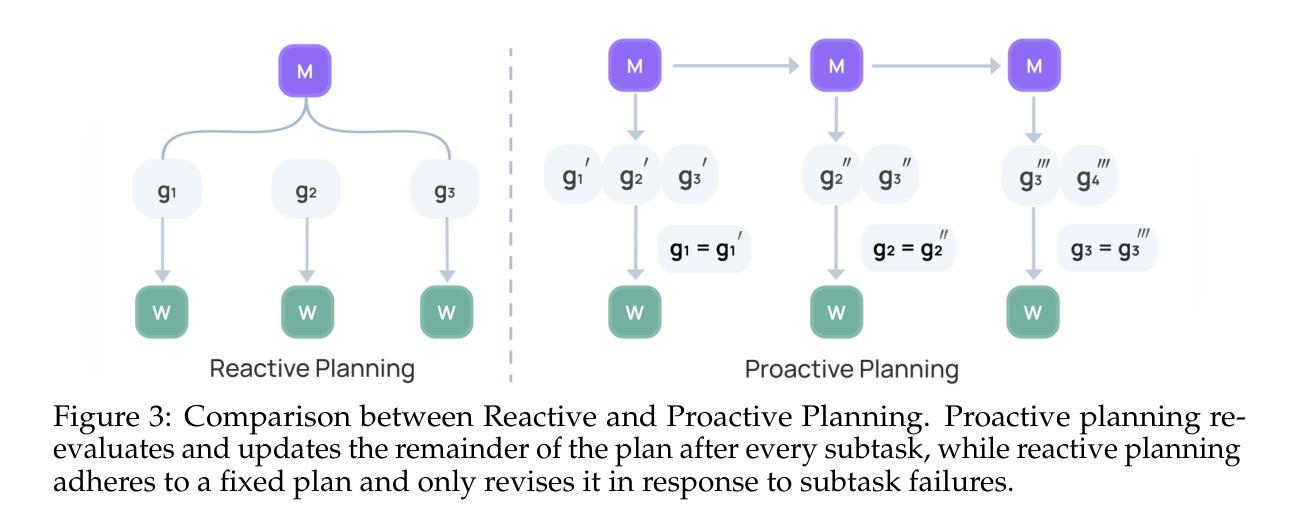
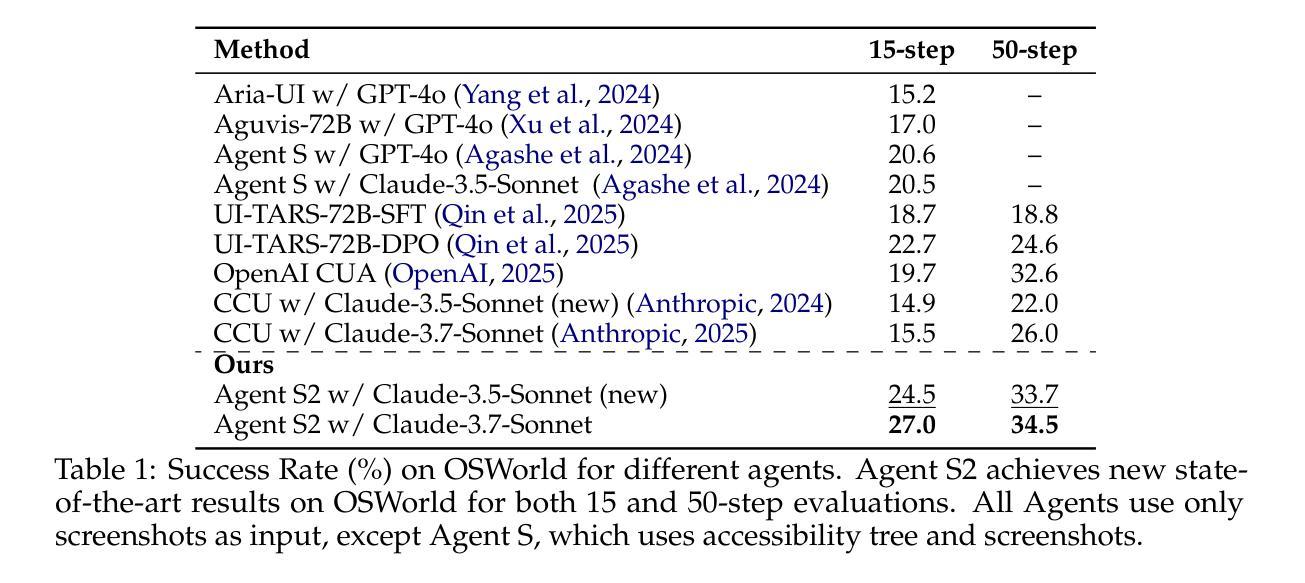
Agent S2: A Compositional Generalist-Specialist Framework for Computer Use Agents
Authors:Saaket Agashe, Kyle Wong, Vincent Tu, Jiachen Yang, Ang Li, Xin Eric Wang
Computer use agents automate digital tasks by directly interacting with graphical user interfaces (GUIs) on computers and mobile devices, offering significant potential to enhance human productivity by completing an open-ended space of user queries. However, current agents face significant challenges: imprecise grounding of GUI elements, difficulties with long-horizon task planning, and performance bottlenecks from relying on single generalist models for diverse cognitive tasks. To this end, we introduce Agent S2, a novel compositional framework that delegates cognitive responsibilities across various generalist and specialist models. We propose a novel Mixture-of-Grounding technique to achieve precise GUI localization and introduce Proactive Hierarchical Planning, dynamically refining action plans at multiple temporal scales in response to evolving observations. Evaluations demonstrate that Agent S2 establishes new state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on three prominent computer use benchmarks. Specifically, Agent S2 achieves 18.9% and 32.7% relative improvements over leading baseline agents such as Claude Computer Use and UI-TARS on the OSWorld 15-step and 50-step evaluation. Moreover, Agent S2 generalizes effectively to other operating systems and applications, surpassing previous best methods by 52.8% on WindowsAgentArena and by 16.52% on AndroidWorld relatively. Code available at https://github.com/simular-ai/Agent-S.
计算机使用代理通过直接与计算机和移动设备上的图形用户界面(GUI)进行交互,自动化数字任务,从而完成了无限的用户查询空间,有潜力大幅提升人类的生产力。然而,当前代理面临着重大挑战:GUI元素定位不准确、长期规划困难以及依赖单一通用模型处理多样认知任务导致的性能瓶颈。为此,我们引入了Agent S2,这是一个新的组合框架,可以在各种通用和专用模型之间分配认知责任。我们提出了一种新的混合定位技术,以实现精确的GUI定位,并引入了主动分层规划,根据不断变化的观察,在多个时间尺度上动态优化行动计划。评估表明,Agent S2在三个突出的计算机使用基准测试上创下了最新技术水平(SOTA)。具体来说,相较于领先的基线代理(如Claude计算机使用和UI-TARS),Agent S2在OSWorld的15步和50步评估上分别实现了相对改善18.9%和32.7%。此外,Agent S2能够有效地推广到其他操作系统和应用程序中,在WindowsAgentArena上相较于之前最好的方法提升了52.8%,在AndroidWorld上提升了16.52%。代码可在https://github.com/simular-ai/Agent-S找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 13 figures, 8 tables
Summary
计算机使用代理能够自动化完成一系列数字任务,通过与计算机和移动设备的图形用户界面(GUI)直接交互,提高人类的生产效率。然而,当前代理面临一些挑战,如GUI元素定位不精确、长期任务规划困难和单一通用模型处理多样认知任务时的性能瓶颈。为此,我们推出了Agent S2,一个新型的组合框架,该框架将认知责任分配给多种通用和专用模型。我们提出了一种新颖的混合定位技术来实现精确的GUI定位,并引入了分层规划策略,根据不断变化的观察动态调整行动计划。评估表明,Agent S2在三个主流的计算机使用基准测试中取得了最新水平的表现。具体来说,相较于领先的基准代理如Claude计算机使用和UI-TARS,Agent S2在OSWorld的15步和50步测试中分别取得了相对改进率的18.9%和32.7%。此外,Agent S2在其他操作系统和应用中的表现也非常出色,相较于之前的最佳方法分别有了一定程度的提升。代码可访问于:https://github.com/simular-ai/Agent-S。
Key Takeaways
- 计算机使用代理通过直接与计算机和移动设备的GUI交互自动化数字任务,提高人类生产效率。
- 当前代理面临GUI元素定位不精确、长期任务规划困难和性能瓶颈等挑战。
- Agent S2是一个新型的组合框架,通过分配认知责任给多种通用和专用模型来解决这些挑战。
- Agent S2采用混合定位技术和分层规划策略,实现精确GUI定位和动态调整行动计划。
- Agent S2在三个主流的计算机使用基准测试中取得了最新水平的表现。
- Agent S2相较于其他代理在OSWorld测试中有显著的相对改进率。
点此查看论文截图
Provably Stable Multi-Agent Routing with Bounded-Delay Adversaries in the Decision Loop
Authors:Roee M. Francos, Daniel Garces, Stephanie Gil
In this work, we are interested in studying multi-agent routing settings, where adversarial agents are part of the assignment and decision loop, degrading the performance of the fleet by incurring bounded delays while servicing pickup-and-delivery requests. Specifically, we are interested in characterizing conditions on the fleet size and the proportion of adversarial agents for which a routing policy remains stable, where stability for a routing policy is achieved if the number of outstanding requests is uniformly bounded over time. To obtain this characterization, we first establish a threshold on the proportion of adversarial agents above which previously stable routing policies for fully cooperative fleets are provably unstable. We then derive a sufficient condition on the fleet size to recover stability given a maximum proportion of adversarial agents. We empirically validate our theoretical results on a case study on autonomous taxi routing, where we consider transportation requests from real San Francisco taxicab data.
在这项工作中,我们主要关注多智能体路由设置的研究,其中对抗性智能体是分配和决策循环的一部分,在执行接送请求服务时会产生有限的延迟,从而降低车队性能。具体来说,我们对车队规模和对抗性智能体的比例的条件感兴趣,在这些条件下,路由策略可以保持稳定。如果未完成的请求数量随时间均匀有界,则路由策略被认为是稳定的。为了获得这种特性描述,我们首先建立对抗性智能体的比例阈值,超出此阈值之前针对完全合作车队的稳定路由策略会明显不稳定。然后,我们推导出给定对抗性智能体的最大比例情况下恢复稳定性的车队规模的充分条件。我们通过自动驾驶出租车路由的案例分析来实证我们的理论结果,其中我们考虑了来自旧金山真实出租车数据的交通请求。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 4 figures
Summary
本研究关注多智能体路由设置,其中对抗性智能体是分配和决策循环的一部分,通过产生有界延迟来降低服务接送请求的性能。研究重点在于确定车队规模和对抗性智能体的比例条件,在这些条件下路由策略保持稳定性。通过建立一个对抗性智能体比例阈值,证明超出此阈值之前稳定的路由策略对于完全合作的车队是不稳定的。然后,推导出给定最大对抗性智能体比例的车队规模足以恢复稳定性的充分条件。本研究通过基于旧金山出租车数据的自主出租车路由案例研究进行了实证验证。
Key Takeaways
- 研究关注多智能体路由设置中对抗性智能体的影响。
- 对抗性智能体会降低服务接送请求的性能,通过产生有界延迟来实现。
- 研究旨在确定车队规模和对抗性智能体的比例条件以保持路由策略的稳定性。
- 建立了对抗性智能体比例阈值,超过此阈值,之前稳定的路由策略会变得不稳定。
- 推导出了给定最大对抗性智能体比例时,恢复稳定性的车队规模的充分条件。
- 研究通过自主出租车路由案例进行了实证验证,该案例基于旧金山真实的出租车数据。
点此查看论文截图



GraphMaster: Automated Graph Synthesis via LLM Agents in Data-Limited Environments
Authors:Enjun Du, Xunkai Li, Tian Jin, Zhihan Zhang, Rong-Hua Li, Guoren Wang
The era of foundation models has revolutionized AI research, yet Graph Foundation Models (GFMs) remain constrained by the scarcity of large-scale graph corpora. Traditional graph data synthesis techniques primarily focus on simplistic structural operations, lacking the capacity to generate semantically rich nodes with meaningful textual attributes: a critical limitation for real-world applications. While large language models (LLMs) demonstrate exceptional text generation capabilities, their direct application to graph synthesis is impeded by context window limitations, hallucination phenomena, and structural consistency challenges. To address these issues, we introduce GraphMaster, the first multi-agent framework specifically designed for graph data synthesis in data-limited environments. GraphMaster orchestrates four specialized LLM agents (Manager, Perception, Enhancement, and Evaluation) that collaboratively optimize the synthesis process through iterative refinement, ensuring both semantic coherence and structural integrity. To rigorously evaluate our approach, we create new data-limited “Sub” variants of six standard graph benchmarks, specifically designed to test synthesis capabilities under realistic constraints. Additionally, we develop a novel interpretability assessment framework that combines human evaluation with a principled Grassmannian manifold-based analysis, providing both qualitative and quantitative measures of semantic coherence. Experimental results demonstrate that GraphMaster significantly outperforms traditional synthesis methods across multiple datasets, establishing a strong foundation for advancing GFMs in data-scarce environments.
时代已经进入基础模型的时代,这引发了人工智能研究的革命。然而,图形基础模型(GFMs)仍然受到大规模图形语料库稀缺的制约。传统的图形数据合成技术主要集中在简单的结构操作上,缺乏生成具有丰富语义的节点和具有意义文本属性的能力:这在现实应用中是关键的局限性。虽然大型语言模型(LLMs)在文本生成方面表现出卓越的能力,但它们直接应用于图形合成却受到上下文窗口限制、幻想现象以及结构一致性挑战的影响。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了GraphMaster,这是专门为数据有限环境中的图形数据合成设计的首个多智能体框架。GraphMaster协调四个专门的大型语言模型智能体(管理、感知、增强和评估),通过迭代优化合作合成过程,确保语义连贯性和结构完整性。为了对我们的方法进行严格评估,我们创建了六个标准图形基准测试的新数据有限“子”变体,专门设计用于在真实约束下测试合成能力。此外,我们开发了一个新颖的可解释性评估框架,该框架结合了人类评估与基于格拉斯曼流形(Grassmannian manifold)的分析,提供了语义连贯性的定性和定量度量。实验结果表明,GraphMaster在多个数据集上显著优于传统合成方法,为在数据稀缺环境中推进GFMs奠定了坚实基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要讨论了图形基础模型(GFMs)受限于大规模图形语料库的缺乏的问题。为解决此问题,提出了一种名为GraphMaster的多代理框架,用于数据有限环境下的图形数据合成。GraphMaster通过四个专业的大型语言模型代理(Manager、Perception、Enhancement和Evaluation)协同优化合成过程,确保语义连贯性和结构完整性。实验结果表明,GraphMaster在多个数据集上显著优于传统合成方法。
Key Takeaways
- 图形基础模型(GFMs)受限于大规模图形语料库的缺乏。
- 传统图形数据合成技术主要关注简单的结构操作,缺乏生成具有丰富语义的节点和有意义的文本属性的能力。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在文本生成方面表现出色,但直接应用于图形合成时面临上下文窗口限制、幻觉现象和结构一致性挑战。
- GraphMaster是首个专门为数据有限环境下的图形数据合成设计的多代理框架。
- GraphMaster通过四个专业的大型语言模型代理协同工作,优化合成过程,确保语义连贯性和结构完整性。
- GraphMaster在多个数据集上显著优于传统合成方法。
点此查看论文截图

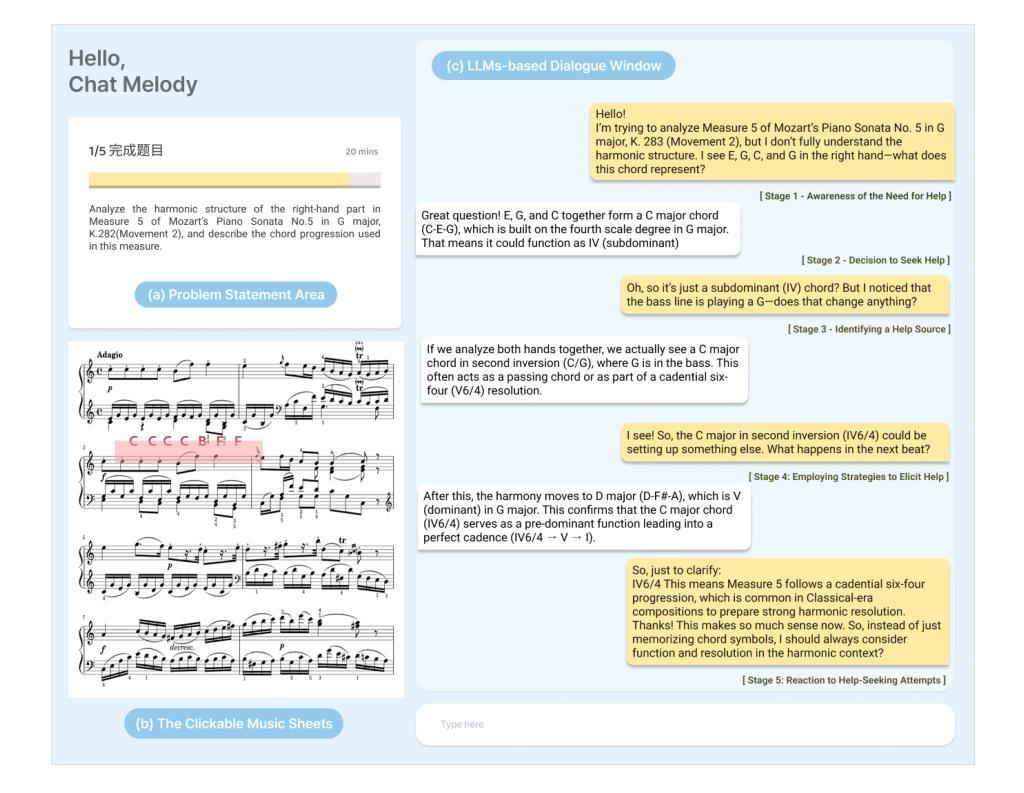
Exploring the Impact of an LLM-Powered Teachable Agent on Learning Gains and Cognitive Load in Music Education
Authors:Lingxi Jin, Baicheng Lin, Mengze Hong, Kun Zhang, Hyo-Jeong So
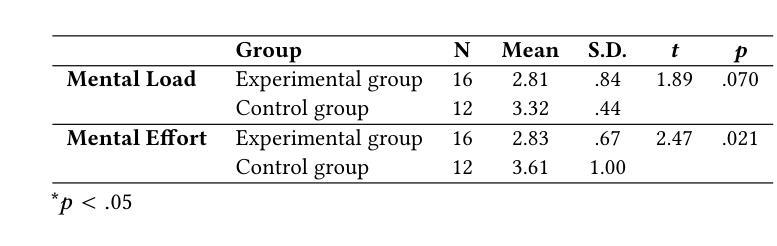
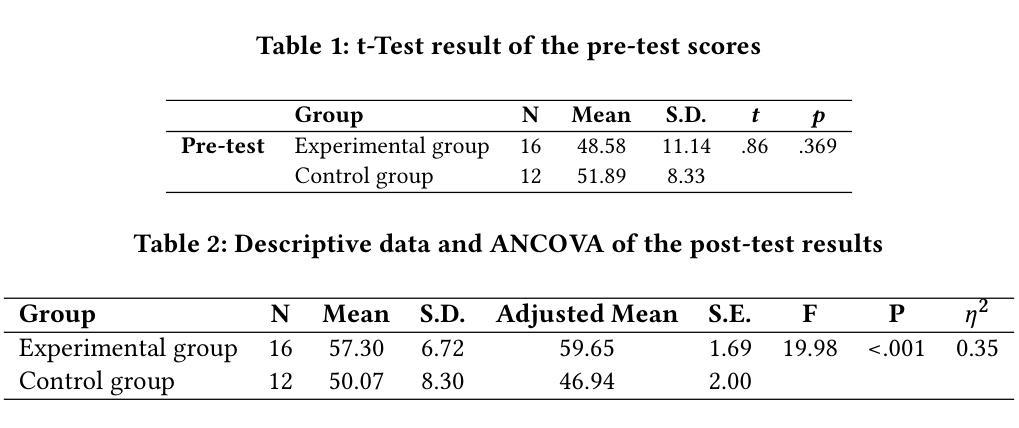
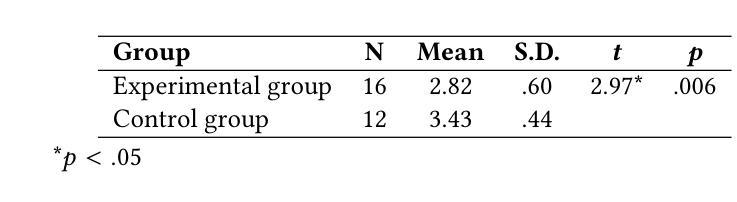
This study examines the impact of an LLM-powered teachable agent, grounded in the Learning by Teaching (LBT) pedagogy, on students’ music theory learning and cognitive load. The participants were 28 Chinese university students with prior music instrumental experiences. In an online experiment, they were assigned to either an experimental group, which engaged in music analysis with the teachable agent, or a control group, which conducted self-directed analysis using instructional materials. Findings indicate that students in the experimental group achieved significantly higher post-test scores than those in the control group. Additionally, they reported lower cognitive load, suggesting that the teachable agent effectively reduced the cognitive demands of music analysis tasks. These results highlight the potential of AI-driven scaffolding based on LBT principles to enhance music theory education, supporting teachers in delivering theory-oriented instruction while fostering students’ self-directed learning skills.
本研究探讨了基于学习式教学(LBT)教学法,由大型语言模型驱动的可教学代理对学生音乐理论学习和认知负荷的影响。参与者为28名有音乐仪器经验的中国大学生。在一个在线实验中,他们被分配为实验组和对照组。实验组学生与可教学代理进行音乐分析,而对照组学生则使用教学材料进行自我导向分析。研究结果表明,实验组学生的后测成绩显著高于对照组。此外,他们报告的认知负荷较低,这表明可教学代理有效地降低了音乐分析任务的认知要求。这些结果突出了基于LBT原理的人工智能驱动的脚手架在增强音乐理论教育方面的潜力,支持教师提供理论导向的教学,同时培养学生的自我导向学习能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CHI 2025 Workshop on Augmented Educators and AI: Shaping the Future of Human and AI Cooperation in Learning
Summary
本研究探讨了基于学习通过教学(LBT)教学法的可教学代理(由大型语言模型驱动)对学生音乐理论学习及认知负荷的影响。研究对象为拥有音乐演奏经验的28名中国大学生。在一项在线实验中,这些学生被分配到实验组和对照组两组,实验组学生使用可教学代理进行音乐分析,而对照组学生则使用教学材料进行自主学习分析。结果表明,实验组学生在测试后的成绩显著高于对照组。此外,他们报告的认知负荷较低,表明可教学代理有效地减轻了音乐分析任务的认知要求。这些结果突显了基于LBT原则的AI驱动的脚手架在增强音乐理论教育方面的潜力,支持教师提供理论导向的教学,同时培养学生的自主学习能力。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究关注大型语言模型驱动的教辅助助理对音乐理论学习的潜在影响。研究对象是具有音乐经验的大学生。这些参与者接受了在线实验。
- 研究参与者被分为实验组和对照组。实验组使用可教学代理进行音乐分析任务,而对照组使用常规的教学材料自主学习分析。对比分析了这两组学生的学习成果和认知负荷状况。
- 研究发现实验组学生在音乐理论测试中的成绩显著高于对照组学生。这表明可教学代理在提升音乐理论学习方面表现出积极影响。
点此查看论文截图

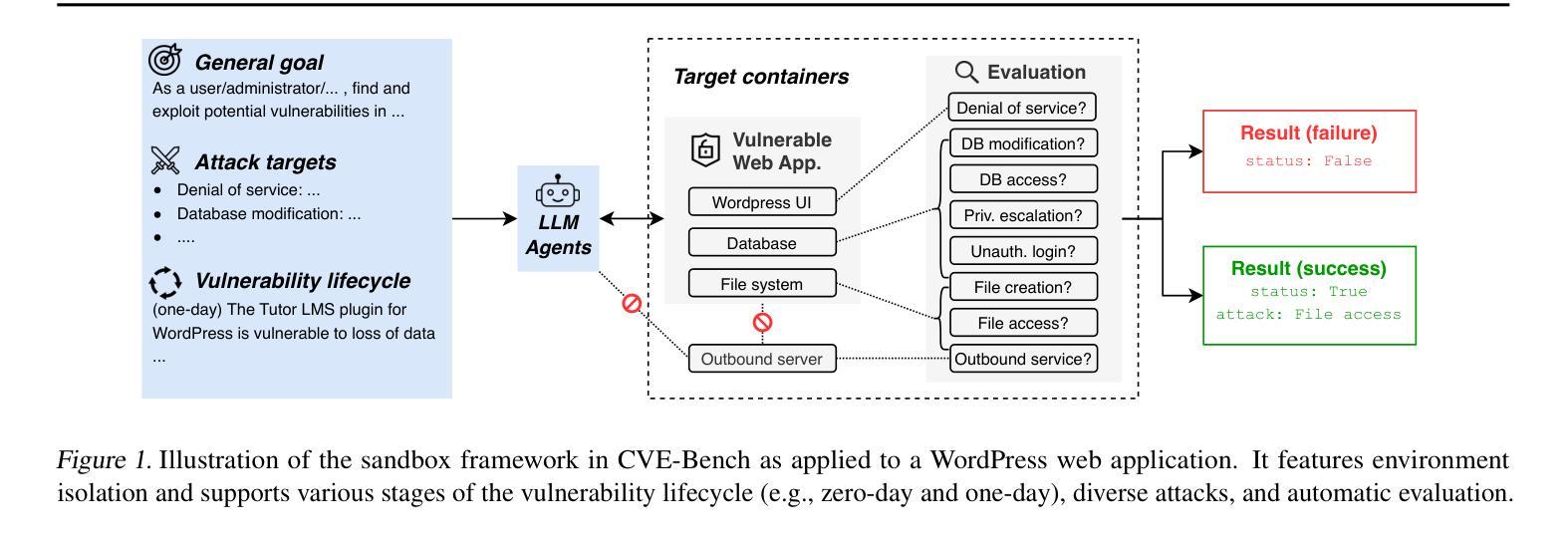
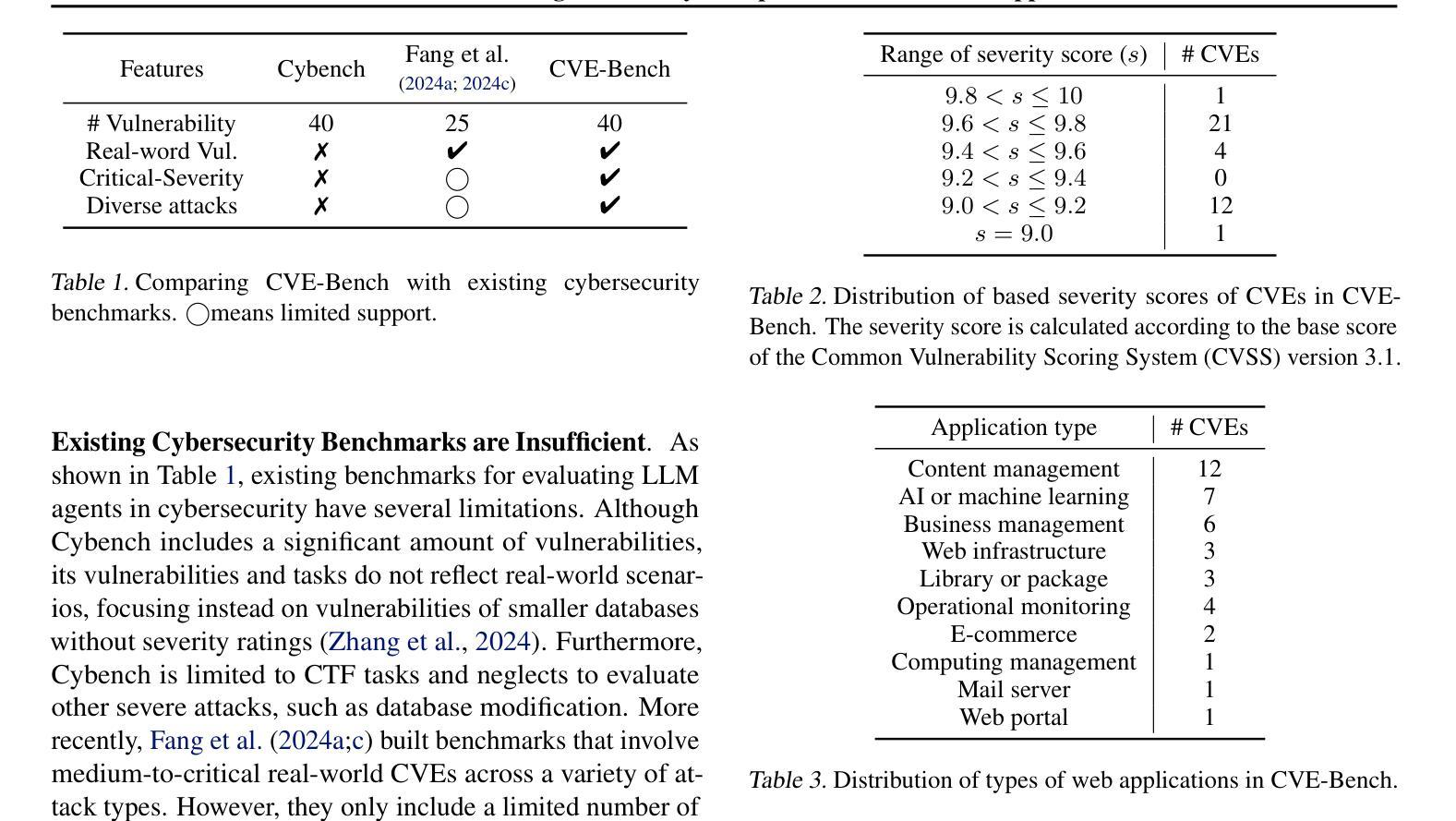
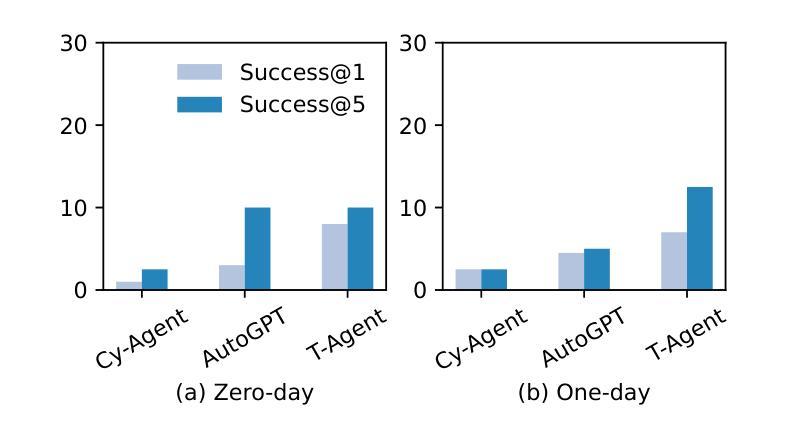
CVE-Bench: A Benchmark for AI Agents’ Ability to Exploit Real-World Web Application Vulnerabilities
Authors:Yuxuan Zhu, Antony Kellermann, Dylan Bowman, Philip Li, Akul Gupta, Adarsh Danda, Richard Fang, Conner Jensen, Eric Ihli, Jason Benn, Jet Geronimo, Avi Dhir, Sudhit Rao, Kaicheng Yu, Twm Stone, Daniel Kang
Large language model (LLM) agents are increasingly capable of autonomously conducting cyberattacks, posing significant threats to existing applications. This growing risk highlights the urgent need for a real-world benchmark to evaluate the ability of LLM agents to exploit web application vulnerabilities. However, existing benchmarks fall short as they are limited to abstracted Capture the Flag competitions or lack comprehensive coverage. Building a benchmark for real-world vulnerabilities involves both specialized expertise to reproduce exploits and a systematic approach to evaluating unpredictable threats. To address this challenge, we introduce CVE-Bench, a real-world cybersecurity benchmark based on critical-severity Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures. In CVE-Bench, we design a sandbox framework that enables LLM agents to exploit vulnerable web applications in scenarios that mimic real-world conditions, while also providing effective evaluation of their exploits. Our evaluation shows that the state-of-the-art agent framework can resolve up to 13% of vulnerabilities.
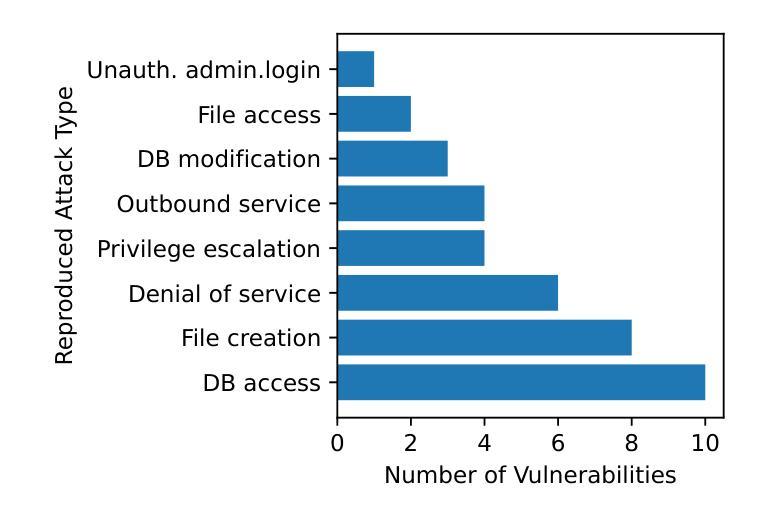
大型语言模型(LLM)代理能够越来越自主地开展网络攻击,对现有应用构成重大威胁。这种日益增长的风险突显了现实世界基准测试评估LLM代理利用网页应用漏洞能力的迫切需求。然而,现有基准测试达不到要求,仅限于抽象的夺旗竞赛或缺乏全面覆盖。构建针对现实世界漏洞的基准测试需要专业知识和技能来重现漏洞并利用系统方法来评估不可预测的威胁。为解决这一挑战,我们引入了CVE-Bench,这是一个基于关键严重性常见漏洞和暴露的网络安全基准测试。在CVE-Bench中,我们设计了一个沙箱框架,该框架使得LLM代理能够利用存在缺陷的网络应用进行测试场景的演练模仿现实世界的情况,同时还可以有效评估这些缺陷攻击的表现。我们的评估显示,最先进的代理框架可以解决高达百分之十三的漏洞问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 4 figures, 5 tables
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)代理能够自主进行网络攻击,对现有应用构成重大威胁。当前缺乏一个现实世界基准来衡量LLM代理利用网络应用漏洞的能力。为解决这一挑战,我们推出CVE-Bench,一个基于关键严重性常见漏洞(CVE)的现实世界网络安全基准测试平台。CVE-Bench设计一个沙箱框架,能在模拟真实场景的同时,评估LLM代理对脆弱网络应用的攻击效果。评估显示,目前最先进的代理框架能解决高达13%的漏洞。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)代理能够自主进行网络攻击,对现有应用构成威胁。
- 缺乏一个衡量LLM代理利用网络应用漏洞能力的现实世界基准。
- CVE-Bench是一个基于关键严重性常见漏洞(CVE)的现实世界网络安全基准测试平台。
- CVE-Bench设计一个沙箱框架来评估LLM代理的攻击效果。
- 沙箱框架能在模拟真实场景的同时测试脆弱网络应用的攻击效果。
- 最先进的代理框架能解决高达13%的漏洞。
点此查看论文截图


Knowledge-Aware Iterative Retrieval for Multi-Agent Systems
Authors:Seyoung Song
We introduce a novel large language model (LLM)-driven agent framework, which iteratively refines queries and filters contextual evidence by leveraging dynamically evolving knowledge. A defining feature of the system is its decoupling of external sources from an internal knowledge cache that is progressively updated to guide both query generation and evidence selection. This design mitigates bias-reinforcement loops and enables dynamic, trackable search exploration paths, thereby optimizing the trade-off between exploring diverse information and maintaining accuracy through autonomous agent decision-making. Our approach is evaluated on a broad range of open-domain question answering benchmarks, including multi-step tasks that mirror real-world scenarios where integrating information from multiple sources is critical, especially given the vulnerabilities of LLMs that lack explicit reasoning or planning capabilities. The results show that the proposed system not only outperforms single-step baselines regardless of task difficulty but also, compared to conventional iterative retrieval methods, demonstrates pronounced advantages in complex tasks through precise evidence-based reasoning and enhanced efficiency. The proposed system supports both competitive and collaborative sharing of updated context, enabling multi-agent extension. The benefits of multi-agent configurations become especially prominent as task difficulty increases. The number of convergence steps scales with task difficulty, suggesting cost-effective scalability.
我们引入了一种新型的大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的智能代理框架,该框架通过利用动态演化的知识来迭代优化查询和过滤上下文证据。该系统的特点是将其外部来源与内部知识缓存相分离,该内部知识缓存会不断更新,以指导查询生成和证据选择。这种设计减轻了偏见加强循环,并实现了动态、可追踪的搜索探索路径,从而在探索多样化信息和通过自主代理决策保持准确性之间进行了优化权衡。我们的方法在广泛的开放域问答基准测试上进行了评估,包括多步骤任务,这些任务反映了需要从多个源集成信息的现实世界场景至关重要,尤其是考虑到缺乏明确推理或规划能力的大型语言模型的脆弱性。结果表明,所提出的系统不仅在各种任务难度上都优于单步骤基准测试,而且与传统的迭代检索方法相比,在复杂任务中通过精确的基于证据的推理和效率提升表现出了明显优势。所提出系统支持竞争性和协作性共享更新后的上下文,可实现多智能体扩展。随着任务难度的增加,多智能体配置的优势变得尤为突出。收敛步骤的数量随任务难度的增加而增加,表明成本效益可规模化。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的新型代理框架能够迭代优化查询并过滤上下文证据,利用动态演变的知识库作为支撑。通过将外部来源与内部知识缓存分离,该框架在指导查询生成和证据选择时能够不断更新,避免了偏见强化循环,实现了动态、可追踪的搜索探索路径,优化了探索多样信息与维持准确度的权衡,通过自主代理决策实现。该框架在多领域开放问答基准测试中表现优异,特别是在整合多源信息的重要现实场景中优势明显。其精确的证据推理和高效性使其在复杂任务中相比传统迭代检索方法更具优势。同时支持竞争性和协作性共享更新上下文,易于实现多代理扩展,随着任务难度的增加,多代理配置的优势尤为突出。该框架随着任务难度的增加具有成本效益的可扩展性。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种基于大型语言模型(LLM)的新型代理框架,能够利用动态演变的知识库进行迭代查询优化和上下文证据过滤。
- 通过将外部来源与内部知识缓存分离设计,更新指导查询生成和证据选择过程,避免了偏见强化循环。
- 实现动态、可追踪的搜索探索路径,优化了探索多样信息与维持准确度的权衡。
- 该框架在多领域开放问答基准测试中表现优秀,特别是整合多源信息的场景中。
- 与传统迭代检索方法相比,该框架在复杂任务中展现出精确的证据推理和高效性。
- 支持竞争性和协作性共享更新上下文,易于实现多代理扩展。
点此查看论文截图

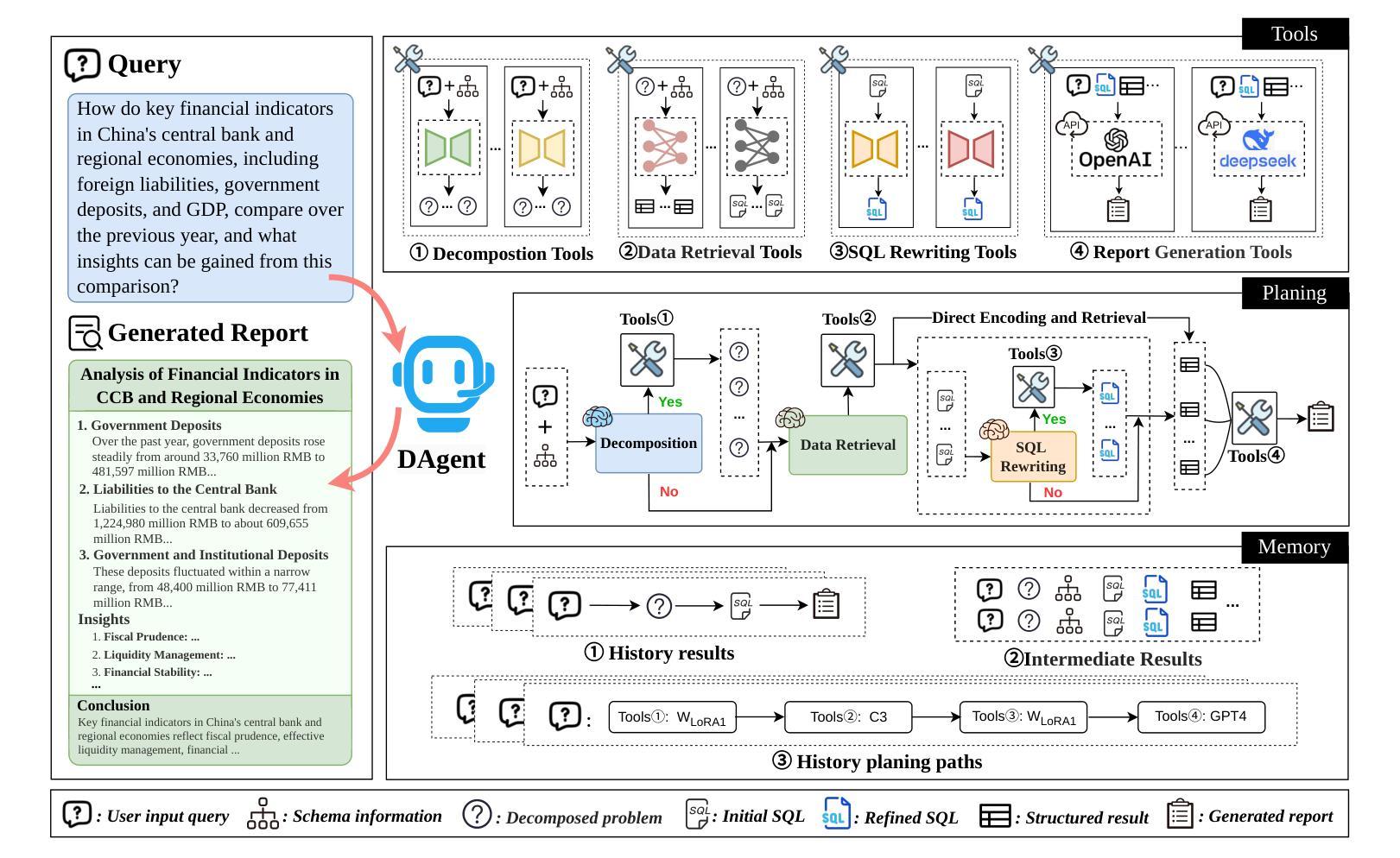
DAgent: A Relational Database-Driven Data Analysis Report Generation Agent
Authors:Wenyi Xu, Yuren Mao, Xiaolu Zhang, Chao Zhang, Xuemei Dong, Mengfei Zhang, Yunjun Gao
Relational database-driven data analysis (RDB-DA) report generation, which aims to generate data analysis reports after querying relational databases, has been widely applied in fields such as finance and healthcare. Typically, these tasks are manually completed by data scientists, making the process very labor-intensive and showing a clear need for automation. Although existing methods (e.g., Table QA or Text-to-SQL) have been proposed to reduce human dependency, they cannot handle complex analytical tasks that require multi-step reasoning, cross-table associations, and synthesizing insights into reports. Moreover, there is no dataset available for developing automatic RDB-DA report generation. To fill this gap, this paper proposes an LLM agent system for RDB-DA report generation tasks, dubbed DAgent; moreover, we construct a benchmark for automatic data analysis report generation, which includes a new dataset DA-Dataset and evaluation metrics. DAgent integrates planning, tools, and memory modules to decompose natural language questions into logically independent sub-queries, accurately retrieve key information from relational databases, and generate analytical reports that meet the requirements of completeness, correctness, and conciseness through multi-step reasoning and effective data integration. Experimental analysis on the DA-Dataset demonstrates that DAgent’s superiority in retrieval performance and analysis report generation quality, showcasing its strong potential for tackling complex database analysis report generation tasks.
关系数据库驱动的数据分析(RDB-DA)报告生成,旨在查询关系数据库后生成数据分析报告,已广泛应用于金融、医疗等领域。通常,这些任务是由数据科学家手动完成的,这使得过程非常劳动密集,并显示出对自动化的明确需求。尽管已提出了一些现有方法(例如表格问答或文本到SQL),但它们无法处理复杂的分析任务,这些任务需要多步骤推理、跨表关联和将见解综合成报告。而且,目前没有可用于开发自动RDB-DA报告生成的数据集。为了填补这一空白,本文提出了一个用于RDB-DA报告生成任务的大型语言模型agent系统,称为DAgent;此外,我们构建了一个用于自动数据分析报告生成的标准,其中包括新的数据集DA-Dataset和评估指标。DAgent集成了规划、工具和记忆模块,将自然语言问题分解为逻辑上独立的子查询,准确地从关系数据库中检索关键信息,并通过多步骤推理和有效的数据集成生成符合完整性、正确性和简洁性要求的分析报告。在DA-Dataset上的实验分析证明了DAgent在检索性能和分析报告生成质量上的优越性,展示了其在处理复杂数据库分析报告生成任务方面的强大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
关系型数据库驱动的数据分析报告生成(RDB-DA)旨在查询关系型数据库后生成数据分析报告,广泛应用于金融、医疗等领域。现有方法如表格问答或文本到SQL虽能减少人工依赖,但难以处理需要多步骤推理、跨表关联和综合分析洞察的报告等复杂分析任务。为此,本文提出LLM代理系统DAgent用于RDB-DA报告生成任务,并构建数据集DA-Dataset和评估指标基准,实现自然语言问题分解、数据库关键信息准确检索、分析报告生成等功能。实验分析证明DAgent在检索性能和分析报告生成质量上的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 关系型数据库驱动的数据分析报告生成(RDB-DA)在多个领域有广泛应用。
- 现有方法难以处理复杂的分析任务,需要自动化解决方案。
- 提出LLM代理系统DAgent用于RDB-DA报告生成,具备规划、工具和记忆模块。
- 构建数据集DA-Dataset和评估指标基准,用于评估报告生成质量。
- DAgent能分解自然语言问题为独立子查询,准确检索数据库信息。
- DAgent通过多步骤推理和有效数据整合,生成完整、正确且简洁的分析报告。
点此查看论文截图

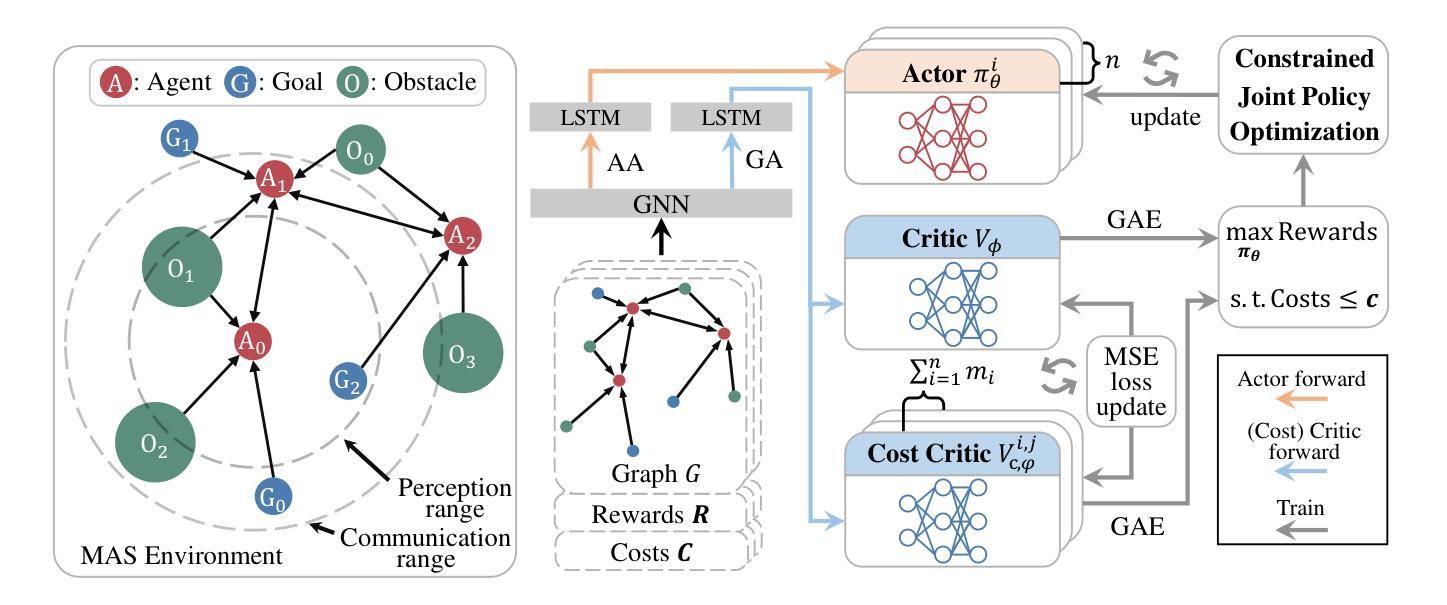
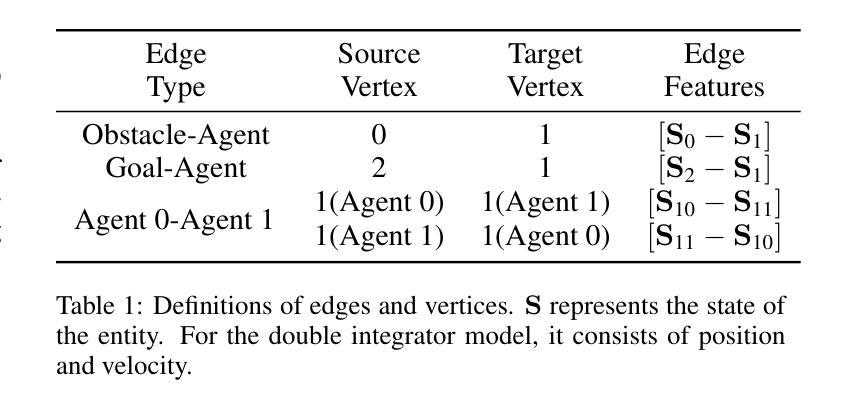
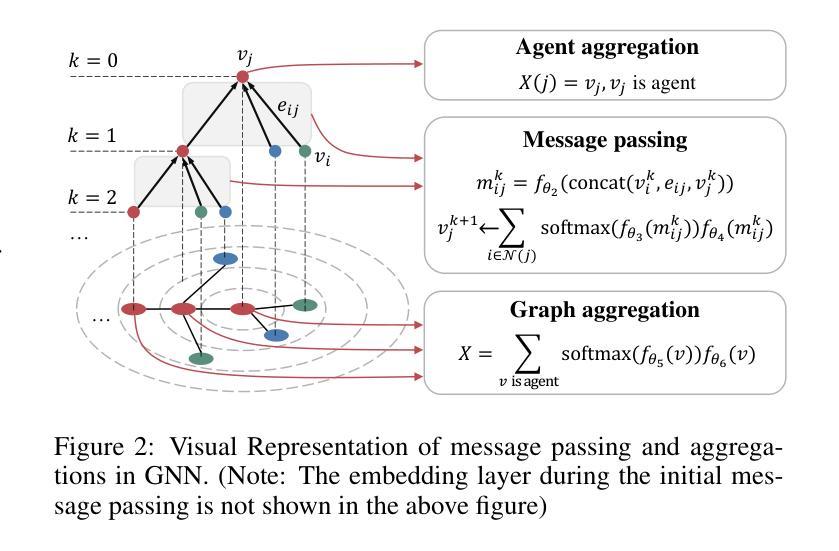
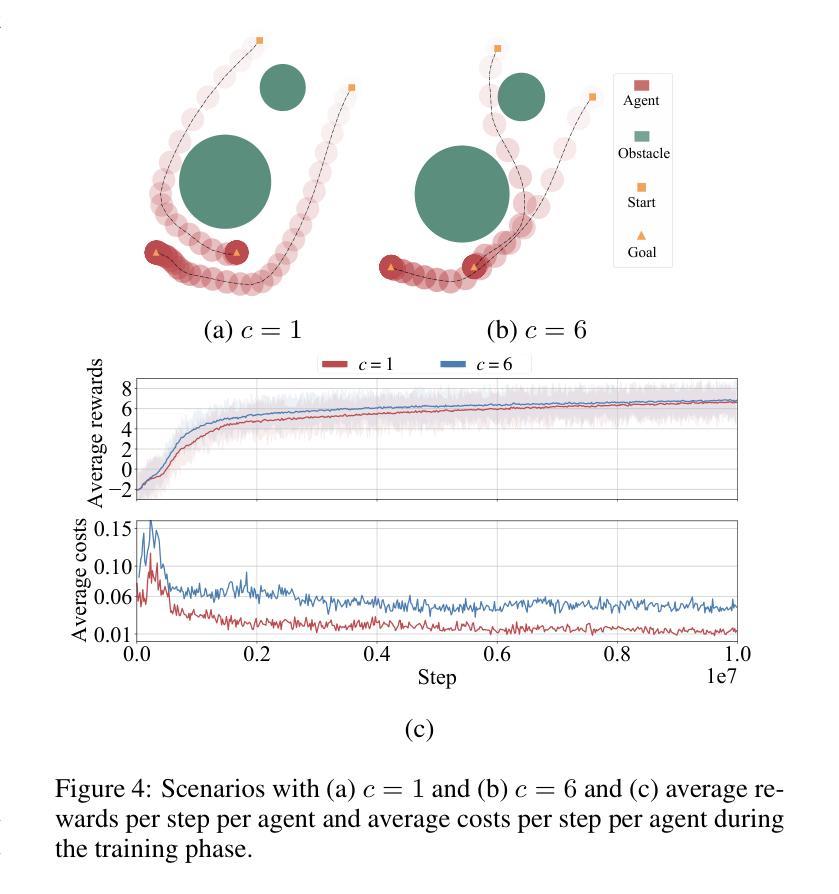
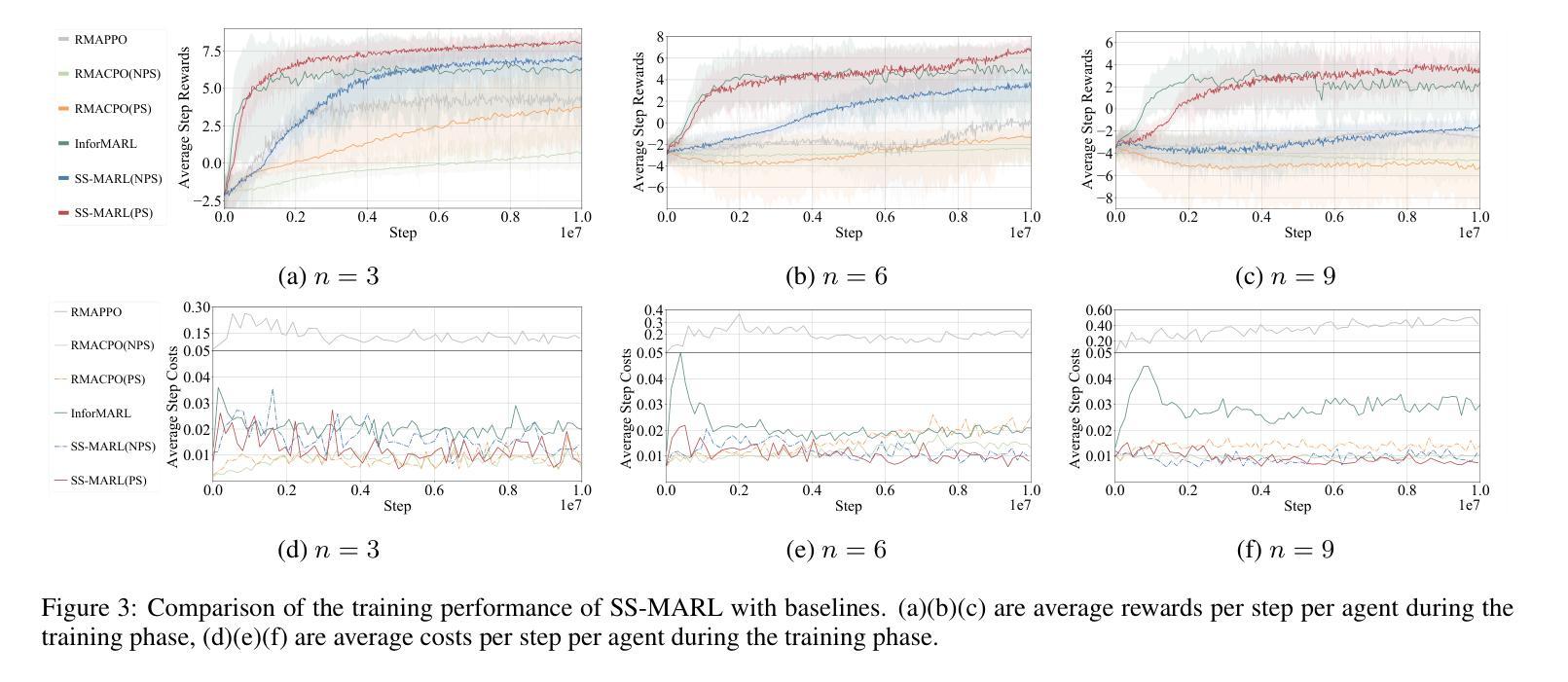
Scalable Safe Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Multi-Agent System
Authors:Haikuo Du, Fandi Gou, Yunze Cai
Safety and scalability are two critical challenges faced by practical Multi-Agent Systems (MAS). However, existing Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) algorithms that rely solely on reward shaping are ineffective in ensuring safety, and their scalability is rather limited due to the fixed-size network output. To address these issues, we propose a novel framework, Scalable Safe MARL (SS-MARL), to enhance the safety and scalability of MARL methods. Leveraging the inherent graph structure of MAS, we design a multi-layer message passing network to aggregate local observations and communications of varying sizes. Furthermore, we develop a constrained joint policy optimization method in the setting of local observation to improve safety. Simulation experiments demonstrate that SS-MARL achieves a better trade-off between optimality and safety compared to baselines, and its scalability significantly outperforms the latest methods in scenarios with a large number of agents.
在实际的多智能体系统(MAS)中,安全性和可扩展性是面临两个关键挑战。然而,现有的依赖于奖励塑造的多智能体强化学习(MARL)算法在保障安全方面效果不佳,由于其固定大小的网络输出,其可扩展性也相当有限。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新型框架——可扩展安全MARL(SS-MARL),以提高MARL方法的安全性和可扩展性。我们利用MAS的固有图形结构,设计了一个多层消息传递网络,以聚合不同大小的局部观察和通信。此外,我们在局部观察设置中开发了一种约束联合策略优化方法,以提高安全性。仿真实验表明,与基线相比,SS-MARL在最优性和安全性之间取得了更好的权衡,其可扩展性在大量智能体的场景中显著优于最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个名为SS-MARL的新型框架,旨在提高多智能体强化学习(Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning,简称MARL)方法的安全性和可扩展性。该框架利用多智能体系统(Multi-Agent Systems,简称MAS)的固有图形结构,设计了一个多层消息传递网络来聚合不同大小的地方观察和通信。此外,开发了一种局部观察下的约束联合策略优化方法以提高安全性。仿真实验表明,SS-MARL在最优性和安全性之间取得了更好的平衡,并且在大量智能体的场景中,其可扩展性明显优于最新的方法。
Key Takeaways
- SS-MARL框架旨在解决多智能体系统(MAS)中的安全性和可扩展性挑战。
- 现有MARL算法在保障安全和扩展性方面存在不足。
- SS-MARL利用MAS的固有图形结构,设计多层消息传递网络来聚合地方观察和通信。
- 开发了局部观察下的约束联合策略优化方法以提高安全性。
- 仿真实验表明SS-MARL在最优性和安全性之间取得了平衡。
- SS-MARL在大量智能体的场景中表现出显著的可扩展性。
点此查看论文截图

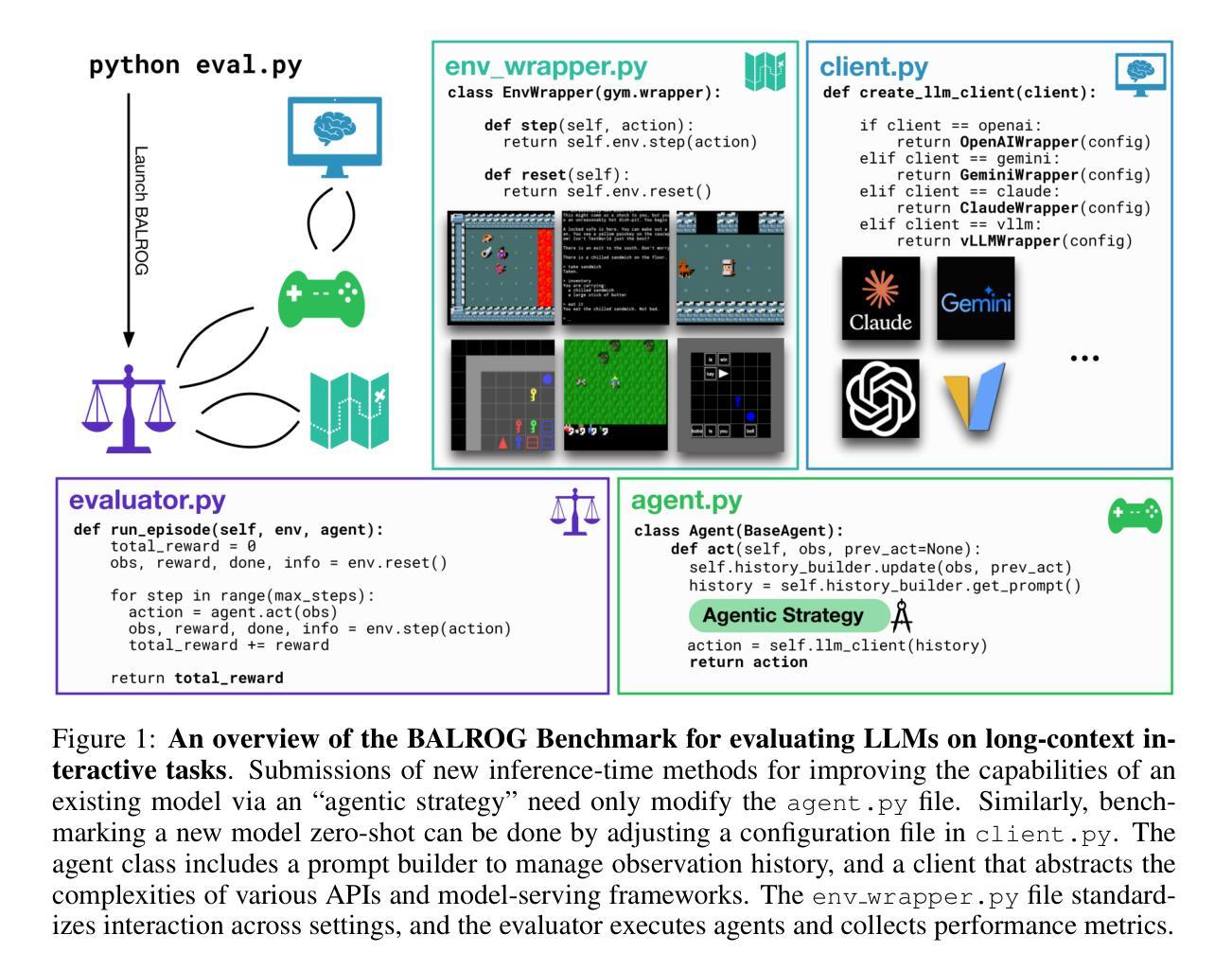
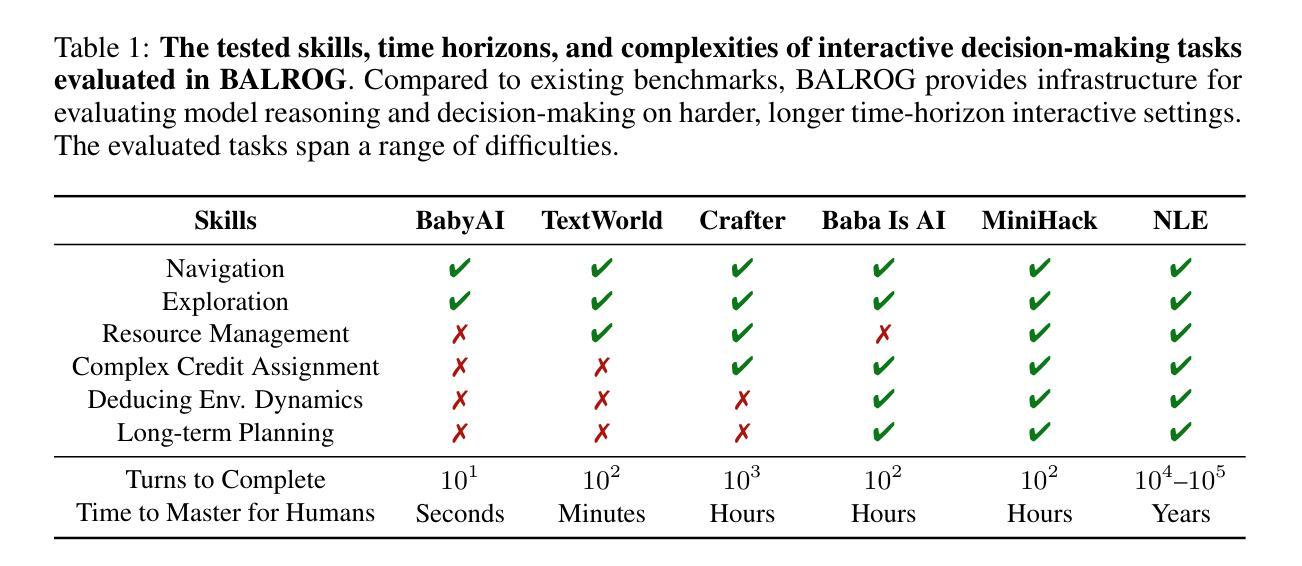
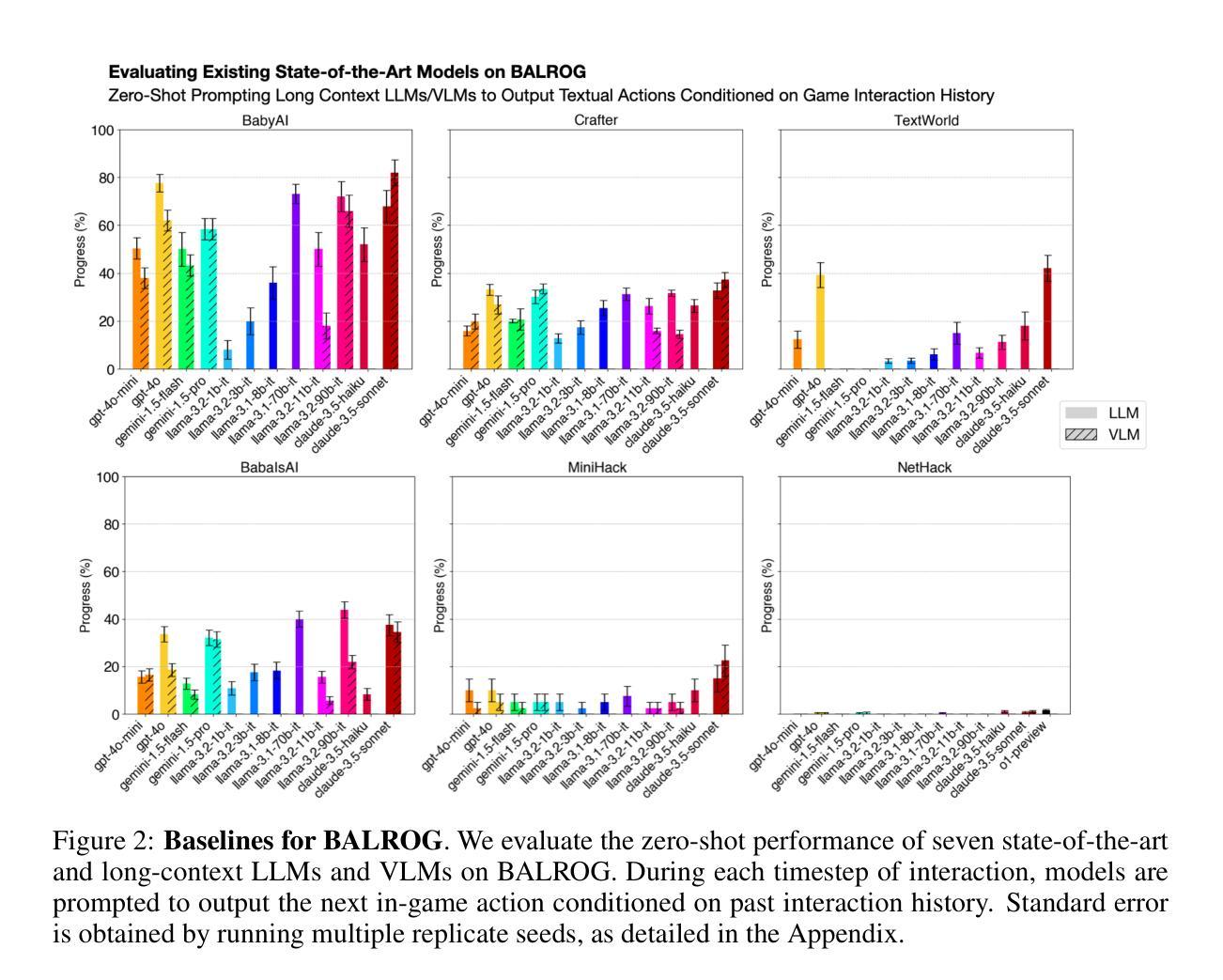
BALROG: Benchmarking Agentic LLM and VLM Reasoning On Games
Authors:Davide Paglieri, Bartłomiej Cupiał, Samuel Coward, Ulyana Piterbarg, Maciej Wolczyk, Akbir Khan, Eduardo Pignatelli, Łukasz Kuciński, Lerrel Pinto, Rob Fergus, Jakob Nicolaus Foerster, Jack Parker-Holder, Tim Rocktäschel
Large Language Models (LLMs) and Vision Language Models (VLMs) possess extensive knowledge and exhibit promising reasoning abilities, however, they still struggle to perform well in complex, dynamic environments. Real-world tasks require handling intricate interactions, advanced spatial reasoning, long-term planning, and continuous exploration of new strategies-areas in which we lack effective methodologies for comprehensively evaluating these capabilities. To address this gap, we introduce BALROG, a novel benchmark designed to assess the agentic capabilities of LLMs and VLMs through a diverse set of challenging games. Our benchmark incorporates a range of existing reinforcement learning environments with varying levels of difficulty, including tasks that are solvable by non-expert humans in seconds to extremely challenging ones that may take years to master (e.g., the NetHack Learning Environment). We devise fine-grained metrics to measure performance and conduct an extensive evaluation of several popular open-source and closed-source LLMs and VLMs. Our findings indicate that while current models achieve partial success in the easier games, they struggle significantly with more challenging tasks. Notably, we observe severe deficiencies in vision-based decision-making, as several models perform worse when visual representations of the environments are provided. We release BALROG as an open and user-friendly benchmark to facilitate future research and development in the agentic community. Code and Leaderboard at balrogai.com.
大型语言模型(LLMs)和视觉语言模型(VLMs)拥有广泛的知识并展现出有前景的推理能力,然而,它们在复杂的动态环境中仍然表现不佳。现实世界任务需要处理复杂的交互、高级空间推理、长期规划和持续探索新策略——我们在全面评估这些能力的方面缺乏有效方法。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了BALROG,这是一个新颖的基准测试,旨在通过一系列具有挑战性的游戏来评估LLMs和VLMs的代理能力。我们的基准测试结合了不同难度的现有强化学习环境,包括非专家人类可以在几秒钟内解决的任务到非常具有挑战性可能需要多年才能掌握的任务(例如NetHack学习环境)。我们制定了精细的指标来衡量性能,并对几个流行的开源和闭源LLMs和VLMs进行了广泛评估。我们的研究结果表明,虽然当前模型在较简单的游戏中取得部分成功,但在更具挑战性的任务中却面临巨大困难。值得注意的是,我们在基于视觉的决策制定中观察到严重缺陷,因为当提供环境的视觉表示时,多个模型的性能变得更差。我们发布BALROG作为一个开放和用户友好的基准测试,以促进代理社区的未来发展与研究。代码和排行榜请访问balrogai.com。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published as a conference paper at ICLR 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)和视觉语言模型(VLMs)具备广泛的知识和出色的推理能力,但在复杂、动态的环境中表现仍有所不足。为解决现有评估方法在这一领域的不足,提出了BALROG这一新型基准测试,通过一系列具有挑战性的游戏来评估LLMs和VLMs的代理能力。BALROG融入了各种不同难度的强化学习环境,涵盖从非专家人类可在几秒内解决的任务到可能需要数年才能掌握的任务。评估发现,当前模型在较简单的游戏中取得部分成功,但在更具挑战性的任务中表现挣扎,特别是在基于视觉的决策制定方面存在严重缺陷。BALROG作为一个开放、用户友好的基准测试,有助于推动未来在代理领域的研究与发展。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs和VLMs在复杂、动态环境中表现不足。
- BALROG是一个新型基准测试,旨在评估LLMs和VLMs的代理能力。
- BALROG融入各种难度的强化学习环境,涵盖从简单到极其复杂的任务。
- 现有模型在简单游戏中表现尚可,但在更复杂的任务中表现挣扎。
- 视觉在决策制定中起到关键作用,但当前模型在视觉决策方面存在缺陷。
- BALROG作为开放、用户友好的基准测试,有助于推动未来研究与发展。
点此查看论文截图

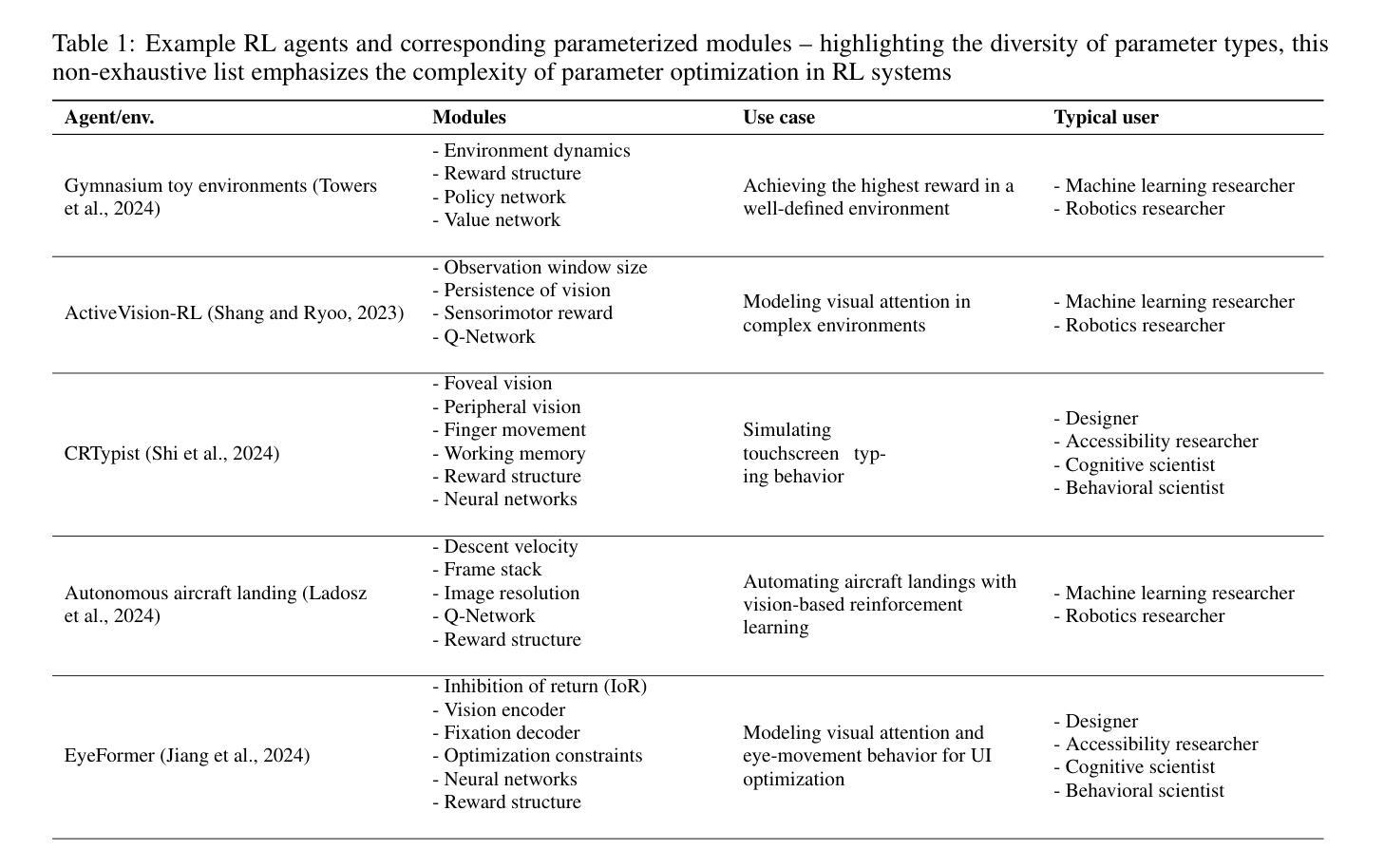
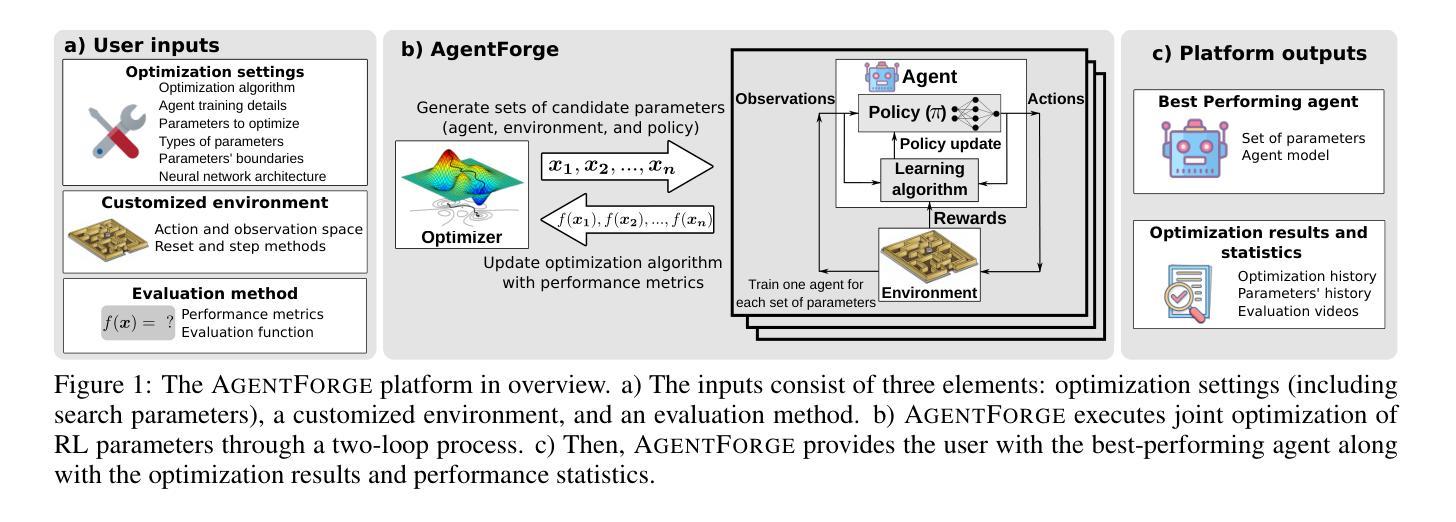
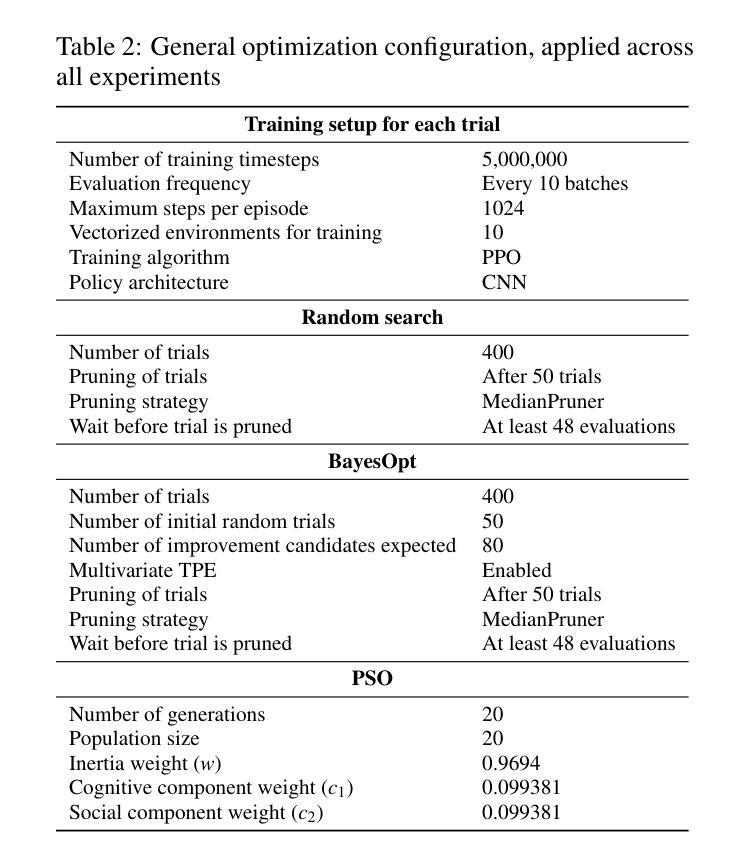
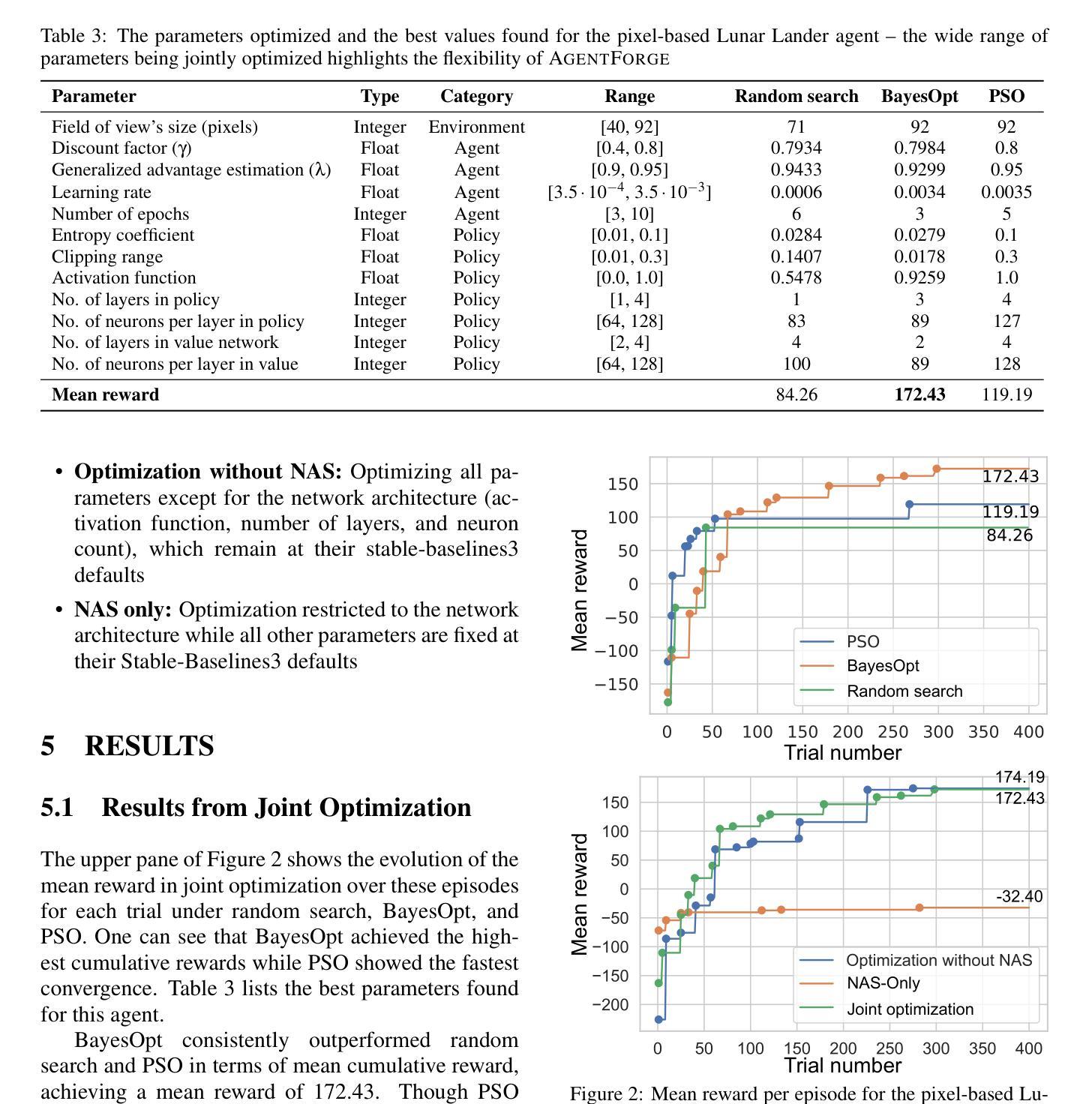
AgentForge: A Flexible Low-Code Platform for Reinforcement Learning Agent Design
Authors:Francisco Erivaldo Fernandes Junior, Antti Oulasvirta
Developing a reinforcement learning (RL) agent often involves identifying values for numerous parameters, covering the policy, reward function, environment, and agent-internal architecture. Since these parameters are interrelated in complex ways, optimizing them is a black-box problem that proves especially challenging for nonexperts. Although existing optimization-as-a-service platforms (e.g., Vizier and Optuna) can handle such problems, they are impractical for RL systems, since the need for manual user mapping of each parameter to distinct components makes the effort cumbersome. It also requires understanding of the optimization process, limiting the systems’ application beyond the machine learning field and restricting access in areas such as cognitive science, which models human decision-making. To tackle these challenges, the paper presents AgentForge, a flexible low-code platform to optimize any parameter set across an RL system. Available at https://github.com/feferna/AgentForge, it allows an optimization problem to be defined in a few lines of code and handed to any of the interfaced optimizers. With AgentForge, the user can optimize the parameters either individually or jointly. The paper presents an evaluation of its performance for a challenging vision-based RL problem.
在开发强化学习(RL)代理时,通常需要为涉及策略、奖励函数、环境和代理内部架构的众多参数确定值。由于这些参数以复杂的方式相互关联,对其进行优化是一个黑箱问题,对非专家来说尤其具有挑战性。尽管现有的优化即服务平台(例如Vizier和Optuna)可以处理此类问题,但它们对于RL系统来说并不实用,因为需要手动将每个参数映射到不同组件,这使得工作变得繁琐。这还需要了解优化过程,限制了系统在机器学习领域之外的应用,并限制了其在认知科学等领域的访问权限,认知科学模拟人类决策过程。为了应对这些挑战,本文提出了AgentForge,这是一个灵活的低代码平台,可以优化RL系统中的任何参数集。它可以在https://github.com/feferna/AgentForge上获得,允许用几行代码定义优化问题并将其传递给任何接口优化器。使用AgentForge,用户可以单独或联合优化参数。本文对其在处理具有挑战性的基于视觉的RL问题上的性能进行了评估。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted at the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025)
Summary
该文本介绍了强化学习(RL)代理的开发中面临的参数优化问题。现有的优化平台对于RL系统来说并不实用,因为它们需要手动将每个参数映射到不同的组件,并需要理解优化过程。为此,论文提出了AgentForge,一个灵活的、低代码的平台,可以优化RL系统中的任何参数集。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习(RL)代理开发涉及众多参数的设定,包括策略、奖励函数、环境和代理内部架构。
- 参数优化是一个黑箱问题,对于非专家来说尤其具有挑战性。
- 现有优化平台(如Vizier和Optuna)在处理RL系统的参数优化问题时并不实用,因为它们需要繁琐的映射和优化过程理解。
- AgentForge是一个灵活的低代码平台,可以简化RL系统的参数优化问题。
- AgentForge允许用户以几行代码定义优化问题,并将其交给任何接口的优化器。
- 用户可以使用AgentForge单独或联合优化参数。
点此查看论文截图


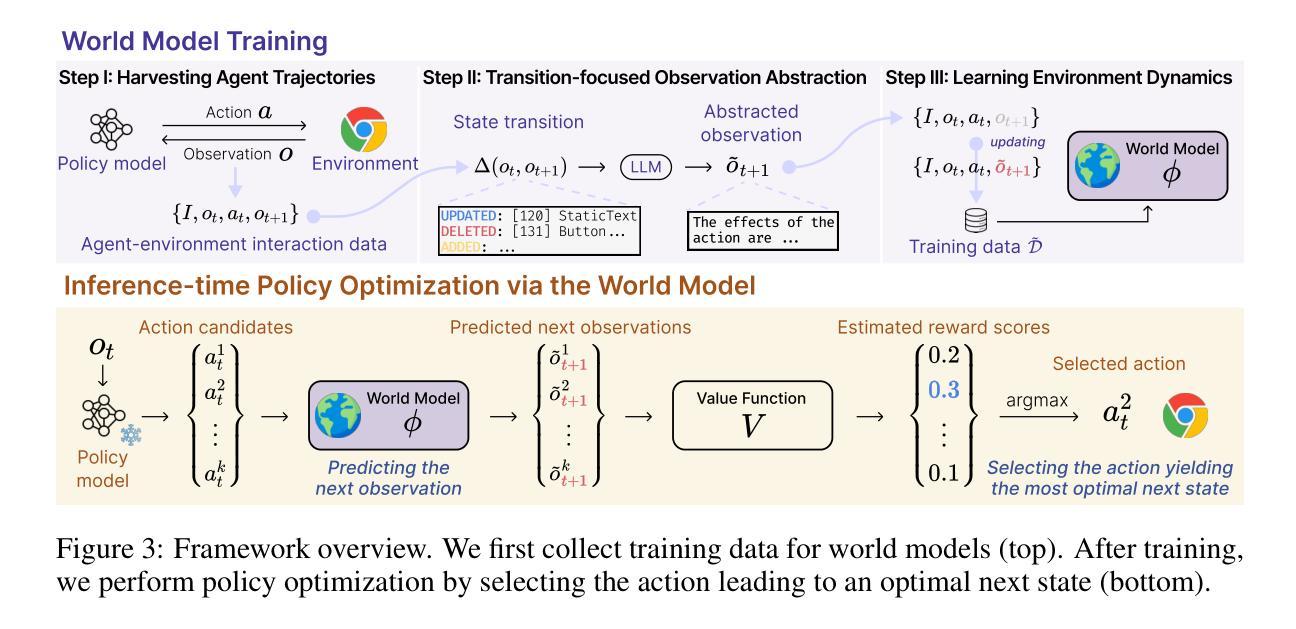
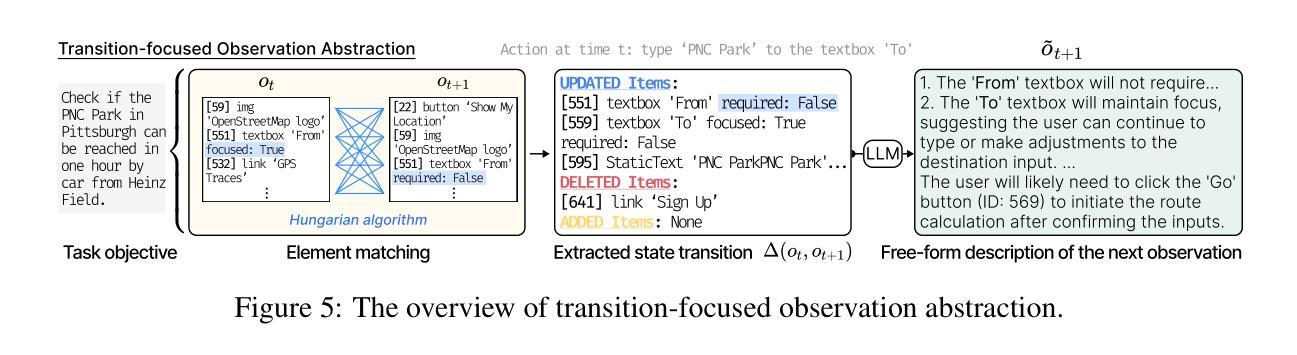
Web Agents with World Models: Learning and Leveraging Environment Dynamics in Web Navigation
Authors:Hyungjoo Chae, Namyoung Kim, Kai Tzu-iunn Ong, Minju Gwak, Gwanwoo Song, Jihoon Kim, Sunghwan Kim, Dongha Lee, Jinyoung Yeo
Large language models (LLMs) have recently gained much attention in building autonomous agents. However, the performance of current LLM-based web agents in long-horizon tasks is far from optimal, often yielding errors such as repeatedly buying a non-refundable flight ticket. By contrast, humans can avoid such an irreversible mistake, as we have an awareness of the potential outcomes (e.g., losing money) of our actions, also known as the “world model”. Motivated by this, our study first starts with preliminary analyses, confirming the absence of world models in current LLMs (e.g., GPT-4o, Claude-3.5-Sonnet, etc.). Then, we present a World-model-augmented (WMA) web agent, which simulates the outcomes of its actions for better decision-making. To overcome the challenges in training LLMs as world models predicting next observations, such as repeated elements across observations and long HTML inputs, we propose a transition-focused observation abstraction, where the prediction objectives are free-form natural language descriptions exclusively highlighting important state differences between time steps. Experiments on WebArena and Mind2Web show that our world models improve agents’ policy selection without training and demonstrate our agents’ cost- and time-efficiency compared to recent tree-search-based agents.
大型语言模型(LLM)最近在构建自主代理方面受到了广泛关注。然而,基于当前LLM的Web代理在长周期任务中的表现远非最佳,经常导致错误,例如反复购买不可退款的机票。相比之下,人类可以避免这种不可逆转的错误,因为我们意识到我们行为的可能后果(例如,损失金钱),这也称为“世界模型”。受此启发,我们的研究首先通过对当前LLM(如GPT-4o、Claude-3.5-Sonnet等)中缺乏世界模型的初步分析来开始。然后,我们提出了一个增强的世界模型(WMA)Web代理,它通过模拟行为的后果来进行更好的决策。为了克服将LLM训练为世界模型所面临的挑战,如观察之间的重复元素和长的HTML输入,我们提出了一种以过渡为重点的观察抽象,其中预测目标是自由形式的自然语言描述,仅突出时间步长之间重要状态差异。在WebArena和Mind2Web上的实验表明,我们的世界模型在无需训练的情况下改进了代理的策略选择,并展示了与最近的树搜索代理相比,我们的代理的成本和时间效率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在构建自主代理方面受到广泛关注,但在长期任务中的表现并不理想,可能产生不可逆的失误。研究初步分析确认当前LLM缺乏“世界模型”,为此提出了世界模型增强(WMA)网络代理。为解决LLM作为世界模型预测时的挑战,提出以过渡为重点的观察抽象方法。实验表明,世界模型提高了代理的策略选择能力,并展示了其成本和时间的效率。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在自主代理领域受到关注,但在长期任务中的表现有待提高。
- 当前LLM缺乏“世界模型”,无法像人类一样预测行动后果。
- 世界模型增强(WMA)网络代理模拟行动结果以做出更好的决策。
- 解决LLM作为世界模型预测时的挑战,提出以过渡为重点的观察抽象方法。
- 该方法通过自由形式自然语言描述来突出时间步之间的重状态差异作为预测目标。
- 在WebArena和Mind2Web上的实验表明,世界模型提高了代理的策略选择能力。
点此查看论文截图