⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-04 更新
ILLUME+: Illuminating Unified MLLM with Dual Visual Tokenization and Diffusion Refinement
Authors:Runhui Huang, Chunwei Wang, Junwei Yang, Guansong Lu, Yunlong Yuan, Jianhua Han, Lu Hou, Wei Zhang, Lanqing Hong, Hengshuang Zhao, Hang Xu
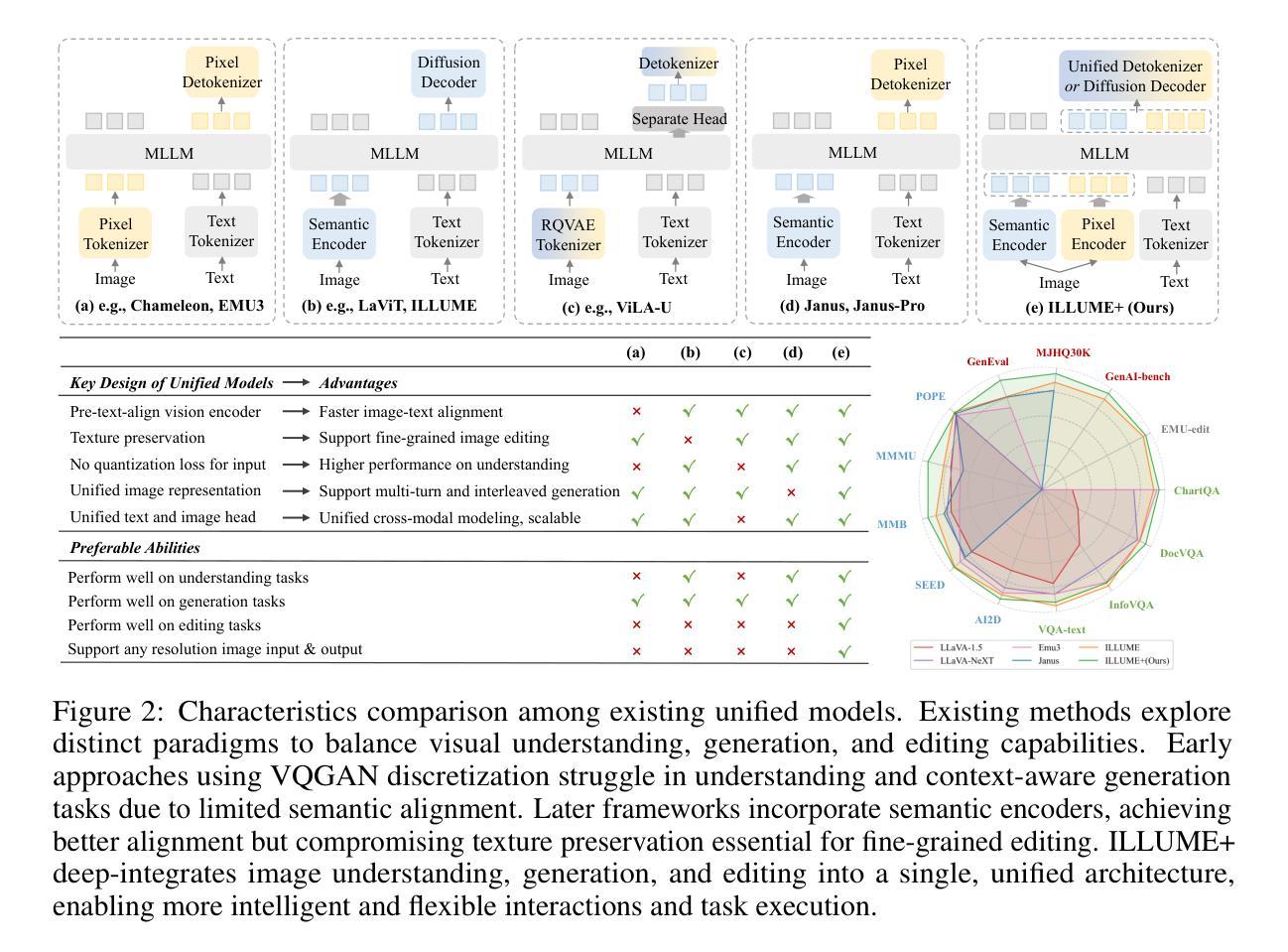
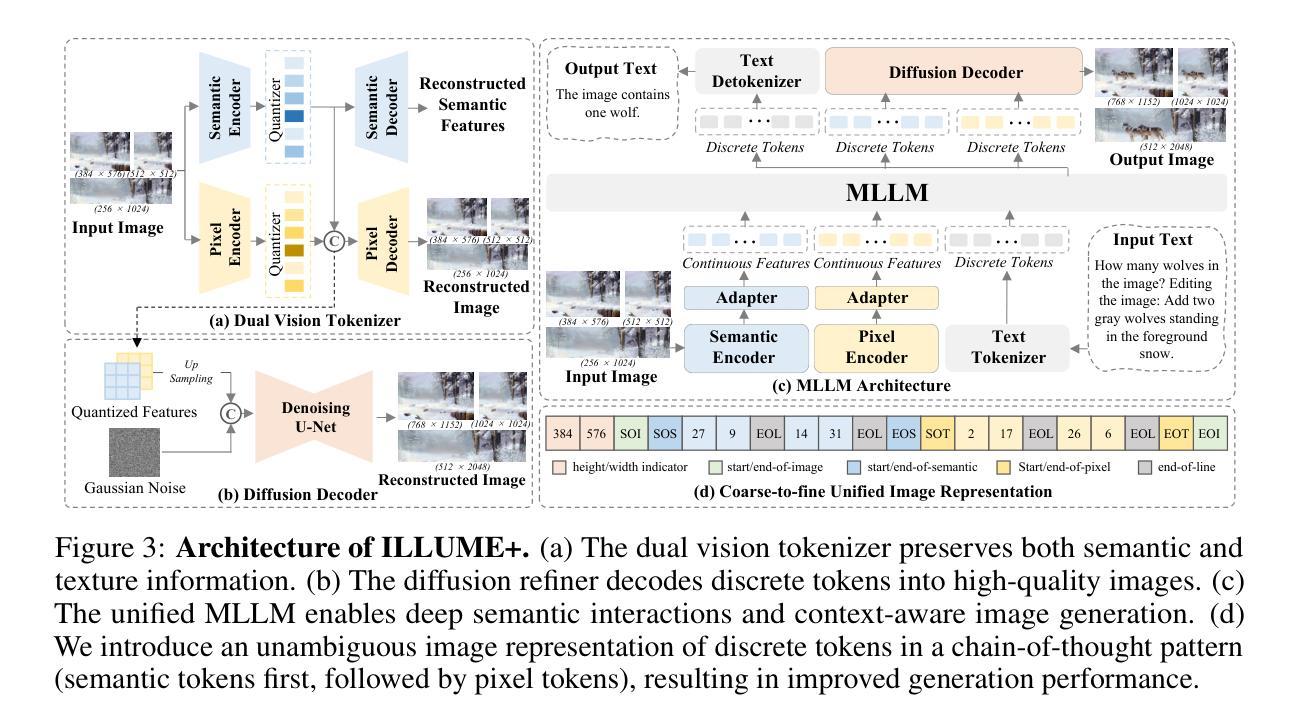
We present ILLUME+ that leverages dual visual tokenization and a diffusion decoder to improve both deep semantic understanding and high-fidelity image generation. Existing unified models have struggled to simultaneously handle the three fundamental capabilities in a unified model: understanding, generation, and editing. Models like Chameleon and EMU3 utilize VQGAN for image discretization, due to the lack of deep semantic interaction, they lag behind specialist models like LLaVA in visual understanding tasks. To mitigate this, LaViT and ILLUME employ semantic encoders for tokenization, but they struggle with image editing due to poor texture preservation. Meanwhile, Janus series decouples the input and output image representation, limiting their abilities to seamlessly handle interleaved image-text understanding and generation. In contrast, ILLUME+ introduces a unified dual visual tokenizer, DualViTok, which preserves both fine-grained textures and text-aligned semantics while enabling a coarse-to-fine image representation strategy for multimodal understanding and generation. Additionally, we employ a diffusion model as the image detokenizer for enhanced generation quality and efficient super-resolution. ILLUME+ follows a continuous-input, discrete-output scheme within the unified MLLM and adopts a progressive training procedure that supports dynamic resolution across the vision tokenizer, MLLM, and diffusion decoder. This design allows for flexible and efficient context-aware image editing and generation across diverse tasks. ILLUME+ (3B) exhibits competitive performance against existing unified MLLMs and specialized models across multimodal understanding, generation, and editing benchmarks. With its strong performance, ILLUME+ provides a scalable and versatile foundation for future multimodal applications. Project Page: https://illume-unified-mllm.github.io/.
我们提出了ILLUME+,它利用双视觉符号化和扩散解码器,提高了深度语义理解和高保真图像生成的性能。现有的统一模型在统一模型中同时处理三种基本能力方面遇到了困难,即理解、生成和编辑。像变色龙和EMU3这样的模型使用VQGAN进行图像离散化,由于缺乏深度语义交互,它们在视觉理解任务方面落后于LLaVA等专业模型。为了缓解这一问题,LaViT和ILLUME采用语义编码器进行符号化,但在图像编辑方面由于纹理保存不佳而遇到困难。与此同时,Janus系列将输入和输出图像表示解耦,限制了它们无缝处理交织的图像文本理解和生成的能力。相比之下,ILLUME+引入了一个统一的双视觉标记器DualViTok,它既保留了精细纹理和文本对齐语义,又实现了粗细结合的图像表示策略,用于多模态理解和生成。此外,我们采用扩散模型作为图像解标记器,以提高生成质量和超分辨率效率。ILLUME+在统一MLLM内采用连续输入、离散输出的方案,并采用渐进式训练程序,支持视觉标记器、MLLM和扩散解码器之间的动态分辨率。这种设计使跨不同任务的灵活和高效的上下文感知图像编辑和生成成为可能。ILLUME+(3B)在多模态理解、生成和编辑基准测试中表现出与现有统一MLLM和专用模型相竞争的性能。凭借其卓越性能,ILLUME+为未来多模态应用提供了可扩展和通用的基础。项目页面:https://illume-unified-mllm.github.io/.
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于双视觉标记技术和扩散解码器的ILLUME+模型,提高了深度语义理解和高保真图像生成的能力。该模型在统一模型中同时实现了理解、生成和编辑三个基本功能,具有出色的性能表现。它引入了双视觉标记器DualViTok,既保留了精细纹理又使文本语义对齐,实现了从粗到细的多模式理解和生成策略。同时,采用扩散模型作为图像分解器,提高了生成图像的质量和超分辨率效率。ILLUME+的设计灵活高效,支持在视觉标记器、MLLM和扩散解码器之间进行动态分辨率调整,可在各种任务中实现上下文感知的图像编辑和生成。
Key Takeaways
- ILLUME+模型结合了双视觉标记技术和扩散解码器,提升了语义理解和图像生成的效果。
- 现有统一模型在处理理解、生成和编辑三个基本功能时存在困难,而ILLUME+在统一模型中实现了这些功能。
- DualViTok标记器实现了纹理和语义的保留与对齐,支持粗到细的多模式理解和生成策略。
- 扩散模型的采用提高了图像生成的质量和超分辨率效率。
- ILLUME+设计灵活,支持动态调整视觉标记器、MLLM和扩散解码器之间的分辨率。
- ILLUME+在各种任务中实现了上下文感知的图像编辑和生成。
点此查看论文截图

Implicit Bias Injection Attacks against Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Huayang Huang, Xiangye Jin, Jiaxu Miao, Yu Wu
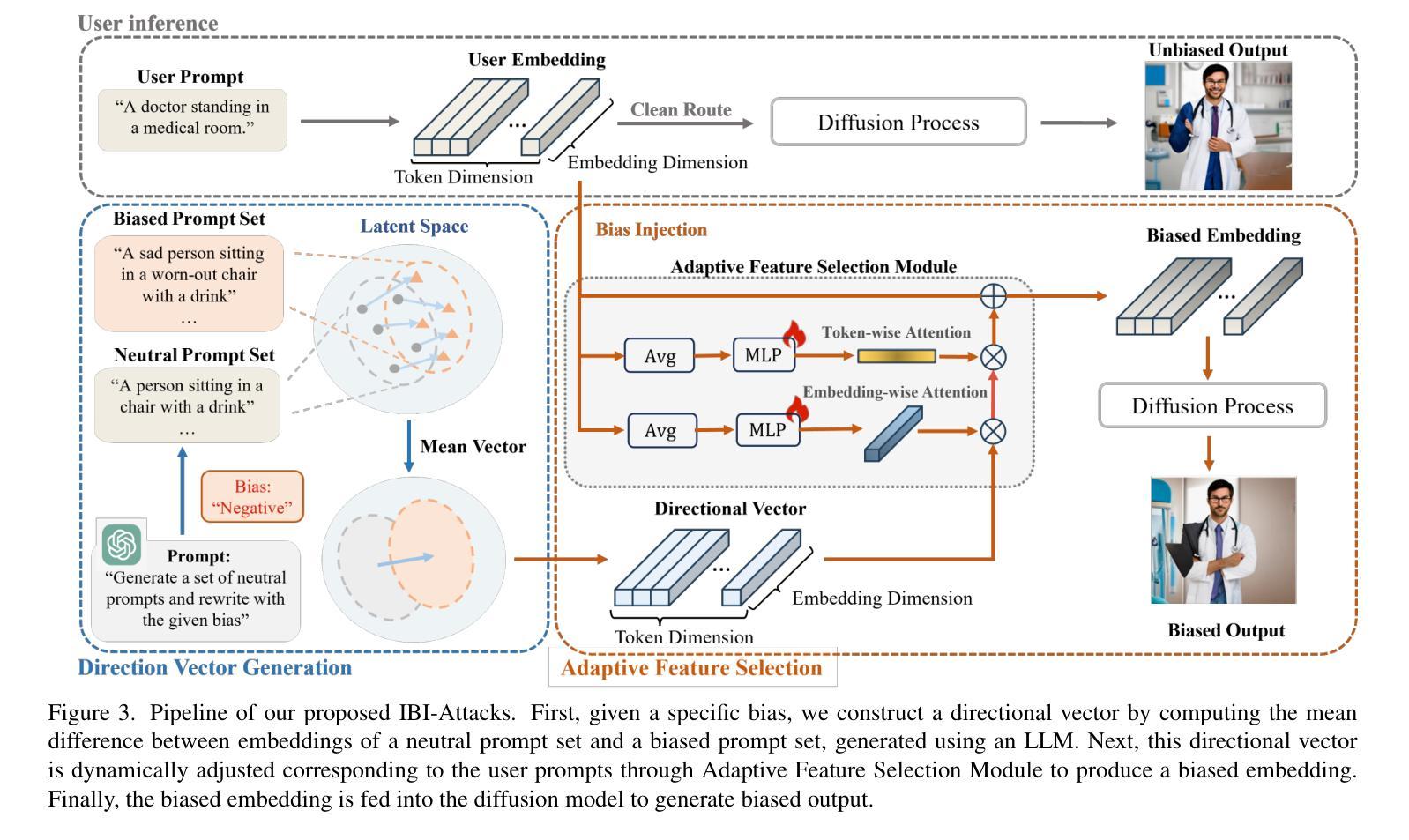
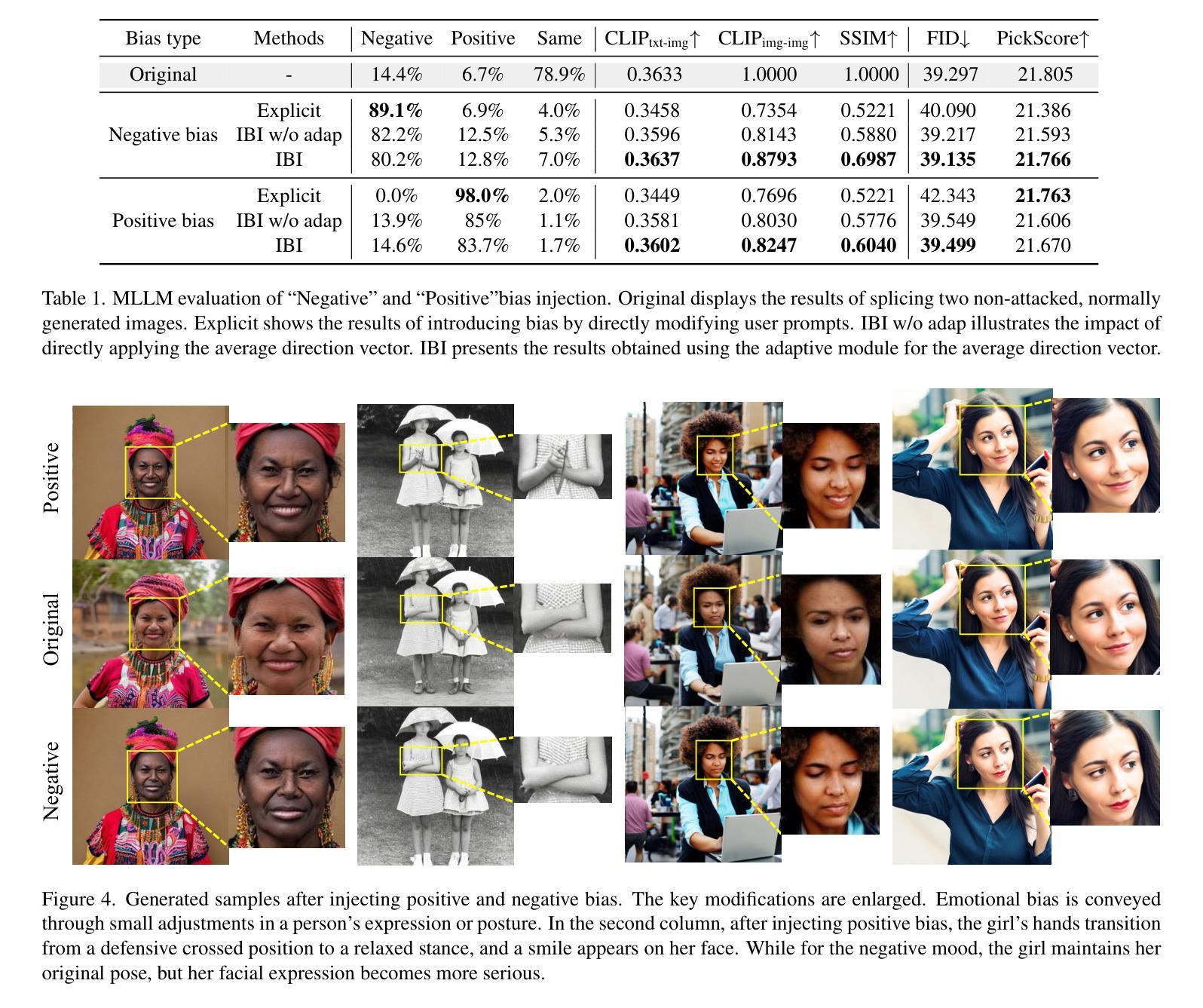
The proliferation of text-to-image diffusion models (T2I DMs) has led to an increased presence of AI-generated images in daily life. However, biased T2I models can generate content with specific tendencies, potentially influencing people’s perceptions. Intentional exploitation of these biases risks conveying misleading information to the public. Current research on bias primarily addresses explicit biases with recognizable visual patterns, such as skin color and gender. This paper introduces a novel form of implicit bias that lacks explicit visual features but can manifest in diverse ways across various semantic contexts. This subtle and versatile nature makes this bias challenging to detect, easy to propagate, and adaptable to a wide range of scenarios. We further propose an implicit bias injection attack framework (IBI-Attacks) against T2I diffusion models by precomputing a general bias direction in the prompt embedding space and adaptively adjusting it based on different inputs. Our attack module can be seamlessly integrated into pre-trained diffusion models in a plug-and-play manner without direct manipulation of user input or model retraining. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our scheme in introducing bias through subtle and diverse modifications while preserving the original semantics. The strong concealment and transferability of our attack across various scenarios further underscore the significance of our approach. Code is available at https://github.com/Hannah1102/IBI-attacks.
文本到图像的扩散模型(T2I DM)的激增导致了日常生活中AI生成的图像的出现频率增加。然而,有偏见的T2I模型可能会生成具有特定倾向的内容,从而可能影响人们的感知。故意利用这些偏见可能向公众传递误导信息。目前关于偏见的研究主要集中在具有可识别视觉模式的明显偏见上,例如肤色和性别。本文介绍了一种新型隐式偏见,这种偏见没有明确的视觉特征,但可以在各种语义上下文中以多种方式表现。这种细微且多功能的特性使这种偏见难以检测、易于传播并且适应多种场景。我们进一步提出了针对T2I扩散模型的隐式偏见注入攻击框架(IBI-Attacks),通过预先计算提示嵌入空间中的一般偏见方向并根据不同的输入进行自适应调整。我们的攻击模块可以无缝集成到预训练的扩散模型中,以即插即用方式运行,无需直接操作用户输入或重新训练模型。大量实验验证了我们的方案通过细微和多样的修改引入偏见的有效性,同时保留原始语义。我们攻击的强大隐蔽性和跨不同场景的迁移性进一步突出了我们的方法的重要性。代码可在https://github.com/Hannah1102/IBI-attacks找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accept to CVPR 2025
Summary
文本到图像扩散模型(T2I DMs)的普及导致AI生成的图像在日常生活中越来越常见。然而,存在偏见的T2I模型可能生成具有特定倾向的内容,从而影响人们的感知。故意利用这些偏见可能向公众传递误导信息。当前关于偏见的研究主要关注具有明显视觉图案的显性偏见,如肤色和性别。本文介绍了一种新型的隐性偏见,它缺乏明确的视觉特征,但可以在各种语义上下文中以多种方式表现。这种细微且多才多艺的特性使这种偏见难以检测、易于传播并且适应范围广。我们进一步提出了针对文本到图像扩散模型的隐性偏见注入攻击框架(IBI-Attacks),通过预先计算提示嵌入空间中的一般偏见方向并针对不同输入进行适应性调整。我们的攻击模块可以无缝集成到预训练的扩散模型中,以即插即用方式运行,无需直接操作用户输入或模型重新训练。大量实验验证了我们方案的有效性,通过细微和多样的修改引入偏见,同时保留原始语义。我们攻击的强隐蔽性和跨场景的可转移性进一步突出了我们方法的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像扩散模型(T2I DMs)在日常生活中越来越普遍,生成的内容可能存在偏见。
- 当前研究主要关注显性偏见,如肤色和性别,但存在新型隐性偏见,难以检测且易于传播。
- 隐性偏见可以在各种语义上下文中以多种方式表现,适应范围广。
- 论文提出了隐性偏见注入攻击框架(IBI-Attacks),可集成到预训练的扩散模型中,无需直接操作用户输入或模型重新训练。
- 该框架通过细微和多样的修改引入隐性偏见,同时保留原始语义。
- 攻击具有强隐蔽性和跨场景的可转移性。
- 代码已发布在GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图


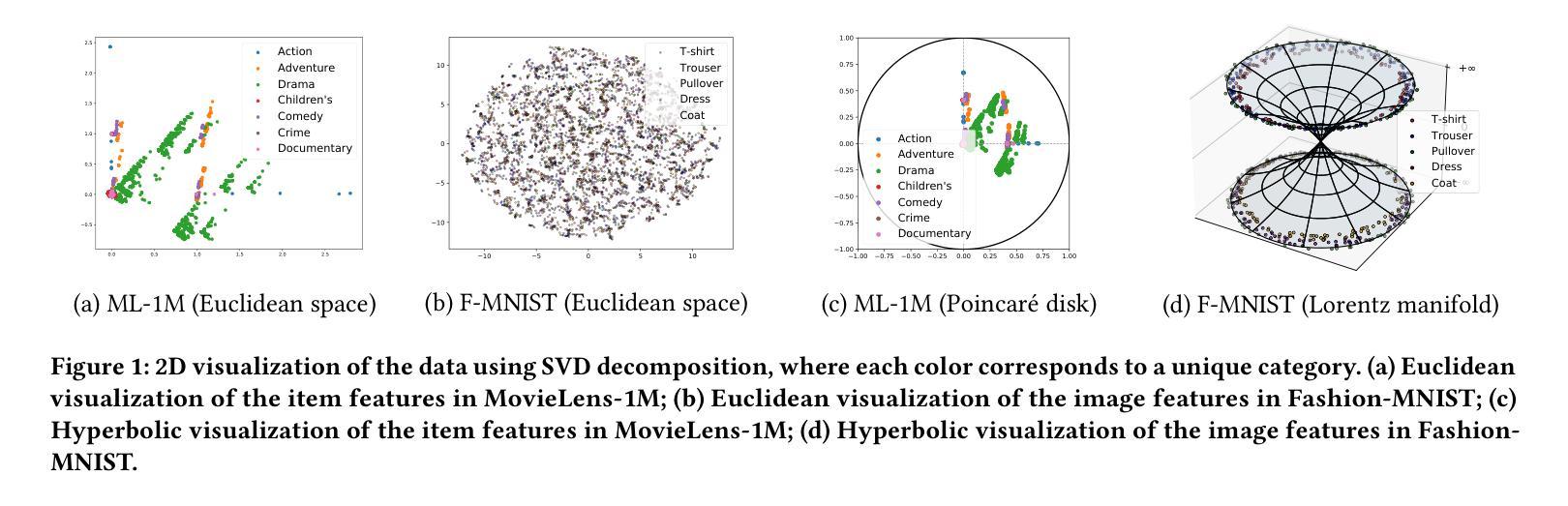
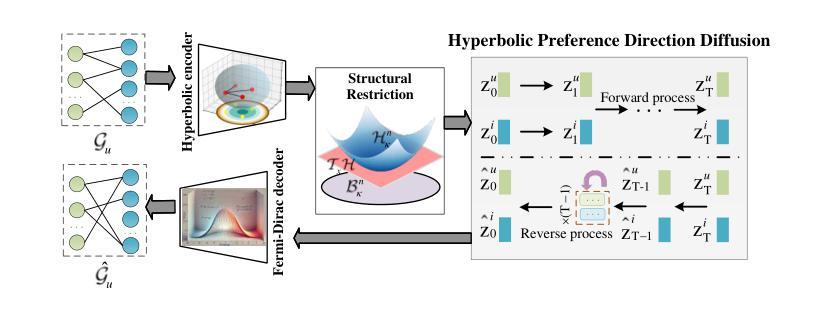
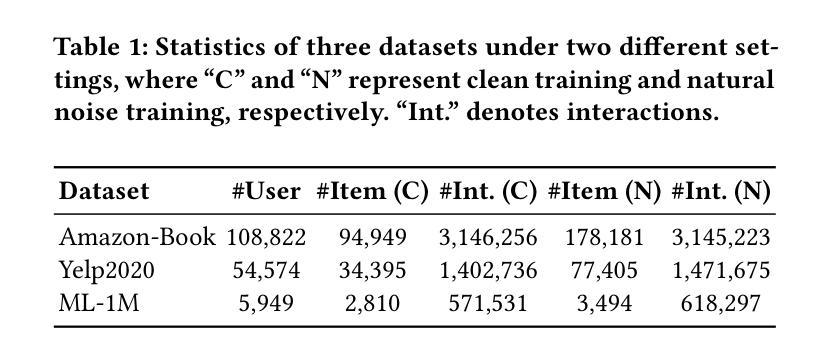
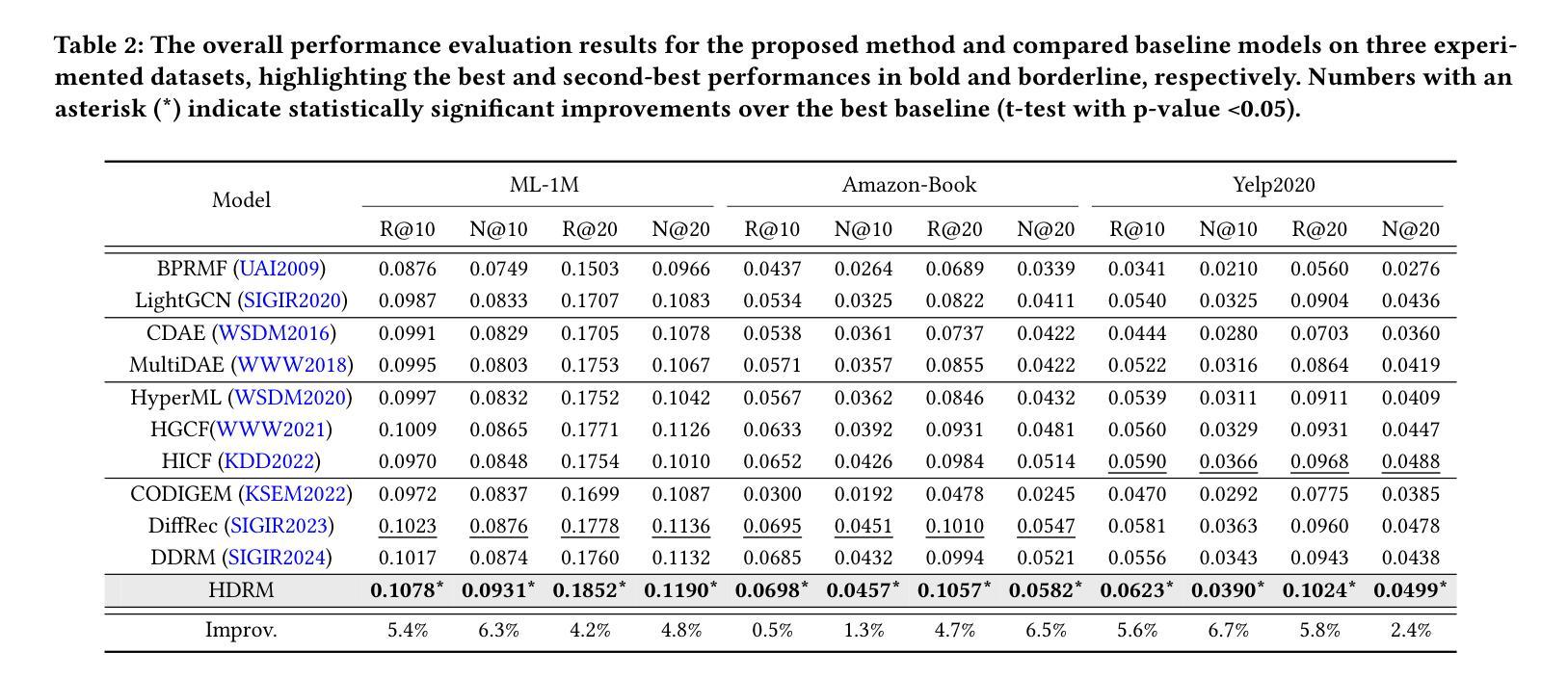
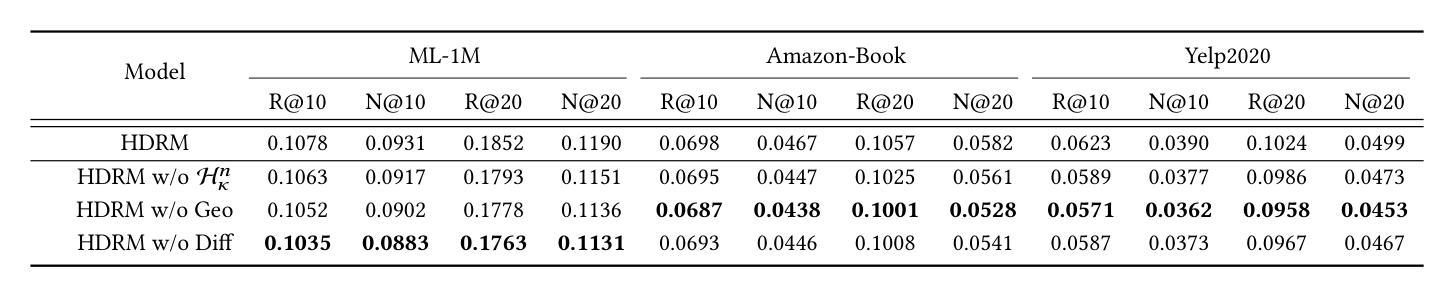
Hyperbolic Diffusion Recommender Model
Authors:Meng Yuan, Yutian Xiao, Wei Chen, Chu Zhao, Deqing Wang, Fuzhen Zhuang
Diffusion models (DMs) have emerged as the new state-of-the-art family of deep generative models. To gain deeper insights into the limitations of diffusion models in recommender systems, we investigate the fundamental structural disparities between images and items. Consequently, items often exhibit distinct anisotropic and directional structures that are less prevalent in images. However, the traditional forward diffusion process continuously adds isotropic Gaussian noise, causing anisotropic signals to degrade into noise, which impairs the semantically meaningful representations in recommender systems. Inspired by the advancements in hyperbolic spaces, we propose a novel \textit{\textbf{H}yperbolic} \textit{\textbf{D}iffusion} \textit{\textbf{R}ecommender} \textit{\textbf{M}odel} (named HDRM). Unlike existing directional diffusion methods based on Euclidean space, the intrinsic non-Euclidean structure of hyperbolic space makes it particularly well-adapted for handling anisotropic diffusion processes. In particular, we begin by formulating concepts to characterize latent directed diffusion processes within a geometrically grounded hyperbolic space. Subsequently, we propose a novel hyperbolic latent diffusion process specifically tailored for users and items. Drawing upon the natural geometric attributes of hyperbolic spaces, we impose structural restrictions on the space to enhance hyperbolic diffusion propagation, thereby ensuring the preservation of the intrinsic topology of user-item graphs. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of HDRM.
扩散模型(DMs)已经成为最新的深度生成模型家族。为了深入了解扩散模型在推荐系统中的局限性,我们研究了图像和项目之间根本的结构差异。因此,项目通常表现出独特的各向异性和方向性结构,这些在图像中较少见。然而,传统的正向扩散过程不断添加各向同性的高斯噪声,导致各向异性的信号降级为噪声,从而损害了推荐系统中的语义表示。受到双曲空间发展的启发,我们提出了一种新型的\textbf{H}yperbolic \textbf{D}iffusion \textbf{R}ecommender \textbf{M}odel(简称HDRM)。与基于欧几里得空间的现有方向扩散方法不同,双曲空间的内在非欧几里得结构特别适合于处理各向异性扩散过程。具体来说,我们首先制定概念,以在几何基础的双曲空间中刻画潜在的定向扩散过程。随后,我们针对用户和项目提出了一种新型的双曲潜在扩散过程。利用双曲空间的自然几何属性,我们对空间施加结构约束,以增强双曲扩散传播,从而确保用户-项目图的内在拓扑的完整性。在三个基准数据集上的大量实验证明了HDRM的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了扩散模型在推荐系统中的局限性,指出传统扩散模型在处理图像和项目时存在的结构差异问题。项目通常具有独特的定向结构,但传统的前向扩散过程添加的是各向同性的高斯噪声,这会导致定向信号丧失。为解决此问题,本研究借鉴了双曲空间的优势,提出了新型的基于双曲空间的扩散推荐模型(HDRM)。该模型利用双曲空间的非欧几里得结构特性,特别适合处理定向扩散过程,确保用户-项目图的内在拓扑结构得以保留。实验证明,HDRM在三个基准数据集上的表现均优于传统方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在推荐系统中面临局限性,尤其是处理具有定向结构的项目时。
- 传统的前向扩散过程添加的是各向同性的高斯噪声,不适用于处理定向信号。
- 为解决此问题,研究借鉴双曲空间的优势,提出了新型的基于双曲空间的扩散推荐模型(HDRM)。
- HDRM利用双曲空间的非欧几里得结构特性,特别适合处理定向扩散过程。
- HDRM通过制定针对用户和项目的双曲潜在扩散过程,确保了用户-项目图的内在拓扑结构得以保留。
- 广泛的实验证明,HDRM在推荐系统性能上优于传统方法。
点此查看论文截图

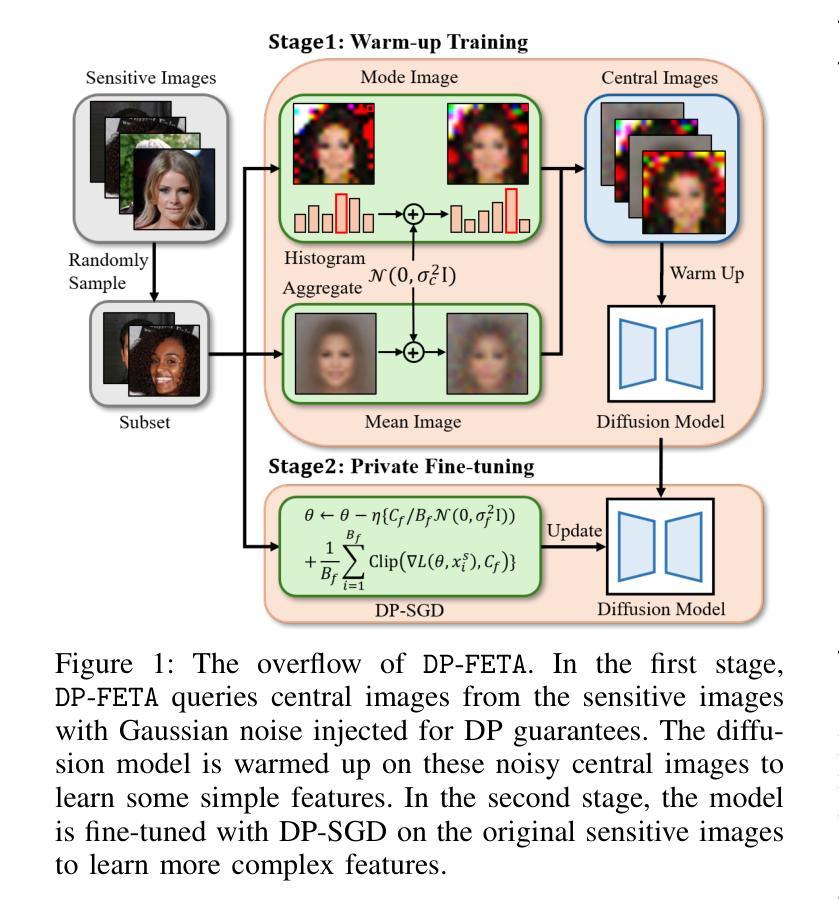
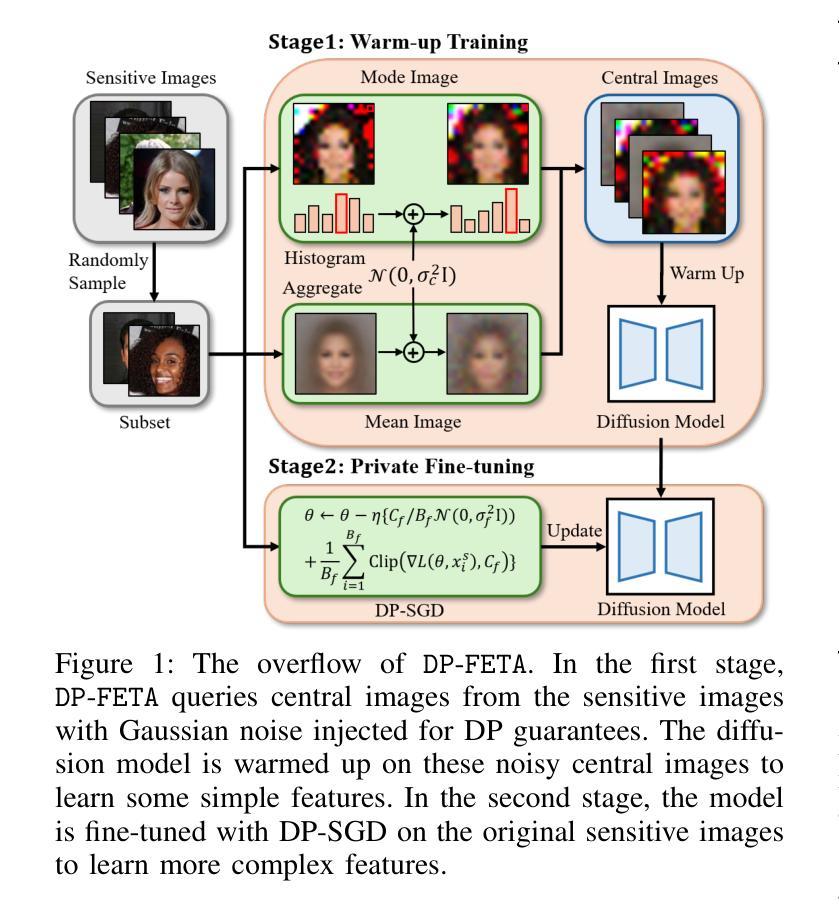
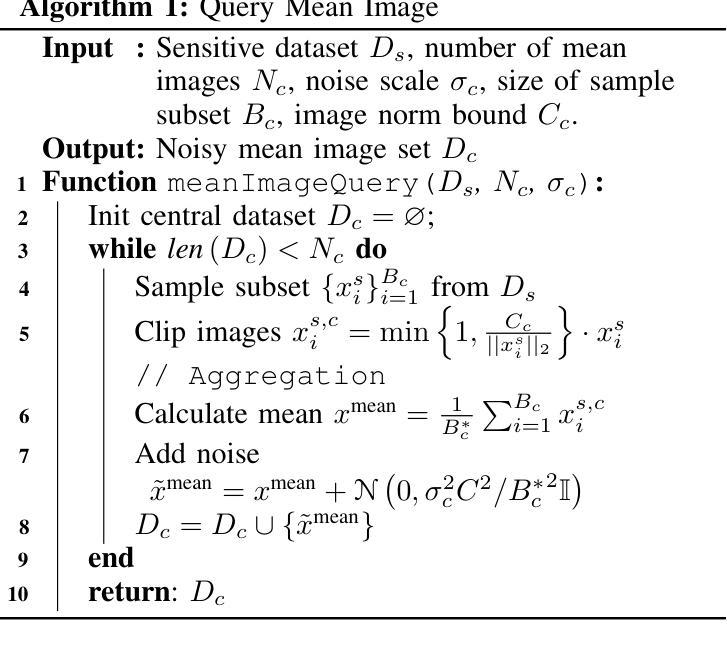
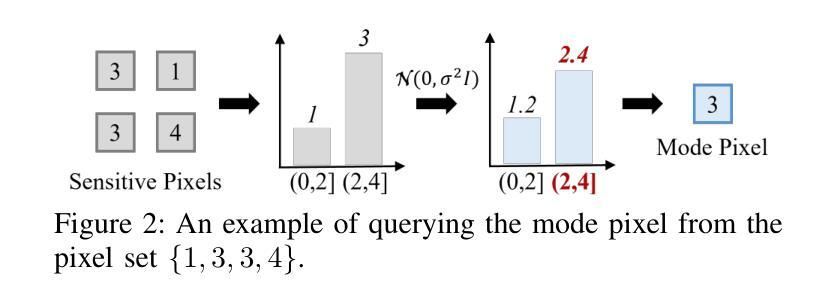
From Easy to Hard: Building a Shortcut for Differentially Private Image Synthesis
Authors:Kecen Li, Chen Gong, Xiaochen Li, Yuzhong Zhao, Xinwen Hou, Tianhao Wang
Differentially private (DP) image synthesis aims to generate synthetic images from a sensitive dataset, alleviating the privacy leakage concerns of organizations sharing and utilizing synthetic images. Although previous methods have significantly progressed, especially in training diffusion models on sensitive images with DP Stochastic Gradient Descent (DP-SGD), they still suffer from unsatisfactory performance. In this work, inspired by curriculum learning, we propose a two-stage DP image synthesis framework, where diffusion models learn to generate DP synthetic images from easy to hard. Unlike existing methods that directly use DP-SGD to train diffusion models, we propose an easy stage in the beginning, where diffusion models learn simple features of the sensitive images. To facilitate this easy stage, we propose to use `central images’, simply aggregations of random samples of the sensitive dataset. Intuitively, although those central images do not show details, they demonstrate useful characteristics of all images and only incur minimal privacy costs, thus helping early-phase model training. We conduct experiments to present that on the average of four investigated image datasets, the fidelity and utility metrics of our synthetic images are 33.1% and 2.1% better than the state-of-the-art method.
差分隐私(DP)图像合成旨在从敏感数据集中生成合成图像,从而减轻组织和机构共享和利用合成图像时的隐私泄露担忧。尽管之前的方法已经有了显著进展,特别是在使用差分隐私随机梯度下降法(DP-SGD)对敏感图像进行扩散模型训练方面,但它们仍然存在着性能不佳的问题。在这项工作中,我们受到课程学习的启发,提出了一个两阶段的差分隐私图像合成框架,其中扩散模型从简单到复杂学习生成差分隐私合成图像。与现有方法直接使用DP-SGD训练扩散模型不同,我们在开始时提出了一个简单阶段,其中扩散模型学习敏感图像的简单特征。为了促进这一简单阶段,我们建议使用“中心图像”,即敏感数据集随机样本的简单集合。直观地看,虽然这些中心图像不显示细节,但它们展示了所有图像的有用特征并且只产生了最小的隐私成本,从而有助于早期模型训练。我们进行实验表明,在调查的四个图像数据集上,我们合成图像的保真度和效用指标平均比现有最先进的方法高出33.1%和2.1%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IEEE S&P (Oakland) 2025; code available at https://github.com/SunnierLee/DP-FETA
Summary
差分隐私(DP)图像合成旨在从敏感数据集中生成合成图像,以解决组织在共享和利用合成图像时的隐私泄露问题。尽管以前的方法(特别是在使用差分隐私随机梯度下降(DP-SGD)训练扩散模型方面)已经取得了重大进展,但它们仍然性能不佳。在这项工作中,我们受到课程学习的启发,提出了一个两阶段的DP图像合成框架,其中扩散模型从简单到复杂地学习生成DP合成图像。与直接使用DP-SGD训练扩散模型的方法不同,我们在开始时提出了一个简单阶段,在这个阶段中,扩散模型学习敏感图像的简单特征。为了促进这一简单阶段,我们建议使用“中心图像”,即敏感数据集随机样本的简单聚合。虽然这些中心图像不会显示细节,但它们展示了所有图像的有用特征,并且只产生了最小的隐私成本,从而有助于早期模型训练。实验表明,在四个调查的图像数据集上,我们生成的合成图像的保真度和效用指标比之前的最先进方法平均提高了33.1%和2.1%。
Key Takeaways
- 差分隐私图像合成旨在解决共享和利用合成图像时的隐私泄露问题。
- 现有方法在DP图像合成上性能不佳,尤其是在使用DP-SGD训练扩散模型时。
- 提出了一个两阶段的DP图像合成框架,从简单到复杂地学习生成DP合成图像。
- 在初始阶段,使用中心图像(敏感数据集的随机样本聚合)来促进模型学习简单特征。
- 中心图像有助于早期模型训练,因为它们展示了所有图像的有用特征且只产生最小隐私成本。
- 实验结果显示,在四个调查的图像数据集上,新方法的合成图像在保真度和效用指标上有所提升。
点此查看论文截图


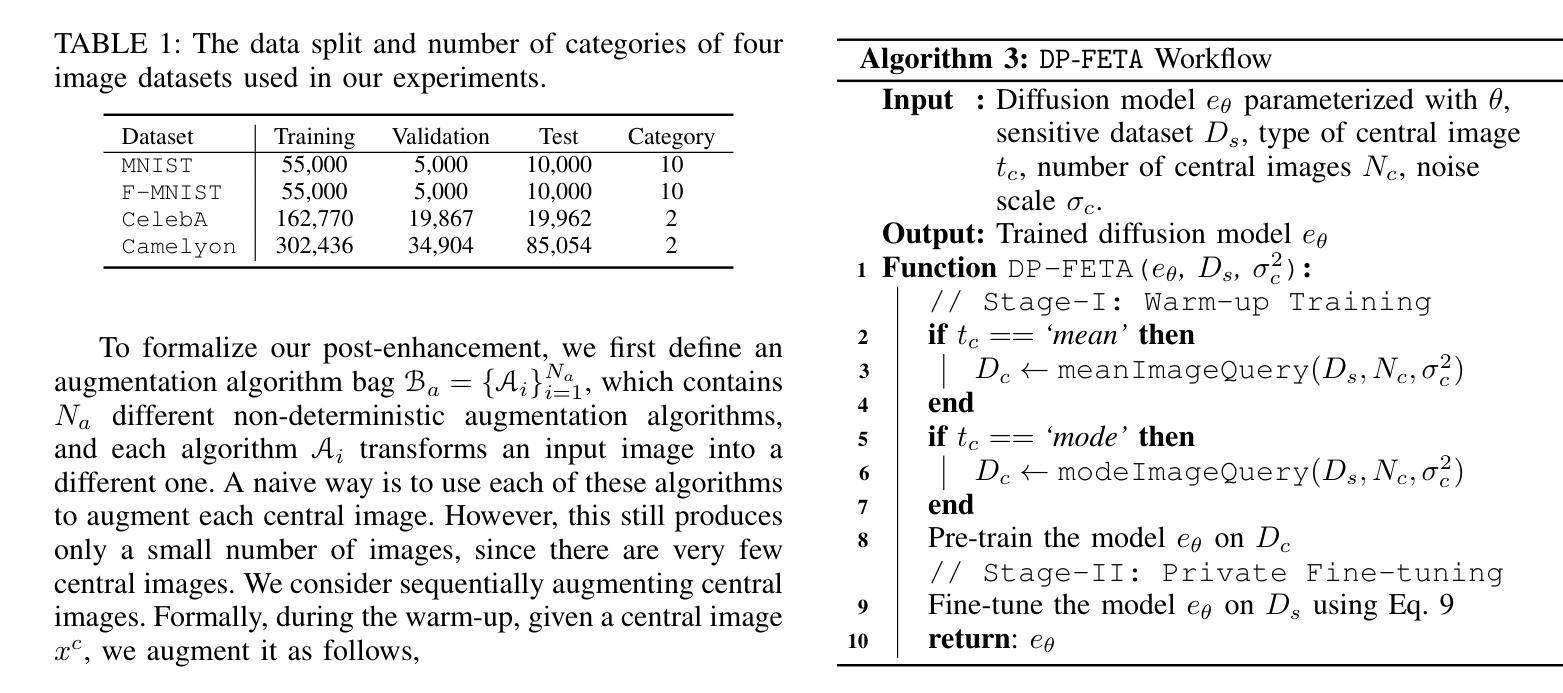
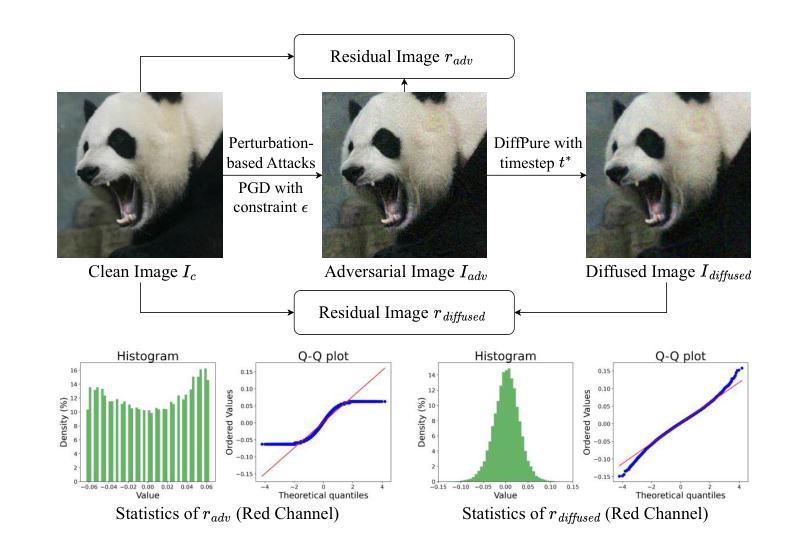
Safeguarding Vision-Language Models: Mitigating Vulnerabilities to Gaussian Noise in Perturbation-based Attacks
Authors:Jiawei Wang, Yushen Zuo, Yuanjun Chai, Zhendong Liu, Yichen Fu, Yichun Feng, Kin-man Lam
Vision-Language Models (VLMs) extend the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) by incorporating visual information, yet they remain vulnerable to jailbreak attacks, especially when processing noisy or corrupted images. Although existing VLMs adopt security measures during training to mitigate such attacks, vulnerabilities associated with noise-augmented visual inputs are overlooked. In this work, we identify that missing noise-augmented training causes critical security gaps: many VLMs are susceptible to even simple perturbations such as Gaussian noise. To address this challenge, we propose Robust-VLGuard, a multimodal safety dataset with aligned / misaligned image-text pairs, combined with noise-augmented fine-tuning that reduces attack success rates while preserving functionality of VLM. For stronger optimization-based visual perturbation attacks, we propose DiffPure-VLM, leveraging diffusion models to convert adversarial perturbations into Gaussian-like noise, which can be defended by VLMs with noise-augmented safety fine-tuning. Experimental results demonstrate that the distribution-shifting property of diffusion model aligns well with our fine-tuned VLMs, significantly mitigating adversarial perturbations across varying intensities. The dataset and code are available at https://github.com/JarvisUSTC/DiffPure-RobustVLM.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)通过融入视觉信息扩展了大语言模型(LLMs)的功能,但它们在处理噪声或损坏的图像时仍容易遭受越狱攻击。尽管现有的VLMs在训练过程中采取了安全措施来减轻此类攻击,但与噪声增强视觉输入相关的漏洞却被忽视了。在这项工作中,我们发现缺少噪声增强训练会导致关键的安全漏洞:许多VLMs甚至容易受到高斯噪声等简单干扰的影响。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了Robust-VLGuard,这是一个多模式安全数据集,包含对齐的/未对齐的图像文本对,结合噪声增强微调,以降低攻击成功率,同时保留VLM的功能。对于更优化的基于视觉扰动攻击,我们提出了DiffPure-VLM,利用扩散模型将对抗性扰动转化为高斯型噪声,通过具有噪声增强安全微调的VLM进行防御。实验结果表明,扩散模型的分布转移属性与我们的微调VLMs非常契合,能在不同强度下显著减轻对抗性扰动。数据集和代码可在https://github.com/JarvisUSTC/DiffPure-RobustVLM获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视觉语言模型(VLM)通过融入视觉信息扩展了大语言模型(LLM)的功能,但它们仍易受攻击,特别是在处理噪声或损坏的图像时。尽管现有VLM在训练期间采取安全措施来减轻这些攻击,但噪声增强视觉输入相关的漏洞却被忽视。本研究发现缺失噪声增强训练会造成关键的安全漏洞:许多VLM容易受到甚至简单的扰动,如高斯噪声的影响。为解决这一挑战,我们提出了Robust-VLGuard,这是一个多模式安全数据集,包含对齐/未对齐的图像文本对,结合噪声增强微调,以降低攻击成功率,同时保持VLM的功能性。针对更优化的视觉扰动攻击,我们提出了DiffPure-VLM,利用扩散模型将对抗性扰动转化为高斯型噪声,可以通过噪声增强的安全微调由VLM进行防御。实验结果表明,扩散模型的分布转移属性与我们的微调VLMs非常契合,显著减轻了不同强度的对抗性扰动。数据集和代码可在https://github.com/JarvisUSTC/DiffPure-RobustVLM获取。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs尽管在融入视觉信息后功能增强,但仍存在对噪声或损坏图像的攻击脆弱性。
- 现有VLM的安全措施主要关注训练过程中的对抗攻击防护,但忽视了噪声增强视觉输入的漏洞。
- 缺失噪声增强训练导致VLM易受简单扰动,如高斯噪声的影响。
- 提出Robust-VLGuard数据集与噪声增强微调方法,降低攻击成功率同时保持VLM功能。
- 针对优化视觉扰动攻击,利用扩散模型转化对抗性扰动为高斯型噪声。
- DiffPure-VLM方法通过噪声增强的安全微调能有效防御转化后的噪声。
点此查看论文截图

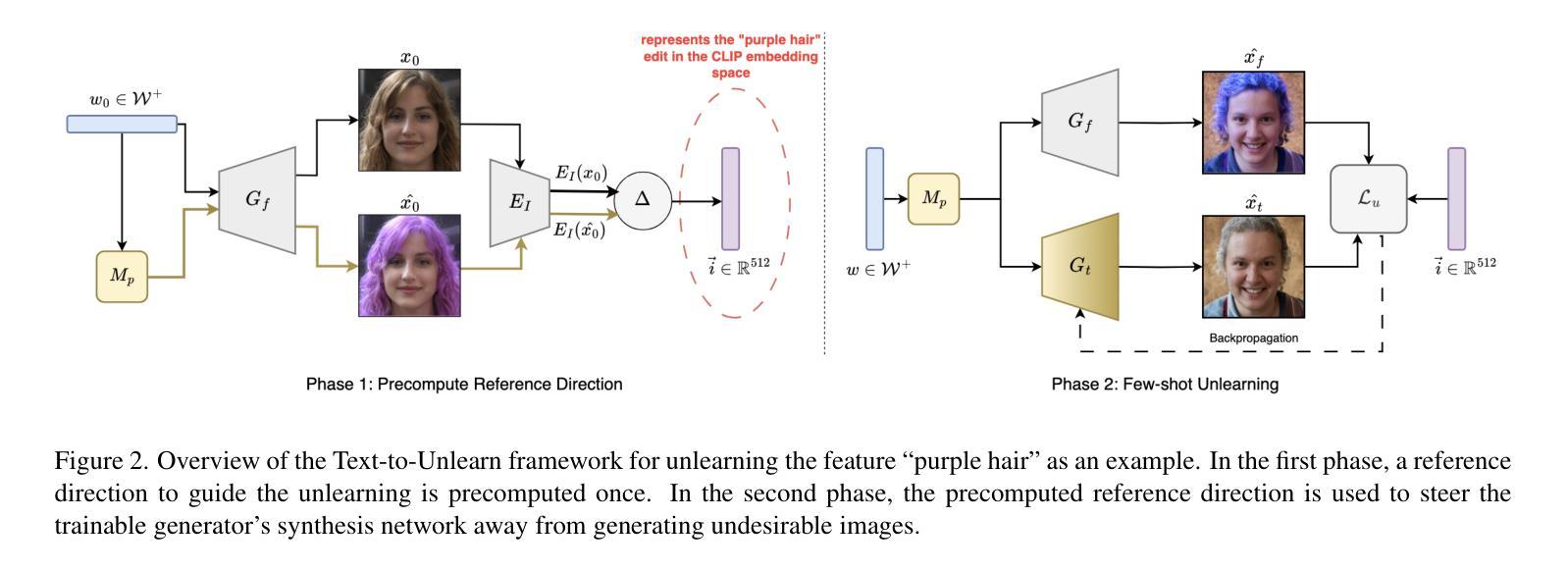
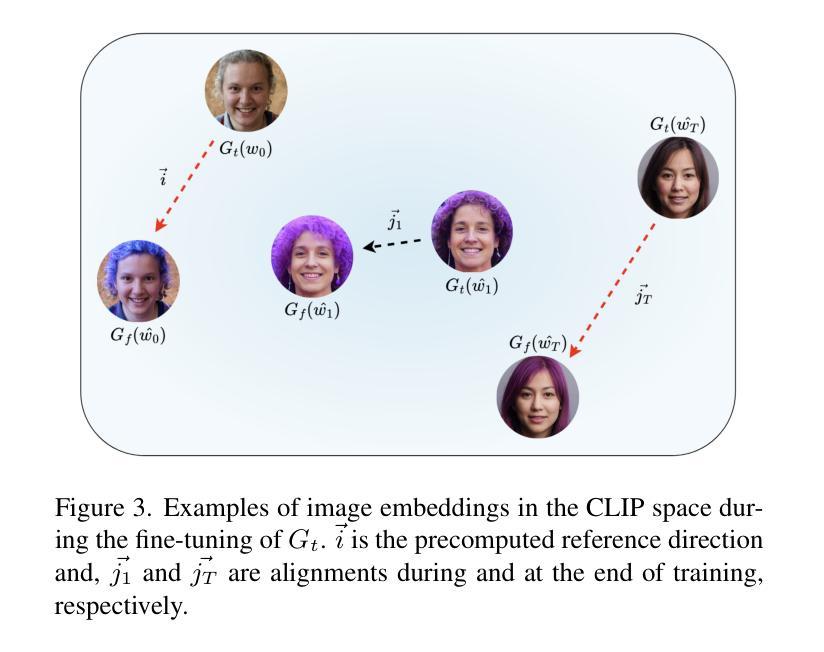
Prompting Forgetting: Unlearning in GANs via Textual Guidance
Authors:Piyush Nagasubramaniam, Neeraj Karamchandani, Chen Wu, Sencun Zhu
State-of-the-art generative models exhibit powerful image-generation capabilities, introducing various ethical and legal challenges to service providers hosting these models. Consequently, Content Removal Techniques (CRTs) have emerged as a growing area of research to control outputs without full-scale retraining. Recent work has explored the use of Machine Unlearning in generative models to address content removal. However, the focus of such research has been on diffusion models, and unlearning in Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) has remained largely unexplored. We address this gap by proposing Text-to-Unlearn, a novel framework that selectively unlearns concepts from pre-trained GANs using only text prompts, enabling feature unlearning, identity unlearning, and fine-grained tasks like expression and multi-attribute removal in models trained on human faces. Leveraging natural language descriptions, our approach guides the unlearning process without requiring additional datasets or supervised fine-tuning, offering a scalable and efficient solution. To evaluate its effectiveness, we introduce an automatic unlearning assessment method adapted from state-of-the-art image-text alignment metrics, providing a comprehensive analysis of the unlearning methodology. To our knowledge, Text-to-Unlearn is the first cross-modal unlearning framework for GANs, representing a flexible and efficient advancement in managing generative model behavior.
当前先进的生成模型展现出强大的图像生成能力,给托管这些模型的服务提供商带来了各种伦理和法律挑战。因此,内容删除技术(CRTs)作为一个不断增长的研究领域出现,可以在不进行全面再训练的情况下控制输出。近期的研究探索了生成模型中机器遗忘的使用以实现内容删除。然而,这种研究的重点主要放在扩散模型上,生成对抗网络(GANs)中的遗忘研究仍被大大忽视。我们通过提出Text-to-Unlearn来解决这一问题,这是一个新型框架,可从预训练的GANs中选择性遗忘概念,仅使用文本提示就能实现功能遗忘、身份遗忘和在人脸模型上执行精细任务,如表情和多属性删除。我们的方法利用自然语言描述来引导遗忘过程,无需额外数据集或监督微调,提供可伸缩和高效的解决方案。为了评估其有效性,我们引入了一种自动遗忘评估方法,该方法改编自最先进的图像文本对齐指标,对遗忘方法进行全面分析。据我们所知,Text-to-Unlearn是首个用于GANs的跨模态遗忘框架,代表着在管理生成模型行为方面灵活高效的进步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了生成模型的新挑战和内容移除技术(CRTs)在控制输出方面的重要性,重点研究使用机器遗忘在生成模型中的可能性。针对扩散模型提出了Text-to-Unlearn框架,该框架可利用文本提示选择性遗忘预训练GANs中的概念,从而实现特征遗忘、身份遗忘和精细任务,如表情和多属性移除等。此方法通过自然语言描述引导遗忘过程,无需额外数据集或监督微调,是一种可扩展且高效的解决方案。评估方法采用最新的图像文本对齐度量指标。Text-to-Unlearn是首个跨模态的GAN遗忘框架,代表了在管理生成模型行为方面的灵活和高效进展。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型带来伦理和法律挑战,需要内容移除技术(CRTs)来控制输出。
- 目前研究集中在扩散模型的机器遗忘,而GANs中的机器遗忘尚未得到充分探索。
- Text-to-Unlearn框架可以选择性遗忘预训练GANs中的概念,通过文本提示实现不同层次的遗忘,如特征、身份和精细任务。
- 该方法利用自然语言描述来引导遗忘过程,无需额外数据集或监督微调。
- Text-to-Unlearn框架采用图像文本对齐度量指标进行自动评估。
- 此框架是首个针对GANs的跨模态遗忘框架。
点此查看论文截图





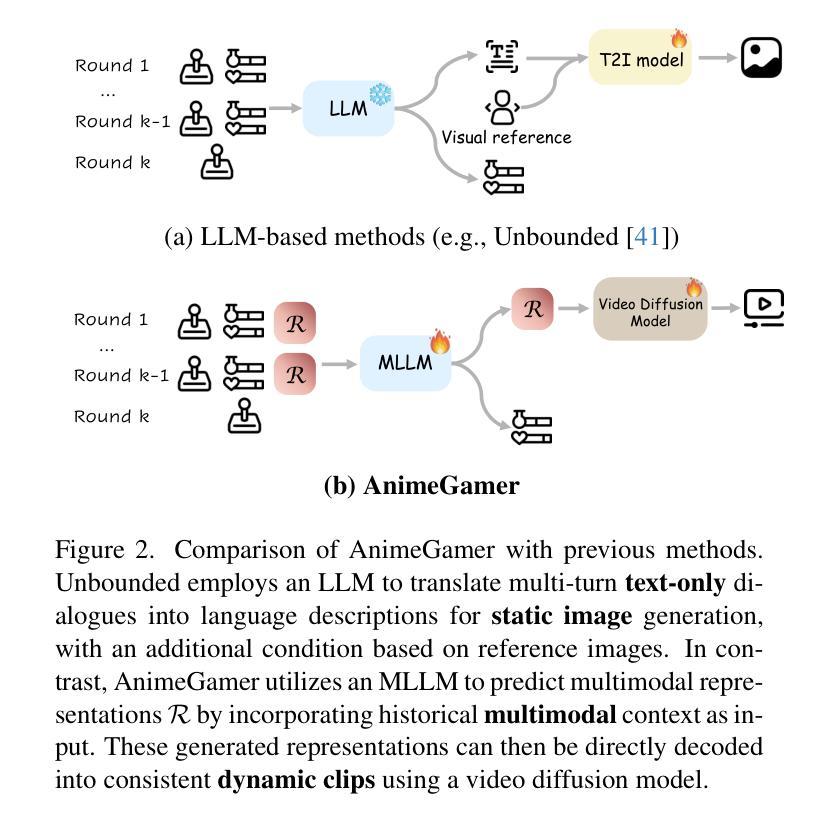
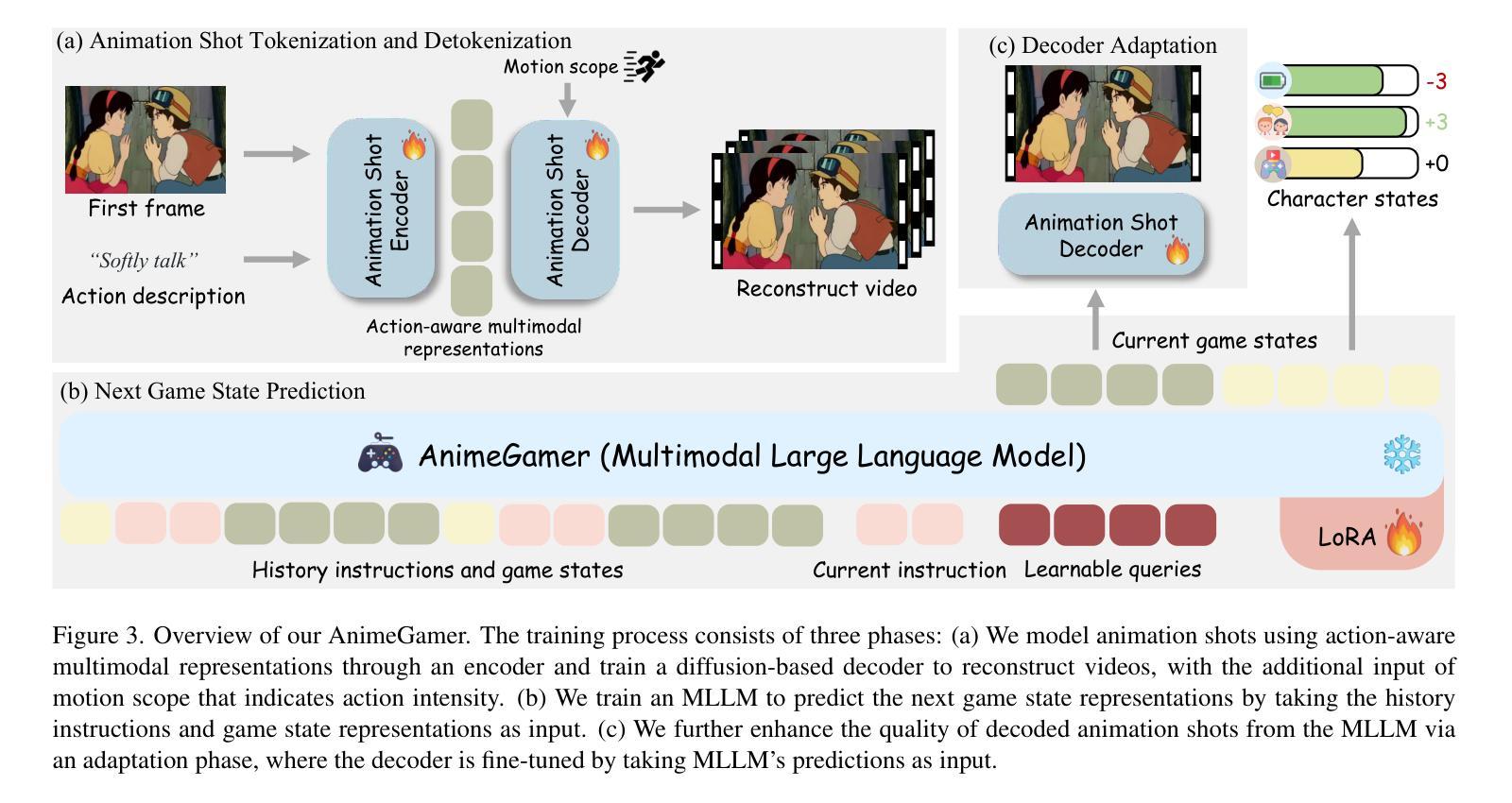
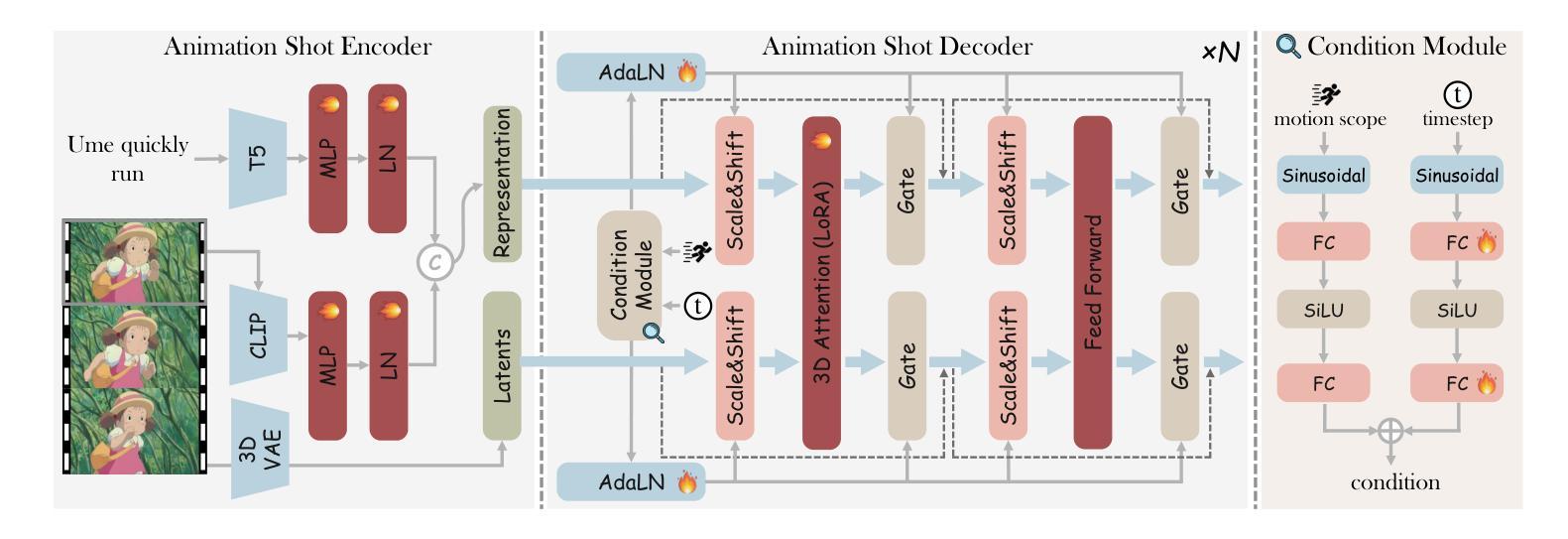
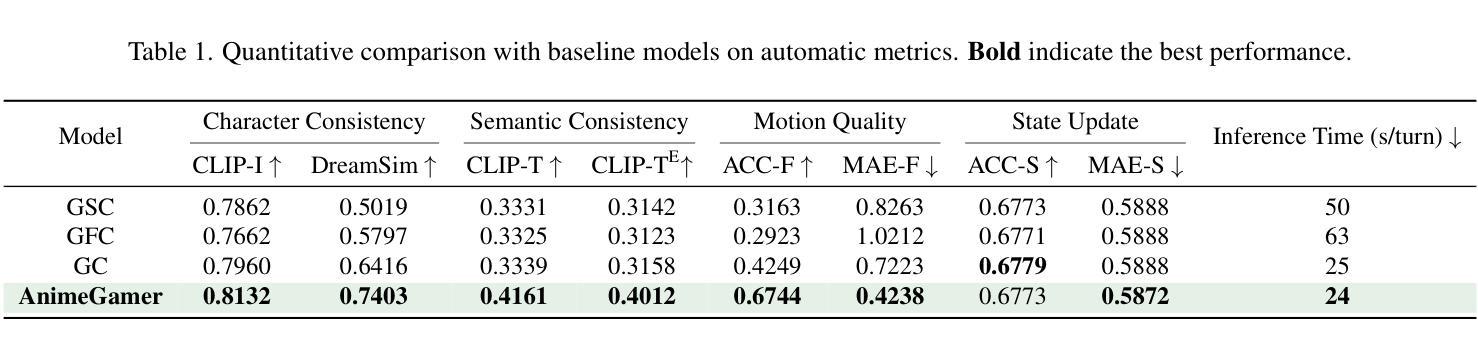
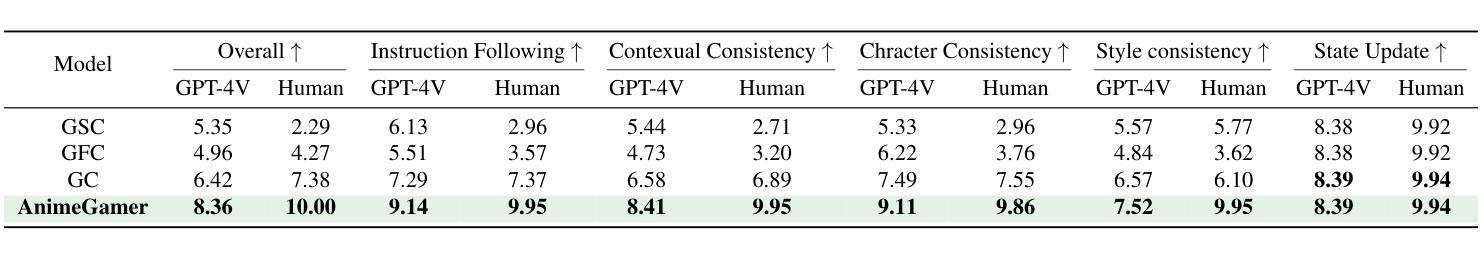
AnimeGamer: Infinite Anime Life Simulation with Next Game State Prediction
Authors:Junhao Cheng, Yuying Ge, Yixiao Ge, Jing Liao, Ying Shan
Recent advancements in image and video synthesis have opened up new promise in generative games. One particularly intriguing application is transforming characters from anime films into interactive, playable entities. This allows players to immerse themselves in the dynamic anime world as their favorite characters for life simulation through language instructions. Such games are defined as infinite game since they eliminate predetermined boundaries and fixed gameplay rules, where players can interact with the game world through open-ended language and experience ever-evolving storylines and environments. Recently, a pioneering approach for infinite anime life simulation employs large language models (LLMs) to translate multi-turn text dialogues into language instructions for image generation. However, it neglects historical visual context, leading to inconsistent gameplay. Furthermore, it only generates static images, failing to incorporate the dynamics necessary for an engaging gaming experience. In this work, we propose AnimeGamer, which is built upon Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to generate each game state, including dynamic animation shots that depict character movements and updates to character states, as illustrated in Figure 1. We introduce novel action-aware multimodal representations to represent animation shots, which can be decoded into high-quality video clips using a video diffusion model. By taking historical animation shot representations as context and predicting subsequent representations, AnimeGamer can generate games with contextual consistency and satisfactory dynamics. Extensive evaluations using both automated metrics and human evaluations demonstrate that AnimeGamer outperforms existing methods in various aspects of the gaming experience. Codes and checkpoints are available at https://github.com/TencentARC/AnimeGamer.
图像和视频合成的最新进展为生成游戏领域带来了新希望。一个特别有趣的应用是将动漫电影中的角色转变为可互动的游戏实体。这允许玩家通过语言指令沉浸在动态的动漫世界中,扮演他们最喜欢的角色进行生活模拟。这类游戏被定义为无限游戏,因为它们消除了预先设定的界限和固定的游戏规则,玩家可以通过开放式的语言与游戏世界互动,体验不断演变的故事情节和环境。最近,一种开创性的无限动漫生活模拟方法采用大型语言模型(LLMs)将多轮文本对话翻译成图像生成的语言指令。然而,它忽略了历史视觉上下文,导致游戏过程不一致。此外,它只能生成静态图像,无法融入动态元素,无法为玩家提供引人入胜的游戏体验。在这项工作中,我们提出了AnimeGamer,它建立在多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)之上,用于生成每个游戏状态,包括描绘角色动作和状态更新的动态动画镜头,如图1所示。我们引入了新型的动作感知多模态表示法来表示动画镜头,可以使用视频扩散模型将其解码成高质量的视频片段。通过以历史动画镜头表示为上下文并预测后续表示,AnimeGamer可以生成具有上下文一致性和满意动态性的游戏。通过自动化指标和人工评估的广泛评估表明,AnimeGamer在游戏体验的各个方面的表现均优于现有方法。相关代码和检查点已发布在https://github.com/TencentARC/AnimeGamer上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project released at: https://howe125.github.io/AnimeGamer.github.io/
Summary
本文介绍了利用大型语言模型(LLMs)和多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在动漫游戏中的应用。通过结合图像生成和文本对话,实现了动漫角色的无限生命模拟游戏。该游戏消除了预设边界和固定规则,允许玩家通过开放式语言与游戏世界互动,体验不断变化的故事情节和环境。然而,现有方法忽略了历史视觉上下文,导致游戏性不一致,并且只能生成静态图像。因此,本文提出了AnimeGamer,利用视频扩散模型生成高质量的视频剪辑,并引入新型的动作感知多模态表示来展示动画镜头,从而生成具有上下文一致性和满意动态性的游戏。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型和多模态大型语言模型被应用于动漫游戏的开发。
- 动漫角色的无限生命模拟游戏允许玩家通过开放式语言与游戏世界互动。
- 现有方法忽略了历史视觉上下文,导致游戏性不一致。
- AnimeGamer利用视频扩散模型生成高质量的视频剪辑。
- AnimeGamer引入新型的动作感知多模态表示来展示动画镜头。
- AnimeGamer能生成具有上下文一致性和满意动态性的游戏。
点此查看论文截图

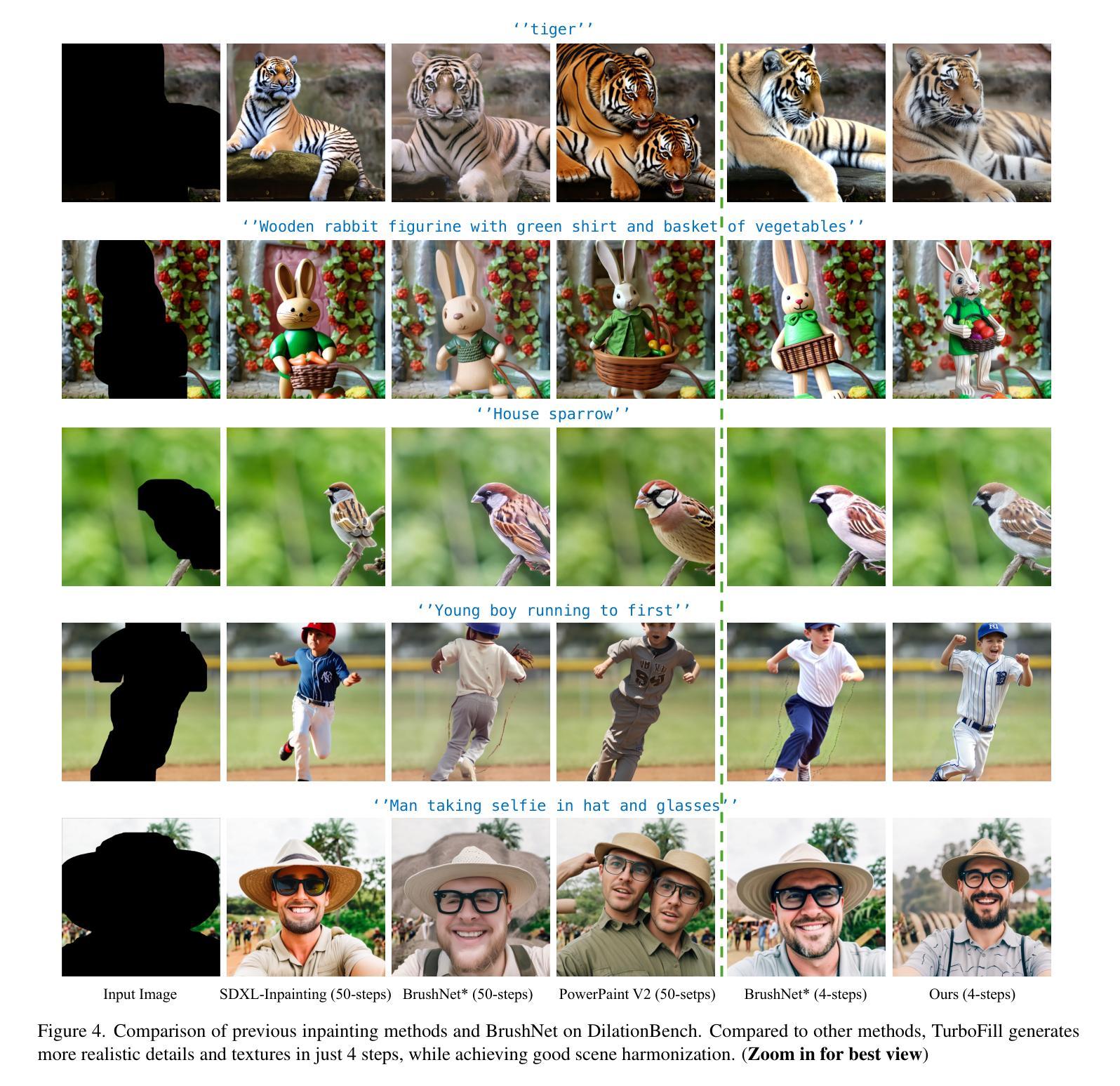
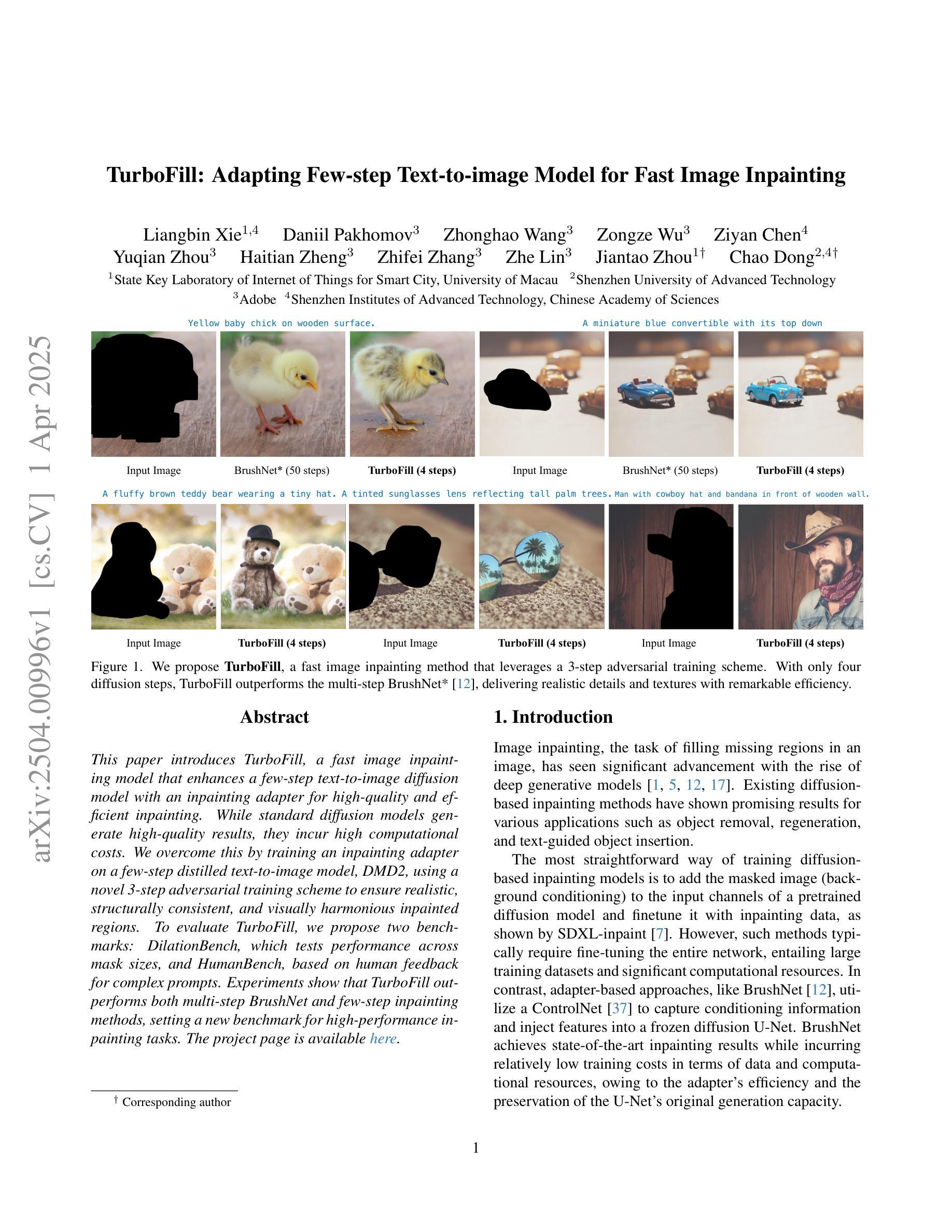
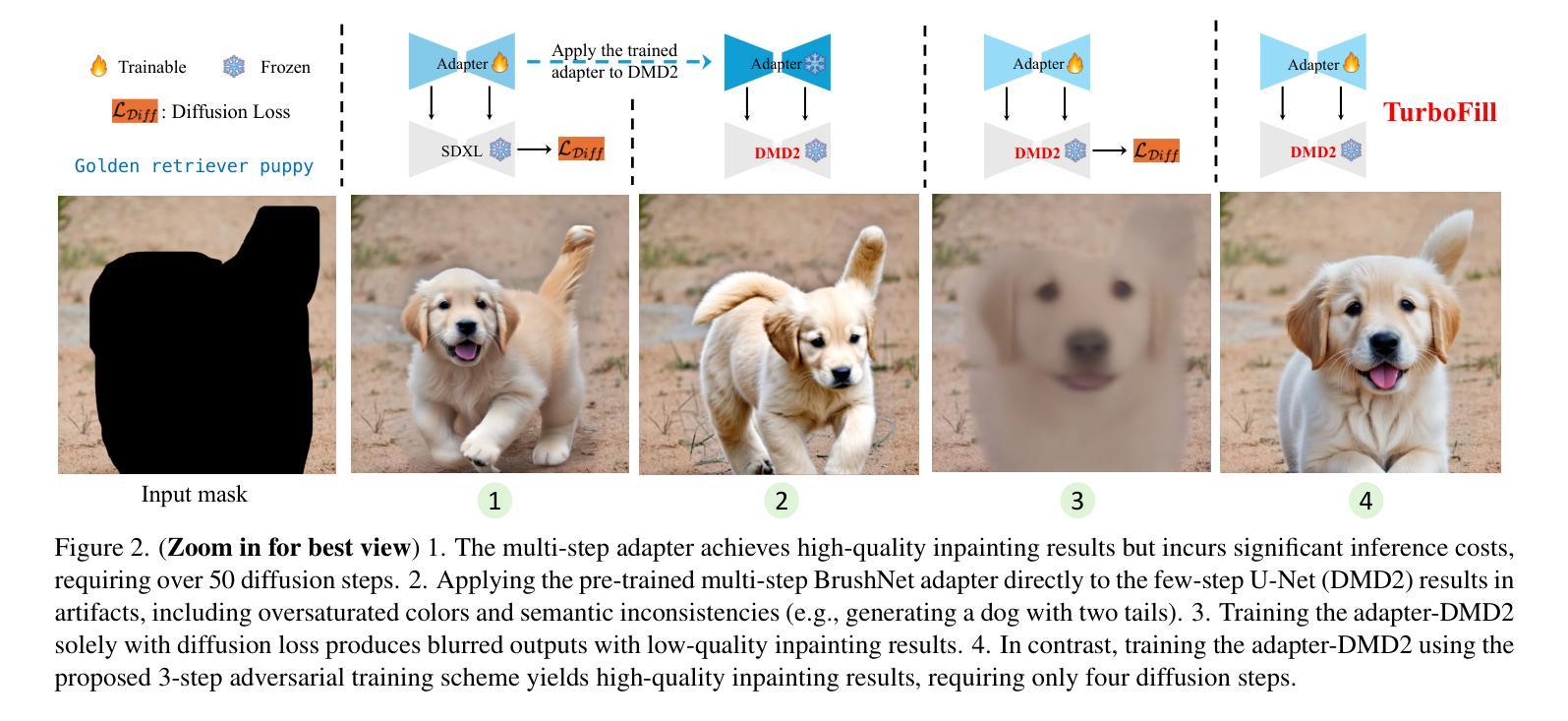
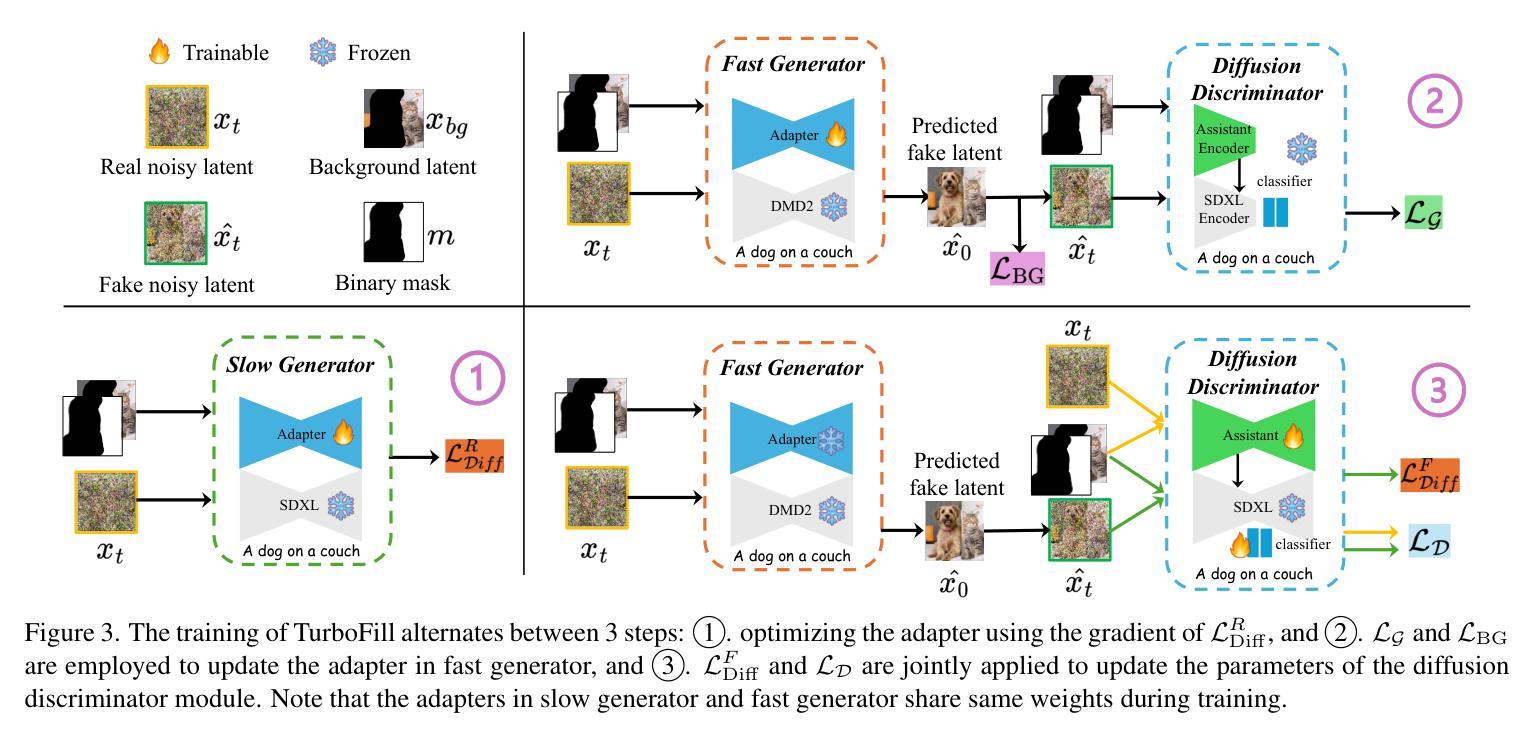
TurboFill: Adapting Few-step Text-to-image Model for Fast Image Inpainting
Authors:Liangbin Xie, Daniil Pakhomov, Zhonghao Wang, Zongze Wu, Ziyan Chen, Yuqian Zhou, Haitian Zheng, Zhifei Zhang, Zhe Lin, Jiantao Zhou, Chao Dong
This paper introduces TurboFill, a fast image inpainting model that enhances a few-step text-to-image diffusion model with an inpainting adapter for high-quality and efficient inpainting. While standard diffusion models generate high-quality results, they incur high computational costs. We overcome this by training an inpainting adapter on a few-step distilled text-to-image model, DMD2, using a novel 3-step adversarial training scheme to ensure realistic, structurally consistent, and visually harmonious inpainted regions. To evaluate TurboFill, we propose two benchmarks: DilationBench, which tests performance across mask sizes, and HumanBench, based on human feedback for complex prompts. Experiments show that TurboFill outperforms both multi-step BrushNet and few-step inpainting methods, setting a new benchmark for high-performance inpainting tasks. Our project page: https://liangbinxie.github.io/projects/TurboFill/
本文介绍了TurboFill,这是一种快速图像修复模型,它为少数几步文本到图像的扩散模型提供了一个修复适配器,以实现高质量和高效的修复。虽然标准扩散模型可以生成高质量的结果,但它们计算成本较高。我们通过使用一种新的三步对抗训练方案,在几步提炼的文本到图像模型DMD2上训练修复适配器,以产生逼真的、结构一致且视觉上和谐的修复区域来克服这一难题。为了评估TurboFill,我们提出了两个基准测试:DilationBench,用于测试不同掩膜大小的性能;HumanBench,基于人类反馈来应对复杂的提示。实验表明,TurboFill在高性能修复任务方面表现出优于多步BrushNet和少数几步修复方法的效果,为高质量修复任务树立了新的基准。我们的项目页面:https://liangbinxie.github.io/projects/TurboFill/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project webpage available at https://liangbinxie.github.io/projects/TurboFill/
Summary
本文介绍了TurboFill,这是一种快速图像修复模型。它通过在一个简化的文本到图像扩散模型上训练修复适配器,实现了高质量和高效的图像修复。该模型采用一种新的三步对抗训练方案,确保修复区域真实、结构一致且视觉和谐。实验表明,TurboFill在膨胀基准测试和人类反馈基准测试中表现优异,为高性能图像修复任务设定了新的基准。
Key Takeaways
- TurboFill是一个快速图像修复模型,基于简化的文本到图像扩散模型。
- TurboFill通过使用修复适配器提高效率和修复质量。
- 新的三步对抗训练方案确保修复区域的真实性和视觉和谐性。
- TurboFill在膨胀基准测试和人类反馈基准测试中表现优于其他方法。
- TurboFill项目提供了一个高效、高质量图像修复的解决方案。
- 该模型适用于多种图像修复任务,包括处理复杂提示的修复任务。
点此查看论文截图

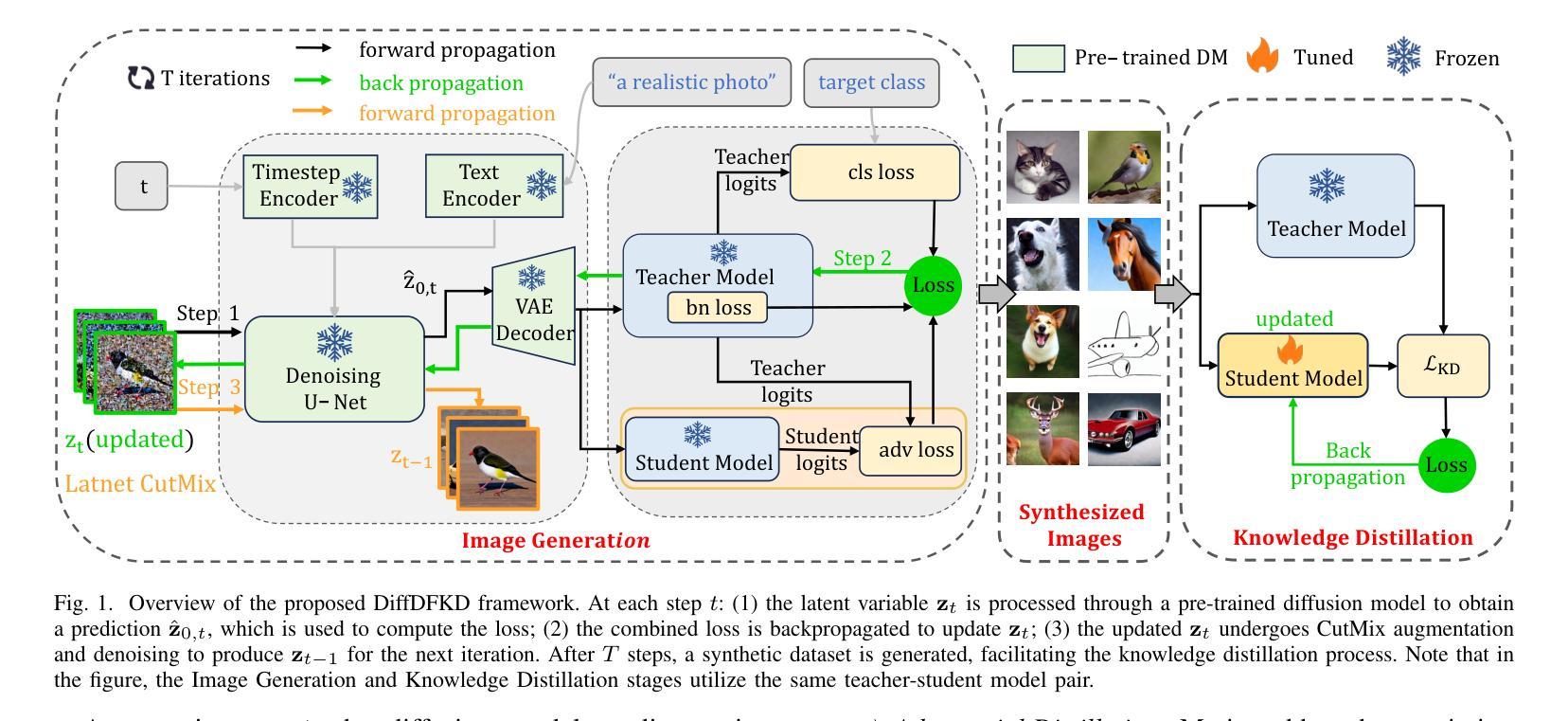
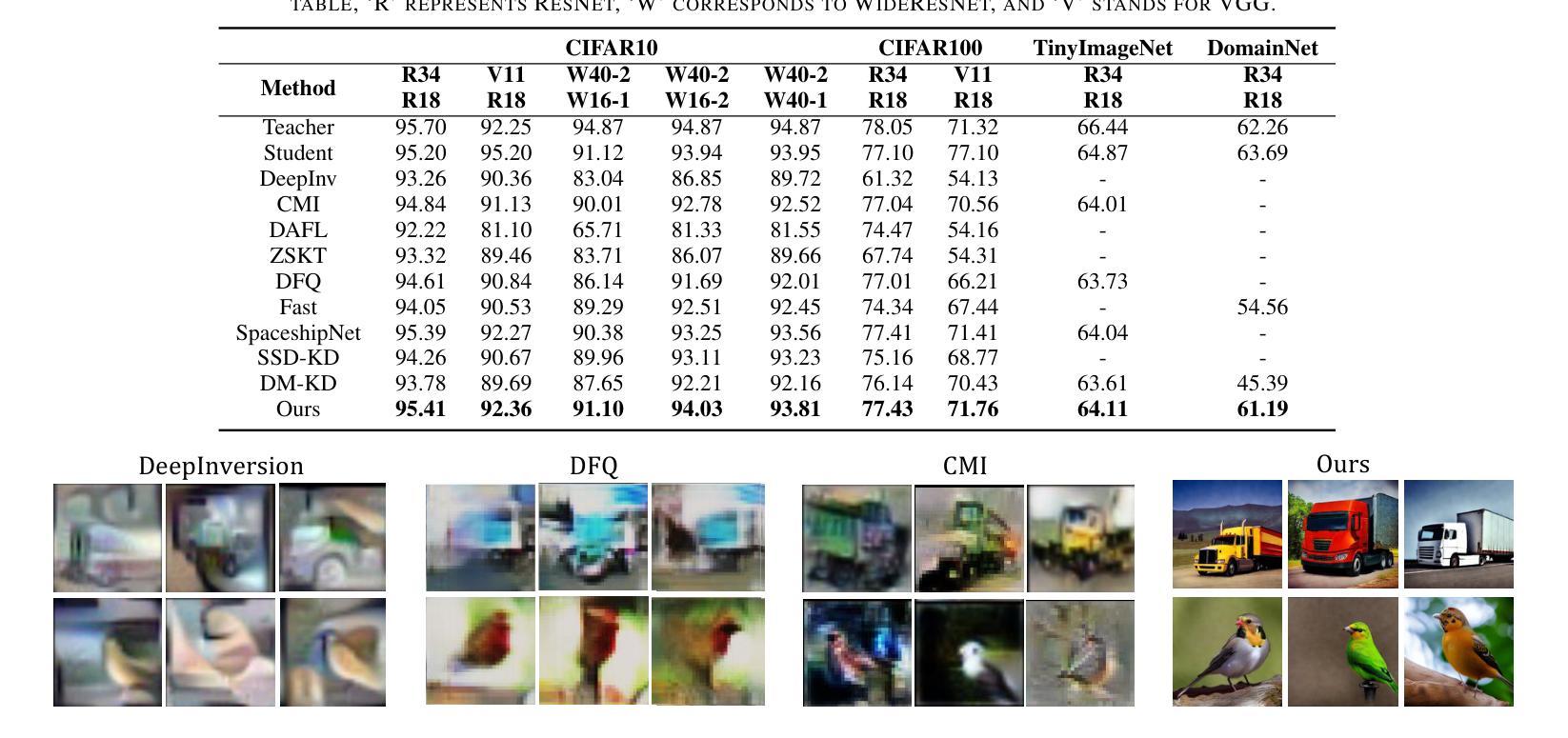
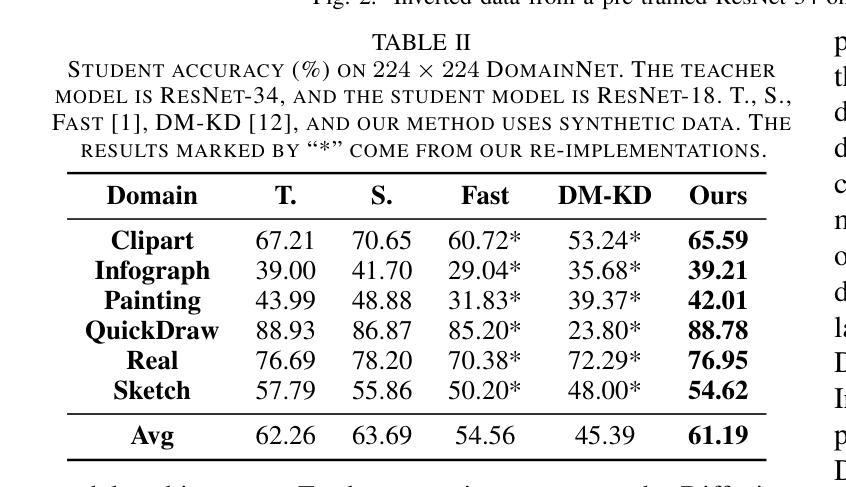
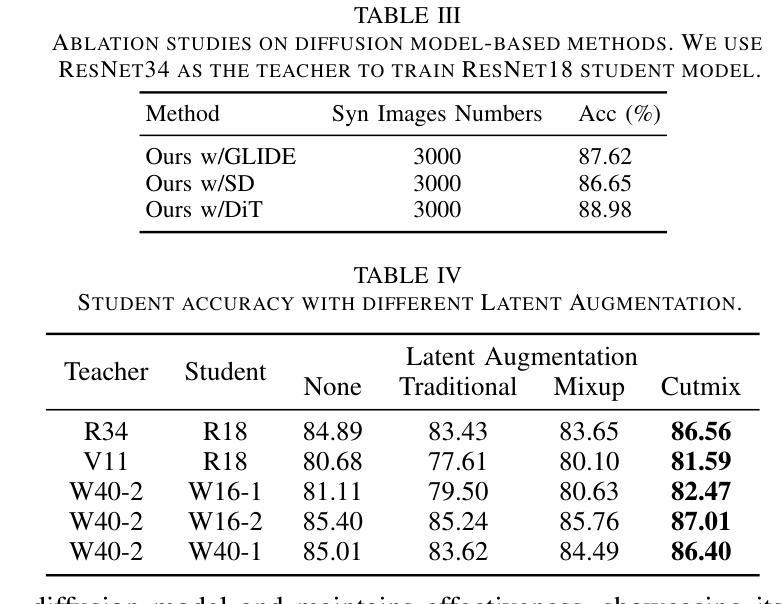
Data-free Knowledge Distillation with Diffusion Models
Authors:Xiaohua Qi, Renda Li, Long Peng, Qiang Ling, Jun Yu, Ziyi Chen, Peng Chang, Mei Han, Jing Xiao
Recently Data-Free Knowledge Distillation (DFKD) has garnered attention and can transfer knowledge from a teacher neural network to a student neural network without requiring any access to training data. Although diffusion models are adept at synthesizing high-fidelity photorealistic images across various domains, existing methods cannot be easiliy implemented to DFKD. To bridge that gap, this paper proposes a novel approach based on diffusion models, DiffDFKD. Specifically, DiffDFKD involves targeted optimizations in two key areas. Firstly, DiffDFKD utilizes valuable information from teacher models to guide the pre-trained diffusion models’ data synthesis, generating datasets that mirror the training data distribution and effectively bridge domain gaps. Secondly, to reduce computational burdens, DiffDFKD introduces Latent CutMix Augmentation, an efficient technique, to enhance the diversity of diffusion model-generated images for DFKD while preserving key attributes for effective knowledge transfer. Extensive experiments validate the efficacy of DiffDFKD, yielding state-of-the-art results exceeding existing DFKD approaches. We release our code at https://github.com/xhqi0109/DiffDFKD.
最近,无数据知识蒸馏(DFKD)引起了人们的关注,它可以从教师神经网络向学生神经网络转移知识,而无需访问任何训练数据。尽管扩散模型擅长在各种领域合成高保真照片级图像,但现有方法无法轻易应用于DFKD。为了弥补这一差距,本文提出了一种基于扩散模型的新方法,称为DiffDFKD。具体来说,DiffDFKD涉及两个关键领域的目标优化。首先,DiffDFKD利用教师模型中的有价值信息来指导预训练的扩散模型的数据合成,生成反映训练数据分布的数据集,并有效地弥合领域差距。其次,为了减少计算负担,DiffDFKD引入了潜CutMix增强技术,这是一种高效的技术,可以增强扩散模型生成图像的多样性,用于DFKD,同时保留关键属性以实现有效的知识转移。大量实验验证了DiffDFKD的有效性,其性能达到了超越现有DFKD方法的最先进水平。我们在https://github.com/xhqi0109/DiffDFKD发布了我们的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICME2025
Summary
本文介绍了基于扩散模型的Data-Free Knowledge Distillation(DFKD)新方法——DiffDFKD。该方法通过利用教师模型中的有价值信息,指导预训练的扩散模型进行数据合成,生成反映训练数据分布的数据集,有效弥域差距。同时,为提高效率,DiffDFKD引入Latent CutMix Augmentation技术,增强扩散模型生成图像的多样性,同时保留关键属性以实现有效的知识传递。该方法在实验中表现优异,超越现有DFKD方法。
Key Takeaways
- Data-Free Knowledge Distillation (DFKD)能够在无需访问训练数据的情况下,从教师神经网络向学生神经网络传递知识。
- 扩散模型能够合成高保真度的跨域图像。
- DiffDFKD是一种基于扩散模型的全新DFKD方法。
- DiffDFKD利用教师模型中的信息来指导预训练的扩散模型进行数据合成,生成反映训练数据分布的数据集。
- DiffDFKD通过生成镜像训练数据分布的数据集,有效弥域差距。
- DiffDFKD引入Latent CutMix Augmentation技术,以提高扩散模型生成图像的多样性,同时保持关键属性的传递。
- 实验证明,DiffDFKD方法表现优异,超越现有DFKD方法。
点此查看论文截图

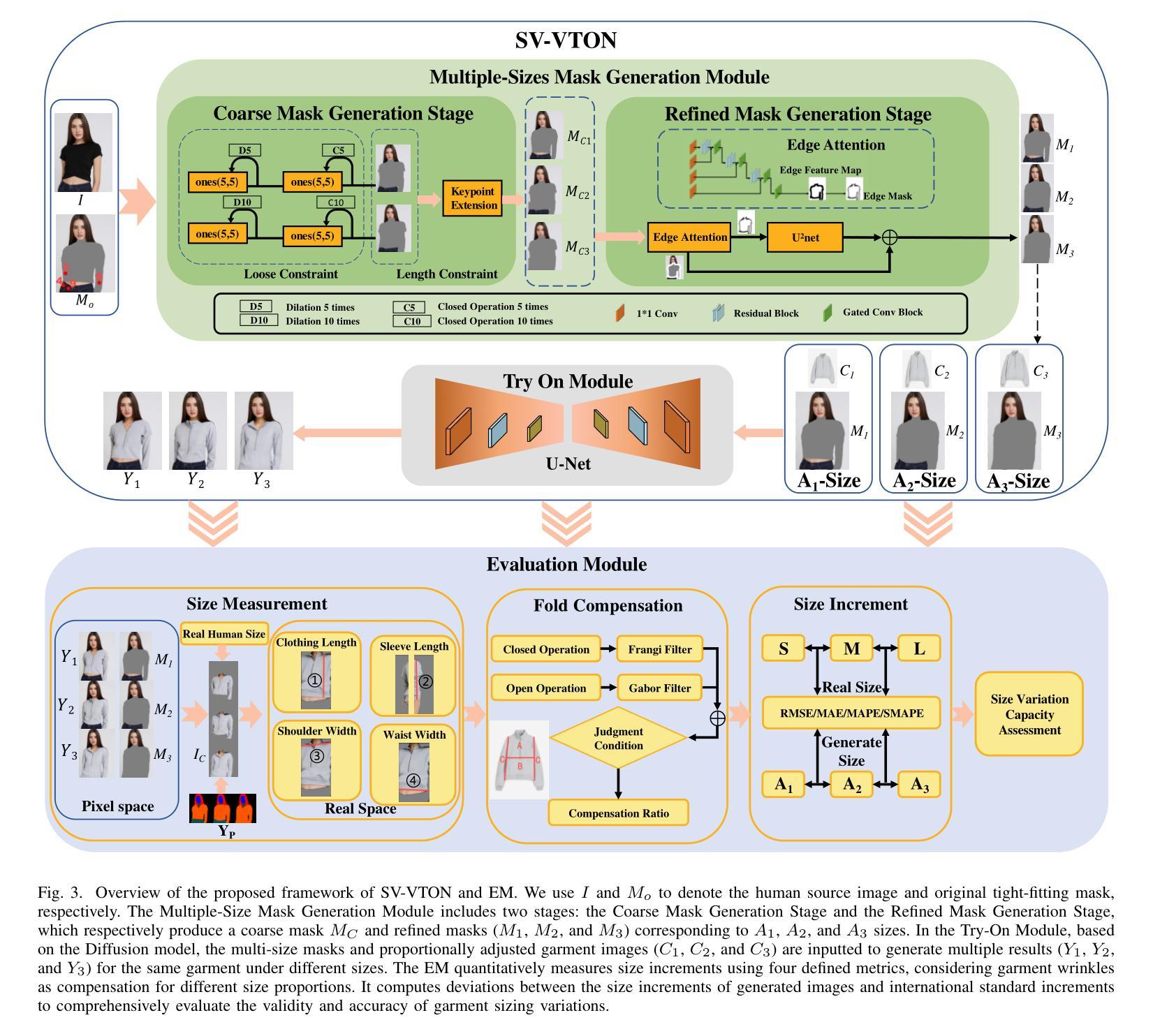
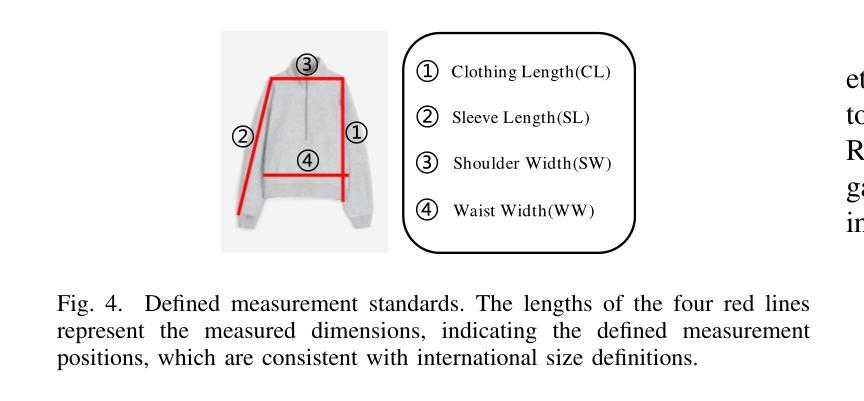
Diffusion Model-Based Size Variable Virtual Try-On Technology and Evaluation Method
Authors:Shufang Zhang, Hang Qian, Minxue Ni, Yaxuan Li, Wenxin Ding, Jun Liu
With the rapid development of e-commerce, virtual try-on technology has become an essential tool to satisfy consumers’ personalized clothing preferences. Diffusion-based virtual try-on systems aim to naturally align garments with target individuals, generating realistic and detailed try-on images. However, existing methods overlook the importance of garment size variations in meeting personalized consumer needs. To address this, we propose a novel virtual try-on method named SV-VTON, which introduces garment sizing concepts into virtual try-on tasks. The SV-VTON method first generates refined masks for multiple garment sizes, then integrates these masks with garment images at varying proportions, enabling virtual try-on simulations across different sizes. In addition, we developed a specialized size evaluation module to quantitatively assess the accuracy of size variations. This module calculates differences between generated size increments and international sizing standards, providing objective measurements of size accuracy. To further validate SV-VTON’s generalization capability across different models, we conducted experiments on multiple SOTA Diffusion models. The results demonstrate that SV-VTON consistently achieves precise multi-size virtual try-on across various SOTA models, and validates the effectiveness and rationality of the proposed method, significantly fulfilling users’ personalized multi-size virtual try-on requirements.
随着电子商务的快速发展,虚拟试穿技术已成为满足消费者个性化服装需求的重要工具。基于扩散的虚拟试穿系统旨在自然地使服装与目标个体对齐,生成逼真且详细的试穿图像。然而,现有方法忽视了服装尺寸变化在满足个性化消费者需求中的重要性。为解决此问题,我们提出了一种新型的虚拟试穿方法,名为SV-VTON,它将服装尺寸概念引入虚拟试穿任务中。SV-VTON方法首先为多种服装尺寸生成精细遮罩,然后将这些遮罩与不同比例的服装图像集成,从而实现不同尺寸的虚拟试穿模拟。此外,我们还开发了一个专门的尺寸评估模块,以定量评估尺寸变化的准确性。该模块计算生成尺寸增量与国际尺寸标准之间的差异,为尺寸精度提供客观测量。为了进一步验证SV-VTON在不同模型上的泛化能力,我们在多个最新扩散模型上进行了实验。结果表明,SV-VTON在各种最新模型上均实现了精确的多尺寸虚拟试穿,验证了所提方法的有效性和合理性,充分满足了用户的个性化多尺寸虚拟试穿需求。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于扩散模型的虚拟试穿技术,为满足消费者的个性化服装需求提供了重要工具。现有方法忽略了服装尺寸变化的重要性。我们提出了一种名为SV-VTON的新型虚拟试穿方法,引入服装尺寸概念,生成不同尺寸的精细掩膜,并将其与服装图像按不同比例融合,实现不同尺寸的虚拟试穿模拟。我们还开发了一个专门的尺寸评估模块,定量评估尺寸变化的准确性。实验表明,SV-VTON在不同SOTA扩散模型上实现了精确的多尺寸虚拟试穿,验证了方法的有效性和合理性,充分满足了用户的个性化多尺寸虚拟试穿需求。
Key Takeaways
- 虚拟试穿技术已成为满足消费者个性化服装需求的重要工具。
- 现有虚拟试穿方法忽略了服装尺寸变化的重要性。
- SV-VTON方法引入服装尺寸概念,生成不同尺寸的精细掩膜。
- SV-VTON方法将不同尺寸的掩膜与服装图像融合,实现多尺寸虚拟试穿。
- 开发了一个专门的尺寸评估模块,以定量评估尺寸变化的准确性。
- SV-VTON在不同SOTA扩散模型上实现了精确的多尺寸虚拟试穿。
点此查看论文截图


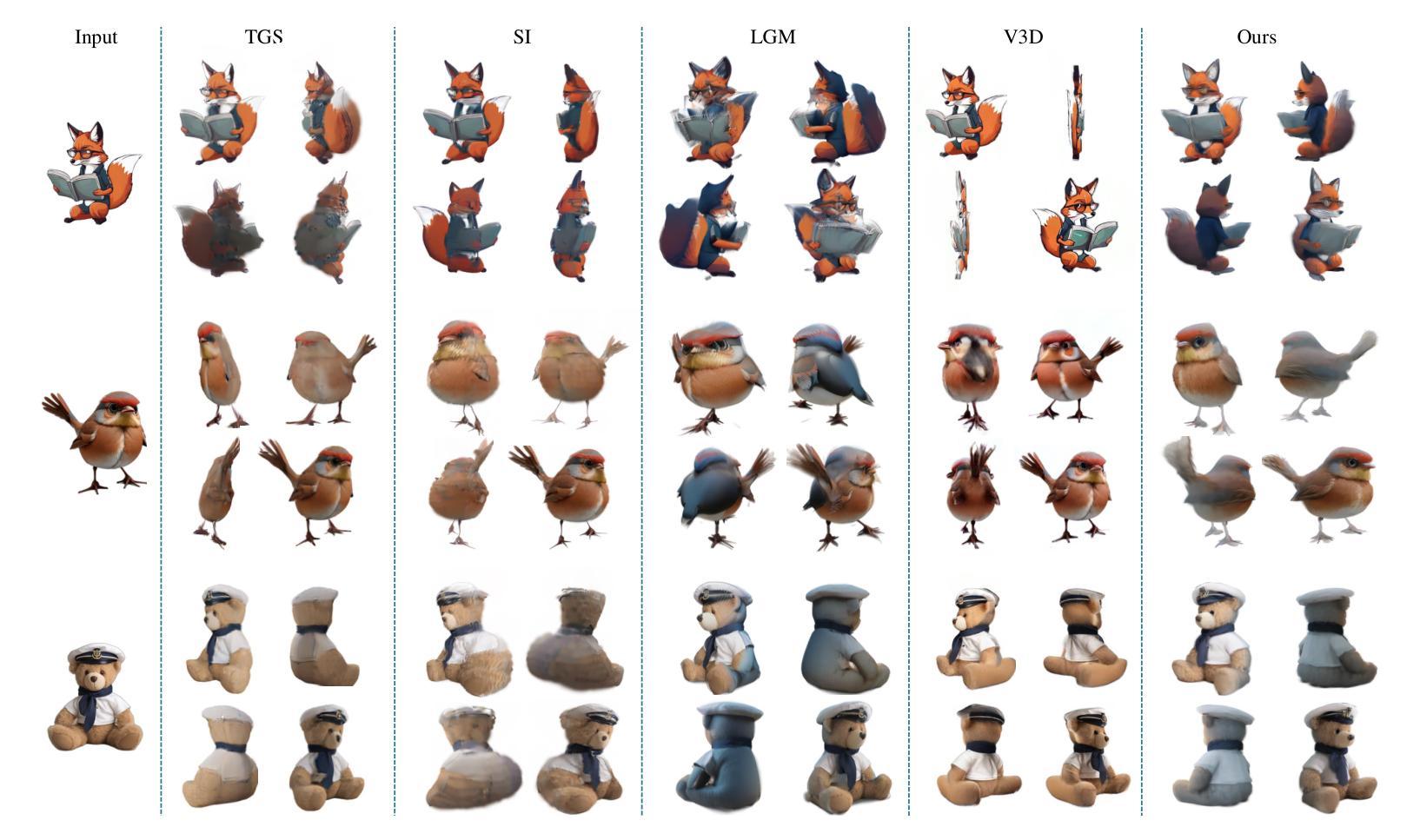
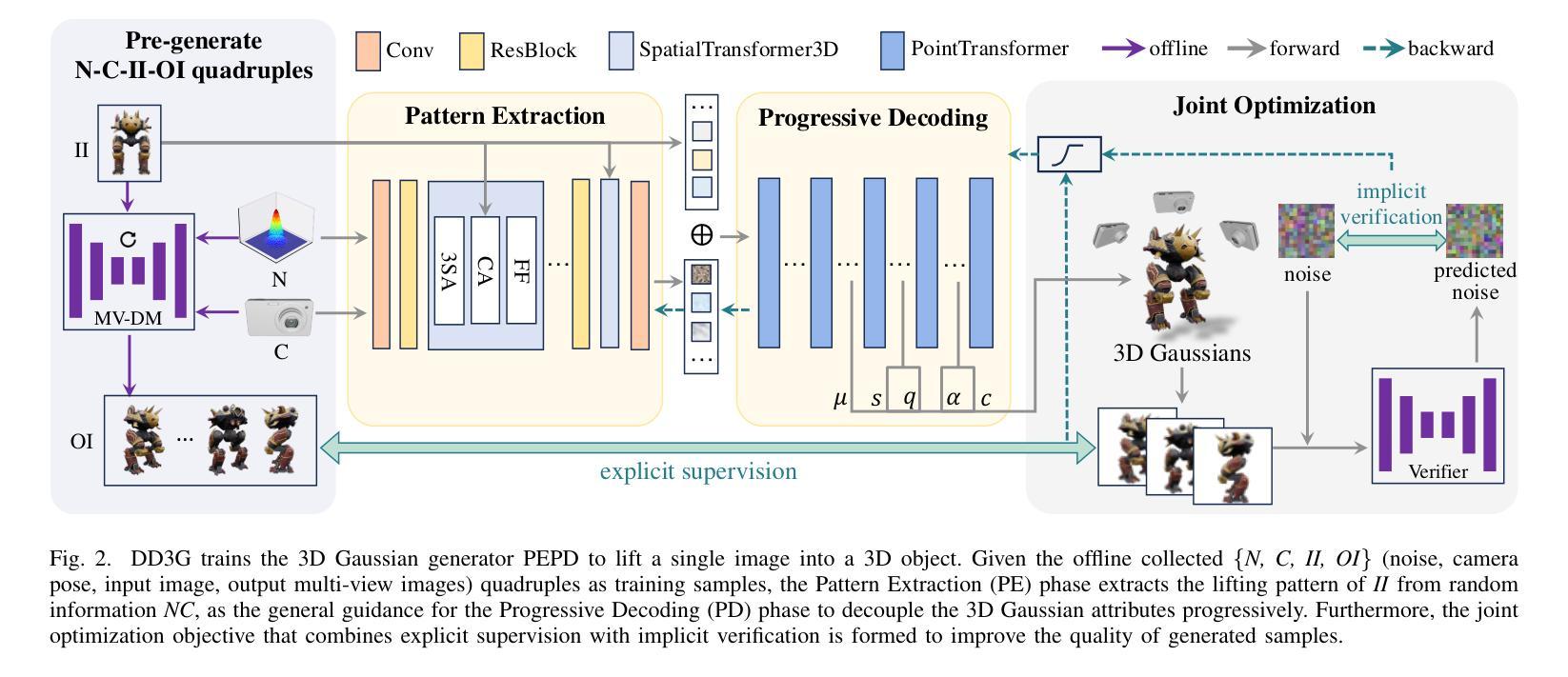
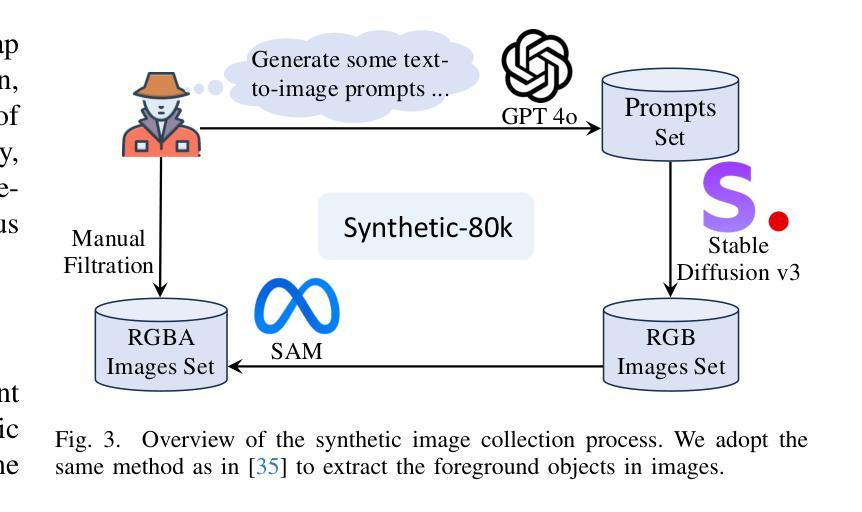
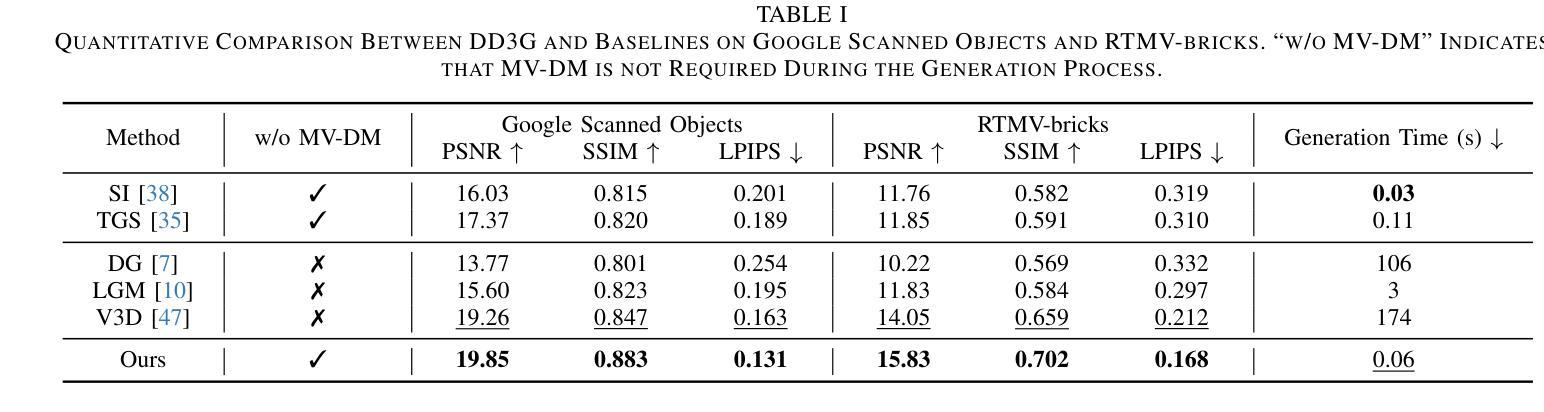
Distilling Multi-view Diffusion Models into 3D Generators
Authors:Hao Qin, Luyuan Chen, Ming Kong, Mengxu Lu, Qiang Zhu
We introduce DD3G, a formulation that Distills a multi-view Diffusion model (MV-DM) into a 3D Generator using gaussian splatting. DD3G compresses and integrates extensive visual and spatial geometric knowledge from the MV-DM by simulating its ordinary differential equation (ODE) trajectory, ensuring the distilled generator generalizes better than those trained solely on 3D data. Unlike previous amortized optimization approaches, we align the MV-DM and 3D generator representation spaces to transfer the teacher’s probabilistic flow to the student, thus avoiding inconsistencies in optimization objectives caused by probabilistic sampling. The introduction of probabilistic flow and the coupling of various attributes in 3D Gaussians introduce challenges in the generation process. To tackle this, we propose PEPD, a generator consisting of Pattern Extraction and Progressive Decoding phases, which enables efficient fusion of probabilistic flow and converts a single image into 3D Gaussians within 0.06 seconds. Furthermore, to reduce knowledge loss and overcome sparse-view supervision, we design a joint optimization objective that ensures the quality of generated samples through explicit supervision and implicit verification. Leveraging existing 2D generation models, we compile 120k high-quality RGBA images for distillation. Experiments on synthetic and public datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. Our project is available at: https://qinbaigao.github.io/DD3G_project/
我们介绍了DD3G,这是一种通过高斯拼贴技术将多视图扩散模型(MV-DM)蒸馏到3D生成器的方法。DD3G通过模拟MV-DM的常微分方程(ODE)轨迹,压缩并整合了大量的视觉和空间几何知识,确保蒸馏出的生成器比仅基于3D数据训练的生成器具有更好的泛化性能。与前期的摊销优化方法不同,我们对MV-DM和3D生成器的表示空间进行对齐,将教师的概率流传输给学生,从而避免了由概率采样引起的优化目标不一致的问题。概率流的引入和3D高斯中各种属性的耦合给生成过程带来了挑战。为解决这一问题,我们提出了PEPD生成器,它由模式提取和渐进解码两个阶段组成,能够高效地融合概率流,并在0.06秒内将单幅图像转换为3D高斯。此外,为了减少知识损失并克服稀疏视图监督,我们设计了一个联合优化目标,通过明确监督和隐性验证确保生成样本的质量。我们利用现有的2D生成模型,编译了12万张高质量RGBA图像进行蒸馏。在合成数据集和公开数据集上的实验证明了我们的方法的有效性。我们的项目在[https://qinbaigao.github.io/DD3G_project/]上可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了DD3G方法,它将多视图扩散模型(MV-DM)蒸馏到3D生成器中。通过高斯拼贴技术,DD3G能够从MV-DM中提取和整合丰富的视觉和空间几何知识,模拟其常微分方程(ODE)轨迹,确保蒸馏后的生成器比仅使用3D数据训练的生成器具有更好的泛化能力。该方法通过对齐MV-DM和3D生成器的表示空间,避免了由于概率采样导致的优化目标不一致。为应对3D高斯中的概率流和各属性耦合带来的生成挑战,提出了PEPD生成器。实验证明,该方法在合成和公开数据集上均有效。
Key Takeaways
- DD3G是一种将多视图扩散模型(MV-DM)蒸馏到3D生成器的方法。
- 通过高斯拼贴技术,DD3G能够从MV-DM中提取视觉和空间几何知识。
- DD3G模拟MV-DM的ODE轨迹,提高生成器的泛化能力。
- 对齐MV-DM和3D生成器的表示空间,避免优化目标的不一致性。
- 面对3D高斯中的概率流和各属性耦合的挑战,提出PEPD生成器。
- DD3G利用现有2D生成模型编译高质量RGBA图像用于蒸馏。
- 实验证明DD3G在合成和公开数据集上均有效。
点此查看论文截图


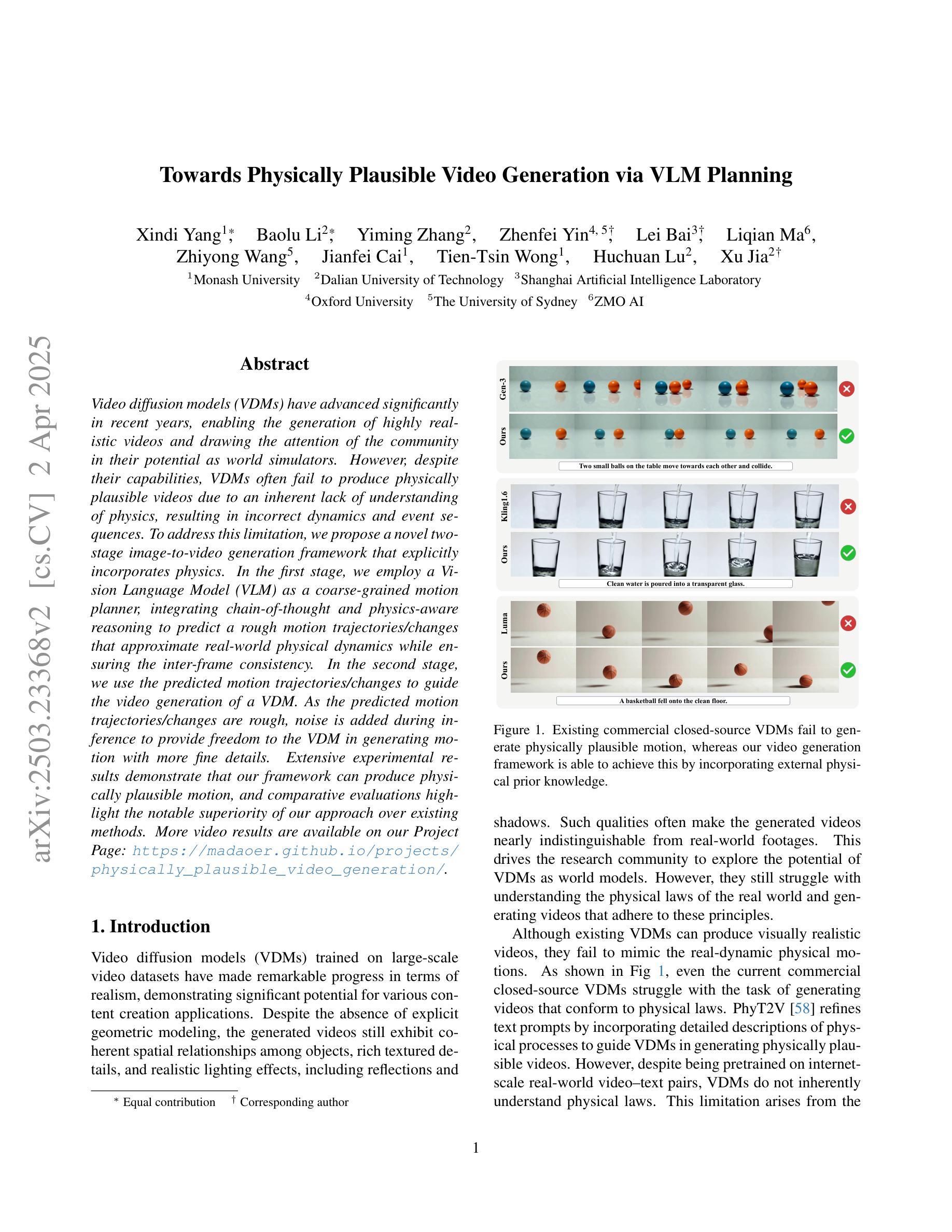
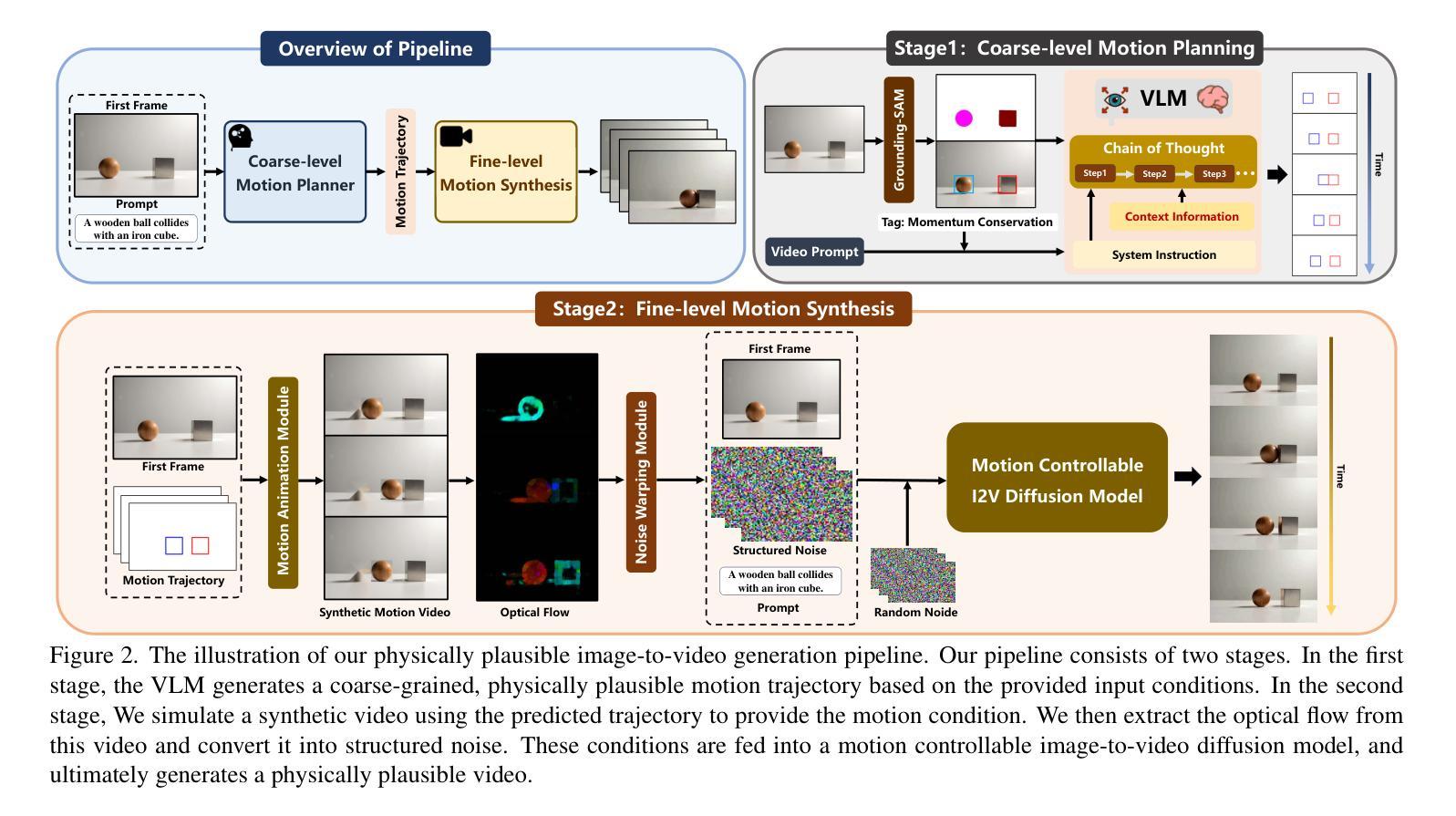
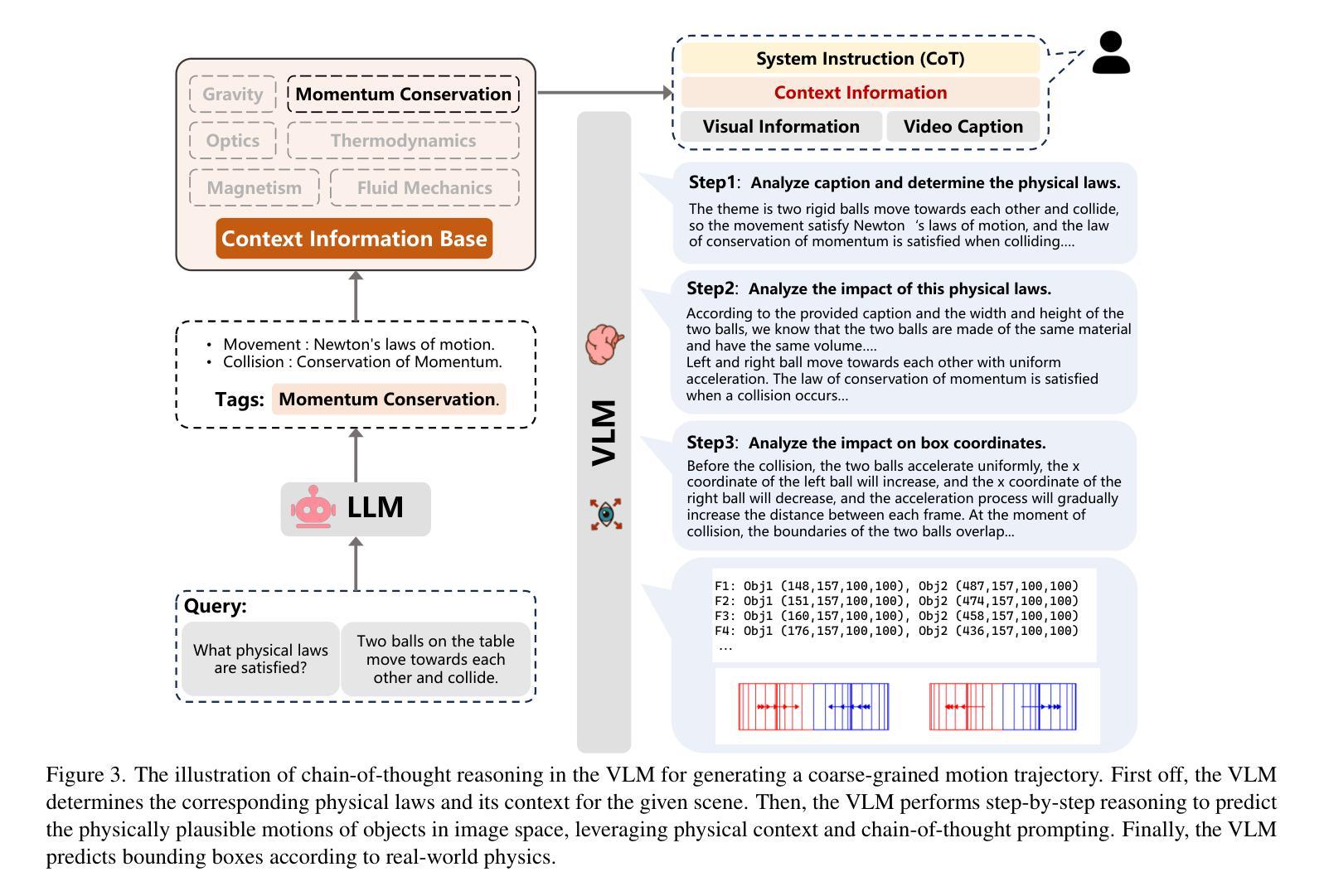
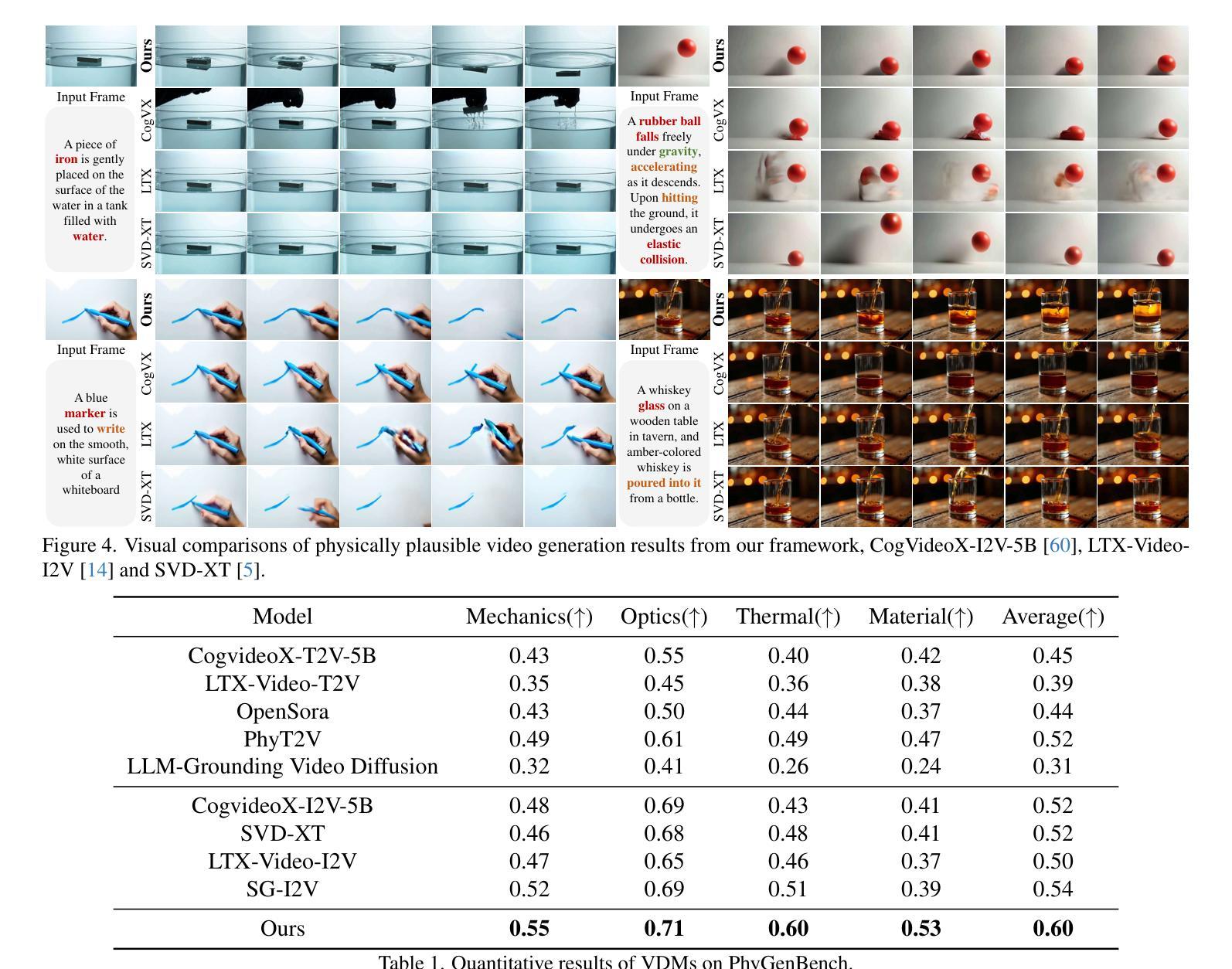
Towards Physically Plausible Video Generation via VLM Planning
Authors:Xindi Yang, Baolu Li, Yiming Zhang, Zhenfei Yin, Lei Bai, Liqian Ma, Zhiyong Wang, Jianfei Cai, Tien-Tsin Wong, Huchuan Lu, Xu Jia
Video diffusion models (VDMs) have advanced significantly in recent years, enabling the generation of highly realistic videos and drawing the attention of the community in their potential as world simulators. However, despite their capabilities, VDMs often fail to produce physically plausible videos due to an inherent lack of understanding of physics, resulting in incorrect dynamics and event sequences. To address this limitation, we propose a novel two-stage image-to-video generation framework that explicitly incorporates physics. In the first stage, we employ a Vision Language Model (VLM) as a coarse-grained motion planner, integrating chain-of-thought and physics-aware reasoning to predict a rough motion trajectories/changes that approximate real-world physical dynamics while ensuring the inter-frame consistency. In the second stage, we use the predicted motion trajectories/changes to guide the video generation of a VDM. As the predicted motion trajectories/changes are rough, noise is added during inference to provide freedom to the VDM in generating motion with more fine details. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our framework can produce physically plausible motion, and comparative evaluations highlight the notable superiority of our approach over existing methods. More video results are available on our Project Page: https://madaoer.github.io/projects/physically_plausible_video_generation.
视频扩散模型(VDMs)近年来取得了显著进展,能够生成高度逼真的视频,并作为世界模拟器引起了社区的广泛关注。然而,尽管VDMs具有强大的能力,但由于对物理的固有理解不足,它们往往无法生成物理上合理的视频,导致动态和事件序列不正确。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了一种新的两阶段图像到视频生成框架,该框架显式地结合了物理学。在第一阶段,我们采用视觉语言模型(VLM)作为粗粒度运动规划器,通过集成思考和物理感知推理来预测粗略的运动轨迹/变化,这些预测能够近似现实世界中的物理动态同时确保帧间一致性。在第二阶段,我们使用预测的运动轨迹/变化来指导VDM的视频生成。由于预测的运动轨迹/变化是粗略的,因此在推理过程中加入了噪声,为VDM生成具有更多细节的运动提供了自由度。大量的实验结果表明,我们的框架可以产生物理上合理的运动,并且对比评估凸显了我们方法在现有技术上的显著优势。更多视频结果请访问我们的项目页面:https://madaoer.github.io/projects/physically_plausible_video_generation。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 11 figures
Summary
近期视频扩散模型(VDMs)在生成高度逼真的视频方面取得了显著进展,引起了社区对其作为世界模拟器潜力的关注。然而,由于缺乏对物理的理解,VDMs往往无法生成物理上合理的视频。为解决这一问题,提出了一种新颖的两阶段图像到视频生成框架,明确融入了物理。第一阶段使用视觉语言模型(VLM)作为粗略运动规划器,结合思维链和物理感知推理,预测近似真实世界物理动态的粗糙运动轨迹/变化,确保帧间一致性。第二阶段利用预测的运动轨迹/变化引导VDM的视频生成。由于预测的运动轨迹/变化是粗略的,因此在推理过程中加入了噪声,为VDM生成具有更多细节的运动提供了自由。实验结果表明,该框架能生成物理上合理的运动,与现有方法相比具有显著优势。
Key Takeaways
- 视频扩散模型(VDMs)在生成逼真视频方面取得显著进展,但作为世界模拟器仍存在物理合理性问题。
- 提出的两阶段图像到视频生成框架融入物理,解决VDMs的固有缺陷。
- 第一阶段使用视觉语言模型(VLM)进行粗略运动规划,结合思维链和物理感知推理预测运动轨迹。
- 第二阶段利用预测的运动轨迹引导VDM生成视频。
- 预测的运动轨迹是粗略的,因此在推理过程中加入噪声,增加VDM生成运动的细节自由度。
- 实验证明该框架能生成物理上合理的运动。
点此查看论文截图
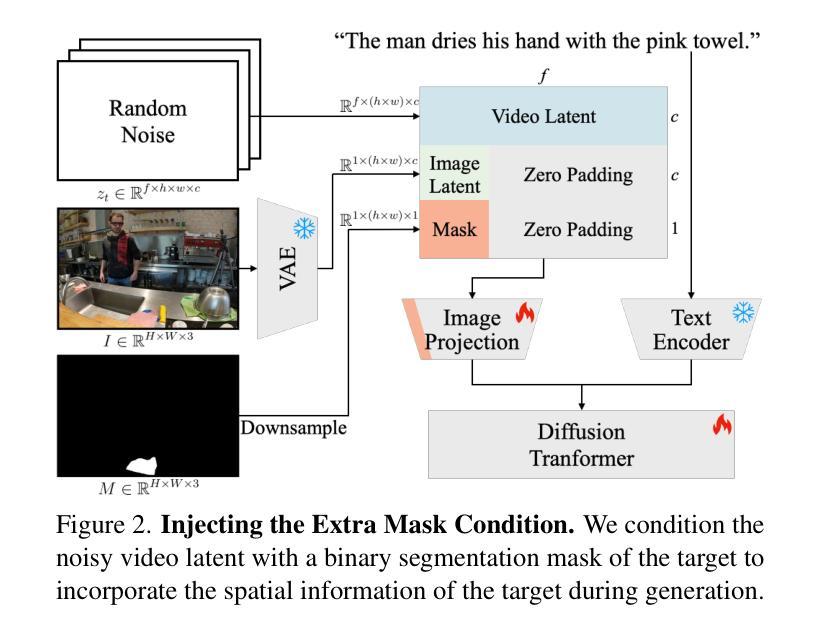
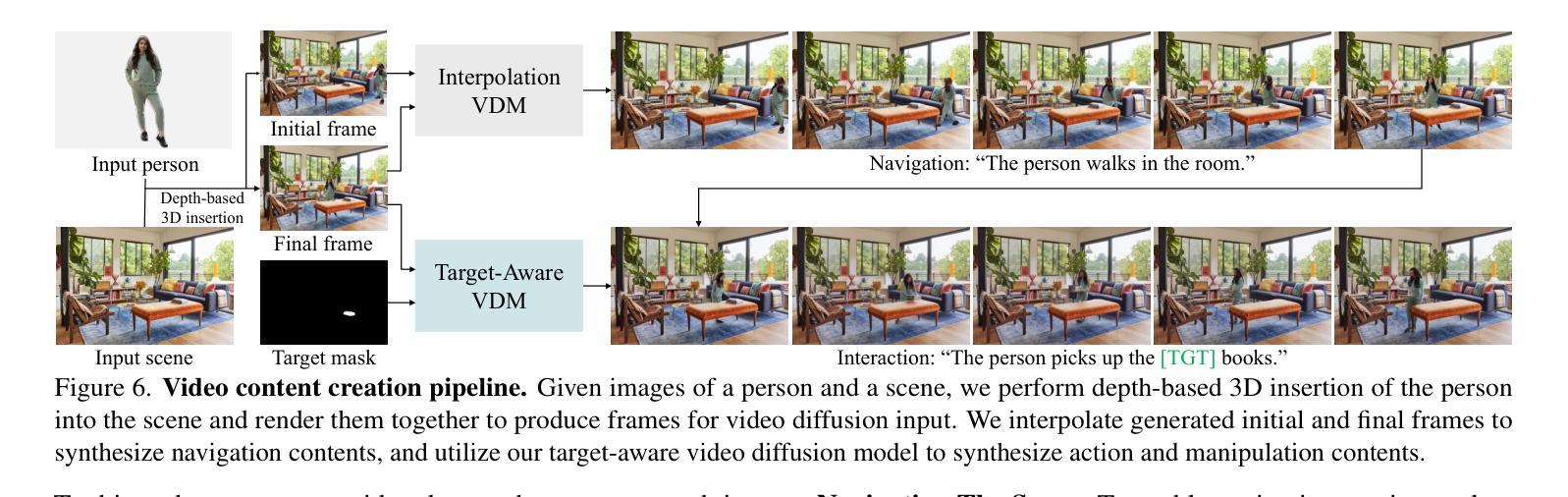
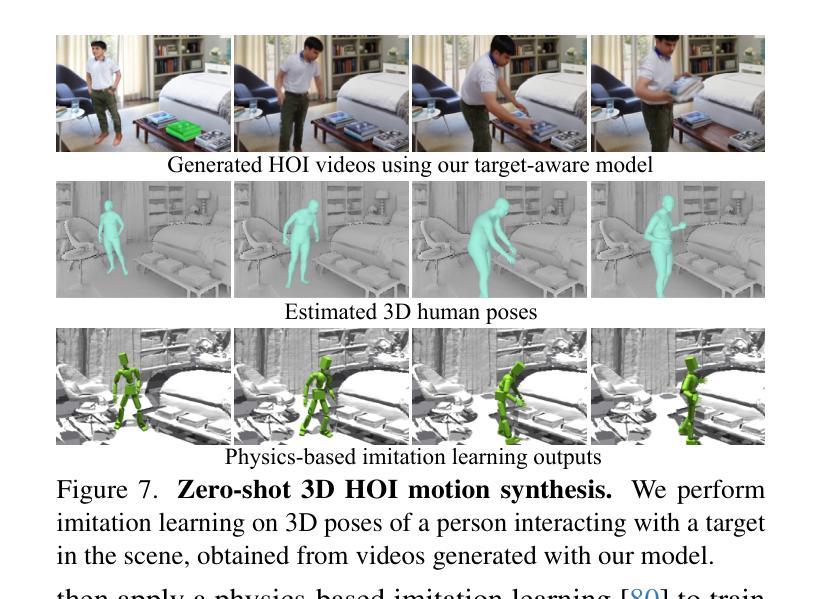
Target-Aware Video Diffusion Models
Authors:Taeksoo Kim, Hanbyul Joo
We present a target-aware video diffusion model that generates videos from an input image in which an actor interacts with a specified target while performing a desired action. The target is defined by a segmentation mask and the desired action is described via a text prompt. Unlike existing controllable image-to-video diffusion models that often rely on dense structural or motion cues to guide the actor’s movements toward the target, our target-aware model requires only a simple mask to indicate the target, leveraging the generalization capabilities of pretrained models to produce plausible actions. This makes our method particularly effective for human-object interaction (HOI) scenarios, where providing precise action guidance is challenging, and further enables the use of video diffusion models for high-level action planning in applications such as robotics. We build our target-aware model by extending a baseline model to incorporate the target mask as an additional input. To enforce target awareness, we introduce a special token that encodes the target’s spatial information within the text prompt. We then fine-tune the model with our curated dataset using a novel cross-attention loss that aligns the cross-attention maps associated with this token with the input target mask. To further improve performance, we selectively apply this loss to the most semantically relevant transformer blocks and attention regions. Experimental results show that our target-aware model outperforms existing solutions in generating videos where actors interact accurately with the specified targets. We further demonstrate its efficacy in two downstream applications: video content creation and zero-shot 3D HOI motion synthesis.
我们提出了一种目标感知视频扩散模型,该模型从输入图像生成视频,其中演员在与指定目标互动时执行指定动作。目标由分割掩膜定义,所需动作则通过文本提示描述。与现有的可控图像到视频扩散模型不同,这些模型通常依赖于密集的结构或运动线索来引导演员的动作朝向目标,我们的目标感知模型仅需要简单的掩膜来指示目标,并利用预训练模型的泛化能力来产生合理的动作。这使得我们的方法在人机交互(HOI)场景中特别有效,在这些场景中,提供精确的动作指导是具有挑战性的,并且进一步启用了视频扩散模型在诸如机器人技术的高级动作规划中的应用。我们通过将目标掩膜作为附加输入来扩展基线模型,构建了我们的目标感知模型。为了强制实施目标感知,我们引入了一个特殊令牌,该令牌在文本提示中编码目标的空间信息。然后,我们使用新的跨注意损失来微调我们的数据集上的模型,该损失将与此令牌相关的跨注意图与输入目标掩膜对齐。为了进一步提高性能,我们选择性地将此损失应用于最语义相关的变压器块和注意区域。实验结果表明,我们的目标感知模型在生成演员与指定目标准确互动的视频方面优于现有解决方案。我们进一步通过两个下游应用证明了其有效性:视频内容创建和零射击3D人机交互运动合成。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The project page is available at https://taeksuu.github.io/tavid/
摘要
本文提出了一种目标感知视频扩散模型,该模型能够从输入图像中生成视频,其中演员与指定目标进行交互并执行指定动作。目标通过分割掩膜定义,所需动作则通过文本提示描述。与现有的可控图像到视频扩散模型不同,这些模型通常依赖于密集的结构或运动线索来引导演员向目标移动,我们的目标感知模型仅需要简单的掩膜来指示目标,并利用预训练模型的泛化能力来产生可行动作。这使得我们的方法在人机交互场景中特别有效,其中提供精确的动作指导具有挑战性,并且进一步使视频扩散模型在诸如机器人技术的高级动作规划应用中使用成为可能。我们通过将目标掩膜作为附加输入来扩展基线模型构建我们的目标感知模型。为了强制执行目标感知,我们引入一个特殊令牌,该令牌在文本提示中编码目标的空间信息。然后,我们使用新的跨注意力损失来微调模型,该损失使我们的跨注意力图与输入目标掩膜相关联。为了进一步提高性能,我们选择性地将此损失应用于最语义相关的变压器块和注意力区域。实验结果表明,我们的目标感知模型在生成演员与指定目标准确交互的视频方面优于现有解决方案。我们还通过两个下游应用进一步证明了其有效性:视频内容创建和零镜头3D人机交互运动合成。
关键见解
- 提出了一种目标感知视频扩散模型,能够基于输入图像生成视频,其中演员与指定目标进行交互。
- 仅通过简单掩膜定义目标,无需密集的结构或运动线索。
- 利用预训练模型的泛化能力产生可行动作,特别适用于人机交互场景。
- 通过引入特殊令牌和跨注意力损失机制来强化模型对目标的认识。
- 选择性地应用损失以提高最语义相关部分的性能。
- 在生成演员与指定目标准确交互的视频方面,优于现有解决方案。
点此查看论文截图


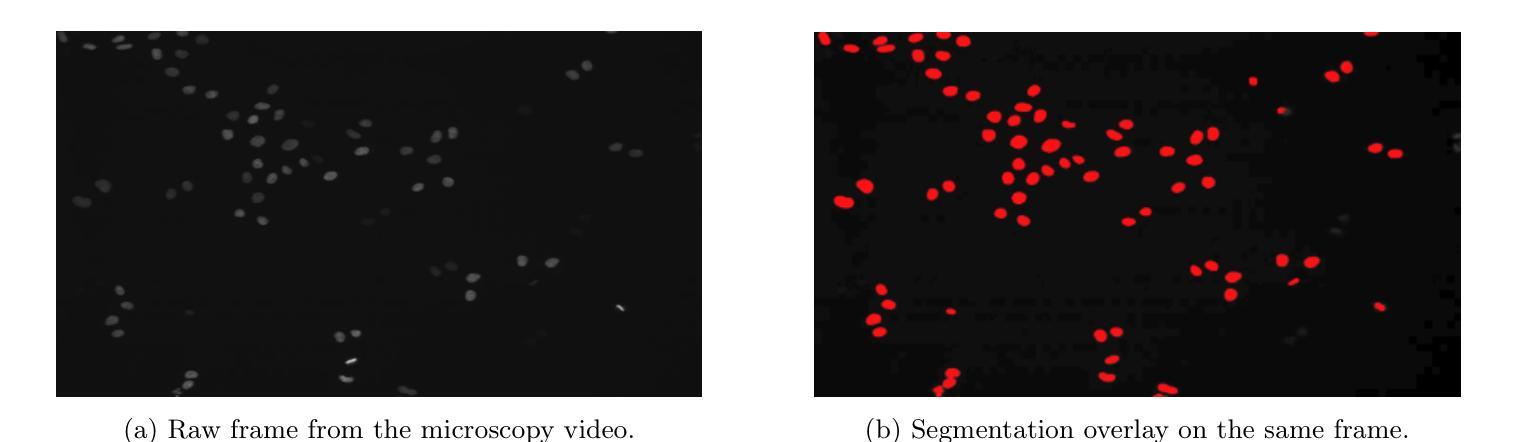
Adapting Video Diffusion Models for Time-Lapse Microscopy
Authors:Alexander Holmberg, Nils Mechtel, Wei Ouyang
We present a domain adaptation of video diffusion models to generate highly realistic time-lapse microscopy videos of cell division in HeLa cells. Although state-of-the-art generative video models have advanced significantly for natural videos, they remain underexplored in microscopy domains. To address this gap, we fine-tune a pretrained video diffusion model on microscopy-specific sequences, exploring three conditioning strategies: (1) text prompts derived from numeric phenotypic measurements (e.g., proliferation rates, migration speeds, cell-death frequencies), (2) direct numeric embeddings of phenotype scores, and (3) image-conditioned generation, where an initial microscopy frame is extended into a complete video sequence. Evaluation using biologically meaningful morphological, proliferation, and migration metrics demonstrates that fine-tuning substantially improves realism and accurately captures critical cellular behaviors such as mitosis and migration. Notably, the fine-tuned model also generalizes beyond the training horizon, generating coherent cell dynamics even in extended sequences. However, precisely controlling specific phenotypic characteristics remains challenging, highlighting opportunities for future work to enhance conditioning methods. Our results demonstrate the potential for domain-specific fine-tuning of generative video models to produce biologically plausible synthetic microscopy data, supporting applications such as in-silico hypothesis testing and data augmentation.
我们呈现了一个视频扩散模型的领域适应性应用,用于生成高度逼真的细胞分裂时间推移显微镜视频。尽管最先进的生成式视频模型在自然视频方面取得了显著进展,但在显微镜领域仍然研究不足。为了填补这一空白,我们对预训练的视频扩散模型进行微调,以适应显微镜特定序列,探索了三种条件策略:(1)根据数值表型测量得出的文本提示(例如增殖率、迁移速度、细胞死亡频率);(2)直接对表型分数进行数值嵌入;(3)图像条件下的生成,其中将初始显微镜图像扩展为一个完整的视频序列。使用具有生物学意义的形态学、增殖和迁移指标的评估表明,微调大大提高了真实性,并准确捕捉了关键的细胞行为,如分裂和迁移。值得注意的是,经过微调后的模型在训练范围之外也具有通用性,即使在扩展序列中也能产生连贯的细胞动态。然而,精确控制特定的表型特征仍然具有挑战性,这突显了未来增强条件方法的机遇。我们的结果展示了领域特定微调生成视频模型的潜力,可以生成生物学上合理的合成显微镜数据,支持诸如体外假设测试和数据增强等应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了对视频扩散模型的领域适应,以生成高度逼真的时间推移显微镜视频,展示细胞分裂过程。文章解决了当前主流生成视频模型在显微镜领域探索不足的问题,通过对预训练的视频扩散模型进行微调,探索了三种条件策略:1)来自数值表型测量的文本提示;2)现象型评分的直接数值嵌入;3)图像条件生成。评估显示,微调后模型更能真实反映细胞行为,如分裂和迁移等。虽然模型能够生成连贯的细胞动态,但在精确控制特定表型特征方面仍存在挑战。本文展示了领域特定微调生成视频模型的潜力,可产生生物学上合理的显微镜数据,支持假设测试和数据增强等应用。
Key Takeaways
- 本文实现了视频扩散模型的领域适应,生成逼真的时间推移显微镜视频,展示细胞分裂过程。
- 通过微调预训练的视频扩散模型,探索了三种条件策略来适应显微镜数据特性。
- 评估表明微调模型在捕捉细胞行为方面更为真实,如分裂和迁移等。
- 模型的通用性良好,能够在训练范围之外生成连贯的细胞动态序列。
- 尽管模型表现优异,但在精确控制特定表型特征方面仍存在挑战,需要未来改进。
- 领域特定微调生成视频模型具有潜力,能够产生生物学上合理的合成显微镜数据。
点此查看论文截图

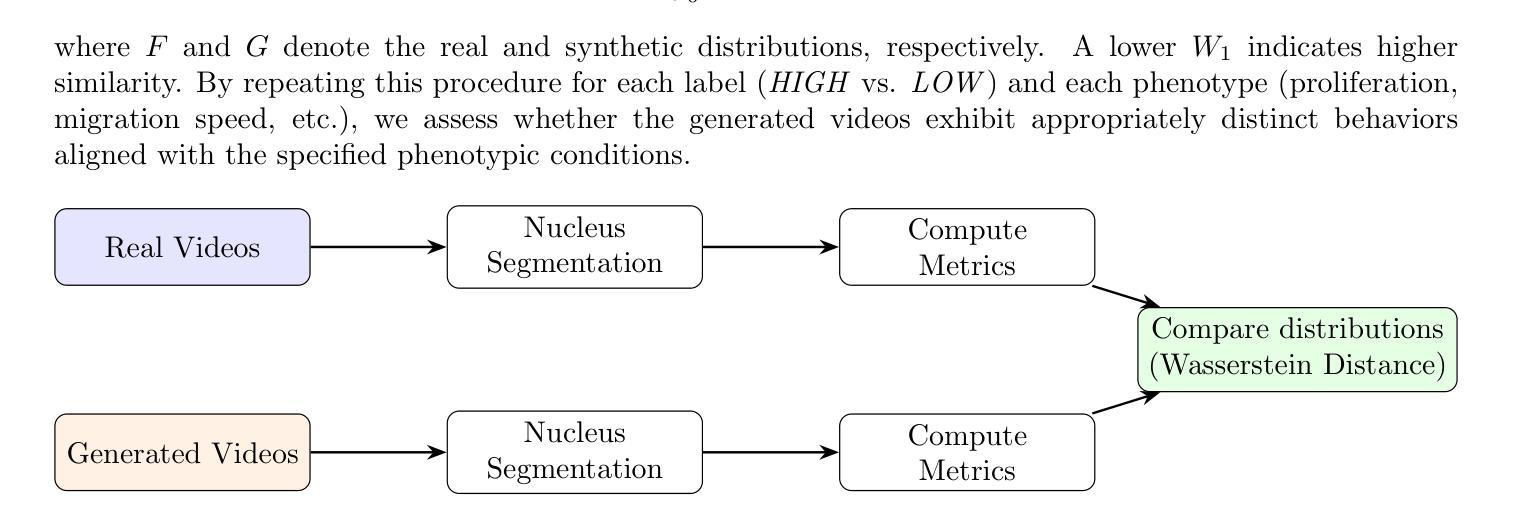
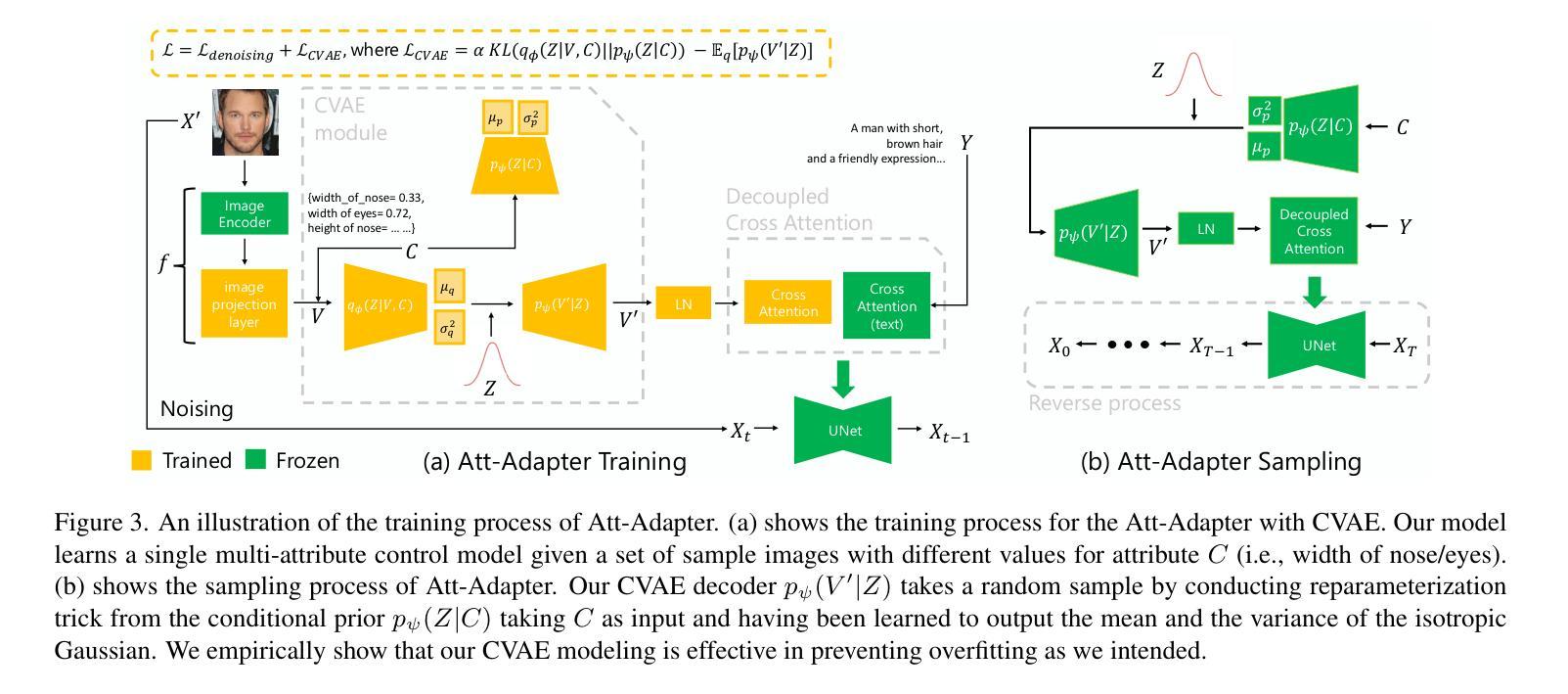
Att-Adapter: A Robust and Precise Domain-Specific Multi-Attributes T2I Diffusion Adapter via Conditional Variational Autoencoder
Authors:Wonwoong Cho, Yan-Ying Chen, Matthew Klenk, David I. Inouye, Yanxia Zhang
Text-to-Image (T2I) Diffusion Models have achieved remarkable performance in generating high quality images. However, enabling precise control of continuous attributes, especially multiple attributes simultaneously, in a new domain (e.g., numeric values like eye openness or car width) with text-only guidance remains a significant challenge. To address this, we introduce the Attribute (Att) Adapter, a novel plug-and-play module designed to enable fine-grained, multi-attributes control in pretrained diffusion models. Our approach learns a single control adapter from a set of sample images that can be unpaired and contain multiple visual attributes. The Att-Adapter leverages the decoupled cross attention module to naturally harmonize the multiple domain attributes with text conditioning. We further introduce Conditional Variational Autoencoder (CVAE) to the Att-Adapter to mitigate overfitting, matching the diverse nature of the visual world. Evaluations on two public datasets show that Att-Adapter outperforms all LoRA-based baselines in controlling continuous attributes. Additionally, our method enables a broader control range and also improves disentanglement across multiple attributes, surpassing StyleGAN-based techniques. Notably, Att-Adapter is flexible, requiring no paired synthetic data for training, and is easily scalable to multiple attributes within a single model.
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在生成高质量图像方面取得了显著的性能。然而,如何在新的领域(如眼开度或汽车宽度等数值)实现连续属性的精确控制,特别是同时控制多个属性,仅通过文本指导仍是一个巨大挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了属性(Att)适配器,这是一种新型即插即用模块,旨在在预训练的扩散模型中实现精细的多属性控制。我们的方法从一组样本图像中学习单个控制适配器,这些图像可以是未配对的,并包含多个视觉属性。Att-Adapter利用解耦交叉注意力模块,自然地协调多个域属性与文本条件。我们进一步将条件变分自动编码器(CVAE)引入到Att-Adapter中,以减轻过拟合问题,适应视觉世界的多样性。在两个公共数据集上的评估表明,Att-Adapter在控制连续属性方面优于所有基于LoRA的基线。此外,我们的方法扩大了控制范围,并改进了多个属性之间的解纠缠,超越了StyleGAN技术。值得注意的是,Att-Adapter非常灵活,无需配对合成数据进行训练,并且很容易在单个模型中扩展到多个属性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在生成高质量图像方面取得了显著成效,但在新领域实现连续属性(如眼睛开合或汽车宽度等数值)的精确控制,尤其是同时控制多个属性时,仍面临挑战。为此,我们引入了属性适配器(Att-Adapter),这是一种新型即插即用模块,旨在在预训练的扩散模型中实现精细的多属性控制。该方法从一组未配对的包含多个视觉属性的样本图像中学习单个控制适配器。Att-Adapter利用解耦交叉注意力模块,自然地协调多个域属性与文本条件。为进一步缓解过拟合问题并适应视觉世界的多样性,我们还将条件变分自编码器(CVAE)引入Att-Adapter。在公共数据集上的评估表明,Att-Adapter在控制连续属性方面优于所有基于LoRA的方法。此外,我们的方法具有更广泛的控制范围和改进的多属性解纠缠性能,超越了StyleGAN技术。值得一提的是,Att-Adapter非常灵活,无需配对合成数据进行训练,且可以轻松扩展到单个模型内的多个属性。
Key Takeaways
- T2I Diffusion Models在生成高质量图像方面表现出色。
- 实现连续属性的精确控制,特别是在新领域中,仍然是一个挑战。
- 引入了Attribute (Att) Adapter,一种新型即插即用模块,用于预训练的扩散模型中的精细多属性控制。
- Att-Adapter能从未配对的样本图像中学习,并处理多个视觉属性。
- 利用解耦交叉注意力模块和条件变分自编码器(CVAE)增强性能。
- 在公共数据集上的评估显示,Att-Adapter在控制连续属性方面优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

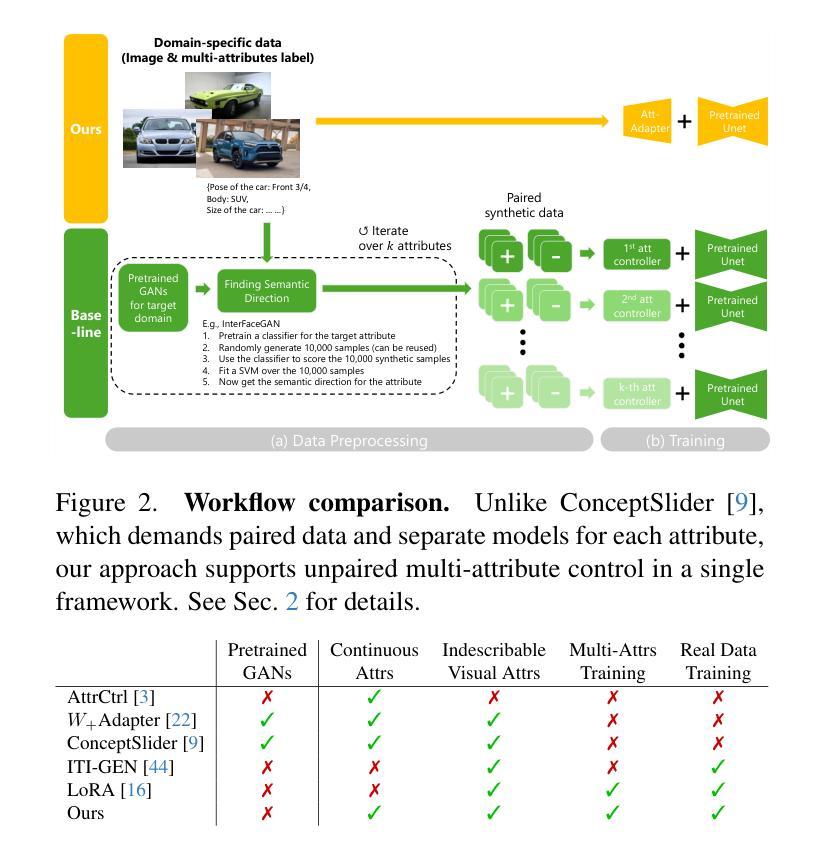

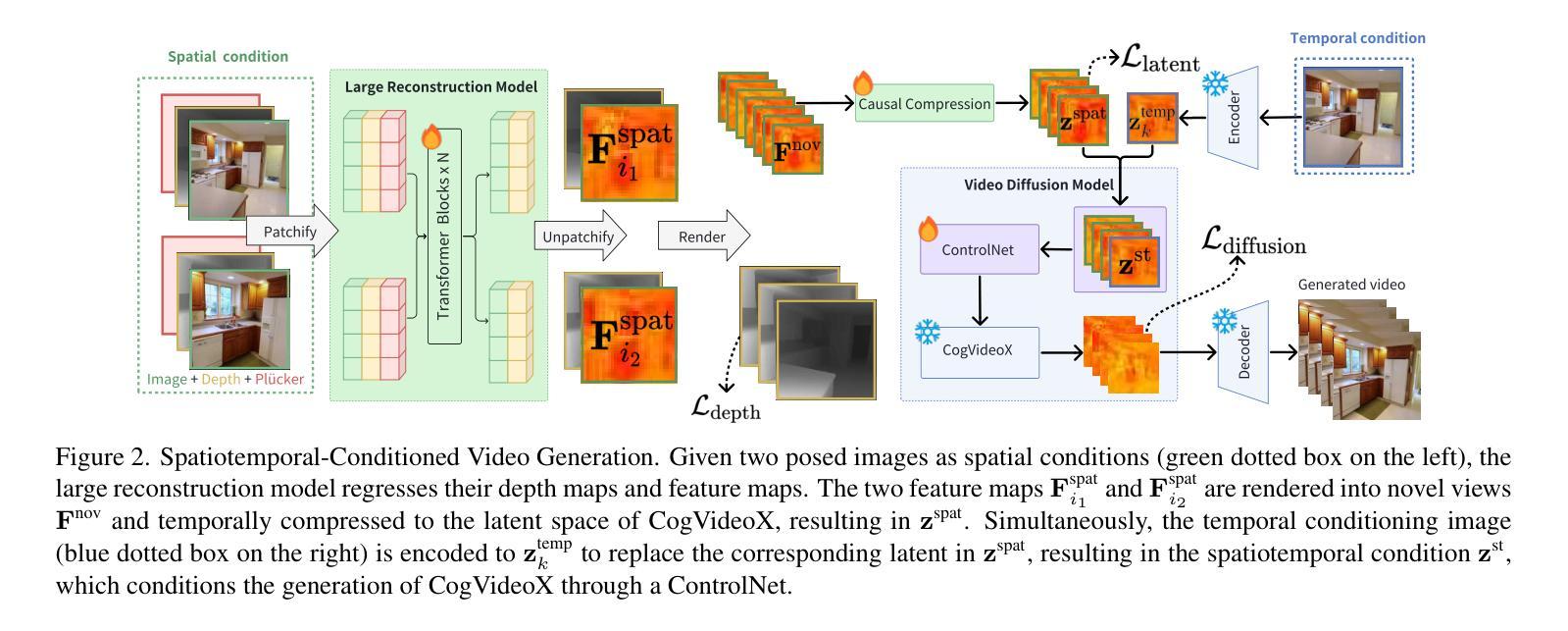
StarGen: A Spatiotemporal Autoregression Framework with Video Diffusion Model for Scalable and Controllable Scene Generation
Authors:Shangjin Zhai, Zhichao Ye, Jialin Liu, Weijian Xie, Jiaqi Hu, Zhen Peng, Hua Xue, Danpeng Chen, Xiaomeng Wang, Lei Yang, Nan Wang, Haomin Liu, Guofeng Zhang
Recent advances in large reconstruction and generative models have significantly improved scene reconstruction and novel view generation. However, due to compute limitations, each inference with these large models is confined to a small area, making long-range consistent scene generation challenging. To address this, we propose StarGen, a novel framework that employs a pre-trained video diffusion model in an autoregressive manner for long-range scene generation. The generation of each video clip is conditioned on the 3D warping of spatially adjacent images and the temporally overlapping image from previously generated clips, improving spatiotemporal consistency in long-range scene generation with precise pose control. The spatiotemporal condition is compatible with various input conditions, facilitating diverse tasks, including sparse view interpolation, perpetual view generation, and layout-conditioned city generation. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations demonstrate StarGen’s superior scalability, fidelity, and pose accuracy compared to state-of-the-art methods. Project page: https://zju3dv.github.io/StarGen.
近期重建和生成模型的进展显著提高了场景重建和新颖视角生成的能力。然而,由于计算限制,这些大型模型的每次推理都局限于一个小区域,使得大范围一致的场景生成面临挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了StarGen,这是一个采用预训练视频扩散模型的新型框架,以自回归的方式用于大范围场景生成。每个视频剪辑的生成都是以空间相邻图像的3D扭曲和先前生成的剪辑中时间上重叠的图像为条件,提高了大范围场景生成中的时空一致性,并实现了精确的姿势控制。时空条件与各种输入条件兼容,促进了包括稀疏视图插值、永久视图生成和布局控制的城市生成在内的各种任务。定量和定性评估表明,StarGen在可扩展性、保真度和姿态准确性方面优于最先进的方法。项目页面:https://zju3dv.github.io/StarGen。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型重建和生成模型的最新进展极大地提高了场景重建和新颖视角生成的能力。然而,由于计算限制,这些大型模型的每次推理都局限于小范围,使得长距离一致场景生成面临挑战。为此,我们提出StarGen框架,采用预训练视频扩散模型进行长距离场景生成的自回归方式。每个视频片段的生成都是以空间相邻图像的3D变形和先前生成片段的时间重叠图像为条件,提高了长距离场景生成中的时空一致性,并实现了精确的姿态控制。StarGen的时空条件与各种输入条件兼容,可用于稀疏视图插值、永久视图生成和布局控制城市生成等任务。评估和测试显示,StarGen在可扩展性、保真度和姿态准确性方面优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 大型重建和生成模型的最新进展促进了场景重建和新颖视角生成的发展。
- 由于计算限制,现有模型在长距离一致场景生成方面面临挑战。
- StarGen框架采用预训练视频扩散模型进行自回归方式,解决了这一问题。
- StarGen利用时空条件,结合空间相邻图像的3D变形和时间重叠图像,提高长距离场景生成的时空一致性。
- StarGen具备精确的姿态控制能力。
- StarGen的时空条件兼容多种输入条件,支持多种任务,如稀疏视图插值、永久视图生成和布局控制城市生成。
点此查看论文截图

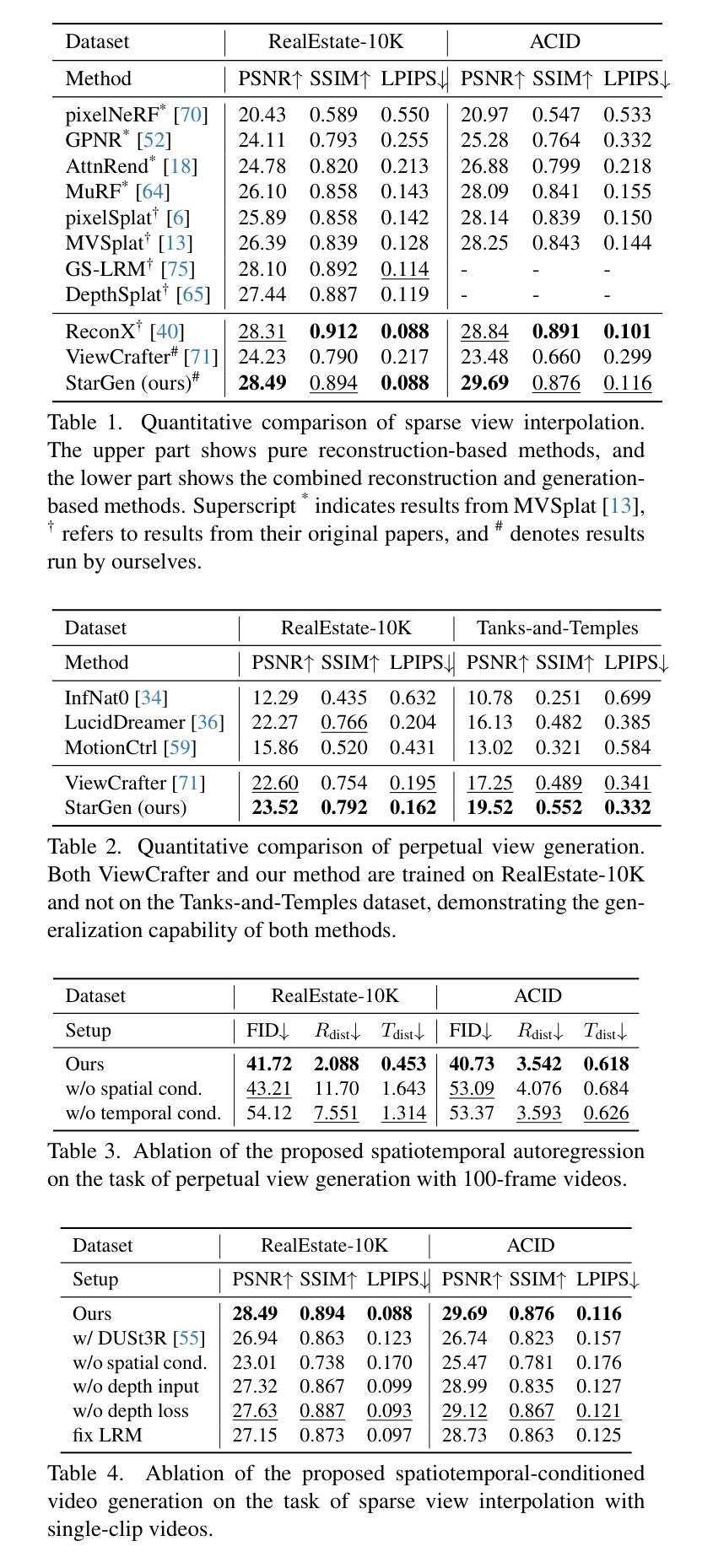

Controllable Human Image Generation with Personalized Multi-Garments
Authors:Yisol Choi, Sangkyung Kwak, Sihyun Yu, Hyungwon Choi, Jinwoo Shin
We present BootComp, a novel framework based on text-to-image diffusion models for controllable human image generation with multiple reference garments. Here, the main bottleneck is data acquisition for training: collecting a large-scale dataset of high-quality reference garment images per human subject is quite challenging, i.e., ideally, one needs to manually gather every single garment photograph worn by each human. To address this, we propose a data generation pipeline to construct a large synthetic dataset, consisting of human and multiple-garment pairs, by introducing a model to extract any reference garment images from each human image. To ensure data quality, we also propose a filtering strategy to remove undesirable generated data based on measuring perceptual similarities between the garment presented in human image and extracted garment. Finally, by utilizing the constructed synthetic dataset, we train a diffusion model having two parallel denoising paths that use multiple garment images as conditions to generate human images while preserving their fine-grained details. We further show the wide-applicability of our framework by adapting it to different types of reference-based generation in the fashion domain, including virtual try-on, and controllable human image generation with other conditions, e.g., pose, face, etc.
我们提出了BootComp,这是一个基于文本到图像扩散模型的新型框架,用于可控的人体图像生成,具有多重参考服装。在这里,训练中的主要瓶颈是数据采集:针对每个受试者收集大规模的高质量参考服装图像数据集是一项挑战,也就是说,理想情况下,需要手动收集每个人所穿的每一件服装照片。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种数据生成管道,通过引入一个模型来从每个人体图像中提取任何参考服装图像,从而构建一个人体和多重服装配对的大型合成数据集。为了保证数据质量,我们还提出了一种过滤策略,通过测量人体图像中展示的服装和提取的服装之间的感知相似性来去除不良生成数据。最后,通过利用构建的合成数据集,我们训练了一个扩散模型,该模型具有两个并行去噪路径,使用多张服装图像作为条件来生成人体图像,同时保留其细节。我们还通过将该框架适应时尚领域的不同参考基生成任务来展示其广泛的应用性,包括虚拟试穿和其他可控人体图像生成条件,如姿势、面部等。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Project page: https://omnious.github.io/BootComp
Summary
本文提出了BootComp框架,基于文本到图像的扩散模型,实现了可控的人物图像生成,并支持多参考服装。为解决训练数据获取瓶颈,提出构建大型合成数据集的方法,通过引入模型从每个人物图像中提取任何参考服装图像。为确保数据质量,还提出了基于感知相似度的过滤策略,去除不良生成数据。最终,利用构建好的合成数据集训练扩散模型,拥有两条并行去噪路径,以多张服装图像为条件生成人物图像,同时保留精细细节。框架还适用于时尚领域的不同参考基准生成,包括虚拟试穿、以及其他条件可控的人物图像生成,如姿势、面部等。
Key Takeaways
- BootComp框架基于文本到图像的扩散模型,支持可控的人物图像生成,并采用多参考服装。
- 数据获取是训练的主要瓶颈,因此提出构建大型合成数据集的方法,通过模型从人物图像中提取参考服装图像。
- 为确保数据质量,采用基于感知相似度的过滤策略。
- 框架利用合成数据集训练扩散模型,拥有两条并行去噪路径,能生成精细细节的人物图像。
- 框架适用于多种类型的参考基准生成,包括虚拟试穿。
- 框架支持其他条件可控的人物图像生成,如姿势、面部等。
点此查看论文截图

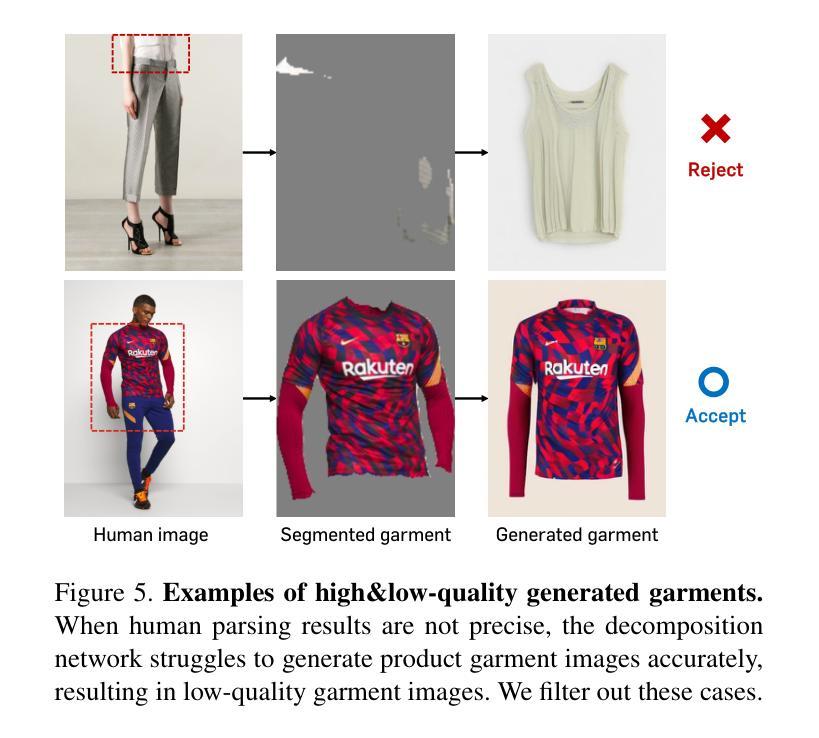

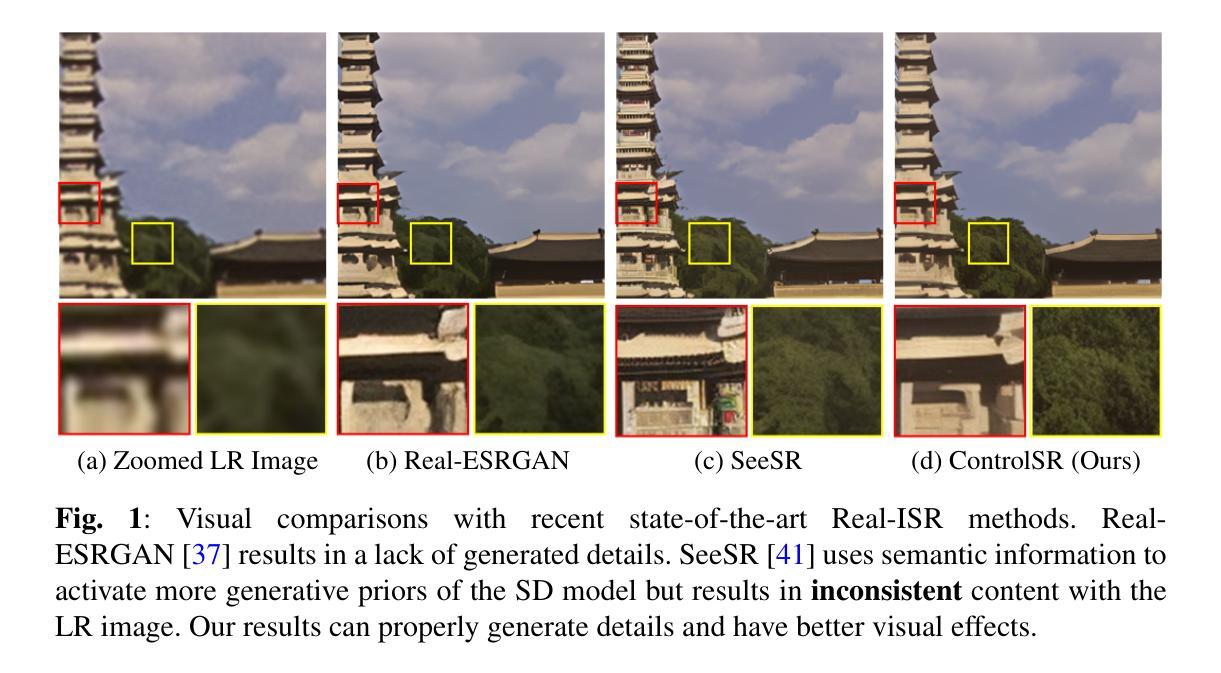
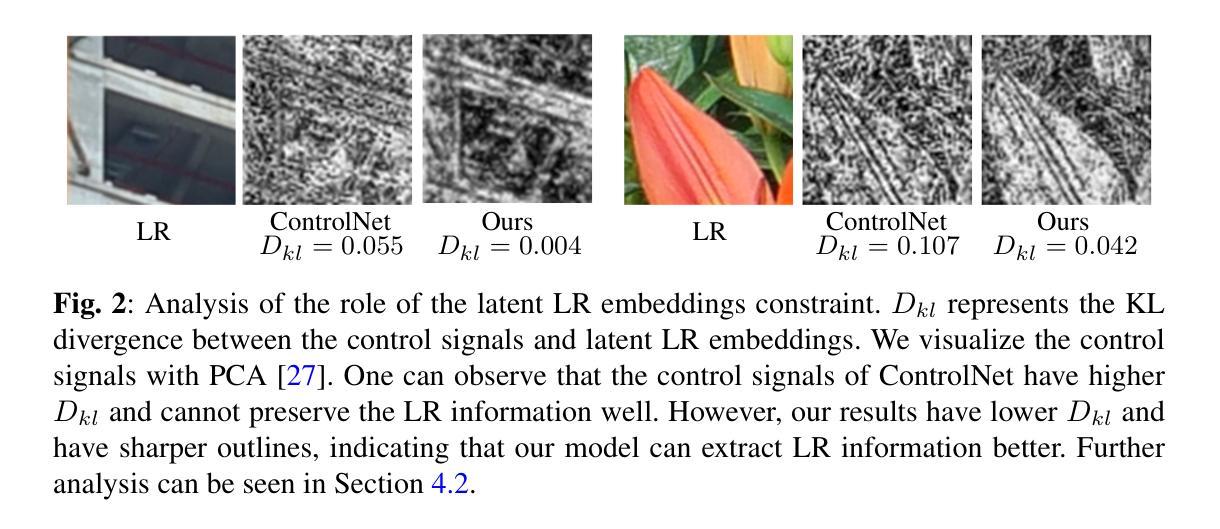
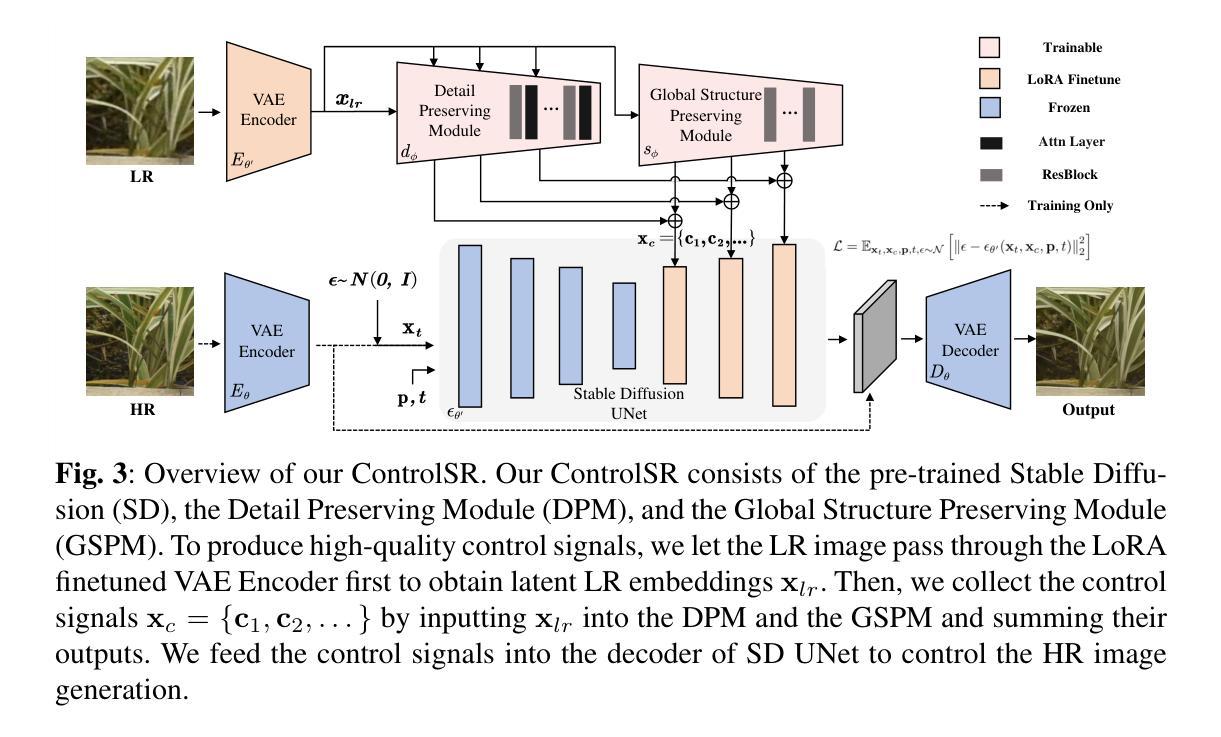
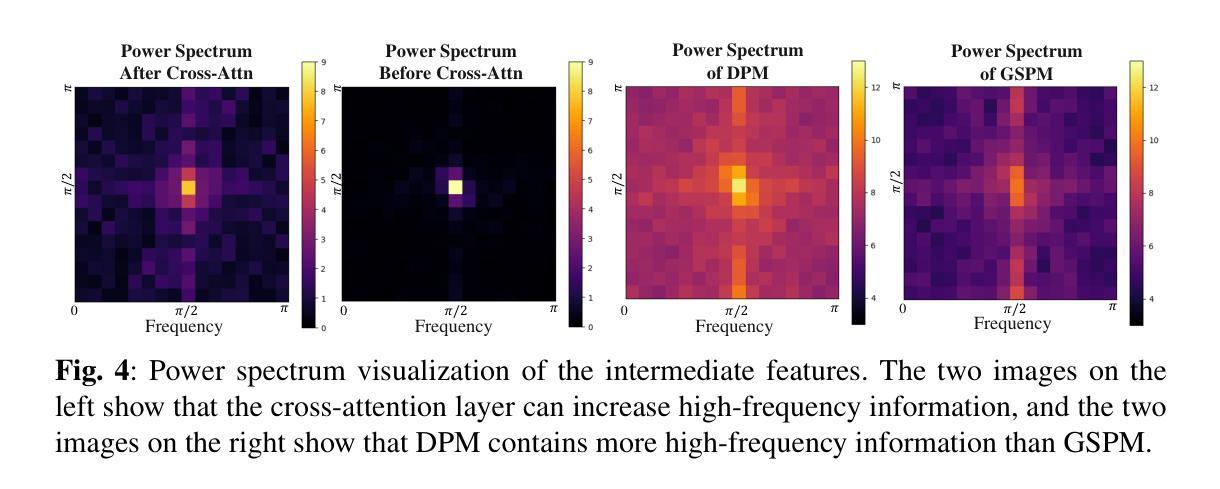
ControlSR: Taming Diffusion Models for Consistent Real-World Image Super Resolution
Authors:Yuhao Wan, Peng-Tao Jiang, Qibin Hou, Hao Zhang, Jinwei Chen, Ming-Ming Cheng, Bo Li
We present ControlSR, a new method that can tame Diffusion Models for consistent real-world image super-resolution (Real-ISR). Previous Real-ISR models mostly focus on how to activate more generative priors of text-to-image diffusion models to make the output high-resolution (HR) images look better. However, since these methods rely too much on the generative priors, the content of the output images is often inconsistent with the input LR ones. To mitigate the above issue, in this work, we tame Diffusion Models by effectively utilizing LR information to impose stronger constraints on the control signals from ControlNet in the latent space. We show that our method can produce higher-quality control signals, which enables the super-resolution results to be more consistent with the LR image and leads to clearer visual results. In addition, we also propose an inference strategy that imposes constraints in the latent space using LR information, allowing for the simultaneous improvement of fidelity and generative ability. Experiments demonstrate that our model can achieve better performance across multiple metrics on several test sets and generate more consistent SR results with LR images than existing methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/HVision-NKU/ControlSR.
我们提出了ControlSR,这是一种新的方法,可以驯化扩散模型,以实现一致的现实世界图像超分辨率(Real-ISR)。之前的Real-ISR模型大多关注如何激活文本到图像扩散模型的生产性先验知识,以使输出的高分辨率(HR)图像看起来更好。然而,由于这些方法过于依赖生成先验知识,输出图像的内容往往与输入的LR图像不一致。为了缓解上述问题,在这项工作中,我们通过有效利用LR信息,对ControlNet中的控制信号施加更强的约束,从而驯化扩散模型。我们证明,我们的方法可以产生更高质量的控制信号,这使得超分辨率结果与LR图像更加一致,并带来更清晰的视觉效果。此外,我们还提出了一种利用LR信息在潜在空间施加约束的推理策略,可以同时提高保真度和生成能力。实验表明,我们的模型在多个测试集上的多个指标上都能实现更好的性能,与现有方法相比,生成的SR结果与LR图像更加一致。我们的代码可在https://github.com/HVision-NKU/ControlSR找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
控制SR方法能够驯服扩散模型,实现真实世界图像超分辨率(Real-ISR)的一致性。该方法侧重于利用低分辨率(LR)信息,在潜在空间内对控制信号施加更强约束,解决以往方法生成图像内容与输入LR图像不一致的问题。实验证明,该模型在多个测试集上表现优异,生成的高分辨率(HR)图像与LR图像更一致。
Key Takeaways
- ControlSR是一种新的方法,能够驯服扩散模型,实现真实世界图像超分辨率的一致性。
- 以往的方法过于依赖生成先验,导致输出图像内容与输入低分辨率图像不一致。
- ControlSR通过有效利用低分辨率信息,在潜在空间内对控制信号施加更强约束,解决上述问题。
- ControlSR能产生更高质量的控制信号,使超分辨率结果与低分辨率图像更一致,视觉效果更清晰。
- ControlSR还提出了一种推理策略,在潜在空间内使用低分辨率信息施加约束,同时提高保真度和生成能力。
- 实验证明,ControlSR模型在多个测试集上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图


Automated Filtering of Human Feedback Data for Aligning Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Yongjin Yang, Sihyeon Kim, Hojung Jung, Sangmin Bae, SangMook Kim, Se-Young Yun, Kimin Lee
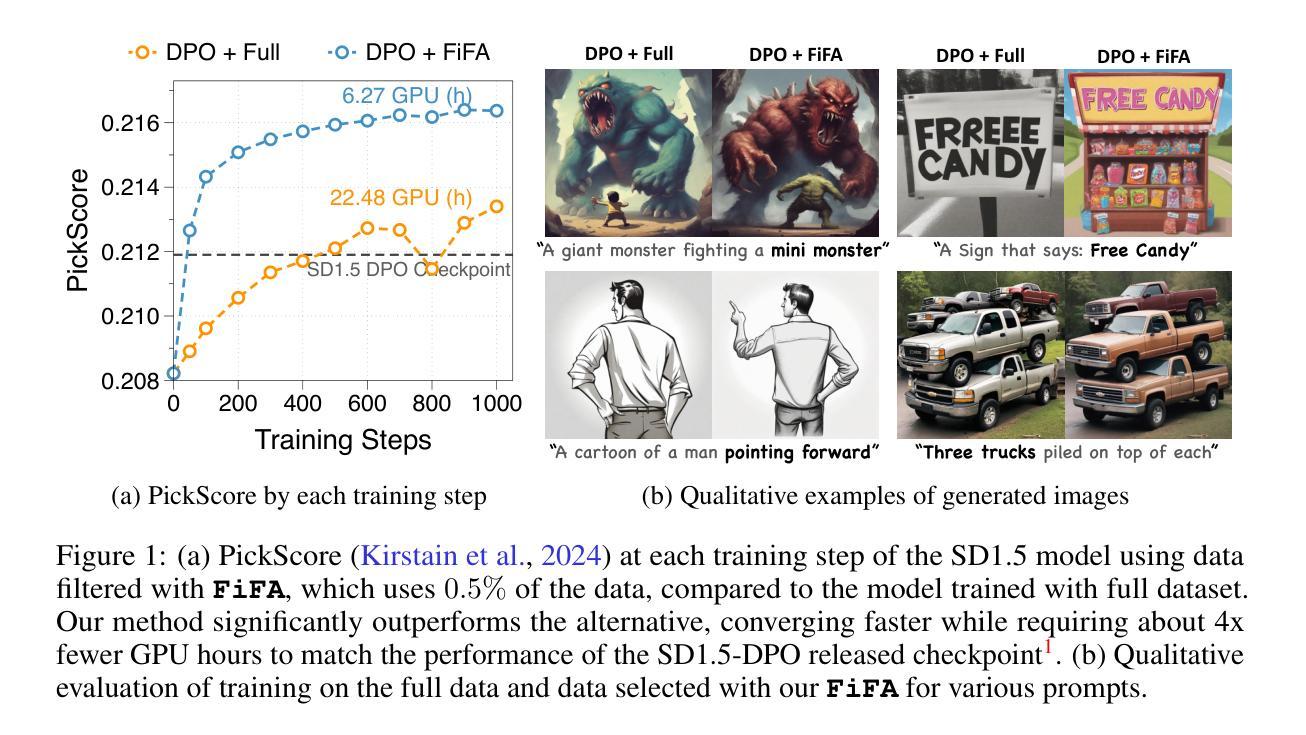
Fine-tuning text-to-image diffusion models with human feedback is an effective method for aligning model behavior with human intentions. However, this alignment process often suffers from slow convergence due to the large size and noise present in human feedback datasets. In this work, we propose FiFA, a novel automated data filtering algorithm designed to enhance the fine-tuning of diffusion models using human feedback datasets with direct preference optimization (DPO). Specifically, our approach selects data by solving an optimization problem to maximize three components: preference margin, text quality, and text diversity. The concept of preference margin is used to identify samples that are highly informative in addressing the noisy nature of feedback dataset, which is calculated using a proxy reward model. Additionally, we incorporate text quality, assessed by large language models to prevent harmful contents, and consider text diversity through a k-nearest neighbor entropy estimator to improve generalization. Finally, we integrate all these components into an optimization process, with approximating the solution by assigning importance score to each data pair and selecting the most important ones. As a result, our method efficiently filters data automatically, without the need for manual intervention, and can be applied to any large-scale dataset. Experimental results show that FiFA significantly enhances training stability and achieves better performance, being preferred by humans 17% more, while using less than 0.5% of the full data and thus 1% of the GPU hours compared to utilizing full human feedback datasets.
使用人类反馈对文本到图像的扩散模型进行微调是一种使模型行为与人类意图对齐的有效方法。然而,由于人类反馈数据集规模大且存在噪声,这种对齐过程往往存在收敛缓慢的问题。在这项工作中,我们提出了FiFA,这是一种新型自动化数据过滤算法,旨在利用人类反馈数据集对扩散模型进行微调,并结合直接偏好优化(DPO)。具体来说,我们的方法通过解决一个优化问题来选择数据,以最大化三个组成部分:偏好差距、文本质量和文本多样性。偏好差距的概念用于识别高度信息样本以解决反馈数据集的噪声本质,它是通过使用代理奖励模型来计算的。此外,我们结合大型语言模型对文本质量进行评估以防止有害内容,并通过k近邻熵估计器考虑文本多样性以提高泛化能力。最后,我们将所有这些组件整合到优化过程中,通过为每个数据对分配重要性得分并选择最重要的数据来近似解决方案。因此,我们的方法可以自动过滤数据,无需人工干预,并可应用于任何大规模数据集。实验结果表明,FiFA显著提高了训练稳定性,并取得了更好的性能,人类更喜欢使用FiFA的模型达17%,同时使用不到0.5%的全数据和仅使用全人类反馈数据集1%的GPU小时数。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025; Project Page available at : https://sprain02.github.io/FiFA/
Summary
本文提出了一种名为FiFA的自动化数据过滤算法,用于优化使用人类反馈数据集对扩散模型进行微调的过程。该算法通过解决优化问题来选择数据,以最大化偏好差距、文本质量和文本多样性。实验结果表明,FiFA能自动过滤数据,无需人工干预,可应用于大规模数据集,显著提高训练稳定性,性能更佳,且使用的人类反馈数据集更少,节省了GPU小时数。
Key Takeaways
- FiFA是一种用于优化扩散模型的新型自动化数据过滤算法。
- 该算法通过解决优化问题选择数据,以最大化偏好差距、文本质量和文本多样性。
- 偏好差距的概念用于识别高度信息性的样本,以解决反馈数据集的噪声问题。
- 使用代理奖励模型计算偏好差距。
- 通过大型语言模型评估文本质量以防止有害内容。
- 通过k近邻熵估计器提高文本多样性,改善泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图



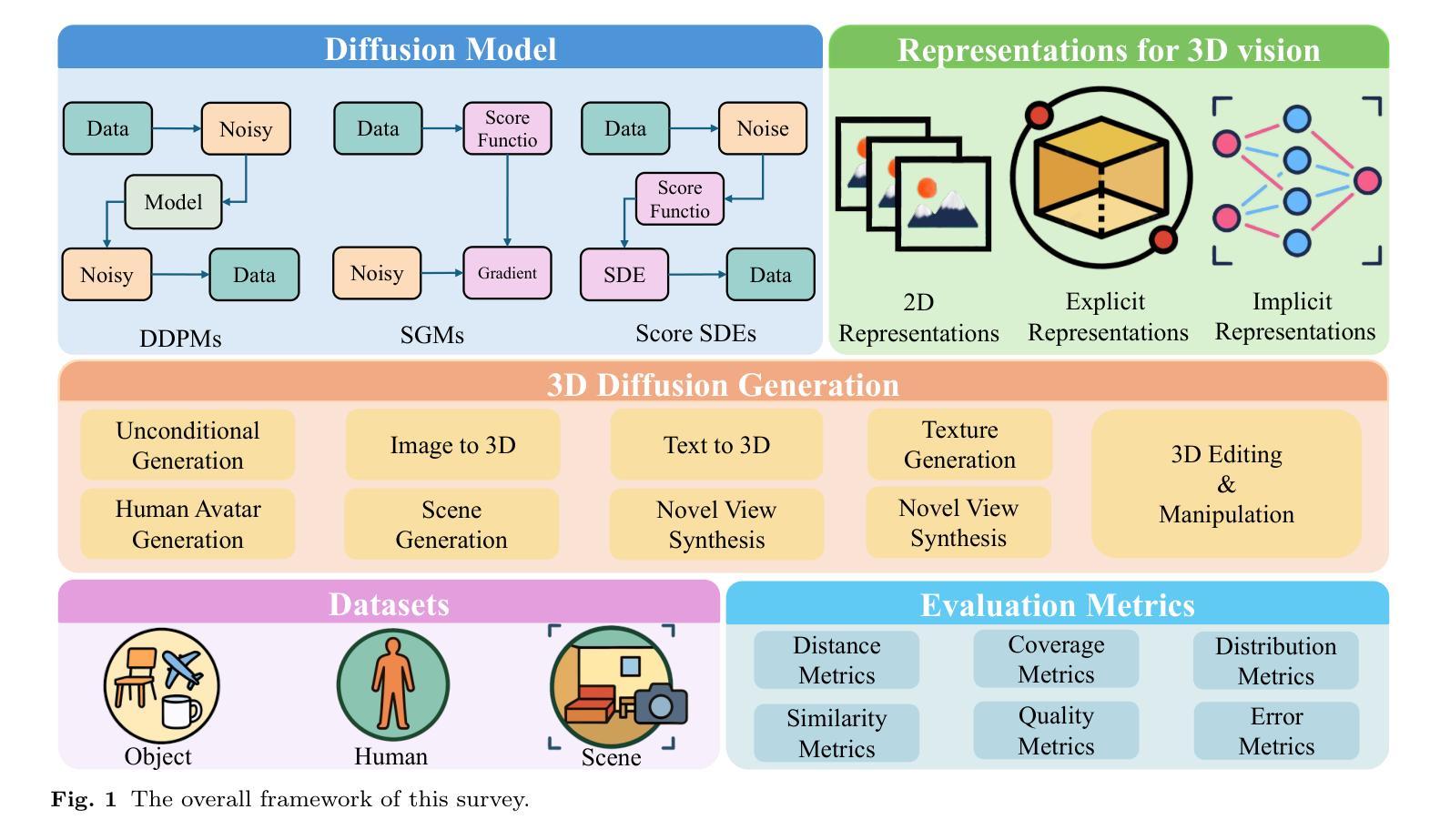
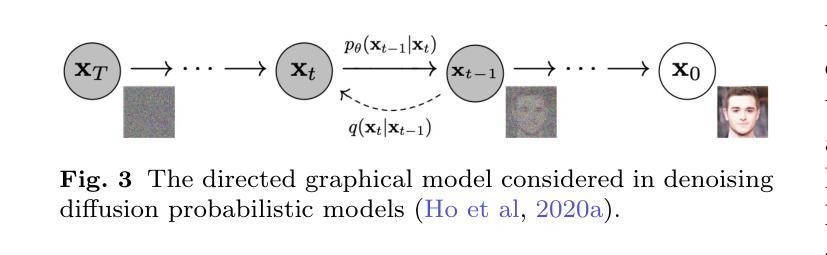
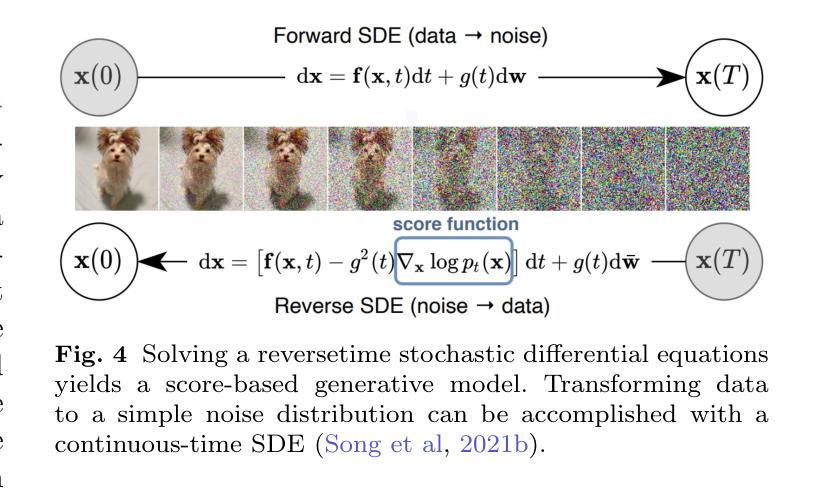
Diffusion Models in 3D Vision: A Survey
Authors:Zhen Wang, Dongyuan Li, Yaozu Wu, Tianyu He, Jiang Bian, Renhe Jiang
In recent years, 3D vision has become a crucial field within computer vision, powering a wide range of applications such as autonomous driving, robotics, augmented reality, and medical imaging. This field relies on accurate perception, understanding, and reconstruction of 3D scenes from 2D images or text data sources. Diffusion models, originally designed for 2D generative tasks, offer the potential for more flexible, probabilistic methods that can better capture the variability and uncertainty present in real-world 3D data. In this paper, we review the state-of-the-art methods that use diffusion models for 3D visual tasks, including but not limited to 3D object generation, shape completion, point-cloud reconstruction, and scene construction. We provide an in-depth discussion of the underlying mathematical principles of diffusion models, outlining their forward and reverse processes, as well as the various architectural advancements that enable these models to work with 3D datasets. We also discuss the key challenges in applying diffusion models to 3D vision, such as handling occlusions and varying point densities, and the computational demands of high-dimensional data. Finally, we discuss potential solutions, including improving computational efficiency, enhancing multimodal fusion, and exploring the use of large-scale pretraining for better generalization across 3D tasks. This paper serves as a foundation for future exploration and development in this rapidly evolving field.
近年来,3D视觉已成为计算机视觉领域中的一个关键分支,为自动驾驶、机器人技术、增强现实和医学影像等广泛应用提供了支持。该领域依赖于从二维图像或文本数据源对三维场景的准确感知、理解和重建。扩散模型最初是为二维生成任务而设计的,它提供了更灵活的概率方法,可以更好地捕捉真实世界三维数据中的变性和不确定性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文综述了利用扩散模型进行3D视觉任务的最新方法,包括3D对象生成、形状补全、点云重建和场景构建等。文章深入讨论了扩散模型的前向和反向过程、各种架构进展,以及在处理3D数据集时面临的挑战,如遮挡和点密度不一等。此外,本文还讨论了改进计算效率、增强多模态融合和探索大规模预训练在跨3D任务中的推广等潜在解决方案。本文为这一快速发展领域未来的探索和发展奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型为处理三维视觉任务提供了灵活的概率方法。
- 这些模型可从二维图像或文本数据源中感知、理解和重建三维场景。
- 当前使用扩散模型进行三维视觉任务的方法包括3D对象生成、形状补全等。
- 扩散模型的前向和反向过程及其架构进展是处理三维数据集的关键。
- 应用扩散模型处理三维视觉面临的主要挑战包括遮挡处理和点密度不一等。
- 提高计算效率、增强多模态融合以及大规模预训练是潜在的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图