⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-04 更新
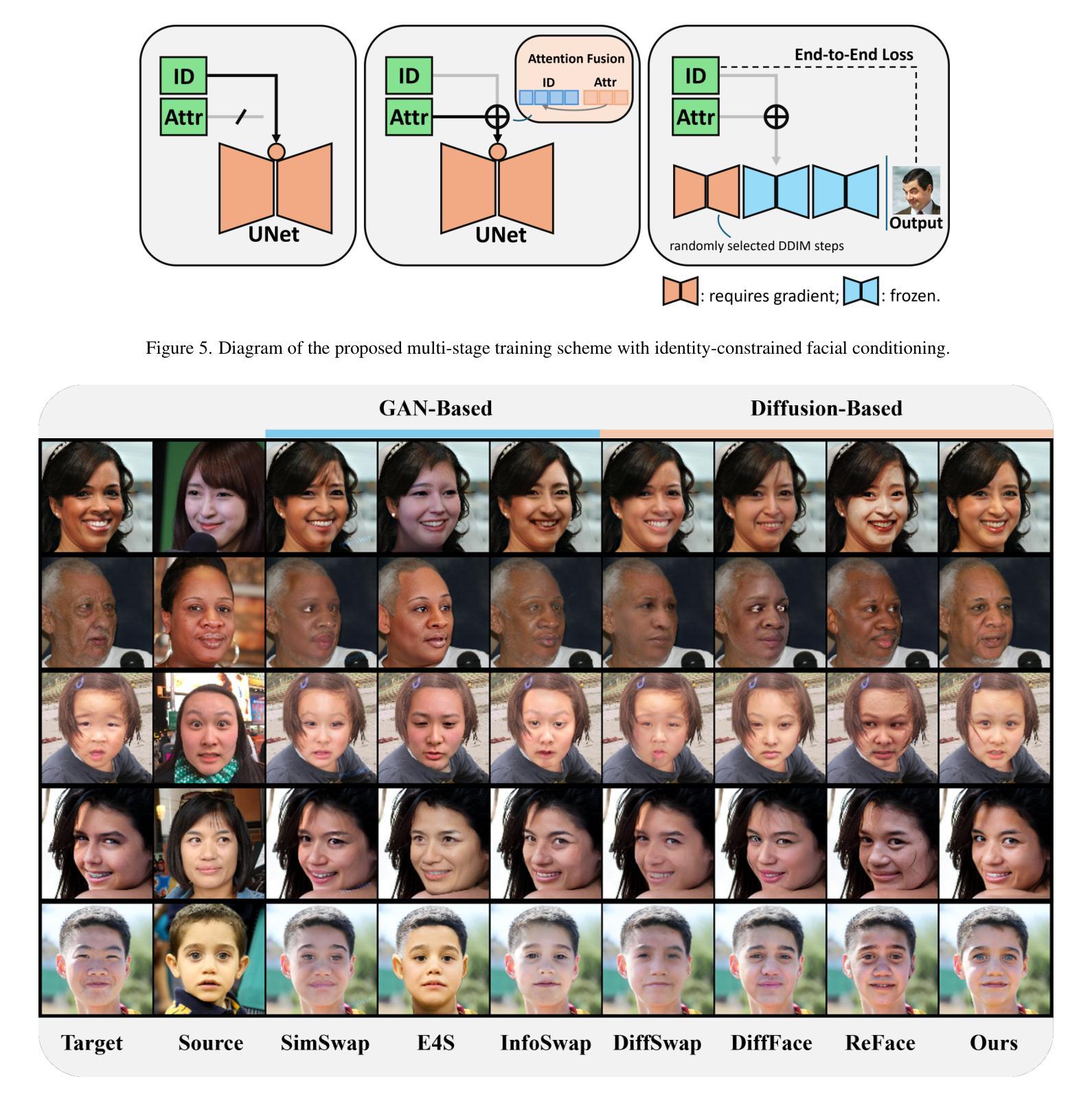
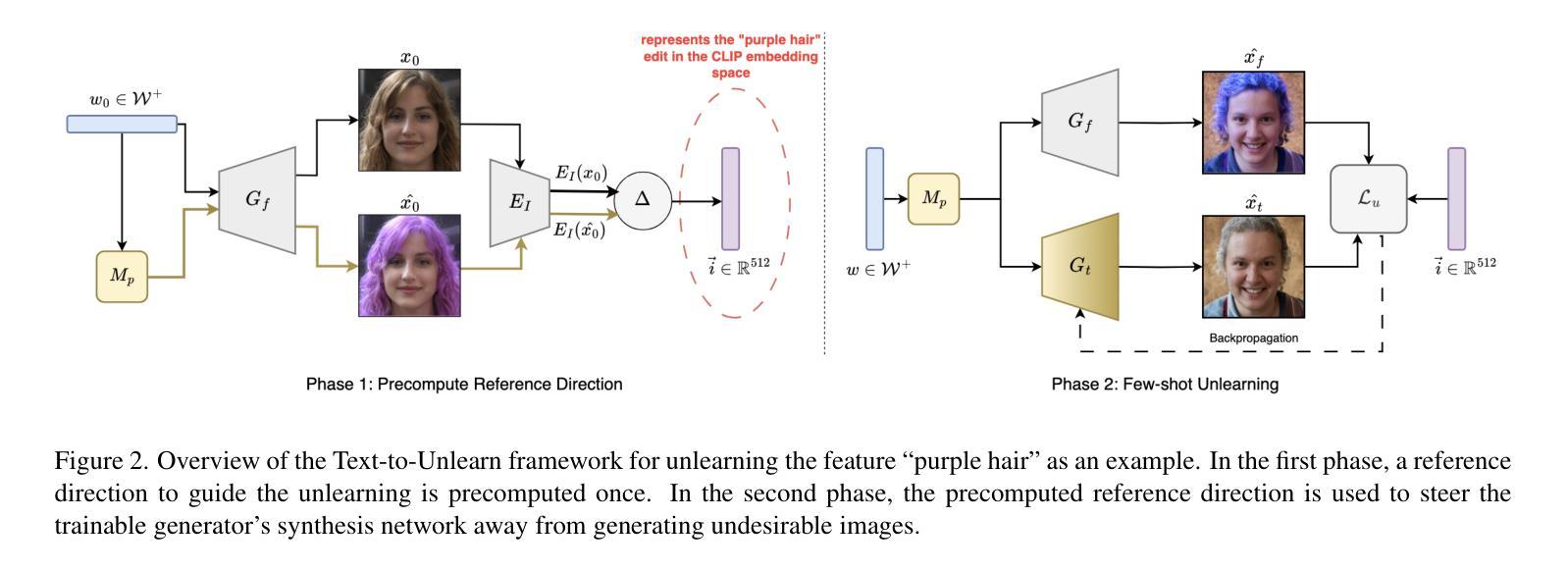
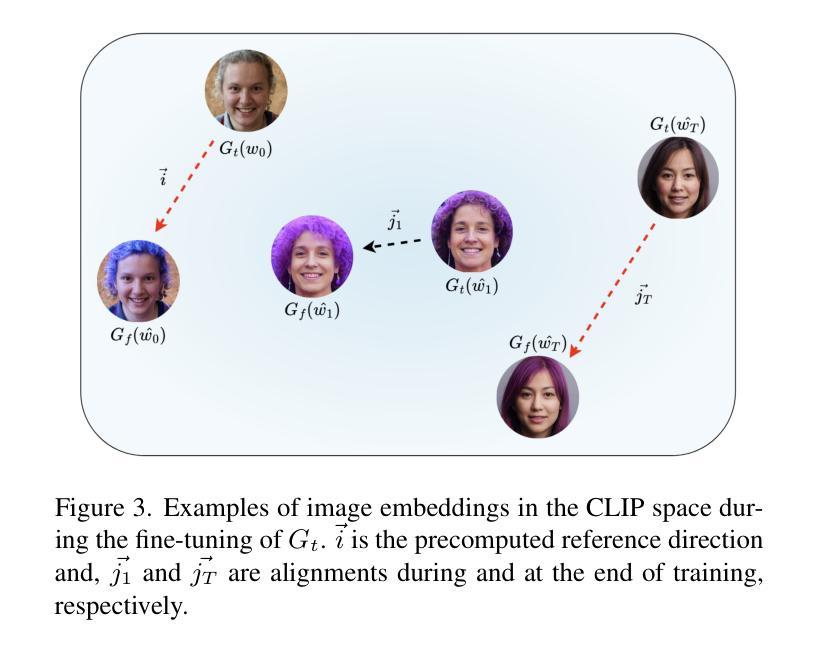
Prompting Forgetting: Unlearning in GANs via Textual Guidance
Authors:Piyush Nagasubramaniam, Neeraj Karamchandani, Chen Wu, Sencun Zhu
State-of-the-art generative models exhibit powerful image-generation capabilities, introducing various ethical and legal challenges to service providers hosting these models. Consequently, Content Removal Techniques (CRTs) have emerged as a growing area of research to control outputs without full-scale retraining. Recent work has explored the use of Machine Unlearning in generative models to address content removal. However, the focus of such research has been on diffusion models, and unlearning in Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) has remained largely unexplored. We address this gap by proposing Text-to-Unlearn, a novel framework that selectively unlearns concepts from pre-trained GANs using only text prompts, enabling feature unlearning, identity unlearning, and fine-grained tasks like expression and multi-attribute removal in models trained on human faces. Leveraging natural language descriptions, our approach guides the unlearning process without requiring additional datasets or supervised fine-tuning, offering a scalable and efficient solution. To evaluate its effectiveness, we introduce an automatic unlearning assessment method adapted from state-of-the-art image-text alignment metrics, providing a comprehensive analysis of the unlearning methodology. To our knowledge, Text-to-Unlearn is the first cross-modal unlearning framework for GANs, representing a flexible and efficient advancement in managing generative model behavior.
当前先进的生成模型展现出强大的图像生成能力,给托管这些模型的服务提供商带来了各种伦理和法律挑战。因此,内容删除技术(CRTs)作为研究的一个增长领域出现,可以在不进行全面再训练的情况下控制输出。近期的工作探讨了生成模型中机器遗忘的使用以解决内容删除问题。然而,此类研究的重点主要集中在扩散模型上,生成对抗网络(GANs)中的遗忘仍被大大忽视。我们通过提出Text-to-Unlearn来解决这一空白,这是一个新的框架,能够仅使用文本提示来选择性遗忘预训练GAN中的概念,实现功能遗忘、身份遗忘,以及在人脸训练模型中的表情和多属性删除等精细任务。我们的方法利用自然语言描述来引导遗忘过程,无需额外的数据集或监督微调,提供可伸缩和高效的解决方案。为了评估其有效性,我们引入了一种自动遗忘评估方法,该方法改编自最先进的图像文本对齐指标,对遗忘方法进行全面分析。据我们所知,Text-to-Unlearn是首个用于GAN的跨模式遗忘框架,代表着在管理生成模型行为方面灵活高效的进步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本介绍了生成模型带来的伦理和法律挑战,以及内容移除技术(CRTs)在控制生成模型输出方面的作用。针对这一问题,文本提出了一种名为Text-to-Unlearn的新型框架,该框架能够通过文本提示选择性地遗忘预训练GAN中的概念,从而实现特征遗忘、身份遗忘以及面部表情和多属性移除等精细任务。此框架使用自然语言描述来引导无学习过程,无需额外的数据集或监督微调,具有可扩展性和高效性。为评估其效果,文本还引入了一种自动无学习评估方法。据文本所述,Text-to-Unlearn是首个跨模态无学习框架,为管理生成模型行为提供了灵活高效的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型带来伦理和法律挑战,需要内容移除技术(CRTs)来控制输出。
- Text-to-Unlearn框架能够选择性地遗忘预训练GAN中的概念。
- 该框架可以通过文本提示实现特征遗忘、身份遗忘以及面部表情和多属性移除等精细任务。
- Text-to-Unlearn使用自然语言描述来引导无学习过程,无需额外数据集或监督微调。
- Text-to-Unlearn是首个跨模态无学习框架,为管理生成模型行为提供灵活高效的解决方案。
- 文本引入了一种自动无学习评估方法,以评估Text-to-Unlearn框架的效果。
点此查看论文截图





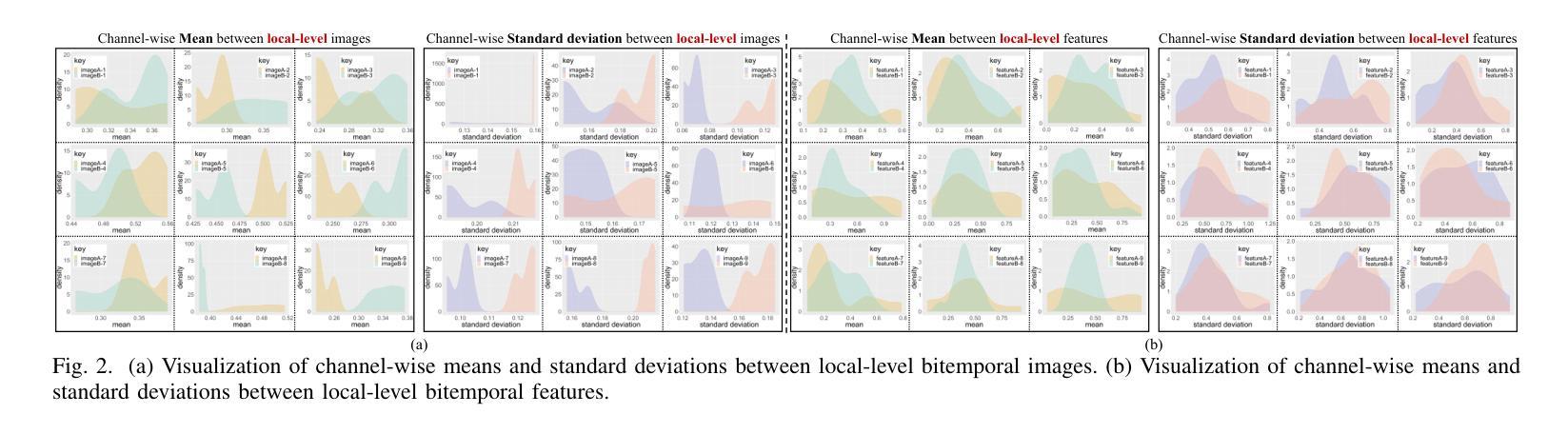
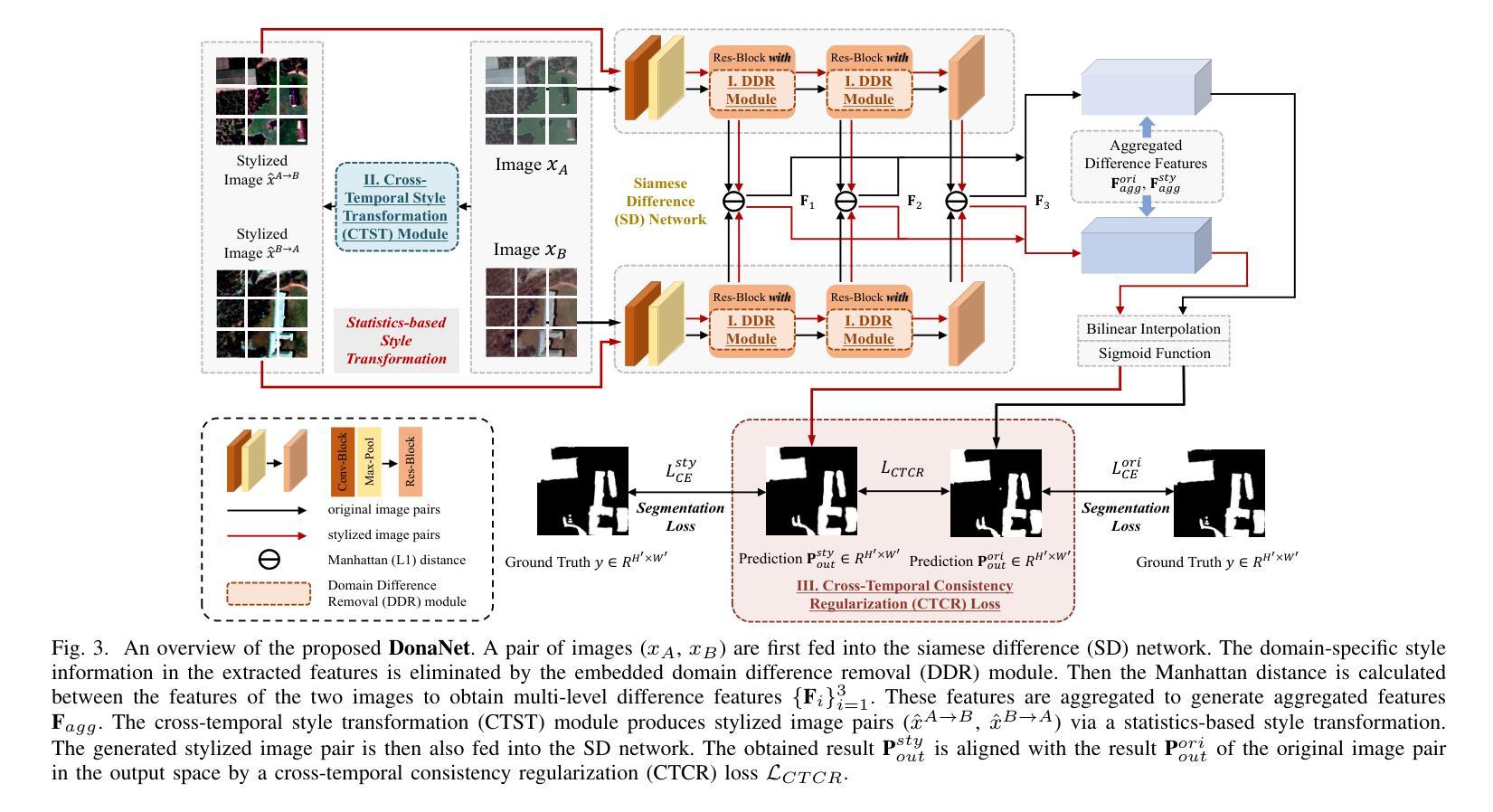
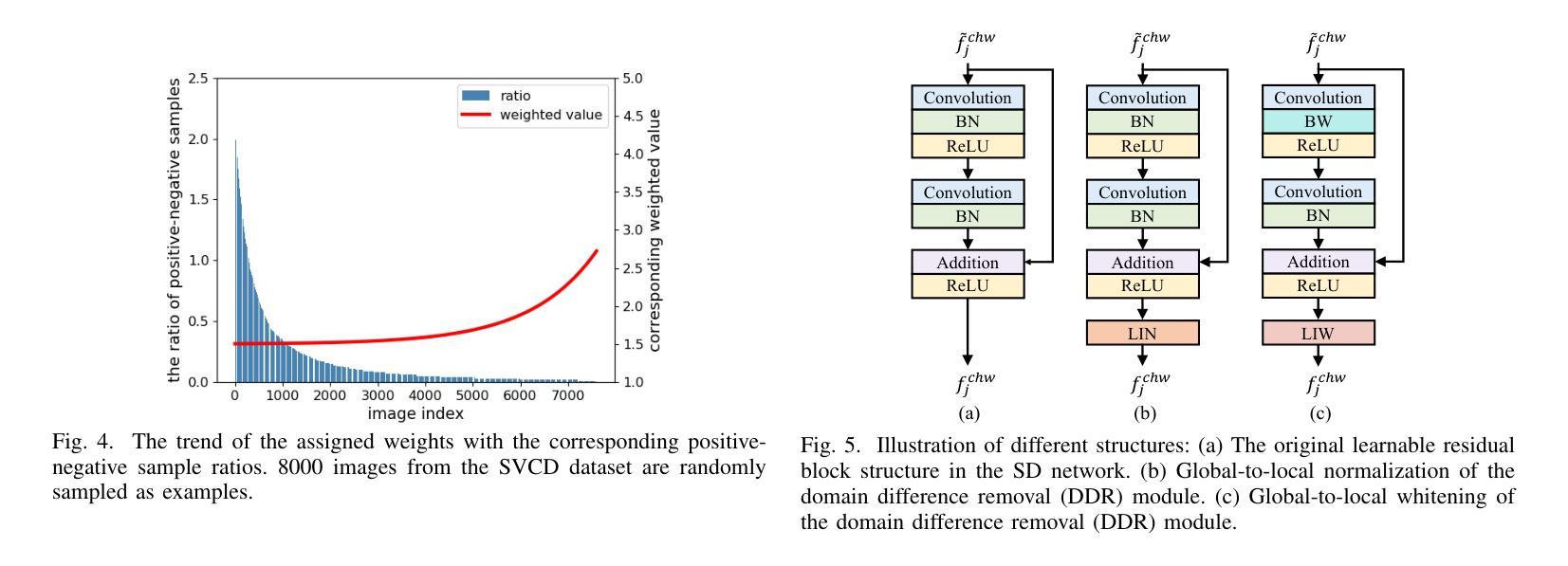
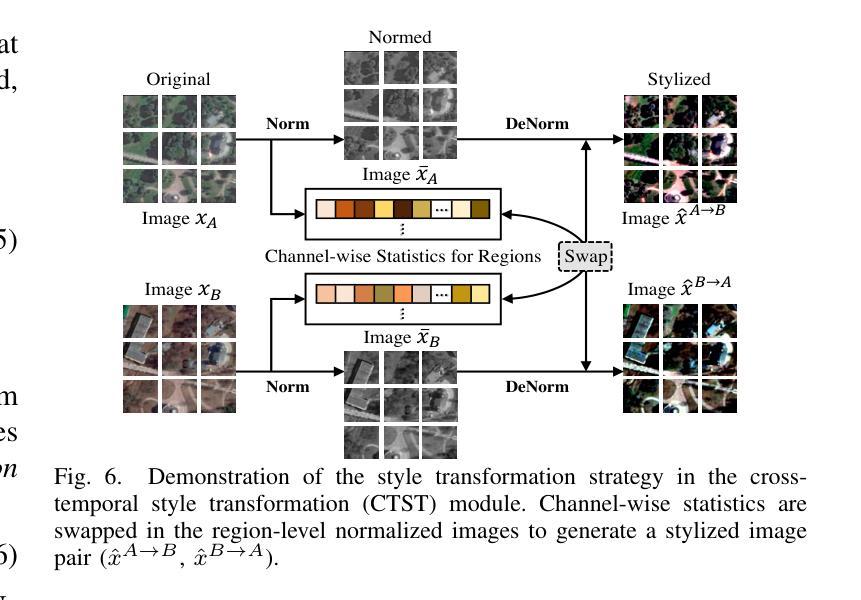
Generalization-aware Remote Sensing Change Detection via Domain-agnostic Learning
Authors:Qi Zang, Shuang Wang, Dong Zhao, Dou Quan, Yang Hu, Licheng Jiao
Change detection has essential significance for the region’s development, in which pseudo-changes between bitemporal images induced by imaging environmental factors are key challenges. Existing transformation-based methods regard pseudo-changes as a kind of style shift and alleviate it by transforming bitemporal images into the same style using generative adversarial networks (GANs). However, their efforts are limited by two drawbacks: 1) Transformed images suffer from distortion that reduces feature discrimination. 2) Alignment hampers the model from learning domain-agnostic representations that degrades performance on scenes with domain shifts from the training data. Therefore, oriented from pseudo-changes caused by style differences, we present a generalizable domain-agnostic difference learning network (DonaNet). For the drawback 1), we argue for local-level statistics as style proxies to assist against domain shifts. For the drawback 2), DonaNet learns domain-agnostic representations by removing domain-specific style of encoded features and highlighting the class characteristics of objects. In the removal, we propose a domain difference removal module to reduce feature variance while preserving discriminative properties and propose its enhanced version to provide possibilities for eliminating more style by decorrelating the correlation between features. In the highlighting, we propose a cross-temporal generalization learning strategy to imitate latent domain shifts, thus enabling the model to extract feature representations more robust to shifts actively. Extensive experiments conducted on three public datasets demonstrate that DonaNet outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods with a smaller model size and is more robust to domain shift.
变化检测对区域发展具有本质意义,其中由成像环境因素引起的双时相图像之间的伪变化是关键挑战。现有基于转换的方法将伪变化视为一种风格转变,并通过使用生成对抗网络(GAN)将双时相图像转换为相同风格来缓解这一问题。然而,他们的努力受限于两个缺点:1)转换后的图像会出现失真,降低了特征辨别能力。2)对齐阻碍了模型学习领域无关的表示,降低了在训练数据领域转移场景上的性能。因此,我们从由风格差异引起的伪变化出发,提出了一种通用的领域无关差异学习网络(DonaNet)。针对缺点1),我们主张使用局部级别的统计信息作为风格代理来帮助对抗领域转移。对于缺点2),DonaNet通过去除编码特征的特定领域风格并突出对象的类特征来学习领域无关的表示。在去除过程中,我们提出了一个领域差异去除模块,以减少特征方差的同时保留判别属性,并提出了其增强版,通过解特征之间的相关性来消除更多风格的可能性。在突出过程中,我们提出了一种跨时间泛化学习策略来模拟潜在领域转移,从而使模型能够更主动地提取对转移更稳健的特征表示。在三个公共数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,DonaNet在更小的模型大小的情况下超过了现有的最先进的方法,并且对领域转移更具鲁棒性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对由环境成像因素引起的时序图像中的伪变化挑战,提出了一个通用的领域无关差异学习网络(DonaNet)。为解决现有转换方法在处理伪变化时的局限,DonaNet通过局部级别统计作为风格代理来对抗领域转移,并通过移除编码特征的特定领域风格和突出对象类别特征来学习领域无关的表示。提出的领域差异移除模块能够在减少特征方差的同时保留判别属性,增强版本则通过解特征间的相关性来消除更多风格。同时,采用跨时序泛化学习策略来模拟潜在领域转移,使模型更能适应领域变化。在三个公开数据集上的实验表明,DonaNet在性能上优于现有最先进的模型,具有更小的模型尺寸且对领域转移更具鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways
- 伪变化在时序图像发展监测中是重要挑战,由于成像环境因素导致的两时序图像间的伪变化影响区域发展检测。
- 现有转换方法将伪变化视为风格转变,并使用生成对抗网络(GANs)将两时序图像转换为同一风格以应对挑战。
- DonaNet网络被提出以解决现有方法的两个局限性:变换图像因失真而降低特征辨别能力,以及模型难以学习领域无关表示导致在场景领域转移时性能下降。
- DonaNet使用局部级别统计作为风格代理来对抗领域转移。
- 提出了领域差异移除模块,可以在减少特征方差的同时保留判别属性。
- 采用跨时序泛化学习策略来模拟潜在领域转移,提升模型的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

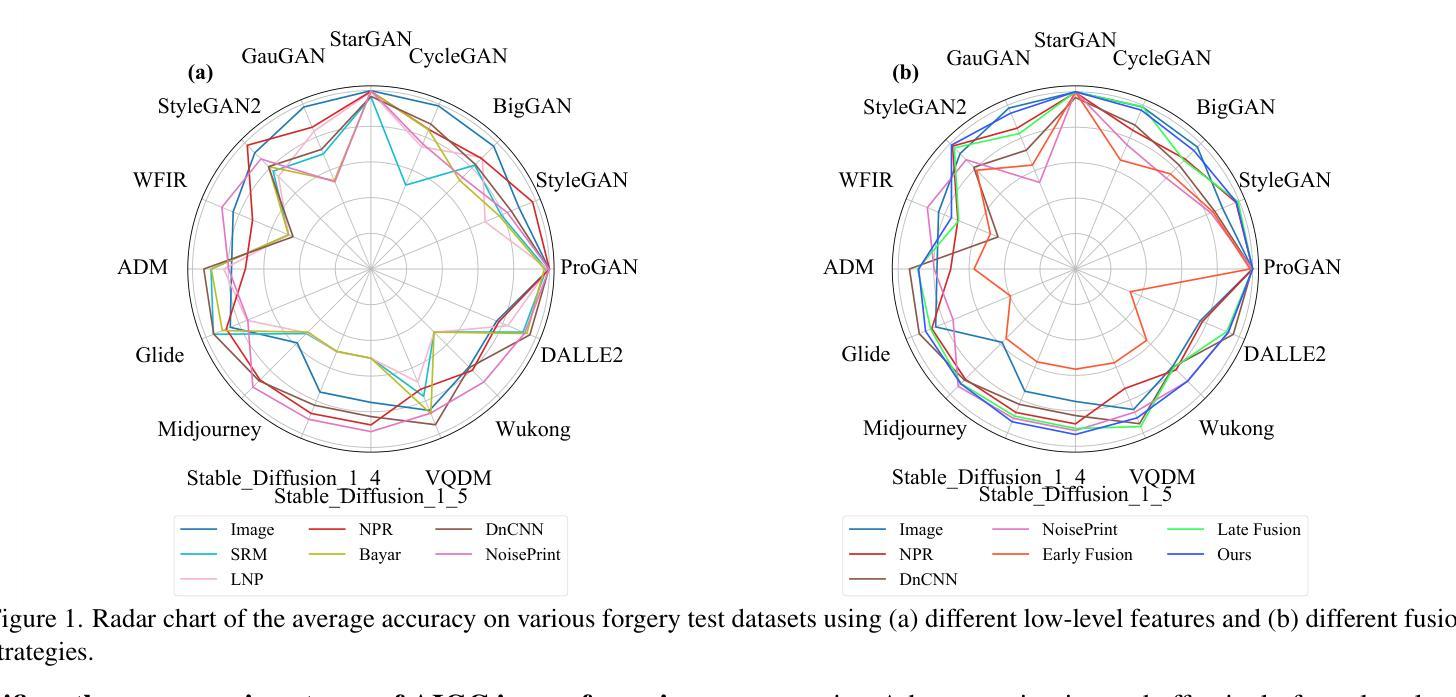
Exploring the Collaborative Advantage of Low-level Information on Generalizable AI-Generated Image Detection
Authors:Ziyin Zhou, Ke Sun, Zhongxi Chen, Xianming Lin, Yunpeng Luo, Ke Yan, Shouhong Ding, Xiaoshuai Sun
Existing state-of-the-art AI-Generated image detection methods mostly consider extracting low-level information from RGB images to help improve the generalization of AI-Generated image detection, such as noise patterns. However, these methods often consider only a single type of low-level information, which may lead to suboptimal generalization. Through empirical analysis, we have discovered a key insight: different low-level information often exhibits generalization capabilities for different types of forgeries. Furthermore, we found that simple fusion strategies are insufficient to leverage the detection advantages of each low-level and high-level information for various forgery types. Therefore, we propose the Adaptive Low-level Experts Injection (ALEI) framework. Our approach introduces Lora Experts, enabling the backbone network, which is trained with high-level semantic RGB images, to accept and learn knowledge from different low-level information. We utilize a cross-attention method to adaptively fuse these features at intermediate layers. To prevent the backbone network from losing the modeling capabilities of different low-level features during the later stages of modeling, we developed a Low-level Information Adapter that interacts with the features extracted by the backbone network. Finally, we propose Dynamic Feature Selection, which dynamically selects the most suitable features for detecting the current image to maximize generalization detection capability. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method, finetuned on only four categories of mainstream ProGAN data, performs excellently and achieves state-of-the-art results on multiple datasets containing unseen GAN and Diffusion methods.
当前最先进的AI生成图像检测方法大多考虑从RGB图像中提取低级信息,以帮助提高AI生成图像检测的泛化能力,例如噪声模式。然而,这些方法通常只考虑一种低级信息,可能导致泛化效果不佳。通过实证分析,我们发现了关键见解:不同的低级信息往往对不同类型的伪造表现出不同的泛化能力。此外,我们发现简单的融合策略不足以利用每种低级和高级信息对不同类型伪造的检测优势。因此,我们提出了自适应低级专家注入(ALEI)框架。我们的方法引入了Lora专家,使训练有高级语义RGB图像的主干网络能够接受和学习来自不同低级信息的知识。我们使用交叉注意方法来自适应地融合中间层的这些特征。为了防止主干网络在建模后期失去对不同低级特征的建模能力,我们开发了一个低级信息适配器,它与主干网络提取的特征进行交互。最后,我们提出了动态特征选择,它动态选择最适合检测当前图像的特征,以最大限度地提高泛化检测能力。大量实验表明,我们的方法仅在四个主流ProGAN数据集上进行微调,就表现出卓越的性能,并在包含未见过的GAN和Diffusion方法的多个数据集上达到了最新技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对当前最先进的AI生成图像检测方法的不足,研究团队发现融合多种低级别信息有助于提高检测不同种类伪造图像的泛化能力。他们提出了自适应低级别专家注入(ALEI)框架,引入多个“低级专家”,并利用交叉注意力方法自适应融合特征。同时,框架还包含防止主干网络丢失不同低级别特征建模能力的信息适配器以及动态特征选择机制。实验证明,该方法在多个数据集上表现优异,达到领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 当前AI生成图像检测方法的局限性:主要依赖单一类型的低级别信息,可能导致泛化能力不足。
- 不同低级别信息对于不同类型伪造图像的泛化能力有所不同。
- ALEI框架引入多个“低级专家”以增强检测性能。
- 利用交叉注意力方法自适应融合特征,提高检测效果。
- 信息适配器用于防止主干网络在后期建模中丢失不同低级别特征的建模能力。
- 动态特征选择机制能最大化泛化检测能力。
点此查看论文截图

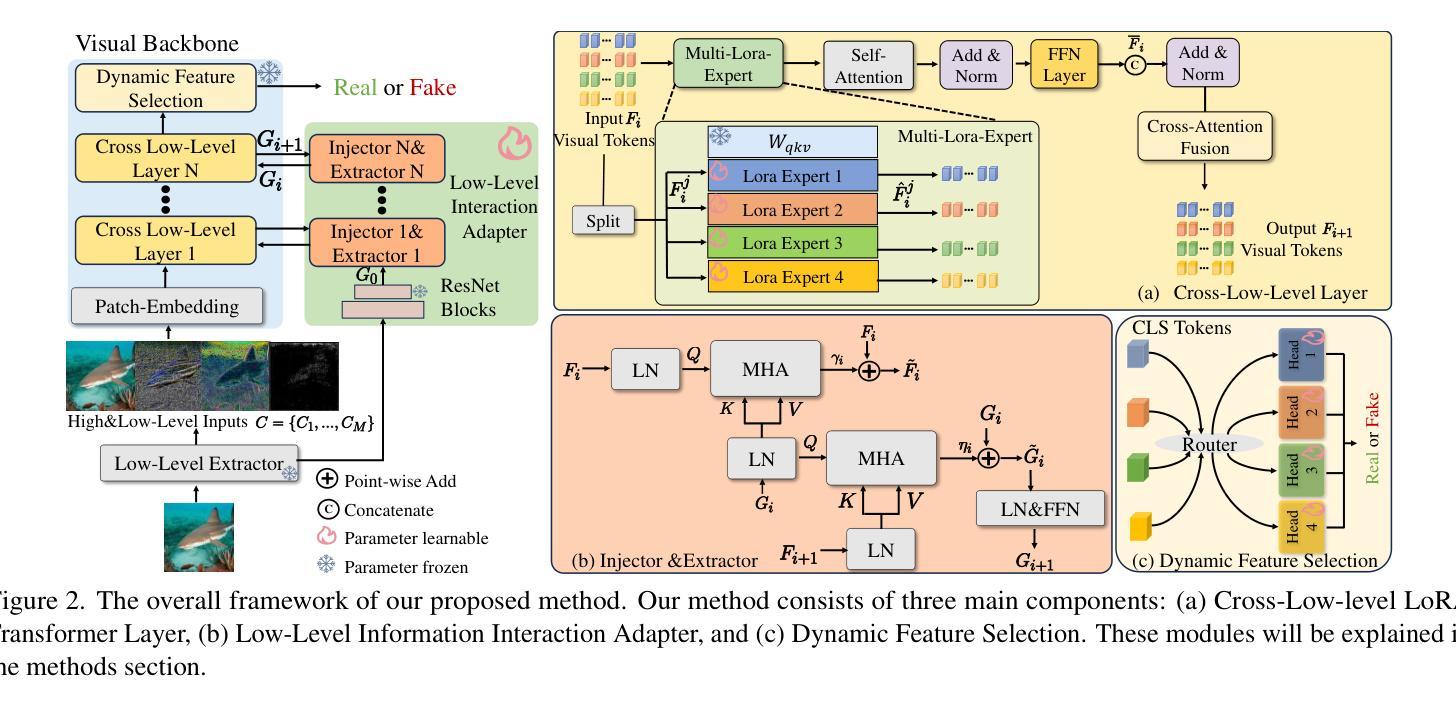
Style Quantization for Data-Efficient GAN Training
Authors:Jian Wang, Xin Lan, Jizhe Zhou, Yuxin Tian, Jiancheng Lv
Under limited data setting, GANs often struggle to navigate and effectively exploit the input latent space. Consequently, images generated from adjacent variables in a sparse input latent space may exhibit significant discrepancies in realism, leading to suboptimal consistency regularization (CR) outcomes. To address this, we propose \textit{SQ-GAN}, a novel approach that enhances CR by introducing a style space quantization scheme. This method transforms the sparse, continuous input latent space into a compact, structured discrete proxy space, allowing each element to correspond to a specific real data point, thereby improving CR performance. Instead of direct quantization, we first map the input latent variables into a less entangled ``style’’ space and apply quantization using a learnable codebook. This enables each quantized code to control distinct factors of variation. Additionally, we optimize the optimal transport distance to align the codebook codes with features extracted from the training data by a foundation model, embedding external knowledge into the codebook and establishing a semantically rich vocabulary that properly describes the training dataset. Extensive experiments demonstrate significant improvements in both discriminator robustness and generation quality with our method.
在有限数据设置下,生成对抗网络(GANs)往往难以导航并有效地利用输入潜在空间。因此,从稀疏输入潜在空间中的相邻变量生成的图像在真实性方面可能存在重大差异,导致次优的一致性正则化(CR)结果。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了SQ-GAN这一新方法,它通过引入风格空间量化方案来增强CR。该方法将稀疏、连续的输入潜在空间转换为一个紧凑、结构化的离散代理空间,使每个元素都能对应一个特定的真实数据点,从而提高CR性能。我们不是直接进行量化,而是首先将输入潜在变量映射到一个不太纠缠的“风格”空间,并使用可学习的代码本进行量化。这使得每个量化代码能够控制不同的变异因素。此外,我们优化了最佳传输距离,将代码本代码与基础模型从训练数据中提取的特征进行对齐,将外部知识嵌入到代码本中,建立一个语义丰富的词汇表,恰当地描述训练数据集。大量实验证明,我们的方法在判别器鲁棒性和生成质量方面都有显著提高。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在有限数据环境下,生成对抗网络(GANs)在输入潜在空间的导航和有效探索方面常常遇到困难。针对这一问题,本文提出了一种名为SQ-GAN的新方法,通过引入风格空间量化方案来增强一致性正则化(CR)性能。该方法将稀疏的连续输入潜在空间转换为一个紧凑、结构化的离散代理空间,使每个元素都能对应一个真实的数据点,从而提高CR性能。实验证明,该方法在判别器鲁棒性和生成质量方面都有显著提高。
Key Takeaways
- 在有限数据环境下,GANs在输入潜在空间导航和有效探索方面遇到困难。
- 提出的SQ-GAN方法通过引入风格空间量化方案增强一致性正则化(CR)性能。
- SQ-GAN将稀疏的连续输入潜在空间转换为一个紧凑、结构化的离散代理空间。
- 使用学习到的代码本进行量化,使每个量化的代码控制不同的变量因素。
- 通过优化传输距离,将代码本代码与基础模型提取的特征对齐,嵌入外部知识,建立语义丰富的词汇表,描述训练数据集。
- SQ-GAN提高了判别器的鲁棒性和生成质量。
点此查看论文截图

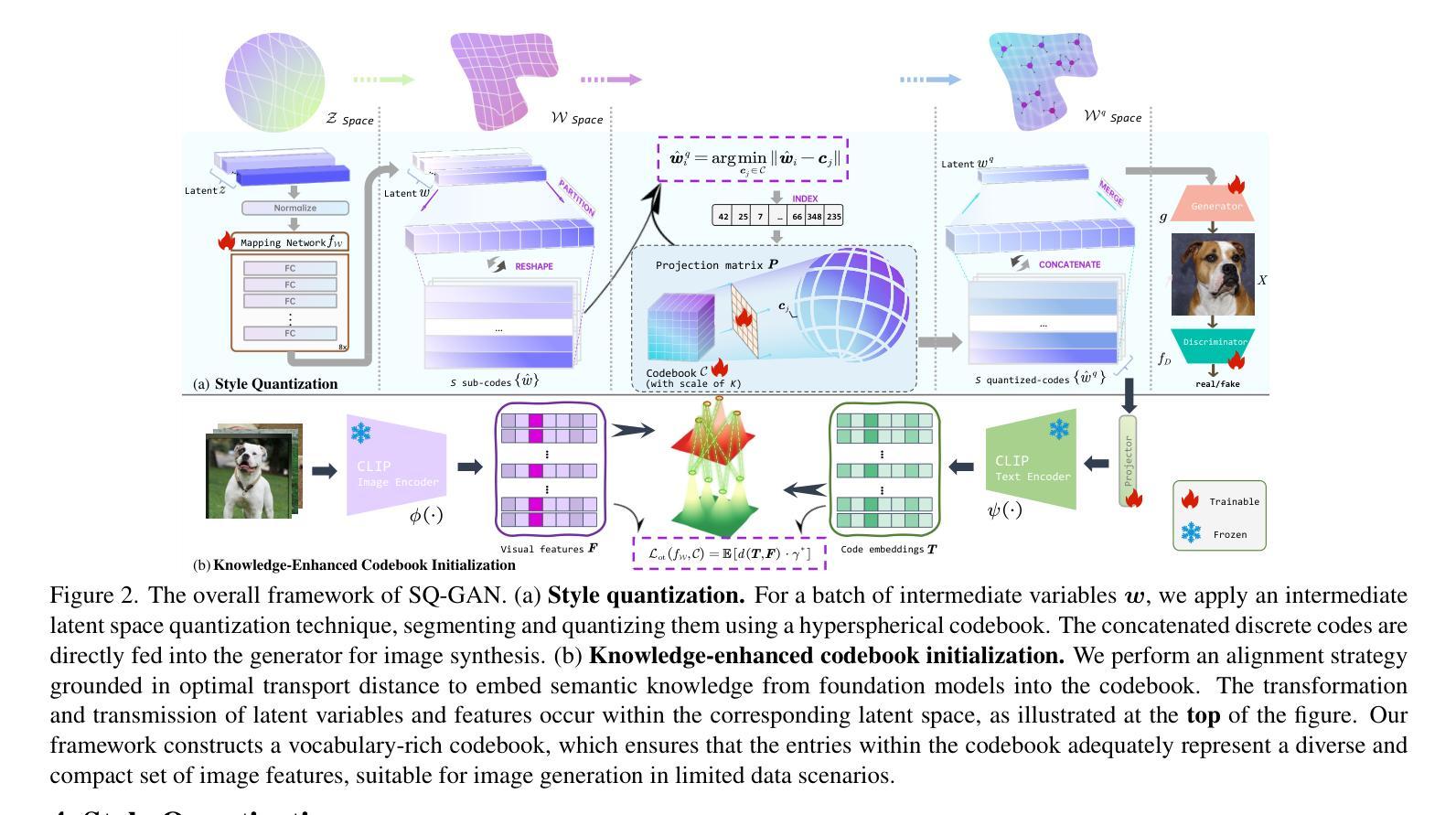
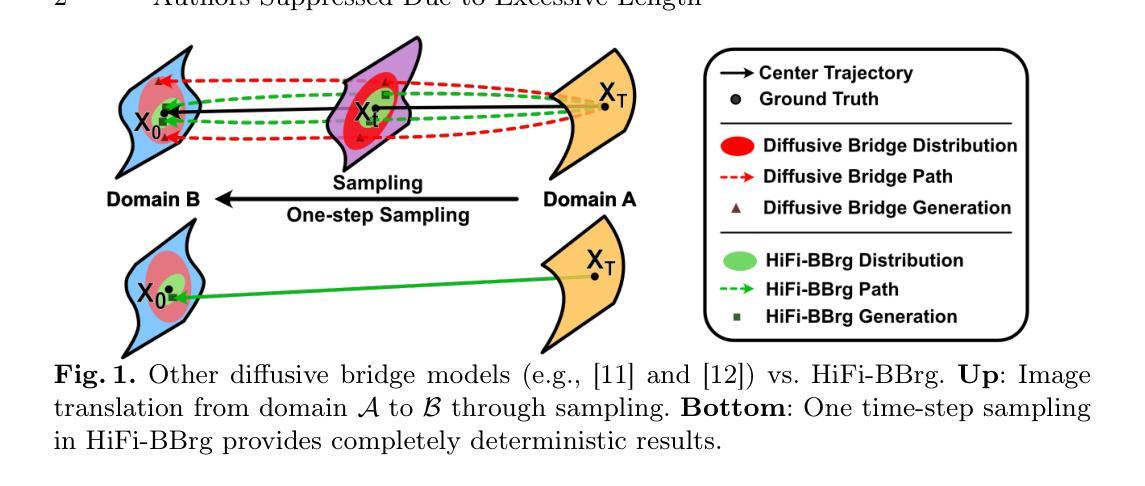
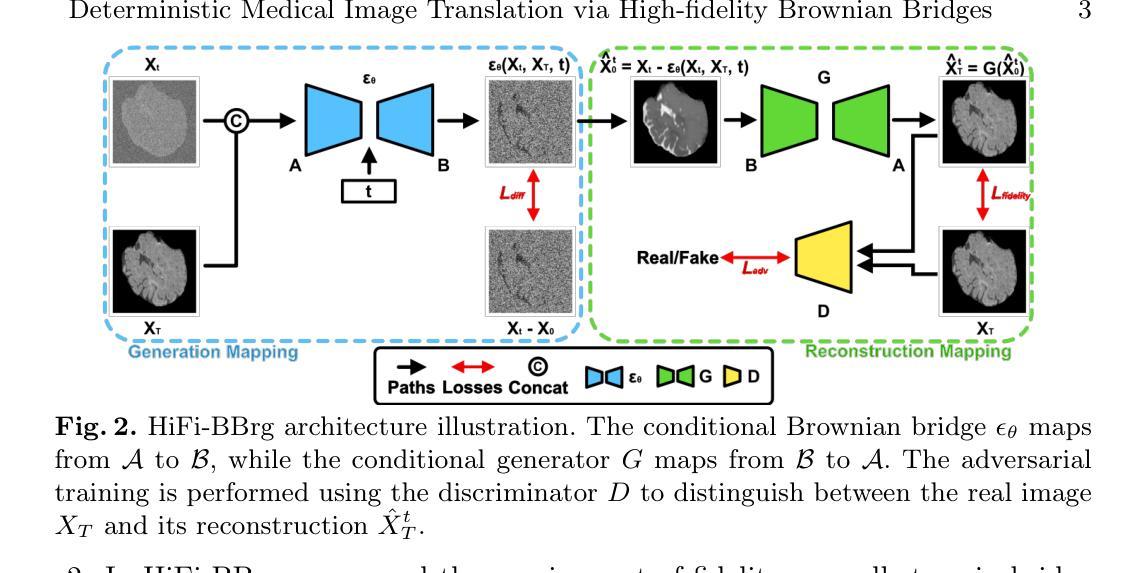
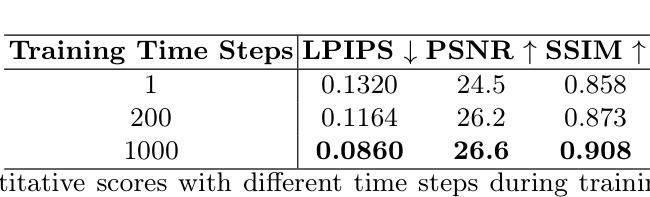
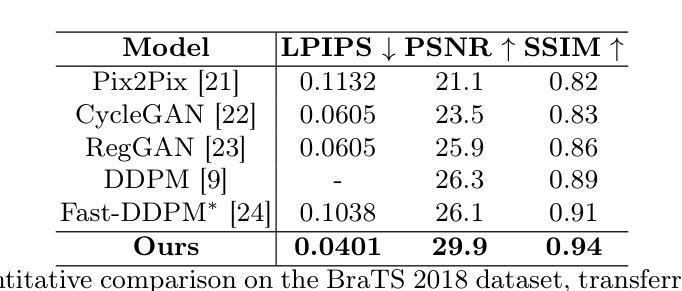
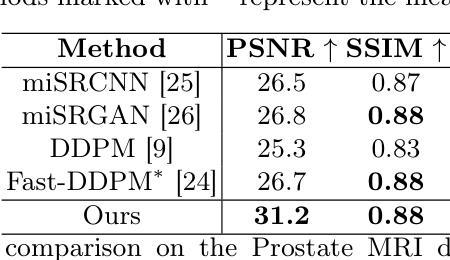
Deterministic Medical Image Translation via High-fidelity Brownian Bridges
Authors:Qisheng He, Nicholas Summerfield, Peiyong Wang, Carri Glide-Hurst, Ming Dong
Recent studies have shown that diffusion models produce superior synthetic images when compared to Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). However, their outputs are often non-deterministic and lack high fidelity to the ground truth due to the inherent randomness. In this paper, we propose a novel High-fidelity Brownian bridge model (HiFi-BBrg) for deterministic medical image translations. Our model comprises two distinct yet mutually beneficial mappings: a generation mapping and a reconstruction mapping. The Brownian bridge training process is guided by the fidelity loss and adversarial training in the reconstruction mapping. This ensures that translated images can be accurately reversed to their original forms, thereby achieving consistent translations with high fidelity to the ground truth. Our extensive experiments on multiple datasets show HiFi-BBrg outperforms state-of-the-art methods in multi-modal image translation and multi-image super-resolution.
最近的研究表明,与生成对抗网络(GANs)相比,扩散模型在生成合成图像方面表现出更优越的性能。然而,由于其内在的随机性,它们的输出通常是非确定的,并且与真实图像的高保真度缺失。在本文中,我们提出了一种用于确定性医学图像翻译的高保真布朗桥模型(HiFi-BBrg)。我们的模型包括两个独特而相互有益的映射:生成映射和重建映射。布朗桥训练过程由重建映射中的保真度损失和对抗性训练引导。这确保了翻译后的图像可以准确地恢复到其原始形式,从而实现与真实图像高度一致的翻译。我们在多个数据集上的广泛实验表明,HiFi-BBrg在跨模态图像翻译和多图像超分辨率方面优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型的高保真布朗桥模型(HiFi-BBrg),用于确定性医学图像翻译。该模型包含两个独特且相辅相成的映射:生成映射和重建映射。通过重建映射中的保真损失和对抗训练来指导布朗桥训练过程,确保翻译后的图像可以准确还原为原始形式,从而实现高保真度的一致翻译。在多个数据集上的实验表明,HiFi-BBrg在模态图像翻译和多图像超分辨率方面优于现有先进技术。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在生成合成图像方面表现出优于生成对抗网络(GANs)的性能,但输出具有非确定性和对真实数据的保真度不足的问题。
- 论文提出了一种新型的高保真布朗桥模型(HiFi-BBrg)用于医学图像翻译,具有确定性和高保真度。
- HiFi-BBrg模型包含两个关键部分:生成映射和重建映射,这两个部分通过相互合作确保图像翻译的准确性和高保真度。
- 模型通过布朗桥训练过程结合保真损失和对抗训练,确保翻译后的图像可以还原为原始形式。
- 该模型在多个数据集上进行了实验验证,展示了其在多模态图像翻译和多图像超分辨率方面的优越性。
- 与现有技术相比,HiFi-BBrg模型具有更高的性能和更准确的图像翻译能力。
点此查看论文截图

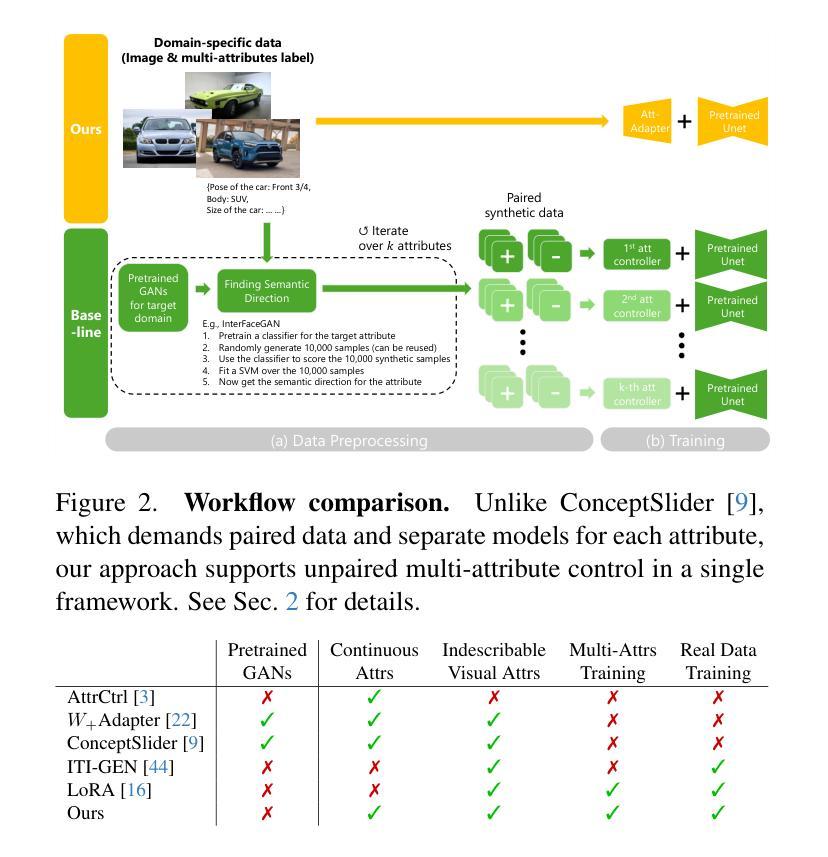
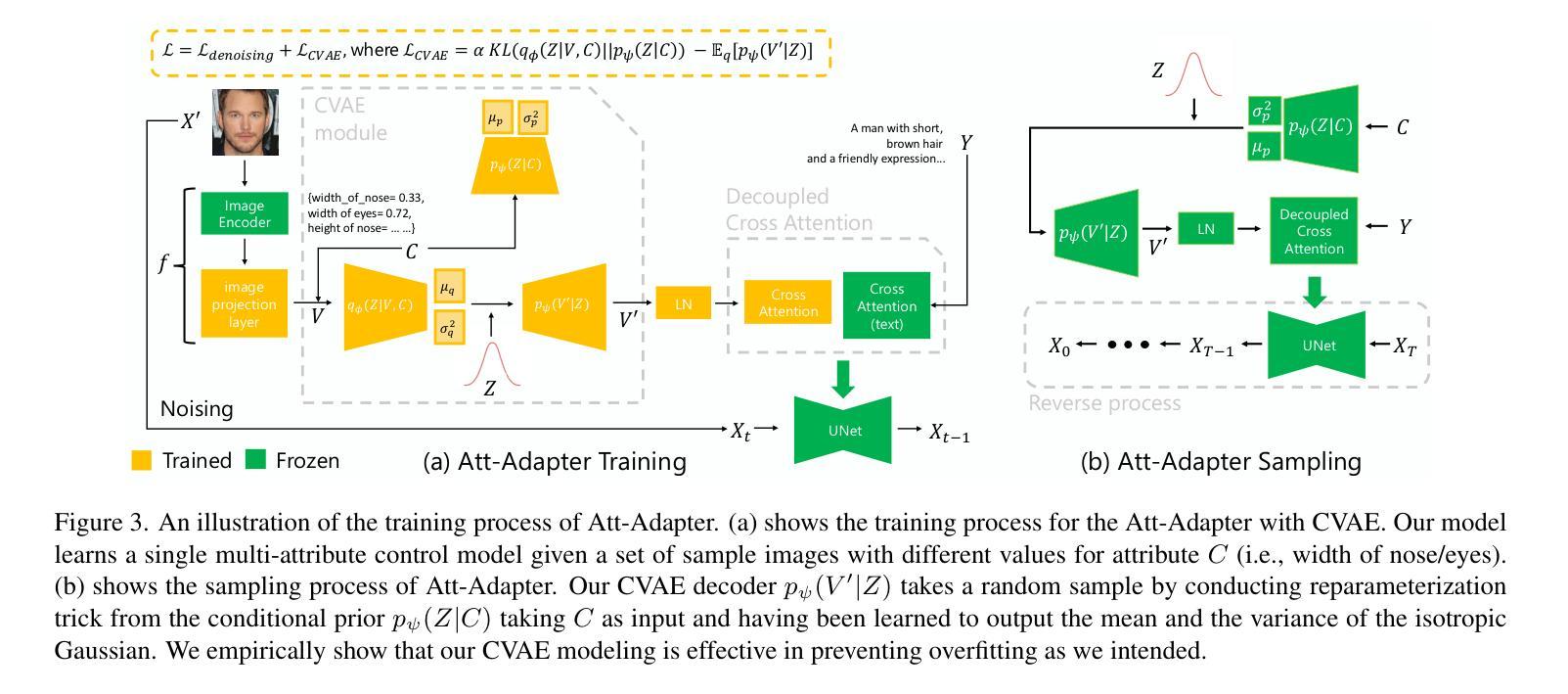
Att-Adapter: A Robust and Precise Domain-Specific Multi-Attributes T2I Diffusion Adapter via Conditional Variational Autoencoder
Authors:Wonwoong Cho, Yan-Ying Chen, Matthew Klenk, David I. Inouye, Yanxia Zhang
Text-to-Image (T2I) Diffusion Models have achieved remarkable performance in generating high quality images. However, enabling precise control of continuous attributes, especially multiple attributes simultaneously, in a new domain (e.g., numeric values like eye openness or car width) with text-only guidance remains a significant challenge. To address this, we introduce the Attribute (Att) Adapter, a novel plug-and-play module designed to enable fine-grained, multi-attributes control in pretrained diffusion models. Our approach learns a single control adapter from a set of sample images that can be unpaired and contain multiple visual attributes. The Att-Adapter leverages the decoupled cross attention module to naturally harmonize the multiple domain attributes with text conditioning. We further introduce Conditional Variational Autoencoder (CVAE) to the Att-Adapter to mitigate overfitting, matching the diverse nature of the visual world. Evaluations on two public datasets show that Att-Adapter outperforms all LoRA-based baselines in controlling continuous attributes. Additionally, our method enables a broader control range and also improves disentanglement across multiple attributes, surpassing StyleGAN-based techniques. Notably, Att-Adapter is flexible, requiring no paired synthetic data for training, and is easily scalable to multiple attributes within a single model.
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在生成高质量图像方面取得了显著的成绩。然而,在全新领域实现连续属性的精确控制,尤其是同时控制多个属性(例如,如眼睛睁开或汽车宽度等数值属性)仅通过文本指导仍然是一个巨大的挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了属性(Att)适配器,这是一种新型即插即用模块,旨在在预训练的扩散模型中实现精细的多属性控制。我们的方法从一组样本图像中学习单个控制适配器,这些图像可以是未配对的,并包含多个视觉属性。Att-Adapter利用解耦的交叉注意力模块,自然地协调多个域属性与文本条件。我们进一步将条件变分自编码器(CVAE)引入到Att-Adapter中,以减轻过拟合问题,适应视觉世界的多样性。在两个公共数据集上的评估表明,Att-Adapter在控制连续属性方面优于所有基于LoRA的方法。此外,我们的方法扩大了控制范围,并改善了多个属性之间的解纠缠,超越了StyleGAN技术。值得注意的是,Att-Adapter非常灵活,无需配对合成数据进行训练,并且很容易在单个模型中扩展到多个属性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型已生成高质量图像方面取得了显著成效。然而,使用纯文本指导在新的领域(如眼睛睁开程度或汽车宽度等数值)实现连续属性的精确控制,尤其是同时控制多个属性,仍然是一个重大挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了属性适配器(Att-Adapter),这是一种新型即插即用模块,旨在在预训练的扩散模型中实现精细粒度的多属性控制。我们的方法从一组未配对的包含多个视觉属性的样本图像中学习单个控制适配器。Att-Adapter利用解耦交叉注意力模块,自然地协调文本条件与多个域属性。我们还引入了条件变分自编码器(CVAE)来减轻过拟合问题,以适应视觉世界的多样性。在公开数据集上的评估表明,Att-Adapter在控制连续属性方面优于所有基于LoRA的方法。此外,我们的方法扩大了控制范围,改进了多个属性之间的解纠缠,超越了StyleGAN技术。值得一提的是,Att-Adapter非常灵活,无需配对合成数据进行训练,且可轻松扩展到单个模型中的多个属性。
Key Takeaways
- T2I扩散模型在高质图像生成方面表现卓越,但在新领域的连续属性控制上仍有挑战。
- 引入属性适配器(Att-Adapter)来解决这一挑战,这是一个新型的即插即用模块,用于预训练扩散模型中的精细粒度多属性控制。
- Att-Adapter通过利用解耦交叉注意力模块和条件变分自编码器(CVAE)来提高性能并适应视觉世界的多样性。
- 在公开数据集上的评估显示,Att-Adapter在控制连续属性方面优于其他方法。
- Att-Adapter扩大了控制范围,改进了多个属性之间的解纠缠。
- Att-Adapter具有灵活性,无需配对合成数据进行训练,且可轻松扩展到多个属性。
点此查看论文截图


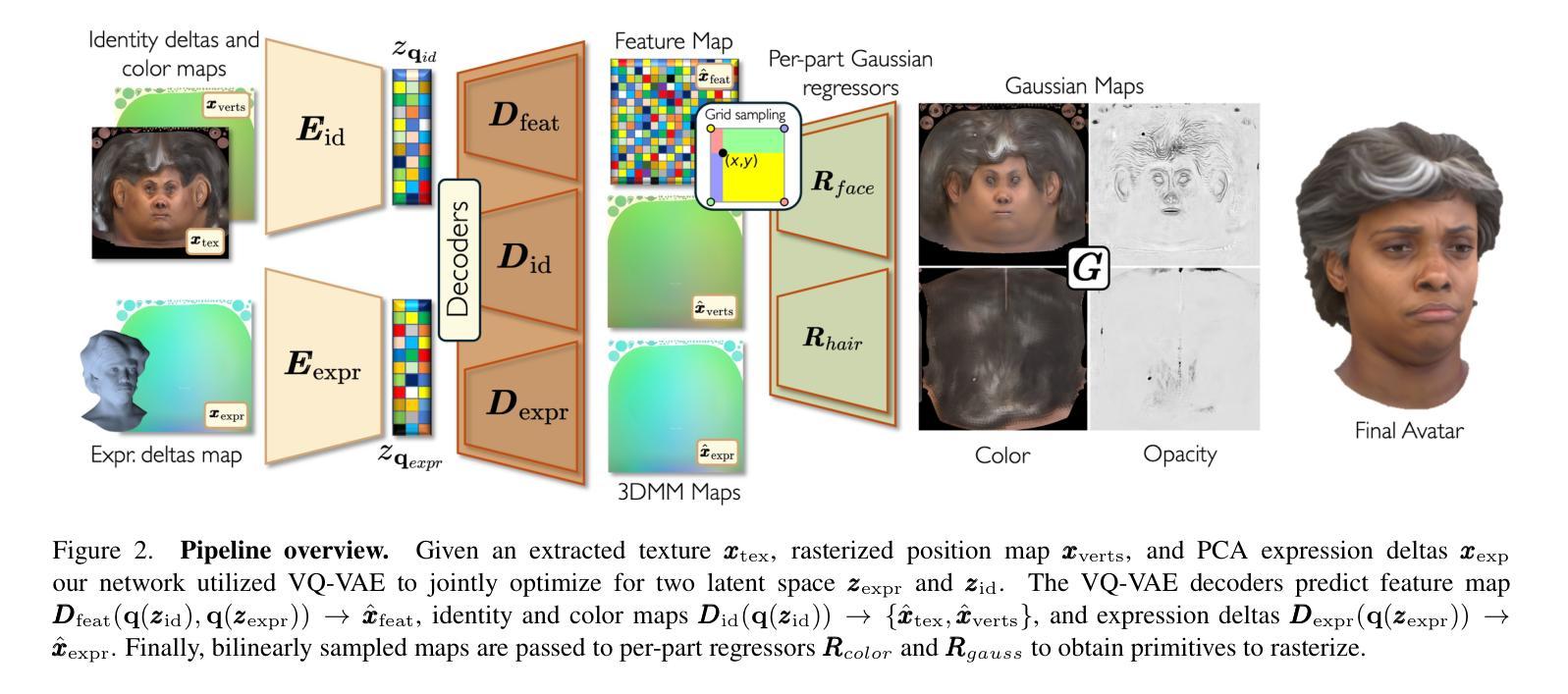
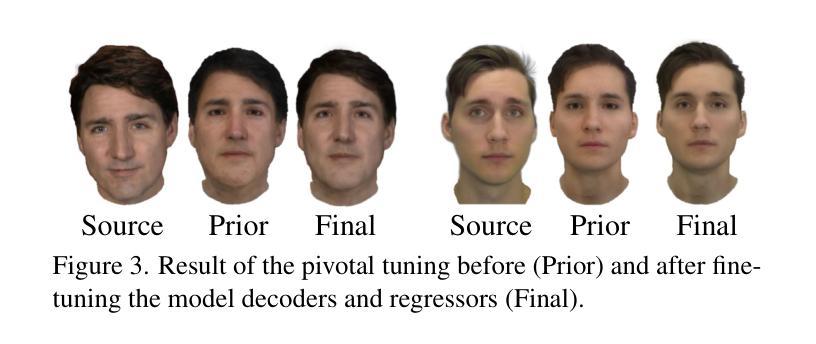
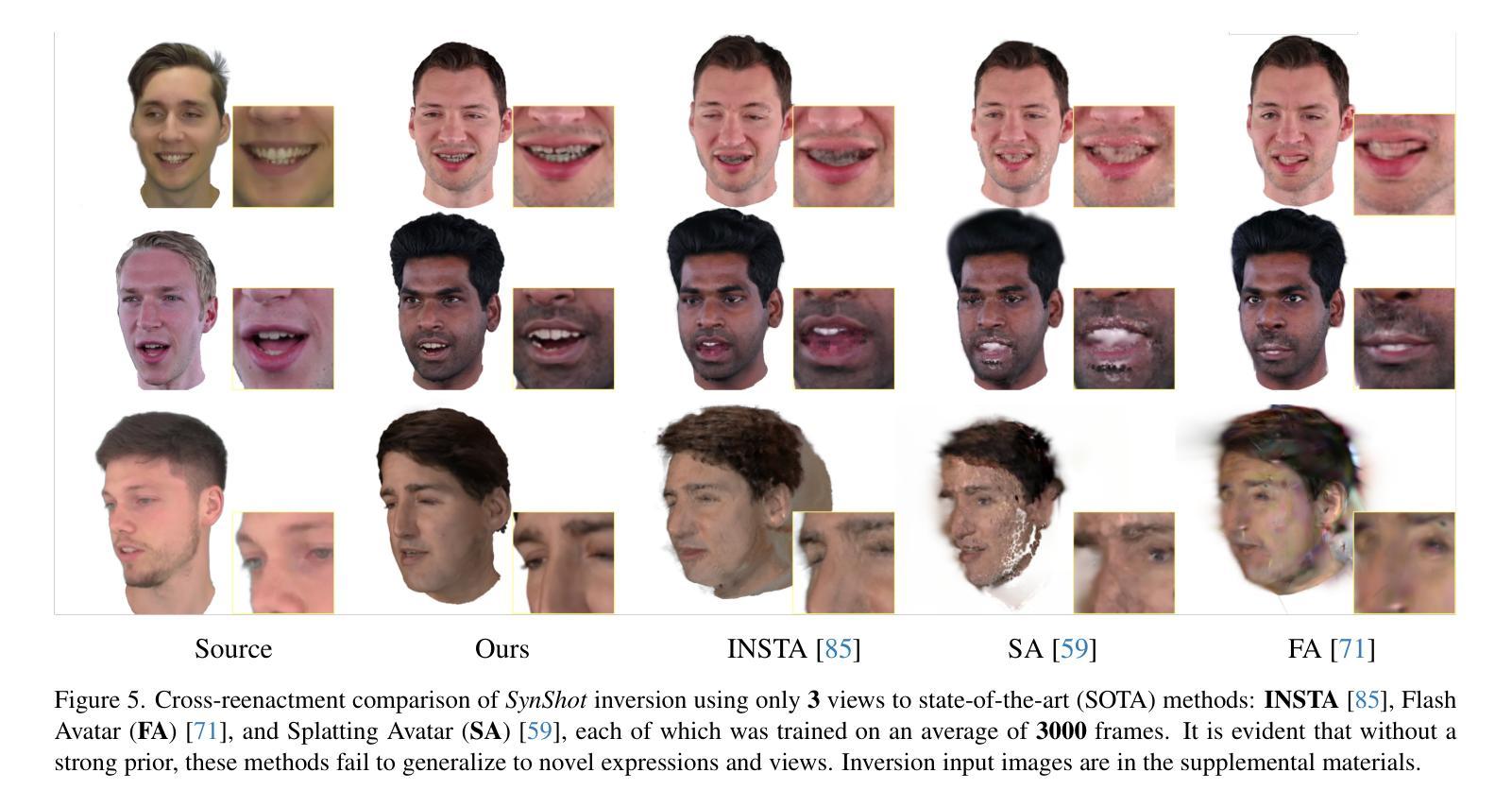
Synthetic Prior for Few-Shot Drivable Head Avatar Inversion
Authors:Wojciech Zielonka, Stephan J. Garbin, Alexandros Lattas, George Kopanas, Paulo Gotardo, Thabo Beeler, Justus Thies, Timo Bolkart
We present SynShot, a novel method for the few-shot inversion of a drivable head avatar based on a synthetic prior. We tackle three major challenges. First, training a controllable 3D generative network requires a large number of diverse sequences, for which pairs of images and high-quality tracked meshes are not always available. Second, the use of real data is strictly regulated (e.g., under the General Data Protection Regulation, which mandates frequent deletion of models and data to accommodate a situation when a participant’s consent is withdrawn). Synthetic data, free from these constraints, is an appealing alternative. Third, state-of-the-art monocular avatar models struggle to generalize to new views and expressions, lacking a strong prior and often overfitting to a specific viewpoint distribution. Inspired by machine learning models trained solely on synthetic data, we propose a method that learns a prior model from a large dataset of synthetic heads with diverse identities, expressions, and viewpoints. With few input images, SynShot fine-tunes the pretrained synthetic prior to bridge the domain gap, modeling a photorealistic head avatar that generalizes to novel expressions and viewpoints. We model the head avatar using 3D Gaussian splatting and a convolutional encoder-decoder that outputs Gaussian parameters in UV texture space. To account for the different modeling complexities over parts of the head (e.g., skin vs hair), we embed the prior with explicit control for upsampling the number of per-part primitives. Compared to SOTA monocular and GAN-based methods, SynShot significantly improves novel view and expression synthesis.
我们提出了一种名为SynShot的新方法,用于基于合成先验的少量驾驶头部半身像翻转。我们解决了三个主要挑战。首先,训练可控的3D生成网络需要大量的不同序列,而这些序列的图像和高品质跟踪网格并不总是可用。其次,真实数据的使用受到严格监管(例如,在《通用数据保护条例》下,当参与者同意撤回时,需要频繁删除模型和数据进行适应)。不受这些约束的合成数据是一个吸引人的选择。第三,最先进的单眼半身像模型在推广到新的视角和表情时遇到困难,缺乏强大的先验知识并且经常过度拟合特定的视角分布。受仅受合成数据训练的机器学习模型的启发,我们提出了一种方法,该方法从包含不同身份、表情和视角的大量合成头部数据中学习先验模型。SynShot使用少量输入图像对预训练的合成先验进行微调,以弥合领域差距,从而建立一个对新颖表情和视角具有普遍性的逼真头部半身像模型。我们使用3D高斯喷绘和卷积编码器-解码器来建立头部半身像模型,该编码器-解码器输出UV纹理空间的高斯参数。为了考虑头部各部分的建模复杂性(例如皮肤和头发),我们在先验中嵌入了一种明确控制方法来增加每部分的基本形态的数量。与最先进单眼和基于GAN的方法相比,SynShot显著提高了新颖的视点和表情合成效果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR25 Website: https://zielon.github.io/synshot/
Summary
基于合成先验数据的新型SynShot方法解决了驾驶头影在少量样本下的倒转问题。解决了三个主要问题:训练可控的3D生成网络需要大量不同的序列数据;真实数据的使用受到严格限制;最新的单眼化身模型缺乏强先验且难以泛化到新视角和表情。SynShot通过从大量合成头部数据中学习先验模型来解决问题,进而利用少量的图像进行微调以填补领域间的差距,从而实现能模拟现实感的头部化身。此法将头部化身建模为三维高斯拼贴,并使用卷积编码器解码器输出UV纹理空间的高斯参数。不同头部部位建模复杂度不同(如皮肤和头发),因此先验模型内置了对各部位原始数量进行上采样的明确控制。相较于现有的单眼和基于GAN的方法,SynShot极大地提高了对新视角和表情的合成能力。
Key Takeaways
- SynShot是一种基于合成先验数据的新方法,用于解决驾驶头影在有限样本下的倒转问题。
- 它解决了三个主要挑战:数据获取困难、真实数据使用的限制以及现有模型在新视角和表情上的泛化能力有限。
- SynShot通过从合成头部数据中学习先验模型来解决这些问题,并利用少量图像进行微调,以生成逼真的头部化身。
- 该方法采用三维高斯拼贴技术,并使用卷积编码器解码器在UV纹理空间中输出高斯参数。
- 对于头部不同部位的建模复杂度,SynShot提供了明确的控制机制,通过上采样各部位的原始数量来适应。
点此查看论文截图


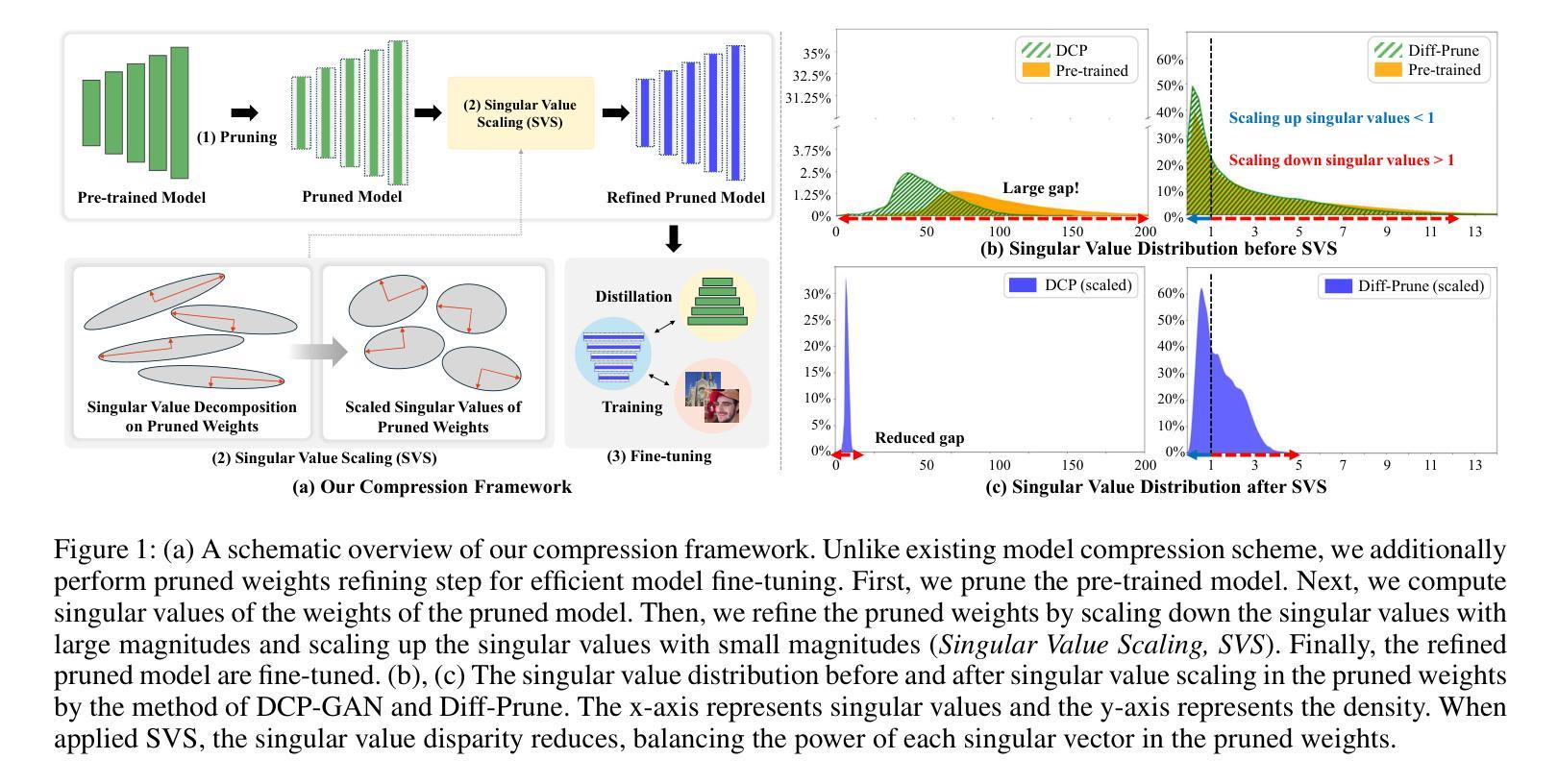
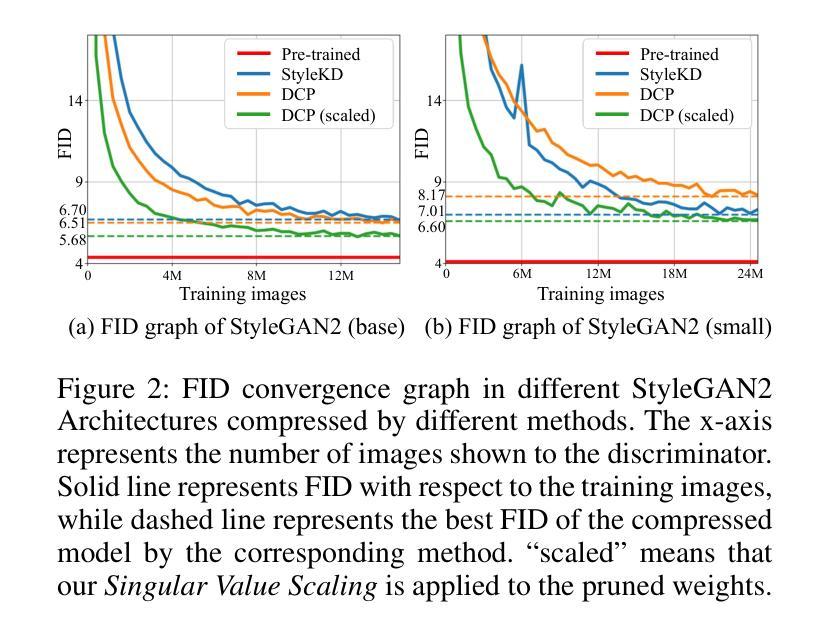
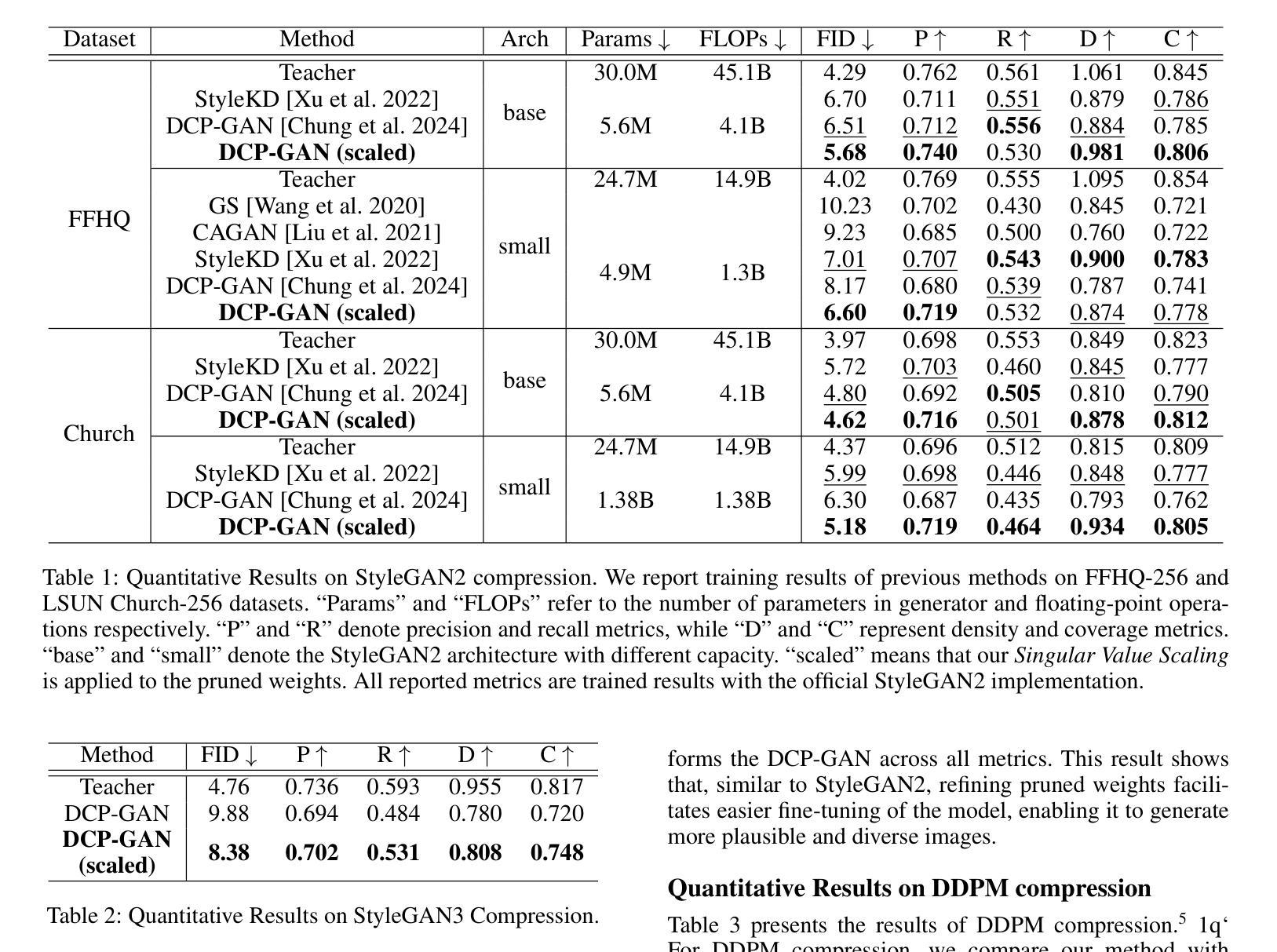
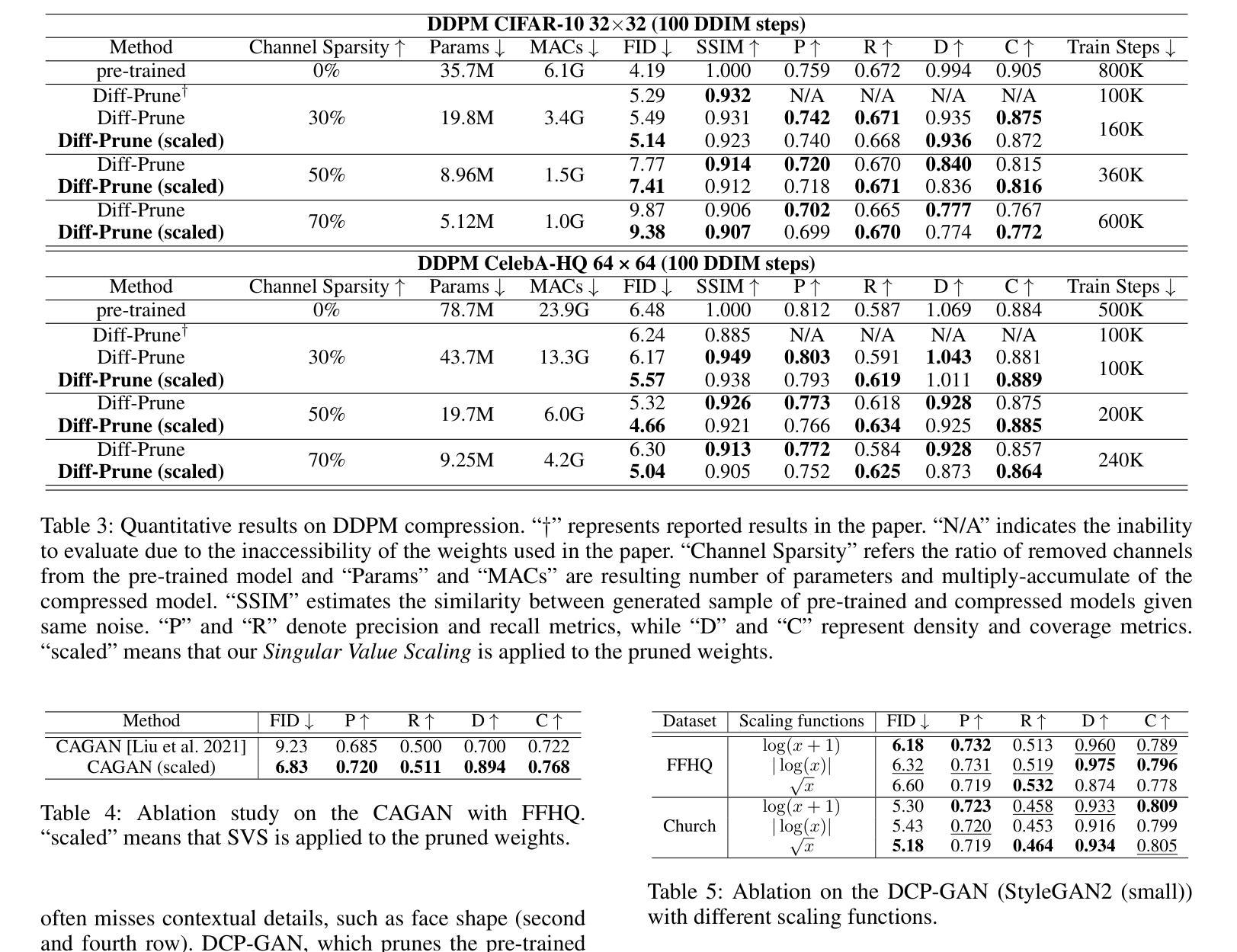
Singular Value Scaling: Efficient Generative Model Compression via Pruned Weights Refinement
Authors:Hyeonjin Kim, Jaejun Yoo
While pruning methods effectively maintain model performance without extra training costs, they often focus solely on preserving crucial connections, overlooking the impact of pruned weights on subsequent fine-tuning or distillation, leading to inefficiencies. Moreover, most compression techniques for generative models have been developed primarily for GANs, tailored to specific architectures like StyleGAN, and research into compressing Diffusion models has just begun. Even more, these methods are often applicable only to GANs or Diffusion models, highlighting the need for approaches that work across both model types. In this paper, we introduce Singular Value Scaling (SVS), a versatile technique for refining pruned weights, applicable to both model types. Our analysis reveals that pruned weights often exhibit dominant singular vectors, hindering fine-tuning efficiency and leading to suboptimal performance compared to random initialization. Our method enhances weight initialization by minimizing the disparities between singular values of pruned weights, thereby improving the fine-tuning process. This approach not only guides the compressed model toward superior solutions but also significantly speeds up fine-tuning. Extensive experiments on StyleGAN2, StyleGAN3 and DDPM demonstrate that SVS improves compression performance across model types without additional training costs. Our code is available at: https://github.com/LAIT-CVLab/Singular-Value-Scaling.
虽然剪枝方法可以有效地保持模型性能而无需额外的训练成本,但它们通常只专注于保留关键连接,而忽视了剪枝权重对后续微调或蒸馏的影响,从而导致效率低下。此外,大多数用于生成模型的压缩技术主要是针对生成对抗网络(GANs)开发的,适合特定的架构(如StyleGAN),而关于扩散模型(Diffusion models)的压缩研究才刚刚开始。更甚者,这些方法通常仅适用于GAN或扩散模型,这突显了对适用于这两种模型类型的方法的需求。在本文中,我们介绍了奇异值缩放(Singular Value Scaling,SVS),这是一种精炼剪枝权重的通用技术,适用于这两种模型类型。我们的分析表明,剪枝权重通常表现出主要的奇异向量,阻碍微调效率,导致与随机初始化相比性能不佳。我们的方法通过最小化剪枝权重的奇异值之间的差异来改进权重初始化,从而改进微调过程。这种方法不仅引导压缩模型走向更好的解决方案,而且显著加快了微调速度。在StyleGAN2、StyleGAN3和DDPM上的大量实验表明,SVS提高了各类模型的压缩性能,且无需额外的训练成本。我们的代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/LAIT-CVlab/Singular-Value-Scaling。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to AAAI 2025
Summary
在文本中,研究人员介绍了一种名为奇异值缩放(Singular Value Scaling,SVS)的技术,该技术能够精炼修剪权重并适用于多种模型类型。研究表明,修剪后的权重常常具有主导奇异向量,影响微调效率并导致性能不佳。SVS技术通过最小化修剪权重的奇异值差异来改进权重初始化,从而提高微调过程的速度和压缩模型的性能。在StyleGAN2、StyleGAN3和DDPM上的实验证明,SVS技术可跨模型类型提升压缩性能,且无需额外训练成本。
Key Takeaways
- 修剪方法在维持模型性能的同时不增加额外训练成本,但往往只关注保留关键连接。
- 修剪后的权重对后续的微调或蒸馏的影响常被忽视,导致效率降低。
- 大多数生成模型的压缩技术主要针对GANs(如StyleGAN)开发,对Diffusion模型的压缩研究才刚刚开始。
- 当前方法通常仅适用于GANs或Diffusion模型,需要开发适用于两种模型类型的方法。
- 引入奇异值缩放(SVS)技术,这是一种精炼修剪权重的通用方法,适用于各种模型。
- 修剪后的权重具有主导奇异向量,影响微调效率和性能。
点此查看论文截图