⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-04 更新
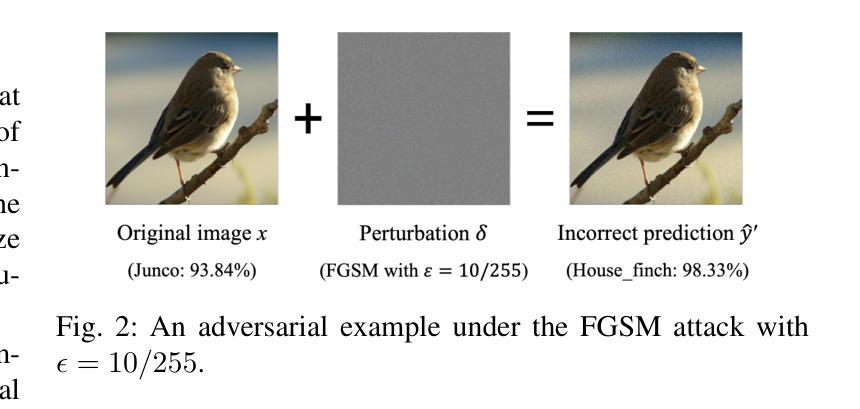
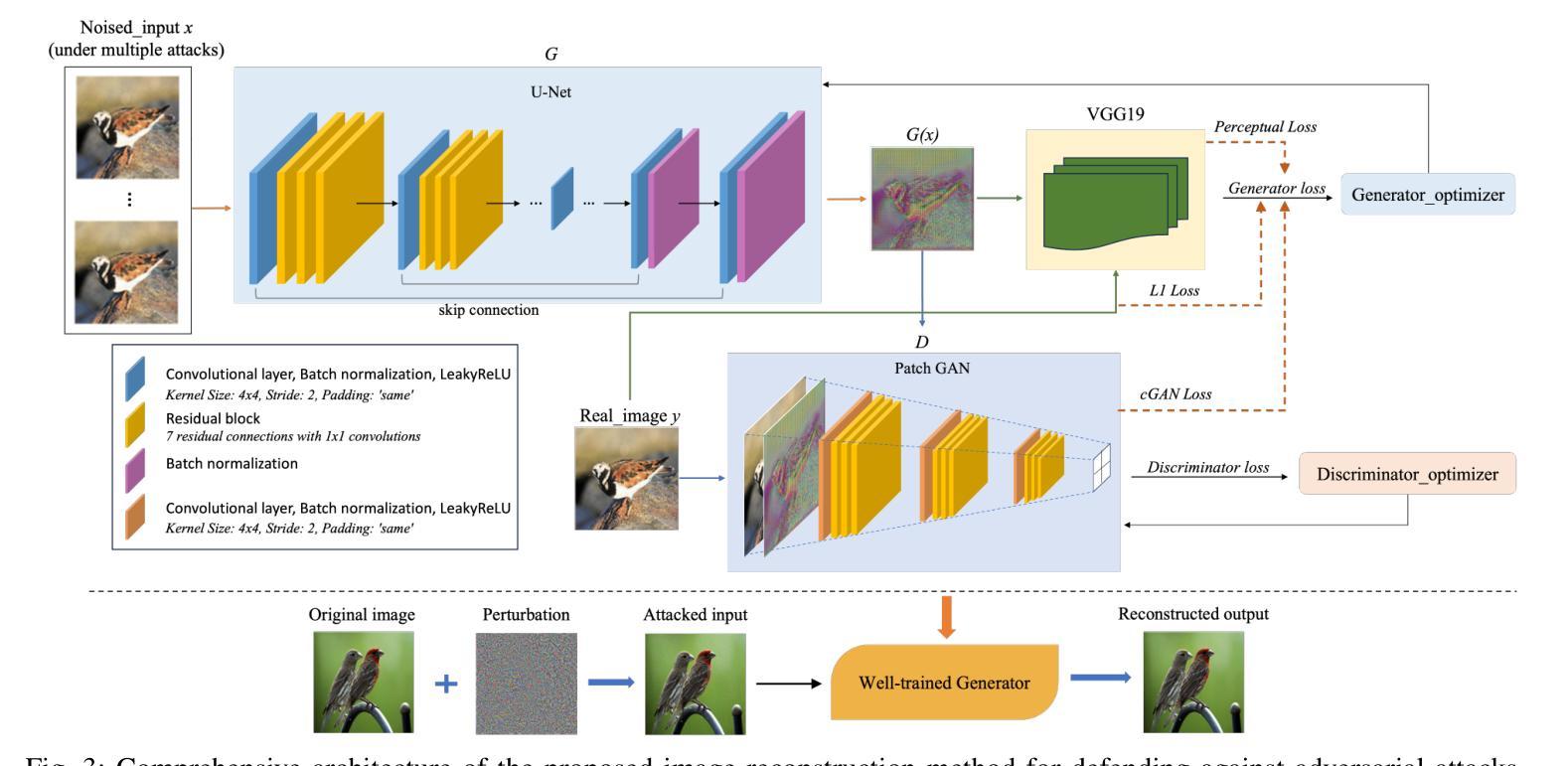
Leveraging Generalizability of Image-to-Image Translation for Enhanced Adversarial Defense
Authors:Haibo Zhang, Zhihua Yao, Kouichi Sakurai, Takeshi Saitoh
In the rapidly evolving field of artificial intelligence, machine learning emerges as a key technology characterized by its vast potential and inherent risks. The stability and reliability of these models are important, as they are frequent targets of security threats. Adversarial attacks, first rigorously defined by Ian Goodfellow et al. in 2013, highlight a critical vulnerability: they can trick machine learning models into making incorrect predictions by applying nearly invisible perturbations to images. Although many studies have focused on constructing sophisticated defensive mechanisms to mitigate such attacks, they often overlook the substantial time and computational costs of training and maintaining these models. Ideally, a defense method should be able to generalize across various, even unseen, adversarial attacks with minimal overhead. Building on our previous work on image-to-image translation-based defenses, this study introduces an improved model that incorporates residual blocks to enhance generalizability. The proposed method requires training only a single model, effectively defends against diverse attack types, and is well-transferable between different target models. Experiments show that our model can restore the classification accuracy from near zero to an average of 72% while maintaining competitive performance compared to state-of-the-art methods.
在人工智能这个快速发展的领域里,机器学习作为一种具有巨大潜力和固有风险的关键技术而崭露头角。这些模型的稳定性和可靠性非常重要,因为它们经常受到安全威胁的侵袭。Ian Goodfellow等人在2013年首次严格定义的对抗性攻击,凸显了一个关键漏洞:他们可以通过对图像施加几乎不可见的扰动,欺骗机器学习模型做出错误的预测。尽管许多研究致力于构建复杂的防御机制来减轻这类攻击,但它们往往忽视了训练和维持这些模型的巨大时间和计算成本。理想的防御方法应该能够在各种甚至未知的对抗性攻击中具有通用性,并且具有最小的额外开销。本研究基于我们之前在基于图像到图像翻译的防御方面的工作,引入了一个改进模型,该模型结合了残差块以增强通用性。所提出的方法只需要训练一个单一模型,就能有效地防御多种攻击类型,并且在不同的目标模型之间具有良好的可迁移性。实验表明,我们的模型可以将分类准确率从接近零恢复到平均72%,同时与最新方法相比保持竞争力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
机器学习模型在人工智能的快速发展中展现出巨大的潜力和固有的风险。模型的稳定性和可靠性尤为重要,因为它们经常面临安全威胁。对抗性攻击是机器学习模型的关键漏洞之一,可以通过对图像施加几乎不可见的扰动来误导模型做出错误的预测。尽管许多研究致力于构建复杂的防御机制来减轻这些攻击,但它们往往忽略了训练和维持这些模型的巨大时间和计算成本。本研究基于我们在图像到图像翻译防御方面的工作,提出了一种改进的模型,该模型结合了残差块以增强通用性。所提出的方法只需要训练一个模型,可以有效地防御多种攻击类型,并且在不同的目标模型之间具有良好的可转移性。实验表明,我们的模型可以将分类准确率从接近于零恢复到平均72%,同时与最先进的方法相比保持竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 机器学习在人工智能领域展现出巨大潜力,但存在对抗性攻击的安全风险。
- 对抗性攻击能够通过几乎不可见的扰动误导机器学习模型做出错误预测。
- 许多防御机制的研究忽略了训练和维持防御模型的巨大时间和计算成本。
- 本研究基于图像到图像翻译防御工作,提出了一个改进的模型。
- 改进模型结合了残差块以增强通用性,能防御多种攻击类型,并在不同目标模型间具有良好的可转移性。
- 实验结果显示,该模型能将分类准确率从近乎零恢复到平均72%。
- 该模型的性能与当前最先进的方法相比具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图

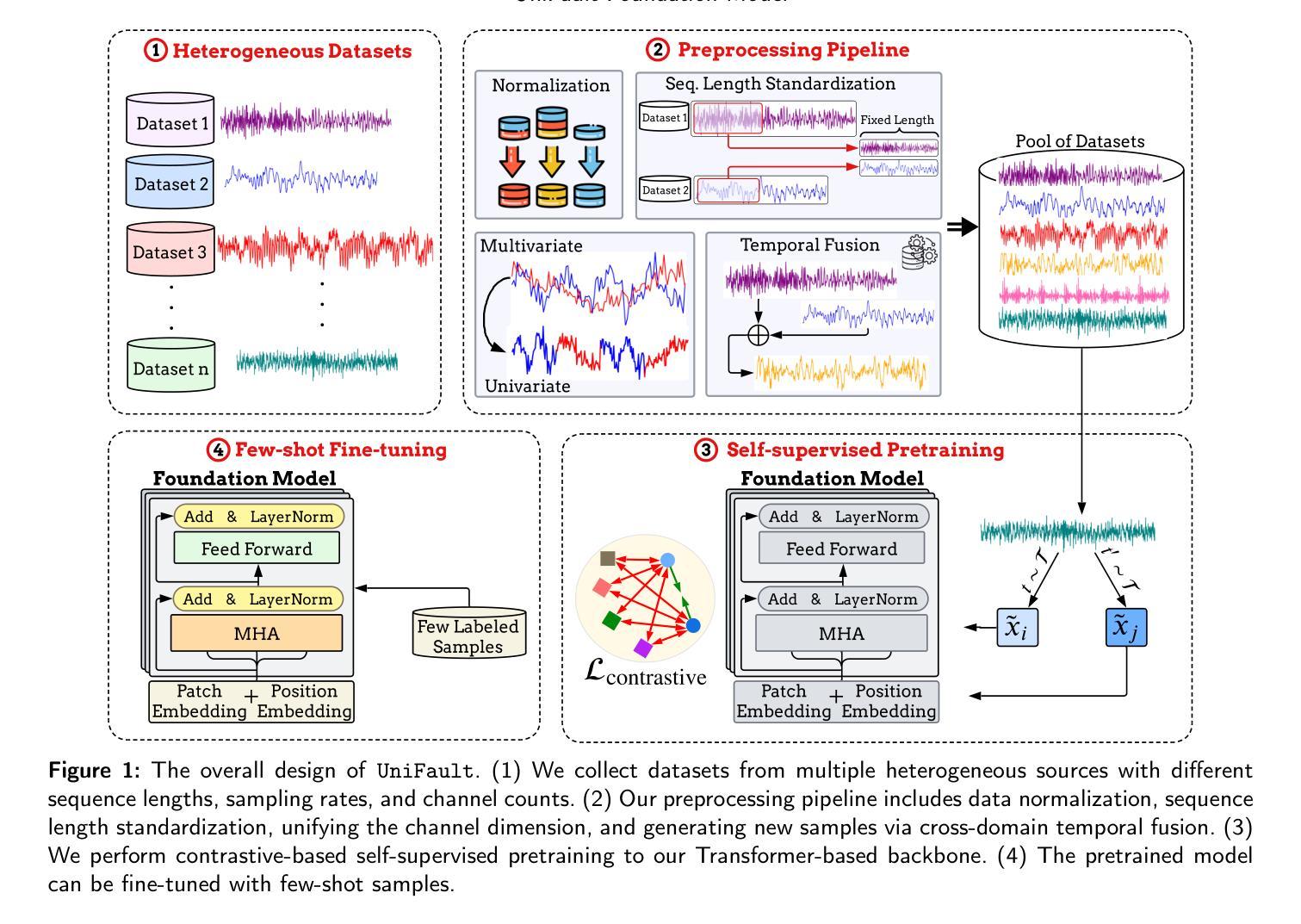
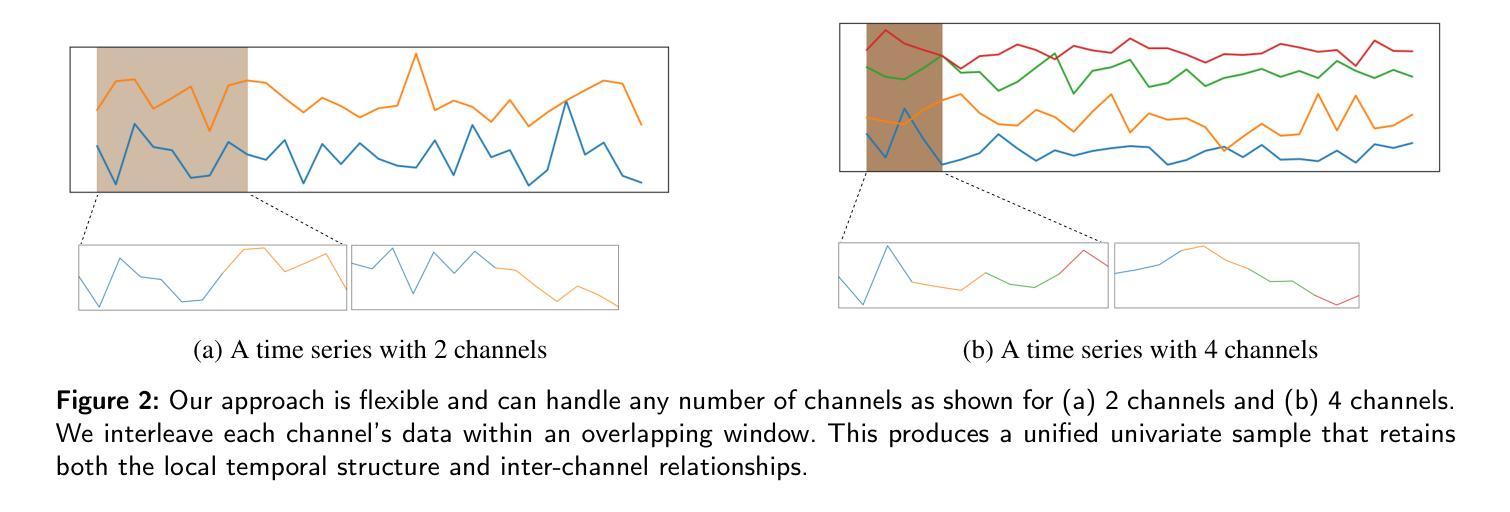
UniFault: A Fault Diagnosis Foundation Model from Bearing Data
Authors:Emadeldeen Eldele, Mohamed Ragab, Xu Qing, Edward, Zhenghua Chen, Min Wu, Xiaoli Li, Jay Lee
Machine fault diagnosis (FD) is a critical task for predictive maintenance, enabling early fault detection and preventing unexpected failures. Despite its importance, existing FD models are operation-specific with limited generalization across diverse datasets. Foundation models (FM) have demonstrated remarkable potential in both visual and language domains, achieving impressive generalization capabilities even with minimal data through few-shot or zero-shot learning. However, translating these advances to FD presents unique hurdles. Unlike the large-scale, cohesive datasets available for images and text, FD datasets are typically smaller and more heterogeneous, with significant variations in sampling frequencies and the number of channels across different systems and applications. This heterogeneity complicates the design of a universal architecture capable of effectively processing such diverse data while maintaining robust feature extraction and learning capabilities. In this paper, we introduce UniFault, a foundation model for fault diagnosis that systematically addresses these issues. Specifically, the model incorporates a comprehensive data harmonization pipeline featuring two key innovations. First, a unification scheme transforms multivariate inputs into standardized univariate sequences while retaining local inter-channel relationships. Second, a novel cross-domain temporal fusion strategy mitigates distribution shifts and enriches sample diversity and count, improving the model generalization across varying conditions. UniFault is pretrained on over 9 billion data points spanning diverse FD datasets, enabling superior few-shot performance. Extensive experiments on real-world FD datasets demonstrate that UniFault achieves SoTA performance, setting a new benchmark for fault diagnosis models and paving the way for more scalable and robust predictive maintenance solutions.
机器故障诊断(FD)是预测性维护中的一项关键任务,能够实现早期故障检测并防止意外故障。尽管其重要性不言而喻,但现有的FD模型都是针对特定操作的,在多种数据集之间的泛化能力有限。基础模型(FM)在视觉和语言领域都表现出了显著的优势,即使在少量数据的情况下,也能通过小样本或零样本学习实现令人印象深刻的泛化能力。然而,将这些进展应用于FD却面临独特的障碍。与可用于图像和文本的规模庞大、连贯的数据集不同,FD数据集通常较小且更异质,不同系统和应用之间的采样频率和数据通道数量存在重大差异。这种异质性使得设计一个能够处理如此多样数据的同时保持稳健的特征提取和学习能力的通用架构变得复杂。在本文中,我们引入了UniFault,这是一个用于故障诊断的基础模型,系统地解决了这些问题。具体来说,该模型结合了一个全面的数据调和管道,包含两个关键的创新点。首先,一个统一方案将多元输入转换为标准化的单变量序列,同时保留局部通道间的关系。其次,一种新的跨域时间融合策略缓解了分布偏移问题并丰富了样本的多样性和数量,提高了模型在不同条件下的泛化能力。UniFault在跨越多种FD数据集的超过9亿个数据点上进行预训练,实现了卓越的小样本性能。在真实世界的FD数据集上的广泛实验表明,UniFault达到了最新的性能水平,为故障诊断模型设定了新的基准,并为更可扩展和稳健的预测性维护解决方案铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
机器故障诊断(FD)是预测性维护中的一项关键任务,能够实现对早期故障的及时检测,避免意外停机情况的出现。虽然故障诊断模型的发展非常重要,但目前存在大量的操作特定模型,这些模型的跨数据集泛化能力受限。基础模型(FM)在视觉和语言领域已经展现出令人瞩目的潜力,通过少量样本学习或零样本学习即可实现令人印象深刻的泛化能力。然而,将这一进展转化为故障诊断面临着独特的挑战。与可用于图像和文本的大规模、连贯数据集相比,故障诊断数据集通常更小、更异质,不同系统和应用之间的采样频率和数据通道数量存在显著差异。这种异质性使得设计一种能够处理此类多样数据同时保持稳健的特征提取和学习能力的通用架构变得复杂。本文介绍了用于故障诊断的基础模型UniFault,该模型系统地解决了这些问题。具体来说,该模型包含全面的数据调和管道,具有两大创新之处。首先,统一方案将多元输入转换为标准化的单变量序列,同时保留局部通道间关系。其次,一种新的跨域时间融合策略缓解了分布偏移问题并丰富了样本多样性和计数,提高了模型在不同条件下的泛化能力。UniFault在跨越多个故障诊断数据集超过9亿个数据点上进行预训练,实现了出色的少量样本性能。在真实世界的故障诊断数据集上进行的大量实验表明,UniFault达到了最先进的性能水平,为故障诊断模型设定了新的基准线,并为更可扩展和稳健的预测性维护解决方案铺平了道路。
要点提炼
- 机器故障诊断(FD)是预测性维护中的核心任务,要求早期故障检测并避免意外停机。
- 当前FD模型操作特定性强,泛化能力受限。
- 基础模型(FM)在视觉和语言领域具有出色的泛化能力。
- 将FM应用于FD面临数据集小、异质性的挑战。
- UniFault模型通过数据调和管道解决这些问题,包括输入数据的统一转换和跨域时间融合策略。
- UniFault模型在大量FD数据集上进行预训练,实现优秀少量样本性能。
点此查看论文截图

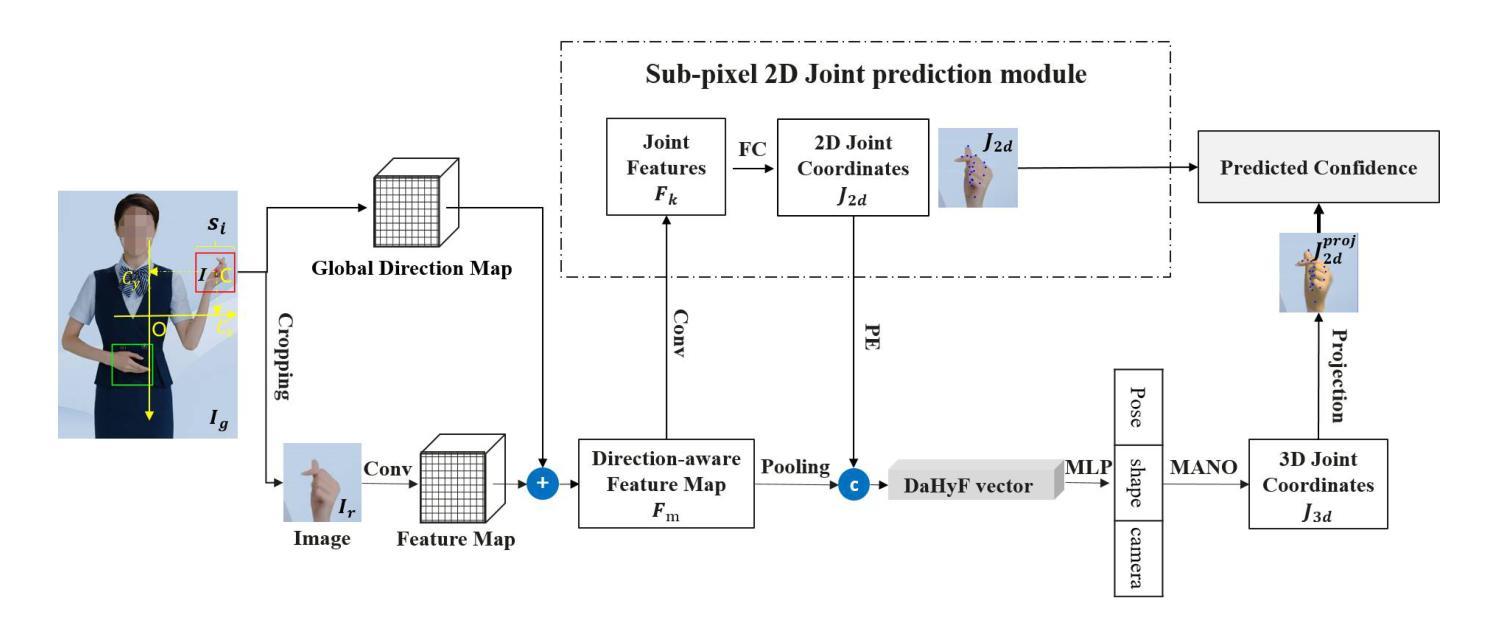
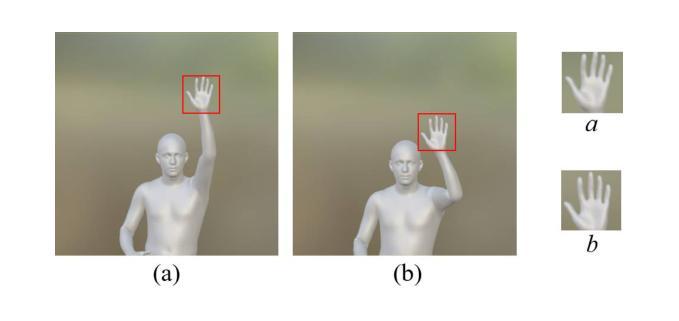
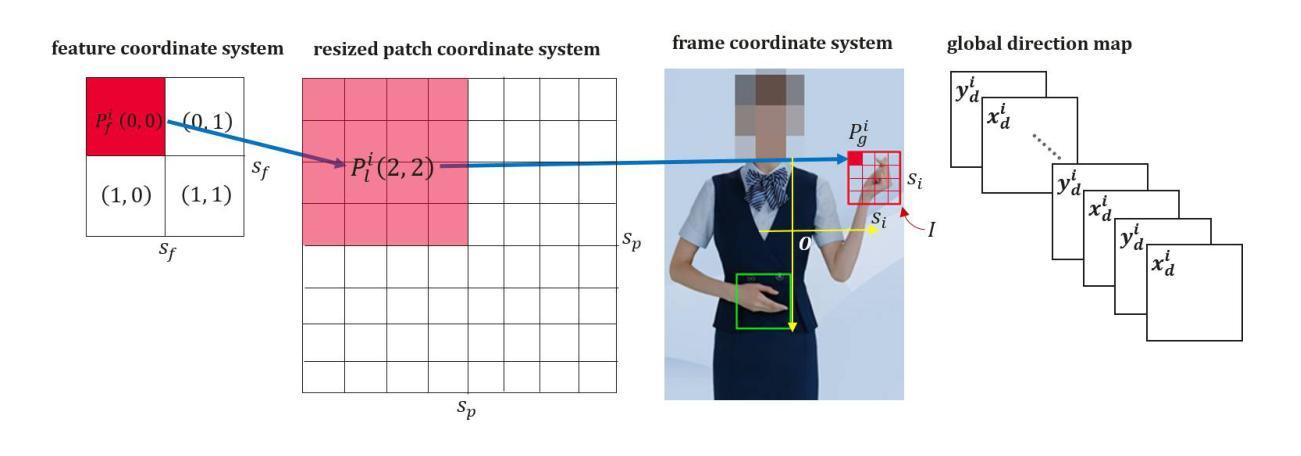
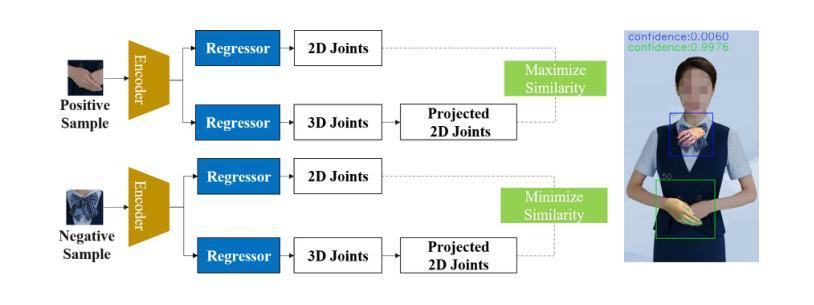
Direction-Aware Hybrid Representation Learning for 3D Hand Pose and Shape Estimation
Authors:Shiyong Liu, Zhihao Li, Xiao Tang, Jianzhuang Liu
Most model-based 3D hand pose and shape estimation methods directly regress the parametric model parameters from an image to obtain 3D joints under weak supervision. However, these methods involve solving a complex optimization problem with many local minima, making training difficult. To address this challenge, we propose learning direction-aware hybrid features (DaHyF) that fuse implicit image features and explicit 2D joint coordinate features. This fusion is enhanced by the pixel direction information in the camera coordinate system to estimate pose, shape, and camera viewpoint. Our method directly predicts 3D hand poses with DaHyF representation and reduces jittering during motion capture using prediction confidence based on contrastive learning. We evaluate our method on the FreiHAND dataset and show that it outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods by more than 33% in accuracy. DaHyF also achieves the top ranking on both the HO3Dv2 and HO3Dv3 leaderboards for the metric of Mean Joint Error (after scale and translation alignment). Compared to the second-best results, the largest improvement observed is 10%. We also demonstrate its effectiveness in real-time motion capture scenarios with hand position variability, occlusion, and motion blur.
大多数基于模型的3D手势姿态和形状估计方法直接通过图像回归参数模型参数,以在弱监督下获得3D关节。然而,这些方法需要解决具有多个局部最小值的复杂优化问题,使得训练变得困难。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了学习方向感知混合特征(DaHyF),该特征融合了隐式图像特征和显式的2D关节坐标特征。这种融合通过相机坐标系中的像素方向信息来增强,以估计姿态、形状和相机视点。我们的方法直接使用DaHyF表示预测3D手势姿态,并利用基于对比学习的预测置信度减少运动捕捉过程中的抖动。我们在FreiHAND数据集上评估了我们的方法,结果表明,在准确性方面,它比现有最先进的方法高出33%以上。DaHyF在HO3Dv2和HO3Dv3排行榜上的平均关节误差指标方面也获得了排名第一。与第二好的结果相比,观察到的最大改进是10%。我们还证明了它在具有手部位置变化、遮挡和运动模糊的实时运动捕捉场景中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025 workshop
Summary
手姿三维姿态及形状估算中,许多模型基于回归图像参数化模型参数来得到三维关节点,但存在训练困难的问题。为解决此问题,我们提出学习方向感知混合特征(DaHyF),融合隐性图像特征和显性二维关节坐标特征,并结合相机坐标系中的像素方向信息来估算姿态、形状和相机视角。该方法可直接预测三维手姿态,通过对比学习减少运动捕捉时的抖动。在FreiHAND数据集上的实验表明,其准确度高于现有先进技术超过33%,在HO3Dv2和HO3Dv3排行榜上的平均关节误差排名也位居前列。对实时运动捕捉场景下的手部位置变化、遮挡和运动模糊等情况进行了验证。
Key Takeaways
- 提出学习方向感知混合特征(DaHyF)以融合隐性图像特征和显性二维关节坐标特征。
- DaHyF结合像素方向信息在相机坐标系中估算姿态、形状和相机视角。
- 方法能减少运动捕捉时的抖动问题,增强预测的准确性。
- 在FreiHAND数据集上的准确度显著提高,准确率超越现有技术至少33%。
- DaHyF在HO3Dv2和HO3Dv3排行榜上的平均关节误差排名名列前茅,相对第二好的结果最高提升了10%。
- DaHyF适用于多种真实场景,包括手部位置变化、遮挡和运动模糊等情况。
点此查看论文截图

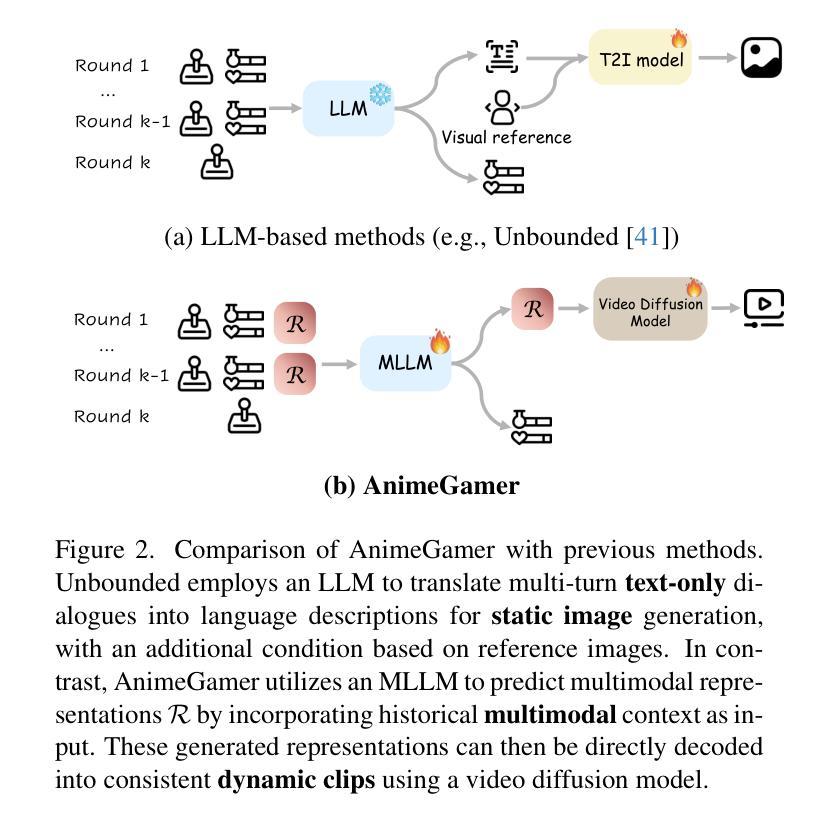
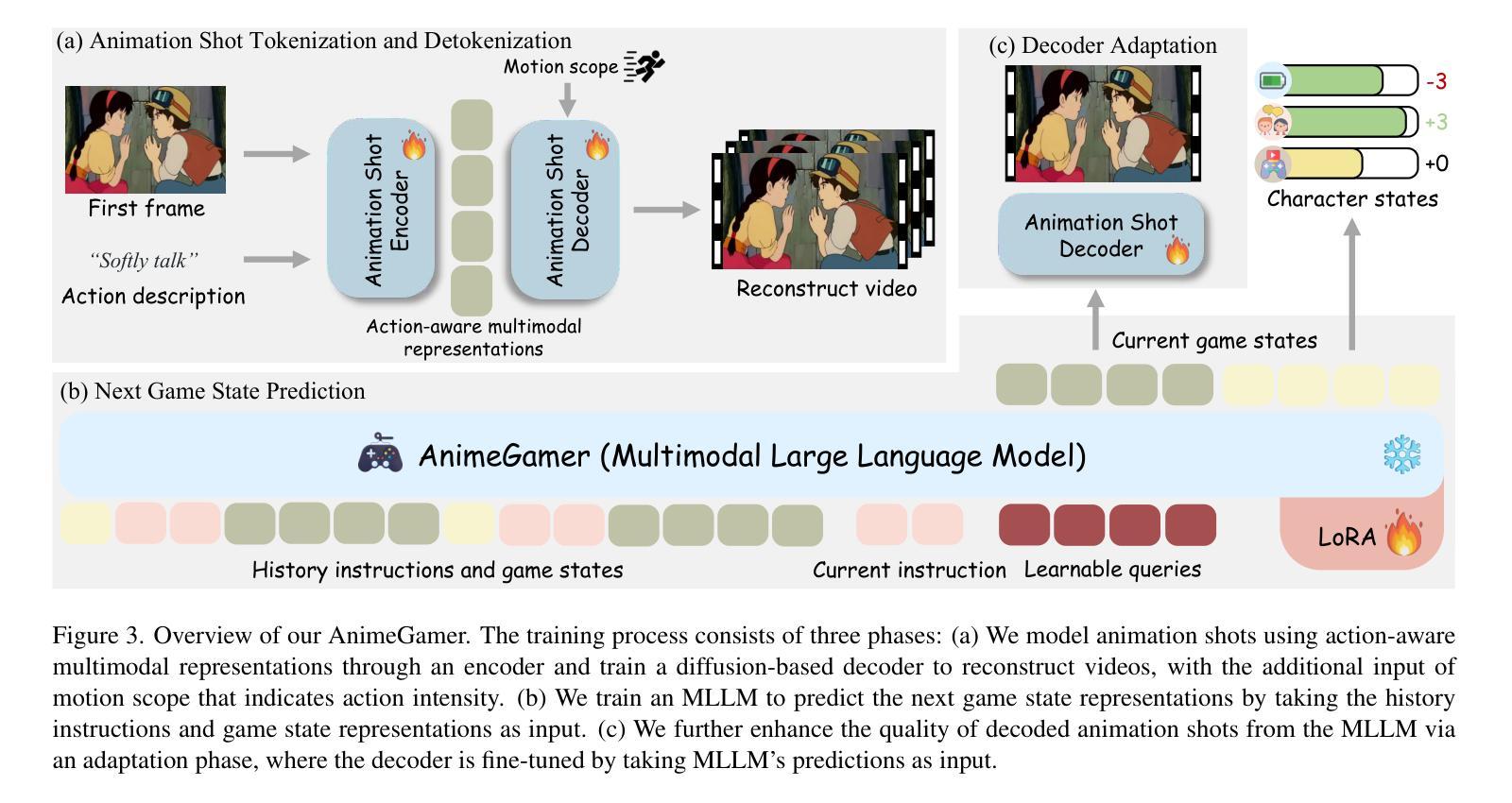
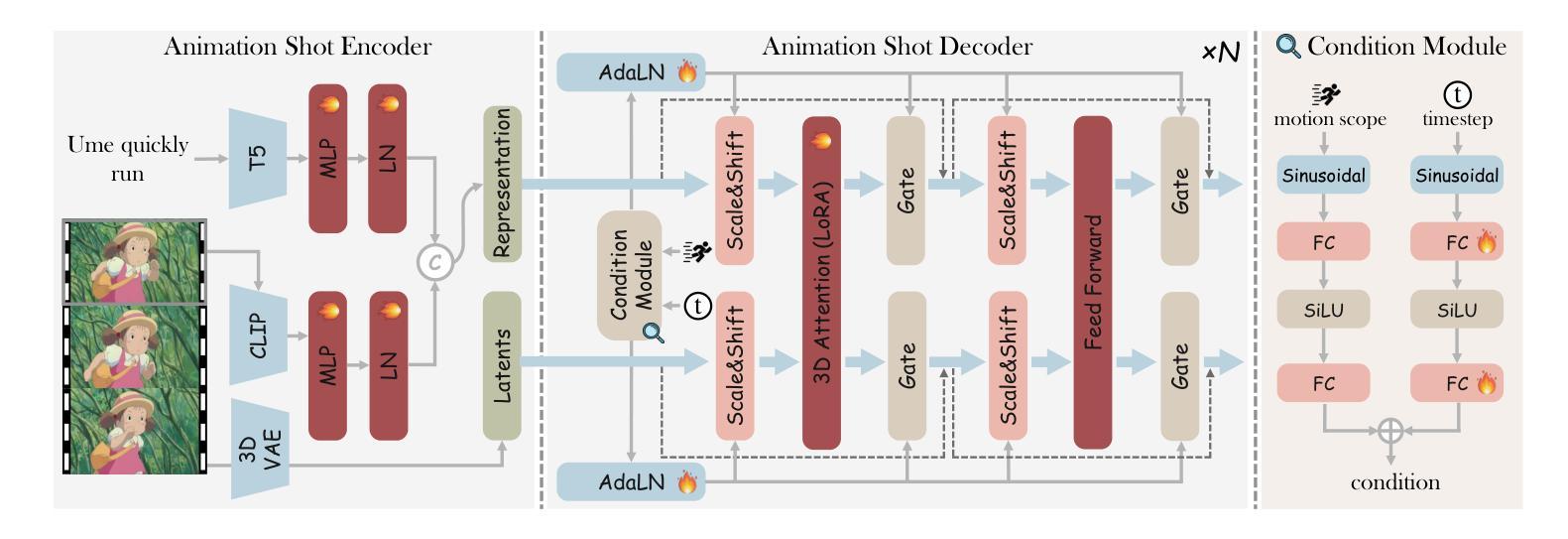
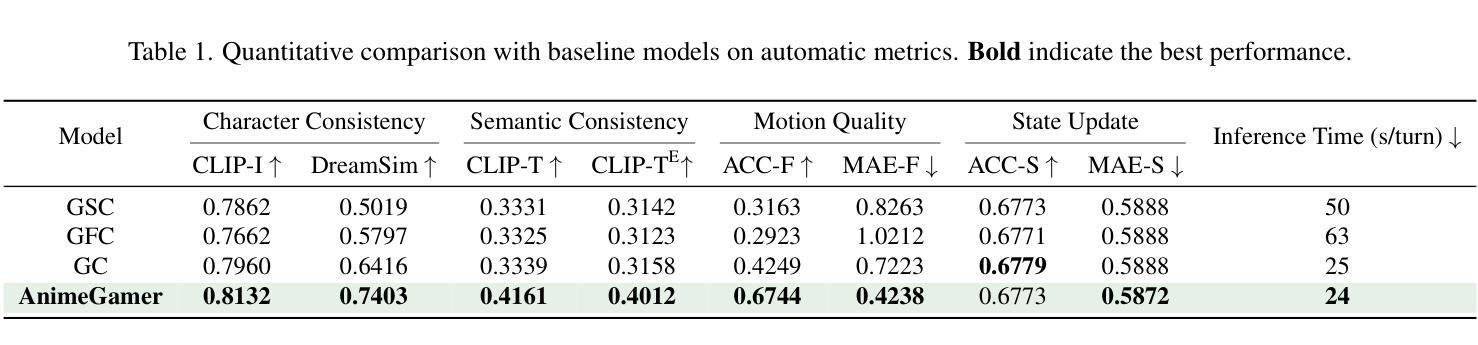
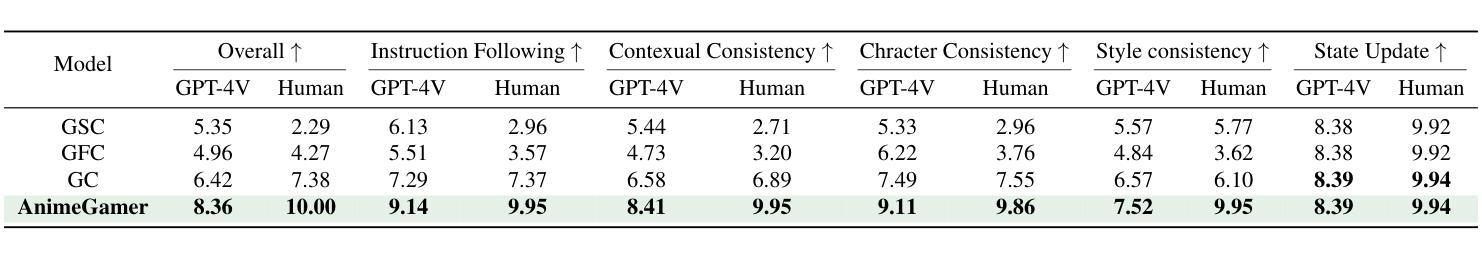
AnimeGamer: Infinite Anime Life Simulation with Next Game State Prediction
Authors:Junhao Cheng, Yuying Ge, Yixiao Ge, Jing Liao, Ying Shan
Recent advancements in image and video synthesis have opened up new promise in generative games. One particularly intriguing application is transforming characters from anime films into interactive, playable entities. This allows players to immerse themselves in the dynamic anime world as their favorite characters for life simulation through language instructions. Such games are defined as infinite game since they eliminate predetermined boundaries and fixed gameplay rules, where players can interact with the game world through open-ended language and experience ever-evolving storylines and environments. Recently, a pioneering approach for infinite anime life simulation employs large language models (LLMs) to translate multi-turn text dialogues into language instructions for image generation. However, it neglects historical visual context, leading to inconsistent gameplay. Furthermore, it only generates static images, failing to incorporate the dynamics necessary for an engaging gaming experience. In this work, we propose AnimeGamer, which is built upon Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to generate each game state, including dynamic animation shots that depict character movements and updates to character states, as illustrated in Figure 1. We introduce novel action-aware multimodal representations to represent animation shots, which can be decoded into high-quality video clips using a video diffusion model. By taking historical animation shot representations as context and predicting subsequent representations, AnimeGamer can generate games with contextual consistency and satisfactory dynamics. Extensive evaluations using both automated metrics and human evaluations demonstrate that AnimeGamer outperforms existing methods in various aspects of the gaming experience. Codes and checkpoints are available at https://github.com/TencentARC/AnimeGamer.
最近图像和视频合成的进展为生成游戏带来了新的前景。一个特别吸引人的应用是将动漫电影中的角色转变为可互动的游戏实体。这允许玩家通过语言指令沉浸在动态的动漫世界中,扮演他们最喜欢的角色进行生活模拟。这类游戏被定义为无限游戏,因为它们消除了预定的边界和固定的游戏规则,玩家可以通过开放式的语言与游戏世界互动,体验不断演变的故事情节和环境。最近,一种用于无限动漫生活模拟的开创性方法采用大型语言模型(LLM)将多轮文本对话翻译为图像生成的语言指令。然而,它忽略了历史视觉上下文,导致游戏体验不一致。此外,它只能生成静态图像,无法融入动态元素,无法提供引人入胜的游戏体验。在这项工作中,我们提出了AnimeGamer,它基于多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)来生成每种游戏状态,包括描绘角色动作和状态更新的动态动画镜头,如图1所示。我们引入了新型的动作感知多模态表示法来表示动画镜头,可以使用视频扩散模型将其解码为高质量的视频片段。通过获取历史动画镜头表示作为上下文并预测随后的表示,AnimeGamer可以生成具有上下文一致性和令人满意的动力学特性的游戏。使用自动化指标和人类评估的广泛评估表明,AnimeGamer在游戏体验的各个方面都优于现有方法。代码和检查点可用于https://github.com/TencentARC/AnimeGamer。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project released at: https://howe125.github.io/AnimeGamer.github.io/
Summary
本文介绍了最新图像和视频合成技术在生成游戏领域的应用,特别是在将动漫角色转化为可互动实体方面的应用。游戏玩家可以通过语言指令沉浸于动态的动漫世界,并扮演他们最喜欢的角色进行生活模拟。提出了一种基于多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)构建的AnimeGamer系统,能够生成游戏状态,包括动态动画镜头和角色状态更新。通过引入新型的动作感知多模态表示方法,并结合视频扩散模型,生成的游戏具有上下文一致性和满意的动态效果。
Key Takeaways
- 最新图像和视频合成技术为生成游戏领域带来新希望。
- 将动漫角色转化为可互动实体是一种引人入胜的应用。
- 玩家可通过语言指令沉浸于动漫世界,扮演喜欢的角色进行生活模拟。
- 提出了一种基于多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的AnimeGamer系统。
- AnimeGamer能生成包括动态动画镜头的游戏状态。
- 通过引入动作感知多模态表示方法,结合视频扩散模型,实现游戏的上下文一致性和动态效果。
点此查看论文截图

SCFANet: Style Distribution Constraint Feature Alignment Network For Pathological Staining Translation
Authors:Zetong Chen, Yuzhuo Chen, Hai Zhong, Xu Qiao
Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining serves as a valuable technique for detecting specific antigens or proteins through antibody-mediated visualization. However, the IHC staining process is both time-consuming and costly. To address these limitations, the application of deep learning models for direct translation of cost-effective Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) stained images into IHC stained images has emerged as an efficient solution. Nevertheless, the conversion from H&E to IHC images presents significant challenges, primarily due to alignment discrepancies between image pairs and the inherent diversity in IHC staining style patterns. To overcome these challenges, we propose the Style Distribution Constraint Feature Alignment Network (SCFANet), which incorporates two innovative modules: the Style Distribution Constrainer (SDC) and Feature Alignment Learning (FAL). The SDC ensures consistency between the generated and target images’ style distributions while integrating cycle consistency loss to maintain structural consistency. To mitigate the complexity of direct image-to-image translation, the FAL module decomposes the end-to-end translation task into two subtasks: image reconstruction and feature alignment. Furthermore, we ensure pathological consistency between generated and target images by maintaining pathological pattern consistency and Optical Density (OD) uniformity. Extensive experiments conducted on the Breast Cancer Immunohistochemical (BCI) dataset demonstrate that our SCFANet model outperforms existing methods, achieving precise transformation of H&E-stained images into their IHC-stained counterparts. The proposed approach not only addresses the technical challenges in H&E to IHC image translation but also provides a robust framework for accurate and efficient stain conversion in pathological analysis.
免疫组织化学(IHC)染色作为一种通过抗体介导的可视化检测特定抗原或蛋白质的有价值的技术。然而,IHC染色过程既耗时又成本高昂。为了解决这些局限性,应用深度学习模型将成本效益高的苏木精和伊红(H&E)染色图像直接翻译成IHC染色图像已成为一种有效的解决方案。然而,从H&E到IHC图像的转换存在重大挑战,主要是由于图像对之间的对齐差异和IHC染色风格模式的固有多样性。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了风格分布约束特征对齐网络(SCFANet),它包含两个创新模块:风格分布约束器(SDC)和特征对齐学习(FAL)。SDC确保生成图像和目标图像之间风格分布的一致性,同时结合循环一致性损失以保持结构一致性。为了减轻直接图像到图像翻译的复杂性,FAL模块将端到端的翻译任务分解为两个子任务:图像重建和特征对齐。此外,我们通过保持病理模式一致性和光学密度(OD)均匀性,确保生成图像和目标图像之间的病理一致性。在乳腺癌免疫组织化学(BCI)数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,我们的SCFANet模型优于现有方法,实现了H&E染色图像到IHC染色图像的精确转换。该方法不仅解决了H&E到IHC图像转换的技术挑战,而且为病理分析中的准确高效染色转换提供了稳健的框架。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
IHC染色技术用于检测特定抗原或蛋白质,但过程耗时且成本高昂。为解决这些问题,研究者利用深度学习模型将经济高效的H&E染色图像直接转换为IHC染色图像。然而,转换过程中存在对齐差异和IHC染色风格模式多样性等挑战。为此,提出SCFANet模型,包括SDC和FAL两个创新模块,确保风格分布和结构性一致性,并分解为图像重建和特征对齐两个子任务。在乳腺癌免疫组织化学数据集上的实验表明,SCFANet模型精确转换H&E染色图像为IHC染色图像,提供稳健的框架进行病理分析中的染色转换。
Key Takeaways
- IHC染色是检测特定抗原或蛋白质的重要技术,但存在时间和成本问题。
- 深度学习模型可用于将H&E染色图像转换为IHC染色图像,提高效率。
- 转换过程中面临图像对齐和IHC染色风格多样性的挑战。
- SCFANet模型通过SDC和FAL模块克服这些挑战,确保风格分布和结构性一致性。
- SCFANet将转换任务分解为图像重建和特征对齐两个子任务。
- 通过维持病理性模式一致性和光学密度均匀性,确保病理一致性。
点此查看论文截图

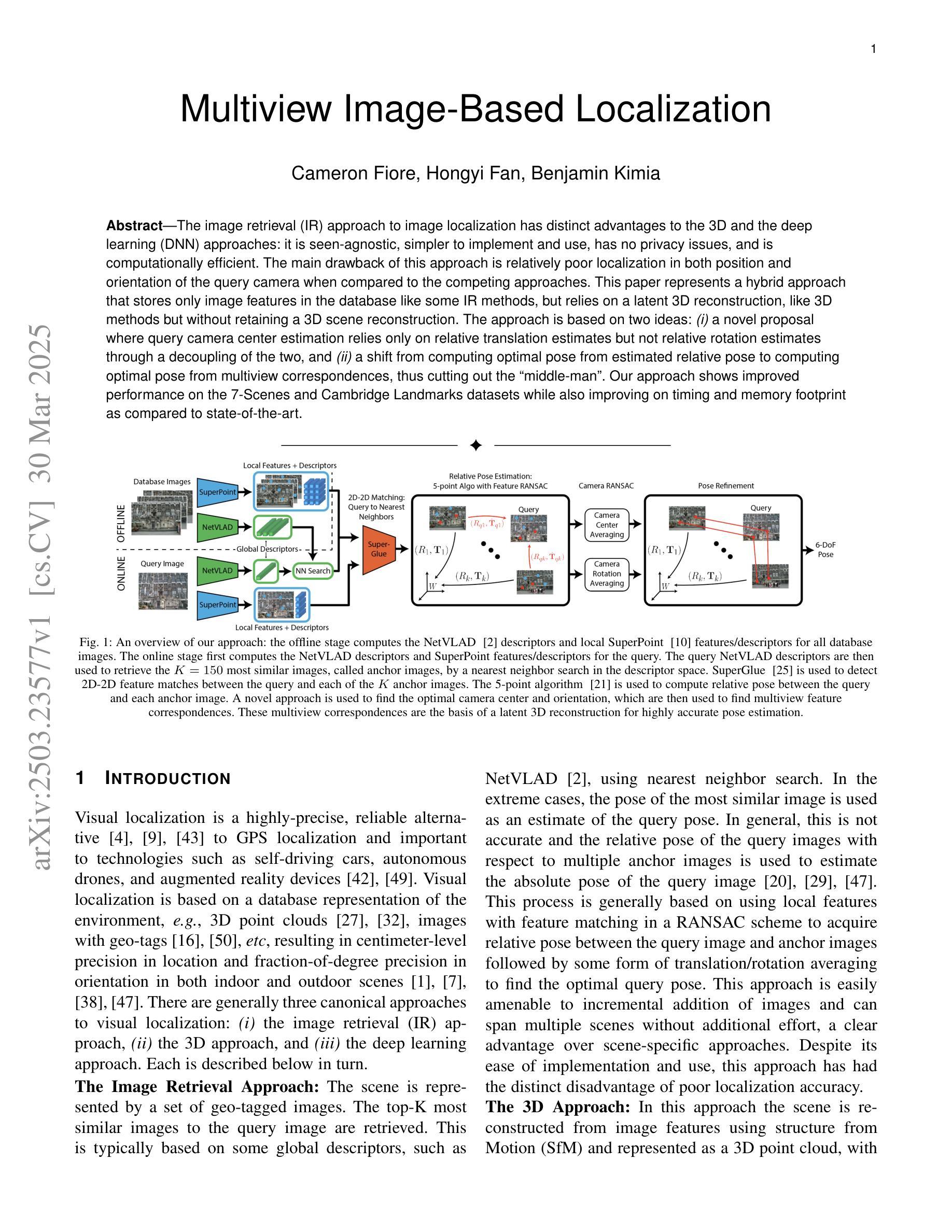
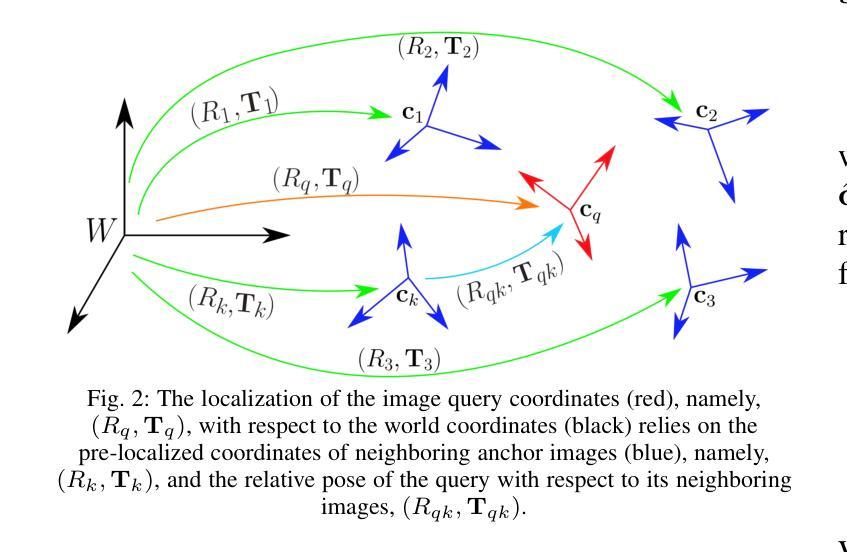
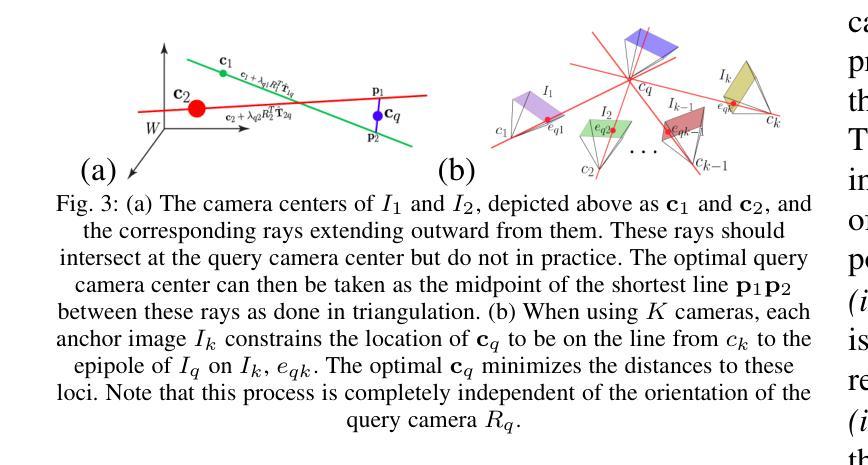
Multiview Image-Based Localization
Authors:Cameron Fiore, Hongyi Fan, Benjamin Kimia
The image retrieval (IR) approach to image localization has distinct advantages to the 3D and the deep learning (DNN) approaches: it is seen-agnostic, simpler to implement and use, has no privacy issues, and is computationally efficient. The main drawback of this approach is relatively poor localization in both position and orientation of the query camera when compared to the competing approaches. This paper represents a hybrid approach that stores only image features in the database like some IR methods, but relies on a latent 3D reconstruction, like 3D methods but without retaining a 3D scene reconstruction. The approach is based on two ideas: {\em (i)} a novel proposal where query camera center estimation relies only on relative translation estimates but not relative rotation estimates through a decoupling of the two, and {\em (ii)} a shift from computing optimal pose from estimated relative pose to computing optimal pose from multiview correspondences, thus cutting out the ``middle-man’’. Our approach shows improved performance on the 7-Scenes and Cambridge Landmarks datasets while also improving on timing and memory footprint as compared to state-of-the-art.
图像检索(IR)方法在图像定位方面具有与3D和深度学习(DNN)方法不同的明显优势:它不受视觉影响,更容易实施和使用,没有隐私问题,计算效率高。这种方法的主要缺点是与竞争方法相比,在查询相机的位置和方位定位方面相对较差。本文代表了一种混合方法,该方法仅将图像特征存储在数据库中,类似于某些IR方法,但依赖于潜在的3D重建,类似于3D方法,但不保留3D场景重建。该方法基于两个思想:(i)一种新型提案,其中查询相机中心估计仅依赖于相对平移估计,而不依赖于通过解耦两者得到的相对旋转估计;(ii)从通过估计的相对姿势计算最佳姿势转向通过多视图对应关系计算最佳姿势,从而省略了“中间人”。我们的方法在7场景和剑桥地标数据集上显示出性能改进,同时在时间和内存占用方面与最新技术相比也有所改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文提出一种图像检索(IR)与深度学习和三维重建技术结合的混合方法,用于图像定位。该方法具有视觉无关性、易于实现和使用、无隐私问题和计算效率高等优点。其主要缺点是与其他方法相比,查询相机的位置和方位定位相对较差。新方法仅在数据库中存储图像特征,依靠潜在的三维重建技术但不保留整个三维场景重建。它通过相对平移估计而非相对旋转估计来估算查询相机中心,并通过从估计的相对姿态计算最优姿态转向多视角对应关系的最优姿态计算,实现了性能提升。在7场景和剑桥地标数据集上,该方法在时间和内存占用方面均优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 图像检索(IR)方法具有视觉无关性、易于实现和使用、无隐私问题和计算效率高等优点。
- 混合方法结合IR和深度学习(DNN)以及三维重建技术用于图像定位。
- 该方法主要缺点在于查询相机的定位和方位定位相对较差。
- 该方法在数据库中仅存储图像特征,依赖潜在的三维重建技术。
- 方法通过相对平移估计而非相对旋转估计来估算查询相机中心。
- 方法从估计的相对姿态计算最优姿态转向多视角对应关系的最优姿态计算。
- 在数据集上,该方法相较于现有技术具有更好的性能和较低的时间和内存占用。
点此查看论文截图

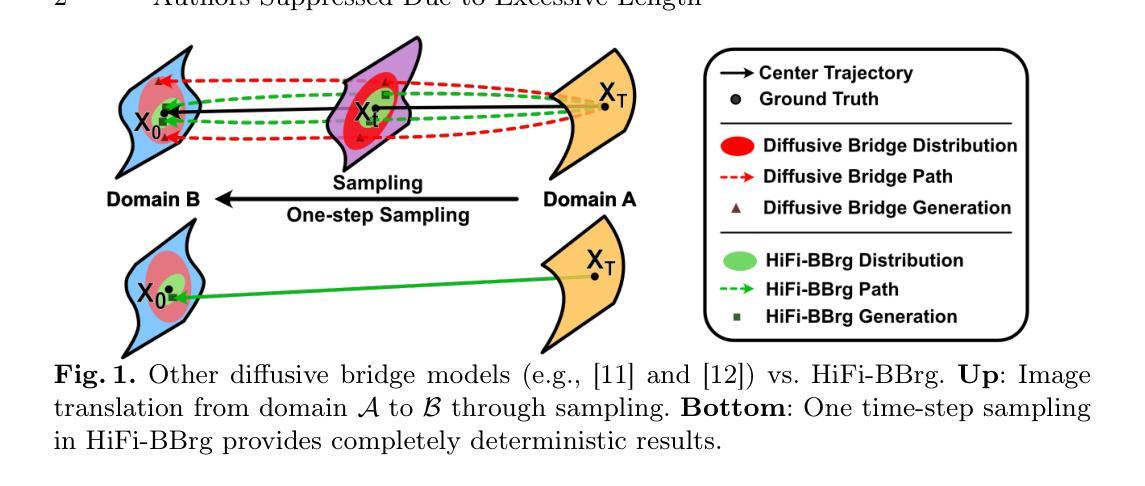
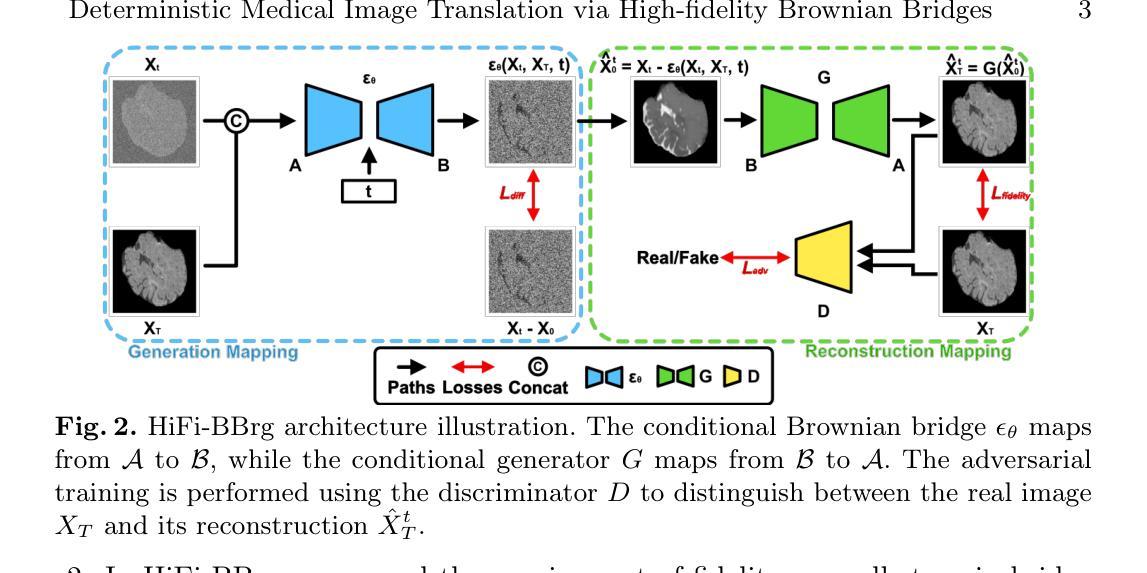
Deterministic Medical Image Translation via High-fidelity Brownian Bridges
Authors:Qisheng He, Nicholas Summerfield, Peiyong Wang, Carri Glide-Hurst, Ming Dong
Recent studies have shown that diffusion models produce superior synthetic images when compared to Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). However, their outputs are often non-deterministic and lack high fidelity to the ground truth due to the inherent randomness. In this paper, we propose a novel High-fidelity Brownian bridge model (HiFi-BBrg) for deterministic medical image translations. Our model comprises two distinct yet mutually beneficial mappings: a generation mapping and a reconstruction mapping. The Brownian bridge training process is guided by the fidelity loss and adversarial training in the reconstruction mapping. This ensures that translated images can be accurately reversed to their original forms, thereby achieving consistent translations with high fidelity to the ground truth. Our extensive experiments on multiple datasets show HiFi-BBrg outperforms state-of-the-art methods in multi-modal image translation and multi-image super-resolution.
最近的研究表明,与生成对抗网络(GANs)相比,扩散模型在生成合成图像方面表现出更优越的性能。然而,它们的输出通常是非确定的,并且由于固有的随机性,对真实数据的保真度不高。在本文中,我们提出了一种用于确定性医学图像翻译的高保真布朗桥模型(HiFi-BBrg)。我们的模型包括两个不同但相互有益的映射:生成映射和重建映射。布朗桥训练过程由重建映射中的保真度损失和对抗性训练引导。这确保了翻译的图像可以准确地恢复到其原始形式,从而实现与真实数据高度一致的翻译。我们在多个数据集上的广泛实验表明,HiFi-BBrg在跨模态图像翻译和多图像超分辨率方面优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
最近的研究表明,扩散模型在生成合成图像方面相较于生成对抗网络(GANs)有优势。然而,其输出通常具有非确定性,并且由于固有的随机性,对真实数据的保真度不高。本文提出了一种新型的用于确定性医学图像翻译的高保真布朗桥模型(HiFi-BBrg)。该模型包含两个独特且相辅相成的映射:生成映射和重建映射。布朗桥训练过程由重建映射中的保真损失和对抗训练引导,确保翻译后的图像可以准确还原为原始形式,从而实现具有与真实数据高保真的一致翻译。在多个数据集上的广泛实验表明,HiFi-BBrg在跨模态图像翻译和多图像超分辨率方面优于现有先进技术。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在合成图像生成方面相较于GANs有优势。
- 扩散模型的输出常具有非确定性,并且对真实数据的保真度不高。
- 提出的HiFi-BBrg模型用于确定性医学图像翻译。
- HiFi-BBrg模型包含生成映射和重建映射两个独特且相辅相成的部分。
- 布朗桥训练过程确保翻译后的图像可以准确还原。
- HiFi-BBrg模型实现了高保真的一致翻译。
点此查看论文截图

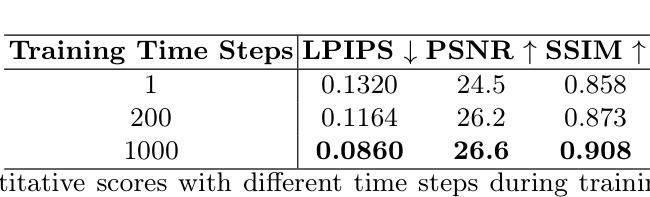
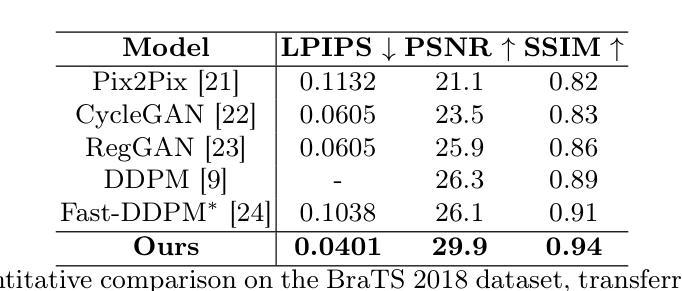
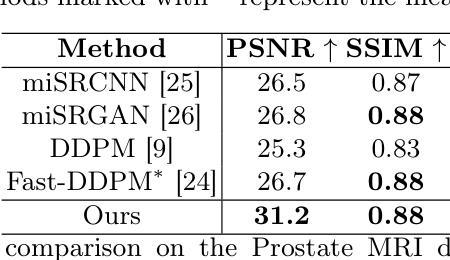
Time-resolved dynamic CBCT reconstruction using prior-model-free spatiotemporal Gaussian representation (PMF-STGR)
Authors:Jiacheng Xie, Hua-Chieh Shao, You Zhang
Time-resolved CBCT imaging, which reconstructs a dynamic sequence of CBCTs reflecting intra-scan motion (one CBCT per x-ray projection without phase sorting or binning), is highly desired for regular and irregular motion characterization, patient setup, and motion-adapted radiotherapy. Representing patient anatomy and associated motion fields as 3D Gaussians, we developed a Gaussian representation-based framework (PMF-STGR) for fast and accurate dynamic CBCT reconstruction. PMF-STGR comprises three major components: a dense set of 3D Gaussians to reconstruct a reference-frame CBCT for the dynamic sequence; another 3D Gaussian set to capture three-level, coarse-to-fine motion-basis-components (MBCs) to model the intra-scan motion; and a CNN-based motion encoder to solve projection-specific temporal coefficients for the MBCs. Scaled by the temporal coefficients, the learned MBCs will combine into deformation vector fields to deform the reference CBCT into projection-specific, time-resolved CBCTs to capture the dynamic motion. Due to the strong representation power of 3D Gaussians, PMF-STGR can reconstruct dynamic CBCTs in a ‘one-shot’ training fashion from a standard 3D CBCT scan, without using any prior anatomical or motion model. We evaluated PMF-STGR using XCAT phantom simulations and real patient scans. Metrics including the image relative error, structural-similarity-index-measure, tumor center-of-mass-error, and landmark localization error were used to evaluate the accuracy of solved dynamic CBCTs and motion. PMF-STGR shows clear advantages over a state-of-the-art, INR-based approach, PMF-STINR. Compared with PMF-STINR, PMF-STGR reduces reconstruction time by 50% while reconstructing less blurred images with better motion accuracy. With improved efficiency and accuracy, PMF-STGR enhances the applicability of dynamic CBCT imaging for potential clinical translation.
时间解析CBCT成像技术重构反映扫描内动态的一系列CBCT图像(每次X射线投影都有一张CBCT,无需相位排序或分组),对于常规和不规则运动特征、患者设置和适应性放疗中的运动需求具有重要意义。我们用三维高斯函数来表示患者解剖结构和相关运动场,并开发了一种基于高斯表示的框架(PMF-STGR),用于快速准确地重建动态CBCT。PMF-STGR主要包括三个组成部分:使用密集的三维高斯集重构动态序列的参考帧CBCT;使用另一个三维高斯集捕捉三级粗细运动基础成分(MBCs),以模拟扫描内的运动;基于CNN的运动编码器用于解决与MBC投影相关的特定时间系数。根据时间系数,学习到的MBC将组合成变形矢量场,将参考CBCT变形为与投影相关的、时间解析的CBCT,以捕捉动态运动。由于三维高斯函数具有很强的表示能力,PMF-STGR可以从标准的3D CBCT扫描中通过“单次”训练的方式重建动态CBCT,无需使用任何先验解剖或运动模型。我们使用XCAT幻影模拟和实际患者扫描对PMF-STGR进行了评估。使用图像相对误差、结构相似性指数度量、肿瘤质量中心误差和地标定位误差等指标来评估求解的动态CBCT和运动准确性。PMF-STGR相比于目前最先进的方法——基于INR的方法PMF-STINR具有明显的优势。与PMF-STINR相比,PMF-STGR在重建时间减少50%的同时,生成了模糊度更低的图像,并提高了运动准确性。凭借更高的效率和准确性,PMF-STGR增强了动态CBCT成像的适用性,具有潜在的临床应用价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages, 5 figures
Summary
动态CBCT成像能够反映无相位排序或无分组的单次扫描中的运动,这对于常规和不规则的运动特性分析、患者设置和自适应放疗具有极大价值。为快速准确地重建动态CBCT序列,研究团队建立了基于高斯表示的框架(PMF-STGR)。该框架通过构建密集的三维高斯集来重建动态序列的参考框架CBCT,并引入另一组三维高斯集捕捉三个级别的运动基础分量(MBCs),从而模拟扫描期间的运动。同时,采用基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的运动编码器计算针对MBCs的投影特定时间系数。基于这些时间系数学习的MBCs会转化为变形向量场,以将参考CBCT变形为适应投影特定时间的动态CBCT图像序列,实现动态运动捕捉。该方法可在一次扫描中使用单个CBCT训练出动态CBCT图像序列,无需使用任何先验解剖或运动模型。通过XCAT幻影模拟和真实患者扫描验证了其性能。评估指标包括图像相对误差、结构相似性指数度量、肿瘤质心误差和地标定位误差等。相较于目前的主流方法PMF-STINR,PMF-STGR具有明显优势,其重建时间缩短了50%,同时生成的图像更清晰且运动准确性更高。这提高了动态CBCT成像在临床应用中的效率和准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 时间解析CBCT成像对于运动表征、患者设置和自适应放疗至关重要。
- 研究团队提出了基于高斯表示的框架(PMF-STGR)进行动态CBCT重建。
- PMF-STGR利用三维高斯集捕捉参考帧和运动中细节。
- 引入CNN解决运动编码问题,生成动态运动的变形向量场。
- PMF-STGR在一次扫描中即可训练出动态CBCT图像序列,无需先验模型。
- 与现有方法相比,PMF-STGR在图像质量和运动准确性方面表现出优势。
点此查看论文截图

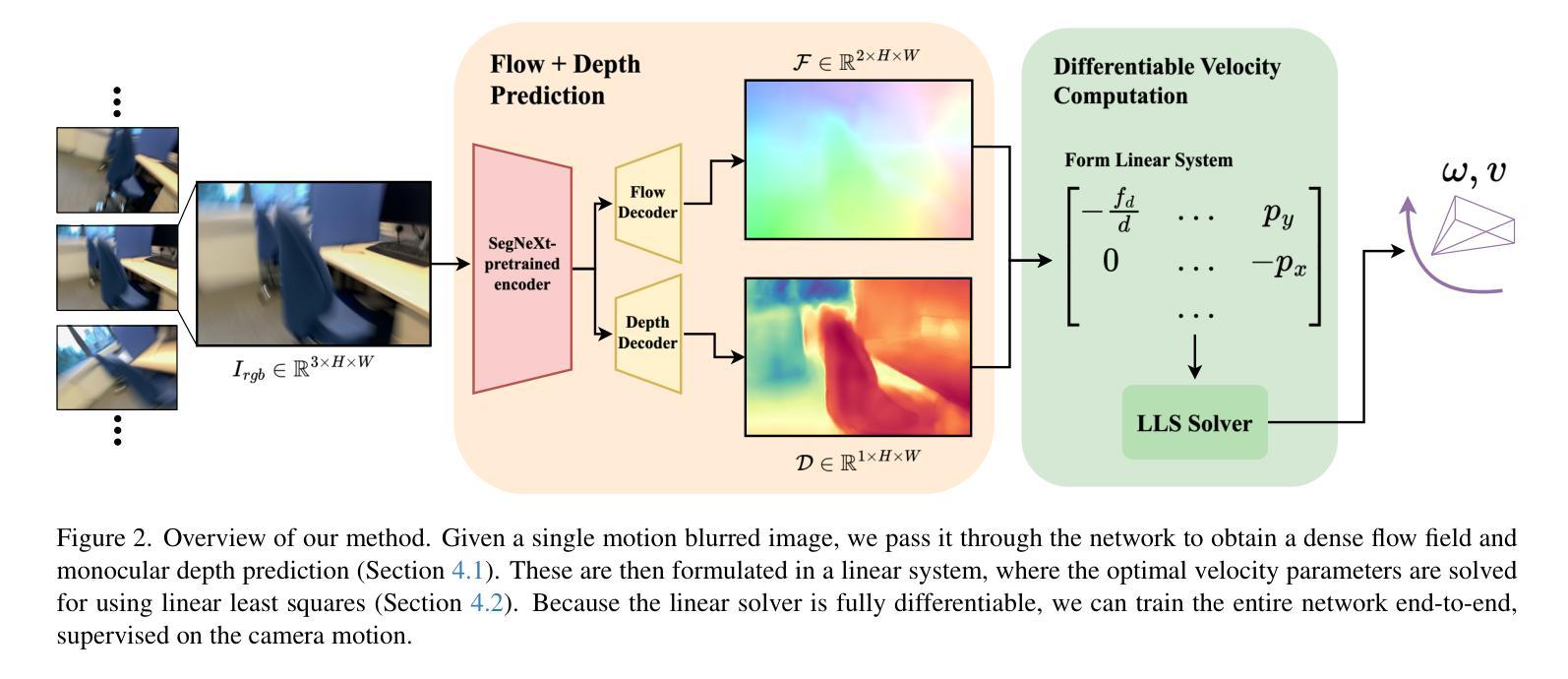
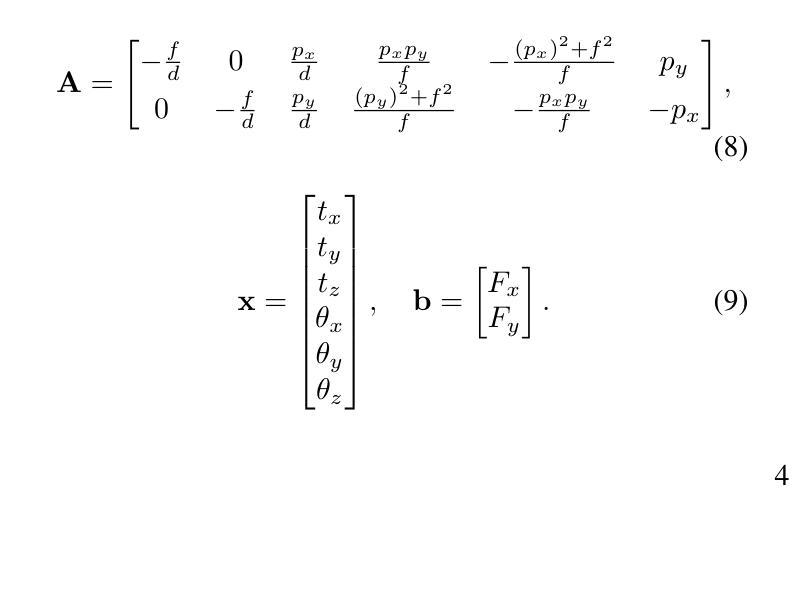
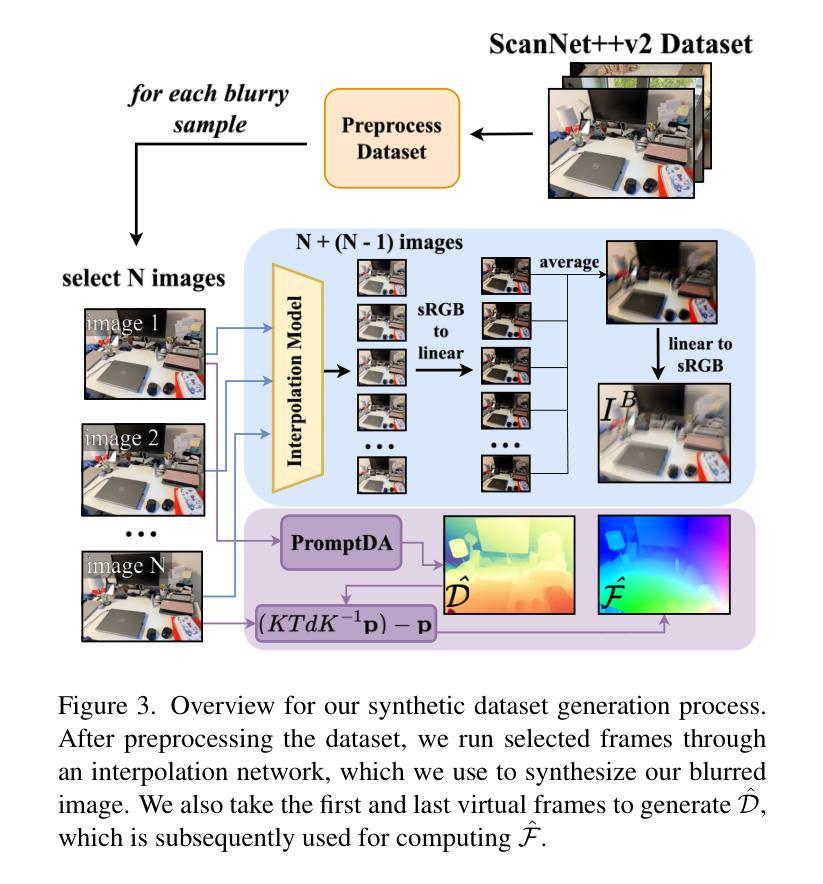
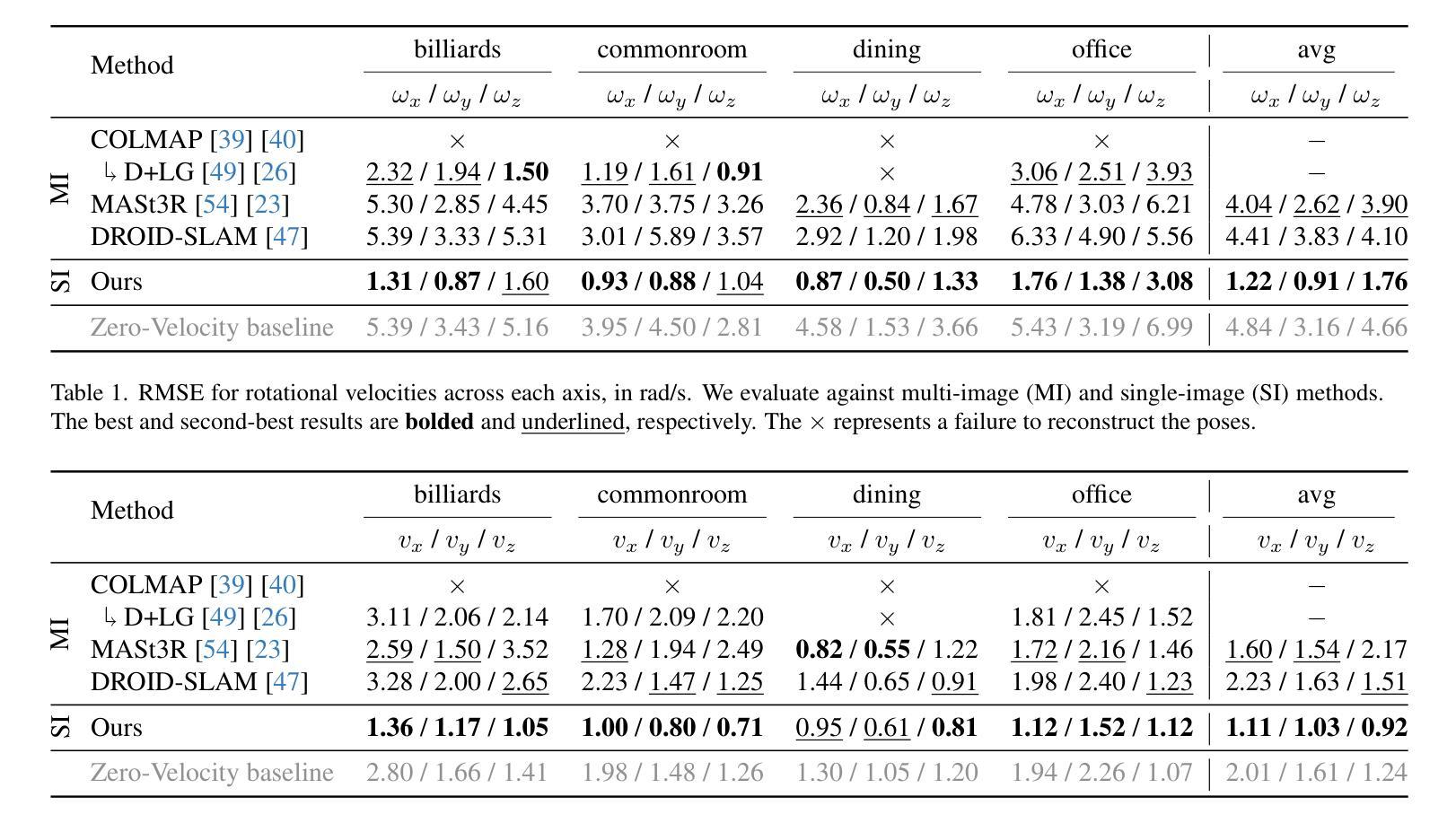
Image as an IMU: Estimating Camera Motion from a Single Motion-Blurred Image
Authors:Jerred Chen, Ronald Clark
In many robotics and VR/AR applications, fast camera motions cause a high level of motion blur, causing existing camera pose estimation methods to fail. In this work, we propose a novel framework that leverages motion blur as a rich cue for motion estimation rather than treating it as an unwanted artifact. Our approach works by predicting a dense motion flow field and a monocular depth map directly from a single motion-blurred image. We then recover the instantaneous camera velocity by solving a linear least squares problem under the small motion assumption. In essence, our method produces an IMU-like measurement that robustly captures fast and aggressive camera movements. To train our model, we construct a large-scale dataset with realistic synthetic motion blur derived from ScanNet++v2 and further refine our model by training end-to-end on real data using our fully differentiable pipeline. Extensive evaluations on real-world benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art angular and translational velocity estimates, outperforming current methods like MASt3R and COLMAP.
在机器人技术和虚拟现实/增强现实应用中,快速相机运动会产生高水平的运动模糊,导致现有的相机姿态估计方法失效。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型框架,该框架利用运动模糊作为运动估计的丰富线索,而不是将其视为不受欢迎的伪像。我们的方法通过直接从单张运动模糊图像预测密集运动流场和单眼深度图来工作。然后,我们在小运动假设下通过解决线性最小二乘问题来恢复瞬时相机速度。本质上,我们的方法产生了一种类似于IMU的测量值,能够稳健地捕获快速且猛烈的相机运动。为了训练我们的模型,我们使用ScanNet++v2构建了具有现实合成运动模糊的大规模数据集,并通过在我们的完全可微管道上对真实数据进行端到端的训练来进一步完善我们的模型。在真实世界基准测试上的广泛评估表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的角速度和线速度估计,优于MASt3R和COLMAP等方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://jerredchen.github.io/image-as-imu/
Summary
该文本提出了一种利用运动模糊作为运动估计的丰富线索的新框架,而不是将其视为不需要的伪影。该框架通过预测从单个运动模糊图像中的密集运动流场和单眼深度图来工作,然后通过解决小运动假设下的线性最小二乘问题来恢复瞬时相机速度。该方法实质上产生了IMU式的测量,能够稳健地捕获快速和激烈的相机运动。
Key Takeaways
- 现有方法在快速相机运动下会出现运动模糊问题,导致姿态估计失败。
- 提出了一种新的框架,利用运动模糊作为运动估计的丰富线索。
- 通过预测密集运动流场和单眼深度图来估计相机运动。
- 通过解决线性最小二乘问题来恢复瞬时相机速度。
- 方法实质上产生了IMU式的测量,稳健地捕获快速和激烈的相机运动。
- 使用ScanNet++v2构建的大规模数据集进行模型训练,并利用完全可微分的管道进行真实数据的端到端训练来进一步优化模型。
点此查看论文截图

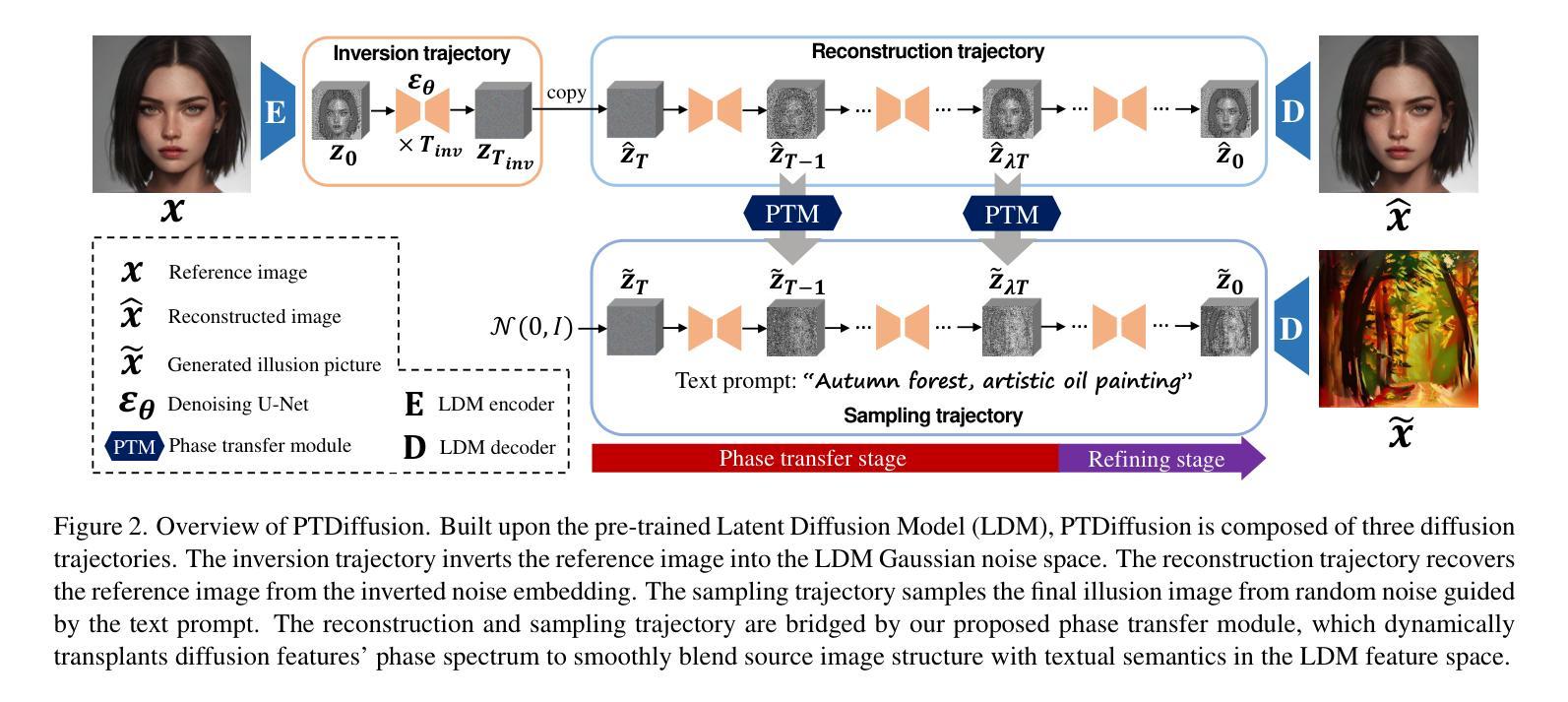
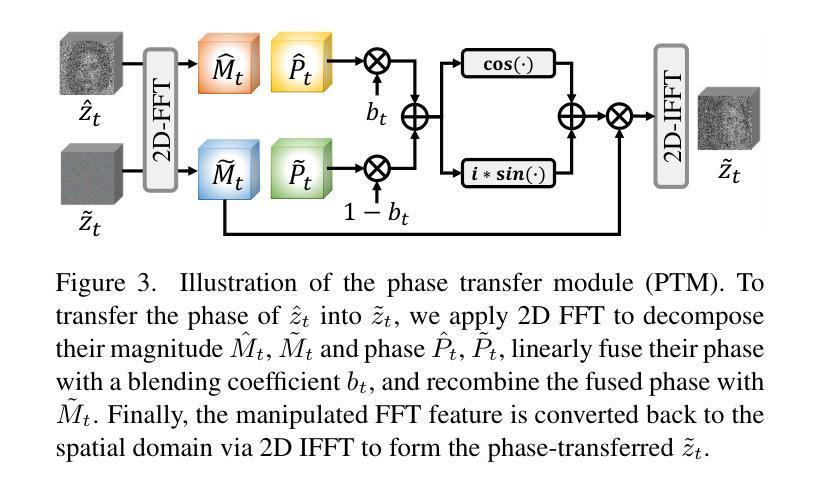
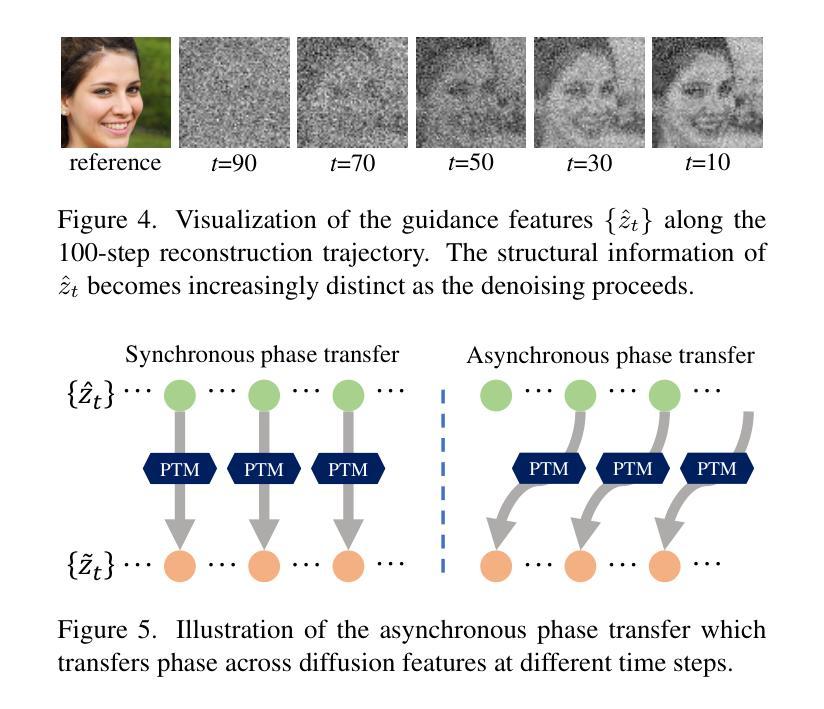
PTDiffusion: Free Lunch for Generating Optical Illusion Hidden Pictures with Phase-Transferred Diffusion Model
Authors:Xiang Gao, Shuai Yang, Jiaying Liu
Optical illusion hidden picture is an interesting visual perceptual phenomenon where an image is cleverly integrated into another picture in a way that is not immediately obvious to the viewer. Established on the off-the-shelf text-to-image (T2I) diffusion model, we propose a novel training-free text-guided image-to-image (I2I) translation framework dubbed as \textbf{P}hase-\textbf{T}ransferred \textbf{Diffusion} Model (PTDiffusion) for hidden art syntheses. PTDiffusion harmoniously embeds an input reference image into arbitrary scenes described by the text prompts, producing illusion images exhibiting hidden visual cues of the reference image. At the heart of our method is a plug-and-play phase transfer mechanism that dynamically and progressively transplants diffusion features’ phase spectrum from the denoising process to reconstruct the reference image into the one to sample the generated illusion image, realizing deep fusion of the reference structural information and the textual semantic information in the diffusion model latent space. Furthermore, we propose asynchronous phase transfer to enable flexible control to the degree of hidden content discernability. Our method bypasses any model training and fine-tuning process, all while substantially outperforming related text-guided I2I methods in image generation quality, text fidelity, visual discernibility, and contextual naturalness for illusion picture synthesis, as demonstrated by extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments. Our project is publically available at \href{https://xianggao1102.github.io/PTDiffusion_webpage/}{this web page}.
光学错觉隐藏图像是一种有趣的视觉感知现象,其中图像被巧妙地集成到另一幅图像中,以至于观众无法立即察觉。我们基于现成的文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型,提出了一种无需训练的文字引导图像到图像(I2I)转换框架,名为阶段转移扩散模型(PTDiffusion),用于合成隐藏艺术。PTDiffusion和谐地将输入参考图像嵌入到文本提示描述的任意场景中,生成显示参考图像的隐藏视觉线索的错觉图像。我们方法的核心是一个即插即用的相位转移机制,该机制动态且渐进地从去噪过程中移植扩散特征的相位谱,将参考图像重建到采样生成的错觉图像中,实现在扩散模型潜在空间中的参考结构信息和文本语义信息的深度融合。此外,我们提出了异步相位转移,以实现灵活控制隐藏内容的可识别程度。我们的方法避开了任何模型训练和微调过程,同时在图像生成质量、文本忠实度、视觉可辨识度和上下文自然度等方面大大优于相关的文本引导I2I方法,用于错觉图像合成。我们的项目已在以下网页公开:网页链接。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2025)
Summary
文本描述了一个名为PTDiffusion的新方法,它是一种无需训练的文本引导的图像到图像(I2I)翻译框架,用于合成隐藏艺术图像。该方法通过将输入参考图像嵌入到由文本提示描述的任意场景中,生成隐藏视觉线索的错觉图像。其核心技术是插播式相位转移机制,实现参考图像与文本语义信息的深度融合。此外,还提出了异步相位转移,以实现灵活控制隐藏内容的识别程度。该方法无需任何模型训练和微调过程,在图像生成质量、文本忠实度、视觉辨识度和上下文自然性方面均大大优于相关文本引导的I2I方法。
Key Takeaways
- PTDiffusion是一种新的文本引导的图像到图像(I2I)翻译框架,用于合成隐藏艺术图像。
- 它通过将参考图像巧妙地嵌入到由文本描述的场景中,生成具有隐藏视觉线索的错觉图像。
- 插播式相位转移机制是PTDiffusion的核心技术,实现了参考图像与文本信息的深度融合。
- 异步相位转移允许灵活控制隐藏内容的识别程度。
- PTDiffusion无需任何模型训练和微调,具有出色的图像生成质量、文本忠实度、视觉辨识度和上下文自然性。
- 该方法对于创建视觉错觉图像具有重要的应用价值。
点此查看论文截图


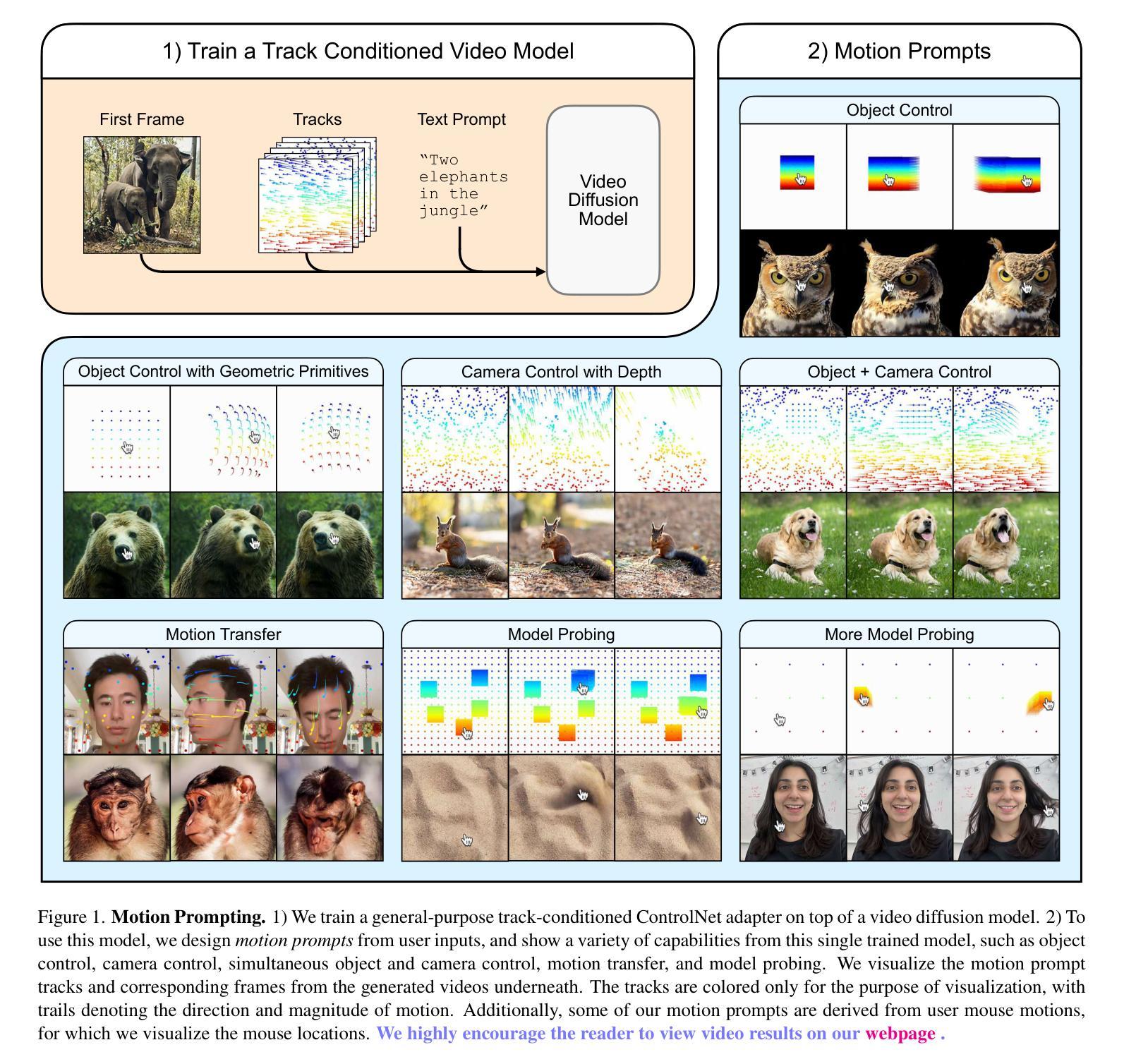
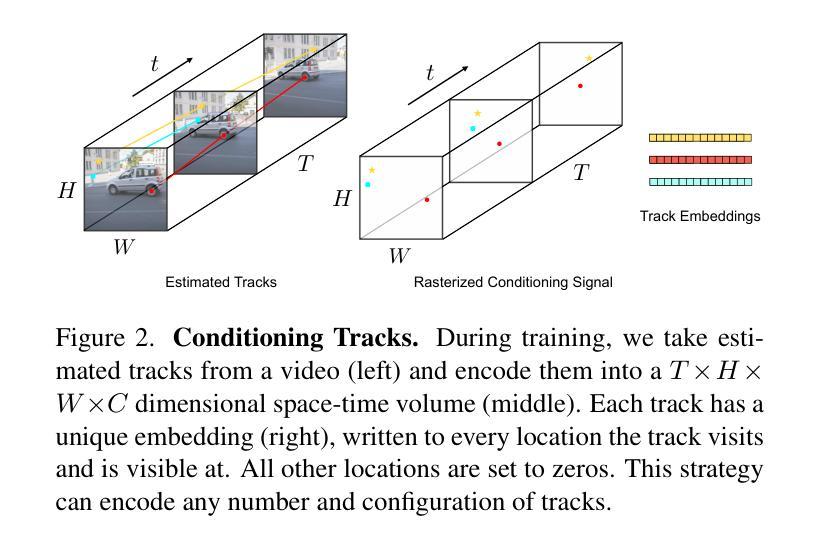
Motion Prompting: Controlling Video Generation with Motion Trajectories
Authors:Daniel Geng, Charles Herrmann, Junhwa Hur, Forrester Cole, Serena Zhang, Tobias Pfaff, Tatiana Lopez-Guevara, Carl Doersch, Yusuf Aytar, Michael Rubinstein, Chen Sun, Oliver Wang, Andrew Owens, Deqing Sun
Motion control is crucial for generating expressive and compelling video content; however, most existing video generation models rely mainly on text prompts for control, which struggle to capture the nuances of dynamic actions and temporal compositions. To this end, we train a video generation model conditioned on spatio-temporally sparse or dense motion trajectories. In contrast to prior motion conditioning work, this flexible representation can encode any number of trajectories, object-specific or global scene motion, and temporally sparse motion; due to its flexibility we refer to this conditioning as motion prompts. While users may directly specify sparse trajectories, we also show how to translate high-level user requests into detailed, semi-dense motion prompts, a process we term motion prompt expansion. We demonstrate the versatility of our approach through various applications, including camera and object motion control, “interacting” with an image, motion transfer, and image editing. Our results showcase emergent behaviors, such as realistic physics, suggesting the potential of motion prompts for probing video models and interacting with future generative world models. Finally, we evaluate quantitatively, conduct a human study, and demonstrate strong performance. Video results are available on our webpage: https://motion-prompting.github.io/
动作控制在生成富有表现力和引人入胜的视频内容方面起着至关重要的作用。然而,现有的大多数视频生成模型主要依赖于文本提示来进行控制,这很难捕捉到动态动作和时序组合的细微差别。为此,我们训练了一种基于时空稀疏或密集运动轨迹的视频生成模型。与之前的工作相比,这种灵活的表示可以编码任意数量的轨迹、特定对象的运动或全局场景的运动,以及时序稀疏的运动。由于其灵活性,我们将这种条件称为运动提示。虽然用户可以直接指定稀疏轨迹,我们还展示了如何将高级用户请求翻译成详细、半密集的运动提示,我们称这个过程为运动提示扩展。我们通过各种应用展示了我们的方法的通用性,包括相机和对象运动控制、“与图像互动”、运动转移和图像编辑等。我们的结果展示了新兴的行为,如逼真的物理效果,这表明运动提示在探查视频模型以及与未来的生成世界模型互动方面具有潜力。最后,我们进行了定量评估、人类研究,并展示了强大的性能。视频结果可在我们的网页上看到:https://motion-prompting.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025 camera ready. Project page: https://motion-prompting.github.io/
Summary
本文主要探讨了动作控制在生成具有表现力和吸引力的视频内容中的重要性。传统的视频生成模型主要依赖于文本提示进行动作控制,难以捕捉动态行为和时序组合的细节。为此,本文训练了一种基于时空稀疏或密集运动轨迹的视频生成模型,并引入了一种灵活的运动提示条件表达。这种表达方式能够编码任意数量的轨迹、物体特定的或全局场景的运动,以及时序稀疏的运动。用户可以直接指定稀疏轨迹,本文还展示了如何将高级用户请求转化为详细的半密集运动提示,称为运动提示扩展。本文通过各种应用展示了该方法的通用性,包括相机和物体运动控制、“与图像互动”、运动转移和图像编辑等。结果展现了新兴的行为,如现实物理现象,显示了运动提示在探测视频模型和与未来生成世界模型互动中的潜力。最后,本文进行了定量评估、人类研究,并展示了强大的性能表现。
Key Takeaways
- 动作控制在生成视频内容中的重要性。
- 现有视频生成模型主要依赖文本提示进行动作控制,存在难以捕捉动态行为和时序组合的细微之处的缺陷。
- 引入了一种基于时空稀疏或密集运动轨迹的视频生成模型,并称之为“运动提示”。
- 运动提示可以编码任意数量的轨迹、物体特定的或全局场景的运动,以及时序稀疏的运动,具有灵活性。
- 用户可以直接指定稀疏轨迹,同时本文还展示了如何将高级用户请求转化为详细的半密集运动提示(运动提示扩展)。
- 该方法具有广泛的应用性,包括相机和物体运动控制、与图像的互动、运动转移和图像编辑等。
点此查看论文截图



A Unified Framework for Forward and Inverse Problems in Subsurface Imaging using Latent Space Translations
Authors:Naveen Gupta, Medha Sawhney, Arka Daw, Youzuo Lin, Anuj Karpatne
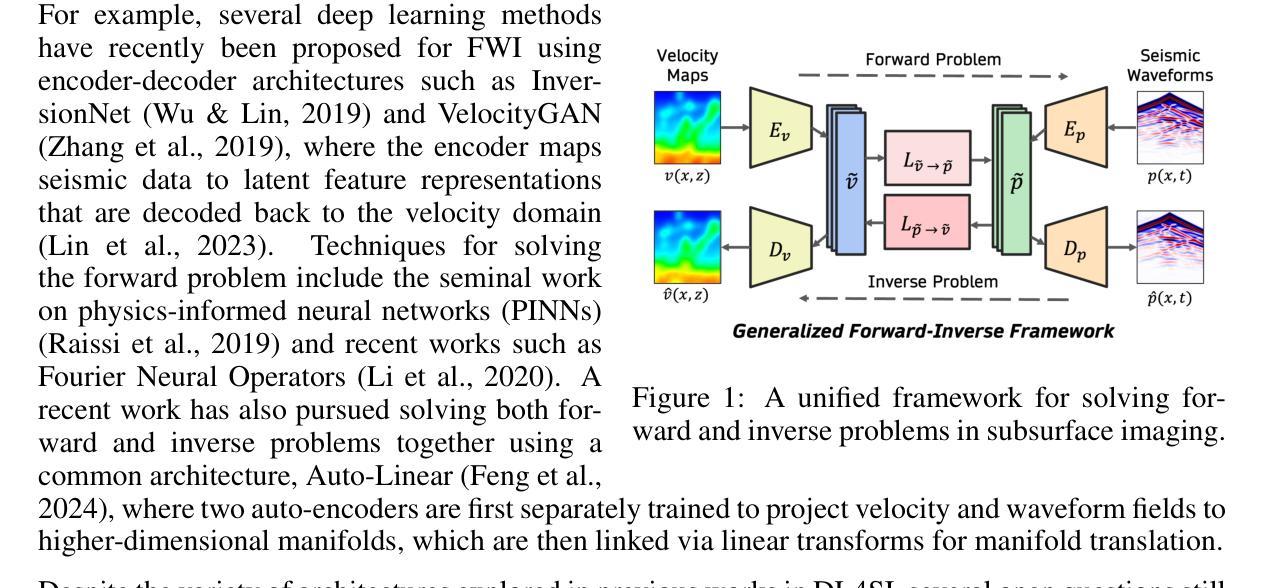
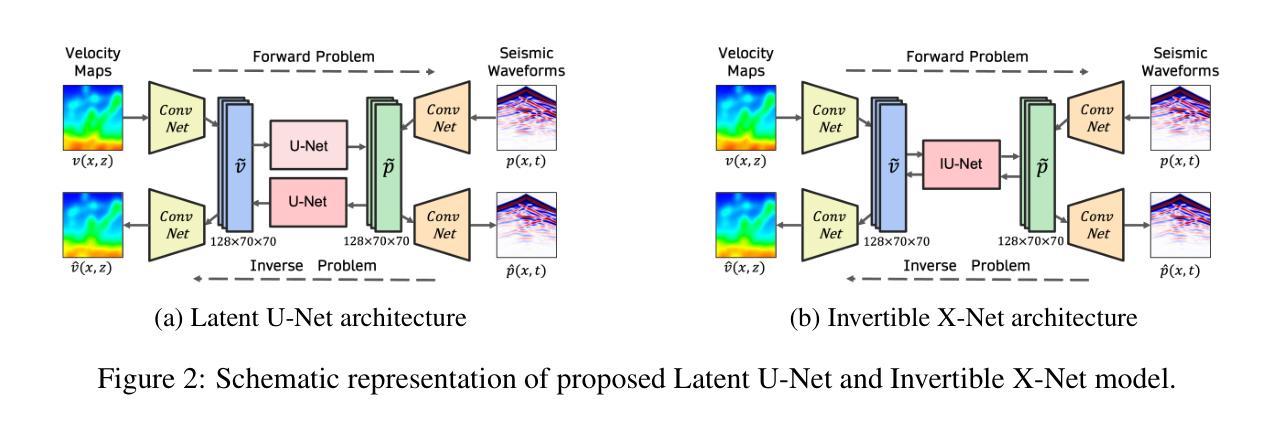
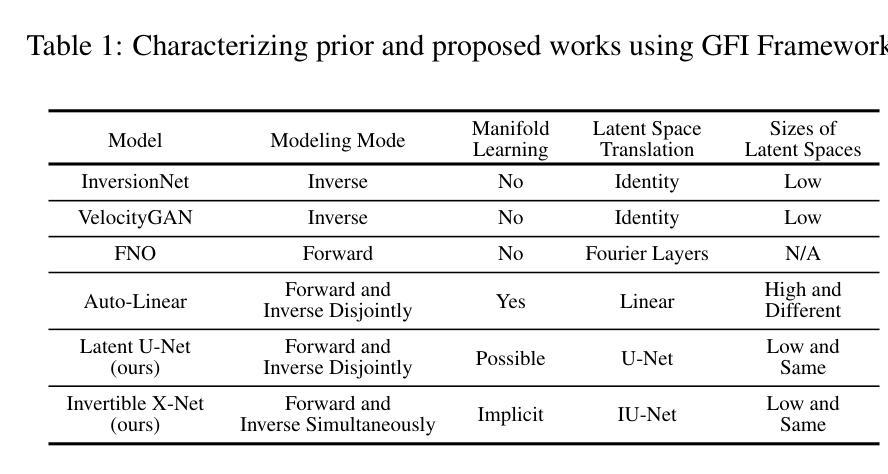
In subsurface imaging, learning the mapping from velocity maps to seismic waveforms (forward problem) and waveforms to velocity (inverse problem) is important for several applications. While traditional techniques for solving forward and inverse problems are computationally prohibitive, there is a growing interest in leveraging recent advances in deep learning to learn the mapping between velocity maps and seismic waveform images directly from data. Despite the variety of architectures explored in previous works, several open questions still remain unanswered such as the effect of latent space sizes, the importance of manifold learning, the complexity of translation models, and the value of jointly solving forward and inverse problems. We propose a unified framework to systematically characterize prior research in this area termed the Generalized Forward-Inverse (GFI) framework, building on the assumption of manifolds and latent space translations. We show that GFI encompasses previous works in deep learning for subsurface imaging, which can be viewed as specific instantiations of GFI. We also propose two new model architectures within the framework of GFI: Latent U-Net and Invertible X-Net, leveraging the power of U-Nets for domain translation and the ability of IU-Nets to simultaneously learn forward and inverse translations, respectively. We show that our proposed models achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance for forward and inverse problems on a wide range of synthetic datasets, and also investigate their zero-shot effectiveness on two real-world-like datasets. Our code is available at https://github.com/KGML-lab/Generalized-Forward-Inverse-Framework-for-DL4SI
在地下成像中,学习从速度图到地震波形(正问题)和从波形到速度(反问题)的映射对于多个应用非常重要。虽然传统解决正问题和反问题的技术在计算上是禁止的,但越来越多的兴趣在于利用深度学习领域的最新进展直接从数据中学习速度图与地震波形图像之间的映射。尽管以前的研究中探索了多种架构,但仍有许多公开问题尚未解决,例如潜在空间大小的影响、流形学习的重要性、翻译模型的复杂性以及联合解决正问题和反问题的价值。我们提出了一个统一框架,旨在系统地刻画这一领域的先前研究,我们称之为广义正反(GFI)框架,它建立在流形和潜在空间翻译假设的基础上。我们表明,GFI涵盖了地下成像深度学习领域的先前研究,这些研究可以看作是GFI的特定实例。在GFI框架下,我们还提出了两种新型模型架构:潜在U-Net和可逆X-Net,它们利用U-Net在领域翻译方面的力量以及IU-Net同时学习正向和逆向翻译的能力。我们展示了我们提出的模型在合成数据集上的正反问题上实现了最先进的性能,并调查了它们在两个类似现实世界数据集上的零样本有效性。我们的代码可在 https://github.com/KGML-lab/Generalized-Forward-Inverse-Framework-for-DL4SI 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICLR 2025
Summary
本文探讨地下成像领域中速度图与地震波形之间的映射问题,包括正问题和反问题。传统解决正反问题的方法计算量大,现多采用深度学习技术直接从数据中学习速度图与地震波形图像之间的映射关系。文章提出一种广义正逆(GFI)框架来系统分析该领域的前期研究,并在此框架下提出两种新型模型架构:潜在U-Net和可逆X-Net。这些模型在合成数据集上表现优异,并在两种模拟现实世界数据集上实现了零样本有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 地下成像中,正问题和反问题的研究重要,涉及速度图到地震波形的映射以及反向过程。
- 传统方法计算量大,现有研究倾向于利用深度学习技术来学习速度图与地震波形之间的直接映射。
- 提出广义正逆(GFI)框架,用于系统分析该领域的前期研究。
- 在GFI框架下,提出两种新型模型架构:潜在U-Net和可逆X-Net。
- 模型在合成数据集上表现优越,达到目前最佳水平(SOTA)。
- 模型在模拟现实世界数据集上实现零样本有效性。
点此查看论文截图

Improving Neural Optimal Transport via Displacement Interpolation
Authors:Jaemoo Choi, Yongxin Chen, Jaewoong Choi
Optimal Transport (OT) theory investigates the cost-minimizing transport map that moves a source distribution to a target distribution. Recently, several approaches have emerged for learning the optimal transport map for a given cost function using neural networks. We refer to these approaches as the OT Map. OT Map provides a powerful tool for diverse machine learning tasks, such as generative modeling and unpaired image-to-image translation. However, existing methods that utilize max-min optimization often experience training instability and sensitivity to hyperparameters. In this paper, we propose a novel method to improve stability and achieve a better approximation of the OT Map by exploiting displacement interpolation, dubbed Displacement Interpolation Optimal Transport Model (DIOTM). We derive the dual formulation of displacement interpolation at specific time $t$ and prove how these dual problems are related across time. This result allows us to utilize the entire trajectory of displacement interpolation in learning the OT Map. Our method improves the training stability and achieves superior results in estimating optimal transport maps. We demonstrate that DIOTM outperforms existing OT-based models on image-to-image translation tasks.
最优传输(OT)理论探究的是将源分布转移到目标分布的成本最小化传输映射。最近,已经出现了几种使用神经网络为给定成本函数学习最优传输映射的方法。我们将这些方法称为OT Map。OT Map为多样的机器学习任务(如生成建模和未配对的图像到图像翻译)提供了强大的工具。然而,现有的使用最大-最小优化方法的方法通常存在训练不稳定和对超参数敏感的问题。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的方法,通过利用位移插值来改善稳定性,并更好地逼近OT Map,被称为位移插值最优传输模型(DIOTM)。我们推导出位移插值在特定时间t的对偶公式,并证明这些对偶问题随时间推移是如何相互关联的。这一结果允许我们利用位移插值的整个轨迹来学习OT Map。我们的方法提高了训练稳定性,并在估计最优传输映射方面取得了更好的结果。我们证明DIOTM在图像到图像翻译任务上优于现有的基于OT的模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages
Summary
本文介绍了最优传输(OT)理论及其在计算机学习中的应用,特别是在生成建模和未配对图像转换等领域的应用。文章提出了一种新的方法,即位移插值最优传输模型(DIOTM),以提高训练稳定性和对最优传输地图的近似精度。该方法通过利用位移插值的整个轨迹来学习最优传输地图,并在图像转换任务上表现出优异性能。
Key Takeaways
- 最优传输(OT)理论是研究如何将源分布转移到目标分布的成本最小化传输图。
- 神经网络已用于学习给定成本函数的最优传输图,但现有方法存在训练不稳定和对超参数敏感的问题。
- 本文提出了一种新的方法,即位移插值最优传输模型(DIOTM),以提高稳定性和对最优传输图的近似精度。
- DIOTM通过推导位移插值在特定时间t的对偶公式,并利用整个位移插值轨迹来学习最优传输图。
- DIOTM方法提高了训练稳定性。
- 在图像转换任务上,DIOTM表现出优于现有基于OT的模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图

AI in radiological imaging of soft-tissue and bone tumours: a systematic review evaluating against CLAIM and FUTURE-AI guidelines
Authors:Douwe J. Spaanderman, Matthew Marzetti, Xinyi Wan, Andrew F. Scarsbrook, Philip Robinson, Edwin H. G. Oei, Jacob J. Visser, Robert Hemke, Kirsten van Langevelde, David F. Hanff, Geert J. L. H. van Leenders, Cornelis Verhoef, Dirk J. Gruühagen, Wiro J. Niessen, Stefan Klein, Martijn P. A. Starmans
Soft-tissue and bone tumours (STBT) are rare, diagnostically challenging lesions with variable clinical behaviours and treatment approaches. This systematic review provides an overview of Artificial Intelligence (AI) methods using radiological imaging for diagnosis and prognosis of these tumours, highlighting challenges in clinical translation, and evaluating study alignment with the Checklist for AI in Medical Imaging (CLAIM) and the FUTURE-AI international consensus guidelines for trustworthy and deployable AI to promote the clinical translation of AI methods. The review covered literature from several bibliographic databases, including papers published before 17/07/2024. Original research in peer-reviewed journals focused on radiology-based AI for diagnosing or prognosing primary STBT was included. Exclusion criteria were animal, cadaveric, or laboratory studies, and non-English papers. Abstracts were screened by two of three independent reviewers for eligibility. Eligible papers were assessed against guidelines by one of three independent reviewers. The search identified 15,015 abstracts, from which 325 articles were included for evaluation. Most studies performed moderately on CLAIM, averaging a score of 28.9$\pm$7.5 out of 53, but poorly on FUTURE-AI, averaging 5.1$\pm$2.1 out of 30. Imaging-AI tools for STBT remain at the proof-of-concept stage, indicating significant room for improvement. Future efforts by AI developers should focus on design (e.g. define unmet clinical need, intended clinical setting and how AI would be integrated in clinical workflow), development (e.g. build on previous work, explainability), evaluation (e.g. evaluating and addressing biases, evaluating AI against best practices), and data reproducibility and availability (making documented code and data publicly available). Following these recommendations could improve clinical translation of AI methods.
软组织及骨肿瘤(STBT)是罕见的、诊断具有挑战性的病变,其临床行为和治疗方式各异。这篇系统性综述概述了使用放射影像学进行诊断和预后的软组织及骨肿瘤的人工智能(AI)方法,强调了临床翻译中的挑战,并评估了研究是否符合医学影像学人工智能(CLAIM)清单以及可信且可部署的人工智能的国际共识指南(FUTURE-AI),以促进AI方法的临床翻译。综述涵盖了多个文献数据库的文献,包括在2024年7月17日之前发表的文章。纳入的原始研究是对基于放射学的AI用于诊断或预测原发性STBT的研究。排除标准是动物、尸体或实验室研究,以及非英语论文。摘要由三名独立评审员中的两名进行资格筛选。合格论文由三名独立评审员之一根据指南进行评估。搜索确定了15015篇摘要,其中325篇文章纳入评估。大多数研究在CLAIM上的表现中等,平均得分为28.9±7.5(满分为53分),但在FUTURE-AI上的表现较差,平均得分为5.1±2.1(满分为30分)。针对STBT的成像AI工具仍处于概念验证阶段,表明还有很大的改进空间。未来人工智能开发者应重点关注设计(如确定未满足的临床需求、预期的临床环境以及AI如何融入临床工作流程)、开发(如基于以往工作进行建设、解释性)、评估(如评估和解决偏见、评估AI是否符合最佳实践)、数据可重复性和可用性(公开提供有记录的代码和数据)。遵循这些建议可能有助于改善AI方法的临床翻译。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages, 6 figures, 8 supplementary figures
Summary
软组织及骨肿瘤诊断与预后的人工智能影像技术系统综述,探讨临床转化挑战,并对照医疗影像人工智能清单(CLAIM)及国际可靠的未来人工智能(FUTURE-AI)指南进行评价。综述涵盖多个文献数据库的研究,重点讨论基于放射学的AI技术在诊断原发性软组织及骨肿瘤(STBT)方面的进展。现有研究在CLAIM上的表现中等,但在FUTURE-AI上的表现不佳。未来人工智能开发者应在设计、开发、评估和数据可重复性方面努力改进。
Key Takeaways
- AI在STBT诊断和预后中的应用得到了系统性回顾。
- AI技术在放射学影像诊断方面的进展受到关注。
- 综述探讨了临床转化中的挑战,并对照医疗影像人工智能清单(CLAIM)和国际指南进行评价。
- 研究在CLAIME表现中等,但在FUTURE-AI指南上表现欠佳。
- 当前影像人工智能工具仍处于概念验证阶段,有巨大的改进空间。
- AI开发者需要在设计、开发、评估和数据的可重复性方面做出努力。
点此查看论文截图

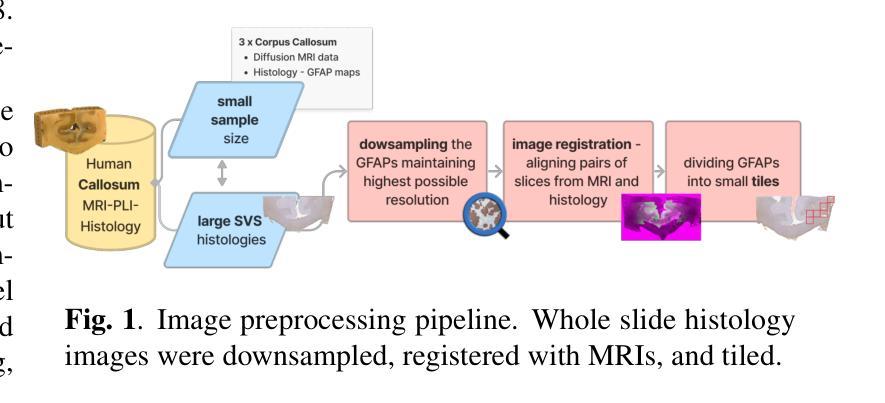
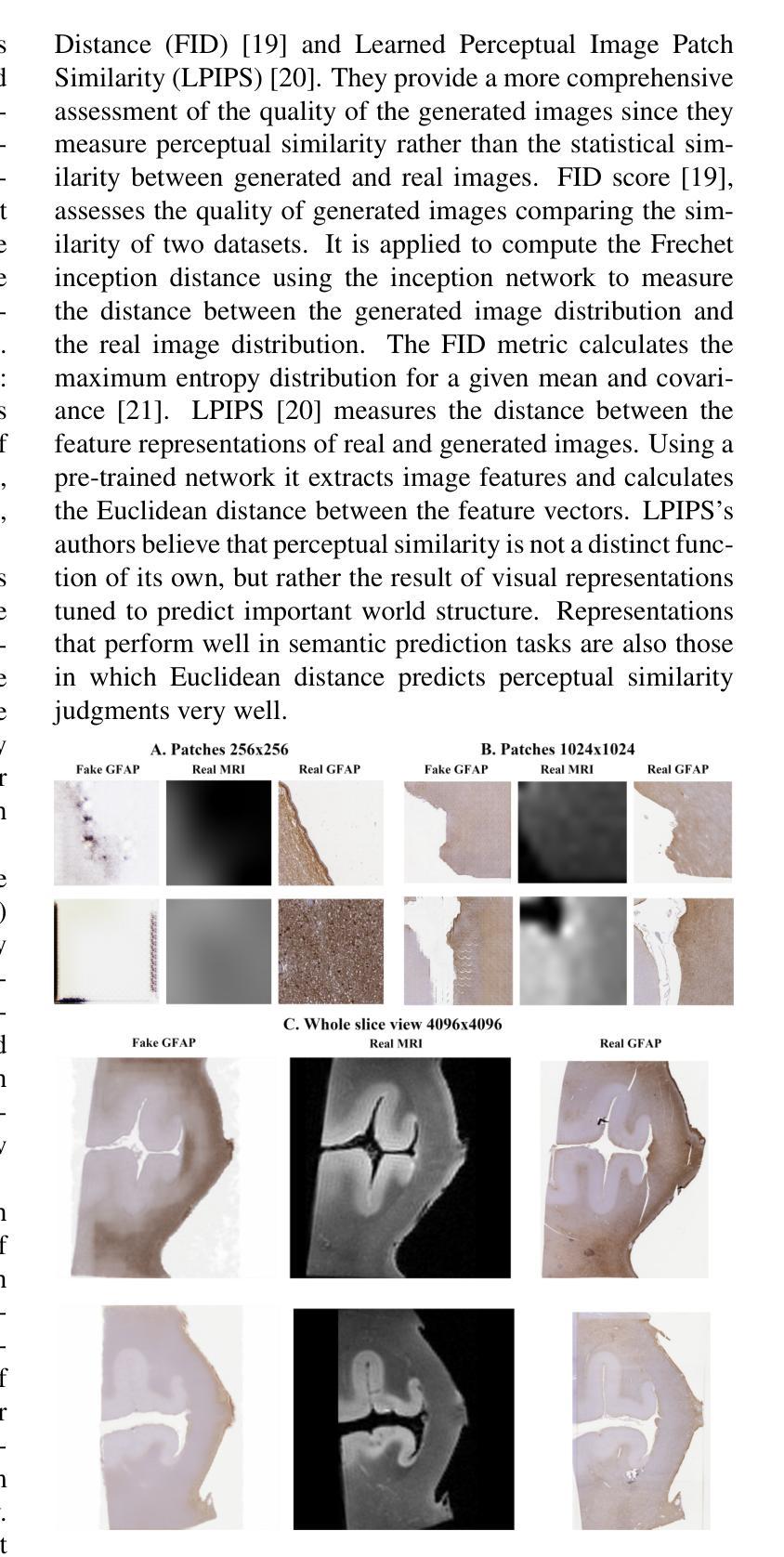
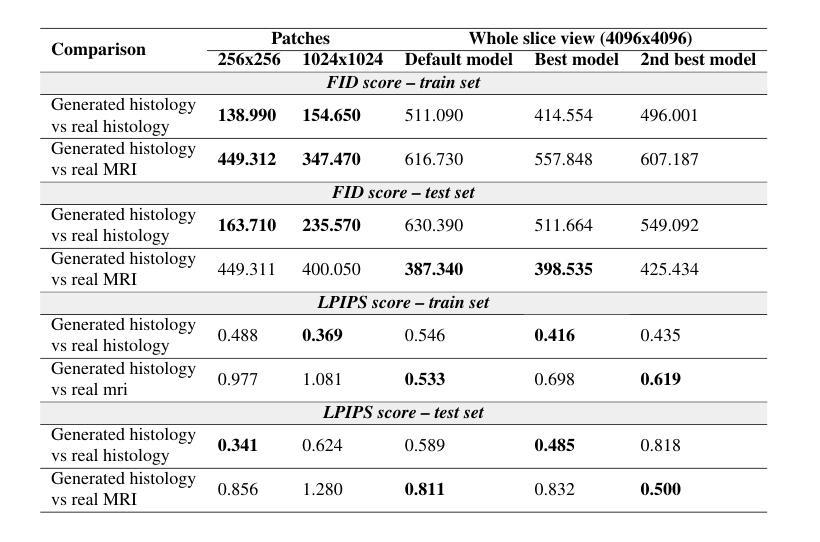
Style transfer between Microscopy and Magnetic Resonance Imaging via Generative Adversarial Network in small sample size settings
Authors:Monika Pytlarz, Adrian Onicas, Alessandro Crimi
Cross-modal augmentation of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and microscopic imaging based on the same tissue samples is promising because it can allow histopathological analysis in the absence of an underlying invasive biopsy procedure. Here, we tested a method for generating microscopic histological images from MRI scans of the corpus callosum using conditional generative adversarial network (cGAN) architecture. To our knowledge, this is the first multimodal translation of the brain MRI to histological volumetric representation of the same sample. The technique was assessed by training paired image translation models taking sets of images from MRI scans and microscopy. The use of cGAN for this purpose is challenging because microscopy images are large in size and typically have low sample availability. The current work demonstrates that the framework reliably synthesizes histology images from MRI scans of corpus callosum, emphasizing the network’s ability to train on high resolution histologies paired with relatively lower-resolution MRI scans. With the ultimate goal of avoiding biopsies, the proposed tool can be used for educational purposes.
基于同一组织样本的磁共振成像(MRI)和显微镜成像的跨模态增强方法前景广阔,因为它可以在没有基本的侵入性活检程序的情况下进行组织病理学分析。在这里,我们测试了一种方法,利用条件生成对抗网络(cGAN)架构,从胼胝体的MRI扫描生成显微镜组织学图像。据我们所知,这是首次将大脑MRI转换为同一样本的组织学体积表示的多模式转换。该技术通过训练配对图像翻译模型来评估,这些模型从MRI扫描和显微镜图像中获取信息。使用cGAN进行此目的具有挑战性,因为显微镜图像尺寸较大且样本通常可用量较少。当前的工作证明该框架可以可靠地从胼胝体的MRI扫描中合成组织学图像,突出了网络在相对较低的分辨率MRI扫描与较高的分辨率组织学配对训练的能力。以最终避免活检为目标,所提议的工具可用于教学目的。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 2023 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP)
Summary:利用条件生成对抗网络(cGAN)架构,首次实现了基于MRI的微观组织学图像生成,展示了从MRI扫描到同一样本组织学体积表示的跨模态转换。尽管面临样本可用性低和图像分辨率高的挑战,但该框架仍成功合成出可靠的组织学图像,可为教育和临床实践提供支持。
Key Takeaways:
- 利用条件生成对抗网络(cGAN)实现了MRI与微观成像的跨模态增强。
- 成功实现从MRI扫描到同一样本组织学体积表示的转变。
- 框架能够在低分辨率MRI扫描上训练,并成功合成高分辨率组织学图像。
- 该技术可应用于教育目的,模拟真实微观环境下的病理变化,以辅助学习和研究。
- 尽管面临样本可用性和图像分辨率的挑战,但该技术仍显示出巨大的潜力。
点此查看论文截图