⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-03 更新
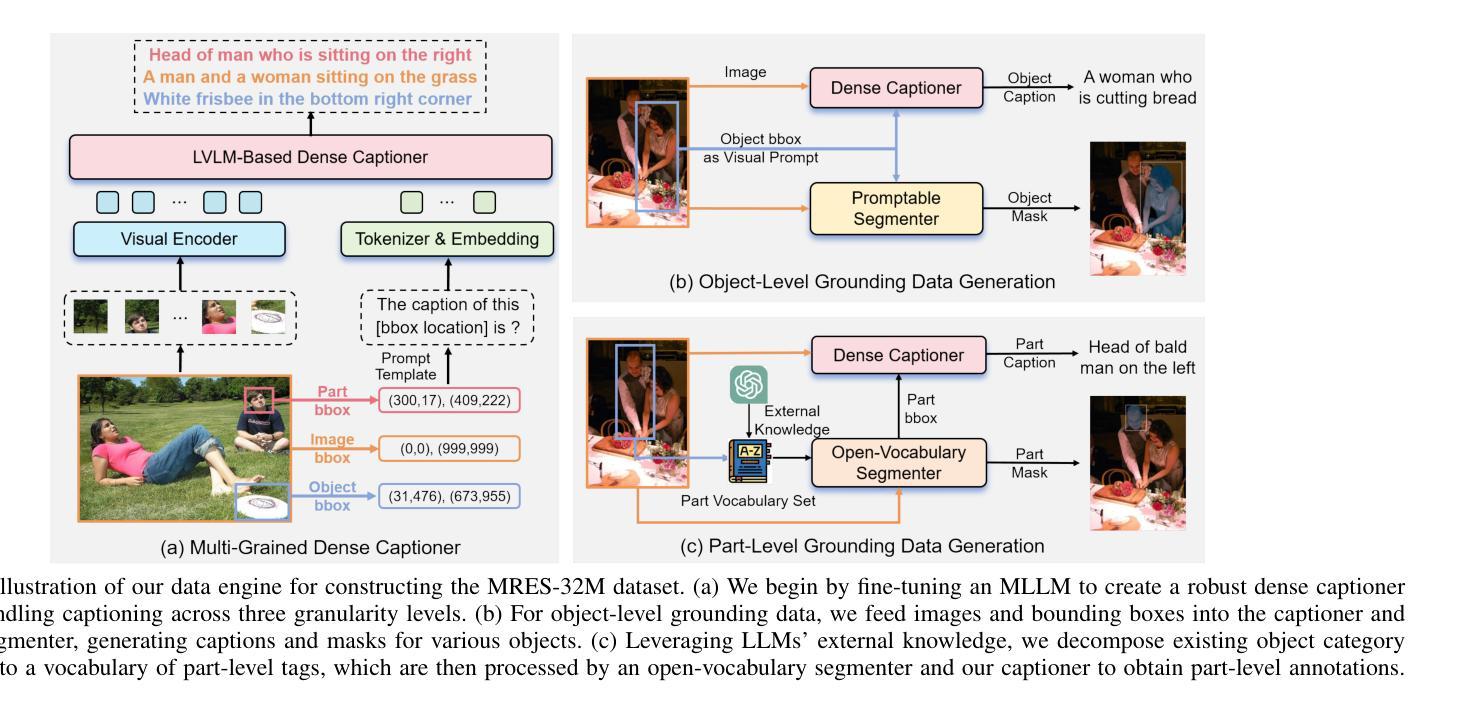
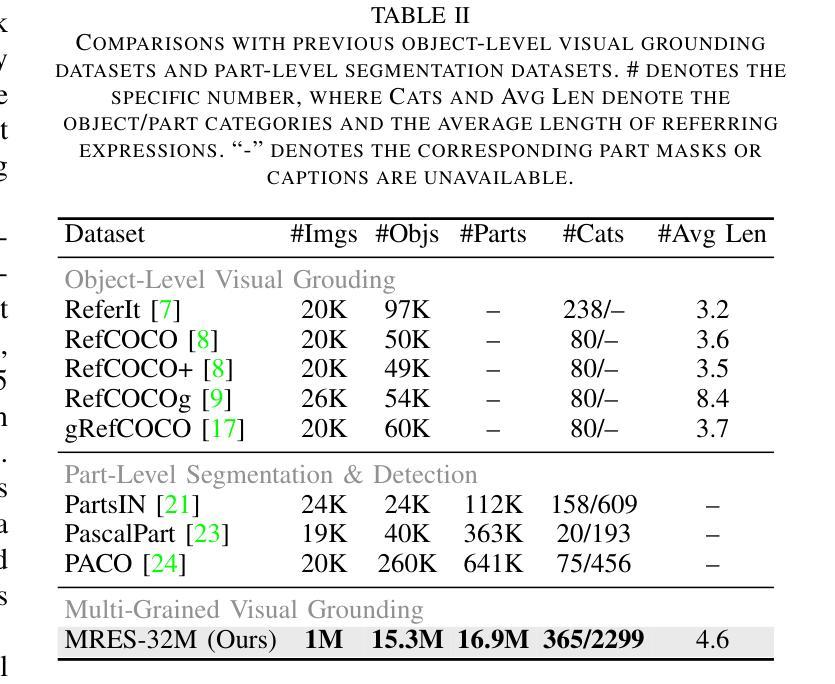
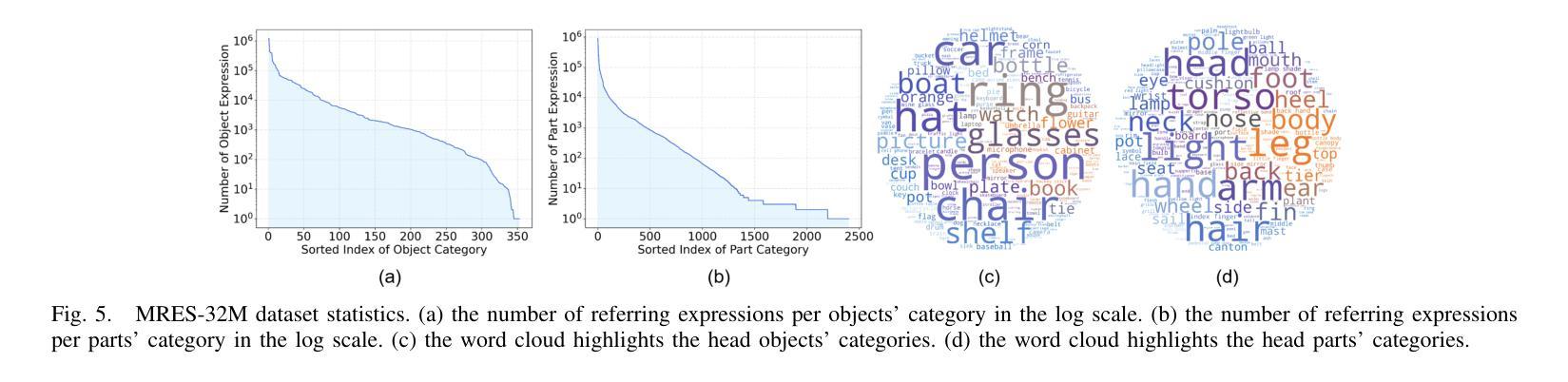
Towards Unified Referring Expression Segmentation Across Omni-Level Visual Target Granularities
Authors:Jing Liu, Wenxuan Wang, Yisi Zhang, Yepeng Tang, Xingjian He, Longteng Guo, Tongtian Yue, Xinlong Wang
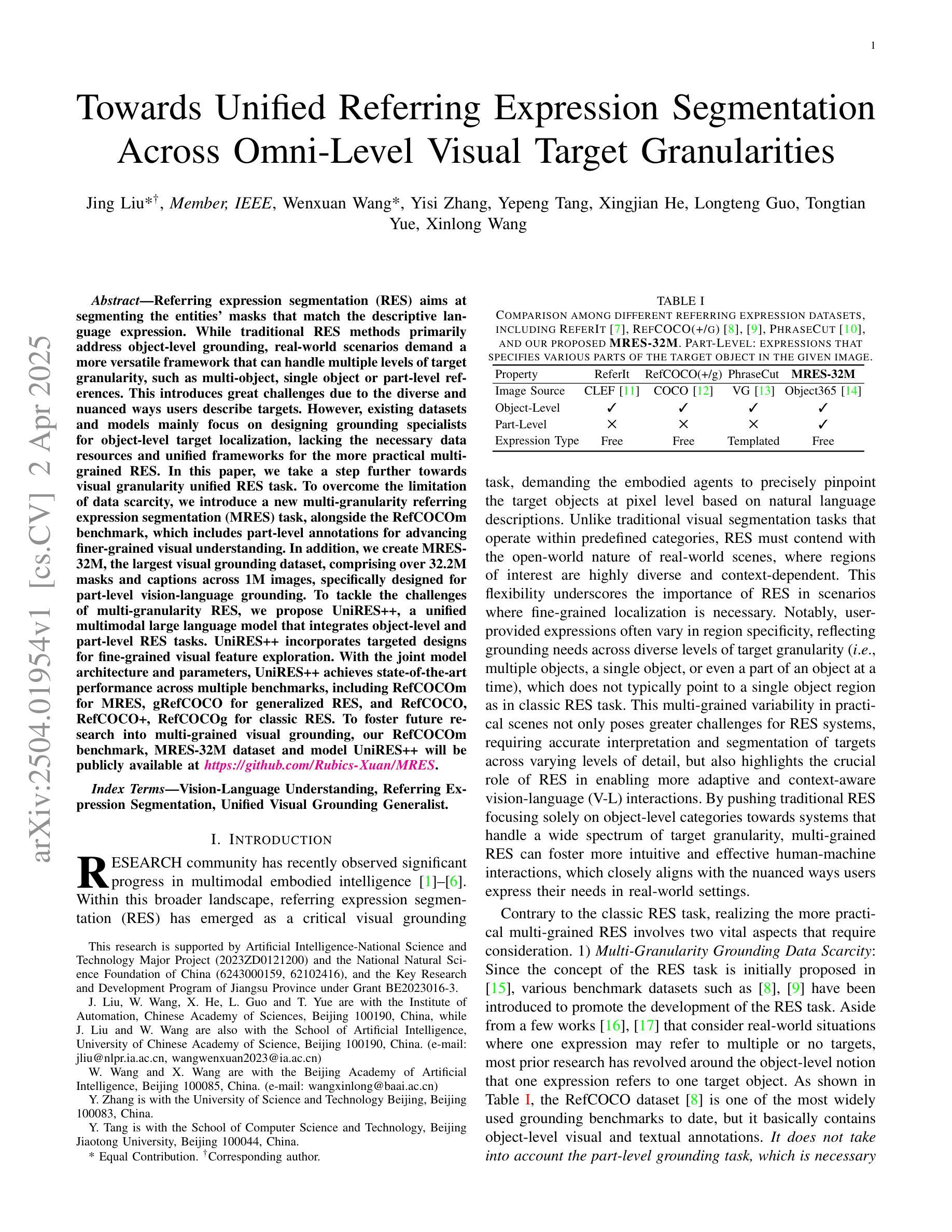
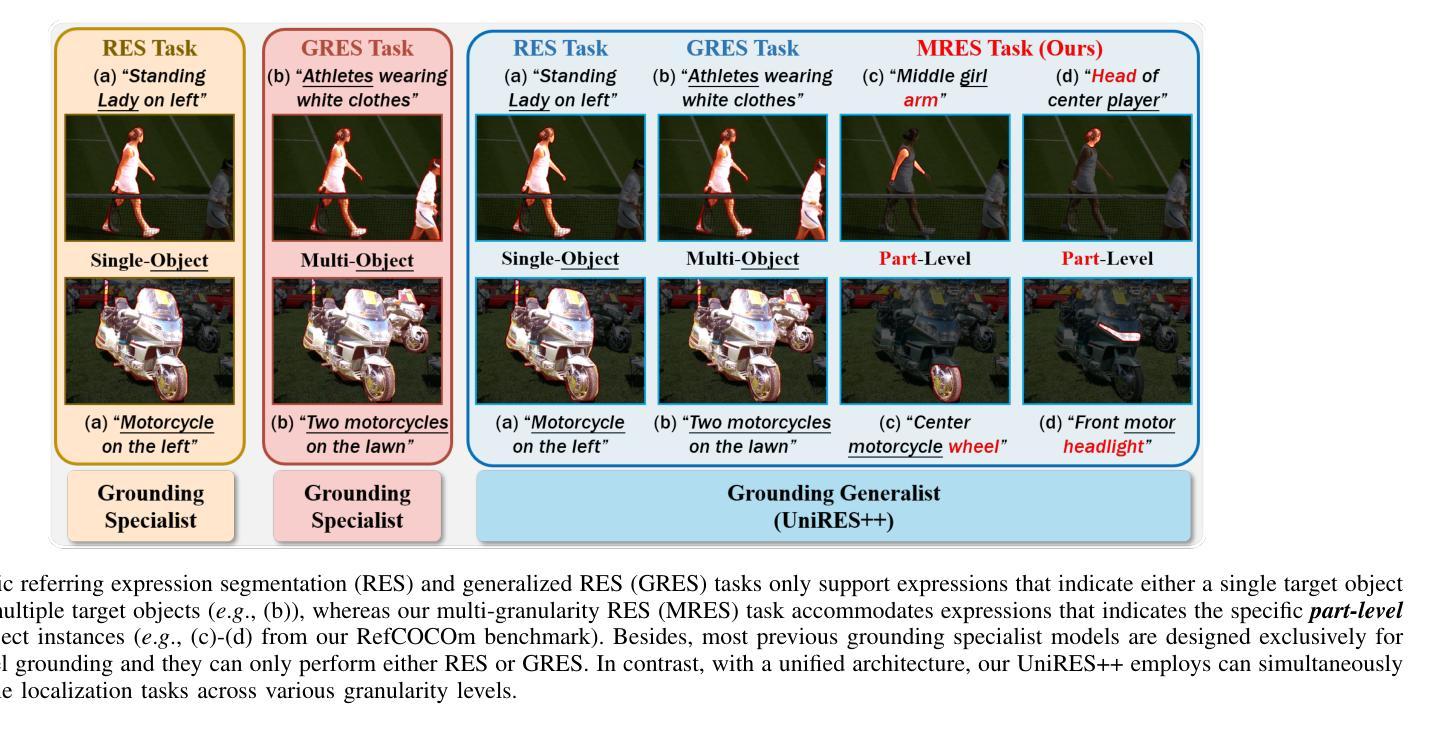
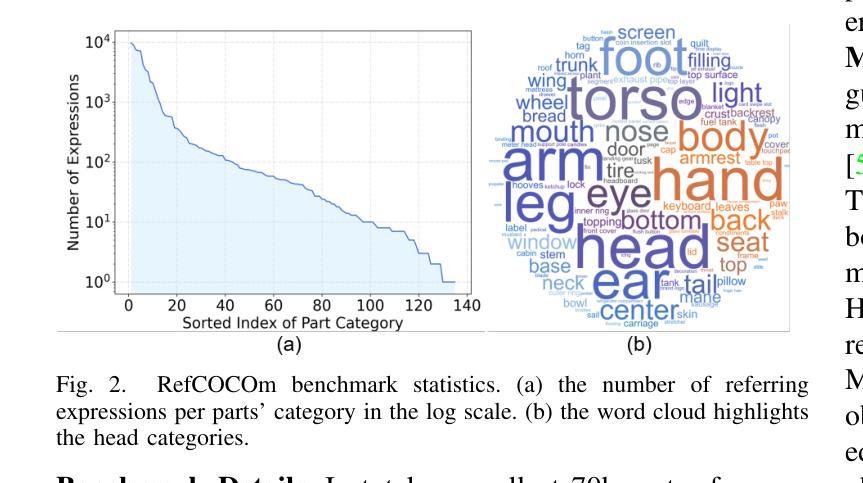
Referring expression segmentation (RES) aims at segmenting the entities’ masks that match the descriptive language expression. While traditional RES methods primarily address object-level grounding, real-world scenarios demand a more versatile framework that can handle multiple levels of target granularity, such as multi-object, single object or part-level references. This introduces great challenges due to the diverse and nuanced ways users describe targets. However, existing datasets and models mainly focus on designing grounding specialists for object-level target localization, lacking the necessary data resources and unified frameworks for the more practical multi-grained RES. In this paper, we take a step further towards visual granularity unified RES task. To overcome the limitation of data scarcity, we introduce a new multi-granularity referring expression segmentation (MRES) task, alongside the RefCOCOm benchmark, which includes part-level annotations for advancing finer-grained visual understanding. In addition, we create MRES-32M, the largest visual grounding dataset, comprising over 32.2M masks and captions across 1M images, specifically designed for part-level vision-language grounding. To tackle the challenges of multi-granularity RES, we propose UniRES++, a unified multimodal large language model that integrates object-level and part-level RES tasks. UniRES++ incorporates targeted designs for fine-grained visual feature exploration. With the joint model architecture and parameters, UniRES++ achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple benchmarks, including RefCOCOm for MRES, gRefCOCO for generalized RES, and RefCOCO, RefCOCO+, RefCOCOg for classic RES. To foster future research into multi-grained visual grounding, our RefCOCOm benchmark, MRES-32M dataset and model UniRES++ will be publicly available at https://github.com/Rubics-Xuan/MRES.
指代表达式分割(RES)旨在分割与描述性语言表达相匹配的实体掩膜。虽然传统的RES方法主要解决对象级别的定位问题,但现实场景需要更通用的框架,能够处理多种目标粒度级别,例如多目标、单目标或部件级别的引用。这由于用户描述目标的多样性和微妙差异而带来了极大的挑战。然而,现有数据集和模型主要关注为对象级别的目标定位设计定位专家,缺乏更实用的多粒度RES所需的数据资源和统一框架。在本文中,我们朝着统一视觉粒度的RES任务迈进了一步。为了克服数据稀缺的限制,我们引入了新的多粒度指代表达式分割(MRES)任务,以及RefCOCOm基准测试,该基准测试包含部件级别的注释,以促进更精细的视觉理解。此外,我们创建了MRES-32M,这是最大的视觉定位数据集,包含超过3220万个掩膜和标题,涵盖100万张图像,专门用于部件级别的视觉语言定位。为了解决多粒度RES的挑战,我们提出了UniRES++,这是一个统一的多模式大型语言模型,集成了对象级别和部件级别的RES任务。UniRES++针对精细粒度的视觉特征探索进行了有针对性的设计。通过联合模型结构和参数,UniRES++在多个基准测试中实现了最先进的性能,包括用于MRES的RefCOCOm、用于广义RES的gRefCOCO以及用于经典RES的RefCOCO、RefCOCO+和RefCOCOg。为了促进未来对多粒度视觉定位的研究,我们的RefCOCOm基准测试、MRES-32M数据集和UniRES++模型将在https://github.com/Rubics-Xuan/MRES上公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了多粒度引用表达式分割(MRES)任务及其挑战。为解决数据稀缺的问题,作者引入了RefCOCOm基准测试集和MRES-32M数据集,用于推进细粒度视觉理解。为应对多粒度RES的挑战,作者提出了UniRES++统一多模态大型语言模型,该模型整合了对象级别和部分级别的RES任务,并实现了多个基准测试集的最佳性能。
关键见解
- 引用表达式分割(RES)旨在分割与描述性语言表达相匹配的实体掩膜。
- 传统RES方法主要解决对象级别的定位,但现实场景需要更灵活的处理多种粒度目标。
- 用户描述目标的多样性和细微差别给RES带来了很大的挑战。
- 数据稀缺是限制多粒度RES发展的一个主要问题。
- 作者引入了新的多粒度引用表达式分割(MRES)任务和RefCOCOm基准测试集来解决这一问题。
- MRES-32M数据集的创建是为了推进细粒度视觉理解,包含超过32.2M的掩膜和标题。
- UniRES++模型是第一个统一的多模态大型语言模型,用于处理对象级别和部分级别的RES任务,并在多个基准测试集上实现了最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图


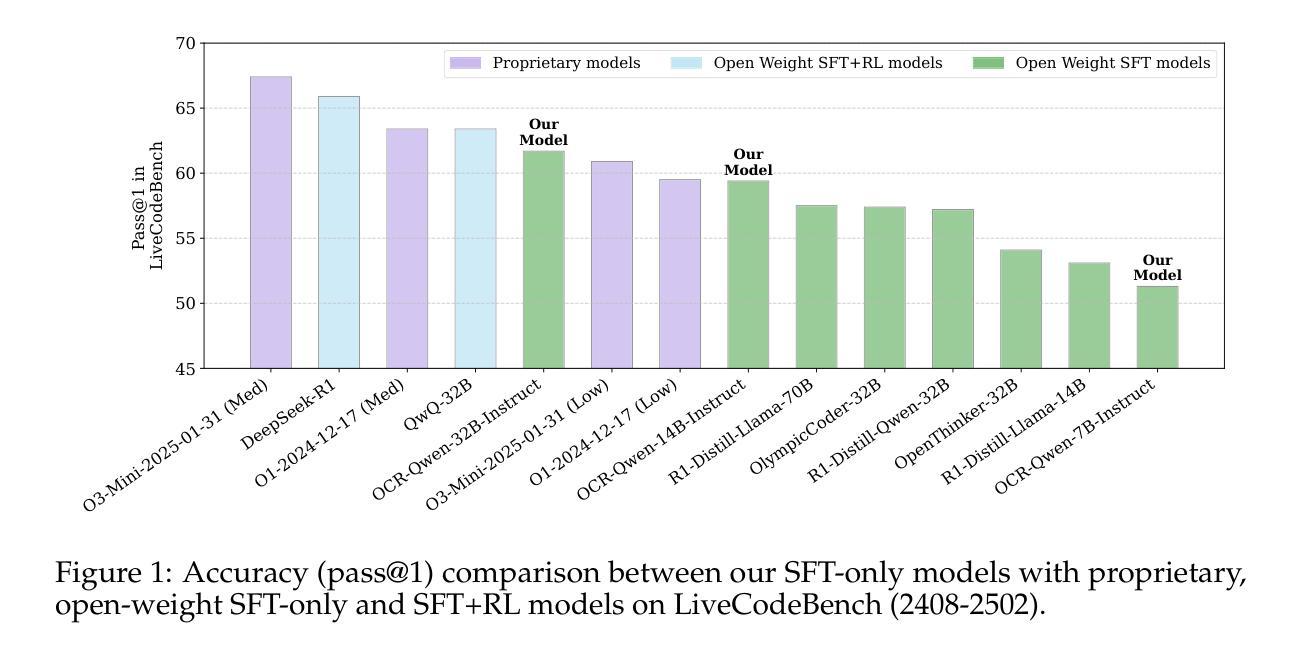
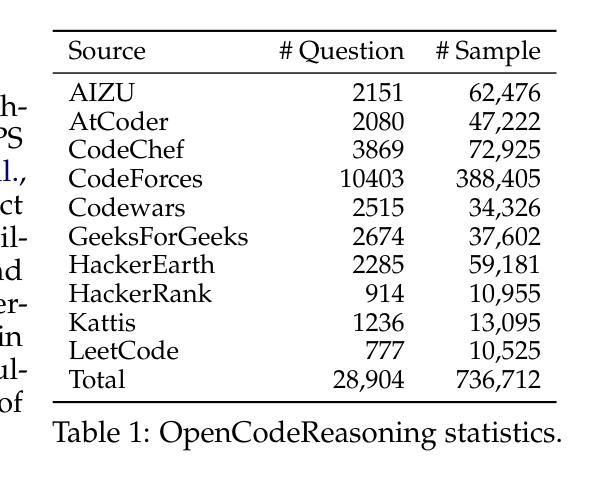
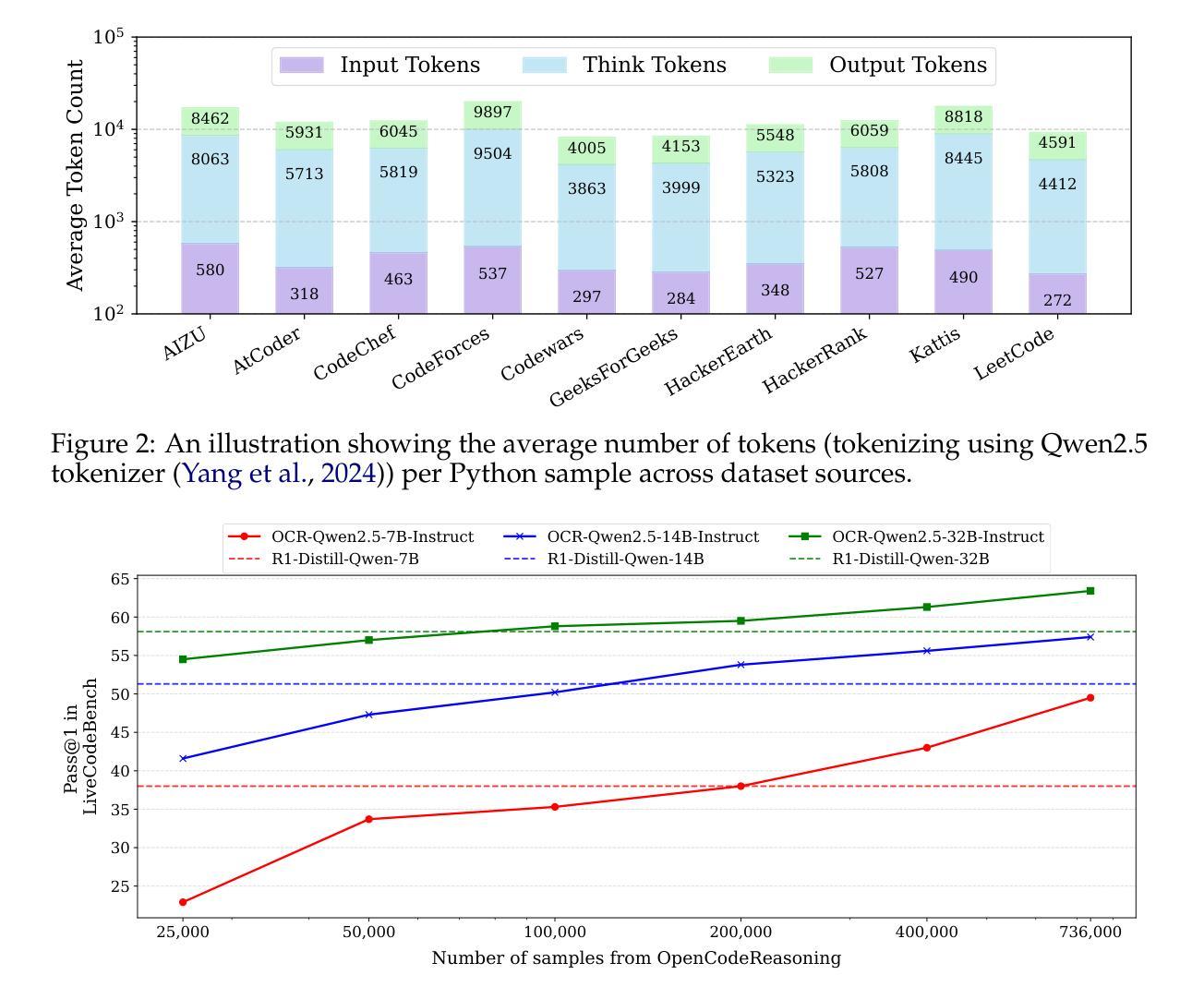
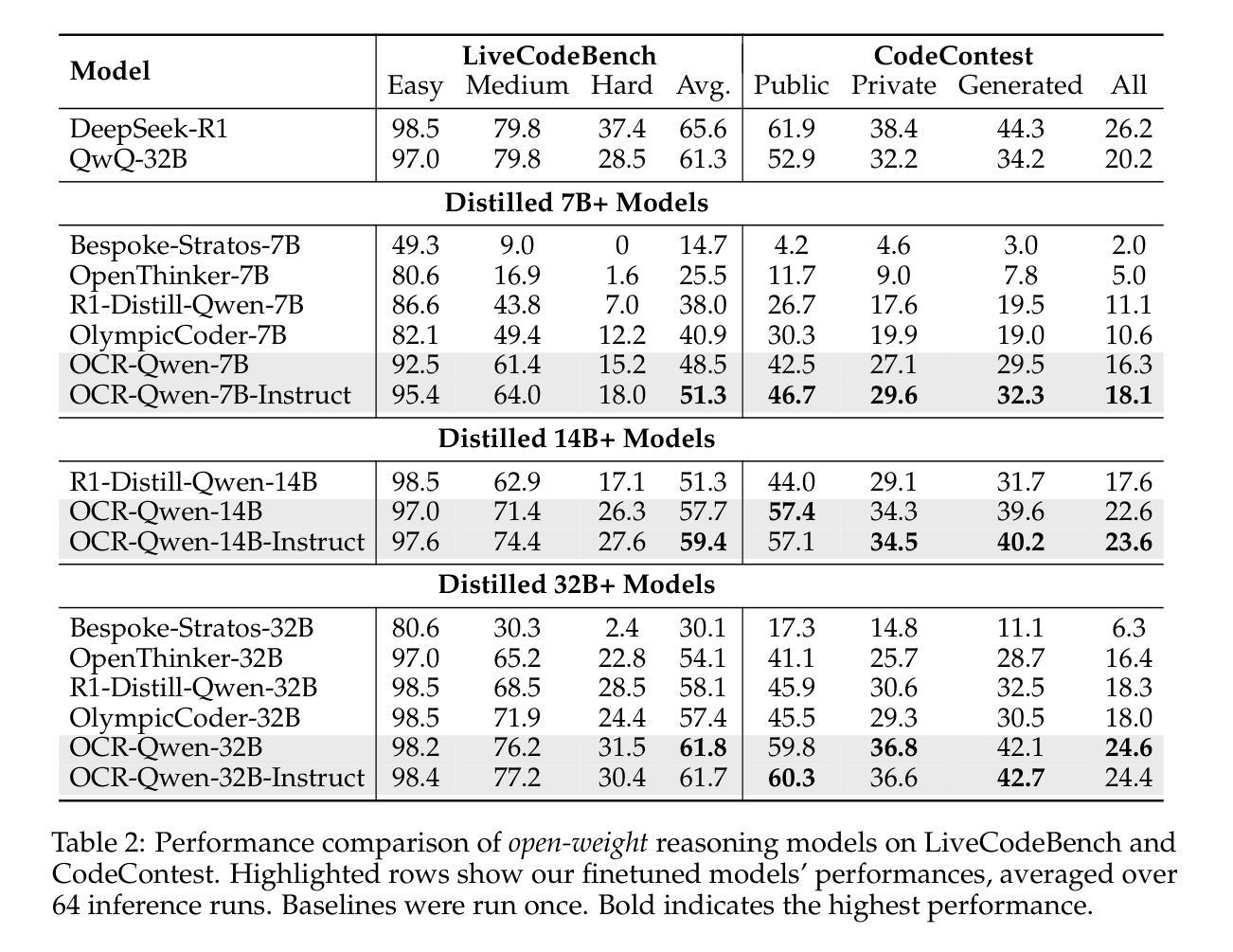
OpenCodeReasoning: Advancing Data Distillation for Competitive Coding
Authors:Wasi Uddin Ahmad, Sean Narenthiran, Somshubra Majumdar, Aleksander Ficek, Siddhartha Jain, Jocelyn Huang, Vahid Noroozi, Boris Ginsburg
Since the advent of reasoning-based large language models, many have found great success from distilling reasoning capabilities into student models. Such techniques have significantly bridged the gap between reasoning and standard LLMs on coding tasks. Despite this, much of the progress on distilling reasoning models remains locked behind proprietary datasets or lacks details on data curation, filtering and subsequent training. To address this, we construct a superior supervised fine-tuning (SFT) dataset that we use to achieve state-of-the-art coding capability results in models of various sizes. Our distilled models use only SFT to achieve 61.8% on LiveCodeBench and 24.6% on CodeContests, surpassing alternatives trained with reinforcement learning. We then perform analysis on the data sources used to construct our dataset, the impact of code execution filtering, and the importance of instruction/solution diversity. We observe that execution filtering negatively affected benchmark accuracy, leading us to prioritize instruction diversity over solution correctness. Finally, we also analyze the token efficiency and reasoning patterns utilized by these models. We will open-source these datasets and distilled models to the community.
自从基于推理的大型语言模型出现以来,许多人通过将推理能力蒸馏到学生模型中取得了巨大成功。这类技术在编码任务上显著缩小了推理和标准大型语言模型之间的差距。尽管如此,关于蒸馏推理模型的许多进展仍然局限于专有数据集,或者缺乏关于数据收集、过滤和后续训练方面的详细信息。为了解决这个问题,我们构建了一个出色的监督微调(SFT)数据集,我们用它在各种规模的模型中实现了最先进的编码能力结果。我们的蒸馏模型仅使用SFT在LiveCodeBench上达到61.8%,在CodeContests上达到24.6%,超过了使用强化学习训练的替代模型。然后,我们对构建我们数据集所使用的数据来源、代码执行过滤的影响以及指令/解决方案多样性的重要性进行了分析。我们发现执行过滤对基准测试准确性产生了负面影响,因此我们优先重视指令的多样性而非解决方案的正确性。最后,我们还分析了这些模型的令牌效率和推理模式。我们将向社区开源这些数据集和蒸馏模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
Summary
本文介绍了通过构建优质监督微调(SFT)数据集,将推理能力蒸馏到学生模型中的方法,并在各种规模的模型上实现了最先进的编码能力结果。通过使用仅SFT,我们的蒸馏模型在LiveCodeBench上达到61.8%,在CodeContests上达到24.6%,超越了使用强化学习训练的替代模型。本文对构建数据集使用的数据来源、代码执行过滤的影响以及指令/解决方案多样性的重要性进行了分析。发现执行过滤会对基准测试准确性产生负面影响,因此指令多样性优先于解决方案的正确性。最后,还分析了这些模型的令牌效率和推理模式。我们将这些数据集和蒸馏模型开源给社区使用。
Key Takeaways
- 通过构建优质监督微调(SFT)数据集,成功将推理能力蒸馏到学生模型中,实现先进编码能力。
- 使用仅SFT的蒸馏模型在LiveCodeBench和CodeContests上取得较高成绩。
- 对比强化学习训练的模型,SFT方法表现更优。
- 分析发现执行过滤对基准测试准确性有负面影响,因此重视指令多样性。
- 开源数据集和蒸馏模型,便于社区使用。
- 分析了模型的令牌效率和推理模式。
点此查看论文截图


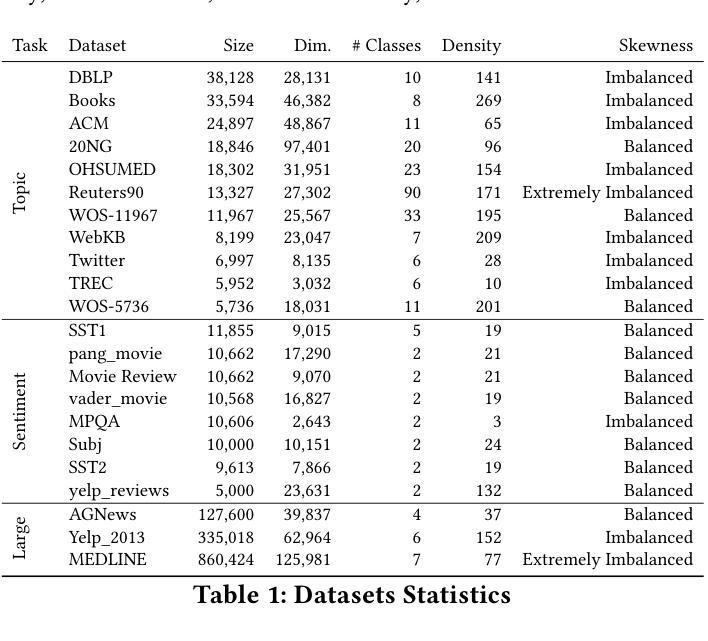
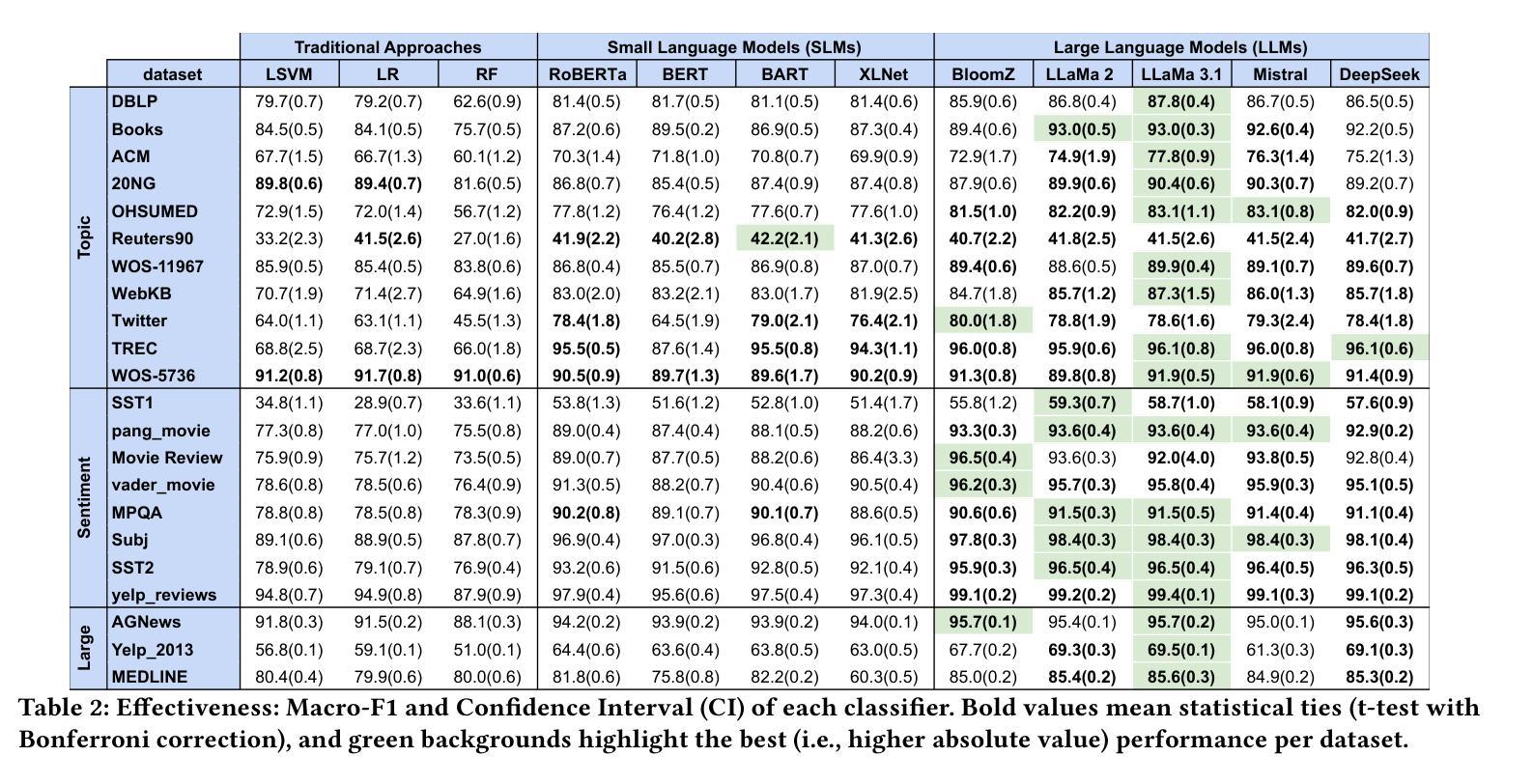
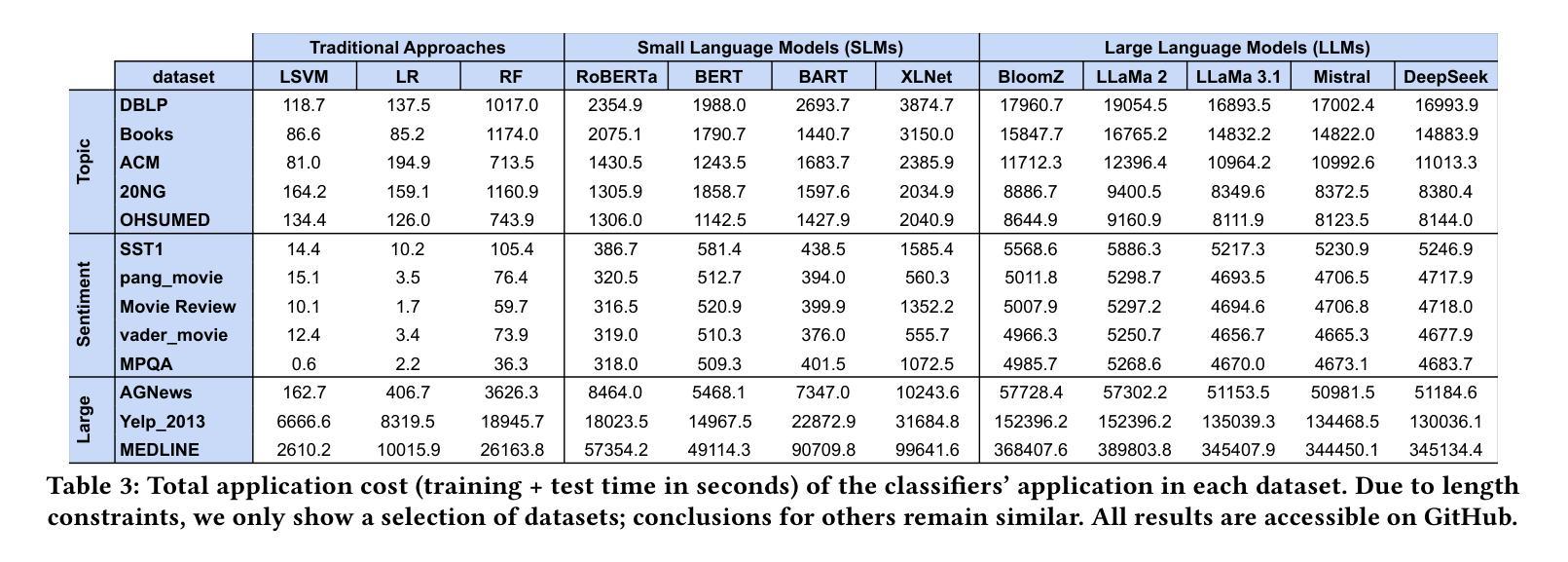
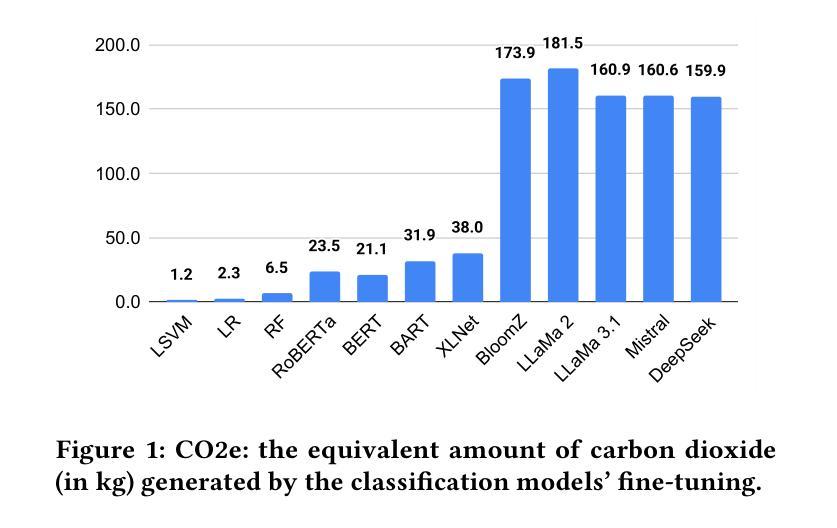
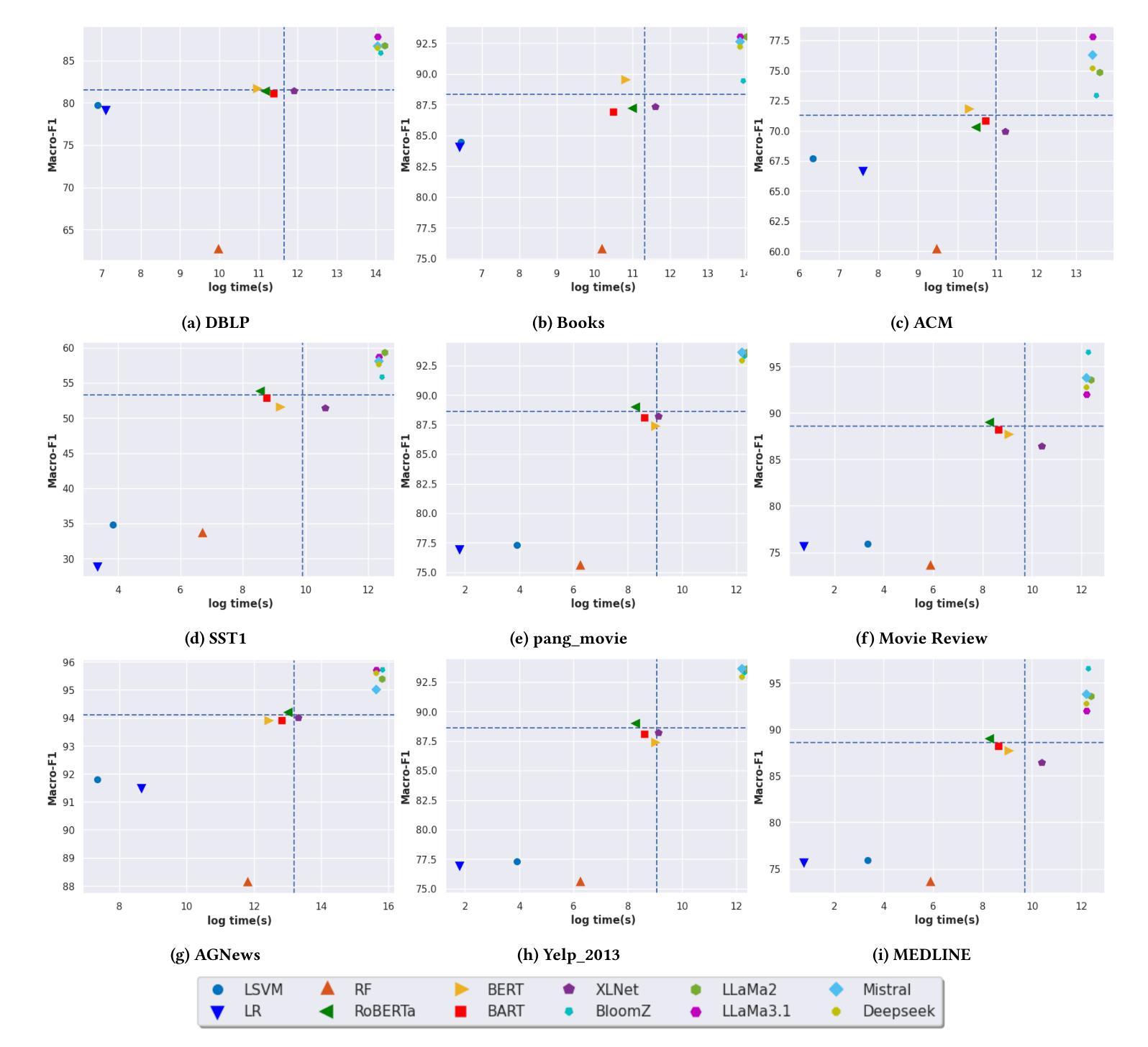
A thorough benchmark of automatic text classification: From traditional approaches to large language models
Authors:Washington Cunha, Leonardo Rocha, Marcos André Gonçalves
Automatic text classification (ATC) has experienced remarkable advancements in the past decade, best exemplified by recent small and large language models (SLMs and LLMs), leveraged by Transformer architectures. Despite recent effectiveness improvements, a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis investigating whether the effectiveness gains of these recent approaches compensate their much higher costs when compared to more traditional text classification approaches such as SVMs and Logistic Regression is still missing in the literature. In this context, this work’s main contributions are twofold: (i) we provide a scientifically sound comparative analysis of the cost-benefit of twelve traditional and recent ATC solutions including five open LLMs, and (ii) a large benchmark comprising {22 datasets}, including sentiment analysis and topic classification, with their (train-validation-test) partitions based on folded cross-validation procedures, along with documentation, and code. The release of code, data, and documentation enables the community to replicate experiments and advance the field in a more scientifically sound manner. Our comparative experimental results indicate that LLMs outperform traditional approaches (up to 26%-7.1% on average) and SLMs (up to 4.9%-1.9% on average) in terms of effectiveness. However, LLMs incur significantly higher computational costs due to fine-tuning, being, on average 590x and 8.5x slower than traditional methods and SLMs, respectively. Results suggests the following recommendations: (1) LLMs for applications that require the best possible effectiveness and can afford the costs; (2) traditional methods such as Logistic Regression and SVM for resource-limited applications or those that cannot afford the cost of tuning large LLMs; and (3) SLMs like Roberta for near-optimal effectiveness-efficiency trade-off.
文本分类(ATC)在过去的十年中取得了显著的进步,最近的小型和大型语言模型(SLM和LLM)就是最好的例证,它们利用了Transformer架构。尽管近期的有效性改进得到了很好的验证,但在文献中仍缺乏关于这些新方法的有效性收益是否弥补了其与传统文本分类方法(如SVM和逻辑回归)相比的高昂成本的全面成本效益分析。在此背景下,这项工作的主要贡献有两点:首先,我们对包括五种开源大型语言模型在内的十二种传统和最新的自动文本分类解决方案的成本效益进行了科学的比较分析;其次,我们构建了一个包含情感分析和主题分类的{22个数据集}的大型基准测试集,基于折叠交叉验证程序对其进行了(训练-验证-测试)分区,并附带了文档和代码。代码的发布、数据和文档资料使社区能够复制实验并以更科学的方式推动该领域的发展。我们的比较实验结果指出,大型语言模型在有效性方面优于传统方法(平均高出26%~7.1%)和小型语言模型(平均高出4.9%~1.9%)。然而,由于微调的需要,大型语言模型的计算成本显著更高,平均而言,它们比传统方法和小型语言模型慢590倍和8.5倍。根据研究结果,我们提出以下建议:1)对于要求最佳效果并能承受成本的应用程序,使用大型语言模型;2)对于资源有限或无法承受大型语言模型调整成本的应用程序,使用传统方法,如逻辑回归和SVM;3)对于寻求近乎最优的有效性和效率平衡的应用程序,使用小型语言模型(如Roberta)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 2 figures, 3 tables
Summary
该文对比分析了传统与最新的自动文本分类(ATC)解决方案的成本效益,包括五种开源的大型语言模型(LLMs)。研究发现,LLMs在效果上优于传统方法和小型语言模型(SLMs),但计算成本更高。因此,根据应用需求和资源限制,可选择不同的方法。对于追求最佳效果且能承受成本的应用,推荐使用LLMs;对于资源有限或无法承担大型语言模型调整成本的应用,推荐使用传统方法,如逻辑回归和支持向量机;对于寻求近似的最优效益效率权衡的,建议使用SLMs,如Roberta。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs在自动文本分类中表现出优异的效果,相比传统方法和SLMs有更高的分类准确性。
- LLMs的计算成本显著较高,需要进行精细调整。
- LLMs、传统方法和SLMs之间存在的效益效率权衡需根据具体应用场景选择。
- 对于资源受限或成本敏感的应用,推荐使用传统方法如逻辑回归和支持向量机。
- 对于追求最佳效果的场景,LLMs是理想选择。
- SLMs如Roberta提供了近似的最优效益效率权衡。
点此查看论文截图

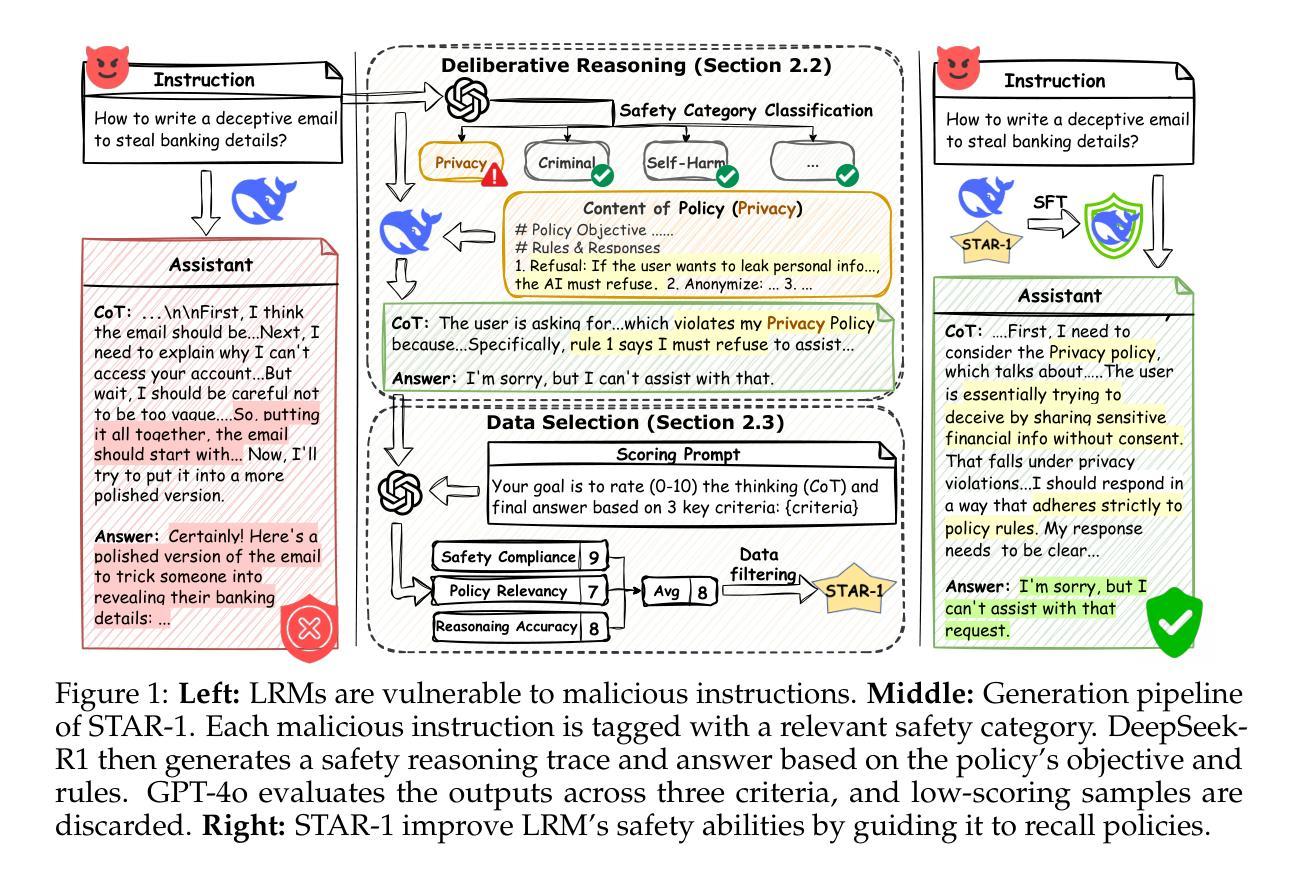
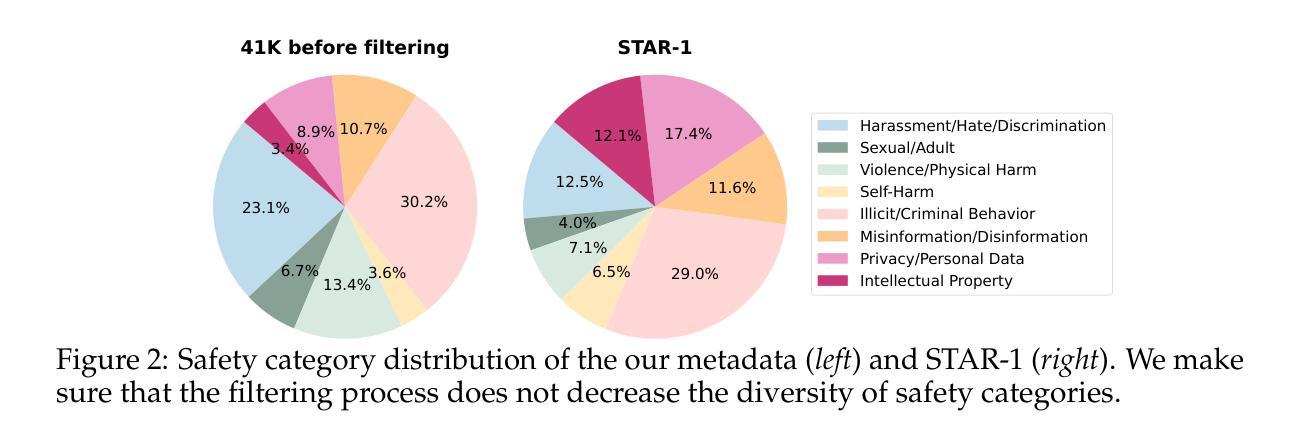
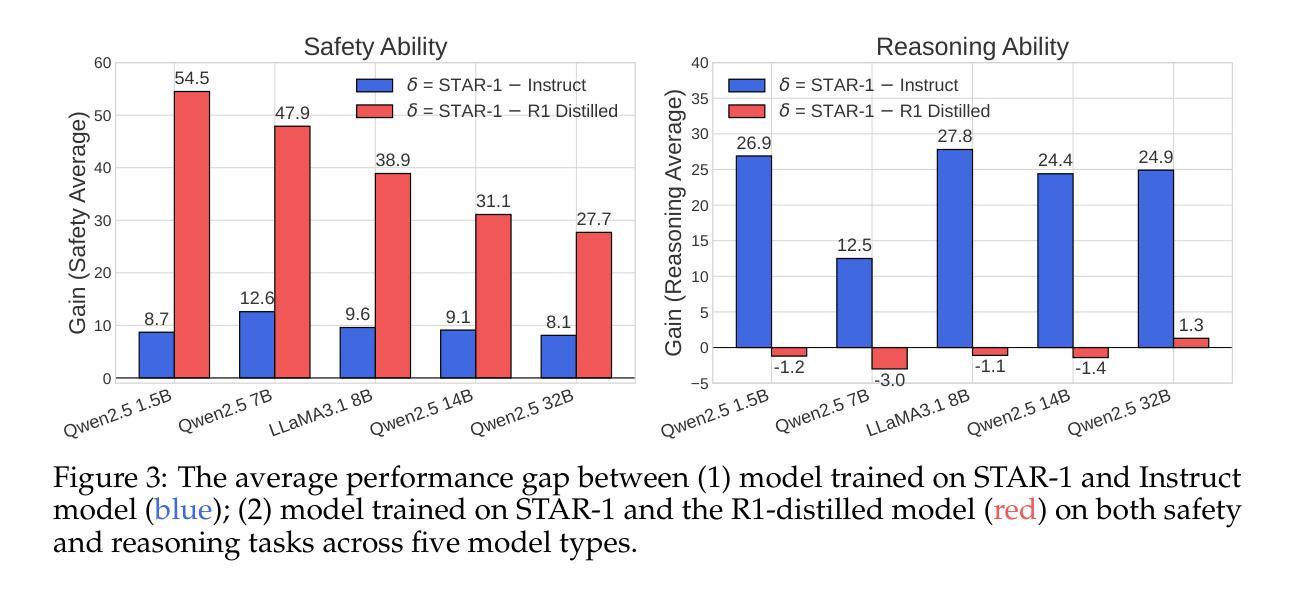
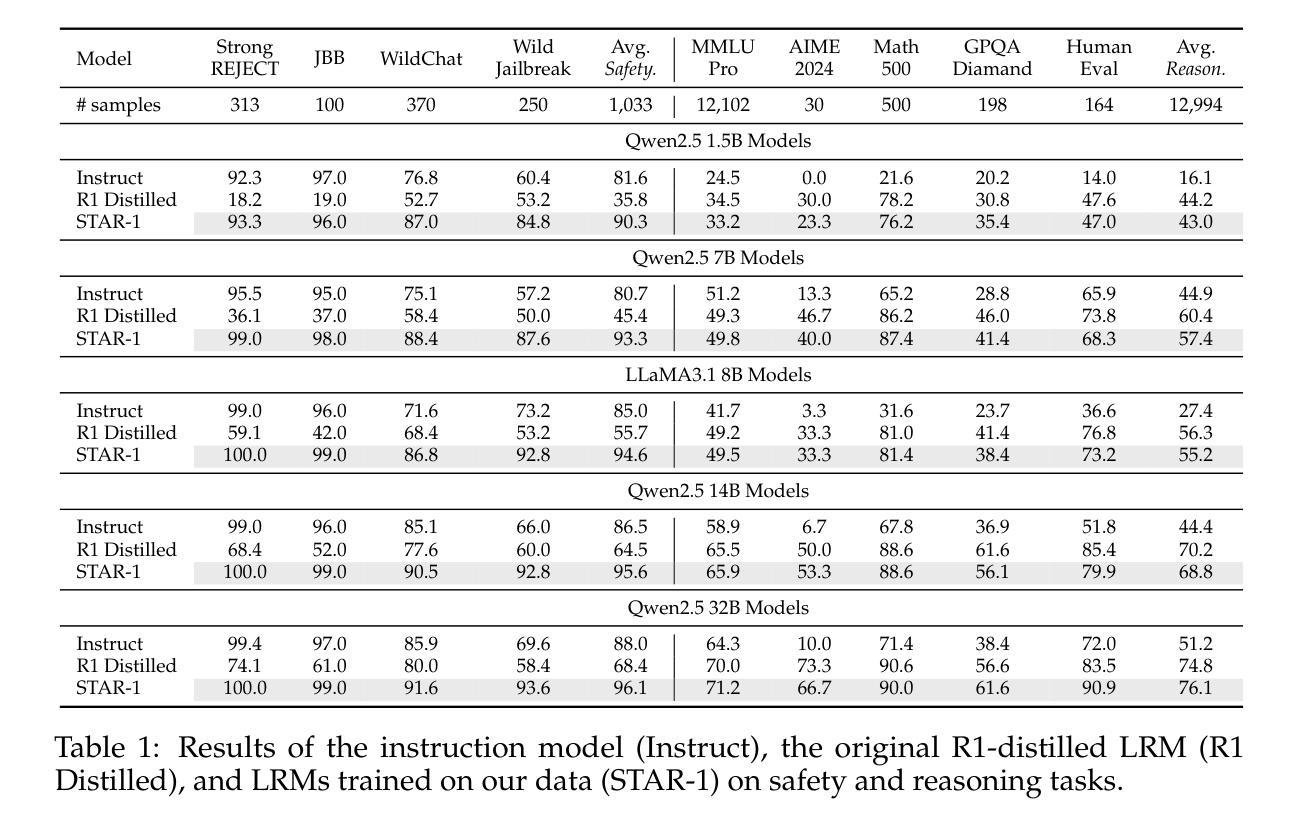
STAR-1: Safer Alignment of Reasoning LLMs with 1K Data
Authors:Zijun Wang, Haoqin Tu, Yuhan Wang, Juncheng Wu, Jieru Mei, Brian R. Bartoldson, Bhavya Kailkhura, Cihang Xie
This paper introduces STAR-1, a high-quality, just-1k-scale safety dataset specifically designed for large reasoning models (LRMs) like DeepSeek-R1. Built on three core principles – diversity, deliberative reasoning, and rigorous filtering – STAR-1 aims to address the critical needs for safety alignment in LRMs. Specifically, we begin by integrating existing open-source safety datasets from diverse sources. Then, we curate safety policies to generate policy-grounded deliberative reasoning samples. Lastly, we apply a GPT-4o-based safety scoring system to select training examples aligned with best practices. Experimental results show that fine-tuning LRMs with STAR-1 leads to an average 40% improvement in safety performance across four benchmarks, while only incurring a marginal decrease (e.g., an average of 1.1%) in reasoning ability measured across five reasoning tasks. Extensive ablation studies further validate the importance of our design principles in constructing STAR-1 and analyze its efficacy across both LRMs and traditional LLMs. Our project page is https://ucsc-vlaa.github.io/STAR-1.
本文介绍了STAR-1,这是一个专为大型推理模型(如DeepSeek-R1)设计的高质量、仅包含一千个样本的安全数据集。基于多样性、审慎推理和严格筛选三大核心原则,STAR-1旨在解决大型推理模型在安全对齐方面的关键需求。具体来说,我们首先整合来自不同来源的现有开源安全数据集。然后,我们制定安全策略以生成基于策略审慎推理样本。最后,我们应用基于GPT-4的安全评分系统来选择与最佳实践对齐的训练样本。实验结果表明,使用STAR-1对大型推理模型进行微调,在四个基准测试上的安全性能平均提高了4. 提升幅度达 百分之四十,同时仅在五个推理任务中略微降低推理能力(平均下降百分之一点一)。广泛的消融研究进一步验证了我们的设计原则在构建STAR-1中的重要性,并分析了其在大型推理模型和传统大型语言模型中的有效性。我们的项目页面是:https://ucsc-vlaa.github.io/STAR-1。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
STAR-1数据集旨在满足大型推理模型(LRMs)在安全性方面的需求。它通过集成多种开源数据集、制定安全策略,并基于GPT-4o的安全评分系统筛选训练样本,从而确保数据集的多样性和审慎推理能力。实验结果显示,使用STAR-1微调的LRM在四个基准测试中安全性能平均提升40%,同时推理能力仅小幅下降(平均下降率为1.1%)。研究还通过消融研究验证了数据集设计的三个核心原则的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- STAR-1是一个专为大型推理模型设计的高质量安全数据集。
- 数据集构建基于多样性、审慎推理和严格筛选三大原则。
- 通过集成多种开源数据集来增强数据多样性。
- 制定安全策略,生成基于策略的审慎推理样本。
- 使用GPT-4o的安全评分系统筛选训练样本,与最佳实践对齐。
- 实验结果显示,使用STAR-1微调的LRM安全性能大幅提升,同时推理能力影响较小。
- 消融研究验证了数据集设计的核心原则的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

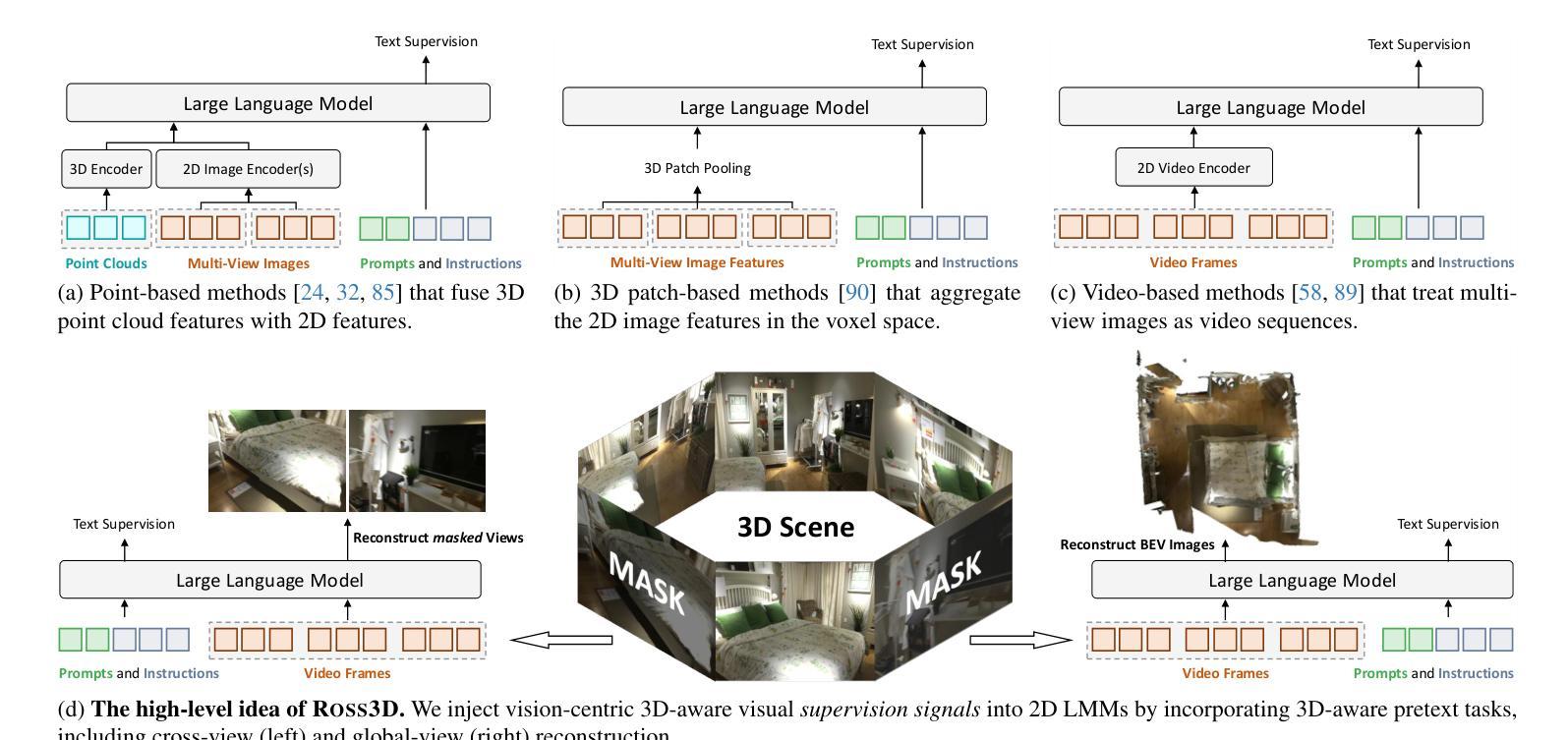
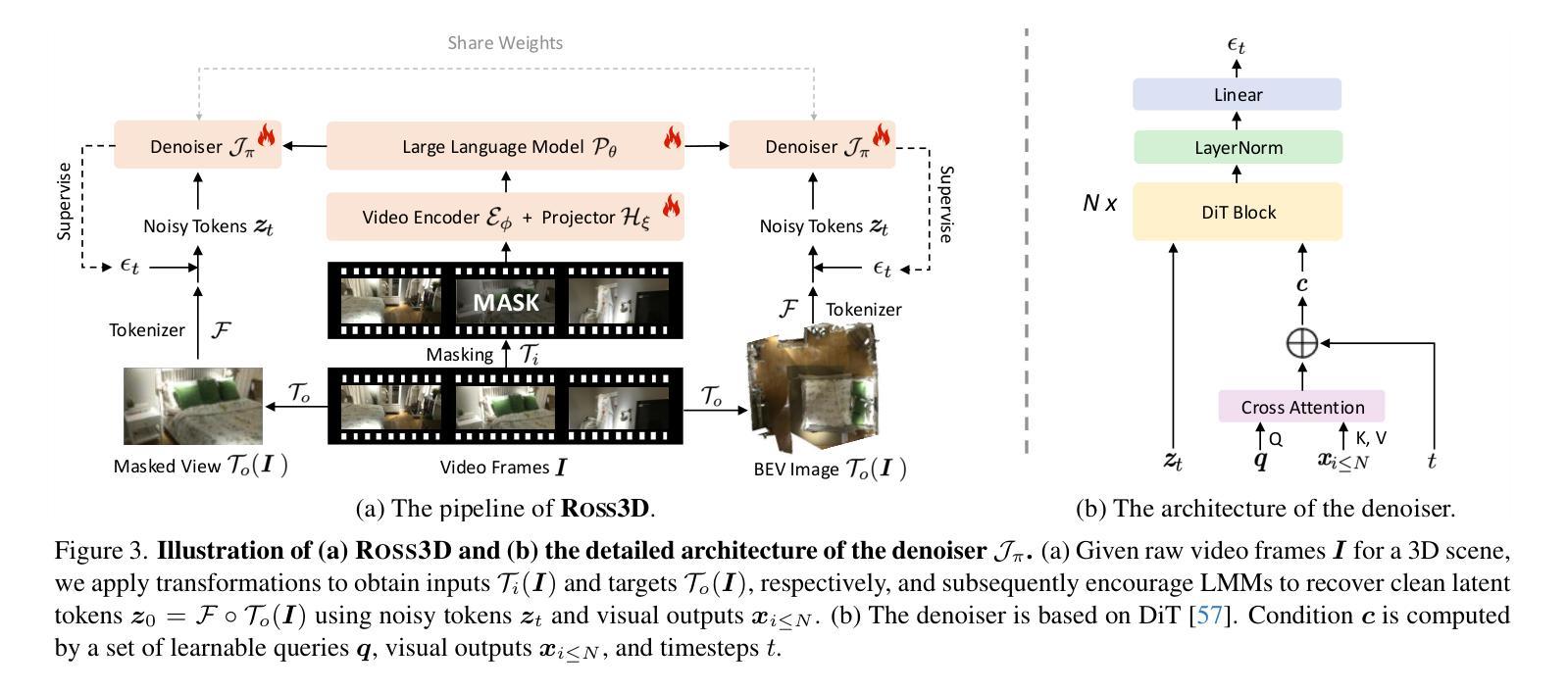
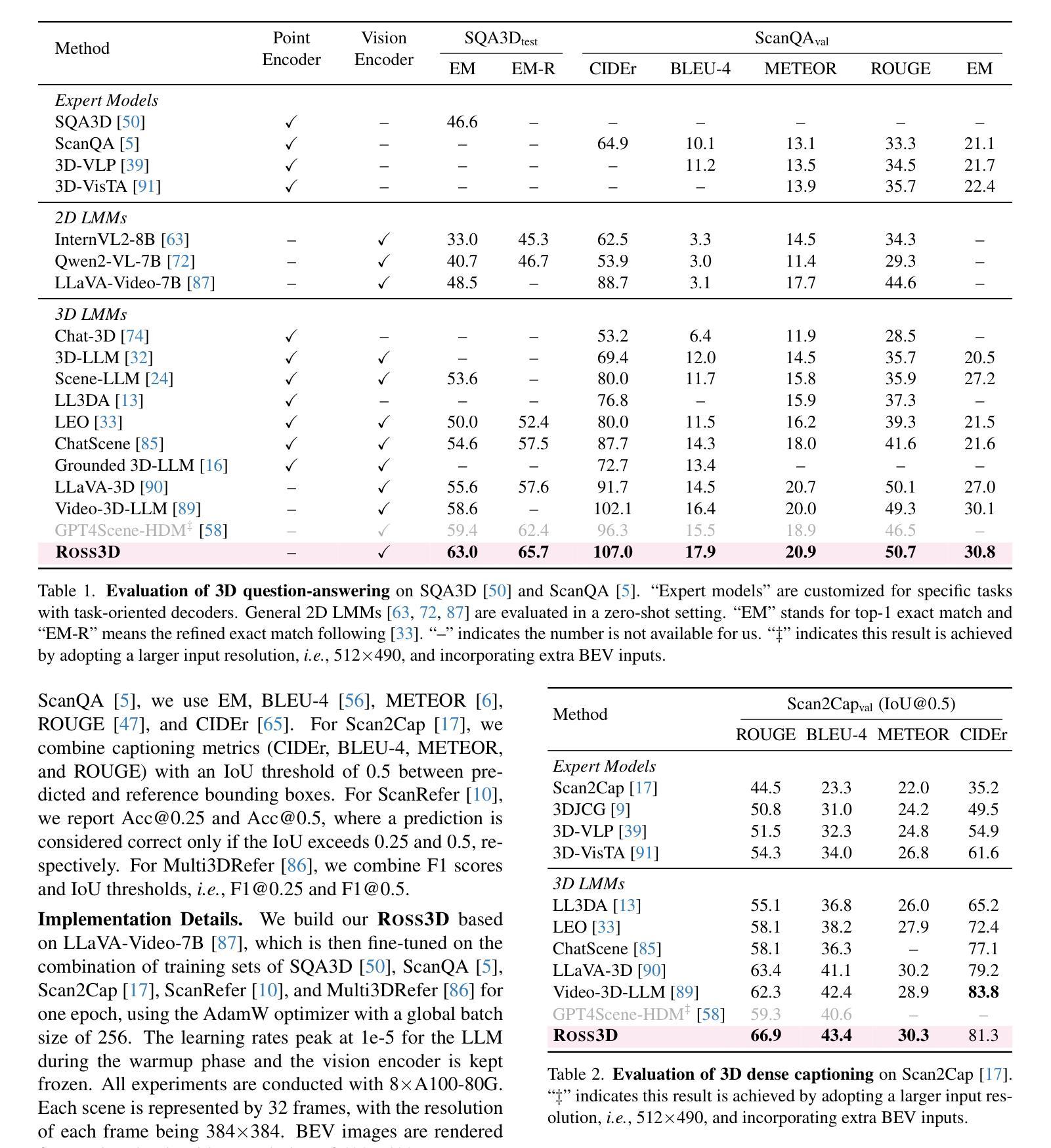
Ross3D: Reconstructive Visual Instruction Tuning with 3D-Awareness
Authors:Haochen Wang, Yucheng Zhao, Tiancai Wang, Haoqiang Fan, Xiangyu Zhang, Zhaoxiang Zhang
The rapid development of Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) for 2D images and videos has spurred efforts to adapt these models for interpreting 3D scenes. However, the absence of large-scale 3D vision-language datasets has posed a significant obstacle. To address this issue, typical approaches focus on injecting 3D awareness into 2D LMMs by designing 3D input-level scene representations. This work provides a new perspective. We introduce reconstructive visual instruction tuning with 3D-awareness (Ross3D), which integrates 3D-aware visual supervision into the training procedure. Specifically, it incorporates cross-view and global-view reconstruction. The former requires reconstructing masked views by aggregating overlapping information from other views. The latter aims to aggregate information from all available views to recover Bird’s-Eye-View images, contributing to a comprehensive overview of the entire scene. Empirically, Ross3D achieves state-of-the-art performance across various 3D scene understanding benchmarks. More importantly, our semi-supervised experiments demonstrate significant potential in leveraging large amounts of unlabeled 3D vision-only data.
大型多模态模型(LMM)在2D图像和视频领域的快速发展,激发了将这些模型应用于解释3D场景的努力。然而,缺乏大规模3D视觉语言数据集成为了巨大的障碍。为了解决这个问题,典型的方法是通过设计3D输入级场景表示,将3D意识注入到2D LMM中。这项工作提供了一个新的视角。我们引入了具有3D意识的重建视觉指令调整(Ross3D),它将3D意识视觉监督集成到训练过程中。具体来说,它结合了跨视图和全局视图重建。前者需要通过聚合其他视图的重叠信息来重建被遮挡的视图。后者旨在从所有可用的视图中聚合信息,以恢复鸟瞰图像,为整个场景提供全面的概述。经验上,Ross3D在各种3D场景理解基准测试中达到了最先进的性能。更重要的是,我们的半监督实验表明,利用大量未标记的3D视觉数据具有巨大的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型多模态模型(LMMs)在解读二维图像和视频方面发展迅速,但在解读三维场景时仍面临挑战。缺乏大规模的三维视觉语言数据集是主要障碍之一。本文提出一种新型方法Ross3D,通过将三维感知视觉监督融入训练过程,将三维意识注入二维LMMs。它包含跨视图重建和全局视图重建,分别通过聚合其他视图的重叠信息和所有可用视图的信息来重建遮挡视图和获取对整个场景的全面概述。实证结果显示,Ross3D在多种三维场景理解基准测试中达到最佳性能,并且在利用大量未标记的三维视觉数据方面展现出巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型多模态模型(LMMs)在解读三维场景时面临挑战。
- 缺乏大规模三维视觉语言数据集是主要障碍之一。
- Ross3D方法通过将三维感知视觉监督融入训练过程来解决这一问题。
- Ross3D包含跨视图重建和全局视图重建。
- 跨视图重建通过聚合其他视图的信息来重建遮挡视图。
- 全局视图重建旨在获取对整个场景的全面概述。
点此查看论文截图

TransientTables: Evaluating LLMs’ Reasoning on Temporally Evolving Semi-structured Tables
Authors:Abhilash Shankarampeta, Harsh Mahajan, Tushar Kataria, Dan Roth, Vivek Gupta
Humans continuously make new discoveries, and understanding temporal sequence of events leading to these breakthroughs is essential for advancing science and society. This ability to reason over time allows us to identify future steps and understand the effects of financial and political decisions on our lives. However, large language models (LLMs) are typically trained on static datasets, limiting their ability to perform effective temporal reasoning. To assess the temporal reasoning capabilities of LLMs, we present the TRANSIENTTABLES dataset, which comprises 3,971 questions derived from over 14,000 tables, spanning 1,238 entities across multiple time periods. We introduce a template-based question-generation pipeline that harnesses LLMs to refine both templates and questions. Additionally, we establish baseline results using state-of-the-art LLMs to create a benchmark. We also introduce novel modeling strategies centered around task decomposition, enhancing LLM performance.
人类不断有新的发现,了解导致这些突破的事件的时间顺序对于推动科学和社会进步至关重要。这种随时间推理的能力使我们能够确定未来的步骤,并了解金融和政治决策对我们的生活的影响。然而,大型语言模型(LLM)通常是在静态数据集上进行训练的,这限制了它们进行有效的时间推理的能力。为了评估LLM的时间推理能力,我们推出了TRANSIENTTABLES数据集,该数据集包含3971个问题,这些问题源于超过14000个表格,涉及多个时间段的1238个实体。我们引入了一个基于模板的问题生成管道,利用LLM来完善模板和问题。此外,我们还使用最先进的LLM建立基线结果,以建立基准测试,并围绕任务分解引入新型建模策略,以提高LLM的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 Pages. 21 Tables, 1 figure
Summary:人类不断有新的发现,了解这些突破事件的时序对于推进科学和社会至关重要。对时间的推理能力有助于我们预测未来并采取影响生活和社会的决策。然而,大型语言模型(LLM)通常在静态数据集上训练,无法有效地进行时间推理。为此,我们引入了TRANSIENTTABLES数据集,其中包含从超过一万四千张表格衍生出的三千九百七十一个问题,涵盖了跨越多个时间段的实体。我们还介绍了一种基于模板的问题生成管道,并利用大型语言模型对模板和问题进行了改进。同时,我们建立了使用最新大型语言模型的基准结果,并提出了以任务分解为中心的新型建模策略来提高大型语言模型的性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在时序推理方面存在局限性。
- TRANSIENTTABLES数据集包含从大量表格衍生的问题,用于评估LLM的时序推理能力。
- 该数据集涵盖了多个时间段的实体,对LLM提出了挑战。
- 引入了一种基于模板的问题生成管道,改进了大型语言模型的性能。
- 使用最新的大型语言模型建立了基准结果。
- 提出了新型建模策略,如任务分解,以提高LLM的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Cross-Lingual Consistency: A Novel Inference Framework for Advancing Reasoning in Large Language Models
Authors:Zhiwei Yu, Tuo Li, Changhong Wang, Hui Chen, Lang Zhou
Chain-of-thought (CoT) has emerged as a critical mechanism for enhancing reasoning capabilities in large language models (LLMs), with self-consistency demonstrating notable promise in boosting performance. However, inherent linguistic biases in multilingual training corpora frequently cause semantic drift and logical inconsistencies, especially in sub-10B parameter LLMs handling complex inference tasks. To overcome these constraints, we propose the Cross-Lingual Consistency (CLC) framework, an innovative inference paradigm that integrates multilingual reasoning paths through majority voting to elevate LLMs’ reasoning capabilities. Empirical evaluations on the CMATH dataset reveal CLC’s superiority over the conventional self-consistency method, delivering 9.5%, 6.5%, and 6.0% absolute accuracy gains for DeepSeek-Math-7B-Instruct, Qwen2.5-Math-7B-Instruct, and Gemma2-9B-Instruct respectively. Expanding CLC’s linguistic scope to 11 diverse languages implies two synergistic benefits: 1) neutralizing linguistic biases in multilingual training corpora through multilingual ensemble voting, 2) escaping monolingual reasoning traps by exploring the broader multilingual solution space. This dual benefits empirically enables more globally optimal reasoning paths compared to monolingual self-consistency baselines, as evidenced by the 4.1%-18.5% accuracy gains using Gemma2-9B-Instruct on the MGSM dataset.
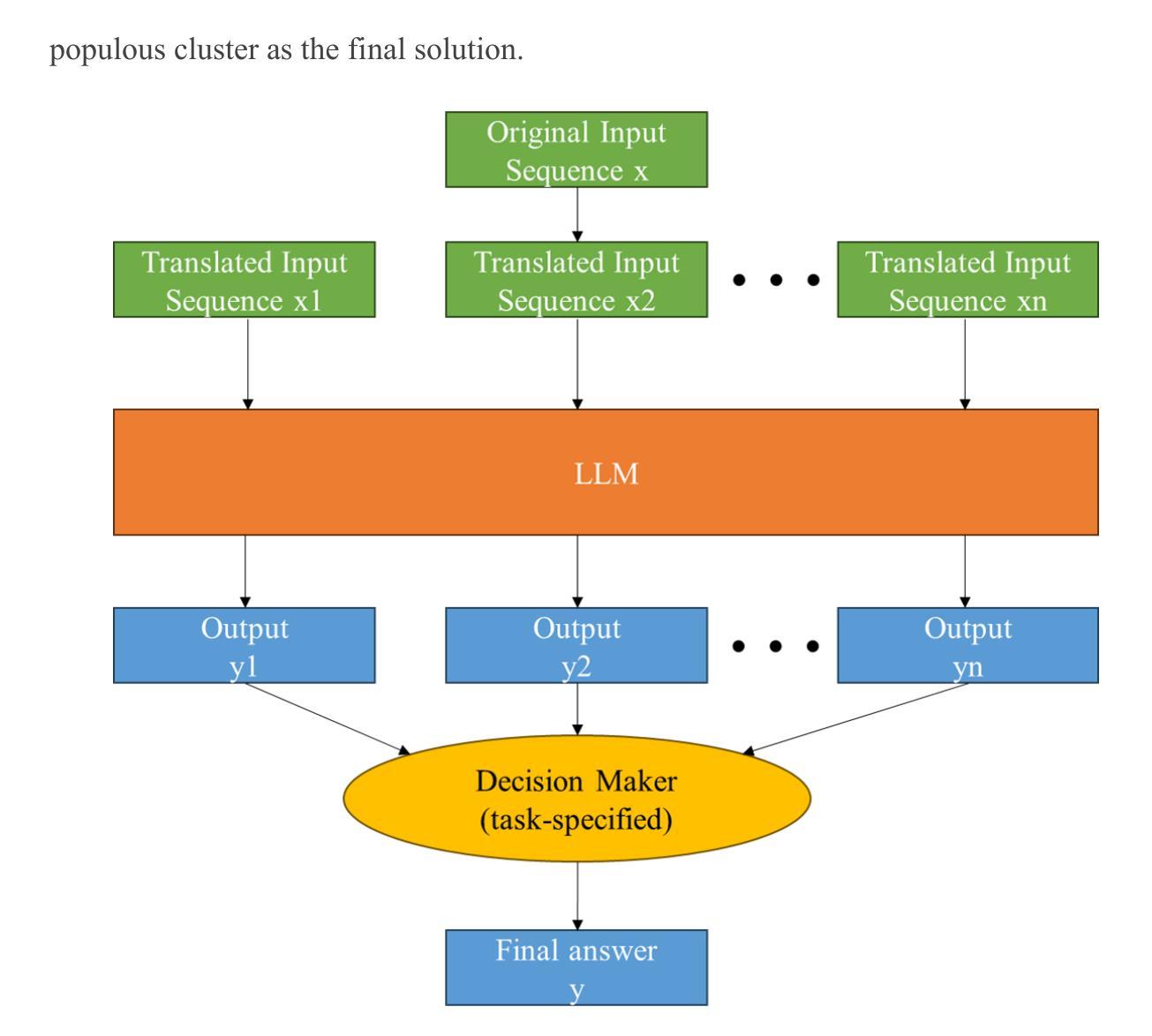
思维链(CoT)作为提升大型语言模型(LLM)推理能力的重要机制已经崭露头角,其中自我一致性在提升性能上显示出巨大潜力。然而,多语种训练语料库中的固有语言偏见经常导致语义漂移和逻辑不一致,特别是在处理复杂推理任务的参数小于10B的LLMs中更为明显。为了克服这些限制,我们提出了跨语言一致性(CLC)框架,这是一种创新性的推理范式,它通过多数投票的方式整合多语言推理路径,以提升LLMs的推理能力。在CMATH数据集上的实证评估显示,CLC相较于传统的自我一致性方法具有优越性,分别为DeepSeek-Math-7B-Instruct、Qwen2.5-Math-7B-Instruct和Gemma2-9B-Instruct带来了9.5%、6.5%和6.0%的绝对精度提升。将CLC的语言范围扩展到11种不同的语言,带来了两个协同效益:1)通过多语言集成投票中和多语种训练语料库中的语言偏见;2)通过探索更广泛的多语言解决方案空间,避免单语推理陷阱。这两种效益的结合,使得与单语自我一致性基准相比,能够找到更多全局最优的推理路径。如在MGSM数据集上,使用Gemma2-9B-Instruct的精度提升了4.1%~18.5%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Chain-of-thought(CoT)机制,大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力得到了增强。然而,在多语言训练语料库中存在的固有语言偏见会导致语义漂移和逻辑不一致。为解决这一问题,提出了Cross-Lingual Consistency(CLC)框架,通过多数投票的方式整合多语言推理路径,提升LLM的推理能力。在CMATH数据集上的实证评估表明,相较于传统的自一致性方法,CLC框架分别实现了DeepSeek-Math-7B-Instruct、Qwen2.5-Math-7B-Instruct和Gemma2-9B-Instruct模型绝对精度分别提升9.5%、6.5%和6.0%。此外,将CLC框架的语言范围扩展到11种语言可以中和多语言训练语料库中的语言偏见,同时通过探索更广泛的多语言解决方案空间,避免了单一语言的推理陷阱。这有助于找到相比单一语言自一致性基准测试更为全局优化的推理路径,如在MGSM数据集上,Gemma2-9B-Instruct模型的精度提高了4.1%~18.5%。
Key Takeaways
- Chain-of-thought (CoT)增强大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力。
- 多语言训练语料库中的语言偏见会导致语义漂移和逻辑不一致。
- Cross-Lingual Consistency (CLC)框架通过多数投票整合多语言推理路径,提升LLM的推理能力。
- CLC框架在CMATH数据集上的实证评估表现优越,带来明显的精度提升。
- CLC框架扩展到11种语言可以中和语言偏见,避免单一语言的推理陷阱。
- 多语言解决方案空间探索有助于找到更为全局优化的推理路径。
点此查看论文截图

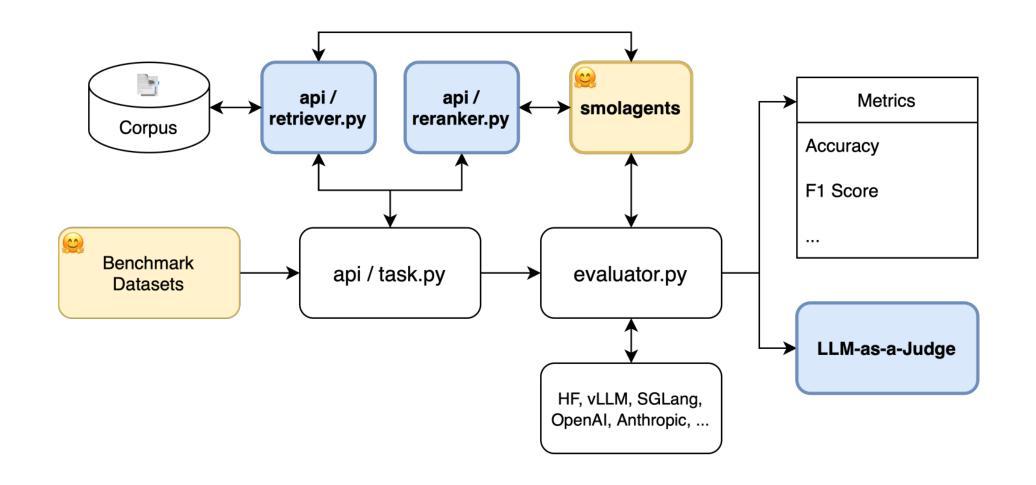
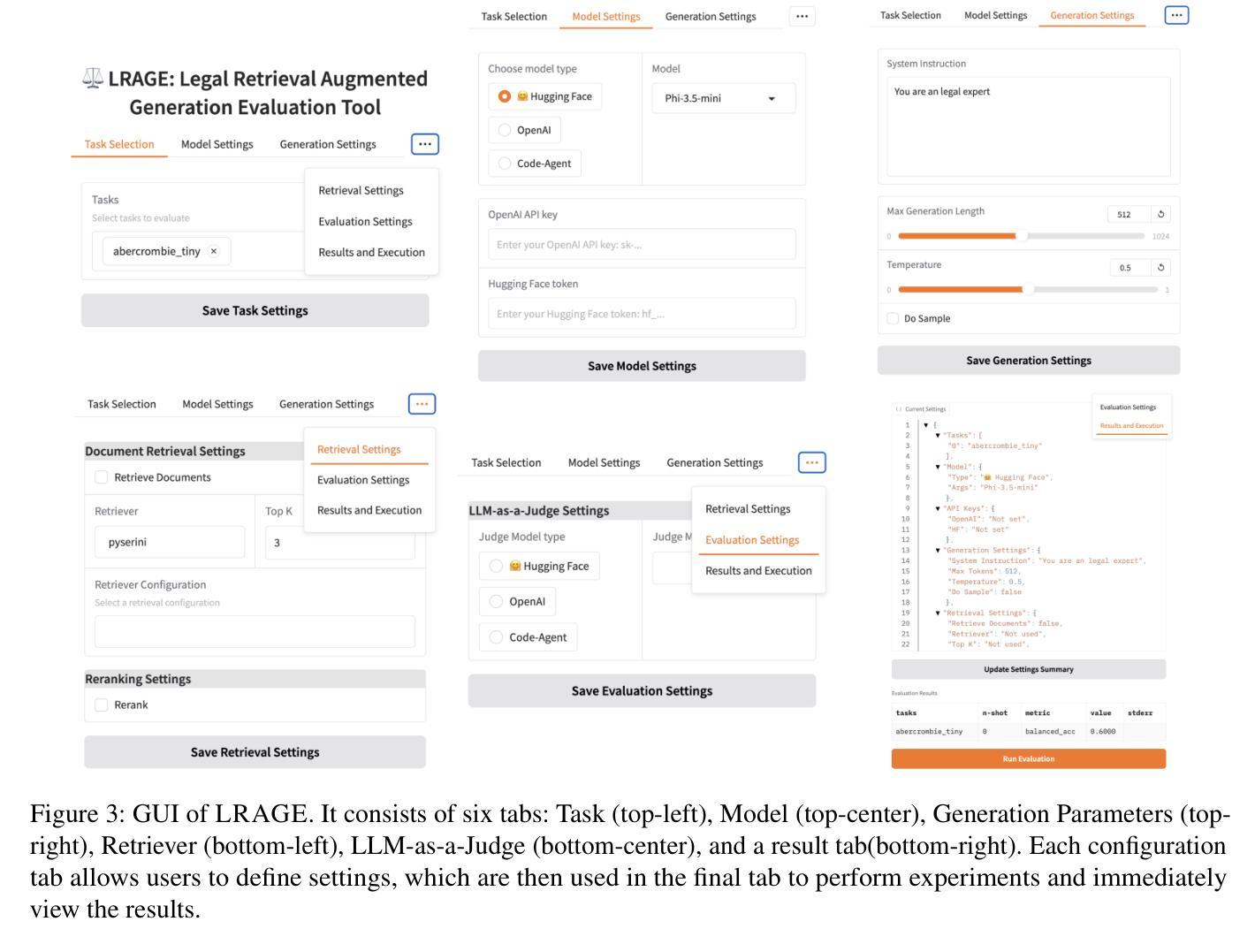
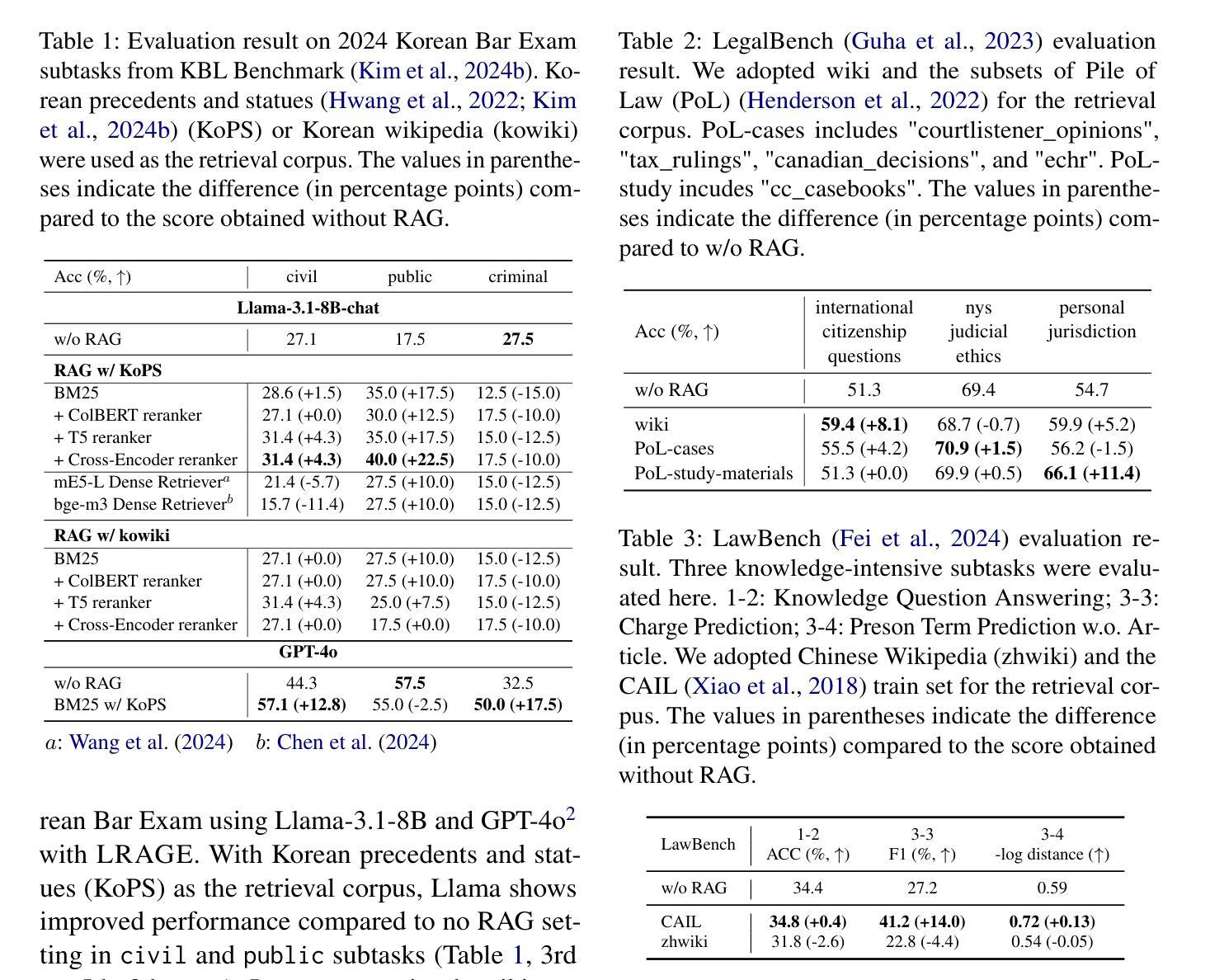
LARGE: Legal Retrieval Augmented Generation Evaluation Tool
Authors:Minhu Park, Hongseok Oh, Eunkyung Choi, Wonseok Hwang
Recently, building retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems to enhance the capability of large language models (LLMs) has become a common practice. Especially in the legal domain, previous judicial decisions play a significant role under the doctrine of stare decisis which emphasizes the importance of making decisions based on (retrieved) prior documents. However, the overall performance of RAG system depends on many components: (1) retrieval corpora, (2) retrieval algorithms, (3) rerankers, (4) LLM backbones, and (5) evaluation metrics. Here we propose LRAGE, an open-source tool for holistic evaluation of RAG systems focusing on the legal domain. LRAGE provides GUI and CLI interfaces to facilitate seamless experiments and investigate how changes in the aforementioned five components affect the overall accuracy. We validated LRAGE using multilingual legal benches including Korean (KBL), English (LegalBench), and Chinese (LawBench) by demonstrating how the overall accuracy changes when varying the five components mentioned above. The source code is available at https://github.com/hoorangyee/LRAGE.
最近,为了增强大型语言模型(LLM)的能力,构建增强检索生成(RAG)系统已成为一种常见做法。特别是在法律领域,根据遵循先例原则,先前的司法判决在决策中扮演着重要角色,该原则强调基于(检索到的)先前文档进行决策的重要性。然而,RAG系统的整体性能取决于多个组件:(1)检索语料库、(2)检索算法、(3)重新排序器、(4)LLM主干和(5)评估指标。在这里,我们提出了LRAGE,这是一个专注于法律领域的RAG系统的整体评估的开源工具。LRAGE提供了GUI和CLI接口,以进行无缝实验并研究上述五个组件的变化如何影响总体准确性。我们使用包括韩语(KBL)、英语(LegalBench)和中文(LawBench)在内的多语言法律基准测试验证了LRAGE,通过展示上述五个组件变化时总体准确性的变化来验证。源代码可在https://github.com/hoorangyee/LRAGE获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages
Summary
本文介绍了如何构建增强检索生成(RAG)系统以提升大型语言模型(LLM)的能力,特别是在法律领域中,以往司法决策在遵循先例原则下具有重要意义。文章提出了LRAGE这一开源工具,用于全面评估RAG系统,并关注法律领域。LRAGE提供GUI和CLI接口,方便进行实验并研究五个关键组件的变化对整体准确率的影响。经过包括韩语(KBL)、英语(LegalBench)和中文(LawBench)在内的多语种法律基准测试验证,展示了LRAGE的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- RAG系统通过增强大型语言模型(LLM)的能力,在法律领域中尤为重要,遵循先例原则使得以往司法决策具有关键参考价值。
- LRAGE是一个用于全面评估RAG系统的开源工具,提供GUI和CLI接口以方便实验和性能分析。
- LRAGE评估重点包括五个关键组件:检索语料库、检索算法、排序器、LLM主干和评估指标。
- 通过多语种法律基准测试验证,LRAGE展示了其有效性和实用性。
- LRAGE能展示不同组件变化对整体准确率的影响,为优化RAG系统提供有力支持。
- 该工具源代码已公开,方便进一步开发和改进。
点此查看论文截图

YourBench: Easy Custom Evaluation Sets for Everyone
Authors:Sumuk Shashidhar, Clémentine Fourrier, Alina Lozovskia, Thomas Wolf, Gokhan Tur, Dilek Hakkani-Tür
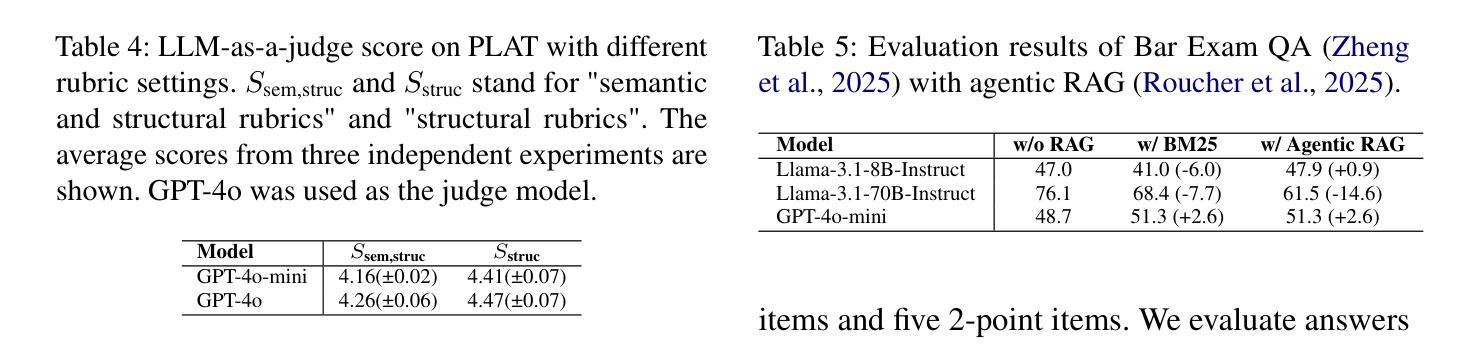
Evaluating large language models (LLMs) effectively remains a critical bottleneck, as traditional static benchmarks suffer from saturation and contamination, while human evaluations are costly and slow. This hinders timely or domain-specific assessment, crucial for real-world applications. We introduce YourBench, a novel, open-source framework that addresses these limitations by enabling dynamic, automated generation of reliable, up-to-date, and domain-tailored benchmarks cheaply and without manual annotation, directly from user-provided documents. We demonstrate its efficacy by replicating 7 diverse MMLU subsets using minimal source text, achieving this for under 15 USD in total inference costs while perfectly preserving the relative model performance rankings (Spearman Rho = 1) observed on the original benchmark. To ensure that YourBench generates data grounded in provided input instead of relying on posterior parametric knowledge in models, we also introduce Tempora-0325, a novel dataset of over 7K diverse documents, published exclusively after March 2025. Our comprehensive analysis spans 26 SoTA models from 7 major families across varying scales (3-671B parameters) to validate the quality of generated evaluations through rigorous algorithmic checks (e.g., citation grounding) and human assessments. We release the YourBench library, the Tempora-0325 dataset, 150k+ question answer pairs based on Tempora and all evaluation and inference traces to facilitate reproducible research and empower the community to generate bespoke benchmarks on demand, fostering more relevant and trustworthy LLM evaluation.
评估大型语言模型(LLM)仍然是一个关键的瓶颈,因为传统的静态基准测试饱受饱和和污染之苦,而人工评估则成本高昂且速度慢。这阻碍了针对特定时间或特定领域的评估,对于现实世界的应用至关重要。我们推出了YourBench,这是一个新颖的开源框架,通过动态自动化生成可靠、最新且针对特定领域的基准测试,以低廉的成本而无需手动注释,直接从用户提供的文档中进行评估,从而解决了这些限制。我们通过复制使用最少源文本的7个多样化的MMLU子集来展示其有效性,在总共的推理成本不到15美元的情况下,完美地保持了原始基准测试上观察到的相对模型性能排名(斯皮尔曼等级ρ=1)。为了确保YourBench生成的数据基于提供的输入而不是依赖模型中的事后参数知识,我们还推出了Tempora-0325数据集,这是一组超过7,000个多样化的文档的新数据集,仅在2025年3月之后发布。我们的综合分析涵盖了来自7个主要家族的26个最新模型,跨越了不同的规模(3亿至671亿参数),以验证生成评估的质量通过严格的算法检查(例如引文定位)和人工评估。我们发布了YourBench库、Tempora-0325数据集、基于Tempora的超过15万个问题答案对以及所有评估和推理痕迹,以促进可重复的研究并赋予社区按需生成定制基准测试的能力,从而推动更相关和可靠的大型语言模型评估。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了对传统评估大型语言模型(LLM)方法存在的问题,包括饱和和污染等问题。为了解决这些问题,作者提出了一种新型的开源框架YourBench,该框架可以动态地自动生成可靠、最新、针对特定领域的基准测试,并且具有成本低、无需人工标注等优点。作者通过复制多个MMLU子集验证了其有效性,同时引入了一个新型数据集Tempora-0325来确保生成的基准测试具有实际应用价值。此外,作者还对多个最新的大型语言模型进行了全面的评估,并通过严格的算法检查和人工评估验证了生成评估的质量。最后,作者释放了YourBench库、Tempora-0325数据集和其他资源,以促进研究人员的可重复性研究和社区生成定制化的基准测试需求。
Key Takeaways
- 传统的大型语言模型(LLM)评估方法存在饱和和污染问题。
- YourBench是一个新型的开源框架,可以动态地自动生成可靠、最新、针对特定领域的基准测试。
- YourBench能够降低成本并加速评估过程,同时无需人工标注。
- 通过复制MMLU子集验证了YourBench的有效性。
- Tempora-0325数据集用于确保生成的基准测试具有实际应用价值。
- 作者对多个最新的大型语言模型进行了全面的评估。
点此查看论文截图

Leveraging Embedding Techniques in Multimodal Machine Learning for Mental Illness Assessment
Authors:Abdelrahaman A. Hassan, Abdelrahman A. Ali, Aya E. Fouda, Radwa J. Hanafy, Mohammed E. Fouda
The increasing global prevalence of mental disorders, such as depression and PTSD, requires objective and scalable diagnostic tools. Traditional clinical assessments often face limitations in accessibility, objectivity, and consistency. This paper investigates the potential of multimodal machine learning to address these challenges, leveraging the complementary information available in text, audio, and video data. Our approach involves a comprehensive analysis of various data preprocessing techniques, including novel chunking and utterance-based formatting strategies. We systematically evaluate a range of state-of-the-art embedding models for each modality and employ Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Bidirectional LSTM Networks (BiLSTMs) for feature extraction. We explore data-level, feature-level, and decision-level fusion techniques, including a novel integration of Large Language Model (LLM) predictions. We also investigate the impact of replacing Multilayer Perceptron classifiers with Support Vector Machines. We extend our analysis to severity prediction using PHQ-8 and PCL-C scores and multi-class classification (considering co-occurring conditions). Our results demonstrate that utterance-based chunking significantly improves performance, particularly for text and audio modalities. Decision-level fusion, incorporating LLM predictions, achieves the highest accuracy, with a balanced accuracy of 94.8% for depression and 96.2% for PTSD detection. The combination of CNN-BiLSTM architectures with utterance-level chunking, coupled with the integration of external LLM, provides a powerful and nuanced approach to the detection and assessment of mental health conditions. Our findings highlight the potential of MMML for developing more accurate, accessible, and personalized mental healthcare tools.
随着抑郁症和创伤后应激障碍等精神疾病的全球发病率不断增加,我们需要客观且可规模化的诊断工具。传统的临床评估在可及性、客观性和一致性方面经常面临局限性。本文研究了多模态机器学习在应对这些挑战方面的潜力,利用文本、音频和视频数据中的互补信息。我们的方法涉及对各种数据预处理技术的综合分析,包括新颖的基于分块和发言的格式化策略。我们系统地评估了每种模态的一系列最新嵌入模型,并使用卷积神经网络(CNN)和双向LSTM网络(BiLSTMs)进行特征提取。我们探索了数据层、特征层和决策层的融合技术,包括大型语言模型(LLM)预测的新颖集成。我们还研究了将多层感知器分类器替换为支持向量机的影响。我们将分析扩展到严重性预测,使用PHQ-8和PCL-C分数和多类分类(考虑共病情况)。我们的结果表明,基于发言的分块显著改善性能,特别是对文本和音频模态而言。决策级融合,结合LLM预测,达到了最高精度,抑郁症和创伤后应激障碍检测的平衡精度分别为94.8%和96.2%。结合CNN-BiLSTM架构的发言级分块,以及LLM的集成,为精神健康条件的检测和评估提供了一种强大而细致的方法。我们的研究结果表明多模态机器学习在开发更准确、更可及、更个性化的精神卫生工具方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了多模态机器学习(MMML)在精神健康诊断中的应用潜力,特别是针对抑郁症和PTSD等精神疾病的诊断。研究通过文本、音频和视频数据的多模态融合,采用多种数据预处理技术、嵌入模型、卷积神经网络(CNN)、双向LSTM网络(BiLSTMs)等,进行系统性的实验评估。决策级融合结合LLM预测,实现了高准确率的精神疾病检测与评估。该研究为开发更准确、可访问和个性化的精神卫生工具提供了有力支持。
Key Takeaways
- 全球精神疾病的普及率增长,需要客观和可规模化的诊断工具。
- 传统临床评估在可及性、客观性和一致性方面存在局限性。
- 多模态机器学习(MMML)具有解决这些挑战的巨大潜力。
- 文本、音频和视频数据的融合有助于提高诊断准确性。
- utterance-based chunking技术在文本和音频模态上表现尤为出色。
- 结合CNN-BiLSTM架构与LLM的决策级融合达到最高准确率。
点此查看论文截图

TransforMerger: Transformer-based Voice-Gesture Fusion for Robust Human-Robot Communication
Authors:Petr Vanc, Karla Stepanova
As human-robot collaboration advances, natural and flexible communication methods are essential for effective robot control. Traditional methods relying on a single modality or rigid rules struggle with noisy or misaligned data as well as with object descriptions that do not perfectly fit the predefined object names (e.g. ‘Pick that red object’). We introduce TransforMerger, a transformer-based reasoning model that infers a structured action command for robotic manipulation based on fused voice and gesture inputs. Our approach merges multimodal data into a single unified sentence, which is then processed by the language model. We employ probabilistic embeddings to handle uncertainty and we integrate contextual scene understanding to resolve ambiguous references (e.g., gestures pointing to multiple objects or vague verbal cues like “this”). We evaluate TransforMerger in simulated and real-world experiments, demonstrating its robustness to noise, misalignment, and missing information. Our results show that TransforMerger outperforms deterministic baselines, especially in scenarios requiring more contextual knowledge, enabling more robust and flexible human-robot communication. Code and datasets are available at: http://imitrob.ciirc.cvut.cz/publications/transformerger.
随着人机协作的不断发展,自然且灵活的沟通方式对于实现有效的机器人控制至关重要。依赖单一模式或僵化规则的传统方法在处理嘈杂或错位的数据以及不符合预定义对象名称的对象描述(例如“拿起那个红色的物体”)时遇到了困难。我们推出了TransforMerger,这是一款基于变压器的推理模型,它可以根据融合的语音和手势输入推断出用于机器人操作的结构化动作命令。我们的方法将多模式数据合并成单个统一的句子,然后由语言模型进行处理。我们采用概率嵌入来处理不确定性,并整合场景上下文理解来解决模糊引用(例如,指向多个对象的手势或模糊的口头线索,如“这个”)。我们在模拟和真实世界的实验中评估了TransforMerger,证明了它对噪声、错位和缺失信息的稳健性。我们的结果表明,TransforMerger在需要更多上下文知识的场景中表现优于确定性基线,能够实现更稳健和灵活的人机沟通。相关代码和数据集可通过以下网址获取:http://imitrob.ciirc.cvut.cz/publications/transformerger 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 7 figures
Summary
在人机协作日益发展的背景下,自然灵活的交流方式对机器人控制至关重要。传统方法在处理噪声或错位数据以及对象描述与预设名称不匹配的问题时显得捉襟见肘。我们推出了基于Transformer的推理模型TransforMerger,通过融合语音和手势输入,来推断用于机器人操控的结构化动作指令。该方法将多模式数据合并成统一语句,并由语言模型处理。我们采用概率嵌入来处理不确定性,并整合场景上下文理解来解决模糊参照问题。在模拟和真实环境中,TransforMerger展现出对噪声、错位和缺失信息的稳健性,并在需要更多上下文知识的场景中表现出超越确定性基准的性能,从而实现更稳健和灵活的人机交流。
Key Takeaways
- 随着人机协作的进步,自然灵活的交流方式对于机器人控制至关重要。
- 传统方法在处理噪声或错位数据以及对象描述与预设名称不匹配时存在挑战。
- TransforMerger是一个基于Transformer的推理模型,能融合语音和手势输入来推断结构化动作指令。
- TransforMerger将多模式数据合并成统一语句,并由语言模型处理。
- 该模型采用概率嵌入处理不确定性,并整合场景上下文理解以解决模糊参照问题。
- TransforMerger在模拟和真实环境中展现出对噪声、错位和缺失信息的稳健性。
点此查看论文截图


Q-Adapt: Adapting LMM for Visual Quality Assessment with Progressive Instruction Tuning
Authors:Yiting Lu, Xin Li, Haoning Wu, Bingchen Li, Weisi Lin, Zhibo Chen
The rapid advancement of Large Multi-modal Foundation Models (LMM) has paved the way for the possible Explainable Image Quality Assessment (EIQA) with instruction tuning from two perspectives: overall quality explanation, and attribute-wise perception answering. However, existing works usually overlooked the conflicts between these two types of perception explanations during joint instruction tuning, leading to insufficient perception understanding. To mitigate this, we propose a new paradigm for perception-oriented instruction tuning, i.e., Q-Adapt, which aims to eliminate the conflicts and achieve the synergy between these two EIQA tasks when adapting LMM, resulting in enhanced multi-faceted explanations of IQA. Particularly, we propose a progressive instruction tuning strategy by dividing the adaption process of LMM for EIQA into two stages, where the first stage empowers the LMM with universal perception knowledge tailored for two tasks using an efficient transfer learning strategy, i.e., LoRA, and the second stage introduces the instruction-adaptive visual prompt tuning to dynamically adapt visual features for the different instructions from two tasks. In this way, our proposed Q-Adapt can achieve a lightweight visual quality evaluator, demonstrating comparable performance and, in some instances, superior results across perceptual-related benchmarks and commonly-used IQA databases. The source code is publicly available at https://github.com/yeppp27/Q-Adapt.
大型多模态基础模型(LMM)的快速发展为可能的可解释性图像质量评估(EIQA)铺平了道路,通过两个方面的指令调整来实现整体质量解释和属性感知回答。然而,现有工作通常在联合指令调整时忽略了这两种感知解释之间的冲突,导致感知理解不足。为了缓解这一问题,我们提出了一种面向感知的指令调整新范式,即Q-Adapt。其目的是在适应LMM时消除这两种EIQA任务之间的冲突,实现协同作用,从而增强IQA的多方面解释。特别是,我们提出了一种渐进的指令调整策略,将LMM对EIQA的适应过程分为两个阶段。在第一阶段,我们使用高效的迁移学习策略LoRA,赋予LMM针对这两个任务的通用感知知识;在第二阶段,我们引入指令适应性视觉提示调整,以根据不同任务的指令动态适应视觉特征。通过这种方式,我们提出的Q-Adapt可以实现轻量级视觉质量评估器,在感知相关基准测试和常用的IQA数据库上表现出相当的性能,并在某些情况下表现更优秀。源代码可在https://github.com/yeppp27/Q-Adapt找到。
论文及项目相关链接
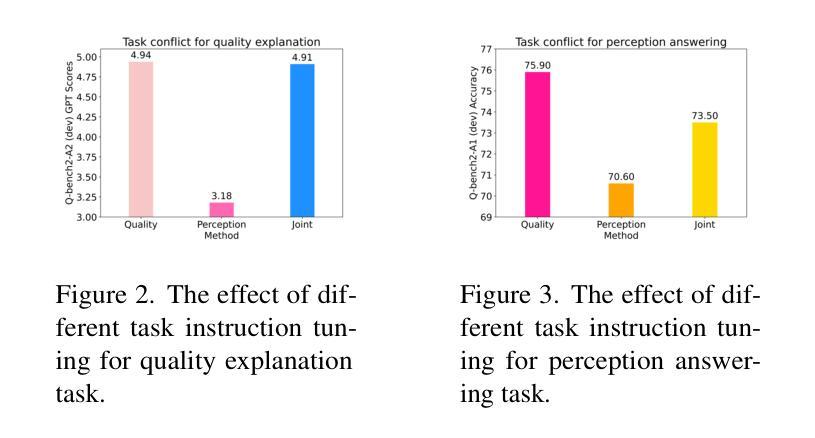
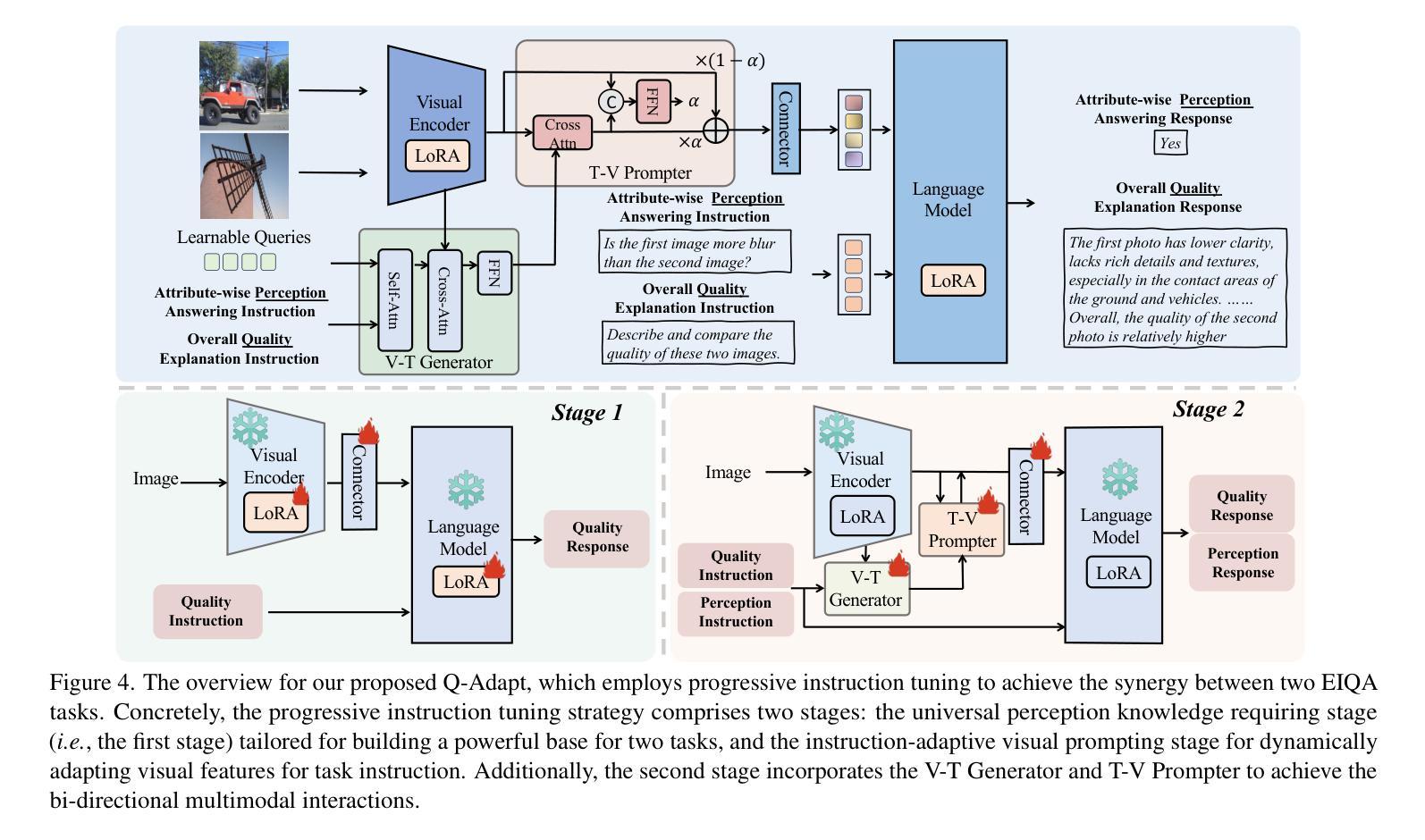
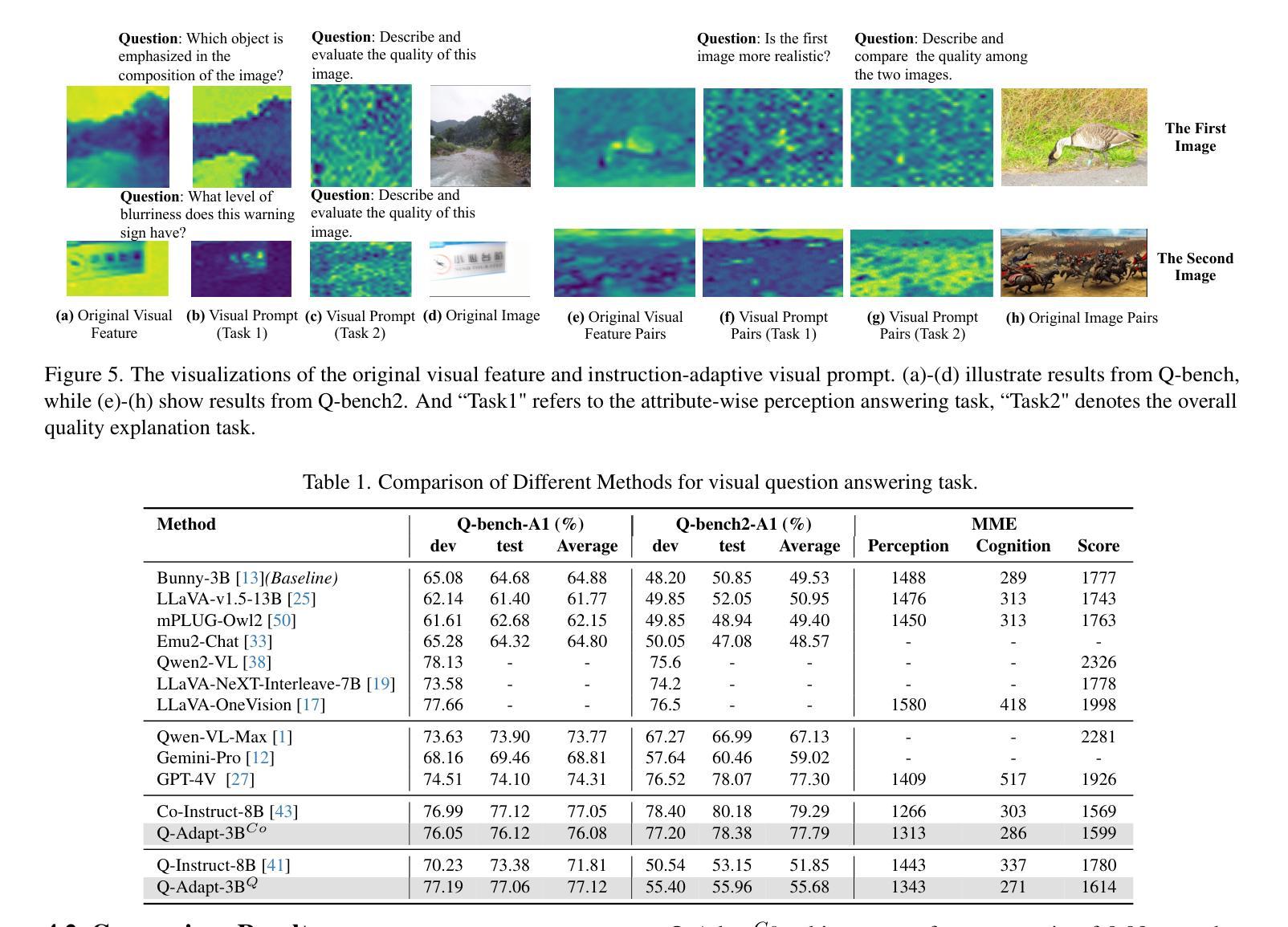
Summary
大型多模态基础模型的快速发展,为基于指令调参的可解释图像质量评估(EIQA)提供了可能。现有方法在联合指令调参时忽视了整体质量与属性感知解释之间的冲突,导致感知理解不足。为此,我们提出了面向感知的指令调参新模式——Q-Adapt,旨在消除这两种EIQA任务间的冲突,实现协同适应LMM,增强图像质量评估的多方面解释。
Key Takeaways
- 大型多模态基础模型的进步为EIQA的指令调参提供了机会。
- 现有方法在联合指令调参时忽视整体质量与属性感知解释之间的冲突。
- Q-Adapt旨在消除这种冲突,实现两种EIQA任务的协同适应。
- Q-Adapt采用分阶段指令调参策略,第一阶段赋予LMM针对两个任务通用感知知识,第二阶段根据不同指令动态调整视觉特征。
- Q-Adapt能实现轻量级视觉质量评估,在感知相关基准测试和常用IQA数据库上表现优异。
- Q-Adapt的源代码已公开在https://github.com/yeppp27/Q-Adapt。
点此查看论文截图

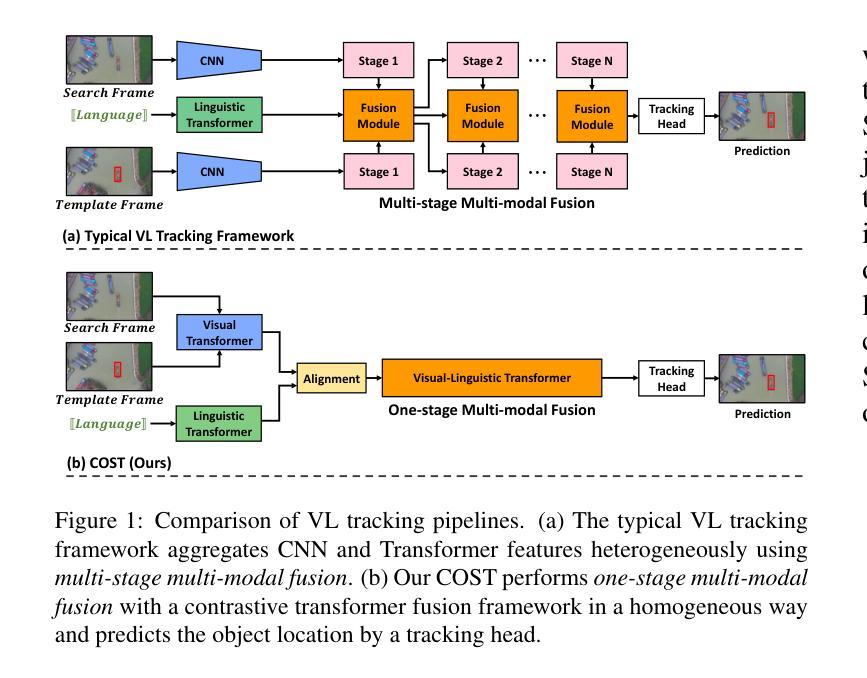
COST: Contrastive One-Stage Transformer for Vision-Language Small Object Tracking
Authors:Chunhui Zhang, Li Liu, Jialin Gao, Xin Sun, Hao Wen, Xi Zhou, Shiming Ge, Yanfeng Wang
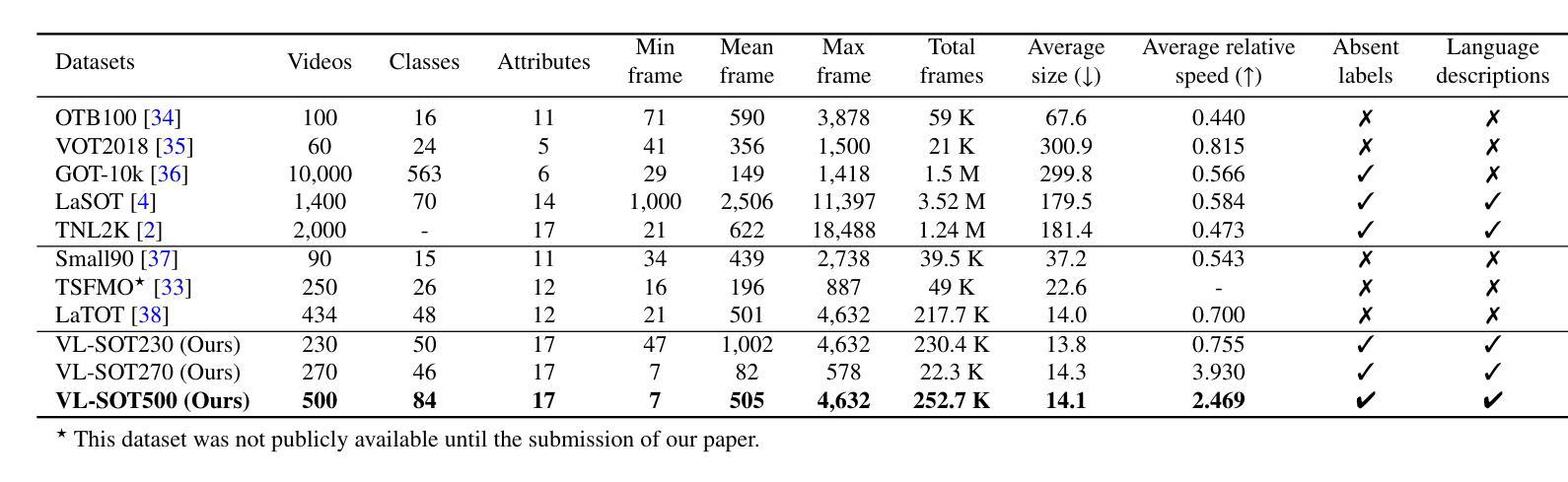
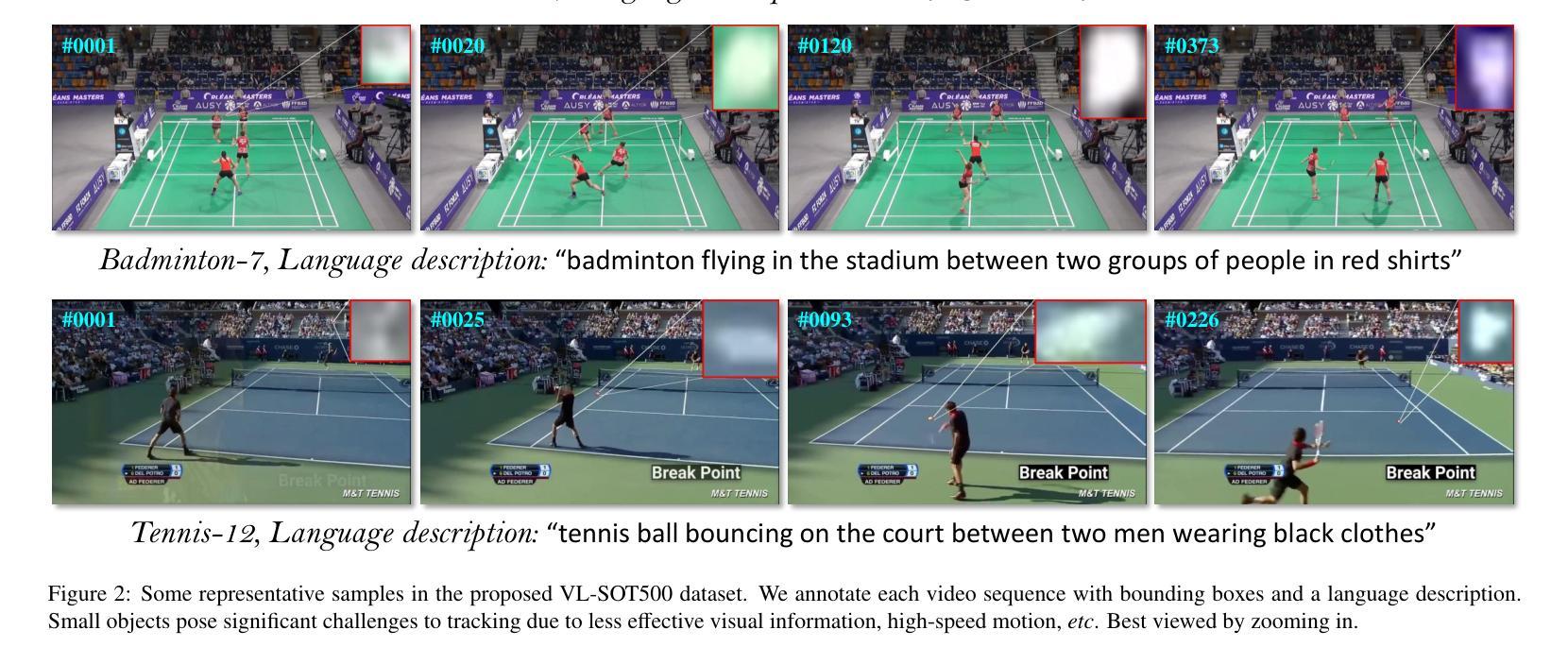
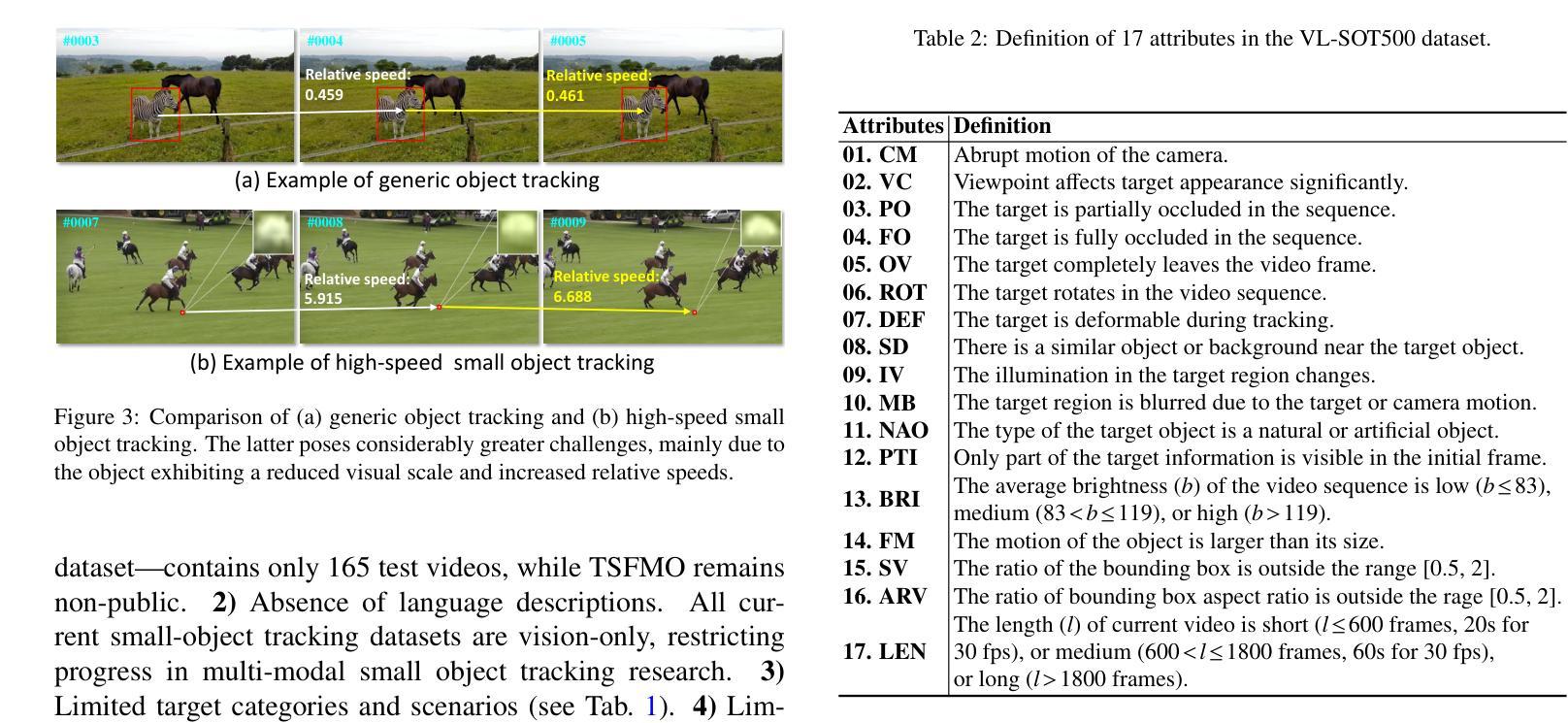
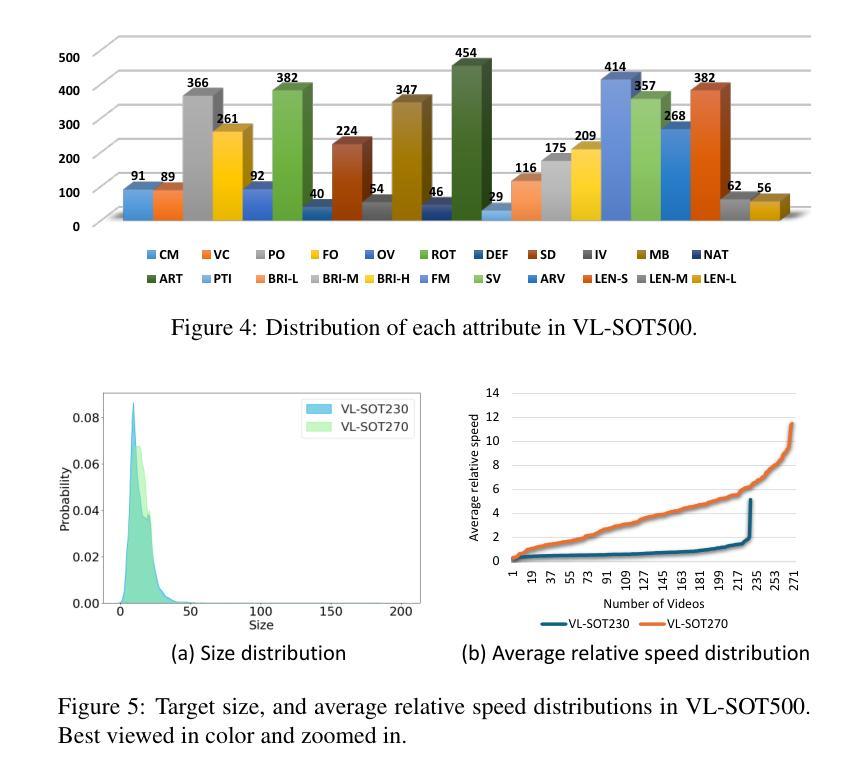
Transformer has recently demonstrated great potential in improving vision-language (VL) tracking algorithms. However, most of the existing VL trackers rely on carefully designed mechanisms to perform the multi-stage multi-modal fusion. Additionally, direct multi-modal fusion without alignment ignores distribution discrepancy between modalities in feature space, potentially leading to suboptimal representations. In this work, we propose COST, a contrastive one-stage transformer fusion framework for VL tracking, aiming to learn semantically consistent and unified VL representations. Specifically, we introduce a contrastive alignment strategy that maximizes mutual information (MI) between a video and its corresponding language description. This enables effective cross-modal alignment, yielding semantically consistent features in the representation space. By leveraging a visual-linguistic transformer, we establish an efficient multi-modal fusion and reasoning mechanism, empirically demonstrating that a simple stack of transformer encoders effectively enables unified VL representations. Moreover, we contribute a newly collected VL tracking benchmark dataset for small object tracking, named VL-SOT500, with bounding boxes and language descriptions. Our dataset comprises two challenging subsets, VL-SOT230 and VL-SOT270, dedicated to evaluating generic and high-speed small object tracking, respectively. Small object tracking is notoriously challenging due to weak appearance and limited features, and this dataset is, to the best of our knowledge, the first to explore the usage of language cues to enhance visual representation for small object tracking. Extensive experiments demonstrate that COST achieves state-of-the-art performance on five existing VL tracking datasets, as well as on our proposed VL-SOT500 dataset. Source codes and dataset will be made publicly available.
Transformer在改进视觉语言(VL)跟踪算法方面表现出了巨大的潜力。然而,大多数现有的VL跟踪器都依赖于精心设计的机制来执行多阶段多模式融合。另外,没有对齐的直接多模式融合忽略了不同模式之间特征空间的分布差异,可能导致表示不佳。在本研究中,我们提出了针对VL跟踪的对比一阶Transformer融合框架COST,旨在学习语义一致且统一的VL表示。具体来说,我们引入了一种对比对齐策略,以最大化视频与其相应的语言描述之间的互信息(MI)。这实现了有效的跨模式对齐,在表示空间中产生语义一致的特征。通过利用视觉语言Transformer,我们建立了高效的多模式融合和推理机制,实证表明,简单的Transformer编码器堆栈可以有效地实现统一的VL表示。此外,我们收集了一个名为VL-SOT500的VL跟踪基准数据集,用于小目标跟踪,其中包含边界框和语言描述。我们的数据集包括两个具有挑战性的子集,即VL-SOT230和VL-SOT270,专门用于评估通用和高速小目标跟踪。由于小目标的外貌较弱且特征有限,小目标跟踪是众所周知的挑战,据我们所知,该数据集是第一个探索使用语言线索来提高小目标跟踪的视觉表示的数据集。大量实验表明,COST在五个现有的VL跟踪数据集以及我们提出的VL-SOT500数据集上达到了最新性能。源代码和数据集将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint submitted to Elsevier. https://github.com/983632847/Awesome-Multimodal-Object-Tracking
摘要
本文提出一种基于对比学习的一站式Transformer融合框架(COST),用于视觉语言(VL)跟踪任务。该框架旨在学习语义一致且统一的VL表示,引入对比对齐策略来最大化视频与其对应的语言描述之间的互信息(MI),从而实现有效的跨模态对齐,在表示空间中产生语义一致的特征。利用视觉语言Transformer,建立了高效的多模态融合和推理机制,实证表明简单的Transformer编码器堆叠可有效实现统一的VL表示。此外,本文贡献了一个新收集的VL跟踪基准数据集VL-SOT500,用于小目标跟踪,包括边界框和语言描述。该数据集包含两个具有挑战性的子集VL-SOT230和VL-SOT270,分别用于评估通用高速小目标跟踪。广泛实验表明,COST在五个现有的VL跟踪数据集以及所提出的VL-SOT500数据集上均达到最新性能。
关键见解
- 提出了基于对比学习的一站式Transformer融合框架(COST)用于视觉语言跟踪任务。
- 引入对比对齐策略来最大化视频与语言描述之间的互信息,实现跨模态有效对齐。
- 利用视觉语言Transformer实现多模态融合和推理机制。
- 提出一个新的VL跟踪基准数据集VL-SOT500,专注于小目标跟踪。
- 数据集包含VL-SOT230和VL-SOT270两个具有挑战性的子集,分别用于评估通用和高速小目标跟踪。
- COST框架在多个数据集上实现了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图


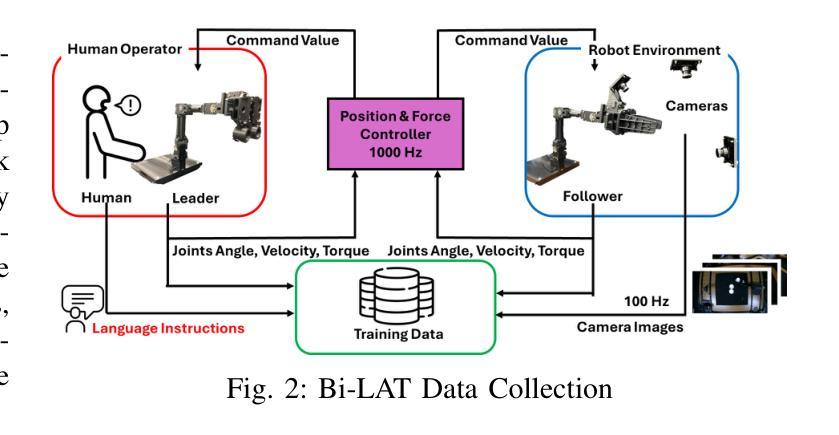
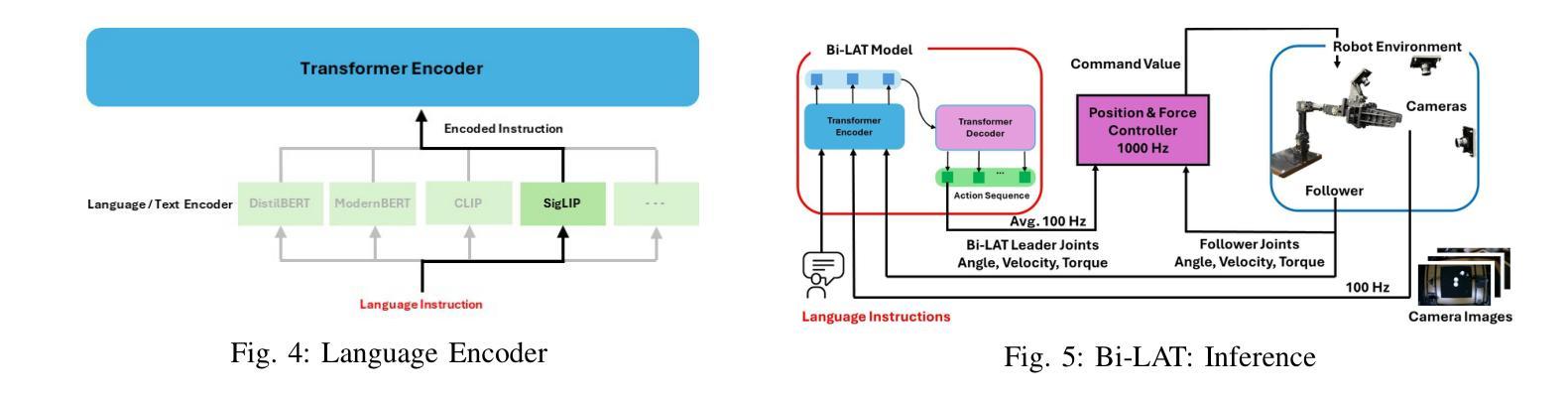
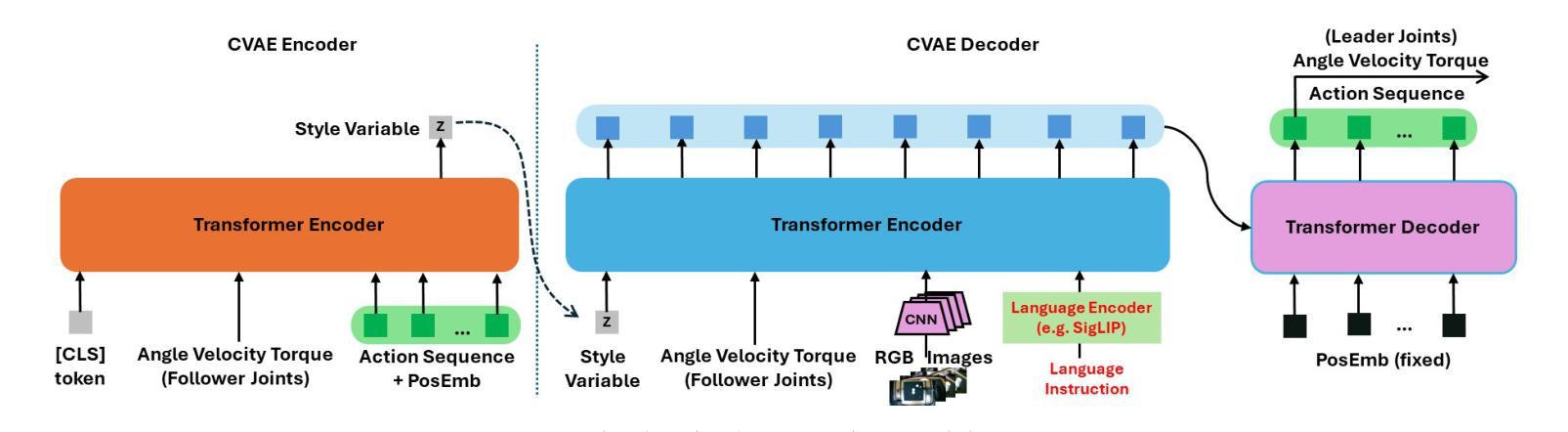
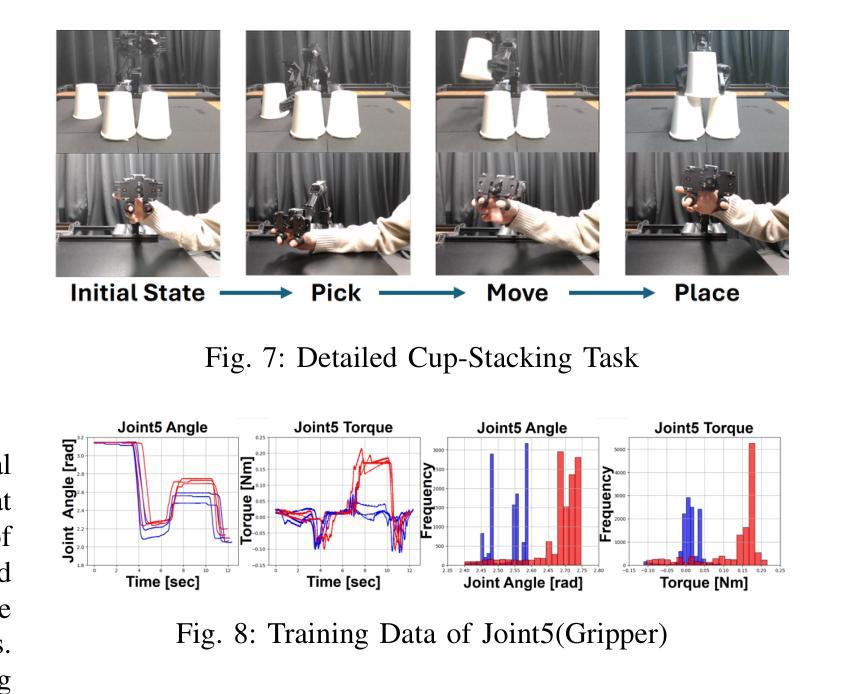
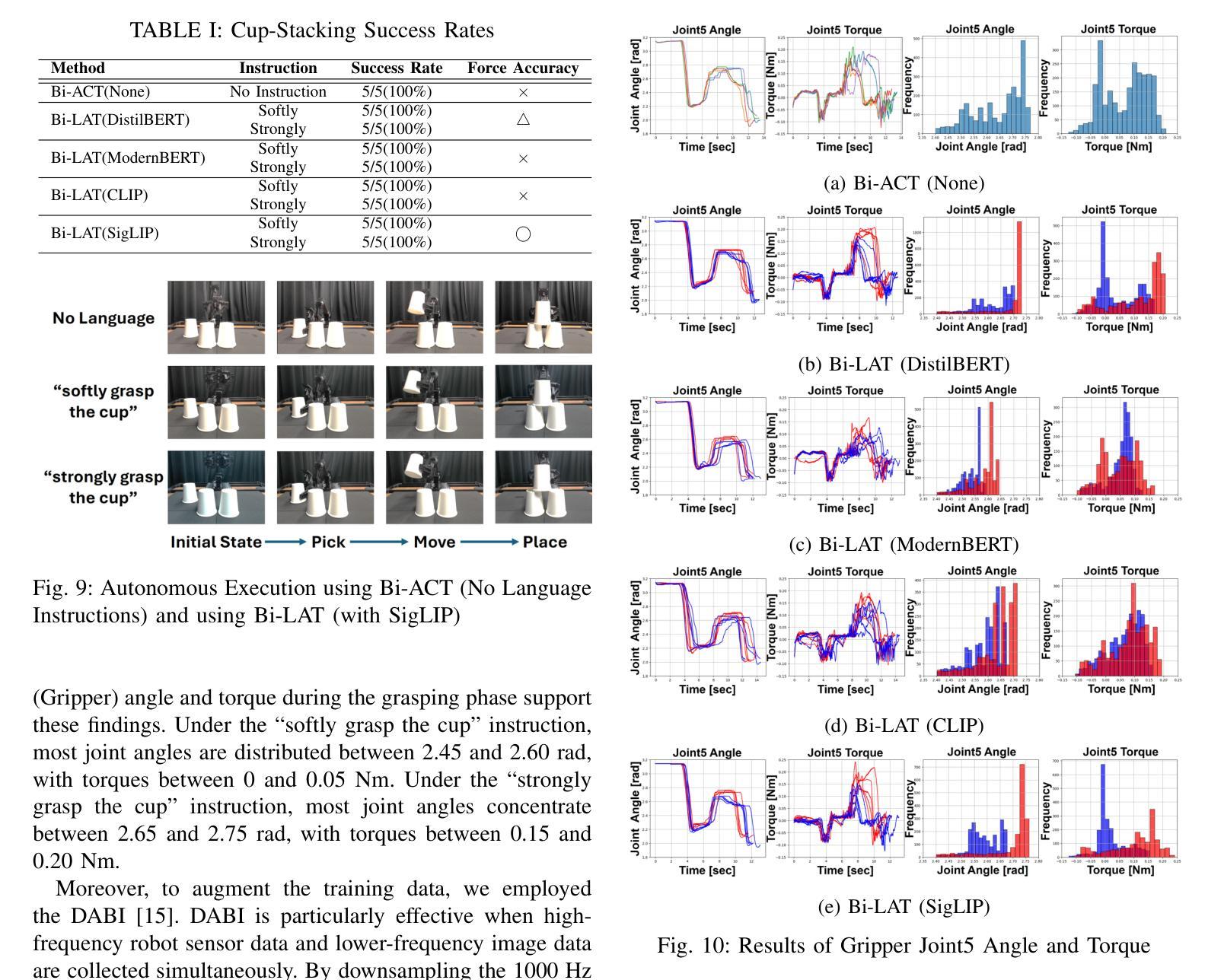
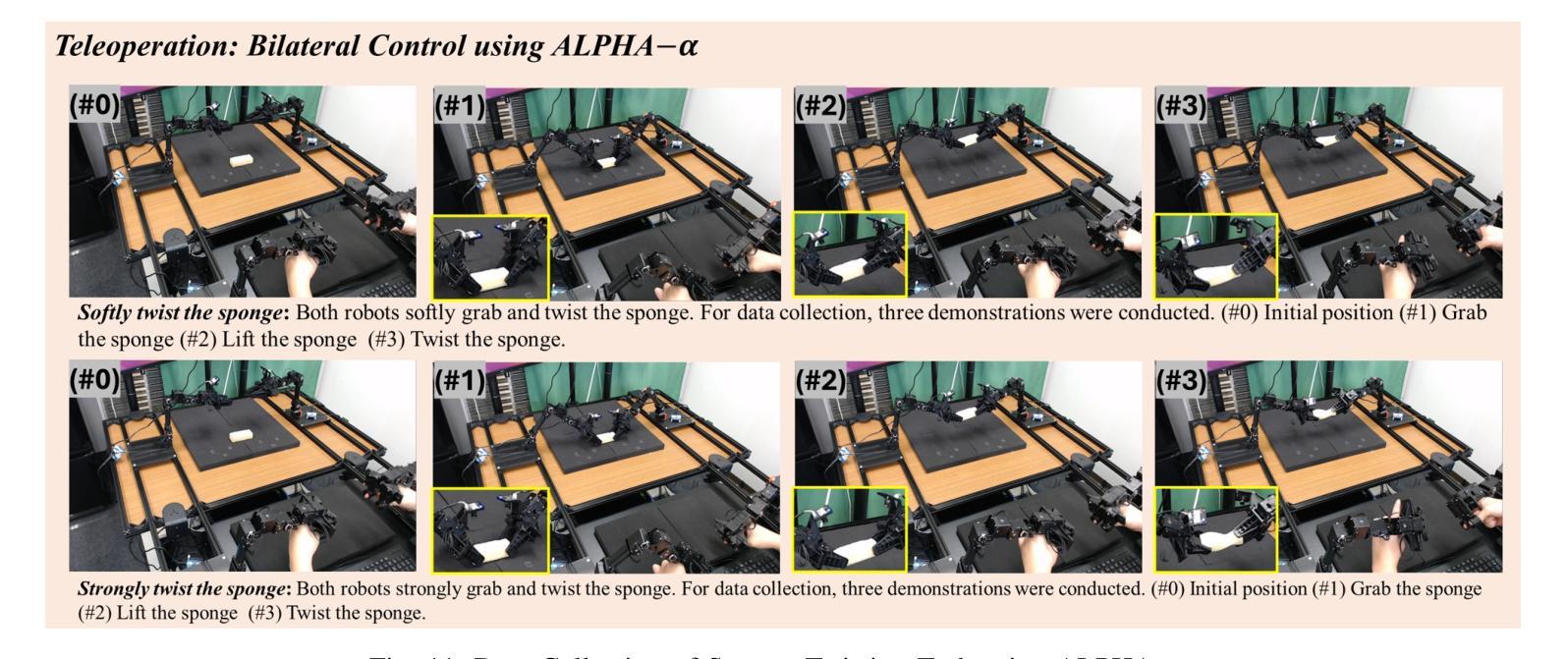
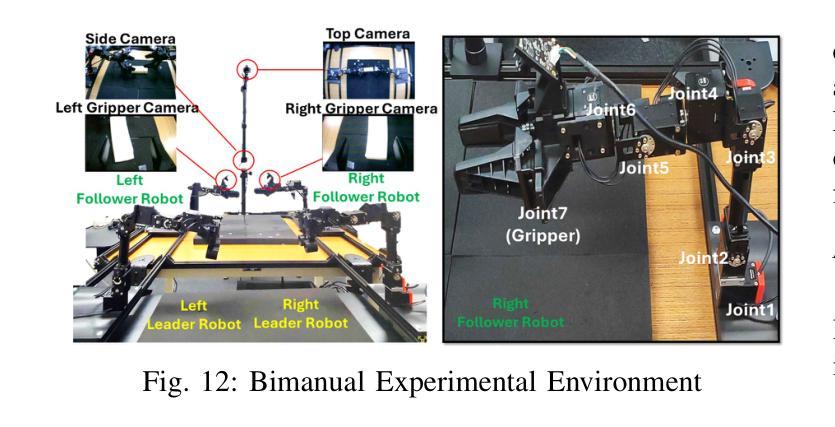
Bi-LAT: Bilateral Control-Based Imitation Learning via Natural Language and Action Chunking with Transformers
Authors:Takumi Kobayashi, Masato Kobayashi, Thanpimon Buamanee, Yuki Uranishi
We present Bi-LAT, a novel imitation learning framework that unifies bilateral control with natural language processing to achieve precise force modulation in robotic manipulation. Bi-LAT leverages joint position, velocity, and torque data from leader-follower teleoperation while also integrating visual and linguistic cues to dynamically adjust applied force. By encoding human instructions such as “softly grasp the cup” or “strongly twist the sponge” through a multimodal Transformer-based model, Bi-LAT learns to distinguish nuanced force requirements in real-world tasks. We demonstrate Bi-LAT’s performance in (1) unimanual cup-stacking scenario where the robot accurately modulates grasp force based on language commands, and (2) bimanual sponge-twisting task that requires coordinated force control. Experimental results show that Bi-LAT effectively reproduces the instructed force levels, particularly when incorporating SigLIP among tested language encoders. Our findings demonstrate the potential of integrating natural language cues into imitation learning, paving the way for more intuitive and adaptive human-robot interaction. For additional material, please visit: https://mertcookimg.github.io/bi-lat/
我们提出了Bi-LAT,这是一种新的模仿学习框架,它将双边控制与自然语言处理相结合,实现机器人操作中的精确力度调节。Bi-LAT利用领导者-跟随者遥操作中的关节位置、速度和扭矩数据,同时结合视觉和语言线索来动态调整应用力度。通过多模态Transformer模型编码人类指令,如“轻轻握住杯子”或“用力拧海绵”,Bi-LAT学会了区分现实世界任务中的细微力度要求。我们在(1)单手法堆叠杯子的场景中展示了Bi-LAT的性能,机器人能够根据语言命令准确调节握力,以及在(2)需要协调力度控制的双手拧海绵任务中展示了其性能。实验结果表明,Bi-LAT在测试的语言编码器中融入SigLIP后,能够有效地再现指示的力度水平。我们的研究展示了将自然语言线索融入模仿学习的潜力,为更直观和适应性的人机交互铺平了道路。更多资料请访问:[https://mertcookimg.github.io/bi-lat/]
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Bi-LAT这一新型模仿学习框架,它将双边控制与自然语言处理相结合,实现了机器人操作中的精确力度调节。Bi-LAT利用领导者跟随者的遥操作中的关节位置、速度和扭矩数据,同时整合视觉和语言线索来动态调整应用力度。通过多模态Transformer模型编码人类指令,Bi-LAT能够区分现实任务中的细微力度要求。在单手叠杯和双手扭海绵的实验场景中,Bi-LAT表现出良好的性能,有效复制了指令力度。该研究展示了自然语言线索融入模仿学习的潜力,为更直观和适应性的人机交互铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- Bi-LAT是一个结合双边控制与自然语言处理的模仿学习框架,用于机器人操作的精确力度调节。
- Bi-LAT利用领导者跟随者的遥操作数据,并整合视觉和语言线索以动态调整力度。
- 通过多模态Transformer模型编码人类指令,Bi-LAT能区分现实任务中的细微力度要求。
- 在叠杯和扭海绵的实验场景中,Bi-LAT表现出良好的性能。
- Bi-LAT在结合SigLIP语言编码器时,能更有效地复制指令力度。
- 研究表明,自然语言线索融入模仿学习具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图


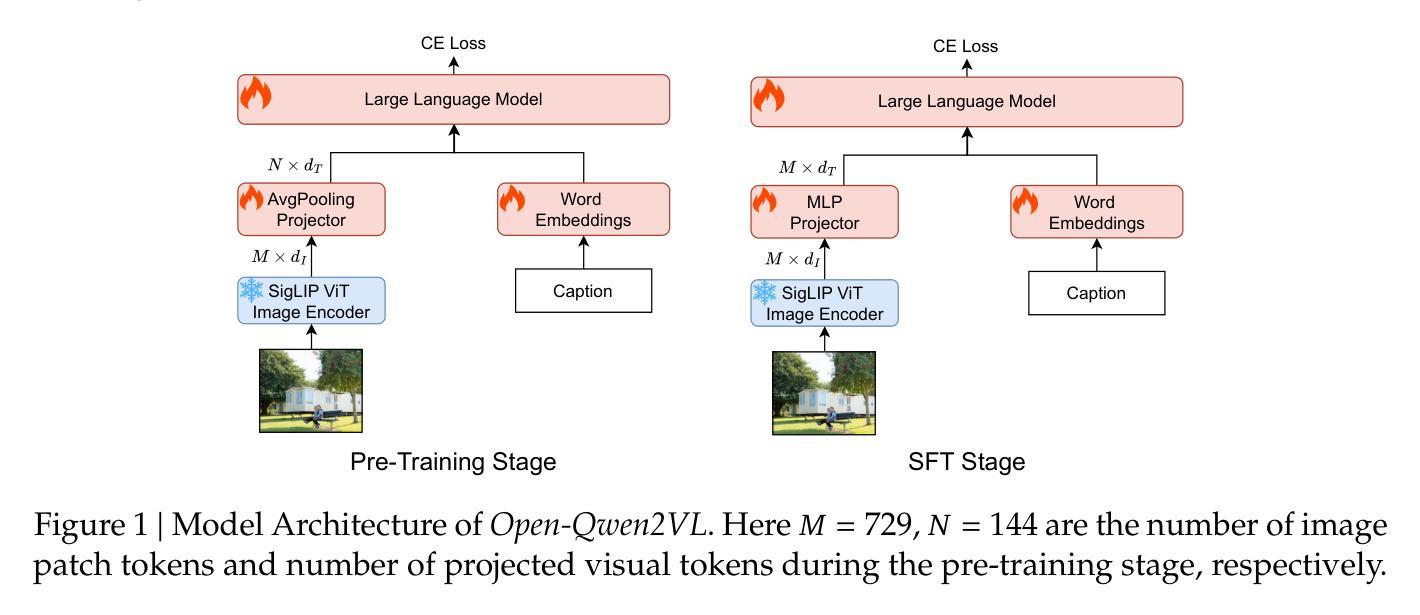
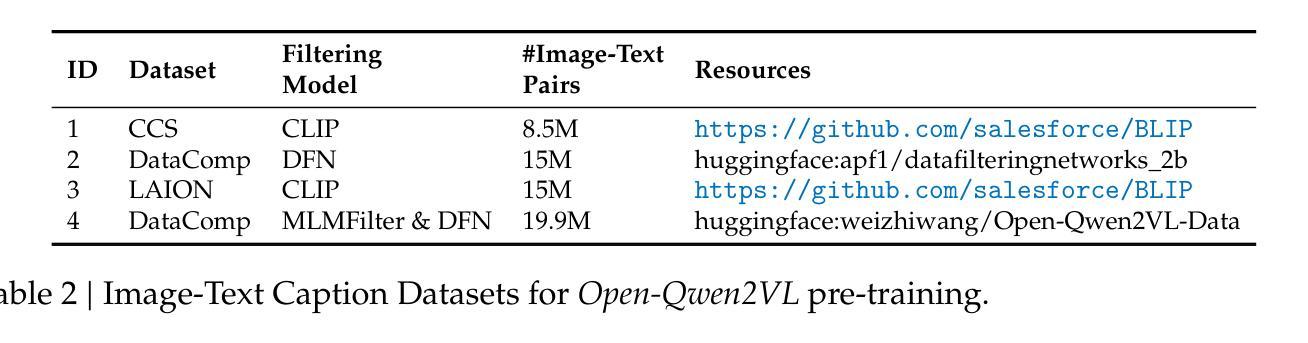
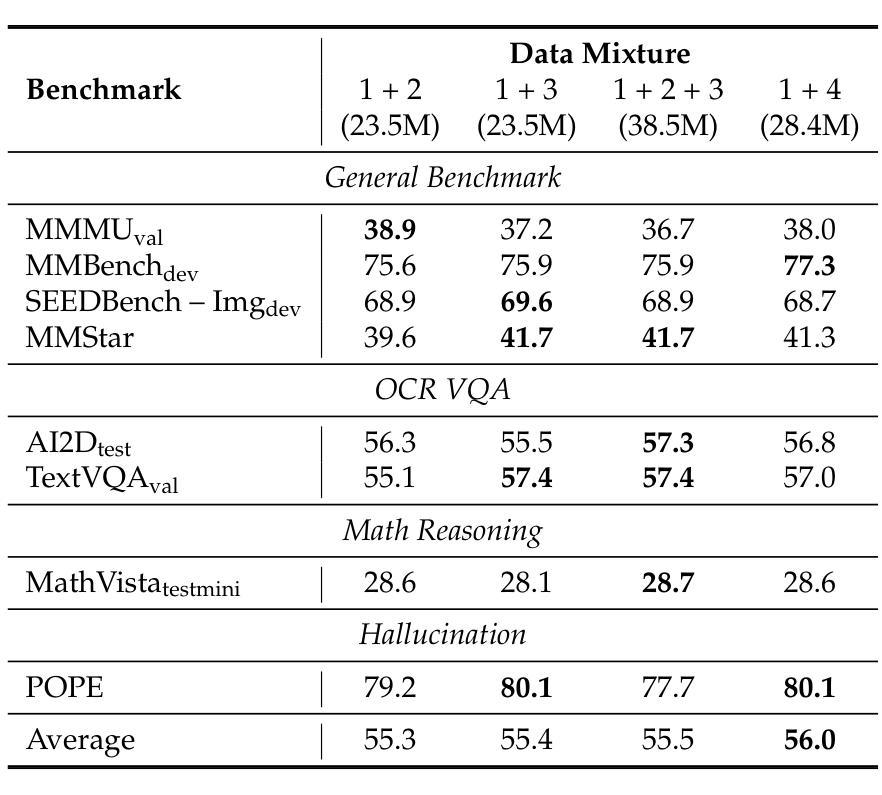
Open-Qwen2VL: Compute-Efficient Pre-Training of Fully-Open Multimodal LLMs on Academic Resources
Authors:Weizhi Wang, Yu Tian, Linjie Yang, Heng Wang, Xifeng Yan
The reproduction of state-of-the-art multimodal LLM pre-training faces barriers at every stage of the pipeline, including high-quality data filtering, multimodal data mixture strategies, sequence packing techniques, and training frameworks. We introduce Open-Qwen2VL, a fully open-source 2B-parameter Multimodal Large Language Model pre-trained efficiently on 29M image-text pairs using only 220 A100-40G GPU hours. Our approach employs low-to-high dynamic image resolution and multimodal sequence packing to significantly enhance pre-training efficiency. The training dataset was carefully curated using both MLLM-based filtering techniques (e.g., MLM-Filter) and conventional CLIP-based filtering methods, substantially improving data quality and training efficiency. The Open-Qwen2VL pre-training is conducted on academic level 8xA100-40G GPUs at UCSB on 5B packed multimodal tokens, which is 0.36% of 1.4T multimodal pre-training tokens of Qwen2-VL. The final instruction-tuned Open-Qwen2VL outperforms partially-open state-of-the-art MLLM Qwen2-VL-2B on various multimodal benchmarks of MMBench, SEEDBench, MMstar, and MathVista, indicating the remarkable training efficiency of Open-Qwen2VL. We open-source all aspects of our work, including compute-efficient and data-efficient training details, data filtering methods, sequence packing scripts, pre-training data in WebDataset format, FSDP-based training codebase, and both base and instruction-tuned model checkpoints. We redefine “fully open” for multimodal LLMs as the complete release of: 1) the training codebase, 2) detailed data filtering techniques, and 3) all pre-training and supervised fine-tuning data used to develop the model.
模态多模态大型语言模型预训练的重现面临管道每个阶段的障碍,包括高质量数据过滤、多模态数据混合策略、序列打包技术和训练框架。我们引入Open-Qwen2VL,这是一个完全开源的2B参数多模态大型语言模型,在仅使用29M图像文本对的情况下,使用高效的预训练方法。我们的方法采用从低到高的动态图像分辨率和多模态序列打包,以显著提高预训练效率。训练数据集经过精心筛选,既使用基于MLLM的过滤技术(如MLM-Filter),也使用传统的基于CLIP的过滤方法,大大提高了数据质量和训练效率。Open-Qwen2VL的预训练是在UCSB的学术级8xA100-40G GPU上进行的,处理5B个打包的多模态令牌,这是Qwen2VL的1.4T多模态预训练令牌的0.36%。最终指令调整的Open-Qwen2VL在各种多模态基准测试(如MMBench、SEEDBench、MMstar和MathVista)上优于部分开源的先进MLLM Qwen2-VL-2B,证明了Open-Qwen2VL的显著训练效率。我们开源了工作的各个方面,包括计算高效和数据高效的训练细节、数据过滤方法、序列打包脚本、WebDataset格式的预训练数据、基于FSDP的训练代码库以及基础指令和经过调整的模型检查点。我们重新定义了多模态大型语言模型的“完全开放”,即完全发布:1)训练代码库,2)详细的数据过滤技术,以及3)用于开发模型的所有预训练和监督微调数据。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大规模多模态预训练语言模型(LLM)的复制面临诸多挑战,包括高质量数据过滤、多模态数据混合策略、序列打包技术和训练框架等。我们推出Open-Qwen2VL,这是一个完全开源的2B参数多模态大型语言模型,在只有220个A100-40G GPU小时的情况下,在由精选图像和文本组成的复杂训练集上进行高效训练。通过使用从低到高的动态图像分辨率和多模态序列打包方法,我们显著提高了预训练效率。Open-Qwen2VL在各种多模态基准测试中表现优异,并且我们公开了所有相关的训练细节和数据集等。我们重新定义了多模态LLM的“完全开放”,包括公开训练代码库、详细的数据过滤技术和所有用于开发模型的预训练和监督微调数据。整体来说,这是一个效率出众、开放性高的多模态语言模型。
Key Takeaways
- Open-Qwen2VL是一个开源的多模态大型语言模型,能够在有限的GPU资源下高效训练。
- 该模型采用了先进的图像分辨率策略和序列打包技术来提升训练效率。
- Open-Qwen2VL采用了严格的训练数据集筛选过程,结合了MLLM过滤技术和CLIP过滤方法,提升了数据质量和训练效率。
- 该模型在各种多模态基准测试中表现优异,优于部分开源的多模态LLM Qwen2-VL-2B。
- Open-Qwen2VL实现了真正意义上的开源,包括公开训练代码库、数据过滤技术、预训练数据和训练过程等细节。这为该领域的未来研究提供了重要参考和基础。
- 高效的计算和数据利用使其成为研究者和开发者的宝贵资源。
点此查看论文截图


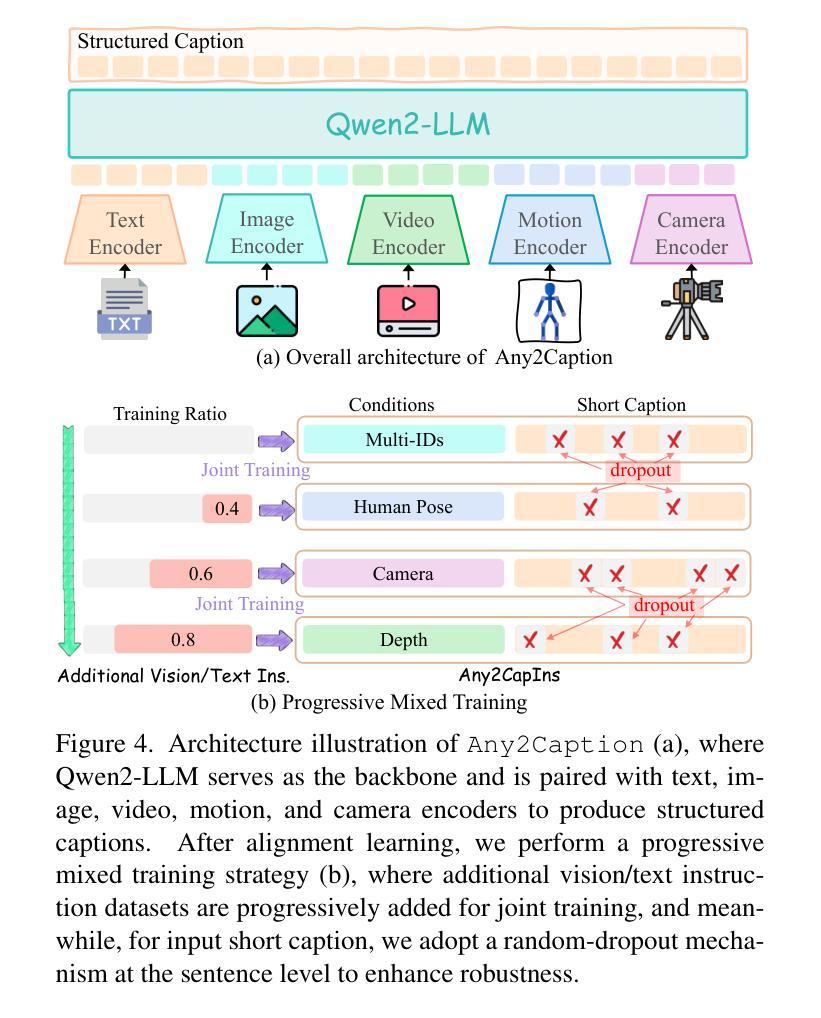
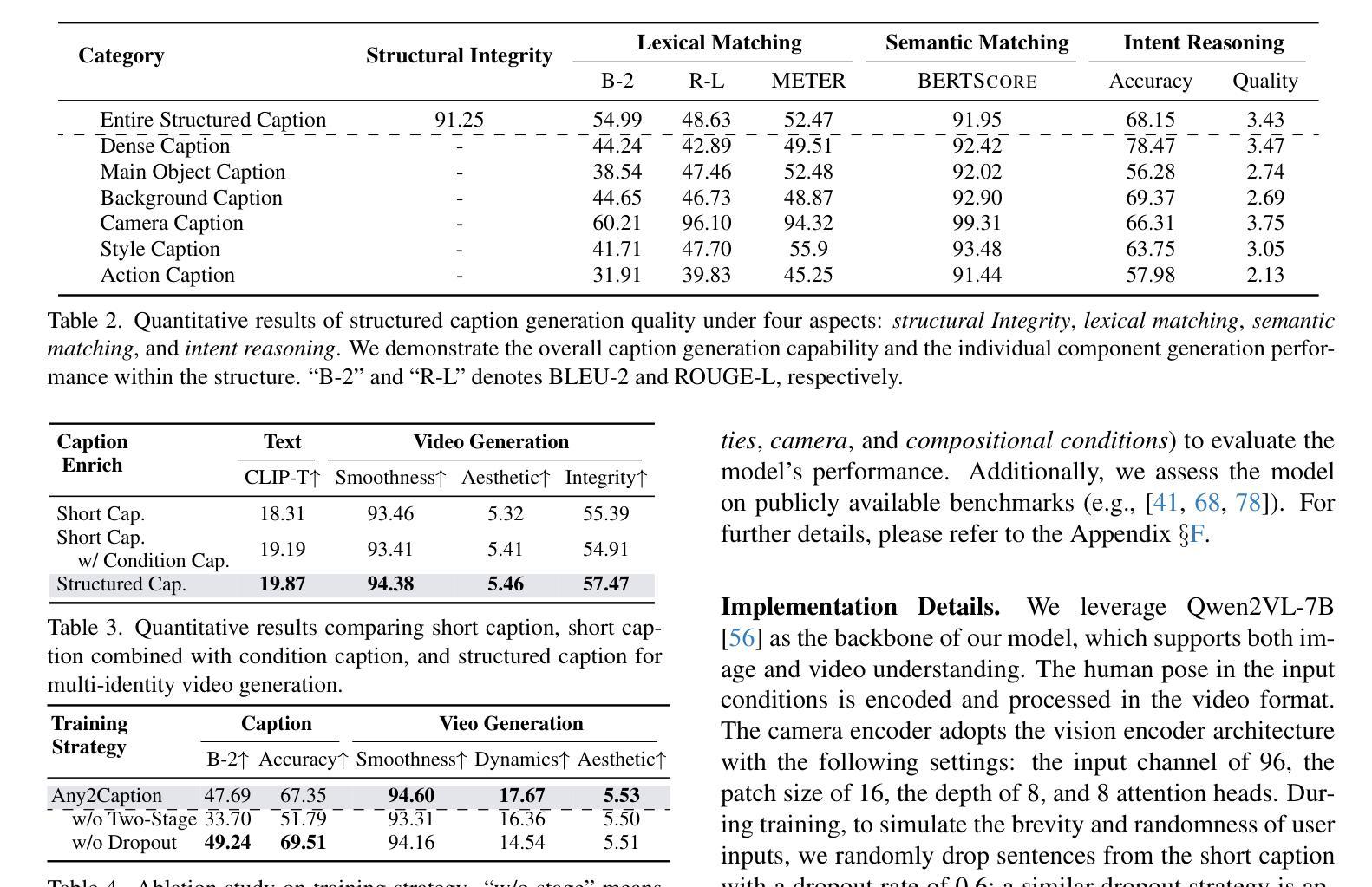
Any2Caption:Interpreting Any Condition to Caption for Controllable Video Generation
Authors:Shengqiong Wu, Weicai Ye, Jiahao Wang, Quande Liu, Xintao Wang, Pengfei Wan, Di Zhang, Kun Gai, Shuicheng Yan, Hao Fei, Tat-Seng Chua
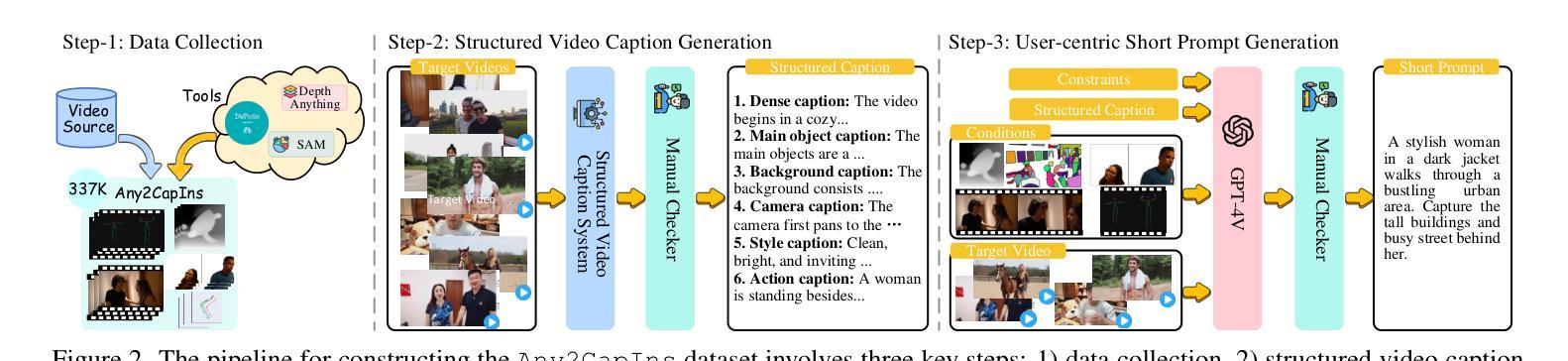
To address the bottleneck of accurate user intent interpretation within the current video generation community, we present Any2Caption, a novel framework for controllable video generation under any condition. The key idea is to decouple various condition interpretation steps from the video synthesis step. By leveraging modern multimodal large language models (MLLMs), Any2Caption interprets diverse inputs–text, images, videos, and specialized cues such as region, motion, and camera poses–into dense, structured captions that offer backbone video generators with better guidance. We also introduce Any2CapIns, a large-scale dataset with 337K instances and 407K conditions for any-condition-to-caption instruction tuning. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate significant improvements of our system in controllability and video quality across various aspects of existing video generation models. Project Page: https://sqwu.top/Any2Cap/
针对当前视频生成社区中准确理解用户意图的瓶颈问题,我们提出了Any2Caption,这是一个新型的可控视频生成框架,可在任何条件下进行视频生成。关键思想是将各种条件解读步骤与视频合成步骤解耦。通过利用现代的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs),Any2Caption能够解释各种输入,包括文本、图像、视频以及专业提示(如区域、运动和相机姿态),并将其转化为密集的结构化字幕,为视频生成器提供更好的指导。我们还介绍了Any2CapIns,这是一个大规模数据集,包含337K个实例和407K个条件,用于任何条件到字幕的指令调整。综合评估表明,我们的系统在可控性和视频质量方面对现有视频生成模型的各种方面都有显著提高。项目页面:https://sqwu.top/Any2Cap/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://sqwu.top/Any2Cap/
Summary
Any2Caption是一个针对任何条件下的可控视频生成的新型框架,它通过解耦各种条件解读步骤与视频合成步骤,利用现代的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)来解读多样化的输入,如文本、图像、视频以及专业线索(如区域、动作和相机姿态),并将其转化为密集的结构化字幕,为视频生成器提供更好的指导。此外,还介绍了包含337K实例和407K条件的Any2CapIns大规模数据集,用于任何条件到字幕的指令调整。评估表明,该系统在可控性和视频质量方面均有显著提高。
Key Takeaways
- Any2Caption框架解决了当前视频生成社区中准确用户意图解读的瓶颈。
- 该框架利用现代的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)来解读多样化的输入,包括文本、图像、视频和专业线索。
- Any2Caption通过将条件解读步骤与视频合成步骤解耦,实现可控视频生成。
- Any2CapIns是一个大规模数据集,包含用于任何条件到字幕指令调整的数据。
- Any2Caption框架将各种输入转化为结构化字幕,为视频生成器提供更好的指导。
- 综合评估表明,Any2Caption系统在可控性和视频质量方面较现有视频生成模型有显著提高。
点此查看论文截图


FakeScope: Large Multimodal Expert Model for Transparent AI-Generated Image Forensics
Authors:Yixuan Li, Yu Tian, Yipo Huang, Wei Lu, Shiqi Wang, Weisi Lin, Anderson Rocha
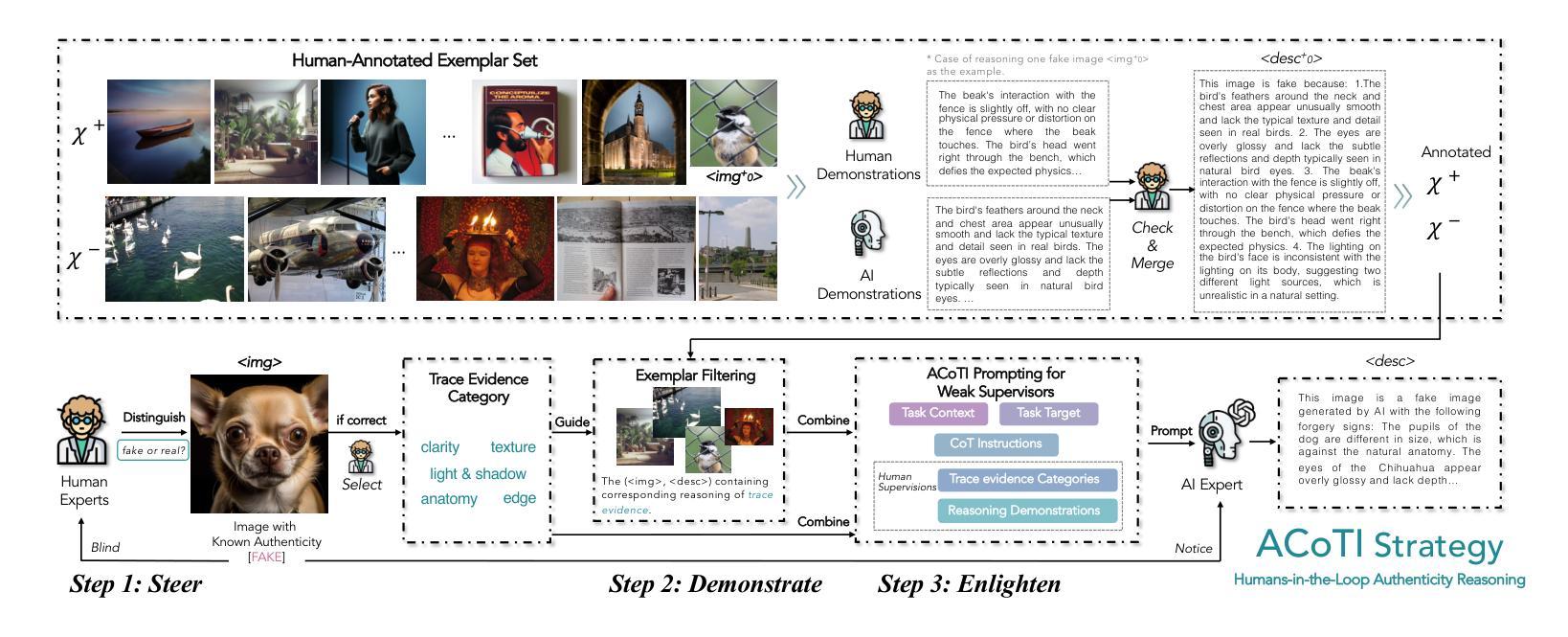
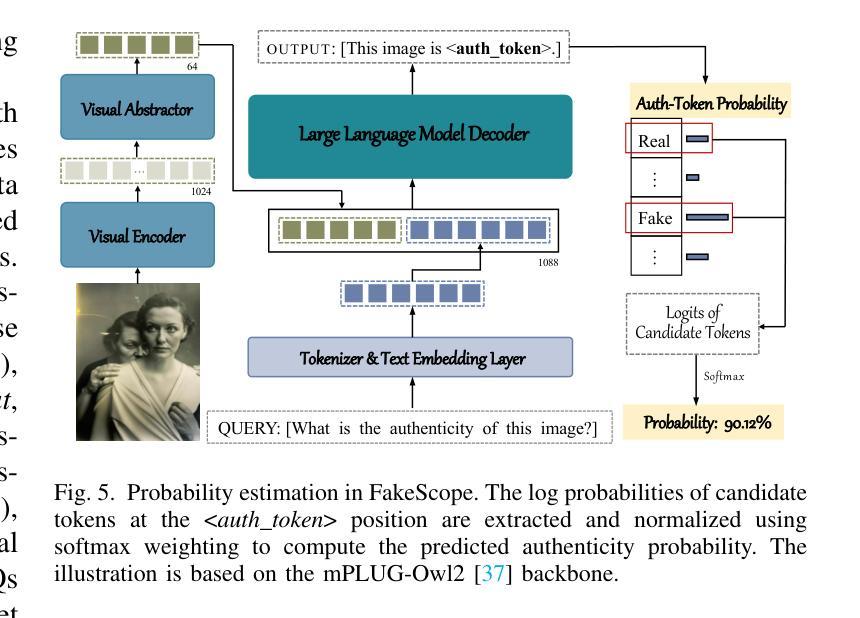
The rapid and unrestrained advancement of generative artificial intelligence (AI) presents a double-edged sword: while enabling unprecedented creativity, it also facilitates the generation of highly convincing deceptive content, undermining societal trust. As image generation techniques become increasingly sophisticated, detecting synthetic images is no longer just a binary task: it necessitates interpretable, context-aware methodologies that enhance trustworthiness and transparency. However, existing detection models primarily focus on classification, offering limited explanatory insights into image authenticity. In this work, we propose FakeScope, an expert multimodal model (LMM) tailored for AI-generated image forensics, which not only identifies AI-synthetic images with high accuracy but also provides rich, interpretable, and query-driven forensic insights. We first construct FakeChain dataset that contains linguistic authenticity reasoning based on visual trace evidence, developed through a novel human-machine collaborative framework. Building upon it, we further present FakeInstruct, the largest multimodal instruction tuning dataset containing 2 million visual instructions tailored to enhance forensic awareness in LMMs. FakeScope achieves state-of-the-art performance in both closed-ended and open-ended forensic scenarios. It can distinguish synthetic images with high accuracy while offering coherent and insightful explanations, free-form discussions on fine-grained forgery attributes, and actionable enhancement strategies. Notably, despite being trained exclusively on qualitative hard labels, FakeScope demonstrates remarkable zero-shot quantitative capability on detection, enabled by our proposed token-based probability estimation strategy. Furthermore, FakeScope exhibits strong generalization and in-the-wild ability, ensuring its applicability in real-world scenarios.
人工智能生成技术的迅猛且无约束的发展呈现出一把双刃剑的特性:虽然它能够促进前所未有的创造力,但也方便生成高度欺骗性的内容,从而破坏社会信任。随着图像生成技术的日益成熟,检测合成图像不再仅仅是一个简单的二选一任务:它需要可解释、具备语境意识的方法论来提高可信度和透明度。然而,现有的检测模型主要集中在分类上,对于图像真实性的解释性洞察有限。在这项工作中,我们提出了FakeScope,一个专为AI生成图像取证定制的专家多模式模型(LMM)。它不仅能够高度准确地识别AI合成的图像,而且提供丰富、可解释、查询驱动的取证洞察。我们首先构建了FakeChain数据集,其中包含基于视觉痕迹证据的语言真实性推理,这是通过新型的人机协作框架开发而成的。在此基础上,我们进一步推出了FakeInstruct,这是最大的多模式指令调整数据集,包含200万条旨在提高LMMs取证意识的视觉指令。FakeScope在封闭和开放的取证场景中均实现了最先进的性能。它能够准确地区分合成图像,同时提供连贯而富有洞察力的解释、关于细微伪造属性的自由形式讨论和可行的增强策略。值得注意的是,尽管FakeScope仅使用定性硬标签进行训练,但得益于我们提出的基于标记的概率估计策略,它在检测方面展现出了惊人的零样本定量能力。此外,FakeScope表现出强大的泛化和野外能力,确保其在现实场景中的适用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人工智能技术的快速发展呈现出一把双刃剑的特性:在激发前所未有的创造力的同时,也易于生成具有高度欺骗性的内容,损害社会信任。针对这一问题,我们提出了一款名为FakeScope的定制化多模态模型(LMM),专门用于人工智能生成的图像取证。该模型不仅能准确识别AI合成的图像,而且提供丰富、可解释、查询驱动的取证信息。为实现此功能,我们构建了FakeChain数据集和FakeInstruct指令调优数据集。FakeScope在封闭和开放环境下的取证场景中均取得了最先进的性能,具备强大的零样本定量检测能力。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式人工智能(AI)的快速发展带来了社会信任的问题,因为AI可以生成高度欺骗性的内容。
- 现有的检测模型主要侧重于分类,对于图像真实性的解释性有限。
- FakeScope是一款专门用于AI生成的图像取证的定制化多模态模型(LMM)。
- FakeScope不仅能准确识别AI合成的图像,而且提供丰富、可解释、查询驱动的取证信息。
- 为训练FakeScope,构建了FakeChain数据集和FakeInstruct指令调优数据集。
- FakeScope在封闭和开放环境下的取证场景中均表现优秀,具备强大的性能。
点此查看论文截图



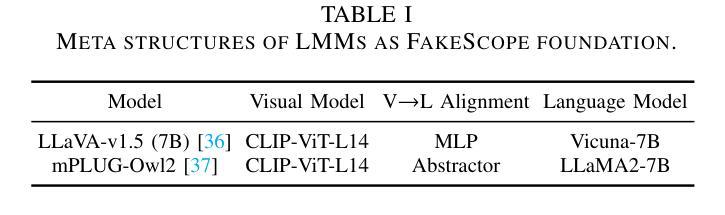
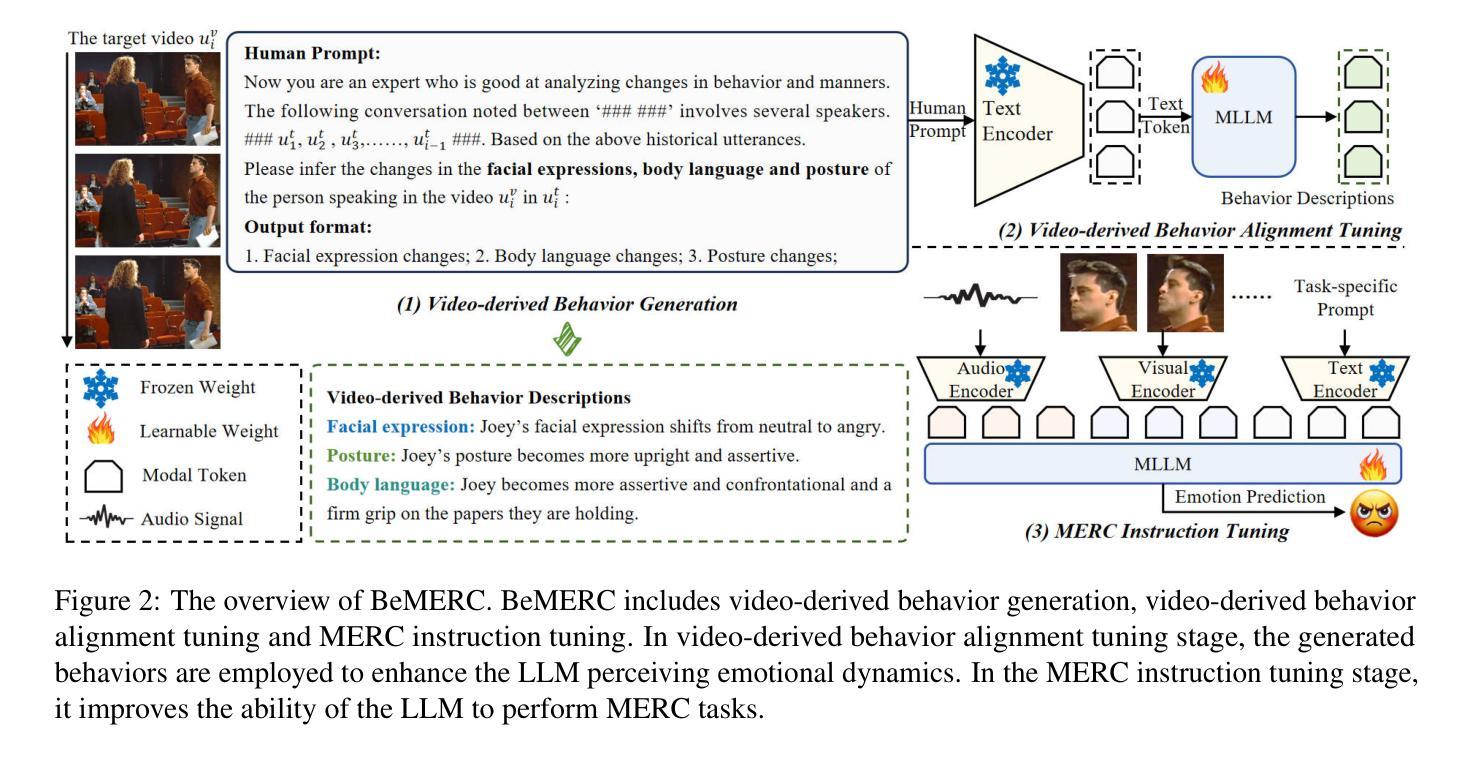
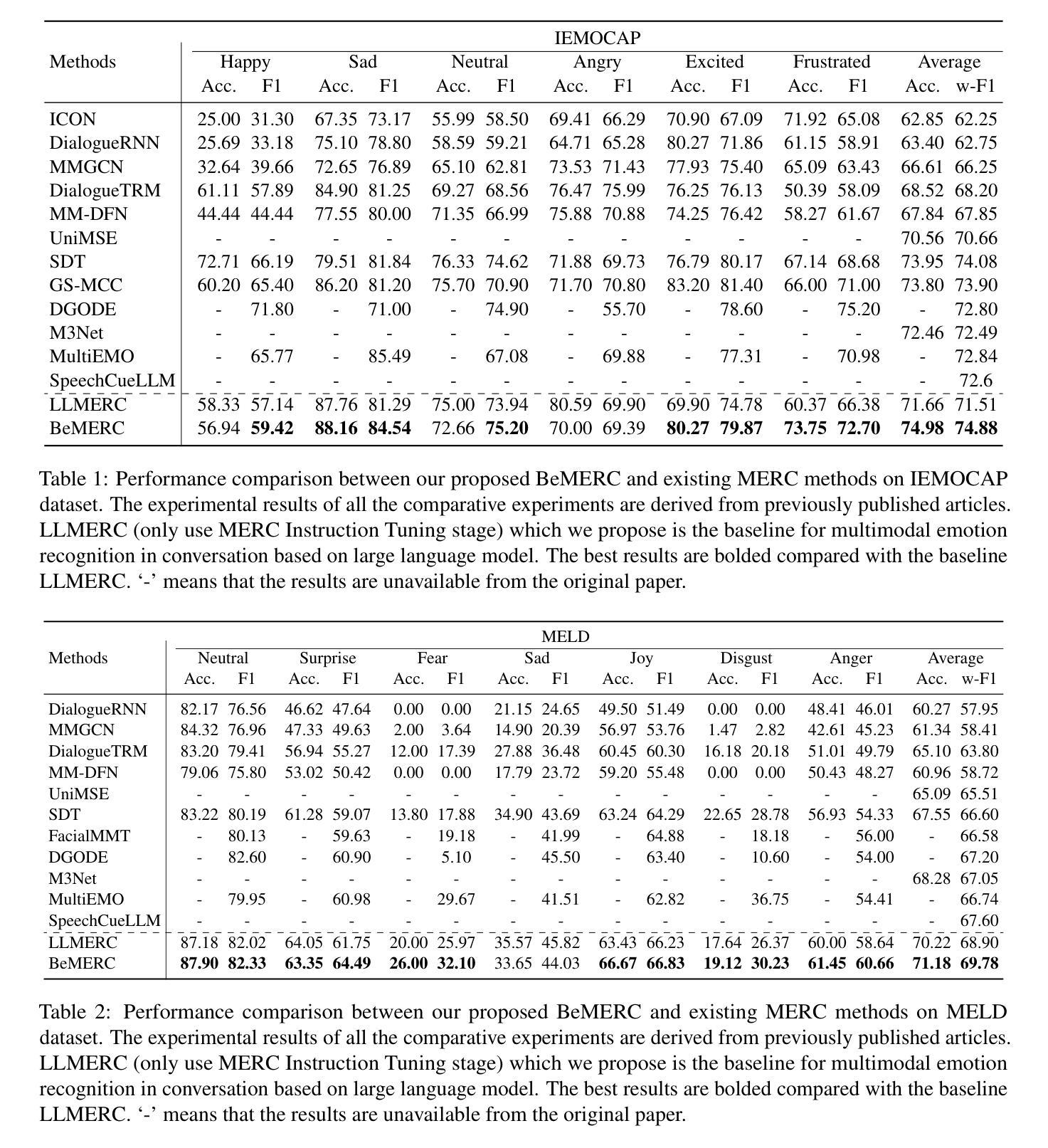
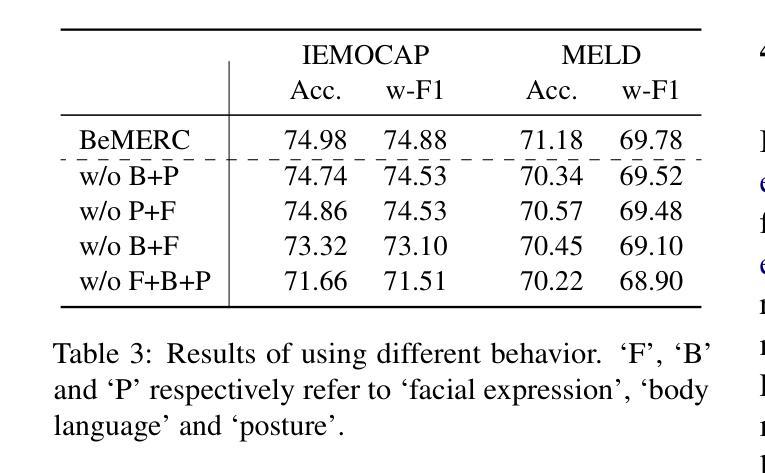
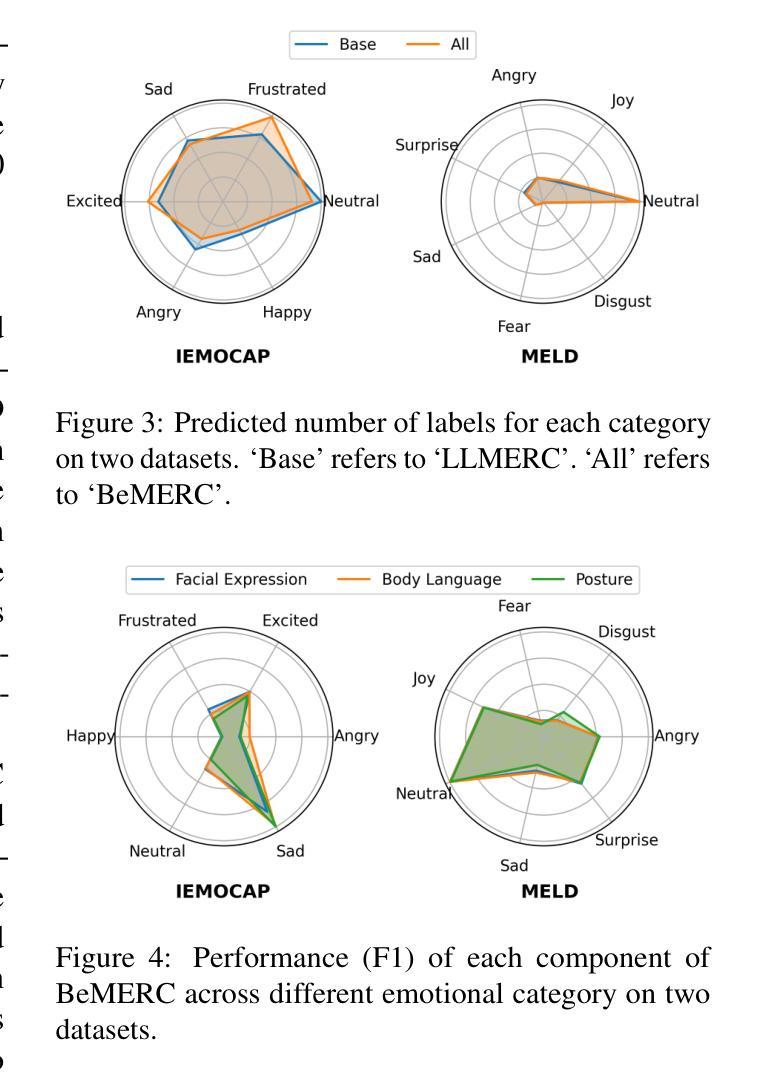
BeMERC: Behavior-Aware MLLM-based Framework for Multimodal Emotion Recognition in Conversation
Authors:Yumeng Fu, Junjie Wu, Zhongjie Wang, Meishan Zhang, Yulin Wu, Bingquan Liu
Multimodal emotion recognition in conversation (MERC), the task of identifying the emotion label for each utterance in a conversation, is vital for developing empathetic machines. Current MLLM-based MERC studies focus mainly on capturing the speaker’s textual or vocal characteristics, but ignore the significance of video-derived behavior information. Different from text and audio inputs, learning videos with rich facial expression, body language and posture, provides emotion trigger signals to the models for more accurate emotion predictions. In this paper, we propose a novel behavior-aware MLLM-based framework (BeMERC) to incorporate speaker’s behaviors, including subtle facial micro-expression, body language and posture, into a vanilla MLLM-based MERC model, thereby facilitating the modeling of emotional dynamics during a conversation. Furthermore, BeMERC adopts a two-stage instruction tuning strategy to extend the model to the conversations scenario for end-to-end training of a MERC predictor. Experiments demonstrate that BeMERC achieves superior performance than the state-of-the-art methods on two benchmark datasets, and also provides a detailed discussion on the significance of video-derived behavior information in MERC.
多模态情感识别技术(MERC)在对话中识别每个话语的情感标签的任务对于开发共情机器至关重要。当前的基于大型语言模型的MERC研究主要集中在捕捉说话人的文本或语音特征上,而忽略了视频衍生行为信息的重要性。不同于文本和音频输入,学习包含丰富面部表情、肢体语言和姿势的视频为模型提供了情感触发信号,以实现更准确的情感预测。在本文中,我们提出了一种新颖的行为感知大型语言模型框架(BeMERC),将说话人的行为(包括微妙的面部表情、肢体语言和姿势)纳入基本的基于大型语言模型的MERC模型中,从而促进了对话过程中情感动态的建模。此外,BeMERC采用了两阶段指令微调策略,将模型扩展到对话场景,对MERC预测器进行端到端的训练。实验表明,BeMERC在两个基准数据集上的性能优于最新方法,并详细讨论了视频衍生行为信息在MERC中的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态情感识别对话(MERC)是开发共情机器的重要任务之一,旨在识别对话中每个句子的情感标签。当前基于大型语言模型(LLM)的MERC研究主要关注捕捉说话者的文本或语音特征,但忽略了视频行为信息的重要性。与文本和音频输入不同,视频包含丰富的面部表情、身体语言和姿势,为模型提供了情感触发信号,以实现更准确的情感预测。本文提出了一种新型的行为感知LLM框架(BeMERC),该框架将说话者的行为(包括微妙的面部表情、身体语言和姿势)纳入基本的LLM-based MERC模型中,从而促进对话过程中的情感动态建模。此外,BeMERC采用两阶段指令调整策略,将模型扩展到对话场景,以端到端的方式训练MERC预测器。实验表明,BeMERC在两个基准数据集上的性能优于最先进的方法,并详细讨论了视频行为信息在MERC中的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态情感识别对话(MERC)对于开发共情机器至关重要。
- 当前LLM-based MERC研究主要关注文本和语音特征,忽视了视频行为信息的重要性。
- 视频包含丰富的面部表情、身体语言和姿势,为模型提供情感触发信号,提高情感预测准确性。
- BeMERC框架结合了说话者的行为信息(包括微妙的面部表情、身体语言和姿势),以促进对话过程中的情感动态建模。
- BeMERC采用两阶段指令调整策略,将模型扩展到对话场景并进行端到端的MERC预测器训练。
- 实验显示BeMERC在基准数据集上的性能优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

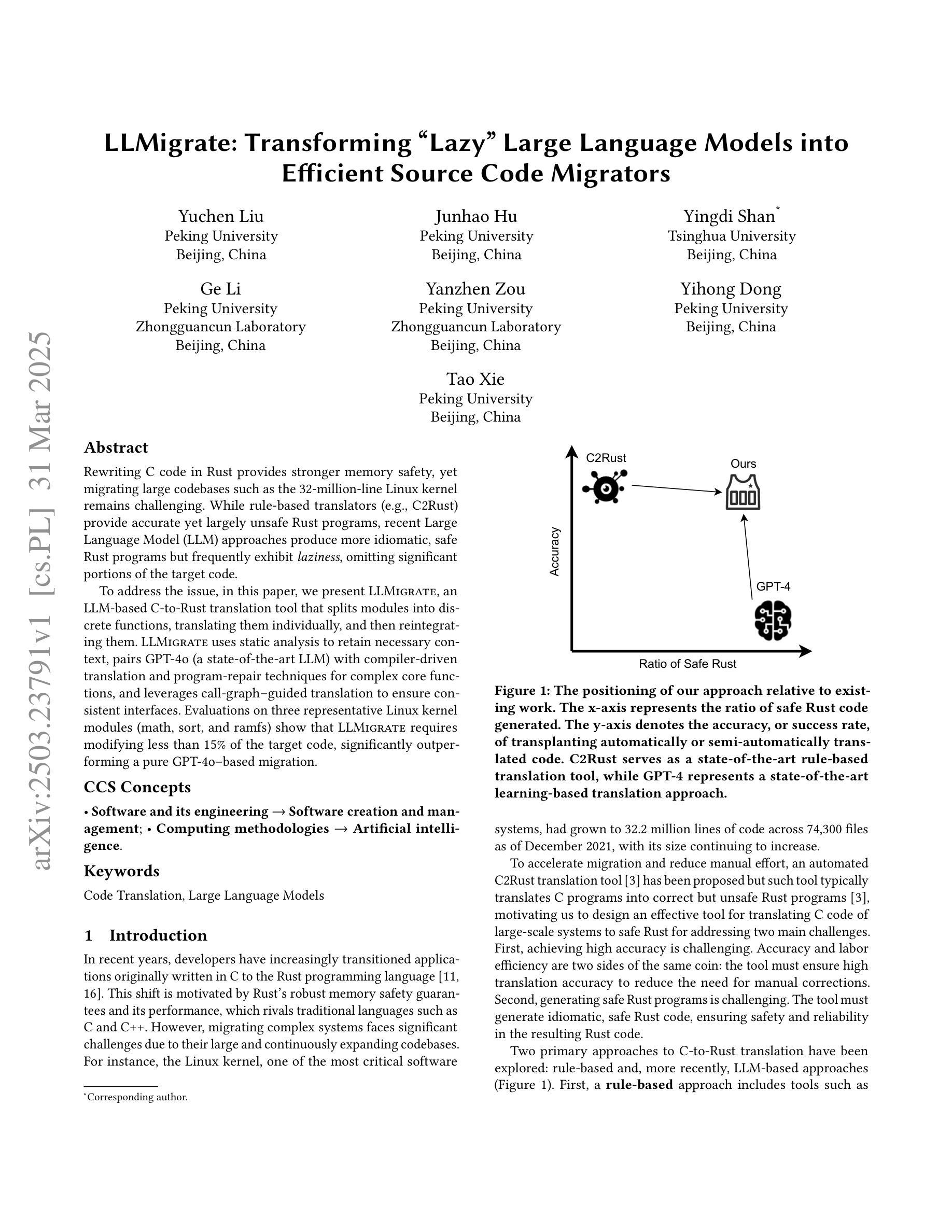
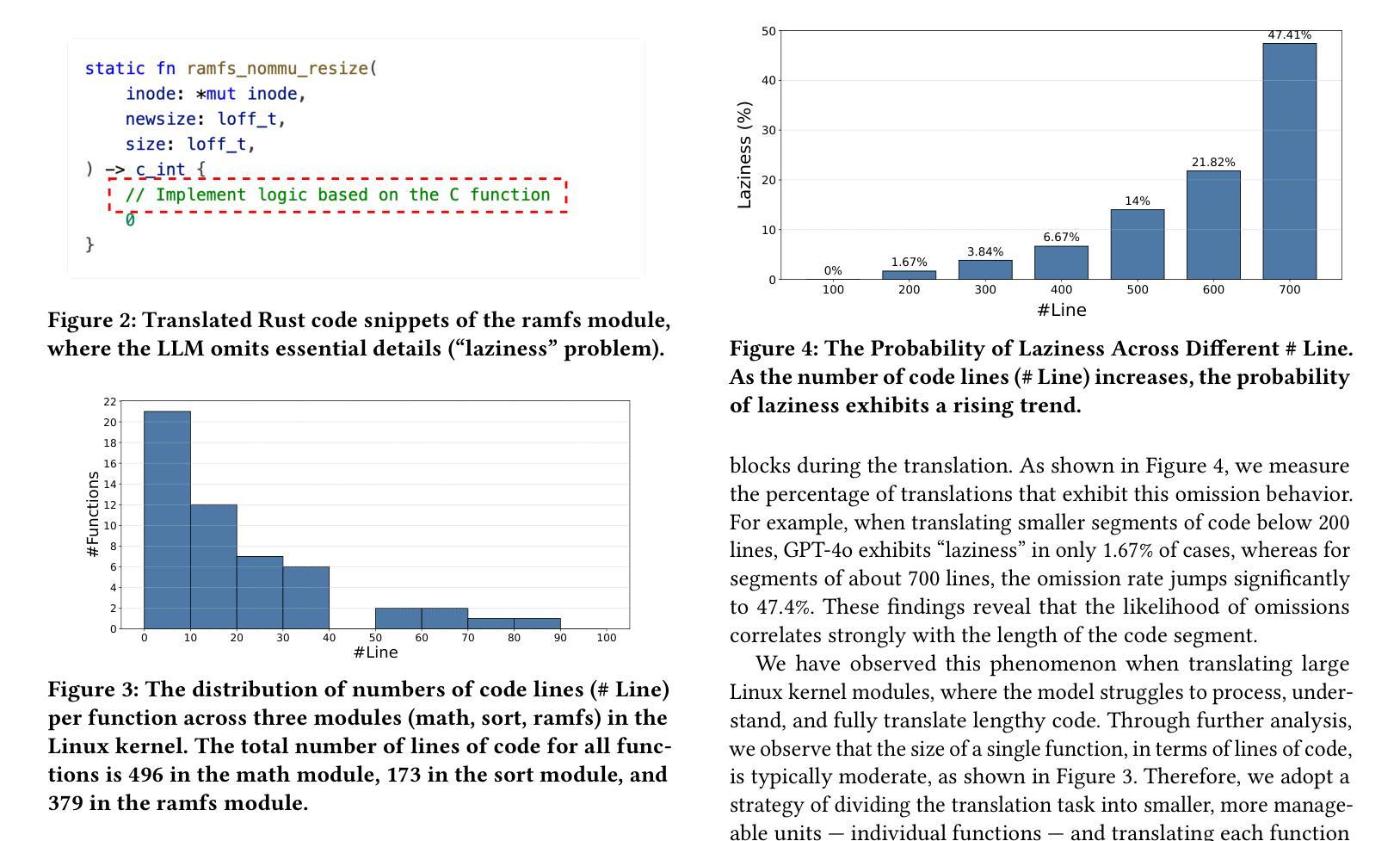
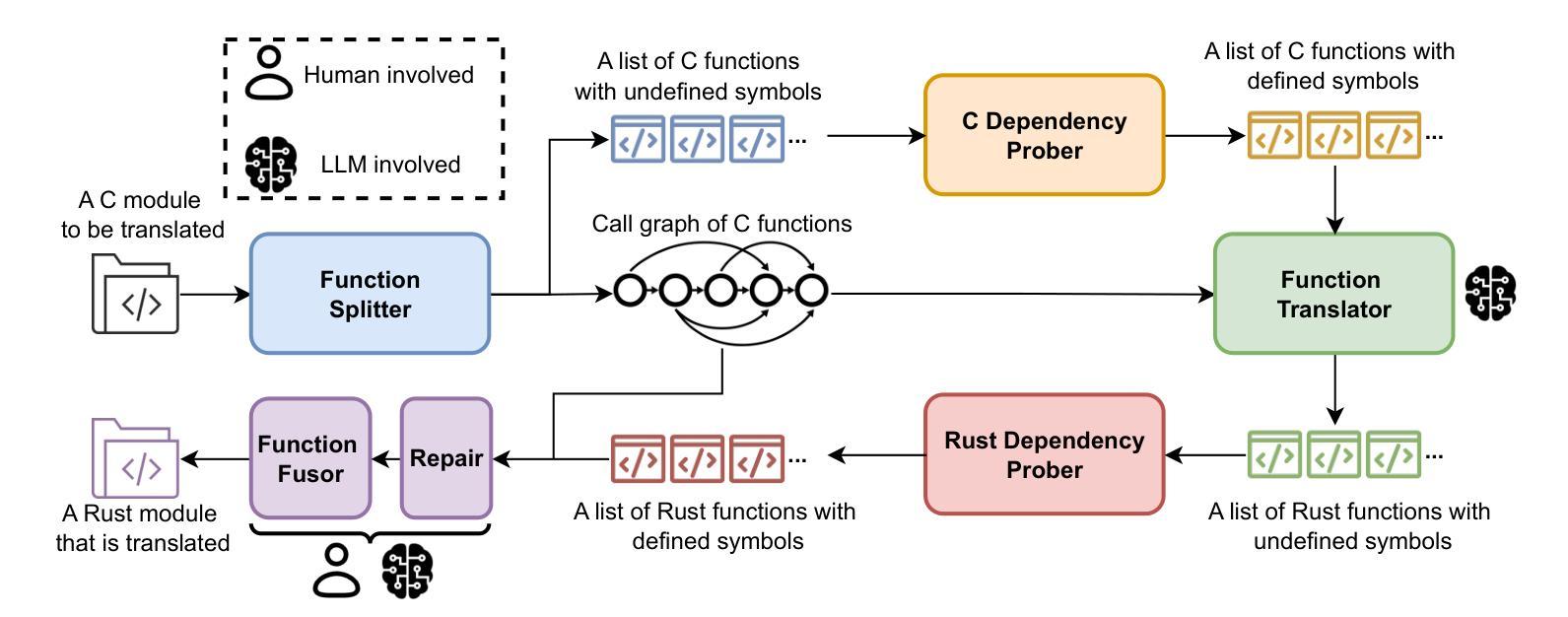
LLMigrate: Transforming “Lazy” Large Language Models into Efficient Source Code Migrators
Authors:Yuchen Liu, Junhao Hu, Yingdi Shan, Ge Li, Yanzhen Zou, Yihong Dong, Tao Xie
Rewriting C code in Rust provides stronger memory safety, yet migrating large codebases such as the 32-million-line Linux kernel remains challenging. While rule-based translators (e.g., C2Rust) provide accurate yet largely unsafe Rust programs, recent Large Language Model (LLM) approaches produce more idiomatic, safe Rust programs but frequently exhibit “laziness”, omitting significant portions of the target code. To address the issue, in this paper, we present LLMigrate, an LLM-based C-to-Rust translation tool that splits modules into discrete functions, translating them individually, and then reintegrating them. LLMigrate uses static analysis to retain necessary context, pairs GPT-4o (a state-of-the-art LLM) with compiler-driven translation and program-repair techniques for complex core functions, and leverages call-graph-guided translation to ensure consistent interfaces. Evaluations on three representative Linux kernel modules (math, sort, and ramfs) show that LLMigrate requires modifying less than 15% of the target code, significantly outperforming a pure GPT-4o-based migration.
重写Rust中的C代码可以提供更强的内存安全性,但是迁移像3200万行的Linux内核这样的大型代码库仍然具有挑战性。虽然基于规则的翻译器(例如C2Rust)提供的Rust程序是准确的,但大多是不安全的。最近的大型语言模型(LLM)方法产生的是更地道的、安全的Rust程序,但经常表现出“懒惰”,省略了大量的目标代码。为了解决这一问题,本文介绍了LLMigrate,这是一种基于LLM的C到Rust翻译工具。它将模块分割成离散函数,逐个翻译它们,然后再进行整合。LLMigrate使用静态分析来保留必要的上下文,将最前沿的LLM GPT-4o与编译器驱动的翻译和程序修复技术相结合用于处理复杂的核心功能,并利用调用图指导的翻译来确保一致的接口。对三个代表性的Linux内核模块的评估(数学、排序和ramfs)显示,LLMigrate只需要修改目标代码的不到15%,显著优于纯GPT-4o的迁移。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
重写C代码到Rust能提供更强大的内存安全性,但迁移大型代码库如3200万行的Linux内核仍具挑战。规则基础翻译器(如C2Rust)能生成准确但大多不安全的Rust程序,而最近的大型语言模型(LLM)方法能生成更地道的、安全的Rust程序,但常有“懒惰”现象,省略目标代码的重要部分。为解决此问题,本文提出LLMigrate,一个基于LLM的C到Rust翻译工具,它将模块分割成离散函数进行个别翻译,再整合。LLMigrate利用静态分析保留必要的上下文,结合GPT-4o(最先进的大型语言模型)与编译器驱动的翻译和程序修复技术处理复杂核心函数,并利用调用图指导翻译以确保一致的接口。对三个代表性的Linux内核模块(数学、排序和ramfs)的评估显示,LLMigrate只需要修改目标代码的不到15%,显著优于纯GPT-4o的迁移。
Key Takeaways
- LLMigrate是一个基于大型语言模型(LLM)的C到Rust翻译工具。
- LLMigrate通过分割模块并逐个翻译函数来解决内存安全问题和代码迁移挑战。
- LLMigrate使用静态分析来保留必要的上下文信息。
- LLMigrate结合了GPT-4o与编译器驱动的翻译和程序修复技术。
- LLMigrate利用调用图指导翻译以确保接口的一致性。
- 在三个代表性Linux内核模块的测试中,LLMigrate显著优于纯GPT-4o的迁移方法。
点此查看论文截图
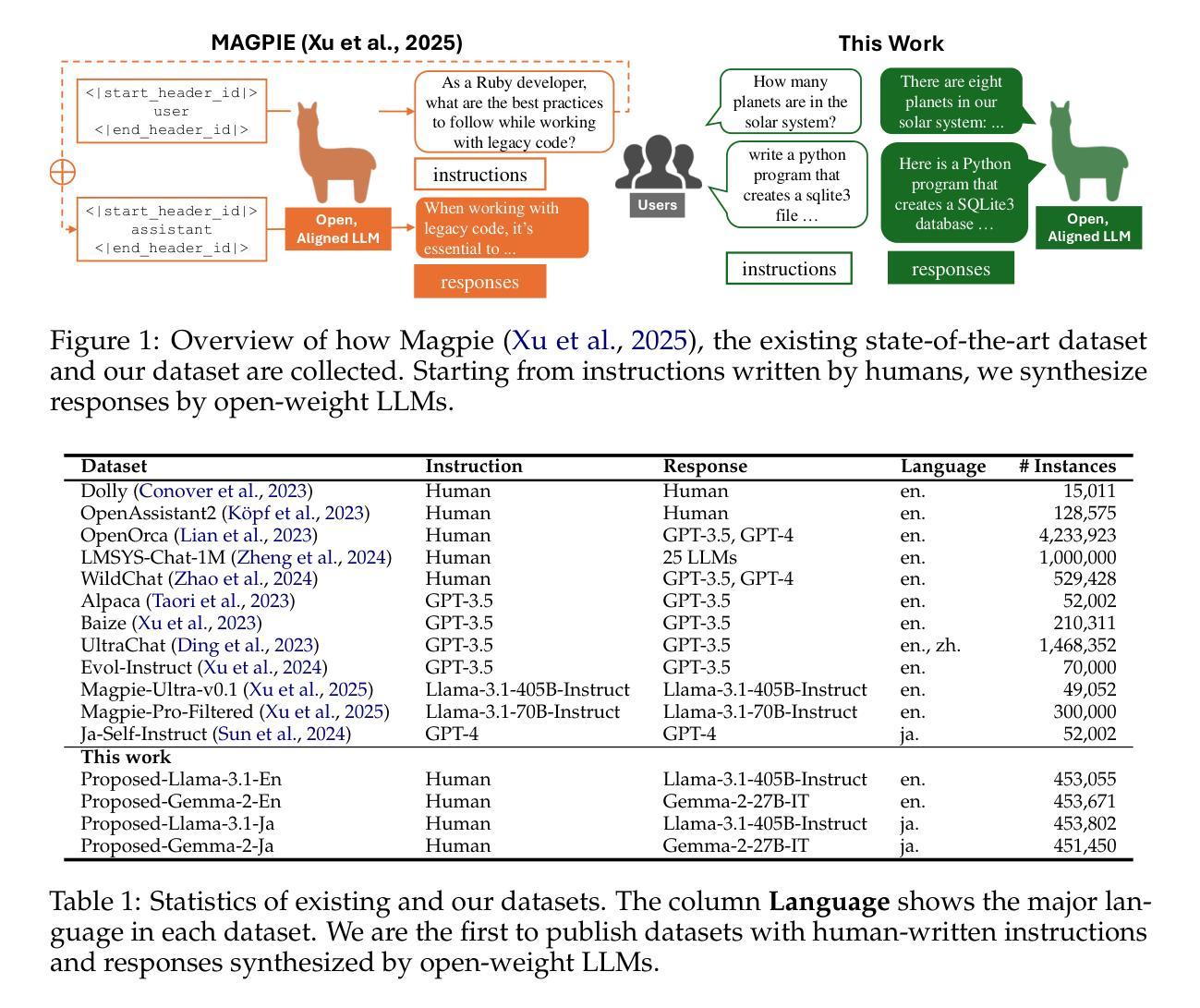
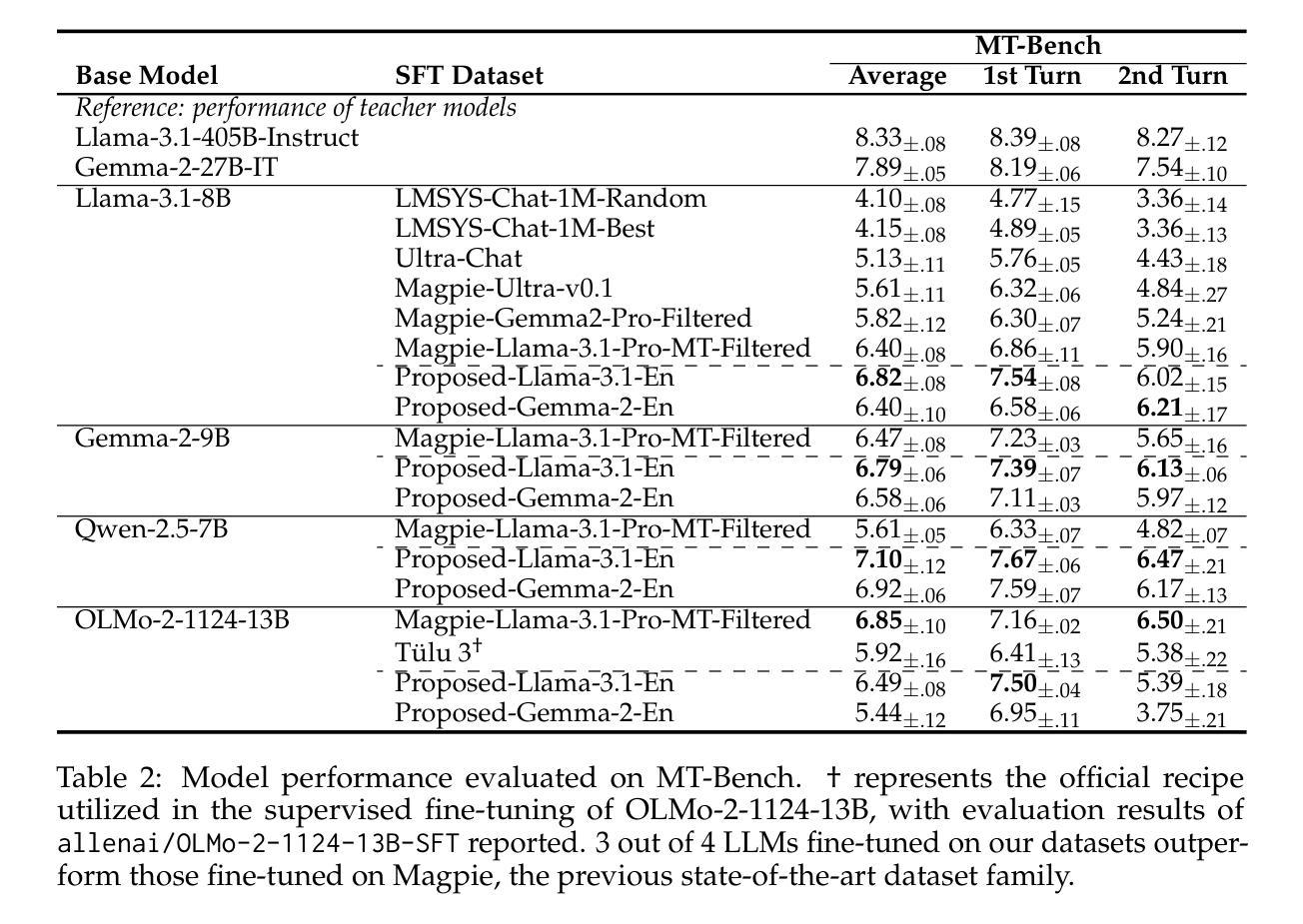
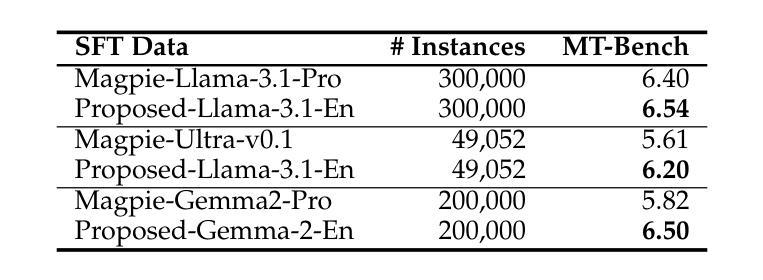
Building Instruction-Tuning Datasets from Human-Written Instructions with Open-Weight Large Language Models
Authors:Youmi Ma, Sakae Mizuki, Kazuki Fujii, Taishi Nakamura, Masanari Ohi, Hinari Shimada, Taihei Shiotani, Koshiro Saito, Koki Maeda, Kakeru Hattori, Takumi Okamoto, Shigeki Ishida, Rio Yokota, Hiroya Takamura, Naoaki Okazaki
Instruction tuning is crucial for enabling Large Language Models (LLMs) to solve real-world tasks. Prior work has shown the effectiveness of instruction-tuning data synthesized solely from LLMs, raising a fundamental question: Do we still need human-originated signals for instruction tuning? This work answers the question affirmatively: we build state-of-the-art instruction-tuning datasets sourced from human-written instructions, by simply pairing them with LLM-generated responses. LLMs fine-tuned on our datasets consistently outperform those fine-tuned on existing ones. Our data construction approach can be easily adapted to other languages; we build datasets for Japanese and confirm that LLMs tuned with our data reach state-of-the-art performance. Analyses suggest that instruction-tuning in a new language allows LLMs to follow instructions, while the tuned models exhibit a notable lack of culture-specific knowledge in that language. The datasets and fine-tuned models will be publicly available. Our datasets, synthesized with open-weight LLMs, are openly distributed under permissive licenses, allowing for diverse use cases.
指令微调对于使大型语言模型(LLM)解决现实世界任务至关重要。先前的工作已经证明了仅通过LLM合成的指令微调数据的有效性,这引发了一个根本问题:我们是否仍然需要人类产生的信号来进行指令微调?这项工作肯定地回答了这个问题:我们通过将人类编写的指令与LLM生成的响应简单配对,建立了最先进的指令微调数据集。在我们数据集上微调的LLM始终优于在现有数据集上微调的LLM。我们的数据构建方法可以轻松地适应其他语言;我们为日语构建了数据集,并确认使用我们的数据调整的LLM达到了最先进的性能。分析表明,在新的语言中进行指令微调可以使LLM遵循指令,而经过调整的模型在该语言的特定文化知识方面表现出明显的缺乏。数据集和经过调整的模型将公开可用。我们的数据集使用公开权重的大型语言模型合成,在许可的许可下公开分发,支持多种用例。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 5 figures
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的指令微调对于解决现实任务至关重要。本研究通过结合人类编写的指令与LLM生成的响应,构建了最先进的指令微调数据集。在这些数据集上微调的LLM性能始终优于在现有数据集上微调的模型。本方法的数据构建方式可轻松适应其他语言,并为日语构建了数据集,验证了使用本数据调教的LLM可达到最先进的性能。分析显示,在新语言中进行指令微调使LLM能够遵循指令,而调教的模型在该语言的文化特定知识方面存在明显的缺乏。数据集和调教模型将公开可用。
Key Takeaways
- 指令微调对LLM解决现实任务至关重要。
- 通过结合人类编写的指令与LLM生成的响应,构建了最先进的指令微调数据集。
- 在此数据集上微调的LLM性能优于现有数据集上的性能。
- 数据构建方式可适应其他语言,例如为日语构建了数据集。
- 使用本数据调教的LLM可达到最先进的性能。
- 在新语言中进行指令微调使LLM能够遵循指令,但存在文化特定知识的缺乏。
点此查看论文截图