⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-04 更新
Foundations and Evaluations in NLP
Authors:Jungyeul Park
This memoir explores two fundamental aspects of Natural Language Processing (NLP): the creation of linguistic resources and the evaluation of NLP system performance. Over the past decade, my work has focused on developing a morpheme-based annotation scheme for the Korean language that captures linguistic properties from morphology to semantics. This approach has achieved state-of-the-art results in various NLP tasks, including part-of-speech tagging, dependency parsing, and named entity recognition. Additionally, this work provides a comprehensive analysis of segmentation granularity and its critical impact on NLP system performance. In parallel with linguistic resource development, I have proposed a novel evaluation framework, the jp-algorithm, which introduces an alignment-based method to address challenges in preprocessing tasks like tokenization and sentence boundary detection (SBD). Traditional evaluation methods assume identical tokenization and sentence lengths between gold standards and system outputs, limiting their applicability to real-world data. The jp-algorithm overcomes these limitations, enabling robust end-to-end evaluations across a variety of NLP tasks. It enhances accuracy and flexibility by incorporating linear-time alignment while preserving the complexity of traditional evaluation metrics. This memoir provides key insights into the processing of morphologically rich languages, such as Korean, while offering a generalizable framework for evaluating diverse end-to-end NLP systems. My contributions lay the foundation for future developments, with broader implications for multilingual resource development and system evaluation.
这篇回忆录探讨了自然语言处理(NLP)的两个基本方面:语言资源的创建和NLP系统性能的评价。过去十年,我的工作主要集中在为韩语开发一种基于词素的标注方案,该方案能够捕捉从形态到语义的语言特性。该方法在各种NLP任务中达到了最新水平,包括词性标注、依存解析和命名实体识别。此外,这项工作还全面分析了分词粒度及其对NLP系统性能的关键影响。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本回忆录探讨了自然语言处理(NLP)的两个基本方面:语言资源的创建和NLP系统性能的评价。作者以过去十年的工作经验为基础,介绍了为韩语开发基于语素的注释方案,该方案在多种NLP任务中取得了最先进的成果,包括词性标注、依存解析和命名实体识别。同时,作者还全面分析了分词粒度对NLP系统性能的关键影响。此外,作者提出了一个新颖的评价框架jp-algorithm,该框架引入了对齐方法,解决了预处理任务中的挑战,如分词和句子边界检测。此回忆录为处理形态丰富的语言(如韩语)提供了关键见解,并为评估多种端到端的NLP系统提供了可推广的框架。
Key Takeaways:
- 作者介绍了其韩语语素注释方案及其在多种NLP任务中的卓越表现。
- 分词粒度对NLP系统性能具有重要影响。
- 作者提出了jp-algorithm评价框架,解决了传统评价方法的局限性。
- jp-algorithm通过引入对齐方法,提高了评估的准确性和灵活性。
- 此回忆录为处理形态丰富的语言提供了重要见解。
- 作者的贡献为未来多语言资源开发和系统评价奠定了基础。
点此查看论文截图

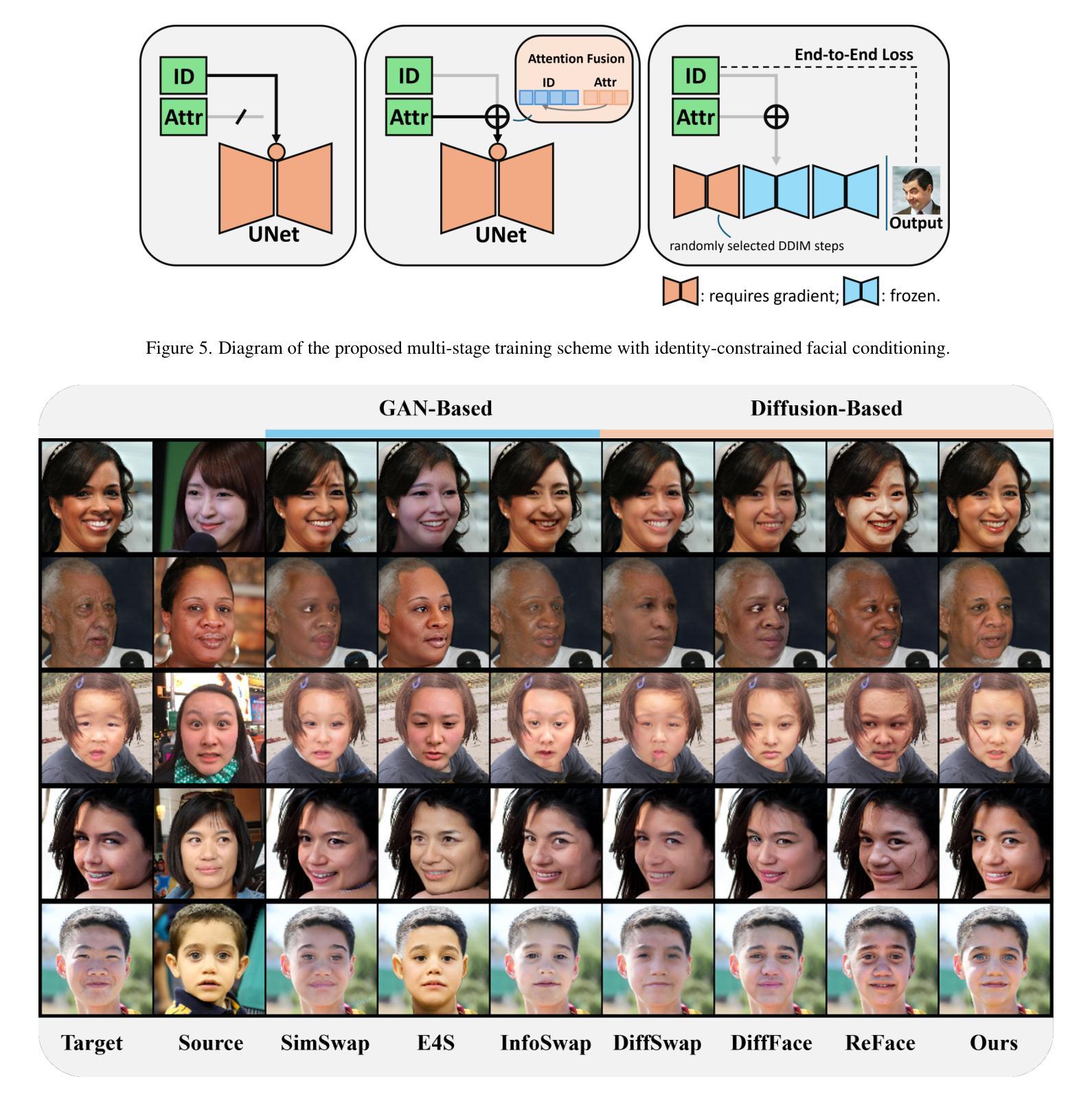
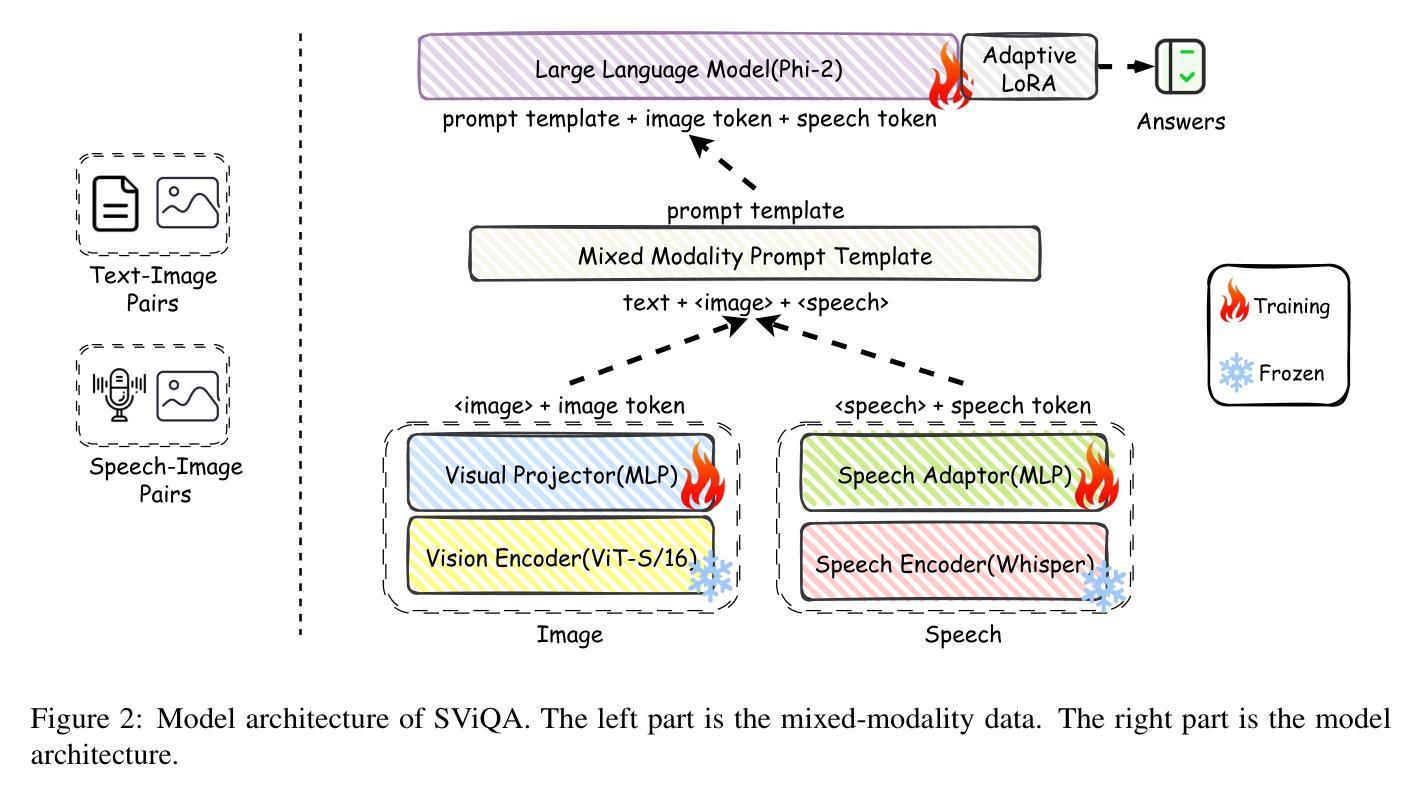
SViQA: A Unified Speech-Vision Multimodal Model for Textless Visual Question Answering
Authors:Bingxin Li
Multimodal models integrating speech and vision hold significant potential for advancing human-computer interaction, particularly in Speech-Based Visual Question Answering (SBVQA) where spoken questions about images require direct audio-visual understanding. Existing approaches predominantly focus on text-visual integration, leaving speech-visual modality gaps underexplored due to their inherent heterogeneity. To this end, we introduce SViQA, a unified speech-vision model that directly processes spoken questions without text transcription. Building upon the LLaVA architecture, our framework bridges auditory and visual modalities through two key innovations: (1) end-to-end speech feature extraction eliminating intermediate text conversion, and (2) cross-modal alignment optimization enabling effective fusion of speech signals with visual content. Extensive experimental results on the SBVQA benchmark demonstrate the proposed SViQA’s state-of-the-art performance, achieving 75.62% accuracy, and competitive multimodal generalization. Leveraging speech-text mixed input boosts performance to 78.85%, a 3.23% improvement over pure speech input, highlighting SViQA’s enhanced robustness and effective cross-modal attention alignment.
多模态模型集成了语音和视觉,在推进人机交互方面拥有巨大潜力,特别是在基于语音的视觉问答(SBVQA)中,关于图像的口语问题需要直接音视频的感知。现有方法主要集中在文本视觉集成上,由于内在异质性导致语音视觉模态差距尚未得到充分探索。为此,我们引入了SViQA,这是一个统一的语音视觉模型,可以直接处理口语问题而无需文本转录。我们的框架建立在LLaVA架构之上,通过两个关键创新点桥梁听觉和视觉模式:(1)端到端的语音特征提取消除了中间文本转换,以及(2)跨模态对齐优化,使语音信号与视觉内容的融合有效。在SBVQA基准测试上的大量实验结果表明,所提出的SViQA具有最先进的性能,达到了75.62%的准确率,并且在多模态推广方面具有竞争力。利用语音文本混合输入将性能提高到78.85%,相较于纯语音输入提高了3.23%,突显了SViQA增强的稳健性和有效的跨模态注意力对齐。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了SViQA模型在多模态语音识别和视觉问答(SBVQA)方面的应用。该模型直接处理语音问题,无需文本转录,通过两个关键创新点——端到端的语音特征提取和跨模态对齐优化,实现了对语音信号与视觉内容的融合。实验结果证明了SViQA模型在SBVQA上的先进性能和对多模态推广的竞争力。混合使用语音和文字输入能进一步提高模型性能。
Key Takeaways
- SViQA模型将语音识别与视觉整合在一个统一框架内,可直接处理语音问题而无需文本转录。
- 通过两个关键创新实现了语音信号与视觉内容的融合:端到端的语音特征提取和跨模态对齐优化。
- 实验结果展示了SViQA在SBVQA上的卓越性能,达到了75.62%的准确率。
- 当使用混合语音和文字输入时,SViQA的性能提升到78.85%,显示出其在跨模态注意力对齐方面的优势。
点此查看论文截图
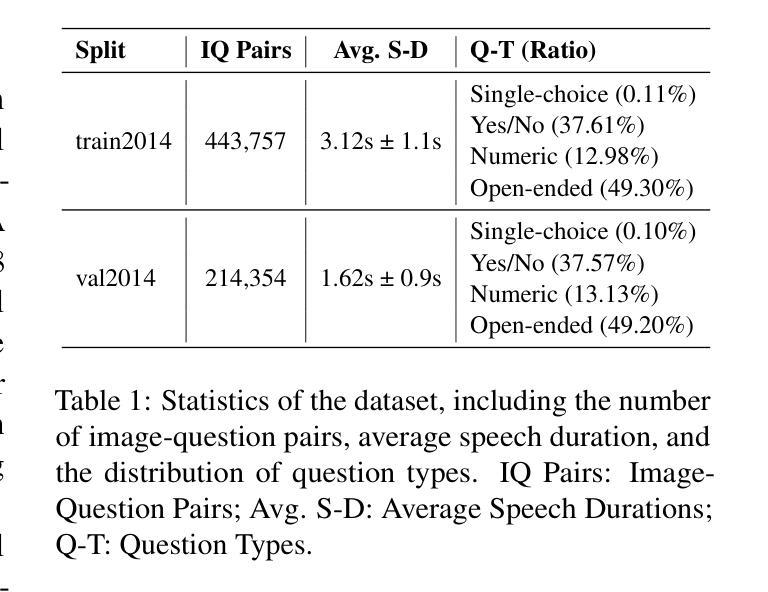

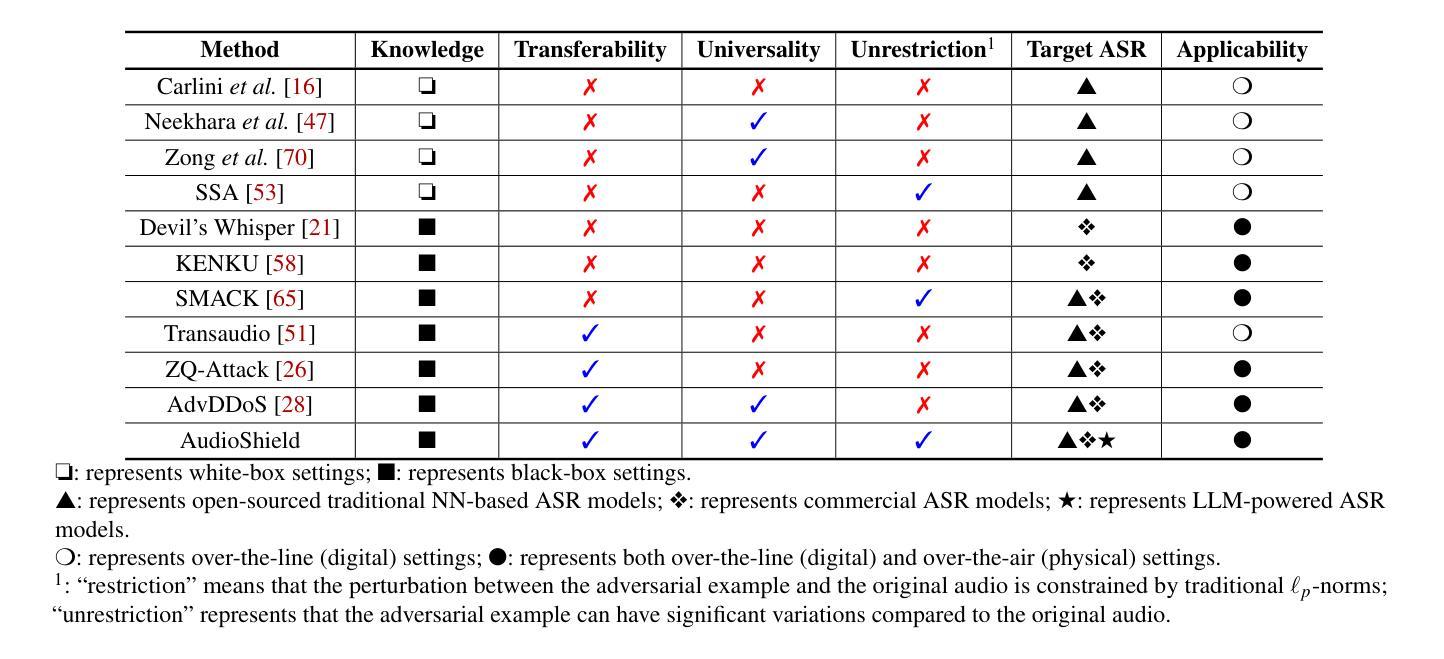
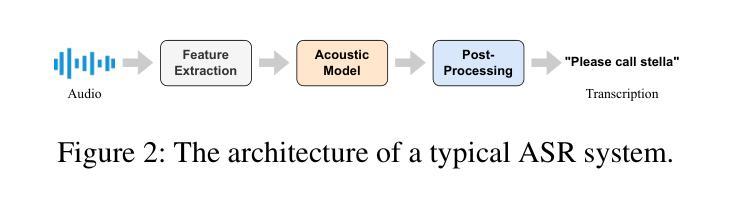
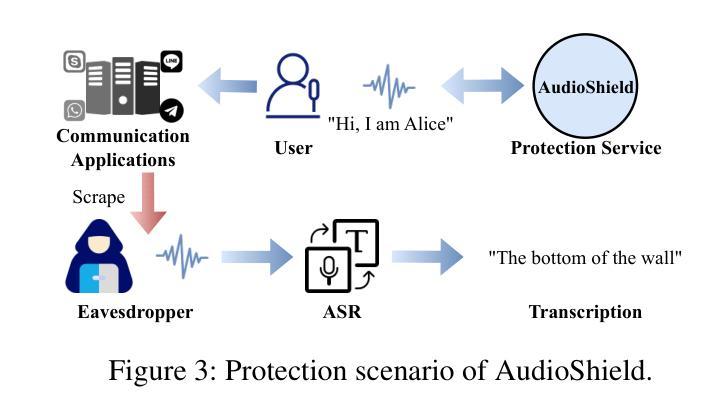
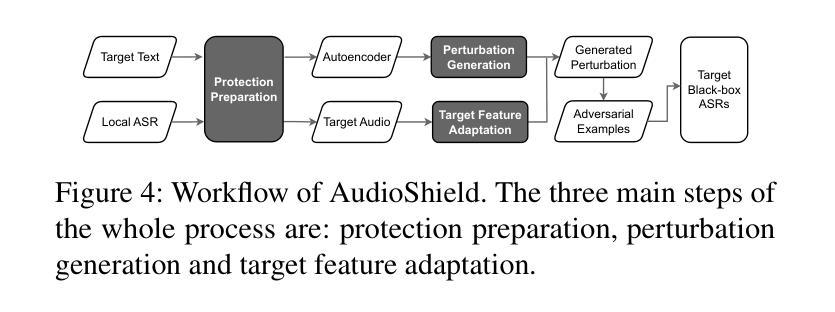
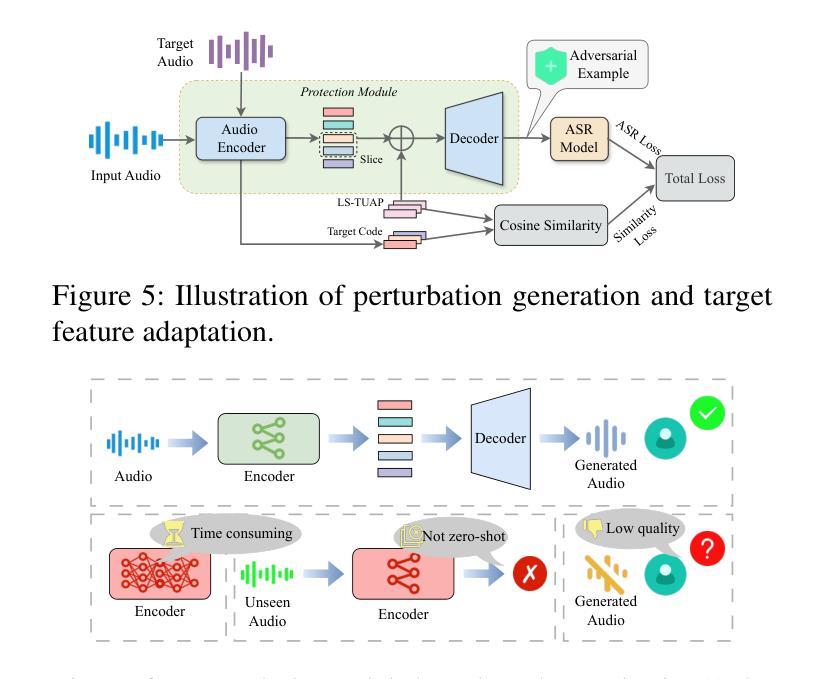
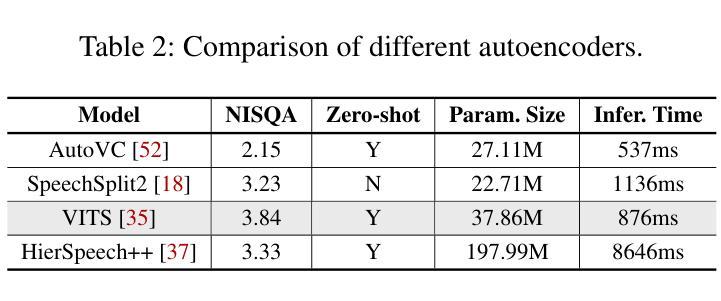
Whispering Under the Eaves: Protecting User Privacy Against Commercial and LLM-powered Automatic Speech Recognition Systems
Authors:Weifei Jin, Yuxin Cao, Junjie Su, Derui Wang, Yedi Zhang, Minhui Xue, Jie Hao, Jin Song Dong, Yixian Yang
The widespread application of automatic speech recognition (ASR) supports large-scale voice surveillance, raising concerns about privacy among users. In this paper, we concentrate on using adversarial examples to mitigate unauthorized disclosure of speech privacy thwarted by potential eavesdroppers in speech communications. While audio adversarial examples have demonstrated the capability to mislead ASR models or evade ASR surveillance, they are typically constructed through time-intensive offline optimization, restricting their practicality in real-time voice communication. Recent work overcame this limitation by generating universal adversarial perturbations (UAPs) and enhancing their transferability for black-box scenarios. However, they introduced excessive noise that significantly degrades audio quality and affects human perception, thereby limiting their effectiveness in practical scenarios. To address this limitation and protect live users’ speech against ASR systems, we propose a novel framework, AudioShield. Central to this framework is the concept of Transferable Universal Adversarial Perturbations in the Latent Space (LS-TUAP). By transferring the perturbations to the latent space, the audio quality is preserved to a large extent. Additionally, we propose target feature adaptation to enhance the transferability of UAPs by embedding target text features into the perturbations. Comprehensive evaluation on four commercial ASR APIs (Google, Amazon, iFlytek, and Alibaba), three voice assistants, two LLM-powered ASR and one NN-based ASR demonstrates the protection superiority of AudioShield over existing competitors, and both objective and subjective evaluations indicate that AudioShield significantly improves the audio quality. Moreover, AudioShield also shows high effectiveness in real-time end-to-end scenarios, and demonstrates strong resilience against adaptive countermeasures.
自动语音识别(ASR)的广泛应用支持大规模语音监控,引发了用户对于隐私的担忧。本文专注于使用对抗性样本减轻语音通信中潜在窃听者擅自泄露语音隐私的问题。虽然音频对抗性样本已展现出干扰ASR模型或躲避ASR监控的能力,但它们通常是通过耗时的离线优化构建的,这限制了它们在实时语音通信中的实用性。最近的工作通过生成通用对抗性扰动(UAPs)并提高其针对黑箱场景的迁移性来克服这一限制。然而,它们引入了过多的噪声,显著降低了音频质量并影响了人类感知,从而限制了它们在实际情况中的有效性。为了解决这一限制并保护实时用户的语音免受ASR系统的影响,我们提出了新型框架AudioShield。该框架的核心概念是潜在空间中的可迁移通用对抗性扰动(LS-TUAP)。通过将扰动转移到潜在空间,可以在很大程度上保留音频质量。此外,我们通过将目标文本特征嵌入到扰动中,提出了目标特征适应方法来增强UAPs的迁移性。对四个商业ASR API(Google、Amazon、iFlytek和Alibaba)、三个语音助手、两个基于大型语言模型的ASR和一个基于神经网络的ASR的全面评估表明,AudioShield的保护性能优于现有竞争对手。客观和主观评估均表明,AudioShield显著提高了音频质量。此外,AudioShield在实时端到端场景中表现出高有效性,并对自适应对策表现出强烈抗性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accept to USENIX Security 2025
摘要
本文主要关注自动语音识别(ASR)在语音通信中对隐私的挑战,并提出了一种新型框架AudioShield,通过利用潜伏空间中的可转移通用对抗扰动(LS-TUAP)来生成音频对抗实例以保护用户实时语音免受ASR系统的侵犯。该方法不仅保护了音频质量,还提高了UAP的迁移性。通过嵌入目标文本特征到扰动中,进一步增强了UAP的迁移性。对现有商业ASR API和语音助手系统的全面评估表明,AudioShield的保护性能优于现有竞品,并在音频质量和保护能力方面取得显著进步。同时,AudioShield在实际场景中表现良好,对自适应对策具有强大的韧性。
关键见解
- 自动语音识别(ASR)的大规模应用引发了关于语音隐私泄露的担忧。
- 对抗实例可用于防止未经授权的语音隐私泄露。
- AudioShield框架使用潜伏空间中的可转移通用对抗扰动(LS-TUAP)来保护实时语音隐私。
- AudioShield通过保留音频质量并嵌入目标文本特征来提高UAP的迁移性。
- AudioShield在多个ASR系统和语音助手上的评估表现优于其他竞争对手。
- AudioShield既有效保护了音频质量,也提高了语音隐私保护能力。
点此查看论文截图

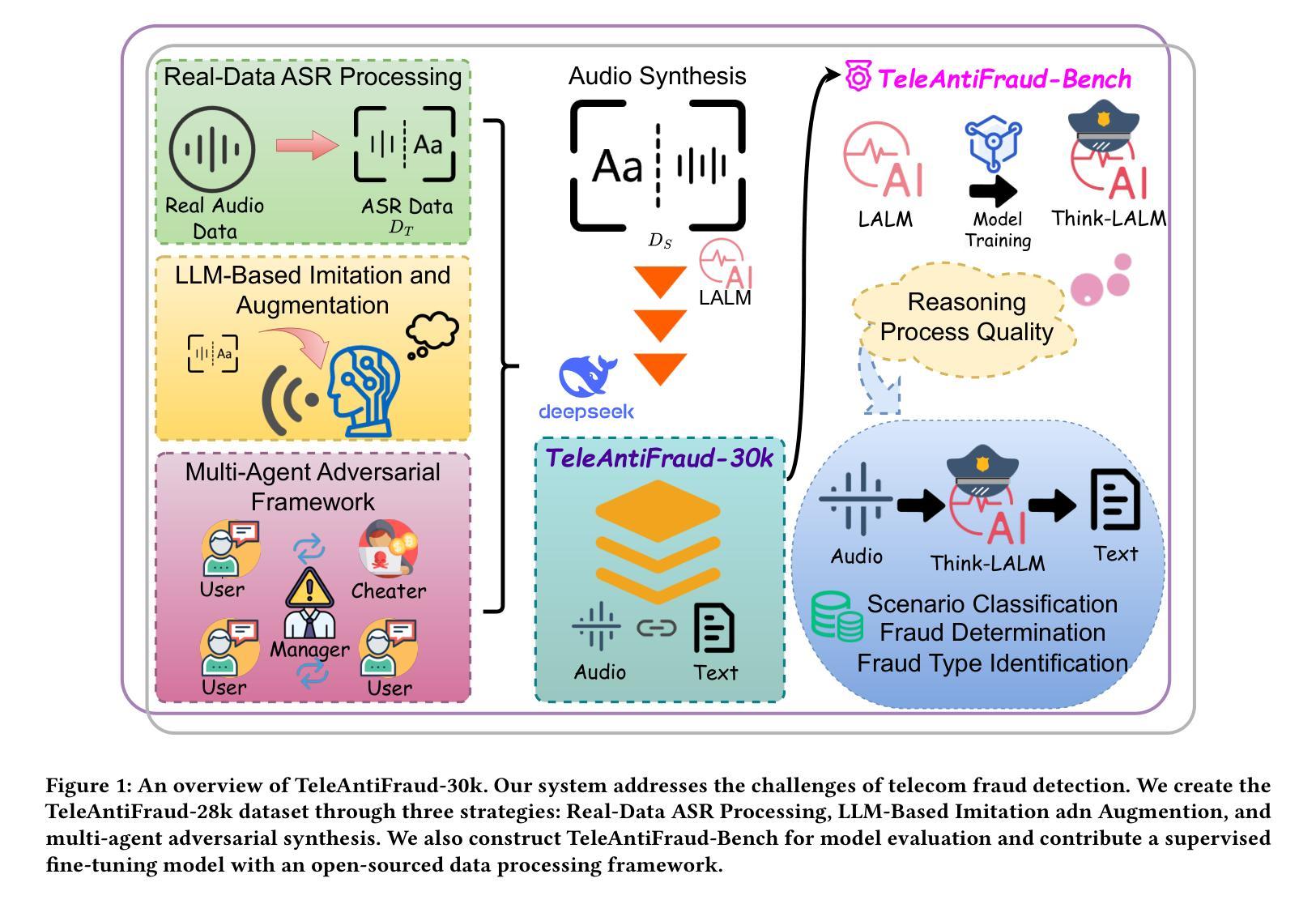
TeleAntiFraud-28k: An Audio-Text Slow-Thinking Dataset for Telecom Fraud Detection
Authors:Zhiming Ma, Peidong Wang, Minhua Huang, Jingpeng Wang, Kai Wu, Xiangzhao Lv, Yachun Pang, Yin Yang, Wenjie Tang, Yuchen Kang
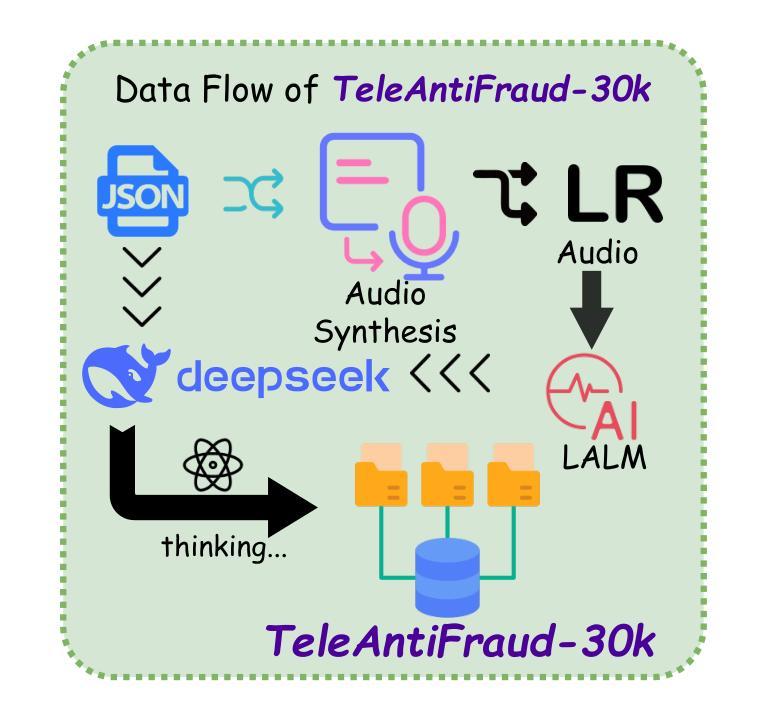
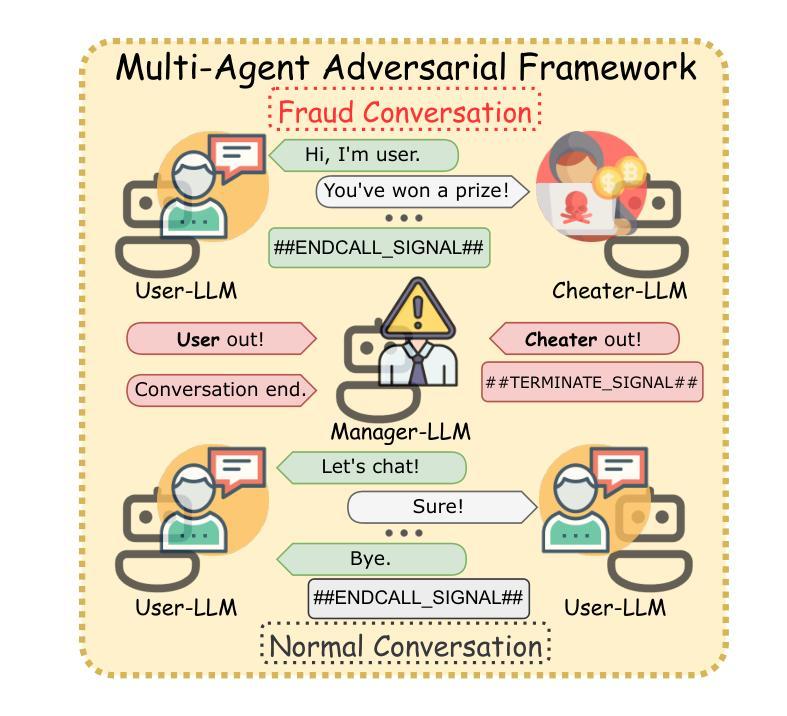
The detection of telecom fraud faces significant challenges due to the lack of high-quality multimodal training data that integrates audio signals with reasoning-oriented textual analysis. To address this gap, we present TeleAntiFraud-28k, the first open-source audio-text slow-thinking dataset specifically designed for automated telecom fraud analysis. Our dataset is constructed through three strategies: (1) Privacy-preserved text-truth sample generation using automatically speech recognition (ASR)-transcribed call recordings (with anonymized original audio), ensuring real-world consistency through text-to-speech (TTS) model regeneration; (2) Semantic enhancement via large language model (LLM)-based self-instruction sampling on authentic ASR outputs to expand scenario coverage; (3) Multi-agent adversarial synthesis that simulates emerging fraud tactics through predefined communication scenarios and fraud typologies. The generated dataset contains 28,511 rigorously processed speech-text pairs, complete with detailed annotations for fraud reasoning. The dataset is divided into three tasks: scenario classification, fraud detection, fraud type classification. Furthermore, we construct TeleAntiFraud-Bench, a standardized evaluation benchmark comprising proportionally sampled instances from the dataset, to facilitate systematic testing of model performance on telecom fraud detection tasks. We also contribute a production-optimized supervised fine-tuning (SFT) model trained on hybrid real/synthetic data, while open-sourcing the data processing framework to enable community-driven dataset expansion. This work establishes a foundational framework for multimodal anti-fraud research while addressing critical challenges in data privacy and scenario diversity. The project will be released at https://github.com/JimmyMa99/TeleAntiFraud.
电信欺诈检测面临着巨大的挑战,主要是由于缺乏高质量的多模式训练数据,无法将音频信号与面向推理的文本分析相结合。为了解决这一空白,我们推出了TeleAntiFraud-28k,这是专门为电信欺诈自动化分析设计的第一个开源音频文本慢思考数据集。我们的数据集通过以下三种策略构建:(1)使用自动语音识别(ASR)转录的通话录音生成隐私保护文本真实样本(带有匿名原始音频),并通过文本到语音(TTS)模型再生确保现实世界的一致性;(2)通过基于大型语言模型(LLM)的自我指令采样对真实的ASR输出进行语义增强,以扩大场景覆盖;(3)模拟新兴欺诈策略的多代理对抗合成,通过预定的通信场景和欺诈类型。生成的数据集包含经过严格处理的28511个语音文本对,带有详细的欺诈推理注释。数据集分为三个任务:场景分类、欺诈检测、欺诈类型分类。此外,我们构建了TeleAntiFraud-Bench,一个标准化的评估基准,其中包含从数据集中按比例采样的实例,以促进电信欺诈检测任务上模型性能的系统测试。我们还为混合真实/合成数据训练的生产优化监督微调(SFT)模型做出了贡献,同时开源数据处理框架,以实现社区驱动的数据集扩展。这项工作为多媒体反欺诈研究建立了基础框架,同时解决了数据隐私和场景多样性方面的关键挑战。该项目将在https://github.com/JimmyMa99/TeleAntiFraud发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了针对电信欺诈检测领域所面临的挑战,提出了一种新的开源音频文本慢思考数据集TeleAntiFraud-28k。该数据集通过三种策略构建,包括隐私保护文本真实样本生成、语义增强以及多代理对抗合成。数据集包含28,511个经过严格处理的语音文本对,带有详细的欺诈推理注释,分为场景分类、欺诈检测和欺诈类型分类三个任务。同时,文章还介绍了TeleAntiFraud-Bench评估基准的构建,以及使用混合真实/合成数据训练的优化监督微调模型。该研究为多媒体抗欺诈研究提供了基础框架,并解决了数据隐私和场景多样性等关键挑战。
Key Takeaways
- TeleAntiFraud-28k是专门为电信欺诈分析设计的首个开源音频文本慢思考数据集。
- 数据集通过隐私保护的文本真实样本生成、语义增强和多代理对抗合成三种策略构建。
- 数据集包含28,511个语音文本对,带有详细的欺诈推理注释,分为场景分类、欺诈检测和欺诈类型分类三个任务。
- 介绍了TeleAntiFraud-Bench评估基准的构建,以系统化测试电信欺诈检测任务的模型性能。
- 公开了一个优化监督微调模型,该模型使用混合真实/合成数据进行训练。
- 研究为多媒体抗欺诈研究提供了基础框架。
点此查看论文截图

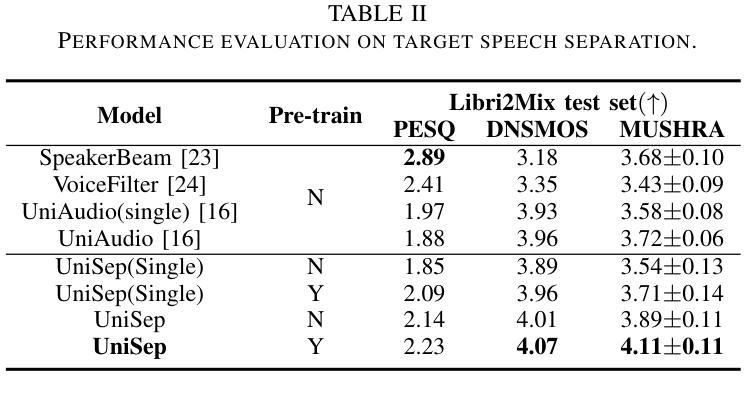
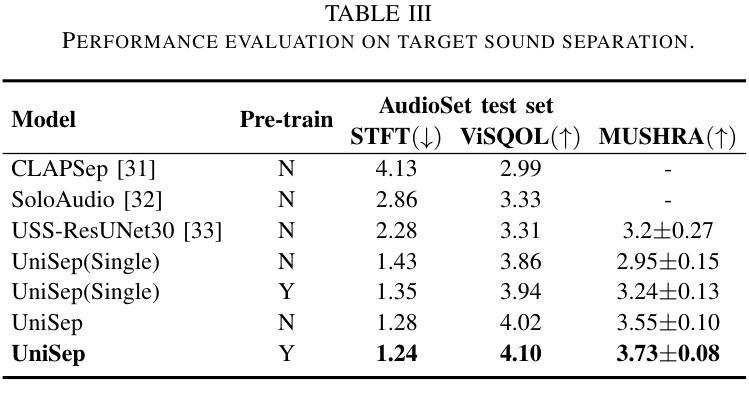
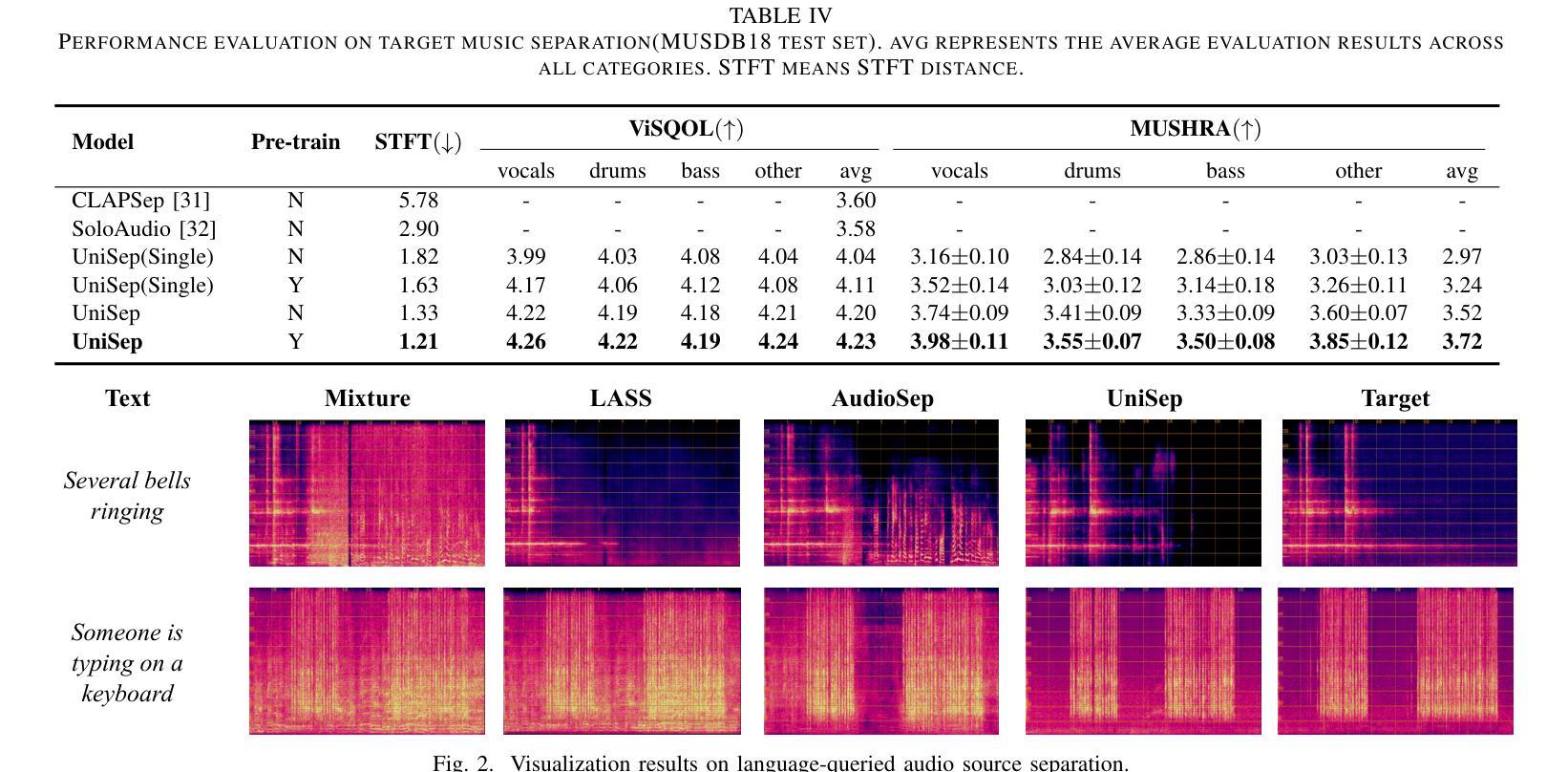
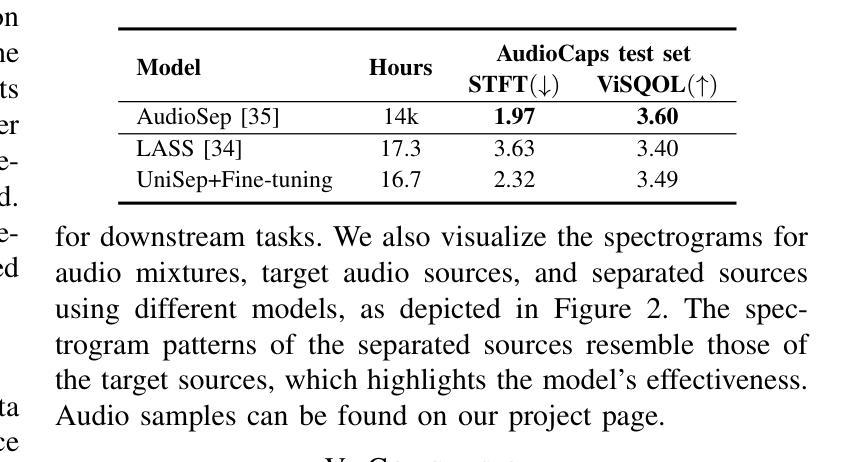
UniSep: Universal Target Audio Separation with Language Models at Scale
Authors:Yuanyuan Wang, Hangting Chen, Dongchao Yang, Weiqin Li, Dan Luo, Guangzhi Li, Shan Yang, Zhiyong Wu, Helen Meng, Xixin Wu
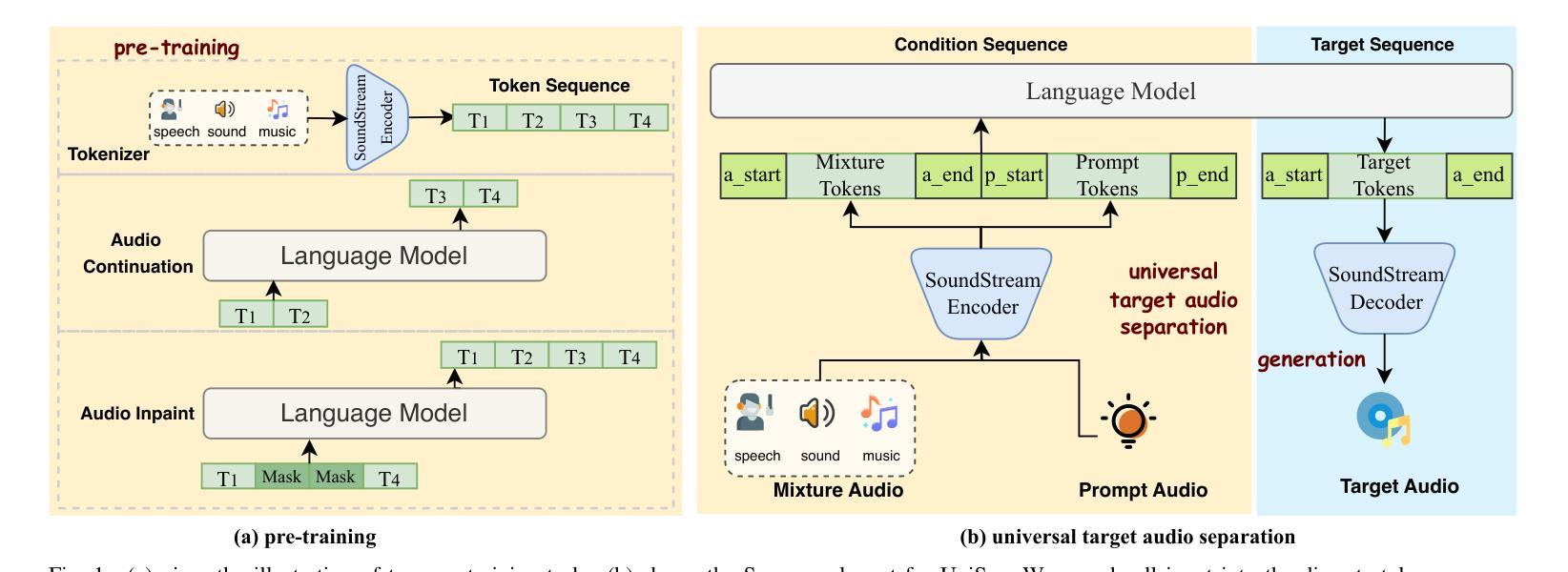
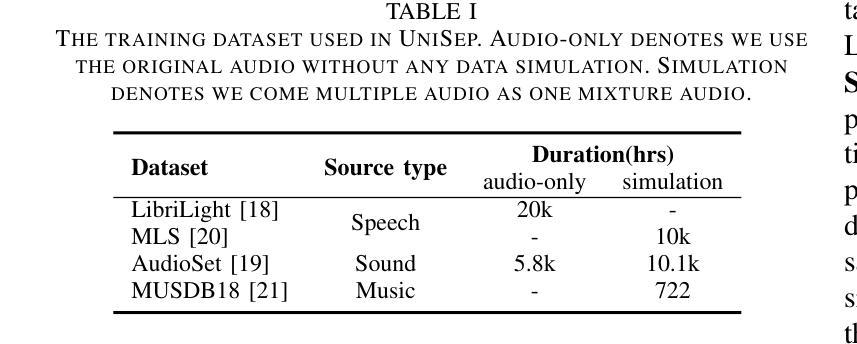
We propose Universal target audio Separation (UniSep), addressing the separation task on arbitrary mixtures of different types of audio. Distinguished from previous studies, UniSep is performed on unlimited source domains and unlimited source numbers. We formulate the separation task as a sequence-to-sequence problem, and a large language model (LLM) is used to model the audio sequence in the discrete latent space, leveraging the power of LLM in handling complex mixture audios with large-scale data. Moreover, a novel pre-training strategy is proposed to utilize audio-only data, which reduces the efforts of large-scale data simulation and enhances the ability of LLMs to understand the consistency and correlation of information within audio sequences. We also demonstrate the effectiveness of scaling datasets in an audio separation task: we use large-scale data (36.5k hours), including speech, music, and sound, to train a universal target audio separation model that is not limited to a specific domain. Experiments show that UniSep achieves competitive subjective and objective evaluation results compared with single-task models.
我们提出了通用目标音频分离(UniSep),解决了不同类型音频的任意混合分离任务。与以前的研究不同,UniSep适用于无限的源域和无限的源数量。我们将分离任务制定为序列到序列的问题,并使用大型语言模型(LLM)对离散潜在空间中的音频序列进行建模,利用LLM在处理复杂混合音频和大规模数据方面的强大功能。此外,我们提出了一种新的预训练策略,只使用音频数据,这减少了大规模数据模拟的努力,增强了LLM理解音频序列内信息一致性和关联性的能力。我们还展示了在音频分离任务中扩大数据集的有效性:我们使用大规模数据(36.5k小时),包括语音、音乐和声音,来训练一个通用的目标音频分离模型,该模型不受特定领域的限制。实验表明,与单任务模型相比,UniSep在主观和客观评估方面都取得了具有竞争力的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICME 2025
Summary
本文提出了Universal目标音频分离(UniSep)方法,解决了不同类型音频的任意混合分离任务。该方法在不限源域和不限源数量的情况下执行分离任务。将分离任务公式化为序列到序列的问题,并使用大型语言模型(LLM)在离散潜在空间中对音频序列进行建模。此外,提出了一种新的预训练策略,利用纯音频数据来降低大规模数据模拟的努力并增强LLM对音频序列中信息的一致性和关联性的理解。实验证明,UniSep在多数据集训练下的效果出色,与单任务模型相比取得了有竞争力的主观和客观评价结果。
Key Takeaways
- UniSep解决了不同类型音频的任意混合分离任务,适用于无限源域和无限源数量。
- 采用序列到序列的公式化方法处理音频分离任务。
- 利用大型语言模型(LLM)在离散潜在空间中对音频序列建模。
- 提出了一种新的预训练策略,利用纯音频数据增强LLM对音频信息的理解。
- 通过使用大规模数据(包括语音、音乐和声音)训练通用目标音频分离模型,不局限于特定领域。
- 实验表明,UniSep在主观和客观评价方面表现出竞争力。
点此查看论文截图

Whisper-LM: Improving ASR Models with Language Models for Low-Resource Languages
Authors:Xabier de Zuazo, Eva Navas, Ibon Saratxaga, Inma Hernáez Rioja
Automatic speech recognition systems have undoubtedly advanced with the integration of multilingual and multitask models such as Whisper, which have shown a promising ability to understand and process speech across a wide range of languages. Despite their robustness, these models often fall short in handling the linguistic distinctions of minority languages. This study addresses this gap by integrating traditional and novel language models with fine-tuned Whisper models to raise their performance in less commonly studied languages. Through rigorous fine-tuning and evaluation across multiple datasets, we demonstrate substantial improvements in word error rate, particularly in low-resource scenarios. Our approach not only does take advantage of the extensive data Whisper was pre-trained on, but also complements its linguistic adaptability by incorporating language models. We obtained improvements up to 51% for in-distribution datasets and up to 34% for out-of-distribution sentences using statistical language models, while large language models provided moderate but consistently robust improvement across diverse linguistic contexts. The findings reveal that, while the integration reliably benefits all model sizes, the extent of improvement varies, highlighting the importance of optimized language model parameters. Finally, we emphasize the importance of selecting appropriate evaluation parameters when reporting the results using transformer-based ASR models. In summary, this research clears the way for more inclusive ASR technologies that perform better across languages by enriching their linguistic knowledge. For further implementation details of this study, the technical documentation and source code are available at http://www.github.com/hitz-zentroa/whisper-lm.
自动语音识别系统无疑已通过整合如whisper等多语言和多任务模型,在理解和处理广泛语言方面表现出了令人瞩目的能力。尽管这些模型具有稳健性,但在处理少数语言的语言差异方面往往表现不足。本研究通过整合传统和新型语言模型与微调过的whisper模型,来解决这一差距,以提高其在较少研究的语言中的性能。通过多个数据集的严格微调与评估,我们证明了在单词错误率方面的显著改进,特别是在资源匮乏的场景下。我们的方法不仅利用了whisper预训练所依赖的大量数据,而且通过融入语言模型来补充其语言适应性。我们在使用统计语言模型的情况下,对内部数据集改进了高达51%,对外部句子改进了高达32%,而大型语言模型在不同的语言环境中提供了适度的但始终稳定的改进。研究结果表明,虽然整合对所有模型规模都有可靠的好处,但改进程度有所不同,这强调了优化语言模型参数的重要性。最后,我们强调了在使用基于变压器的ASR模型报告结果时,选择适当的评估参数的重要性。总之,本研究为开发更具包容性的ASR技术铺平了道路,这些技术通过丰富其语言知识,在跨语言方面表现更好。有关本研究的进一步实施细节,技术文档和源代码可在http://www.github.com/hitz-zentroa/whisper-lm处获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 26 pages, 6 figures, includes supplementary materials. Will be submitted to IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing
Summary
本文研究了自动语音识别系统(ASR)在处理少数语言时的局限性,并探讨了通过集成传统和新型语言模型来提高预训练whisper模型性能的可行性。研究结果表明,整合模型显著提高了单词错误率,特别是在资源有限的情况下。该研究为增强ASR技术的语言适应性并提高其跨语言的性能开辟了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 多语言多任务模型如Whisper能理解和处理多种语言的语音。
- 在处理少数语言时,现有模型如Whisper可能存在局限性。
- 通过整合传统和新型语言模型,可以提高whisper模型的性能。
- 整合模型在多个数据集上的严格精细调整和评价显示,单词错误率显著提高。
- 在资源有限的情况下,改进尤为显著。
- 大型语言模型在多种语言环境下提供了稳健但适中的改进。
点此查看论文截图

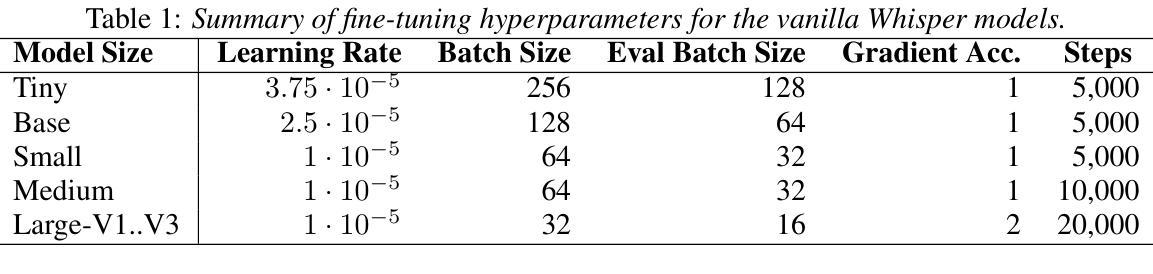
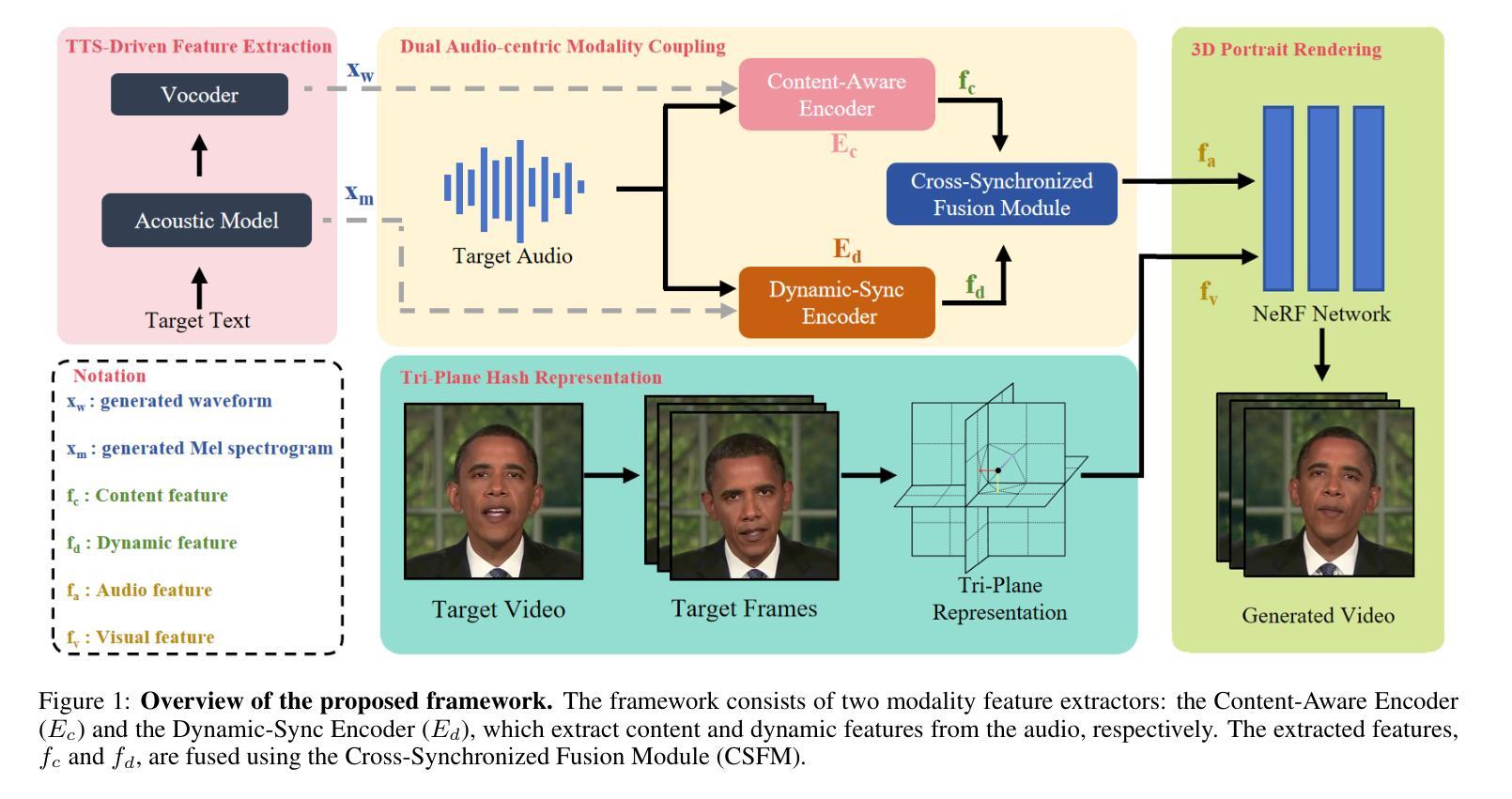
Dual Audio-Centric Modality Coupling for Talking Head Generation
Authors:Ao Fu, Ziqi Ni, Yi Zhou
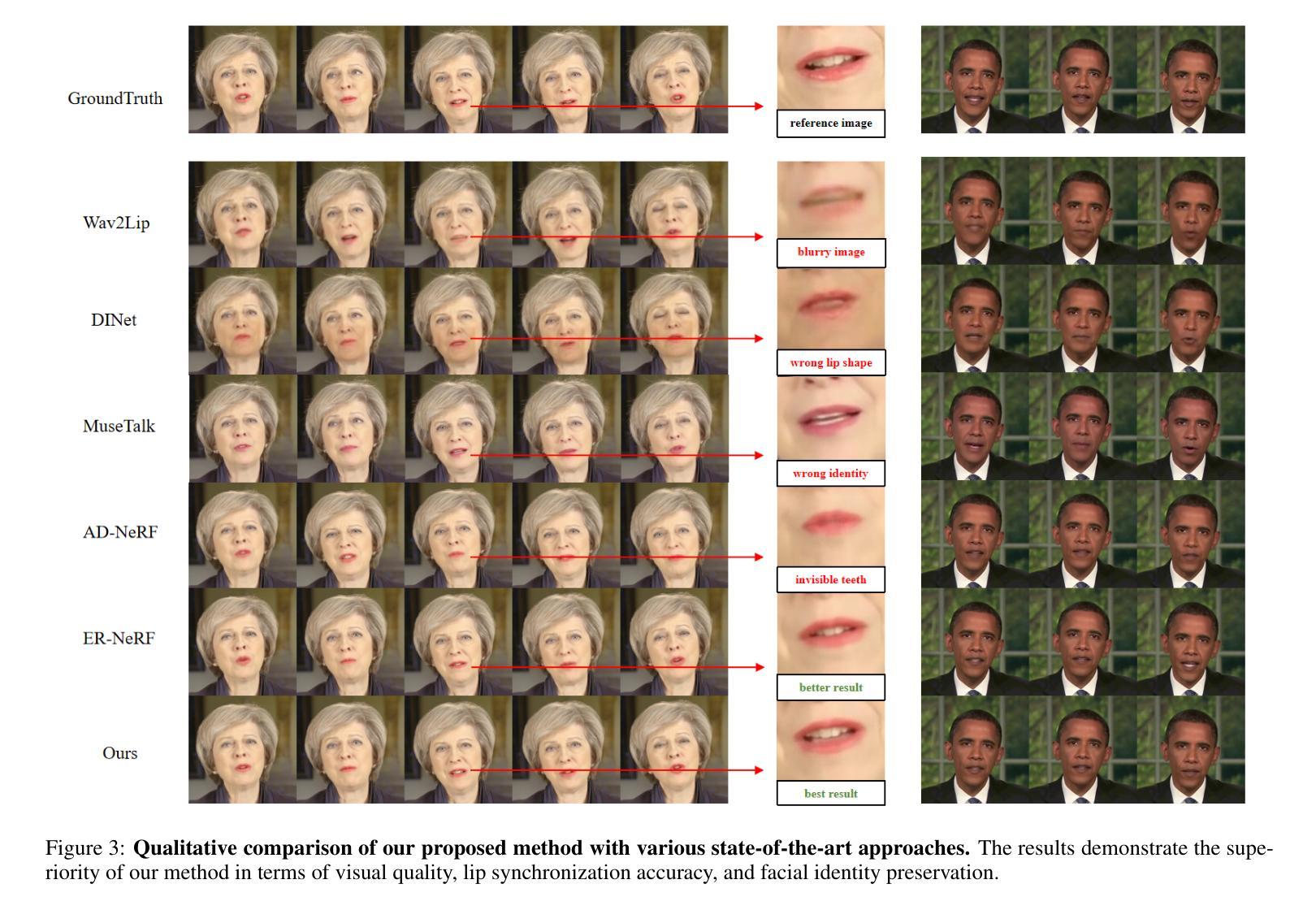
The generation of audio-driven talking head videos is a key challenge in computer vision and graphics, with applications in virtual avatars and digital media. Traditional approaches often struggle with capturing the complex interaction between audio and facial dynamics, leading to lip synchronization and visual quality issues. In this paper, we propose a novel NeRF-based framework, Dual Audio-Centric Modality Coupling (DAMC), which effectively integrates content and dynamic features from audio inputs. By leveraging a dual encoder structure, DAMC captures semantic content through the Content-Aware Encoder and ensures precise visual synchronization through the Dynamic-Sync Encoder. These features are fused using a Cross-Synchronized Fusion Module (CSFM), enhancing content representation and lip synchronization. Extensive experiments show that our method outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches in key metrics such as lip synchronization accuracy and image quality, demonstrating robust generalization across various audio inputs, including synthetic speech from text-to-speech (TTS) systems. Our results provide a promising solution for high-quality, audio-driven talking head generation and present a scalable approach for creating realistic talking heads.
音频驱动的说话人头部视频生成是计算机视觉和图形学领域的关键挑战,在虚拟化身和数字媒体中有广泛的应用。传统的方法往往难以捕捉音频和面部动态之间的复杂交互,导致唇同步和视觉质量问题。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于NeRF的新型框架——双音频中心模态耦合(DAMC),它有效地整合了来自音频输入的内容和动态特征。通过利用双编码器结构,DAMC通过内容感知编码器捕获语义内容,并通过动态同步编码器确保精确的视觉同步。这些特征使用跨同步融合模块(CSFM)进行融合,增强了内容表示和唇同步。大量实验表明,我们的方法在唇同步准确性和图像质量等关键指标上优于现有的最先进的方法,展示了在各种音频输入上的稳健泛化能力,包括来自文本到语音(TTS)系统的合成语音。我们的结果为高质量音频驱动的说话人头部生成提供了有前景的解决方案,并展示了一种创建逼真说话人头部的可扩展方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 4 figures
Summary
音频驱动的人头动画生成是计算机视觉和图形学领域的关键挑战,应用于虚拟角色和数字媒体。传统方法难以捕捉音频与面部动态的复杂交互,导致唇部同步和视觉质量问题。本文提出基于NeRF的双音频中心模态耦合(DAMC)框架,有效整合音频输入的内容和动态特征。通过双编码器结构,DAMC通过内容感知编码器捕捉语义内容,并通过动态同步编码器确保精确视觉同步。这些特征通过交叉同步融合模块(CSFM)融合,提高内容表达和唇部同步。实验表明,该方法在唇部同步准确性和图像质量等关键指标上优于现有先进方法,并在各种音频输入上表现出强大的泛化能力,包括文本到语音(TTS)系统的合成语音。
Key Takeaways
- 音频驱动的人头动画生成是计算机视觉和图形领域的重要挑战,具有广泛的应用于虚拟角色和数字媒体。
- 传统方法难以捕捉音频与面部动态的复杂交互,导致唇部同步和视觉质量问题。
- 本文提出了一个基于NeRF的双音频中心模态耦合(DAMC)框架来解决这个问题。
- DAMC通过内容感知编码器和动态同步编码器有效整合音频输入的内容和动态特征。
- 通过交叉同步融合模块(CSFM)融合内容和动态特征,提高内容表达和唇部同步。
- 实验表明,DAMC在关键指标上优于现有方法,如唇部同步准确性和图像质量。
点此查看论文截图

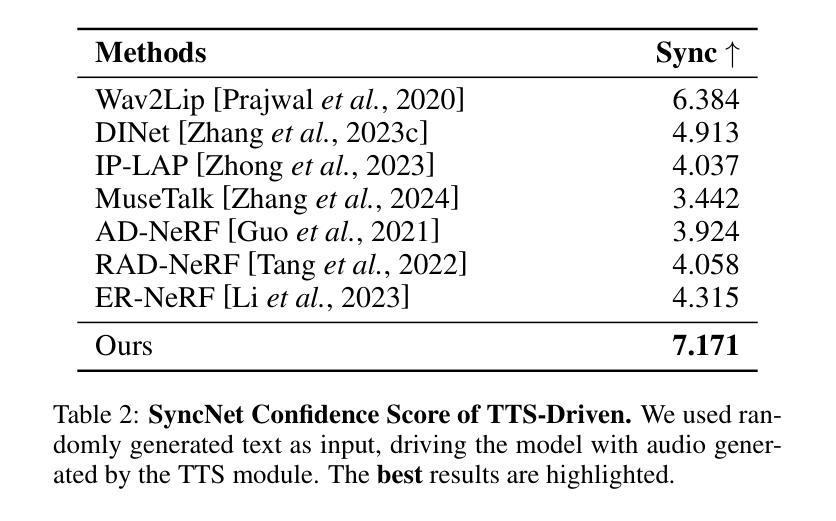

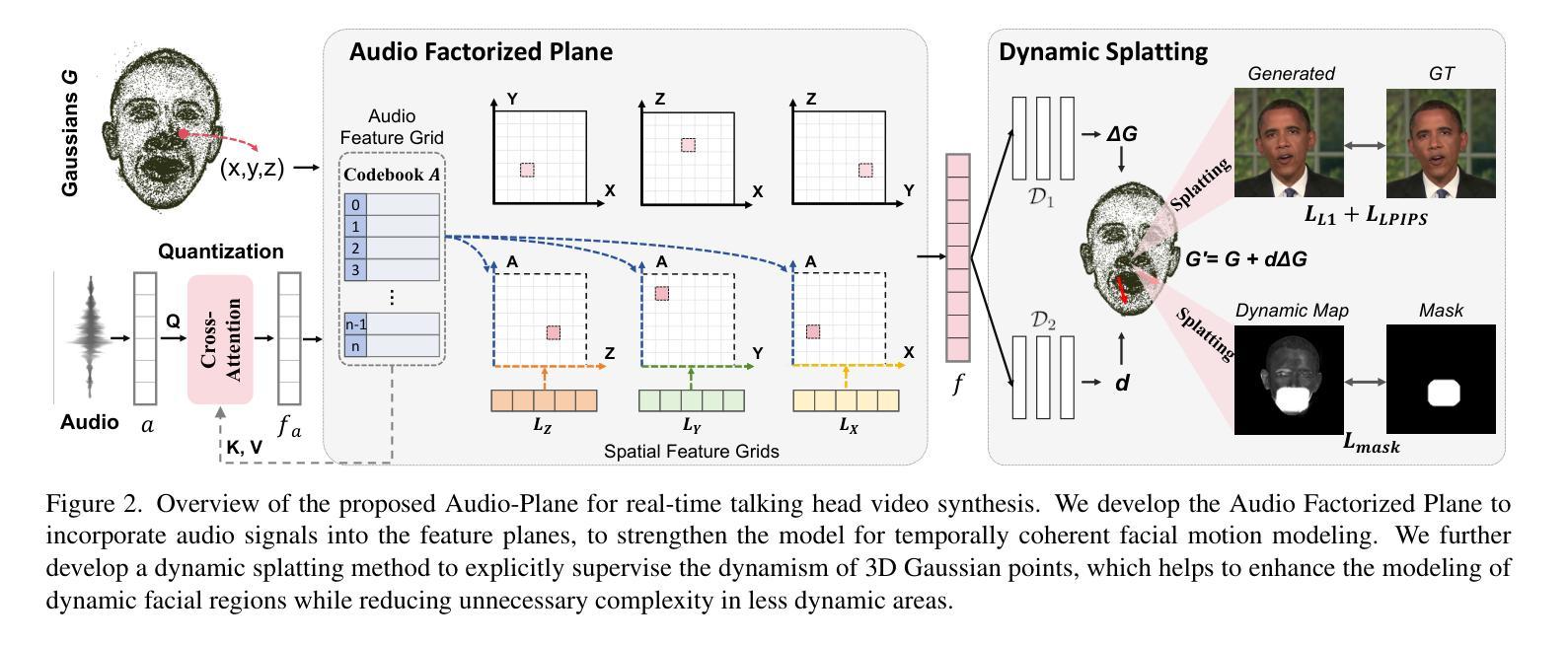
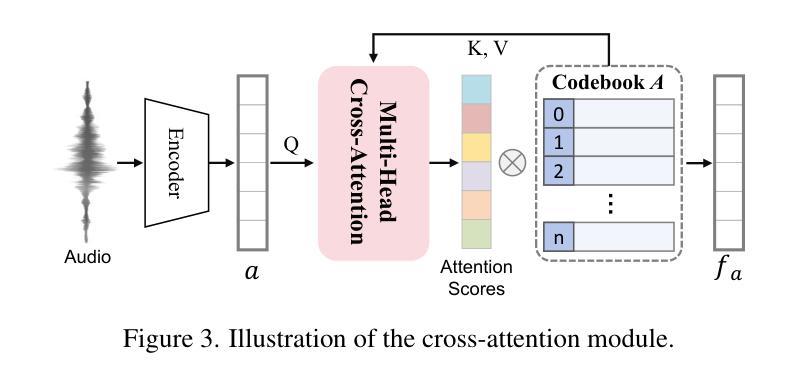
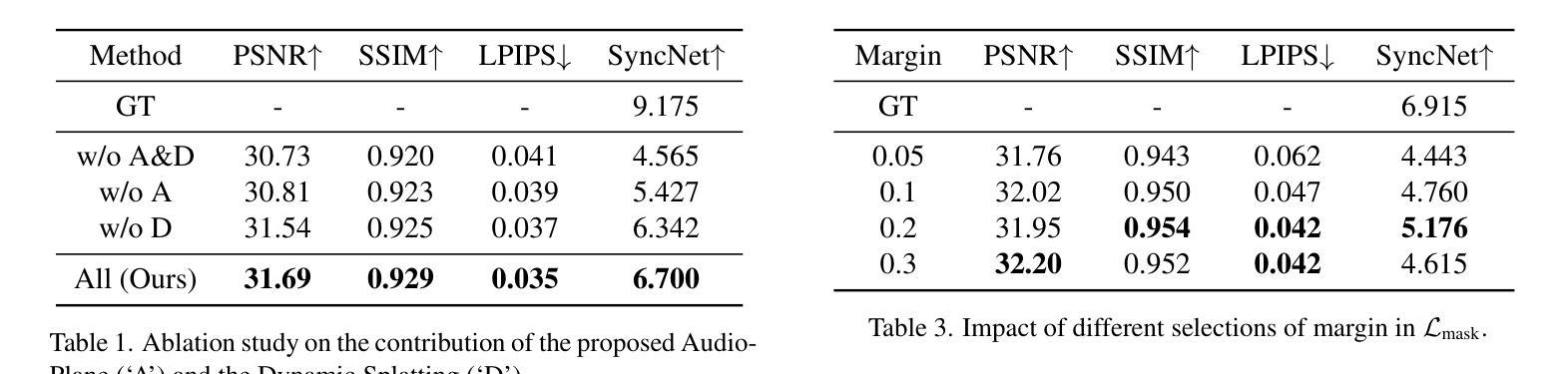
Audio-Plane: Audio Factorization Plane Gaussian Splatting for Real-Time Talking Head Synthesis
Authors:Shuai Shen, Wanhua Li, Yunpeng Zhang, Weipeng Hu, Yap-Peng Tan
Talking head synthesis has become a key research area in computer graphics and multimedia, yet most existing methods often struggle to balance generation quality with computational efficiency. In this paper, we present a novel approach that leverages an Audio Factorization Plane (Audio-Plane) based Gaussian Splatting for high-quality and real-time talking head generation. For modeling a dynamic talking head, 4D volume representation is needed. However, directly storing a dense 4D grid is impractical due to the high cost and lack of scalability for longer durations. We overcome this challenge with the proposed Audio-Plane, where the 4D volume representation is decomposed into audio-independent space planes and audio-dependent planes. This provides a compact and interpretable feature representation for talking head, facilitating more precise audio-aware spatial encoding and enhanced audio-driven lip dynamic modeling. To further improve speech dynamics, we develop a dynamic splatting method that helps the network more effectively focus on modeling the dynamics of the mouth region. Extensive experiments demonstrate that by integrating these innovations with the powerful Gaussian Splatting, our method is capable of synthesizing highly realistic talking videos in real time while ensuring precise audio-lip synchronization. Synthesized results are available in https://sstzal.github.io/Audio-Plane/.
头部说话合成已成为计算机图形学和多媒体领域的一个关键研究方向,然而,大多数现有方法往往难以在生成质量和计算效率之间取得平衡。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于音频分解平面(Audio-Plane)的高斯涂抹技术的新方法,用于高质量实时头部说话生成。为了模拟动态的说话头部,需要4D体积表示。然而,由于成本高昂和长期缺乏可扩展性,直接存储密集的4D网格并不实用。我们克服了这一挑战,提出了音频平面(Audio-Plane),其中将4D体积表示分解为独立于音频的空间平面和依赖于音频的平面。这为说话的头部提供了一个紧凑且可解释的特征表示,促进了更精确的声音感知空间编码和增强的音频驱动唇部动态建模。为了进一步提高语音动态效果,我们开发了一种动态涂抹方法,帮助网络更有效地专注于唇部区域的动态建模。大量实验表明,通过将这些创新与强大的高斯涂抹技术相结合,我们的方法能够在保证精确音频唇部同步的情况下,实时合成高度逼真的说话视频。合成结果可在https://sstzal.github.io/Audio-Plane/查看。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文提出了一种利用音频分解平面(Audio-Plane)高斯模糊技术实现高质量实时动态谈话头生成的新方法。通过分解四维体积表示法为音频独立空间平面和音频依赖平面,解决了直接存储密集四维网格的不切实际和缺乏可扩展性的问题。该方法为谈话头提供了紧凑且可解释的特征表示,促进了更精确的音频感知空间编码和增强的音频驱动唇动态建模。为了进一步提高语音动态,开发了一种动态模糊方法,帮助网络更有效地专注于唇部区域的动态建模。实验证明,通过将这些创新与强大的高斯模糊技术相结合,该方法能够实时合成高度逼真的谈话视频,同时确保精确的音频-唇部同步。
Key Takeaways
- 本论文提出了利用音频分解平面(Audio-Plane)技术实现高质量实时谈话头生成的方法。
- 通过将四维体积表示分解为音频独立和依赖的平面,解决了存储密集四维网格的问题。
- Audio-Plane技术提供了紧凑且可解释的谈话头特征表示。
- 该方法促进了更精确的音频感知空间编码和增强的音频驱动唇动态建模。
- 通过动态模糊方法,提高了语音动态建模的效果。
- 实验证明该方法能够合成高度逼真的谈话视频,并确保音频与唇部的精确同步。
点此查看论文截图


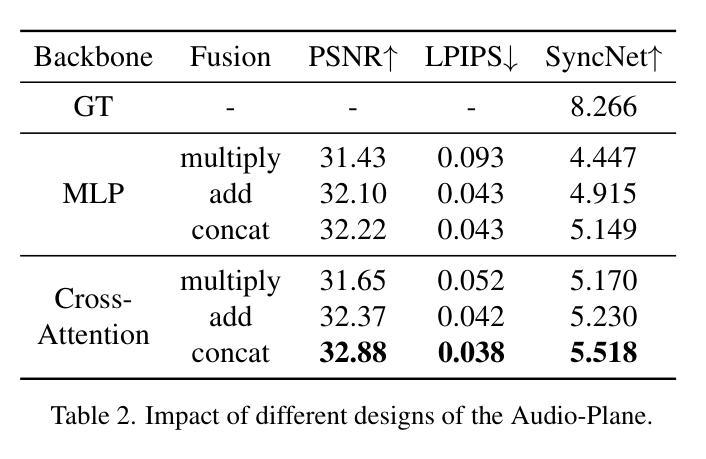
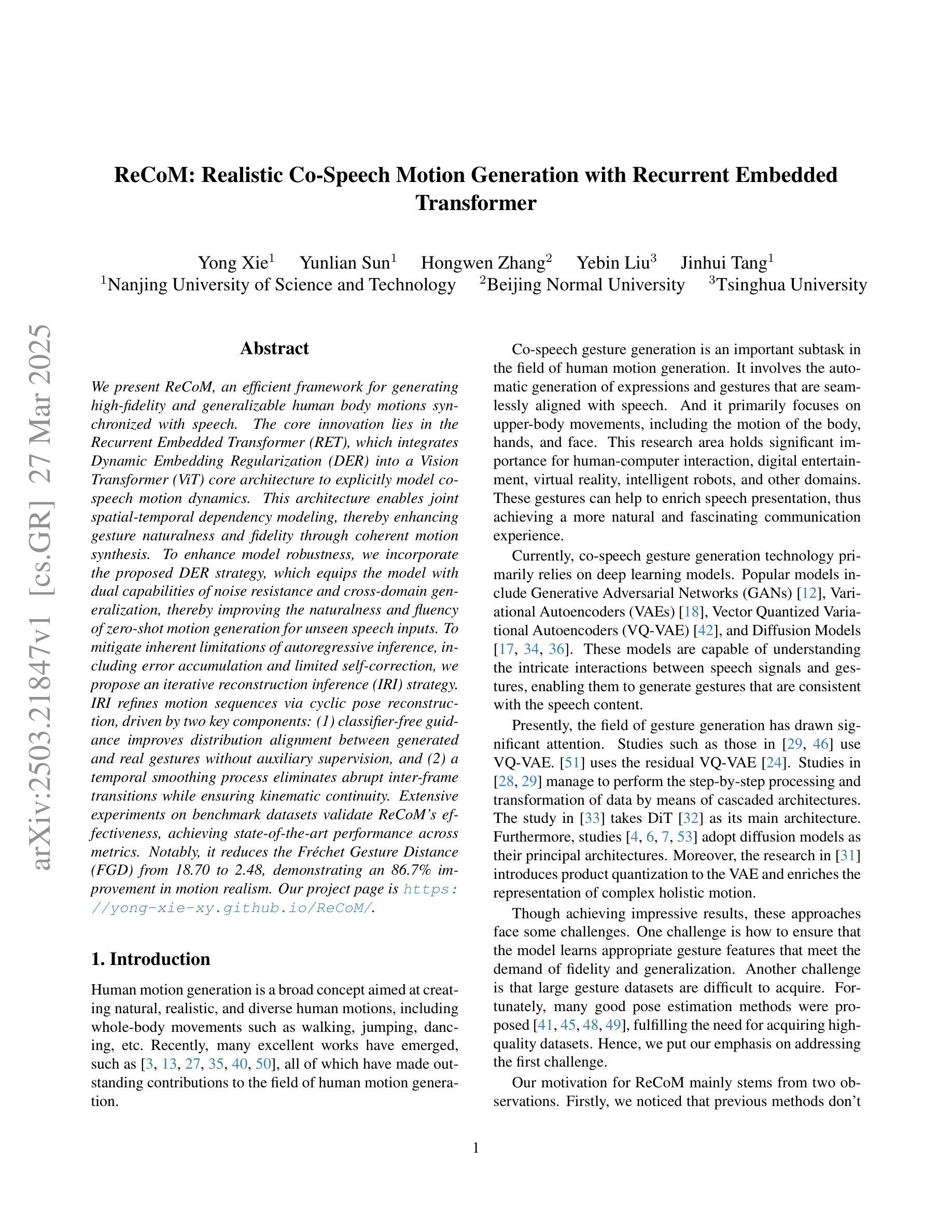
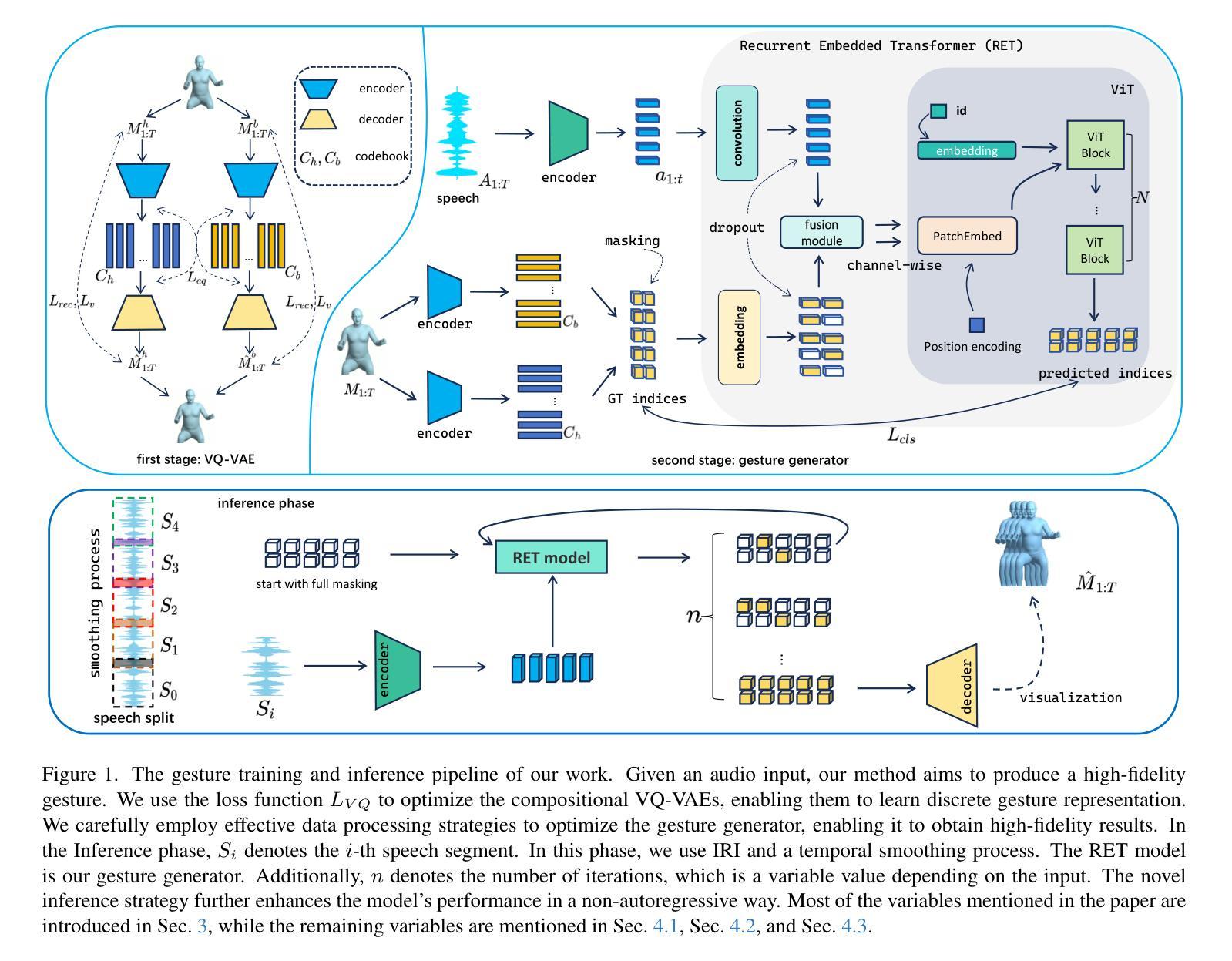
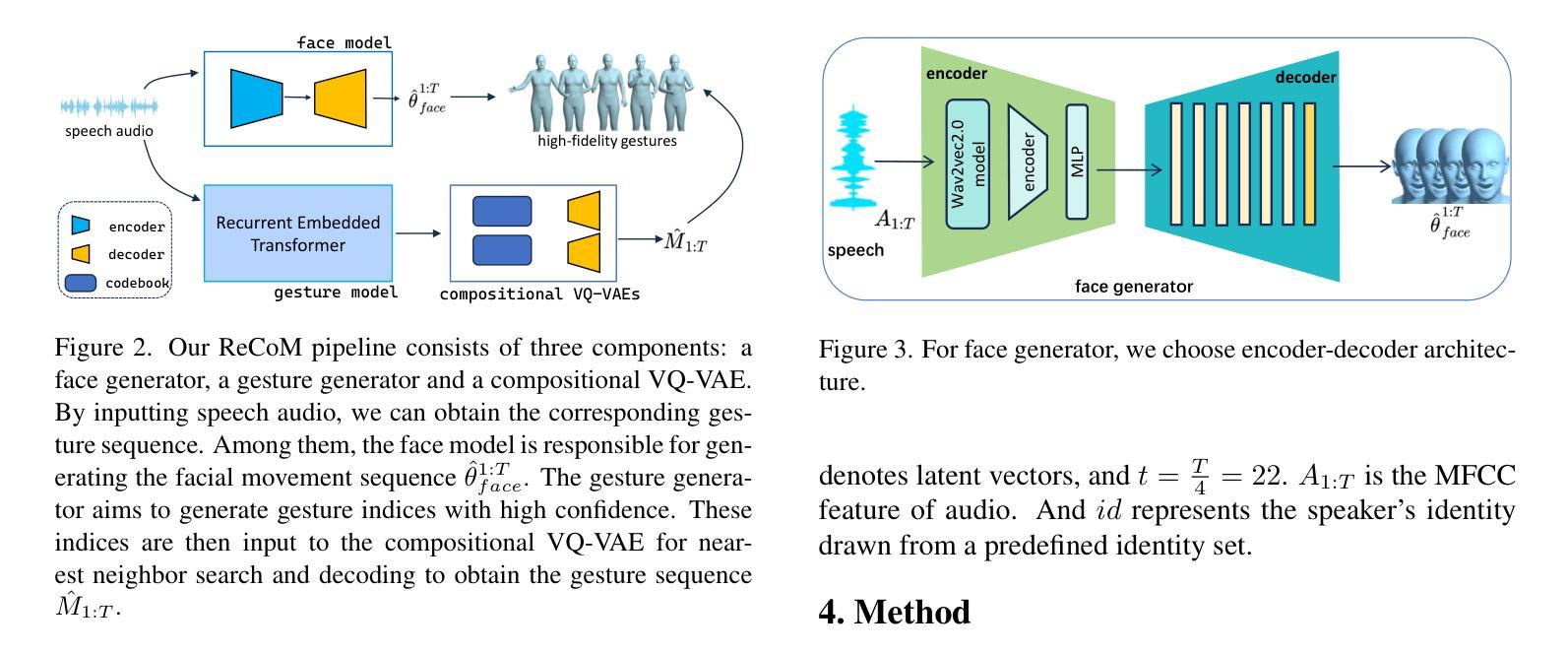
ReCoM: Realistic Co-Speech Motion Generation with Recurrent Embedded Transformer
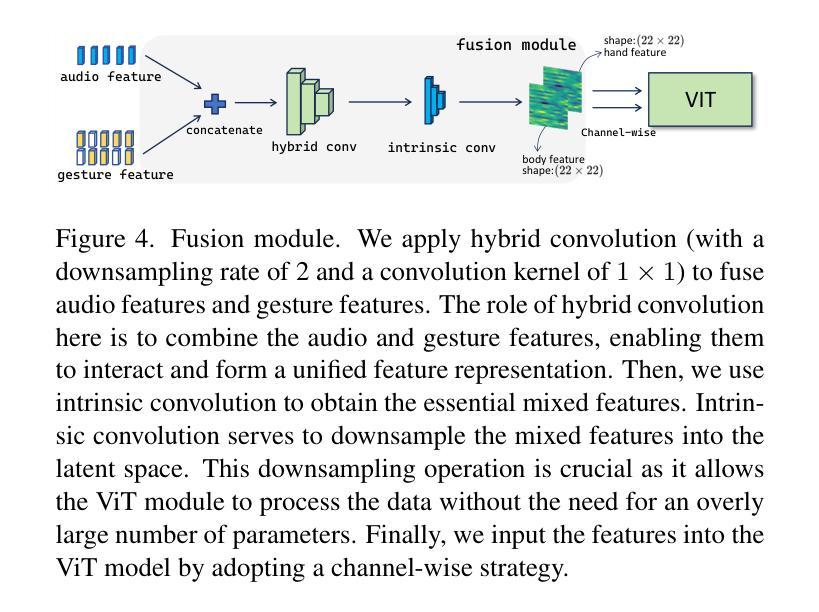
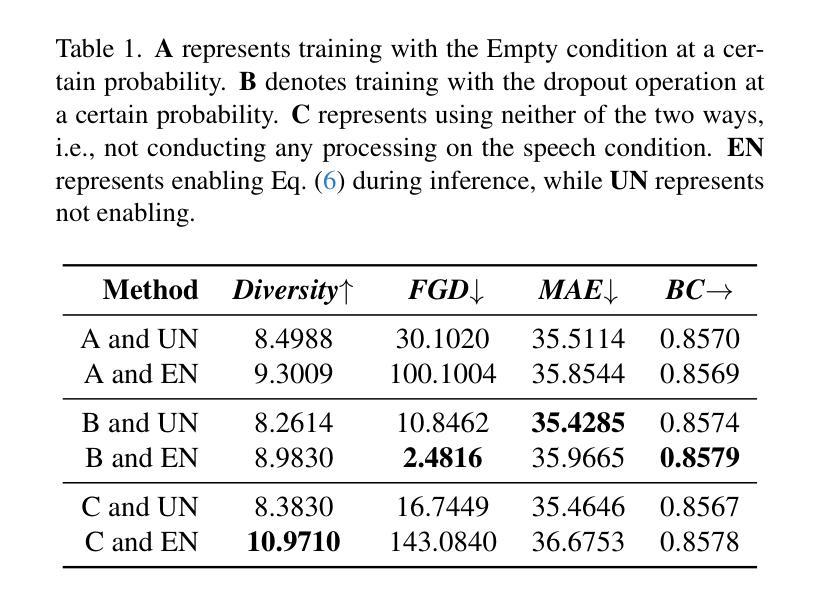
Authors:Yong Xie, Yunlian Sun, Hongwen Zhang, Yebin Liu, Jinhui Tang
We present ReCoM, an efficient framework for generating high-fidelity and generalizable human body motions synchronized with speech. The core innovation lies in the Recurrent Embedded Transformer (RET), which integrates Dynamic Embedding Regularization (DER) into a Vision Transformer (ViT) core architecture to explicitly model co-speech motion dynamics. This architecture enables joint spatial-temporal dependency modeling, thereby enhancing gesture naturalness and fidelity through coherent motion synthesis. To enhance model robustness, we incorporate the proposed DER strategy, which equips the model with dual capabilities of noise resistance and cross-domain generalization, thereby improving the naturalness and fluency of zero-shot motion generation for unseen speech inputs. To mitigate inherent limitations of autoregressive inference, including error accumulation and limited self-correction, we propose an iterative reconstruction inference (IRI) strategy. IRI refines motion sequences via cyclic pose reconstruction, driven by two key components: (1) classifier-free guidance improves distribution alignment between generated and real gestures without auxiliary supervision, and (2) a temporal smoothing process eliminates abrupt inter-frame transitions while ensuring kinematic continuity. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets validate ReCoM’s effectiveness, achieving state-of-the-art performance across metrics. Notably, it reduces the Fr'echet Gesture Distance (FGD) from 18.70 to 2.48, demonstrating an 86.7% improvement in motion realism. Our project page is https://yong-xie-xy.github.io/ReCoM/.
我们提出了ReCoM,这是一个高效框架,用于生成与语音同步的高保真和可推广的人体动作。核心创新点在于循环嵌入转换器(RET),它将动态嵌入正则化(DER)集成到视觉转换器(ViT)核心架构中,以显式地建模共语音运动动力学。该架构能够联合建模时空依赖性,从而通过连贯的运动合成增强手势的自然性和保真度。为了提高模型的稳健性,我们采用了提出的DER策略,该策略使模型具备抗噪声和跨域推广的双重能力,从而提高了未见语音输入的零样本运动生成的自然性和流畅性。为了减轻自回归推理的固有局限性,包括误差累积和有限的自我校正能力,我们提出了一种迭代重建推理(IRI)策略。IRI通过循环姿势重建来优化运动序列,这由两个关键组件驱动:(1)无分类器指导改善了生成手势和真实手势之间的分布对齐,无需辅助监督;(2)时间平滑过程消除了帧间突兀的过渡,同时确保了运动学连续性。在基准数据集上的广泛实验验证了ReCoM的有效性,其在各项指标上均达到了最新技术水平。值得注意的是,它将Fréchet手势距离(FGD)从18.70减少到2.48,显示出运动真实性的86.7%改进。我们的项目页面是https://yong-xie-xy.github.io/ReCoM/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 6 figures, Project Page: https://yong-xie-xy.github.io/ReCoM/
Summary
本文介绍了ReCoM框架,它能生成与语音同步的高保真、可推广的人体动作。核心创新在于Recurrent Embedded Transformer(RET),它将Dynamic Embedding Regularization(DER)集成到Vision Transformer(ViT)核心架构中,以显式地模拟动作与语音的协同动态。通过联合空间时间依赖性建模,提高了手势的自然性和保真性,并通过连贯的动作合成实现了逼真运动。为提高模型稳健性,结合了DER策略,使模型具有抗噪声和跨域推广能力,提高了未见语音输入的零样本运动生成的流畅性和自然性。为缓解自回归推理的固有局限性,如误差累积和有限的自我校正能力,提出了迭代重建推理(IRI)策略。通过循环姿势重建优化动作序列,由无监督分类器引导和临时平滑过程驱动,消除了帧间突兀过渡,确保了运动学连续性。在基准数据集上的广泛实验验证了ReCoM的有效性,实现了跨指标的先进性能。显著地,它将Fr’echet Gesture Distance(FGD)从18.70降低到2.48,显示出动作真实性的86.7%提升。
Key Takeaways
- ReCoM是一个高效框架,用于生成与语音同步的高保真和可推广的人体动作。
- 核心创新是Recurrent Embedded Transformer(RET),集成了Dynamic Embedding Regularization(DER)和Vision Transformer(ViT)。
- RET能显式地模拟动作与语音的协同动态,通过联合空间时间依赖性建模提高手势的自然性和保真性。
- DER策略提高了模型的稳健性,具有抗噪声和跨域推广能力。
- 迭代重建推理(IRI)策略缓解自回归推理的局限性,如误差累积和有限的自我校正能力。
- IRI通过循环姿势重建优化动作序列,由无监督分类器引导和临时平滑过程驱动。
点此查看论文截图
QualiSpeech: A Speech Quality Assessment Dataset with Natural Language Reasoning and Descriptions
Authors:Siyin Wang, Wenyi Yu, Xianzhao Chen, Xiaohai Tian, Jun Zhang, Lu Lu, Yu Tsao, Junichi Yamagishi, Yuxuan Wang, Chao Zhang
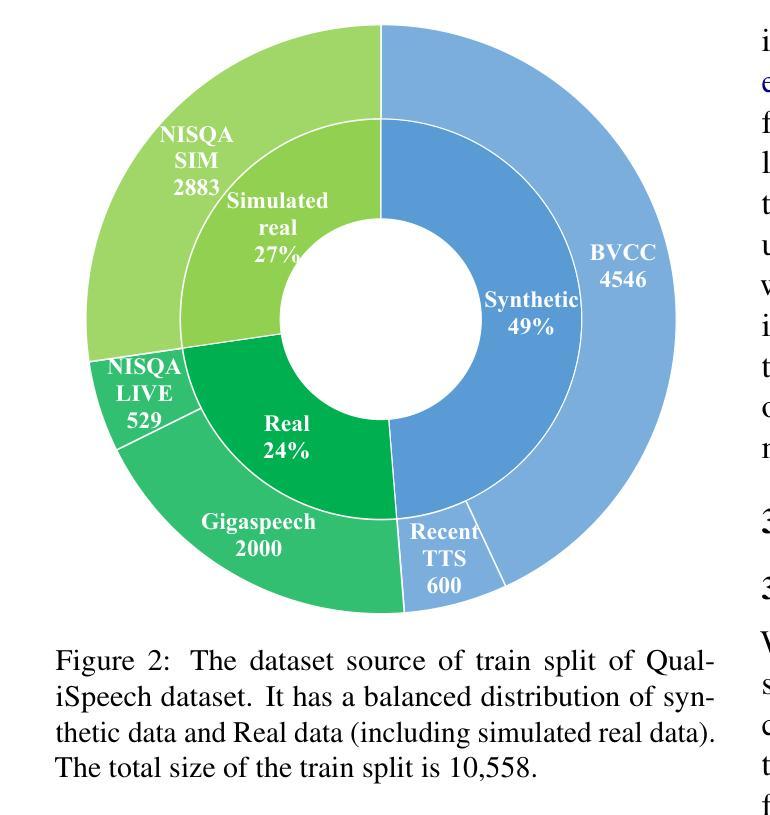
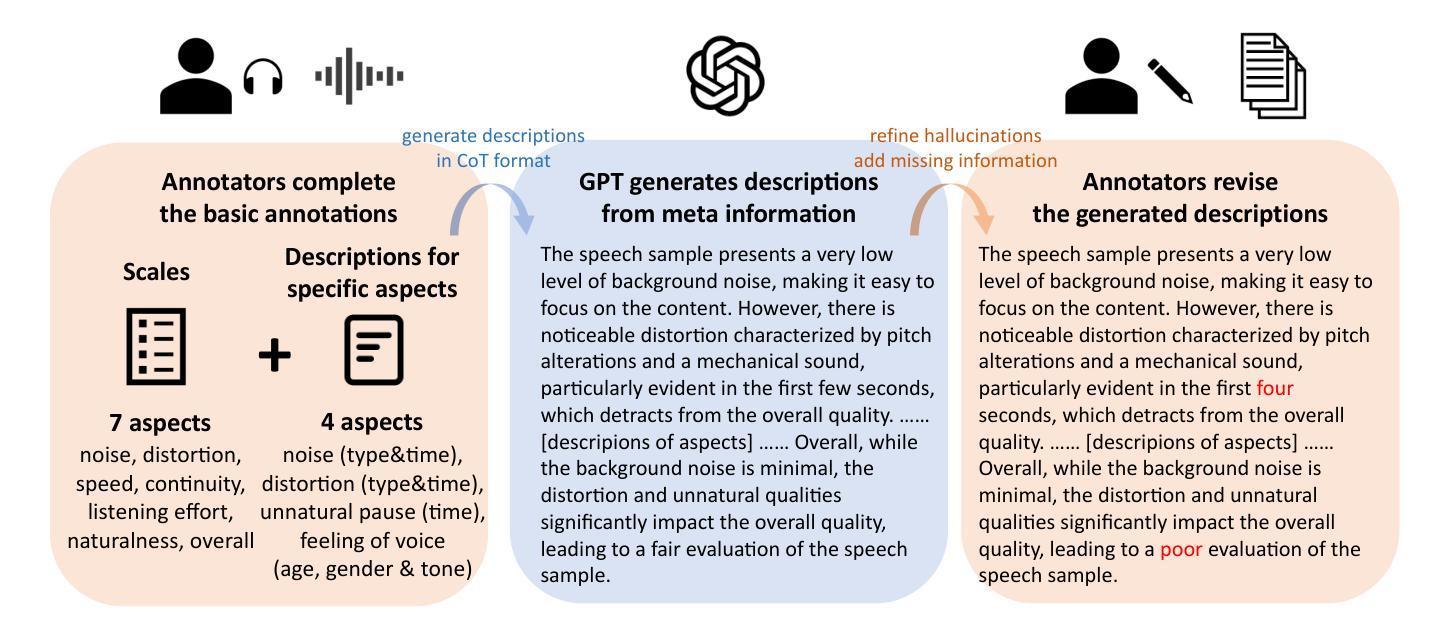
This paper explores a novel perspective to speech quality assessment by leveraging natural language descriptions, offering richer, more nuanced insights than traditional numerical scoring methods. Natural language feedback provides instructive recommendations and detailed evaluations, yet existing datasets lack the comprehensive annotations needed for this approach. To bridge this gap, we introduce QualiSpeech, a comprehensive low-level speech quality assessment dataset encompassing 11 key aspects and detailed natural language comments that include reasoning and contextual insights. Additionally, we propose the QualiSpeech Benchmark to evaluate the low-level speech understanding capabilities of auditory large language models (LLMs). Experimental results demonstrate that finetuned auditory LLMs can reliably generate detailed descriptions of noise and distortion, effectively identifying their types and temporal characteristics. The results further highlight the potential for incorporating reasoning to enhance the accuracy and reliability of quality assessments. The dataset will be released at https://huggingface.co/datasets/tsinghua-ee/QualiSpeech.
本文探索了一种利用自然语言描述进行语音质量评估的新视角,提供了比传统数字评分方法更丰富、更细微的见解。自然语言反馈提供了指导性的建议和详细的评价,但现有数据集缺乏这种评估方法所需的全面注释。为了弥补这一差距,我们推出了QualiSpeech数据集,这是一个全面的低级别语音质量评估数据集,涵盖了11个关键方面和包含推理和上下文洞察的自然语言详细注释。此外,我们提出了QualiSpeech基准测试,以评估听觉大型语言模型(LLM)对低级别语音的理解能力。实验结果表明,经过微调后的听觉LLM可以可靠地描述噪声和失真的细节,有效地识别它们的类型和时间特征。结果还强调了结合推理提高质量评估准确性和可靠性的潜力。该数据集将在https://huggingface.co/datasets/tsinghua-ee/QualiSpeech发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 16 figures
摘要
本文利用自然语言描述,从新的角度探讨语音质量评估,提供比传统数字评分方法更丰富、更细微的见解。自然语言反馈提供指导性的建议和详细的评价,但现有数据集缺乏全面注释,无法支持此方法。为了弥补这一差距,我们推出了QualiSpeech数据集,它涵盖了低层次的语音质量评估的11个关键方面,包含推理和上下文洞察的自然语言评论。此外,我们提出了QualiSpeech基准测试,以评估听觉大型语言模型(LLM)对低层次语音的理解能力。实验结果表明,经过微调的大型语言模型能够可靠地描述噪声和失真细节,有效识别它们的类型和时间特征。结果还表明,结合推理可以提高质量评估的准确性和可靠性。该数据集将在https://huggingface.co/datasets/tsinghua-ee/QualiSpeech上发布。
关键见解
- 利用自然语言描述提供了一个新的语音质量评估视角,更丰富且细微。
- 自然语言反馈能提供指导性的建议和详细的评价。
- 现有数据集缺乏全面注释,无法支持基于自然语言描述的语音质量评估方法。
- 推出QualiSpeech数据集,涵盖低层次语音质量评估的多个方面和详细自然语言评论。
- 提出QualiSpeech基准测试以评估听觉大型语言模型对低层次语音的理解能力。
- 实验表明,经过训练的大型语言模型能够详细描述语音中的噪声和失真。
点此查看论文截图


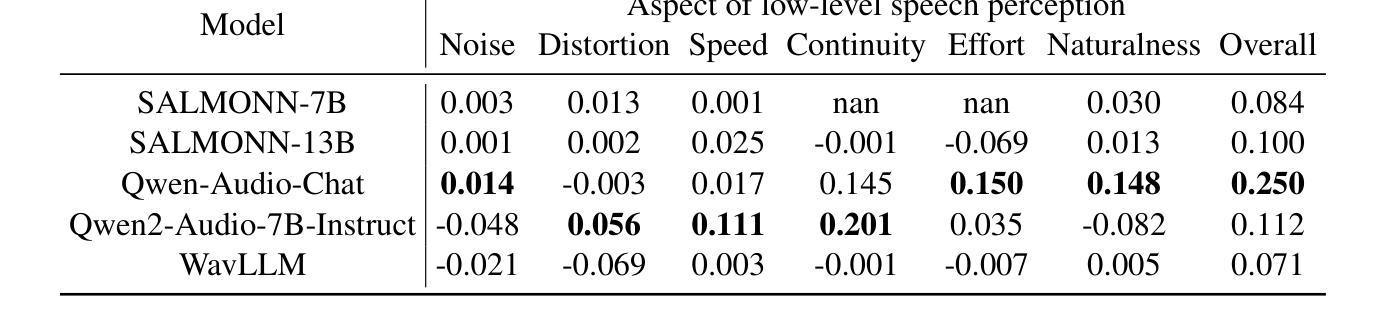
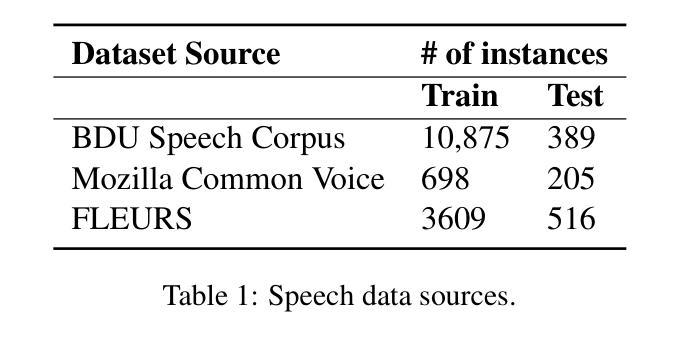
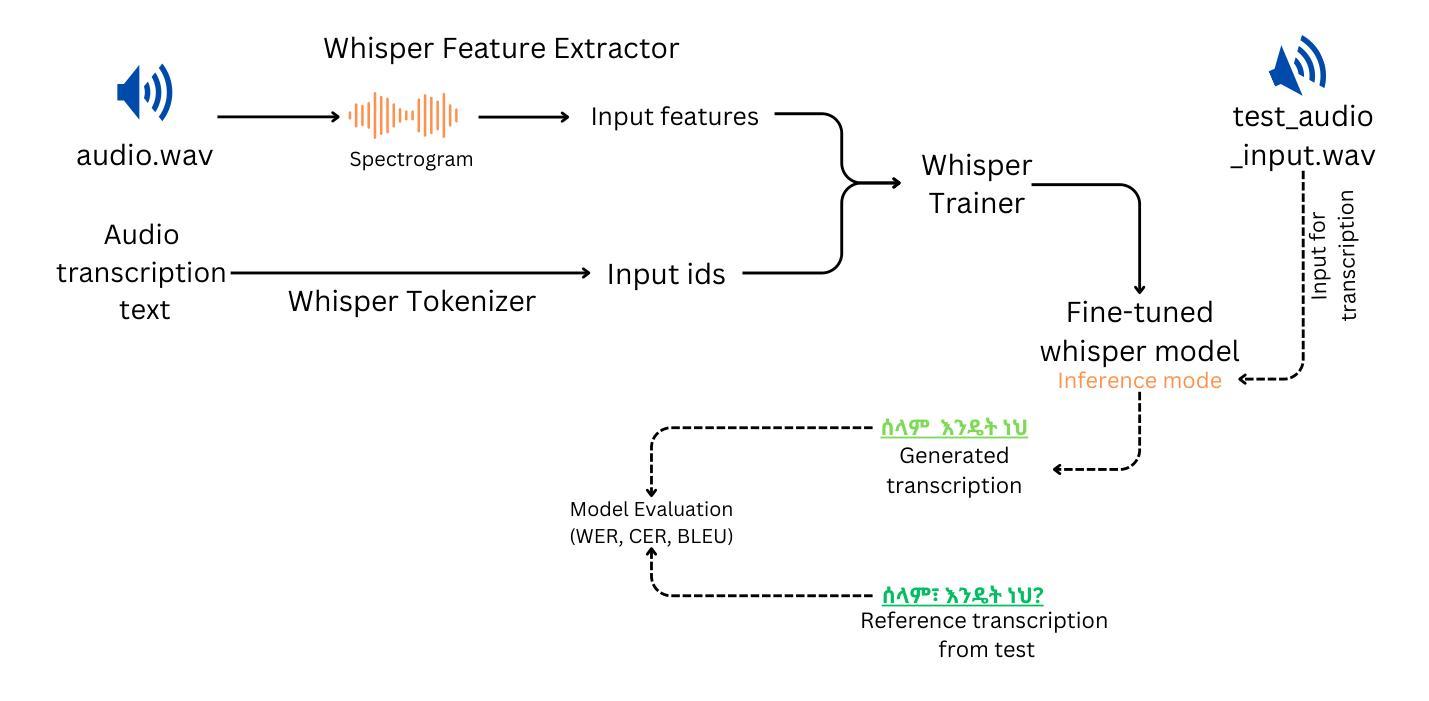
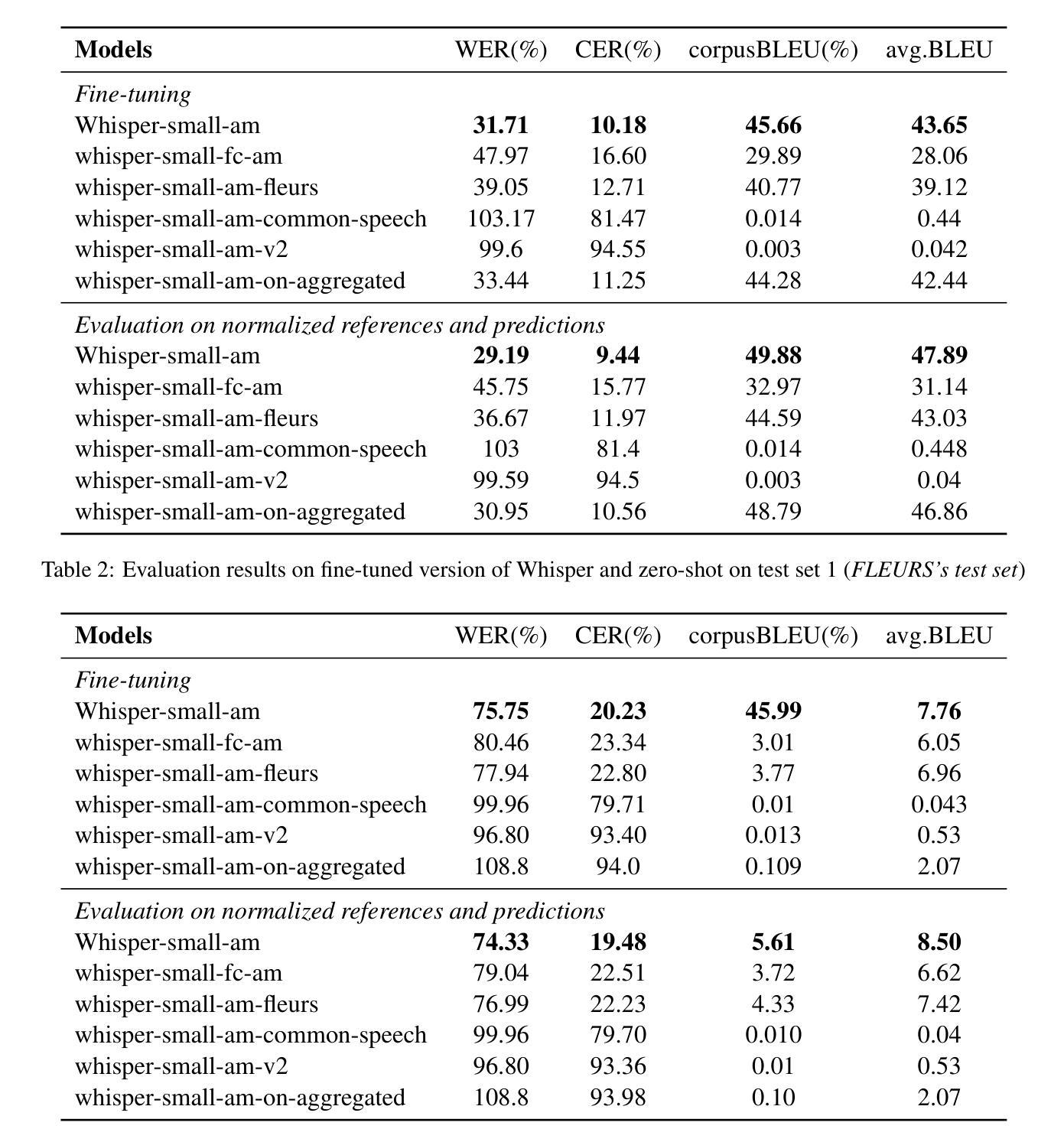
Whispering in Amharic: Fine-tuning Whisper for Low-resource Language
Authors:Dawit Ketema Gete, Bedru Yimam Ahmed, Tadesse Destaw Belay, Yohannes Ayana Ejigu, Sukairaj Hafiz Imam, Alemu Belay Tessema, Mohammed Oumer Adem, Tadesse Amare Belay, Robert Geislinger, Umma Aliyu Musa, Martin Semmann, Shamsuddeen Hassan Muhammad, Henning Schreiber, Seid Muhie Yimam
This work explores fine-tuning OpenAI’s Whisper automatic speech recognition (ASR) model for Amharic, a low-resource language, to improve transcription accuracy. While the foundational Whisper model struggles with Amharic due to limited representation in its training data, we fine-tune it using datasets like Mozilla Common Voice, FLEURS, and the BDU-speech dataset. The best-performing model, Whispersmall-am, significantly improves when finetuned on a mix of existing FLEURS data and new, unseen Amharic datasets. Training solely on new data leads to poor performance, but combining it with FLEURS data reinforces the model, enabling better specialization in Amharic. We also demonstrate that normalizing Amharic homophones significantly enhances Word Error Rate (WER) and Bilingual Evaluation Understudy (BLEU) scores. This study underscores the importance of fine-tuning strategies and dataset composition for improving ASR in low-resource languages, providing insights for future Amharic speech recognition research.
这项工作探讨了针对阿姆哈拉语(一种低资源语言)对OpenAI的自动语音识别(ASR)模型Whisper进行微调,以提高转录准确性。尽管基础Whisper模型在阿姆哈拉语方面由于其训练数据中的有限表示而面临挑战,但我们使用Mozilla Common Voice、FLEURS和BDU-speech等数据集对其进行微调。表现最佳的模型Whispersmall-am,在现有的FLEURS数据和新的未见过的阿姆哈拉语数据集的混合上微调时,性能得到了显著提升。仅在新数据上进行训练会导致性能不佳,但将其与FLEURS数据相结合可以加强模型,使阿姆哈拉语的专业化能力更强。我们还证明,对阿姆哈拉语的同音字进行归一化处理可以显著提高单词错误率(WER)和双语评估下研究(BLEU)的得分。这项研究强调了微调策略和数据集组成在提高低资源语言的语音识别中的重要性,为未来阿姆哈拉语语音识别研究提供了见解。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
本文探讨了针对阿姆哈拉语这种资源贫乏的语言,如何对OpenAI的Whisper自动语音识别(ASR)模型进行微调,以提高转录准确性。使用Mozilla Common Voice、FLEURS和BDU-speech等数据集对基础Whisper模型进行微调,解决了模型在阿姆哈拉语方面的识别困难。在现有FLEURS数据和新、未见过的阿姆哈拉语数据集的混合上训练的Whispersmall-am模型表现最佳。仅在新数据上训练会导致性能不佳,但与FLEURS数据相结合,强化了模型的性能,使其在阿姆哈拉语方面更加专业化。同时证明,对阿姆哈拉语的同音字进行归一化处理可以显著提高单词错误率和双语评估研究得分。本研究强调了微调策略和数据集组成在改进低资源语言的语音识别中的重要性,为未来阿姆哈拉语语音识别研究提供了启示。
关键见解
- OpenAI的Whisper模型在资源贫乏的阿姆哈拉语上的表现有待提高。
- 使用Mozilla Common Voice、FLEURS和BDU-speech等数据集的微调策略能有效提升模型在阿姆哈拉语上的性能。
- 混合使用现有和新数据集进行微调,特别是FLEURS数据与新数据的结合,能显著提高模型的性能。
- 仅在新数据集上训练ASR模型可能导致性能不佳。
- 对阿姆哈拉语的同音字进行归一化处理能改善语音识别结果的准确性。
- 有效的微调策略和选择合适的数据集组成对于提高低资源语言的语音识别至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

Automatic Speech Recognition for Non-Native English: Accuracy and Disfluency Handling
Authors:Michael McGuire
Automatic speech recognition (ASR) has been an essential component of computer assisted language learning (CALL) and computer assisted language testing (CALT) for many years. As this technology continues to develop rapidly, it is important to evaluate the accuracy of current ASR systems for language learning applications. This study assesses five cutting-edge ASR systems’ recognition of non-native accented English speech using recordings from the L2-ARCTIC corpus, featuring speakers from six different L1 backgrounds (Arabic, Chinese, Hindi, Korean, Spanish, and Vietnamese), in the form of both read and spontaneous speech. The read speech consisted of 2,400 single sentence recordings from 24 speakers, while the spontaneous speech included narrative recordings from 22 speakers. Results showed that for read speech, Whisper and AssemblyAI achieved the best accuracy with mean Match Error Rates (MER) of 0.054 and 0.056 respectively, approaching human-level accuracy. For spontaneous speech, RevAI performed best with a mean MER of 0.063. The study also examined how each system handled disfluencies such as filler words, repetitions, and revisions, finding significant variation in performance across systems and disfluency types. While processing speed varied considerably between systems, longer processing times did not necessarily correlate with better accuracy. By detailing the performance of several of the most recent, widely-available ASR systems on non-native English speech, this study aims to help language instructors and researchers understand the strengths and weaknesses of each system and identify which may be suitable for specific use cases.
多年来,语音识别技术(ASR)一直是计算机辅助语言学习(CALL)和计算机辅助语言测试(CALT)的重要组成部分。随着这项技术的快速发展,评估当前语音识别系统在语言学习应用中的准确性至关重要。本研究评估了五种前沿的语音识别系统对非母语英语口音的识别能力,使用了L2-ARCTIC语料库中的录音,该语料库包含了来自六个不同母语背景(阿拉伯语、中文、印地语、韩语、西班牙语和越南语)的发音人的朗读和即兴演讲。朗读部分由24名发音人的2400个单句录音组成,而即兴演讲部分则包含来自22名发音人的叙述录音。结果表明,在朗读部分,whisper和AssemblyAI取得了最佳准确性,平均匹配错误率(MER)分别为0.054和0.056,接近人类水平的准确性。在即兴演讲部分,RevAI表现最佳,平均MER为0.063。该研究还探讨了各系统如何处理不流畅现象,如填充词、重复和修正等,发现系统之间的性能差异很大。虽然处理速度在不同系统之间存在显著差异,但处理时间的长短并不一定与准确性相关。通过对几个最新且广泛可用的语音识别系统在非母语英语发音上的表现进行详细分析,本研究旨在帮助语言教师和研究者了解各系统的优缺点,并确定哪些系统适用于特定的用例。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 26 pages, 10 figures
Summary
本文主要研究了五种前沿的自动语音识别系统在非母语英语口音识别方面的性能。通过采用L2-ARCTIC语料库中的录音,研究评估了这些系统对不同母语背景的说话者的识别能力,包括阅读语和自发性口语。各系统在阅读语和自发性口语的识别准确率上存在差异,其中某些系统表现出接近人类水平的性能。此外,研究还探讨了各系统对口语不流畅现象的处理能力,如填充词、重复和修订等。结果显示,各系统在处理不同不流畅现象方面的表现差异显著。同时,系统处理速度与识别准确率并不完全相关。本研究旨在为语言教师和研究人员了解各系统的优缺点以及选择合适系统提供参考。
Key Takeaways
- 五种前沿的ASR系统被评估在非母语英语口音识别上的性能。
- 这些系统在阅读语和自发性口语的识别上都表现出差异。
- Whisper和AssemblyAI在阅读语的识别上表现最佳,接近人类水平。
- RevAI在自发性口语的识别上表现最好。
- 各系统在处理口语不流畅现象(如填充词、重复和修订)方面的表现差异显著。
- ASR系统的处理速度并不直接关联其识别准确率。
点此查看论文截图

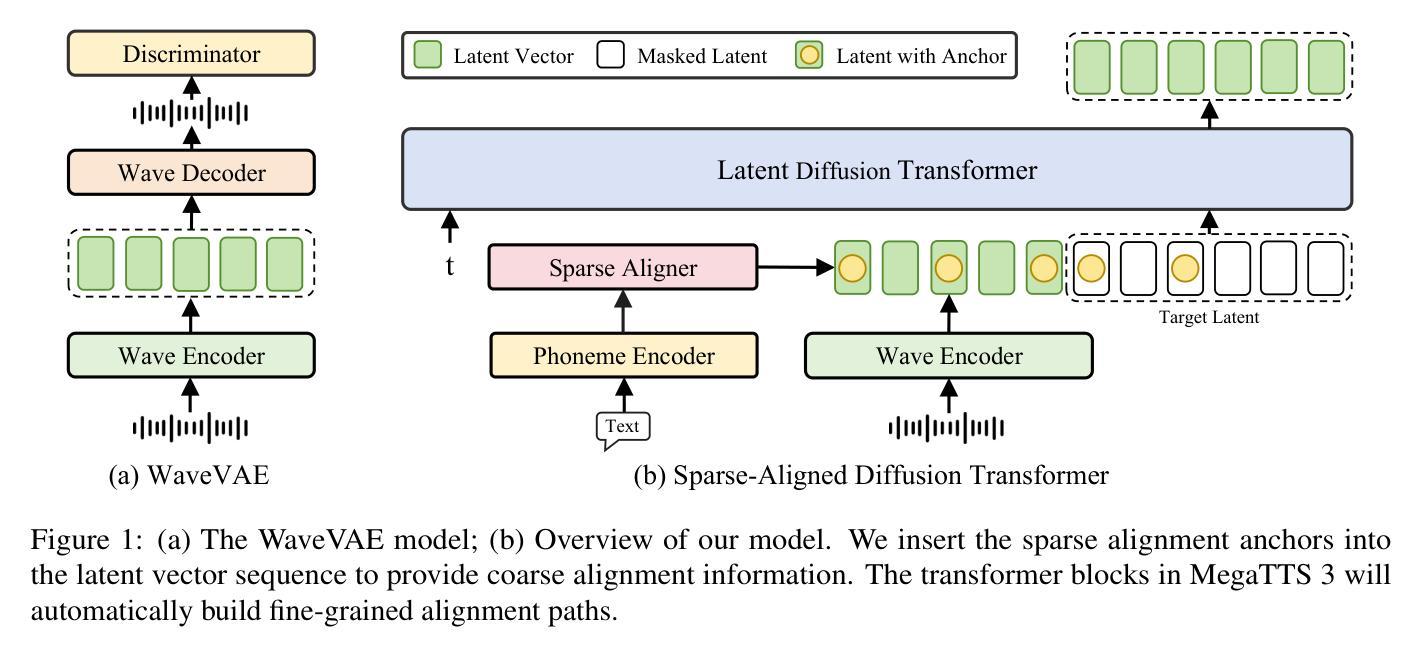
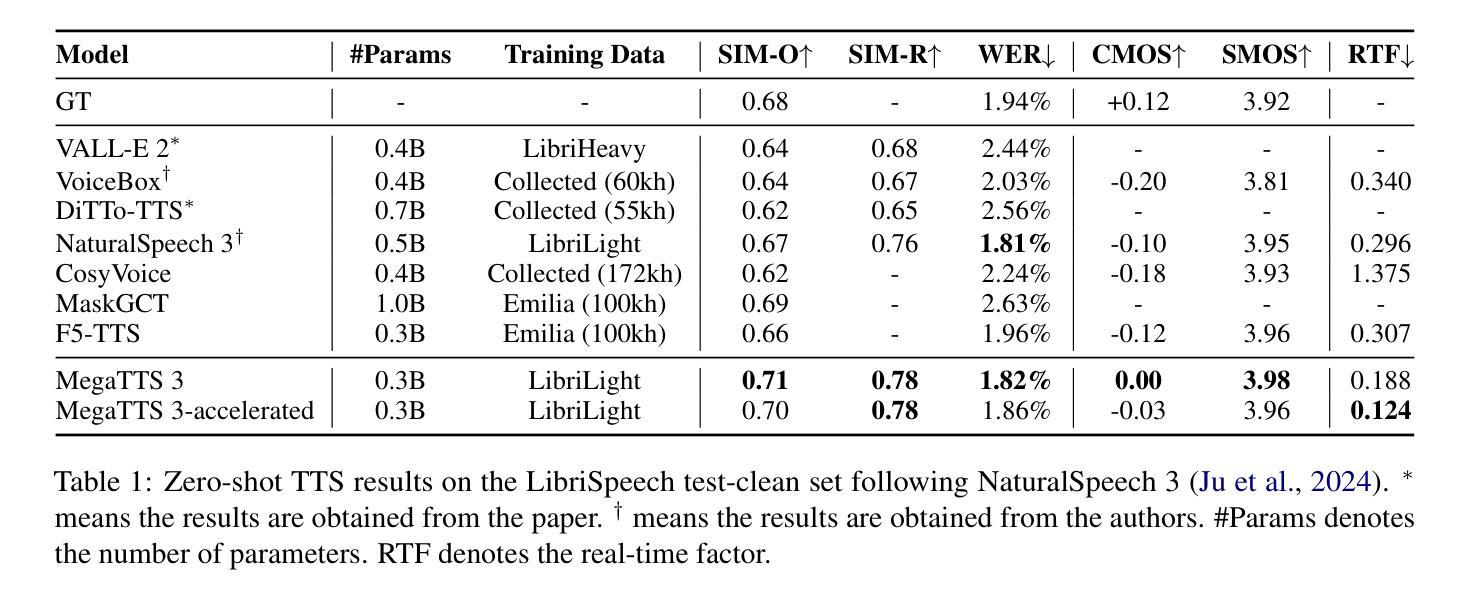
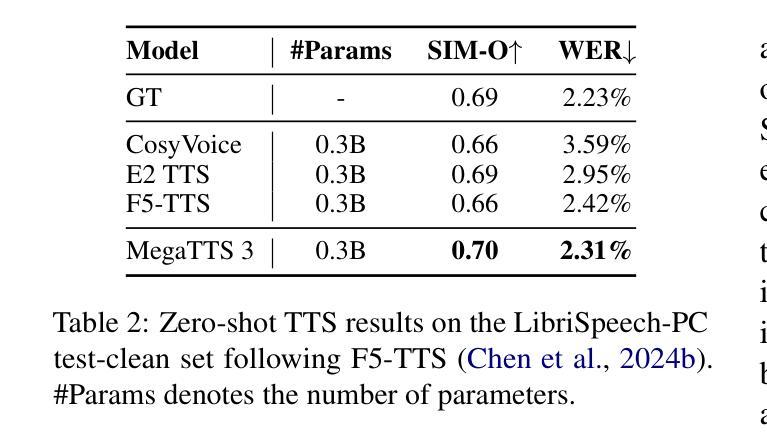
MegaTTS 3: Sparse Alignment Enhanced Latent Diffusion Transformer for Zero-Shot Speech Synthesis
Authors:Ziyue Jiang, Yi Ren, Ruiqi Li, Shengpeng Ji, Boyang Zhang, Zhenhui Ye, Chen Zhang, Bai Jionghao, Xiaoda Yang, Jialong Zuo, Yu Zhang, Rui Liu, Xiang Yin, Zhou Zhao
While recent zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) models have significantly improved speech quality and expressiveness, mainstream systems still suffer from issues related to speech-text alignment modeling: 1) models without explicit speech-text alignment modeling exhibit less robustness, especially for hard sentences in practical applications; 2) predefined alignment-based models suffer from naturalness constraints of forced alignments. This paper introduces \textit{MegaTTS 3}, a TTS system featuring an innovative sparse alignment algorithm that guides the latent diffusion transformer (DiT). Specifically, we provide sparse alignment boundaries to MegaTTS 3 to reduce the difficulty of alignment without limiting the search space, thereby achieving high naturalness. Moreover, we employ a multi-condition classifier-free guidance strategy for accent intensity adjustment and adopt the piecewise rectified flow technique to accelerate the generation process. Experiments demonstrate that MegaTTS 3 achieves state-of-the-art zero-shot TTS speech quality and supports highly flexible control over accent intensity. Notably, our system can generate high-quality one-minute speech with only 8 sampling steps. Audio samples are available at https://sditdemo.github.io/sditdemo/.
近期,零样本文本到语音(TTS)模型在语音质量和表达力方面有了显著的提升,但主流系统仍然面临与语音文本对齐建模相关的问题:1)没有明确的语音文本对齐建模的模型表现出较低的稳健性,特别是在实际应用中的难句;2)基于预定义对齐的模型受到强制对齐的自然性约束。本文介绍了MegaTTS 3,这是一个具有创新稀疏对齐算法的TTS系统,用于指导潜在扩散变压器(DiT)。具体来说,我们为MegaTTS 3提供稀疏对齐边界,以减少对齐的难度,同时不限制搜索空间,从而实现高自然度。此外,我们采用多条件无分类指导策略来调整口音强度,并采用分段整流流技术来加速生成过程。实验表明,MegaTTS 3达到了最先进的零样本TTS语音质量,并对口音强度实现了高度灵活的控制。值得注意的是,我们的系统只需8个采样步骤就能生成高质量的一分钟语音。音频样本可在https://sditdemo.github.io/sditdemo/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了新一代的文本转语音(TTS)系统——MegaTTS 3。该系统采用创新的稀疏对齐算法,指导潜在扩散变压器(DiT)进行语音和文本的对齐。通过提供稀疏对齐边界,MegaTTS 3在降低对齐难度的同时不限制搜索空间,实现了高度的自然性。此外,还采用了多条件无分类指导策略来调整口音强度,并采用分段整流流技术加速生成过程。实验表明,MegaTTS 3达到了零样本TTS的先进语音质量,并高度灵活控制口音强度。尤其值得关注的是,该系统可以在仅8个采样步骤内生成高质量的一分钟语音。
Key Takeaways
- MegaTTS 3是一个新型的文本转语音(TTS)系统,主要解决现有TTS系统语音和文本对齐的问题。
- 通过引入创新的稀疏对齐算法,MegaTTS 3能够更有效地进行语音和文本的对齐,提高了系统的鲁棒性。
- 系统采用多条件无分类指导策略,允许灵活调整口音强度。
- 分段整流流技术的运用加速了语音生成的流程。
- 实验结果表明,MegaTTS 3的语音质量达到了零样本TTS的先进水平。
- MegaTTS 3能够在短时间内生成高质量的语音,例如仅8个采样步骤生成一分钟的语音。
点此查看论文截图

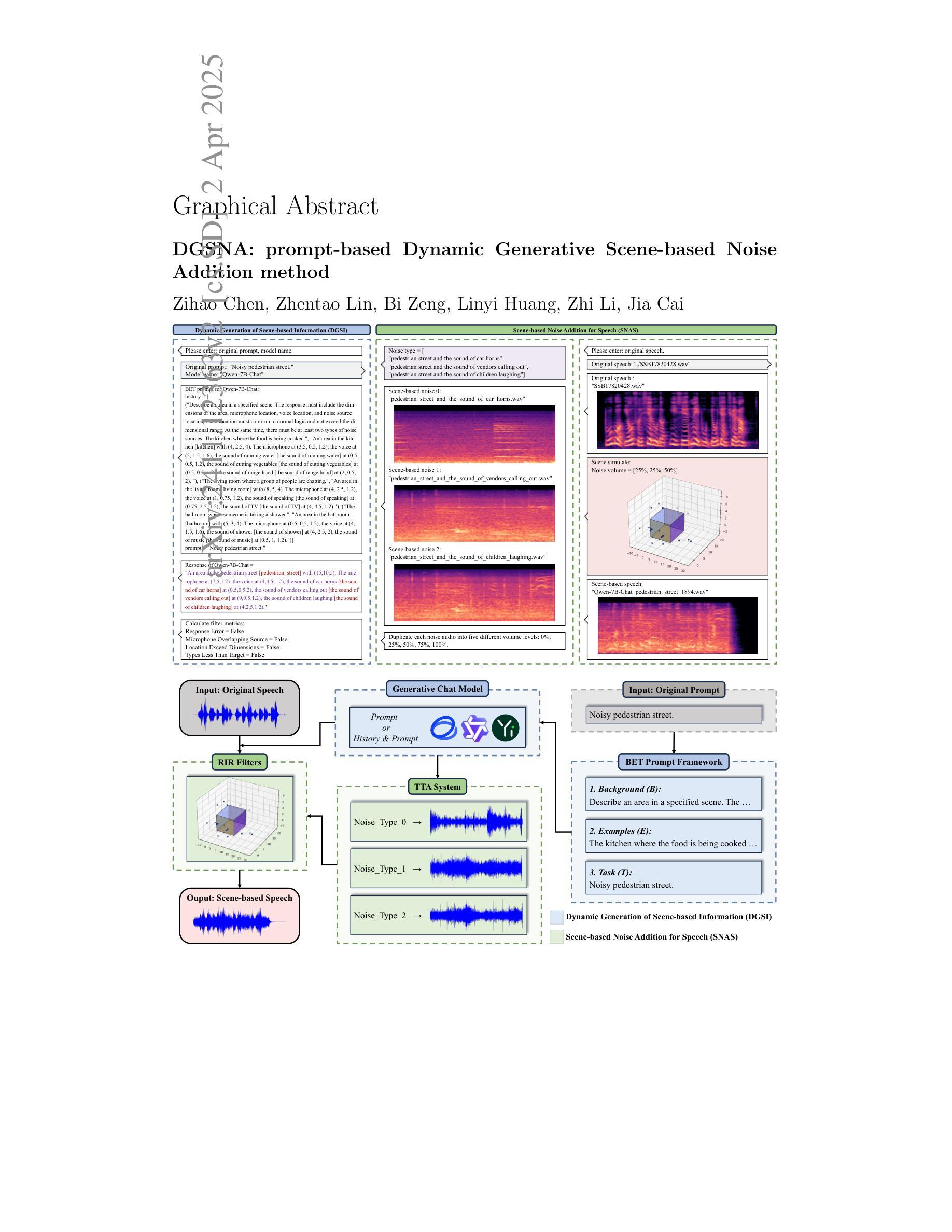
DGSNA: prompt-based Dynamic Generative Scene-based Noise Addition method
Authors:Zihao Chen, Zhentao Lin, Bi Zeng, Linyi Huang, Zhi Li, Jia Cai
To ensure the reliable operation of speech systems across diverse environments, noise addition methods have emerged as the prevailing solution. However, existing methods offer limited coverage of real-world noisy scenes and depend on pre-existing scene-based information and noise. This paper presents prompt-based Dynamic Generative Scene-based Noise Addition (DGSNA), a novel noise addition methodology that integrates Dynamic Generation of Scene-based Information (DGSI) with Scene-based Noise Addition for Speech (SNAS). This integration facilitates automated scene-based noise addition by transforming clean speech into various noise environments, thereby providing a more comprehensive and realistic simulation of diverse noise conditions. Experimental results demonstrate that DGSNA significantly enhances the robustness of speech recognition and keyword spotting models across various noise conditions, achieving a relative improvement of up to 11.21%. Furthermore, DGSNA can be effectively integrated with other noise addition methods to enhance performance. Our implementation and demonstrations are available at https://dgsna.github.io.
为了确保跨不同环境中的语音系统可靠运行,噪声添加方法已经成为了一种主流的解决方案。然而,现有方法提供的真实世界噪声场景的覆盖范围有限,并依赖于基于场景的信息和噪声。本文提出了基于提示的动态生成场景噪声添加(DGSNA),这是一种新型噪声添加方法,它将基于场景的动态信息生成(DGSI)与基于场景的语音噪声添加(SNAS)相结合。这种结合通过转换干净语音为各种噪声环境,实现了基于场景的自动噪声添加,从而提供了更全面和现实的多种噪声条件模拟。实验结果表明,DGSNA显著提高了各种噪声条件下的语音识别和关键词识别模型的稳健性,相对改进率最高可达11.21%。此外,DGSNA可以与其他噪声添加方法有效结合以提高性能。我们的实现和演示可在https://dgsna.github.io查看。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本提出了一种基于提示的动态生成场景噪声添加方法(DGSNA),该方法结合了场景信息的动态生成(DGSI)和基于场景的噪声添加技术(SNAS)。DGSNA可自动将干净语音转换为各种噪声环境,提供更全面和现实的噪声条件模拟。实验结果表明,DGSNA可显著提高语音识别和关键词识别模型在各种噪声条件下的稳健性,相对改进率最高可达11.21%。
Key Takeaways
- DGSNA是一种新的噪声添加方法,它结合了DGSI和SNAS技术。
- DGSNA能自动将干净语音转化为各种噪声环境,实现更全面和现实的噪声条件模拟。
- 实验结果表明,DGSNA能显著提高语音识别和关键词识别模型在多种噪声条件下的稳健性。
- DGSNA的相对改进率最高可达11.21%。
- DGSNA与其他噪声添加方法结合使用,可进一步提升性能。
- DGSNA的实施和演示可在指定网站找到。
点此查看论文截图
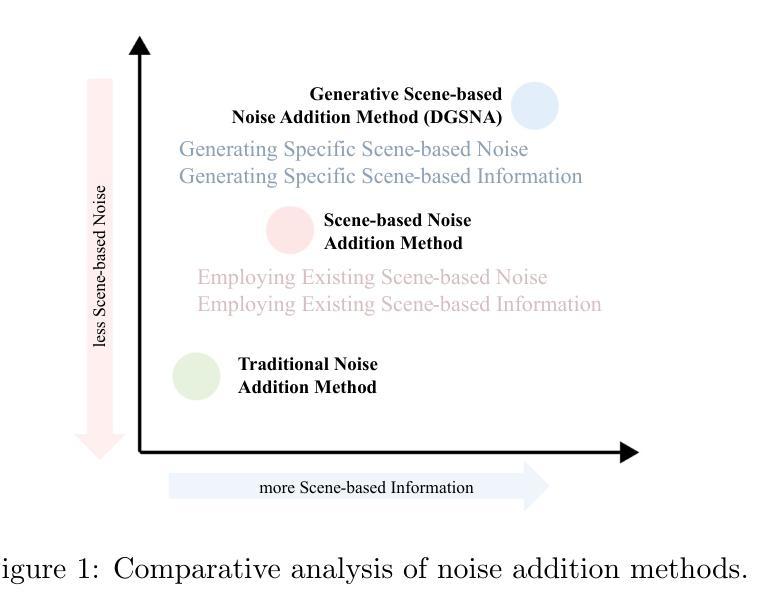
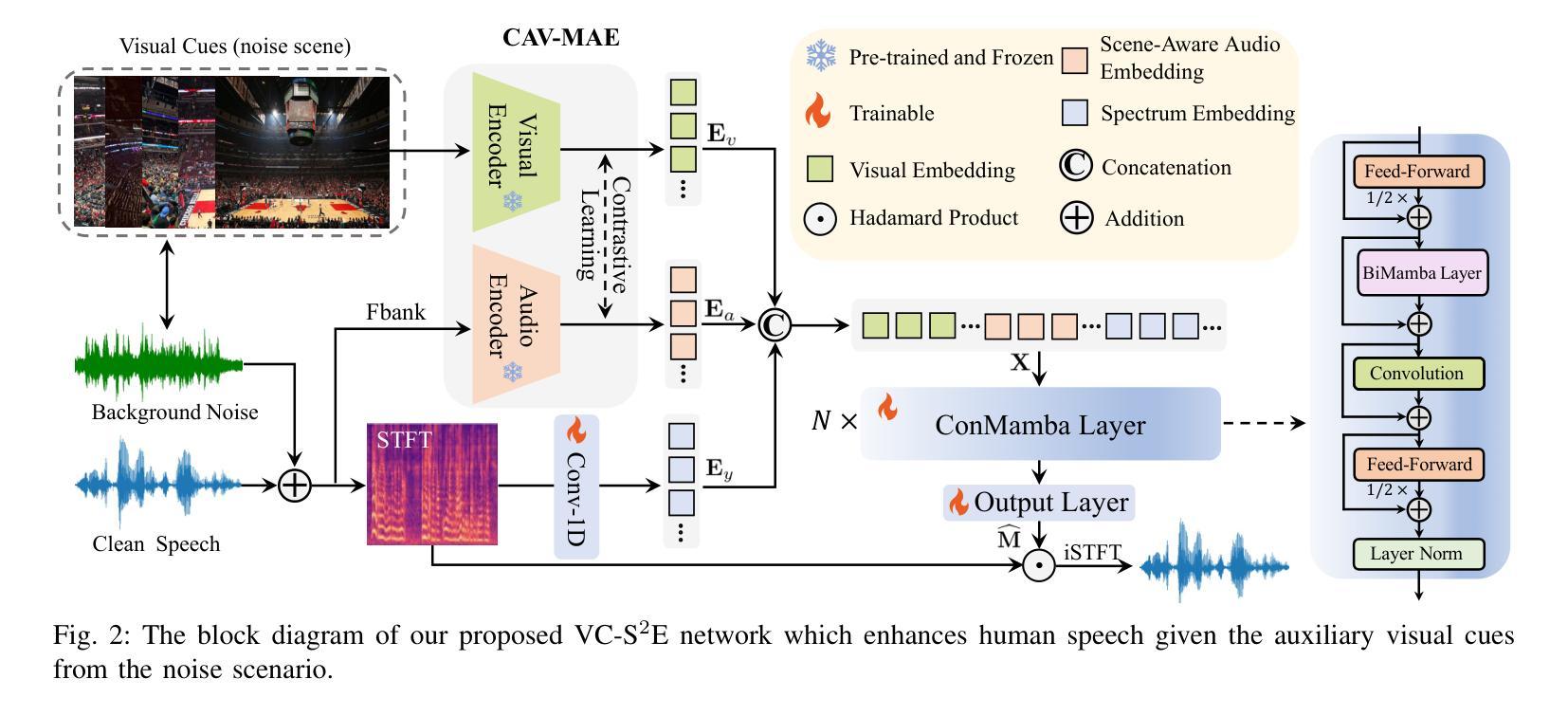
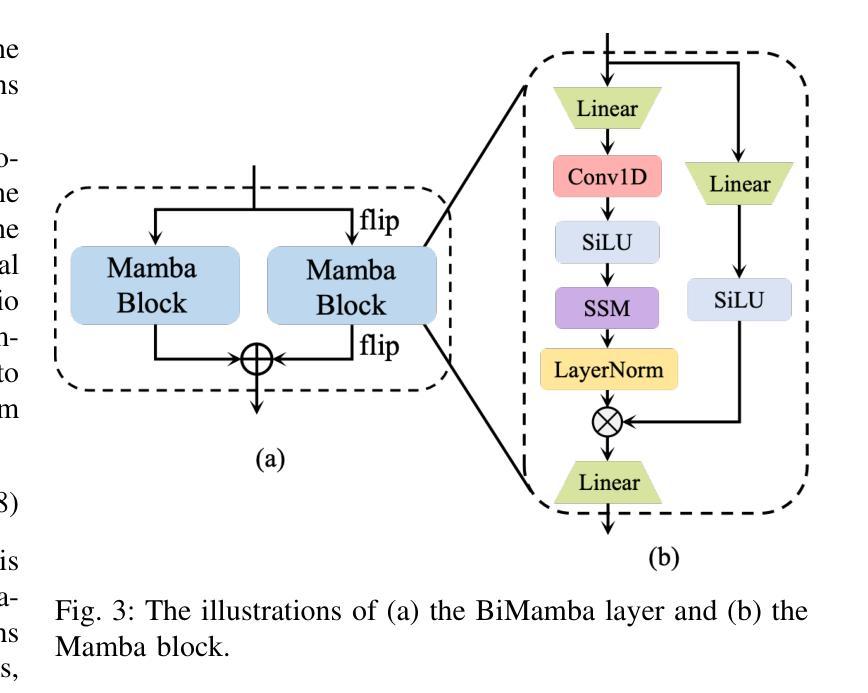
SAV-SE: Scene-aware Audio-Visual Speech Enhancement with Selective State Space Model
Authors:Xinyuan Qian, Jiaran Gao, Yaodan Zhang, Qiquan Zhang, Hexin Liu, Leibny Paola Garcia, Haizhou Li
Speech enhancement plays an essential role in various applications, and the integration of visual information has been demonstrated to bring substantial advantages. However, the majority of current research concentrates on the examination of facial and lip movements, which can be compromised or entirely inaccessible in scenarios where occlusions occur or when the camera view is distant. Whereas contextual visual cues from the surrounding environment have been overlooked: for example, when we see a dog bark, our brain has the innate ability to discern and filter out the barking noise. To this end, in this paper, we introduce a novel task, i.e. SAV-SE. To our best knowledge, this is the first proposal to use rich contextual information from synchronized video as auxiliary cues to indicate the type of noise, which eventually improves the speech enhancement performance. Specifically, we propose the VC-S$^2$E method, which incorporates the Conformer and Mamba modules for their complementary strengths. Extensive experiments are conducted on public MUSIC, AVSpeech and AudioSet datasets, where the results demonstrate the superiority of VC-S$^2$E over other competitive methods. We will make the source code publicly available. Project demo page: https://AVSEPage.github.io/
语音增强在各类应用中扮演着重要角色,而视觉信息的融合已证明可以带来巨大的优势。然而,当前大多数研究主要关注面部和嘴唇动作的检查,这些在遮挡发生或摄像头视角较远的情况下可能会受到损害或完全无法获取。而周围环境中的上下文视觉线索却被忽视了:例如,当我们看到狗叫时,我们的大脑就有天生的能力去辨别和过滤掉吠叫噪音。因此,本文介绍了一项新任务,即SAV-SE。据我们所知,这是首次提出利用来自同步视频中的丰富上下文信息作为辅助线索,以指示噪声类型,最终提高语音增强性能。具体来说,我们提出了VC-S$^2$E方法,该方法结合了Conformer和Mamba模块,以发挥它们的互补优势。在公共MUSIC、AVSpeech和AudioSet数据集上进行了大量实验,结果表明VC-S$^2$E优于其他竞争方法。我们将公开源代码。项目演示页面:https://AVSEPage.github.io/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted by IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing
Summary
语音增强在各种应用中发挥着重要作用,集成视觉信息可以带来明显的优势。当前研究多集中在面部和嘴唇动作的观察上,但在遮挡或远距离拍摄时,这些信息可能受限或无法获取。相较之下,环境中的上下文视觉线索常被忽视。本文介绍了一种新型任务——SAV-SE,旨在利用同步视频中的丰富上下文信息作为辅助线索,以识别噪声类型,从而提高语音增强的性能。具体提出了VC-S$^2$E方法,结合了Conformer和Mamba模块的优势。在公共MUSIC、AVSpeech和AudioSet数据集上的实验结果表明,VC-S$^2$E优于其他竞争方法。
Key Takeaways
- 语音增强集成视觉信息至关重要,能带来显著优势。
- 当前研究主要关注面部和嘴唇动作,但在特定情境下存在局限性。
- 上下文视觉线索(如环境中的声音与视觉信号的关联)在语音增强中扮演重要角色。
- SAV-SE旨在利用同步视频的丰富上下文信息识别噪声类型,提高语音增强性能。
- VC-S$^2$E方法结合了Conformer和Mamba模块的优势。
- 在多个公共数据集上的实验证明了VC-S$^2$E方法的优越性。
点此查看论文截图

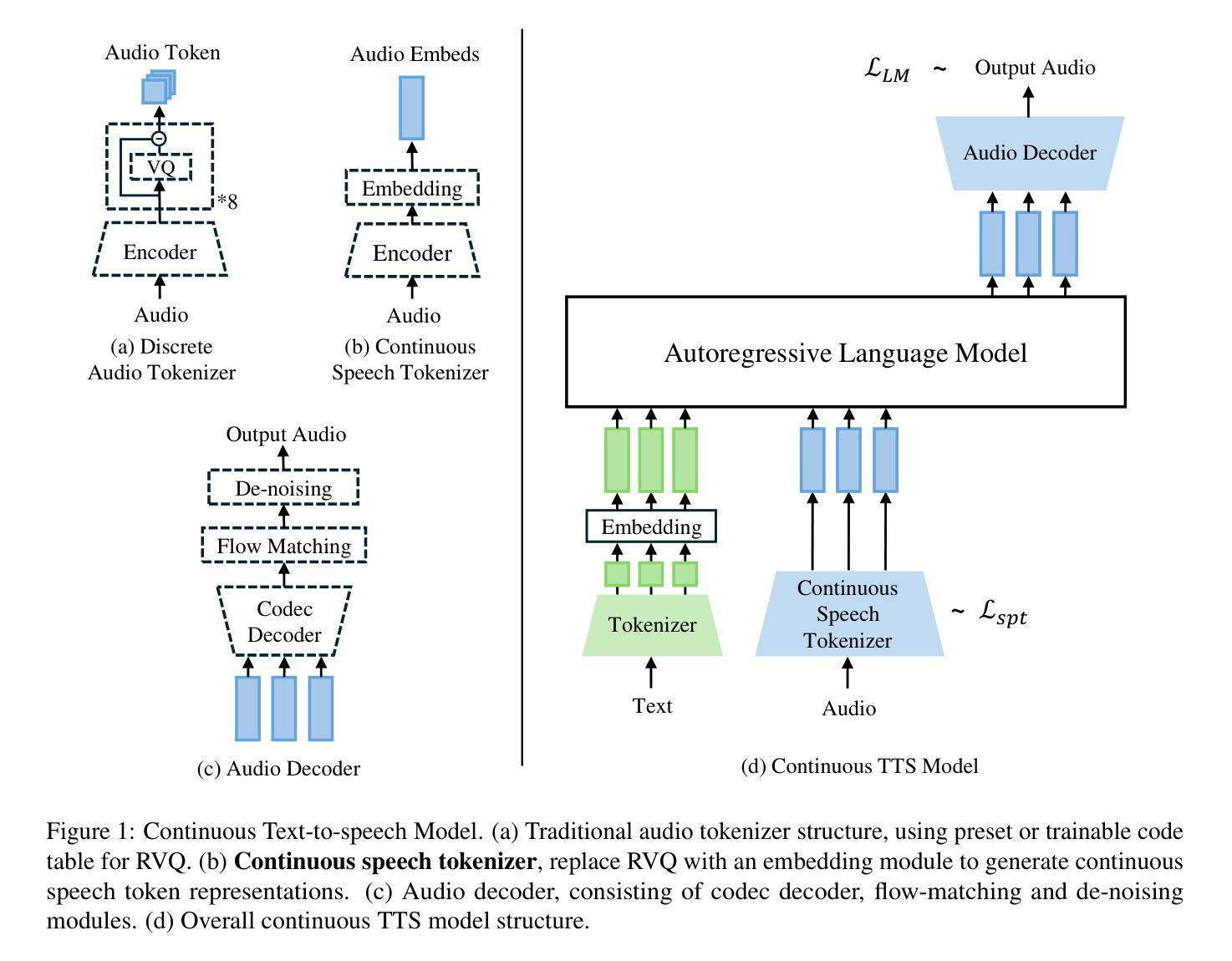
Continuous Speech Tokenizer in Text To Speech
Authors:Yixing Li, Ruobing Xie, Xingwu Sun, Yu Cheng, Zhanhui Kang
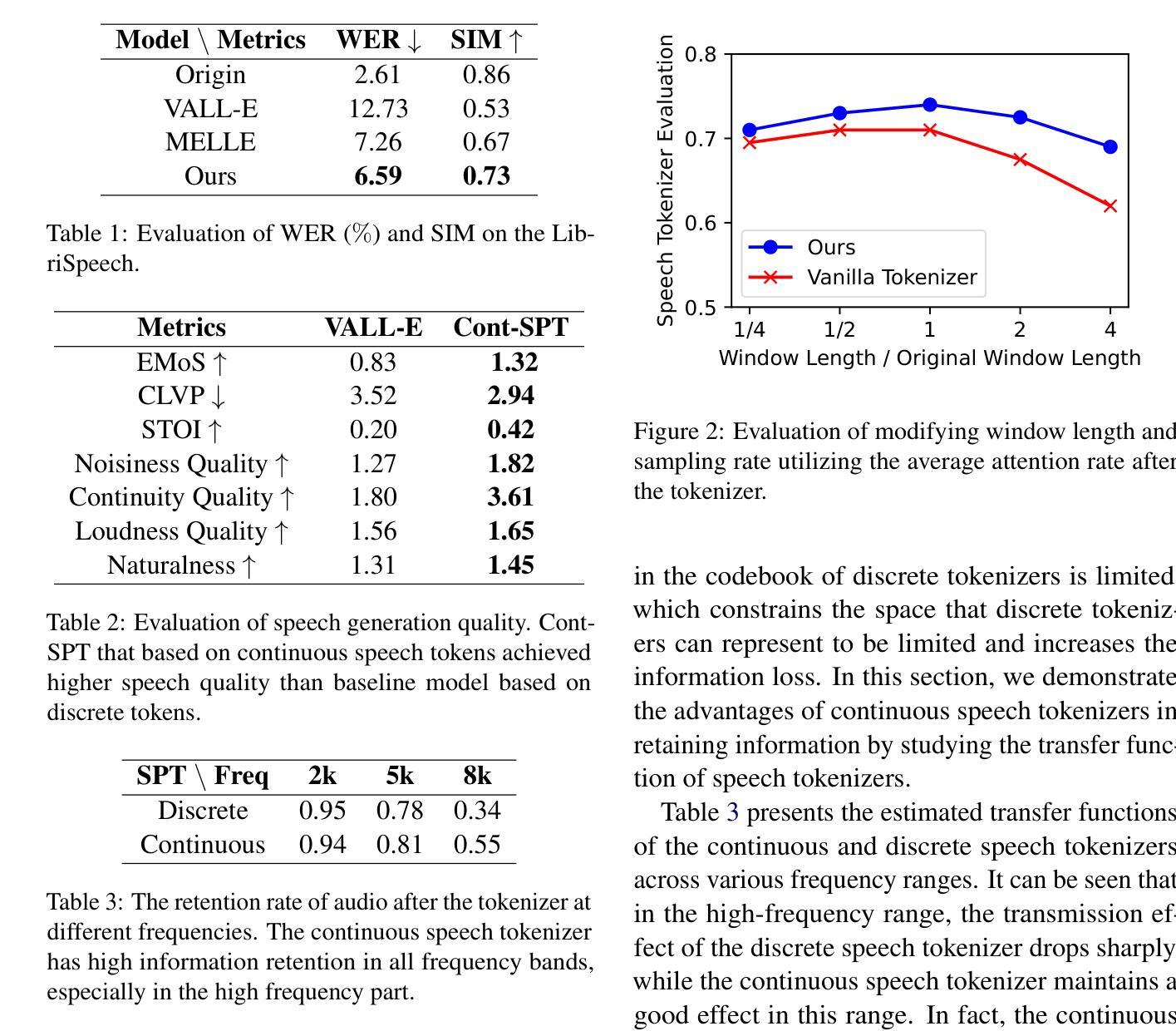
The fusion of speech and language in the era of large language models has garnered significant attention. Discrete speech token is often utilized in text-to-speech tasks for speech compression and portability, which is convenient for joint training with text and have good compression efficiency. However, we found that the discrete speech tokenizer still suffers from information loss. Therefore, we propose a simple yet effective continuous speech tokenizer named Cont-SPT, and a text-to-speech model based on continuous speech tokens. Our results show that the speech language model based on the continuous speech tokenizer has better continuity and higher estimated Mean Opinion Scores (MoS). This enhancement is attributed to better information preservation rate of the continuous speech tokenizer across both low and high frequencies in the frequency domain. The code and resources for Cont-SPT can be found in https://github.com/Yixing-Li/Continuous-Speech-Tokenizer
在大型语言模型时代,语音和语言的融合引起了人们的广泛关注。离散语音令牌通常用于文本到语音的任务,以实现语音压缩和便携性,这便于与文本进行联合训练并具有良好的压缩效率。然而,我们发现离散语音令牌化仍然存在信息丢失的问题。因此,我们提出了一种简单有效的连续语音令牌化方法,命名为Cont-SPT,以及一种基于连续语音令牌的文本到语音模型。结果表明,基于连续语音令牌的语音语言模型具有更好的连续性和更高的预估平均意见得分(MoS)。这种增强功能归因于连续语音令牌化在低频和高频域都能更好地保持信息。Cont-SPT的代码和资源可在https://github.com/Yixing-Li/Continuous-Speech-Tokenizer找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NAACL 2025 Findings Poster
总结
随着大型语言模型的兴起,语音和语言的融合引起了人们的广泛关注。离散语音令牌在文本到语音任务中常用于语音压缩和便携性,便于与文本进行联合训练,并具有良好的压缩效率。然而,研究发现离散语音分词器仍存在信息丢失的问题。为此,我们提出了一种简单有效的连续语音分词器Cont-SPT,以及基于连续语音令牌的文本到语音模型。结果表明,基于连续语音分词器的语音语言模型具有更好的连续性和更高的预估平均意见得分(MoS)。这一改进归因于连续语音分词器在频域中低频和高频段的信息保持率更高。Cont-SPT的代码和资源可在https://github.com/Yixing-Li/Continuous-Speech-Tokenizer找到。
关键见解
- 语音和语言融合在大型语言模型时代备受关注。
- 离散语音令牌在文本到语音任务中用于语音压缩和便携性。
- 离散语音分词器存在信息丢失的问题。
- 提出了名为Cont-SPT的连续语音分词器。
- 基于连续语音令牌的文本到语音模型表现出更好的连续性和更高的预估平均意见得分(MoS)。
- 连续语音分词器在频域中具有较高的信息保持率。
点此查看论文截图

Multi-modal Speech Transformer Decoders: When Do Multiple Modalities Improve Accuracy?
Authors:Yiwen Guan, Viet Anh Trinh, Vivek Voleti, Jacob Whitehill
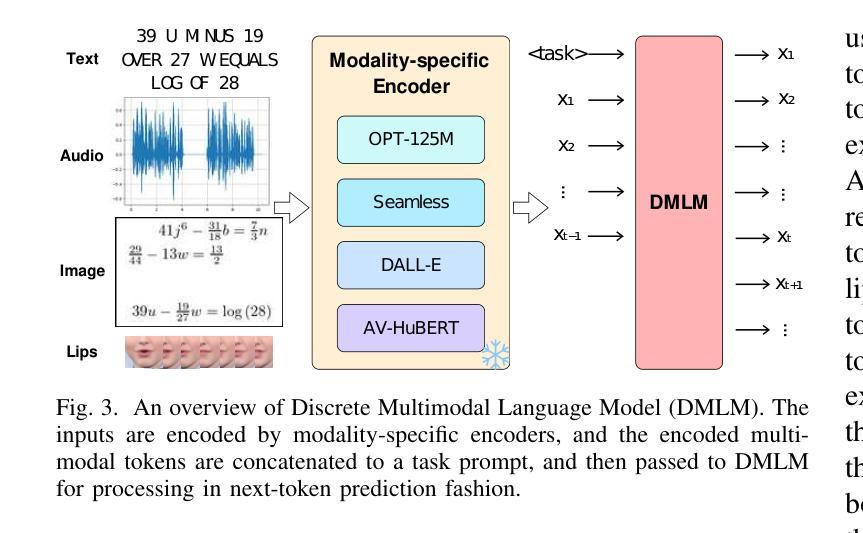
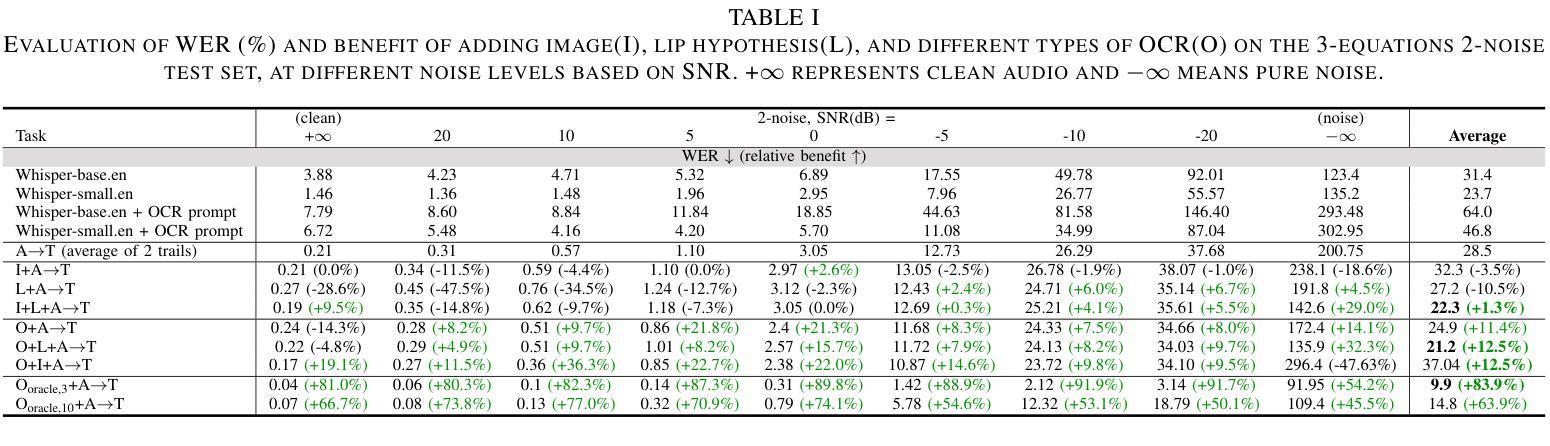
Decoder-only discrete-token language models have recently achieved significant success in automatic speech recognition. However, systematic analyses of how different modalities impact performance in specific scenarios remain limited. In this paper, we investigate the effects of multiple modalities on recognition accuracy on both synthetic and real-world datasets. Our experiments suggest that: (1) Integrating more modalities can increase accuracy; in particular, our paper is, to our best knowledge, the first to show the benefit of combining audio, image context, and lip information; (2) Images as a supplementary modality for speech recognition provide the greatest benefit at moderate noise levels, moreover, they exhibit a different trend compared to inherently synchronized modalities like lip movements; (3) Performance improves on both synthetic and real-world datasets when the most relevant visual information is filtered as a preprocessing step.
在自动语音识别领域,仅使用解码器的离散令牌语言模型最近取得了重大成功。然而,关于不同模态如何在特定场景中影响性能的系统性分析仍然有限。在本文中,我们研究了多种模态对合成和现实世界数据集上识别准确性的影响。我们的实验表明:(1)集成更多模态可以提高准确性;特别是,据我们所知,本文首次展示了结合音频、图像上下文和嘴唇信息的益处;(2)图像作为语音识别的辅助模态,在中等噪声水平下提供的效益最大,而且与嘴唇动作等内在同步模态相比,它们表现出不同的趋势;(3)当最相关的视觉信息作为预处理步骤进行过滤时,合成和现实世界数据集上的性能都会提高。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了多模态在合成和真实世界数据集上语音识别准确性的影响。研究发现,整合多模态信息能提高识别准确性,特别是结合音频、图像背景和唇语信息;图像作为语音识别的辅助模态在中等噪声水平下提供最大帮助,并且与唇动等内在同步模态展现出不同趋势;在过滤最相关的视觉信息作为预处理步骤时,合成和真实世界数据集上的性能均有所提高。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态信息的整合能提高语音识别准确性。
- 结合音频、图像背景和唇语信息能带来最佳识别效果。
- 图像作为语音识别辅助模态在中等噪声环境下效益最大。
- 与内在同步模态如唇动相比,图像模态展现出不同趋势。
- 过滤最相关的视觉信息作为预处理能提高识别性能。
- 上述发现在合成和真实世界数据集上都得到了验证。
- 该研究为语音识别中的多模态融合提供了新见解。
点此查看论文截图


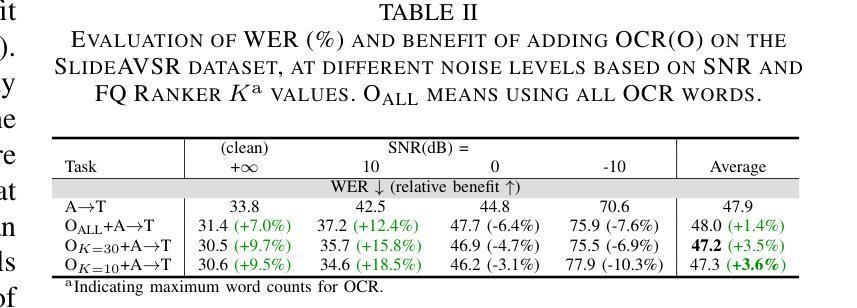
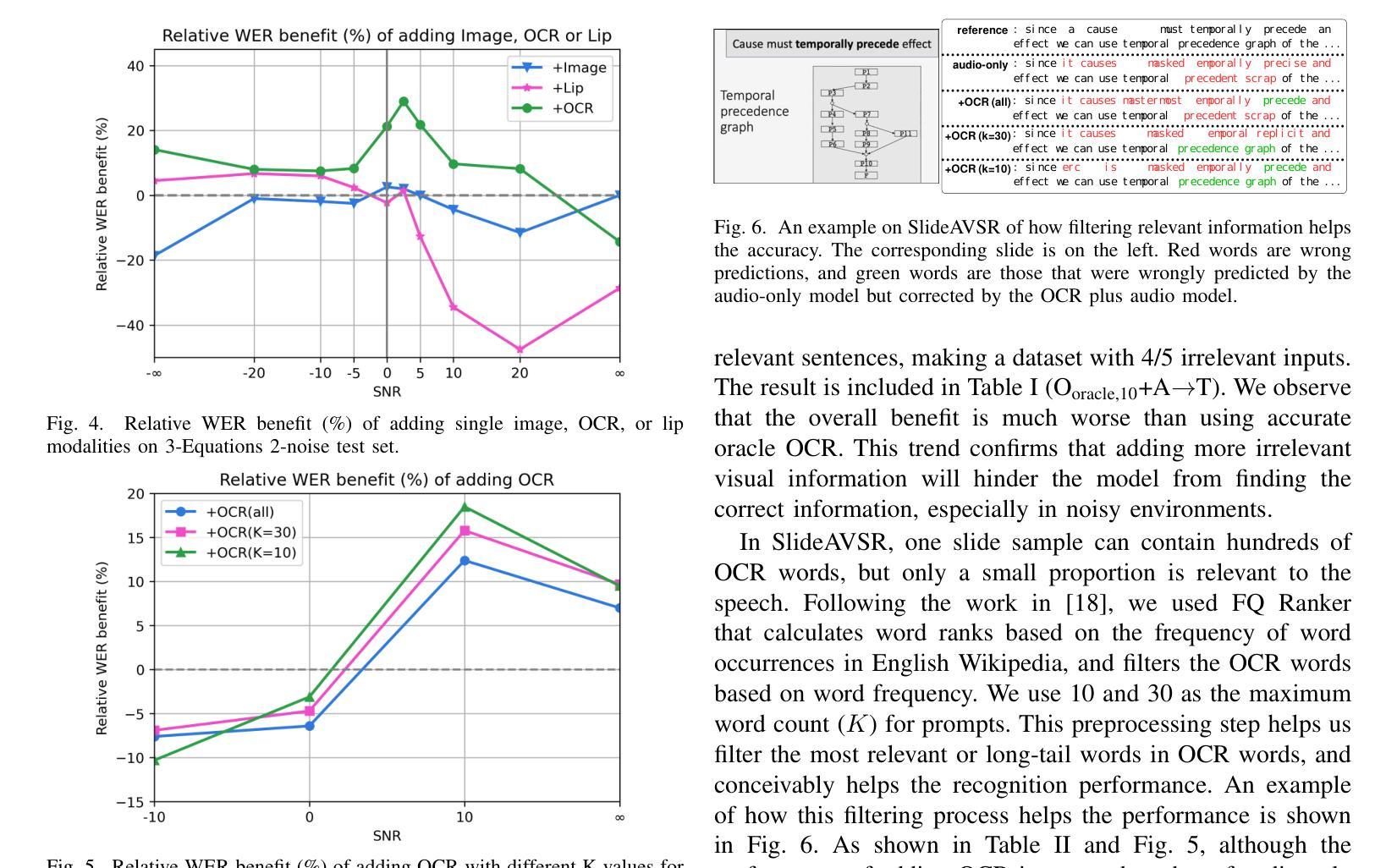
Large Language Model Can Transcribe Speech in Multi-Talker Scenarios with Versatile Instructions
Authors:Lingwei Meng, Shujie Hu, Jiawen Kang, Zhaoqing Li, Yuejiao Wang, Wenxuan Wu, Xixin Wu, Xunying Liu, Helen Meng
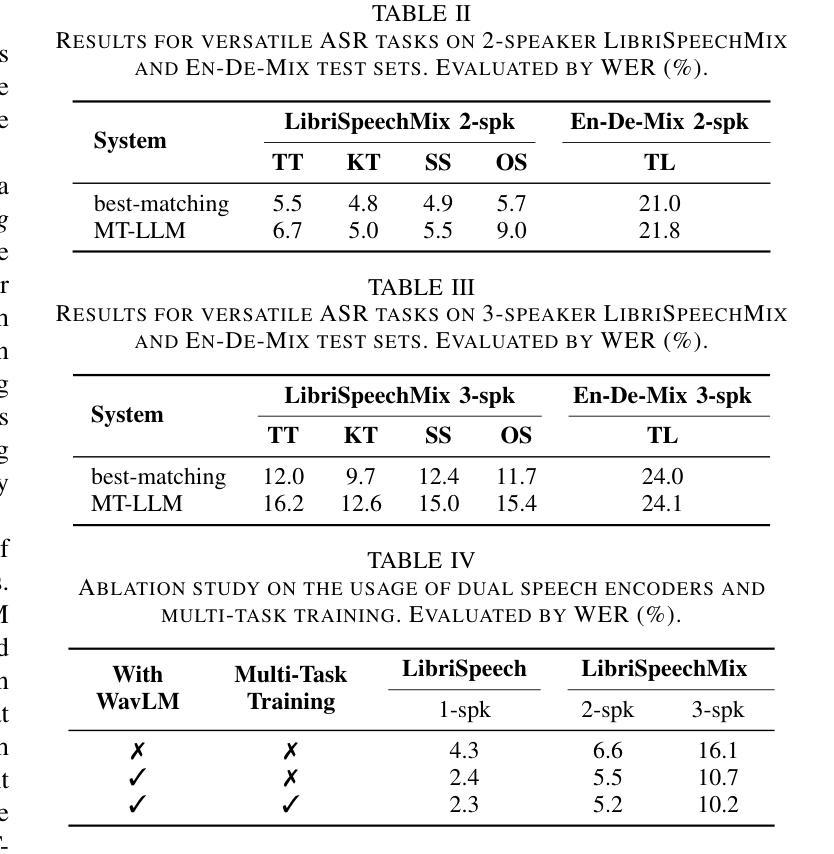
Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized various domains, bringing significant progress and new opportunities. Despite progress in speech-related tasks, LLMs have not been sufficiently explored in multi-talker scenarios. In this work, we present a pioneering effort to investigate the capability of LLMs in transcribing speech in multi-talker environments, following versatile instructions related to multi-talker automatic speech recognition (ASR), target talker ASR, and ASR based on specific talker attributes such as sex, occurrence order, language, and keyword spoken. Our approach utilizes WavLM and Whisper encoder to extract multi-faceted speech representations that are sensitive to speaker characteristics and semantic context. These representations are then fed into an LLM fine-tuned using LoRA, enabling the capabilities for speech comprehension and transcription. Comprehensive experiments reveal the promising performance of our proposed system, MT-LLM, in cocktail party scenarios, highlighting the potential of LLM to handle speech-related tasks based on user instructions in such complex settings. The code, model, and samples are available at https://github.com/cuhealthybrains/MT-LLM.
近期大型语言模型(LLM)的进步已经颠覆了多个领域,带来了显著的进步和新机遇。尽管在语音相关任务上有所进展,但LLM在多说话人场景中的应用尚未得到充分探索。在这项工作中,我们率先研究了LLM在多说话人环境下的语音识别能力。我们遵循与多说话人自动语音识别(ASR)、目标说话人ASR以及基于特定说话人属性(如性别、发言顺序、语言和关键词)的ASR相关的通用指令。我们的方法利用WavLM和Whisper编码器提取多面语音表示,这些表示对说话人特性和语义上下文敏感。然后,这些表示被输入到使用LoRA微调过的LLM中,以实现语音理解和转录功能。综合实验表明,我们提出的MT-LLM系统在鸡尾酒会场景中表现出有前景的性能,突显了LLM在复杂环境中根据用户指令处理语音相关任务的潜力。代码、模型和样本可在https://github.com/cuhealthybrains/MT-LLM找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE ICASSP 2025. Update code link
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的近期进展为各领域带来了革命性的变革,促进了显著进步并为新的机会敞开了大门。尽管在语音相关任务方面有所进展,但LLM在多说话人场景中的转录应用尚未得到充分探索。本研究致力于探索LLM在多变环境下的语音转录能力,包括与多说话人自动语音识别(ASR)、目标说话人ASR以及基于特定说话人属性(如性别、发生顺序、语言和关键词)的ASR相关的灵活指令。我们的方法利用WavLM和Whisper编码器提取多面语音表示,这些表示对发言者的特性和语义上下文都很敏感。然后,通过LoRA微调这些表示,使其具备理解并转录语音的能力。综合实验显示,我们的系统MT-LLM在鸡尾酒会场景中表现优异,突显了LLM在复杂环境中处理基于用户指令的语音相关任务的潜力。代码、模型和样本可在GitHub上获取:https://github.com/cuhealthybrains/MT-LLM。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在语音相关任务中的应用正在快速发展。
- LLM在多说话人场景中的语音转录尚未充分探索。
- 本研究探索了LLM在多说话人环境中的语音转录能力。
- 利用WavLM和Whisper编码器提取多面语音表示以区分不同说话者。
- 利用LoRA微调LLM以理解并转录语音。
- 综合实验显示MT-LLM系统在复杂场景下的出色表现。
点此查看论文截图

Medical Spoken Named Entity Recognition
Authors:Khai Le-Duc, David Thulke, Hung-Phong Tran, Long Vo-Dang, Khai-Nguyen Nguyen, Truong-Son Hy, Ralf Schlüter
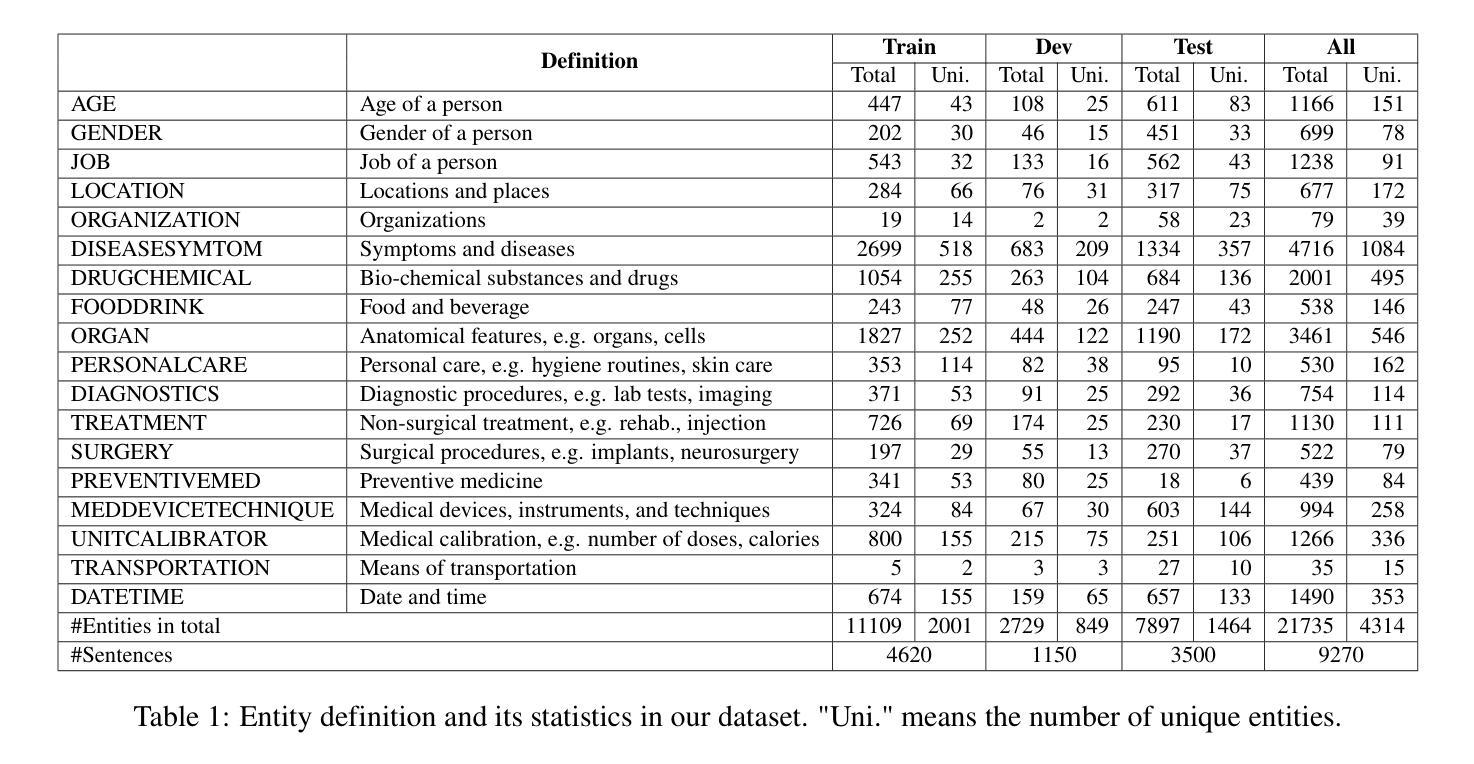
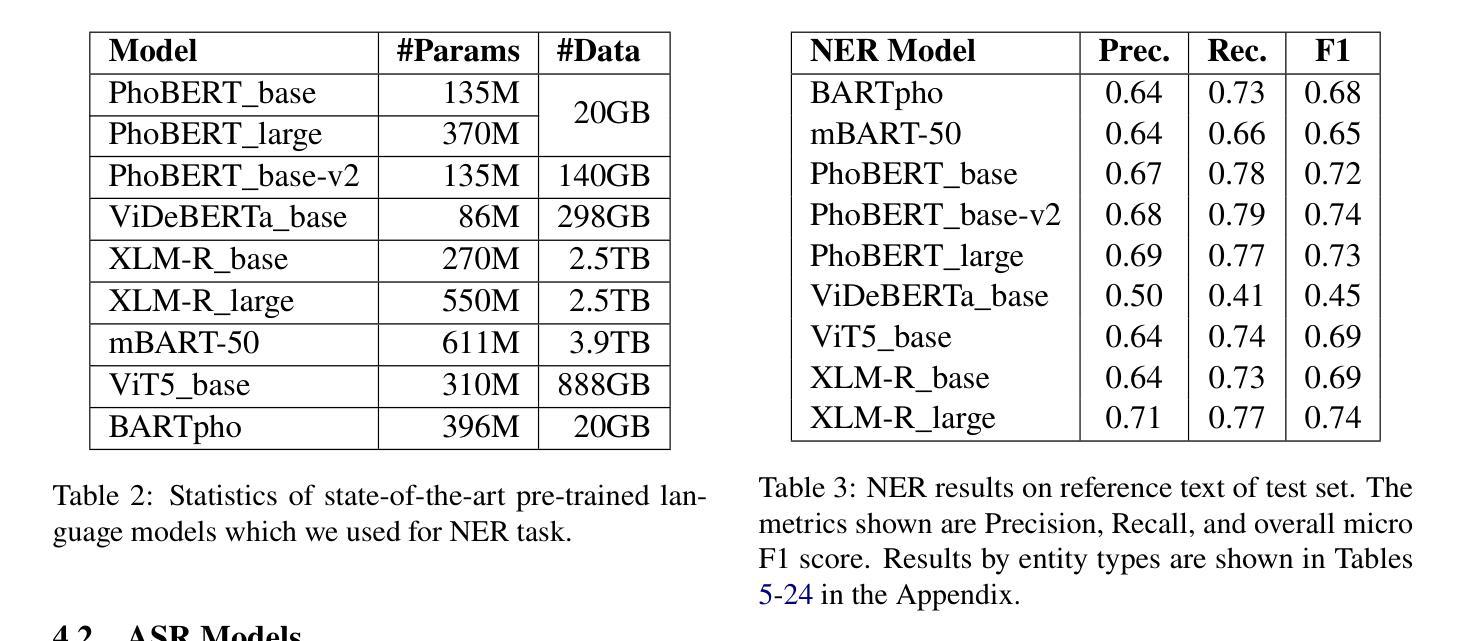
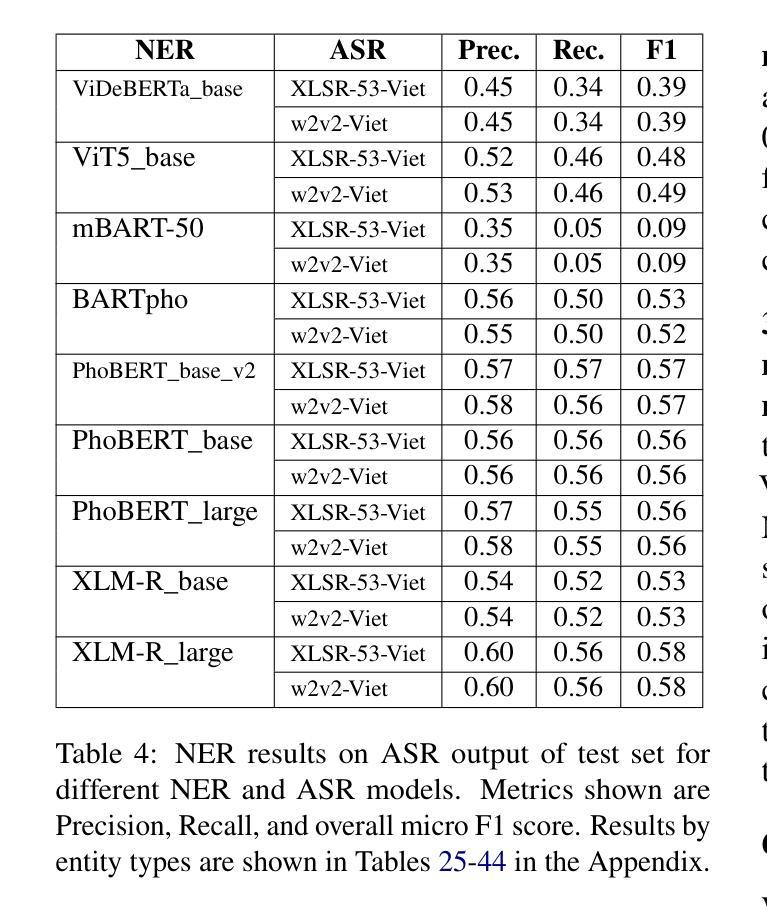
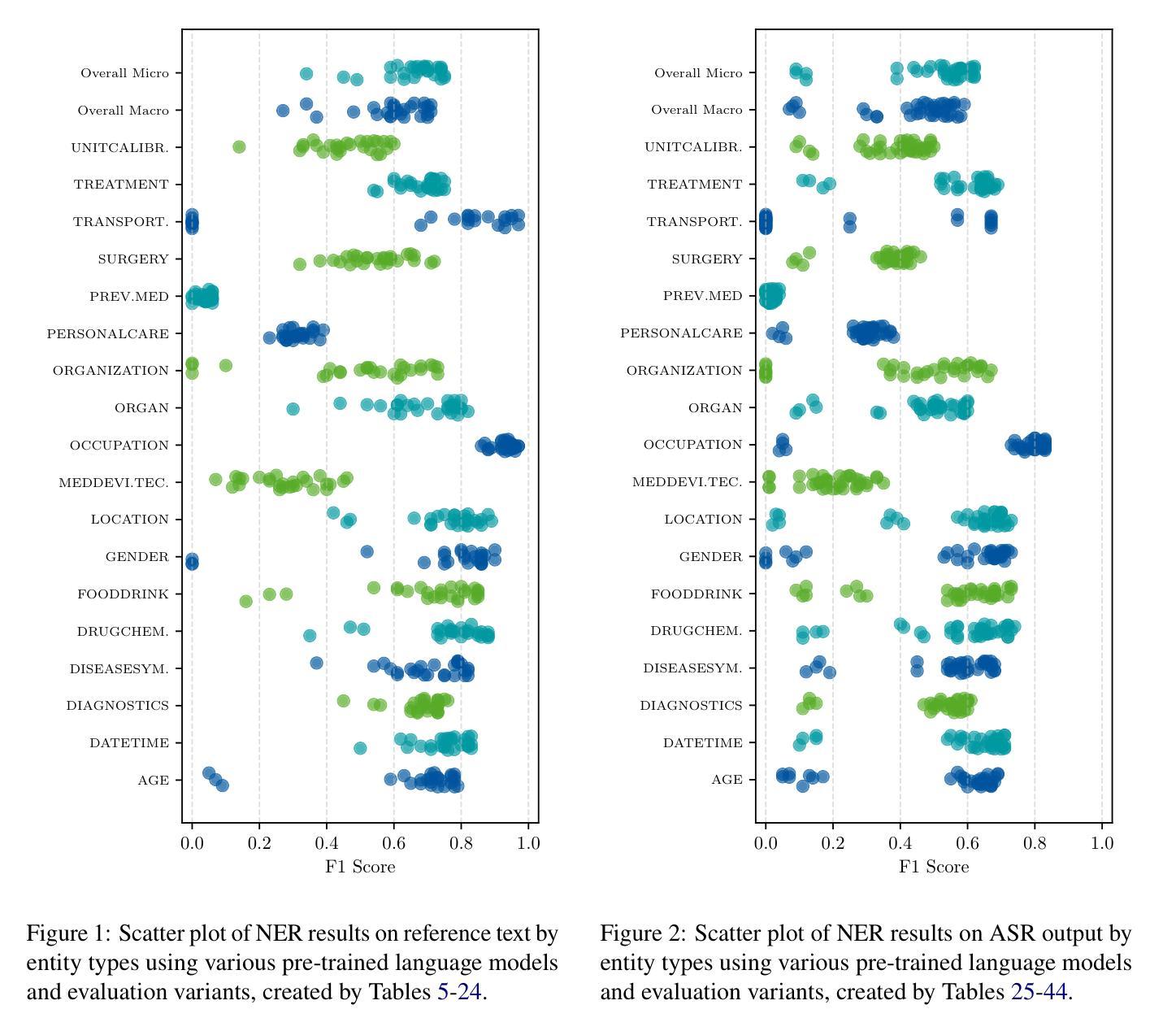
Spoken Named Entity Recognition (NER) aims to extract named entities from speech and categorise them into types like person, location, organization, etc. In this work, we present VietMed-NER - the first spoken NER dataset in the medical domain. To our knowledge, our Vietnamese real-world dataset is the largest spoken NER dataset in the world regarding the number of entity types, featuring 18 distinct types. Furthermore, we present baseline results using various state-of-the-art pre-trained models: encoder-only and sequence-to-sequence; and conduct quantitative and qualitative error analysis. We found that pre-trained multilingual models generally outperform monolingual models on reference text and ASR output and encoders outperform sequence-to-sequence models in NER tasks. By translating the transcripts, the dataset can also be utilised for text NER in the medical domain in other languages than Vietnamese. All code, data and models are publicly available: https://github.com/leduckhai/MultiMed/tree/master/VietMed-NER.
语音命名实体识别(NER)旨在从语音中提取命名实体,并将其分类为人物、地点、组织等类型。在这项工作中,我们推出了VietMed-NER——医疗领域的首个语音NER数据集。据我们所知,我们的越南现实数据集是世界上实体类型数量最多的语音NER数据集,具有18种不同的类型。此外,我们使用各种最先进的预训练模型展示了基线结果:仅编码器模型和序列到序列模型;并进行定量和定性误差分析。我们发现,在参考文本和ASR输出上,预训练的多语言模型通常优于单语言模型,并且在NER任务中,编码器模型的性能优于序列到序列模型。通过翻译录音,该数据集也可用于除越南语以外的其他语言的医疗领域文本NER。所有代码、数据和模型可公开访问:https://github.com/leduckhai/MultiMed/tree/master/VietMed-NER。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NAACL 2025, 60 pages
Summary
越南语医疗领域口语命名实体识别数据集VietMed-NER面世,包含18种不同实体类型,为世界上最大的医疗领域口语NER数据集。研究采用最新预训练模型,发现多语言预训练模型在参考文本和自动语音识别输出上通常优于单语言模型,编码器在命名实体识别任务上表现优于序列到序列模型。数据集可通过翻译转录本用于其他语言医疗文本命名实体识别研究。
Key Takeaways
1.VietMed-NER是医疗领域的首个越南语口语命名实体识别数据集。
2.VietMed-NER包含18种不同的实体类型,为世界上最大的医疗领域口语NER数据集。
3.研究使用了最新的预训练模型,包括编码器模型和序列到序列模型。
4.多语言预训练模型在参考文本和自动语音识别输出上的表现通常优于单语言模型。
5.编码器在命名实体识别任务上的表现优于序列到序列模型。
6.VietMed-NER数据集通过翻译转录本也可用于其他语言的医疗文本命名实体识别研究。
点此查看论文截图