⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-04 更新
Prompting Medical Vision-Language Models to Mitigate Diagnosis Bias by Generating Realistic Dermoscopic Images
Authors:Nusrat Munia, Abdullah-Al-Zubaer Imran
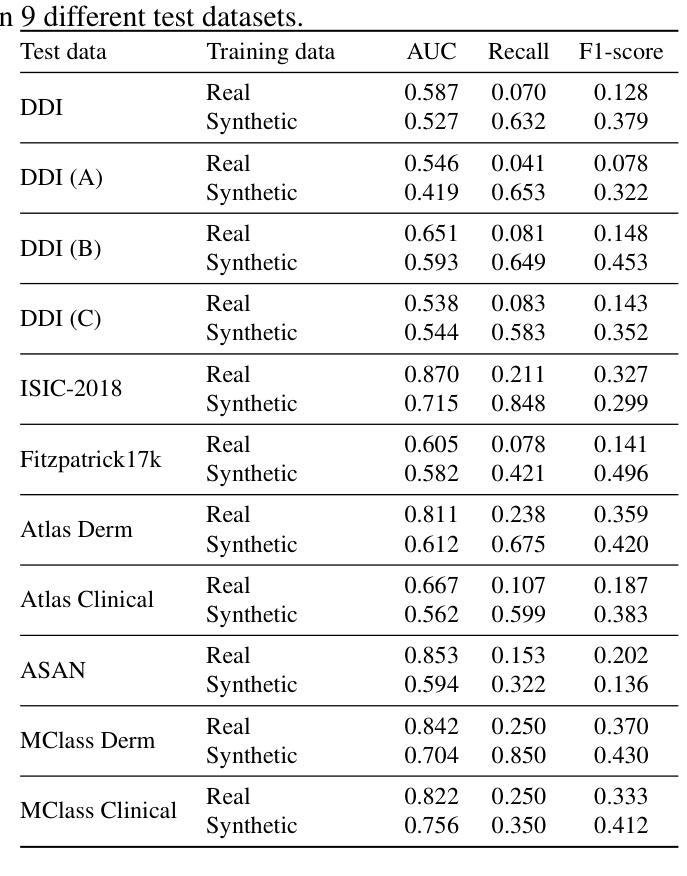
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in skin disease diagnosis has improved significantly, but a major concern is that these models frequently show biased performance across subgroups, especially regarding sensitive attributes such as skin color. To address these issues, we propose a novel generative AI-based framework, namely, Dermatology Diffusion Transformer (DermDiT), which leverages text prompts generated via Vision Language Models and multimodal text-image learning to generate new dermoscopic images. We utilize large vision language models to generate accurate and proper prompts for each dermoscopic image which helps to generate synthetic images to improve the representation of underrepresented groups (patient, disease, etc.) in highly imbalanced datasets for clinical diagnoses. Our extensive experimentation showcases the large vision language models providing much more insightful representations, that enable DermDiT to generate high-quality images. Our code is available at https://github.com/Munia03/DermDiT
人工智能(AI)在皮肤病诊断中的应用已经取得了显著进步,但一个主要问题是这些模型在子群体中的表现经常存在偏见,特别是在肤色等敏感属性方面。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新型的基于生成式人工智能的框架,即皮肤病扩散转换器(DermDiT)。它利用通过视觉语言模型生成的文本提示和跨模态文本图像学习来生成新的皮肤镜图像。我们利用大型视觉语言模型为每张皮肤镜图像生成准确恰当的提示,这有助于生成合成图像,以改善高度不平衡数据集中代表性不足的群体(患者、疾病等)的临床诊断表示。我们的大量实验表明,大型视觉语言模型提供了更有洞察力的表示,使DermDiT能够生成高质量图像。我们的代码可在https://github.com/Munia03/DermDiT找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper accepted at International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2025)
Summary
本文介绍了针对皮肤疾病诊断中人工智能模型存在的偏见问题,提出了一种基于生成式人工智能的新型框架——皮肤病扩散转换器(DermDiT)。该框架利用视觉语言模型生成文本提示,并通过多模态文本图像学习生成新的皮肤镜图像。DermDiT通过大型视觉语言模型为每张皮肤镜图像生成准确的提示,有助于生成代表性不足的群体的合成图像,从而改进高度不均衡数据集中的临床诊断。实验表明,大型视觉语言模型提供了更有洞察力的表示,使DermDiT能够生成高质量图像。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能在皮肤疾病诊断中的应用已经取得了显著进步。
- 现有模型在针对不同子群体的性能上经常表现出偏见,特别是在涉及皮肤颜色等敏感属性方面。
- 提出了一种新型生成式AI框架——皮肤病扩散转换器(DermDiT)来解决这一问题。
- DermDiT利用视觉语言模型生成文本提示,并通过多模态文本-图像学习来生成新的皮肤镜图像。
- 该框架通过为每张皮肤镜图像生成准确的提示,有助于改善代表性不足的群体(如患者、疾病等)在高度不均衡数据集中的表示。
- 大型视觉语言模型为DermDiT生成高质量图像提供了更有洞察力的表示。
点此查看论文截图

STPNet: Scale-aware Text Prompt Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Dandan Shan, Zihan Li, Yunxiang Li, Qingde Li, Jie Tian, Qingqi Hong
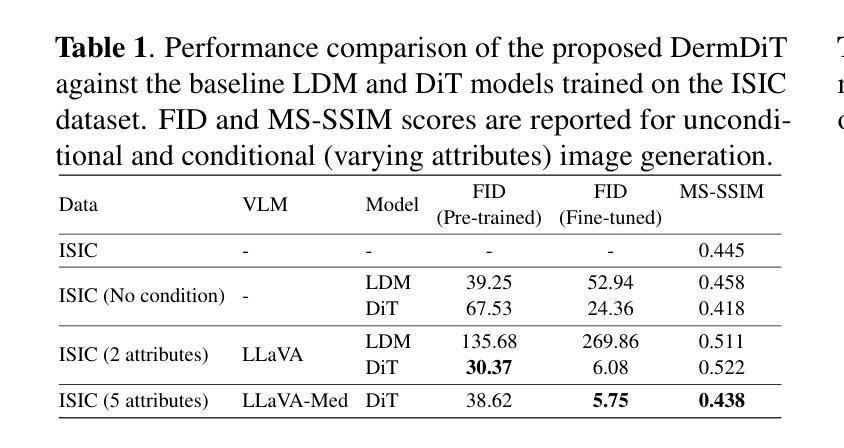
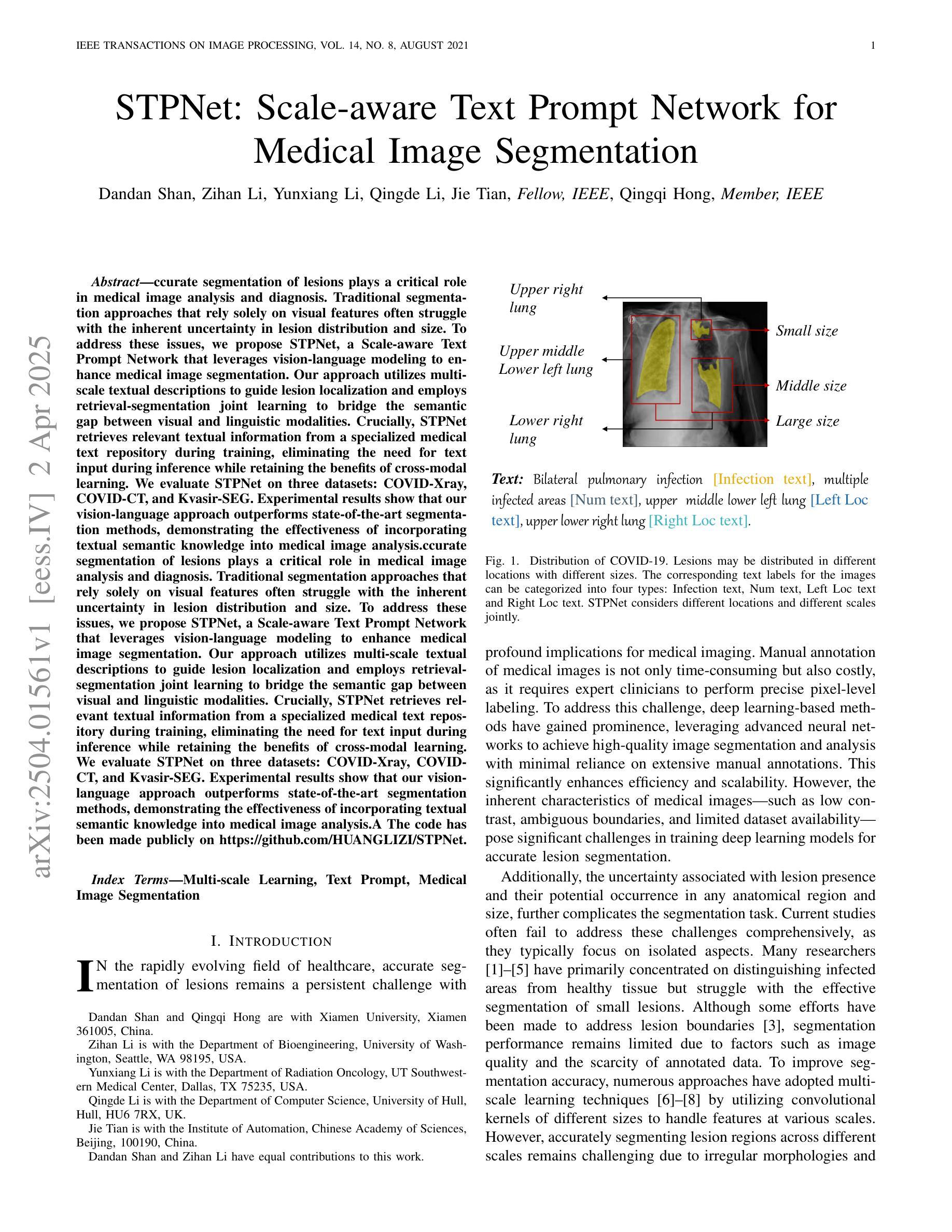
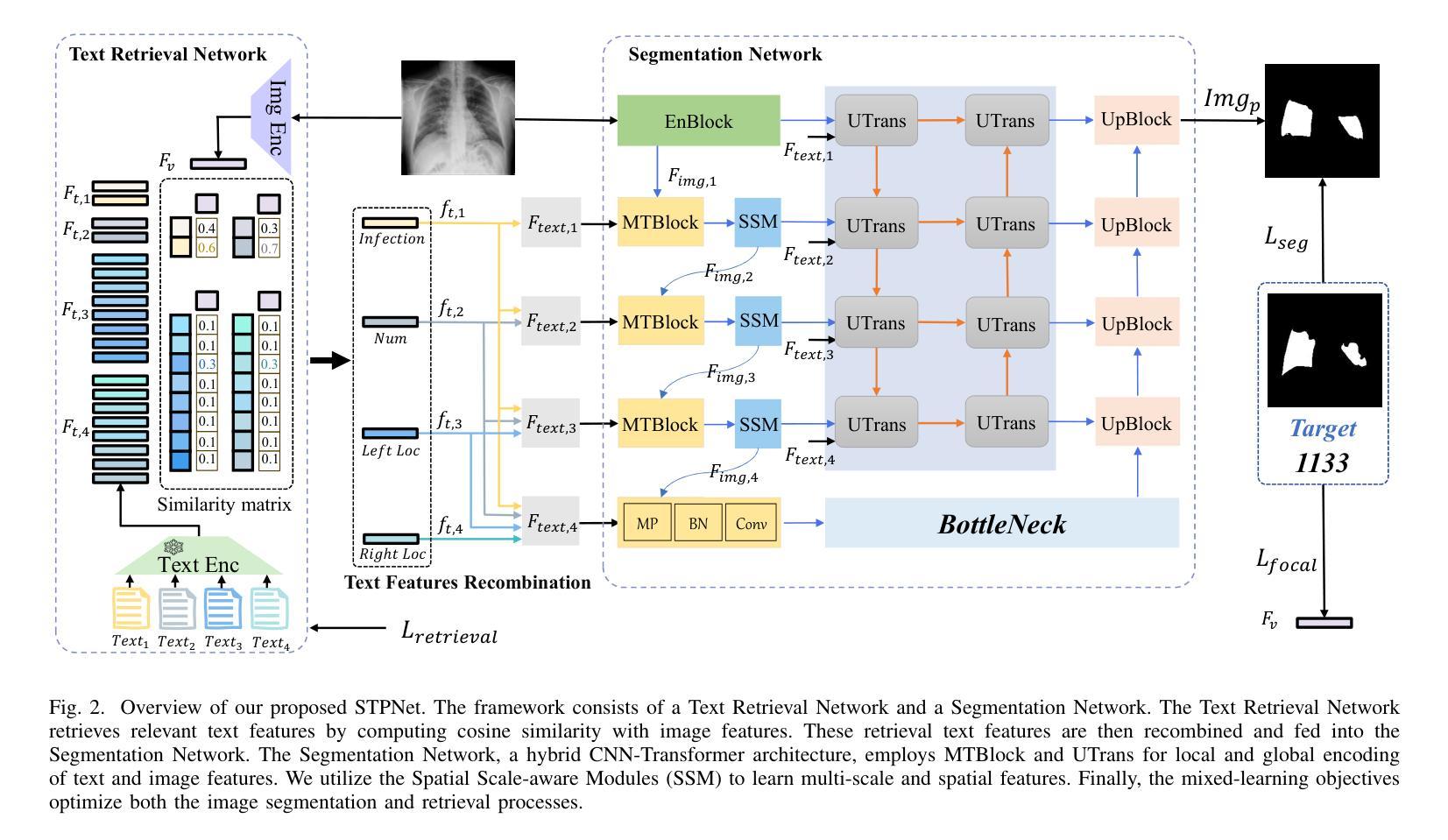
Accurate segmentation of lesions plays a critical role in medical image analysis and diagnosis. Traditional segmentation approaches that rely solely on visual features often struggle with the inherent uncertainty in lesion distribution and size. To address these issues, we propose STPNet, a Scale-aware Text Prompt Network that leverages vision-language modeling to enhance medical image segmentation. Our approach utilizes multi-scale textual descriptions to guide lesion localization and employs retrieval-segmentation joint learning to bridge the semantic gap between visual and linguistic modalities. Crucially, STPNet retrieves relevant textual information from a specialized medical text repository during training, eliminating the need for text input during inference while retaining the benefits of cross-modal learning. We evaluate STPNet on three datasets: COVID-Xray, COVID-CT, and Kvasir-SEG. Experimental results show that our vision-language approach outperforms state-of-the-art segmentation methods, demonstrating the effectiveness of incorporating textual semantic knowledge into medical image analysis. The code has been made publicly on https://github.com/HUANGLIZI/STPNet.
在医学图像分析和诊断中,精确地分割病变部位起着至关重要的作用。传统的仅依赖于视觉特征的分割方法通常难以处理病变分布和大小中的固有不确定性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了STPNet,这是一个利用视觉语言建模来提高医学图像分割的尺度感知文本提示网络。我们的方法利用多尺度文本描述来指导病变部位的定位,并采用检索分割联合学习来弥合视觉和语言模态之间的语义鸿沟。重要的是,STPNet在训练过程中从专用的医学文本存储库中检索相关的文本信息,从而在推理过程中不需要文本输入,同时保留跨模态学习的优点。我们在三个数据集上评估了STPNet:COVID-Xray、COVID-CT和Kvasir-SEG。实验结果表明,我们的视觉语言方法优于最先进的分割方法,证明了将文本语义知识融入医学图像分析中的有效性。代码已公开在https://github.com/HUANGLIZI/STPNet。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
STPNet是一个利用视觉语言建模增强医学图像分割的规模感知文本提示网络。它利用多尺度文本描述引导病变定位,并采用检索分割联合学习来缩小视觉和语言模态之间的语义鸿沟。STPNet在训练过程中从专业医学文本存储库中检索相关文本信息,在推理过程中无需文本输入,同时保留跨模态学习的优势。在三个数据集上的实验结果表明,STPNet在医学图像分析领域优于最先进的分割方法,融入文本语义知识效果显著。
Key Takeaways
- STPNet是一个针对医学图像分割的规模感知文本提示网络。
- 该网络利用多尺度文本描述来引导病变定位。
- STPNet采用检索分割联合学习,缩小了视觉和语言模态之间的语义鸿沟。
- STPNet在训练过程中从专业医学文本存储库中检索相关文本信息。
- 在推理过程中,STPNet不需要额外的文本输入。
- STPNet在三个数据集上的实验表现优于其他最先进的分割方法。
- 融入文本语义知识在医学图像分析中具有显著效果。
点此查看论文截图
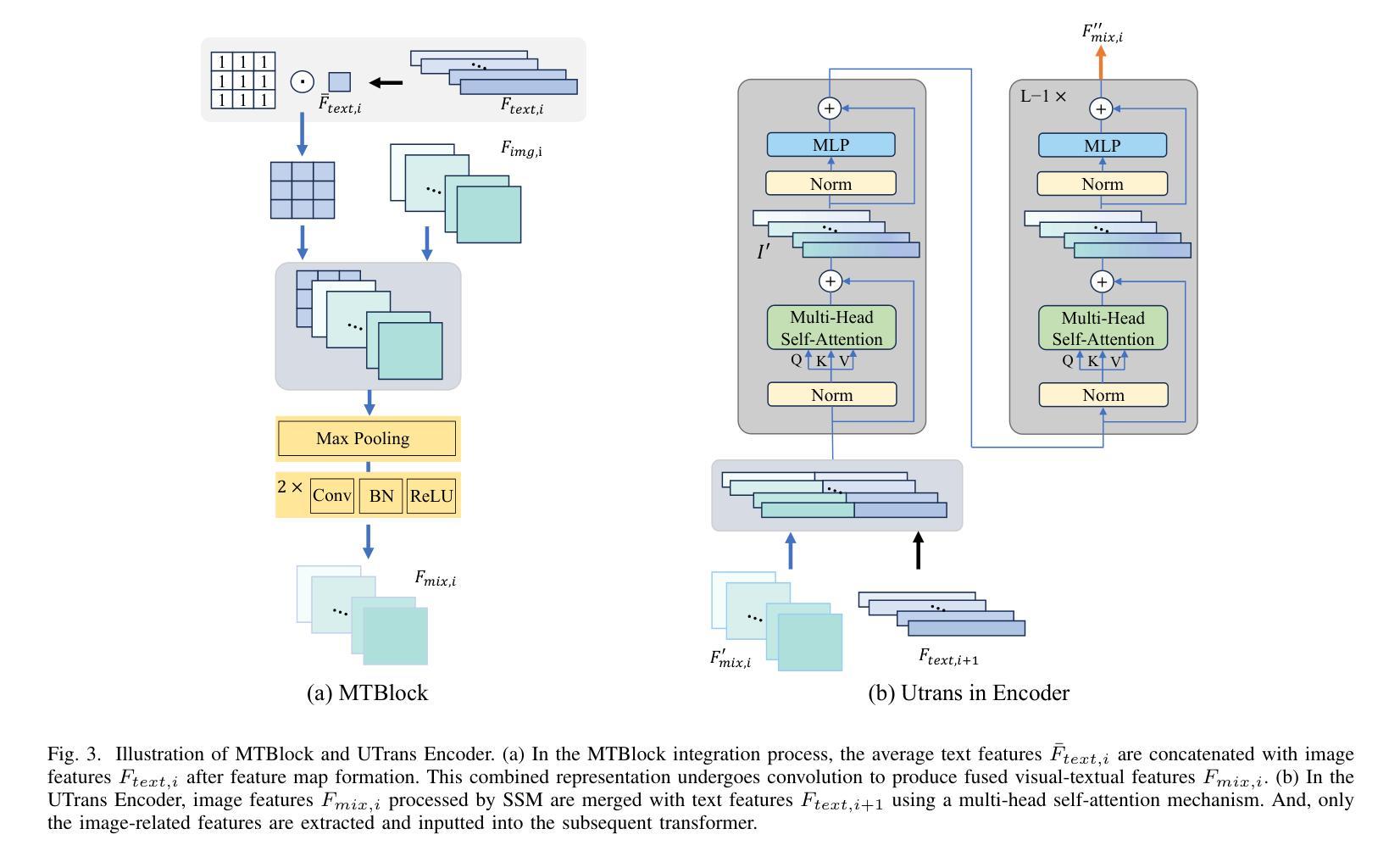
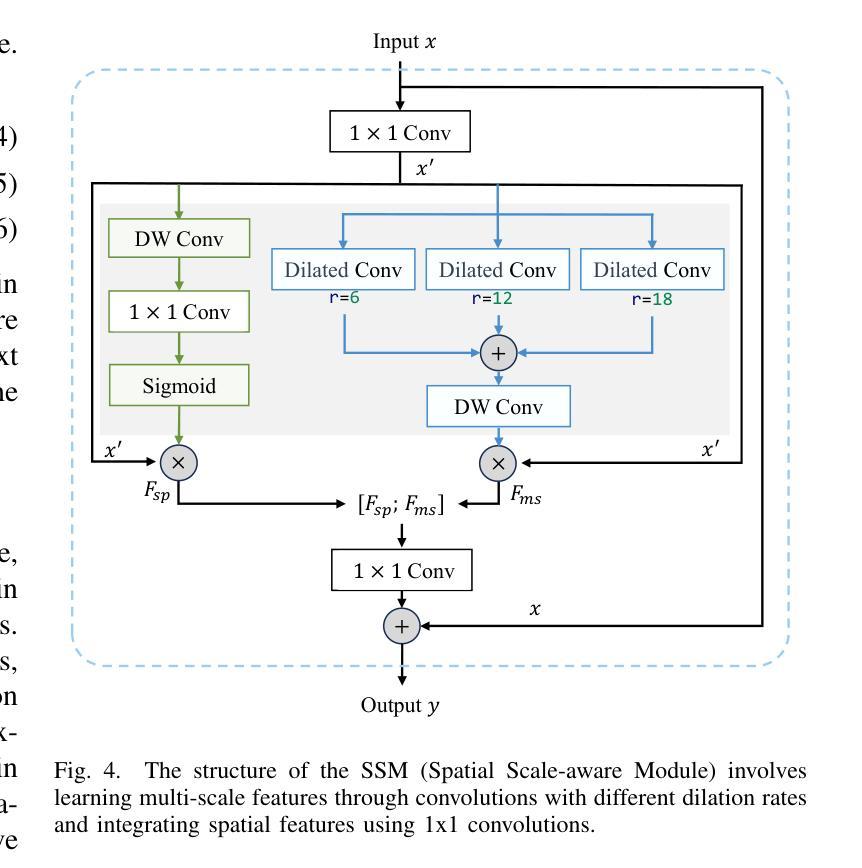
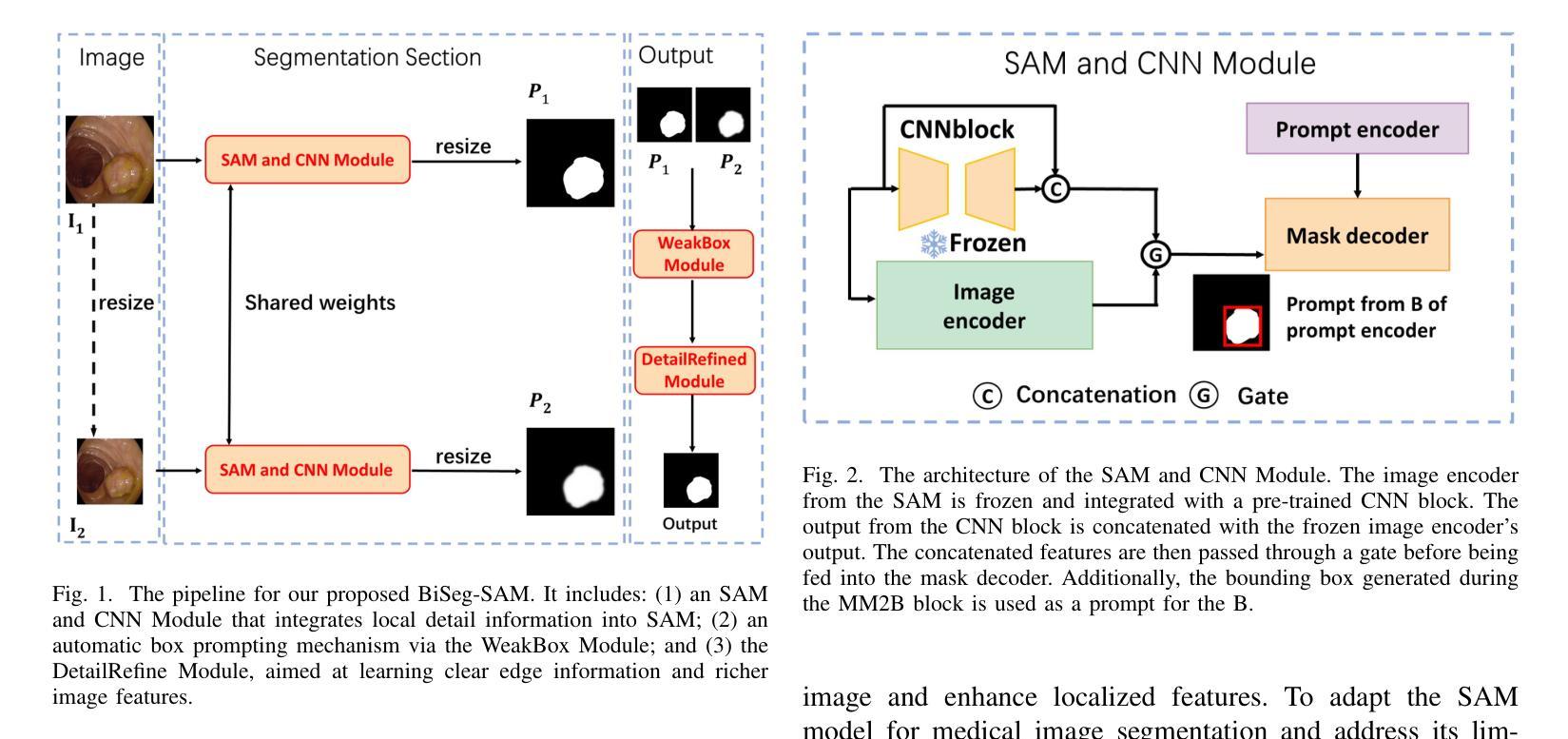
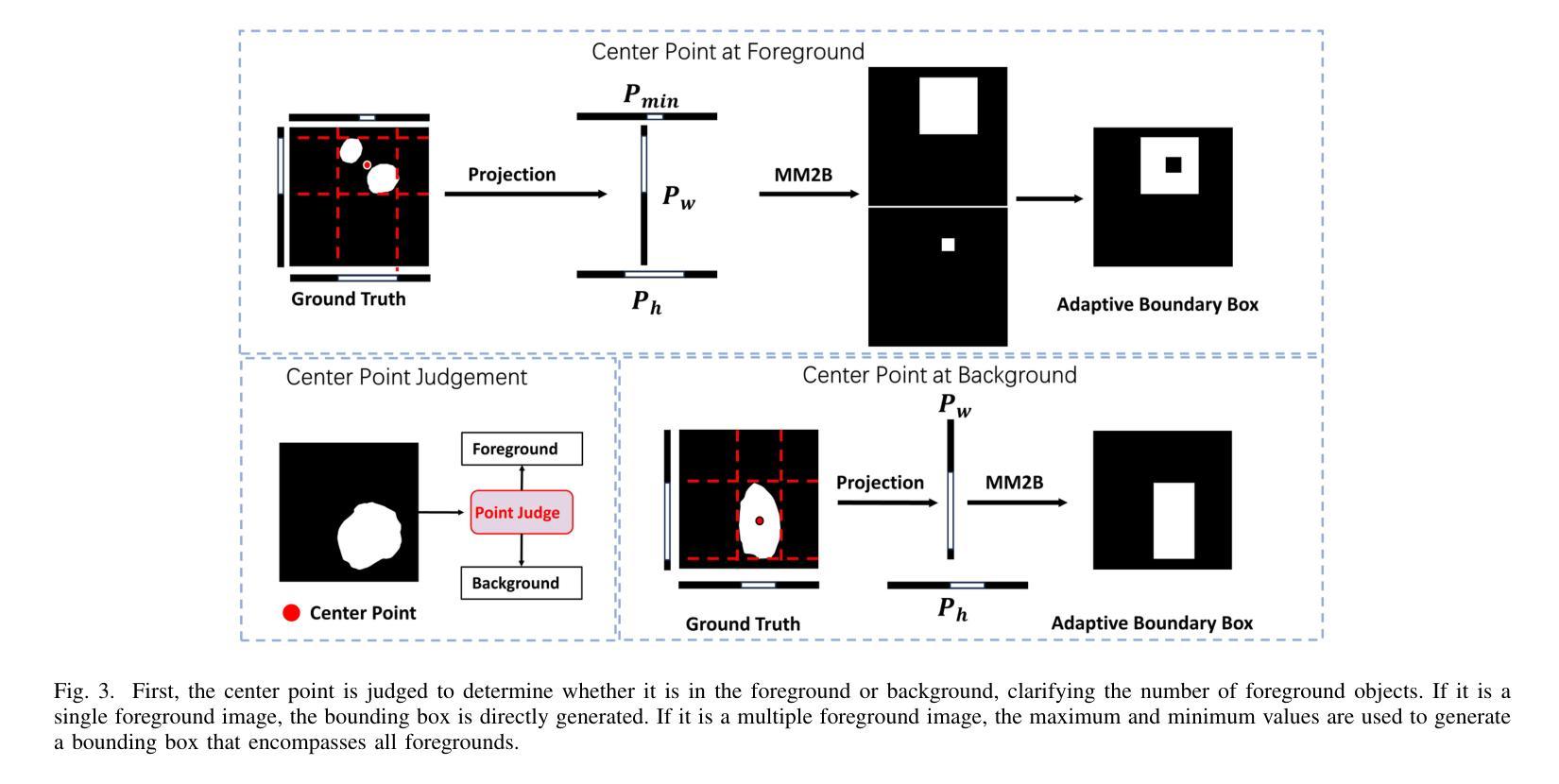
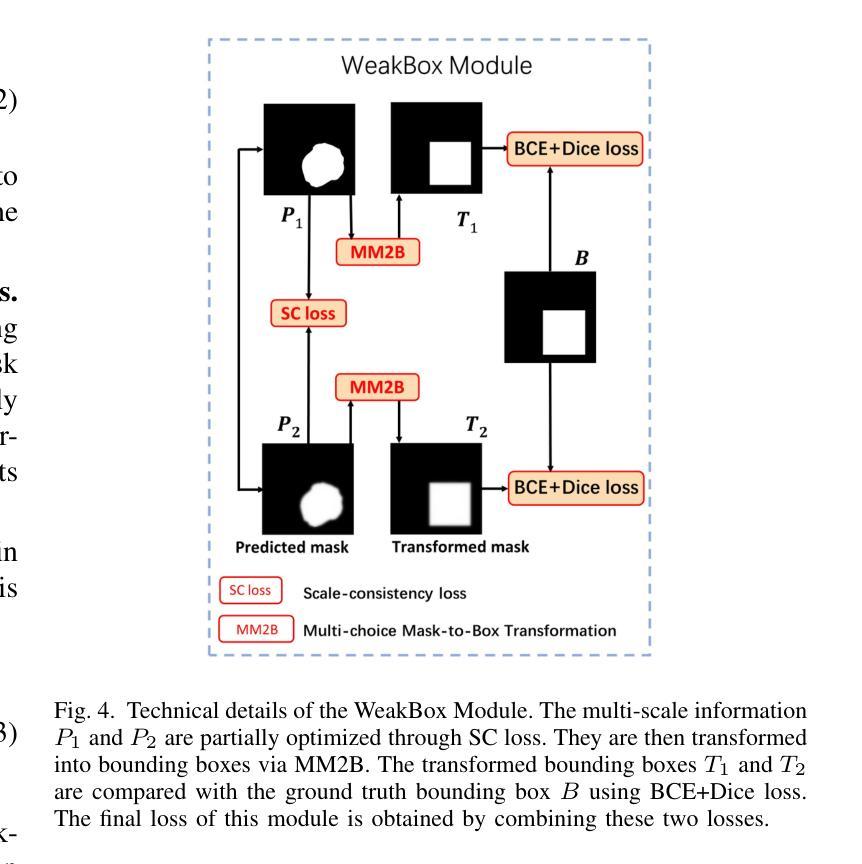
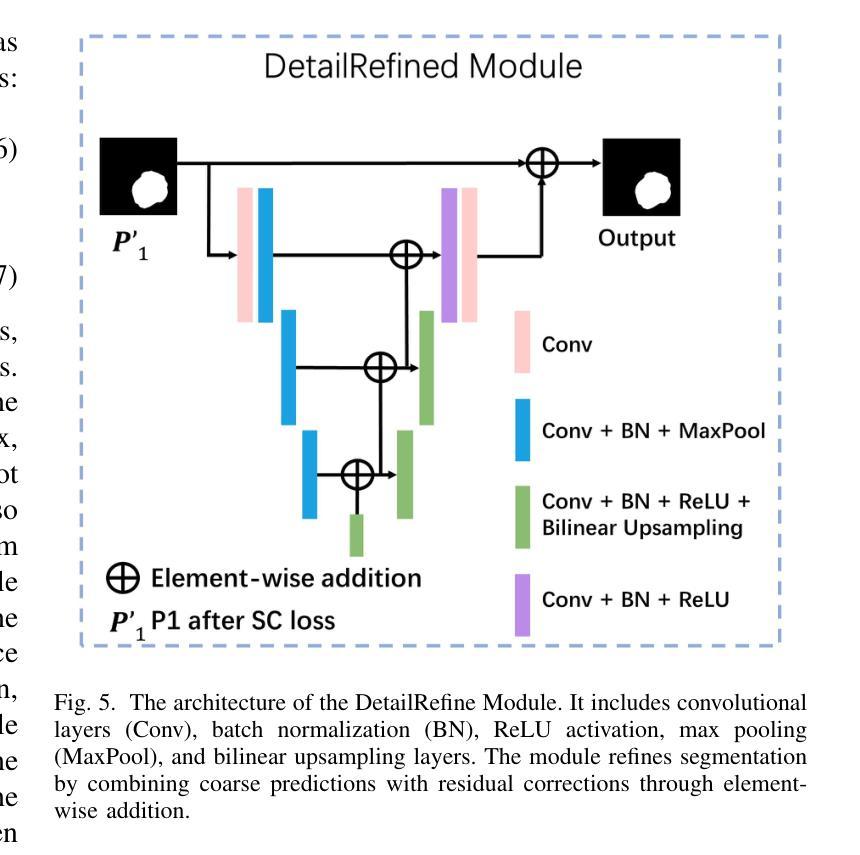
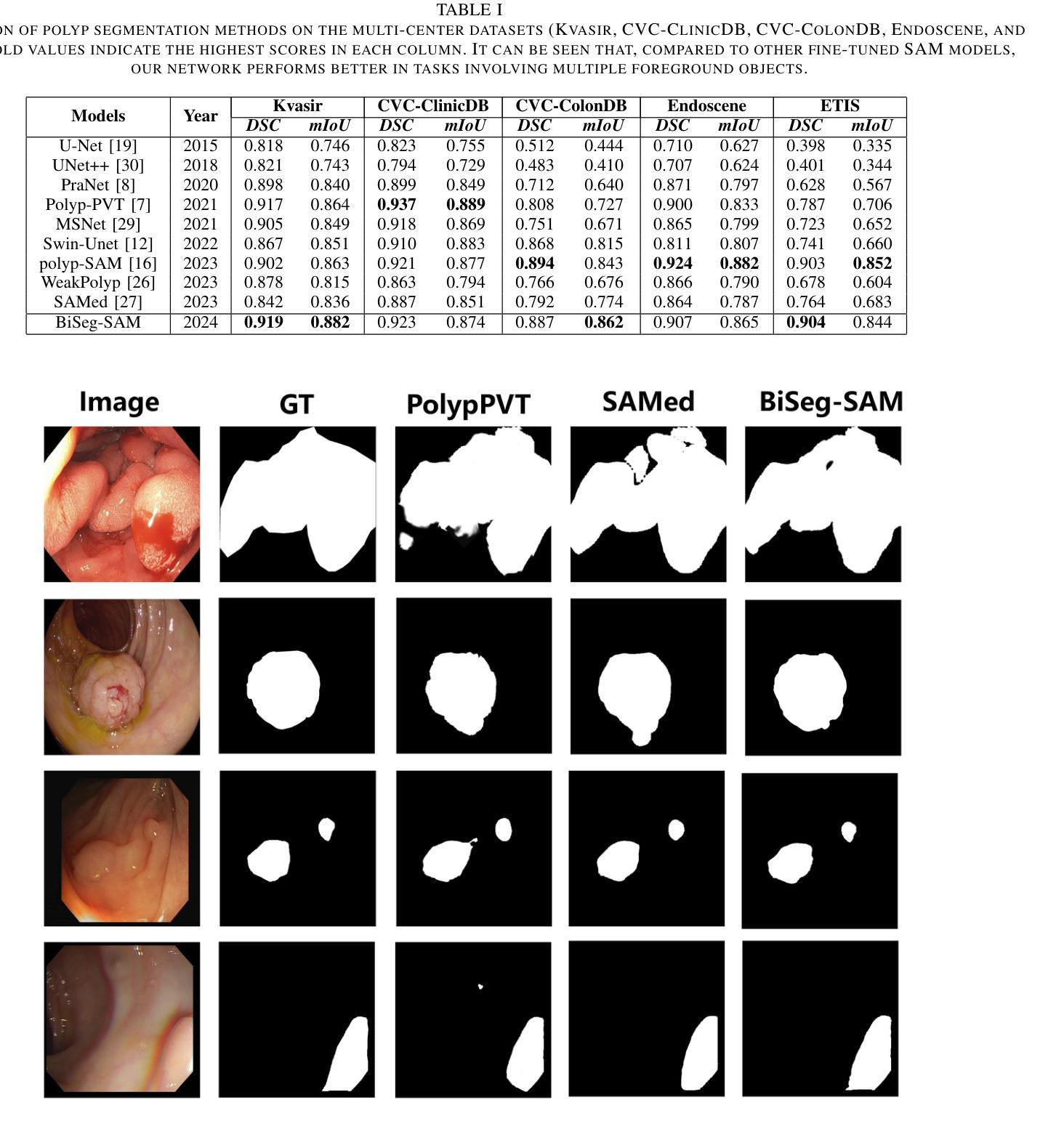
BiSeg-SAM: Weakly-Supervised Post-Processing Framework for Boosting Binary Segmentation in Segment Anything Models
Authors:Encheng Su, Hu Cao, Alois Knoll
Accurate segmentation of polyps and skin lesions is essential for diagnosing colorectal and skin cancers. While various segmentation methods for polyps and skin lesions using fully supervised deep learning techniques have been developed, the pixel-level annotation of medical images by doctors is both time-consuming and costly. Foundational vision models like the Segment Anything Model (SAM) have demonstrated superior performance; however, directly applying SAM to medical segmentation may not yield satisfactory results due to the lack of domain-specific medical knowledge. In this paper, we propose BiSeg-SAM, a SAM-guided weakly supervised prompting and boundary refinement network for the segmentation of polyps and skin lesions. Specifically, we fine-tune SAM combined with a CNN module to learn local features. We introduce a WeakBox with two functions: automatically generating box prompts for the SAM model and using our proposed Multi-choice Mask-to-Box (MM2B) transformation for rough mask-to-box conversion, addressing the mismatch between coarse labels and precise predictions. Additionally, we apply scale consistency (SC) loss for prediction scale alignment. Our DetailRefine module enhances boundary precision and segmentation accuracy by refining coarse predictions using a limited amount of ground truth labels. This comprehensive approach enables BiSeg-SAM to achieve excellent multi-task segmentation performance. Our method demonstrates significant superiority over state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods when tested on five polyp datasets and one skin cancer dataset.
准确地对息肉和皮肤病变进行分割对于诊断结肠癌和皮肤癌至关重要。虽然已经开发了各种使用完全监督深度学习的息肉和皮肤病变分割方法,但医生对医疗图像进行像素级注释既耗时又成本高昂。像分段任何事情模型(SAM)这样的基础视觉模型已经表现出了卓越的性能;然而,直接将SAM应用于医学分割可能无法产生令人满意的结果,这是由于缺乏特定领域的医学知识。在本文中,我们提出了BiSeg-SAM,这是一个由SAM引导的弱监督提示和边界细化网络,用于息肉和皮肤病变的分割。具体来说,我们结合了SAM和CNN模块进行微调,以学习局部特征。我们引入了一个WeakBox,它具有两个功能:自动为SAM模型生成框提示,并使用我们提出的Multi-choice Mask-to-Box(MM2B)转换进行粗略的遮罩到框转换,解决粗标签和精确预测之间的不匹配问题。此外,我们还应用了尺度一致性(SC)损失来进行预测尺度对齐。我们的DetailRefine模块通过利用有限数量的真实标签对粗略预测进行细化,提高了边界精度和分割准确性。这一综合方法使BiSeg-SAM在五个息肉数据集和一个皮肤癌数据集上取得了出色的多任务分割性能。我们的方法在测试时显示出对最先进方法的显著优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 2024 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM)
Summary
本文提出一种基于Segment Anything Model(SAM)的弱监督提示和边界细化网络BiSeg-SAM,用于息肉和皮肤病变的分割。针对医疗图像分割中像素级标注耗时耗资的问题,BiSeg-Sam通过结合SAM和CNN模块学习局部特征,引入WeakBox自动生成SAM模型的box提示,并采用Multi-choice Mask-to-Box转换解决粗标签与精确预测之间的不匹配问题。此外,通过应用尺度一致性损失实现预测尺度对齐,并借助DetailRefine模块使用少量真实标签提高边界精度和分割准确性。在五个息肉数据集和皮肤癌数据集上的测试结果表明,该方法优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 提出BiSeg-SAM网络,结合SAM和CNN模块进行医疗图像分割。
- WeakBox自动为SAM模型生成box提示,并解决了粗标签与精确预测之间的不匹配问题。
- 采用Multi-choice Mask-to-Box转换进行粗略的mask-to-box转换。
- 应用尺度一致性损失以提高预测尺度的准确性。
- DetailRefine模块使用少量真实标签提高边界精度和分割准确性。
点此查看论文截图
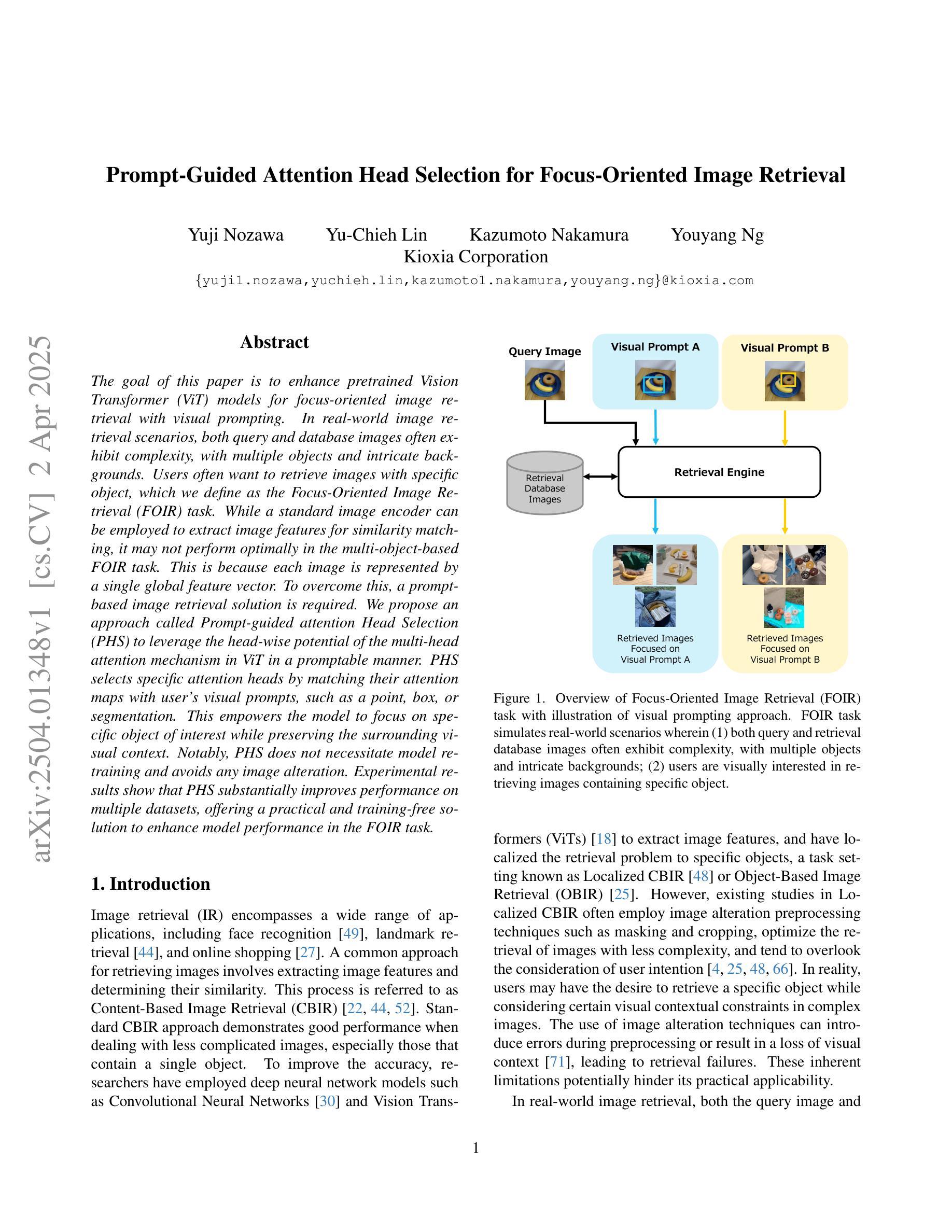
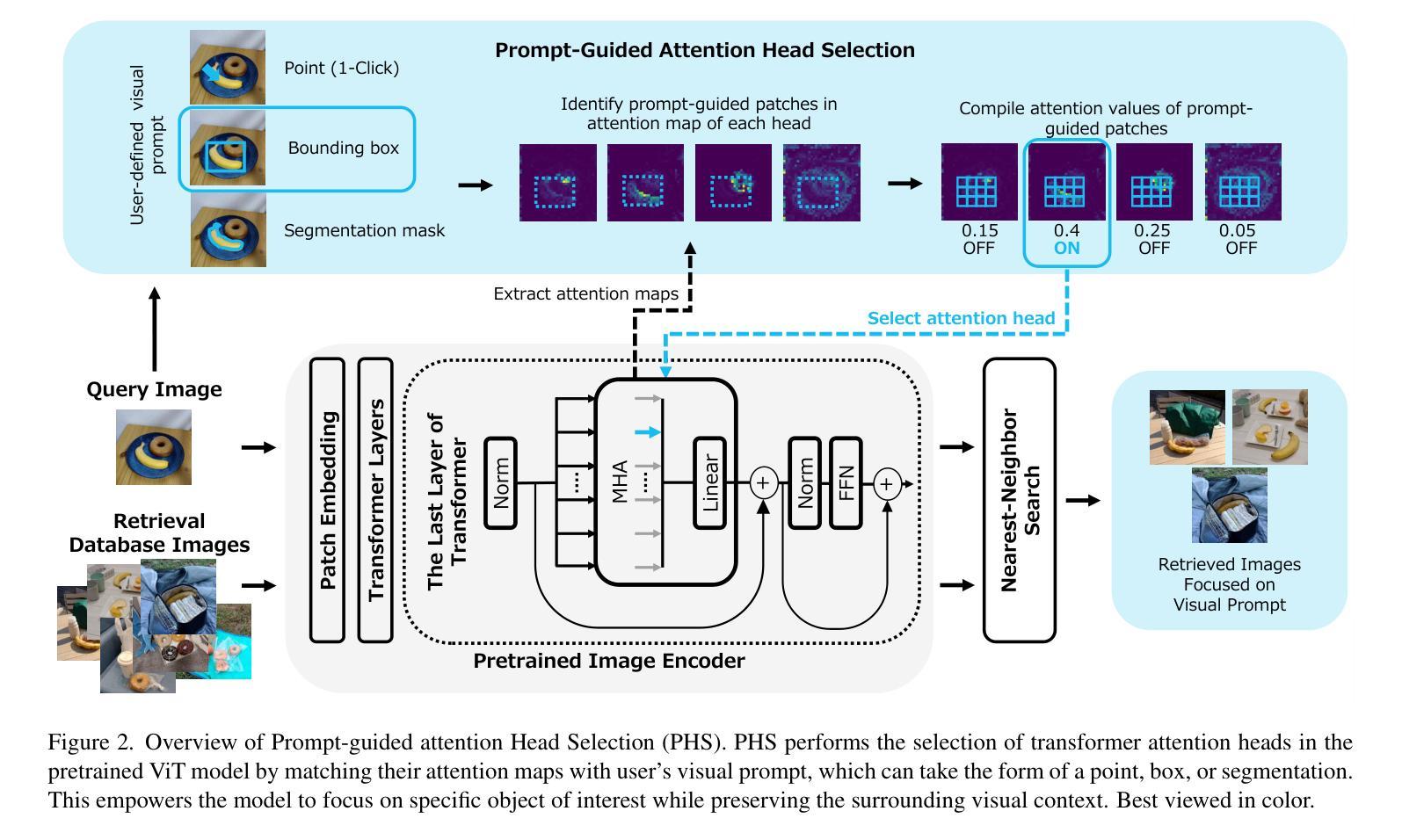
Prompt-Guided Attention Head Selection for Focus-Oriented Image Retrieval
Authors:Yuji Nozawa, Yu-Chieh Lin, Kazumoto Nakamura, Youyang Ng
The goal of this paper is to enhance pretrained Vision Transformer (ViT) models for focus-oriented image retrieval with visual prompting. In real-world image retrieval scenarios, both query and database images often exhibit complexity, with multiple objects and intricate backgrounds. Users often want to retrieve images with specific object, which we define as the Focus-Oriented Image Retrieval (FOIR) task. While a standard image encoder can be employed to extract image features for similarity matching, it may not perform optimally in the multi-object-based FOIR task. This is because each image is represented by a single global feature vector. To overcome this, a prompt-based image retrieval solution is required. We propose an approach called Prompt-guided attention Head Selection (PHS) to leverage the head-wise potential of the multi-head attention mechanism in ViT in a promptable manner. PHS selects specific attention heads by matching their attention maps with user’s visual prompts, such as a point, box, or segmentation. This empowers the model to focus on specific object of interest while preserving the surrounding visual context. Notably, PHS does not necessitate model re-training and avoids any image alteration. Experimental results show that PHS substantially improves performance on multiple datasets, offering a practical and training-free solution to enhance model performance in the FOIR task.
本文的目标是增强面向焦点的图像检索任务的预训练Vision Transformer(ViT)模型,使用视觉提示来实现。在现实世界的图像检索场景中,查询图像和数据库图像通常具有复杂性,包含多个对象和复杂的背景。用户通常希望检索具有特定对象的图像,我们将其定义为面向焦点的图像检索(FOIR)任务。虽然可以使用标准的图像编码器来提取图像特征以进行相似性匹配,但在基于多对象的FOIR任务中,其性能可能并不最佳。这是因为每张图像都由单个全局特征向量表示。为了克服这一点,需要一种基于提示的图像检索解决方案。我们提出了一种名为Prompt-guided attention Head Selection(PHS)的方法,以提示的方式利用ViT中多头注意力机制的头部潜力。PHS通过匹配用户的视觉提示(如点、框或分割)与特定的注意力头来选取注意力头,使用户能够关注特定的感兴趣对象,同时保留周围的视觉上下文。值得注意的是,PHS不需要模型重新训练,并且避免了任何图像修改。实验结果表明,PHS在多个数据集上的性能得到了显著提高,为FOIR任务中增强模型性能提供了实用且无需训练的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025 PixFoundation Workshop
Summary
该论文旨在改进预训练的Vision Transformer(ViT)模型,以进行面向焦点的图像检索。针对现实世界中的图像检索场景,论文提出了一种名为Prompt-guided attention Head Selection(PHS)的方法,利用ViT的多头注意力机制的头部潜力,通过匹配用户的视觉提示(如点、框或分割)来选择特定的注意力头。此方法可在不重新训练模型或更改图像的情况下,提高模型在面向焦点的图像检索任务上的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 论文旨在改进预训练的Vision Transformer(ViT)模型,用于面向焦点的图像检索任务。
- 现有图像编码器在面向焦点的图像检索任务中可能表现不佳,因为每个图像仅由一个全局特征向量表示。
- 提出了一种名为Prompt-guided attention Head Selection(PHS)的方法,利用ViT的多头注意力机制。
- PHS通过匹配注意力图与用户视觉提示(如点、框或分割)来选择特定注意力头。
- PHS方法使模型能够关注特定目标对象,同时保留周围视觉上下文。
- PHS不需要模型重新训练,避免了图像修改。
点此查看论文截图
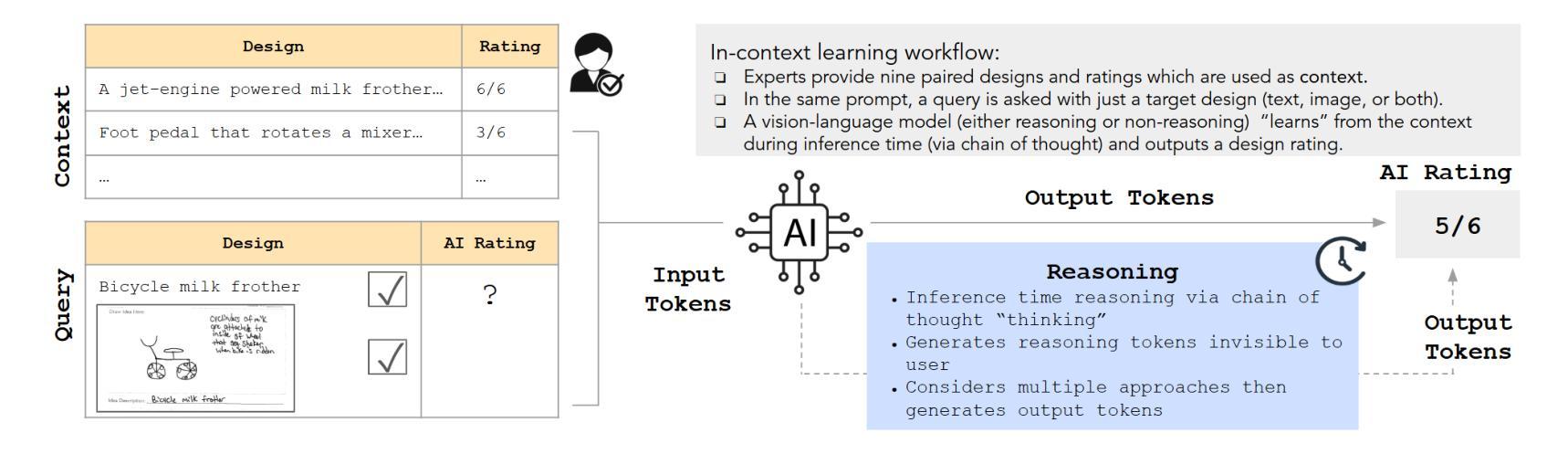
AI Judges in Design: Statistical Perspectives on Achieving Human Expert Equivalence With Vision-Language Models
Authors:Kristen M. Edwards, Farnaz Tehranchi, Scarlett R. Miller, Faez Ahmed
The subjective evaluation of early stage engineering designs, such as conceptual sketches, traditionally relies on human experts. However, expert evaluations are time-consuming, expensive, and sometimes inconsistent. Recent advances in vision-language models (VLMs) offer the potential to automate design assessments, but it is crucial to ensure that these AI ``judges’’ perform on par with human experts. However, no existing framework assesses expert equivalence. This paper introduces a rigorous statistical framework to determine whether an AI judge’s ratings match those of human experts. We apply this framework in a case study evaluating four VLM-based judges on key design metrics (uniqueness, creativity, usefulness, and drawing quality). These AI judges employ various in-context learning (ICL) techniques, including uni- vs. multimodal prompts and inference-time reasoning. The same statistical framework is used to assess three trained novices for expert-equivalence. Results show that the top-performing AI judge, using text- and image-based ICL with reasoning, achieves expert-level agreement for uniqueness and drawing quality and outperforms or matches trained novices across all metrics. In 6/6 runs for both uniqueness and creativity, and 5/6 runs for both drawing quality and usefulness, its agreement with experts meets or exceeds that of the majority of trained novices. These findings suggest that reasoning-supported VLM models can achieve human-expert equivalence in design evaluation. This has implications for scaling design evaluation in education and practice, and provides a general statistical framework for validating AI judges in other domains requiring subjective content evaluation.
早期阶段工程设计的主观评估,如概念草图,传统上依赖于人类专家。然而,专家评估耗时、成本高,且有时评估结果不一致。最近,视觉语言模型(VLM)的进步为自动化设计评估提供了潜力,但确保这些人工智能“判官”的表现与专家相当至关重要。然而,没有现有的框架来评估专家等同程度。本文引入了一个严格的统计框架,以确定人工智能判官的评分是否与专家相当。我们在此框架中进行了一项案例研究,评估了四位基于VLM的判官在主要设计指标(独特性、创造性、实用性和绘图质量)上的表现。这些AI判官采用了各种上下文学习(ICL)技术,包括单模态与多模态提示和推理时间推理。同一统计框架也用于评估三名训练有素的新手是否达到专家水平。结果表明,表现最佳的人工智能判官,采用基于文本和图像的ICL与推理技术,在独特性和绘图质量方面达到了专家级协议,并在所有指标上优于或匹配训练有素的新手。在独特性和创造力的6次运行中以及在绘图质量和实用性的5次运行中,其与专家的协议达到或超过了大多数训练有素的新手。这些发现表明,支持推理的VLM模型可以在设计评估中实现与人类专家的等同水平。这对扩大教育和实践中的设计评估规模具有影响,并提供了一个通用的统计框架,可用于验证其他需要进行主观内容评估领域的AI判官。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 8 tables, 6 figures, 8 tables in the appendix
Summary
本文介绍了一个评估人工智能在设计评价中是否达到专家水平的统计框架。该框架应用于评估基于视觉语言模型的四个AI评委在关键设计指标上的表现,如独特性、创造力、实用性和绘图质量。结果表明,最优秀的人工智能评委使用基于文本和图像的上下文学习并加上推理技术,能够达到专家级别的协议,在某些指标上甚至超过受过训练的新手。这为设计评价的可扩展性在教育和实践领域提供了启示,也为验证AI评委在其他需要进行主观内容评价领域的能力提供了一个通用的统计框架。
Key Takeaways
- 传统的工程设计评估依赖于人类专家,但存在耗时、成本高昂和不一致的问题。
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)的近期进展为自动化设计评估提供了潜力。
- 论文引入了一个统计框架来评估AI评委的表现是否达到专家水平。
- 在关键设计指标上,最优秀的人工智能评委达到了与专家一致的水平,甚至在某些指标上超过了受过训练的新手。
- 人工智能在设计评价中的表现对于教育和实践领域具有启示作用。
- 该研究提供了一个通用的统计框架,用于验证AI评委在其他主观内容评价领域的能力。
点此查看论文截图

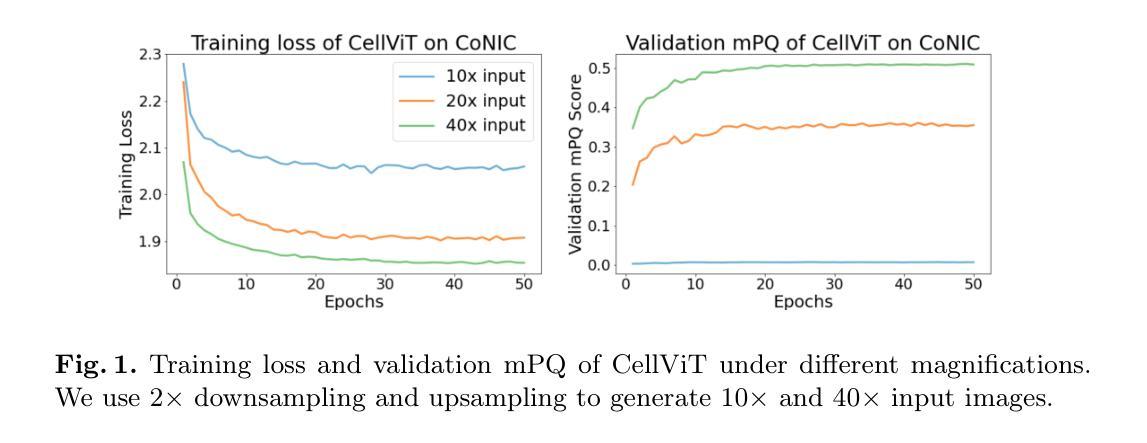
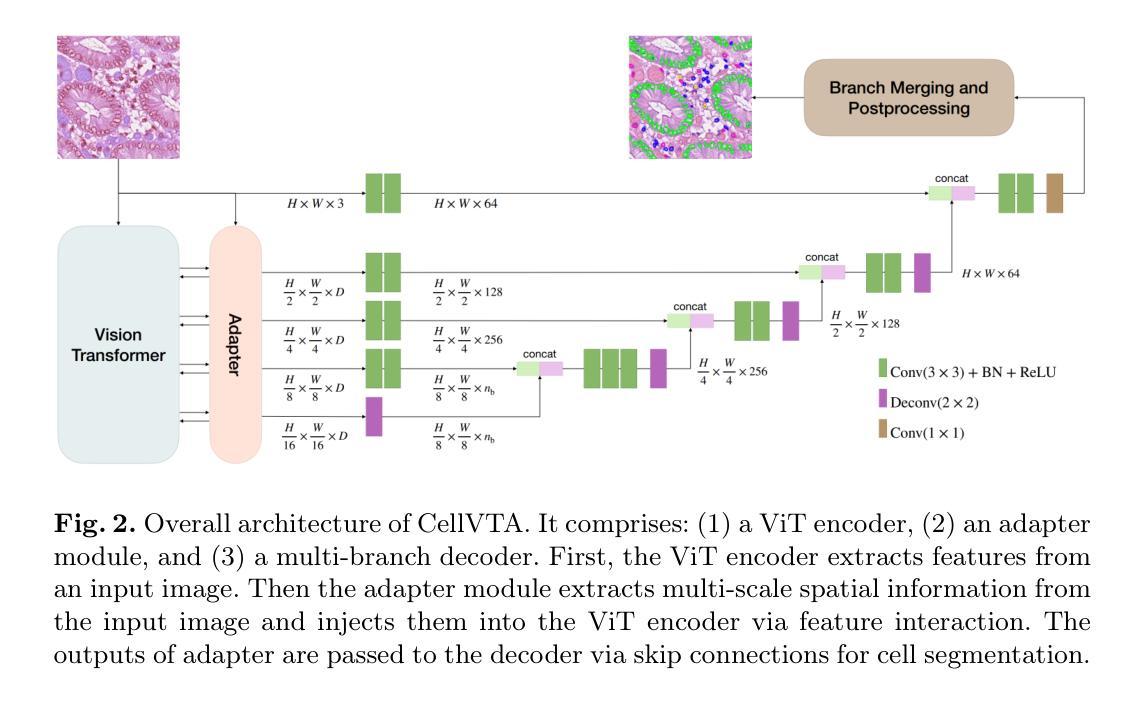
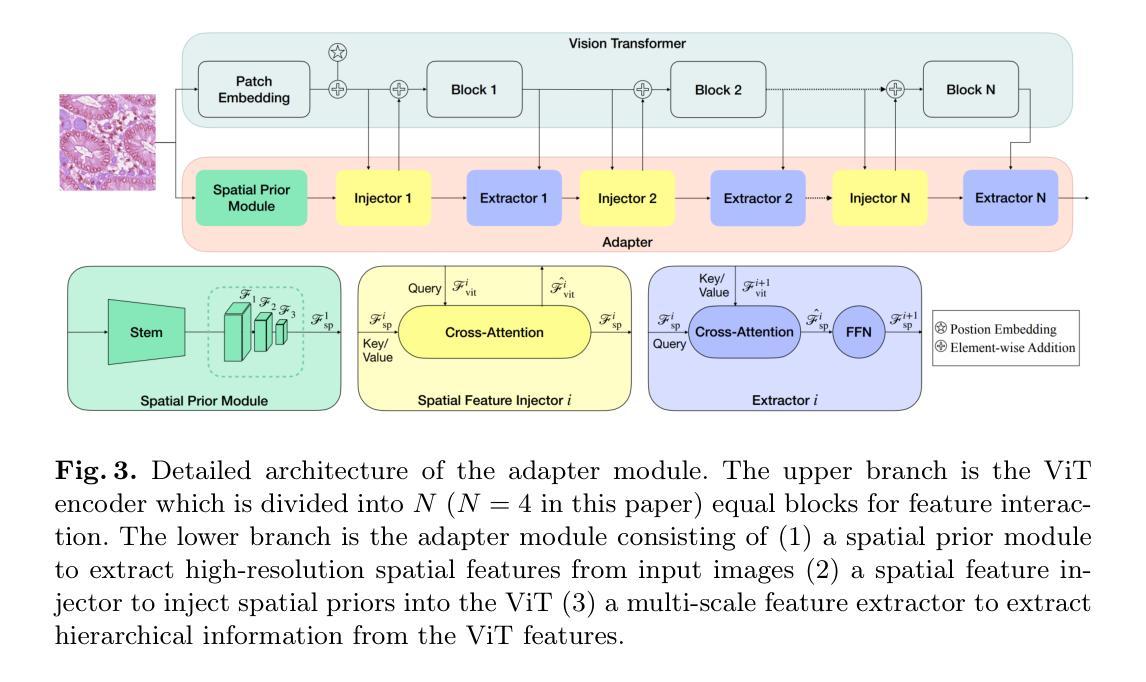
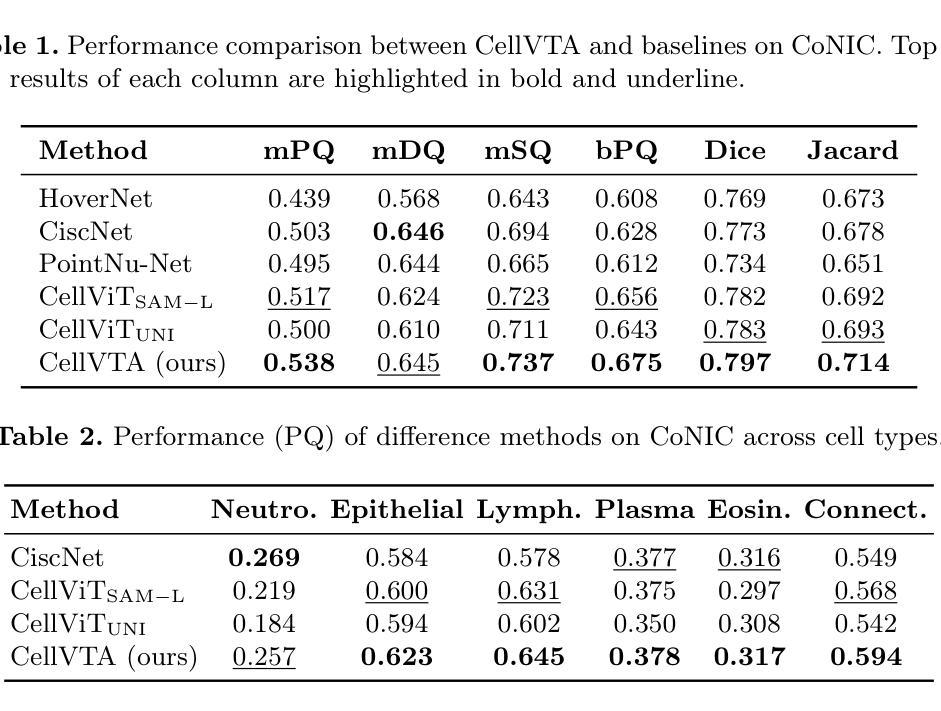
CellVTA: Enhancing Vision Foundation Models for Accurate Cell Segmentation and Classification
Authors:Yang Yang, Xijie Xu, Yixun Zhou, Jie Zheng
Cell instance segmentation is a fundamental task in digital pathology with broad clinical applications. Recently, vision foundation models, which are predominantly based on Vision Transformers (ViTs), have achieved remarkable success in pathology image analysis. However, their improvements in cell instance segmentation remain limited. A key challenge arises from the tokenization process in ViTs, which substantially reduces the spatial resolution of input images, leading to suboptimal segmentation quality, especially for small and densely packed cells. To address this problem, we propose CellVTA (Cell Vision Transformer with Adapter), a novel method that improves the performance of vision foundation models for cell instance segmentation by incorporating a CNN-based adapter module. This adapter extracts high-resolution spatial information from input images and injects it into the ViT through a cross-attention mechanism. Our method preserves the core architecture of ViT, ensuring seamless integration with pretrained foundation models. Extensive experiments show that CellVTA achieves 0.538 mPQ on the CoNIC dataset and 0.506 mPQ on the PanNuke dataset, which significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art cell segmentation methods. Ablation studies confirm the superiority of our approach over other fine-tuning strategies, including decoder-only fine-tuning and full fine-tuning. Our code and models are publicly available at https://github.com/JieZheng-ShanghaiTech/CellVTA.
细胞实例分割是数字病理学中的一项基本任务,在临床应用中具有广泛的应用。最近,基于视觉转换器(ViT)的视觉基础模型在病理学图像分析方面取得了显著的成功。然而,它们在细胞实例分割方面的改进仍然有限。一个关键挑战来自于ViT中的令牌化过程,该过程大大降低了输入图像的空间分辨率,导致分割质量不佳,尤其是针对小而密集包装的细胞。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了CellVTA(带适配器的细胞视觉转换器),这是一种通过结合基于CNN的适配器模块来提高视觉基础模型在细胞实例分割方面的性能的新方法。该适配器从输入图像中提取高分辨率的空间信息,并通过交叉注意机制将其注入ViT。我们的方法保留了ViT的核心架构,确保与预训练的基础模型无缝集成。大量实验表明,CellVTA在CoNIC数据集上实现了0.538的mPQ,在PanNuke数据集上实现了0.506的mPQ,显著优于最先进的细胞分割方法。消融研究证实了我们的方法优于其他微调策略,包括仅解码器微调和全微调。我们的代码和模型可在https://github.com/JieZheng-ShanghaiTech/CellVTA公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Vision Transformer的模型在数字病理学中的细胞实例分割任务中取得了显著的成功,但仍有提升空间。为提高分割质量,尤其是针对小且密集排列的细胞,提出了CellVTA方法。该方法通过引入CNN适配器模块,提取高分辨率空间信息并注入ViT中。实验证明,CellVTA在CoNIC和PanNuke数据集上的性能优于现有细胞分割方法。
Key Takeaways
- Vision foundation models based on Vision Transformers (ViTs) have achieved notable success in pathology image analysis.
- A key challenge in cell instance segmentation is the tokenization process in ViTs, leading to reduced spatial resolution and suboptimal segmentation quality.
- CellVTA addresses this challenge by incorporating a CNN-based adapter module to extract high-resolution spatial information.
- CellVTA preserves the core architecture of ViT, ensuring seamless integration with pretrained foundation models.
- CellVTA achieves significant performance improvements over state-of-the-art cell segmentation methods, with mPQ scores of 0.538 on the CoNIC dataset and 0.506 on the PanNuke dataset.
- Ablation studies confirm the superiority of CellVTA over other fine-tuning strategies, including decoder-only fine-tuning and full fine-tuning.
点此查看论文截图

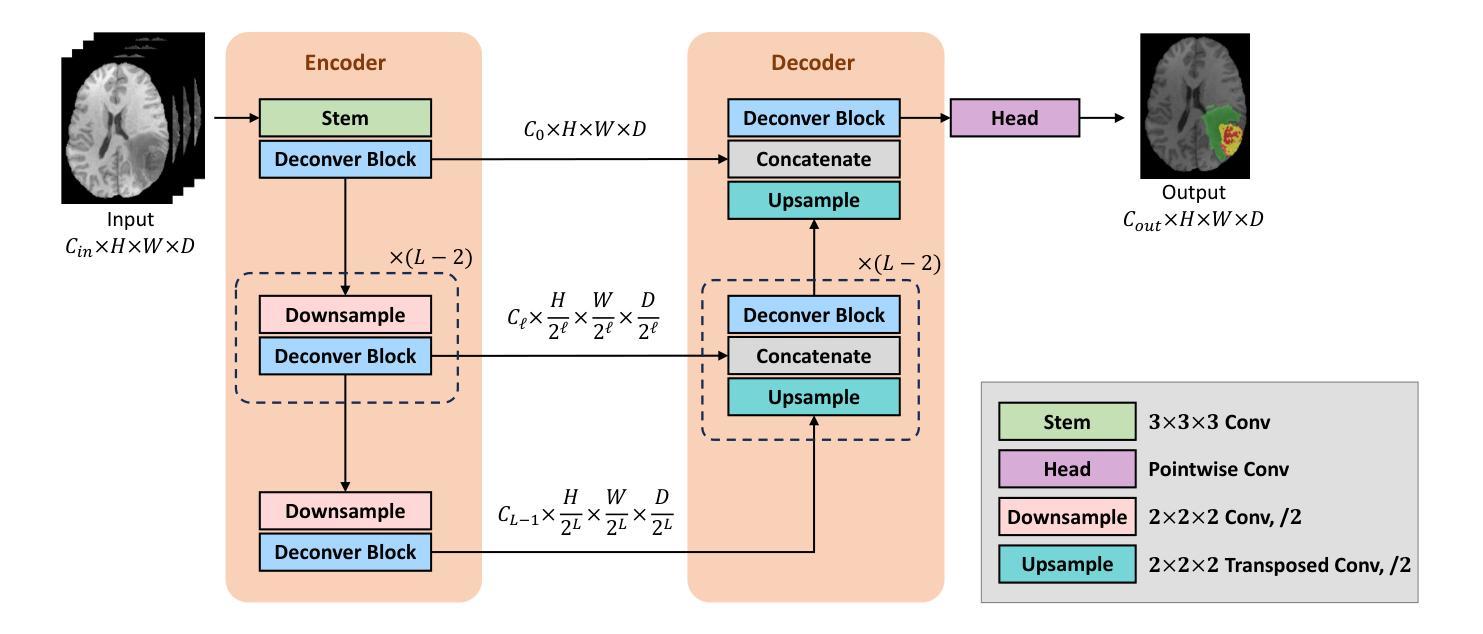
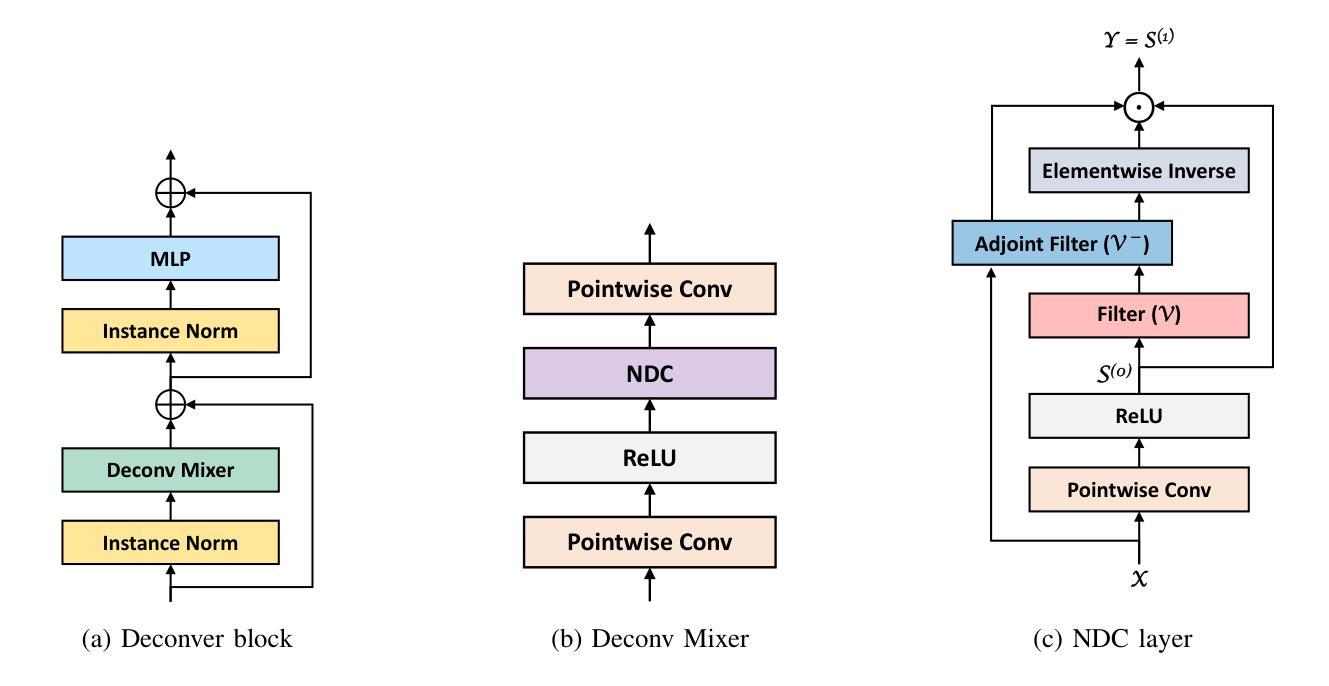
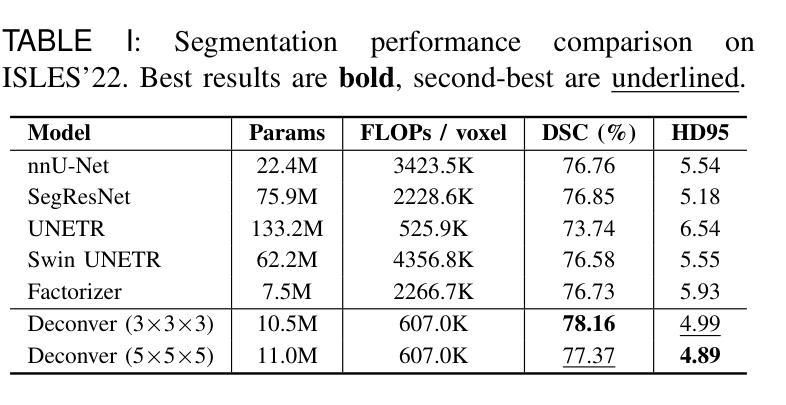
Deconver: A Deconvolutional Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Pooya Ashtari, Shahryar Noei, Fateme Nateghi Haredasht, Jonathan H. Chen, Giuseppe Jurman, Aleksandra Pizurica, Sabine Van Huffel
While convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformers (ViTs) have advanced medical image segmentation, they face inherent limitations such as local receptive fields in CNNs and high computational complexity in ViTs. This paper introduces Deconver, a novel network that integrates traditional deconvolution techniques from image restoration as a core learnable component within a U-shaped architecture. Deconver replaces computationally expensive attention mechanisms with efficient nonnegative deconvolution (NDC) operations, enabling the restoration of high-frequency details while suppressing artifacts. Key innovations include a backpropagation-friendly NDC layer based on a provably monotonic update rule and a parameter-efficient design. Evaluated across four datasets (ISLES’22, BraTS’23, GlaS, FIVES) covering both 2D and 3D segmentation tasks, Deconver achieves state-of-the-art performance in Dice scores and Hausdorff distance while reducing computational costs (FLOPs) by up to 90% compared to leading baselines. By bridging traditional image restoration with deep learning, this work offers a practical solution for high-precision segmentation in resource-constrained clinical workflows. The project is available at https://github.com/pashtari/deconver.
虽然卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)已经推动了医学图像分割的发展,但它们也面临着固有的局限性,如CNN的局部感受野和ViT的高计算复杂度。本文介绍了Deconver,这是一种新型网络,它将图像恢复中的传统反卷积技术集成到一个U形架构中的核心可学习组件。Deconver用高效的非负反卷积(NDC)操作取代了计算昂贵的注意力机制,能够在恢复高频细节的同时抑制伪影。主要创新包括基于可证明单调更新规则的有利于反向传播的NDC层以及参数高效的设计。在涵盖二维和三维分割任务的四个数据集(ISLES’22、BraTS’23、GlaS、FIVES)上进行了评估,Deconver在Dice得分和Hausdorff距离方面达到了最先进的性能,与领先的基础模型相比,计算成本(FLOPs)降低了高达90%。通过桥接传统图像恢复和深度学习,这项工作为资源受限的临床工作流程中的高精度分割提供了实用解决方案。该项目可在https://github.com/pashtari/deconver获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 6 figures, 5 tables
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为Deconver的新型网络,它将传统的解卷积技术作为核心学习组件集成到U型架构中,以解决医疗图像分割面临的挑战。通过采用基于解卷积操作的正面传播算法和高效的参数设计,Deconver能够在恢复高频细节的同时抑制伪影。在多个数据集上的评估表明,它在Dice得分和Hausdorff距离方面达到了最新技术水平,并降低了高达90%的计算成本。该研究为资源受限的临床工作流程提供了高精度分割的实用解决方案。
Key Takeaways
以下是该文的关键要点总结:
- CNN和ViT在医疗图像分割方面存在局限性,如CNN的局部感受野和ViT的高计算复杂性。
- Deconver网络结合了传统解卷积技术,作为一种核心学习组件,以解决这些问题。
- Deconver使用高效非负解卷积(NDC)操作替代了计算成本高昂的注意力机制。
- NDC层基于可证明的单调更新规则,有利于反向传播。
- Deconver实现了参数高效的设计,能够在恢复高频细节的同时抑制伪影。
- 在多个数据集上的评估表明,Deconver在Dice得分和Hausdorff距离方面达到了最新技术水平。
- Deconver降低了高达90%的计算成本,为资源受限的临床工作流程提供了实用解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

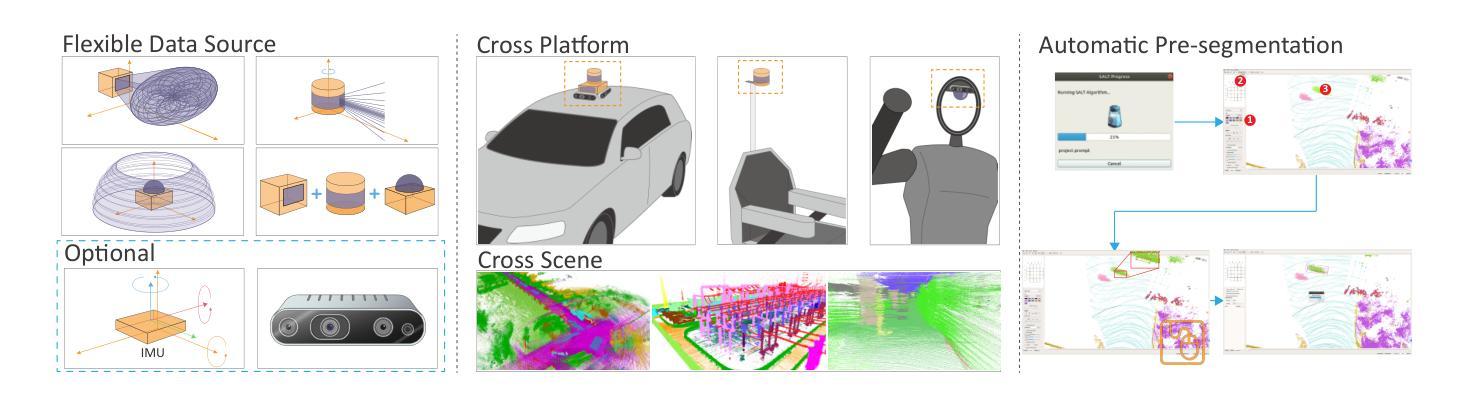
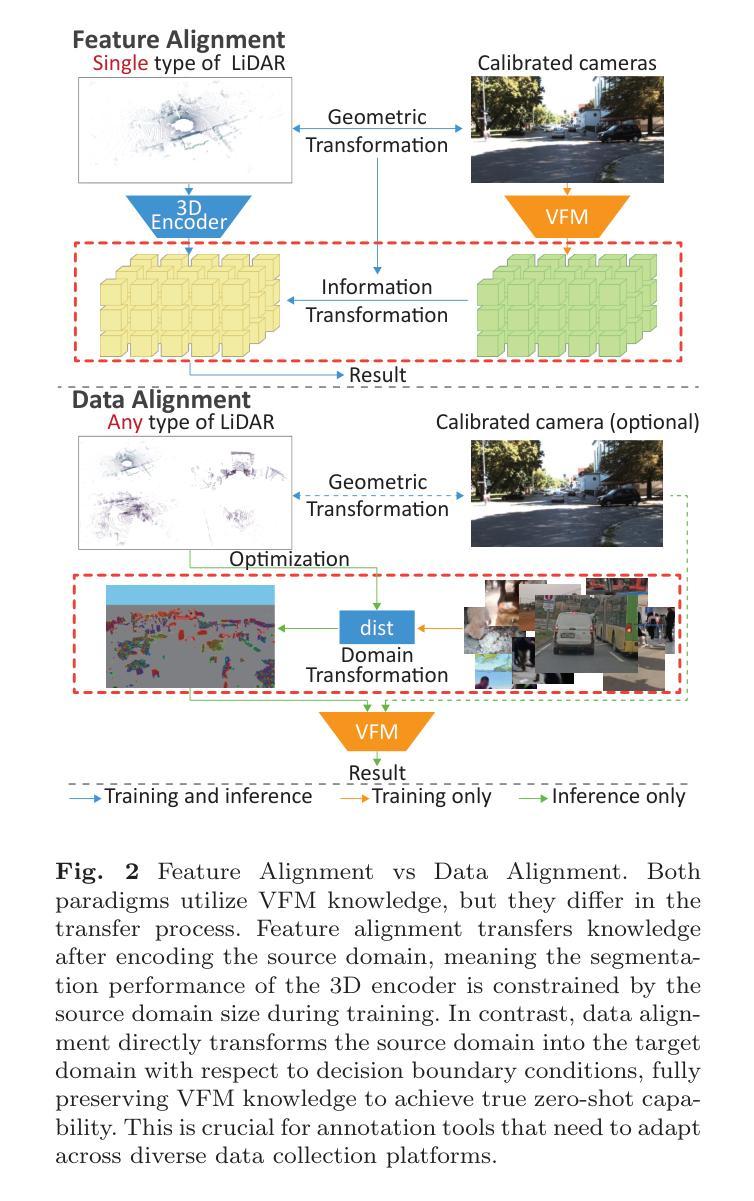
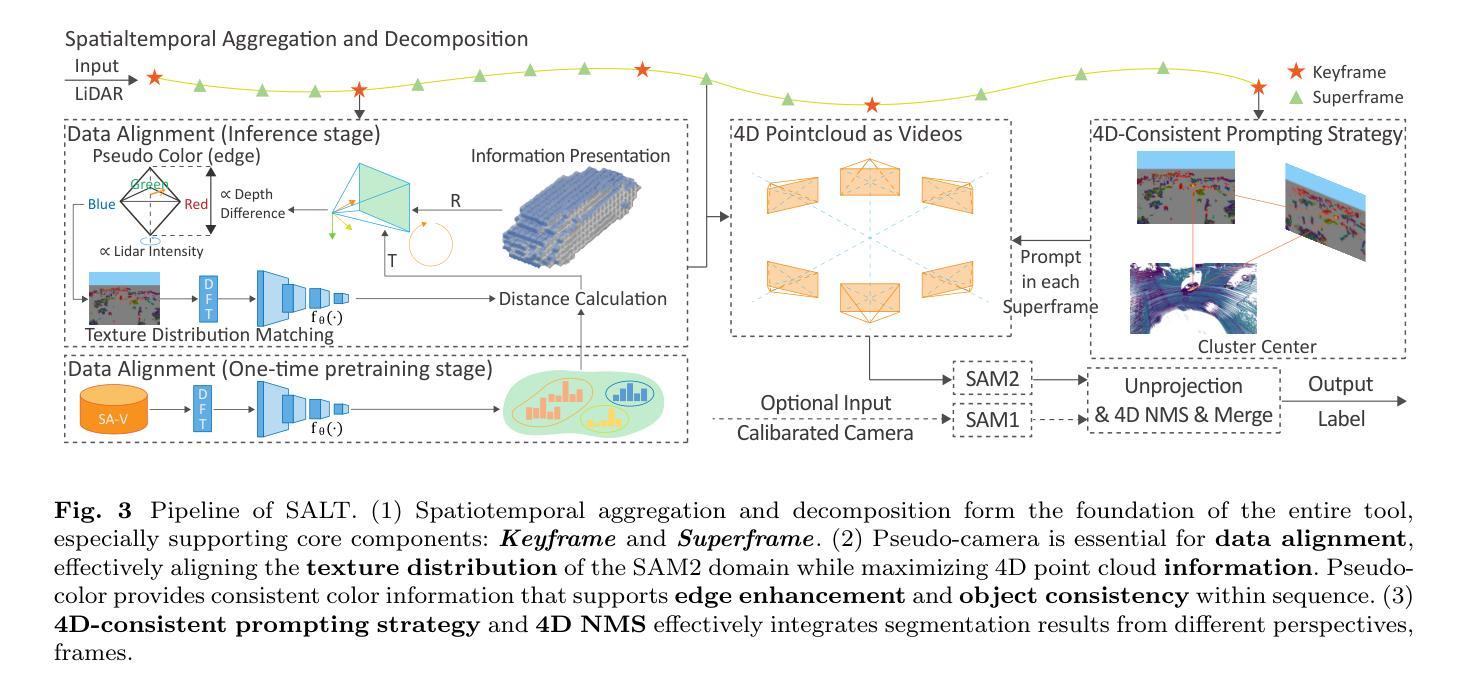
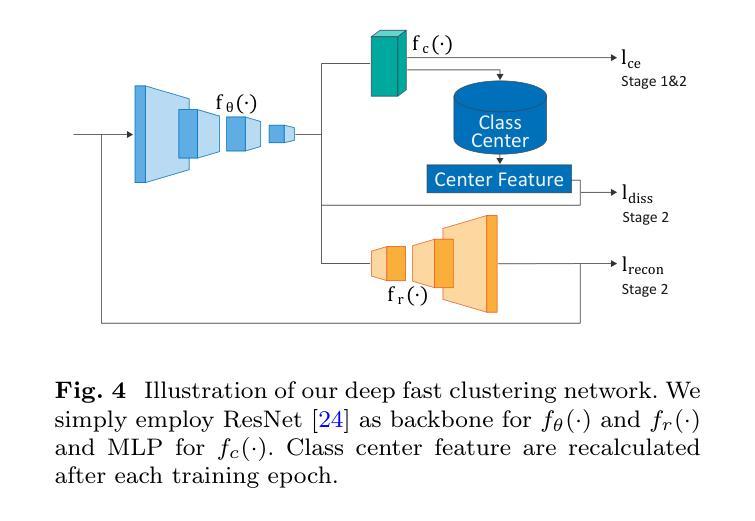
SALT: A Flexible Semi-Automatic Labeling Tool for General LiDAR Point Clouds with Cross-Scene Adaptability and 4D Consistency
Authors:Yanbo Wang, Yongtao Chen, Chuan Cao, Tianchen Deng, Wentao Zhao, Jingchuan Wang, Weidong Chen
We propose a flexible Semi-Automatic Labeling Tool (SALT) for general LiDAR point clouds with cross-scene adaptability and 4D consistency. Unlike recent approaches that rely on camera distillation, SALT operates directly on raw LiDAR data, automatically generating pre-segmentation results. To achieve this, we propose a novel zero-shot learning paradigm, termed data alignment, which transforms LiDAR data into pseudo-images by aligning with the training distribution of vision foundation models. Additionally, we design a 4D-consistent prompting strategy and 4D non-maximum suppression module to enhance SAM2, ensuring high-quality, temporally consistent presegmentation. SALT surpasses the latest zero-shot methods by 18.4% PQ on SemanticKITTI and achieves nearly 40-50% of human annotator performance on our newly collected low-resolution LiDAR data and on combined data from three LiDAR types, significantly boosting annotation efficiency. We anticipate that SALT’s open-sourcing will catalyze substantial expansion of current LiDAR datasets and lay the groundwork for the future development of LiDAR foundation models. Code is available at https://github.com/Cavendish518/SALT.
我们提出了一种灵活的半自动标注工具(SALT),适用于一般的激光雷达点云,具有跨场景适应性和4D一致性。与最近依赖于相机蒸馏的方法不同,SALT直接在原始激光雷达数据上运行,自动生成预分割结果。为了实现这一点,我们提出了一种新的零样本学习范式,称为数据对齐,通过将激光雷达数据与视觉基础模型的训练分布对齐,将激光雷达数据转换为伪图像。此外,我们设计了4D一致提示策略和4D非最大抑制模块,以增强SAM2,确保高质量、时间一致的预分割。SALT在SemanticKITTI上的PQ得分超过最新零样本方法18.4%,在我们新收集的低分辨率激光雷达数据和三种激光雷达类型组合的数据上,达到人类标注师性能的近40-50%,大大提高了标注效率。我们预计SALT的开源将极大地推动当前激光雷达数据集的发展,并为未来激光雷达基础模型的开发奠定基础。代码可在https://github.com/Cavendish518/SALT找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种灵活的半自动标注工具(SALT),适用于一般的激光雷达点云数据,具有跨场景适应性和4D一致性。SALT直接在原始激光雷达数据上操作,自动生成预分割结果,不同于依赖相机蒸馏的现有方法。为实现这一点,本文提出了一种名为数据对齐的新型零样本学习范式,通过将激光雷达数据与视觉基础模型的训练分布对齐,将激光雷达数据转换为伪图像。同时,设计了4D一致的提示策略和4D非最大抑制模块,增强SAM2,确保高质量、时间一致的预分割。SALT在SemanticKITTI上的PQ得分比最新的零样本方法高出18.4%,在新收集的低分辨率激光雷达数据和三种激光雷达类型的组合数据上,达到了人类标注器性能的近40-50%,显著提高了标注效率。
Key Takeaways
- SALT是一种适用于一般激光雷达点云的半自动标注工具,具有跨场景适应性和4D一致性。
- SALT直接在原始激光雷达数据上操作,自动生成预分割结果,不依赖相机蒸馏。
- 提出了一种新型零样本学习范式——数据对齐,将激光雷达数据转换为伪图像。
- 设计了4D一致的提示策略和4D非最大抑制模块,以增强SAM2的性能。
- SALT在SemanticKITTI数据集上的性能优于最新的零样本方法,PQ得分提高18.4%。
- SALT在新收集的低分辨率激光雷达数据和多种激光雷达类型组合的数据上表现出良好的性能,达到了人类标注器性能的近40-50%。
点此查看论文截图

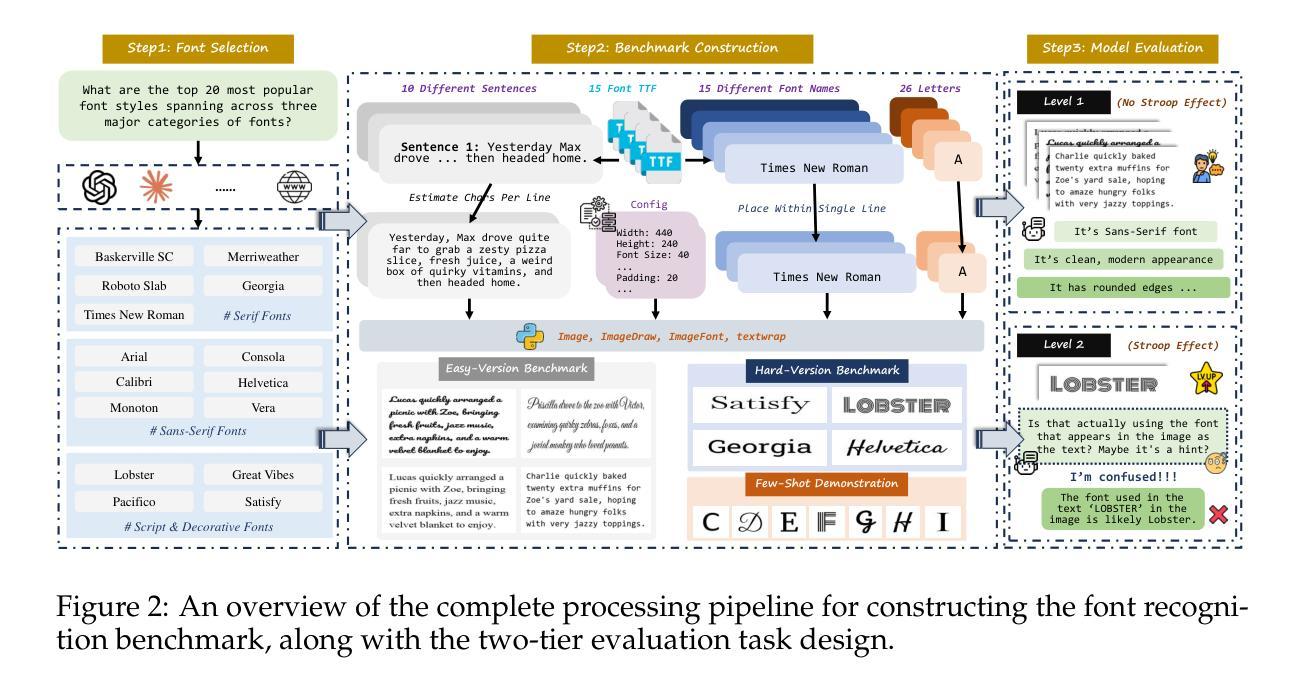
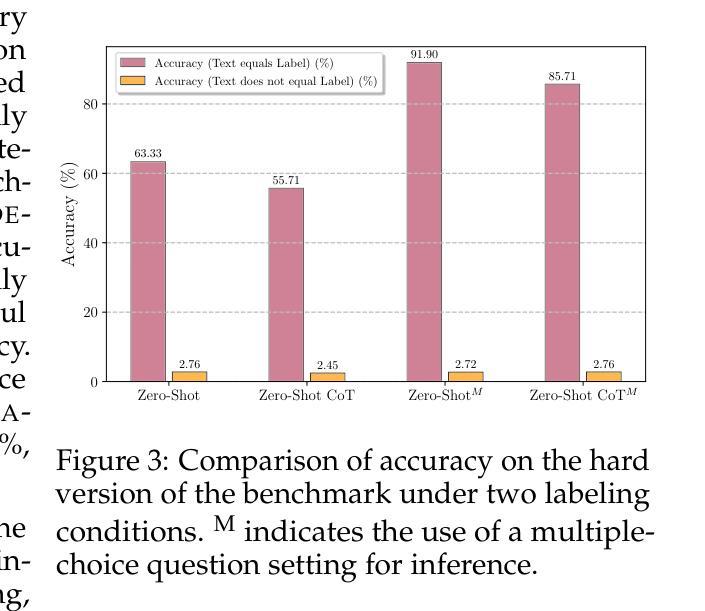
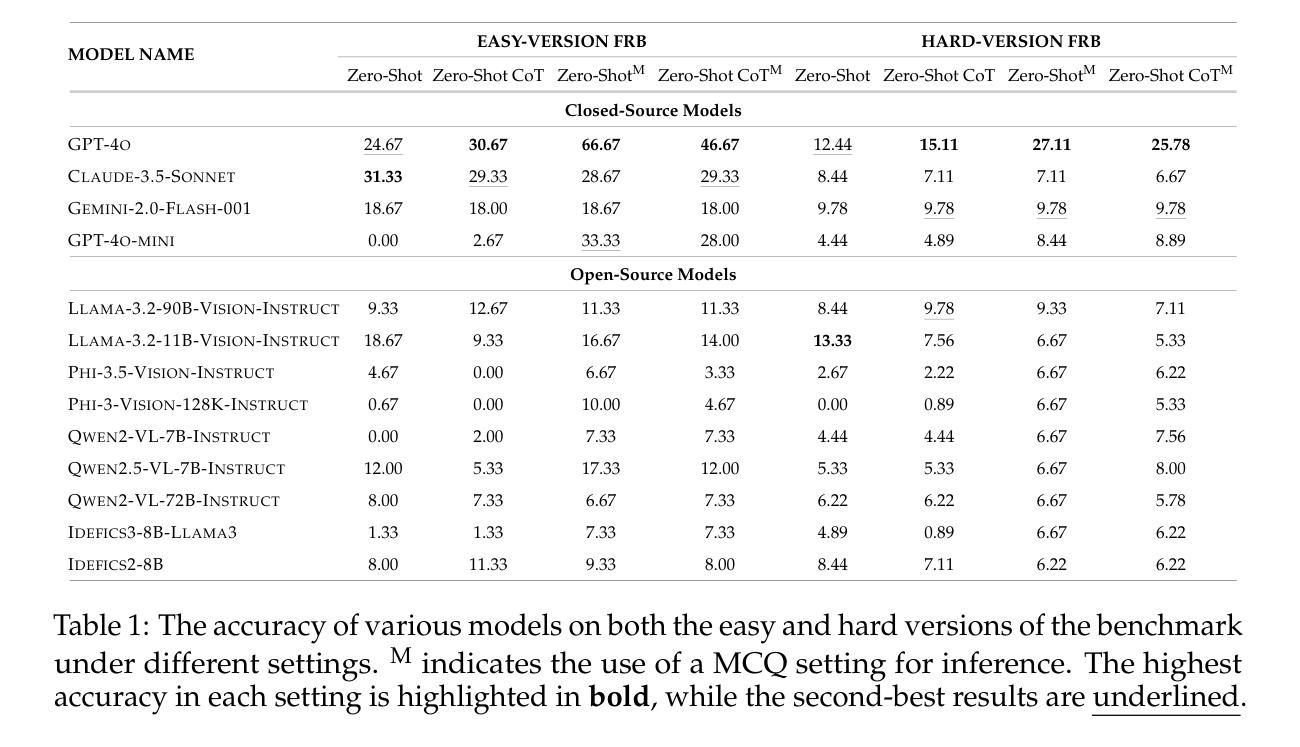
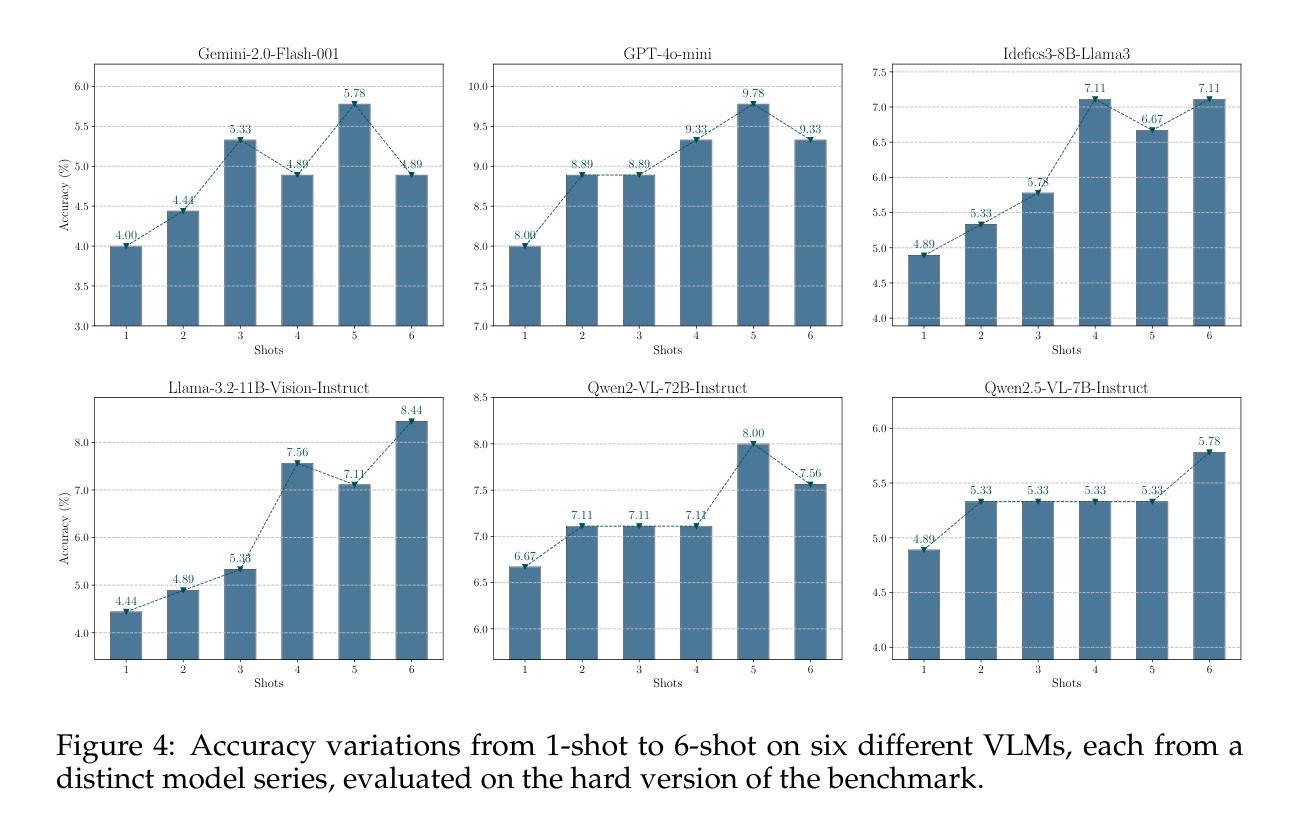
Texture or Semantics? Vision-Language Models Get Lost in Font Recognition
Authors:Zhecheng Li, Guoxian Song, Yujun Cai, Zhen Xiong, Junsong Yuan, Yiwei Wang
Modern Vision-Language Models (VLMs) exhibit remarkable visual and linguistic capabilities, achieving impressive performance in various tasks such as image recognition and object localization. However, their effectiveness in fine-grained tasks remains an open question. In everyday scenarios, individuals encountering design materials, such as magazines, typography tutorials, research papers, or branding content, may wish to identify aesthetically pleasing fonts used in the text. Given their multimodal capabilities and free accessibility, many VLMs are often considered potential tools for font recognition. This raises a fundamental question: Do VLMs truly possess the capability to recognize fonts? To investigate this, we introduce the Font Recognition Benchmark (FRB), a compact and well-structured dataset comprising 15 commonly used fonts. FRB includes two versions: (i) an easy version, where 10 sentences are rendered in different fonts, and (ii) a hard version, where each text sample consists of the names of the 15 fonts themselves, introducing a stroop effect that challenges model perception. Through extensive evaluation of various VLMs on font recognition tasks, we arrive at the following key findings: (i) Current VLMs exhibit limited font recognition capabilities, with many state-of-the-art models failing to achieve satisfactory performance. (ii) Few-shot learning and Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting provide minimal benefits in improving font recognition accuracy across different VLMs. (iii) Attention analysis sheds light on the inherent limitations of VLMs in capturing semantic features.
现代视觉语言模型(VLMs)表现出令人瞩目的视觉和语言能力,在图像识别、目标定位等任务中取得了令人印象深刻的表现。然而,它们在精细任务中的有效性仍然是一个悬而未决的问题。在日常场景中,个人在遇到设计材料,如杂志、排版教程、研究论文或品牌内容时,可能希望识别文本中使用的吸引人的字体。考虑到它们的多模态能力和自由可访问性,许多VLMs通常被认为是字体识别的潜在工具。这引发了一个根本性的问题:VLMs真的具有识别字体的能力吗?为了调查这一点,我们引入了字体识别基准测试(FRB),这是一个包含15种常用字体的紧凑且结构良好的数据集。FRB包括两个版本:(i)一个容易的版本,其中10个句子以不同的字体呈现;(ii)一个困难的版本,其中每个文本样本由15种字体的名称本身组成,引入一种斯特鲁普效应,挑战模型的感知能力。通过对各种VLMs在字体识别任务上的广泛评估,我们得出以下关键发现:(i)当前的VLMs在字体识别能力方面表现有限,许多最先进的模型无法取得令人满意的性能。(ii)小样本学习和思维链提示(CoT)在改善不同VLMs的字体识别准确度方面提供有限的益处。(iii)注意力分析揭示了VLMs在捕获语义特征方面的内在局限性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了现代视觉语言模型(VLMs)在字体识别任务上的表现。为调查VLMs的真正字体识别能力,引入了字体识别基准测试(FRB)。通过评估发现,当前VLMs在字体识别方面能力有限,顶尖模型表现不佳,且少样本学习与Chain-of-Thought提示对提升字体识别准确率作用有限。注意力分析揭示了VLMs捕捉语义特征的内在局限。
Key Takeaways
- 现代视觉语言模型(VLMs)在字体识别任务上的表现引人注目,但在精细任务上的效果仍有待提高。
- 为调查VLMs的字体识别能力,引入了字体识别基准测试(FRB),包括简易版和困难版,分别用于评估模型的基本和极限识别能力。
- 当前VLMs在字体识别方面存在局限,顶尖模型表现并不理想。
- 少样本学习与Chain-of-Thought提示在提升VLMs的字体识别准确率方面作用有限。
- 注意力分析显示,VLMs在捕捉语义特征方面存在内在局限。
- FRB基准测试为评估和改进VLMs的字体识别能力提供了重要依据。
点此查看论文截图


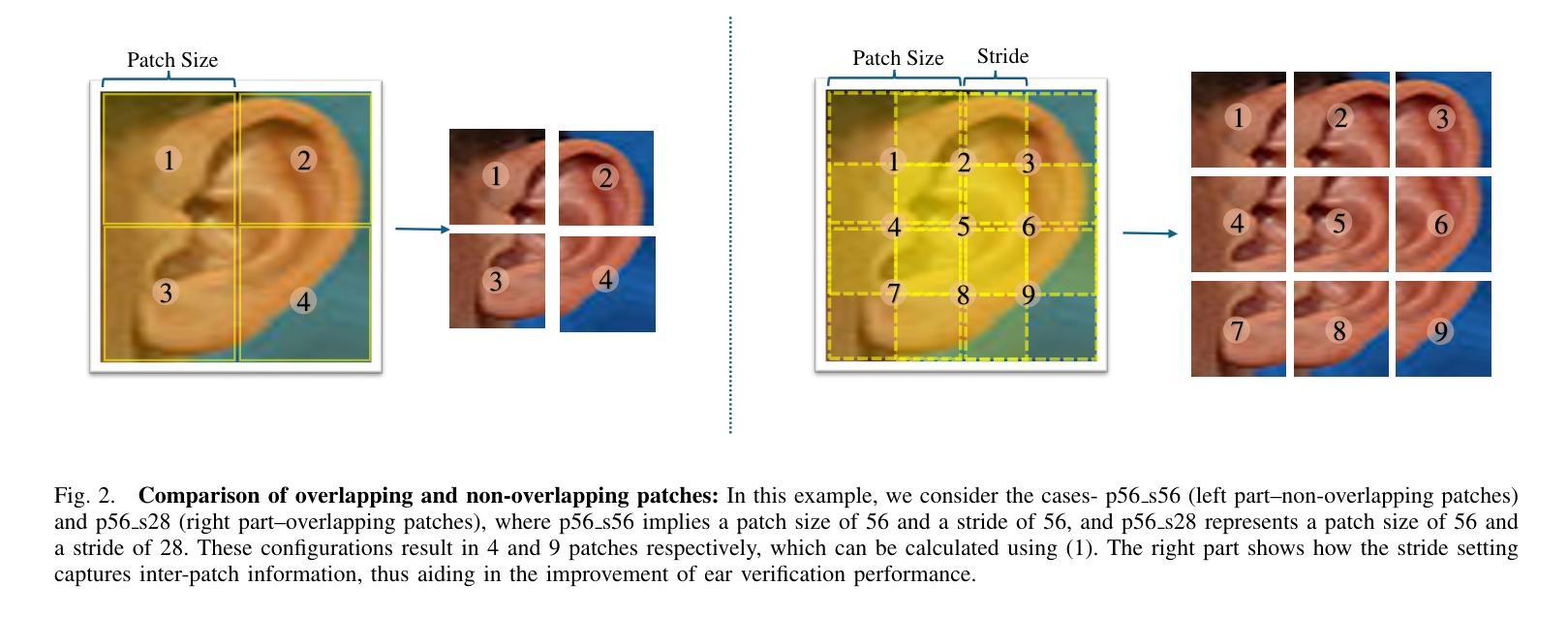
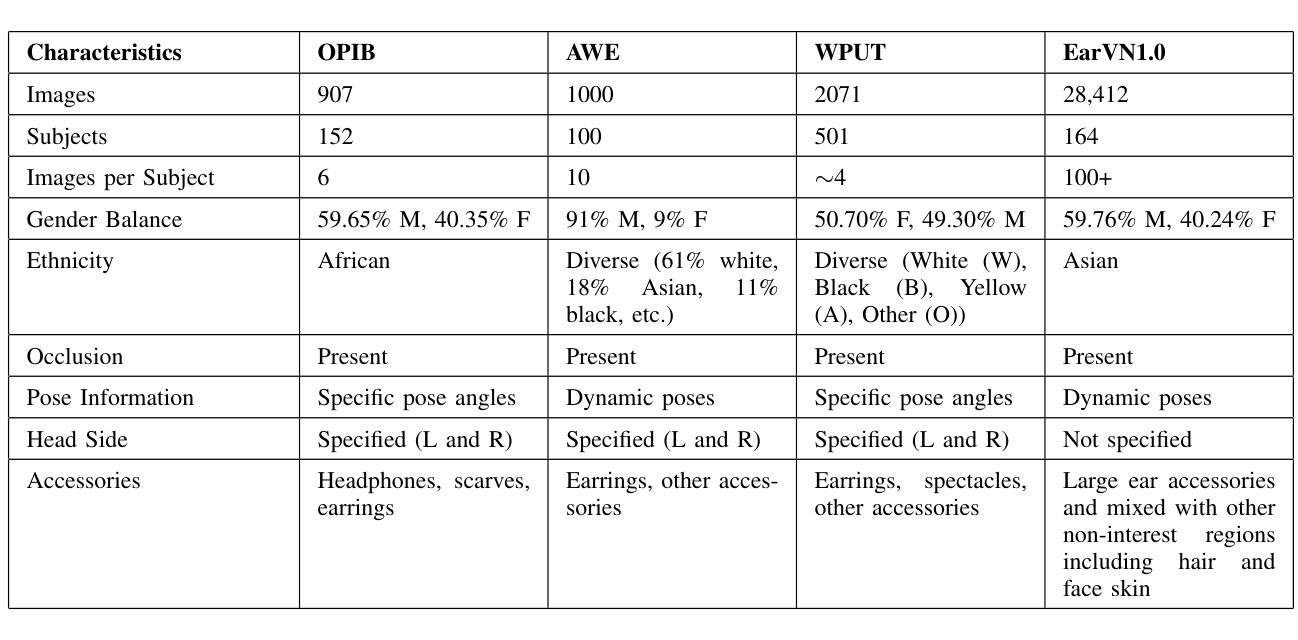
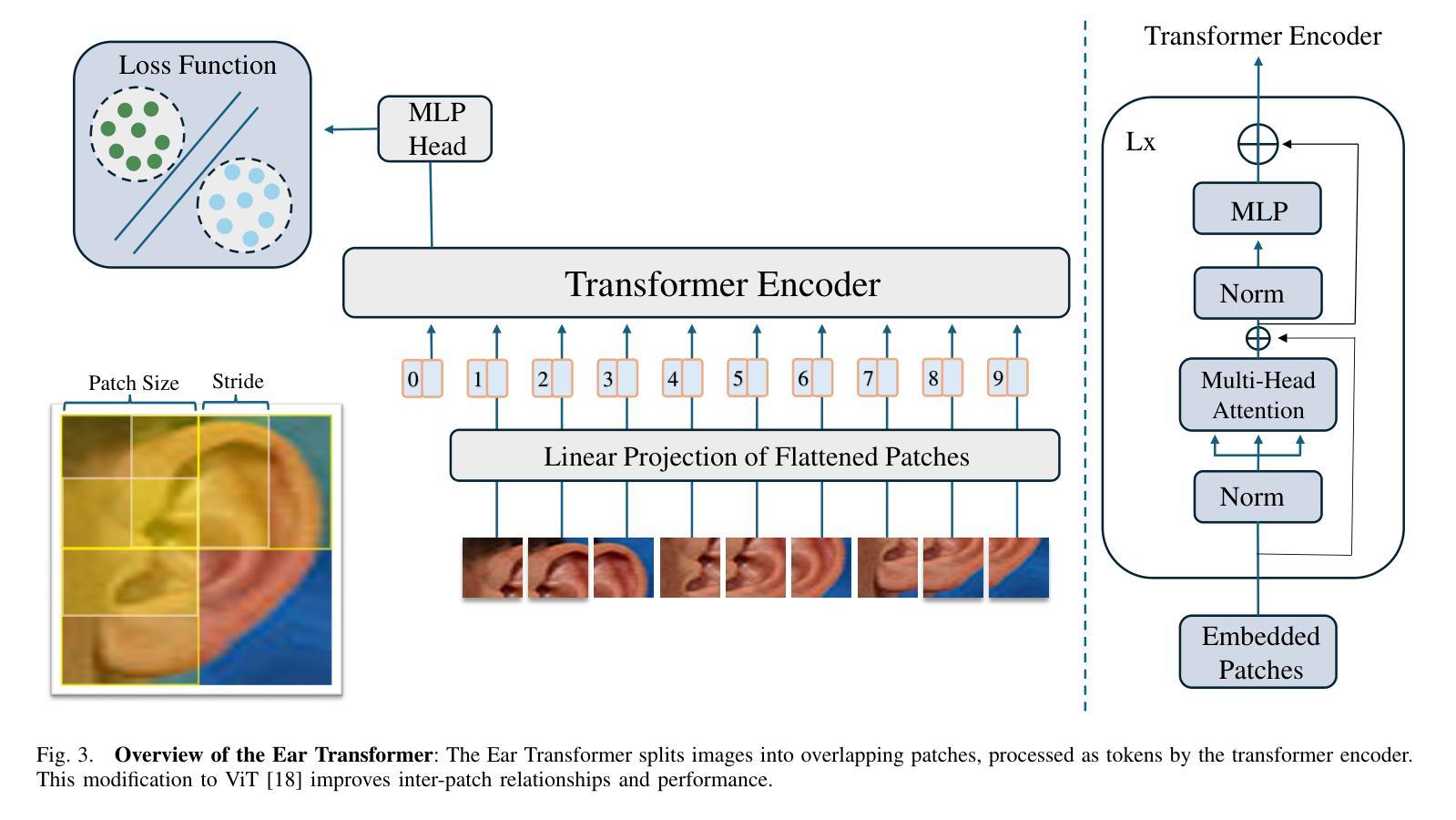
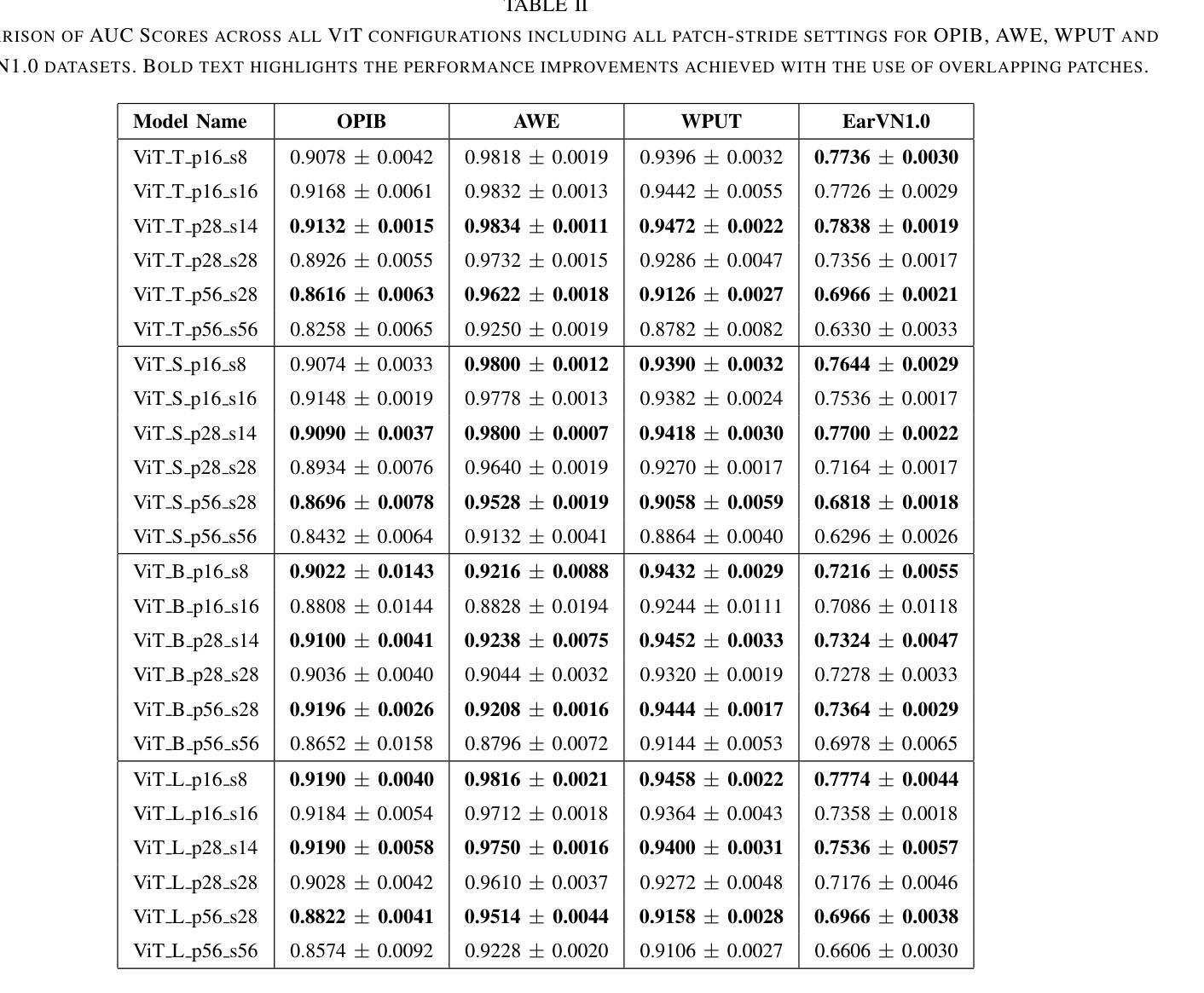
Improved Ear Verification with Vision Transformers and Overlapping Patches
Authors:Deeksha Arun, Kagan Ozturk, Kevin W. Bowyer, Patrick Flynn
Ear recognition has emerged as a promising biometric modality due to the relative stability in appearance during adulthood. Although Vision Transformers (ViTs) have been widely used in image recognition tasks, their efficiency in ear recognition has been hampered by a lack of attention to overlapping patches, which is crucial for capturing intricate ear features. In this study, we evaluate ViT-Tiny (ViT-T), ViT-Small (ViT-S), ViT-Base (ViT-B) and ViT-Large (ViT-L) configurations on a diverse set of datasets (OPIB, AWE, WPUT, and EarVN1.0), using an overlapping patch selection strategy. Results demonstrate the critical importance of overlapping patches, yielding superior performance in 44 of 48 experiments in a structured study. Moreover, upon comparing the results of the overlapping patches with the non-overlapping configurations, the increase is significant, reaching up to 10% for the EarVN1.0 dataset. In terms of model performance, the ViT-T model consistently outperformed the ViT-S, ViT-B, and ViT-L models on the AWE, WPUT, and EarVN1.0 datasets. The highest scores were achieved in a configuration with a patch size of 28x28 and a stride of 14 pixels. This patch-stride configuration represents 25% of the normalized image area (112x112 pixels) for the patch size and 12.5% of the row or column size for the stride. This study confirms that transformer architectures with overlapping patch selection can serve as an efficient and high-performing option for ear-based biometric recognition tasks in verification scenarios.
耳部识别因成年后外观的相对稳定性而成为一种有前景的生物识别方式。尽管视觉变压器(ViT)已广泛应用于图像识别任务,但在耳部识别方面,由于对重叠斑块缺乏关注,其效率受到阻碍,这对于捕获复杂的耳部特征至关重要。在这项研究中,我们采用重叠斑块选择策略,评估了ViT-Tiny(ViT-T)、ViT-Small(ViT-S)、ViT-Base(ViT-B)和ViT-Large(ViT-L)配置在OPIB、AWE、WPUT和EarVN1.0等多个数据集上的性能。结果表明重叠斑块至关重要,在结构化的48次实验中,有44次实验表现出优越的性能。此外,将重叠斑块的结果与非重叠配置进行比较,其增长幅度显著,对于EarVN1.0数据集而言,增长幅度高达10%。就模型性能而言,ViT-T模型在AWE、WPUT和EarVN1.0数据集上持续优于ViT-S、ViT-B和ViT-L模型。在补丁大小为28x28、步幅为14像素的配置中取得了最高分数。该补丁步幅配置代表补丁大小的图像区域占归一化图像面积的25%(即112x112像素),步幅占行或列大小的12.5%。这项研究证实,采用重叠斑块选择的变压器架构可作为验证场景中基于耳朵的生物识别任务的高效且高性能选择。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了使用Vision Transformers(ViT)在耳部识别中的效率问题。研究发现在使用ViT模型时,采用重叠补丁选择策略能显著提高性能,特别是在耳部识别任务中。实验结果显示,重叠补丁策略在多个数据集上的表现均优于非重叠配置,且最高分数出现在补丁大小为28x28,步长为14像素的配置下。研究确认了采用重叠补丁选择的转换器架构可作为验证场景中基于耳朵的生物识别的高效且高性能选择。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers (ViTs) 在耳部识别任务中的效率受到关注。
- 重叠补丁选择策略对于捕捉耳朵的精细特征至关重要。
- 在多个数据集上进行的实验表明,重叠补丁策略显著提高了性能。
- ViT-Tiny模型在多个数据集上表现最佳。
- 最佳性能是在补丁大小为28x28,步长为14像素的配置下实现的。
- 重叠补丁策略能提高模型性能高达10%。
点此查看论文截图

4D LangSplat: 4D Language Gaussian Splatting via Multimodal Large Language Models
Authors:Wanhua Li, Renping Zhou, Jiawei Zhou, Yingwei Song, Johannes Herter, Minghan Qin, Gao Huang, Hanspeter Pfister
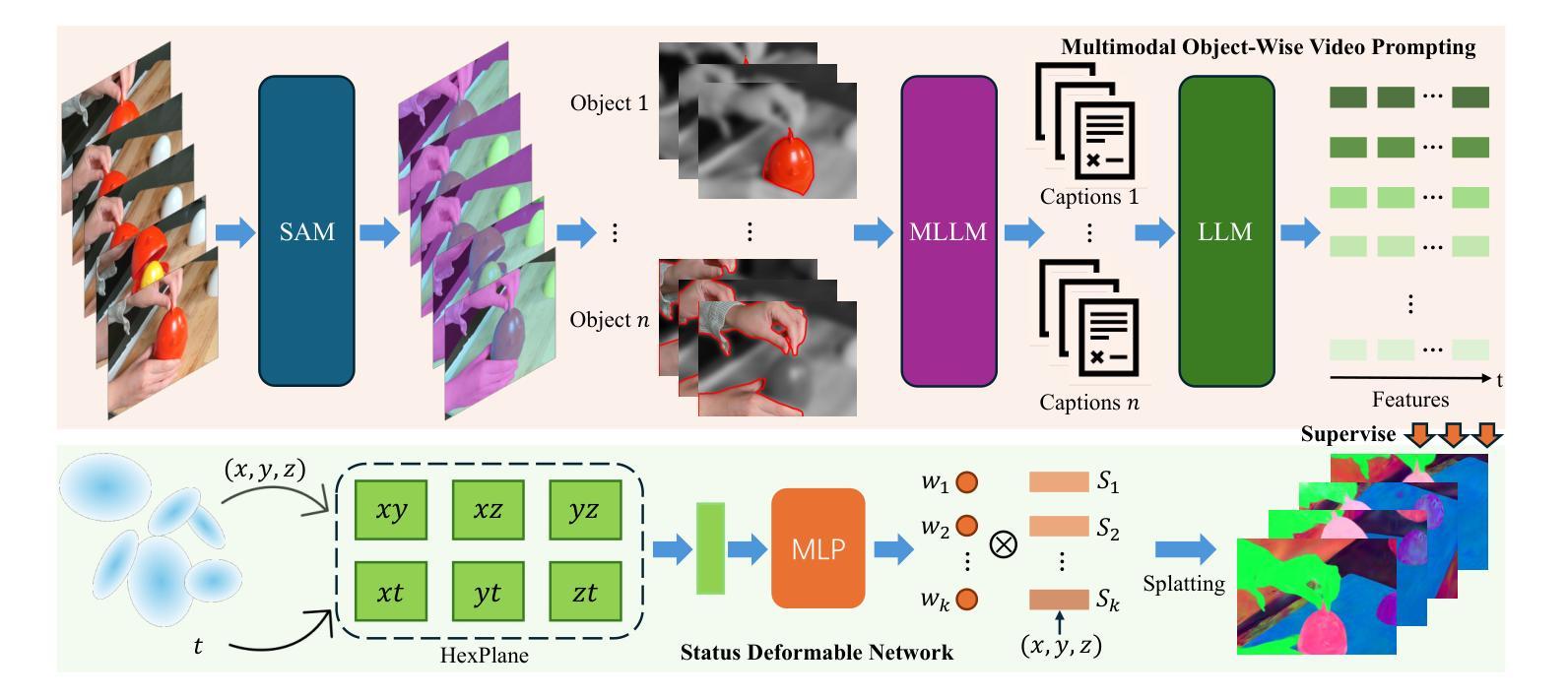
Learning 4D language fields to enable time-sensitive, open-ended language queries in dynamic scenes is essential for many real-world applications. While LangSplat successfully grounds CLIP features into 3D Gaussian representations, achieving precision and efficiency in 3D static scenes, it lacks the ability to handle dynamic 4D fields as CLIP, designed for static image-text tasks, cannot capture temporal dynamics in videos. Real-world environments are inherently dynamic, with object semantics evolving over time. Building a precise 4D language field necessitates obtaining pixel-aligned, object-wise video features, which current vision models struggle to achieve. To address these challenges, we propose 4D LangSplat, which learns 4D language fields to handle time-agnostic or time-sensitive open-vocabulary queries in dynamic scenes efficiently. 4D LangSplat bypasses learning the language field from vision features and instead learns directly from text generated from object-wise video captions via Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). Specifically, we propose a multimodal object-wise video prompting method, consisting of visual and text prompts that guide MLLMs to generate detailed, temporally consistent, high-quality captions for objects throughout a video. These captions are encoded using a Large Language Model into high-quality sentence embeddings, which then serve as pixel-aligned, object-specific feature supervision, facilitating open-vocabulary text queries through shared embedding spaces. Recognizing that objects in 4D scenes exhibit smooth transitions across states, we further propose a status deformable network to model these continuous changes over time effectively. Our results across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that 4D LangSplat attains precise and efficient results for both time-sensitive and time-agnostic open-vocabulary queries.
学习4D语言场,以实现在动态场景中进行时间敏感和无限制的开放语言查询,对于许多实际应用至关重要。虽然LangSplat成功地将CLIP特性融入3D高斯表示中,在3D静态场景中实现了精度和效率,但它缺乏处理动态4D场的能力,因为CLIP是为静态图像文本任务设计的,无法捕捉视频中的时间动态。现实世界的环境本质上是动态的,物体语义会随时间演变。要建立精确的4D语言场,必须获得像素对齐的、面向对象的视频特征,而当前的视觉模型很难做到这一点。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了4D LangSplat,它学习4D语言场,以高效地处理动态场景中的时间无关或时间敏感的无限制词汇查询。4D LangSplat绕过从视觉特征学习语言场的步骤,而是直接从通过多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)生成的面向对象的视频字幕中学习。具体来说,我们提出了一种多模态面向对象视频提示方法,包括视觉和文本提示,引导MLLMs为视频中的对象生成详细、时间一致、高质量的字幕。这些字幕使用大型语言模型进行编码,以生成高质量的句子嵌入,然后作为像素对齐的、面向对象的特征监督,通过共享嵌入空间进行开放词汇文本查询。我们认识到4D场景中的对象在状态之间呈现出平滑的过渡,因此进一步提出了一个状态可变形网络,以有效地对这些随时间变化的连续变化进行建模。我们在多个基准测试上的结果表明,4D LangSplat对于时间敏感和时间无关的无限制词汇查询都达到了精确和高效的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Project Page: https://4d-langsplat.github.io
Summary
本文提出了一个新的模型——4D LangSplat,用于学习处理动态场景中的时间敏感性和非时间敏感性开放式词汇查询的4D语言字段。通过直接从基于对象的视频字幕生成文本,使用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)学习语言字段,并引入模态对象视频提示方法,生成详细、时间连贯的高质量对象字幕。这些字幕被编码成高质量句子嵌入,作为像素对齐的对象特定特征监督,支持通过共享嵌入空间进行开放式文本查询。此外,模型还引入了状态可变形网络来模拟对象在连续时间内的变化。实验结果表明,4D LangSplat对于时间敏感性和非时间敏感性的开放式词汇查询都能达到精确和高效的结果。
Key Takeaways
- 4D LangSplat模型可以学习处理动态场景中的时间敏感性和非时间敏感性开放式词汇查询的4D语言字段。
- 模型通过直接从基于对象的视频字幕生成文本,使用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)学习语言字段。
- 模型引入了模态对象视频提示方法,生成详细、时间连贯的高质量对象字幕。
- 高质量句子嵌入是通过大型语言模型编码生成的,这为开放式文本查询提供了支持。
- 模型引入了状态可变形网络来模拟对象在连续时间内的变化。
点此查看论文截图

InPK: Infusing Prior Knowledge into Prompt for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Shuchang Zhou, Jiwei Wei, Shiyuan He, Yuyang Zhou, Chaoning Zhang, Jie Zou, Ning Xie, Yang Yang
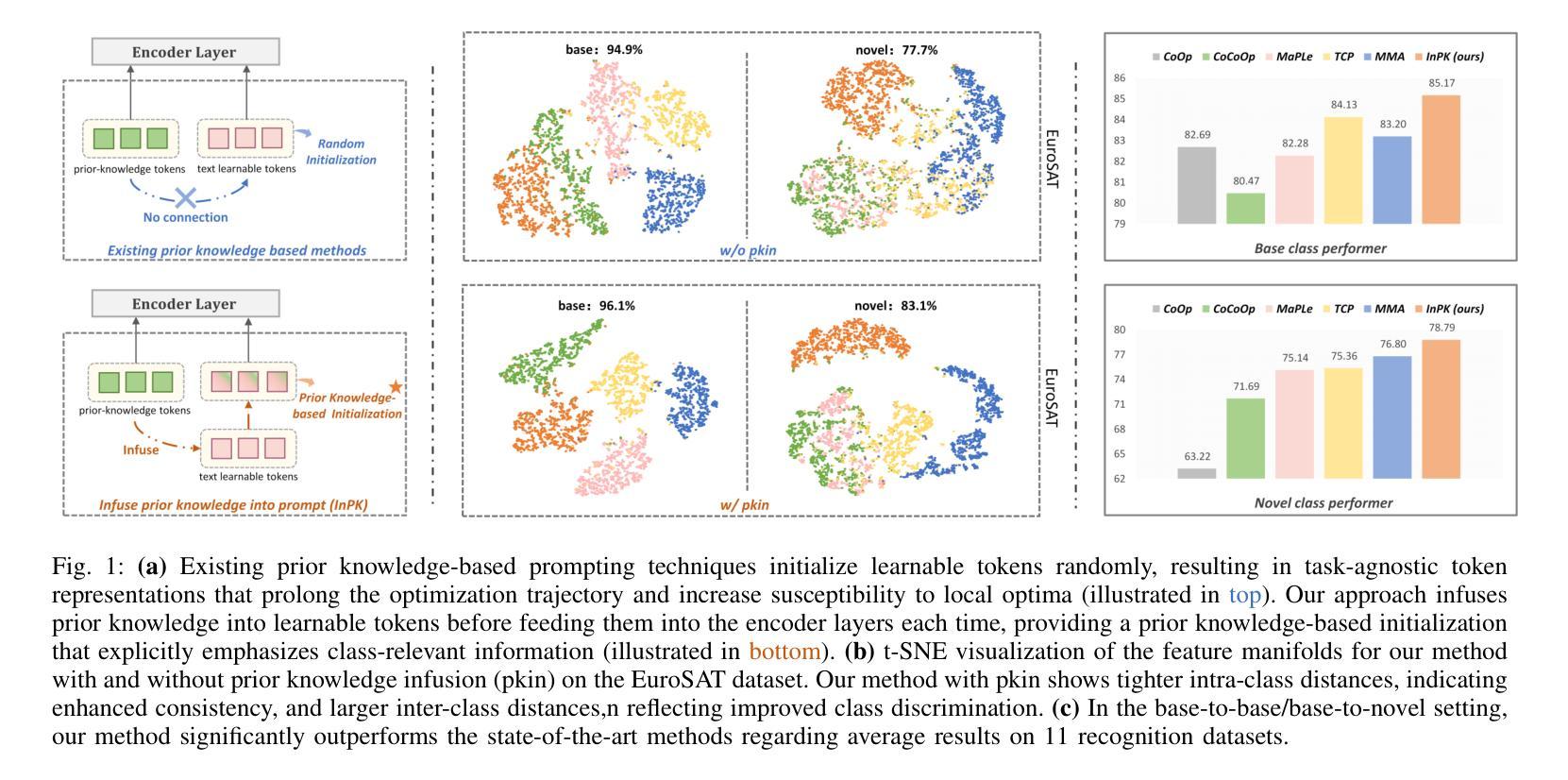
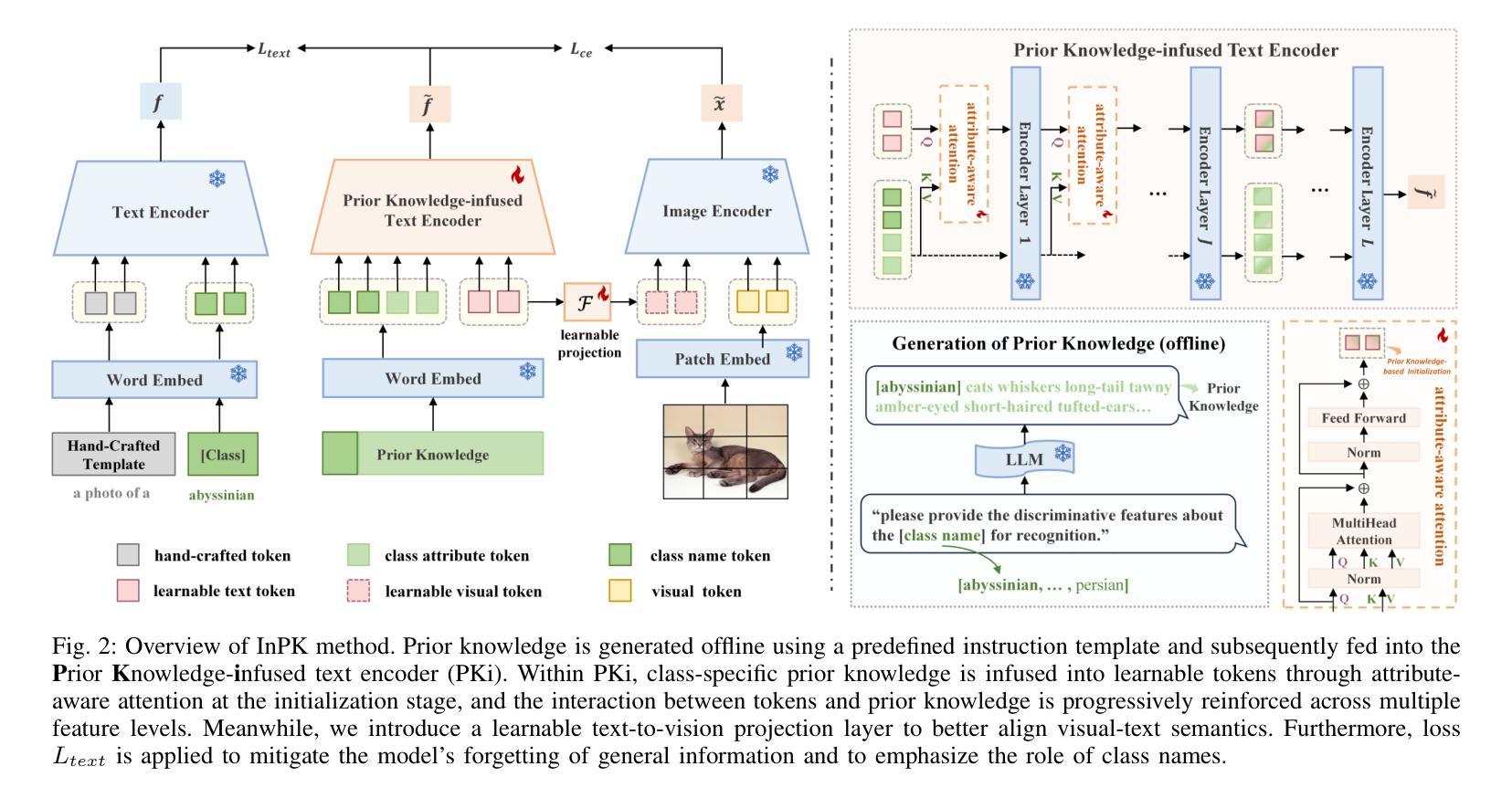
Prompt tuning has become a popular strategy for adapting Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to zero/few-shot visual recognition tasks. Some prompting techniques introduce prior knowledge due to its richness, but when learnable tokens are randomly initialized and disconnected from prior knowledge, they tend to overfit on seen classes and struggle with domain shifts for unseen ones. To address this issue, we propose the InPK model, which infuses class-specific prior knowledge into the learnable tokens during initialization, thus enabling the model to explicitly focus on class-relevant information. Furthermore, to mitigate the weakening of class information by multi-layer encoders, we continuously reinforce the interaction between learnable tokens and prior knowledge across multiple feature levels. This progressive interaction allows the learnable tokens to better capture the fine-grained differences and universal visual concepts within prior knowledge, enabling the model to extract more discriminative and generalized text features. Even for unseen classes, the learned interaction allows the model to capture their common representations and infer their appropriate positions within the existing semantic structure. Moreover, we introduce a learnable text-to-vision projection layer to accommodate the text adjustments, ensuring better alignment of visual-text semantics. Extensive experiments on 11 recognition datasets show that InPK significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in multiple zero/few-shot image classification tasks.
在视觉语言模型(VLMs)中,提示调整已成为适应零/少样本视觉识别任务的流行策略。一些提示技术由于其丰富性而引入了先验知识,但是当可学习令牌随机初始化并与先验知识断开连接时,它们往往会对已见类别产生过拟合,并在未见类别上遇到领域偏移问题。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了InPK模型,该模型在初始化过程中将特定类别的先验知识注入可学习令牌中,从而使模型能够显式地关注类别相关的信息。此外,为了减轻多层编码器对类别信息的削弱,我们不断强化了可学习令牌与先验知识在多个特征层次之间的交互。这种渐进的交互使可学习令牌能够更好地捕捉先验知识中的细微差别和通用视觉概念,使模型能够提取更具鉴别力和普遍性的文本特征。即使对于未见过的类别,学习到的交互也允许模型捕获它们的共同表示并推断它们在现有语义结构中的适当位置。此外,我们引入了一个可学习的文本到视觉投影层来适应文本调整,确保视觉文本语义的更好对齐。在11个识别数据集上的大量实验表明,InPK在多个零/少样本图像分类任务中显著优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对视觉语言模型(VLMs)在零样本或少样本视觉识别任务中的适应性问题,提出了一种名为InPK的模型。该模型通过初始化时融入类别特定的先验知识,解决了学习符号随机初始化导致的过拟合问题。此外,为了缓解多层编码器对类别信息的削弱,模型在多级特征上不断强化了学习符号和先验知识间的交互。实验证明,InPK模型在多个零样本/少样本图像分类任务中显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- InPK模型通过初始化时融入类别特定的先验知识,解决学习符号随机初始化导致的过拟合问题。
- InPK模型在多级特征上强化了学习符号和先验知识间的交互,提升模型性能。
- 引入的文本到视觉投影层确保视觉文本语义的更好对齐。
- InPK模型通过明确关注类别相关信息,能够提取更具区分性和通用性的文本特征。
- 对于未见过的类别,InPK模型能够捕捉其通用表示并定位其在现有语义结构中的位置。
- InPK模型在多个零样本/少样本图像分类任务中显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

DH-Mamba: Exploring Dual-domain Hierarchical State Space Models for MRI Reconstruction
Authors:Yucong Meng, Zhiwei Yang, Zhijian Song, Yonghong Shi
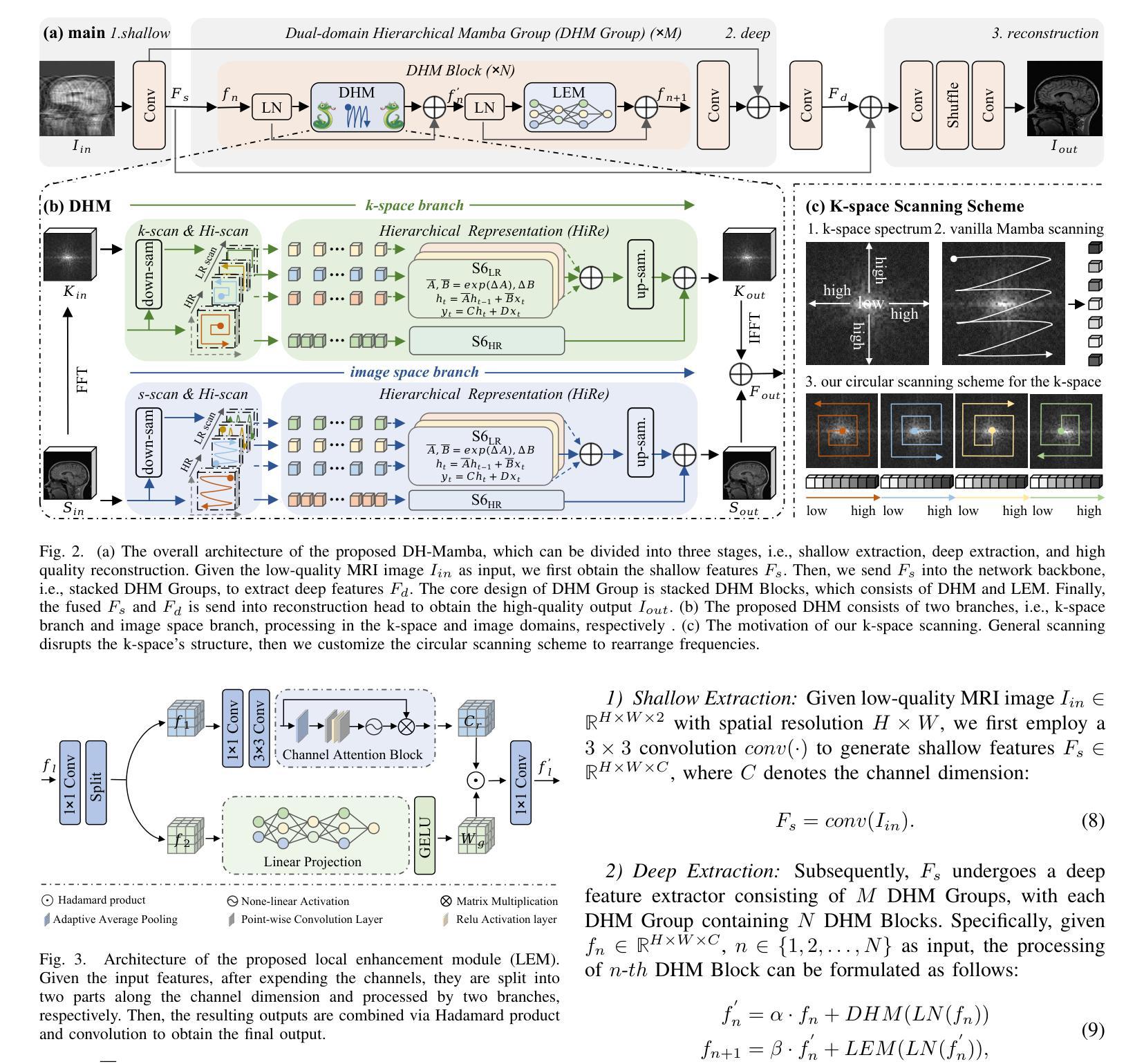
The accelerated MRI reconstruction poses a challenging ill-posed inverse problem due to the significant undersampling in k-space. Deep neural networks, such as CNNs and ViTs, have shown substantial performance improvements for this task while encountering the dilemma between global receptive fields and efficient computation. To this end, this paper explores selective state space models (Mamba), a new paradigm for long-range dependency modeling with linear complexity, for efficient and effective MRI reconstruction. However, directly applying Mamba to MRI reconstruction faces three significant issues: (1) Mamba typically flattens 2D images into distinct 1D sequences along rows and columns, disrupting k-space’s unique spectrum and leaving its potential in k-space learning unexplored. (2) Existing approaches adopt multi-directional lengthy scanning to unfold images at the pixel level, leading to long-range forgetting and high computational burden. (3) Mamba struggles with spatially-varying contents, resulting in limited diversity of local representations. To address these, we propose a dual-domain hierarchical Mamba for MRI reconstruction from the following perspectives: (1) We pioneer vision Mamba in k-space learning. A circular scanning is customized for spectrum unfolding, benefiting the global modeling of k-space. (2) We propose a hierarchical Mamba with an efficient scanning strategy in both image and k-space domains. It mitigates long-range forgetting and achieves a better trade-off between efficiency and performance. (3) We develop a local diversity enhancement module to improve the spatially-varying representation of Mamba. Extensive experiments are conducted on three public datasets for MRI reconstruction under various undersampling patterns. Comprehensive results demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods with lower computational cost.
加速MRI重建是一个具有挑战性的不适定反问题,主要是由于k空间中的显著欠采样。深度神经网络,如卷积神经网络和视觉转换器,在此任务上显示出实质性的性能改进,但面临着全局感受野和高效计算之间的困境。为此,本文探讨了选择性状态空间模型(Mamba)这一具有线性复杂度的长距离依赖建模新范式,用于高效且有效的MRI重建。然而,直接将Mamba应用于MRI重建面临三个重大问题:(1)Mamba通常将2D图像压平为沿行和列的独立1D序列,破坏了k空间的独特频谱,并且没有探索其在k空间学习的潜力。(2)现有方法采用多方向长扫描以在像素级别展开图像,这导致长距离遗忘和高计算负担。(3)Mamba在处理空间变化内容时遇到困难,导致局部表示多样性有限。为解决这些问题,我们从以下角度提出了用于MRI重建的双域分层Mamba:(1)我们在k空间学习中开创了视觉Mamba的先河。为频谱展开定制了循环扫描,有利于k空间的全局建模。(2)我们提出了在图像和k空间域中都采用分层Mamba和有效的扫描策略。它减轻了长距离遗忘,并在效率和性能之间实现了更好的权衡。(3)我们开发了一个局部多样性增强模块,以提高Mamba的空间变化表示。在三个公共数据集上进行了大量MRI重建实验,实验结果表明,在各种欠采样模式下,我们的方法显著优于最先进的方法,且计算成本更低。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了一种新型的针对MRI重建的选择性状态空间模型(Mamba)。然而,直接应用于MRI重建存在三个主要问题。为应对这些问题,该文从以下角度提出了双域分层Mamba方法:探索愿景Mamba在k空间学习中的应用,定制循环扫描以促进k空间的全局建模;提出具有高效扫描策略的分层Mamba,在图像和k空间域上减轻远程遗忘,实现效率和性能的更好平衡;开发局部多样性增强模块,提高Mamba的空间变化表示能力。在三个公共数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,该方法在较低的计算成本下显著优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 论文介绍了针对MRI重建的选择性状态空间模型(Mamba)的新范式。
- Mamba直接应用于MRI重建面临三个主要问题,包括破坏k空间的独特光谱、远程遗忘和高计算负担以及空间变化内容的处理不足。
- 为解决这些问题,论文提出了双域分层Mamba方法,包括在k空间学习中的愿景Mamba应用、具有高效扫描策略的分层Mamba以及局部多样性增强模块的开发。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在多种欠采样模式下显著优于现有技术,且计算成本较低。
点此查看论文截图

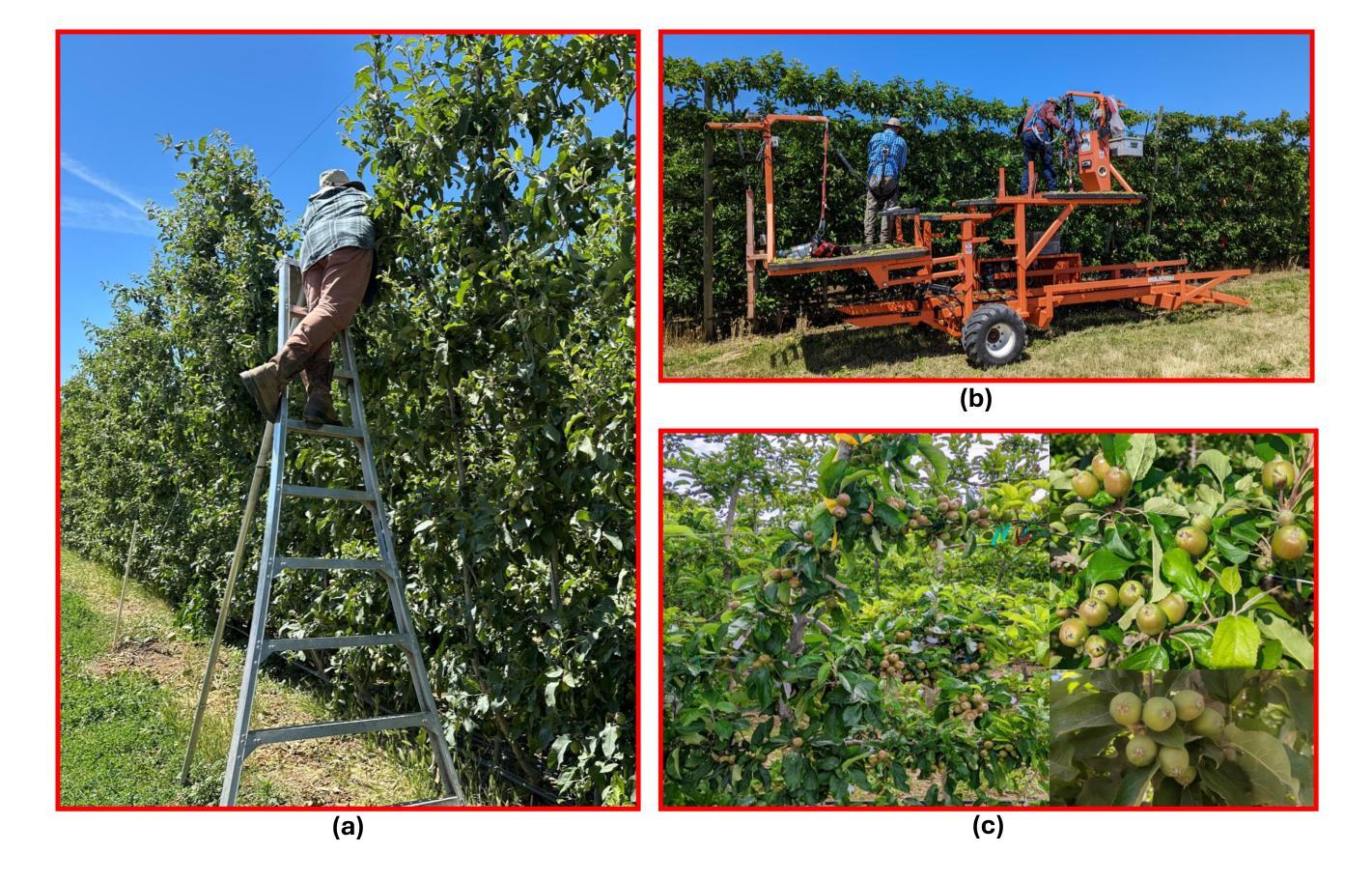
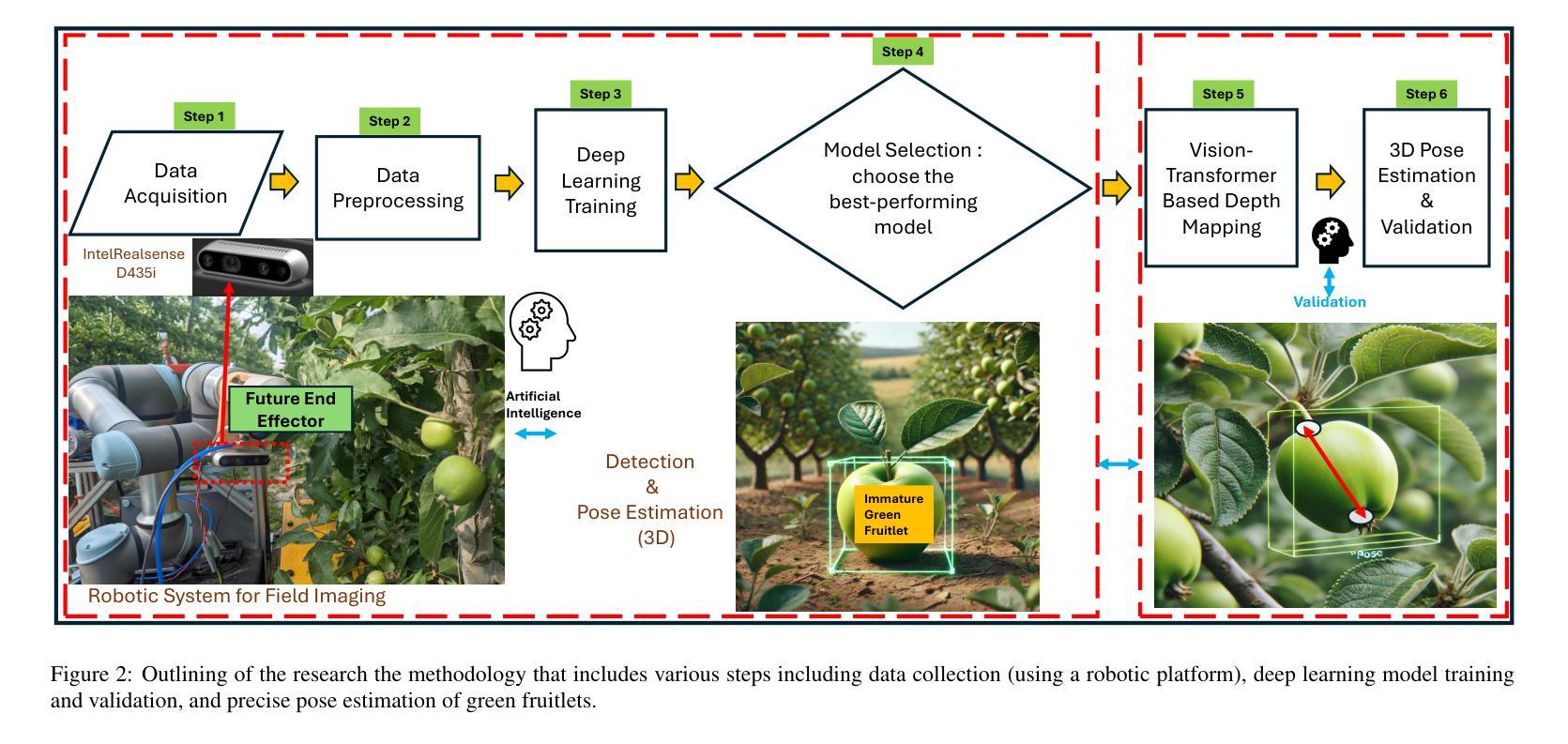
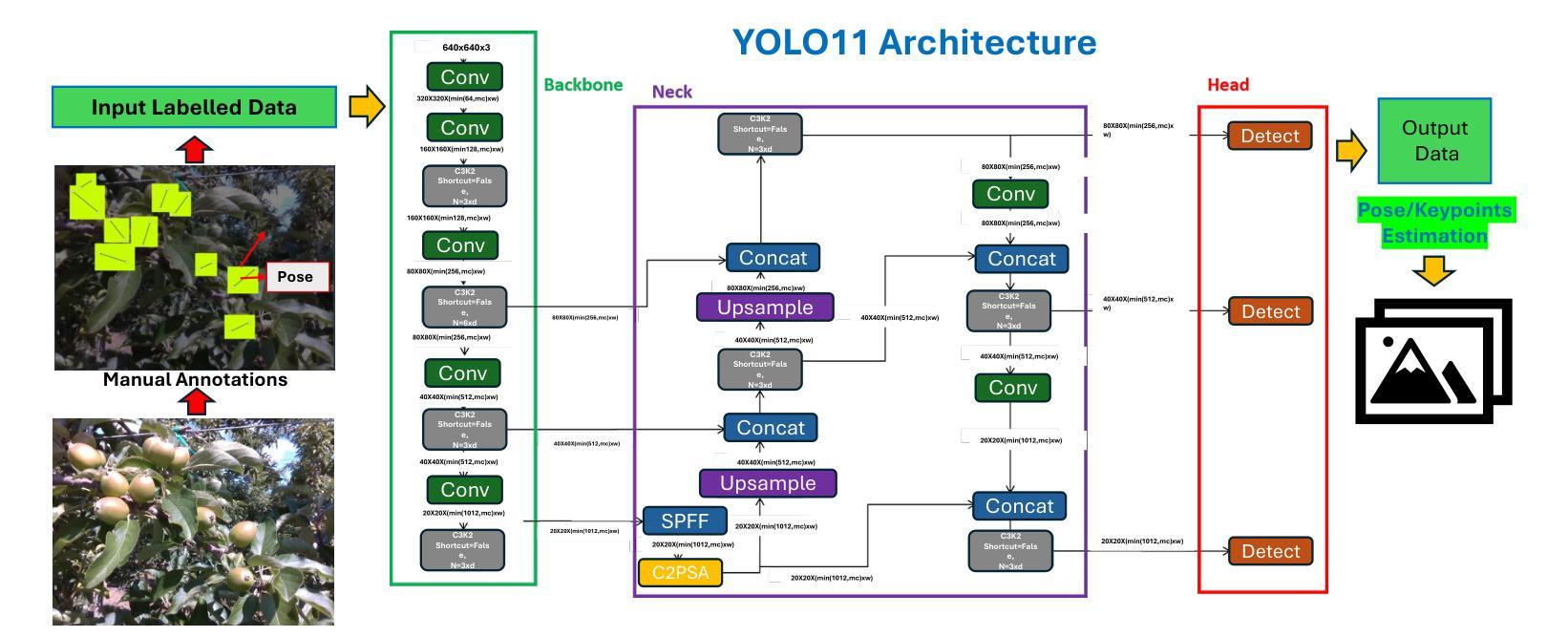
YOLO11 and Vision Transformers based 3D Pose Estimation of Immature Green Fruits in Commercial Apple Orchards for Robotic Thinning
Authors:Ranjan Sapkota, Manoj Karkee
In this study, a robust method for 3D pose estimation of immature green apples (fruitlets) in commercial orchards was developed, utilizing the YOLO11(or YOLOv11) object detection and pose estimation algorithm alongside Vision Transformers (ViT) for depth estimation (Dense Prediction Transformer (DPT) and Depth Anything V2). For object detection and pose estimation, performance comparisons of YOLO11 (YOLO11n, YOLO11s, YOLO11m, YOLO11l and YOLO11x) and YOLOv8 (YOLOv8n, YOLOv8s, YOLOv8m, YOLOv8l and YOLOv8x) were made under identical hyperparameter settings among the all configurations. It was observed that YOLO11n surpassed all configurations of YOLO11 and YOLOv8 in terms of box precision and pose precision, achieving scores of 0.91 and 0.915, respectively. Conversely, YOLOv8n exhibited the highest box and pose recall scores of 0.905 and 0.925, respectively. Regarding the mean average precision at 50% intersection over union (mAP@50), YOLO11s led all configurations with a box mAP@50 score of 0.94, while YOLOv8n achieved the highest pose mAP@50 score of 0.96. In terms of image processing speed, YOLO11n outperformed all configurations with an impressive inference speed of 2.7 ms, significantly faster than the quickest YOLOv8 configuration, YOLOv8n, which processed images in 7.8 ms. Subsequent integration of ViTs for the green fruit’s pose depth estimation revealed that Depth Anything V2 outperformed Dense Prediction Transformer in 3D pose length validation, achieving the lowest Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of 1.52 and Mean Absolute Error (MAE) of 1.28, demonstrating exceptional precision in estimating immature green fruit lengths. Integration of YOLO11 and Depth Anything Model provides a promising solution to 3D pose estimation of immature green fruits for robotic thinning applications. (YOLOv11 pose detection, YOLOv11 Pose, YOLOv11 Keypoints detection, YOLOv11 pose estimation)
在这项研究中,开发了一种利用YOLO11(或YOLOv11)目标检测与姿态估计算法以及用于深度估计的Vision Transformers(ViT)(包括Dense Prediction Transformer(DPT)和Depth Anything V2)对商业果园中未成熟绿色苹果(也称为幼果)进行3D姿态估计的稳健方法。在目标检测和姿态估计方面,对YOLO11(YOLO11n、YOLO11s、YOLO11m、YOLO11l和YOLO11x)和YOLOv8(YOLOv8n、YOLOv8s、YOLOv8m、YOLOv8l和YOLOv8x)的所有配置进行了相同的超参数设置下的性能比较。观察发现,YOLO11n在框精度和姿态精度方面超越了所有YOLO11和YOLOv8的配置,分别达到了0.91和0.915。相反,YOLOv8n在盒子和姿态的召回率方面表现出最佳,分别达到了0.905和0.925。在50%交集联合的平均精度(mAP@50)方面,YOLO11s在所有配置中领先,其盒子mAP@50得分为0.94,而YOLOv8n的姿态mAP@50得分最高,为0.96。在图像处理速度方面,YOLO11n表现最佳,其推理速度为2.7毫秒,显著快于最快的YOLOv8配置(YOLOv8n),后者处理图像需要7.8毫秒。随后对绿色水果的姿态深度估计整合ViTs的研究显示,Depth Anything V2在3D姿态长度验证方面表现优于Dense Prediction Transformer,达到了最低的均方根误差(RMSE)为1.52和平均绝对误差(MAE)为1.28,显示出在估算未成熟绿色水果长度方面的出色精确度。整合YOLO11和Depth Anything模型为解决机器人疏果应用中未成熟绿色水果的3D姿态估计问题提供了有前途的解决方案。(YOLOv11姿态检测、YOLOv11姿态、YOLOv11关键点检测、YOLOv11姿态估计)
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 Pages, 13 Figures, 1 Table
Summary
本研究利用YOLOv11进行苹果幼果的三维姿态估计,并与YOLOv8进行比较。结果显示YOLOv11在框精度和姿态精度上表现更佳,同时处理速度更快。此外,整合Vision Transformers(ViT)的深度估计模型Depth Anything V2对苹果幼果的长度估计展现出极高的精确度。该研究为机器人自动疏果应用中的苹果幼果三维姿态估计提供了有力支持。
Key Takeaways
- 研究利用YOLOv11进行苹果幼果的三维姿态估计,涉及对象检测和姿态估计。
- YOLOv11的不同配置在框精度和姿态精度上进行了比较,其中YOLO11n表现最佳。
- YOLOv8在召回率方面表现出较高的性能。
- Vision Transformers(ViT)被整合用于深度估计,其中Depth Anything V2在长度估计方面表现出高精确度。
- YOLOv11处理图像的速度非常快,为实际应用提供了良好的实时性能。
- 该研究提供了一个有前途的解决方案,即整合YOLOv11和Depth Anything Model进行苹果幼果的三维姿态估计。
点此查看论文截图


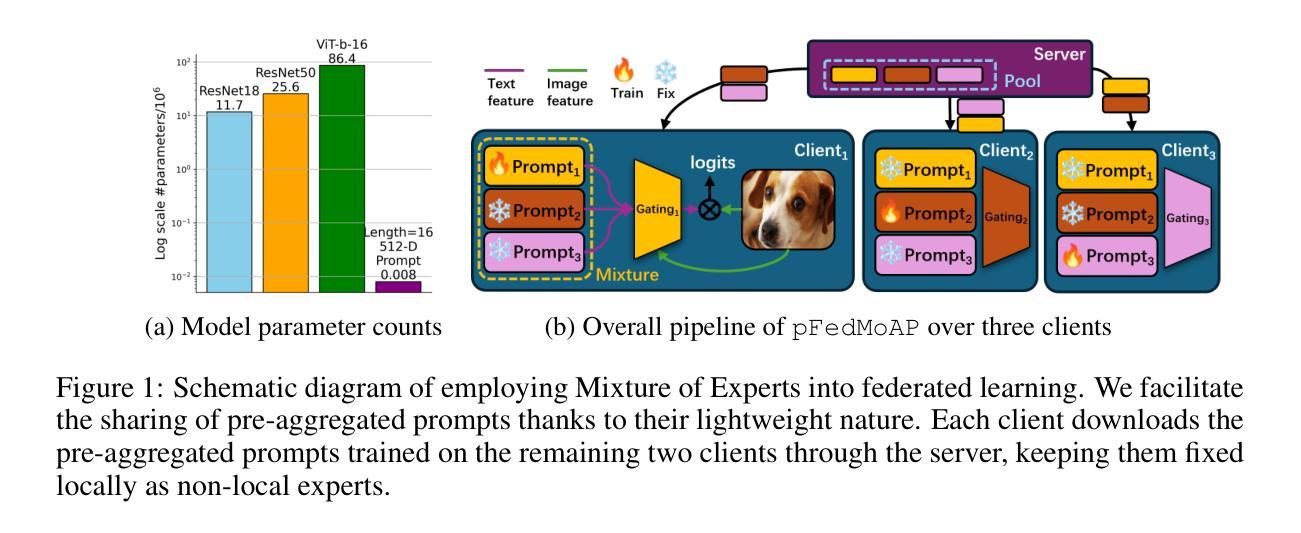
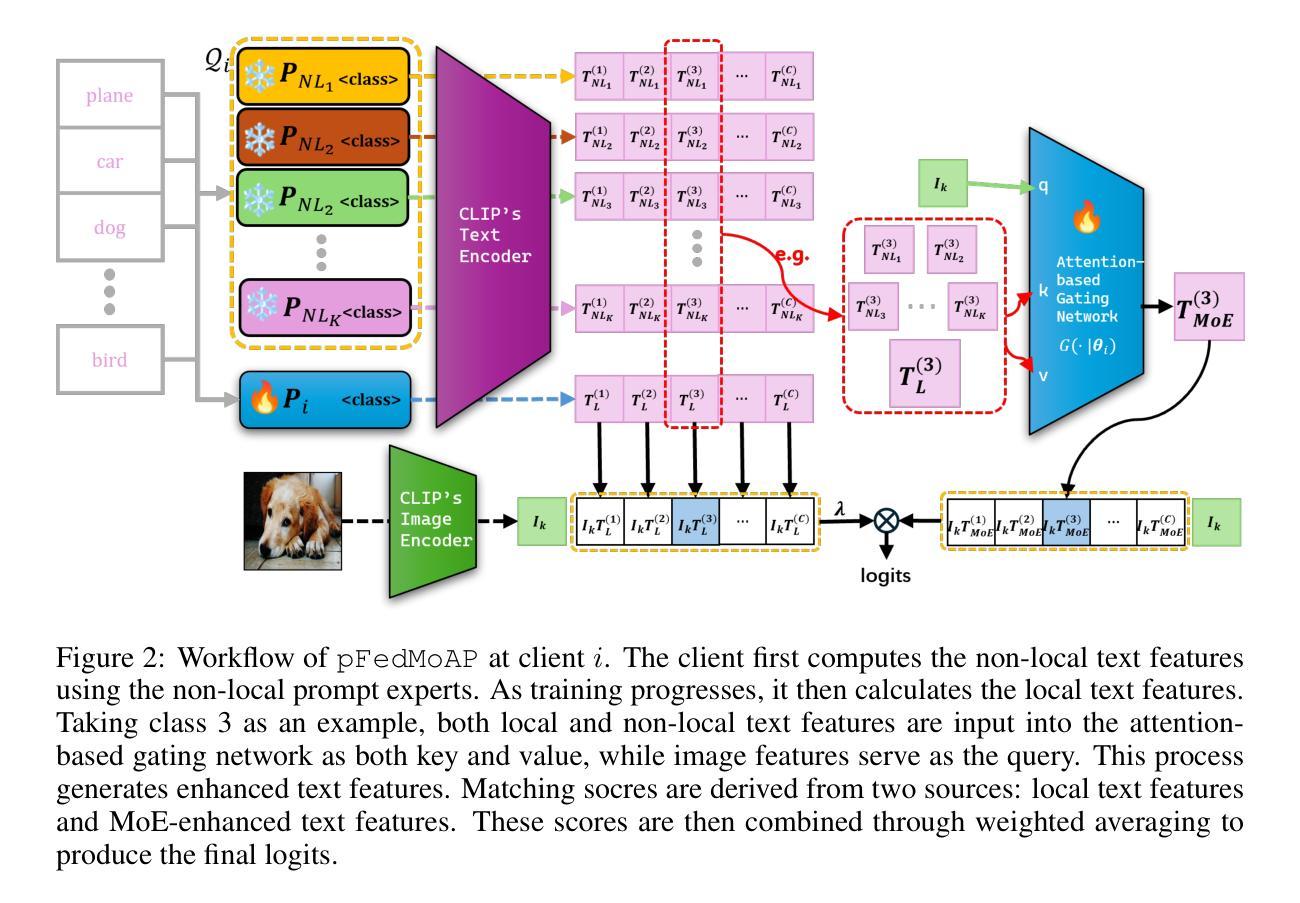
Mixture of Experts Made Personalized: Federated Prompt Learning for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Jun Luo, Chen Chen, Shandong Wu
Federated prompt learning benefits federated learning with CLIP-like Vision-Language Model’s (VLM’s) robust representation learning ability through prompt learning. However, current federated prompt learning methods are habitually restricted to the traditional FL paradigm, where the participating clients are generally only allowed to download a single globally aggregated model from the server. While justifiable for training full-sized models under federated settings, in this work, we argue that this paradigm is ill-suited for lightweight prompts. By facilitating the clients to download multiple pre-aggregated prompts as fixed non-local experts, we propose Personalized Federated Mixture of Adaptive Prompts (pFedMoAP), a novel FL framework that personalizes the prompt learning process through the lens of Mixture of Experts (MoE). pFedMoAP implements a local attention-based gating network that learns to generate enhanced text features for better alignment with local image data, benefiting from both local and downloaded non-local adaptive prompt experts. Extensive experiments on 9 datasets under various federated settings demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed pFedMoAP algorithm. The code is available at https://github.com/ljaiverson/pFedMoAP.
联邦提示学习通过提示学习能力增强了联邦学习在CLIP类视觉语言模型(VLM)中的稳健表示学习能力。然而,当前的联邦提示学习方法通常受限于传统的联邦学习(FL)范式,在这种范式下,参与客户端通常只能从服务器下载单个全局聚合模型。虽然在联邦设置下训练全尺寸模型时这种做法是合理的,但在这项工作中,我们认为这种范式不适合轻量级提示。通过促进客户端下载多个预先聚合的提示作为固定的非局部专家,我们提出了个性化联邦混合自适应提示(pFedMoAP),这是一种通过专家混合(MoE)视角个性化提示学习过程的新型联邦学习框架。pFedMoAP实现了一个基于本地注意力的门控网络,学习生成增强的文本特征,以更好地与本地图像数据对齐,受益于本地和下载的非局部自适应提示专家。在多种联邦设置下的9个数据集上进行的广泛实验证明了所提出的pFedMoAP算法的有效性。代码可在https://github.com/ljaiverson/pFedMoAP找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
基于CLIP类似的视觉语言模型(VLM)的鲁棒表示学习能力,联邦提示学习(Federated Prompt Learning)为联邦学习带来了好处。然而,当前的联邦提示学习方法通常受限于传统的联邦学习(FL)范式,其中参与客户端通常仅允许从服务器下载单个全局聚合模型。然而在该研究中,我们认为该范式不适合用于轻量级提示。通过允许客户端下载多个预先聚合的提示作为固定的非局部专家,我们提出了个性化联邦混合自适应提示(pFedMoAP)这一新型FL框架,它通过专家混合的视角个性化提示学习过程。pFedMoAP实现了基于本地注意力机制的网关网络,学习生成增强的文本特征以更好地与本地图像数据对齐,受益于本地和下载的非局部自适应提示专家。在多种联邦设置下的九个数据集上的广泛实验证明了pFedMoAP算法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦提示学习结合了视觉语言模型(VLM)的鲁棒表示学习能力,为联邦学习带来了好处。
- 当前联邦提示学习方法受限于传统联邦学习范式,仅允许下载单一全局模型。
- pFedMoAP框架允许客户端下载多个预先聚合的提示,作为固定的非局部专家。
- pFedMoAP个性化提示学习过程,借鉴了混合专家的视角。
- pFedMoAP通过实现基于本地注意力机制的网关网络,生成增强的文本特征以更好地与本地图像数据对齐。
- pFedMoAP受益于本地和下载的非局部自适应提示专家。
- 在九个数据集上的实验证明了pFedMoAP算法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

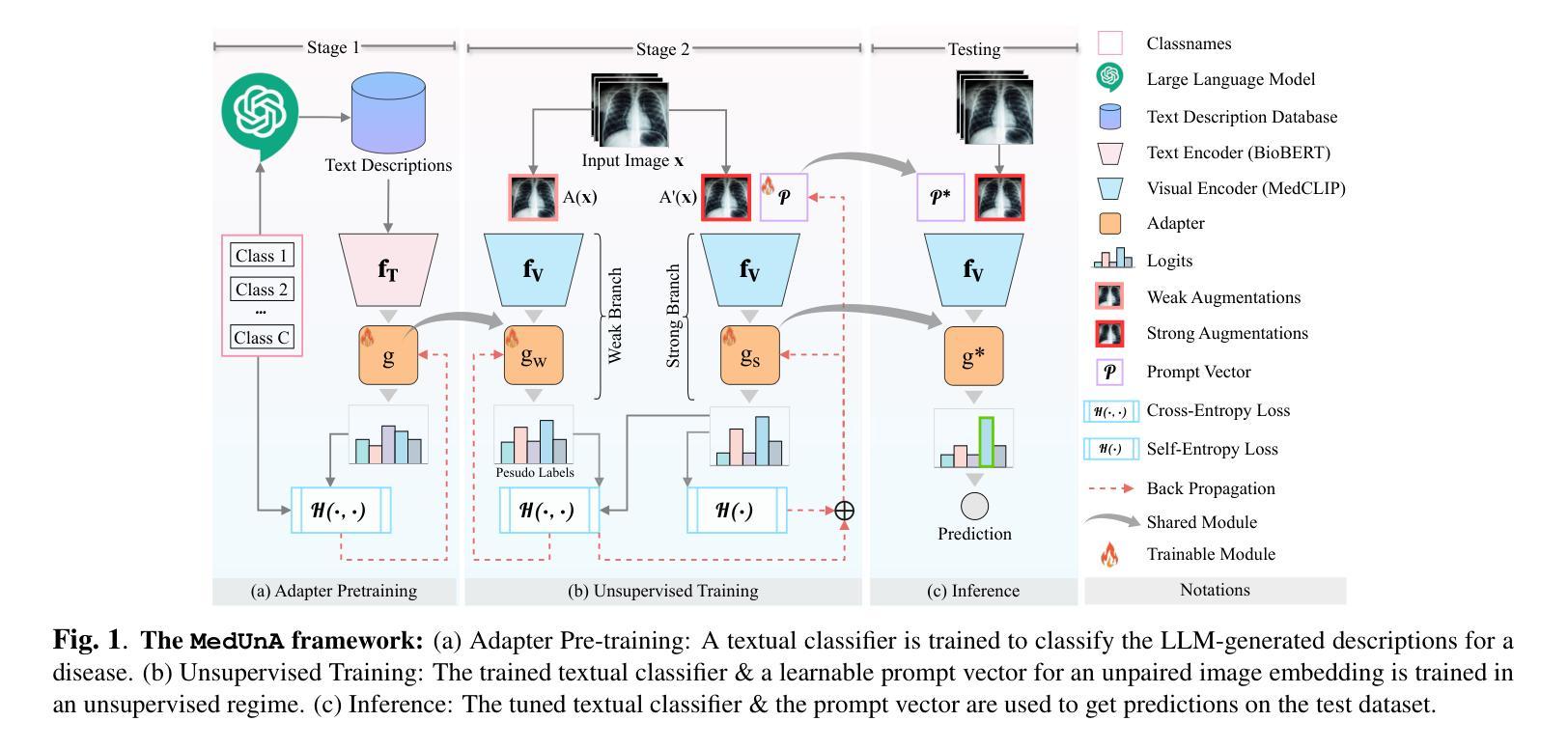
Can language-guided unsupervised adaptation improve medical image classification using unpaired images and texts?
Authors:Umaima Rahman, Raza Imam, Mohammad Yaqub, Boulbaba Ben Amor, Dwarikanath Mahapatra
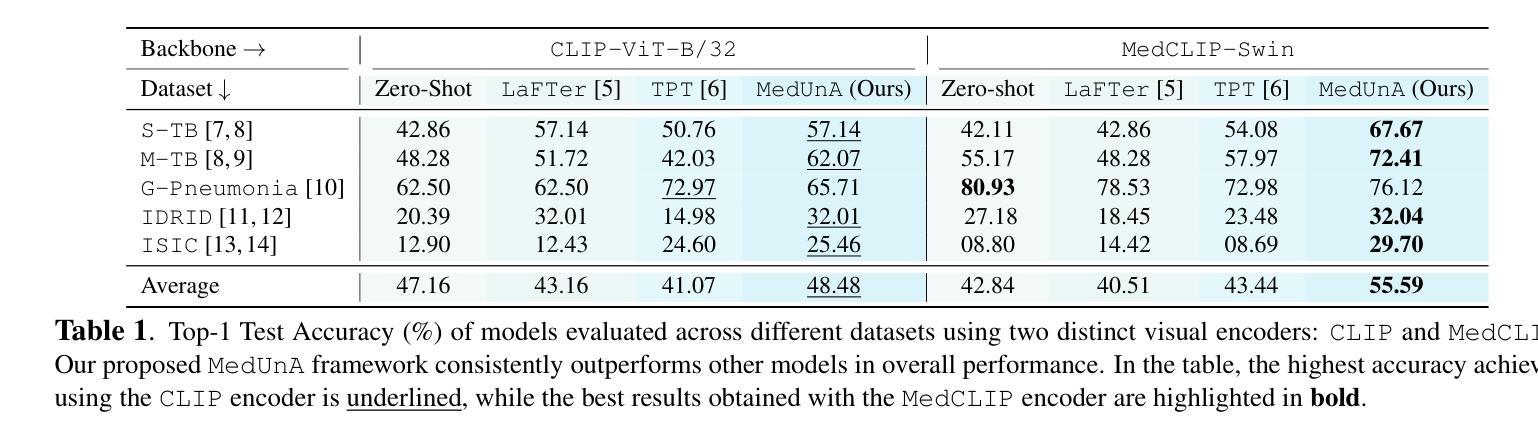
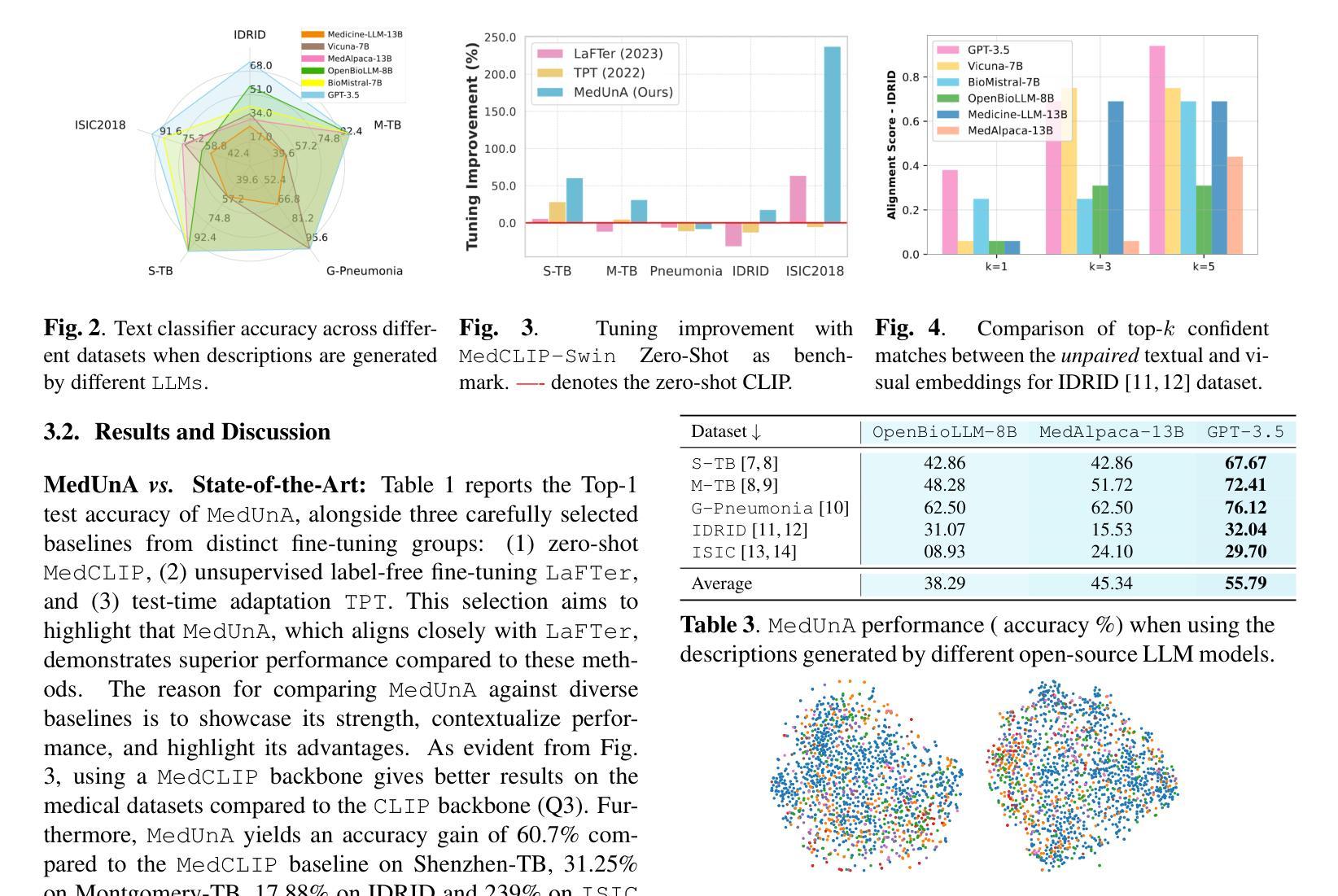
In medical image classification, supervised learning is challenging due to the scarcity of labeled medical images. To address this, we leverage the visual-textual alignment within Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to enable unsupervised learning of a medical image classifier. In this work, we propose \underline{Med}ical \underline{Un}supervised \underline{A}daptation (\texttt{MedUnA}) of VLMs, where the LLM-generated descriptions for each class are encoded into text embeddings and matched with class labels via a cross-modal adapter. This adapter attaches to a visual encoder of \texttt{MedCLIP} and aligns the visual embeddings through unsupervised learning, driven by a contrastive entropy-based loss and prompt tuning. Thereby, improving performance in scenarios where textual information is more abundant than labeled images, particularly in the healthcare domain. Unlike traditional VLMs, \texttt{MedUnA} uses \textbf{unpaired images and text} for learning representations and enhances the potential of VLMs beyond traditional constraints. We evaluate the performance on three chest X-ray datasets and two multi-class datasets (diabetic retinopathy and skin lesions), showing significant accuracy gains over the zero-shot baseline. Our code is available at https://github.com/rumaima/meduna.
在医学图像分类中,由于缺乏标记的医学图像,监督学习面临挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)中的视觉文本对齐功能,实现医学图像分类器的无监督学习。在这项工作中,我们提出了医疗无监督适配(MedUnA)的方法,其中大型语言模型(LLM)为每一类别生成的描述被编码为文本嵌入,并通过跨模态适配器与类别标签相匹配。该适配器附加到MedCLIP的视觉编码器上,并通过无监督学习对齐视觉嵌入,以对比熵损失和提示调整为基础进行驱动。因此,在文本信息比标记图像更丰富的情况下,特别是在医疗领域,提高了性能。与传统的VLMs不同,MedUnA使用非配对图像和文本来学习表示,并提高了VLMs超越传统约束的潜力。我们在三个胸部X射线数据集和两个多类数据集(糖尿病视网膜病变和皮肤病变)上评估了性能,相较于零样本基线,显示出显著的准确性提升。我们的代码位于https://github.com/rumaima/meduna。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Conference paper at International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2025
Summary
医学图像分类中监督学习因缺乏标注医学图像而具有挑战性。本研究提出利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)中的视觉文本对齐来实现医学图像分类器的无监督学习。提出Medical UnA方法,将大型语言模型生成的各类描述编码为文本嵌入,通过跨模态适配器与类标签匹配。该适配器连接到MedCLIP的视觉编码器,通过对无监督学习驱动的对齐生成对比熵损失和提示调整,从而提高在文本信息丰富于标注图像的场景中的性能,特别是在医疗领域。相较于传统VLMs,MedUnA使用非配对图像和文本学习表征,突破了传统约束,提高了VLMs的潜力。在三个胸X光数据集和两个多类数据集(糖尿病视网膜病变和皮肤病变)上的评估显示,相较于零样本基线有显著精度提升。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分类面临监督学习挑战,因缺乏标注医学图像。
- 利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)的视觉文本对齐实现无监督学习。
- 提出Medical UnA方法,结合大型语言模型的类描述与跨模态适配器。
- 适配器与MedCLIP的视觉编码器结合,通过对比熵损失和提示调整实现视觉嵌入对齐。
- 在文本信息丰富于标注图像的场景中表现优异,特别是在医疗领域。
- MedUnA使用非配对图像和文本学习表征,突破传统VLMs的约束。
- 在多个数据集上的评估显示,相较于零样本基线有显著精度提升。
点此查看论文截图

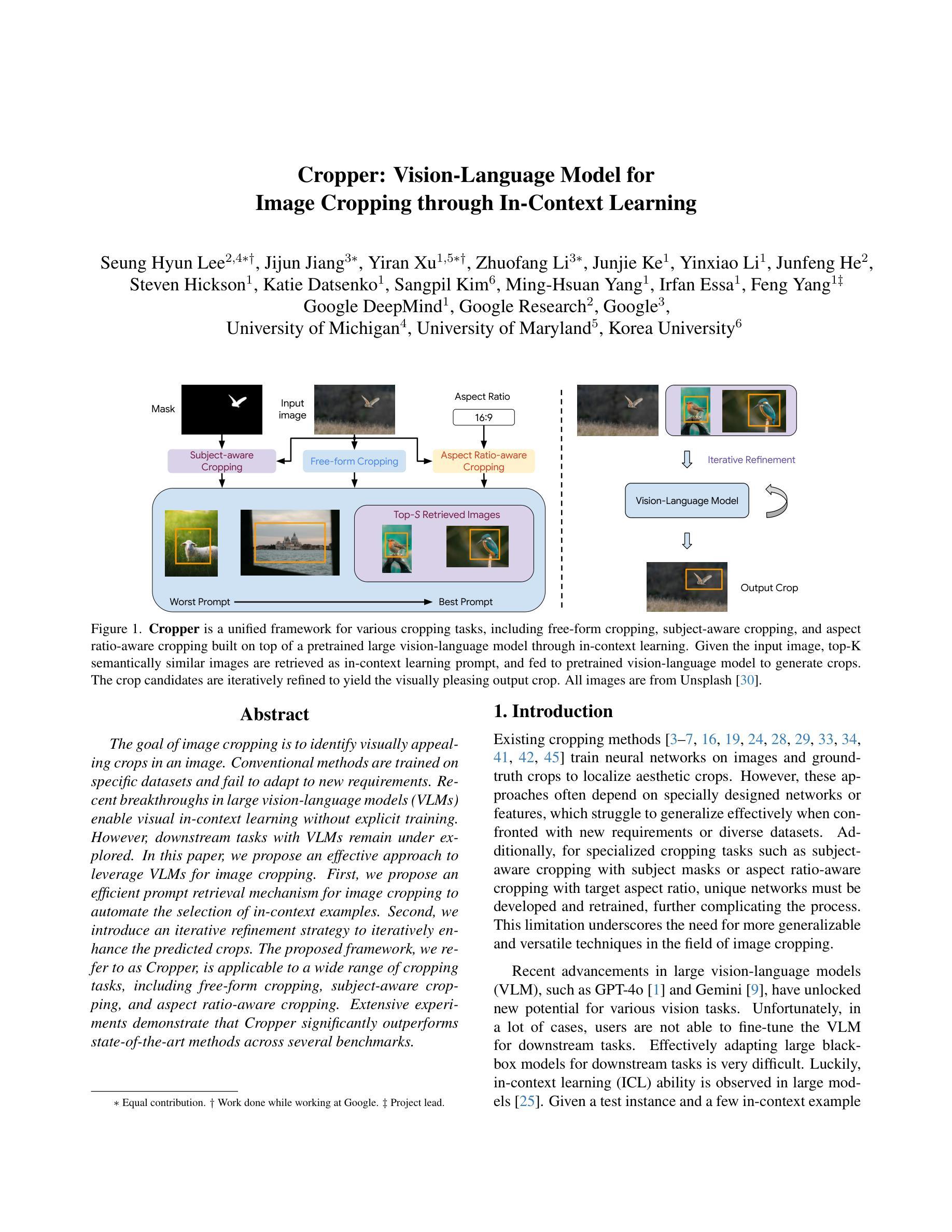
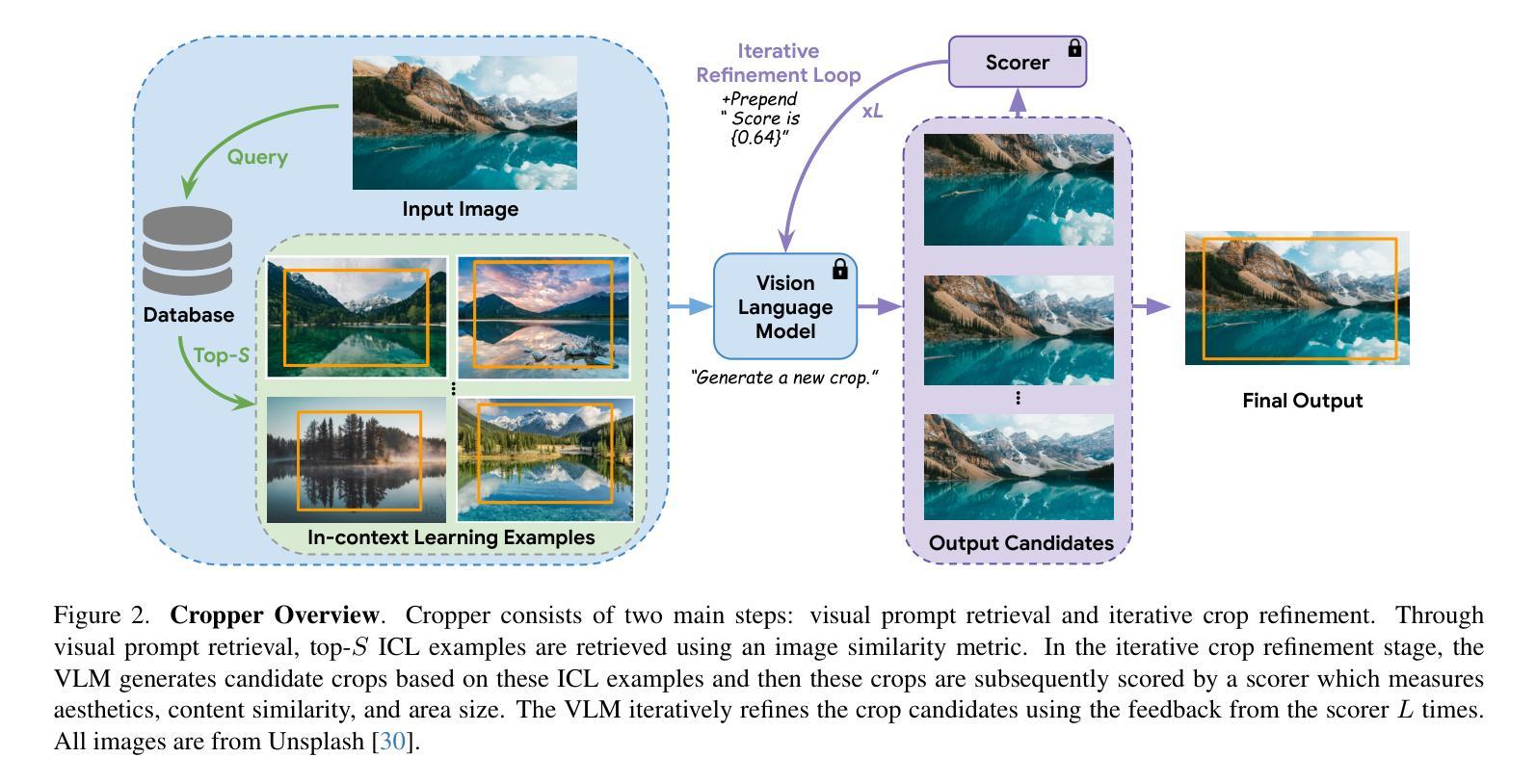
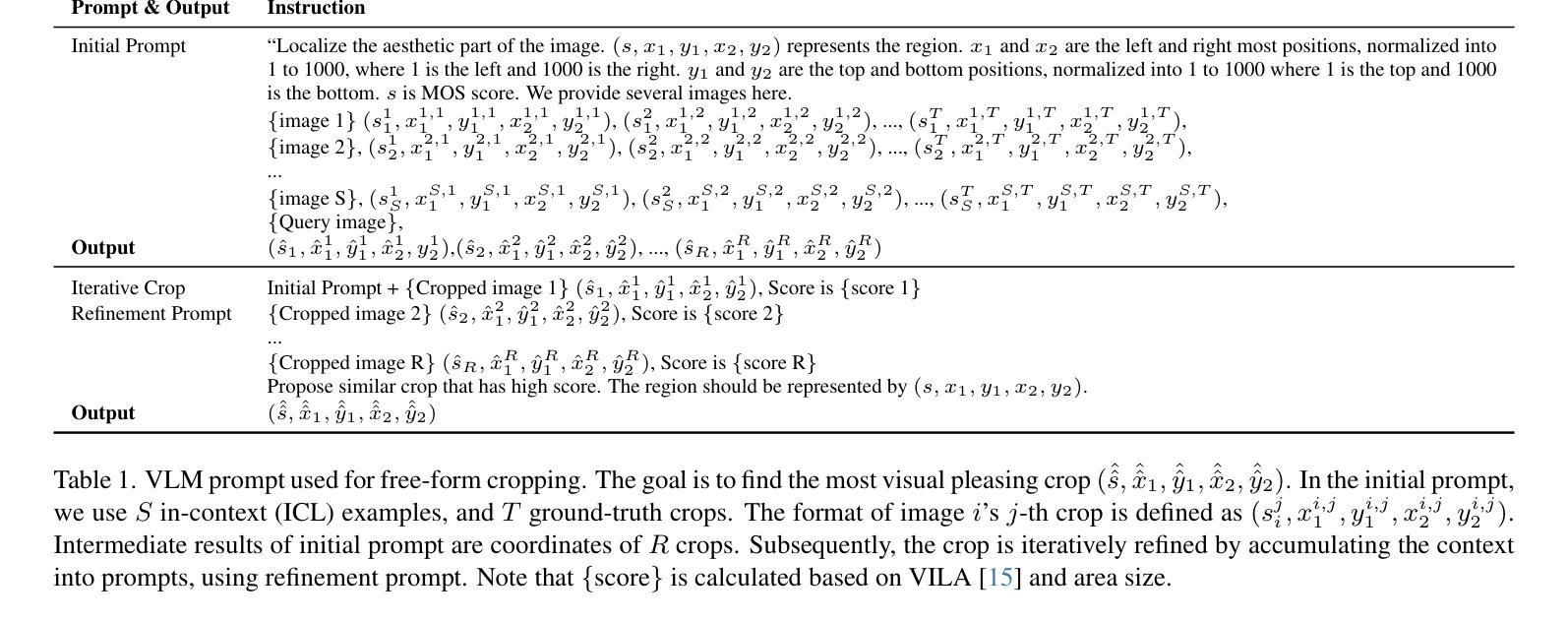
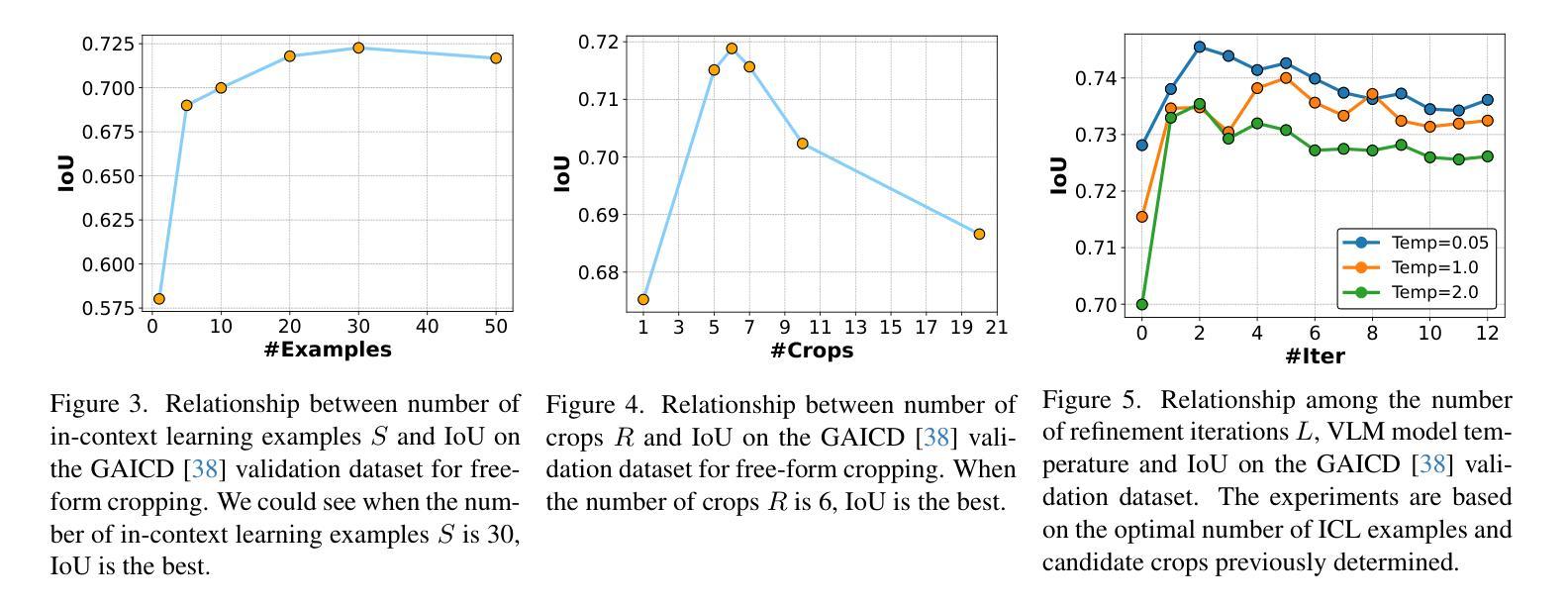
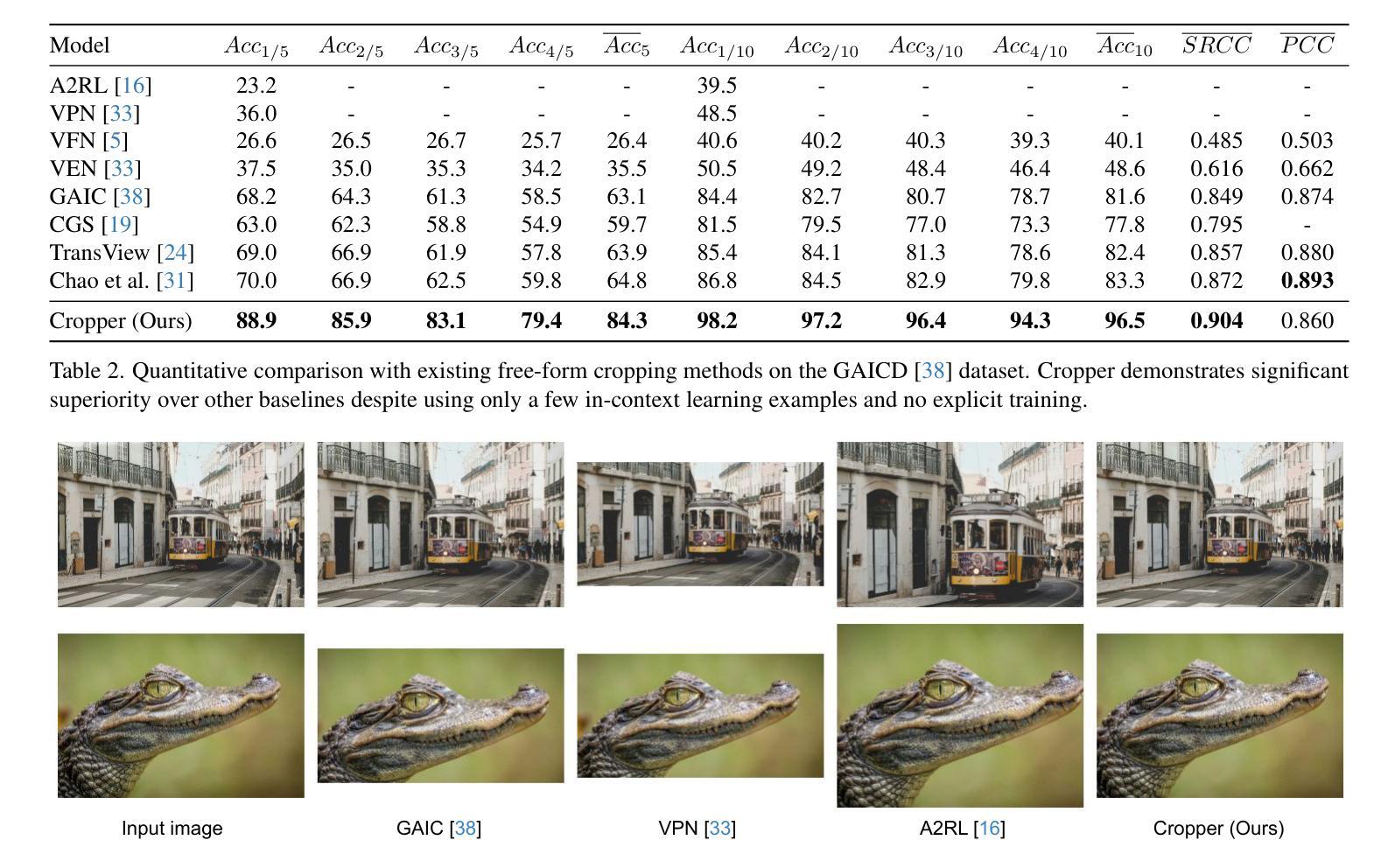
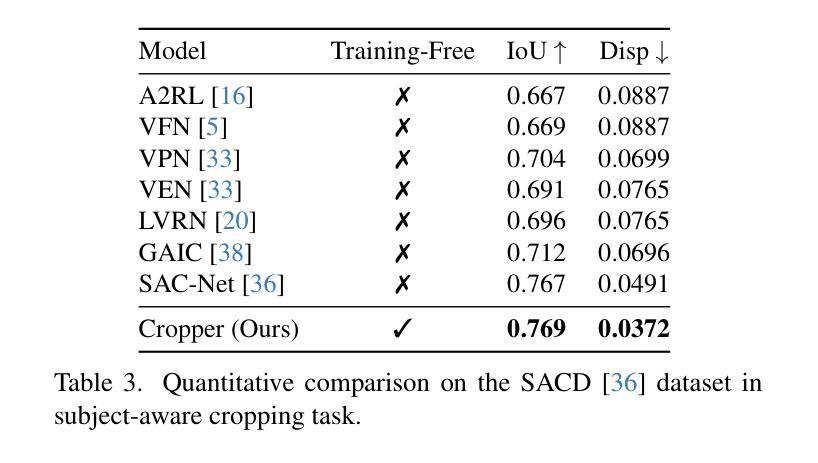
Cropper: Vision-Language Model for Image Cropping through In-Context Learning
Authors:Seung Hyun Lee, Jijun Jiang, Yiran Xu, Zhuofang Li, Junjie Ke, Yinxiao Li, Junfeng He, Steven Hickson, Katie Datsenko, Sangpil Kim, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Irfan Essa, Feng Yang
The goal of image cropping is to identify visually appealing crops in an image. Conventional methods are trained on specific datasets and fail to adapt to new requirements. Recent breakthroughs in large vision-language models (VLMs) enable visual in-context learning without explicit training. However, downstream tasks with VLMs remain under explored. In this paper, we propose an effective approach to leverage VLMs for image cropping. First, we propose an efficient prompt retrieval mechanism for image cropping to automate the selection of in-context examples. Second, we introduce an iterative refinement strategy to iteratively enhance the predicted crops. The proposed framework, we refer to as Cropper, is applicable to a wide range of cropping tasks, including free-form cropping, subject-aware cropping, and aspect ratio-aware cropping. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Cropper significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods across several benchmarks.
图像裁剪的目标是识别图像中视觉吸引力强的部分。传统方法是在特定数据集上进行训练,无法适应新的要求。最近大型视觉语言模型(VLM)的突破使得无需明确训练即可进行视觉上下文学习。然而,使用VLM的下游任务仍然有待探索。在本文中,我们提出了一种利用VLM进行图像裁剪的有效方法。首先,我们提出了一种高效的提示检索机制,用于自动选择上下文示例来进行图像裁剪。其次,我们引入了一种迭代优化策略,以逐步改进预测的裁剪部分。我们称提出的框架为“裁剪器(Cropper)”,适用于各种裁剪任务,包括自由形式裁剪、主题感知裁剪和比例感知裁剪。大量实验表明,Cropper在多个基准测试上的表现均优于最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
图像裁剪的目标是识别图像中的视觉吸引力区域。传统方法依赖于特定数据集的训练,难以适应新要求。最近的大型视觉语言模型(VLMs)的突破实现了无需明确训练的视觉上下文学习。然而,对于VLMs的下游任务仍有待探索。本文提出了一种有效利用VLMs进行图像裁剪的方法。首先,我们提出了有效的提示检索机制,以自动化选择上下文示例进行图像裁剪。其次,我们引入了一种迭代优化策略,以逐步改进预测的裁剪区域。我们称所提出的框架为“Cropper”,适用于多种裁剪任务,包括自由形式裁剪、主题感知裁剪和比例感知裁剪。大量实验表明,Cropper在多个基准测试中显著优于最新方法。
Key Takeaways
- 图像裁剪的目标是识别图像中的视觉吸引力区域。
- 传统图像裁剪方法依赖于特定数据集的训练,难以适应新要求。
- 大型视觉语言模型(VLMs)的突破实现了视觉上下文学习的自动化。
- 本文提出了有效的提示检索机制和迭代优化策略来进行图像裁剪。
- Cropper框架适用于多种图像裁剪任务,包括自由形式、主题感知和比例感知裁剪。
- 实验结果表明,Cropper在多个基准测试中显著优于现有方法。
- 该研究为利用VLMs在图像裁剪任务中的潜力开辟了新的道路。
点此查看论文截图
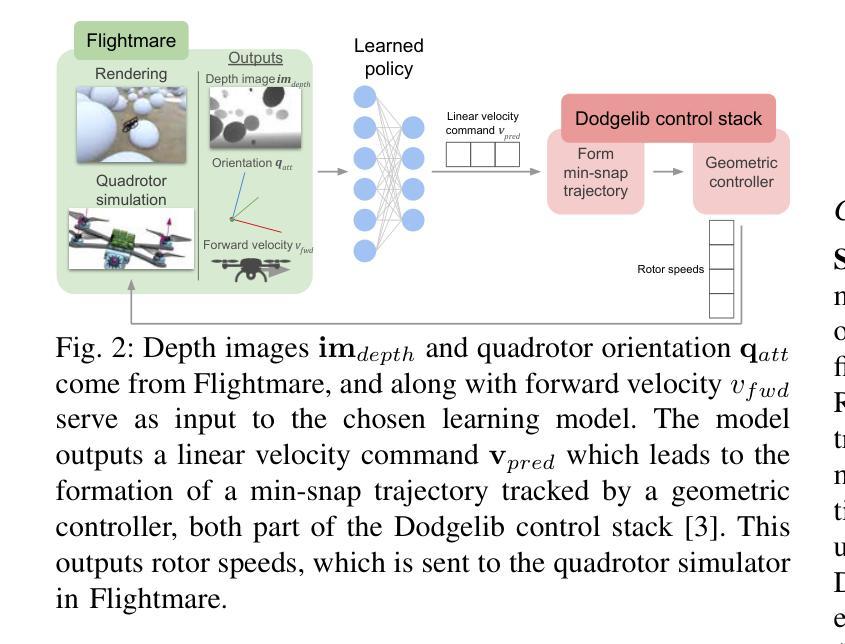
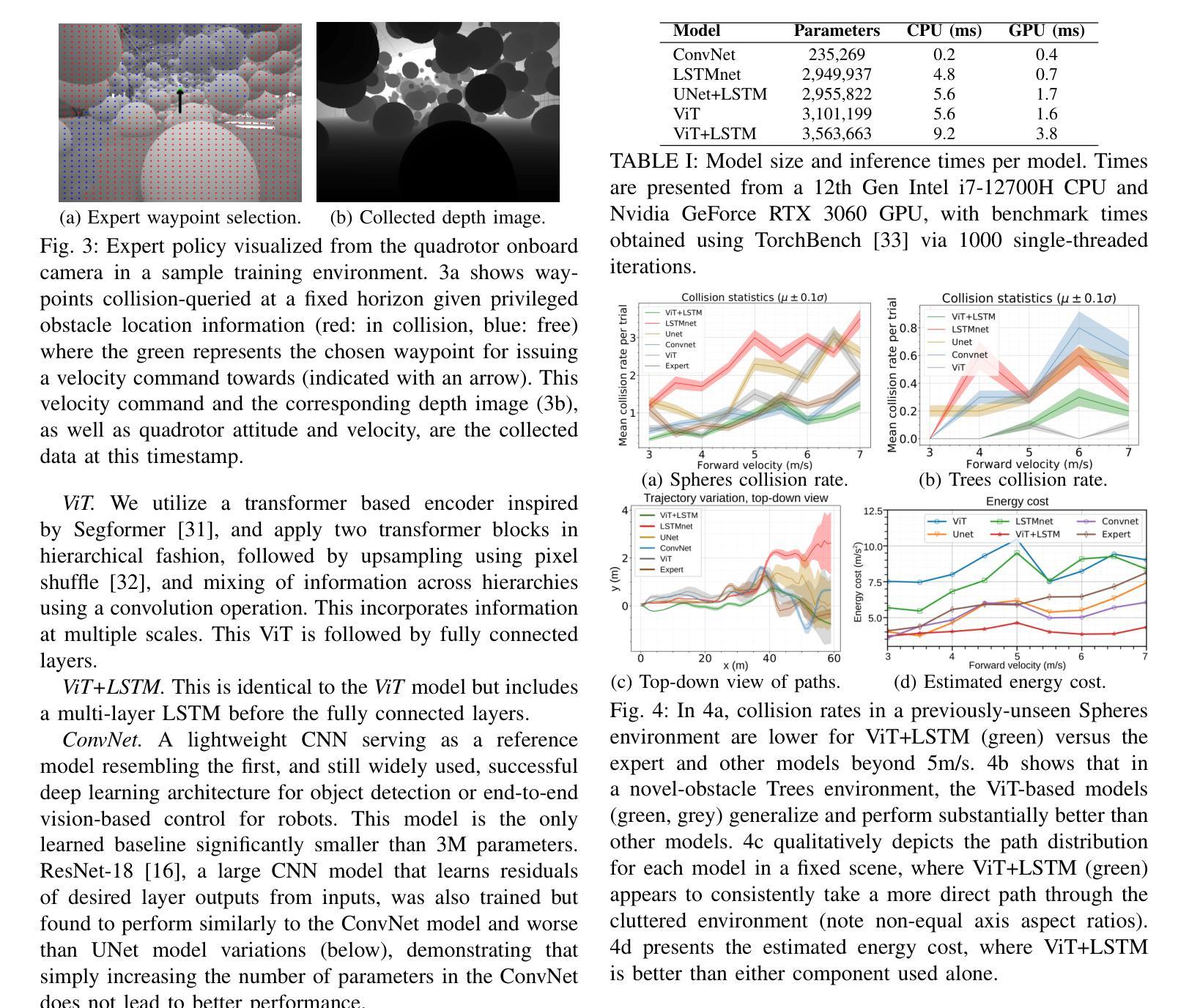
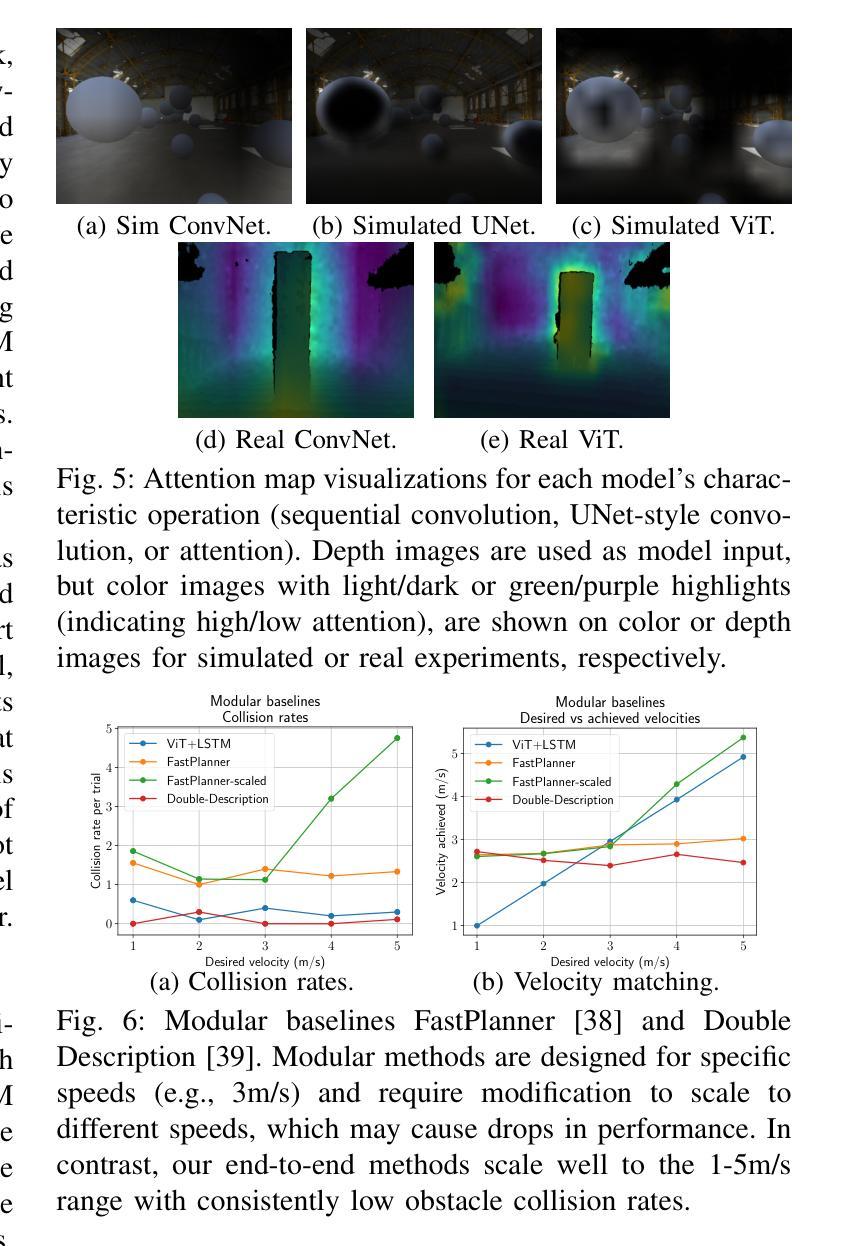
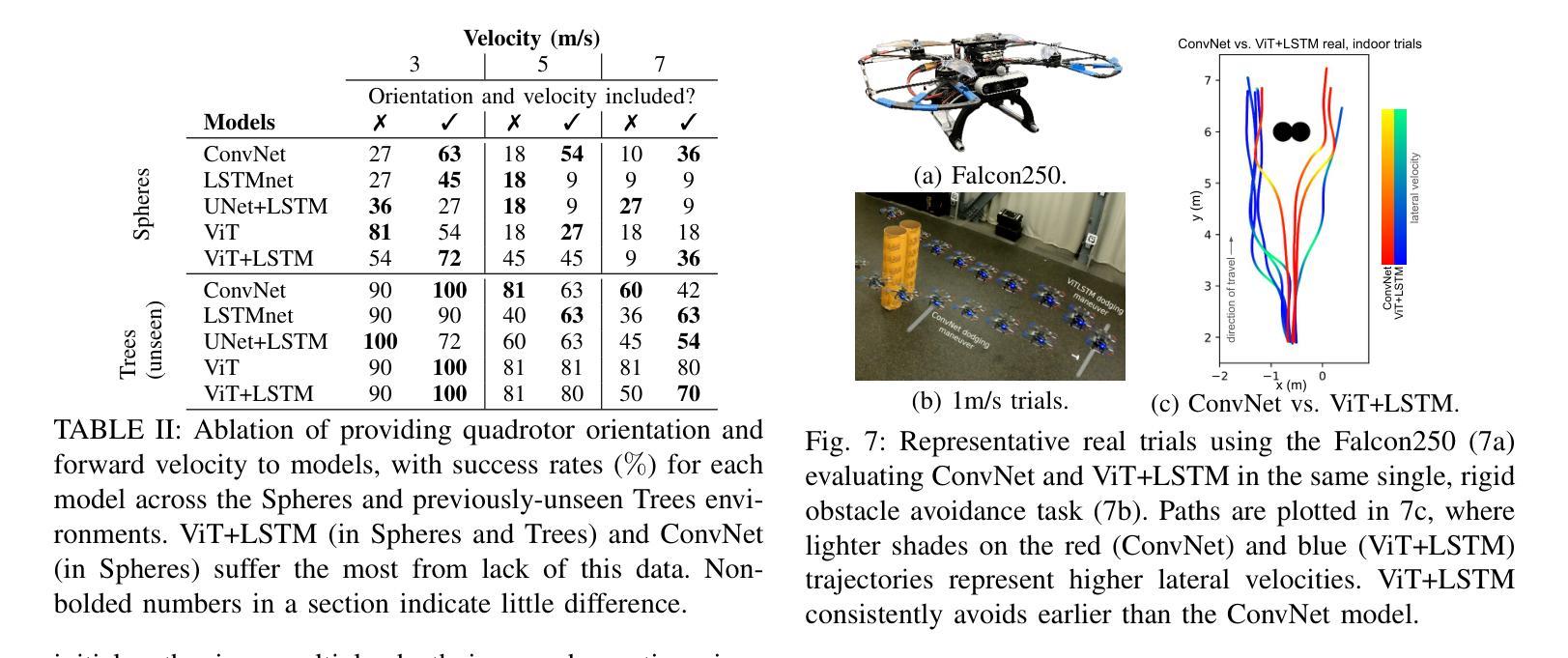
Vision Transformers for End-to-End Vision-Based Quadrotor Obstacle Avoidance
Authors:Anish Bhattacharya, Nishanth Rao, Dhruv Parikh, Pratik Kunapuli, Yuwei Wu, Yuezhan Tao, Nikolai Matni, Vijay Kumar
We demonstrate the capabilities of an attention-based end-to-end approach for high-speed vision-based quadrotor obstacle avoidance in dense, cluttered environments, with comparison to various state-of-the-art learning architectures. Quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have tremendous maneuverability when flown fast; however, as flight speed increases, traditional model-based approaches to navigation via independent perception, mapping, planning, and control modules breaks down due to increased sensor noise, compounding errors, and increased processing latency. Thus, learning-based, end-to-end vision-to-control networks have shown to have great potential for online control of these fast robots through cluttered environments. We train and compare convolutional, U-Net, and recurrent architectures against vision transformer (ViT) models for depth image-to-control in high-fidelity simulation, observing that ViT models are more effective than others as quadrotor speeds increase and in generalization to unseen environments, while the addition of recurrence further improves performance while reducing quadrotor energy cost across all tested flight speeds. We assess performance at speeds of up to 7m/s in simulation and hardware. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to utilize vision transformers for end-to-end vision-based quadrotor control.
我们展示了一种基于注意力的端到端方法,用于高速视觉无人机在密集杂乱环境中的避障能力,并与各种最新学习架构进行了比较。四旋翼无人机在高速飞行时具有巨大的机动性;然而,随着飞行速度的增加,基于独立感知、映射、规划和控制模块的基于传统模型的方法由于传感器噪声增加、误差累积和处理延迟增加而失效。因此,基于学习的端到端视觉控制网络对于通过这些杂乱环境的快速机器人的在线控制显示出巨大潜力。我们在高保真模拟中对卷积、U-Net和递归架构与视觉Transformer(ViT)模型进行了深度图像控制方面的训练和比较,观察到随着四旋翼无人机速度的增加以及在未见过环境的泛化中,ViT模型的效果比其他模型更有效,而递归的加入进一步提高了性能,同时降低了所有测试飞行速度下的四旋翼能量成本。我们在模拟和硬件中以最高7米/秒的速度评估性能。据我们所知,这是首次利用视觉Transformer进行端到端的基于视觉的四旋翼无人机控制的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 18 figures, 3 tables (with supplementary)
Summary
基于注意力的端到端方法,展示了在密集杂乱环境中高速无人机视觉避障的能力,并与各种最新学习架构进行了比较。随着无人机飞行速度的增加,传统基于模型的导航方法因传感器噪声增加、误差累积和处理延迟而出现瓶颈。因此,基于学习的端到端视觉控制网络在控制这些快速机器人穿越杂乱环境方面具有巨大潜力。在仿真环境中对卷积神经网络、U-Net网络和递归架构进行了对比评估,发现随着无人机速度的增加以及推广到未见的环境,使用ViT模型的性能更优秀。所研究速度达到最高7米每秒左右,该项工作是首次将视觉转换器应用于端到端的无人机视觉控制。
Key Takeaways
以下是基于文本的重要见解列表:
- 展示了注意力机制在高速无人机视觉避障中的有效性。
- 对比了多种学习架构,发现ViT模型在仿真环境中性能优越。
- 随着无人机飞行速度的增加,传统导航方法存在局限性。
- 基于学习的端到端视觉控制网络具有巨大潜力。
- 在高保真仿真和硬件测试中都评估了模型性能。
- Vision Transformer在高速环境下的性能优异并具备良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

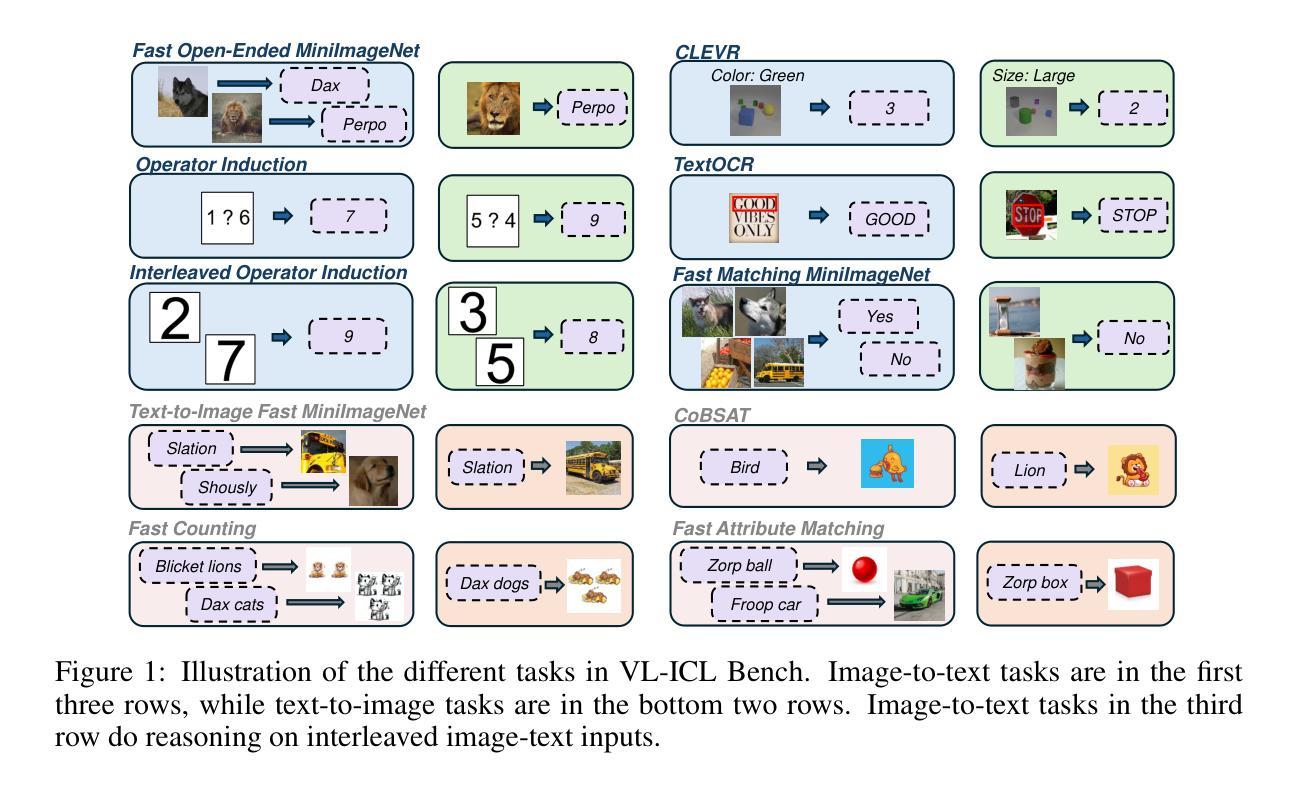
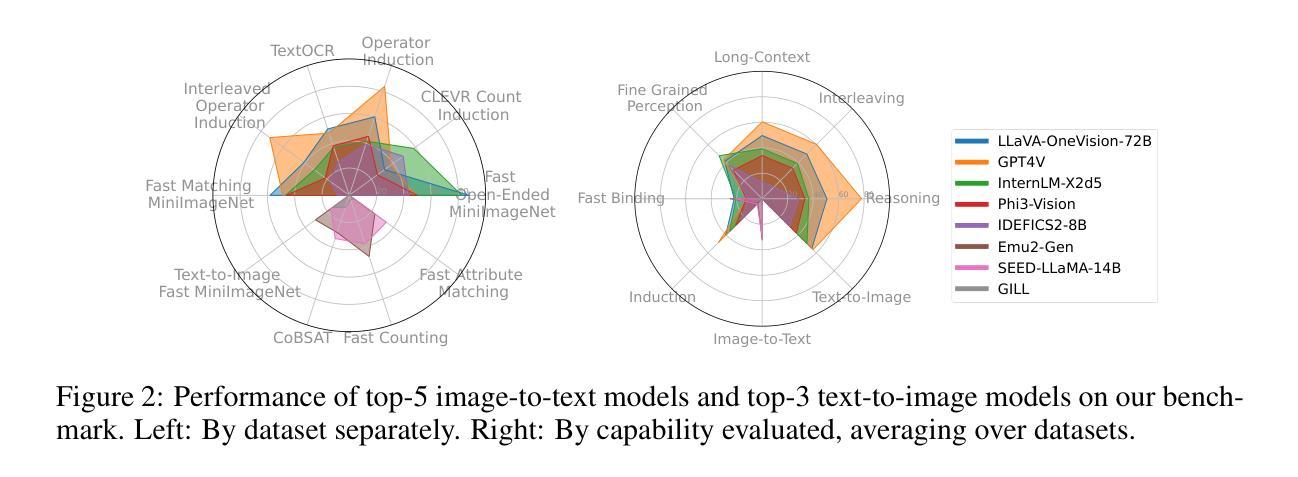
VL-ICL Bench: The Devil in the Details of Multimodal In-Context Learning
Authors:Yongshuo Zong, Ondrej Bohdal, Timothy Hospedales
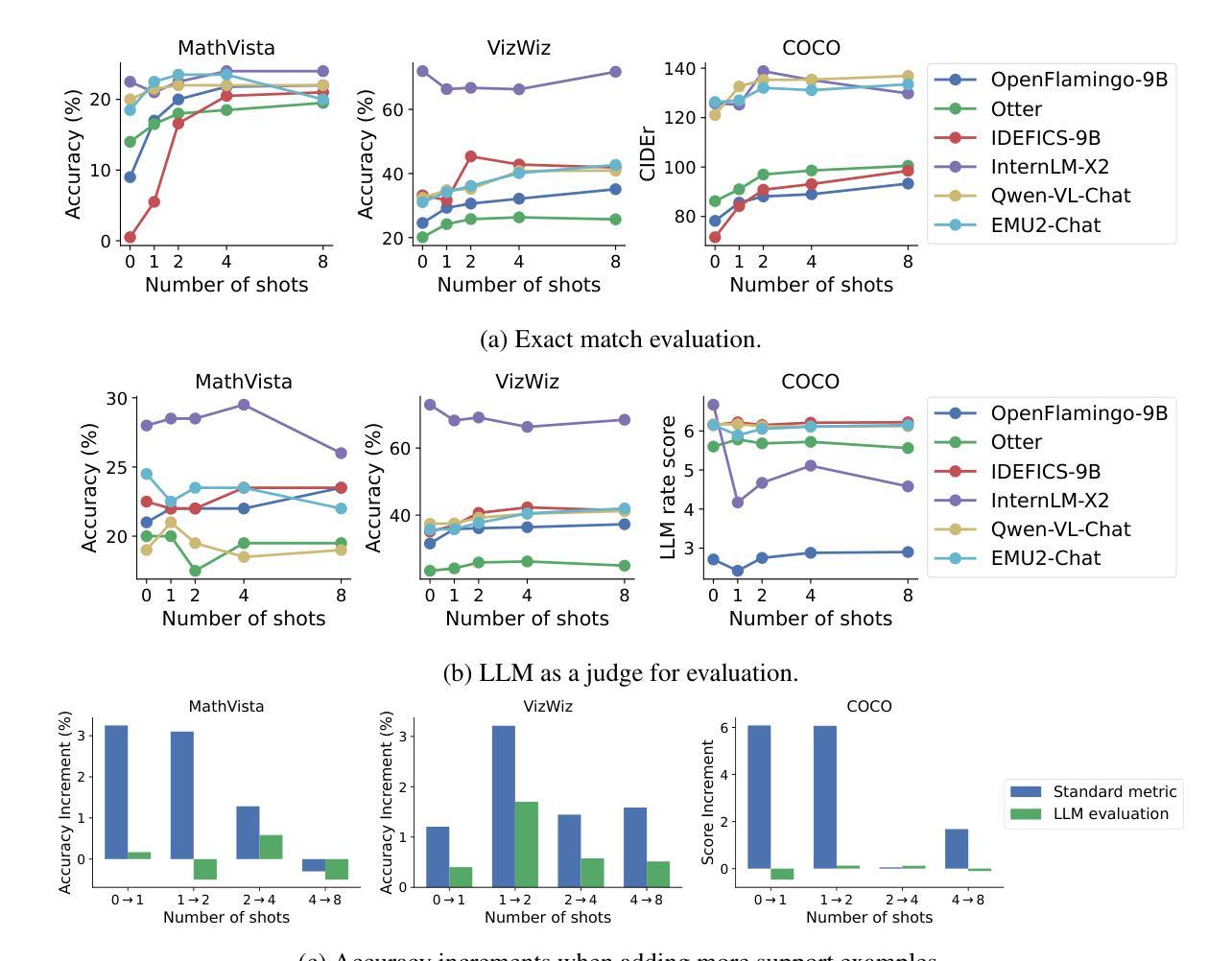
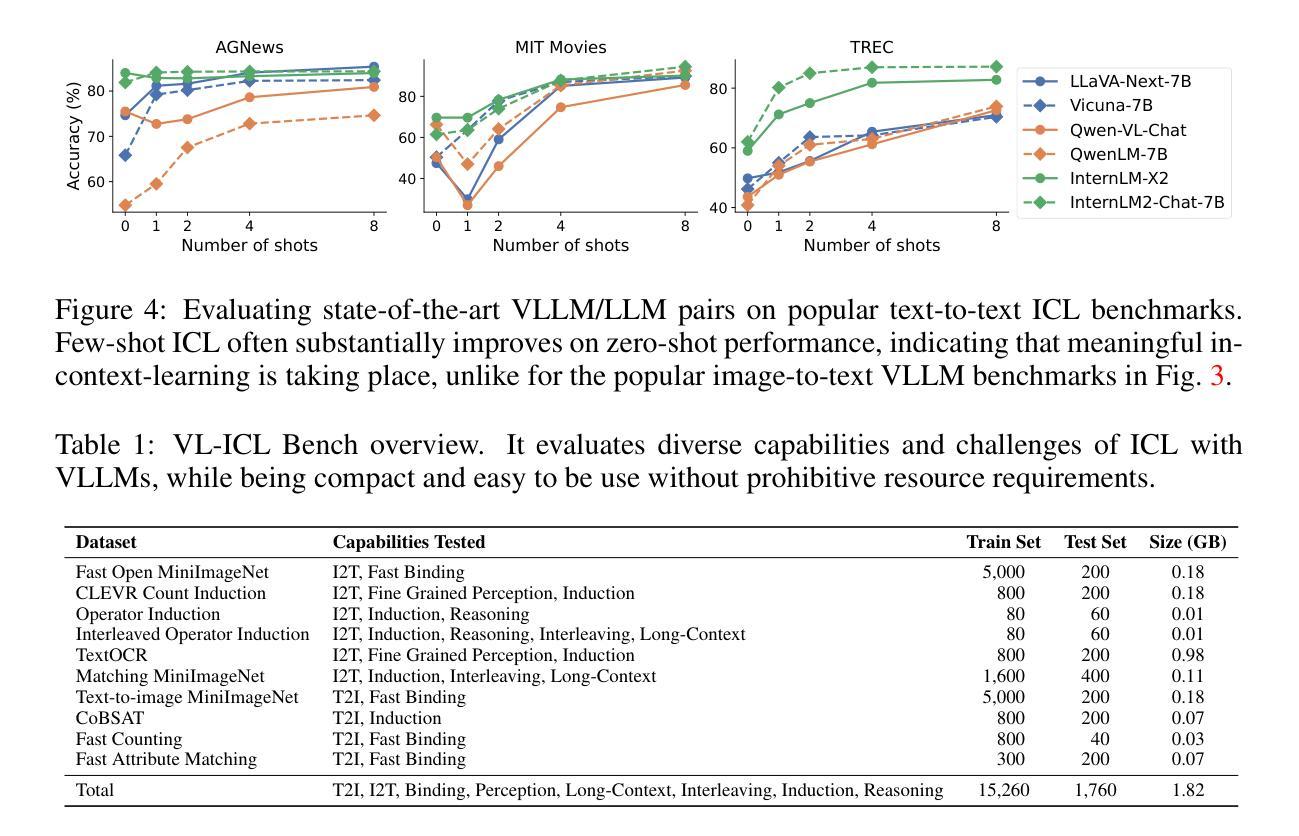
Large language models (LLMs) famously exhibit emergent in-context learning (ICL) – the ability to rapidly adapt to new tasks using few-shot examples provided as a prompt, without updating the model’s weights. Built on top of LLMs, vision large language models (VLLMs) have advanced significantly in areas such as recognition, reasoning, and grounding. However, investigations into \emph{multimodal ICL} have predominantly focused on few-shot visual question answering (VQA), and image captioning, which we will show neither exploit the strengths of ICL, nor test its limitations. The broader capabilities and limitations of multimodal ICL remain under-explored. In this study, we introduce a comprehensive benchmark VL-ICL Bench for multimodal in-context learning, encompassing a broad spectrum of tasks that involve both images and text as inputs and outputs, and different types of challenges, from {perception to reasoning and long context length}. We evaluate the abilities of state-of-the-art VLLMs against this benchmark suite, revealing their diverse strengths and weaknesses, and showing that even the most advanced models, such as GPT-4, find the tasks challenging. By highlighting a range of new ICL tasks, and the associated strengths and limitations of existing models, we hope that our dataset will inspire future work on enhancing the in-context learning capabilities of VLLMs, as well as inspire new applications that leverage VLLM ICL. The code and dataset are available at https://github.com/ys-zong/VL-ICL.
大型语言模型(LLM)表现出突出的上下文环境学习(ICL)能力——即使用作为提示提供的少量示例快速适应新任务的能力,而无需更新模型的权重。建立在大型语言模型之上的视觉大型语言模型(VLLM)在识别、推理和接地等领域取得了显著进展。然而,对多模态ICL的调查主要集中在少量的视觉问答和图像描述上,我们将展示这两者都没有利用ICL的优势,也没有测试其局限性。多模态ICL的更广泛的能力和局限性尚未被充分探索。在这项研究中,我们引入了全面的多模态上下文学习基准测试VL-ICL Bench,涵盖了一系列涉及图像和文本作为输入和输出的任务,以及从感知到推理和长上下文长度的不同类型挑战。我们评估了最先进VLLM对此基准测试套件的能力,揭示了它们各自的优势和劣势,并表明即使是最先进的模型,如GPT-4,也会发现这些任务具有挑战性。通过突出一系列新的ICL任务以及现有模型的关联优势和局限性,我们希望我们的数据集将激励未来对增强VLLM的上下文学习能力的进一步研究,并激发利用VLLM ICL的新应用。代码和数据集可在https://github.com/ys-zong/VL-ICL获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了对多模态上下文学习(ICL)的深入研究。针对视觉大型语言模型(VLLM)的能力与局限,建立了一个全面的基准测试VL-ICL Bench。该基准测试涵盖了广泛的涉及图像和文本的任务,从感知到推理和长语境长度等不同类型挑战。通过对最新VLLM的评估,揭示了它们的优势和不足,并指出即使是最先进的模型如GPT-4也面临挑战。本文旨在通过突出新的ICL任务以及现有模型的优缺点来启发未来工作,以增强VLLM的上下文学习能力并推动新应用的发展。代码和数据集可在https://github.com/ys-zong/VL-ICL找到。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)展现出上下文学习能力(ICL),能快速适应新任务,且无需更新模型权重。
- 视觉大型语言模型(VLLMs)在识别、推理和接地等领域有显著进展。
- 多模态ICL的研究主要集中于视觉问答和图像描述生成,但这并未充分利用ICL的优势,也未测试其局限性。
- 引入了一个全面的基准测试VL-ICL Bench,涵盖涉及图像和文本的多模态ICL的广泛任务,包括感知、推理和长语境长度等挑战。
- 评估了最新VLLM的能力,揭示了其优势和不足,并指出GPT-4等先进模型也面临挑战。
- 希望此基准测试能启发未来对增强VLLM的上下文学习能力的研究和新应用的开发。
点此查看论文截图

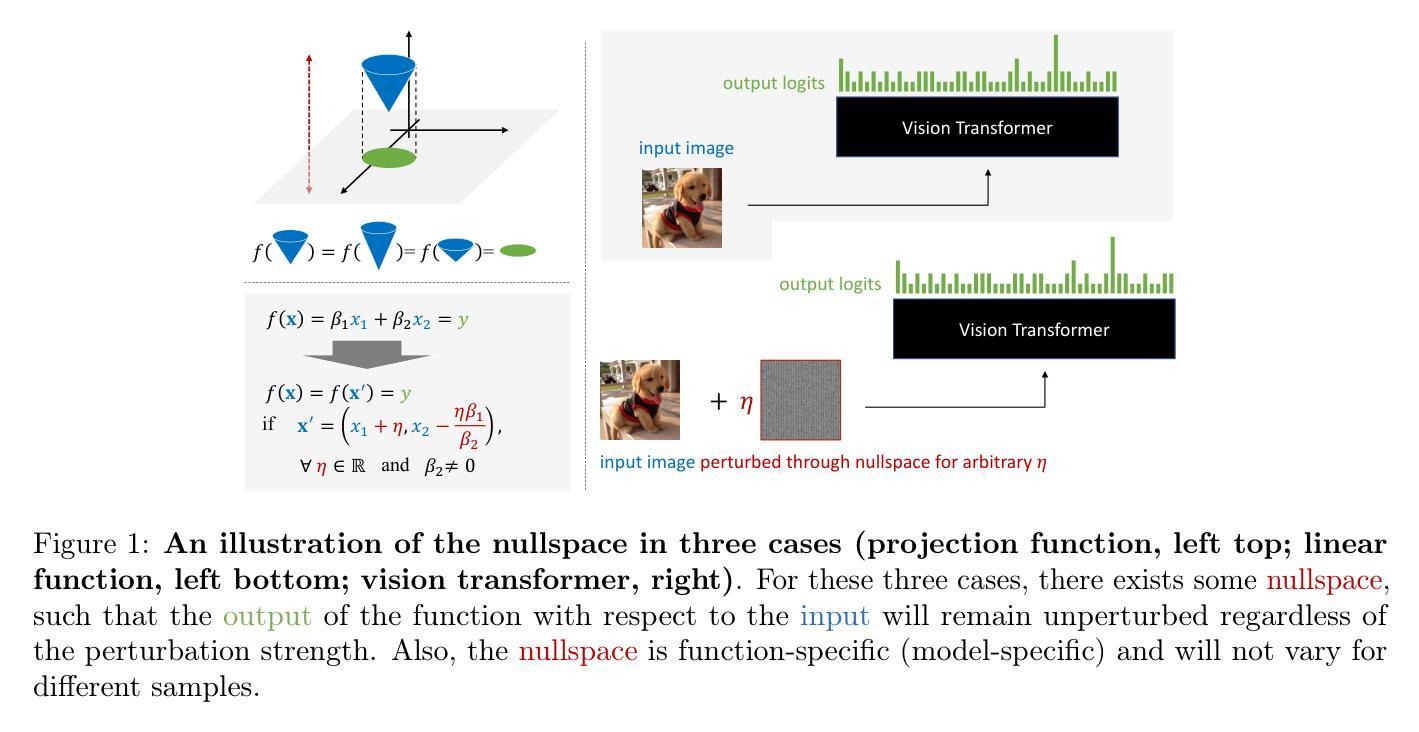
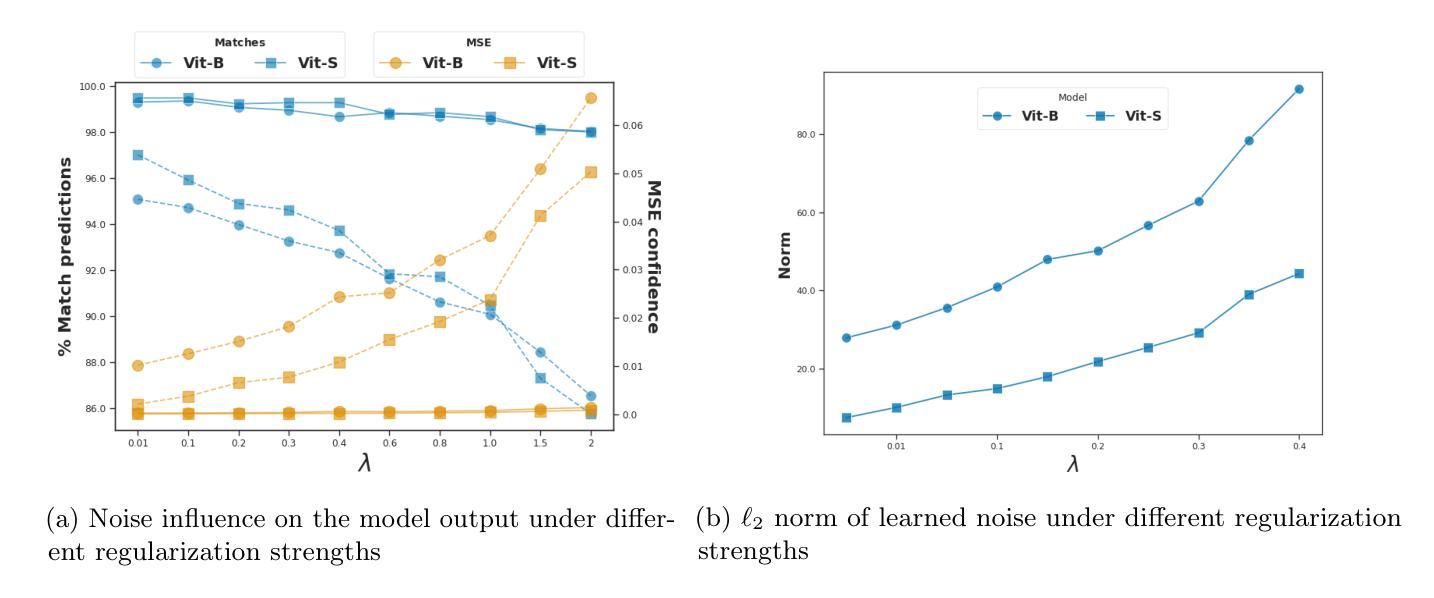
Approximate Nullspace Augmented Finetuning for Robust Vision Transformers
Authors:Haoyang Liu, Aditya Singh, Yijiang Li, Haohan Wang
Enhancing the robustness of deep learning models, particularly in the realm of vision transformers (ViTs), is crucial for their real-world deployment. In this work, we provide a finetuning approach to enhance the robustness of vision transformers inspired by the concept of nullspace from linear algebra. Our investigation centers on whether a vision transformer can exhibit resilience to input variations akin to the nullspace property in linear mappings, which would imply that perturbations sampled from this nullspace do not influence the model’s output when added to the input. We start from the observation that many existing ViTs satisfy this property because their patch embedding layer has a non-trivial nullspace. Then, we extend the notion of nullspace to nonlinear settings and demonstrate that it is possible to synthesize approximate nullspace elements for ViT’s encoder blocks through optimization. Finally, we propose a finetuning strategy for ViTs wherein we augment the training data with synthesized approximate nullspace noise. We find that our finetuning approach significantly improves the models’ robustness to both adversarial and natural image perturbations.\footnote{Code is available at: https://github.com/Liu-Hy/ns-vit.
增强深度学习模型的稳健性,特别是在视觉转换器(ViTs)领域,对于它们在现实世界中的部署至关重要。在这项工作中,我们提供了一种基于线性代数中零空间概念的微调方法,以增强视觉转换器的稳健性。我们的调查重点是视觉转换器是否能表现出对输入变化的抵抗力,类似于线性映射中的零空间属性,这意味着从该零空间采样的扰动在添加到输入时不会影响模型的输出。我们从观察许多现有ViTs具有此属性开始,因为它们的补丁嵌入层具有非平凡的零空间。然后,我们将零空间的概念扩展到非线性环境,并证明可以通过优化为ViT的编码器块合成近似零空间元素。最后,我们提出了一种针对ViTs的微调策略,其中我们通过在训练数据中增加合成的近似零空间噪声来增强模型。我们发现我们的微调方法显著提高了模型对对抗性和自然图像扰动的稳健性。注释:代码可在https://github.com/Liu-Hy/ns-vit找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CPAL 2025, Oral
Summary
本文探讨了如何通过利用线性代数中的零空间概念,对视觉转换器(ViTs)进行微调以提高其稳健性。文章观察到许多现有的ViTs具有非平凡的零空间,进而将零空间的概念扩展到非线性环境,并通过优化为ViT的编码器块合成近似零空间元素。最后,提出了一种针对ViTs的微调策略,通过增加合成近似零空间噪声来增强模型的稳健性。实验表明,该方法显著提高了模型对对抗性和自然图像扰动的稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 利用零空间概念提高视觉转换器(ViTs)的稳健性。
- 观察到许多现有ViTs具有非平凡的零空间。
- 将零空间概念扩展到非线性环境,并为ViT合成近似零空间元素。
- 提出一种针对ViTs的微调策略,通过增加合成近似零空间噪声来增强模型的稳健性。
- 该方法显著提高了模型对对抗性和自然图像扰动的稳健性。
- 该研究提供了一种新的视角来理解视觉转换器的内在性质,并为其优化提供了新思路。
点此查看论文截图