⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-04 更新
View-Invariant Pixelwise Anomaly Detection in Multi-object Scenes with Adaptive View Synthesis
Authors:Subin Varghese, Vedhus Hoskere
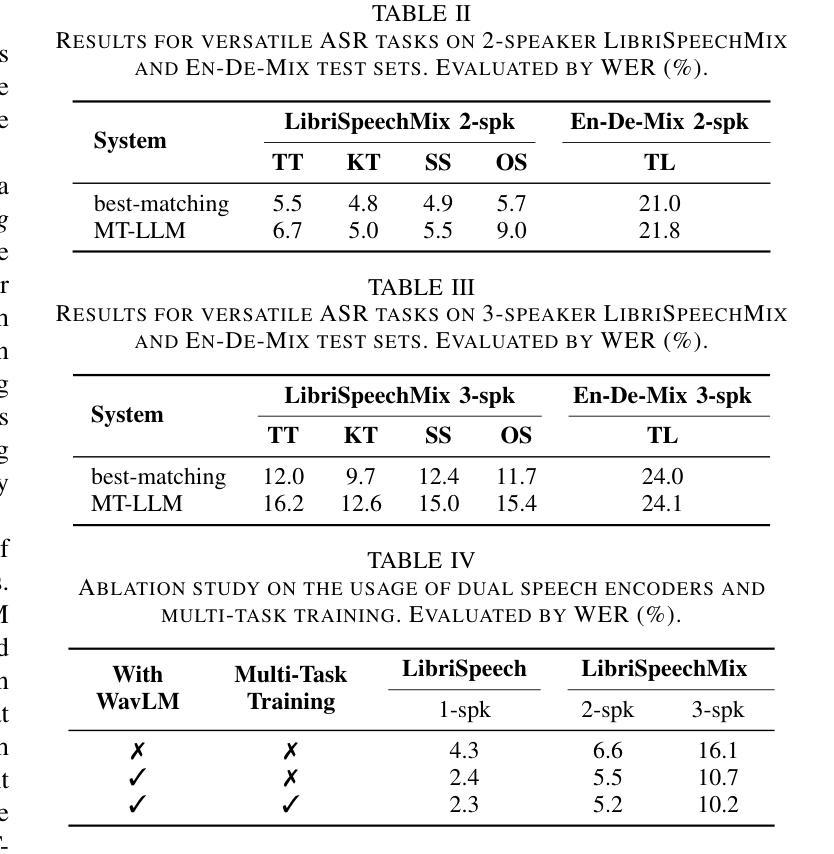
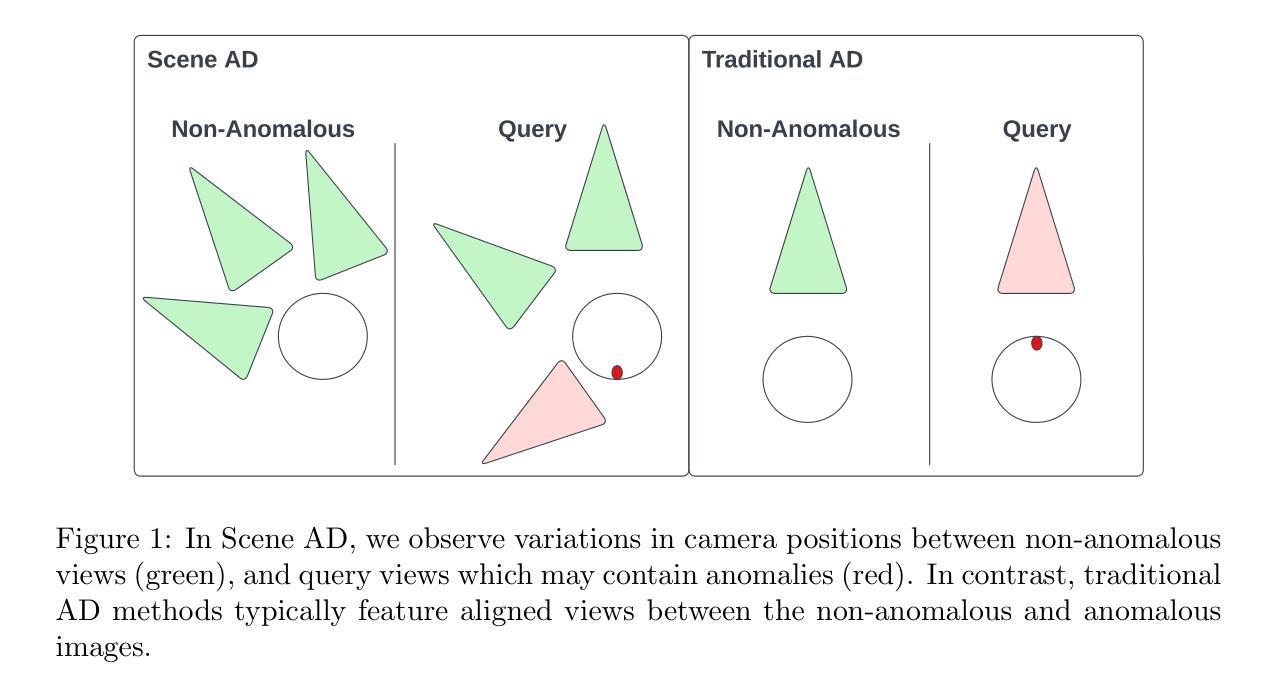
Visual anomaly detection in the built environment is a valuable tool for applications such as infrastructure assessment, construction monitoring, security surveillance, and urban planning. Anomaly detection approaches are typically unsupervised and work by detecting deviations from an expected state where no assumptions are made exact type of deviation. Unsupervised pixel-level anomaly detection methods have been developed to successfully recognize and segment anomalies; however, existing techniques are designed for industrial settings with a fixed camera position. In the built environment, images are periodically captured by a camera operated manually or mounted on aerial or ground vehicles. The camera pose between successive collections may vary widely voiding a fundamental assumption in existing anomaly detection approaches. To address this gap, we introduce the problem of Scene Anomaly Detection (Scene AD), where the goal is to detect anomalies from two sets of images: one set without anomalies and one set that may or may not contain anomalies. No labeled semantic segmentation data are provided for training. We propose a novel network, OmniAD, to tackle Scene AD by refining the reverse distillation anomaly detection method, leading to a 40% improvement in pixel-level anomaly detection. Additionally, we introduce two new data augmentation strategies that leverage novel view synthesis and camera localization to enhance generalization. We evaluate our approach both qualitatively and quantitatively on a new dataset, ToyCity the first Scene AD dataset featuring multiple objects as well as on the established single object centric dataset, MAD. Our method demonstrates marked improvement over baseline approaches, paving the way for robust anomaly detection in scenes with real-world camera pose variations commonly observed in the built environment. https://drags99.github.io/OmniAD/
在构建环境中进行视觉异常检测,对于基础设施评估、施工监测、安全监控和城市规划等应用来说是一项有价值的工具。异常检测方法是典型的无监督方法,通过检测与预期状态的偏差来工作,而不假定确切类型的偏差。为了成功识别和分割异常值,已经开发出了无监督的像素级异常检测方法;然而,现有技术是针对工业环境中固定相机位置设计的。在构建环境中,图像是定期通过手动操作或安装在空中的车辆上的相机捕获的。连续采集之间的相机姿态可能变化很大,从而避免了现有异常检测方法的基本假设。为了解决这一差距,我们引入了场景异常检测(Scene AD)问题,其目标是从两组图像中检测异常值:一组没有异常值,另一组可能包含也可能不包含异常值。不提供用于训练的有标签语义分割数据。我们提出了一种新的网络OmniAD来解决场景AD问题,通过改进反向蒸馏异常检测方法,实现了像素级异常检测的40%改进。此外,我们引入两种新的数据增强策略,利用新型视图合成和相机定位来提高泛化能力。我们在新的数据集ToyCity(首个多对象场景AD数据集)以及公认的单对象中心数据集MAD上进行了定性和定量评估。我们的方法在基线方法上取得了显著改进,为在具有现实世界相机姿态变化的场景中实现稳健的异常检测铺平了道路。如需了解更多信息,请访问:链接地址。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了视觉异常检测在建成环境中的应用价值,包括基础设施评估、施工监测、安全监控和城市规划等领域。针对现有异常检测方法在固定相机位置工业环境中的局限性,文章提出了场景异常检测(Scene AD)问题,旨在从两组图像中检测异常。为此,文章提出了一种名为OmniAD的新网络,改进了反向蒸馏异常检测方法,提高了像素级异常检测的准确性。此外,还引入两种新的数据增强策略,通过合成新视角和相机定位技术增强模型的泛化能力。实验结果显示,新方法在多个数据集上的表现优于基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉异常检测在建成环境中有广泛应用,如基础设施评估、施工监测等。
- 现有异常检测方法大多局限于固定相机位置的工业环境。
- 文章提出了场景异常检测(Scene AD)问题,旨在处理两组图像中的异常检测。
- OmniAD网络通过改进反向蒸馏异常检测方法,提高了像素级异常检测的准确性。
- 引入两种新的数据增强策略以增强模型的泛化能力。
- 方法在多个数据集上的表现优于基线方法。
点此查看论文截图

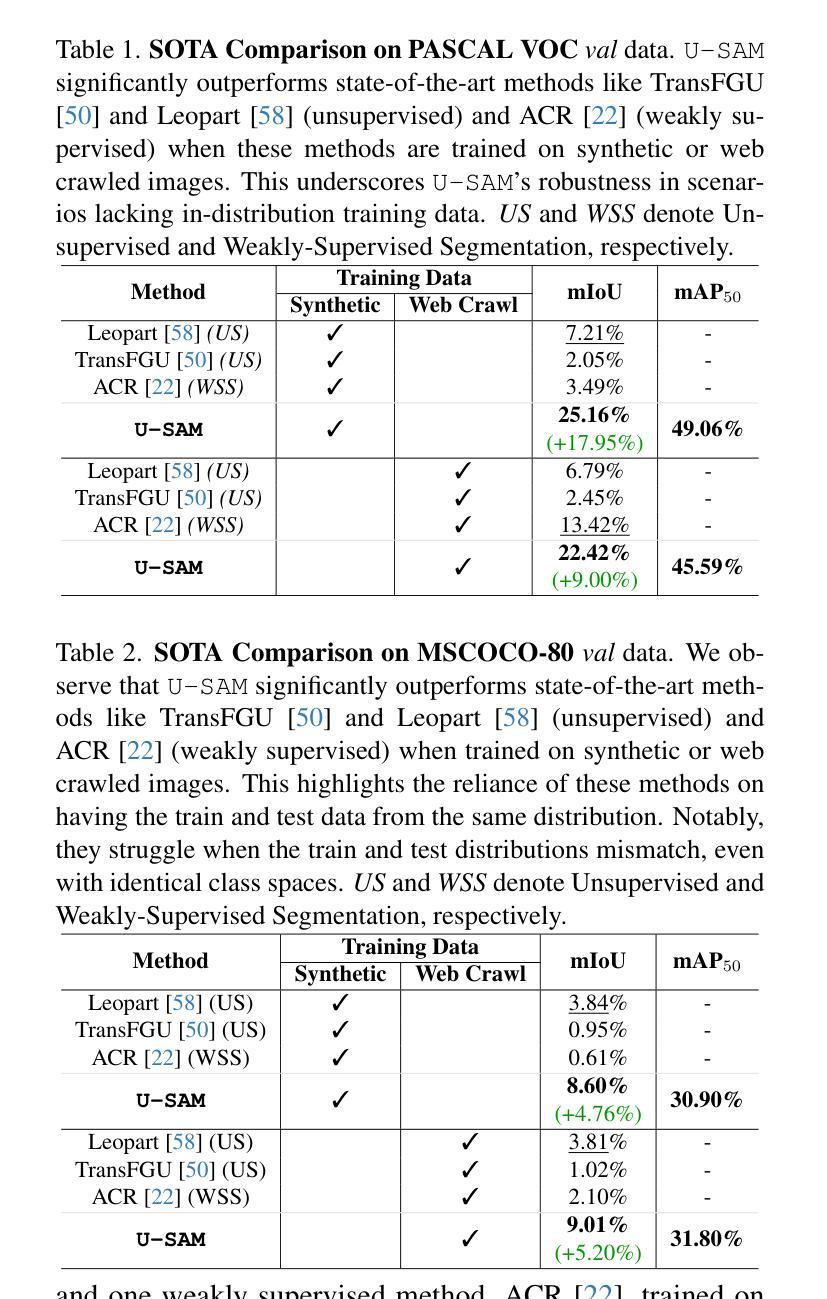
Repurposing SAM for User-Defined Semantics Aware Segmentation
Authors:Rohit Kundu, Sudipta Paul, Arindam Dutta, Amit K. Roy-Chowdhury
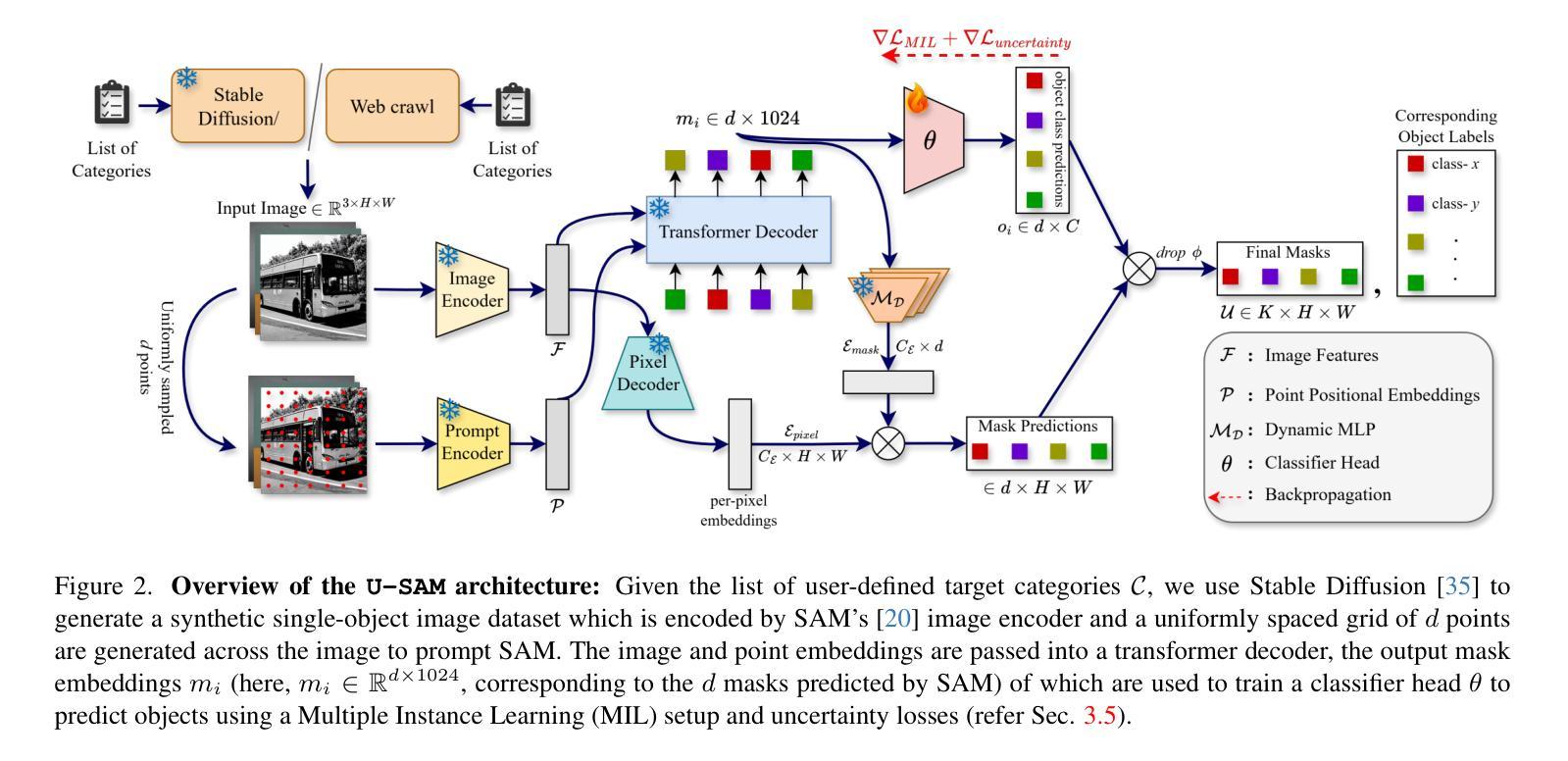
The Segment Anything Model (SAM) excels at generating precise object masks from input prompts but lacks semantic awareness, failing to associate its generated masks with specific object categories. To address this limitation, we propose U-SAM, a novel framework that imbibes semantic awareness into SAM, enabling it to generate targeted masks for user-specified object categories. Given only object class names as input from the user, U-SAM provides pixel-level semantic annotations for images without requiring any labeled/unlabeled samples from the test data distribution. Our approach leverages synthetically generated or web crawled images to accumulate semantic information about the desired object classes. We then learn a mapping function between SAM’s mask embeddings and object class labels, effectively enhancing SAM with granularity-specific semantic recognition capabilities. As a result, users can obtain meaningful and targeted segmentation masks for specific objects they request, rather than generic and unlabeled masks. We evaluate U-SAM on PASCAL VOC 2012 and MSCOCO-80, achieving significant mIoU improvements of +17.95% and +5.20%, respectively, over state-of-the-art methods. By transforming SAM into a semantically aware segmentation model, U-SAM offers a practical and flexible solution for pixel-level annotation across diverse and unseen domains in a resource-constrained environment.
Segment Anything Model(SAM)在根据输入提示生成精确对象掩膜方面表现出色,但缺乏语义意识,无法将其生成的掩膜与特定对象类别相关联。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了U-SAM,这是一个将语义意识融入SAM的新型框架,使其能够针对用户指定的对象类别生成定向掩膜。U-SAM仅接收用户提供的对象类别名称作为输入,为图像提供像素级语义注释,而无需测试数据分布中的任何有标签或无标签样本。我们的方法利用合成生成或网络爬虫图像来积累有关所需对象类别的语义信息。然后,我们学习SAM的掩膜嵌入和对象类别标签之间的映射函数,有效地增强SAM的粒度特定语义识别能力。因此,用户可以获取他们请求的具体对象的有意义和定向分割掩膜,而不是通用和无标签的掩膜。我们在PASCAL VOC 2012和MSCOCO-80上评估了U-SAM,与最新方法相比,mIoU分别提高了+17.95%和+5.20%。通过将SAM转变为语义感知分割模型,U-SAM为资源受限环境中的多样和未见领域的像素级注释提供了实用且灵活解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
U-SAM框架通过引入语义感知能力,解决了SAM模型无法对特定对象类别生成精确掩膜的问题。U-SAM利用合成图像或网络爬虫图像累积关于目标类别的语义信息,并在SAM的掩膜嵌入和目标类别标签之间建立映射关系。这使得用户可以获取特定对象的具有意义且有针对性的分割掩膜,而不是通用且无标签的掩膜。在PASCAL VOC 2012和MSCOCO-80上的评估结果表明,U-SAM较现有方法显著提高了mIoU指标。
Key Takeaways
- U-SAM框架解决了SAM模型缺乏语义感知能力的问题。
- U-SAM通过合成图像或网络爬虫图像累积目标类别的语义信息。
- U-SAM建立SAM的掩膜嵌入和目标类别标签之间的映射关系。
- U-SAM使用户能够获取特定对象的具有意义且有针对性的分割掩膜。
- U-SAM在PASCAL VOC 2012和MSCOCO-80上的mIoU指标显著提高。
- U-SAM将SAM模型转化为具有语义感知能力的分割模型。
点此查看论文截图

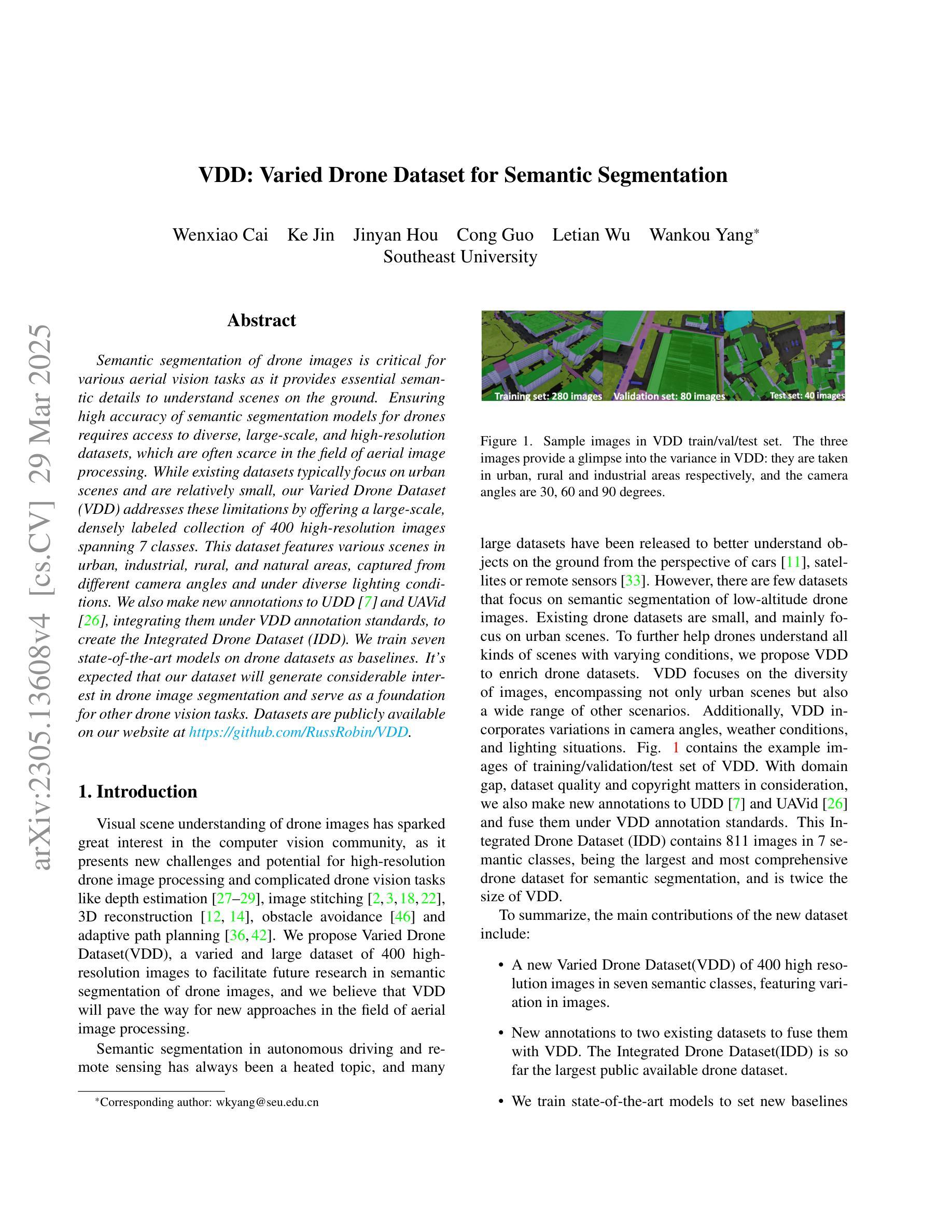
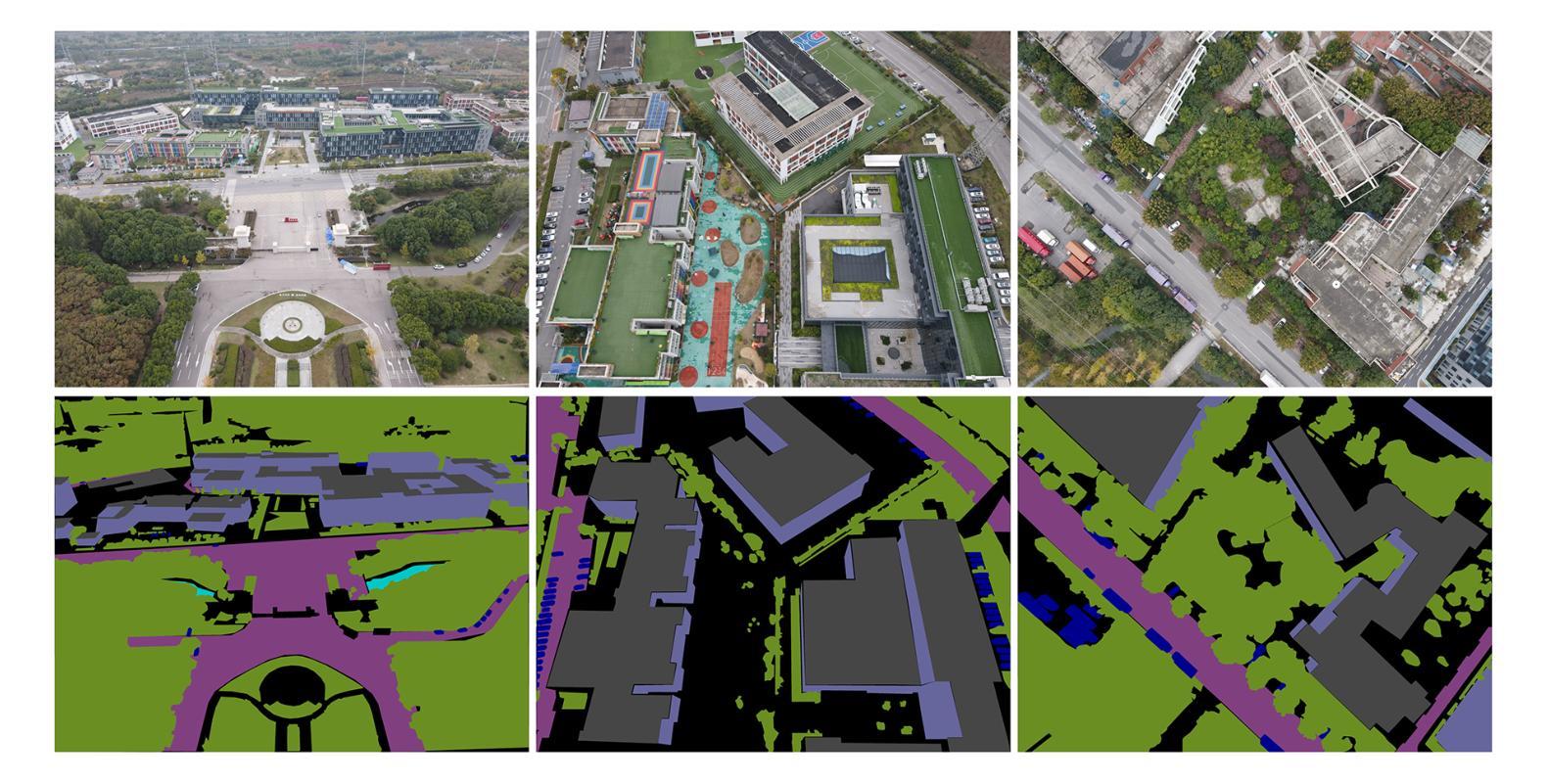
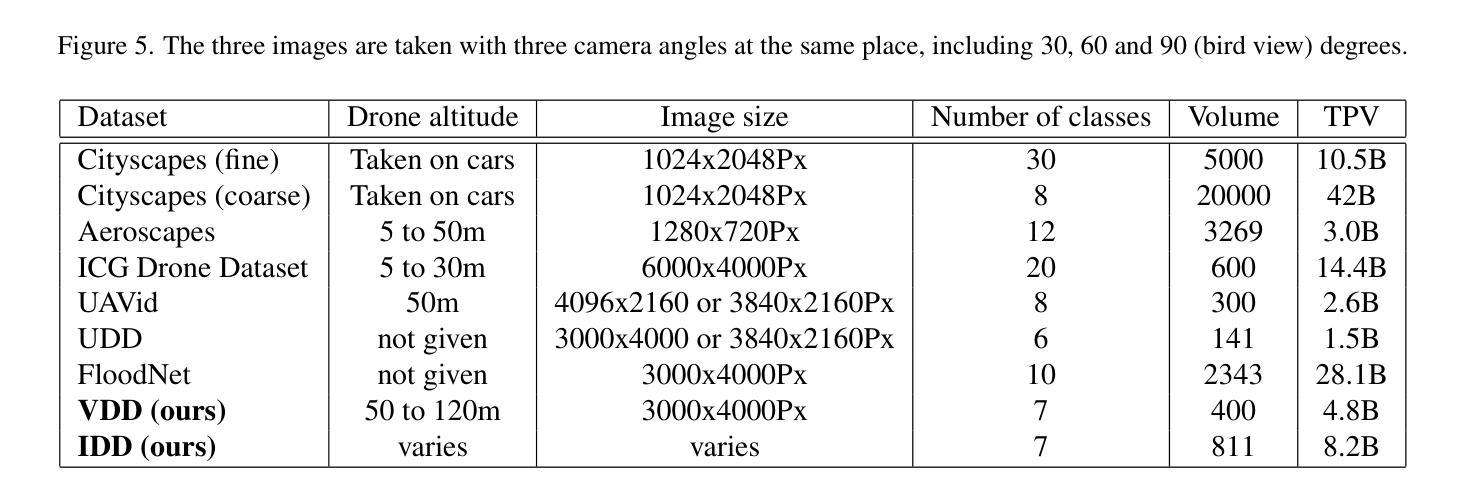
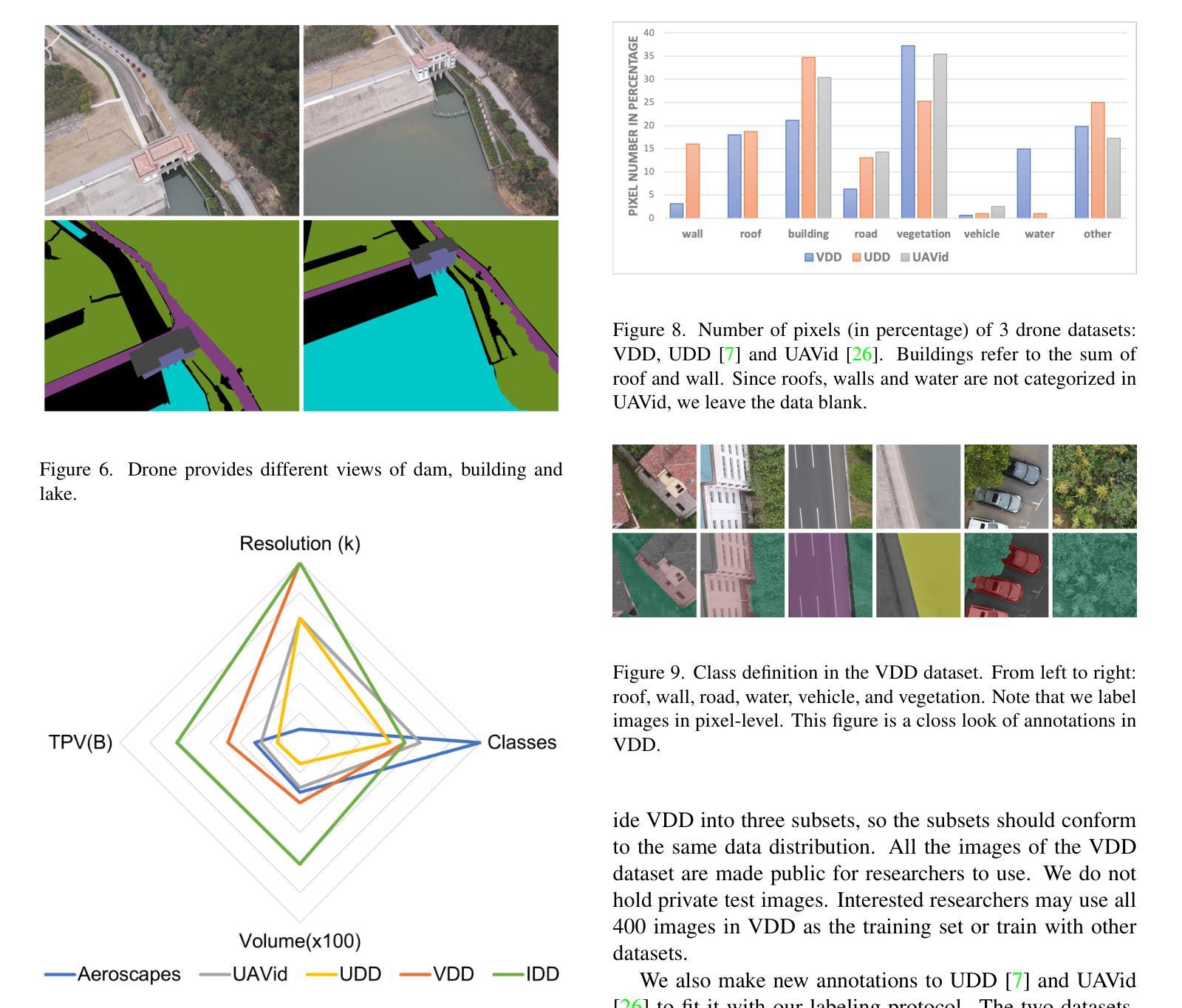
VDD: Varied Drone Dataset for Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Wenxiao Cai, Ke Jin, Jinyan Hou, Cong Guo, Letian Wu, Wankou Yang
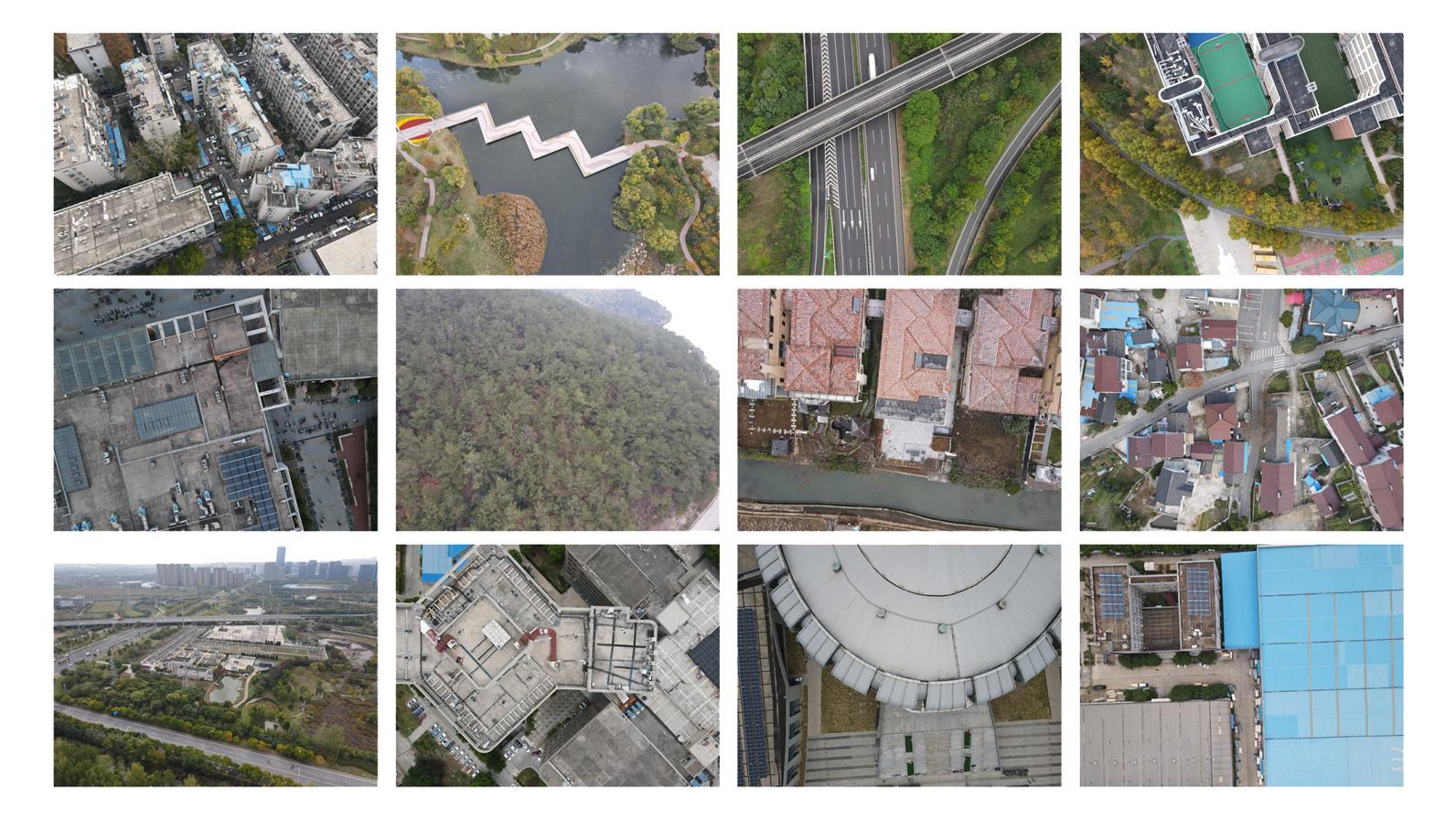
Semantic segmentation of drone images is critical for various aerial vision tasks as it provides essential semantic details to understand scenes on the ground. Ensuring high accuracy of semantic segmentation models for drones requires access to diverse, large-scale, and high-resolution datasets, which are often scarce in the field of aerial image processing. While existing datasets typically focus on urban scenes and are relatively small, our Varied Drone Dataset (VDD) addresses these limitations by offering a large-scale, densely labeled collection of 400 high-resolution images spanning 7 classes. This dataset features various scenes in urban, industrial, rural, and natural areas, captured from different camera angles and under diverse lighting conditions. We also make new annotations to UDD and UAVid, integrating them under VDD annotation standards, to create the Integrated Drone Dataset (IDD). We train seven state-of-the-art models on drone datasets as baselines. It’s expected that our dataset will generate considerable interest in drone image segmentation and serve as a foundation for other drone vision tasks. Datasets are publicly available at \href{our website}{https://github.com/RussRobin/VDD}.
无人机图像的语义分割对于各种空中视觉任务至关重要,因为它提供了理解地面场景的基本语义细节。要确保无人机语义分割模型的高准确性,需要访问多样、大规模、高分辨率的数据集,这在航空图像处理领域通常很稀缺。虽然现有数据集主要关注城市场景且相对较小,但我们的多样化无人机数据集(VDD)通过提供包含7类的大规模高密度标记的400张高分辨率图像来解决这些限制。该数据集以城市、工业、乡村和自然区域的多种场景为特色,从不同相机角度拍摄,并在各种照明条件下获取。我们还对UDD和UAVid进行了新注释,将它们整合到VDD注释标准下,以创建综合无人机数据集(IDD)。我们在无人机数据集上训练了七个最先进的模型作为基线。预计我们的数据集将引起对无人机图像分割的极大兴趣,并作为其他无人机视觉任务的基础。数据集可在我们的网站上公开获取(https://github.com/RussRobin/VDD)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
无人机图像语义分割对于各种空中视觉任务至关重要,它为理解地面场景提供了必要的语义细节。为满足无人机语义分割模型的高准确性需求,亟需多样、大规模、高分辨率的数据集,而现有数据集通常专注于城市场景且规模相对较小。我们的变无人机数据集(VDD)通过提供包含400张高分辨率图像的大规模密集标签集合,涵盖7个类别,解决了这一问题。该数据集的特点是涵盖城市、工业、乡村和自然区域的多种场景,从不同角度拍摄并在各种光照条件下呈现。此外,我们对UDD和UAVid进行了新注释,将其整合到VDD注释标准下,创建了综合无人机数据集(IDD)。我们在无人机数据集上训练了七个最先进的模型作为基准线。预计我们的数据集将在无人机图像分割领域引起广泛关注,并为其他无人机视觉任务奠定基础。数据集可在我们的网站上公开获取。
Key Takeaways
- 无人机图像语义分割对于空中视觉任务至关重要,需要高准确性的模型。
- 现有数据集存在多样性和规模上的不足,难以满足需求。
- 变无人机数据集(VDD)包含400张高分辨率图像,覆盖多个类别和场景。
- VDD涵盖了城市、工业、乡村和自然区域的多种场景,拍摄角度和光照条件多样。
- 综合无人机数据集(IDD)是通过整合UDD和UAVid并添加新注释创建的。
- 在无人机数据集上训练了七个最先进的模型作为性能基准。
点此查看论文截图