⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-04 更新
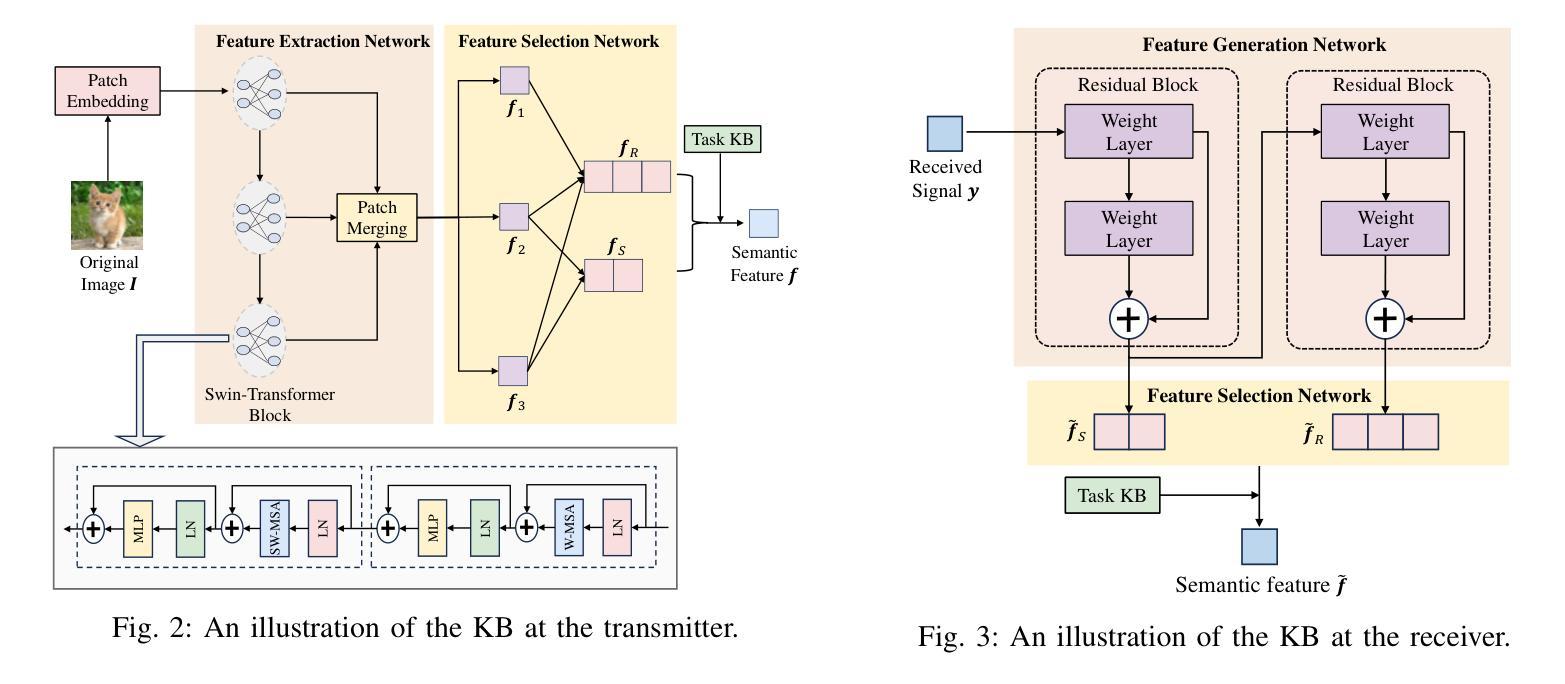
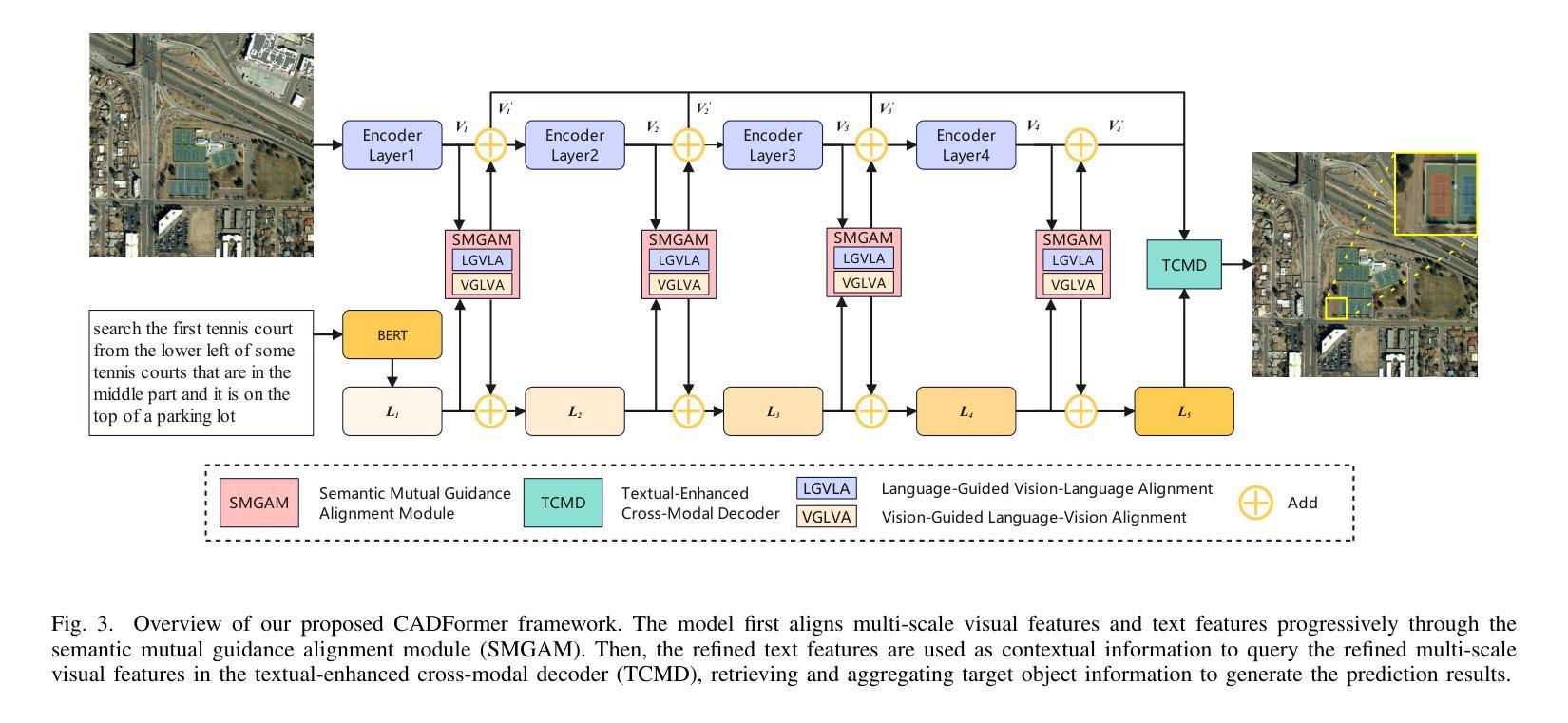
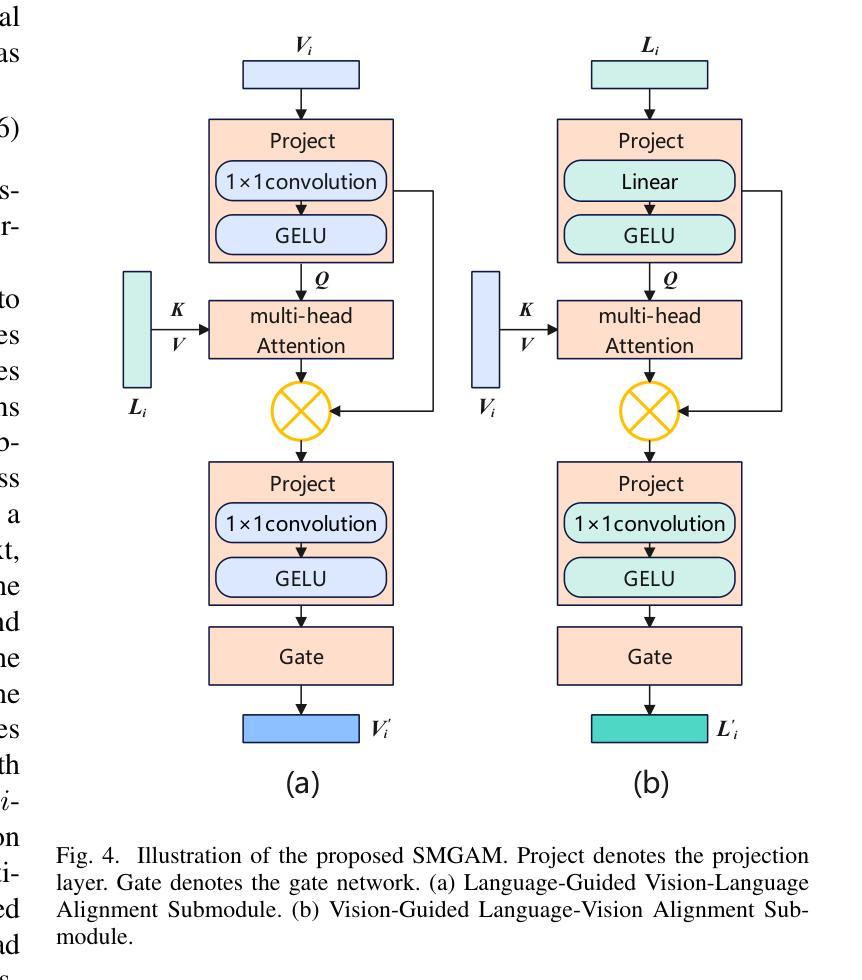
CADFormer: Fine-Grained Cross-modal Alignment and Decoding Transformer for Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation
Authors:Maofu Liu, Xin Jiang, Xiaokang Zhang
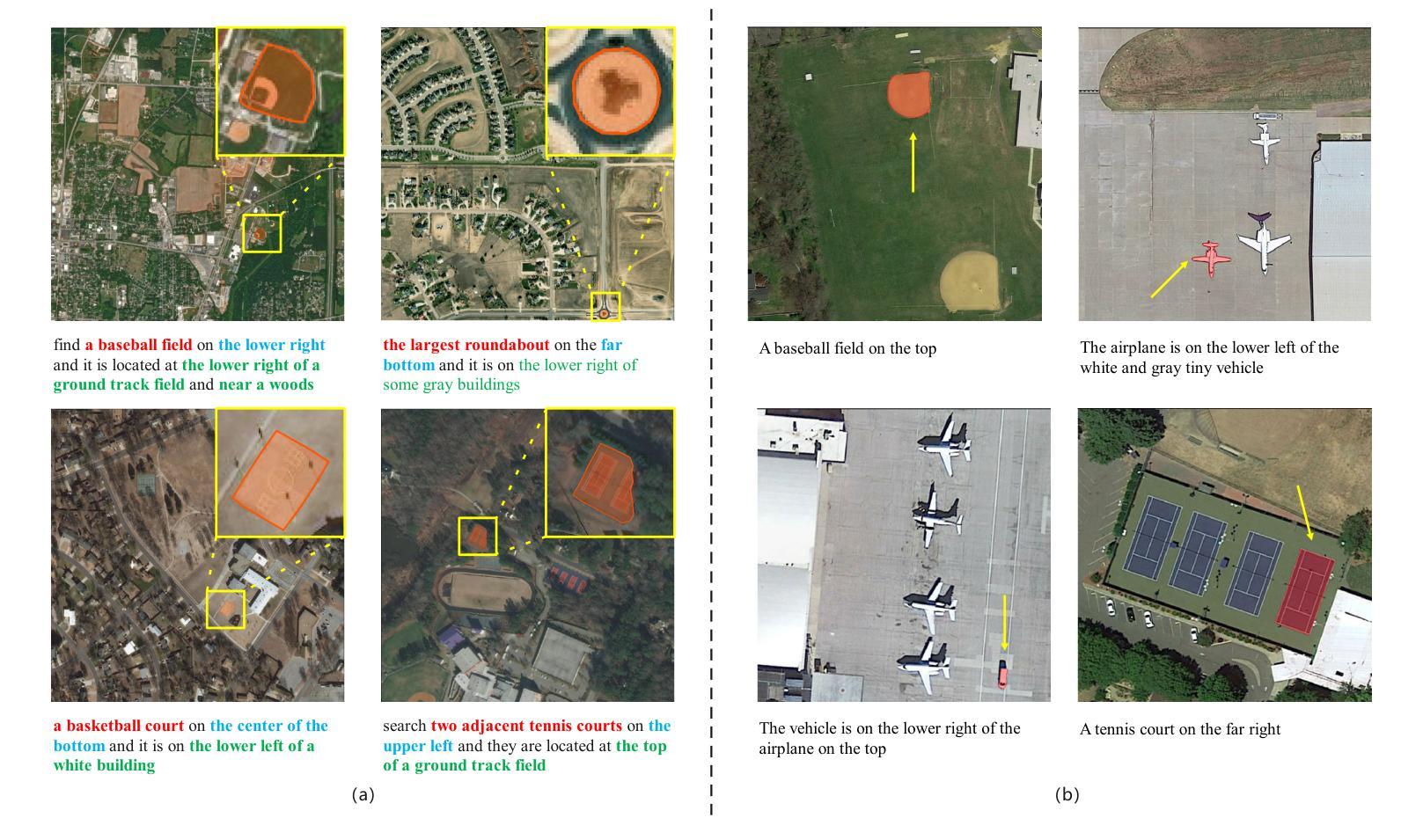
Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation (RRSIS) is a challenging task, aiming to segment specific target objects in remote sensing (RS) images based on a given language expression. Existing RRSIS methods typically employ coarse-grained unidirectional alignment approaches to obtain multimodal features, and they often overlook the critical role of language features as contextual information during the decoding process. Consequently, these methods exhibit weak object-level correspondence between visual and language features, leading to incomplete or erroneous predicted masks, especially when handling complex expressions and intricate RS image scenes. To address these challenges, we propose a fine-grained cross-modal alignment and decoding Transformer, CADFormer, for RRSIS. Specifically, we design a semantic mutual guidance alignment module (SMGAM) to achieve both vision-to-language and language-to-vision alignment, enabling comprehensive integration of visual and textual features for fine-grained cross-modal alignment. Furthermore, a textual-enhanced cross-modal decoder (TCMD) is introduced to incorporate language features during decoding, using refined textual information as context to enhance the relationship between cross-modal features. To thoroughly evaluate the performance of CADFormer, especially for inconspicuous targets in complex scenes, we constructed a new RRSIS dataset, called RRSIS-HR, which includes larger high-resolution RS image patches and semantically richer language expressions. Extensive experiments on the RRSIS-HR dataset and the popular RRSIS-D dataset demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of CADFormer. Datasets and source codes will be available at https://github.com/zxk688.
远程遥感图像分割(RRSIS)是一项具有挑战性的任务,旨在根据给定的语言表达对遥感(RS)图像中的特定目标对象进行分割。现有的RRSIS方法通常采用粗粒度单向对齐方法获得多模态特征,但它们往往忽略了语言特征在解码过程中的关键作用作为上下文信息。因此,这些方法在视觉和语言特征之间表现出较弱的对象级对应关系,导致预测掩膜不完整或错误,尤其是在处理复杂的表达式和遥感的细腻图像场景时。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种针对RRSIS的精细粒度跨模态对齐和解码Transformer,名为CADFormer。具体来说,我们设计了一个语义相互引导对齐模块(SMGAM)来实现视觉到语言以及语言到视觉的对齐,实现对视觉和文本特征的全面融合,实现精细粒度的跨模态对齐。此外,还引入了一种文本增强跨模态解码器(TCMD),在解码过程中融入语言特征,利用精炼的文本信息作为上下文,增强跨模态特征之间的关系。为了全面评估CADFormer的性能,尤其是针对复杂场景中不明显的目标,我们构建了一个新的RRSIS数据集,名为RRSIS-HR,该数据集包括更大的高分辨率RS图像补丁和语义更丰富的语言表达。在RRSIS-HR数据集和流行的RRSIS-D数据集上的大量实验证明了CADFormer的有效性和优越性。数据集和源代码将在https://github.com/zxk688上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对远程遥感图像分割任务(RRSIS)中的挑战,本文提出了一种精细的跨模态对齐与解码Transformer(CADFormer)。它设计了语义互导向对齐模块(SMGAM)实现视觉与语言的双向对齐,并引入了文本增强跨模态解码器(TCMD)在解码过程中融入语言特征。为评估模型性能,构建了新的RRSIS数据集RRSIS-HR。实验表明,CADFormer在RRSIS-HR及流行数据集RRSIS-D上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- RRSIS是一个挑战性任务,旨在根据给定的语言表达对遥感图像中的特定目标对象进行分割。
- 现有方法通常使用粗粒度的单向对齐方法获得多模态特征,忽视了语言特征作为上下文信息的重要性。
- CADFormer通过设计SMGAM模块实现视觉与语言的双向精细对齐。
- TCMD解码器在解码过程中融入了语言特征,利用精炼的文本信息作为上下文,增强了跨模态特征之间的关系。
- 为评估模型性能,构建了新的RRSIS数据集RRSIS-HR,包含大尺度高分辨率遥感图像和丰富的语言表达。
- 在RRSIS-HR及RRSIS-D数据集上的实验表明CADFormer具有优越性能。
点此查看论文截图


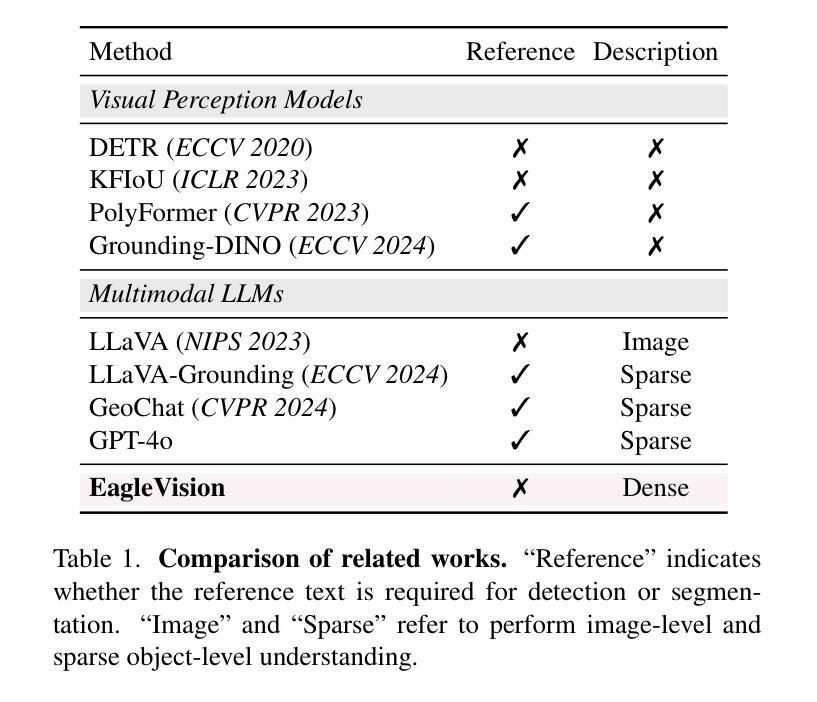
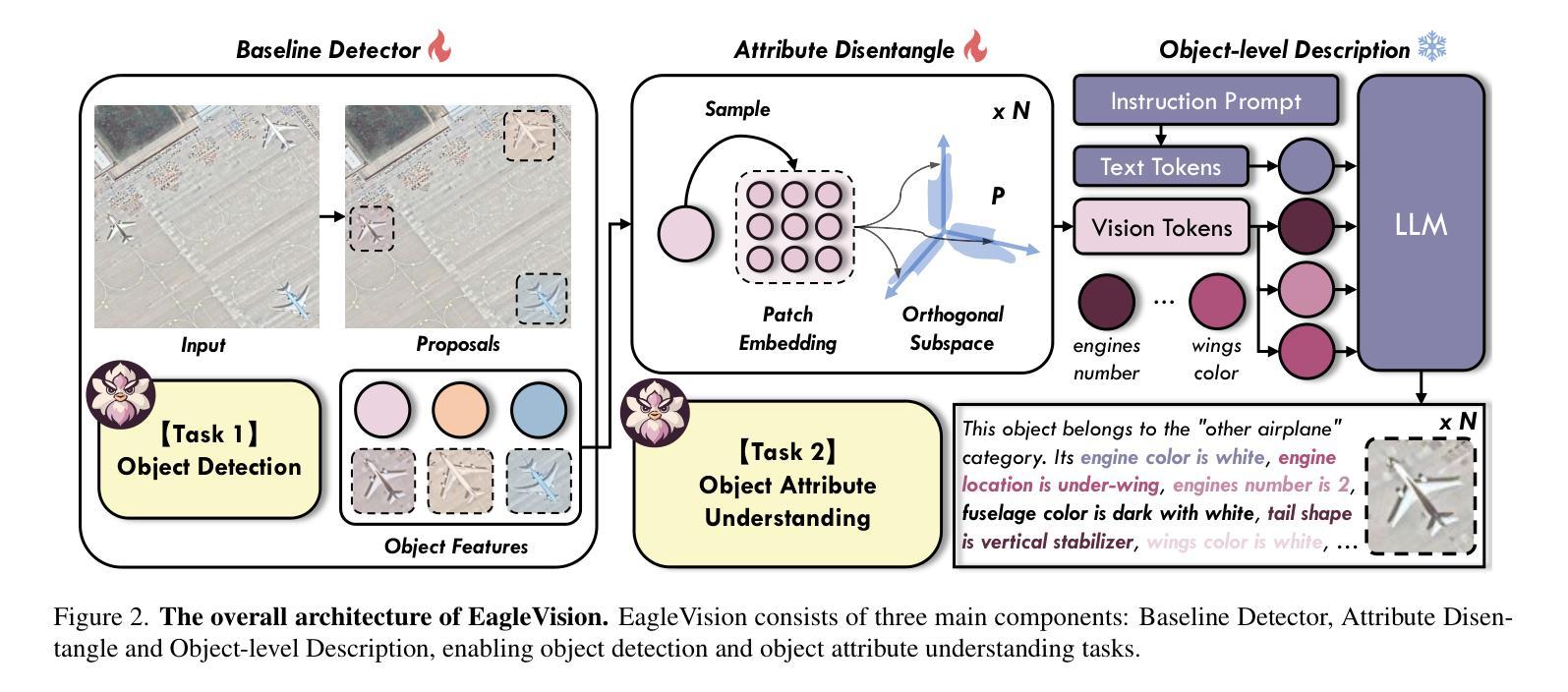
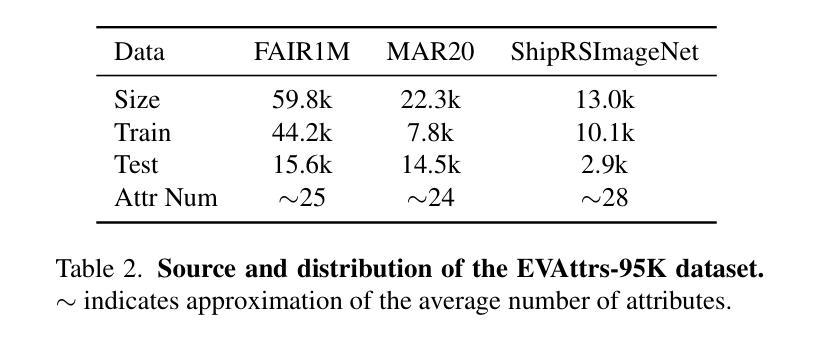
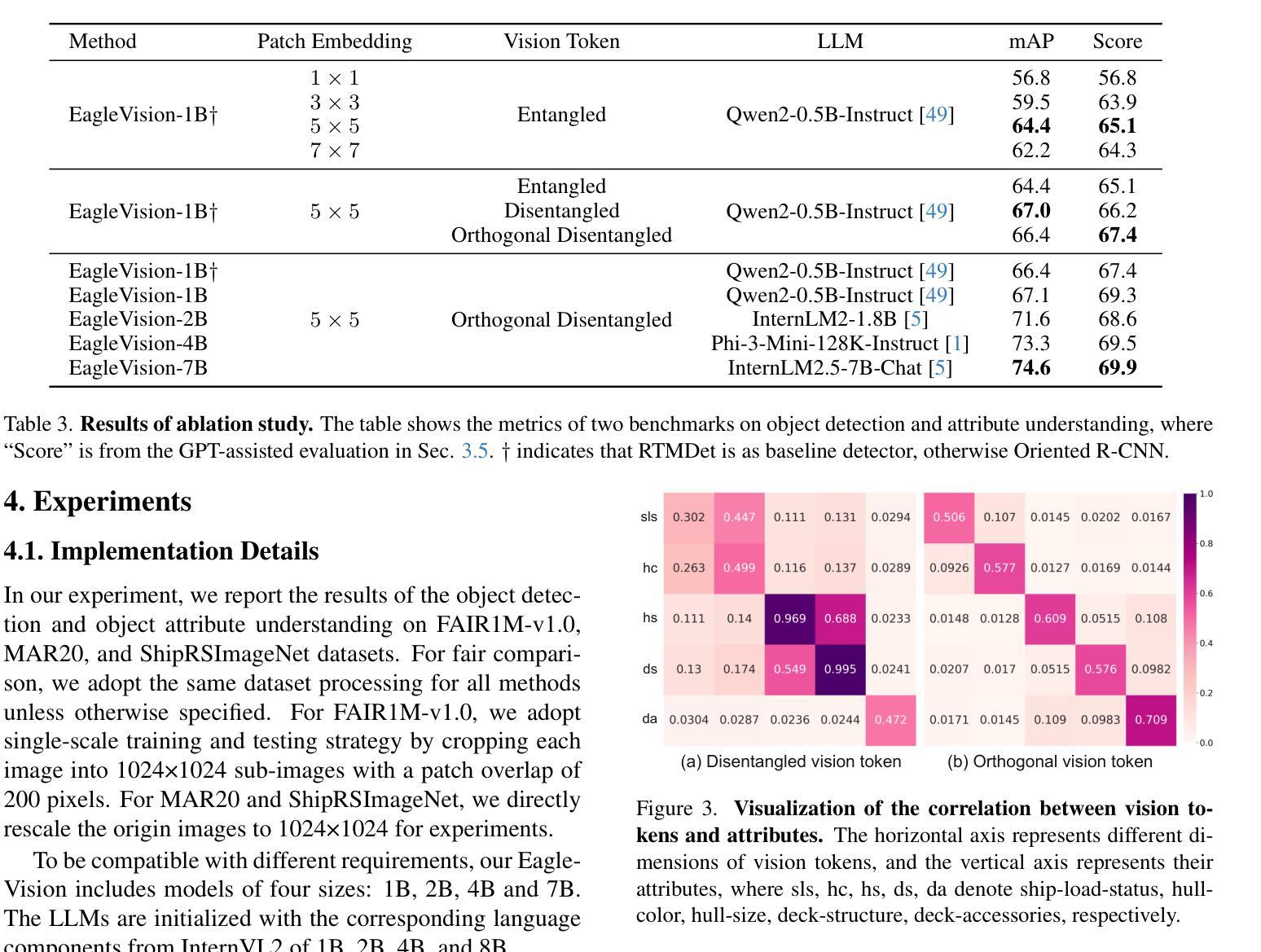
EagleVision: Object-level Attribute Multimodal LLM for Remote Sensing
Authors:Hongxiang Jiang, Jihao Yin, Qixiong Wang, Jiaqi Feng, Guo Chen
Recent advances in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have demonstrated impressive results in various visual tasks. However, in remote sensing (RS), high resolution and small proportion of objects pose challenges to existing MLLMs, which struggle with object-centric tasks, particularly in precise localization and fine-grained attribute description for each object. These RS MLLMs have not yet surpassed classical visual perception models, as they only provide coarse image understanding, leading to limited gains in real-world scenarios. To address this gap, we establish EagleVision, an MLLM tailored for remote sensing that excels in object detection and attribute comprehension. Equipped with the Attribute Disentangle module, EagleVision learns disentanglement vision tokens to express distinct attributes. To support object-level visual-language alignment, we construct EVAttrs-95K, the first large-scale object attribute understanding dataset in RS for instruction tuning, along with a novel evaluation benchmark, EVBench. EagleVision achieves state-of-the-art performance on both fine-grained object detection and object attribute understanding tasks, highlighting the mutual promotion between detection and understanding capabilities in MLLMs. The code, model, data, and demo will be available at https://github.com/XiangTodayEatsWhat/EagleVision.
最近的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的进展在各种视觉任务中取得了令人印象深刻的结果。然而,在遥感(RS)领域,高分辨率和小比例的对象对现有的MLLMs构成了挑战,它们在以对象为中心的任务上表现挣扎,特别是在每个对象的精确定位和精细粒度属性描述方面。这些用于遥感的MLLMs尚未超越经典视觉感知模型,因为它们只提供粗略的图像理解,导致在真实场景中的收益有限。为了解决这一差距,我们建立了EagleVision,这是一个针对遥感定制的大型语言模型,擅长对象检测和属性理解。配备了属性分离模块后,EagleVision学习分离视觉令牌以表达不同的属性。为了支持对象级别的视觉语言对齐,我们构建了EVAttrs-95K数据集,这是遥感领域中用于指令调整的第一个大规模对象属性理解数据集,以及一个新的评估基准EVBench。EagleVision在精细粒度对象检测和对象属性理解任务上都实现了最先进的性能,这凸显出在大型语言模型中检测和理解能力之间的相互促进。代码、模型、数据和演示将发布在https://github.com/XiangTodayEatsWhat/EagleVision。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under Review
Summary
大语言模型在遥感领域面临挑战,如精确定位和精细属性描述等对象中心任务。为此,我们提出了EagleVision模型,并设计了Attribute Disentangle模块以进行精细化对象属性理解。我们建立了EVAttrs-95K数据集和EVBench评估基准以支持对象级视觉语言对齐。EagleVision在精细粒度对象检测和对象属性理解任务上取得了最新性能表现。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在遥感(RS)领域的对象中心任务上遇到了挑战,特别是在精确定位和精细属性描述方面。
- 现有MLLMs在遥感应用中尚未超越经典视觉感知模型,因为它们仅提供粗略的图像理解。
- EagleVision是一个针对遥感领域的MLLM,擅长对象检测和属性理解。
- Attribute Disentangle模块使EagleVision能够学习解纠缠的视觉令牌以表达不同的属性。
- 为支持对象级视觉语言对齐,建立了EVAttrs-95K数据集和EVBench评估基准。
- EagleVision在精细粒度对象检测和对象属性理解任务上取得了最新性能。
- 检测和理解能力在MLLMs中相互促进。
点此查看论文截图

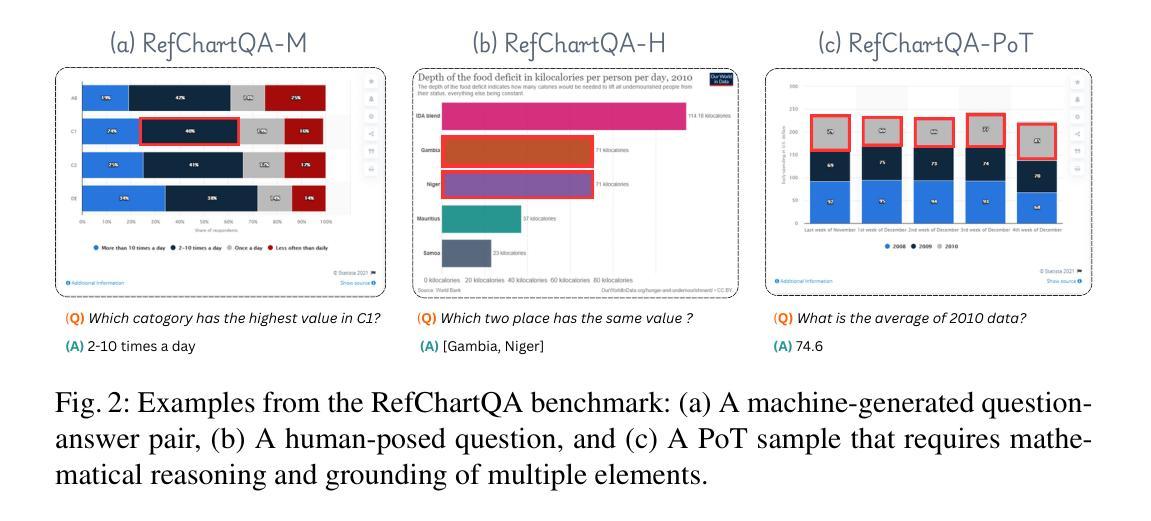
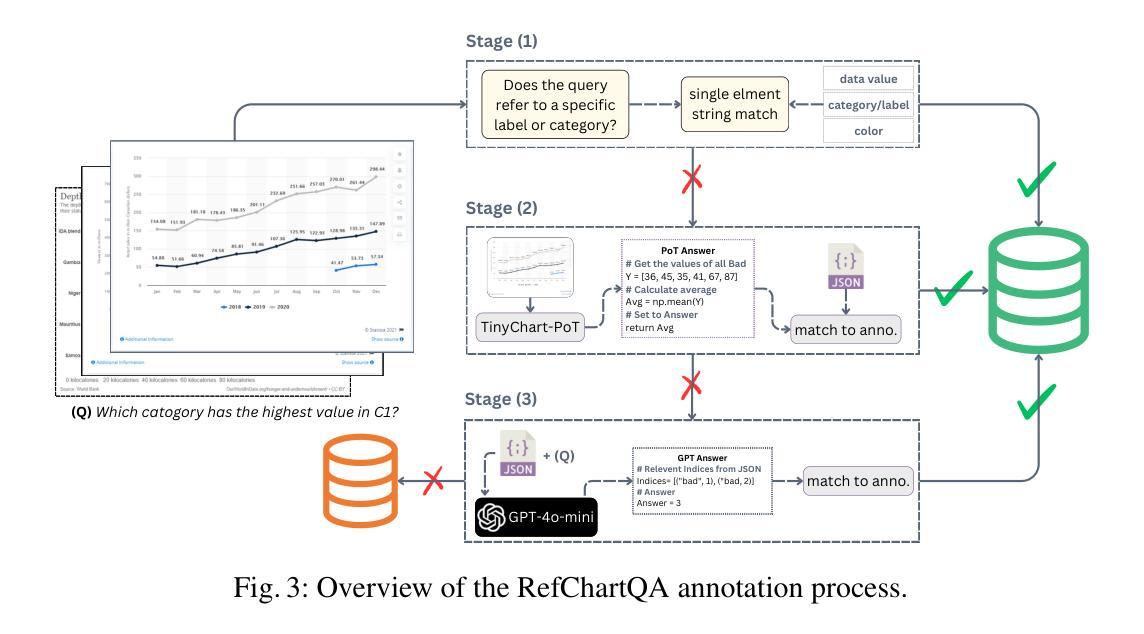
RefChartQA: Grounding Visual Answer on Chart Images through Instruction Tuning
Authors:Alexander Vogel, Omar Moured, Yufan Chen, Jiaming Zhang, Rainer Stiefelhagen
Recently, Vision Language Models (VLMs) have increasingly emphasized document visual grounding to achieve better human-computer interaction, accessibility, and detailed understanding. However, its application to visualizations such as charts remains under-explored due to the inherent complexity of interleaved visual-numerical relationships in chart images. Existing chart understanding methods primarily focus on answering questions without explicitly identifying the visual elements that support their predictions. To bridge this gap, we introduce RefChartQA, a novel benchmark that integrates Chart Question Answering (ChartQA) with visual grounding, enabling models to refer elements at multiple granularities within chart images. Furthermore, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation by instruction-tuning 5 state-of-the-art VLMs across different categories. Our experiments demonstrate that incorporating spatial awareness via grounding improves response accuracy by over 15%, reducing hallucinations, and improving model reliability. Additionally, we identify key factors influencing text-spatial alignment, such as architectural improvements in TinyChart, which leverages a token-merging module for enhanced feature fusion. Our dataset is open-sourced for community development and further advancements. All models and code will be publicly available at https://github.com/moured/RefChartQA.
最近,视觉语言模型(VLMs)越来越强调文档的视觉定位,以实现更好的人机交互、可访问性和深入理解。然而,由于其图表图像中交织的视觉数字关系固有的复杂性,其在图表等可视化中的应用仍待探索。现有的图表理解方法主要关注回答问题,而没有明确识别支持其预测的视觉元素。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了RefChartQA,这是一个将图表问答(ChartQA)与视觉定位相结合的新型基准测试,使模型能够在图表图像内的多个粒度上参考元素。此外,我们通过指令调整了5个不同类别的最先进VLMs进行了全面评估。我们的实验表明,通过定位融入空间意识提高了超过15%的响应准确性,减少了幻觉,提高了模型可靠性。另外,我们还确定了影响文本空间对齐的关键因素,如TinyChart中的架构改进,它利用令牌合并模块增强特征融合。我们的数据集已开源供社区发展和进一步进步。所有模型和代码将在https://github.com/moured/RefChartQA上公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF All models and code will be publicly available at https://github.com/moured/RefChartQA
Summary:视觉语言模型(VLMs)正逐渐重视文档视觉定位,以提高人机交互、可访问性和深入理解。然而,由于图表图像中视觉与数值关系的固有复杂性,其在图表等可视化方面的应用仍被忽视。为了弥补这一空白,引入了RefChartQA基准测试,它将图表问答(ChartQA)与视觉定位相结合,使模型能够在图表图像中的多个粒度级别上引用元素。实验表明,通过定位融入空间意识可以提高响应准确性超过15%,减少幻觉并提高模型可靠性。此外,公开的数据集可供社区开发和进一步进展之用。
Key Takeaways:
- Vision Language Models (VLMs) 强调文档视觉定位的重要性,以增强人机交互和深入理解。
- VLMs在图表可视化方面的应用仍处于探索阶段,因为需要处理视觉与数值关系的复杂性。
- RefChartQA是一个新的基准测试,结合了图表问答(ChartQA)和视觉定位。
- 通过融入空间意识,定位可以提高响应准确性超过15%,并减少幻觉。
- RefChartQA数据集公开供社区使用,促进进一步的发展。
- 实验评估了五种最新VLMs的不同类别,显示模型在定位方面的改进对结果有积极影响。
点此查看论文截图

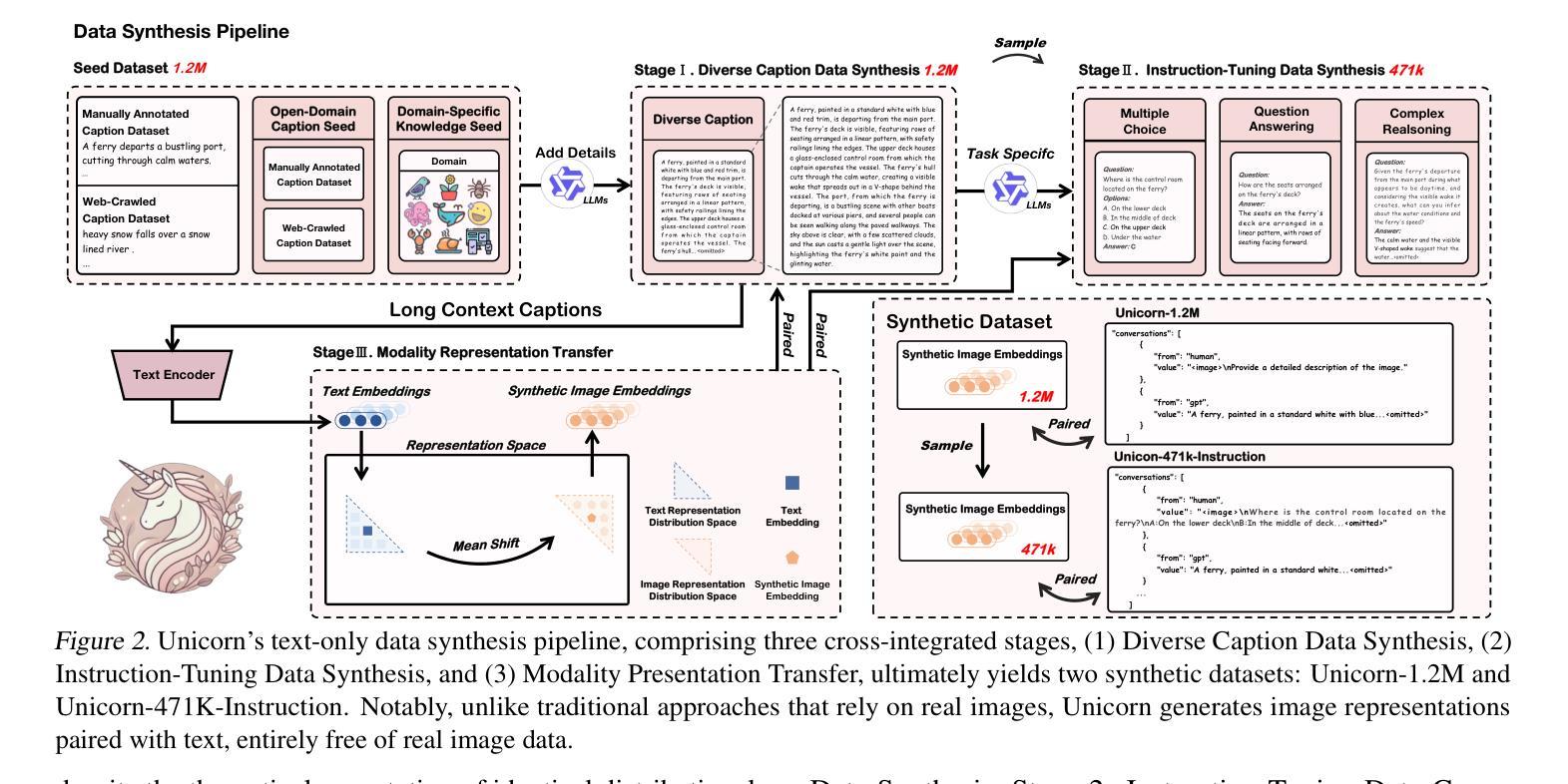
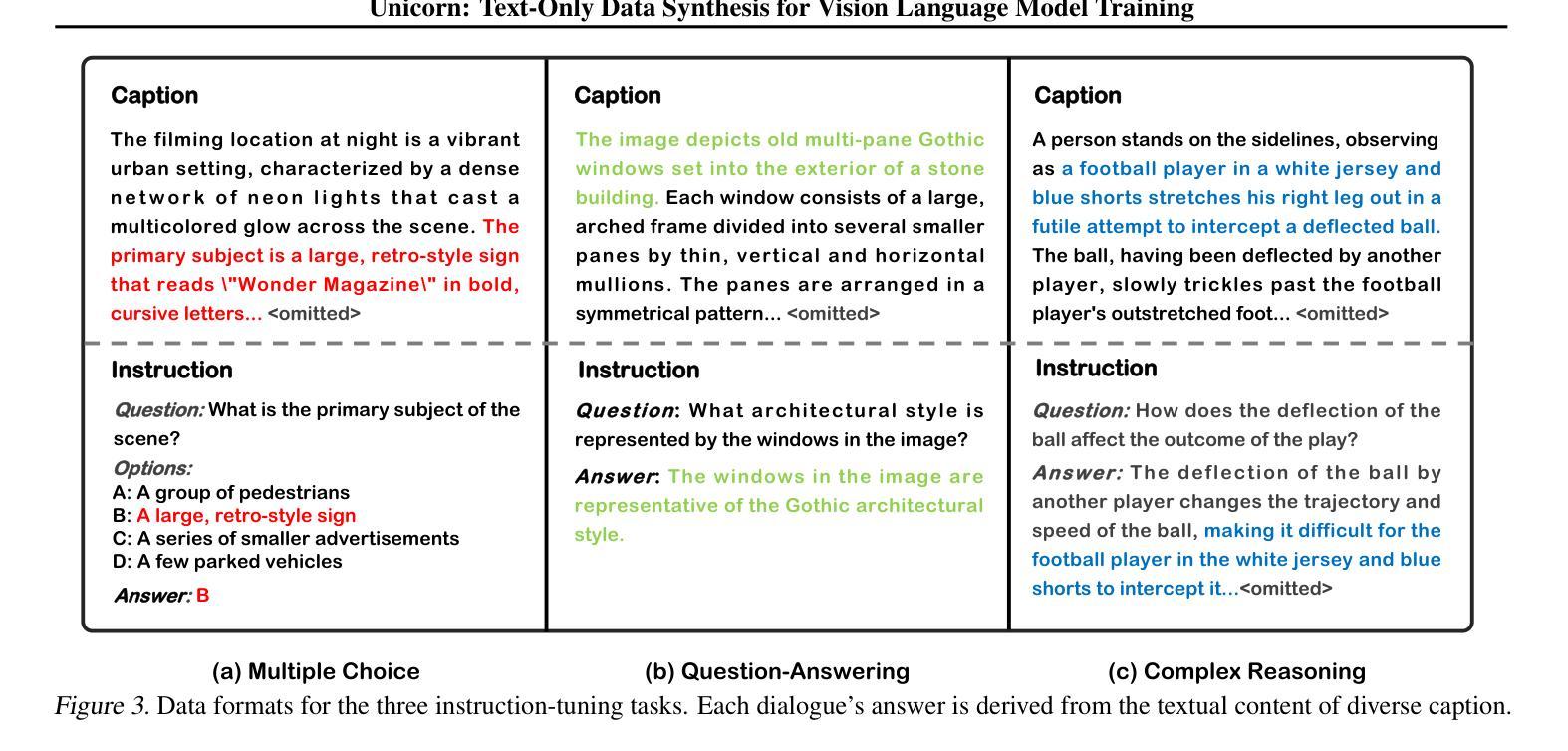
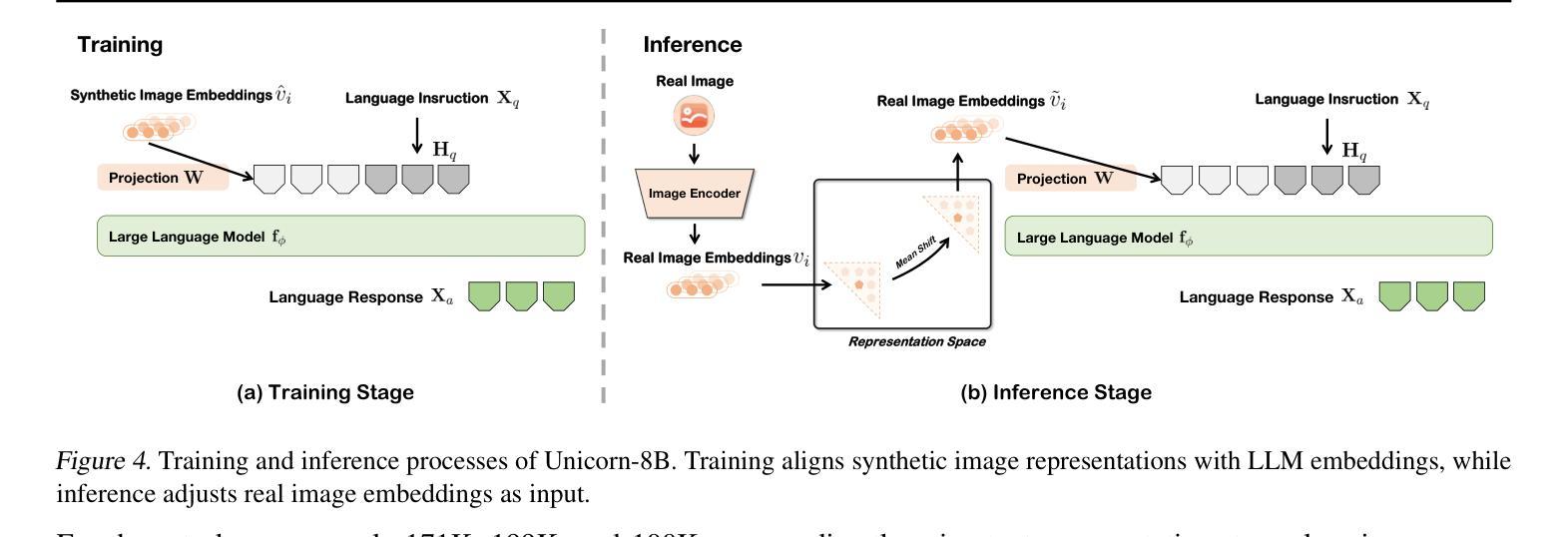
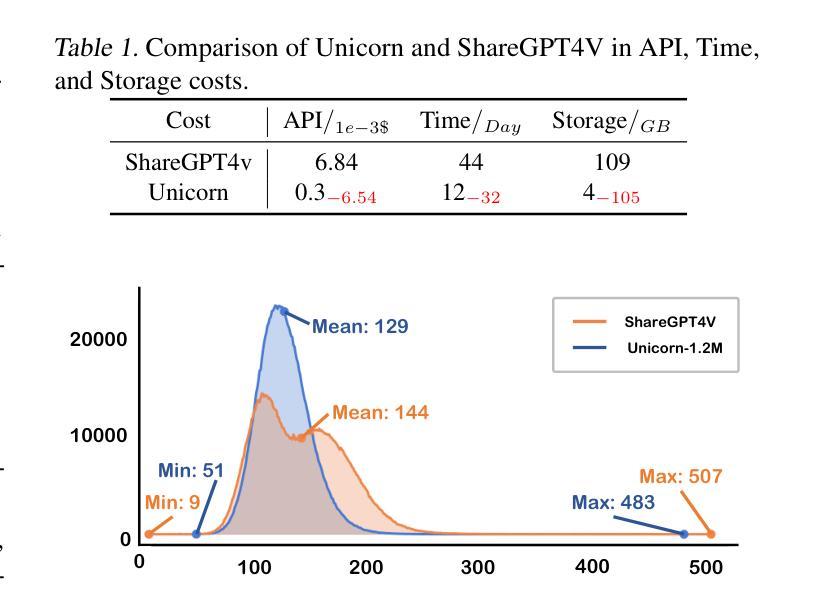
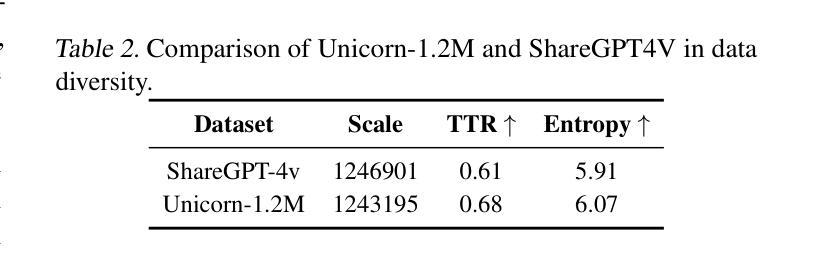
Unicorn: Text-Only Data Synthesis for Vision Language Model Training
Authors:Xiaomin Yu, Pengxiang Ding, Wenjie Zhang, Siteng Huang, Songyang Gao, Chengwei Qin, Kejian Wu, Zhaoxin Fan, Ziyue Qiao, Donglin Wang
Training vision-language models (VLMs) typically requires large-scale, high-quality image-text pairs, but collecting or synthesizing such data is costly. In contrast, text data is abundant and inexpensive, prompting the question: can high-quality multimodal training data be synthesized purely from text? To tackle this, we propose a cross-integrated three-stage multimodal data synthesis framework, which generates two datasets: Unicorn-1.2M and Unicorn-471K-Instruction. In Stage 1: Diverse Caption Data Synthesis, we construct 1.2M semantically diverse high-quality captions by expanding sparse caption seeds using large language models (LLMs). In Stage 2: Instruction-Tuning Data Generation, we further process 471K captions into multi-turn instruction-tuning tasks to support complex reasoning. Finally, in Stage 3: Modality Representation Transfer, these textual captions representations are transformed into visual representations, resulting in diverse synthetic image representations. This three-stage process enables us to construct Unicorn-1.2M for pretraining and Unicorn-471K-Instruction for instruction-tuning, without relying on real images. By eliminating the dependency on real images while maintaining data quality and diversity, our framework offers a cost-effective and scalable solution for VLMs training. Code is available at https://github.com/Yu-xm/Unicorn.git.
训练视觉语言模型(VLM)通常需要大规模、高质量的图文对数据,但收集或合成这样的数据成本很高。相比之下,文本数据非常丰富且价格低廉,这引发了一个问题:是否可以从纯文本合成高质量的多模态训练数据?为解决这一问题,我们提出了一个跨融合的三阶段多模态数据合成框架,该框架生成了两个数据集:Unicorn-1.2M和Unicorn-471K-Instruction。在第一阶段:多样化标题数据合成中,我们通过利用大型语言模型(LLM)扩展稀疏标题种子来构建120万张语义丰富的高质量图片标题。在第二阶段:指令调整数据生成中,我们将47.1万张图片的标题进一步处理成多轮指令调整任务,以支持复杂推理。最后,在第三阶段:模态表示转换中,这些文本标题表示被转换成视觉表示,从而产生多样化的合成图像表示。这三阶段的过程使我们能够构建用于预训练的Unicorn-1.2M和用于指令调整的Unicorn-471K-Instruction,而无需依赖真实图像。通过消除对真实图像的依赖,同时保持数据的质量和多样性,我们的框架为VLMs训练提供了成本低廉且可扩展的解决方案。代码可通过https://github.com/Yu-xm/Unicorn.git获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种跨融合的三阶段多媒体数据合成框架,用于生成用于视觉语言模型训练的数据集。该框架通过纯文本方式合成高质量的多模态训练数据,分为三个阶段:多样化标题数据合成、指令调整数据生成和模态表示转移。最终构建了用于预训练的Unicorn-1.2M数据集和用于指令调整的Unicorn-471K-Instruction数据集。该框架消除了对真实图像的依赖,同时保持了数据的质量和多样性,为视觉语言模型训练提供了成本效益高且可扩展的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种跨融合的三阶段多媒体数据合成框架,用于生成视觉语言模型训练数据集。
- 框架分为三个阶段:多样化标题数据合成、指令调整数据生成和模态表示转移。
- 通过纯文本方式合成高质量的多模态训练数据,无需依赖真实图像。
- 构建了用于预训练的Unicorn-1.2M数据集和用于指令调整的Unicorn-471K-Instruction数据集。
- 框架能够保持数据的质量和多样性,同时提高成本效益和可扩展性。
- 利用大型语言模型(LLMs)进行稀疏标题种子的扩展,生成语义上多样化的高质量标题。
点此查看论文截图

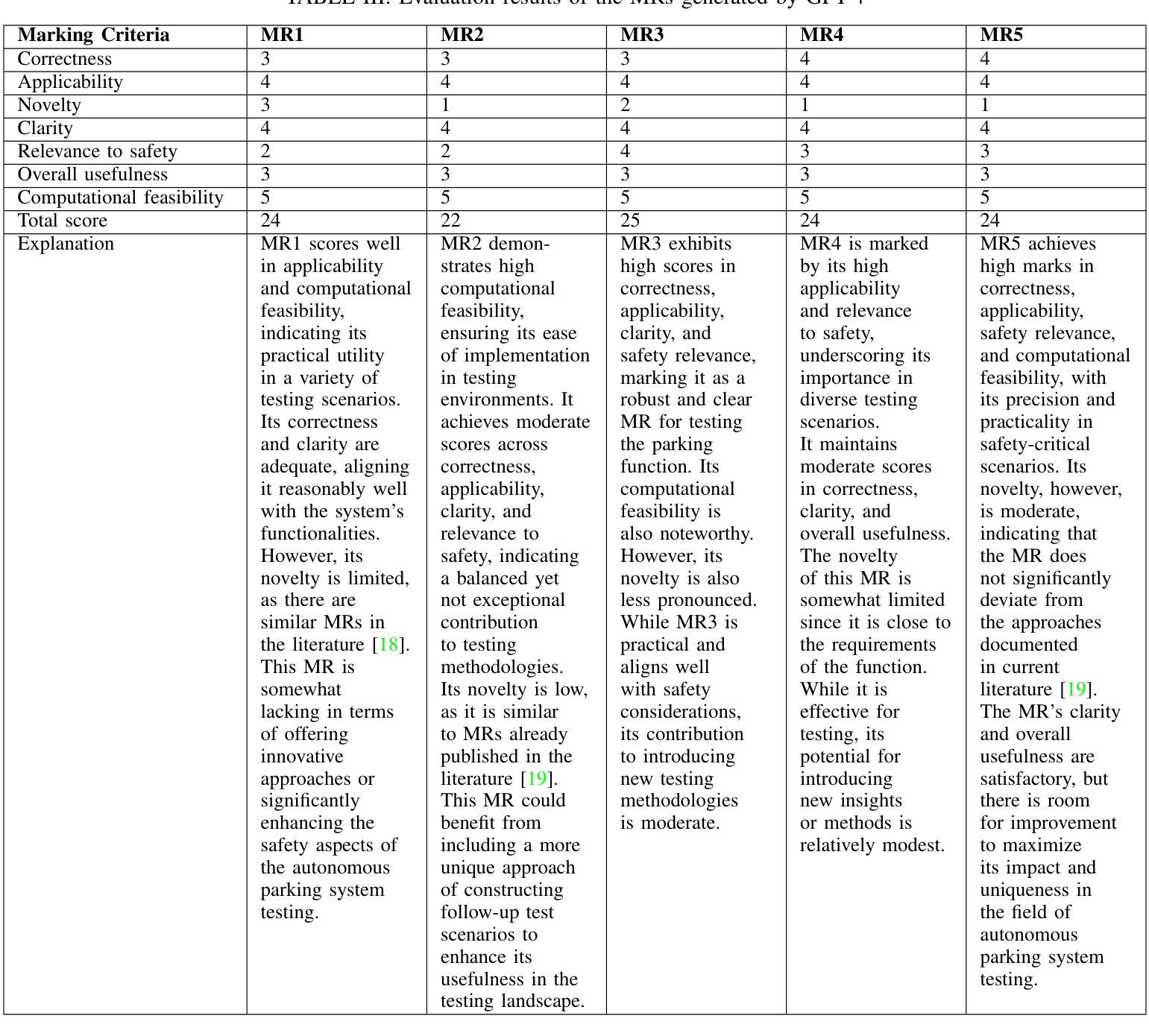
Integrating Artificial Intelligence with Human Expertise: An In-depth Analysis of ChatGPT’s Capabilities in Generating Metamorphic Relations
Authors:Yifan Zhang, Dave Towey, Matthew Pike, Quang-Hung Luu, Huai Liu, Tsong Yueh Chen
Context: This paper provides an in-depth examination of the generation and evaluation of Metamorphic Relations (MRs) using GPT models developed by OpenAI, with a particular focus on the capabilities of GPT-4 in software testing environments. Objective: The aim is to examine the quality of MRs produced by GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 for a specific System Under Test (SUT) adopted from an earlier study, and to introduce and apply an improved set of evaluation criteria for a diverse range of SUTs. Method: The initial phase evaluates MRs generated by GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 using criteria from a prior study, followed by an application of an enhanced evaluation framework on MRs created by GPT-4 for a diverse range of nine SUTs, varying from simple programs to complex systems incorporating AI/ML components. A custom-built GPT evaluator, alongside human evaluators, assessed the MRs, enabling a direct comparison between automated and human evaluation methods. Results: The study finds that GPT-4 outperforms GPT-3.5 in generating accurate and useful MRs. With the advanced evaluation criteria, GPT-4 demonstrates a significant ability to produce high-quality MRs across a wide range of SUTs, including complex systems incorporating AI/ML components. Conclusions: GPT-4 exhibits advanced capabilities in generating MRs suitable for various applications. The research underscores the growing potential of AI in software testing, particularly in the generation and evaluation of MRs, and points towards the complementarity of human and AI skills in this domain.
本文深入探讨了使用OpenAI开发的GPT模型(特别是GPT-4)在软件测试环境中生成和评价Metamorphic Relations (MRs)的方法。文章旨在研究GPT-3.5和GPT-4在特定系统测试(SUT)环境下生成MRs的质量,并为多种SUTs引入和应用了一套改进的评价标准。初始阶段,我们根据先前的研究标准评估了GPT-3.5和GPT-4生成的MRs,然后应用了一个增强的评价框架对GPT-4为九种不同的SUTs生成的MRs进行了评价,这些系统从简单的程序到复杂的包含人工智能/机器学习组件的系统不等。我们自定义的GPT评价工具和人类评价者共同对MRs进行了评估,实现了自动化和人类评价方法之间的直接比较。研究发现,GPT-4在生成准确有用的MRs方面优于GPT-3.5。通过先进的评价标准,GPT-4显示出在各种SUTs上生成高质量MRs的显著能力,包括复杂的包含人工智能/机器学习组件的系统。这表明GPT-4在各种应用中生成MRs方面表现出高级能力。该研究强调了人工智能在软件测试领域(特别是在生成和评价MRs方面)的巨大潜力,并指出了人类和人工智能技能在这个领域的互补性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to Information and Software Technology
摘要
本文深入探讨了使用OpenAI开发的GPT模型生成和评估形态关系(MRs)的过程,重点研究了GPT-4在软件测试环境中的能力。文章旨在评估GPT-3.5和GPT-4对特定系统(采用早期研究中的系统)生成MRs的质量,并为多种系统引入并应用改进的评价标准。研究方法包括使用早期研究的标准对GPT-3.5和GPT-4生成的MRs进行评估,以及对GPT-4为九种不同系统生成的MRs应用改进的评价框架。结合自定义的GPT评估器和人类评估者,对MRs进行了评估,实现了自动与人类评估方法的直接比较。研究发现,GPT-4在生成准确和有用的MRs方面优于GPT-3.5。使用改进的评价标准,GPT-4显示出在各种系统(包括包含人工智能/机器学习组件的复杂系统)中产生高质量MRs的重要能力。本文的结论是,GPT-4在生成适用于各种应用的MRs方面展现了先进的性能,强调人工智能在软件测试领域的潜力,特别是在生成和评估MRs方面。它表明人类和人工智能的技能在这个领域的互补性。
关键见解
- GPT-4在生成形态关系(MRs)方面表现出优于GPT-3.5的性能。
- GPT-4能够在各种系统(包括包含AI/ML组件的复杂系统)中产生高质量的MRs。
- 文章通过使用自定义的GPT评估器和人类评估者,实现了自动化和人类评估方法的直接比较。
- GPT模型在软件测试领域具有潜力,特别是在生成和评估MRs方面。
- 研究强调了人工智能在软件测试中的成长潜力。
- 在生成和评估MRs方面,人类和AI的技能表现出互补性。
点此查看论文截图


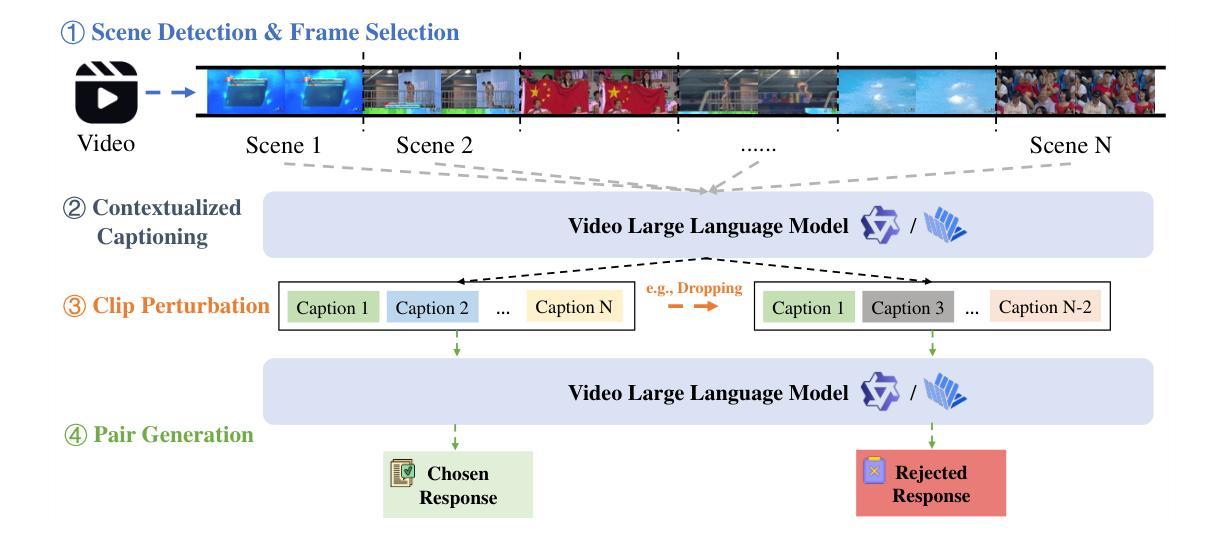
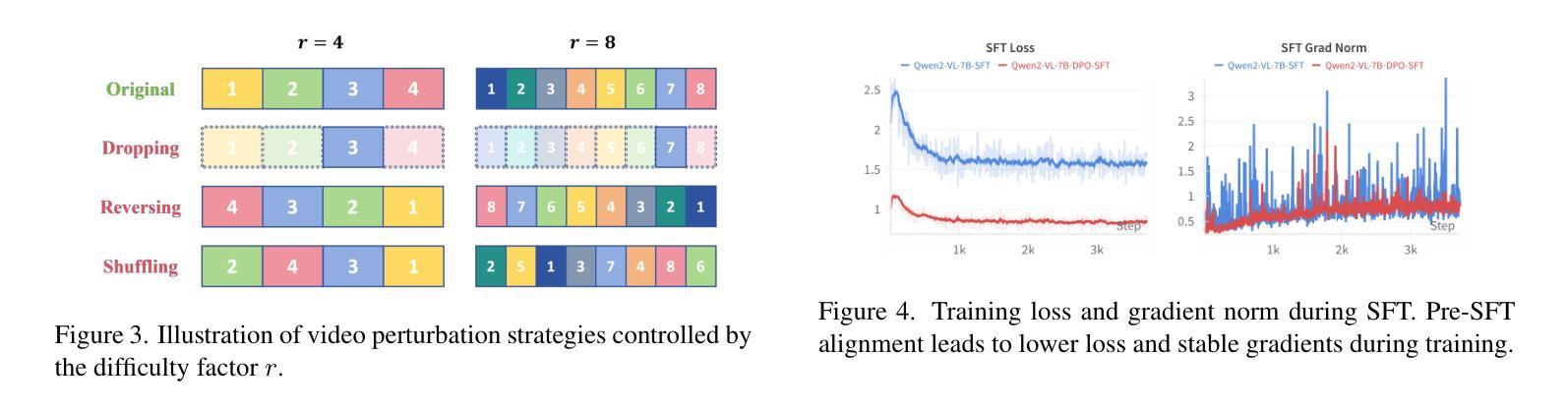
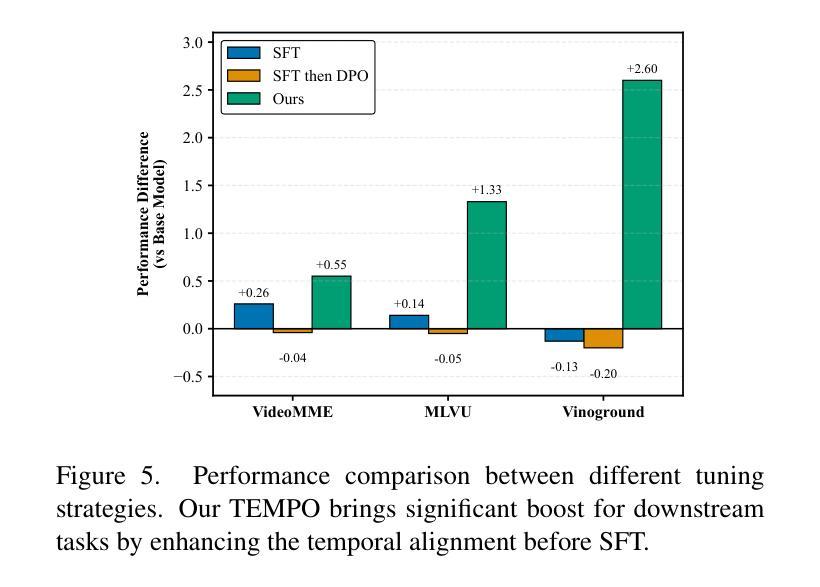
TEMPLE:Temporal Preference Learning of Video LLMs via Difficulty Scheduling and Pre-SFT Alignment
Authors:Shicheng Li, Lei Li, Kun Ouyang, Shuhuai Ren, Yuanxin Liu, Yuanxing Zhang, Fuzheng Zhang, Lingpeng Kong, Qi Liu, Xu Sun
Video Large Language Models (Video LLMs) have achieved significant success by leveraging a two-stage paradigm: pretraining on large-scale video-text data for vision-language alignment, followed by supervised fine-tuning (SFT) for task-specific capabilities. However, existing approaches struggle with temporal reasoning due to weak temporal correspondence in the data and reliance on the next-token prediction paradigm during training. To address these limitations, we propose TEMPLE (TEMporal Preference Learning), a systematic framework that enhances Video LLMs’ temporal reasoning capabilities through Direct Preference Optimization (DPO). To facilitate this, we introduce an automated preference data generation pipeline that systematically constructs preference pairs by selecting videos that are rich in temporal information, designing video-specific perturbation strategies, and finally evaluating model responses on clean and perturbed video inputs. Our temporal alignment features two key innovations: curriculum learning which that progressively increases perturbation difficulty to improve model robustness and adaptability; and “Pre-SFT Alignment’’, applying preference optimization before instruction tuning to prioritize fine-grained temporal comprehension. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach consistently improves Video LLM performance across multiple benchmarks with a relatively small set of self-generated DPO data. We further analyze the transferability of DPO data across architectures and the role of difficulty scheduling in optimization. Our findings highlight our TEMPLE as a scalable and efficient complement to SFT-based methods, paving the way for developing reliable Video LLMs. Code is available at https://github.com/lscpku/TEMPLE.
视频大语言模型(Video LLMs)通过采用两阶段范式取得了显著的成功:首先在大规模视频文本数据上进行预训练,以实现视觉语言对齐,然后通过监督微调(SFT)获得特定任务的能力。然而,现有方法由于数据中的时间对应关系较弱以及在训练过程中依赖于下一个标记预测范式,因此在时间推理方面遇到了困难。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了TEMPLE(时空偏好学习),这是一个系统框架,它通过直接偏好优化(DPO)增强视频LLM的时间推理能力。为了促进这一点,我们引入了一个自动化偏好数据生成管道,该管道通过选择时间信息丰富的视频、设计针对视频的扰动策略,以及评估模型对干净和扰动视频输入的响应来系统地构建偏好对。我们的时间对齐有两个关键的创新点:课程学习,逐步增加扰动难度以提高模型的鲁棒性和适应性;以及“Pre-SFT对齐”,在指令调整之前应用偏好优化,以优先进行精细的时间理解。大量实验表明,我们的方法在使用相对较少自我生成的DPO数据时,能够在多个基准测试上持续提高视频LLM的性能。我们还分析了DPO数据在不同架构之间的可迁移性以及难度调度在优化中的角色。我们的研究结果表明,TEMPLE可以作为基于SFT的方法的可扩展和高效的补充,为开发可靠的视频LLM铺平了道路。代码可在https://github.com/lscpku/TEMPLE找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了TEMPLE框架,通过直接偏好优化(DPO)提升视频大型语言模型(Video LLMs)的时间推理能力。该框架通过自动化偏好数据生成管道,选择富含时间信息的视频、设计视频特定扰动策略,并评估模型对干净和扰动视频输入的响应。引入课程学习机制和“Pre-SFT对齐”,在指令微调之前应用偏好优化,优先提高精细粒度的时间理解能力。实验证明,该方法在多个基准测试上提高了Video LLM的性能,且使用自我生成的DPO数据集相对较小。
Key Takeaways
- Video LLMs采用两阶段范式:预训练大规模视频文本数据实现视觉语言对齐,然后通过监督微调(SFT)获得特定任务能力。
- 现有方法面临时间推理困难,因数据中的时间对应关系较弱,且训练时依赖下一个标记预测范式。
- TEMPLE框架通过直接偏好优化(DPO)提升Video LLMs的时间推理能力。
- TEMPLE引入自动化偏好数据生成管道,包括选择富含时间信息的视频、设计视频特定扰动策略,并评估模型响应。
- 课程学习机制和“Pre-SFT对齐”是提高模型对时间信息理解的关键创新。
- 实验证明TEMPLE方法在多个基准测试上提高了Video LLM性能,且使用自我生成的DPO数据集相对较小。
点此查看论文截图


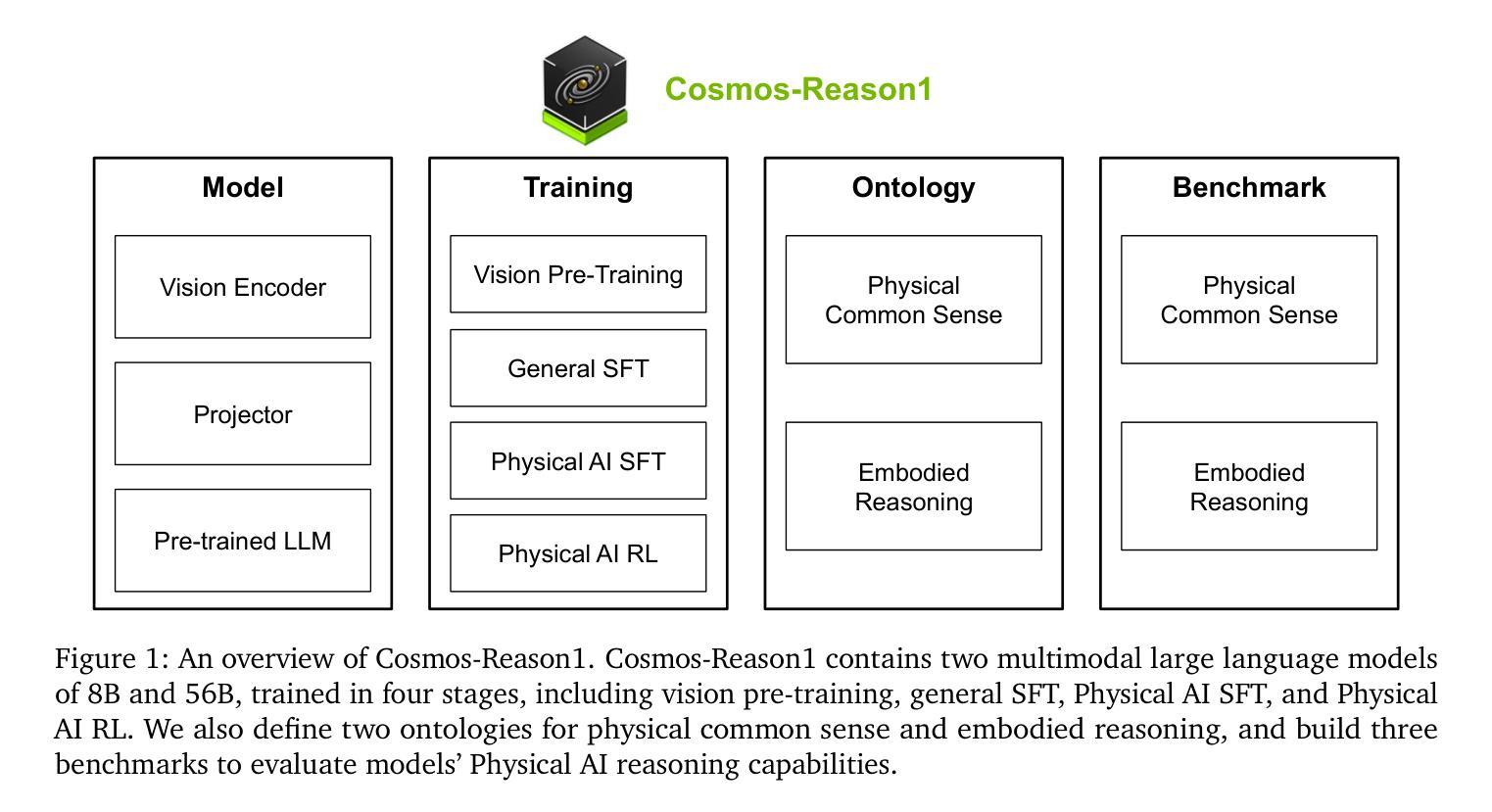
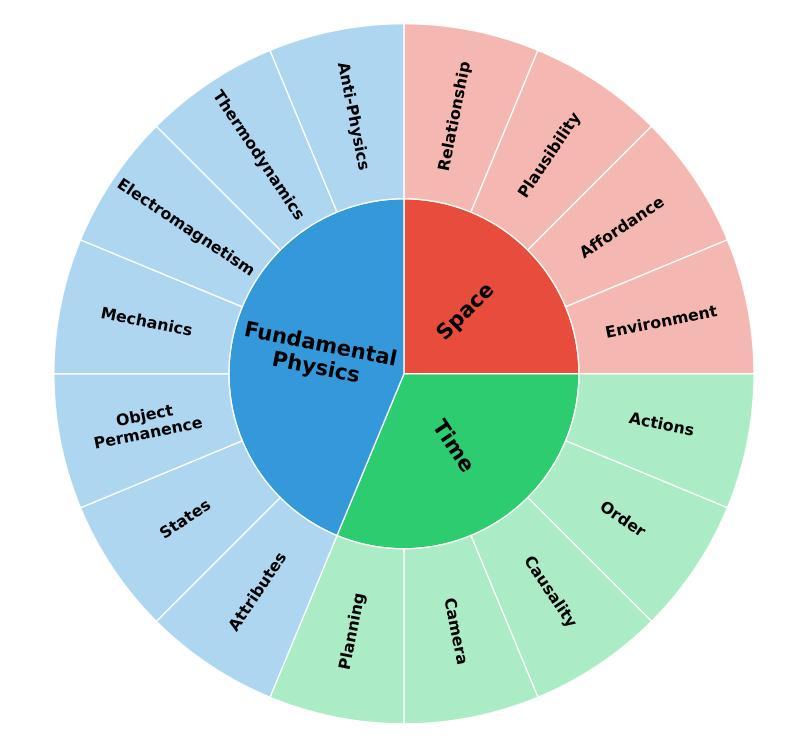
Cosmos-Reason1: From Physical Common Sense To Embodied Reasoning
Authors: NVIDIA, :, Alisson Azzolini, Hannah Brandon, Prithvijit Chattopadhyay, Huayu Chen, Jinju Chu, Yin Cui, Jenna Diamond, Yifan Ding, Francesco Ferroni, Rama Govindaraju, Jinwei Gu, Siddharth Gururani, Imad El Hanafi, Zekun Hao, Jacob Huffman, Jingyi Jin, Brendan Johnson, Rizwan Khan, George Kurian, Elena Lantz, Nayeon Lee, Zhaoshuo Li, Xuan Li, Tsung-Yi Lin, Yen-Chen Lin, Ming-Yu Liu, Alice Luo, Andrew Mathau, Yun Ni, Lindsey Pavao, Wei Ping, David W. Romero, Misha Smelyanskiy, Shuran Song, Lyne Tchapmi, Andrew Z. Wang, Boxin Wang, Haoxiang Wang, Fangyin Wei, Jiashu Xu, Yao Xu, Xiaodong Yang, Zhuolin Yang, Xiaohui Zeng, Zhe Zhang
Physical AI systems need to perceive, understand, and perform complex actions in the physical world. In this paper, we present the Cosmos-Reason1 models that can understand the physical world and generate appropriate embodied decisions (e.g., next step action) in natural language through long chain-of-thought reasoning processes. We begin by defining key capabilities for Physical AI reasoning, with a focus on physical common sense and embodied reasoning. To represent physical common sense, we use a hierarchical ontology that captures fundamental knowledge about space, time, and physics. For embodied reasoning, we rely on a two-dimensional ontology that generalizes across different physical embodiments. Building on these capabilities, we develop two multimodal large language models, Cosmos-Reason1-8B and Cosmos-Reason1-56B. We curate data and train our models in four stages: vision pre-training, general supervised fine-tuning (SFT), Physical AI SFT, and Physical AI reinforcement learning (RL) as the post-training. To evaluate our models, we build comprehensive benchmarks for physical common sense and embodied reasoning according to our ontologies. Evaluation results show that Physical AI SFT and reinforcement learning bring significant improvements. To facilitate the development of Physical AI, we will make our code and pre-trained models available under the NVIDIA Open Model License at https://github.com/nvidia-cosmos/cosmos-reason1.
物理人工智能系统需要在物理世界中感知、理解和执行复杂的动作。在本文中,我们介绍了Cosmos-Reason1模型,该模型能够通过一系列长思考过程理解物理世界,并以自然语言生成适当的决策(例如下一步行动)。我们首先定义物理人工智能推理的关键能力,重点关注物理常识和实体推理。为了表示物理常识,我们使用层次本体来捕获关于空间、时间和物理的基本常识。为了进行实体推理,我们依赖于一个二维本体,该本体可以概括不同的物理实体。基于这些能力,我们开发了两个多模态大型语言模型,即Cosmos-Reason1-8B和Cosmos-Reason1-56B。我们在四个阶段对数据进行整理并对模型进行训练:视觉预训练、一般监督微调(SFT)、物理人工智能SFT和物理人工智能强化学习(RL)作为后训练。为了评估我们的模型,我们根据我们的本体论建立了物理常识和实体推理的综合基准测试。评估结果表明,物理人工智能SFT和强化学习带来了显著的改进。为了方便物理人工智能的开发,我们将在NVIDIA Open Model License下提供我们的代码和预训练模型:https://github.com/nvidia-cosmos/cosmos-reason1。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文介绍了针对物理AI系统的研究,重点介绍了Cosmos-Reason1模型。该模型具备理解物理世界并生成适当决策的能力,通过长链思维推理过程实现。论文定义了物理AI推理的关键能力,侧重于物理常识和体现推理。为表达物理常识,采用层次化本体论捕捉关于空间、时间和物理学的根本知识。为体现推理,依赖二维本体论,在不同物理体现中概括共性。基于此,开发了两个多模态大型语言模型Cosmos-Reason1-8B和Cosmos-Reason1-56B。模型训练分四阶段:视觉预训练、一般监督微调、物理AI监督和物理AI强化学习。评估模型时,根据本体论建立了物理常识和体现推理的综合基准测试。结果显示,物理AI监督和强化学习带来显著改进。为方便物理AI的发展,模型和代码将在NVIDIA Open Model License下提供。
Key Takeaways
- Cosmos-Reason1模型具备理解物理世界并生成适当决策的能力,通过长链思维推理过程实现。
- 论文定义了物理AI推理的关键能力,包括物理常识和体现推理。
- 采用层次化本体论和二维本体论来代表物理常识和体现推理。
- 开发了两个多模态大型语言模型Cosmos-Reason1-8B和Cosmos-Reason1-56B。
- 模型训练包括四个阶段:视觉预训练、一般监督微调、物理AI监督、物理AI强化学习。
- 评估模型时,建立了基于本体论的物理常识和体现推理的综合基准测试。
点此查看论文截图

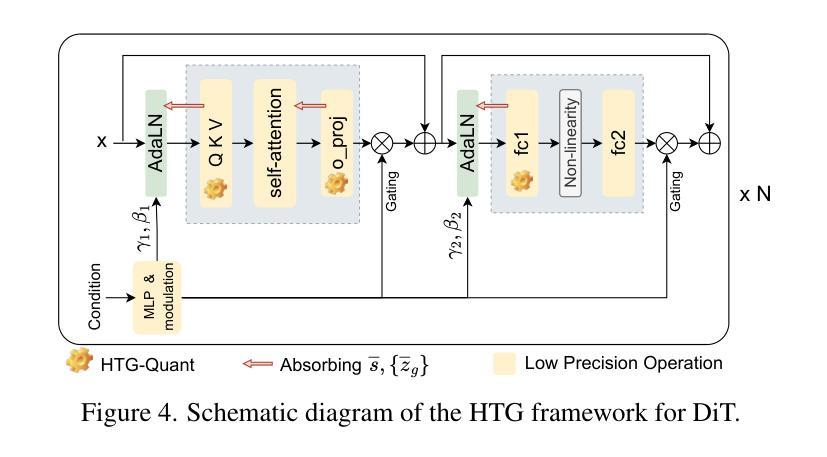
Post-Training Quantization for Diffusion Transformer via Hierarchical Timestep Grouping
Authors:Ning Ding, Jing Han, Yuchuan Tian, Chao Xu, Kai Han, Yehui Tang
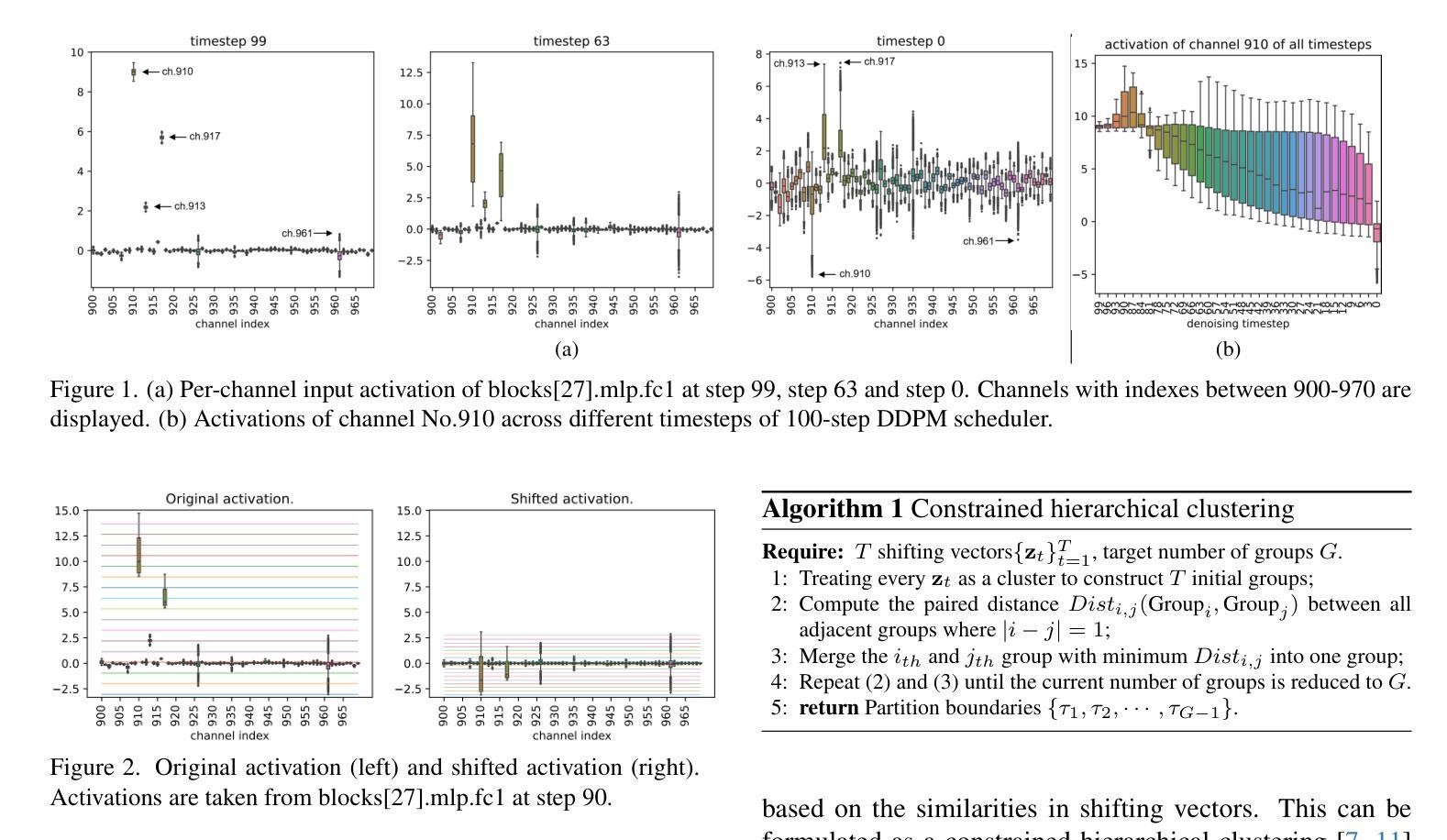
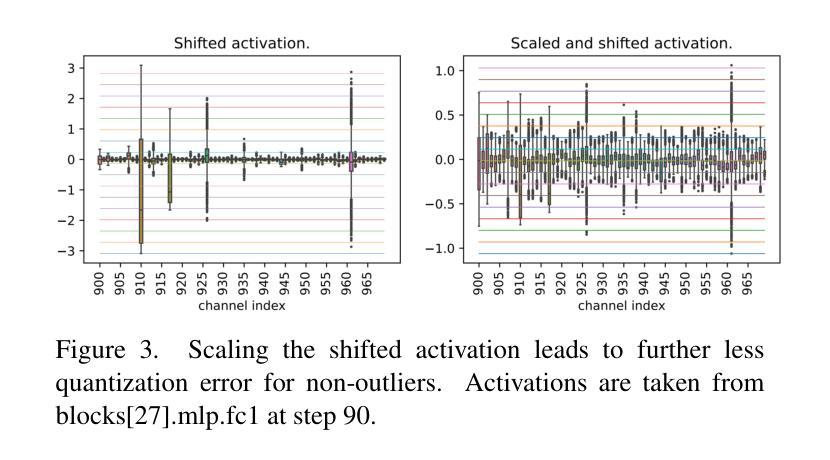
Diffusion Transformer (DiT) has now become the preferred choice for building image generation models due to its great generation capability. Unlike previous convolution-based UNet models, DiT is purely composed of a stack of transformer blocks, which renders DiT excellent in scalability like large language models. However, the growing model size and multi-step sampling paradigm bring about considerable pressure on deployment and inference. In this work, we propose a post-training quantization framework tailored for Diffusion Transforms to tackle these challenges. We firstly locate that the quantization difficulty of DiT mainly originates from the time-dependent channel-specific outliers. We propose a timestep-aware shift-and-scale strategy to smooth the activation distribution to reduce the quantization error. Secondly, based on the observation that activations of adjacent timesteps have similar distributions, we utilize a hierarchical clustering scheme to divide the denoising timesteps into multiple groups. We further design a re-parameterization scheme which absorbs the quantization parameters into nearby module to avoid redundant computations. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that out PTQ method successfully quantize the Diffusion Transformer into 8-bit weight and 8-bit activation (W8A8) with state-of-the-art FiD score. And our method can further quantize DiT model into 4-bit weight and 8-bit activation (W4A8) without sacrificing generation quality.
扩散转换器(DiT)由于其强大的生成能力,现已成为构建图像生成模型的首选。与之前的基于卷积的UNet模型不同,DiT完全由一堆转换器块组成,这使得DiT在可扩展性方面表现出色,就像大型语言模型一样。然而,不断增长的模型大小和多步采样范式给部署和推理带来了巨大的压力。在这项工作中,我们针对扩散转换提出了一种后训练量化框架,以解决这些挑战。我们首先发现DiT的量化难度主要源于时间依赖的特定通道异常值。我们提出了一种时间感知移位和缩放策略,以平滑激活分布,从而减少量化误差。其次,基于相邻时间步的激活具有相似分布的观测,我们采用分层聚类方案将去噪时间步分为多个组。我们进一步设计了一种重新参数化方案,将量化参数吸收到附近的模块中,以避免冗余计算。综合实验表明,我们的PTQ方法成功地将扩散转换器量化到8位权重和8位激活(W8A8),具有最先进的FID分数。我们的方法还可以将DiT模型进一步量化到4位权重和8位激活(W4A8),而不会牺牲生成质量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对扩散变换器(DiT)的定制后训练量化框架,解决了模型部署和推理中的压力问题。研究发现,DiT模型的量化难度主要来源于时序特定的通道异常值。针对此问题,本文提出了一个时序感知移位缩放策略来平滑激活分布以降低量化误差。此外,利用相邻时序激活分布的相似性进行层次聚类分组,设计了参数化方案以避免冗余计算。实验表明,该量化方法可将扩散变换器模型成功量化为权重和激活均为8位的模型(W8A8),且FID得分领先。同时,该方法还能将DiT模型进一步量化为权重为4位、激活为8位的模型(W4A8),且不影响生成质量。
Key Takeaways
- Diffusion Transformer (DiT)已成为图像生成模型的优选方案,其强大的生成能力得到广泛认可。
- DiT面临模型规模扩大和多步采样带来的部署和推理压力。
- 针对DiT的量化难度,研究发现主要源于时序特定的通道异常值。
- 提出时序感知移位缩放策略以平滑激活分布,降低量化误差。
- 利用相邻时序激活分布的相似性进行层次聚类分组。
- 设计了避免冗余计算的参数化方案。
点此查看论文截图

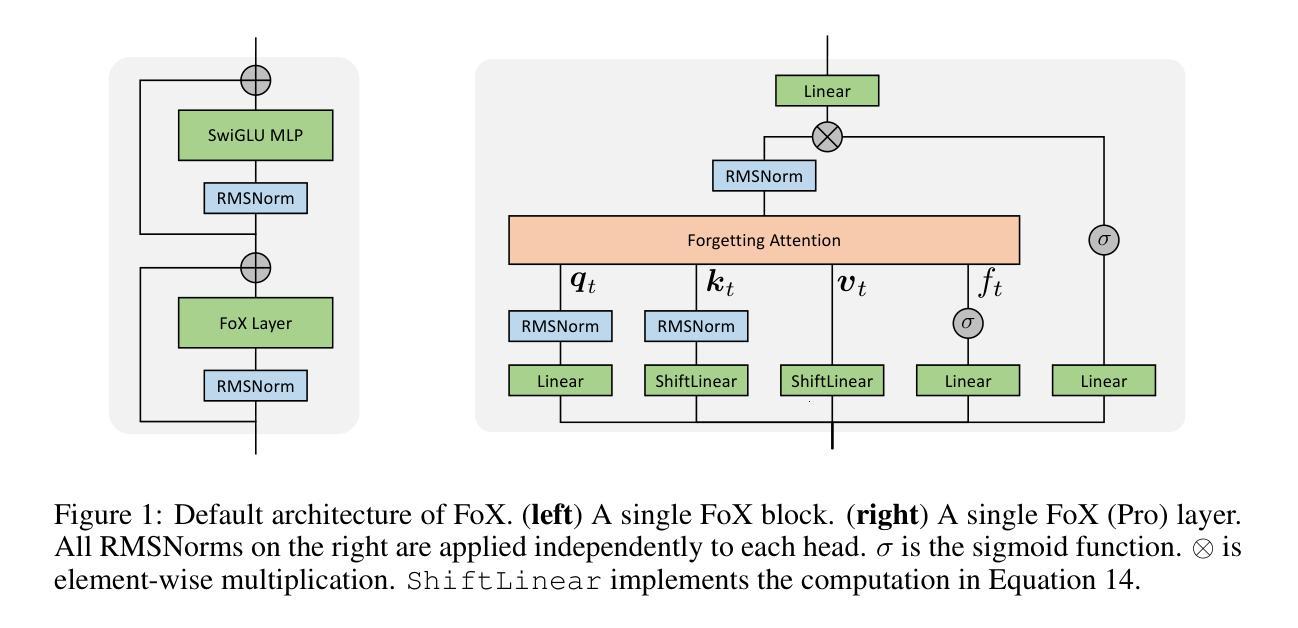
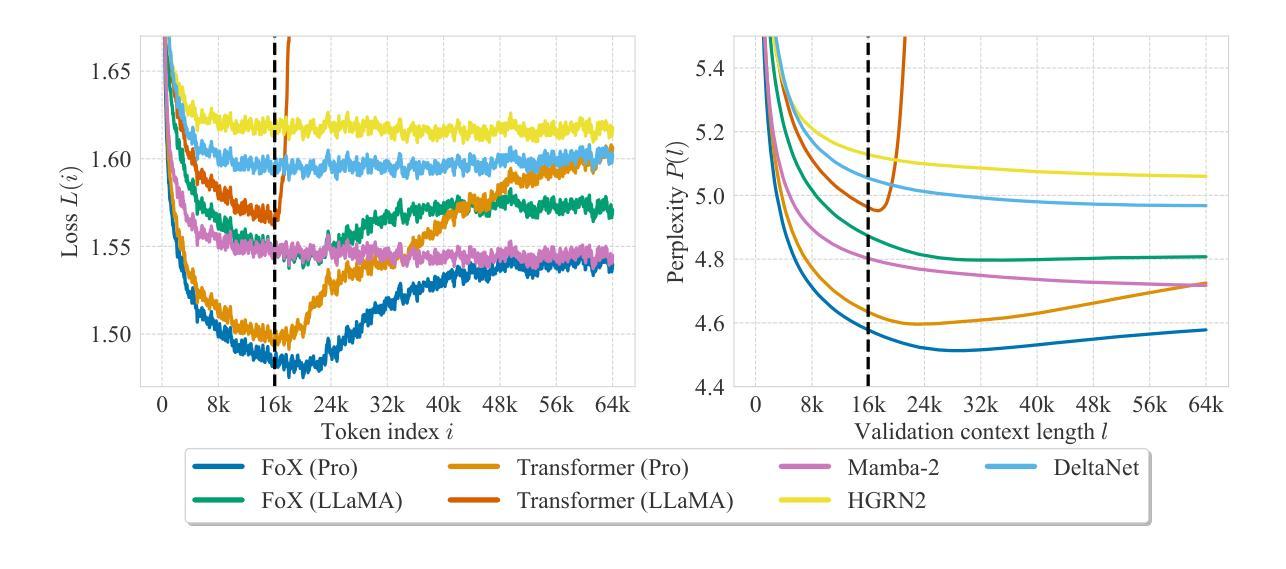
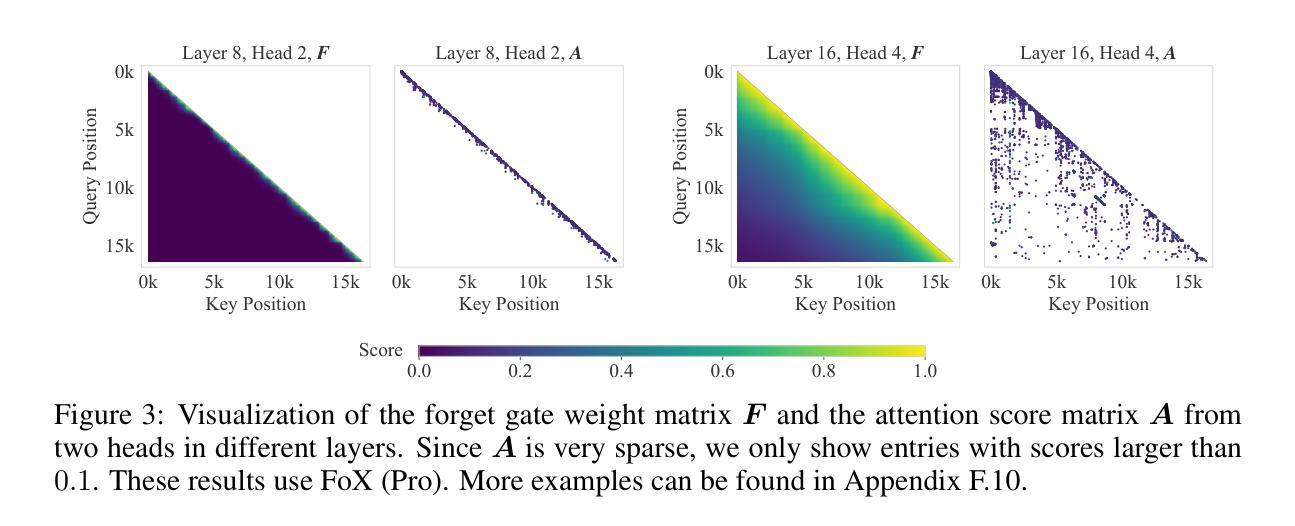
Forgetting Transformer: Softmax Attention with a Forget Gate
Authors:Zhixuan Lin, Evgenii Nikishin, Xu Owen He, Aaron Courville
An essential component of modern recurrent sequence models is the forget gate. While Transformers do not have an explicit recurrent form, we show that a forget gate can be naturally incorporated into Transformers by down-weighting the unnormalized attention scores in a data-dependent way. We name this attention mechanism Forgetting Attention and the resulting model the Forgetting Transformer (FoX). We show that FoX outperforms the Transformer on long-context language modeling, length extrapolation, and short-context downstream tasks, while performing on par with the Transformer on long-context downstream tasks. Moreover, it is compatible with the FlashAttention algorithm and does not require any positional embeddings. Several analyses, including the needle-in-the-haystack test, show that FoX also retains the Transformer’s superior long-context capabilities over recurrent sequence models such as Mamba-2, HGRN2, and DeltaNet. We also introduce a “Pro” block design that incorporates some common architectural components in recurrent sequence models and find it significantly improves the performance of both FoX and the Transformer. Our code is available at https://github.com/zhixuan-lin/forgetting-transformer.
现代循环序列模型的一个重要组成部分是遗忘门。虽然Transformer没有明确的递归形式,我们展示了一种通过数据相关的方式降低未归一化的注意力分数,自然地将遗忘门纳入Transformer的方法。我们将这种注意力机制命名为遗忘注意力,并将得到的模型命名为遗忘转换器(FoX)。我们展示FoX在长上下文语言建模、长度扩展和短上下文下游任务上的性能优于Transformer,同时在长上下文下游任务上的表现与Transformer相当。此外,它与FlashAttention算法兼容,不需要任何位置嵌入。包括“海底捞针”测试在内的几项分析表明,FoX在保持Transformer在长上下文方面的优势的同时,也优于循环序列模型如Mamba-2、HGRN2和DeltaNet等。我们还引入了一种“专业”块设计,它结合了循环序列模型中的一些常见架构组件,发现它能显著提高FoX和Transformer的性能。我们的代码位于https://github.com/zhixuan-lin/forgetting-transformer。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published as a conference paper at ICLR 2025; Fixed an issue with the attention map visualization
Summary
本文介绍了在Transformer模型中引入遗忘门(Forget Gate)的机制,称为遗忘注意力(Forgetting Attention),并由此提出了遗忘变压器(FoX)模型。FoX模型在长文本语言建模、长度扩展和短文本下游任务上优于Transformer,同时在长文本下游任务上的表现与Transformer相当。此外,FoX与FlashAttention算法兼容,无需位置嵌入。分析和测试显示,FoX保留了Transformer在长文本上下文方面的优势,超越了某些递归序列模型。同时,本文还引入了一种结合递归序列模型常见架构组件的“Pro”块设计,显著提高了FoX和Transformer的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 遗忘门机制被自然地融入到Transformer模型中,通过数据相关的方式对未标准化的注意力分数进行下权重处理。
- 提出的FoX模型在长文本语言建模、长度扩展和短文本下游任务上表现出优于Transformer的性能。
- FoX模型与FlashAttention算法兼容,且不需要使用位置嵌入。
- 分析表明,FoX模型保留了Transformer在长文本上下文方面的优势。
- 与某些递归序列模型相比,FoX模型表现更优。
- 引入的“Pro”块设计结合了递归序列模型的常见架构组件,显著提高了FoX和Transformer的性能。
点此查看论文截图

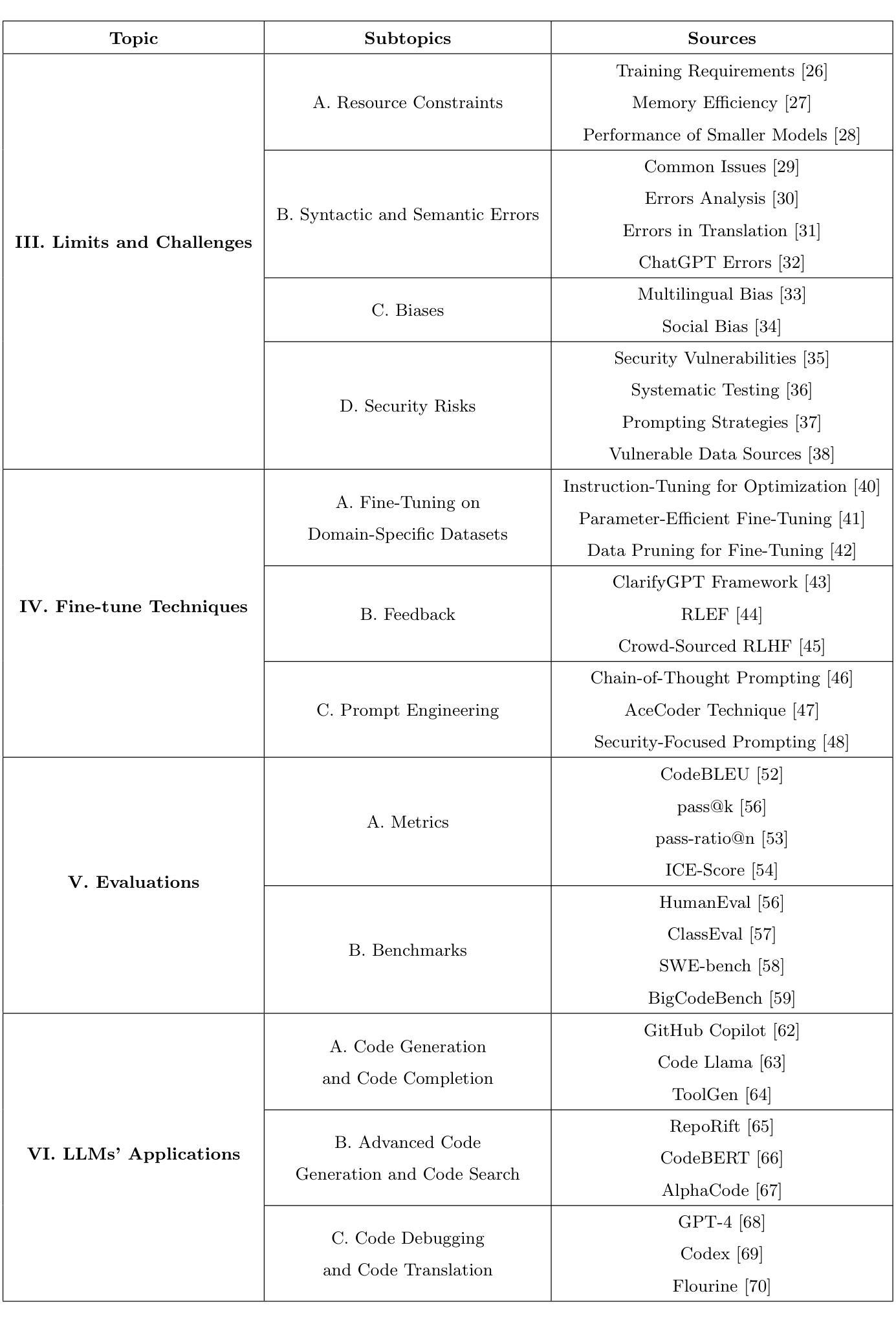
Large Language Models for Code Generation: A Comprehensive Survey of Challenges, Techniques, Evaluation, and Applications
Authors:Nam Huynh, Beiyu Lin
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated their remarkable capabilities in numerous fields. This survey focuses on how LLMs empower users, regardless of their technical background, to use human languages to automatically generate executable code. We begin with understanding LLMs’ limitations and challenges in automated code generation. Subsequently, we review various fine-tuning techniques designed to enhance both the performance and adaptability of LLMs in code generation tasks. We then review the existing metrics and benchmarks for evaluations to assess model performance based on fine-tuning techniques. Finally, we explore the applications of LLMs (e.g. CodeLlama, GitHub Copilot, ToolGen) in code generation tasks to illustrate their roles and functionalities. This survey provides a comprehensive overview of LLMs for code generation, helps researchers in diverse fields better understand the current state-of-the-art technologies, and offers the potential of effectively leveraging LLMs for code generation tasks.
大型语言模型(LLM)已在多个领域展示了其卓越的能力。这篇综述的重点是,无论用户的技术背景如何,LLM如何赋能用户使用自然语言自动生成可执行代码。我们首先了解LLM在自动代码生成方面的局限性和挑战。随后,我们回顾了各种微调技术,旨在提高LLM在代码生成任务中的性能和适应性。然后我们回顾了基于微调技术的评估现有指标和基准测试,以评估模型性能。最后,我们探讨了LLM(例如CodeLlama、GitHub Copilot、ToolGen)在代码生成任务中的应用,以说明它们的作用和功能。这篇综述为代码生成领域的LLM提供了全面的概述,有助于不同领域的研究者更好地了解当前最新技术,并提供了有效利用LLM进行代码生成任务的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在多个领域展现了卓越的能力,特别是在赋能用户利用自然语言自动生成可执行代码方面。本综述先探讨LLMs在自动化代码生成方面的局限和挑战,再评述各种增强模型性能和适应性的微调技术,并评价基于这些技术的模型性能评估指标和基准测试。最后,展示LLMs在代码生成任务中的应用实例(如CodeLlama、GitHub Copilot、ToolGen等),帮助不同领域的研究者了解最新技术,并为有效利用LLMs进行代码生成任务提供潜力。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs已在多个领域展现出强大的能力,特别是在用户利用自然语言自动生成代码方面。
- LLMs在自动化代码生成方面存在局限和挑战,需要研究有效的微调技术来提高性能和适应性。
- 存在多种评估LLMs在代码生成任务中性能的指标和基准测试。
- LLMs在代码生成任务中的应用实例包括CodeLlama、GitHub Copilot和ToolGen等。
- 这些应用展示了LLMs在赋能用户、提高开发效率和促进自动化方面的巨大潜力。
- 综合评述LLMs在代码生成方面的应用有助于研究者了解当前最新技术。
点此查看论文截图


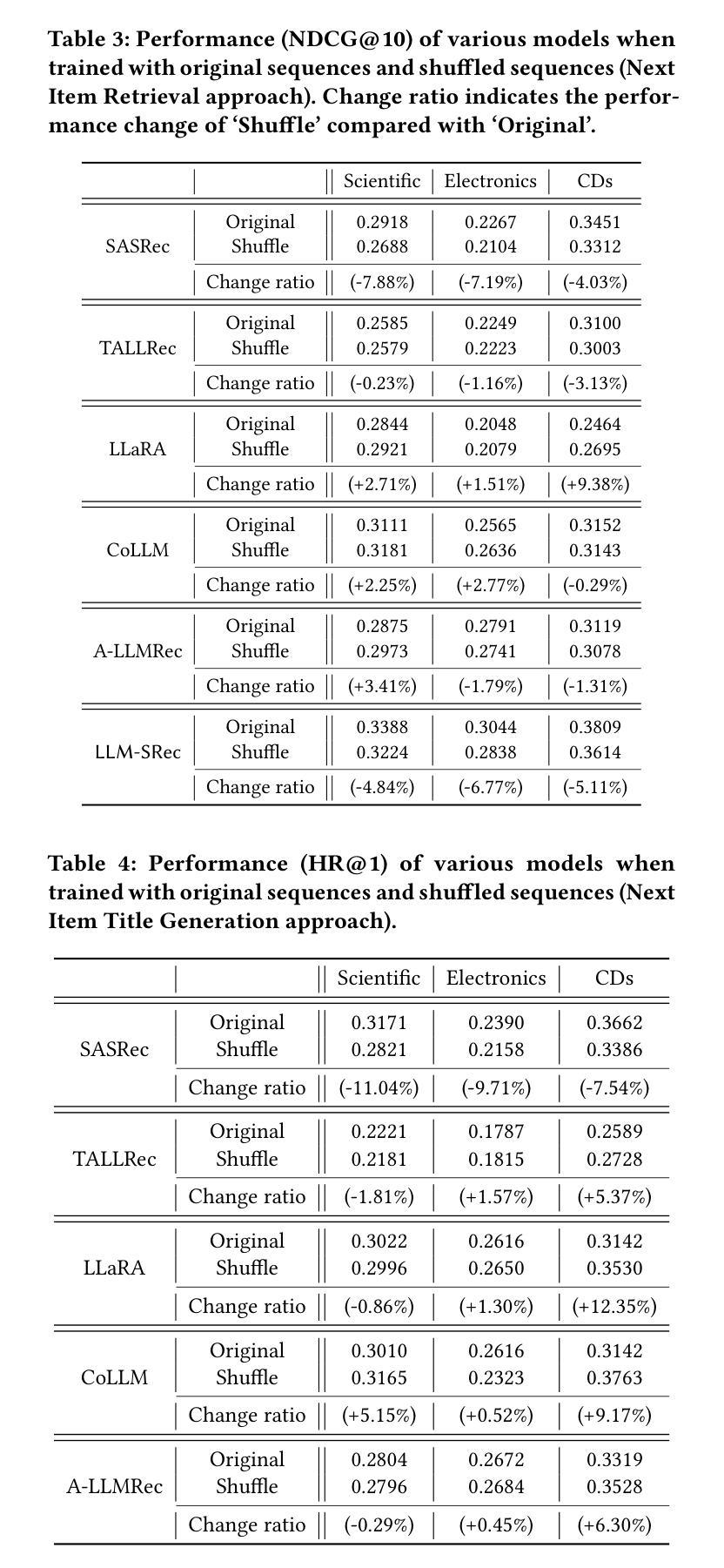
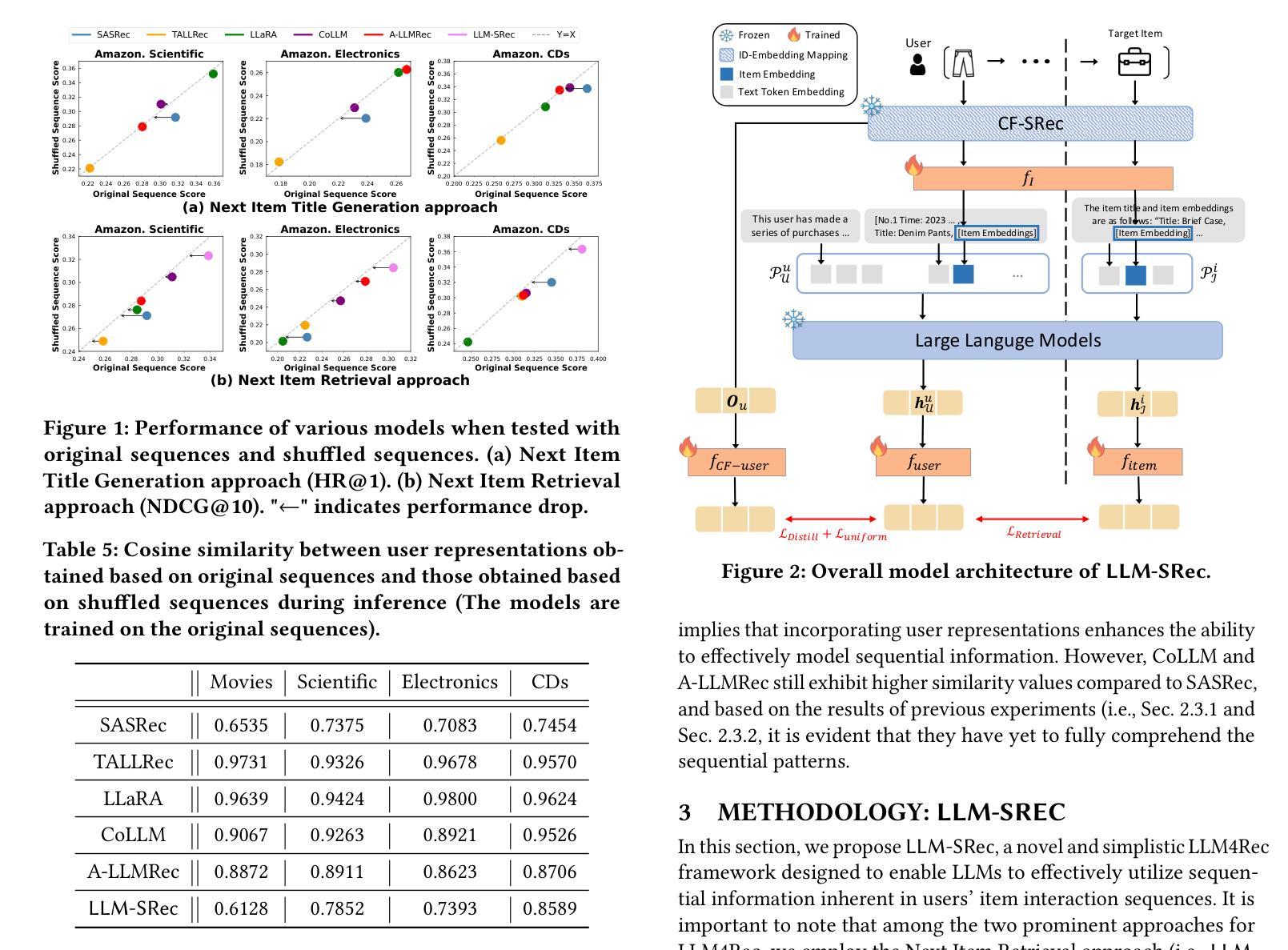
Lost in Sequence: Do Large Language Models Understand Sequential Recommendation?
Authors:Sein Kim, Hongseok Kang, Kibum Kim, Jiwan Kim, Donghyun Kim, Minchul Yang, Kwangjin Oh, Julian McAuley, Chanyoung Park
Large Language Models (LLMs) have recently emerged as promising tools for recommendation thanks to their advanced textual understanding ability and context-awareness. Despite the current practice of training and evaluating LLM-based recommendation (LLM4Rec) models under a sequential recommendation scenario, we found that whether these models understand the sequential information inherent in users’ item interaction sequences has been largely overlooked. In this paper, we first demonstrate through a series of experiments that existing LLM4Rec models do not fully capture sequential information both during training and inference. Then, we propose a simple yet effective LLM-based sequential recommender, called LLM-SRec, a method that enhances the integration of sequential information into LLMs by distilling the user representations extracted from a pre-trained CF-SRec model into LLMs. Our extensive experiments show that LLM-SRec enhances LLMs’ ability to understand users’ item interaction sequences, ultimately leading to improved recommendation performance. Furthermore, unlike existing LLM4Rec models that require fine-tuning of LLMs, LLM-SRec achieves state-of-the-art performance by training only a few lightweight MLPs, highlighting its practicality in real-world applications. Our code is available at https://github.com/Sein-Kim/LLM-SRec.
大型语言模型(LLM)由于其先进的文本理解能力和上下文意识,最近被公认为推荐工具中的有前途的工具。尽管当前在顺序推荐场景下训练和评估基于LLM的推荐(LLM4Rec)模型,但我们发现这些模型是否理解用户项目交互序列中固有的顺序信息却被大大忽视了。在本文中,我们首先通过一系列实验证明,现有的LLM4Rec模型在训练和推理过程中都没有完全捕获顺序信息。然后,我们提出了一种简单有效的基于LLM的顺序推荐器,称为LLM-SRec。这是一种通过蒸馏从预训练的CF-SRec模型中提取的用户表示到LLM中,增强顺序信息融入LLM的方法。我们的大量实验表明,LLM-SRec增强了LLM理解用户项目交互序列的能力,最终提高了推荐性能。此外,与现有的需要微调LLM的LLM4Rec模型不同,LLM-SRec仅通过训练一些轻量级的MLP就实现了最先进的性能,这凸显了其在现实世界应用中的实用性。我们的代码位于https://github.com/Sein-Kim/LLM-SRec。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LLMs用于推荐系统具有先进文本理解和语境感知能力,但现有LLM4Rec模型忽略了对用户物品交互序列中的顺序信息的理解。本文提出一种简单有效的基于LLM的顺序推荐器LLM-SRec,通过蒸馏预训练CF-SRec模型中的用户表示到LLMs中,增强了对顺序信息的整合能力,提高推荐性能,且只需训练少量轻量级MLPs,实用性较高。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs在推荐系统中展现出强大的文本理解和语境感知能力。
- 现有LLM4Rec模型忽略了用户物品交互序列中的顺序信息。
- 本文通过实验证明现有LLM4Rec模型在训练和推理过程中未能充分捕捉顺序信息。
- 提出一种基于LLM的顺序推荐器LLM-SRec,能有效整合顺序信息。
- LLM-SRec通过蒸馏预训练CF-SRec模型中的用户表示到LLMs中,增强了理解用户物品交互序列的能力。
- LLM-SRec提高了推荐性能,达到最新水平。
- LLM-SRec只需训练少量轻量级MLPs,具有实用性,适用于真实世界应用。
点此查看论文截图


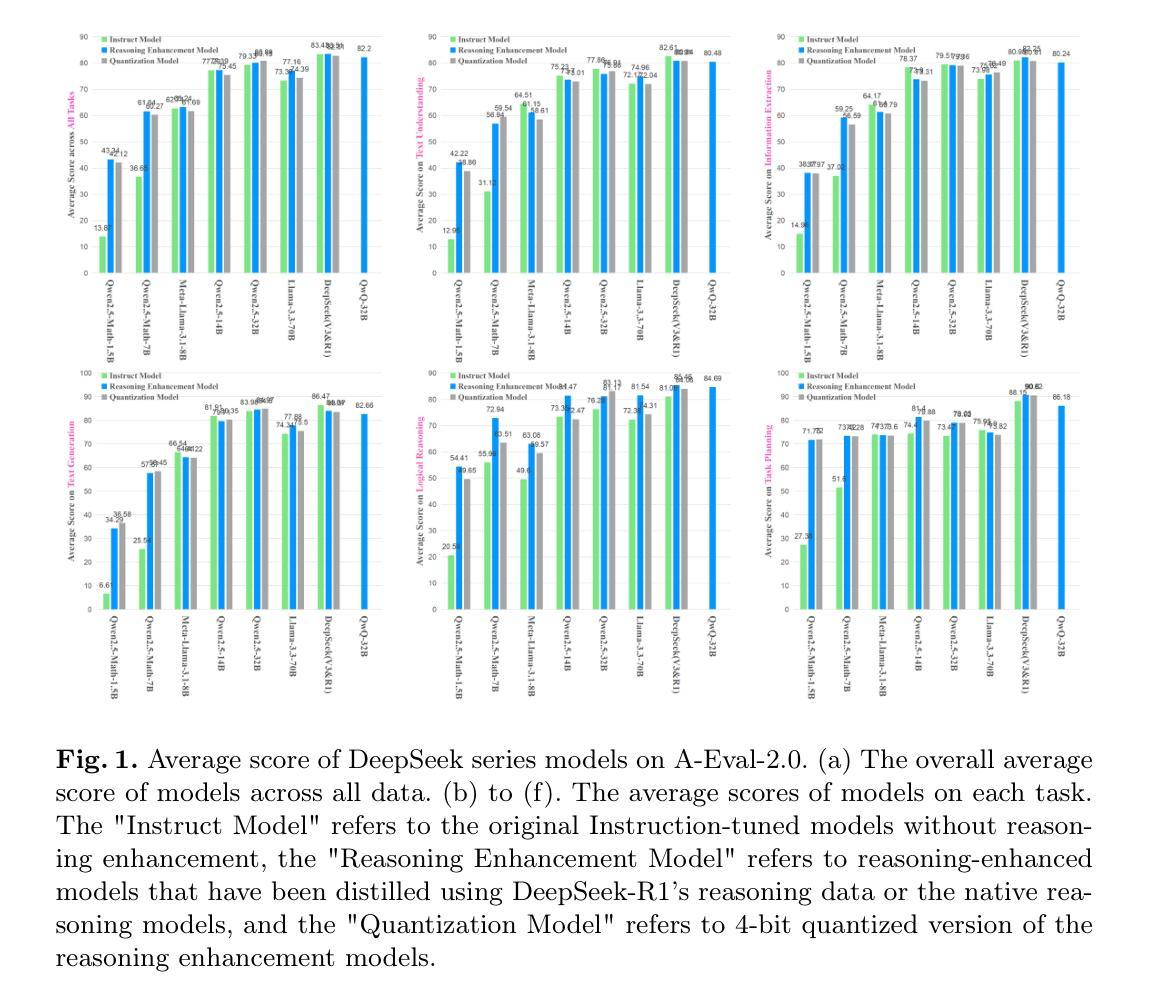
Quantifying the Capability Boundary of DeepSeek Models: An Application-Driven Performance Analysis
Authors:Kaikai Zhao, Zhaoxiang Liu, Xuejiao Lei, Jiaojiao Zhao, Zhenhong Long, Zipeng Wang, Ning Wang, Meijuan An, Qingliang Meng, Peijun Yang, Minjie Hua, Chaoyang Ma, Wen Liu, Kai Wang, Shiguo Lian
DeepSeek-R1, known for its low training cost and exceptional reasoning capabilities, has achieved state-of-the-art performance on various benchmarks. However, detailed evaluations for DeepSeek Series models from the perspective of real-world applications are lacking, making it challenging for users to select the most suitable DeepSeek models for their specific needs. To address this gap, we conduct a systematic evaluation of the DeepSeek-V3, DeepSeek-R1, DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen series, DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama series, their corresponding 4-bit quantized models, and the reasoning model QwQ-32B using the enhanced A-Eval benchmark, A-Eval-2.0. Through a comparative analysis of original instruction-tuned models and their distilled counterparts, we investigate how reasoning enhancements impact performance across diverse practical tasks. To assist users in model selection, we quantify the capability boundary of DeepSeek models through performance tier classifications. Based on the quantification results, we develop a model selection handbook that clearly illustrates the relation among models, their capabilities and practical applications. This handbook enables users to select the most cost-effective models without efforts, ensuring optimal performance and resource efficiency in real-world applications. It should be noted that, despite our efforts to establish a comprehensive, objective, and authoritative evaluation benchmark, the selection of test samples, characteristics of data distribution, and the setting of evaluation criteria may inevitably introduce certain biases into the evaluation results. We will continuously optimize the evaluation benchmarks and periodically update this paper to provide more comprehensive and accurate evaluation results. Please refer to the latest version of the paper for the most current results and conclusions.
DeepSeek-R1以其低训练成本和出色的推理能力而著称,已在各种基准测试上达到了最先进的性能。然而,针对DeepSeek系列模型从现实应用角度的详细评估仍然缺乏,这使得用户难以为其特定需求选择最合适的DeepSeek模型。为了弥补这一空白,我们对DeepSeek-V3、DeepSeek-R1、DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen系列、DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama系列、其对应的4位量化模型以及推理模型QwQ-32B进行了系统的评估,使用的是增强的A-Eval基准测试,即A-Eval-2.0。通过对原始指令调整模型与其蒸馏对应物的比较分析,我们研究了推理增强如何影响各种实际任务上的性能。为了协助用户进行模型选择,我们通过性能分级分类量化了DeepSeek模型的能力边界。基于量化结果,我们开发了模型选择手册,该手册清晰地说明了各模型之间的关系、其能力和实际应用。该手册使用户能够轻松选择最具成本效益的模型,确保在真实应用中的最佳性能和资源效率。值得注意的是,尽管我们努力建立全面、客观、权威的评价基准,但测试样本的选择、数据分布的特征以及评价标准的设定不可避免地会给评价结果带来一定的偏差。我们将不断优化评估基准,并定期更新本文,以提供更全面和准确的评估结果。最新的结果和结论请参考本文的最新版本。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
DeepSeek-R1模型以其低训练成本与出色的推理能力而知名,在各种基准测试中表现卓越。然而,关于DeepSeek系列模型在真实世界应用中的详细评估仍然不足,使得用户难以选择最适合自身需求的DeepSeek模型。为解决此问题,我们对DeepSeek-V3、DeepSeek-R1、DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen系列、DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama系列、其对应的4位量化模型以及推理模型QwQ-32B进行了系统性的评估,采用了增强的A-Eval基准测试,即A-Eval-2.0。我们比较分析了原始指令调整模型与其蒸馏对应物,探讨推理增强如何影响各种实际任务的性能。为了帮助用户选择模型,我们通过性能分级量化了DeepSeek模型的能力边界,并据此开发了模型选择手册,清晰地说明了各模型之间的关系、其能力和实际应用。该手册旨在帮助用户轻松选择最具成本效益的模型,确保在真实世界应用中实现最佳性能和资源效率。需要指出的是,尽管我们努力建立全面、客观、权威的评估基准,但测试样本的选择、数据分布的特征以及评估标准的设定可能会给评估结果带来一定的偏差。我们将持续优化评估基准并定期更新本文,以提供更全面、准确的评估结果。最新结果和结论请参阅本文最新版本。
关键见解
- DeepSeek-R1模型在多种基准测试中表现卓越,但其在实际应用中的性能评估仍然不足。
- 通过对DeepSeek系列模型的全面评估,采用了增强的A-Eval基准测试,即A-Eval-2.0。
- 比较分析了原始指令调整模型与蒸馏模型的推理能力,展示了其在实际任务中的性能差异。
- 通过性能分级量化模型能力边界,为用户提供更清晰的模型选择依据。
- 开发了模型选择手册,帮助用户轻松选择最适合其需求的成本效益高的模型。
- 评估过程中存在的偏差主要源于测试样本选择、数据分布特征以及评估标准设定。
点此查看论文截图

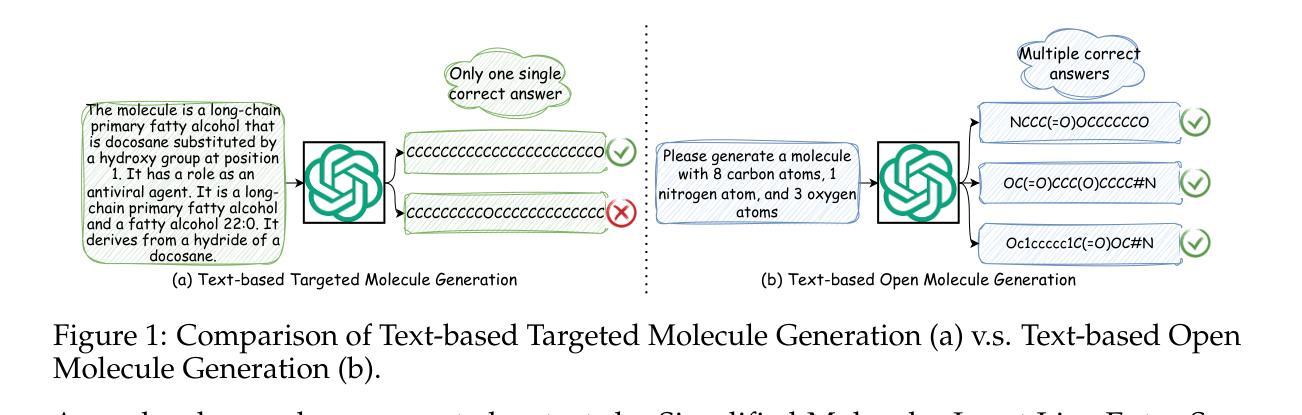
TOMG-Bench: Evaluating LLMs on Text-based Open Molecule Generation
Authors:Jiatong Li, Junxian Li, Yunqing Liu, Dongzhan Zhou, Qing Li
In this paper, we propose Text-based Open Molecule Generation Benchmark (TOMG-Bench), the first benchmark to evaluate the open-domain molecule generation capability of LLMs. TOMG-Bench encompasses a dataset of three major tasks: molecule editing (MolEdit), molecule optimization (MolOpt), and customized molecule generation (MolCustom). Each major task further contains three subtasks, while each subtask comprises 5,000 test samples. Given the inherent complexity of open molecule generation evaluation, we also developed an automated evaluation system that helps measure both the quality and the accuracy of the generated molecules. Our comprehensive benchmarking of 25 LLMs reveals the current limitations as well as potential areas for improvement in text-guided molecule discovery. Furthermore, we propose OpenMolIns, a specialized instruction tuning dataset established for solving challenges raised by TOMG-Bench. Fine-tuned on OpenMolIns, Llama3.1-8B could outperform all the open-source general LLMs, even surpassing GPT-3.5-turbo by 46.5% on TOMG-Bench. Our codes and datasets are available through https://github.com/phenixace/TOMG-Bench.
本文提出了基于文本的开放分子生成基准测试(TOMG-Bench),这是第一个评估大型语言模型在开放域分子生成能力方面的基准测试。TOMG-Bench包含三大任务的数据集:分子编辑(MolEdit)、分子优化(MolOpt)和定制分子生成(MolCustom)。每个主要任务还包括三个子任务,每个子任务包含5000个测试样本。考虑到开放分子生成评价的固有复杂性,我们还开发了一个自动评估系统,帮助衡量生成分子的质量和准确性。我们对25个大型语言模型进行的全面基准测试揭示了当前文本指导分子发现方面的局限性以及潜在的改进领域。此外,我们提出了OpenMolIns,这是一个专门为解决TOMG-Bench提出的挑战而建立的专业指令调整数据集。在OpenMolIns上微调的Llama3.1-8B能够超越所有开源的大型语言模型,在TOMG-Bench上的表现甚至超过了GPT-3.5 Turbo的46.5%。我们的代码和数据集可通过https://github.com/phenixace/TOMG-Bench获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The first benchmark for text-based open molecule generation
Summary:
本文提出了基于文本的开放分子生成基准测试(TOMG-Bench),这是第一个评估大型语言模型(LLMs)在开放域分子生成能力方面的基准测试。TOMG-Bench包括三个主要任务:分子编辑(MolEdit)、分子优化(MolOpt)和定制分子生成(MolCustom)。每个主要任务包含三个子任务,每个子任务包含5000个测试样本。为评估生成的分子质量和准确性,还开发了自动化评估系统。对25个LLMs的全面基准测试揭示了文本引导分子发现领域的当前局限性和潜在改进方向。此外,为应对TOMG-Bench提出的挑战,还推出了OpenMolIns专用指令调整数据集。在OpenMolIns上经过微调的Llama3.1-8B性能超越所有开源通用LLMs,在TOMG-Bench上的表现比GPT-3.5-turbo高出46.5%。相关代码和数据集可通过https://github.com/phenixace/TOMG-Bench获取。
Key Takeaways:
- 提出了基于文本的开放分子生成基准测试(TOMG-Bench),用于评估LLMs在开放域分子生成方面的能力。
- TOMG-Bench包含三个主要任务:分子编辑、分子优化和定制分子生成。
- 开发了自动化评估系统,以衡量生成分子的质量和准确性。
- 对25个LLMs的基准测试揭示了文本引导分子发现领域的局限性和潜在改进方向。
- 推出了OpenMolIns专用指令调整数据集,以应对TOMG-Bench的挑战。
- Llama3.1-8B在OpenMolIns上经过微调后,性能超越其他LLMs,在TOMG-Bench上的表现显著。
点此查看论文截图

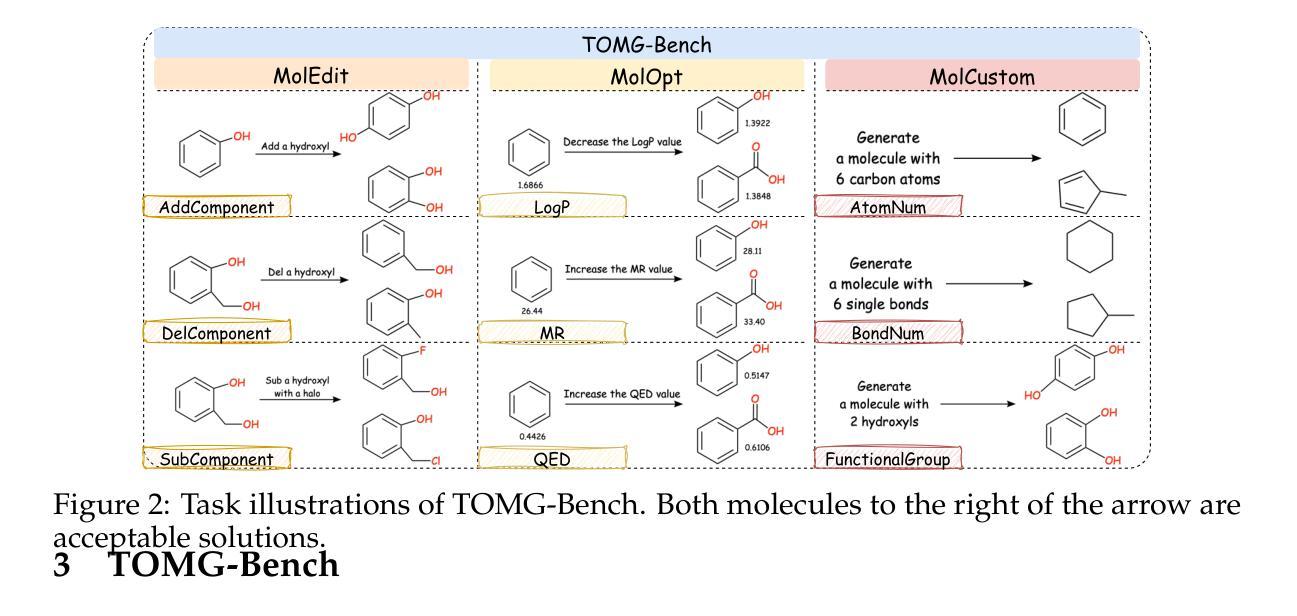

VERA: Explainable Video Anomaly Detection via Verbalized Learning of Vision-Language Models
Authors:Muchao Ye, Weiyang Liu, Pan He
The rapid advancement of vision-language models (VLMs) has established a new paradigm in video anomaly detection (VAD): leveraging VLMs to simultaneously detect anomalies and provide comprehendible explanations for the decisions. Existing work in this direction often assumes the complex reasoning required for VAD exceeds the capabilities of pretrained VLMs. Consequently, these approaches either incorporate specialized reasoning modules during inference or rely on instruction tuning datasets through additional training to adapt VLMs for VAD. However, such strategies often incur substantial computational costs or data annotation overhead. To address these challenges in explainable VAD, we introduce a verbalized learning framework named VERA that enables VLMs to perform VAD without model parameter modifications. Specifically, VERA automatically decomposes the complex reasoning required for VAD into reflections on simpler, more focused guiding questions capturing distinct abnormal patterns. It treats these reflective questions as learnable parameters and optimizes them through data-driven verbal interactions between learner and optimizer VLMs, using coarsely labeled training data. During inference, VERA embeds the learned questions into model prompts to guide VLMs in generating segment-level anomaly scores, which are then refined into frame-level scores via the fusion of scene and temporal contexts. Experimental results on challenging benchmarks demonstrate that the learned questions of VERA are highly adaptable, significantly improving both detection performance and explainability of VLMs for VAD.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)的快速发展为视频异常检测(VAD)建立了一种新的范式:利用VLMs同时检测异常并为决策提供可理解的解释。现有工作往往假设VAD所需的复杂推理超出了预训练VLMs的能力。因此,这些方法要么在推理过程中融入了专门的推理模块,要么通过额外的训练依赖于指令调整数据集来适应VLMs进行VAD。然而,这些策略通常会导致巨大的计算成本或数据注释开销。为了应对可解释VAD中的这些挑战,我们引入了一种名为VERA的言语化学习框架,它使VLMs能够执行VAD而无需修改模型参数。具体来说,VERA自动将VAD所需的复杂推理分解为对更简单、更集中的引导问题的反思,捕捉不同的异常模式。它将这些反思问题视为可学习的参数,通过学习者与优化器VLMs之间的数据驱动言语交互来优化它们,使用粗略标记的训练数据。在推理过程中,VERA将学习到的问题嵌入到模型提示中,以指导VLMs生成分段级别的异常分数,然后通过场景和时态上下文的融合将这些分数细化为帧级别分数。在具有挑战性的基准测试上的实验结果表明,VERA学习的问题高度自适应,显著提高了VLMs在VAD方面的检测性能和解释性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了视觉语言模型(VLMs)在视频异常检测(VAD)中的新应用模式。传统方法常常需要额外的推理模块或指令调整数据集来适应VAD需求,这带来了大量的计算成本或数据标注负担。为解决这些问题,本文提出了一种名为VERA的言语化学习框架,使VLMs能够在无需修改模型参数的情况下进行VAD。VERA通过数据驱动的言语交互,将复杂的VAD推理分解为对简单指导问题的反思,进而优化这些反思问题。在推理过程中,VERA将学习的问题嵌入模型提示中,指导VLMs生成分段级别的异常分数,并通过场景和时间上下文的融合,将其细化为帧级别的分数。实验结果表明,VERA学习的问题具有高度适应性,显著提高了VLMs在VAD中的检测性能和解释性。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)在视频异常检测(VAD)中建立了新的应用模式。
- 现有方法常常需要额外的推理模块或指令调整数据集,带来计算成本和数据标注负担。
- VERA框架使VLMs无需修改模型参数即可进行VAD。
- VERA通过数据驱动的言语交互自动分解复杂的VAD推理,并优化反映问题。
- VERA将学习的问题嵌入模型提示中,指导生成分段级别的异常分数。
- 通过场景和时间上下文的融合,VERA将异常分数细化为帧级别的分数。
点此查看论文截图

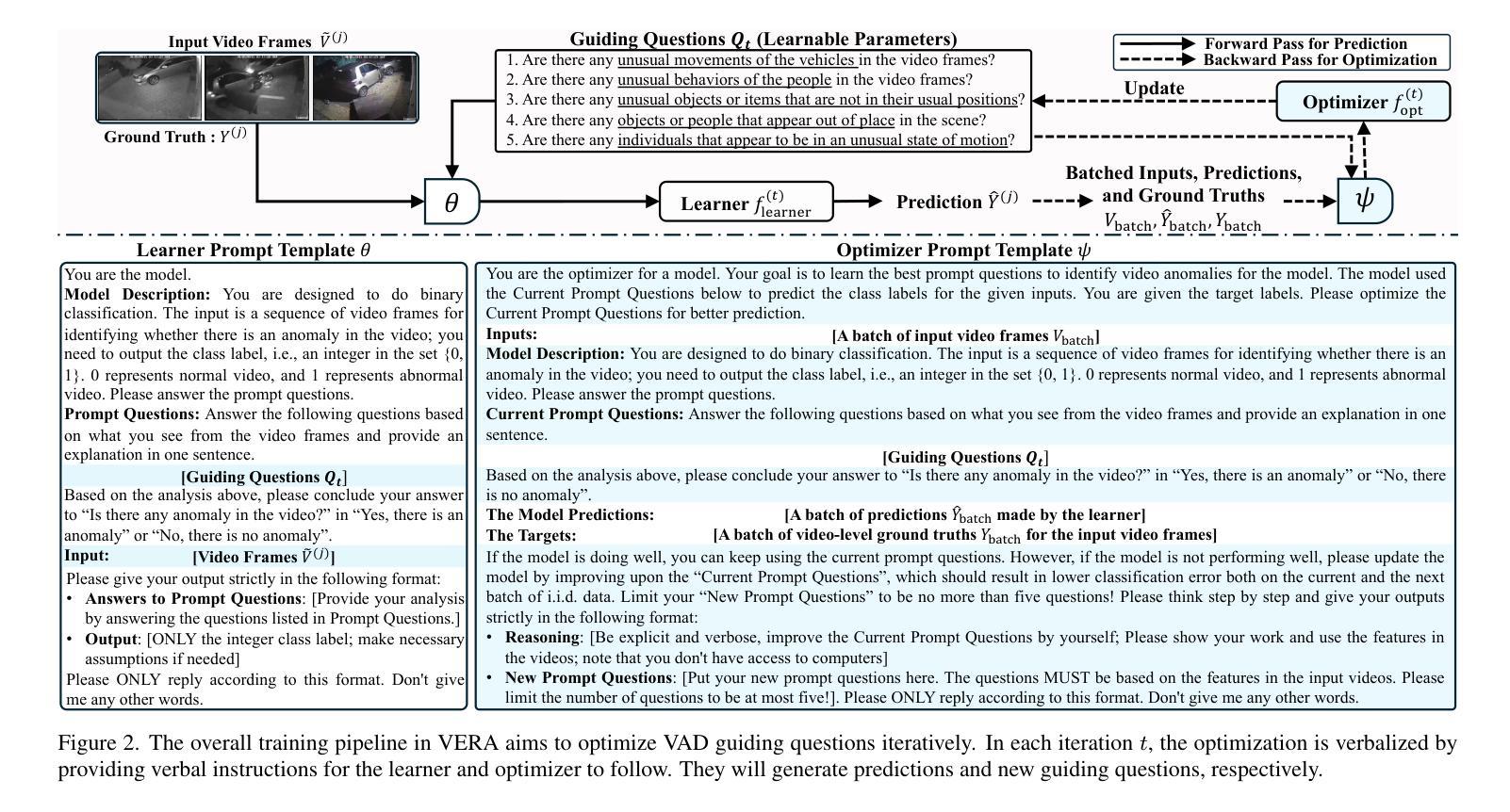
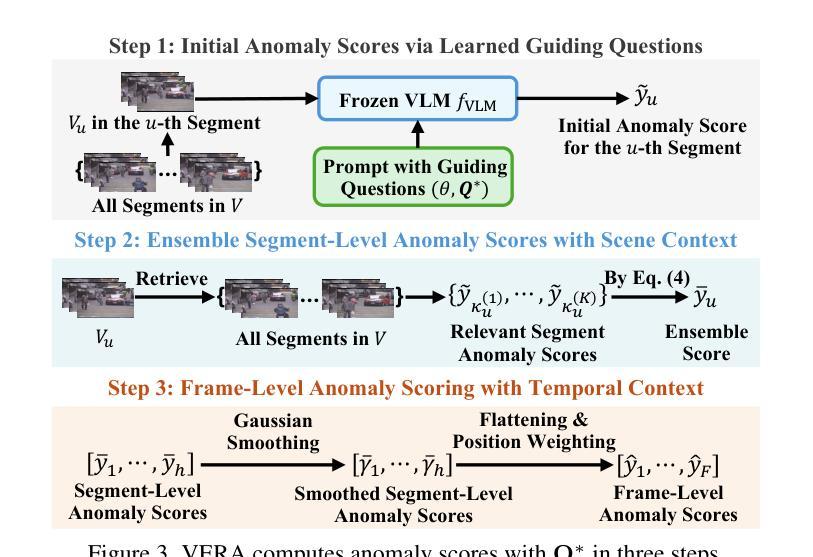
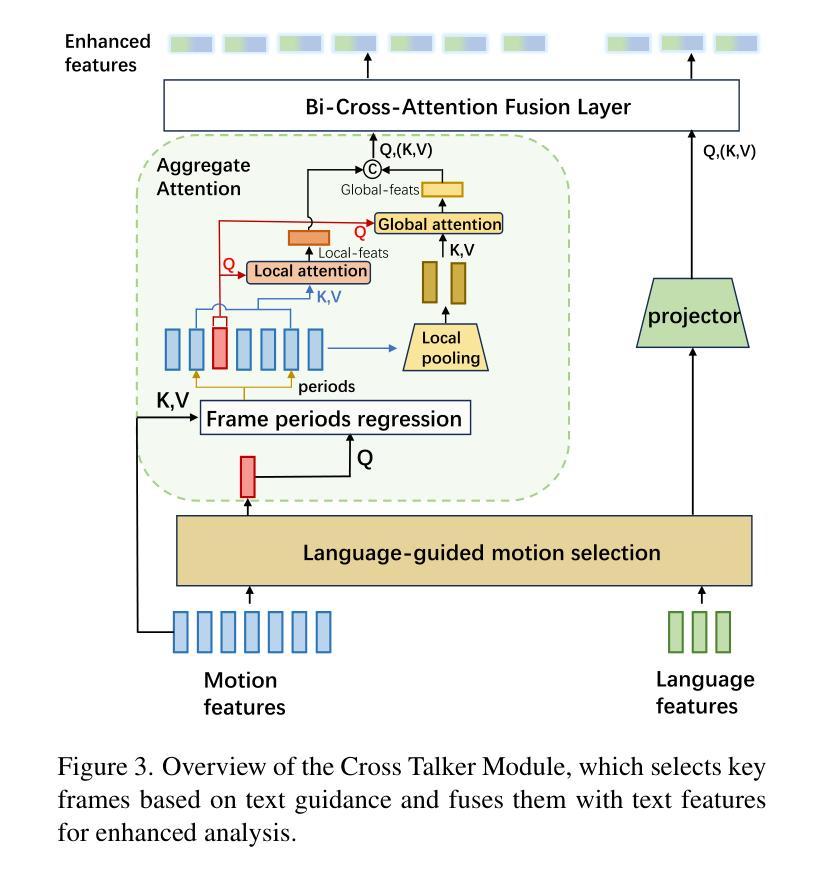
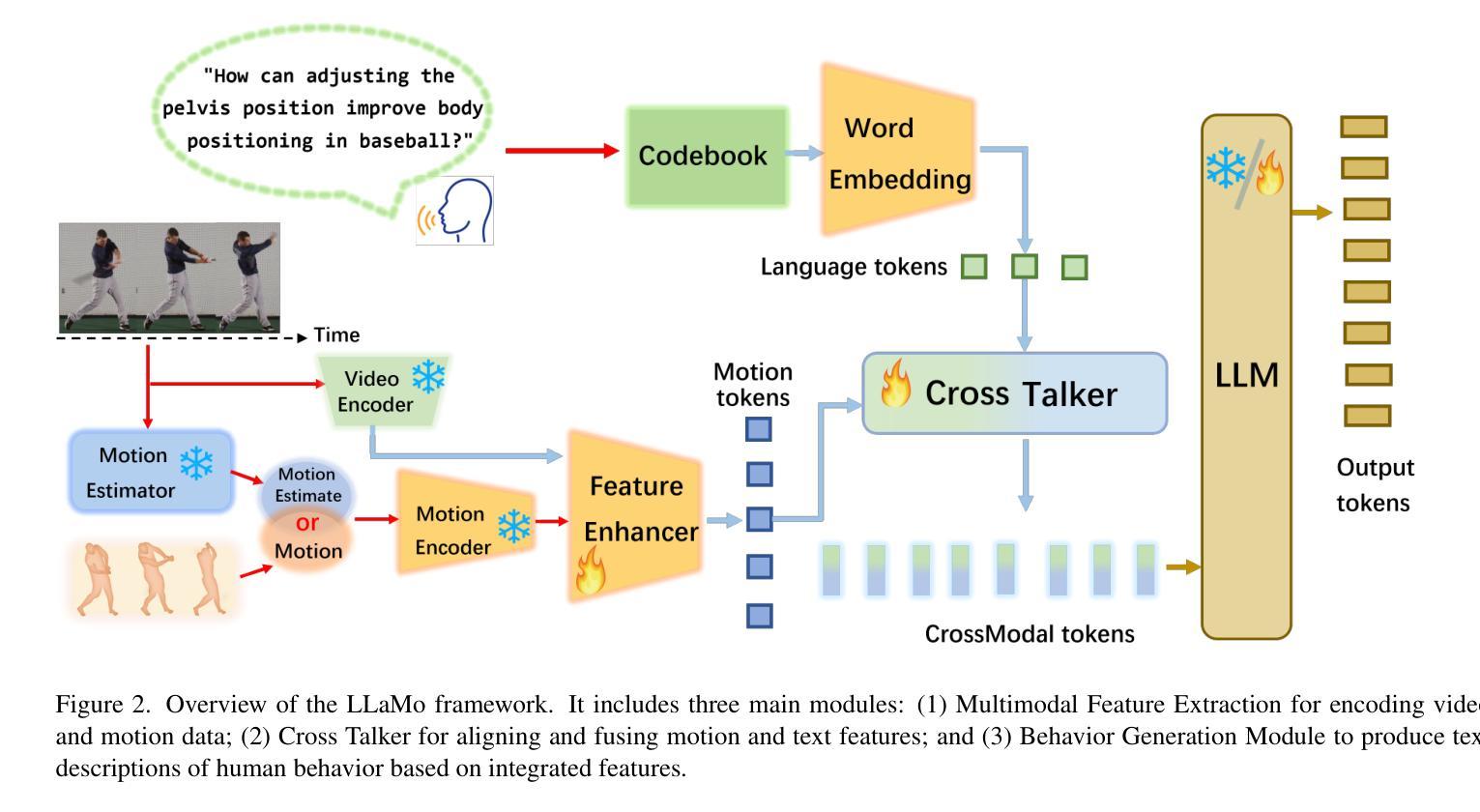
Human Motion Instruction Tuning
Authors:Lei Li, Sen Jia, Jianhao Wang, Zhongyu Jiang, Feng Zhou, Ju Dai, Tianfang Zhang, Zongkai Wu, Jenq-Neng Hwang
This paper presents LLaMo (Large Language and Human Motion Assistant), a multimodal framework for human motion instruction tuning. In contrast to conventional instruction-tuning approaches that convert non-linguistic inputs, such as video or motion sequences, into language tokens, LLaMo retains motion in its native form for instruction tuning. This method preserves motion-specific details that are often diminished in tokenization, thereby improving the model’s ability to interpret complex human behaviors. By processing both video and motion data alongside textual inputs, LLaMo enables a flexible, human-centric analysis. Experimental evaluations across high-complexity domains, including human behaviors and professional activities, indicate that LLaMo effectively captures domain-specific knowledge, enhancing comprehension and prediction in motion-intensive scenarios. We hope LLaMo offers a foundation for future multimodal AI systems with broad applications, from sports analytics to behavioral prediction. Our code and models are available on the project website: https://github.com/ILGLJ/LLaMo.
本文介绍了LLaMo(大型语言和人类运动助理),这是一个用于人类运动指令调整的多模式框架。与传统的将非语言输入(如视频或运动序列)转换为语言标记的指令调整方法不同,LLaMo以原始形式保留运动来进行指令调整。这种方法保留了运动特定的细节,这些细节在标记化时往往会减少,从而提高了模型解释复杂人类行为的能力。通过同时处理视频和运动数据以及文本输入,LLaMo实现了以人为中心的分析灵活性。在人类行为和专业活动等高复杂度领域的实验评估表明,LLaMo有效地捕获了特定领域的知识,提高了运动密集型场景中的理解和预测能力。我们希望LLaMo能为从体育分析到行为预测具有广泛应用领域的未来多模式AI系统提供基础。我们的代码和模型可在项目网站上获得:https://github.com/ILGLJ/LLaMo。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
LLaMo框架是一种用于人类运动指令调整的多模态框架,能够保持运动的本体形式进行指令调整,提升模型对人类复杂行为的解读能力。
Key Takeaways
- LLaMo是一种多模态框架,用于人类运动指令调整。
- 与传统将非语言输入转换为语言标记的指令调整方法不同,LLaMo保持运动的本体形式进行指令调整。
- LLaMo通过处理视频和运动数据与文本输入,实现了灵活、以人类为中心的分析。
- LLaMo能有效捕捉高复杂度领域的特定知识,提升在运动密集型场景中的理解和预测能力。
- LLaMo框架在诸如体育分析和行为预测等领域具有广泛的应用前景。
- LLaMo的代码和模型已发布在项目的网站上。
点此查看论文截图
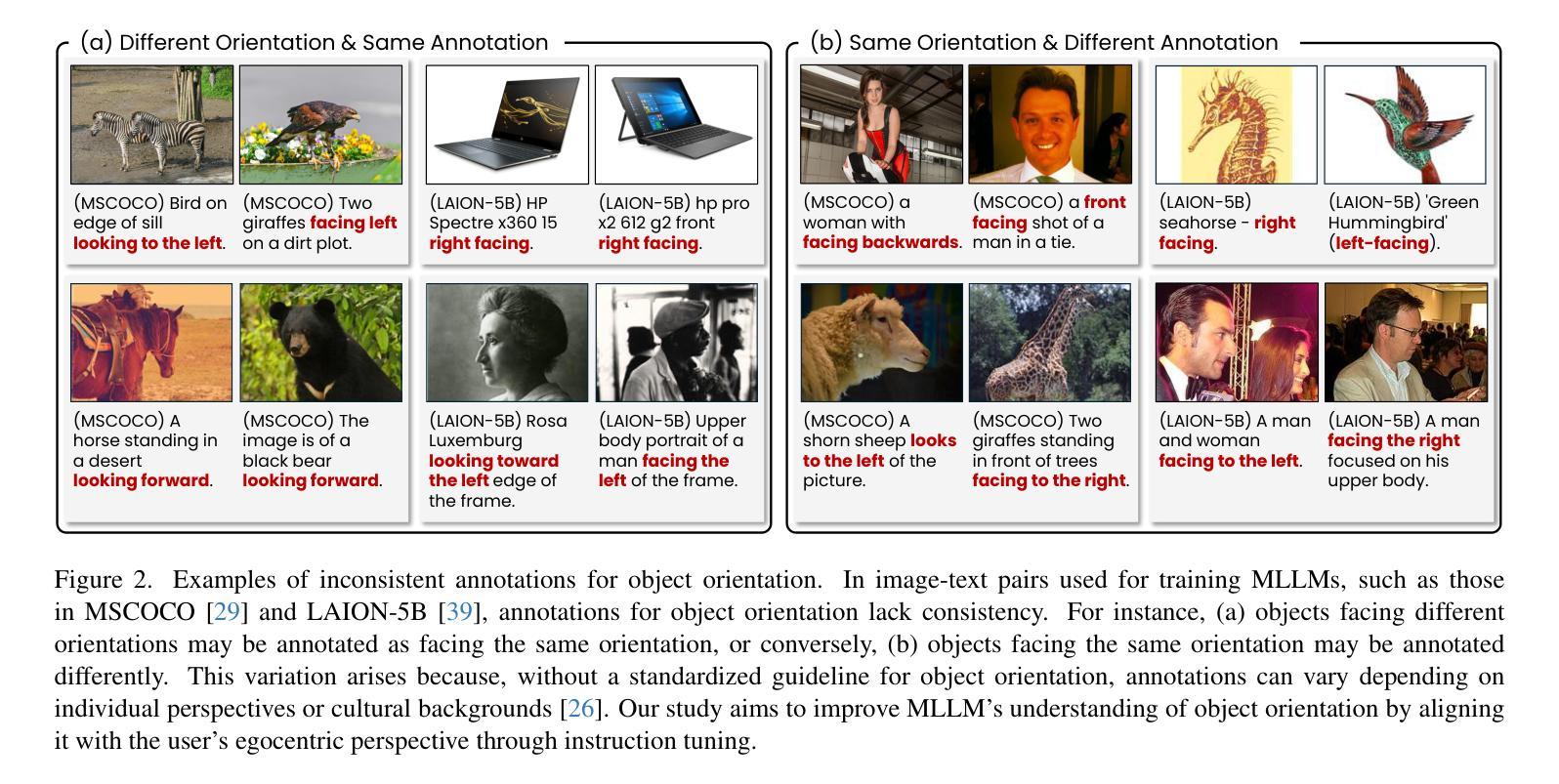
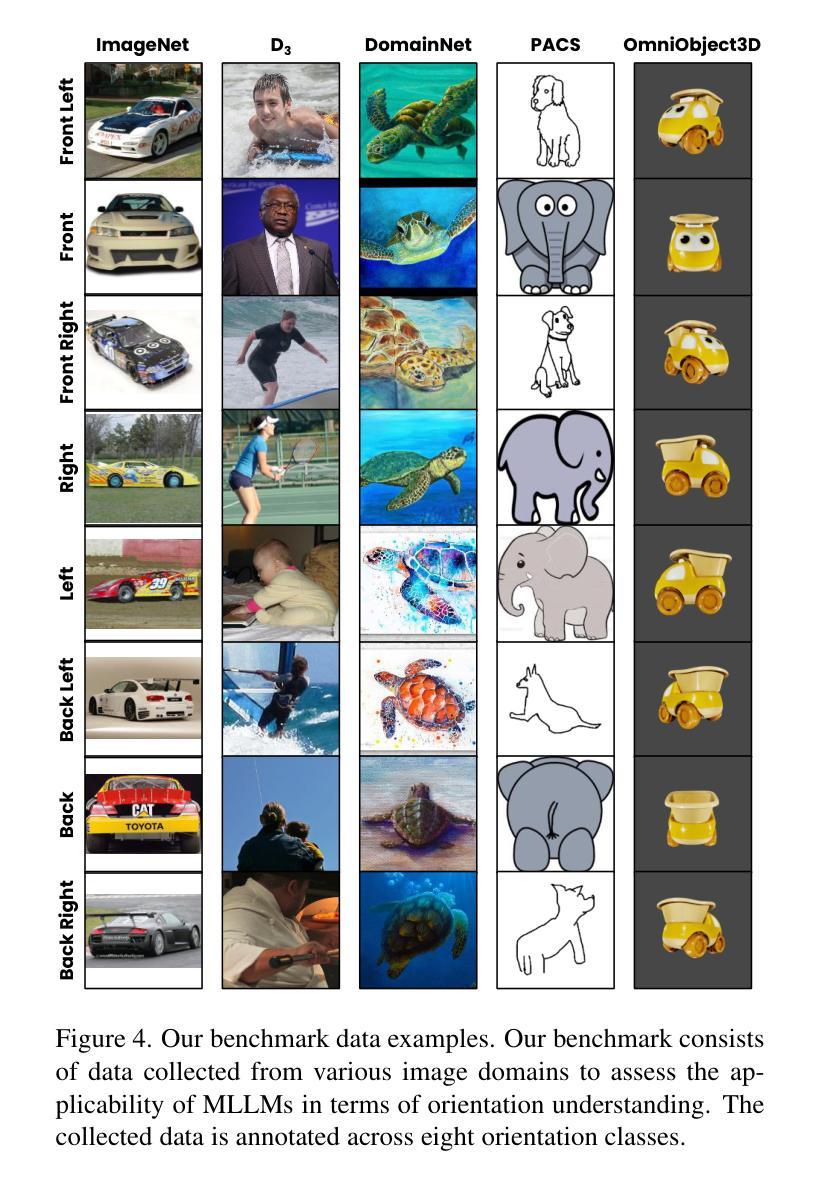
Is ‘Right’ Right? Enhancing Object Orientation Understanding in Multimodal Large Language Models through Egocentric Instruction Tuning
Authors:Ji Hyeok Jung, Eun Tae Kim, Seoyeon Kim, Joo Ho Lee, Bumsoo Kim, Buru Chang
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) act as essential interfaces, connecting humans with AI technologies in multimodal applications. However, current MLLMs face challenges in accurately interpreting object orientation in images due to inconsistent orientation annotations in training data, hindering the development of a coherent orientation understanding. To overcome this, we propose egocentric instruction tuning, which aligns MLLMs’ orientation understanding with the user’s perspective, based on a consistent annotation standard derived from the user’s egocentric viewpoint. We first generate egocentric instruction data that leverages MLLMs’ ability to recognize object details and applies prior knowledge for orientation understanding. Using this data, we perform instruction tuning to enhance the model’s capability for accurate orientation interpretation. In addition, we introduce EgoOrientBench, a benchmark that evaluates MLLMs’ orientation understanding across three tasks using images collected from diverse domains. Experimental results on this benchmark show that egocentric instruction tuning significantly improves orientation understanding without compromising overall MLLM performance. The instruction data and benchmark dataset are available on our project page at https://github.com/jhCOR/EgoOrientBench.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)作为人类与多模态应用程序中的AI技术之间的重要接口。然而,由于训练数据中的方向标注不一致,当前的MLLMs在准确解释图像中的对象方向方面面临挑战,这阻碍了连贯的方向理解的发展。为了克服这一问题,我们提出了以自我为中心(第一人称视角)的指令调整方法,它将MLLMs的方向理解与用户的视角对齐,基于从用户的自我中心视角得出的一致标注标准。我们首先生成利用MLLMs识别对象细节和应用方向理解的先验知识的自我中心指令数据。使用这些数据,我们执行指令调整,以增强模型对准确方向解释的能力。此外,我们还介绍了EgoOrientBench基准测试,该基准测试通过从多个领域收集的图像对MLLMs的方向理解能力进行评估,包括三个任务。在此基准测试上的实验结果表明,以自我为中心的指令调整在不影响MLLM整体性能的前提下,显著提高了方向理解能力。指令数据和基准数据集可在我们的项目页面https://github.com/jhCOR/EgoOrientBench上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR2025 Camera-ready
Summary
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)作为人类与AI技术之间的关键接口,在多模态应用中扮演着重要角色。然而,由于训练数据中方位标注的不一致性,MLLMs在准确解释图像中的对象方位方面存在挑战,制约了其方位理解的连贯性发展。为解决这个问题,我们提出了以用户视角为中心的指令调整方法,基于用户视角的一致标注标准来对齐MLLMs的方位理解。我们首先生成以用户为中心的指令数据,利用MLLMs识别对象细节的能力,并应用方位理解的先验知识。利用这些数据,我们进行指令调整,提高模型准确解释方位的能力。此外,我们还介绍了EgoOrientBench基准测试,该测试在三个任务中评估MLLMs的方位理解,使用了来自不同领域的图像。在EgoOrientBench上的实验结果表明,以用户视角为中心的指令调整在显著提高方位理解的同时,不损害MLLM的整体性能。
Key Takeaways
- MLLMs在多模态应用中作为人类与AI之间的接口,具有关键作用。
- 训练数据中方位标注的不一致性影响了MLLMs准确解释图像中的对象方位。
- 提出以用户视角为中心的指令调整方法,以改善MLLMs的方位理解连贯性。
- 利用生成的以用户为中心的指令数据,结合MLLMs的识别能力和先验知识。
- 通过指令调整提高模型准确解释方位的能力。
- 引入EgoOrientBench基准测试,评估MLLMs在不同任务中的方位理解性能。
点此查看论文截图


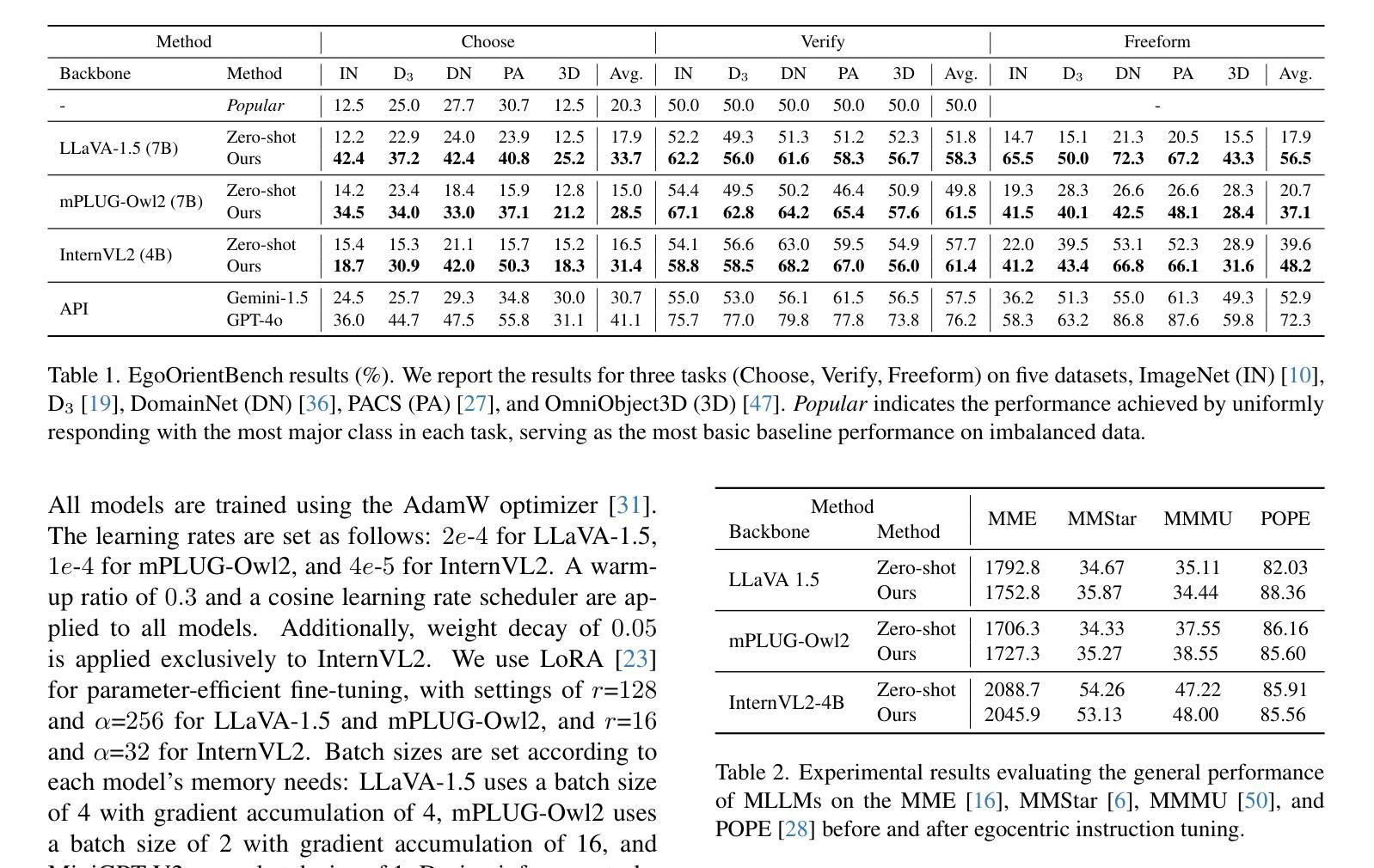
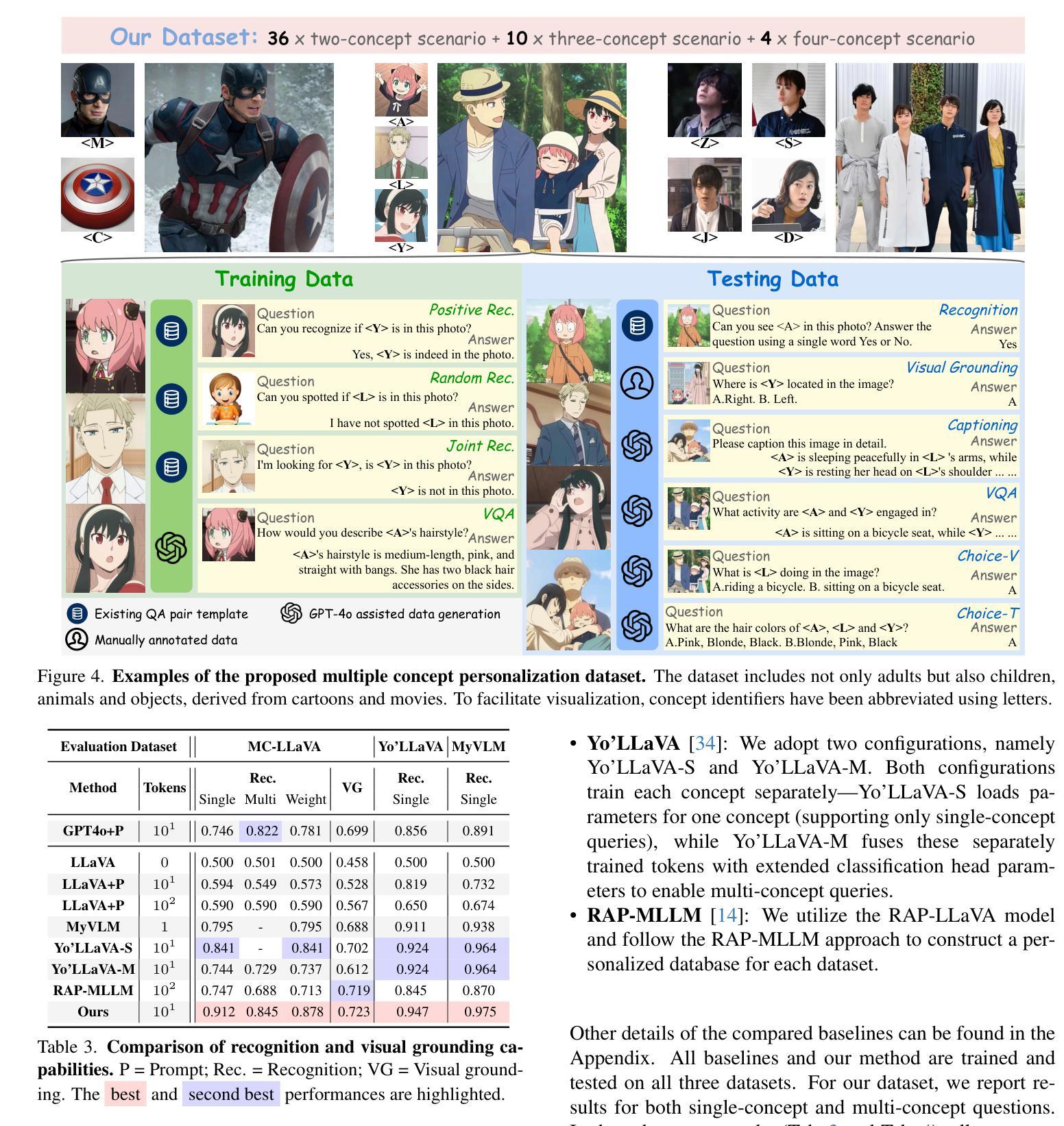
MC-LLaVA: Multi-Concept Personalized Vision-Language Model
Authors:Ruichuan An, Sihan Yang, Ming Lu, Renrui Zhang, Kai Zeng, Yulin Luo, Jiajun Cao, Hao Liang, Ying Chen, Qi She, Shanghang Zhang, Wentao Zhang
Current vision-language models (VLMs) show exceptional abilities across diverse tasks, such as visual question answering. To enhance user experience, recent studies investigate VLM personalization to understand user-provided concepts. However, they mainly focus on single-concept personalization, neglecting the existence and interplay of multiple concepts, which limits real-world applicability. This paper proposes the first multi-concept personalization paradigm, MC-LLaVA. Specifically, MC-LLaVA employs a multi-concept instruction tuning strategy, effectively integrating multiple concepts in a single training step. To reduce the costs related to joint training, we propose a personalized textual prompt that uses visual token information to initialize concept tokens. Additionally, we introduce a personalized visual prompt during inference, aggregating location confidence maps for enhanced recognition and grounding capabilities. To advance multi-concept personalization research, we further contribute a high-quality instruction tuning dataset. We carefully collect images with multiple characters and objects from movies and manually generate question-answer samples for multi-concept scenarios, featuring superior diversity. Comprehensive qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate that MC-LLaVA can achieve impressive multi-concept personalized responses, paving the way for VLMs to become better user-specific assistants. The code and dataset will be publicly available at https://github.com/arctanxarc/MC-LLaVA.
当前的语言视觉模型(VLMs)在多种任务中表现出卓越的能力,如视觉问答。为了提升用户体验,近期的研究致力于对VLM进行个性化,以理解用户提供的概念。然而,它们主要关注单一概念的个性化,忽略了多个概念的存在和相互作用,这限制了其在现实世界中的应用性。本文提出了首个多概念个性化范式MC-LLaVA。具体来说,MC-LLaVA采用了一种多概念指令调整策略,能够在单个训练步骤中有效地集成多个概念。为了降低联合训练的成本,我们提出了一种个性化的文本提示,利用视觉令牌信息来初始化概念令牌。此外,我们在推理过程中引入了个性化的视觉提示,通过汇总位置置信图来增强识别和接地能力。为了推动多概念个性化研究的发展,我们进一步贡献了一个高质量的指令调整数据集。我们从电影中精心收集了含有多个角色和对象的图像,并手动为多个概念场景生成问答样本,具有出色的多样性。综合的定性和定量实验表明,MC-LLaVA可以实现令人印象深刻的多概念个性化响应,为VLMs成为更好的用户特定助手铺平了道路。代码和数据集将在https://github.com/arctanxarc/MC-LLaVA上公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多概念个性化视觉语言模型研究。针对现有模型忽略多概念的问题,提出MC-LLaVA模型,采用多概念指令调整策略,在单一训练步骤中有效整合多个概念。利用视觉标记信息初始化概念标记,降低联合训练成本。引入个性化文本提示和个性化视觉提示,提高识别和多模态定位能力。贡献高质量指令调整数据集,促进多概念个性化研究的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 当前视觉语言模型(VLMs)在多种任务上表现出卓越的能力,如视觉问答。
- 近期研究着眼于VLM个性化,以理解用户提供的概念。
- 现有研究主要关注单概念个性化,忽略了多概念的存在和相互作用。
- MC-LLaVA模型首次提出多概念个性化范式。
- MC-LLaVA采用多概念指令调整策略,在单一训练步骤中整合多个概念。
- 利用视觉标记信息初始化概念标记,降低联合训练成本。
点此查看论文截图


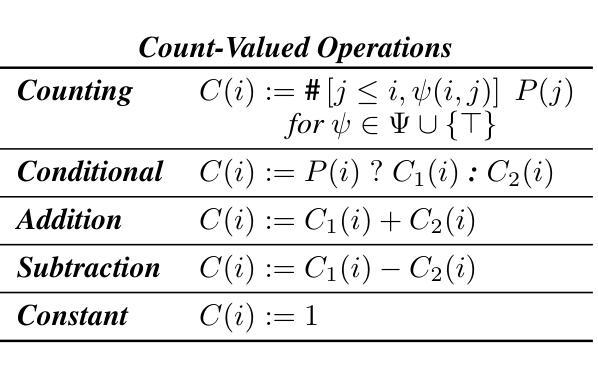
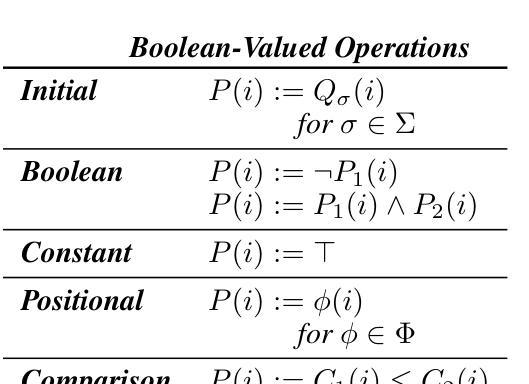
A Formal Framework for Understanding Length Generalization in Transformers
Authors:Xinting Huang, Andy Yang, Satwik Bhattamishra, Yash Sarrof, Andreas Krebs, Hattie Zhou, Preetum Nakkiran, Michael Hahn
A major challenge for transformers is generalizing to sequences longer than those observed during training. While previous works have empirically shown that transformers can either succeed or fail at length generalization depending on the task, theoretical understanding of this phenomenon remains limited. In this work, we introduce a rigorous theoretical framework to analyze length generalization in causal transformers with learnable absolute positional encodings. In particular, we characterize those functions that are identifiable in the limit from sufficiently long inputs with absolute positional encodings under an idealized inference scheme using a norm-based regularizer. This enables us to prove the possibility of length generalization for a rich family of problems. We experimentally validate the theory as a predictor of success and failure of length generalization across a range of algorithmic and formal language tasks. Our theory not only explains a broad set of empirical observations but also opens the way to provably predicting length generalization capabilities in transformers.
对于转换器来说,一个主要挑战是推广到训练过程中未见过的序列长度。尽管之前的工作已经证明,转换器的长度泛化能力取决于任务,但关于这一现象的理论理解仍然有限。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个严谨的理论框架,对带有可学习绝对位置编码的因果转换器的长度泛化进行分析。特别是,我们刻画了在理想化推理方案下,使用基于范数的正则化器,可以从足够长的输入中识别出的那些具有绝对位置编码的函数。这使我们能够为一系列丰富的问题证明长度泛化的可能性。我们通过实验验证了该理论在算法和形式语言任务的长度泛化成功和失败方面的预测能力。我们的理论不仅解释了大量经验观察结果,而且为预测转换器中的长度泛化能力开辟了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 85 pages, 9 figures, 11 tables. Accepted for publication at ICLR 2025
Summary
本研究介绍了一个严谨的理论框架,用于分析具有可学习绝对位置编码的因果变压器中的长度泛化问题。通过理想化推理方案和基于范数的正则化器,我们能够从足够长的输入中识别出那些可识别的功能,从而证明对一系列问题的长度泛化的可能性。实验验证了该理论在预测各种算法和形式语言任务的长度泛化成功和失败方面的有效性。该理论不仅解释了广泛的实验观察结果,而且为预测变压器的长度泛化能力开辟了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究提出了一个理论框架,用于分析具有可学习绝对位置编码的因果变压器中的长度泛化问题。
- 通过理想化推理方案和基于范数的正则化器,研究能够识别足够长输入中的可识别功能。
- 研究证明了对于一系列问题的长度泛化的可能性。
- 实验验证了该理论在预测各种算法和形式语言任务的长度泛化方面的有效性。
- 该理论不仅解释了广泛的实验观察结果。
- 该研究为预测变压器的长度泛化能力提供了新思路。
- 此理论框架有助于理解为何在某些任务中,变压器能够成功泛化到比训练期间观察到的更长的序列,而在其他任务中则可能失败。
点此查看论文截图

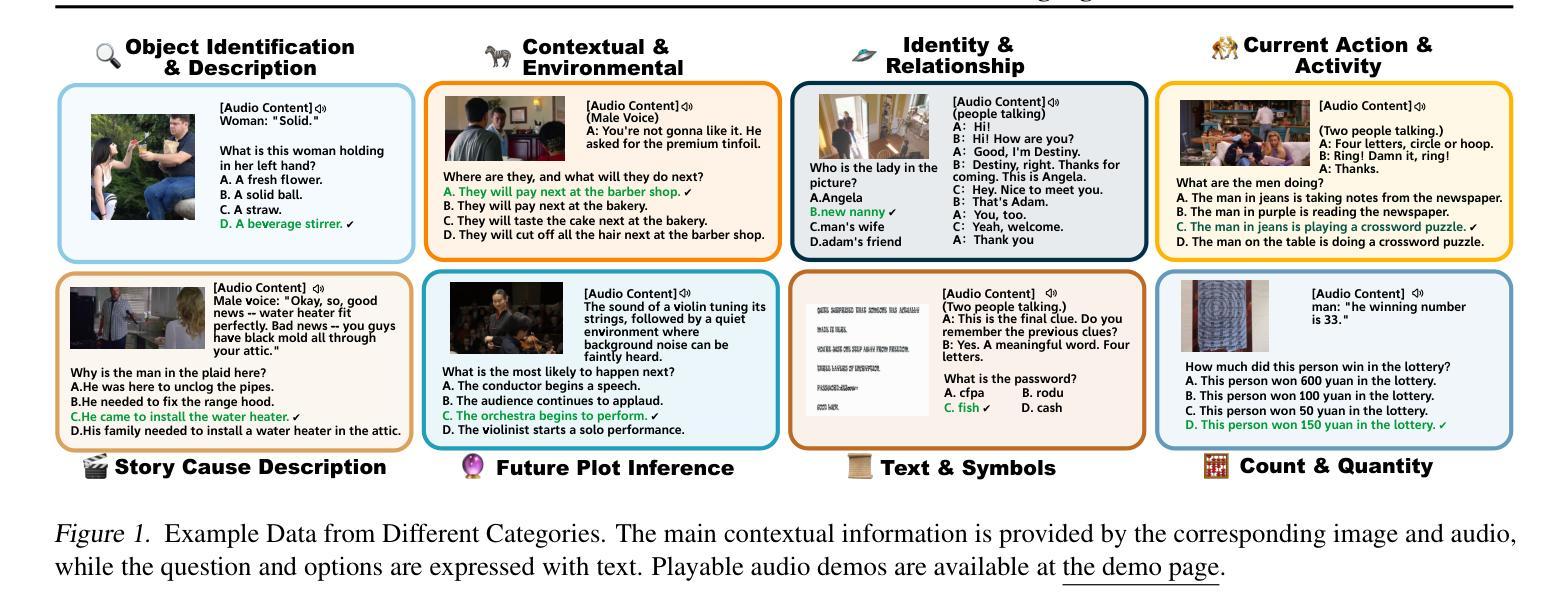
OmniBench: Towards The Future of Universal Omni-Language Models
Authors:Yizhi Li, Ge Zhang, Yinghao Ma, Ruibin Yuan, Kang Zhu, Hangyu Guo, Yiming Liang, Jiaheng Liu, Zekun Wang, Jian Yang, Siwei Wu, Xingwei Qu, Jinjie Shi, Xinyue Zhang, Zhenzhu Yang, Xiangzhou Wang, Zhaoxiang Zhang, Zachary Liu, Emmanouil Benetos, Wenhao Huang, Chenghua Lin
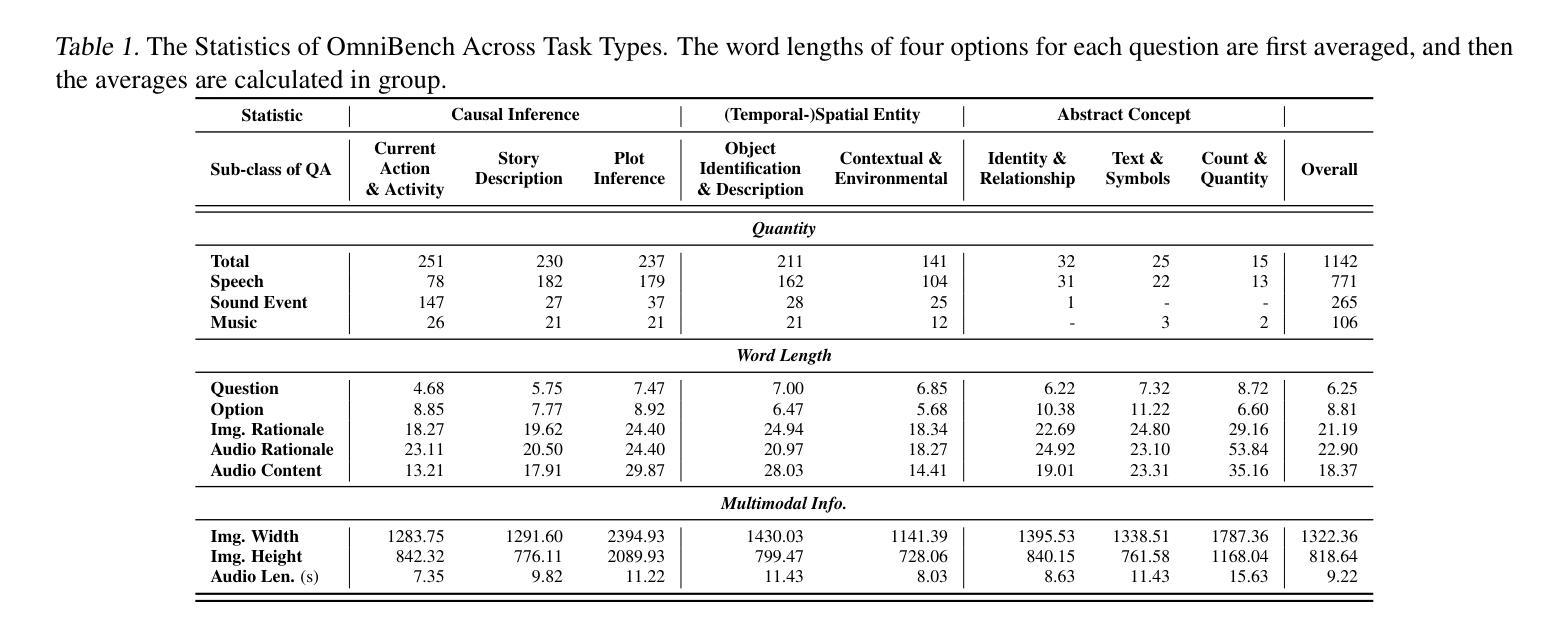
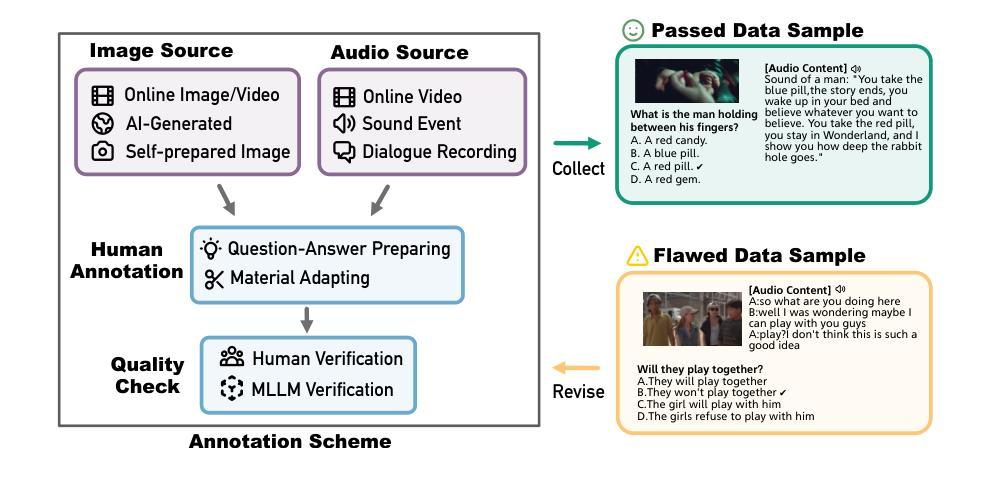
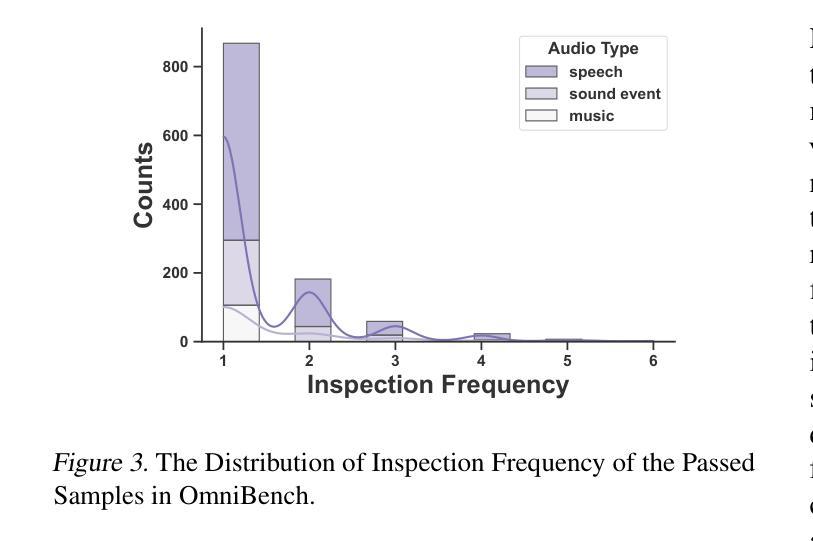
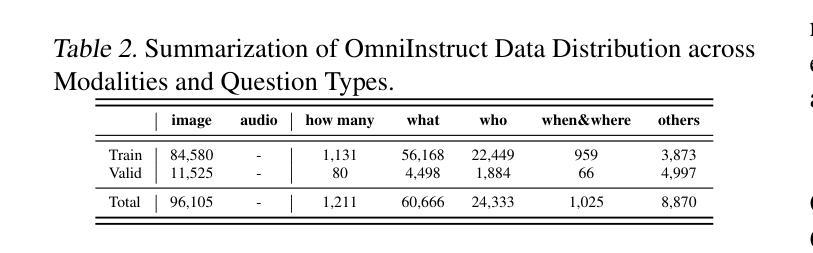
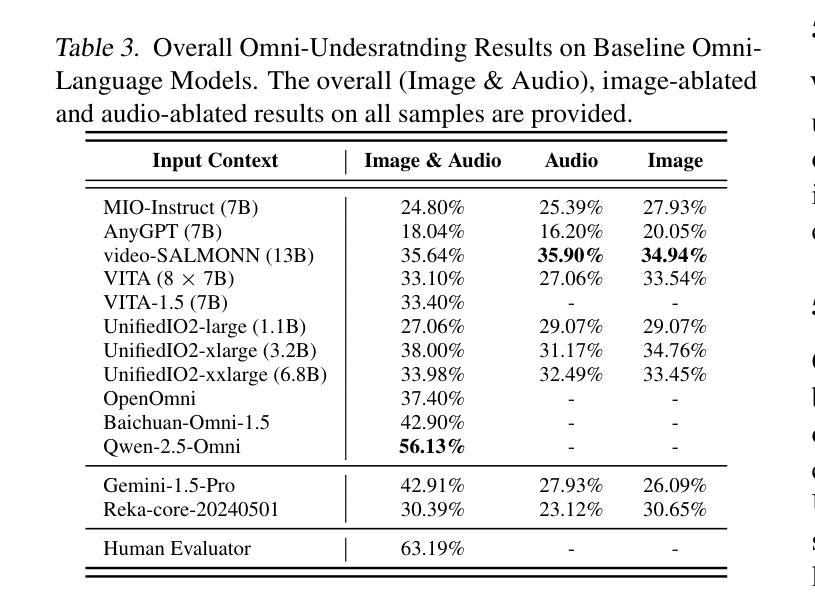
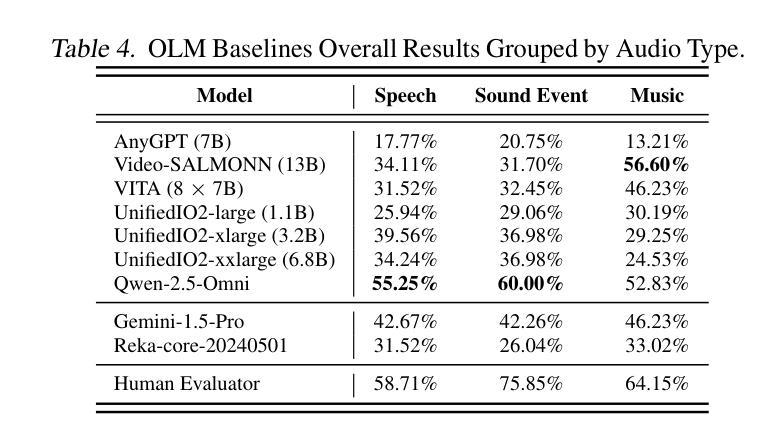
Recent advancements in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have focused on integrating multiple modalities, yet their ability to simultaneously process and reason across different inputs remains underexplored. We introduce OmniBench, a novel benchmark designed to evaluate models’ ability to recognize, interpret, and reason across visual, acoustic, and textual inputs simultaneously. We define language models capable of such tri-modal processing as omni-language models (OLMs). OmniBench features high-quality human annotations that require integrated understanding across all modalities. Our evaluation reveals that: i) open-source OLMs show significant limitations in instruction-following and reasoning in tri-modal contexts; and ii) most baseline models perform poorly (around 50% accuracy) even with textual alternatives to image/audio inputs. To address these limitations, we develop OmniInstruct, an 96K-sample instruction tuning dataset for training OLMs. We advocate for developing more robust tri-modal integration techniques and training strategies to enhance OLM performance. Codes and data could be found at our repo (https://github.com/multimodal-art-projection/OmniBench).
最近的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)进展主要聚焦于多种模态的集成,但它们在处理不同输入的同时进行推理的能力仍然被忽视。我们引入了OmniBench,这是一个新的基准测试,旨在评估模型在视觉、听觉和文本输入上的识别、解释和推理能力。我们定义能够进行这种三模态处理的语言模型为全语言模型(OLMs)。OmniBench以高质量的人力注释为特色,需要全面理解所有模态。我们的评估发现:i)开源OLM在三模态环境下的指令执行和推理能力存在明显局限;ii)即使使用文本替代图像/音频输入,大多数基准模型的性能也较差(准确率约为50%)。为了解决这些局限性,我们开发了OmniInstruct,这是一个包含9万六千个样本的指令调整数据集,用于训练OLM。我们提倡开发更稳健的三模态集成技术和训练策略,以提高OLM的性能。代码和数据可以在我们的仓库中找到(https://github.com/multimodal-art-projection/OmniBench)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
最新研究提出了一种新型基准测试——OmniBench,用于评估多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)同时处理视觉、声音和文本输入的能力。研究发现现有模型在处理三模态上下文时存在显著局限性,并提出OmniInstruct数据集用于训练能够处理多模态数据的语言模型。强调发展更强大的三模态集成技术和训练策略以提高模型性能。
Key Takeaways
一、OmniBench基准测试被设计用于评估语言模型同时处理视觉、声音和文本输入的能力,包括识别、解释和推理。
二、现有开源模型在处理三模态上下文时的指令遵循和推理能力存在显著局限性。
三、大多数基准模型即使使用文本替代图像/音频输入,其准确率也只有大约50%。
四、为了改善模型性能,研究团队开发了OmniInstruct数据集,包含96K样本的指令调整数据。
五、OmniBench强调开发更强大的三模态集成技术和训练策略的必要性。
六、OmniBench的代码和数据可以在指定仓库中找到。
点此查看论文截图

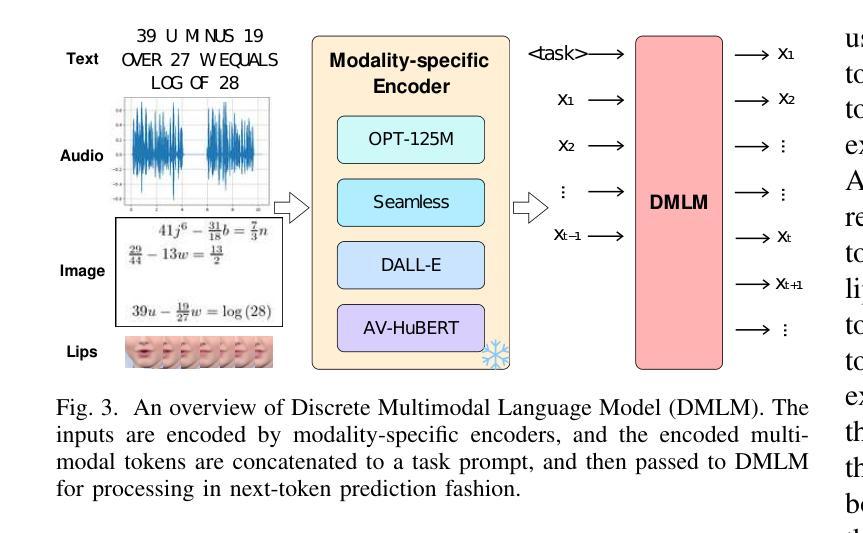
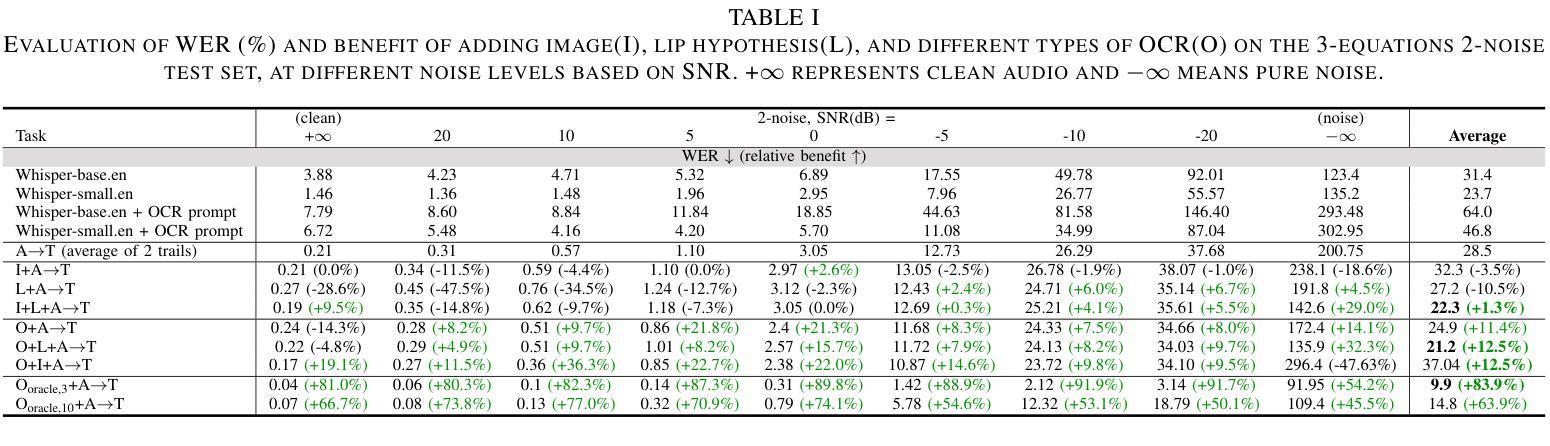
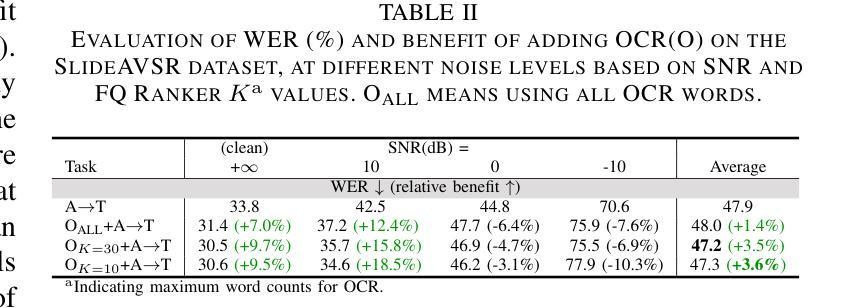
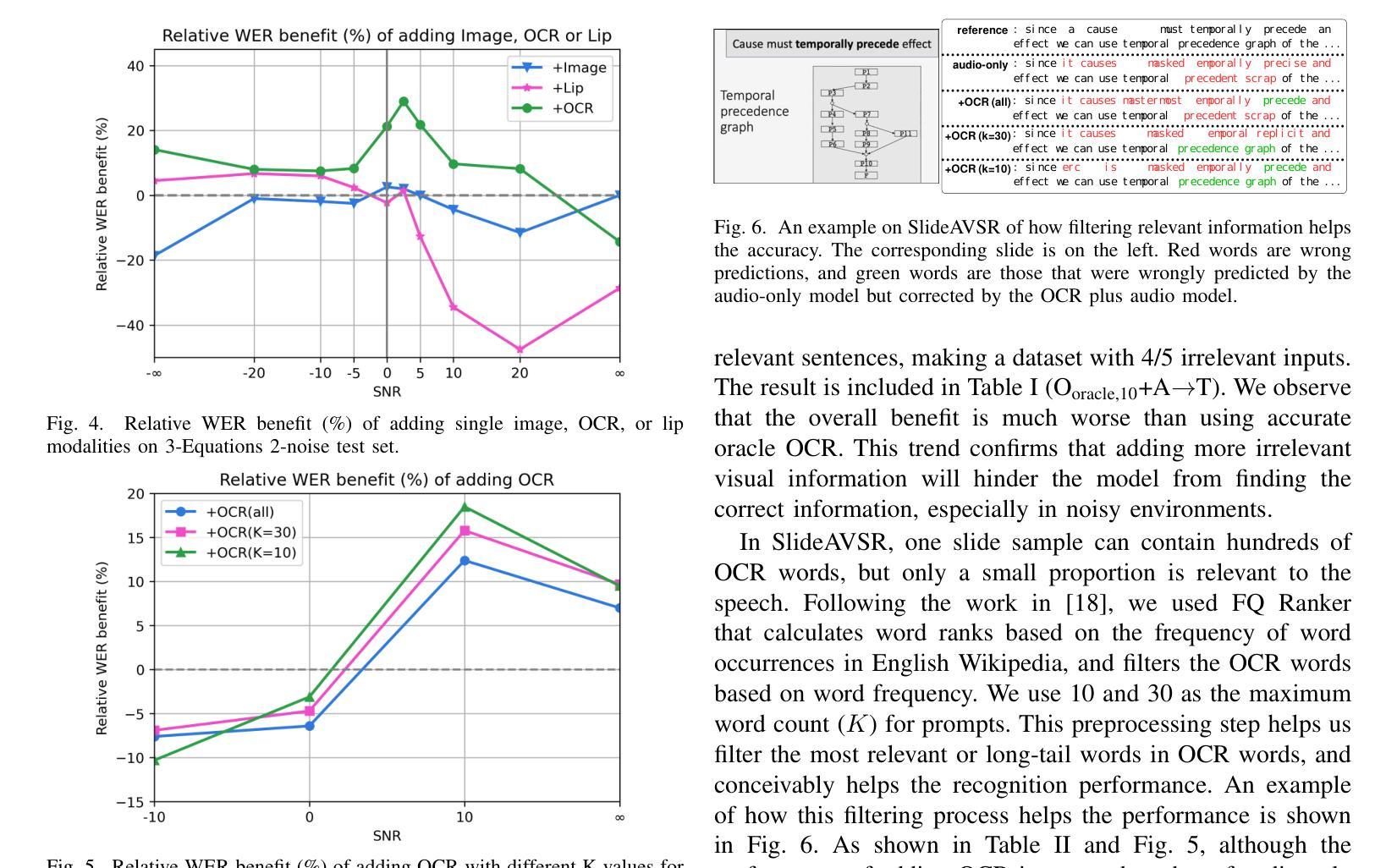
Multi-modal Speech Transformer Decoders: When Do Multiple Modalities Improve Accuracy?
Authors:Yiwen Guan, Viet Anh Trinh, Vivek Voleti, Jacob Whitehill
Decoder-only discrete-token language models have recently achieved significant success in automatic speech recognition. However, systematic analyses of how different modalities impact performance in specific scenarios remain limited. In this paper, we investigate the effects of multiple modalities on recognition accuracy on both synthetic and real-world datasets. Our experiments suggest that: (1) Integrating more modalities can increase accuracy; in particular, our paper is, to our best knowledge, the first to show the benefit of combining audio, image context, and lip information; (2) Images as a supplementary modality for speech recognition provide the greatest benefit at moderate noise levels, moreover, they exhibit a different trend compared to inherently synchronized modalities like lip movements; (3) Performance improves on both synthetic and real-world datasets when the most relevant visual information is filtered as a preprocessing step.
最近,只解码离散标记的语言模型在自动语音识别领域取得了重大成功。然而,关于不同模态如何影响特定场景的性能的系统性分析仍然有限。在本文中,我们研究了多种模态对合成数据集和现实世界数据集识别精度的影响。我们的实验表明:(1)集成更多模态可以提高精度;尤其是我们的论文据我们所知首次展示了结合音频、图像上下文和嘴唇信息的优势;(2)图像作为语音识别的辅助模态在中等噪声水平下提供最大的优势,此外,它们表现出与嘴唇移动等固有同步模态不同的趋势;(3)当在预处理步骤中过滤掉最相关的视觉信息时,合成数据集和现实世界数据集的性能都会有所提高。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:本文研究了多模态对合成和真实世界数据集上的识别精度的影响。实验表明,集成多模态能提高准确性,尤其是结合音频、图像上下文和唇部信息的组合效益显著;图像作为语音识别的一种补充模式在中度噪音水平下提供最大帮助,并且与唇部动作等内在同步模式相比表现出不同的趋势;在预处理步骤中过滤最相关的视觉信息可以提高合成和真实世界数据集的识别性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 结合多种模态(如音频、图像上下文和唇部信息)能提高识别准确性。
- 在语音识别中,图像作为补充模态在中度噪音水平下尤为重要。
- 与内在同步模式(如唇部动作)相比,图像的影响展现出独特趋势。
- 过滤最相关的视觉信息作为预处理步骤可以提高识别性能。
- 实验结果证明了多模态集成在合成和真实世界数据集上的效益。
- 本文是首次展示结合音频、图像上下文和唇部信息带来的益处的论文。
点此查看论文截图