⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-04 更新
Diffusion-Guided Gaussian Splatting for Large-Scale Unconstrained 3D Reconstruction and Novel View Synthesis
Authors:Niluthpol Chowdhury Mithun, Tuan Pham, Qiao Wang, Ben Southall, Kshitij Minhas, Bogdan Matei, Stephan Mandt, Supun Samarasekera, Rakesh Kumar
Recent advancements in 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) and Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have achieved impressive results in real-time 3D reconstruction and novel view synthesis. However, these methods struggle in large-scale, unconstrained environments where sparse and uneven input coverage, transient occlusions, appearance variability, and inconsistent camera settings lead to degraded quality. We propose GS-Diff, a novel 3DGS framework guided by a multi-view diffusion model to address these limitations. By generating pseudo-observations conditioned on multi-view inputs, our method transforms under-constrained 3D reconstruction problems into well-posed ones, enabling robust optimization even with sparse data. GS-Diff further integrates several enhancements, including appearance embedding, monocular depth priors, dynamic object modeling, anisotropy regularization, and advanced rasterization techniques, to tackle geometric and photometric challenges in real-world settings. Experiments on four benchmarks demonstrate that GS-Diff consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines by significant margins.
近期,在三维高斯展布(3DGS)和神经辐射场(NeRF)方面的进展,已在实时三维重建和新型视角合成领域取得了令人印象深刻的结果。然而,这些方法在大规模、无约束的环境中表现较差,稀疏和不均匀的输入覆盖、暂时的遮挡、外观变化和不一致的相机设置导致质量下降。我们提出了GS-Diff,这是一种新型的多视角扩散模型引导下的三维高斯展布框架,旨在解决这些局限性。通过生成基于多视角输入的伪观察结果,我们的方法将缺乏约束的三维重建问题转化为定义明确的问题,即使在稀疏数据的情况下也能实现稳健优化。GS-Diff还融合了多种增强功能,包括外观嵌入、单目深度先验、动态对象建模、各向异性正则化和先进的渲染技术,以应对现实环境中的几何和光度挑战。在四个基准测试上的实验表明,GS-Diff始终显著优于最新基线。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF WACV ULTRRA Workshop 2025
摘要
基于高斯绘制技术和神经辐射场的最新进展,已经成功应用于实时三维重建和新颖视角合成。然而,这些方法在大规模、无约束环境中面临挑战,如稀疏和不均匀输入覆盖、瞬时遮挡、外观变化和不一致的相机设置导致质量下降。我们提出GS-Diff,一种新型的多视角扩散模型引导的三维高斯绘制框架,以解决这些局限性。通过生成基于多视角输入的伪观察结果,我们的方法将约束不足的三维重建问题转化为结构良好的问题,即使在稀疏数据下也能实现稳健优化。GS-Diff进一步结合了外观嵌入、单目深度先验、动态对象建模、异向性正则化和高级光栅化技术等多个改进点,以解决真实环境中的几何和光度挑战。在四项基准测试上的实验表明,GS-Diff显著优于最先进的基线方法。
要点
- 引入了一种新型三维高斯绘制框架GS-Diff,适用于实时三维重建和新颖视角合成。
- GS-Diff通过生成伪观察结果解决了现有方法在大型无约束环境中的局限性。
- 方法采用多视角扩散模型,将约束不足的三维重建问题转化为结构良好的问题。
- GS-Diff集成了多种技术改进,包括外观嵌入、单目深度先验、动态对象建模等,以应对真实环境中的挑战。
点此查看论文截图


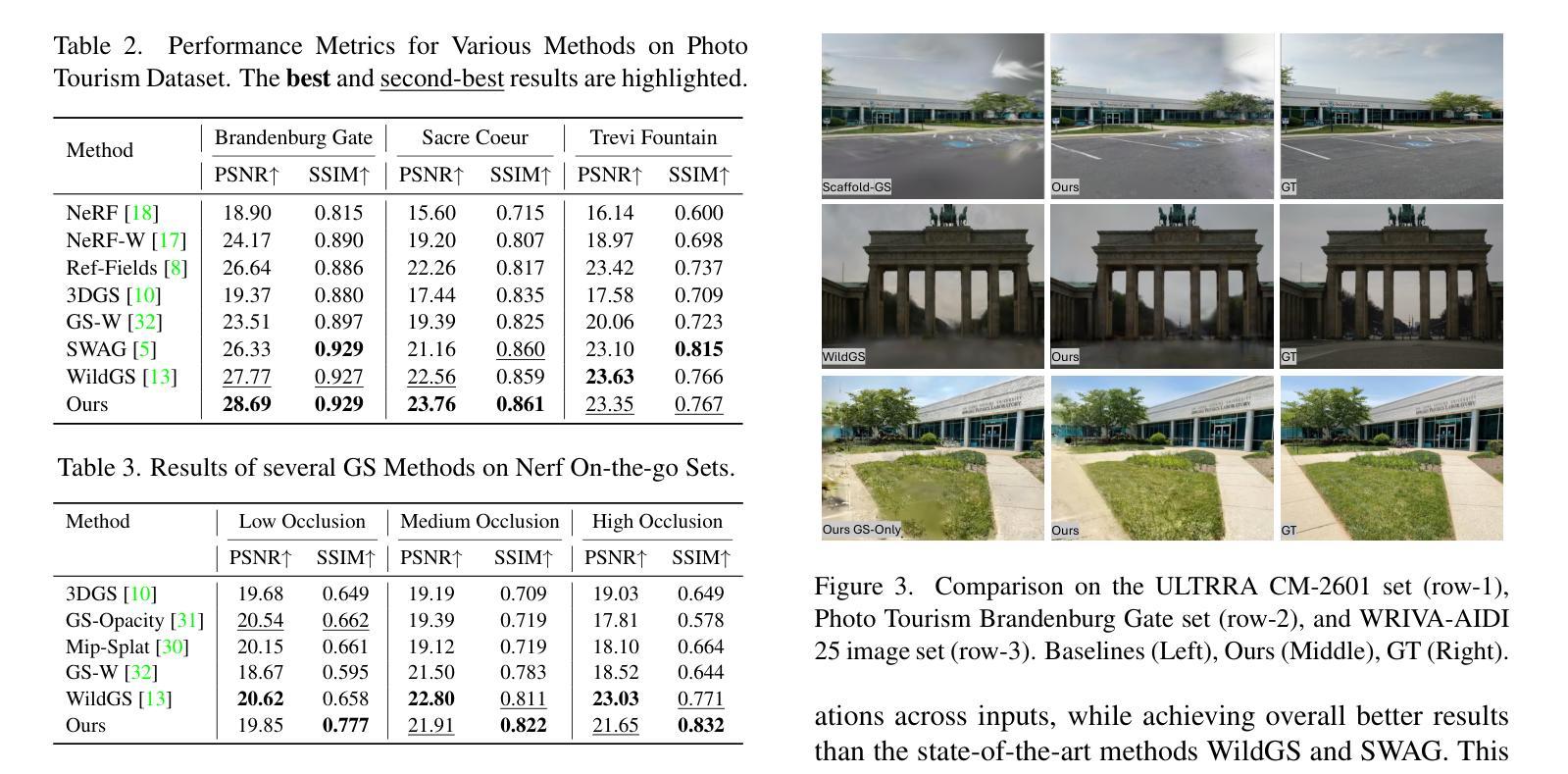
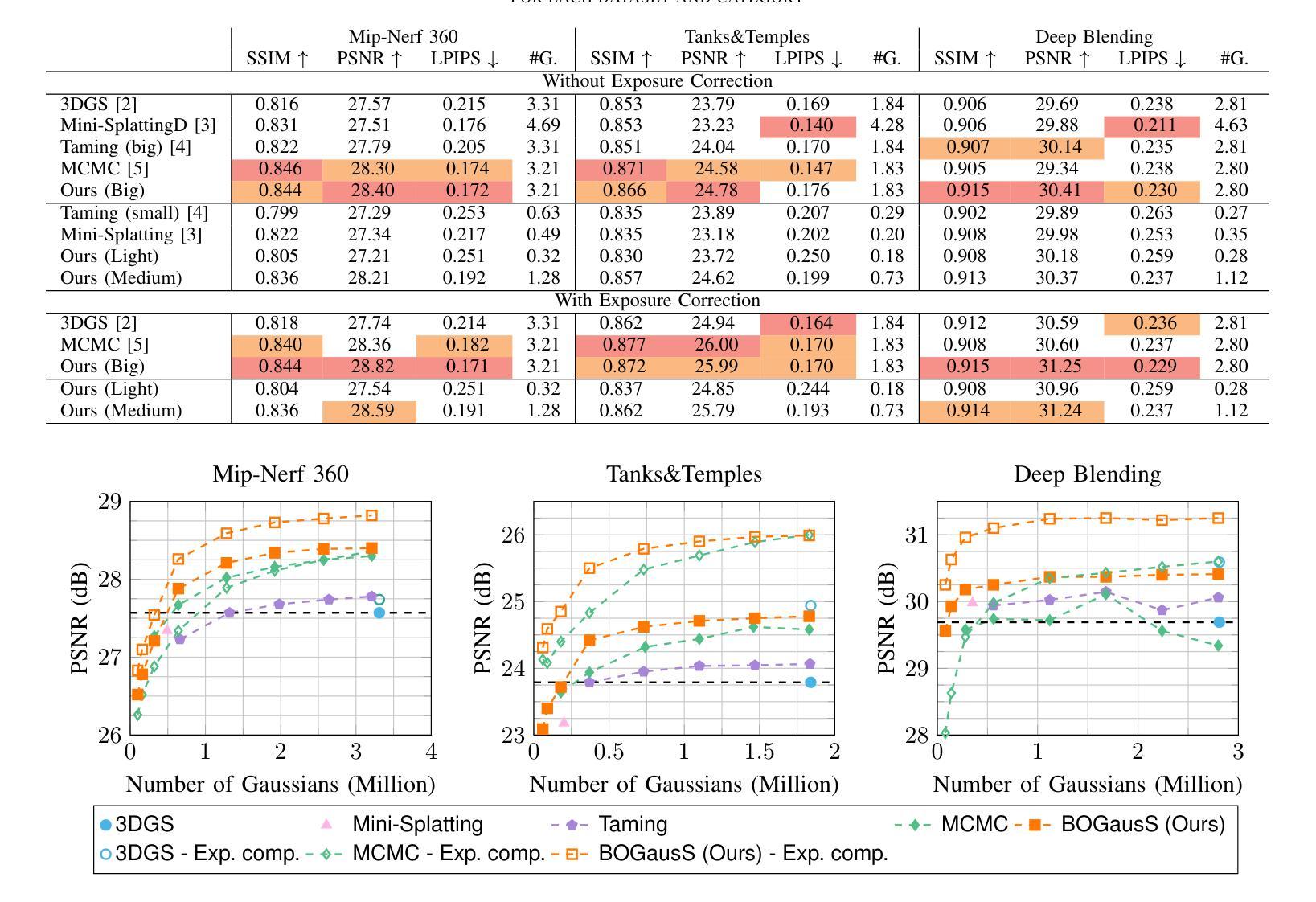
BOGausS: Better Optimized Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Stéphane Pateux, Matthieu Gendrin, Luce Morin, Théo Ladune, Xiaoran Jiang
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) proposes an efficient solution for novel view synthesis. Its framework provides fast and high-fidelity rendering. Although less complex than other solutions such as Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), there are still some challenges building smaller models without sacrificing quality. In this study, we perform a careful analysis of 3DGS training process and propose a new optimization methodology. Our Better Optimized Gaussian Splatting (BOGausS) solution is able to generate models up to ten times lighter than the original 3DGS with no quality degradation, thus significantly boosting the performance of Gaussian Splatting compared to the state of the art.
本文提出了针对新型视角合成的有效解决方案,即三维高斯贴图技术(3DGS)。其框架可实现快速且高保真渲染。虽然相较于其他解决方案(如神经辐射场NeRF)复杂度较低,但在构建不牺牲质量的小型模型方面仍存在挑战。本研究对3DGS训练过程进行了详细分析,并提出了一种新的优化方法。我们的更好优化高斯贴图技术(BOGausS)解决方案生成的模型重量为原始三维高斯贴图的十分之一且没有任何质量降级,从而极大地提高了高斯贴图技术在当前领域的性能表现。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于所提供文本,该研究提出了一种改进的三维高斯模糊技术(BOGausS),优化了现有的3DGS模型的训练过程。通过新型优化策略,该方法可以生成重量比原始模型轻十倍的模型,且没有质量损失,显著提升了高斯模糊技术的性能。这项新技术适用于高质量的三维场景渲染。
Key Takeaways
以下是从文本中提取的七个主要见解:
- 研究人员深入分析了现有的三维高斯模糊技术(3DGS)训练过程,并提出了一种新的优化方法。
- 新方法命名为BOGausS,能够在不牺牲质量的前提下生成重量仅为原始模型十分之一的模型。
- BOGausS显著提升了高斯模糊技术的性能,使其更加高效和灵活。
- BOGausS在新型视合成领域表现出卓越的性能,能够高质量地渲染三维场景。
- 新方法针对较小的模型设计,为解决在模型大小与质量之间的权衡问题提供了新的思路。
- 该研究挑战了现有的模型优化理论,并提供了有价值的参考和启示。
点此查看论文截图

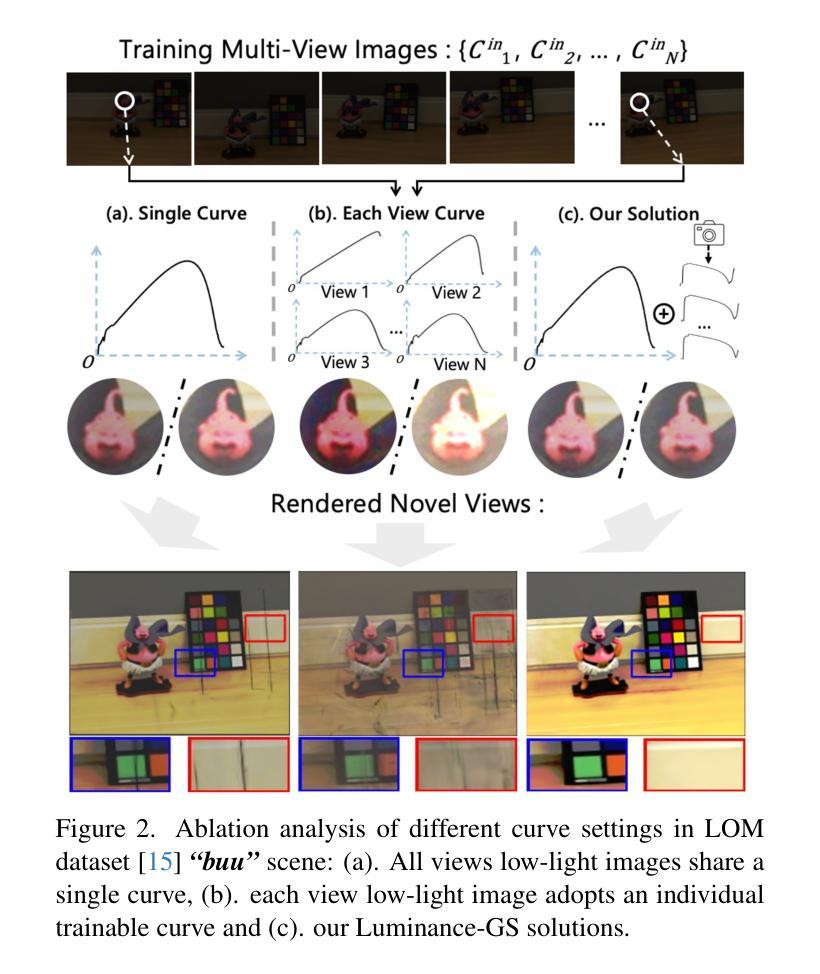
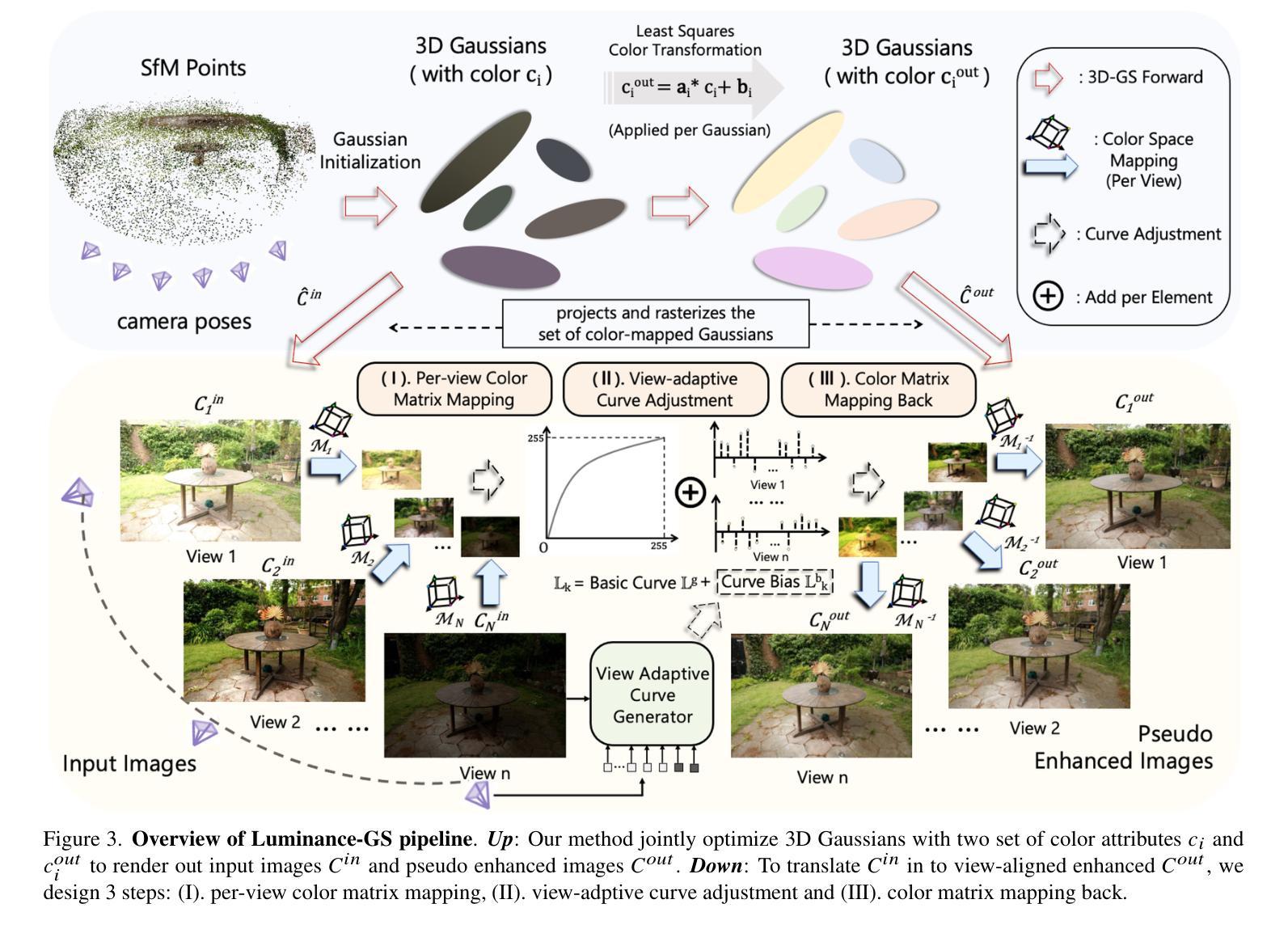
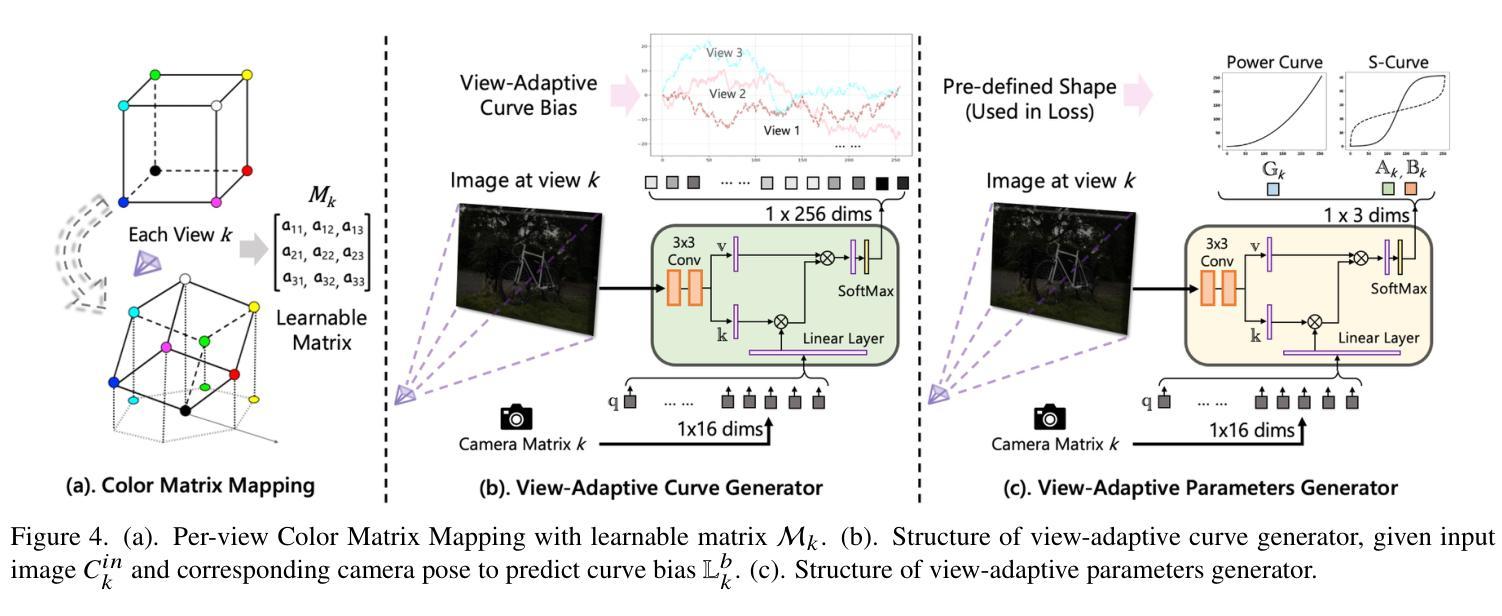
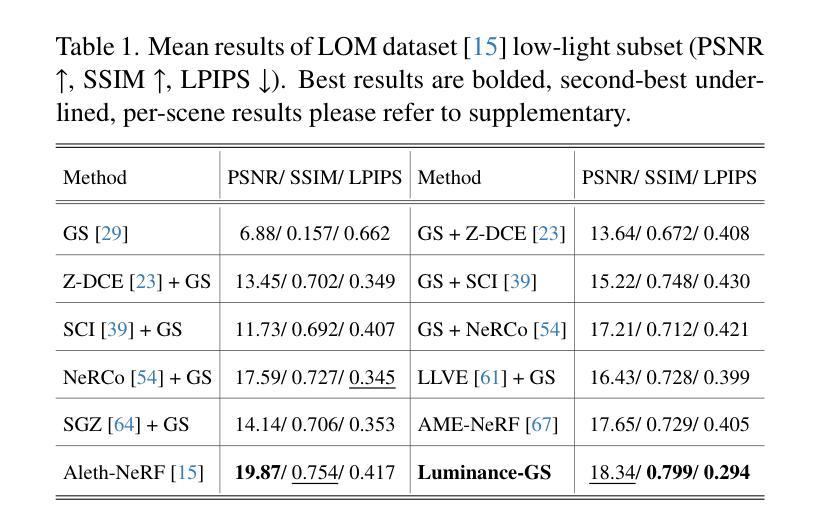
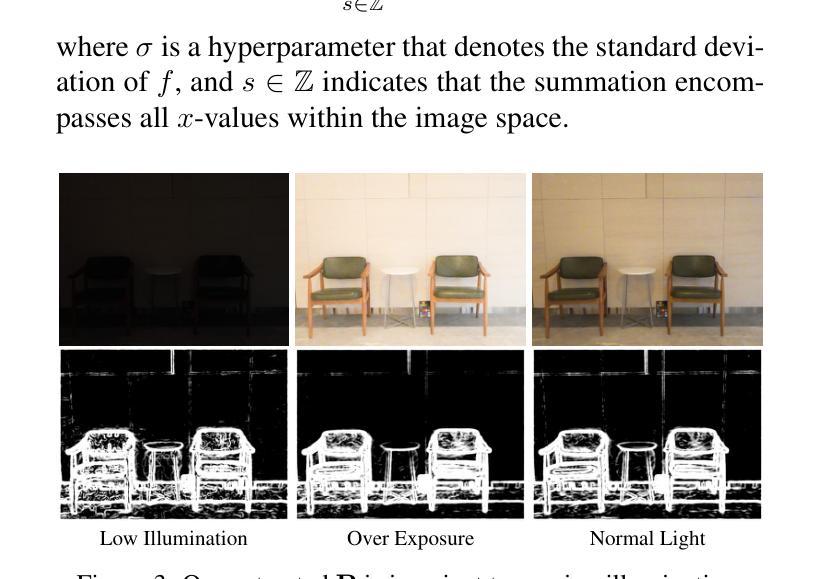
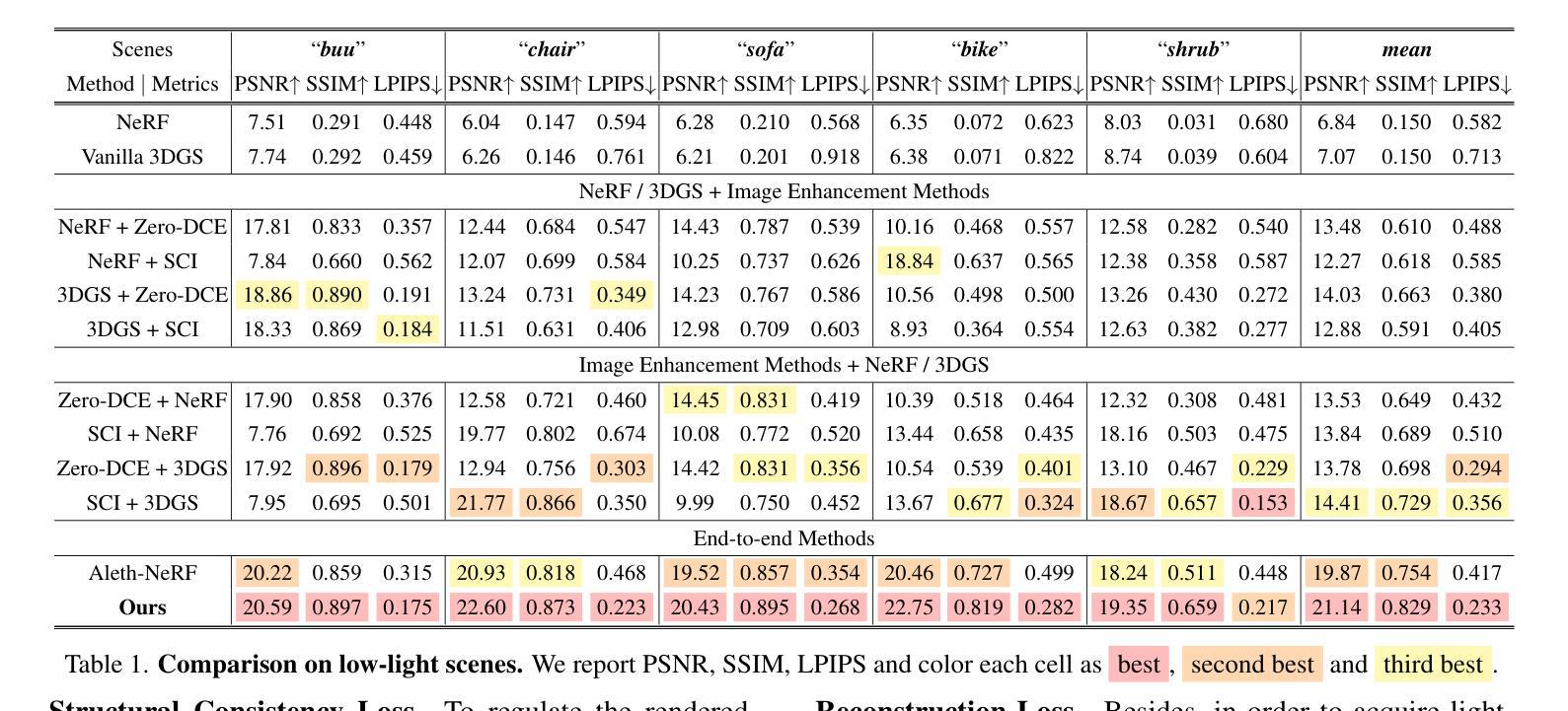
Luminance-GS: Adapting 3D Gaussian Splatting to Challenging Lighting Conditions with View-Adaptive Curve Adjustment
Authors:Ziteng Cui, Xuangeng Chu, Tatsuya Harada
Capturing high-quality photographs under diverse real-world lighting conditions is challenging, as both natural lighting (e.g., low-light) and camera exposure settings (e.g., exposure time) significantly impact image quality. This challenge becomes more pronounced in multi-view scenarios, where variations in lighting and image signal processor (ISP) settings across viewpoints introduce photometric inconsistencies. Such lighting degradations and view-dependent variations pose substantial challenges to novel view synthesis (NVS) frameworks based on Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). To address this, we introduce Luminance-GS, a novel approach to achieving high-quality novel view synthesis results under diverse challenging lighting conditions using 3DGS. By adopting per-view color matrix mapping and view-adaptive curve adjustments, Luminance-GS achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) results across various lighting conditions – including low-light, overexposure, and varying exposure – while not altering the original 3DGS explicit representation. Compared to previous NeRF- and 3DGS-based baselines, Luminance-GS provides real-time rendering speed with improved reconstruction quality.
在多种真实世界光照条件下捕获高质量照片是一个挑战,因为自然光照(例如低光环境)和相机曝光设置(例如曝光时间)都会显著影响图像质量。在多视角场景中,这一挑战更为突出,不同视角的光照和图像信号处理(ISP)设置变化会引入光度不一致性。这种光照退化和视角相关的变化给基于神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯描画(3DGS)的新视角合成(NVS)框架带来了巨大挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了Luminance-GS,这是一种利用三维高斯描画在多种具有挑战性的光照条件下实现高质量新视角合成结果的新方法。通过采用每视图颜色矩阵映射和视图自适应曲线调整,Luminance-GS在各种光照条件下实现了最先进的成果,包括低光、过曝光和可变曝光,同时不改变原始三维高斯描画的显式表示。与之前的NeRF和3DGS基线相比,Luminance-GS提供了实时的渲染速度,并提高了重建质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025, project page: https://cuiziteng.github.io/Luminance_GS_web/
Summary
高难度光照条件下的多视角合成是一项挑战,新的Luminance-GS方法利用3DGS实现高质量合成。通过每视角色彩矩阵映射和视差自适应曲线调整,Luminance-GS在多种光照条件下取得最优结果,包括低光、过曝和不同的曝光。该方法保持原始3DGS显式表示不变,同时提供实时渲染速度和改善的重建质量。
Key Takeaways
- 光照条件对图像质量有显著影响,特别是在多视角场景中,引起光度不一致性。
- 传统NeRF和3DGS方法在面临各种复杂光照条件时存在挑战。
- 新方法Luminance-GS通过每视角色彩矩阵映射和视差自适应曲线调整,成功应对多种复杂光照条件。
- Luminance-GS在多种光照条件下取得最优结果,包括低光、过曝和不同的曝光环境。
- 该方法维持原始3DGS的显式表示不变。
- 与之前的NeRF和3DGS基线相比,Luminance-GS提供实时渲染速度。
点此查看论文截图

Prompting Forgetting: Unlearning in GANs via Textual Guidance
Authors:Piyush Nagasubramaniam, Neeraj Karamchandani, Chen Wu, Sencun Zhu
State-of-the-art generative models exhibit powerful image-generation capabilities, introducing various ethical and legal challenges to service providers hosting these models. Consequently, Content Removal Techniques (CRTs) have emerged as a growing area of research to control outputs without full-scale retraining. Recent work has explored the use of Machine Unlearning in generative models to address content removal. However, the focus of such research has been on diffusion models, and unlearning in Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) has remained largely unexplored. We address this gap by proposing Text-to-Unlearn, a novel framework that selectively unlearns concepts from pre-trained GANs using only text prompts, enabling feature unlearning, identity unlearning, and fine-grained tasks like expression and multi-attribute removal in models trained on human faces. Leveraging natural language descriptions, our approach guides the unlearning process without requiring additional datasets or supervised fine-tuning, offering a scalable and efficient solution. To evaluate its effectiveness, we introduce an automatic unlearning assessment method adapted from state-of-the-art image-text alignment metrics, providing a comprehensive analysis of the unlearning methodology. To our knowledge, Text-to-Unlearn is the first cross-modal unlearning framework for GANs, representing a flexible and efficient advancement in managing generative model behavior.
最先进的生成模型展现出强大的图像生成能力,给托管这些模型的服务提供商带来了各种伦理和法律挑战。因此,内容删除技术(CRTs)作为控制输出而无需全面再训练的研究领域正日益兴起。近期的工作探索了在生成模型中使用机器遗忘(Machine Unlearning)来解决内容删除问题。然而,此类研究的重点主要集中在扩散模型上,生成对抗网络(GANs)中的遗忘仍然被大大忽视。我们通过提出Text-to-Unlearn来解决这一问题,这是一种新型框架,能够仅使用文本提示从预训练的GANs中选择性遗忘概念,实现特征遗忘、身份遗忘和在人脸训练模型中的表情和多属性移除等精细任务。我们的方法利用自然语言描述来引导遗忘过程,无需额外的数据集或监督微调,提供了一种可扩展且高效的解决方案。为了评估其有效性,我们从最先进的图像文本对齐指标中引入了一种自动遗忘评估方法,对遗忘方法进行了综合分析。据我们所知,Text-to-Unlearn是首个用于GANs的跨模态遗忘框架,在管理生成模型行为方面代表了灵活而高效的进步。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于预训练的GANs模型,我们提出了一种名为Text-to-Unlearn的新型框架,它能够通过文本提示有选择地遗忘概念,实现特征遗忘、身份遗忘以及在人脸模型上执行表情和多属性移除等精细任务。该方法利用自然语言描述指导无学习流程,无需额外的数据集或监督微调,提供可伸缩且高效的解决方案。我们的自动无学习评估方法基于先进的图像文本对齐指标,全面分析无学习方法的有效性。Text-to-Unlearn是首个跨模态的GANs无学习框架,灵活高效地管理生成模型的行为。
要点解析
- Text-to-Unlearn框架能够在预训练的GANs模型中通过文本提示选择性遗忘概念。
- 该框架可实现特征遗忘、身份遗忘等精细任务,如人脸模型上的表情和多属性移除。
- 利用自然语言描述指导无学习流程,无需额外的数据集或监督微调。
- 提出一种基于图像文本对齐指标的自动无学习评估方法,全面评估无学习方法的有效性。
- Text-to-Unlearn是首个针对GANs的跨模态无学习框架。
- 该框架为管理生成模型行为提供了灵活高效的解决方案。
- 目前该工作解决了长期以来在生成对抗网络(GANs)中未被充分研究的无学习问题。
点此查看论文截图


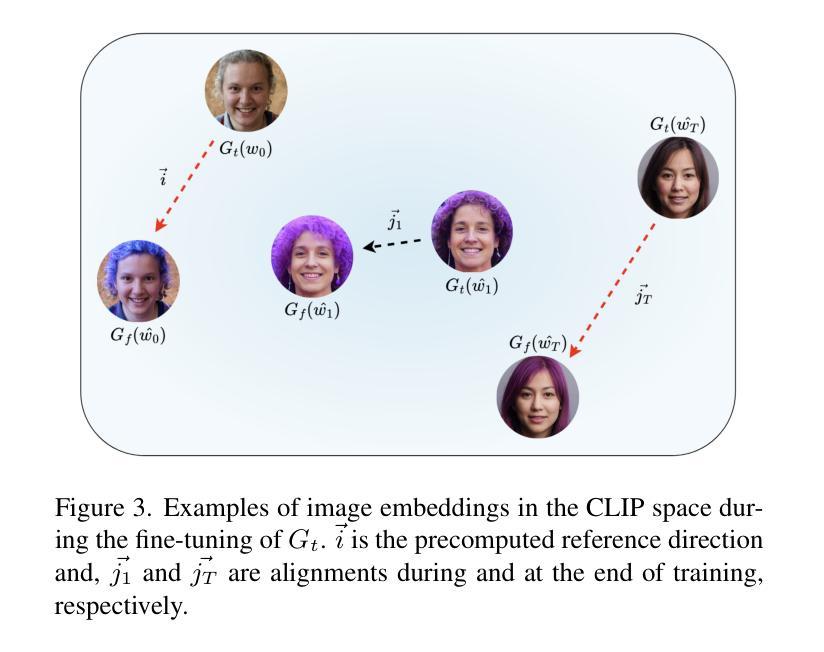



Neural Pruning for 3D Scene Reconstruction: Efficient NeRF Acceleration
Authors:Tianqi Ding, Dawei Xiang, Pablo Rivas, Liang Dong
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have become a popular 3D reconstruction approach in recent years. While they produce high-quality results, they also demand lengthy training times, often spanning days. This paper studies neural pruning as a strategy to address these concerns. We compare pruning approaches, including uniform sampling, importance-based methods, and coreset-based techniques, to reduce the model size and speed up training. Our findings show that coreset-driven pruning can achieve a 50% reduction in model size and a 35% speedup in training, with only a slight decrease in accuracy. These results suggest that pruning can be an effective method for improving the efficiency of NeRF models in resource-limited settings.
神经辐射场(NeRF)近年来已成为流行的3D重建方法。虽然它们能产生高质量的结果,但也需要长时间的训练,通常持续数天。本文针对神经修剪作为一种解决这些问题的策略进行了研究。我们比较了修剪方法,包括均匀采样、基于重要性的方法和基于核心集的技术,以减小模型大小并加快训练速度。我们的研究结果表明,基于核心集的修剪可以实现模型大小减少50%,训练速度提高35%,同时仅略微降低准确性。这些结果暗示,在资源受限的环境中,修剪可能是提高NeRF模型效率的有效方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 4 figures, accepted by International Conference on the AI Revolution: Research, Ethics, and Society (AIR-RES 2025)
摘要
神经辐射场(NeRF)是近年来流行的3D重建方法,虽然能产生高质量结果,但训练时间较长,常需数日。本文研究了通过神经剪枝策略来解决这些问题。我们比较了不同的剪枝方法,包括均匀采样、基于重要性的方法和基于核心集的技巧,以减小模型大小并加速训练。研究发现,基于核心集的剪枝方法能在保持轻微精度损失的前提下,实现模型大小减少50%,训练速度提升35%。这表明在资源受限的环境中,剪枝是提升NeRF模型效率的有效方法。
要点分析
- NeRF已成为流行的3D重建方法,但训练时间长是其一大挑战。
- 神经剪枝作为一种策略被研究,旨在解决训练时间长和模型体积大的问题。
- 对比了多种剪枝方法,包括均匀采样、基于重要性和基于核心集的技巧。
- 基于核心集的剪枝方法能在减小模型大小(50%)和加速训练(35%)方面取得显著成果。
- 剪枝方法在资源受限的环境中能有效提升NeRF模型的效率。
- 轻微精度损失是剪枝策略需要平衡的问题。
点此查看论文截图


Data Cleansing for GANs
Authors:Naoyuki Terashita, Hiroki Ohashi, Satoshi Hara
As the application of generative adversarial networks (GANs) expands, it becomes increasingly critical to develop a unified approach that improves performance across various generative tasks. One effective strategy that applies to any machine learning task is identifying harmful instances, whose removal improves the performance. While previous studies have successfully estimated these harmful training instances in supervised settings, their approaches are not easily applicable to GANs. The challenge lies in two requirements of the previous approaches that do not apply to GANs. First, previous approaches require that the absence of a training instance directly affects the parameters. However, in the training for GANs, the instances do not directly affect the generator’s parameters since they are only fed into the discriminator. Second, previous approaches assume that the change in loss directly quantifies the harmfulness of the instance to a model’s performance, while common types of GAN losses do not always reflect the generative performance. To overcome the first challenge, we propose influence estimation methods that use the Jacobian of the generator’s gradient with respect to the discriminator’s parameters (and vice versa). Such a Jacobian represents the indirect effect between two models: how removing an instance from the discriminator’s training changes the generator’s parameters. Second, we propose an instance evaluation scheme that measures the harmfulness of each training instance based on how a GAN evaluation metric (e.g., Inception score) is expected to change by the instance’s removal. Furthermore, we demonstrate that removing the identified harmful instances significantly improves the generative performance on various GAN evaluation metrics.
随着生成对抗网络(GANs)的应用不断扩大,开发一种适用于各种生成任务的统一方法变得至关重要。适用于任何机器学习任务的有效的策略是识别有害实例,移除它们可以提高性能。虽然以前的研究已经在有监督环境中成功地估计了这些有害的训练实例,但它们的方法并不易于应用于GANs。挑战在于以前的方法的两个要求不适用于GANs。首先,以前的方法要求训练实例的缺失直接影响参数。然而,在GANs的训练中,实例并不会直接影响生成器的参数,因为它们只输入到判别器中。其次,以前的方法假设损失的变化直接量化实例对模型性能的危害性,而常见的GAN损失并不总是反映生成性能。为了克服第一个挑战,我们提出了使用生成器梯度相对于判别器参数的雅可比(以及反之)来估计影响的方法。这样的雅可比代表了两个模型之间的间接影响:移除实例对判别器训练如何改变生成器的参数。其次,我们提出了一种实例评估方案,该方案基于GAN评估指标(例如Inception分数)的预期变化来测量每个训练实例的危害性。此外,我们证明,移除已识别出的有害实例可以显著提高各种GAN评估指标的生成性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems (TNNLS, 2025). Journal extention of https://openreview.net/forum?id=opHLcXxYTC_
Summary
本文介绍了在生成对抗网络(GANs)的应用中,识别并移除有害实例的重要性。以往的研究方法无法直接应用于GANs,因此提出通过计算生成器与判别器参数间的雅可比矩阵来估计影响的方法,并设计了一种基于GAN评价指标变化来评估每个训练实例危害性的方案。实验证明,移除有害实例能显著提高GAN的生成性能。
Key Takeaways
- GANs在生成任务中的应用日益广泛,需要开发一种统一的方法来提高其在各种任务中的性能。
- 识别并移除有害实例是一种有效提高机器学习性能的策略。
- 以往的研究方法无法直接应用于GANs,因为GANs的训练过程中实例不直接影响生成器的参数。
- 提出通过计算雅可比矩阵来估计实例对GAN性能的影响,该矩阵表示生成器和判别器参数之间的间接影响。
- 设计了一种基于GAN评价指标变化来评估每个训练实例危害性的方案。
- 实验证明,移除有害实例能显著提高GAN的生成性能在各种评价指标上的表现。
点此查看论文截图


LITA-GS: Illumination-Agnostic Novel View Synthesis via Reference-Free 3D Gaussian Splatting and Physical Priors
Authors:Han Zhou, Wei Dong, Jun Chen
Directly employing 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) on images with adverse illumination conditions exhibits considerable difficulty in achieving high-quality, normally-exposed representations due to: (1) The limited Structure from Motion (SfM) points estimated in adverse illumination scenarios fail to capture sufficient scene details; (2) Without ground-truth references, the intensive information loss, significant noise, and color distortion pose substantial challenges for 3DGS to produce high-quality results; (3) Combining existing exposure correction methods with 3DGS does not achieve satisfactory performance due to their individual enhancement processes, which lead to the illumination inconsistency between enhanced images from different viewpoints. To address these issues, we propose LITA-GS, a novel illumination-agnostic novel view synthesis method via reference-free 3DGS and physical priors. Firstly, we introduce an illumination-invariant physical prior extraction pipeline. Secondly, based on the extracted robust spatial structure prior, we develop the lighting-agnostic structure rendering strategy, which facilitates the optimization of the scene structure and object appearance. Moreover, a progressive denoising module is introduced to effectively mitigate the noise within the light-invariant representation. We adopt the unsupervised strategy for the training of LITA-GS and extensive experiments demonstrate that LITA-GS surpasses the state-of-the-art (SOTA) NeRF-based method while enjoying faster inference speed and costing reduced training time. The code is released at https://github.com/LowLevelAI/LITA-GS.
直接对不良照明条件下的图像应用三维高斯贴片(3DGS)在实现高质量的正常曝光表示方面存在相当大的困难,原因如下:(1)在不良照明场景中估计的运动结构(SfM)点有限,无法捕获足够的场景细节;(2)没有地面真实参考,密集的信息丢失、显著的噪声和颜色失真给3DGS带来很大挑战,难以产生高质量的结果;(3)将现有的曝光校正方法与3DGS相结合并不能实现令人满意的性能,因为它们的个别增强处理过程导致从不同视角增强的图像之间照明不一致。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了LITA-GS,这是一种新型的无照明参考新视角合成方法,通过无参考的3DGS和物理先验来实现。首先,我们引入了一种光照不变物理先验提取管道。其次,基于提取的稳健空间结构先验,我们开发了光照无关的结构渲染策略,这有助于优化场景结构和物体外观。此外,还引入了一个渐进的去噪模块,以有效地减轻光不变表示中的噪声。我们采用无监督策略对LITA-GS进行训练,大量实验表明,LITA-GS超越了基于神经辐射场表示(NeRF)的最新方法,同时享有更快的推理速度和减少的训练时间。代码已发布在https://github.com/LowLevelAI/LITA-GS。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025. 3DGS, Adverse illumination conditions, Reference-free, Physical priors
Summary
该文本主要介绍了在不良光照条件下直接应用3D高斯平铺(3DGS)的困难,并提出了相应的解决方案。针对结构从运动(SfM)点估计不足、信息丢失严重、噪声和色彩失真等问题,提出一种名为LITA-GS的新型无参考3DGS方法。该方法引入照明不变物理先验提取管道,开发照明无关结构渲染策略,并引入渐进降噪模块。实验表明,LITA-GS在NeRF方法的基础上超越了最新技术,同时提高了推理速度和降低了训练时间。相关代码已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 在不良光照条件下直接应用3D高斯平铺(3DGS)面临困难,如结构从运动(SfM)点估计不足、信息丢失严重等。
- LITA-GS方法引入照明不变物理先验提取管道,解决上述问题。
- LITA-GS基于提取的稳健空间结构先验,开发照明无关结构渲染策略,优化场景结构和物体外观。
- LITA-GS采用渐进降噪模块,有效减轻光照不变表示中的噪声。
- LITA-GS采用无监督策略进行训练,实验表明其性能超越现有NeRF方法,同时提高推理速度和降低训练时间。
- LITA-GS的代码已发布在GitHub上,供公众访问和使用。
点此查看论文截图

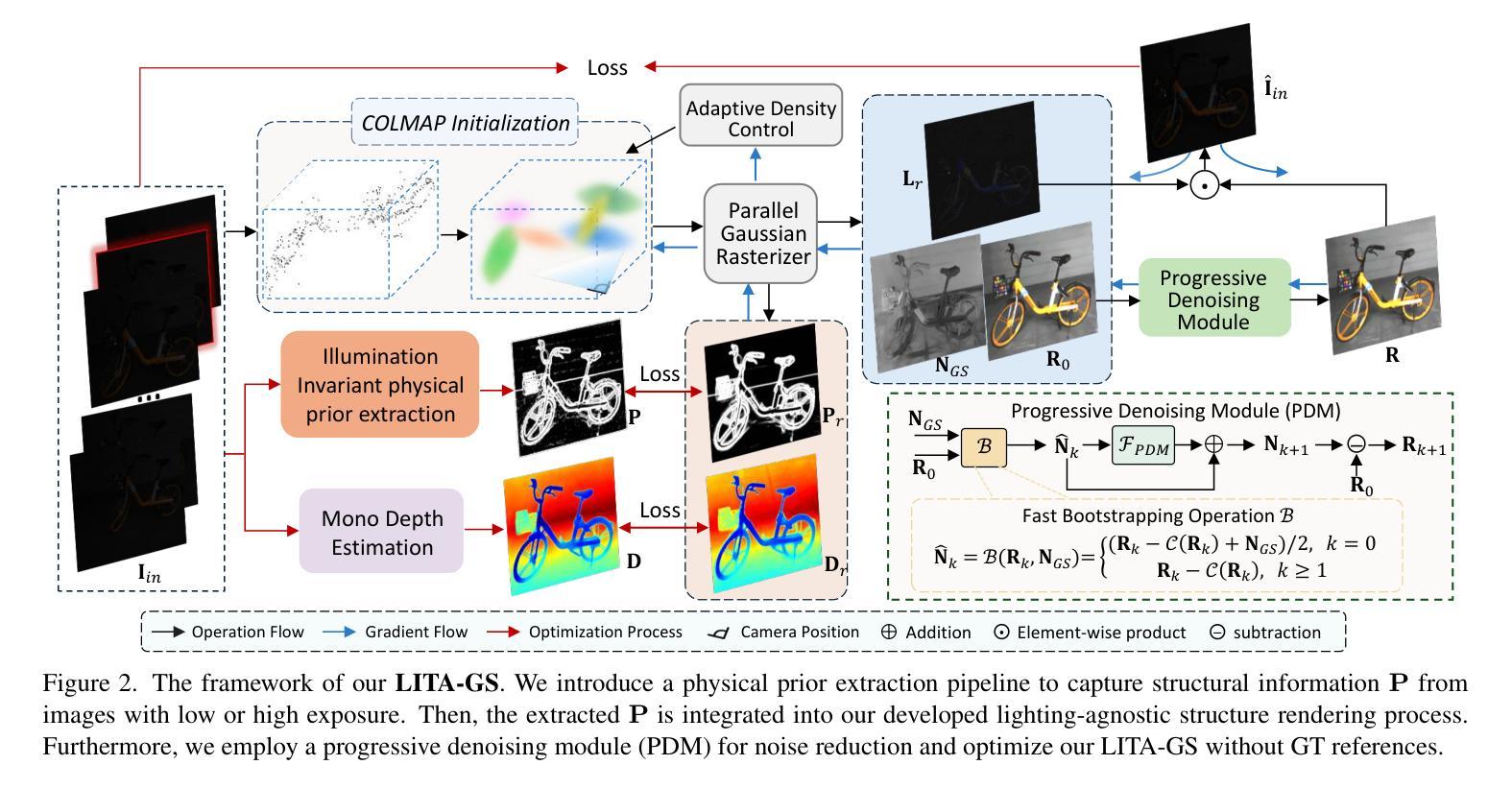
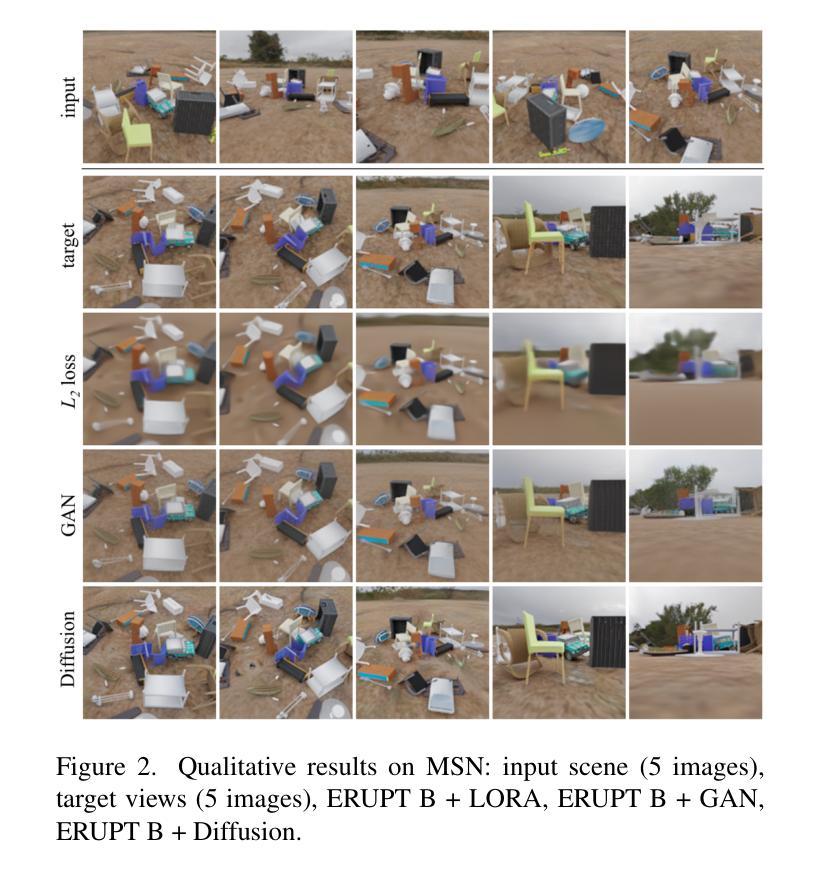
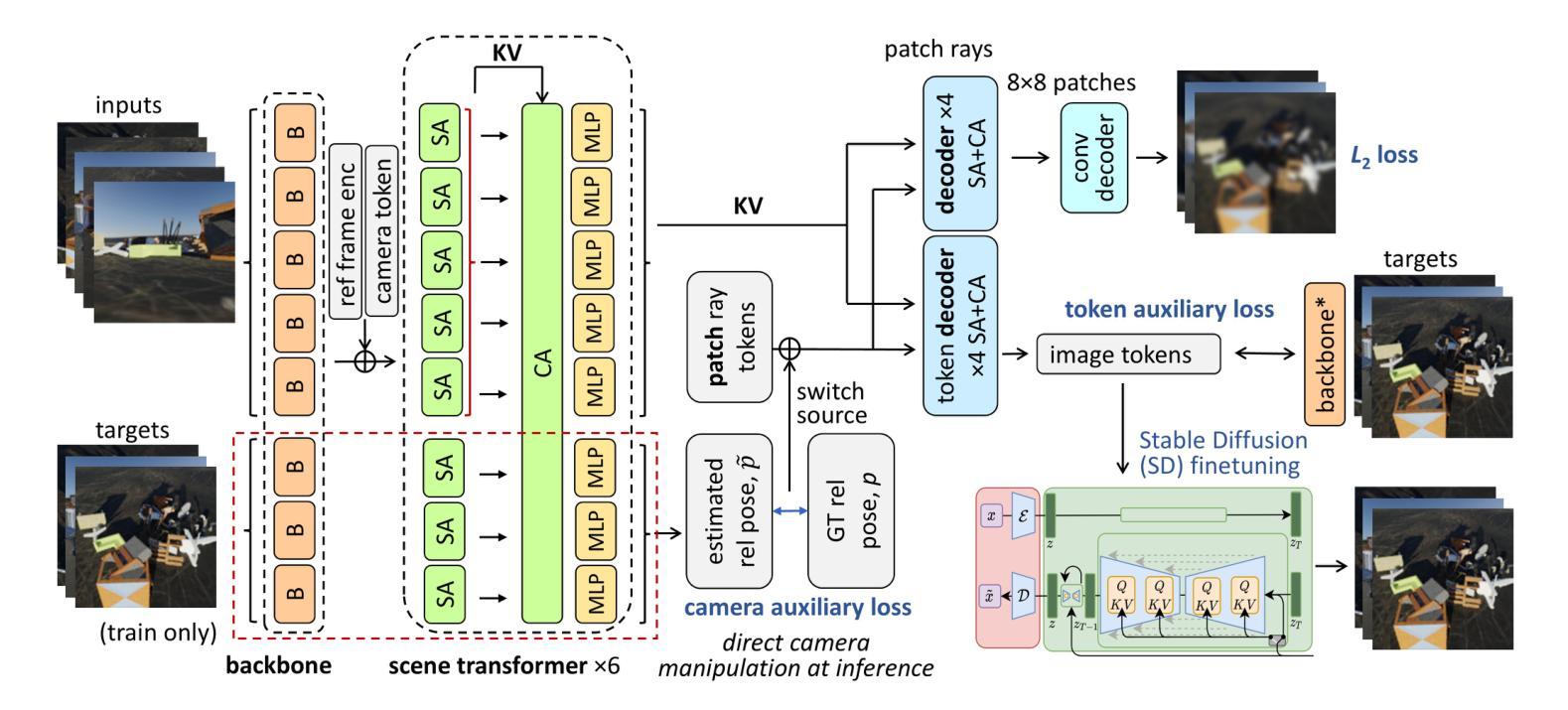
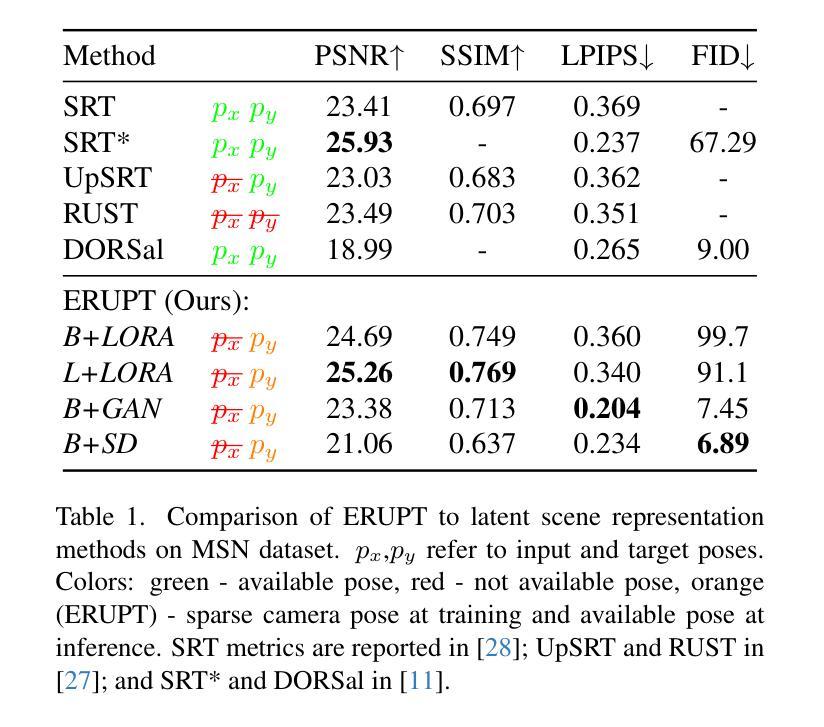
ERUPT: Efficient Rendering with Unposed Patch Transformer
Authors:Maxim V. Shugaev, Vincent Chen, Maxim Karrenbach, Kyle Ashley, Bridget Kennedy, Naresh P. Cuntoor
This work addresses the problem of novel view synthesis in diverse scenes from small collections of RGB images. We propose ERUPT (Efficient Rendering with Unposed Patch Transformer) a state-of-the-art scene reconstruction model capable of efficient scene rendering using unposed imagery. We introduce patch-based querying, in contrast to existing pixel-based queries, to reduce the compute required to render a target view. This makes our model highly efficient both during training and at inference, capable of rendering at 600 fps on commercial hardware. Notably, our model is designed to use a learned latent camera pose which allows for training using unposed targets in datasets with sparse or inaccurate ground truth camera pose. We show that our approach can generalize on large real-world data and introduce a new benchmark dataset (MSVS-1M) for latent view synthesis using street-view imagery collected from Mapillary. In contrast to NeRF and Gaussian Splatting, which require dense imagery and precise metadata, ERUPT can render novel views of arbitrary scenes with as few as five unposed input images. ERUPT achieves better rendered image quality than current state-of-the-art methods for unposed image synthesis tasks, reduces labeled data requirements by ~95% and decreases computational requirements by an order of magnitude, providing efficient novel view synthesis for diverse real-world scenes.
本文解决了从小型RGB图像集合中对多样场景进行新型视角合成的问题。我们提出了ERUPT(无预设补丁转换器高效渲染)模型,这是一种最先进的场景重建模型,能够在无预设图像中实现高效场景渲染。我们引入了基于补丁的查询,与现有的基于像素的查询相比,减少了渲染目标视图所需的计算量。这使得我们的模型在训练和推理过程中都非常高效,能够在商用硬件上以600帧/秒的速度进行渲染。值得注意的是,我们的模型采用学习到的潜在相机姿态,这允许在数据集上使用无预设目标进行训练,即使数据集具有稀疏或不准确的真实相机姿态。我们证明了我们的方法可以在大型真实世界数据上进行泛化,并使用从Mapillary收集的街道视图图像引入了新的基准数据集(MSVS-1M)用于潜在视角合成。与需要密集图像和精确元数据的NeRF和Gaussian Splatting相比,ERUPT仅使用五张无预设输入图像就能渲染任意场景的新视角。ERUPT在无预设图像合成任务方面实现了比当前最先进方法更好的渲染图像质量,将标注数据需求减少了约95%,并将计算需求减少了一个数量级,为多样化的真实世界场景提供了高效的新型视角合成。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
本文提出一种名为ERUPT(基于无姿态图像块的Transformer高效渲染)的场景重建模型,用于解决从不同RGB图像集合中合成新视角的问题。该模型引入基于图像块的查询方式,相较于现有的基于像素的查询,大幅降低了渲染目标视角所需的计算量,同时在训练和推理过程中都表现出极高的效率,可在商用硬件上实现600帧的渲染速度。此外,该模型采用学习到的潜在相机姿态,可在数据集稀疏或地面真实相机姿态不准确的情况下进行训练。ERUPT模型能够在大型真实世界数据上进行推广,并引入新的基准数据集MSVS-1M,用于潜在视角合成的街道视图图像采集。相较于需要密集图像和精确元数据的NeRF和高斯贴图方法,ERUPT仅需少量无姿态输入图像就能合成新的视角。此外,ERUPT在无姿态图像合成任务上达到了优于当前最先进的渲染质量,将标记数据需求降低了约95%,并将计算需求降低了一个数量级,为多样化的真实世界场景提供了高效的新视角合成解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- ERUPT模型解决了从不同RGB图像集合中合成新视角的问题。
- ERUPT引入基于图像块的查询方式,提高渲染效率。
- ERUPT模型在训练和推理过程中都表现出极高的效率,可在商用硬件上实现高速渲染。
- ERUPT采用学习到的潜在相机姿态,适应数据集姿态信息不准确的情况。
- ERUPT模型能够在大型真实世界数据上进行推广,并引入新的基准数据集MSVS-1M。
- ERUPT模型相较于其他方法,在无姿态图像合成任务上达到了更好的渲染质量。
点此查看论文截图


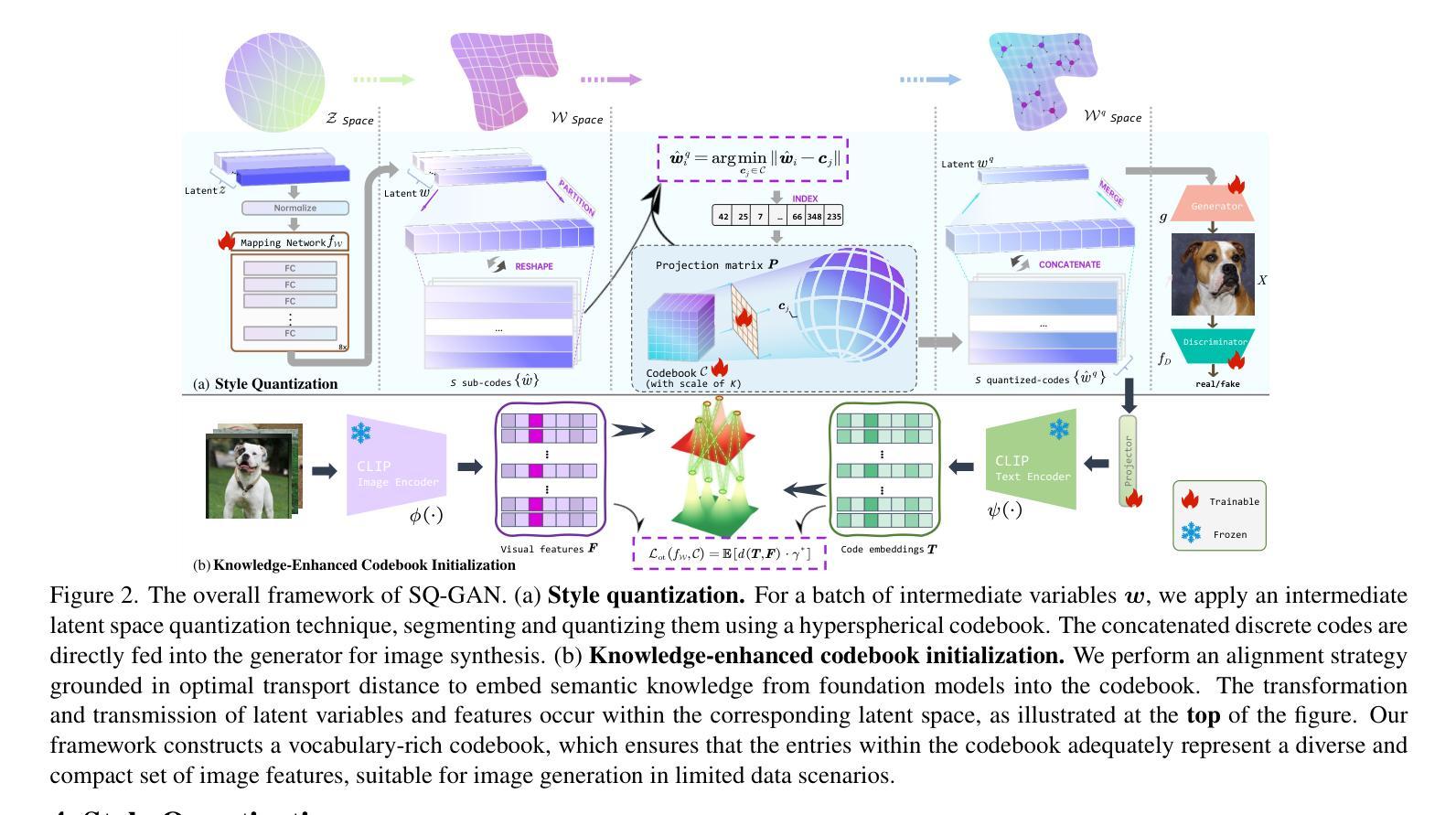
Style Quantization for Data-Efficient GAN Training
Authors:Jian Wang, Xin Lan, Jizhe Zhou, Yuxin Tian, Jiancheng Lv
Under limited data setting, GANs often struggle to navigate and effectively exploit the input latent space. Consequently, images generated from adjacent variables in a sparse input latent space may exhibit significant discrepancies in realism, leading to suboptimal consistency regularization (CR) outcomes. To address this, we propose \textit{SQ-GAN}, a novel approach that enhances CR by introducing a style space quantization scheme. This method transforms the sparse, continuous input latent space into a compact, structured discrete proxy space, allowing each element to correspond to a specific real data point, thereby improving CR performance. Instead of direct quantization, we first map the input latent variables into a less entangled ``style’’ space and apply quantization using a learnable codebook. This enables each quantized code to control distinct factors of variation. Additionally, we optimize the optimal transport distance to align the codebook codes with features extracted from the training data by a foundation model, embedding external knowledge into the codebook and establishing a semantically rich vocabulary that properly describes the training dataset. Extensive experiments demonstrate significant improvements in both discriminator robustness and generation quality with our method.
在有限数据设置下,生成对抗网络(GANs)通常难以导航并有效地利用输入潜在空间。因此,在稀疏输入潜在空间中从相邻变量生成的图像在真实性方面可能存在重大差异,导致次优的一致性正则化(CR)结果。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了SQ-GAN这一新方法,通过引入风格空间量化方案增强CR。该方法将稀疏、连续的输入潜在空间转换为紧凑、结构化的离散代理空间,使每个元素对应一个特定的真实数据点,从而提高CR性能。我们不是直接进行量化,而是首先将输入潜在变量映射到不那么纠缠的“风格”空间,然后使用可学习的代码本进行量化。这使得每个量化代码能够控制不同的变量因素。此外,我们优化了最佳传输距离,将代码本代码与基础模型从训练数据中提取的特征进行对齐,将外部知识嵌入到代码本中,并建立语义丰富的词汇表,适当描述训练数据集。大量实验表明,我们的方法在判别器稳健性和生成质量方面都有显著提高。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在有限数据环境下,生成对抗网络(GANs)在导航和有效探索输入潜在空间方面常常遇到困难。当在稀疏的输入潜在空间中从相邻变量生成图像时,可能会出现现实感的显著差异,导致次优的一致性正则化(CR)结果。为解决这一问题,我们提出了SQ-GAN这一新方法,通过引入风格空间量化方案,增强CR效果。它将稀疏的连续输入潜在空间转化为紧凑的结构化离散代理空间,使每个元素都能对应一个真实的数据点,从而提高CR性能。我们采用可学习的代码本进行量化,而非直接量化,首先将输入潜在变量映射到一个较少纠缠的“风格”空间。此外,我们还优化了运输距离,使代码本代码与基础模型从训练数据中提取的特征保持一致,将外部知识嵌入代码本中,建立了丰富的语义词汇表来描述训练数据集。实验证明,我们的方法在判别器稳健性和生成质量方面都有显著提高。
Key Takeaways
- GANs在有限数据环境下在探索和导航潜在空间时遇到困难。
- 在稀疏的输入潜在空间中生成的图像可能显示出显著的现实感差异。
- 提出SQ-GAN方法,通过风格空间量化增强一致性正则化效果。
- 将连续输入潜在空间转化为离散代理空间,提高CR性能。
- 采用可学习的代码本进行量化,使每个量化代码对应一个真实数据点。
- 优化运输距离以对齐代码本代码与训练数据的特征,嵌入外部知识并丰富语义词汇表。
点此查看论文截图

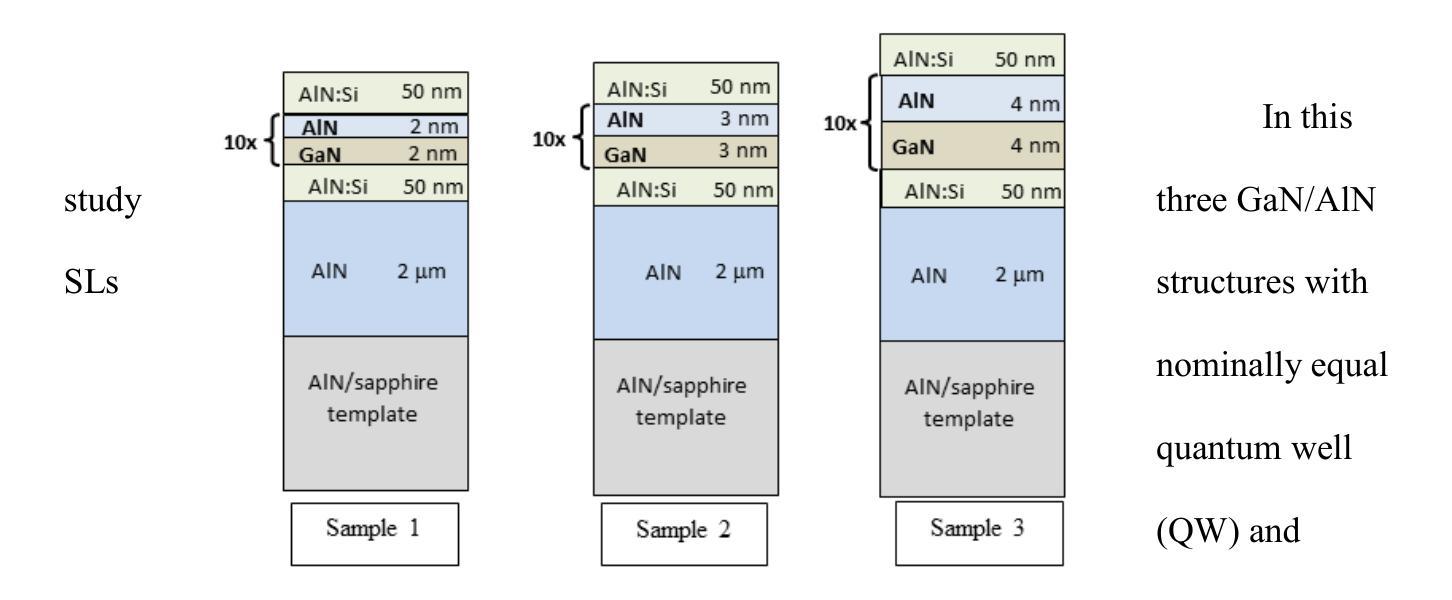
Strain distribution in GaN/AlN superlattices grown on AlN/sapphire templates: comparison of X-ray diffraction and photoluminescence studies
Authors:Aleksandra Wierzbicka, Agata Kaminska, Kamil Sobczak, Dawid Jankowski, Kamil Koronski, Pawel Strak, Marta Sobanska, Zbigniew R. Zytkiewicz
Series of GaN/AlN superlattices (SLs) with various periods and the same thicknesses of GaN quantum wells and AlN barriers have been investigated. X-ray diffraction, photoluminescence (PL) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) techniques were used to study the influence of thickness of AlN and GaN sublayers on strain distribution in GaN/AlN SL structures. Detailed X-ray diffraction measurements demonstrate that the strain occurring in SLs generally decreases with an increase of well/barrier thickness. Fitting of X-ray diffraction curves allowed determining the real thicknesses of the GaN wells and AlN barriers. Since blurring of the interfaces causes deviation of calculated data from experimental results the quality of the interfaces has been evaluated as well and compared with results of TEM measurements. For the samples with thinner wells/barriers the presence of pin-holes and threading dislocations has been observed in TEM measurements. The best quality of interfaces has been found for the sample with a well/barrier thickness of 3 nm. Finally, PL spectra showed that due to Quantum-Confined Stark Effect the PL peak energies of the SLs decreased with increasing the width of the GaN quantum wells and AlN barriers. The effect is well modelled by ab initio calculations based on the density functional theory applied for tetragonally strained structures of the same geometry using a full tensorial representation of the strain in the SLs.
已经研究了具有不同周期和相同GaN量子阱和AlN势垒厚度的GaN/AlN超晶格(SLs)系列。使用X射线衍射、光致发光(PL)和透射电子显微镜(TEM)技术,研究了AlN和GaN亚层厚度对GaN/AlN SL结构中应变分布的影响。详细的X射线衍射测量结果表明,SLs中的应变通常会随着阱/势垒厚度的增加而减小。通过拟合X射线衍射曲线,可以确定GaN阱和AlN势垒的实际厚度。由于界面模糊导致计算数据与实验结果之间存在偏差,因此还对界面质量进行了评估,并将其与TEM测量结果进行了比较。在较薄阱/势垒的样品中,通过TEM测量观察到存在针孔和贯穿位错。在阱/势垒厚度为3nm的样品中发现界面质量最佳。最后,PL光谱显示,由于量子限制斯塔克效应,SLs的PL峰能量随着GaN量子阱和AlN势垒宽度的增加而降低。该效应可以通过基于密度泛函理论的第一性原理计算进行很好的模拟,该计算适用于具有相同几何形状的四边形应变结构,并使用SLs中的应变的全张量表示。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文研究了不同周期的GaN/AlN超晶格(SLs)结构,采用X射线衍射、光致发光和透射电子显微镜技术,探讨了AlN和GaN亚层厚度对GaN/AlN超晶格结构应变分布的影响。研究发现,随着阱/势垒厚度的增加,超晶格中的应变一般会减小。通过X射线衍射曲线的拟合,确定了GaN阱和AlN势垒的实际厚度。同时,对界面的质量进行了评估,并与透射电子显微镜的测量结果进行了比较。在较薄的阱/势垒样品中,透射电子显微镜观察到存在针孔和螺纹位错。在阱/势垒厚度为3nm的样品中获得了最佳界面质量。此外,光致发光光谱表明,由于量子限制斯塔克效应,SLs的发光峰能量随着GaN量子阱和AlN势垒宽度的增加而降低。这一效应通过基于密度泛函理论的第一性原理计算得到了很好的模拟。
Key Takeaways
- GaN/AlN超晶格系列的周期和量子阱厚度对比研究表明,应变随阱/势垒厚度的增加而减小。
- 通过X射线衍射测量确定了GaN阱和AlN势垒的实际厚度。
- 界面质量的评估发现,较薄阱/势垒的样品中存在针孔和螺纹位错。
- 最佳界面质量在阱/势垒厚度为3nm的样品中发现。
- 光致发光光谱揭示了量子限制斯塔克效应在超晶格中的重要作用。
- 随着GaN量子阱和AlN势垒宽度的增加,发光峰能量降低。
点此查看论文截图

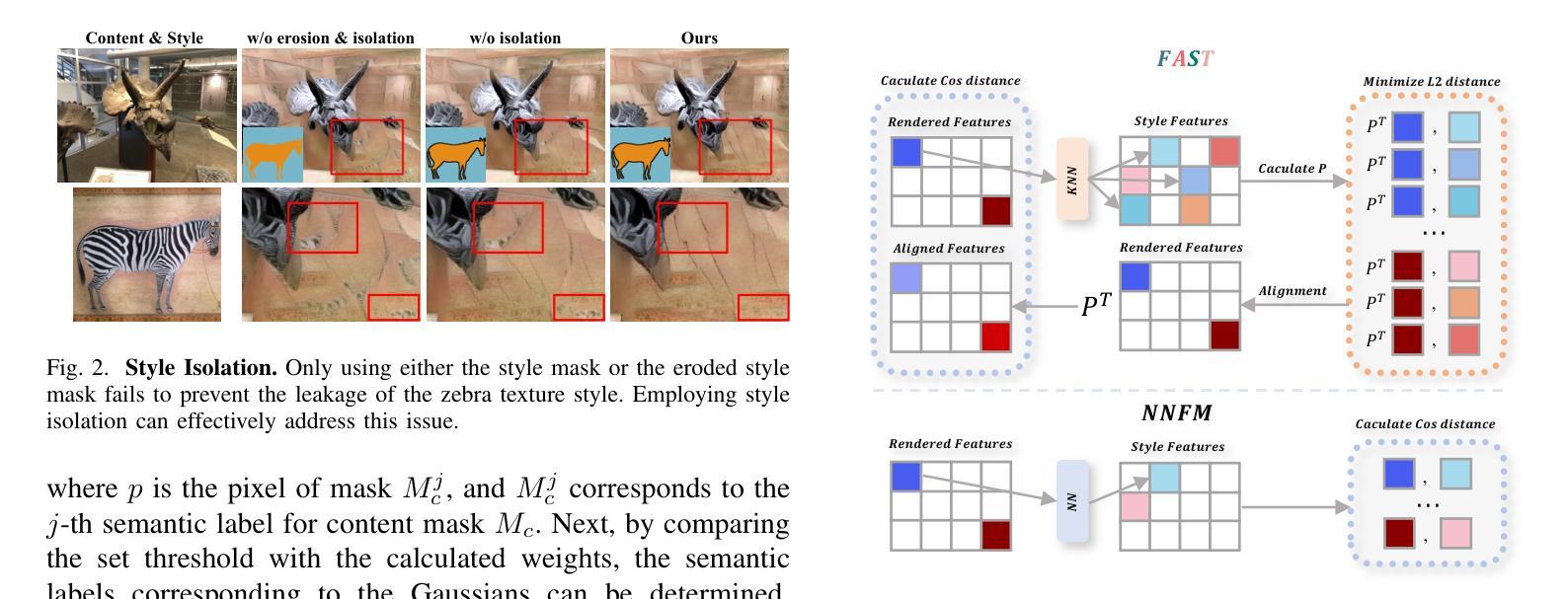
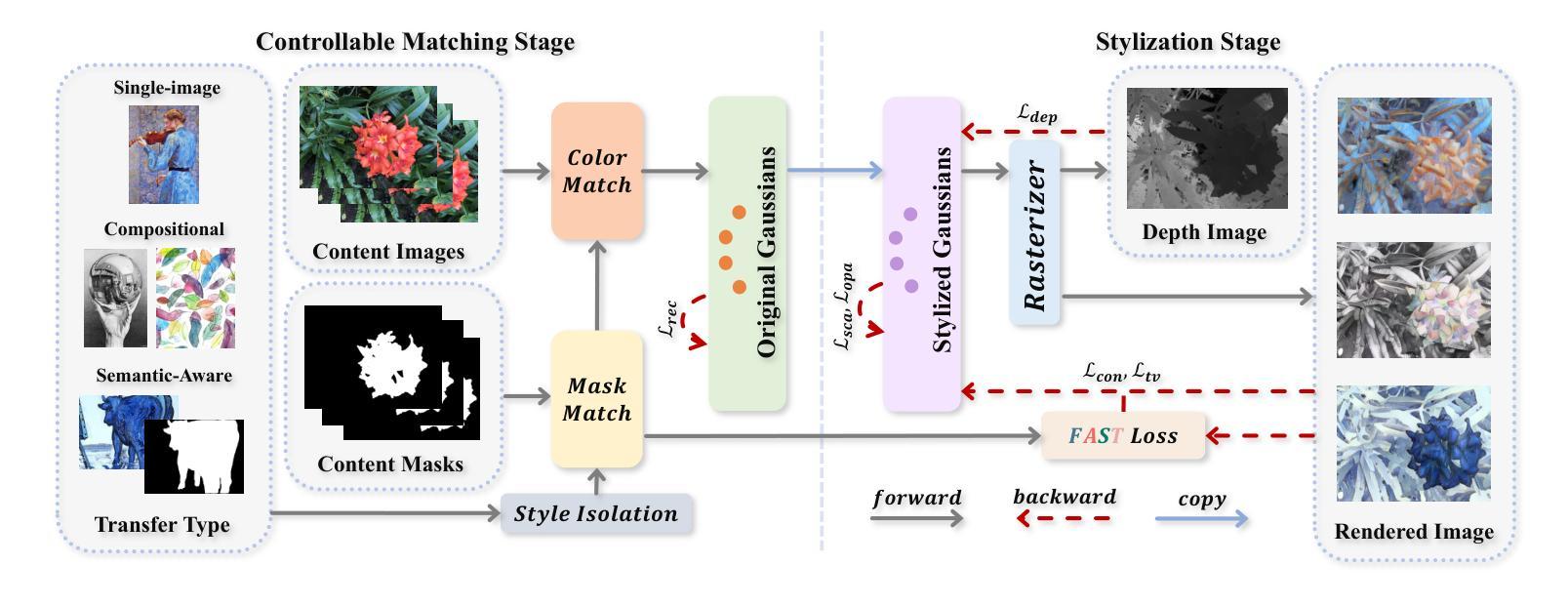
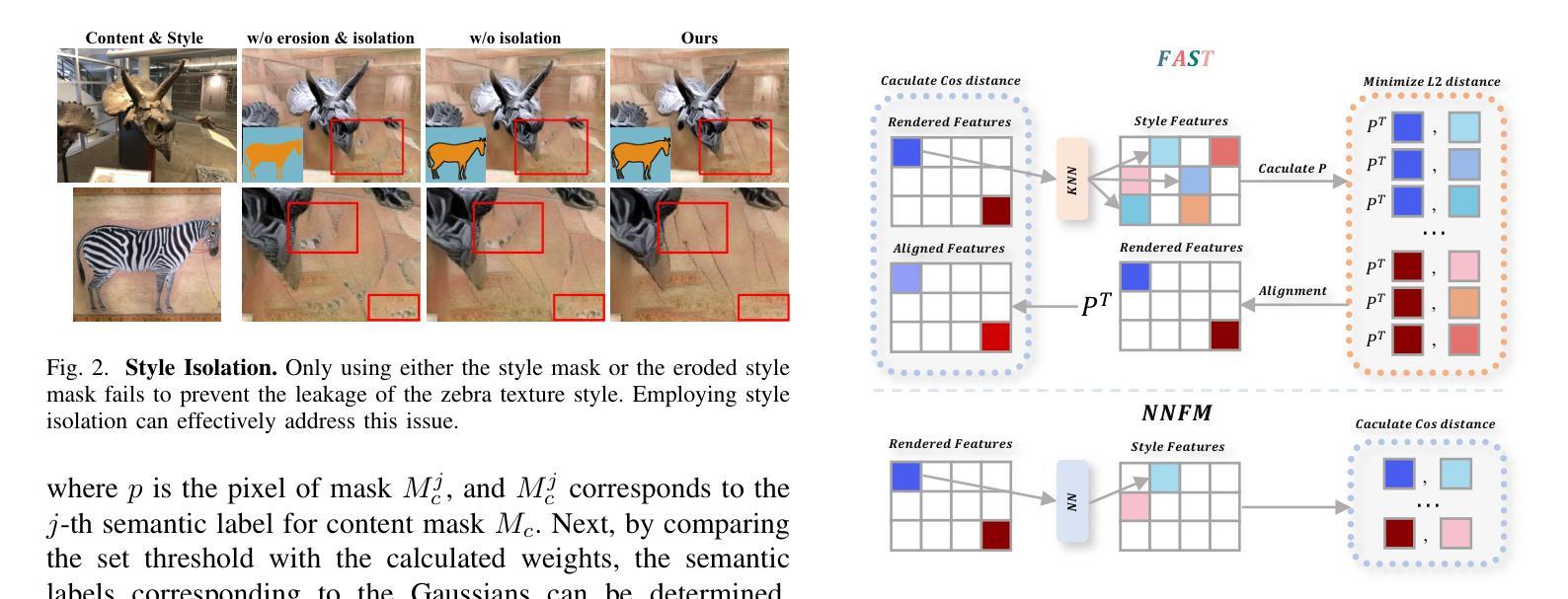
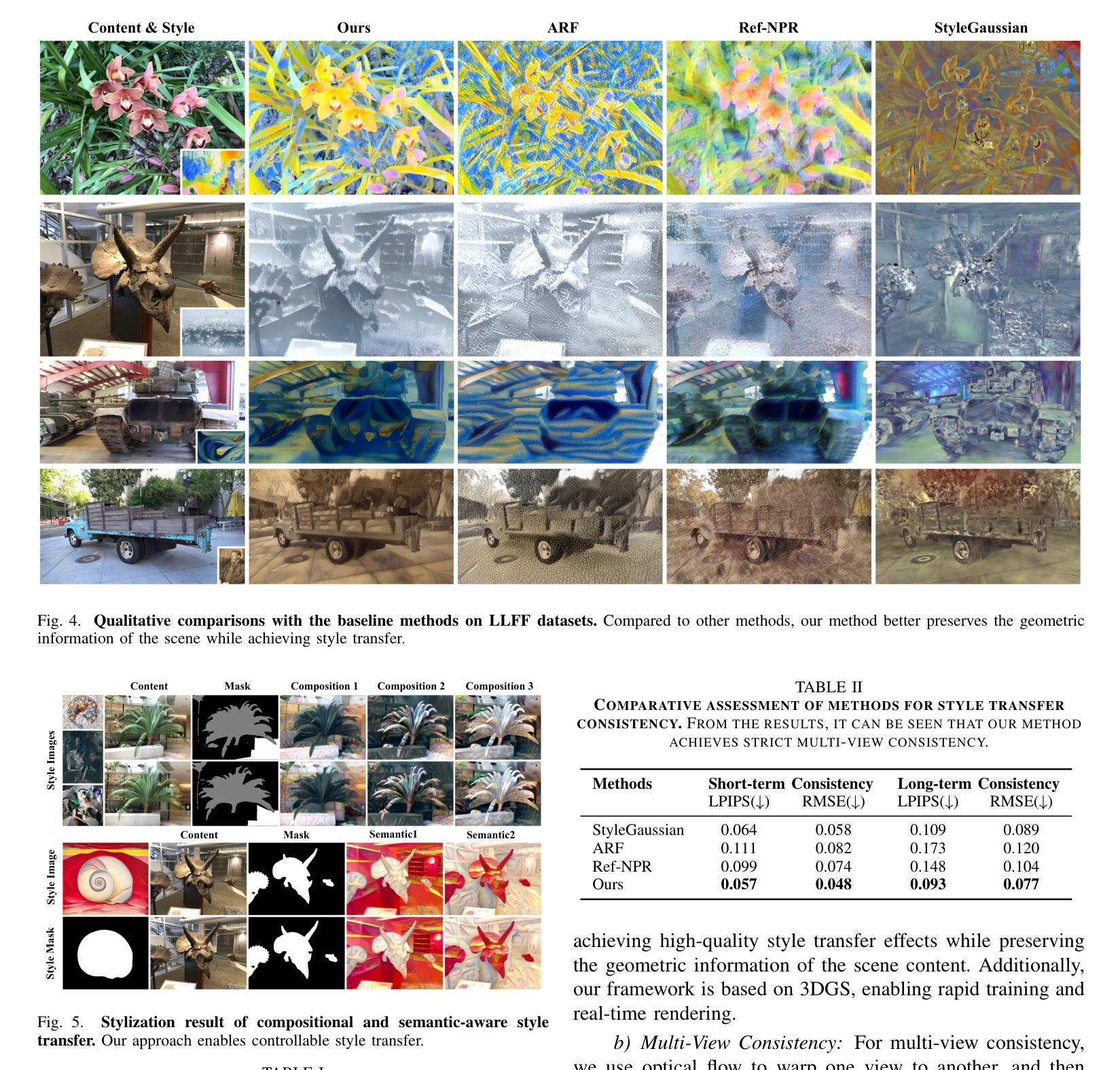
ABC-GS: Alignment-Based Controllable Style Transfer for 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Wenjie Liu, Zhongliang Liu, Xiaoyan Yang, Man Sha, Yang Li
3D scene stylization approaches based on Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) achieve promising results by optimizing with Nearest Neighbor Feature Matching (NNFM) loss. However, NNFM loss does not consider global style information. In addition, the implicit representation of NeRF limits their fine-grained control over the resulting scenes. In this paper, we introduce ABC-GS, a novel framework based on 3D Gaussian Splatting to achieve high-quality 3D style transfer. To this end, a controllable matching stage is designed to achieve precise alignment between scene content and style features through segmentation masks. Moreover, a style transfer loss function based on feature alignment is proposed to ensure that the outcomes of style transfer accurately reflect the global style of the reference image. Furthermore, the original geometric information of the scene is preserved with the depth loss and Gaussian regularization terms. Extensive experiments show that our ABC-GS provides controllability of style transfer and achieves stylization results that are more faithfully aligned with the global style of the chosen artistic reference. Our homepage is available at https://vpx-ecnu.github.io/ABC-GS-website.
基于神经辐射场(NeRF)的3D场景风格化方法通过最近邻特征匹配(NNFM)损失进行优化,取得了有前景的结果。然而,NNFM损失并没有考虑全局风格信息。此外,NeRF的隐式表示限制了其对结果场景的细粒度控制。在本文中,我们介绍了ABC-GS,一个基于3D高斯喷涂的新型框架,以实现高质量的三维风格转移。为此,设计了一个可控的匹配阶段,通过分割掩膜实现场景内容与风格特征的精确对齐。此外,提出了一种基于特征对齐的风格转移损失函数,以确保风格转移的结果准确反映参考图像的全局风格。此外,通过深度损失和高斯正则化项保留了场景的原几何信息。大量实验表明,我们的ABC-GS提供了风格转移的控制能力,并实现了与所选艺术参考的全局风格更忠实对齐的风格化结果。我们的主页可在https://vpx-ecnu.github.io/ABC-GS-website访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 14 figures
Summary
基于NeRF的3D场景风格化方法通过采用最近邻特征匹配(NNFM)损失进行优化,取得了有前景的结果。但NNFM损失没有考虑全局风格信息,且NeRF的隐式表示限制了场景的精细控制。本文提出ABC-GS框架,基于3D高斯拼贴实现高质量3D风格转移。设计可控匹配阶段,通过分割掩膜实现场景内容与风格特征的精确对齐。提出基于特征对齐的风格转移损失函数,确保风格转移结果准确反映参考图像的全局风格。同时保留场景的原始几何信息,通过深度损失和高斯正则化项实现。
Key Takeaways
- 3D场景风格化方法基于NeRF和NNFM损失优化取得进展。
- NNFM损失不考虑全局风格信息,NeRF的隐式表示限制了精细控制。
- ABC-GS框架实现高质量3D风格转移,基于3D高斯拼贴技术。
- 引入可控匹配阶段,通过分割掩膜精确对齐场景内容与风格特征。
- 提出基于特征对齐的风格转移损失函数,确保反映全局风格。
- 保留原始场景的几何信息,通过深度损失和高斯正则化项实现。
点此查看论文截图

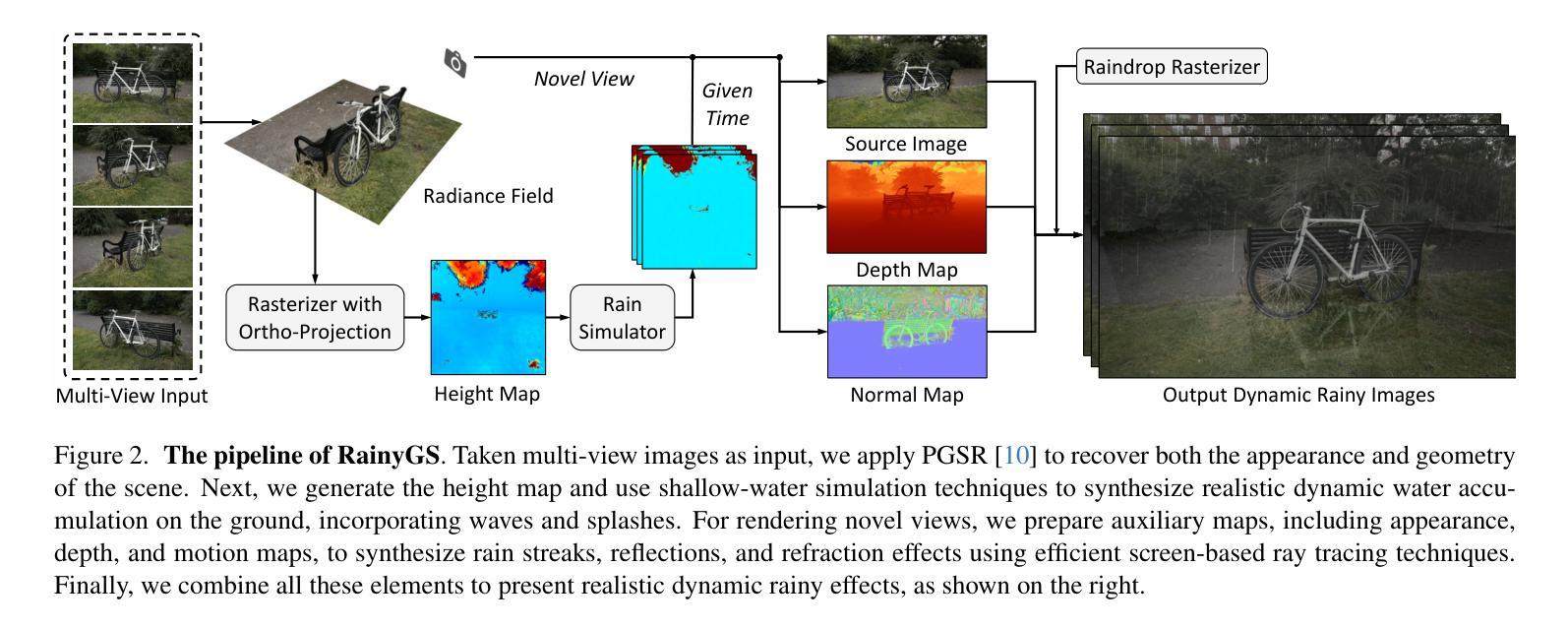
RainyGS: Efficient Rain Synthesis with Physically-Based Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Qiyu Dai, Xingyu Ni, Qianfan Shen, Wenzheng Chen, Baoquan Chen, Mengyu Chu
We consider the problem of adding dynamic rain effects to in-the-wild scenes in a physically-correct manner. Recent advances in scene modeling have made significant progress, with NeRF and 3DGS techniques emerging as powerful tools for reconstructing complex scenes. However, while effective for novel view synthesis, these methods typically struggle with challenging scene editing tasks, such as physics-based rain simulation. In contrast, traditional physics-based simulations can generate realistic rain effects, such as raindrops and splashes, but they often rely on skilled artists to carefully set up high-fidelity scenes. This process lacks flexibility and scalability, limiting its applicability to broader, open-world environments. In this work, we introduce RainyGS, a novel approach that leverages the strengths of both physics-based modeling and 3DGS to generate photorealistic, dynamic rain effects in open-world scenes with physical accuracy. At the core of our method is the integration of physically-based raindrop and shallow water simulation techniques within the fast 3DGS rendering framework, enabling realistic and efficient simulations of raindrop behavior, splashes, and reflections. Our method supports synthesizing rain effects at over 30 fps, offering users flexible control over rain intensity – from light drizzles to heavy downpours. We demonstrate that RainyGS performs effectively for both real-world outdoor scenes and large-scale driving scenarios, delivering more photorealistic and physically-accurate rain effects compared to state-of-the-art methods. Project page can be found at https://pku-vcl-geometry.github.io/RainyGS/
我们考虑以物理正确的方式给自然场景添加动态雨水效果的问题。最近场景建模方面的进展已经取得了重大突破,NeRF和3DGS技术作为重建复杂场景的强大工具而崭露头角。然而,虽然这些方法在合成新视角方面很有效,但它们通常在处理具有挑战性的场景编辑任务(如基于物理的雨水模拟)时遇到困难。相比之下,传统的基于物理的模拟可以产生逼真的雨水效果,如雨滴和飞溅的水花,但它们通常依赖于熟练的艺术家来仔细设置高保真场景。这个过程缺乏灵活性和可扩展性,限制了其在更广泛、开放世界环境中的适用性。在这项工作中,我们介绍了RainyGS,这是一种新颖的方法,它结合了基于物理的建模和3DGS的优点,以在开放世界场景中生成具有物理准确性的逼真动态雨水效果。我们的方法的核心是在快速的3DGS渲染框架内整合基于物理的雨滴和浅水模拟技术,能够实现雨滴行为、飞溅和水面反射的逼真和高效模拟。我们的方法支持以超过30帧/秒的速度合成雨水效果,让用户可以灵活控制雨水的强度,从轻微的细雨到倾盆大雨。我们证明了RainyGS在真实户外场景和大规模驾驶场景中的有效性,与最新方法相比,它提供了更逼真和更物理准确的雨水效果。项目页面可在https://pku-vcl-geometry.github.io/RainyGS/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
本文主要研究在复杂场景中添加动态雨效的难题,并介绍了一种结合物理建模和3DGS技术的新型方法RainyGS。该方法能够在开放世界场景中生成具有物理准确性的高逼真度动态雨效,融合了基于物理的雨滴和浅水模拟技术,在快速3DGS渲染框架内实现了对雨滴行为、溅起和反射的逼真且高效的模拟。用户可灵活控制雨势强度,并支持在真实户外场景和大规模驾驶场景中的有效应用。
Key Takeaways
- 本文考虑在野外场景中增加具有物理正确性的动态雨效问题。
- 介绍了RainyGS方法,该方法结合了物理建模和3DGS技术来生成逼真的动态雨效。
- RainyGS方法能够在开放世界场景中生成具有物理准确性的高逼真度雨效。
- 该方法融合了基于物理的雨滴和浅水模拟技术,在快速3DGS渲染框架内实现了对雨滴行为等的逼真模拟。
- 用户可以灵活控制雨势强度,实现从细雨到大雨的模拟。
- RainyGS在真实户外场景和大规模驾驶场景中的应用效果良好。
点此查看论文截图

LandMarkSystem Technical Report
Authors:Zhenxiang Ma, Zhenyu Yang, Miao Tao, Yuanzhen Zhou, Zeyu He, Yuchang Zhang, Rong Fu, Hengjie Li
3D reconstruction is vital for applications in autonomous driving, virtual reality, augmented reality, and the metaverse. Recent advancements such as Neural Radiance Fields(NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have transformed the field, yet traditional deep learning frameworks struggle to meet the increasing demands for scene quality and scale. This paper introduces LandMarkSystem, a novel computing framework designed to enhance multi-scale scene reconstruction and rendering. By leveraging a componentized model adaptation layer, LandMarkSystem supports various NeRF and 3DGS structures while optimizing computational efficiency through distributed parallel computing and model parameter offloading. Our system addresses the limitations of existing frameworks, providing dedicated operators for complex 3D sparse computations, thus facilitating efficient training and rapid inference over extensive scenes. Key contributions include a modular architecture, a dynamic loading strategy for limited resources, and proven capabilities across multiple representative algorithms.This comprehensive solution aims to advance the efficiency and effectiveness of 3D reconstruction tasks.To facilitate further research and collaboration, the source code and documentation for the LandMarkSystem project are publicly available in an open-source repository, accessing the repository at: https://github.com/InternLandMark/LandMarkSystem.
三维重建在自动驾驶、虚拟现实、增强现实和元宇宙等应用中具有重要意义。最近的进展,如神经网络辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯溅射(3DGS),已经推动了该领域的发展,但传统的深度学习框架难以满足日益增长的场景质量和规模的需求。本文介绍了LandMarkSystem,这是一种新型计算框架,旨在提高多尺度场景重建和渲染。通过利用组件化模型适配层,LandMarkSystem支持各种NeRF和3DGS结构,同时通过分布式并行计算和模型参数卸载优化计算效率。我们的系统解决了现有框架的局限性,为复杂的三维稀疏计算提供了专用操作符,从而实现了大规模场景的快速训练和推理。主要贡献包括模块化架构、有限资源的动态加载策略以及在多种代表性算法中的能力验证。该全面解决方案旨在提高三维重建任务的效率和效果。为了方便进一步的研究和合作,LandMarkSystem项目的源代码和文档已在开源仓库中公开可用,可通过以下链接访问:https://github.com/InternLandMark/LandMarkSystem。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
新一代三维重建计算框架LandMarkSystem研究提出。采用组件化模型自适应层技术,结合NeRF与多种传统框架的优点提升场景渲染效果与效率。支持分布式并行计算与模型参数卸载,实现模块化架构与动态加载策略,面向大规模场景提供高效训练和推理能力。该项目公开源代码与文档,促进进一步研究和合作。
Key Takeaways
- LandMarkSystem是一个新型三维重建计算框架,利用NeRF和3DGS技术的优点增强多尺度场景重建和渲染。
- 引入组件化模型自适应层技术,优化计算效率并支持多种NeRF和3DGS结构。
- 通过分布式并行计算和模型参数卸载解决现有框架的限制。
- 实现模块化架构和动态加载策略,适用于资源有限的场景。
- 在大规模场景上提供高效训练和推理能力。
- 项目公开源代码和文档,便于进一步研究和合作。
点此查看论文截图

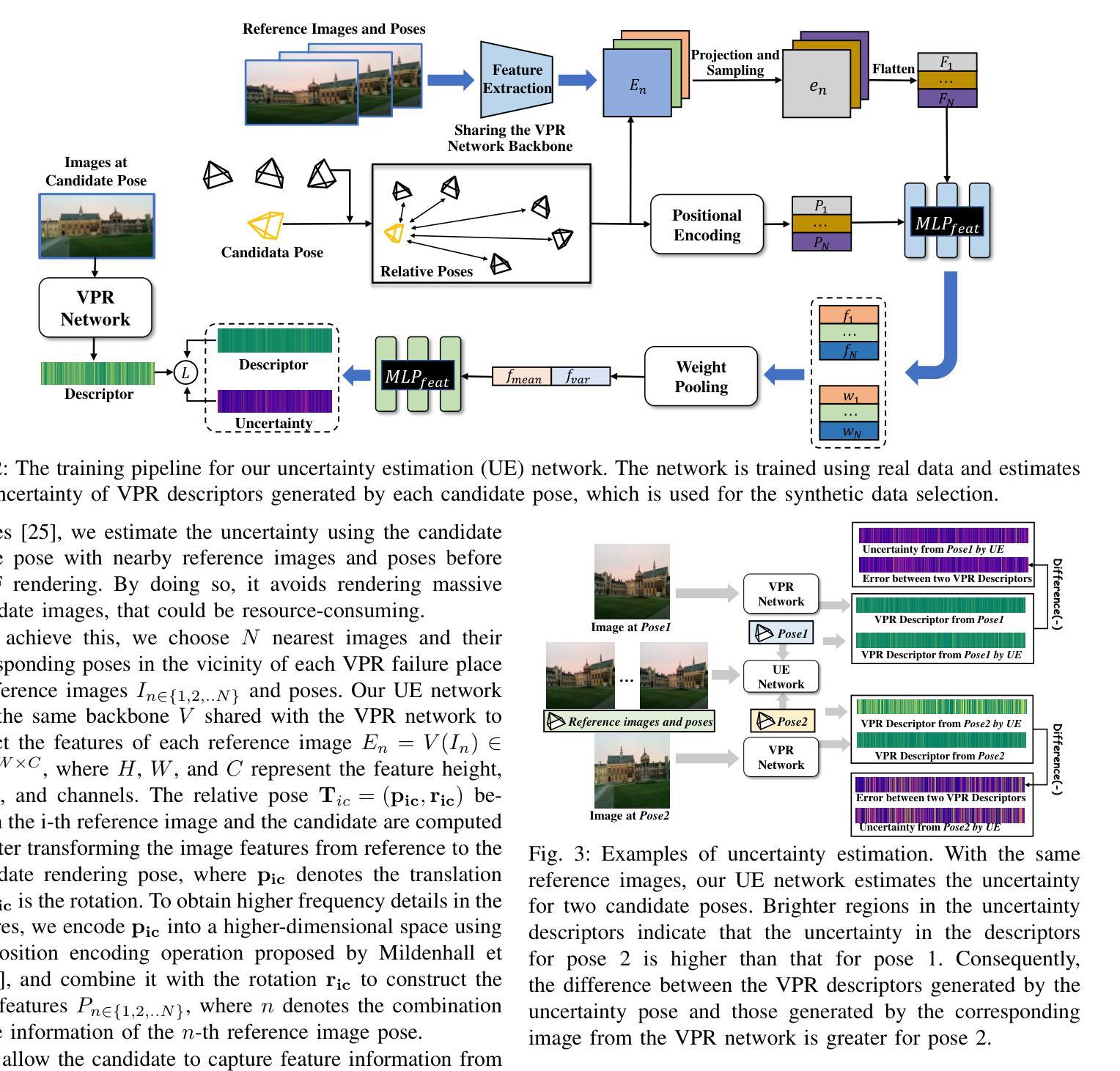
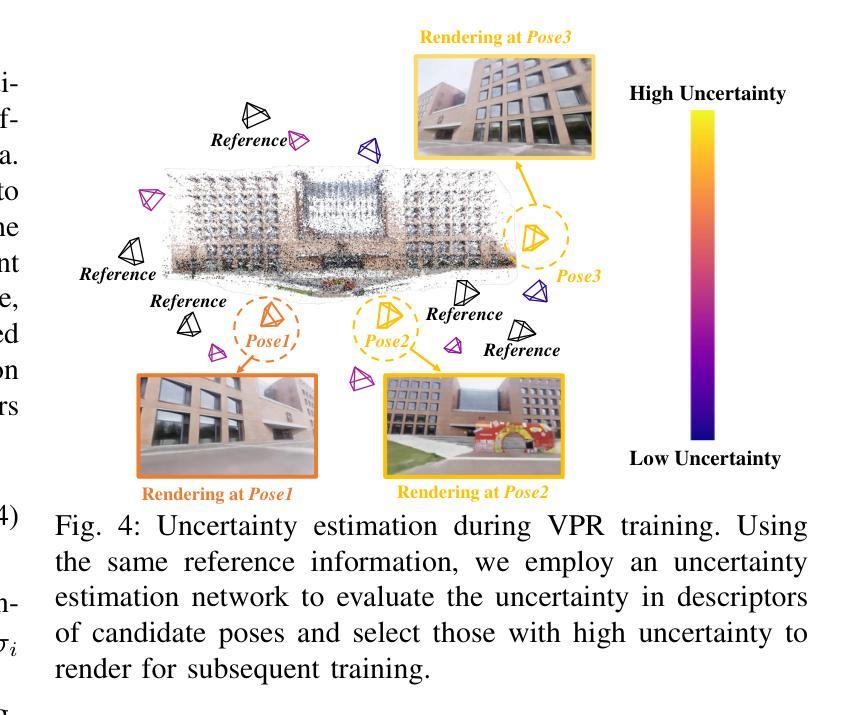
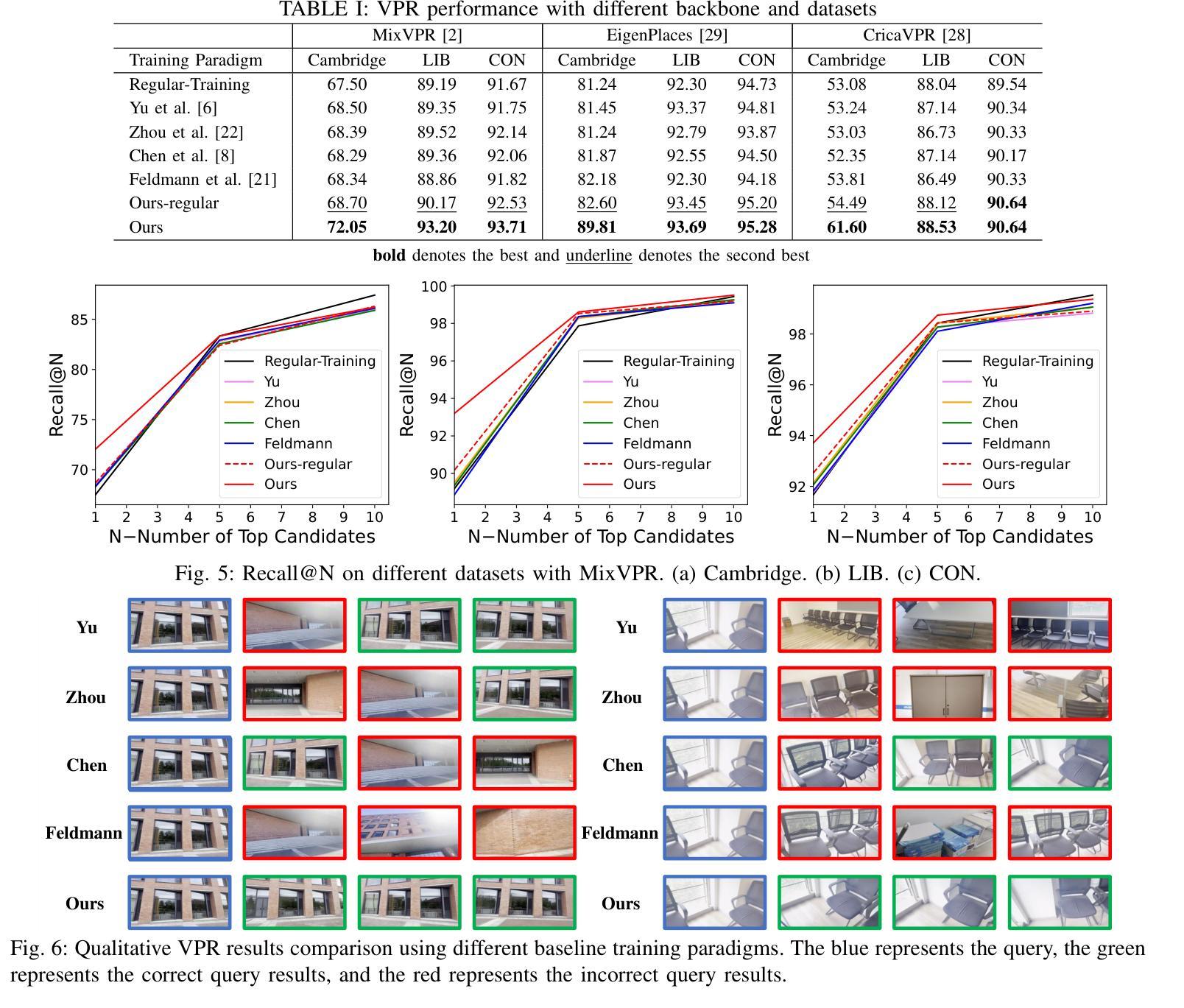
UGNA-VPR: A Novel Training Paradigm for Visual Place Recognition Based on Uncertainty-Guided NeRF Augmentation
Authors:Yehui Shen, Lei Zhang, Qingqiu Li, Xiongwei Zhao, Yue Wang, Huimin Lu, Xieyuanli Chen
Visual place recognition (VPR) is crucial for robots to identify previously visited locations, playing an important role in autonomous navigation in both indoor and outdoor environments. However, most existing VPR datasets are limited to single-viewpoint scenarios, leading to reduced recognition accuracy, particularly in multi-directional driving or feature-sparse scenes. Moreover, obtaining additional data to mitigate these limitations is often expensive. This paper introduces a novel training paradigm to improve the performance of existing VPR networks by enhancing multi-view diversity within current datasets through uncertainty estimation and NeRF-based data augmentation. Specifically, we initially train NeRF using the existing VPR dataset. Then, our devised self-supervised uncertainty estimation network identifies places with high uncertainty. The poses of these uncertain places are input into NeRF to generate new synthetic observations for further training of VPR networks. Additionally, we propose an improved storage method for efficient organization of augmented and original training data. We conducted extensive experiments on three datasets and tested three different VPR backbone networks. The results demonstrate that our proposed training paradigm significantly improves VPR performance by fully utilizing existing data, outperforming other training approaches. We further validated the effectiveness of our approach on self-recorded indoor and outdoor datasets, consistently demonstrating superior results. Our dataset and code have been released at \href{https://github.com/nubot-nudt/UGNA-VPR}{https://github.com/nubot-nudt/UGNA-VPR}.
视觉定位(VPR)对于机器人识别先前访问过的位置至关重要,在室内和室外环境的自主导航中发挥着重要作用。然而,大多数现有的VPR数据集仅限于单一视点的场景,导致识别精度降低,特别是在多方向驾驶或特征稀疏的场景中。此外,获取额外的数据来缓解这些限制通常成本高昂。本文引入了一种新的训练范式,通过不确定性估计和基于NeRF的数据增强来提高现有VPR网络性能,增强当前数据集内的多视图多样性。具体来说,我们首先使用现有的VPR数据集训练NeRF。然后,我们设计的自监督不确定性估计网络会识别出不确定性较高的位置。这些不确定位置的姿势被输入到NeRF中,以生成新的合成观察结果,用于进一步训练VPR网络。此外,我们还提出了一种改进的数据存储方法,用于有效地组织增强和原始训练数据。我们在三个数据集上进行了大量实验,并测试了三种不同的VPR主干网络。结果表明,我们提出的训练范式充分利用了现有数据,显著提高了VPR性能,超过了其他训练方法。我们在自己收集的室内和室外数据集上进一步验证了我们的方法的有效性,始终表现出优越的结果。我们的数据集和代码已发布在https://github.com/nubot-nudt/UGNA-VPR。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L)
Summary
本文提出一种新颖的训练范式,通过不确定性估计和基于NeRF的数据增强技术,增强现有VPR网络的多视角多样性,提高其在多方向驾驶和特征稀疏场景中的识别准确性。通过训练NeRF使用现有VPR数据集,引入自我监督的不确定性估计网络来识别高不确定性地点,并将其姿态输入NeRF生成新的合成观测数据,用于进一步训练VPR网络。同时,提出了一种改进存储方法,以便更有效地组织原始和增强训练数据。实验证明,该方法能充分利用现有数据,显著提高VPR性能。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种新的训练范式,旨在提高视觉场所识别(VPR)网络的性能。
- 通过不确定性估计和NeRF技术增强多视角多样性,克服现有VPR数据集的单视角局限。
- 利用自我监督的不确定性估计网络识别高不确定性地点,并通过NeRF生成新的合成观测数据。
- 提出一种改进存储方法,有效组织原始和增强训练数据。
- 在三个数据集上进行广泛实验,测试三种不同的VPR骨干网络,证明该方法显著提高了VPR性能。
- 在自录的室内和室外数据集上验证了该方法的有效性,均取得优越结果。
点此查看论文截图

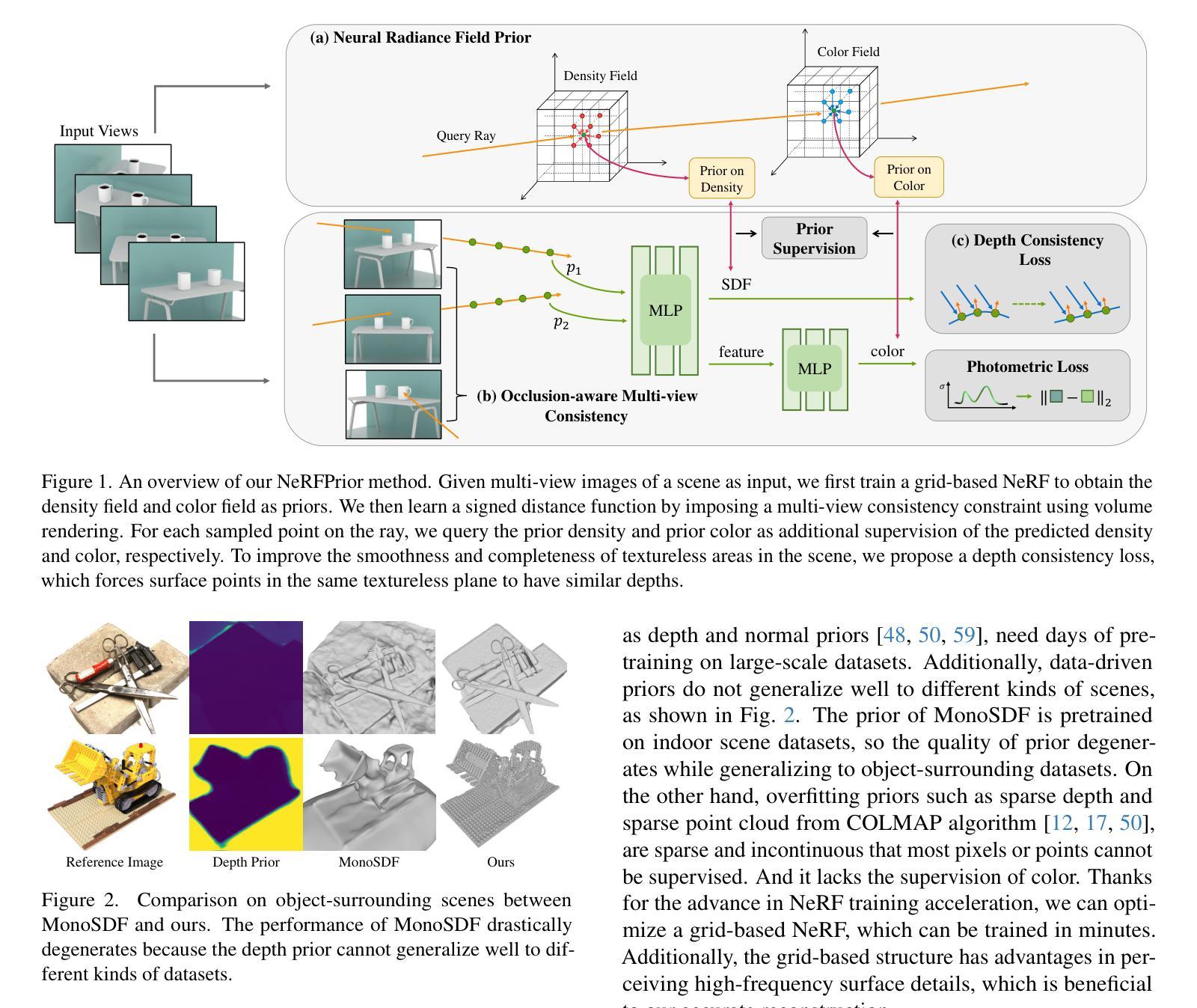
NeRFPrior: Learning Neural Radiance Field as a Prior for Indoor Scene Reconstruction
Authors:Wenyuan Zhang, Emily Yue-ting Jia, Junsheng Zhou, Baorui Ma, Kanle Shi, Yu-Shen Liu, Zhizhong Han
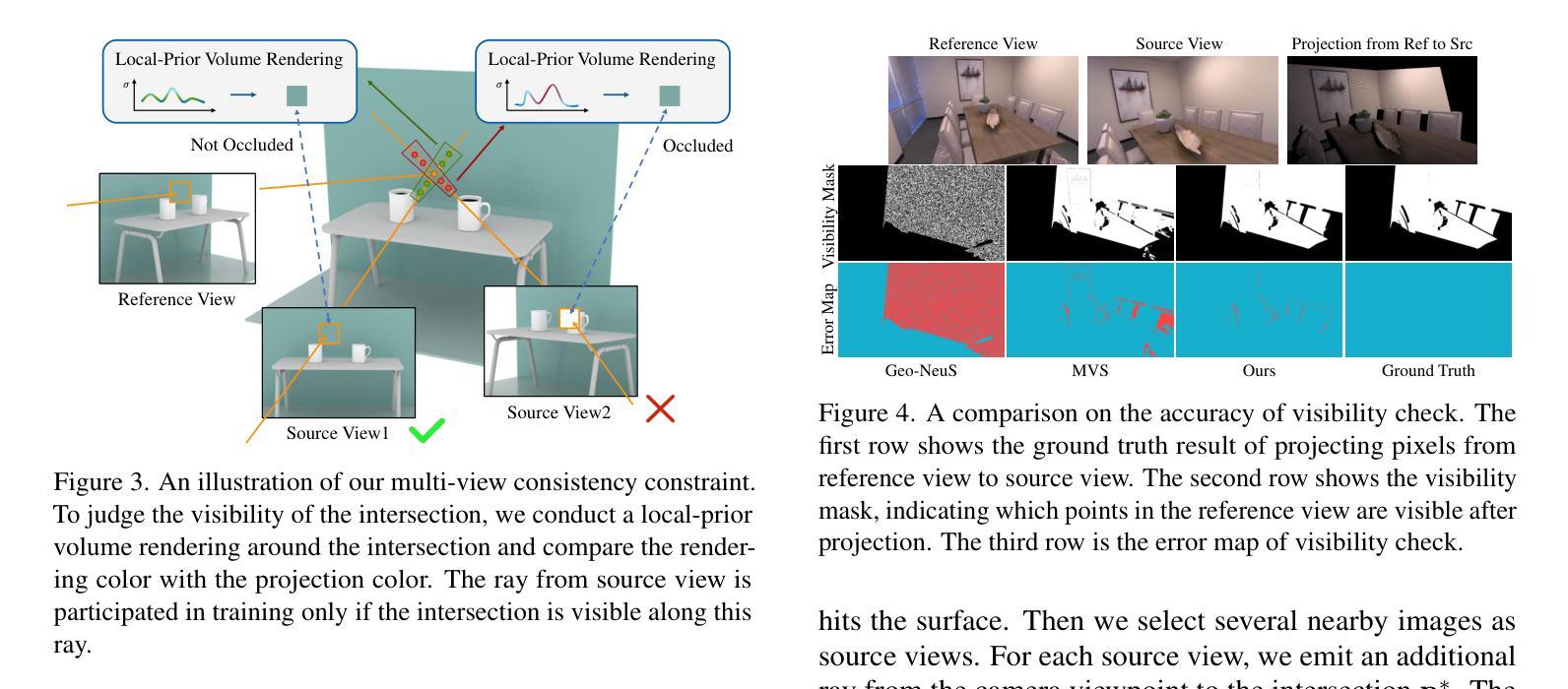
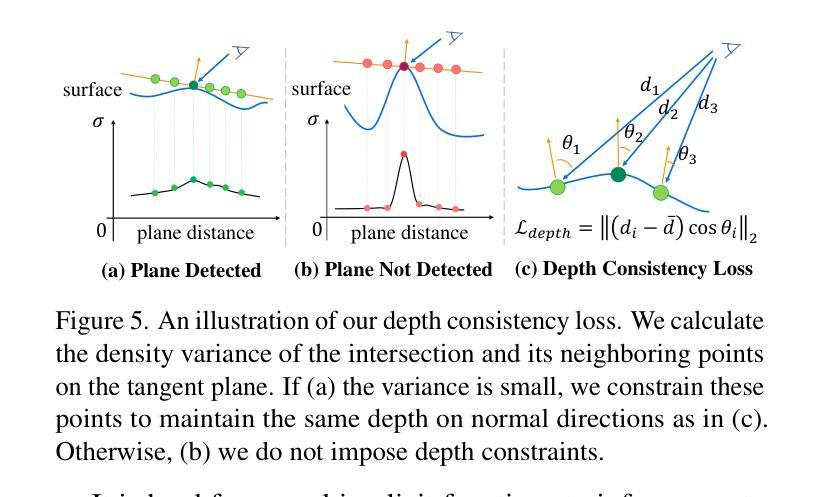
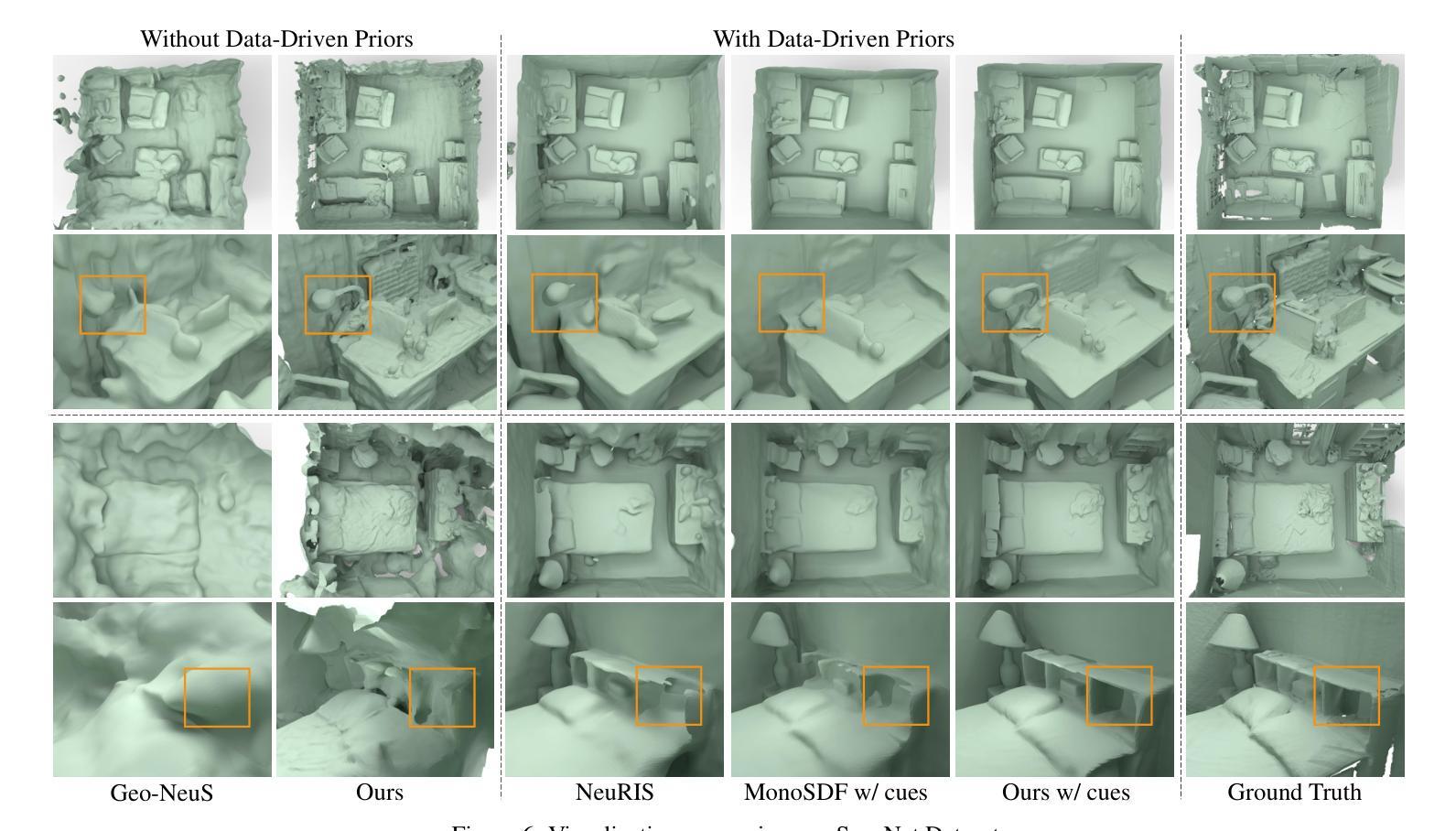
Recently, it has shown that priors are vital for neural implicit functions to reconstruct high-quality surfaces from multi-view RGB images. However, current priors require large-scale pre-training, and merely provide geometric clues without considering the importance of color. In this paper, we present NeRFPrior, which adopts a neural radiance field as a prior to learn signed distance fields using volume rendering for surface reconstruction. Our NeRF prior can provide both geometric and color clues, and also get trained fast under the same scene without additional data. Based on the NeRF prior, we are enabled to learn a signed distance function (SDF) by explicitly imposing a multi-view consistency constraint on each ray intersection for surface inference. Specifically, at each ray intersection, we use the density in the prior as a coarse geometry estimation, while using the color near the surface as a clue to check its visibility from another view angle. For the textureless areas where the multi-view consistency constraint does not work well, we further introduce a depth consistency loss with confidence weights to infer the SDF. Our experimental results outperform the state-of-the-art methods under the widely used benchmarks.
最近,研究表明先验知识对于神经隐式函数从多视角RGB图像重建高质量表面至关重要。然而,当前先验知识需要大量预训练,并且仅提供几何线索,而未考虑颜色的重要性。在本文中,我们提出了NeRFPrior,它采用神经辐射场作为先验知识,使用体积渲染来学习有向距离场进行表面重建。我们的NeRF先验可以提供几何和颜色线索,并且在同一场景下无需额外数据即可快速进行训练。基于NeRF先验,我们能够通过在每条射线交点处显式施加多视角一致性约束来学习有向距离函数(SDF)进行表面推断。具体来说,在每条射线交点处,我们使用先验中的密度作为粗略的几何估计,同时使用接近表面的颜色作为从另一个视角检查其可见性的线索。对于纹理缺失区域,多视角一致性约束无法良好工作,我们进一步引入了带有置信权重的深度一致性损失来推断SDF。我们的实验结果超过了在广泛使用的基准测试上的最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025. Project page: https://wen-yuan-zhang.github.io/NeRFPrior/
Summary
本论文提出了NeRFPrior,使用神经辐射场作为先验来学习符号距离场,通过体积渲染进行表面重建。NeRFPrior不仅能提供几何和颜色线索,还在同一场景下无需额外数据即可快速训练。通过明确对每条射线交点施加多视角一致性约束,实现表面推断学习符号距离函数(SDF)。在纹理缺失区域,引入带有置信权重的深度一致性损失来推断SDF,实验结果优于现有前沿方法。
Key Takeaways
- NeRFPrior使用神经辐射场作为先验,能同时提供几何和颜色线索。
- 无需大规模预训练和额外数据,NeRFPrior能快速适应同一场景。
- 通过体积渲染和符号距离场学习表面重建。
- 引入多视角一致性约束来学习符号距离函数(SDF)。
- 在纹理缺失区域,使用深度一致性损失来推断SDF。
- NeRFPrior的实验结果优于现有方法,在广泛使用的基准测试上表现突出。
点此查看论文截图

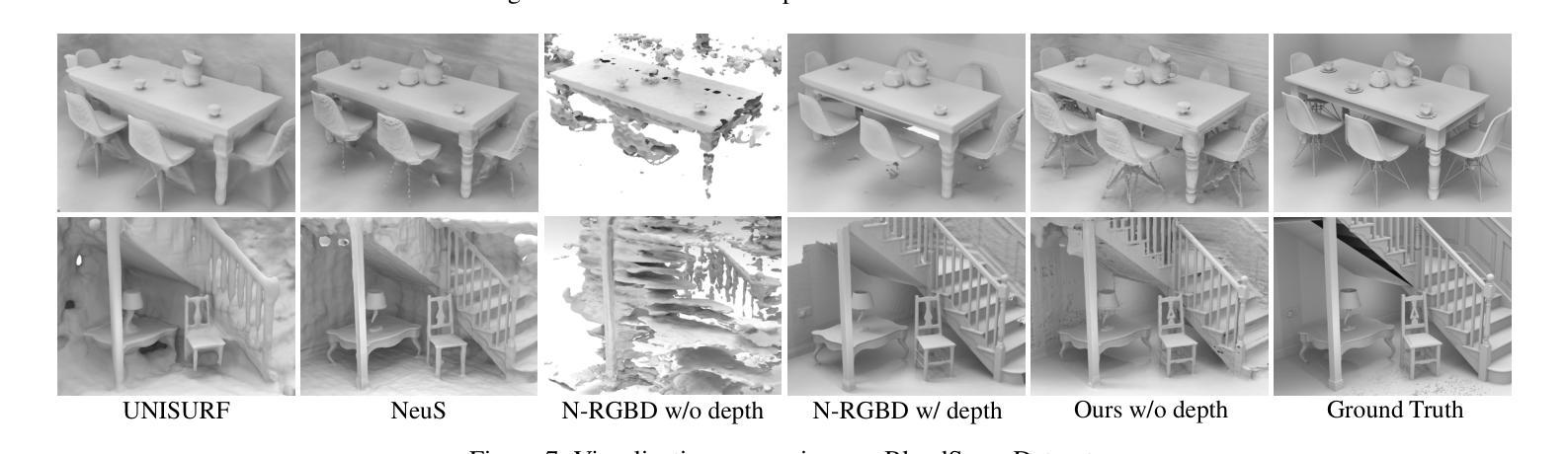
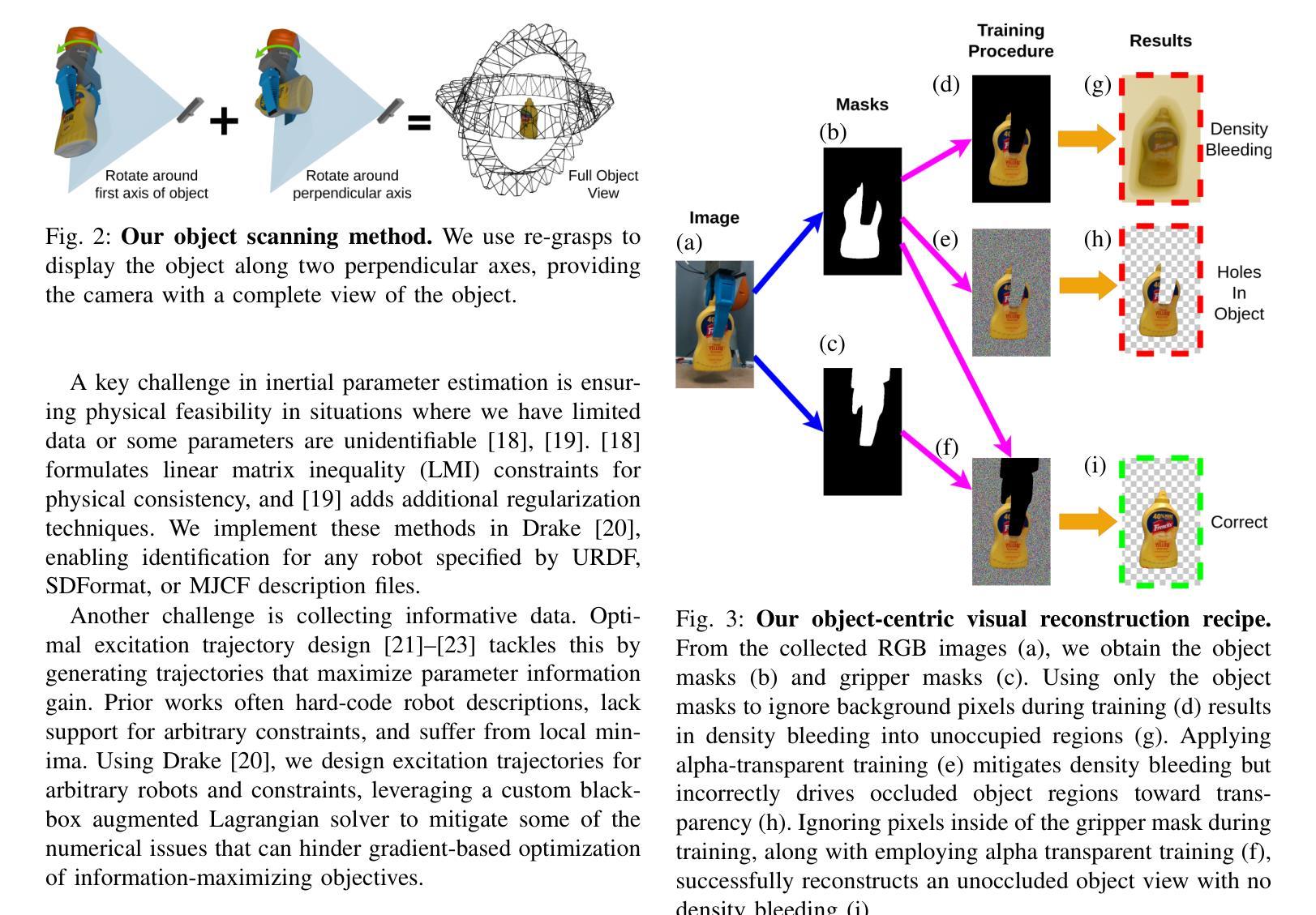
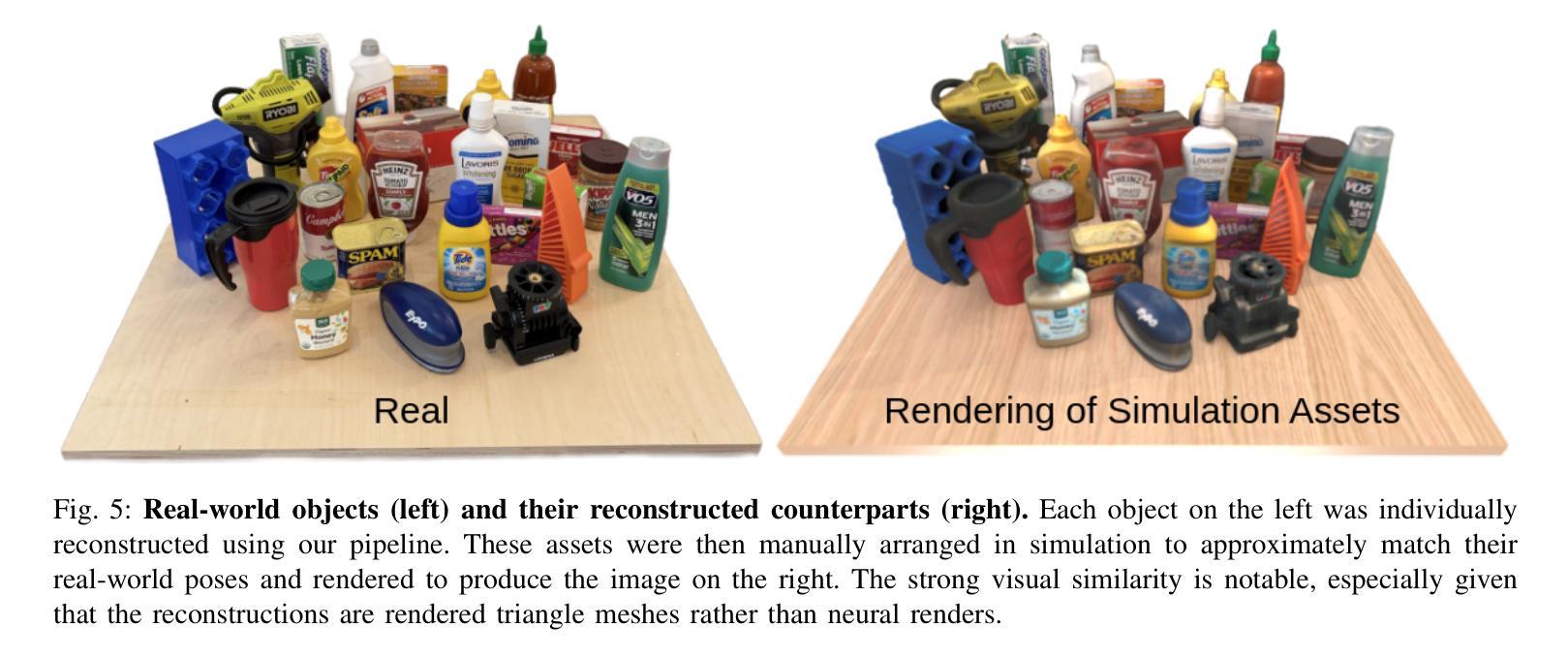
Scalable Real2Sim: Physics-Aware Asset Generation Via Robotic Pick-and-Place Setups
Authors:Nicholas Pfaff, Evelyn Fu, Jeremy Binagia, Phillip Isola, Russ Tedrake
Simulating object dynamics from real-world perception shows great promise for digital twins and robotic manipulation but often demands labor-intensive measurements and expertise. We present a fully automated Real2Sim pipeline that generates simulation-ready assets for real-world objects through robotic interaction. Using only a robot’s joint torque sensors and an external camera, the pipeline identifies visual geometry, collision geometry, and physical properties such as inertial parameters. Our approach introduces a general method for extracting high-quality, object-centric meshes from photometric reconstruction techniques (e.g., NeRF, Gaussian Splatting) by employing alpha-transparent training while explicitly distinguishing foreground occlusions from background subtraction. We validate the full pipeline through extensive experiments, demonstrating its effectiveness across diverse objects. By eliminating the need for manual intervention or environment modifications, our pipeline can be integrated directly into existing pick-and-place setups, enabling scalable and efficient dataset creation. Project page (with code and data): https://scalable-real2sim.github.io/.
通过从现实世界感知模拟物体动态,数字孪生和机器人操作领域展现出巨大的潜力,但这通常需要劳动密集型的测量和专业知识。我们提出了一种全自动的Real2Sim管道,通过机器人交互为现实世界物体生成模拟就绪资产。仅使用机器人的关节扭矩传感器和外部相机,该管道可以识别视觉几何、碰撞几何以及物理属性(例如惯性参数)。我们的方法引入了一种通用方法,通过采用alpha透明训练,利用光度重建技术(例如NeRF、高斯喷绘)提取高质量的对象中心网格,同时明确区分前景遮挡和背景减法。我们通过大量实验验证了整个管道的有效性,证明了其在各种对象中的有效性。通过消除对人工干预或环境修改的需求,我们的管道可以直接集成到现有的拾取和放置设置中,从而实现可扩展和高效的数据库创建。项目页面(含代码和数据):https://scalable-real2sim.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Website: https://scalable-real2sim.github.io/
Summary
该文章介绍了一种全自动的Real2Sim管道,用于通过机器人交互为真实世界物体生成模拟仿真资产。利用机器人的关节扭矩传感器和外部相机,该管道能够识别物体的视觉几何、碰撞几何和物理属性(如惯性参数)。文章还提出了一种采用alpha透明训练法从光度重建技术(如NeRF、高斯拼接技术)中提取高质量物体中心网格的方法,并能明确区分前景遮挡和背景减法。经过广泛的实验验证,该管道在多种物体上都展现出了良好的效果。它能够直接集成现有的拾取和放置设置,无需人工干预或环境改动,从而实现了可扩展且高效的数据集创建。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一种全自动的Real2Sim管道,用于生成模拟仿真资产。
- 通过机器人交互,利用机器人的关节扭矩传感器和外部相机进行识别。
- 能够识别物体的视觉几何、碰撞几何和物理属性(如惯性参数)。
- 采用了alpha透明训练法,能够从光度重建技术中提取高质量物体中心网格。
- 能够明确区分前景遮挡和背景减法。
- 经过广泛实验验证,该管道在多种物体上都展现出了良好效果。
点此查看论文截图



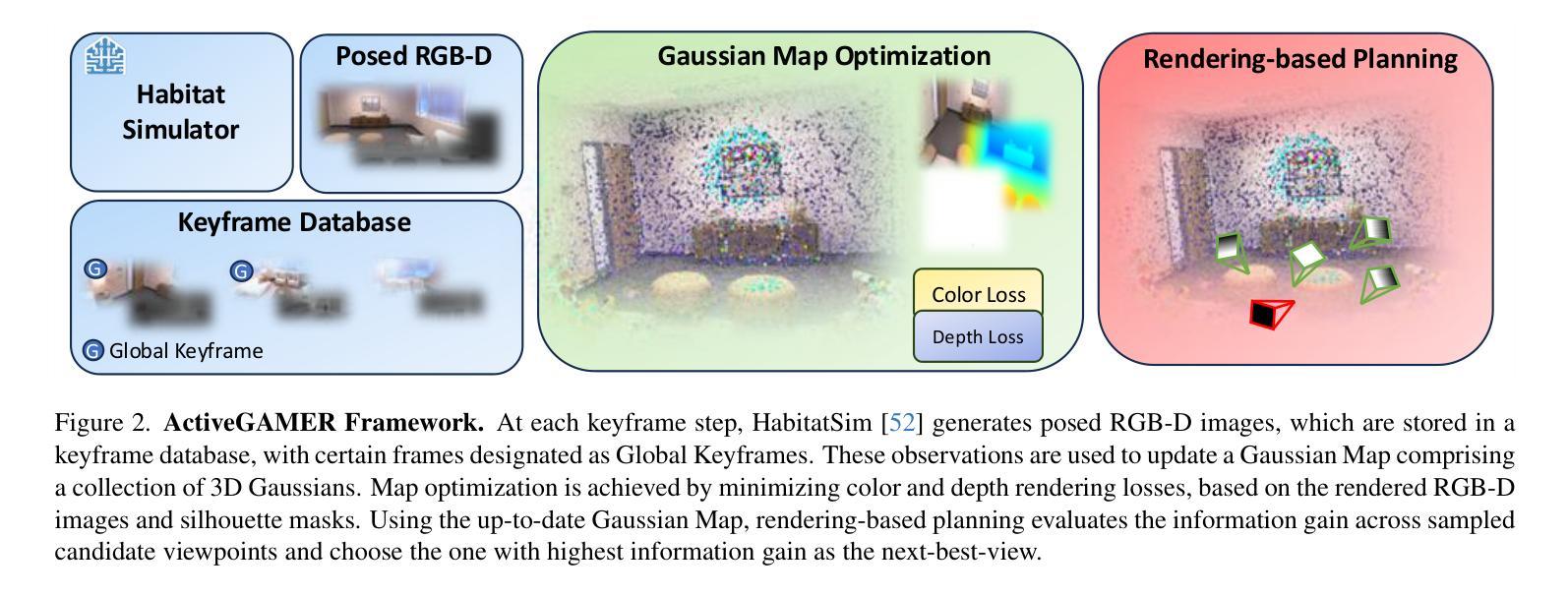
ActiveGAMER: Active GAussian Mapping through Efficient Rendering
Authors:Liyan Chen, Huangying Zhan, Kevin Chen, Xiangyu Xu, Qingan Yan, Changjiang Cai, Yi Xu
We introduce ActiveGAMER, an active mapping system that utilizes 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) to achieve high-quality, real-time scene mapping and exploration. Unlike traditional NeRF-based methods, which are computationally demanding and restrict active mapping performance, our approach leverages the efficient rendering capabilities of 3DGS, allowing effective and efficient exploration in complex environments. The core of our system is a rendering-based information gain module that dynamically identifies the most informative viewpoints for next-best-view planning, enhancing both geometric and photometric reconstruction accuracy. ActiveGAMER also integrates a carefully balanced framework, combining coarse-to-fine exploration, post-refinement, and a global-local keyframe selection strategy to maximize reconstruction completeness and fidelity. Our system autonomously explores and reconstructs environments with state-of-the-art geometric and photometric accuracy and completeness, significantly surpassing existing approaches in both aspects. Extensive evaluations on benchmark datasets such as Replica and MP3D highlight ActiveGAMER’s effectiveness in active mapping tasks.
我们介绍了ActiveGAMER,这是一个利用3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)实现高质量、实时场景映射和探索的主动映射系统。与传统的基于NeRF的方法不同,这些方法计算量大,限制了主动映射的性能,我们的方法利用3DGS的高效渲染能力,能够在复杂环境中实现有效且高效的探索。我们的系统的核心是基于渲染的信息增益模块,该模块能够动态地识别最具信息量的观点,用于规划下一个最佳视图,提高几何和光度重建的精度。ActiveGAMER还集成了一个精心平衡的方案,结合了从粗到细的探索、后期优化以及全局局部关键帧选择策略,以最大化重建的完整性和保真度。我们的系统以最先进的几何和光度精度和完整性自主地探索和重建环境,在这两个方面都显著超越了现有方法。在Replica和MP3D等基准数据集上的广泛评估凸显了ActiveGAMER在主动映射任务中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR2025
Summary
ActiveGAMER是一种利用3D高斯拼贴技术实现高质量实时场景映射和探索的主动映射系统。相较于传统计算量大且限制主动映射性能的NeRF方法,ActiveGAMER采用高效的渲染能力,在复杂环境中实现有效且高效的探索。其核心是基于渲染的信息增益模块,能动态识别最具信息量的视角进行下一步最佳视角规划,提高几何和光度重建的准确性。ActiveGAMER还结合了粗到细的探索、后期优化和全局局部关键帧选择策略,旨在最大化重建的完整性和逼真度。该系统在几何和光度准确性和完整性方面达到业界领先,显著超越了现有方法。在基准数据集上的评估表明ActiveGAMER在主动映射任务中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- ActiveGAMER利用3D高斯拼贴技术实现高质量实时场景映射和探索。
- 与传统NeRF方法相比,ActiveGAMER采用高效渲染技术优化复杂环境的探索。
- 核心基于渲染的信息增益模块可动态识别最佳视角以优化几何和光度重建准确性。
- ActiveGAMER结合了多种策略,如粗到细探索、后期优化和全局局部关键帧选择,以最大化重建质量。
- 系统在几何和光度准确性和完整性方面表现优异,显著超越现有方法。
点此查看论文截图


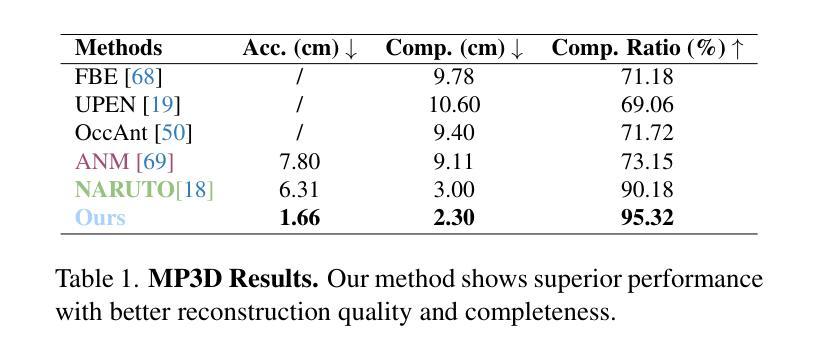
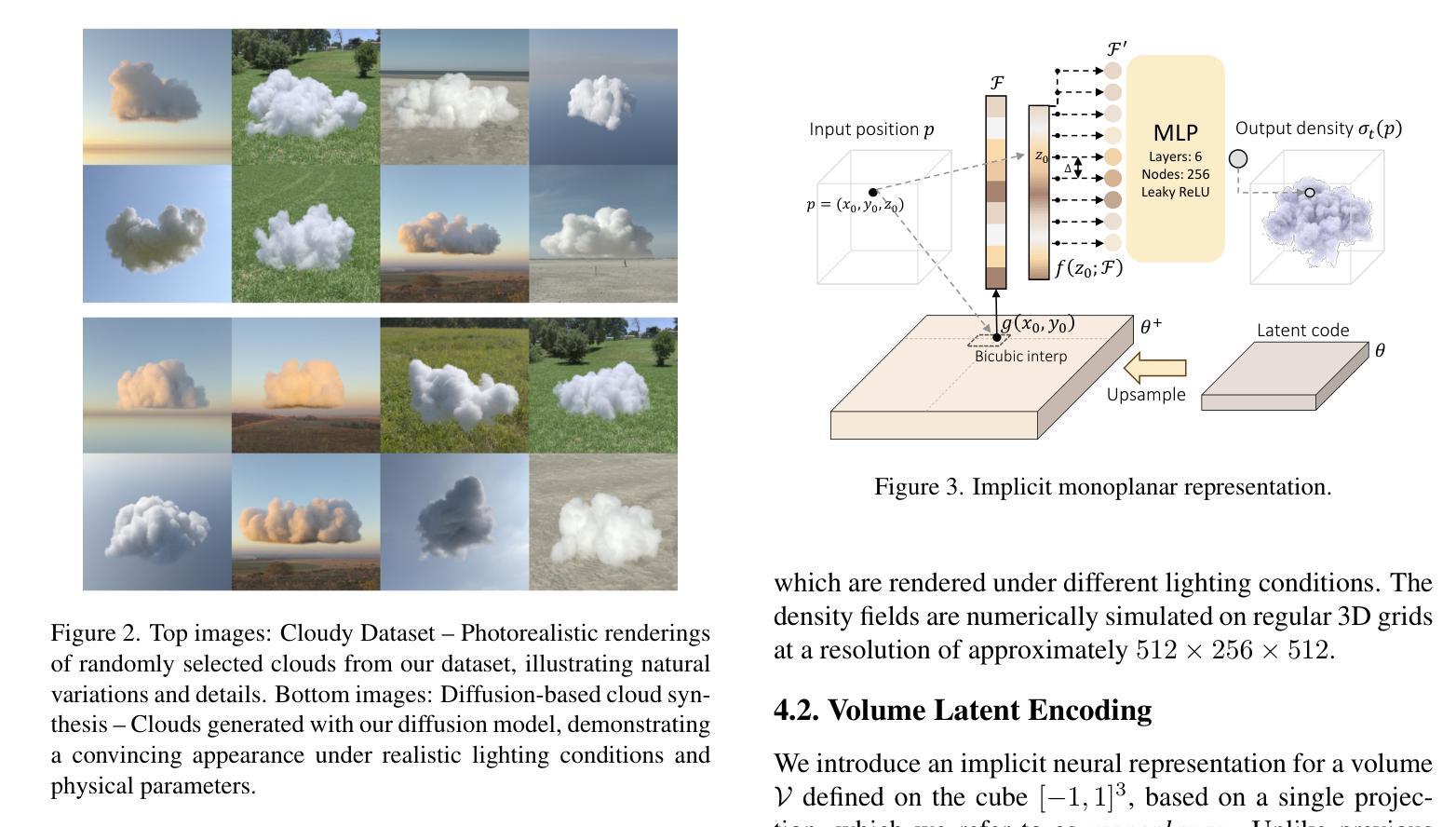
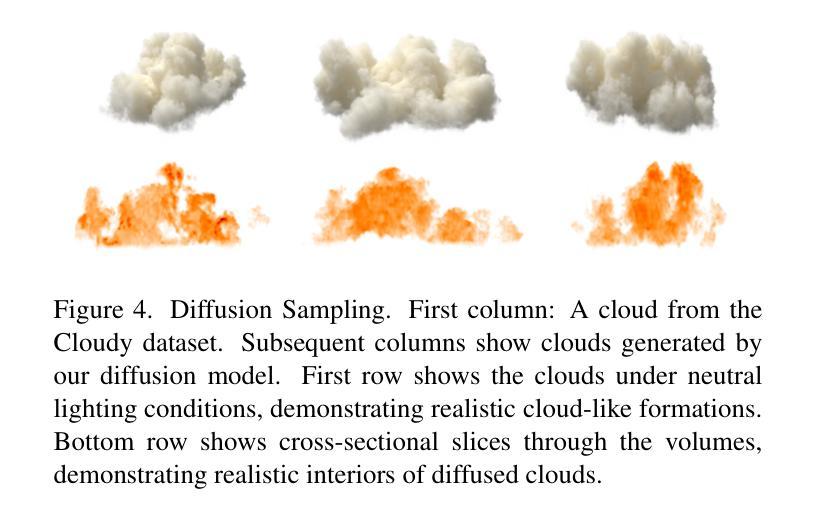
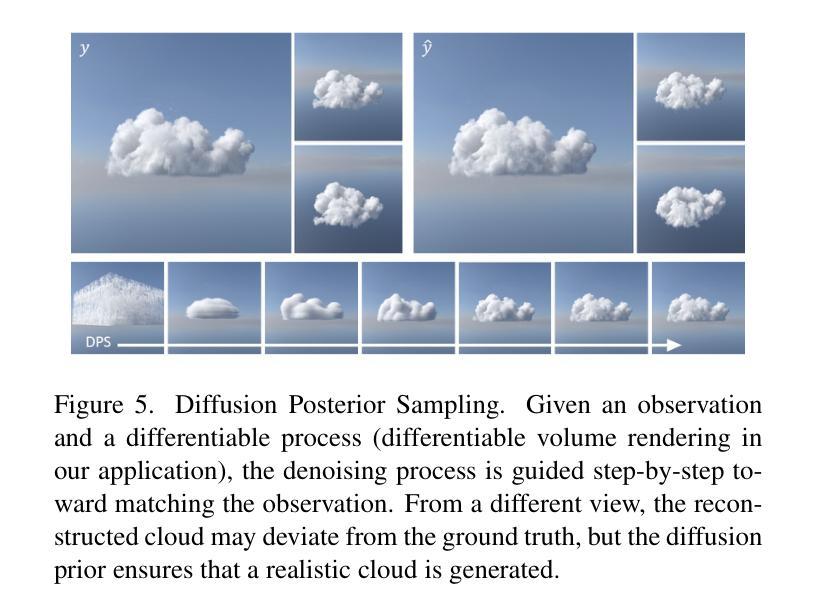
Light Transport-aware Diffusion Posterior Sampling for Single-View Reconstruction of 3D Volumes
Authors:Ludwic Leonard, Nils Thuerey, Ruediger Westermann
We introduce a single-view reconstruction technique of volumetric fields in which multiple light scattering effects are omnipresent, such as in clouds. We model the unknown distribution of volumetric fields using an unconditional diffusion model trained on a novel benchmark dataset comprising 1,000 synthetically simulated volumetric density fields. The neural diffusion model is trained on the latent codes of a novel, diffusion-friendly, monoplanar representation. The generative model is used to incorporate a tailored parametric diffusion posterior sampling technique into different reconstruction tasks. A physically-based differentiable volume renderer is employed to provide gradients with respect to light transport in the latent space. This stands in contrast to classic NeRF approaches and makes the reconstructions better aligned with observed data. Through various experiments, we demonstrate single-view reconstruction of volumetric clouds at a previously unattainable quality.
我们介绍了一种体积场单视图重建技术,该技术普遍存在多次散射效应,如云层中的情况。我们使用无条件扩散模型对体积场的未知分布进行建模,该模型是在新型基准数据集上训练的,该数据集包含1000个合成模拟的体积密度场。神经扩散模型是在一种新型的、对扩散友好的单平面表示的潜在代码上进行训练的。生成模型被用于将定制的参数化扩散后采样技术融入不同的重建任务中。采用基于物理的可微体积渲染器,以提供潜在空间中关于光传输的梯度。这与传统的NeRF方法形成对比,使重建结果更好地与观测数据对齐。通过各种实验,我们展示了体积云的单视图重建,达到了前所未有的质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种单视图重建技术,该技术可以重建出充满多重散射效果的体积场,如云层。该研究采用基于无条件扩散模型的建模方法,利用新型基准数据集训练模型,该数据集包含一千个合成模拟的体积密度场。研究团队还使用了一种针对扩散的个性化参数化重建技术,并结合使用基于物理的可微体积渲染器。这改善了传统NeRF方法的不足,使重建结果更加贴近真实数据观测结果,实现了前所未有的高质量单视图重建云层效果。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了一种单视图重建体积场的重建技术,该技术能够处理多重散射效应。
- 研究采用无条件扩散模型对体积场进行建模。
- 研究使用新型基准数据集进行模型训练,该数据集包含合成模拟的体积密度场。
- 研究团队利用针对扩散的个性化参数化重建技术进行优化。
- 采用基于物理的可微体积渲染器,使重建结果更加贴近真实数据观测结果。
- 该技术实现了高质量的重建云层效果。
点此查看论文截图

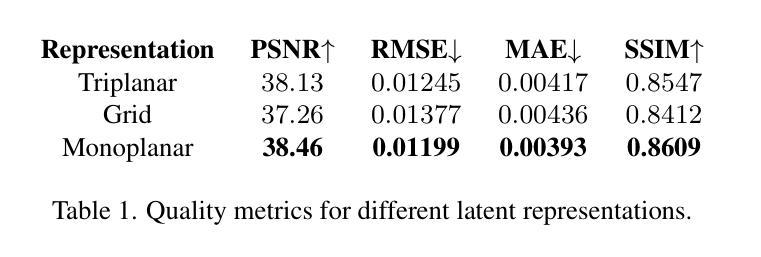
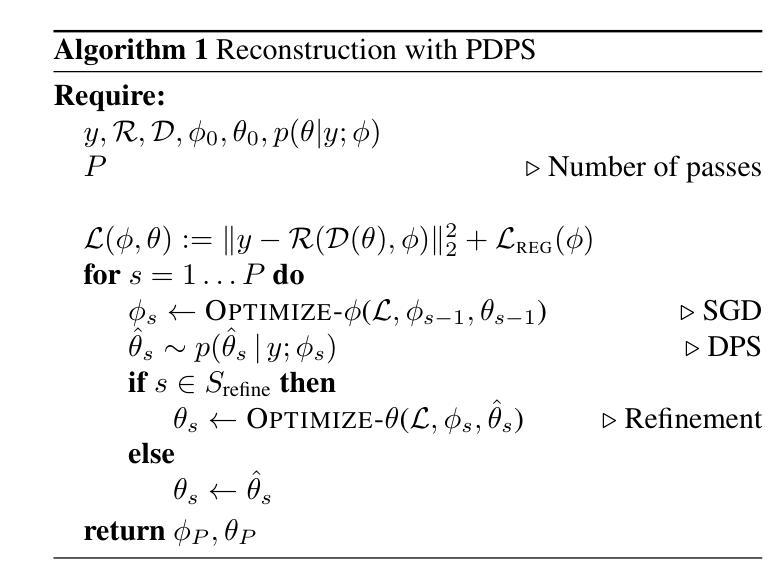
Self-Calibrating 4D Novel View Synthesis from Monocular Videos Using Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Fang Li, Hao Zhang, Narendra Ahuja
Gaussian Splatting (GS) has significantly elevated scene reconstruction efficiency and novel view synthesis (NVS) accuracy compared to Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), particularly for dynamic scenes. However, current 4D NVS methods, whether based on GS or NeRF, primarily rely on camera parameters provided by COLMAP and even utilize sparse point clouds generated by COLMAP for initialization, which lack accuracy as well are time-consuming. This sometimes results in poor dynamic scene representation, especially in scenes with large object movements, or extreme camera conditions e.g. small translations combined with large rotations. Some studies simultaneously optimize the estimation of camera parameters and scenes, supervised by additional information like depth, optical flow, etc. obtained from off-the-shelf models. Using this unverified information as ground truth can reduce robustness and accuracy, which does frequently occur for long monocular videos (with e.g. > hundreds of frames). We propose a novel approach that learns a high-fidelity 4D GS scene representation with self-calibration of camera parameters. It includes the extraction of 2D point features that robustly represent 3D structure, and their use for subsequent joint optimization of camera parameters and 3D structure towards overall 4D scene optimization. We demonstrate the accuracy and time efficiency of our method through extensive quantitative and qualitative experimental results on several standard benchmarks. The results show significant improvements over state-of-the-art methods for 4D novel view synthesis. The source code will be released soon at https://github.com/fangli333/SC-4DGS.
高斯采样(GS)与神经网络辐射场(NeRF)相比,显著提高了场景重建效率和新型视图合成(NVS)的准确性,特别是对于动态场景。然而,当前的四维NVS方法,无论是基于GS还是NeRF,主要依赖于COLMAP提供的相机参数,甚至使用COLMAP生成的稀疏点云进行初始化,这在精度和时间上都存在不足。这有时会导致对动态场景的表示不佳,特别是在大型物体移动或极端相机条件下(例如,小平移与大幅旋转)。一些研究同时优化相机参数的估计和场景,通过现成的模型获得深度、光流等额外信息进行监督。使用未经验证的信息作为真实标准可能会降低稳健性和准确性,这在长单目视频(例如数百帧)中经常发生。我们提出了一种新颖的方法,通过自我校准相机参数学习高保真四维GS场景表示。它包括提取稳健地代表三维结构的二维点特征,以及它们随后的联合优化相机参数和三维结构以进行整体的四维场景优化。我们通过几项标准基准测试进行了大量定量和定性的实验结果,证明了我们的方法在准确性和时间效率方面的表现。结果表明,与最新四维新型视图合成方法相比,我们的方法取得了显著改进。源代码很快将在https://github.com/fangli333/SC-4DGS发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF GitHub Page: https://github.com/fangli333/SC-4DGS
Summary
本文提出一种基于高斯涂抹(GS)的4D场景表示新方法,能自学修正相机参数,提高动态场景的重建效率和新型视角合成(NVS)的准确性。该方法通过提取稳健的2D点特征来代表3D结构,并对其进行联合优化相机参数和3D结构,达到整体的4D场景优化。实验结果显示,该方法在多个标准基准测试上显著优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- Gaussian Splatting (GS)提升了场景重建效率和新型视角合成(NVS)的准确性,特别是在动态场景方面。
- 现有的4D NVS方法主要依赖COLMAP提供的相机参数,导致精度和时间效率上的问题。
- 文中提出的方法能自学修正相机参数,实现高保真度的4D GS场景表示。
- 该方法通过提取2D点特征来稳健地代表3D结构,并对其进行联合优化。
- 方法在多个标准基准测试上经过广泛的定量和定性实验验证,结果显著优于现有技术。
- 该方法的源代码将很快在https://github.com/fangli333/SC-4DGS上发布。
点此查看论文截图

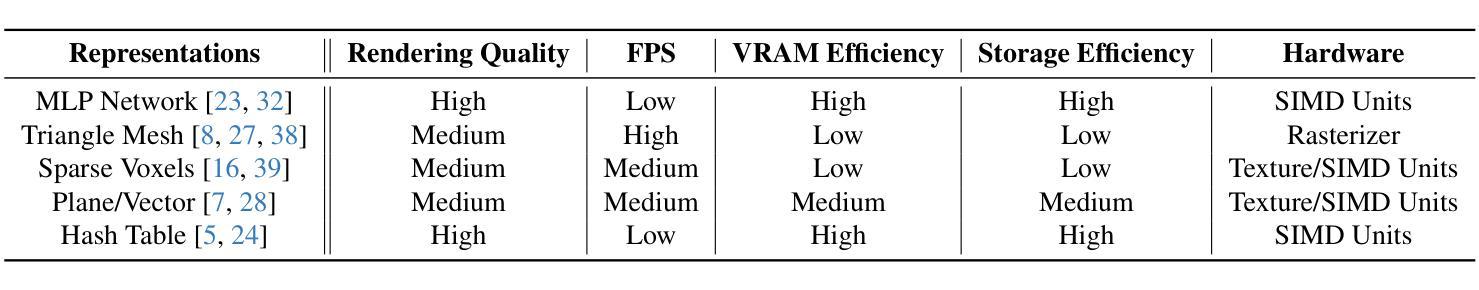
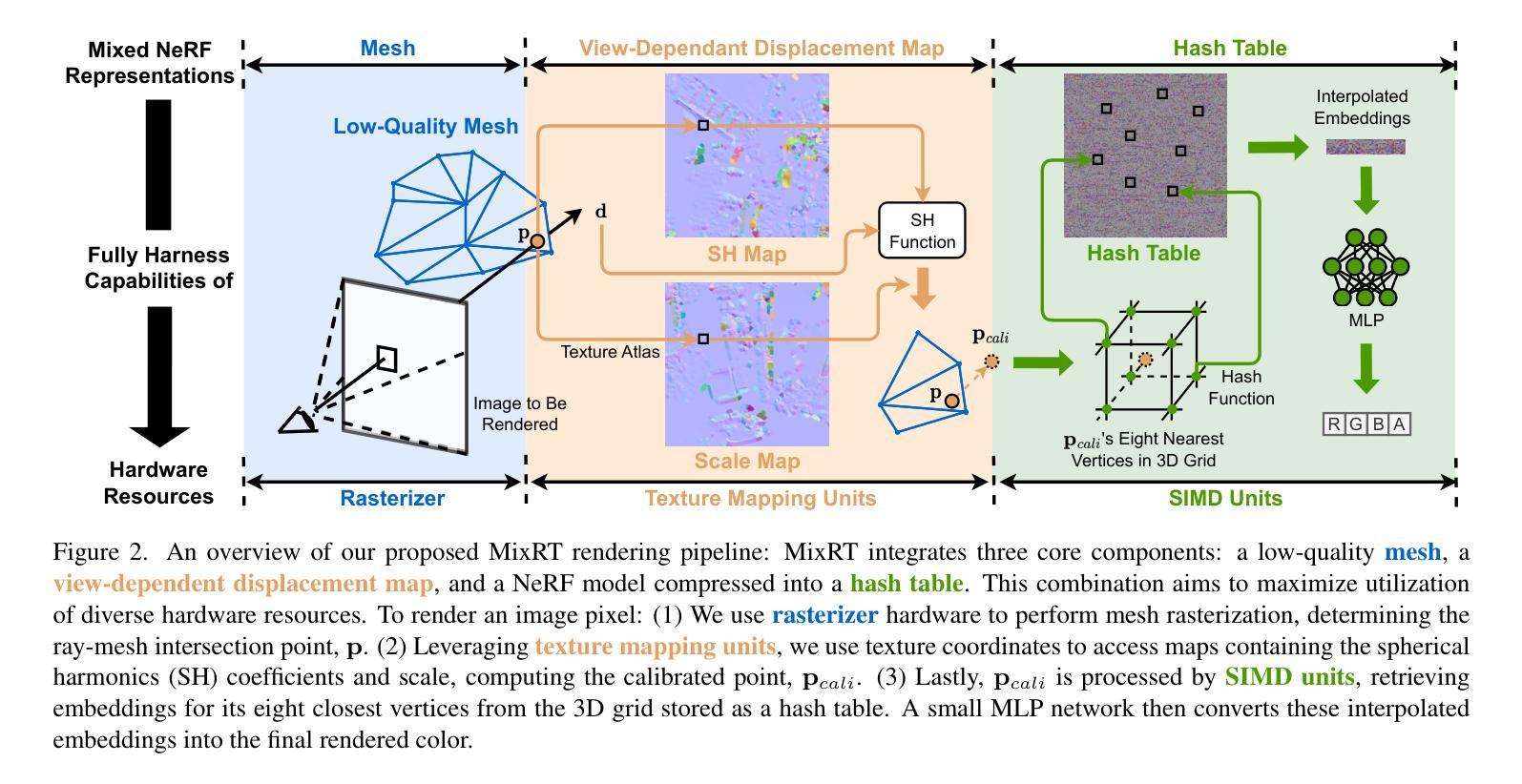
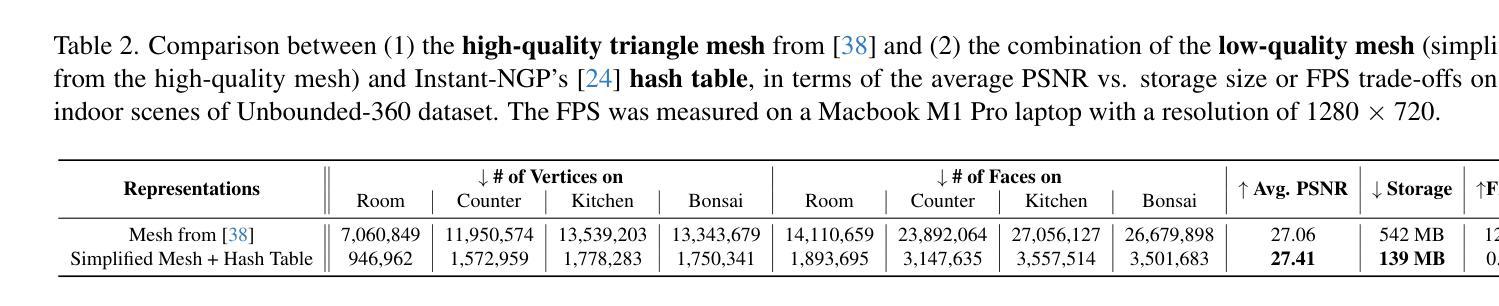
MixRT: Mixed Neural Representations For Real-Time NeRF Rendering
Authors:Chaojian Li, Bichen Wu, Peter Vajda, Yingyan Celine Lin
Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) has emerged as a leading technique for novel view synthesis, owing to its impressive photorealistic reconstruction and rendering capability. Nevertheless, achieving real-time NeRF rendering in large-scale scenes has presented challenges, often leading to the adoption of either intricate baked mesh representations with a substantial number of triangles or resource-intensive ray marching in baked representations. We challenge these conventions, observing that high-quality geometry, represented by meshes with substantial triangles, is not necessary for achieving photorealistic rendering quality. Consequently, we propose MixRT, a novel NeRF representation that includes a low-quality mesh, a view-dependent displacement map, and a compressed NeRF model. This design effectively harnesses the capabilities of existing graphics hardware, thus enabling real-time NeRF rendering on edge devices. Leveraging a highly-optimized WebGL-based rendering framework, our proposed MixRT attains real-time rendering speeds on edge devices (over 30 FPS at a resolution of 1280 x 720 on a MacBook M1 Pro laptop), better rendering quality (0.2 PSNR higher in indoor scenes of the Unbounded-360 datasets), and a smaller storage size (less than 80% compared to state-of-the-art methods).
神经辐射场(NeRF)已经成为一种领先的新型视图合成技术,因其令人印象深刻的逼真重建和渲染能力。然而,在大规模场景中实现实时NeRF渲染却存在挑战,通常会导致采用复杂的烘焙网格表示法,其中包含大量的三角形,或者采用资源密集型的烘焙表示中的光线行进技术。我们挑战这些传统观念,观察到高质量的几何形状,由包含大量三角形的网格表示,并不是实现逼真渲染质量所必需的。因此,我们提出了MixRT,这是一种新型的NeRF表示方法,包括低质量网格、视差图(view-dependent displacement map)和压缩NeRF模型。这种设计有效地利用了现有图形硬件的功能,从而在边缘设备上实现了实时NeRF渲染。借助高度优化的WebGL渲染框架,我们提出的MixRT在边缘设备上实现了实时渲染速度(在MacBook M1 Pro笔记本电脑上以1280 x 720的分辨率超过30 FPS),更好的渲染质量(在Unbounded-360数据集室内场景中高出0.2 PSNR),以及更小的存储大小(与最先进的方法相比减少了不到80%)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by 3DV’24. Project Page: https://licj15.github.io/MixRT/
Summary
本文介绍了Neural Radiance Field(NeRF)技术在新型视图合成方面的前沿应用,提出一种名为MixRT的新型NeRF表示方法,结合低质量网格、视图相关位移图和压缩NeRF模型,实现了实时NeRF渲染。MixRT利用优化的WebGL渲染框架在边缘设备上实现实时渲染速度,同时提高渲染质量和减小存储大小。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF技术已成为新型视图合成的领先技术,具有惊人的逼真重建和渲染能力。
- 实现大规模场景中的实时NeRF渲染具有挑战,通常采用复杂的烘焙网格表示法或资源密集型的射线追踪方法。
- 本文挑战了这些传统方法,指出高质量几何形状(由大量三角形构成的网格表示)并不是实现逼真渲染质量的必要条件。
- 提出了MixRT,一种新型的NeRF表示方法,包括低质量网格、视图相关位移图和压缩NeRF模型,有效结合现有图形硬件的能力。
- MixRT利用高度优化的WebGL渲染框架,在边缘设备上实现实时渲染速度,可在MacBook M1 Pro笔记本电脑上以超过30 FPS的速率进行1280 x 720分辨率的渲染。
- MixRT的渲染质量优于现有方法,在室内场景的Unbounded-360数据集上PSNR值提高了0.2。
点此查看论文截图