⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-04 更新
LEP3: A High-Luminosity e+e- Higgs and ElectroweakFactory in the LHC Tunnel
Authors:C. Anastopoulos, R. Assmann, A. Ball, O. Bruning, O. Buchmueller, T. Camporesi, P. Collier, J Dainton, G. Davies, J. R. Ellis, B. Goddard, L. Gouskos, M. Klute, M. Koratzinos, G. Landsberg, K. Long, L. Malgeri, F. Maltoni, F. Moortgat, C. Mariotti, S. Myers, J. A. Osborne, M. Pierini, D. R. Tovey, D. Treille, T. S. Virdee, N. Wardle, M. Zanetti
As stated in the 2019 European Strategy for Particle Physics (ESPP), it is of the utmost importance that the HL-LHC upgrade of the accelerator and the experiments be successfully completed in a timely manner. All necessary efforts should be devoted to achieving this goal. We also recall two of the principal recommendations of the 2019 ESPP for future accelerator initiatives, namely that 1) An electron-positron Higgs factory is the highest priority for the next collider (Rec. c). 2) Europe, together with its international partners, should investigate the technical and financial feasibility of a future hadron collider at CERN with a centre-of-mass energy of at least 100 TeV and with an electron-positron Higgs and electroweak factory as a possible first stage (Rec. e). A major objective in particle physics is always to operate an accelerator that allows a leap of an order of magnitude in the constituent centre-of-mass energy with respect to the previous one. We support FCC-ee and FCC-hh as the preferred option for CERN future, as it addresses both of the above recommendations. The guidance for the 2025 ESPP requests, in addition to the preferred option, the inclusion of ``prioritised alternatives to be pursued if the chosen preferred option turns out not to be feasible or competitive’’. Proposed alternatives to the preferred FCC option include linear, muon colliders and LHeC accelerators. In response to this request we propose reusing the existing LHC tunnel for an electron-positron collider, called LEP3, as a back-up alternative if the FCC cannot proceed. LEP3 leverages much of the R&D conducted for FCC-ee, offers high-precision studies of Z, W, and Higgs bosons below the tt threshold, and offers potential physics performance comparable or superior to other fallback options at a lower cost while supporting continued R&D towards a next-generation energy frontier machine.
如2019年欧洲粒子物理策略(ESPP)所述,及时成功完成HL-LHC加速器及实验的升级至关重要。我们应该付出一切努力来实现这个目标。我们还回顾了2019年ESPP关于未来加速器倡议的两个主要建议,即:1) 电子正电子希格斯工厂是下一个对撞机的首要选择(建议c)。2) 欧洲应与其国际合作伙伴共同研究在CERN建造未来强子对撞机的技术和经济可行性,其对撞机的质心能量至少应达到100TeV,并以电子正电子希格斯和电弱工厂作为可能的第一阶段(建议e)。粒子物理的一个主要目标始终是运行一种加速器,这种加速器能够使质心能量的构成实现数量级的飞跃。我们支持FCC-ee和FCC-hh作为CERN未来的首选方案,因为它符合上述两个建议。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 3 tables
Summary
欧洲粒子物理战略(ESPP)强调,大型强子对撞机(LHC)的升级工作和实验需及时成功完成。对于未来的加速器倡议,优先电子正负电子希格斯工厂以及研究在欧洲核研究组织建造一个至少拥有中心质量能量达到百TeV级别的大型未来粒子对撞机。FCC选项备选方案包括线性加速器、缪子对撞机和LHC电子正负电子希格斯工厂作为后备方案。如果首选方案不可行或缺乏竞争力,可以将其用作替代方案。其主要目标是在保证高性能物理学研究的同时不断研发下一代粒子加速器。
Key Takeaways
- 完成HL-LHC加速器及其实验的升级至关重要,应全力以赴实现这一目标。
- ESPP建议优先建设电子正负电子希格斯工厂作为未来碰撞机。
- 欧洲应该与国际伙伴共同探索未来粒子加速器的技术可行性,尤其是在中心质量能量达到至少百TeV级别的方面。
- FCC选项的备选方案包括线性加速器、缪子对撞机和LHeC加速器等。
- 如果首选的FCC方案不可行或不具竞争力,应考虑使用LEP3作为后备方案。
- LEP3可以充分利用已有的LHC隧道资源,进行电子正负电子希格斯工厂建设的高精度物理研究。它对下一代粒子加速器的发展也有极大的帮助作用。对于特定的研究,可能可以实现相对于其他备选方案的性能优势或成本优势。
点此查看论文截图

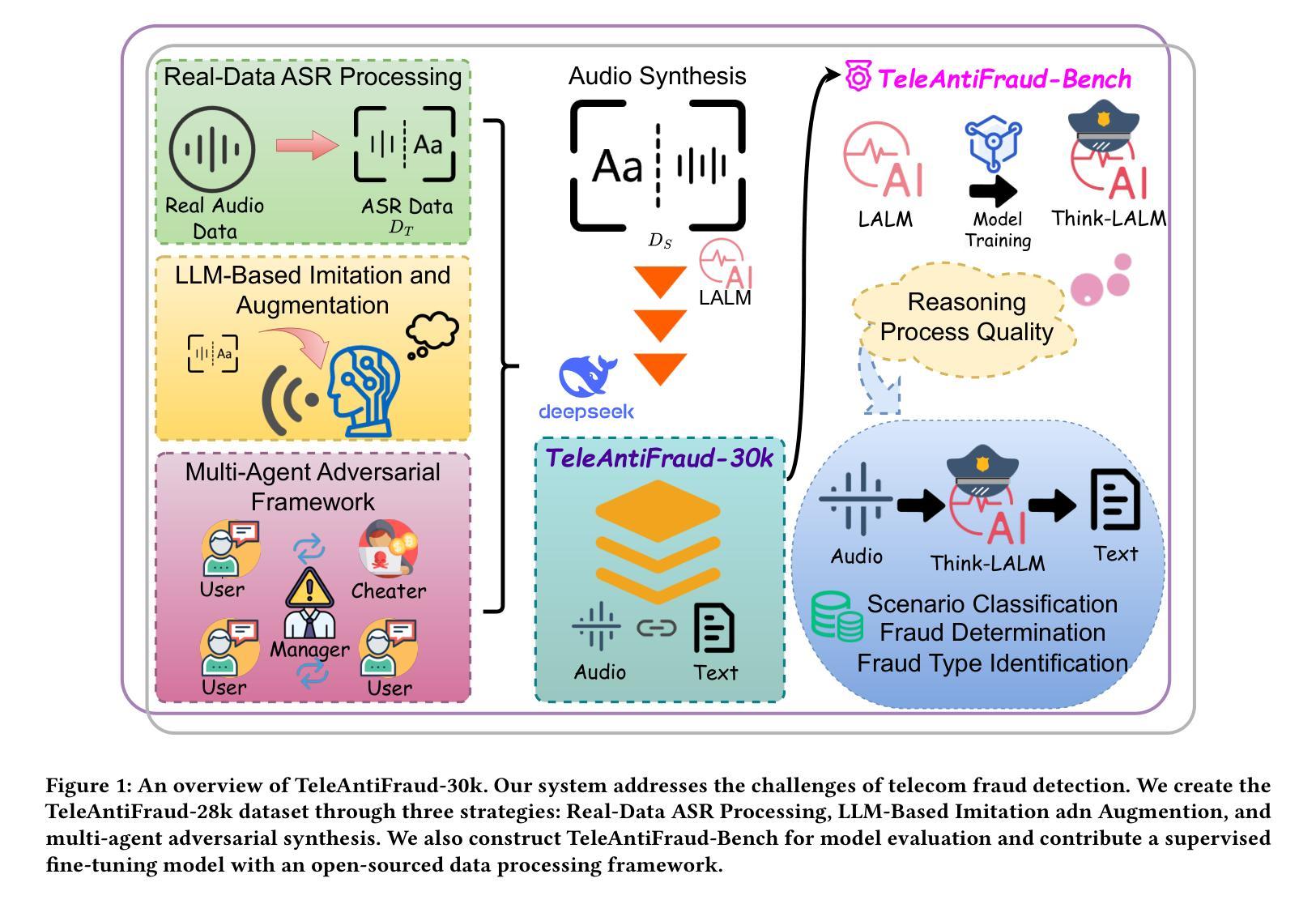
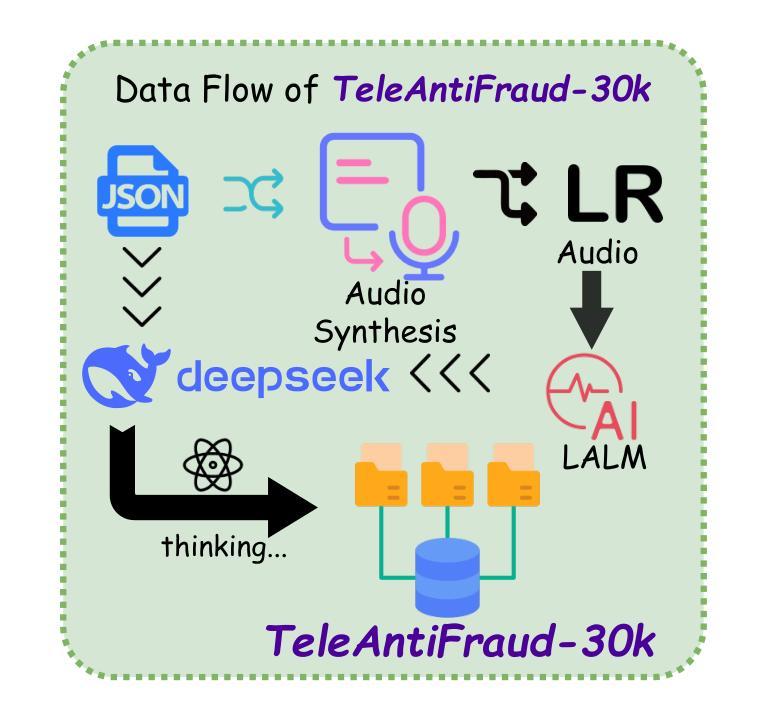
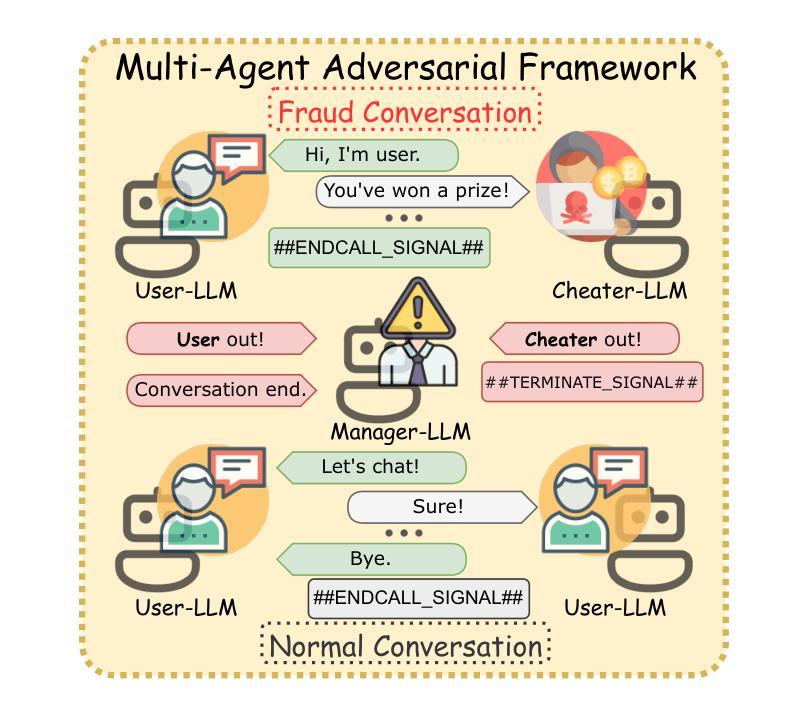
TeleAntiFraud-28k: An Audio-Text Slow-Thinking Dataset for Telecom Fraud Detection
Authors:Zhiming Ma, Peidong Wang, Minhua Huang, Jingpeng Wang, Kai Wu, Xiangzhao Lv, Yachun Pang, Yin Yang, Wenjie Tang, Yuchen Kang
The detection of telecom fraud faces significant challenges due to the lack of high-quality multimodal training data that integrates audio signals with reasoning-oriented textual analysis. To address this gap, we present TeleAntiFraud-28k, the first open-source audio-text slow-thinking dataset specifically designed for automated telecom fraud analysis. Our dataset is constructed through three strategies: (1) Privacy-preserved text-truth sample generation using automatically speech recognition (ASR)-transcribed call recordings (with anonymized original audio), ensuring real-world consistency through text-to-speech (TTS) model regeneration; (2) Semantic enhancement via large language model (LLM)-based self-instruction sampling on authentic ASR outputs to expand scenario coverage; (3) Multi-agent adversarial synthesis that simulates emerging fraud tactics through predefined communication scenarios and fraud typologies. The generated dataset contains 28,511 rigorously processed speech-text pairs, complete with detailed annotations for fraud reasoning. The dataset is divided into three tasks: scenario classification, fraud detection, fraud type classification. Furthermore, we construct TeleAntiFraud-Bench, a standardized evaluation benchmark comprising proportionally sampled instances from the dataset, to facilitate systematic testing of model performance on telecom fraud detection tasks. We also contribute a production-optimized supervised fine-tuning (SFT) model trained on hybrid real/synthetic data, while open-sourcing the data processing framework to enable community-driven dataset expansion. This work establishes a foundational framework for multimodal anti-fraud research while addressing critical challenges in data privacy and scenario diversity. The project will be released at https://github.com/JimmyMa99/TeleAntiFraud.
电信欺诈检测面临着由于缺乏高质量的多模式训练数据,难以将音频信号与面向推理的文本分析相结合的重大挑战。为了弥补这一空白,我们推出了TeleAntiFraud-28k,这是专门为电信欺诈分析自动化设计的第一个开源音频文本慢思考数据集。我们的数据集通过以下三种策略构建:(1)使用自动语音识别(ASR)转录的录音(带有匿名原始音频)进行隐私保护的文本真实样本生成,并通过文本到语音(TTS)模型的再生确保现实世界的一致性;(2)通过基于大型语言模型(LLM)的自我指令采样对真实的ASR输出进行语义增强,以扩大场景覆盖;(3)模拟新兴欺诈策略的多代理对抗合成通过预设的通信场景和欺诈类型。生成的数据集包含经过严格处理的28,511个语音文本对,以及用于欺诈推理的详细注释。数据集分为三个任务:场景分类、欺诈检测、欺诈类型分类。此外,我们构建了TeleAntiFraud-Bench,一个标准化的评估基准,其中包含数据集的按比例采样的实例,以促进电信欺诈检测任务上模型性能的系统测试。我们还贡献了一个在混合真实/合成数据上进行优化监督微调(SFT)的模型,同时开源数据处理框架以推动社区驱动的数据集扩展。这项工作为跨模态反欺诈研究建立了基础框架,同时解决了数据隐私和场景多样性方面的关键挑战。该项目将在https://github.com/JimmyMa99/TeleAntiFraud发布。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
针对电信欺诈检测面临的挑战,如缺乏高质量的多模式训练数据,我们推出了TeleAntiFraud-28k数据集。该数据集通过三种策略构建,包括隐私保护文本样本生成、语义增强和基于多代理的对抗性合成。它包含用于欺诈推理的详细注释的语音文本对。此外,我们还构建了TeleAntiFraud-Bench评估基准,以测试模型在电信欺诈检测任务上的性能。我们的工作为多模式反欺诈研究提供了基础框架,同时解决了数据隐私和场景多样性等挑战。
关键见解
- 缺乏高质量的多模式训练数据是电信欺诈检测的主要挑战之一。
- TeleAntiFraud-28k数据集是专门为自动化电信欺诈分析设计的第一份开源音频文本慢思考数据集。
- 数据集通过隐私保护的文本样本生成、语义增强和多代理对抗性合成三种策略构建。
- 数据集包含用于欺诈推理的详细注释的语音文本对,并分为情景分类、欺诈检测和欺诈类型分类三个任务。
- TeleAntiFraud-Bench评估基准的建立,促进了模型在电信欺诈检测任务上的系统性测试。
- 贡献了一个经过优化的监督微调模型,该模型在混合现实/合成数据上进行训练,并公开了数据处理框架,以便社区进行数据集扩展。
点此查看论文截图

SupertonicTTS: Towards Highly Scalable and Efficient Text-to-Speech System
Authors:Hyeongju Kim, Jinhyeok Yang, Yechan Yu, Seunghun Ji, Jacob Morton, Frederik Bous, Joon Byun, Juheon Lee
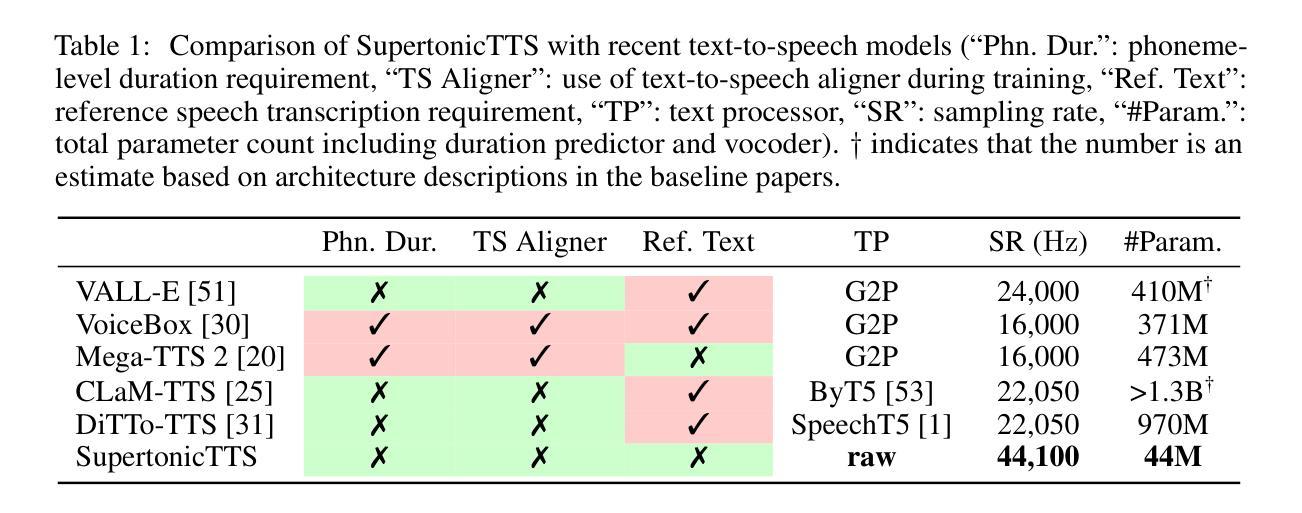
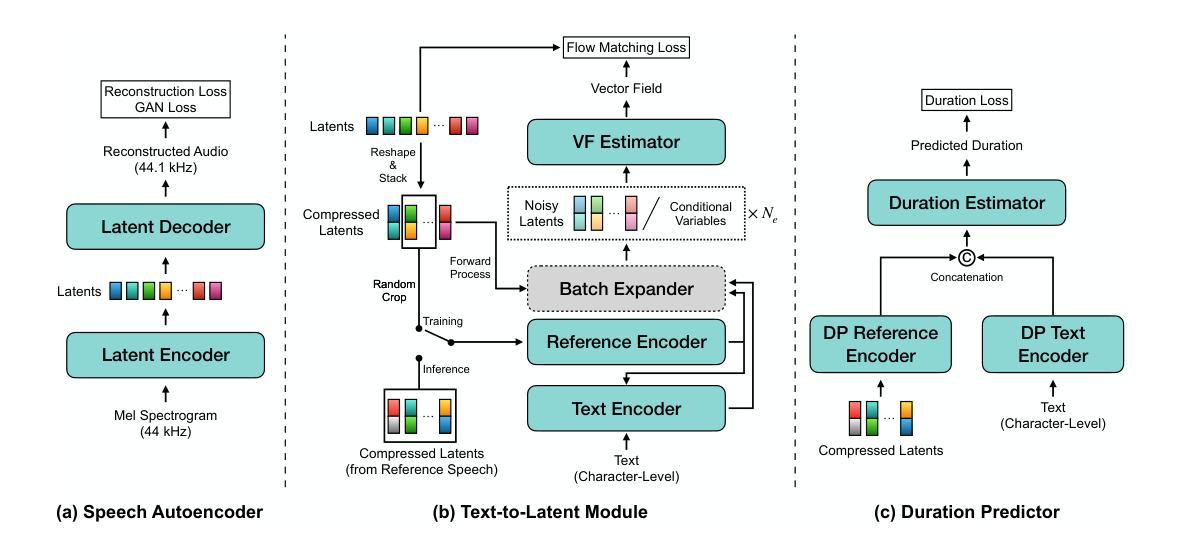
We present a novel text-to-speech (TTS) system, namely SupertonicTTS, for improved scalability and efficiency in speech synthesis. SupertonicTTS is comprised of three components: a speech autoencoder for continuous latent representation, a text-to-latent module leveraging flow-matching for text-to-latent mapping, and an utterance-level duration predictor. To enable a lightweight architecture, we employ a low-dimensional latent space, temporal compression of latents, and ConvNeXt blocks. We further simplify the TTS pipeline by operating directly on raw character-level text and employing cross-attention for text-speech alignment, thus eliminating the need for grapheme-to-phoneme (G2P) modules and external aligners. In addition, we introduce context-sharing batch expansion that accelerates loss convergence and stabilizes text-speech alignment. Experimental results demonstrate that SupertonicTTS achieves competitive performance while significantly reducing architectural complexity and computational overhead compared to contemporary TTS models. Audio samples demonstrating the capabilities of SupertonicTTS are available at: https://supertonictts.github.io/.
我们提出了一种新型文本到语音(TTS)系统,即SupertonicTTS,以提高语音合成的可扩展性和效率。SupertonicTTS由三个组件组成:用于连续潜在表示的语音自编码器、利用流匹配进行文本到潜在映射的文本到潜在模块,以及句子级别的持续时间预测器。为了实现轻量级架构,我们采用了低维潜在空间、潜在时间的临时压缩和ConvNeXt块。我们通过对原始字符级文本进行直接操作并采用跨注意力进行文本语音对齐,进一步简化了TTS管道,从而消除了对字母到音素(G2P)模块和外部对齐器的需求。此外,我们引入了上下文共享批量扩展,这加速了损失收敛并稳定了文本语音对齐。实验结果表明,SupertonicTTS在达到竞争性能的同时,与当代TTS模型相比,显著降低了架构复杂性和计算开销。有关展示SupertonicTTS功能的音频样本,请访问:https://supertonictts.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, preprint
Summary
提出一种新型文本到语音(TTS)系统SupertonicTTS,用于提高语音合成的可扩展性和效率。该系统包含三个组件:用于连续潜在表示的语音自动编码器、利用流匹配进行文本到潜在映射的文本到潜在模块,以及句子级别的持续时间预测器。通过采用低维潜在空间、潜在时间的压缩和ConvNeXt块,实现了轻量级架构。此外,通过直接操作字符级文本并采用跨注意力进行文本语音对齐,简化了TTS管道,从而消除了对grapheme-to-phoneme(G2P)模块和外部对齐器的需求。还引入了上下文共享批量扩展,以加速损失收敛并稳定文本语音对齐。实验结果表明,SupertonicTTS在达到竞争性能的同时,显著降低了架构复杂性和计算开销,相较于现有的TTS模型有着明显的优势。
Key Takeaways
- SupertonicTTS是一种新型的文本到语音(TTS)系统,旨在提高语音合成的可扩展性和效率。
- 系统包含三个主要组件:语音自动编码器、文本到潜在模块和句子级别持续时间预测器。
- 通过采用低维潜在空间、潜在时间的压缩和ConvNeXt块,实现了系统的轻量化。
- 简化了TTS管道,通过直接操作字符级文本并采用跨注意力机制进行文本语音对齐,无需使用G2P模块和外部对齐器。
- 引入了上下文共享批量扩展,以加速损失收敛并改善文本语音对齐的稳定性。
- 实验结果表明,SupertonicTTS在性能上具有竞争力,相较于其他TTS模型,其架构更简单,计算开销更低。
点此查看论文截图
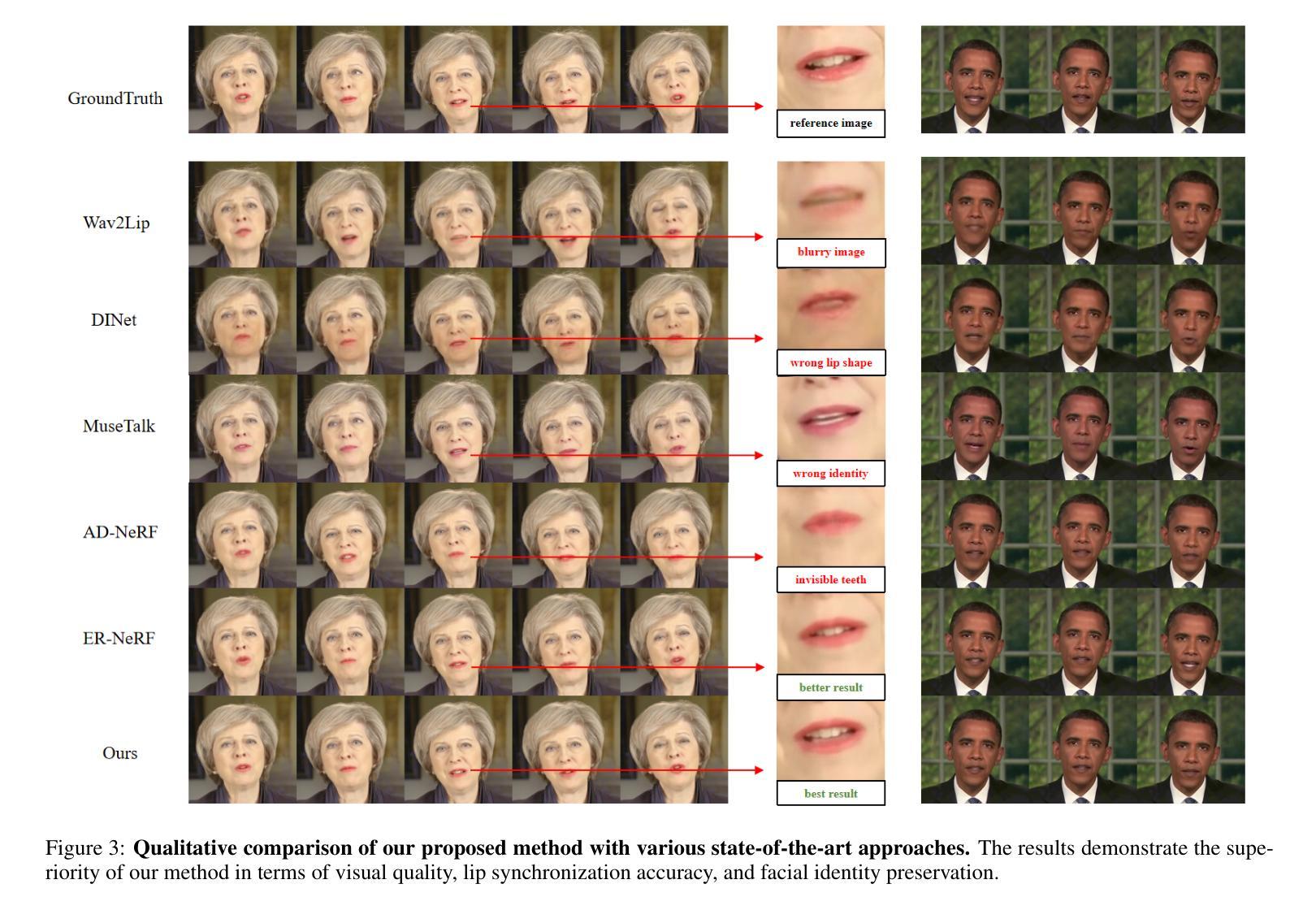
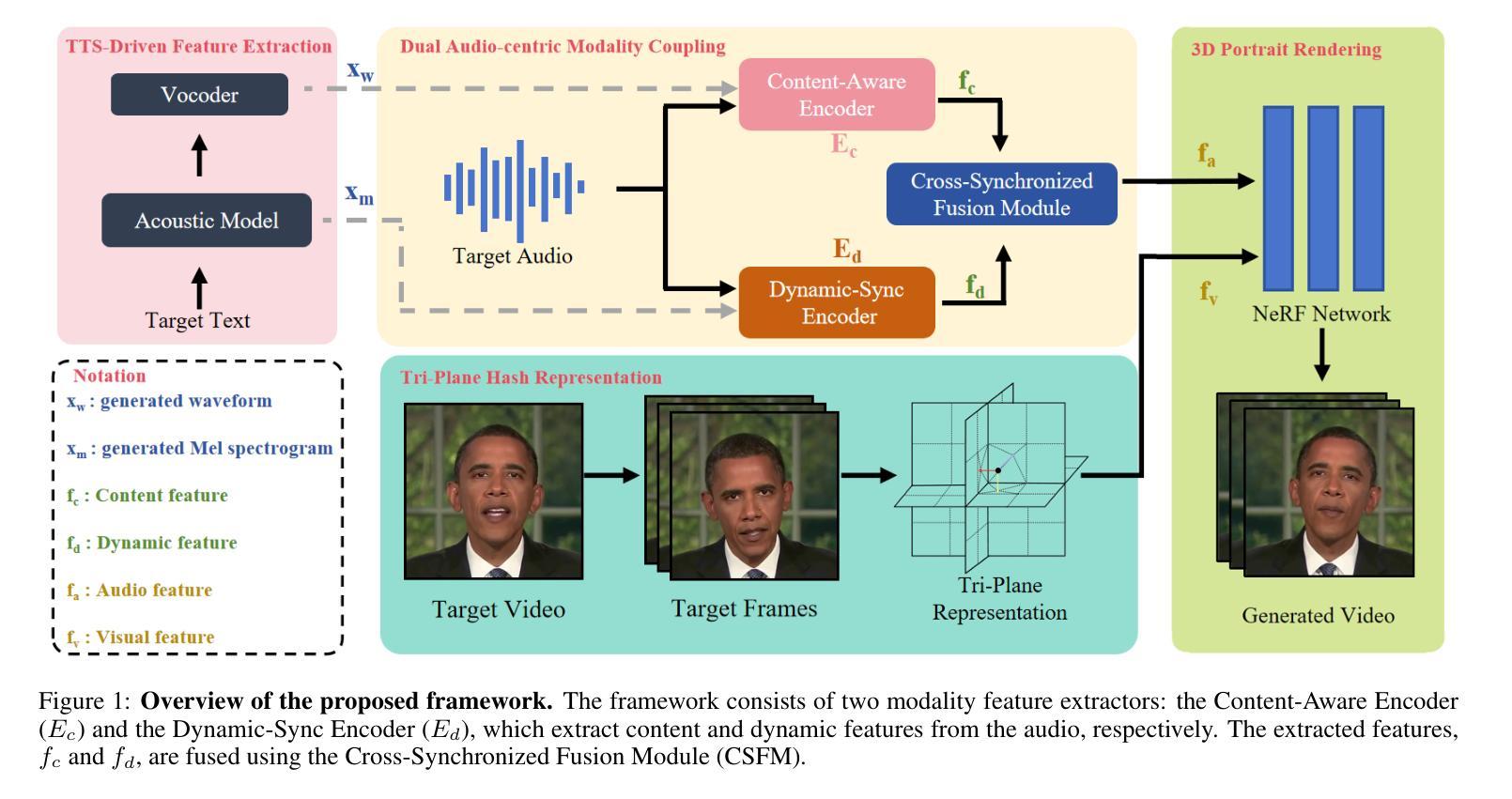
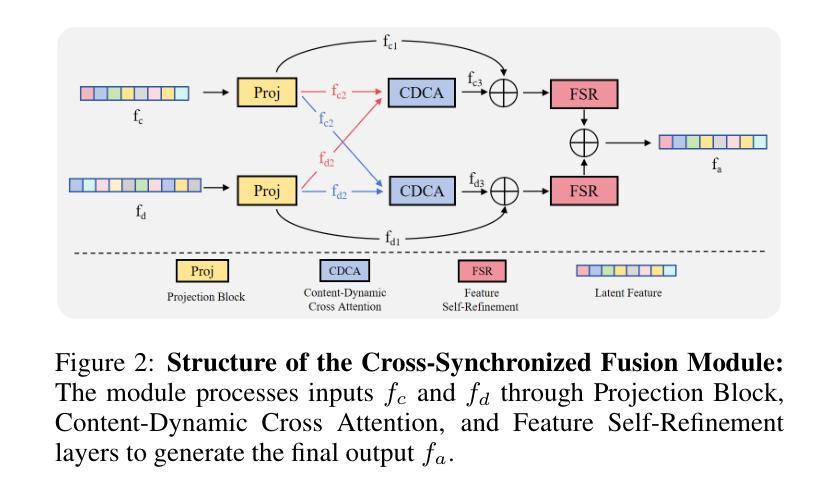
Dual Audio-Centric Modality Coupling for Talking Head Generation
Authors:Ao Fu, Ziqi Ni, Yi Zhou
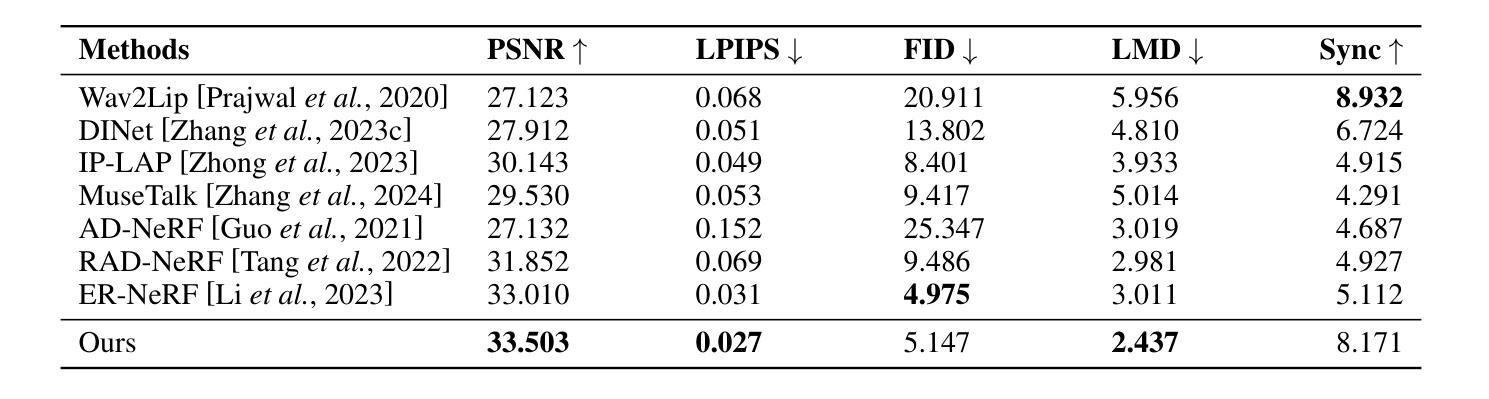
The generation of audio-driven talking head videos is a key challenge in computer vision and graphics, with applications in virtual avatars and digital media. Traditional approaches often struggle with capturing the complex interaction between audio and facial dynamics, leading to lip synchronization and visual quality issues. In this paper, we propose a novel NeRF-based framework, Dual Audio-Centric Modality Coupling (DAMC), which effectively integrates content and dynamic features from audio inputs. By leveraging a dual encoder structure, DAMC captures semantic content through the Content-Aware Encoder and ensures precise visual synchronization through the Dynamic-Sync Encoder. These features are fused using a Cross-Synchronized Fusion Module (CSFM), enhancing content representation and lip synchronization. Extensive experiments show that our method outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches in key metrics such as lip synchronization accuracy and image quality, demonstrating robust generalization across various audio inputs, including synthetic speech from text-to-speech (TTS) systems. Our results provide a promising solution for high-quality, audio-driven talking head generation and present a scalable approach for creating realistic talking heads.
音频驱动的说话人头部的视频生成是计算机视觉和图形学领域的关键挑战,在虚拟化身和数字媒体中有广泛的应用。传统的方法往往难以捕捉音频和面部动态之间的复杂交互,导致唇同步和视觉质量问题。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于NeRF的新型框架——双音频中心模态耦合(DAMC),它能够有效地整合音频输入的内容和动态特征。通过利用双编码器结构,DAMC通过内容感知编码器捕获语义内容,并通过动态同步编码器确保精确的视觉同步。这些特征使用跨同步融合模块(CSFM)进行融合,增强了内容表示和唇同步。大量实验表明,我们的方法在唇同步准确性和图像质量等关键指标上优于现有的最先进的方法,证明了在各种音频输入上的稳健泛化能力,包括来自文本到语音(TTS)系统的合成语音。我们的研究结果为高质量、音频驱动的说话人头部的生成提供了有前景的解决方案,并展示了一种创建逼真说话头部的可扩展方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 4 figures
Summary
新一代音频驱动的对话视频生成是计算机视觉和图形领域的一个关键挑战,广泛应用于虚拟化身和数字媒体。本文提出了一种基于NeRF的双音频中心模态耦合(DAMC)框架,有效整合音频输入的内容和动态特征。通过双编码器结构,DAMC通过内容感知编码器和动态同步编码器捕捉语义内容和确保精确的视觉同步。这些特征通过交叉同步融合模块(CSFM)融合,增强了内容表达和唇同步。实验表明,该方法在唇同步精度和图像质量等关键指标上优于现有先进技术,对各种音频输入具有良好的泛化能力,包括文本到语音(TTS)系统的合成语音。该研究为高质量音频驱动的对话视频生成提供了可行的解决方案,并提出了一种可规模化的方法来创建逼真的对话人物。
Key Takeaways
- 音频驱动的对话视频生成是计算机视觉和图形领域的核心挑战,广泛应用于虚拟化身和数字媒体。
- 传统方法难以捕捉音频和面部动态的复杂交互,导致唇同步和视觉质量问题。
- DAMC框架基于NeRF技术,有效整合音频输入的内容和动态特征。
- 双编码器结构包括内容感知编码器和动态同步编码器,分别捕捉语义内容和确保精确视觉同步。
- 交叉同步融合模块(CSFM)融合了内容和动态特征,增强了内容表达和唇同步。
- 实验表明,DAMC在唇同步精度和图像质量等方面优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

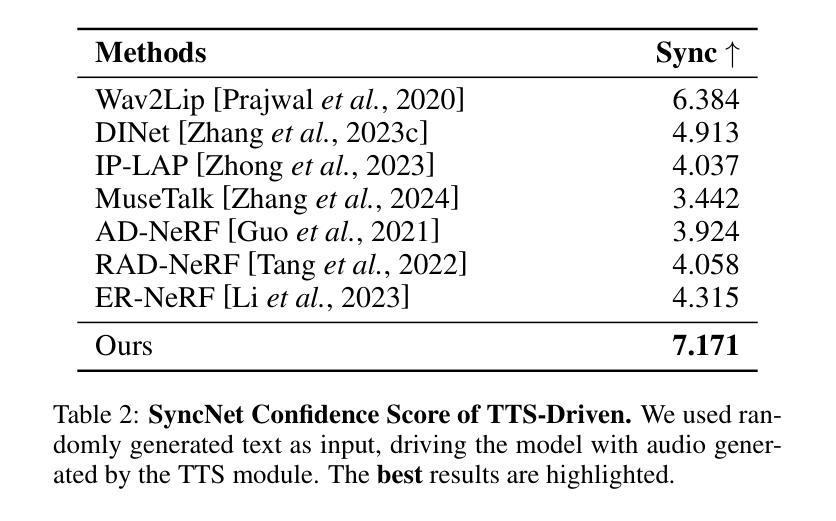

DeepAudio-V1:Towards Multi-Modal Multi-Stage End-to-End Video to Speech and Audio Generation
Authors:Haomin Zhang, Chang Liu, Junjie Zheng, Zihao Chen, Chaofan Ding, Xinhan Di
Currently, high-quality, synchronized audio is synthesized using various multi-modal joint learning frameworks, leveraging video and optional text inputs. In the video-to-audio benchmarks, video-to-audio quality, semantic alignment, and audio-visual synchronization are effectively achieved. However, in real-world scenarios, speech and audio often coexist in videos simultaneously, and the end-to-end generation of synchronous speech and audio given video and text conditions are not well studied. Therefore, we propose an end-to-end multi-modal generation framework that simultaneously produces speech and audio based on video and text conditions. Furthermore, the advantages of video-to-audio (V2A) models for generating speech from videos remain unclear. The proposed framework, DeepAudio, consists of a video-to-audio (V2A) module, a text-to-speech (TTS) module, and a dynamic mixture of modality fusion (MoF) module. In the evaluation, the proposed end-to-end framework achieves state-of-the-art performance on the video-audio benchmark, video-speech benchmark, and text-speech benchmark. In detail, our framework achieves comparable results in the comparison with state-of-the-art models for the video-audio and text-speech benchmarks, and surpassing state-of-the-art models in the video-speech benchmark, with WER 16.57% to 3.15% (+80.99%), SPK-SIM 78.30% to 89.38% (+14.15%), EMO-SIM 66.24% to 75.56% (+14.07%), MCD 8.59 to 7.98 (+7.10%), MCD SL 11.05 to 9.40 (+14.93%) across a variety of dubbing settings.
当前,高质量的同步音频是使用各种多模态联合学习框架合成,利用视频和可选文本输入。在视频到音频的基准测试中,视频到音频的质量、语义对齐和音视频同步都得到有效实现。然而,在真实场景中,语音和音频经常同时在视频中共存,而基于视频和文本条件的端到端同步语音和音频生成的研究尚不充分。因此,我们提出了一种端到端的多模态生成框架,该框架可根据视频和文本条件同时生成语音和音频。此外,视频到音频(V2A)模型在生成语音方面的优势尚不清楚。所提出的框架DeepAudio由视频到音频(V2A)模块、文本到语音(TTS)模块以及动态模态融合(MoF)模块组成。在评估中,所提出的端到端框架在视频音频基准测试、视频语音基准测试和文本语音基准测试中均达到了最先进的性能。具体来说,我们的框架在与视频音频和文本语音基准测试的最先进模型的比较中取得了相当的结果,并在视频语音基准测试中超越了最先进模型,其中字词错误率从16.57%降至3.15%(+80.99%),语音相似性从78.30%提升至89.38%(+14.15%),情绪相似性从66.24%提升至75.56%(+14.07%),MCD指标从8.59降至7.98(+7.10%),MCD SL指标从11.05降至9.40(+14.93%),跨越了各种配音环境的设置。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 5 figures
Summary
该文本介绍了当前高质量同步音频的合成方法,主要是通过多模态联合学习框架实现,利用视频和可选文本输入来生成音频。文章提出了一个端到端的多模态生成框架,能同时基于视频和文本条件生成语音和音频。此外,文章还介绍了DeepAudio框架的结构及其在视频音频、视频语音和文本语音基准测试上的性能表现。
Key Takeaways
- 当前高质量同步音频的合成主要使用多模态联合学习框架,借助视频和可选文本输入实现。
- 文章提出了一个端到端的多模态生成框架,能同时生成语音和音频。
- DeepAudio框架包含视频到音频(V2A)模块、文本到语音(TTS)模块以及动态模态融合(MoF)模块。
- 在视频音频、视频语音和文本语音基准测试中,DeepAudio框架实现了最先进的性能表现。
- 在对比实验中,DeepAudio框架在视频语音基准测试上超越了现有最先进的模型,并且在其他基准测试中表现也相当或更好。
- 端到端的生成框架对于处理真实世界中语音和音频在视频中的共存问题具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图

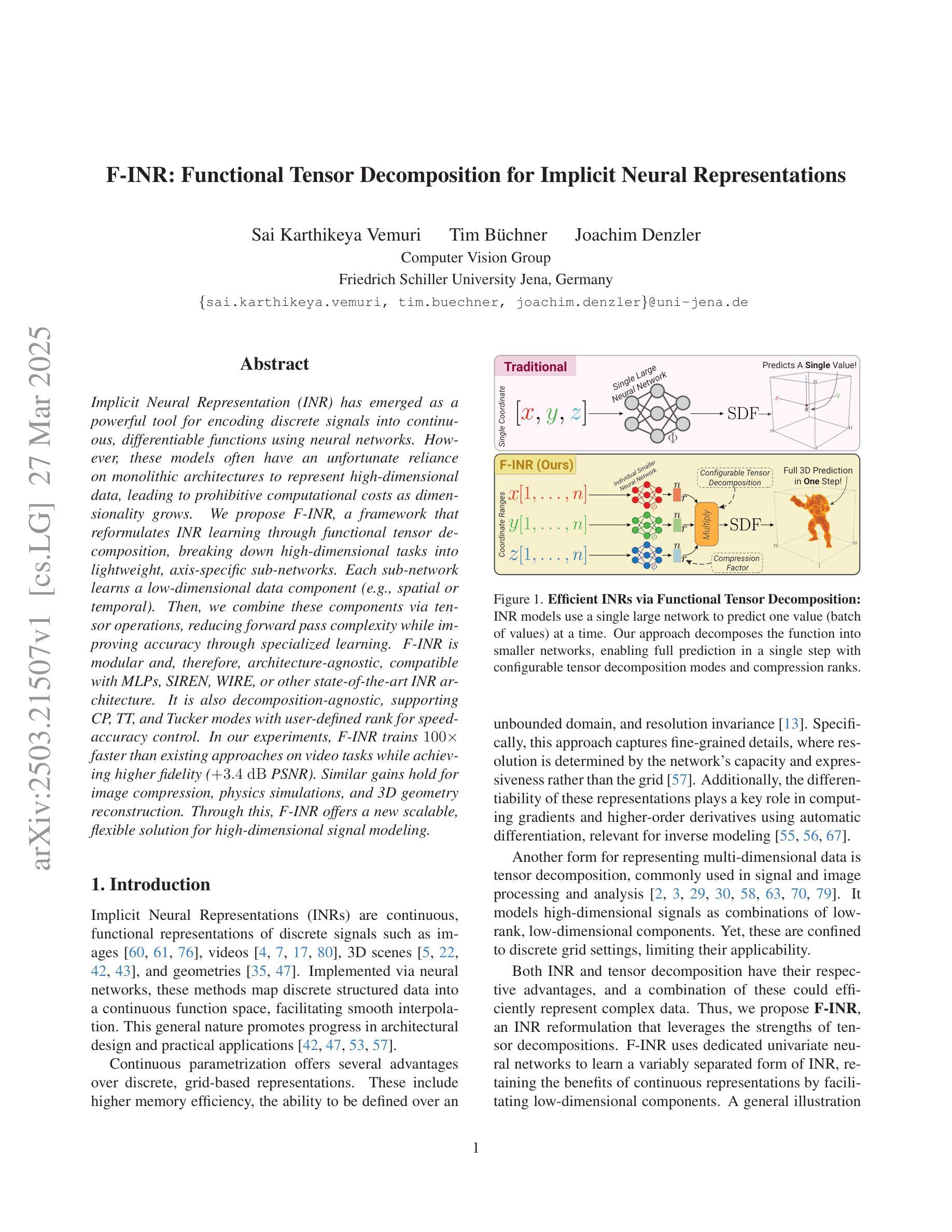
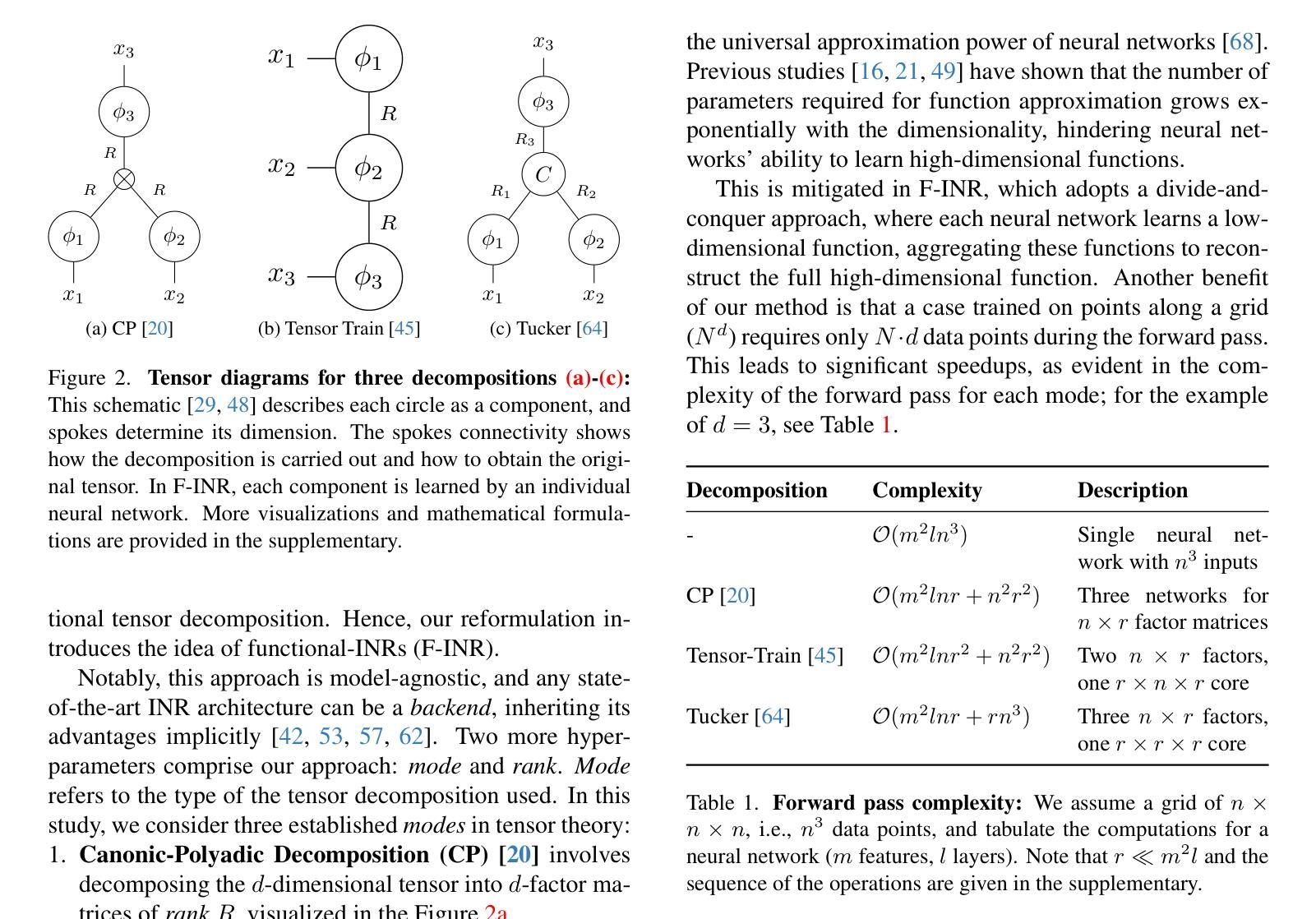
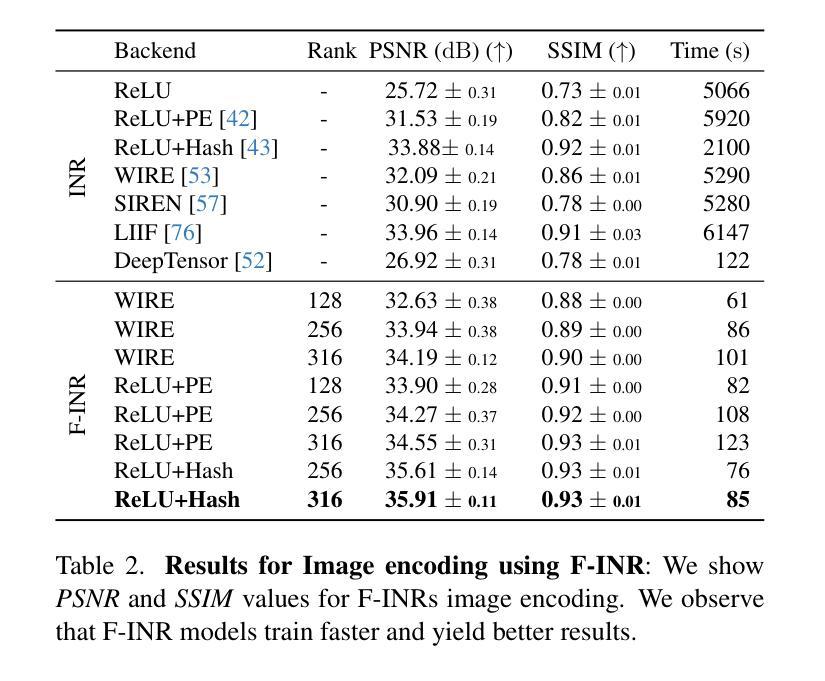
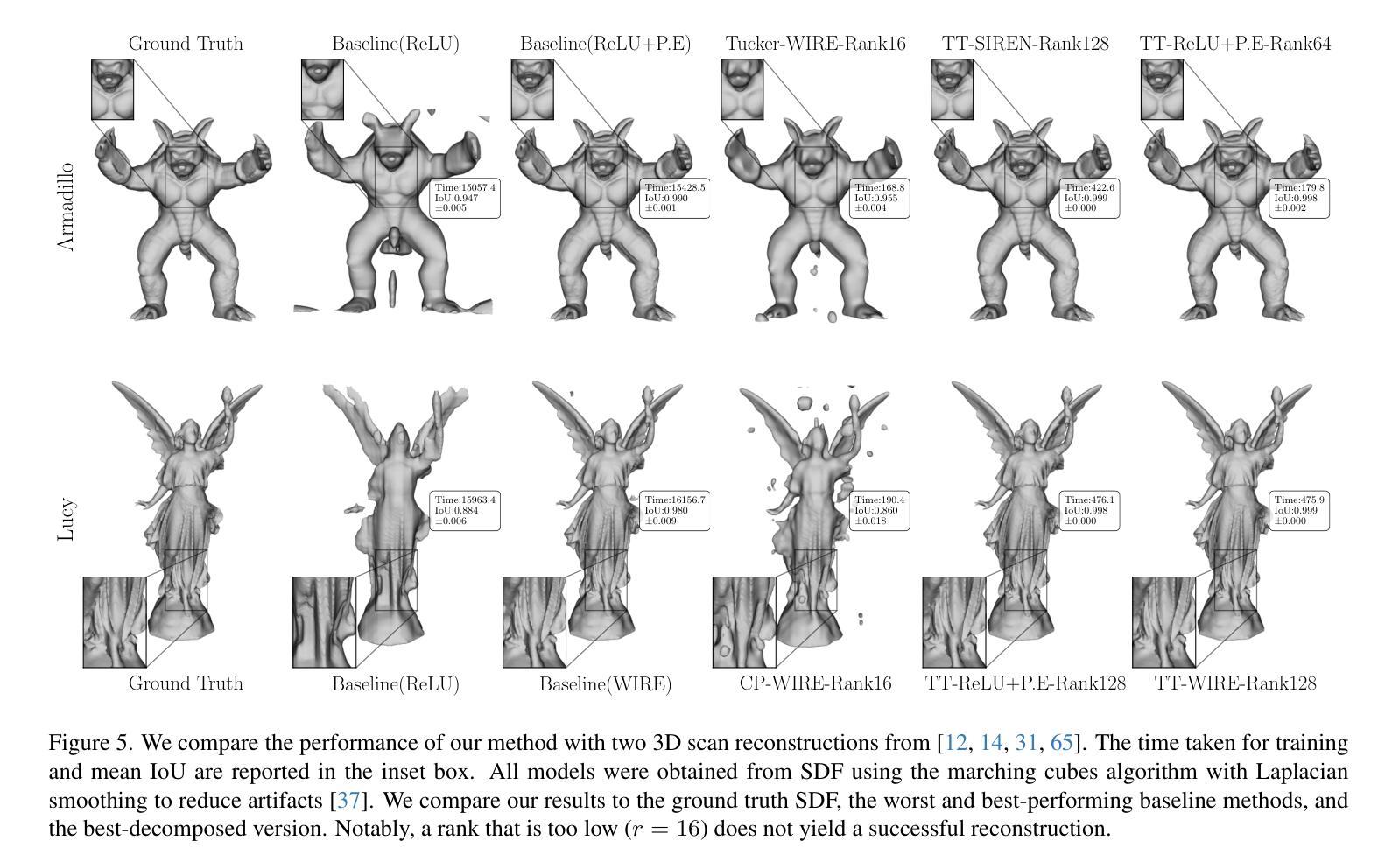
F-INR: Functional Tensor Decomposition for Implicit Neural Representations
Authors:Sai Karthikeya Vemuri, Tim Büchner, Joachim Denzler
Implicit Neural Representation (INR) has emerged as a powerful tool for encoding discrete signals into continuous, differentiable functions using neural networks. However, these models often have an unfortunate reliance on monolithic architectures to represent high-dimensional data, leading to prohibitive computational costs as dimensionality grows. We propose F-INR, a framework that reformulates INR learning through functional tensor decomposition, breaking down high-dimensional tasks into lightweight, axis-specific sub-networks. Each sub-network learns a low-dimensional data component (e.g., spatial or temporal). Then, we combine these components via tensor operations, reducing forward pass complexity while improving accuracy through specialized learning. F-INR is modular and, therefore, architecture-agnostic, compatible with MLPs, SIREN, WIRE, or other state-of-the-art INR architecture. It is also decomposition-agnostic, supporting CP, TT, and Tucker modes with user-defined rank for speed-accuracy control. In our experiments, F-INR trains $100\times$ faster than existing approaches on video tasks while achieving higher fidelity (+3.4 dB PSNR). Similar gains hold for image compression, physics simulations, and 3D geometry reconstruction. Through this, F-INR offers a new scalable, flexible solution for high-dimensional signal modeling.
隐式神经网络表示(INR)已经成为一种强大的工具,能够利用神经网络将离散信号编码为连续、可微分的函数。然而,这些模型往往依赖单一的架构来表示高维数据,随着维度的增长,计算成本也急剧增加。我们提出了F-INR框架,它通过函数张量分解重新定义了INR学习,将高维任务分解为轻量、针对轴的子网络。每个子网络学习低维数据组件(例如,空间或时间)。然后,我们通过张量操作组合这些组件,降低前向传递的复杂性,同时通过专门学习提高准确性。F-INR是模块化的,因此它是与架构无关的,与MLP、SIREN、WIRE或其他最先进的INR架构兼容。它也是与分解无关的,支持CP、TT和Tucker模式,用户定义的等级可用于控制速度与准确性的平衡。在我们的实验中,F-INR在视频任务上的训练速度是现有方法的100倍,同时实现了更高的保真度(+3.4分贝峰值信噪比)。类似的增益也适用于图像压缩、物理模拟和3D几何重建。因此,F-INR为高密度信号建模提供了一种新的可扩展、灵活解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 26 pages, 33 figures, 12 tables
Summary
F-INR框架通过功能张量分解重新定义了隐神经表示(INR)学习,将高维任务分解为轻量级的、针对轴的子网络。子网络学习低维数据组件,然后通过张量操作组合,降低前向传播复杂度,同时通过专项学习提高准确性。F-INR具有模块化、通用性强的特点,兼容多种INR架构和分解模式,实验表明在视频任务上训练速度比现有方法快100倍,同时实现更高的保真度。
Key Takeaways
- F-INR框架使用功能张量分解重新定义了隐神经表示(INR)学习。
- 通过将高维任务分解为轻量级的子网络,降低了计算复杂性。
- 子网络针对轴特定,学习低维数据组件(如空间或时间)。
- 使用张量操作组合数据组件,以提高准确性和效率。
- F-INR框架具有模块化、通用性强的特点,兼容多种INR架构。
- F-INR支持多种分解模式,包括CP、TT和Tucker模式,并提供用户定义的等级以控制速度和准确性。
点此查看论文截图


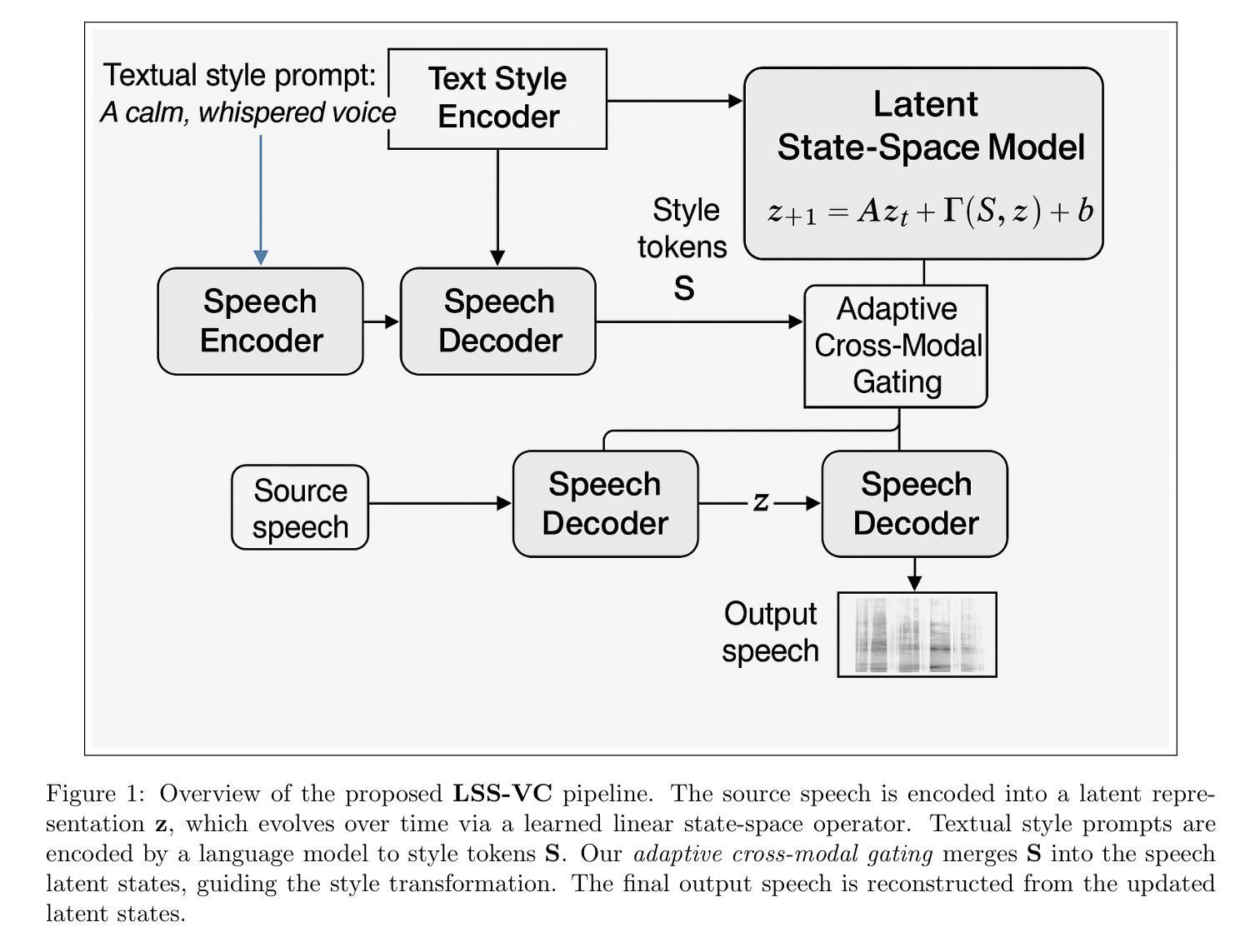
Text-Driven Voice Conversion via Latent State-Space Modeling
Authors:Wen Li, Sofia Martinez, Priyanka Shah
Text-driven voice conversion allows customization of speaker characteristics and prosodic elements using textual descriptions. However, most existing methods rely heavily on direct text-to-speech training, limiting their flexibility in controlling nuanced style elements or timbral features. In this paper, we propose a novel \textbf{Latent State-Space} approach for text-driven voice conversion (\textbf{LSS-VC}). Our method treats each utterance as an evolving dynamical system in a continuous latent space. Drawing inspiration from mamba, which introduced a state-space model for efficient text-driven \emph{image} style transfer, we adapt a loosely related methodology for \emph{voice} style transformation. Specifically, we learn a voice latent manifold where style and content can be manipulated independently by textual style prompts. We propose an adaptive cross-modal fusion mechanism to inject style information into the voice latent representation, enabling interpretable and fine-grained control over speaker identity, speaking rate, and emphasis. Extensive experiments show that our approach significantly outperforms recent baselines in both subjective and objective quality metrics, while offering smoother transitions between styles, reduced artifacts, and more precise text-based style control.
文本驱动的声音转换技术允许使用文本描述来定制说话人的特征和韵律元素。然而,现有的大多数方法严重依赖于直接的文本到语音训练,这在控制微妙的风格元素或音色特征方面限制了其灵活性。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的潜在状态空间文本驱动声音转换方法(LSS-VC)。我们的方法将每个话语视为一个在不断变化的潜在空间中的动态系统。我们从mamba(一种用于高效文本驱动的图像风格转换的状态空间模型)中汲取灵感,将一种松散相关的方法应用于声音风格转换。具体来说,我们学习一个声音潜在流形,其中风格和内容可以通过文本风格提示独立操纵。我们提出了一种自适应的跨模态融合机制,将风格信息注入声音潜在表示中,实现对说话人身份、语速和强调的可解释性和精细控制。大量实验表明,我们的方法在主观和客观质量指标上均显著优于最新的基线方法,同时在风格之间提供平滑过渡、减少伪影和更精确的文本基于风格控制。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本驱动的声音转换技术可以通过使用文本描述来定制说话人的特性和韵律元素。然而,大多数现有方法严重依赖于直接的文本到语音训练,这在控制微妙的风格元素或音色特征方面的灵活性有限。本文提出了一种新型的潜状态空间方法,用于文本驱动的声音转换(LSS-VC)。我们的方法将每个句子视为一个不断变化的潜态空间中的动态系统。从引入状态空间模型的mamba中汲取灵感,我们将其用于文本驱动的图像风格转移,并适应一种松散相关的方法用于声音风格转换。具体来说,我们学习一个声音潜变量流形,其中风格和可以通过文本风格提示独立操作。我们提出了一种自适应跨模态融合机制,将风格信息注入声音潜表示中,实现对说话人身份、语速和强调的直观和精细控制。大量实验表明,我们的方法在主观和客观质量指标上都显著优于最新基线,同时提供平滑的风格过渡、减少的伪影和更精确的文本风格控制。
Key Takeaways
- 文本驱动的声音转换技术可以定制说话人的特性和韵律元素。
- 大多数现有方法依赖文本到语音的直接训练,在控制细微风格元素上有限制。
- 提出了新型的潜状态空间方法(LSS-VC)进行文本驱动的声音转换。
- 将每个句子视为潜态空间中的动态系统,借鉴了mamba的灵感并将其应用于声音风格转换。
- 学习声音潜变量流形,实现风格和内容的独立操作。
- 通过自适应跨模态融合机制注入风格信息到声音潜表示中,实现对说话人身份、语速和强调的精细控制。
点此查看论文截图

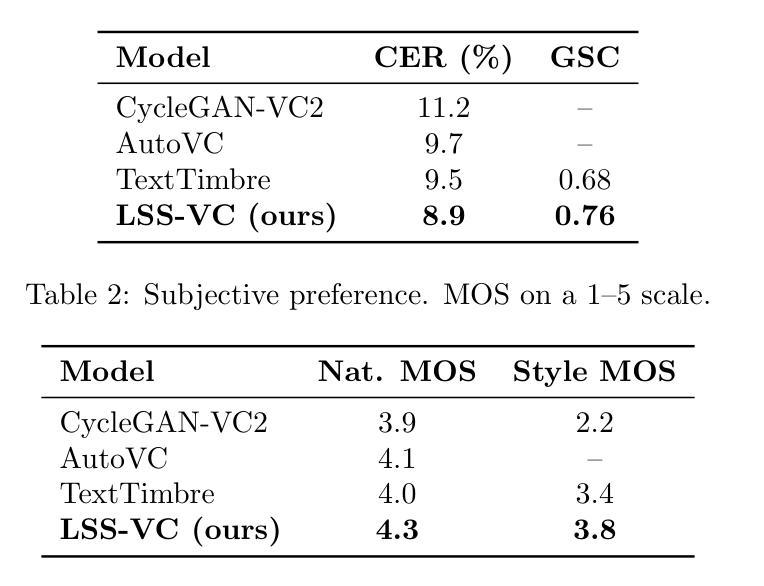
Video-T1: Test-Time Scaling for Video Generation
Authors:Fangfu Liu, Hanyang Wang, Yimo Cai, Kaiyan Zhang, Xiaohang Zhan, Yueqi Duan
With the scale capability of increasing training data, model size, and computational cost, video generation has achieved impressive results in digital creation, enabling users to express creativity across various domains. Recently, researchers in Large Language Models (LLMs) have expanded the scaling to test-time, which can significantly improve LLM performance by using more inference-time computation. Instead of scaling up video foundation models through expensive training costs, we explore the power of Test-Time Scaling (TTS) in video generation, aiming to answer the question: if a video generation model is allowed to use non-trivial amount of inference-time compute, how much can it improve generation quality given a challenging text prompt. In this work, we reinterpret the test-time scaling of video generation as a searching problem to sample better trajectories from Gaussian noise space to the target video distribution. Specifically, we build the search space with test-time verifiers to provide feedback and heuristic algorithms to guide searching process. Given a text prompt, we first explore an intuitive linear search strategy by increasing noise candidates at inference time. As full-step denoising all frames simultaneously requires heavy test-time computation costs, we further design a more efficient TTS method for video generation called Tree-of-Frames (ToF) that adaptively expands and prunes video branches in an autoregressive manner. Extensive experiments on text-conditioned video generation benchmarks demonstrate that increasing test-time compute consistently leads to significant improvements in the quality of videos. Project page: https://liuff19.github.io/Video-T1
随着训练数据、模型规模和计算成本的规模能力不断提升,视频生成在数字创作中取得了令人印象深刻的结果,使用户能够在各种领域表达创造力。最近,大型语言模型(LLM)的研究人员将规模扩展到了测试时间,通过增加推理时间的计算量,可以显著提高LLM的性能。我们并非通过昂贵的训练成本来扩展视频基础模型的规模,而是探索视频生成中的测试时间缩放(TTS)能力,旨在回答以下问题:如果视频生成模型允许使用非微不足道的推理时间计算量,那么在具有挑战性的文本提示下,它能提高多少生成质量。在这项工作中,我们将测试时的视频生成缩放重新解释为搜索问题,从高斯噪声空间中采样更好的轨迹以接近目标视频分布。具体来说,我们构建了一个搜索空间,其中包含测试时间验证器以提供反馈和启发式算法来指导搜索过程。给定一个文本提示,我们首先探索一种直观的线性搜索策略,通过在推理时间增加噪声候选物来进行。由于同时完全去除所有帧的噪声需要大量的测试时间计算成本,因此我们进一步设计了一种更有效的用于视频生成的TTS方法,称为“帧树”(ToF),该方法以自回归的方式自适应地扩展和修剪视频分支。在文本条件视频生成基准测试上的大量实验表明,增加测试时间的计算量可以持续提高视频质量。项目页面:https://liuff19.github.io/Video-T1
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://liuff19.github.io/Video-T1
Summary
视频生成领域通过扩大训练数据、模型规模和计算成本,实现了令人印象深刻的成果。最近,大型语言模型(LLM)的研究者将扩展能力扩展到测试阶段,通过更多的推理时间计算显著提高LLM性能。本研究探索了视频生成中的测试时间缩放(TTS)能力,将视频生成的测试时间缩放重新解释为搜索问题,从高斯噪声空间采样更好的轨迹到目标视频分布。本研究建立了一个带有测试时间验证器的搜索空间,为搜索过程提供反馈和启发式算法。实验表明,增加测试时间计算一致地显著提高了视频质量。
Key Takeaways
- 视频生成领域通过扩大训练数据、模型规模和计算成本取得了显著进步,使用户能够在不同领域表达创造力。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的测试时间缩放(TTS)能够显著提高LLM性能,通过更多的推理时间计算来改善模型表现。
- 本研究将视频生成的测试时间缩放解释为搜索问题,从高斯噪声空间采样轨迹以接近目标视频分布。
- 研究建立了带有测试时间验证器的搜索空间,为搜索过程提供反馈和启发式算法。
- 采用了一种直观的线性搜索策略,通过在推理时间增加噪声候选物来探索视频生成。
- 为了降低测试时的计算成本,研究进一步设计了一种更有效的视频生成TTS方法,称为Tree-of-Frames (ToF),该方法以自回归的方式自适应地扩展和修剪视频分支。
点此查看论文截图

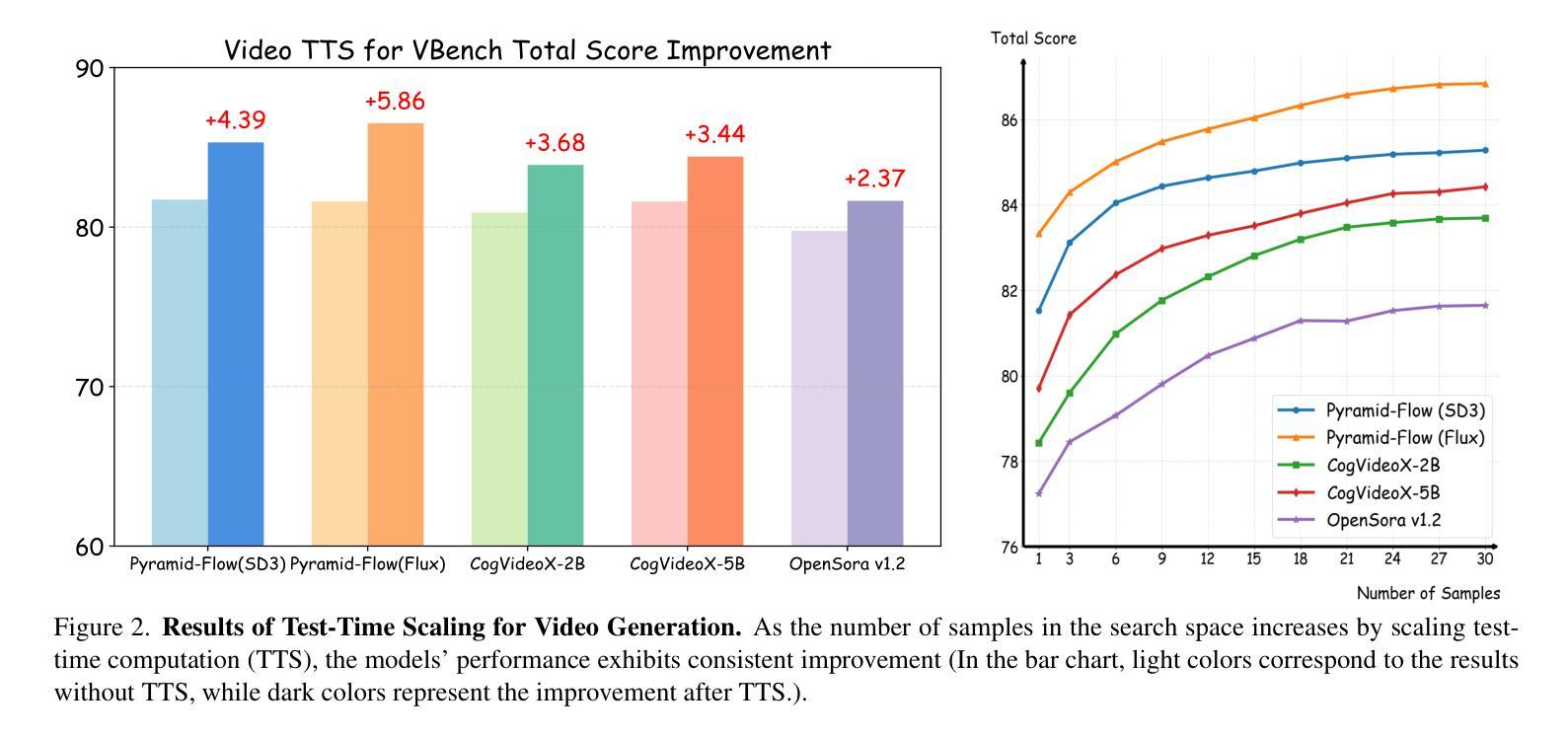
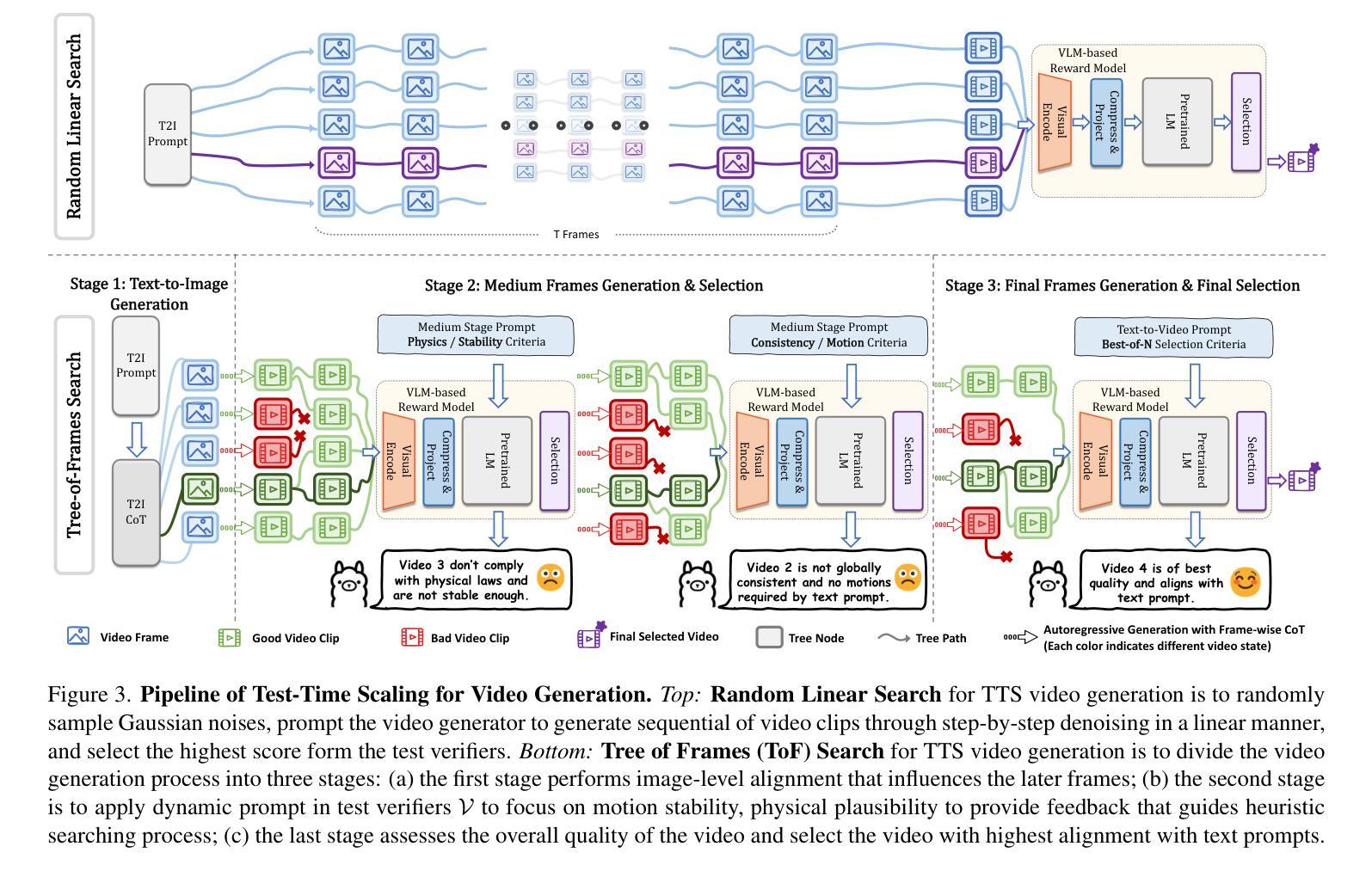
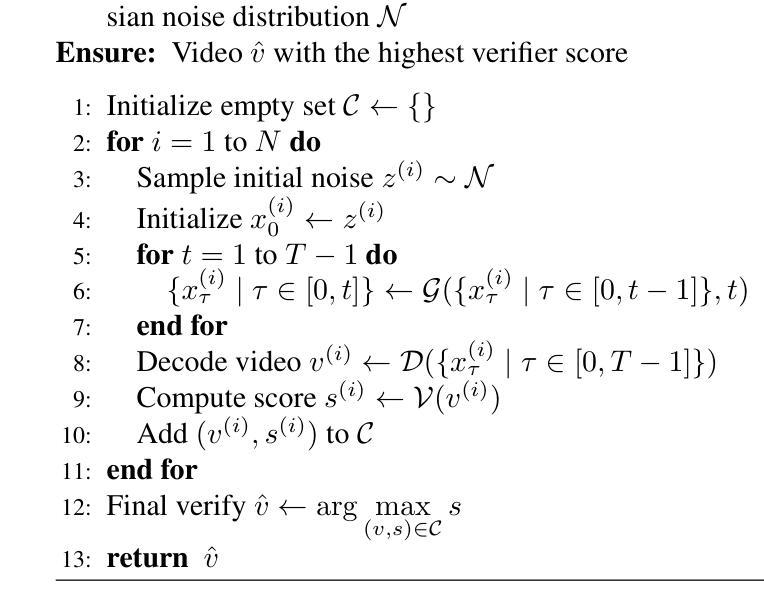
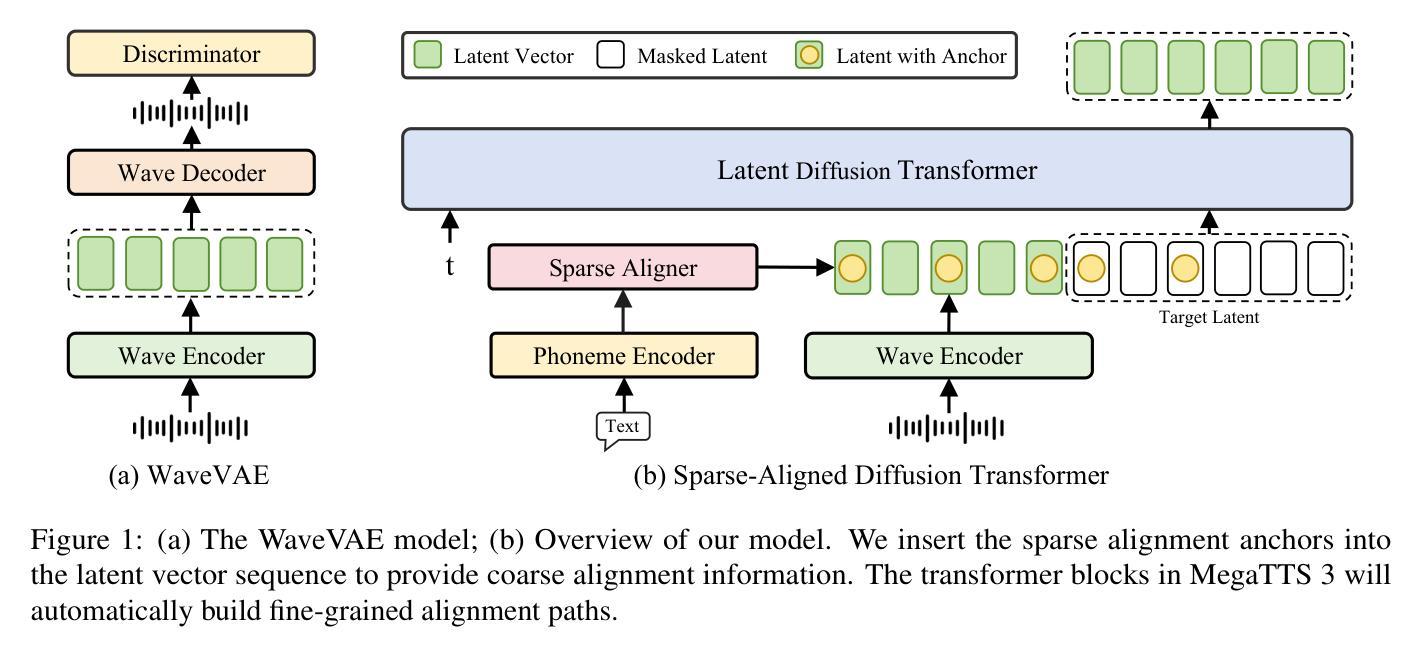
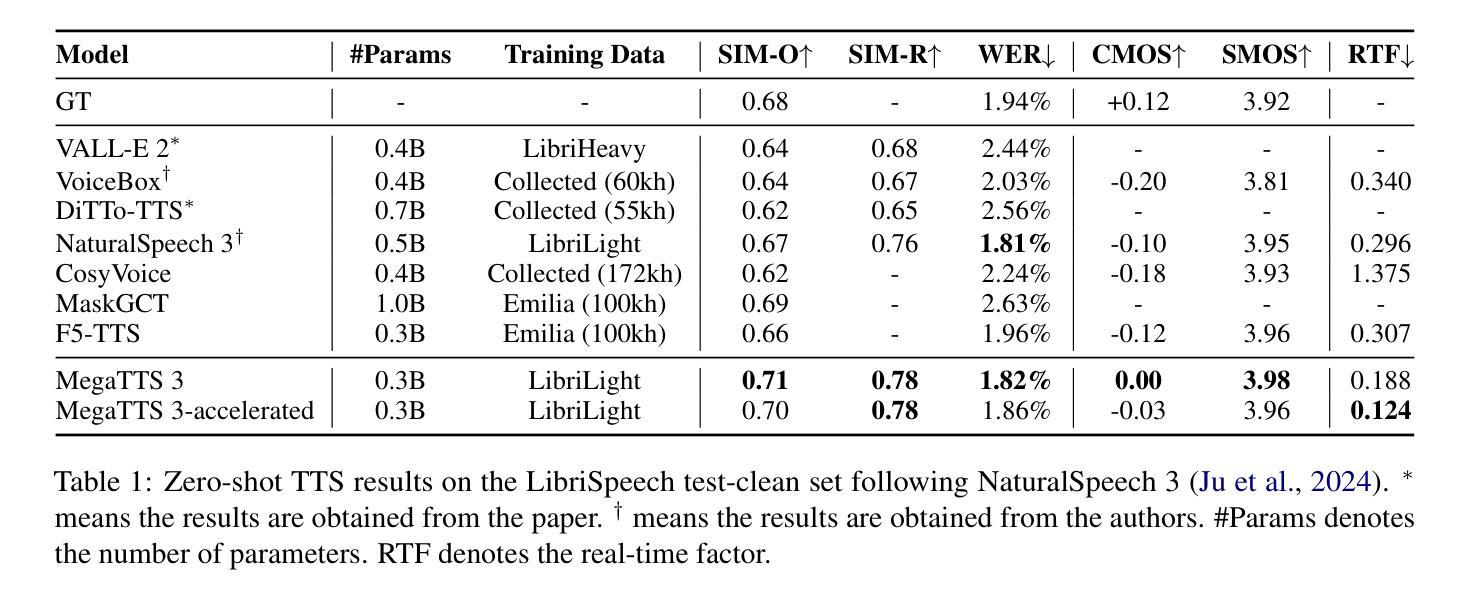
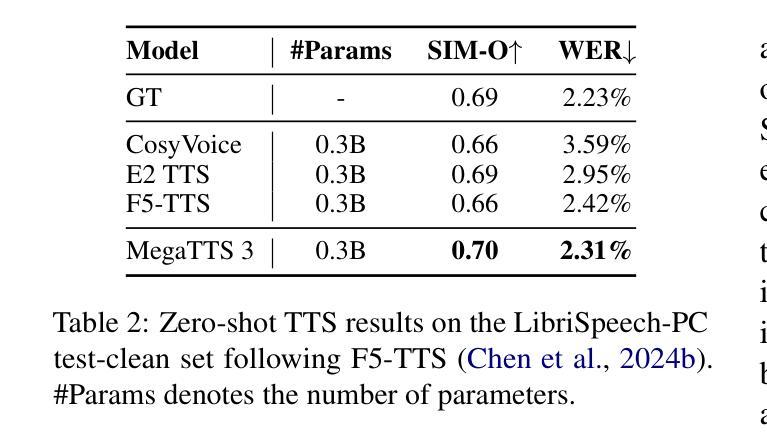
MegaTTS 3: Sparse Alignment Enhanced Latent Diffusion Transformer for Zero-Shot Speech Synthesis
Authors:Ziyue Jiang, Yi Ren, Ruiqi Li, Shengpeng Ji, Boyang Zhang, Zhenhui Ye, Chen Zhang, Bai Jionghao, Xiaoda Yang, Jialong Zuo, Yu Zhang, Rui Liu, Xiang Yin, Zhou Zhao
While recent zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) models have significantly improved speech quality and expressiveness, mainstream systems still suffer from issues related to speech-text alignment modeling: 1) models without explicit speech-text alignment modeling exhibit less robustness, especially for hard sentences in practical applications; 2) predefined alignment-based models suffer from naturalness constraints of forced alignments. This paper introduces \textit{MegaTTS 3}, a TTS system featuring an innovative sparse alignment algorithm that guides the latent diffusion transformer (DiT). Specifically, we provide sparse alignment boundaries to MegaTTS 3 to reduce the difficulty of alignment without limiting the search space, thereby achieving high naturalness. Moreover, we employ a multi-condition classifier-free guidance strategy for accent intensity adjustment and adopt the piecewise rectified flow technique to accelerate the generation process. Experiments demonstrate that MegaTTS 3 achieves state-of-the-art zero-shot TTS speech quality and supports highly flexible control over accent intensity. Notably, our system can generate high-quality one-minute speech with only 8 sampling steps. Audio samples are available at https://sditdemo.github.io/sditdemo/.
近期零样本文本到语音(TTS)模型在语音质量和表达力方面有了显著的提升,但主流系统仍然面临与语音文本对齐建模相关的问题:1)没有明确的语音文本对齐建模的模型表现出较低的稳健性,特别是在实际应用中的难句;2)基于预定义对齐的模型受到强制对齐的自然性约束的影响。本文介绍了MegaTTS 3,一个具有创新稀疏对齐算法的TTS系统,该系统指导潜在扩散变压器(DiT)。具体来说,我们为MegaTTS 3提供稀疏对齐边界,以减少对齐的难度,同时不限制搜索空间,从而实现高自然度。此外,我们采用多条件无分类指导策略进行口音强度调整,并采用分段整流流技术加速生成过程。实验表明,MegaTTS 3达到了最先进的零样本TTS语音质量,并支持对口音强度进行高度灵活的控制。值得注意的是,我们的系统只需8个采样步骤就能生成高质量的一分钟语音。音频样本可在https://sditdemo.github.io/sditdemo/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了MegaTTS 3系统,一个采用创新稀疏对齐算法的零样本文本转语音(TTS)系统。该系统通过提供稀疏对齐边界,减少了对齐的难度,同时不限制搜索空间,实现了高自然度。此外,还采用了多条件无分类引导策略进行口音强度调整,并采用分段整流流技术加速生成过程。实验表明,MegaTTS 3达到了零样本TTS的先进语音质量,并高度灵活地控制了口音强度。
Key Takeaways
- MegaTTS 3是一个零样本TTS系统,显著提高了语音质量和表达力。
- 系统采用稀疏对齐算法,减少了对齐难度,同时保持搜索空间的高自由度。
- 多条件无分类引导策略用于口音强度调整,使语音更自然。
- 分段整流流技术用于加速语音生成过程。
- MegaTTS 3实现了高度灵活的口音强度控制。
- 系统可生成高质量的一分钟语音,仅需要8个采样步骤。
点此查看论文截图

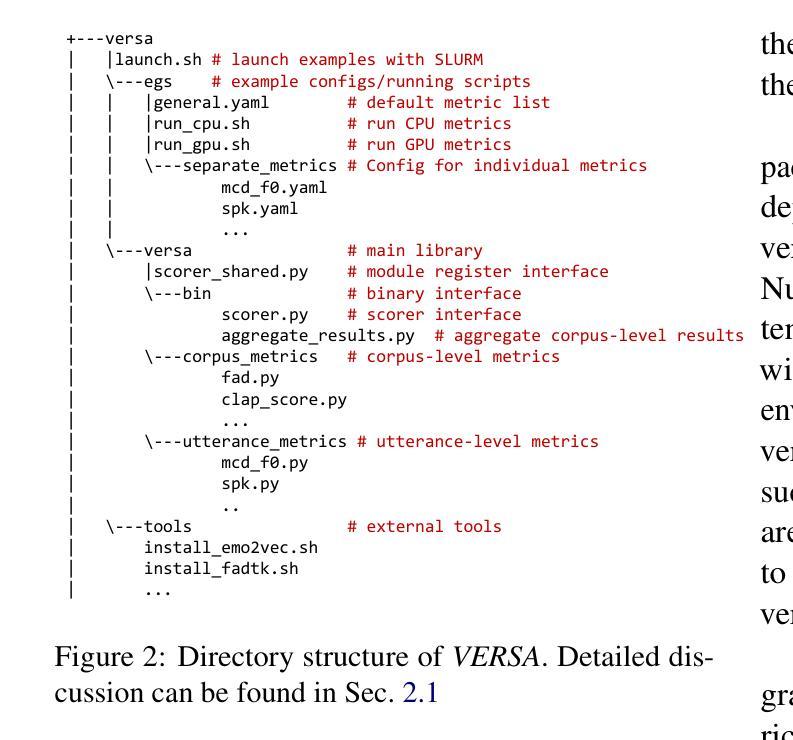
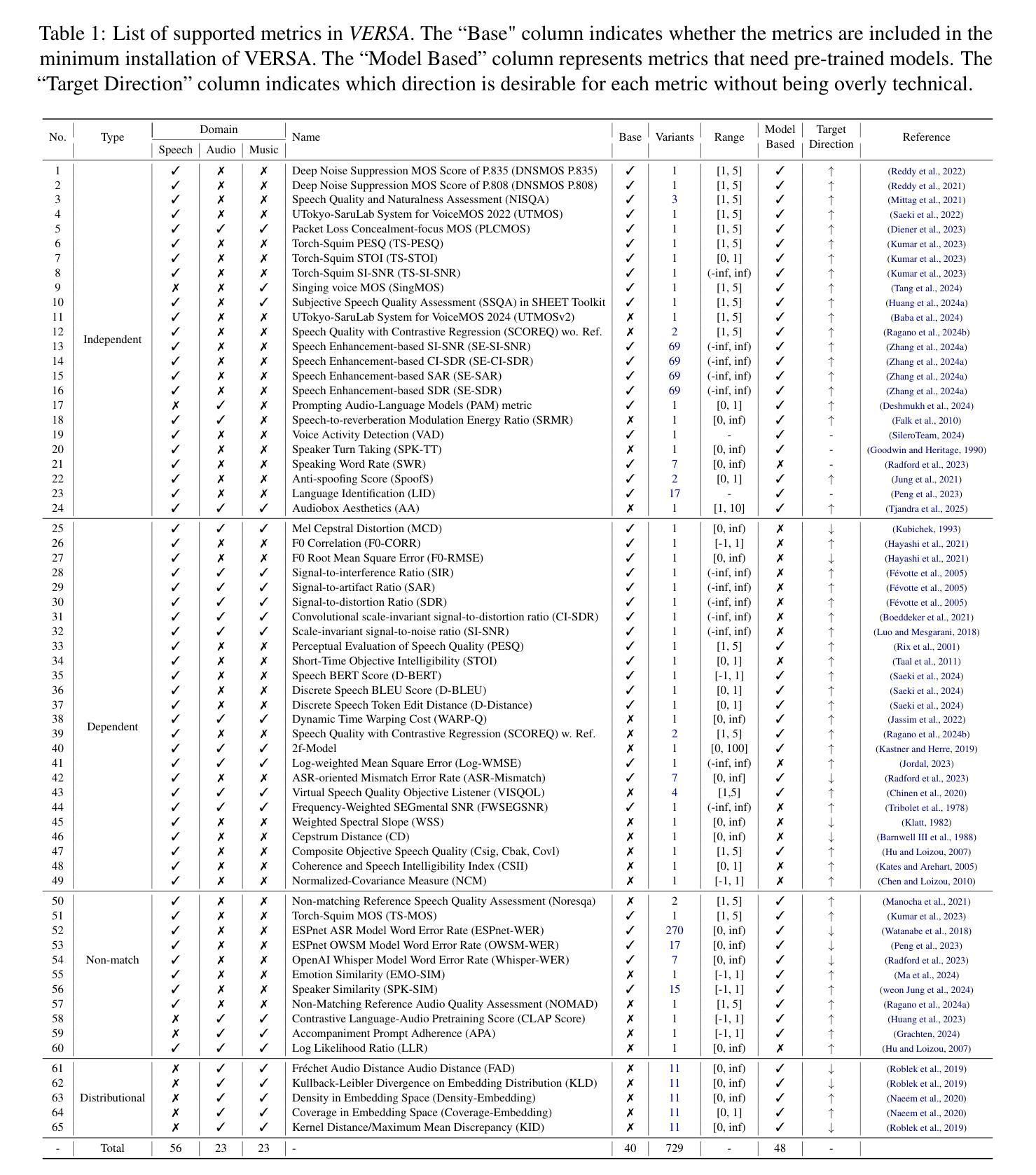
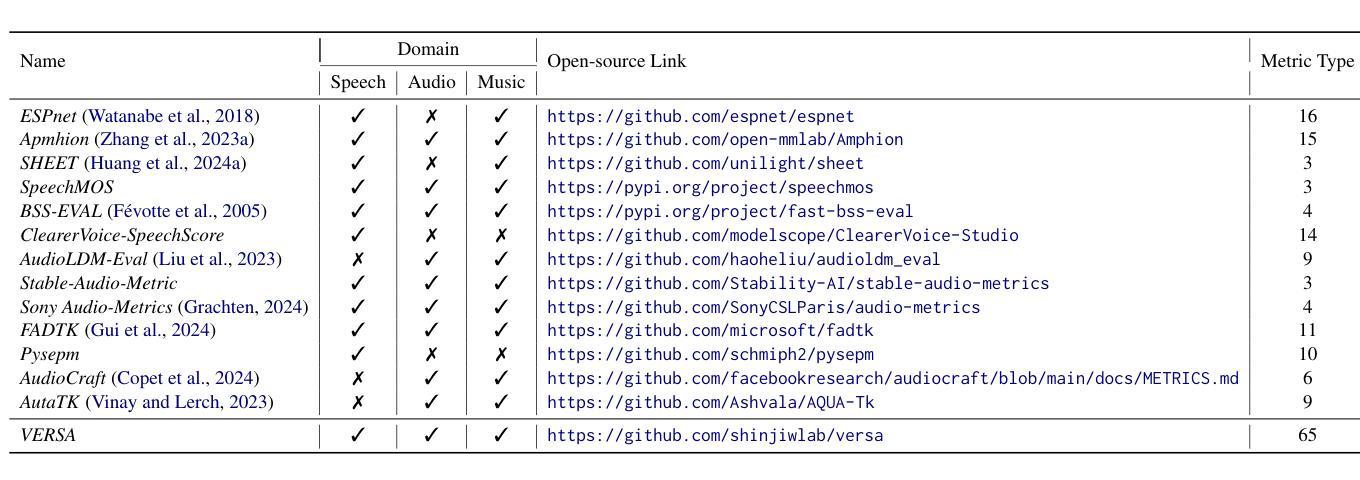
VERSA: A Versatile Evaluation Toolkit for Speech, Audio, and Music
Authors:Jiatong Shi, Hye-jin Shim, Jinchuan Tian, Siddhant Arora, Haibin Wu, Darius Petermann, Jia Qi Yip, You Zhang, Yuxun Tang, Wangyou Zhang, Dareen Safar Alharthi, Yichen Huang, Koichi Saito, Jionghao Han, Yiwen Zhao, Chris Donahue, Shinji Watanabe
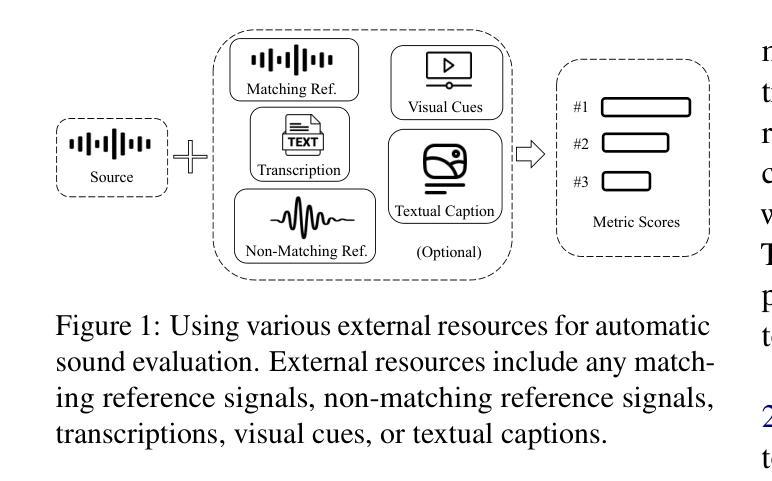
In this work, we introduce VERSA, a unified and standardized evaluation toolkit designed for various speech, audio, and music signals. The toolkit features a Pythonic interface with flexible configuration and dependency control, making it user-friendly and efficient. With full installation, VERSA offers 65 metrics with 729 metric variations based on different configurations. These metrics encompass evaluations utilizing diverse external resources, including matching and non-matching reference audio, text transcriptions, and text captions. As a lightweight yet comprehensive toolkit, VERSA is versatile to support the evaluation of a wide range of downstream scenarios. To demonstrate its capabilities, this work highlights example use cases for VERSA, including audio coding, speech synthesis, speech enhancement, singing synthesis, and music generation. The toolkit is available at https://github.com/wavlab-speech/versa.
在这项工作中,我们介绍了VERSA,这是一个为语音、音频和音乐信号设计的统一、标准化的评估工具包。该工具包具有Python风格的接口,具有灵活的配置和依赖控制,使其友好且高效。完全安装后,VERSA提供基于不同配置的65种指标和729种指标变体。这些指标涵盖了利用多种外部资源的评估,包括匹配和非匹配的参考音频、文本转录和文本标题。作为一个轻便而全面的工具包,VERSA支持对各种下游场景的评估。为了证明其能力,这项工作重点介绍了VERSA的示例用例,包括音频编码、语音合成、语音增强、歌唱合成和音乐生成。该工具包可在https://github.com/wavlab-speech/versa找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
VERSA是一个统一、标准化的语音、音频和音乐信号评估工具包,具有Pythonic接口、灵活的配置和依赖控制,提供多种评估指标,支持多种下游场景的评价。
Key Takeaways
- VERSA是一个针对语音、音频和音乐信号评估的工具包。
- 它提供了一个Pythonic接口,具有灵活的配置和依赖控制。
- VERSA包含65种评估指标,以及基于不同配置的729种指标变化。
- 该工具包可以利用各种外部资源进行评估,包括匹配和非匹配的参考音频、文本转录和文本标题。
- VERSA支持多种下游场景的评价,如音频编码、语音合成、语音增强、歌唱合成和音乐生成等。
- VERSA工具包可在https://github.com/wavlab-speech/versa上获取。
点此查看论文截图

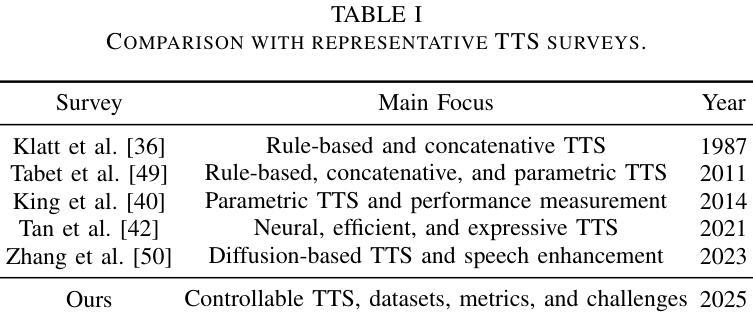
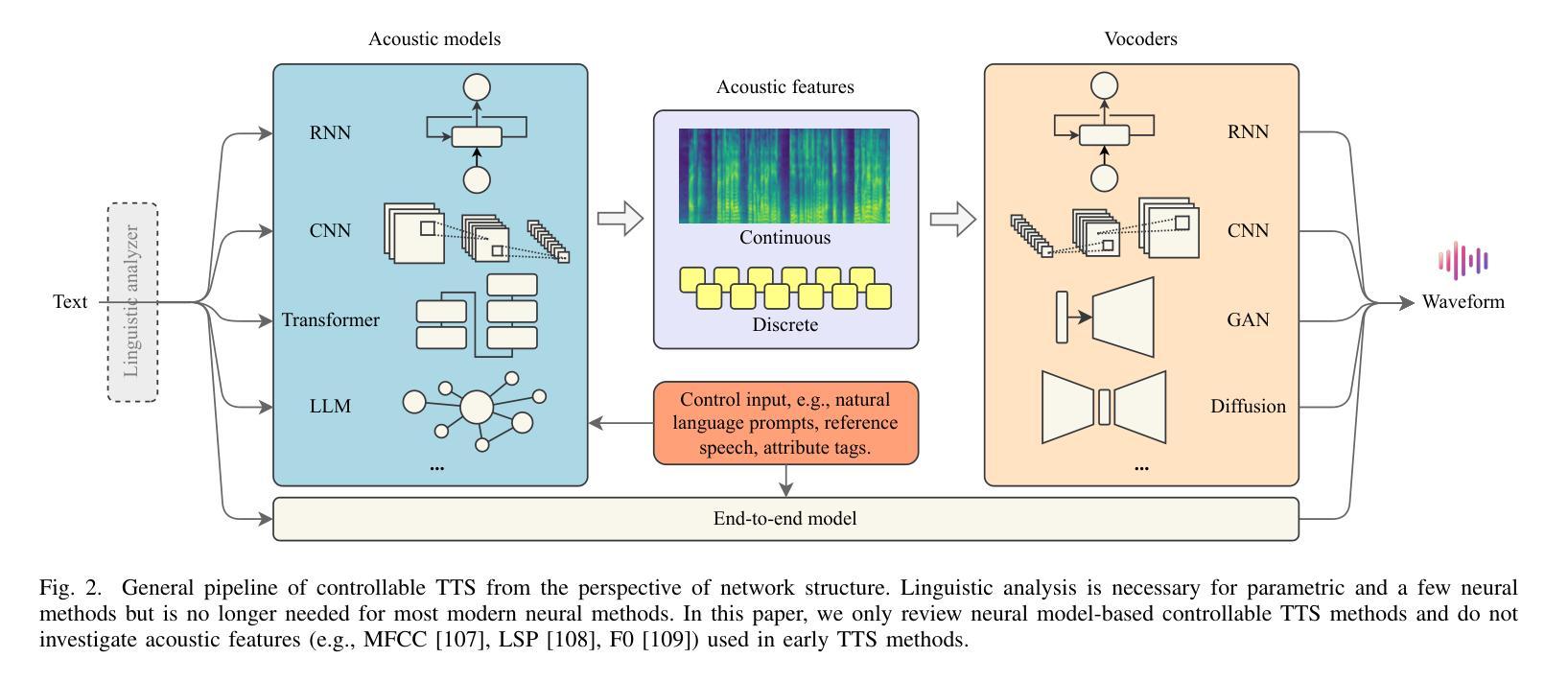
Towards Controllable Speech Synthesis in the Era of Large Language Models: A Survey
Authors:Tianxin Xie, Yan Rong, Pengfei Zhang, Wenwu Wang, Li Liu
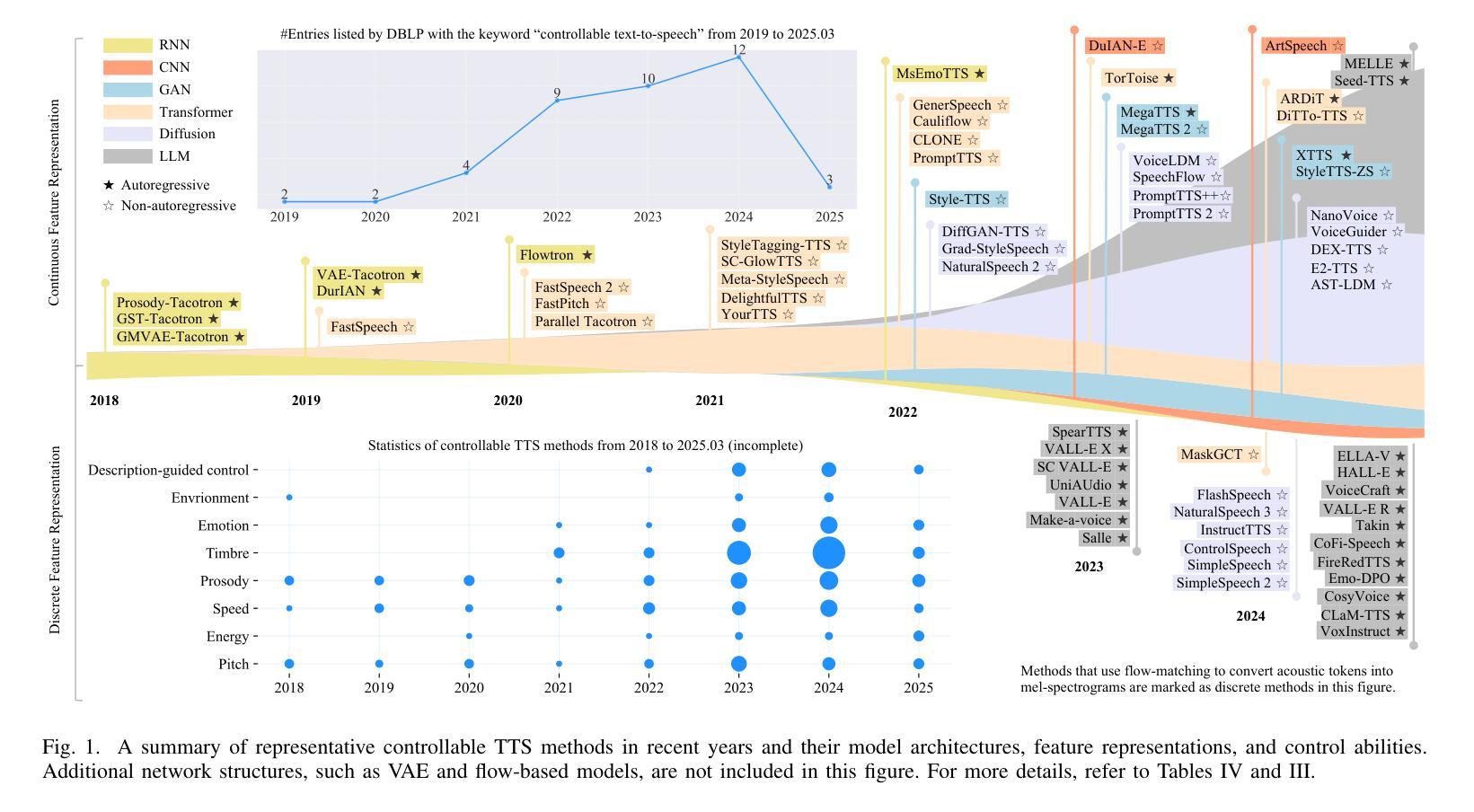
Text-to-speech (TTS), also known as speech synthesis, is a prominent research area that aims to generate natural-sounding human speech from text. Recently, with the increasing industrial demand, TTS technologies have evolved beyond synthesizing human-like speech to enabling controllable speech generation. This includes fine-grained control over various attributes of synthesized speech such as emotion, prosody, timbre, and duration. In addition, advancements in deep learning, such as diffusion and large language models, have significantly enhanced controllable TTS over the past several years. In this work, we conduct a comprehensive survey of controllable TTS, covering approaches ranging from basic control techniques to methods utilizing natural language prompts, aiming to provide a clear understanding of the current state of research. We examine the general controllable TTS pipeline, challenges, model architectures, and control strategies, offering a comprehensive and clear taxonomy of existing methods. Additionally, we provide a detailed summary of datasets and evaluation metrics and shed some light on the applications and future directions of controllable TTS. To the best of our knowledge, this survey paper provides the first comprehensive review of emerging controllable TTS methods, which can serve as a beneficial resource for both academic researchers and industrial practitioners.
文本转语音(TTS),也被称为语音合成,是一个旨在从文本生成自然语音的重要研究领域。最近,随着工业需求的增加,TTS技术已经超越了合成类似人类语音的能力,实现了可控的语音生成。这包括合成语音的各种属性的精细控制,如情感、语调、音质和持续时间。此外,深度学习领域的进步,如扩散和大型语言模型,在过去的几年里显著增强了可控TTS的性能。在这项工作中,我们对可控TTS进行了全面的调查,涵盖了从基本控制技术到利用自然语言提示的方法等各种方法,旨在提供对研究现状的清晰理解。我们考察了可控TTS的一般流程、挑战、模型架构和控制策略,提供了现有方法的全面清晰的分类。此外,我们还详细总结了数据集和评价指标,并对可控TTS的应用和未来发展方向进行了一些探讨。据我们所知,这篇综述论文对新兴的可控TTS方法进行了首次全面的回顾,对学术研究人员和工业从业者都有很大的参考价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF A comprehensive survey on controllable TTS, 26 pages, 7 tables, 6 figures, 317 references. Under review
Summary
文本转语音(TTS)是生成自然语音的关键研究领域。近年来,随着工业需求的增长,TTS技术已进化为可控语音生成,包括精细控制合成语音的各种属性,如情感、语调、音质和时长等。深度学习领域的进展,如扩散和大型语言模型,极大地推动了可控TTS的发展。本文全面综述了可控TTS,涵盖从基本控制技术到利用自然语言提示的方法,旨在提供对当前研究状态的清晰理解。包括一般可控TTS管道、挑战、模型架构和控制策略的综合分类。此外,本文还详细总结了数据集和评估指标,并指出了可控TTS的应用和未来发展方向。本文是对新兴可控TTS方法的首次全面综述,对学术研究人员和工业从业者都有益。
Key Takeaways
- TTS是生成自然语音的重要研究领域。
- 近期TTS技术已扩展至可控语音生成,涉及合成语音的各种属性控制。
- 深度学习领域的进展显著提升了可控TTS的性能。
- 本文全面概述了可控TTS的研究现状,包括其管道、挑战、模型架构和控制策略。
- 文章详细总结了相关的数据集和评估指标。
- 文章还探讨了可控TTS的应用和未来发展方向。
点此查看论文截图

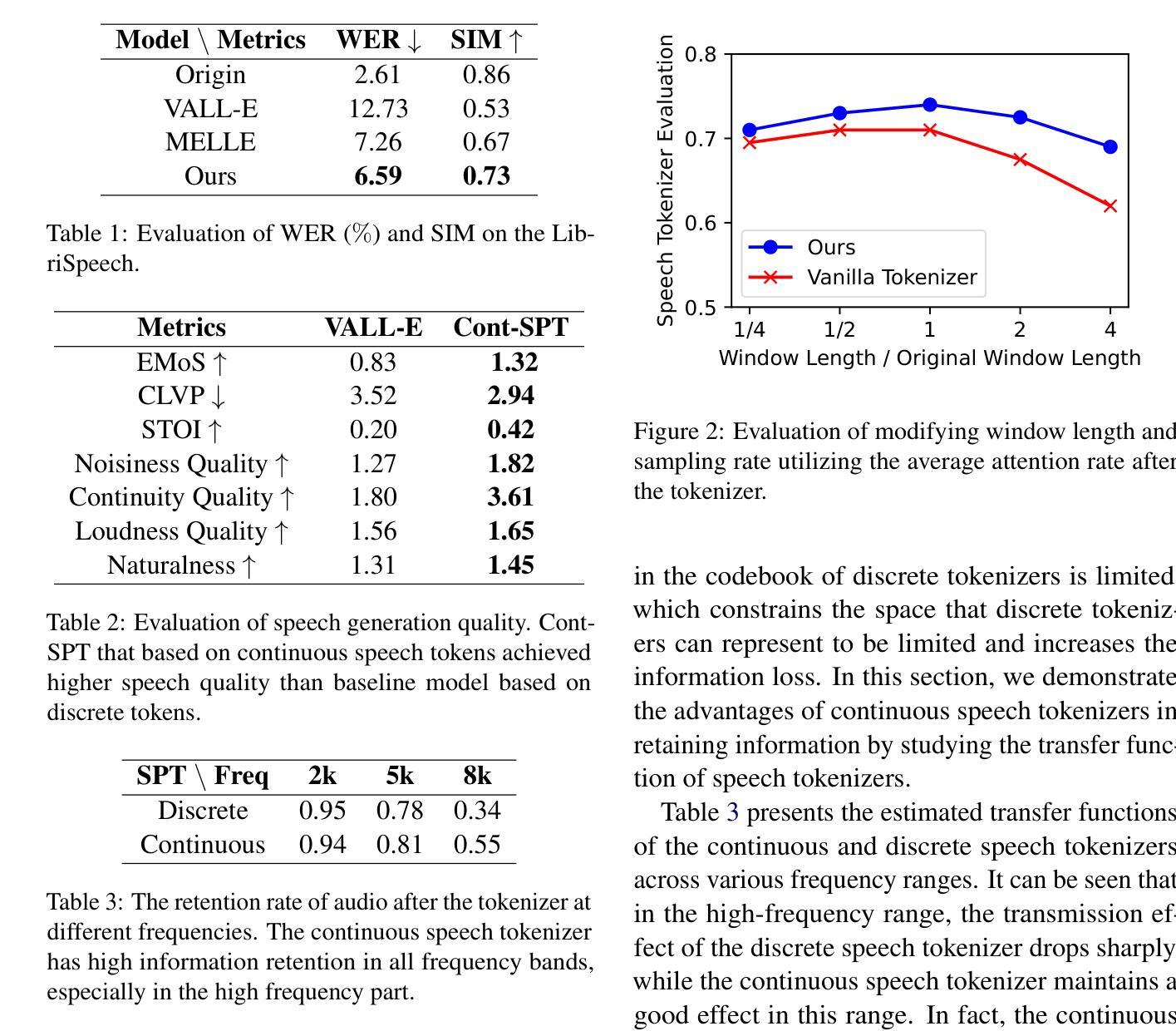
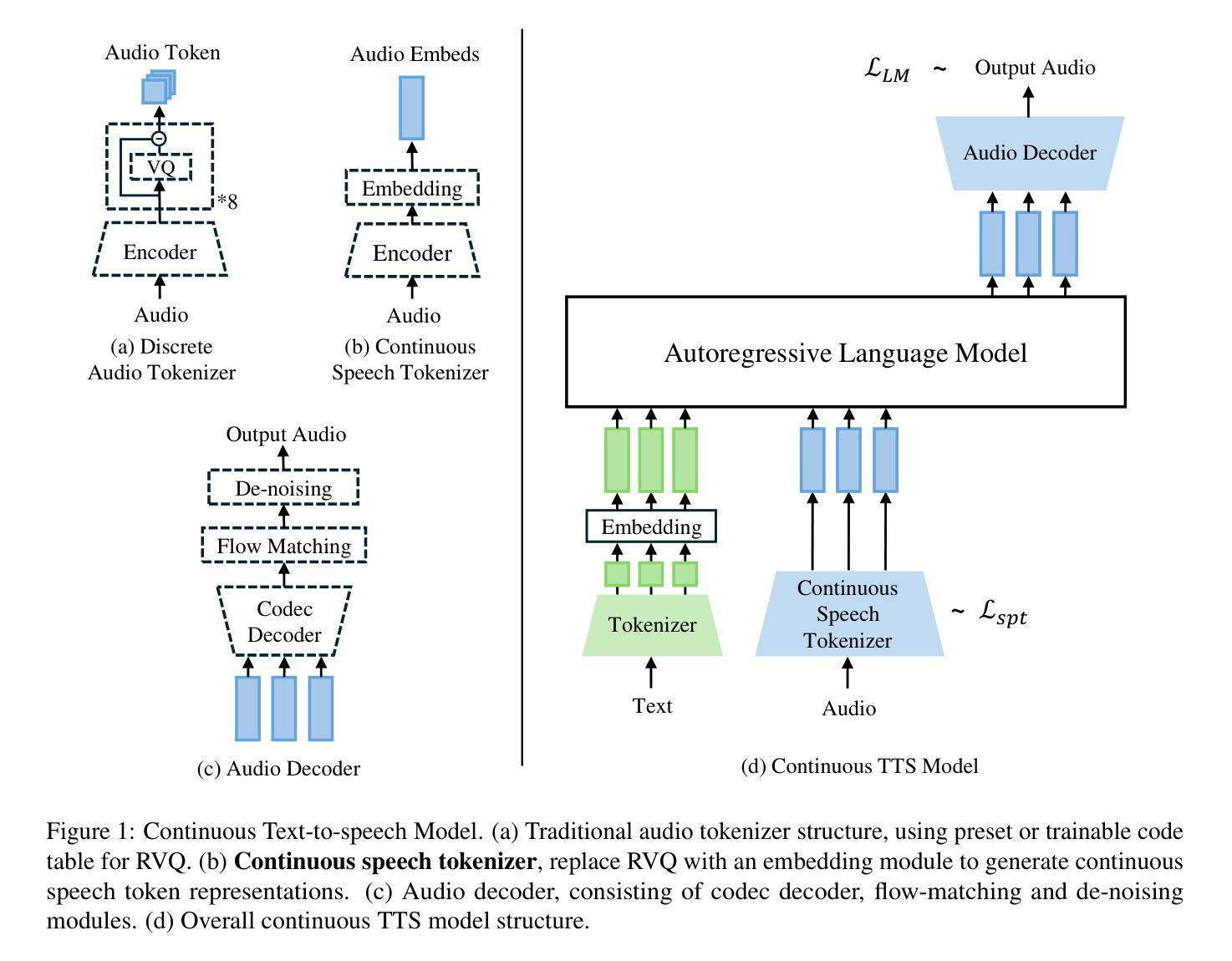
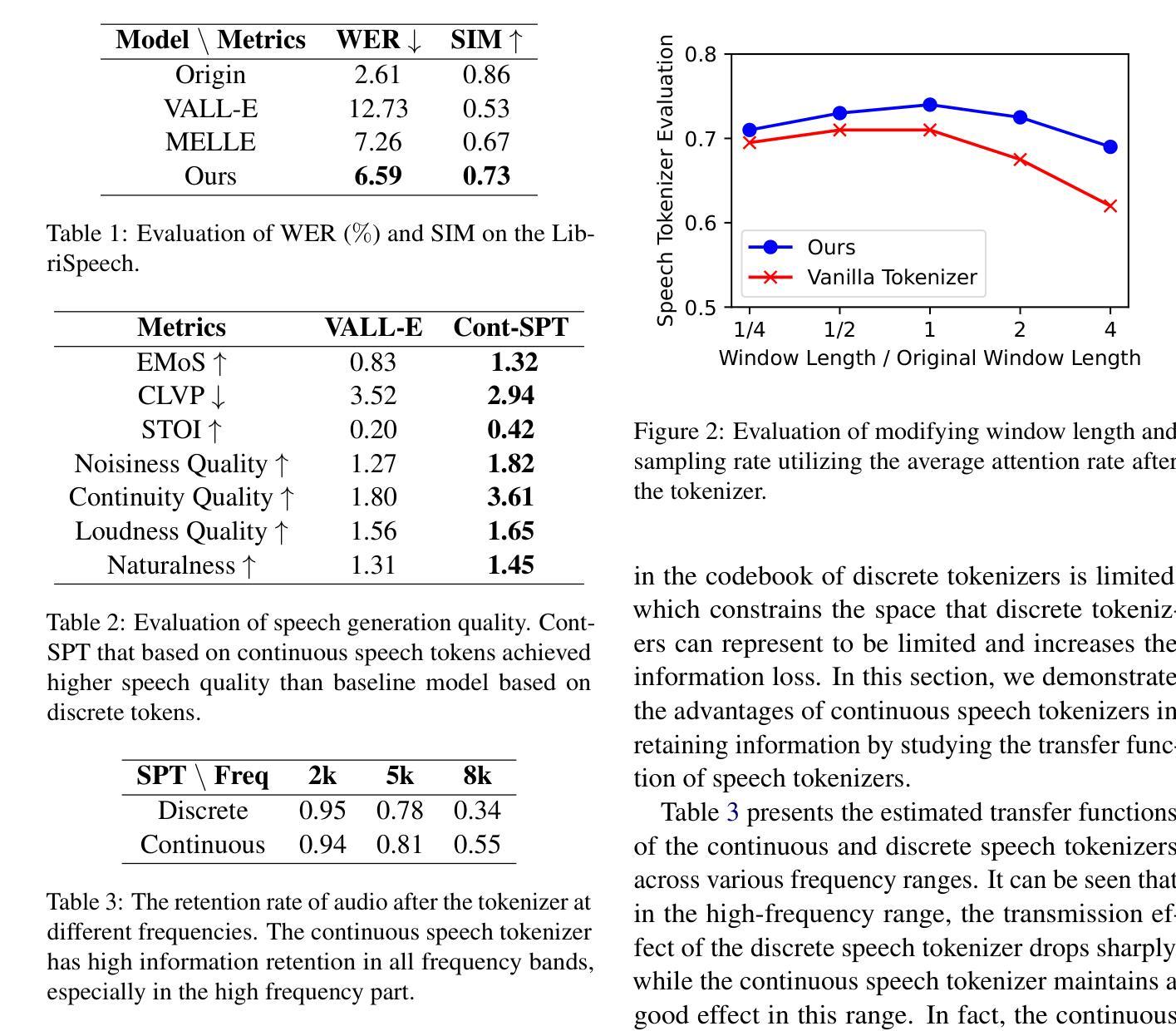
Continuous Speech Tokenizer in Text To Speech
Authors:Yixing Li, Ruobing Xie, Xingwu Sun, Yu Cheng, Zhanhui Kang
The fusion of speech and language in the era of large language models has garnered significant attention. Discrete speech token is often utilized in text-to-speech tasks for speech compression and portability, which is convenient for joint training with text and have good compression efficiency. However, we found that the discrete speech tokenizer still suffers from information loss. Therefore, we propose a simple yet effective continuous speech tokenizer named Cont-SPT, and a text-to-speech model based on continuous speech tokens. Our results show that the speech language model based on the continuous speech tokenizer has better continuity and higher estimated Mean Opinion Scores (MoS). This enhancement is attributed to better information preservation rate of the continuous speech tokenizer across both low and high frequencies in the frequency domain. The code and resources for Cont-SPT can be found in https://github.com/Yixing-Li/Continuous-Speech-Tokenizer
在大型语言模型时代,语音和语言的融合引起了人们的广泛关注。在文本到语音的任务中,离散语音令牌通常用于语音压缩和便携性,这便于与文本进行联合训练并具有很好的压缩效率。然而,我们发现离散语音令牌化仍存在信息丢失的问题。因此,我们提出了一种简单有效的连续语音令牌化方法,命名为Cont-SPT,以及一种基于连续语音令牌的文本到语音模型。结果表明,基于连续语音令牌的语音语言模型具有更好的连续性和更高的预估平均意见得分(MoS)。这种改进归因于连续语音令牌化在低频和高频域中更好的信息保持率。Cont-SPT的代码和资源可在https://github.com/Yixing-Li/Continuous-Speech-Tokenizer中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NAACL 2025 Findings Poster
总结
在大型语言模型的时代,语音和语言的融合引起了广泛关注。离散语音令牌在文本到语音任务中常用于语音压缩和便携性,便于与文本进行联合训练,并具有良好的压缩效率。然而,研究人员发现离散语音分词器仍存在信息丢失的问题。因此,他们提出了一种简单有效的连续语音分词器Cont-SPT和基于连续语音令牌的文本到语音模型。研究表明,基于连续语音分词器的语音语言模型具有更好的连续性和更高的预估平均意见得分(MoS)。这种改进归因于连续语音分词器在频域中低频和高频信息的更好保留率。Cont-SPT的代码和资源可在https://github.com/Yixing-Li/Continuous-Speech-Tokenizer找到。
关键见解
- 语音和语言融合在大型语言模型时代受到关注。
- 离散语音令牌在文本到语音任务中用于语音压缩和便携性。
- 离散语音分词器存在信息丢失的问题。
- 提出了名为Cont-SPT的连续语音分词器。
- 基于连续语音令牌的文本到语音模型表现出更好的连续性和更高的预估平均意见得分(MoS)。
- 连续语音分词器在频域中低频和高频信息的保留率更高。
点此查看论文截图

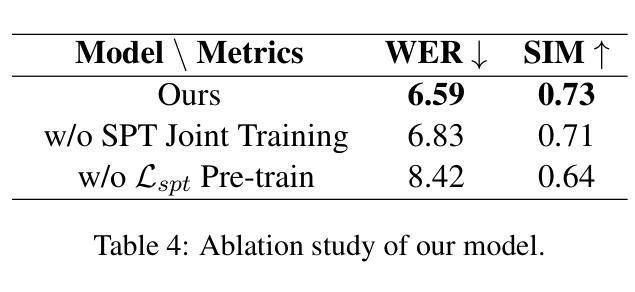
SF-Speech: Straightened Flow for Zero-Shot Voice Clone
Authors:Xuyuan Li, Zengqiang Shang, Hua Hua, Peiyang Shi, Chen Yang, Li Wang, Pengyuan Zhang
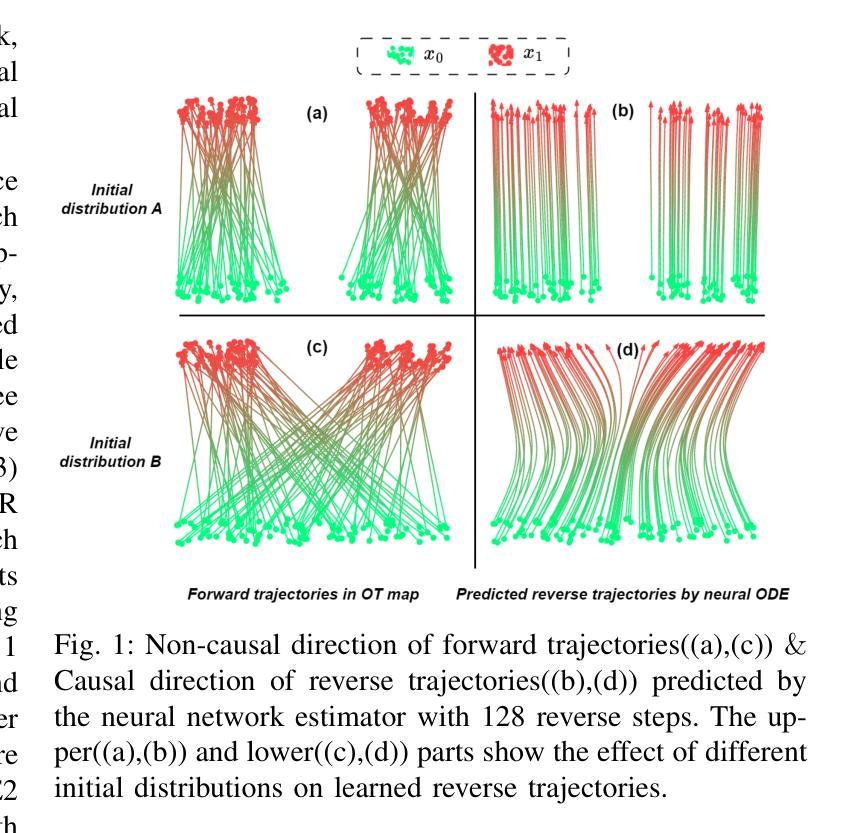
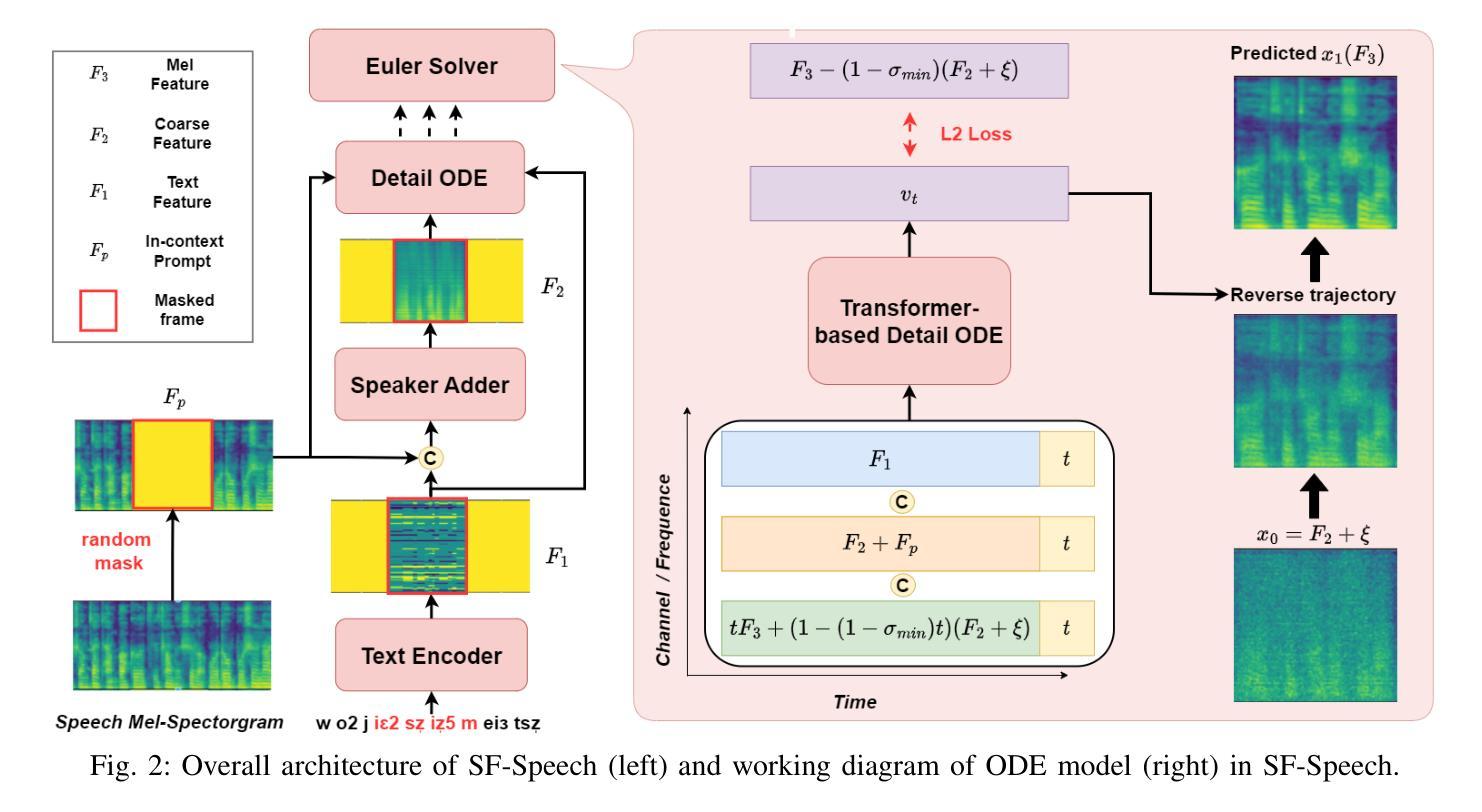
Recently, neural ordinary differential equations (ODE) models trained with flow matching have achieved impressive performance on the zero-shot voice clone task. Nevertheless, postulating standard Gaussian noise as the initial distribution of ODE gives rise to numerous intersections within the fitted targets of flow matching, which presents challenges to model training and enhances the curvature of the learned generated trajectories. These curved trajectories restrict the capacity of ODE models for generating desirable samples with a few steps. This paper proposes SF-Speech, a novel voice clone model based on ODE and in-context learning. Unlike the previous works, SF-Speech adopts a lightweight multi-stage module to generate a more deterministic initial distribution for ODE. Without introducing any additional loss function, we effectively straighten the curved reverse trajectories of the ODE model by jointly training it with the proposed module. Experiment results on datasets of various scales show that SF-Speech outperforms the state-of-the-art zero-shot TTS methods and requires only a quarter of the solver steps, resulting in a generation speed approximately 3.7 times that of Voicebox and E2 TTS. Audio samples are available at the demo page\footnote{[Online] Available: https://lixuyuan102.github.io/Demo/}.
最近,使用流匹配训练的神经常微分方程(ODE)模型在零样本语音克隆任务上取得了令人印象深刻的表现。然而,假设标准高斯噪声作为ODE的初始分布会导致流匹配的拟合目标内部出现许多交点,这给模型训练带来了挑战,并增强了学习生成轨迹的曲率。这些弯曲的轨迹限制了ODE模型在几步内生成理想样本的能力。本文提出了SF-Speech,这是一种基于ODE和上下文学习的新型语音克隆模型。不同于以前的工作,SF-Speech采用轻量级的多阶段模块来为ODE生成更确定的初始分布。我们没有引入任何额外的损失函数,而是通过联合训练所提出的模块,有效地拉直了ODE模型的弯曲反向轨迹。在各种规模数据集上的实验结果表明,SF-Speech优于最先进的零样本文本到语音转换方法,并且所需的求解器步骤仅为四分之一,生成速度大约是Voicebox和E2 TTS的3.7倍。音频样本可在演示页面获得^[在线可用:https://lixuyuan102.github.io/Demo/]^。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing
Summary
神经网络常微分方程(ODE)模型在零样本语音克隆任务上取得了令人印象深刻的性能表现。然而,将标准高斯噪声设为ODE的初始分布会导致流匹配的目标拟合中出现许多交点,给模型训练带来挑战,并增强学习轨迹的曲率。曲率大的轨迹限制了ODE模型在几步内生成理想样本的能力。本文提出一种基于ODE和上下文学习的SF-Speech新型语音克隆模型。不同于以往的工作,SF-Speech采用轻量级的多阶段模块来为ODE生成更确定的初始分布。我们无需引入任何额外的损失函数,就可以通过联合训练模块有效地纠正ODE模型的弯曲反向轨迹。在多种规模数据集上的实验结果表明,SF-Speech优于最先进的零样本文本到语音转换方法,且所需的求解器步骤仅为四分之一,生成速度大约是Voicebox和E2 TTS的3.7倍。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络常微分方程(ODE)模型在语音克隆任务上表现出色。
- 标准高斯噪声作为ODE初始分布会导致流匹配中的交点问题,增加模型训练难度和轨迹曲率。
- SF-Speech是一种基于ODE和上下文学习的新型语音克隆模型。
- SF-Speech采用轻量级多阶段模块生成更确定的ODE初始分布。
- 联合训练模块可有效纠正ODE模型的弯曲反向轨迹,无需额外损失函数。
- SF-Speech在多种数据集上的实验表现优于现有方法,且生成速度更快。
点此查看论文截图

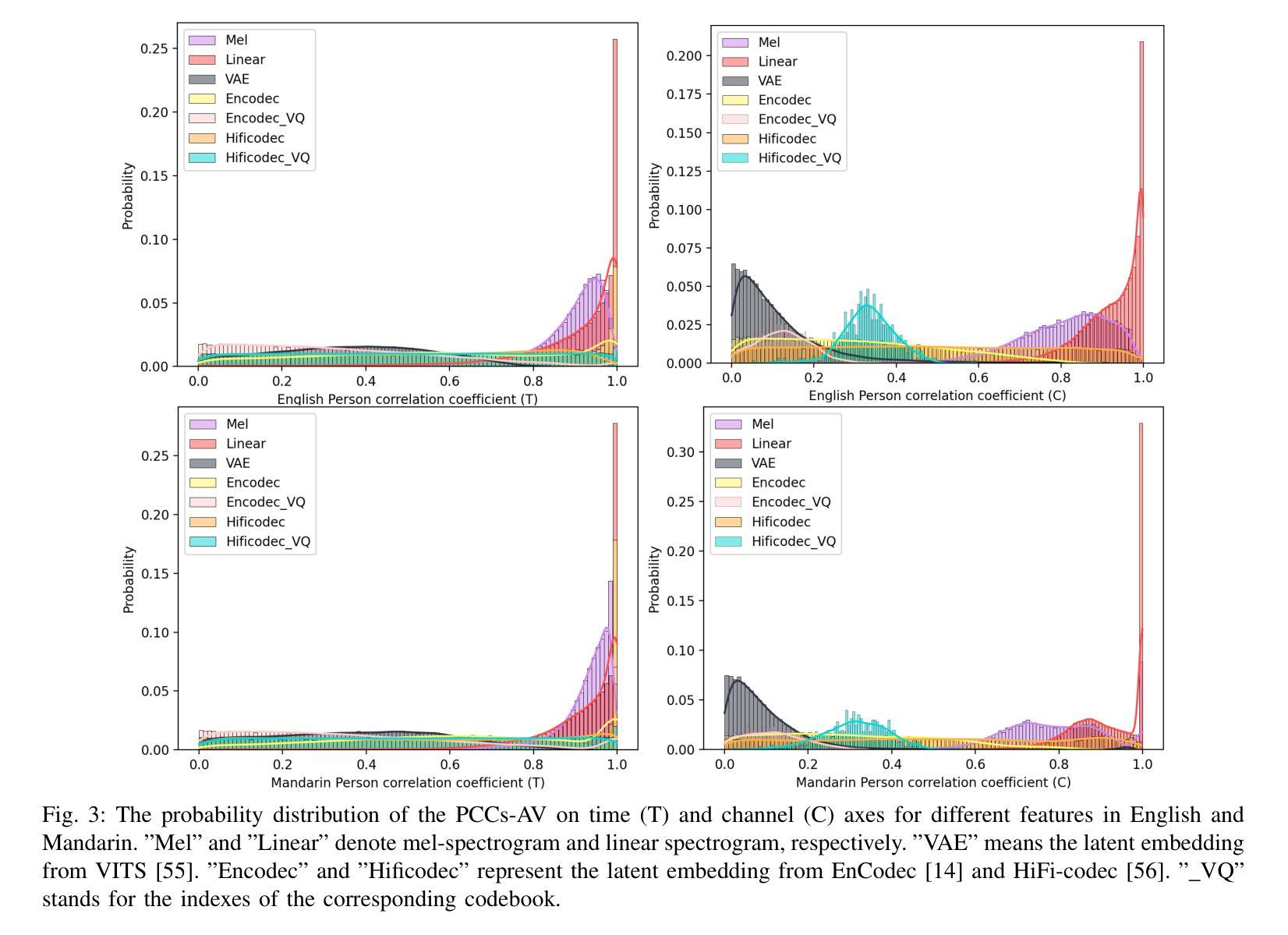
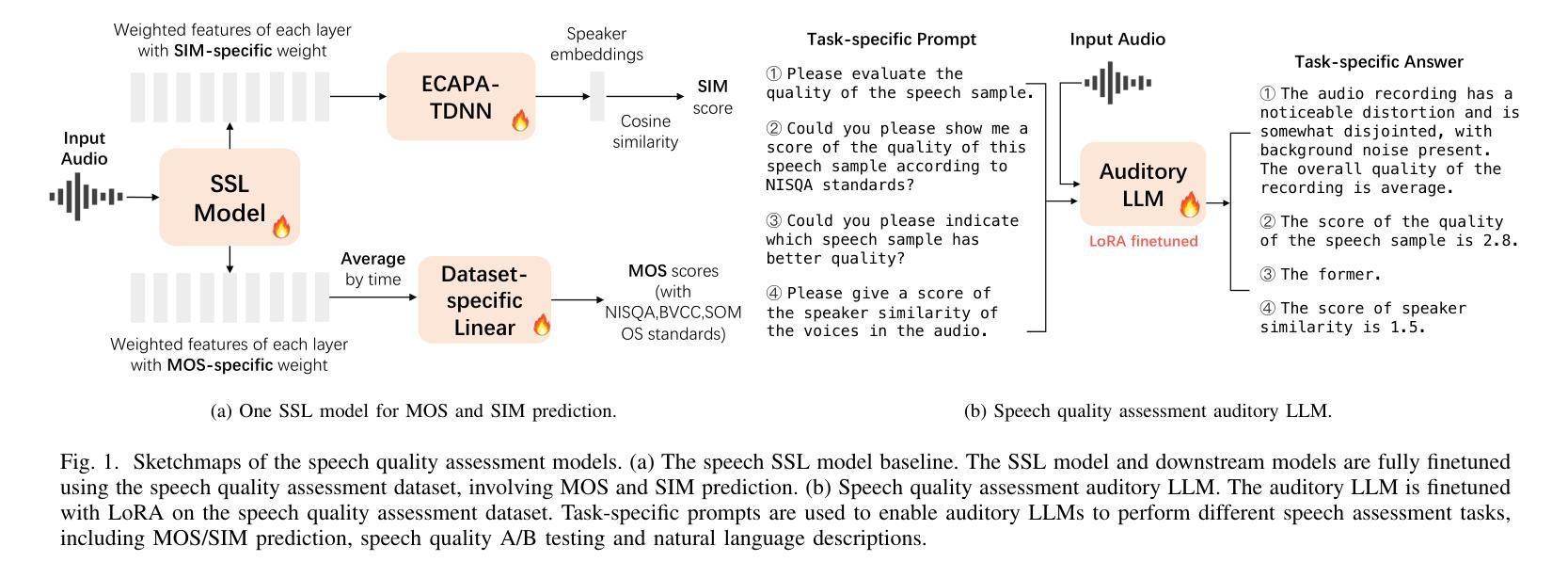
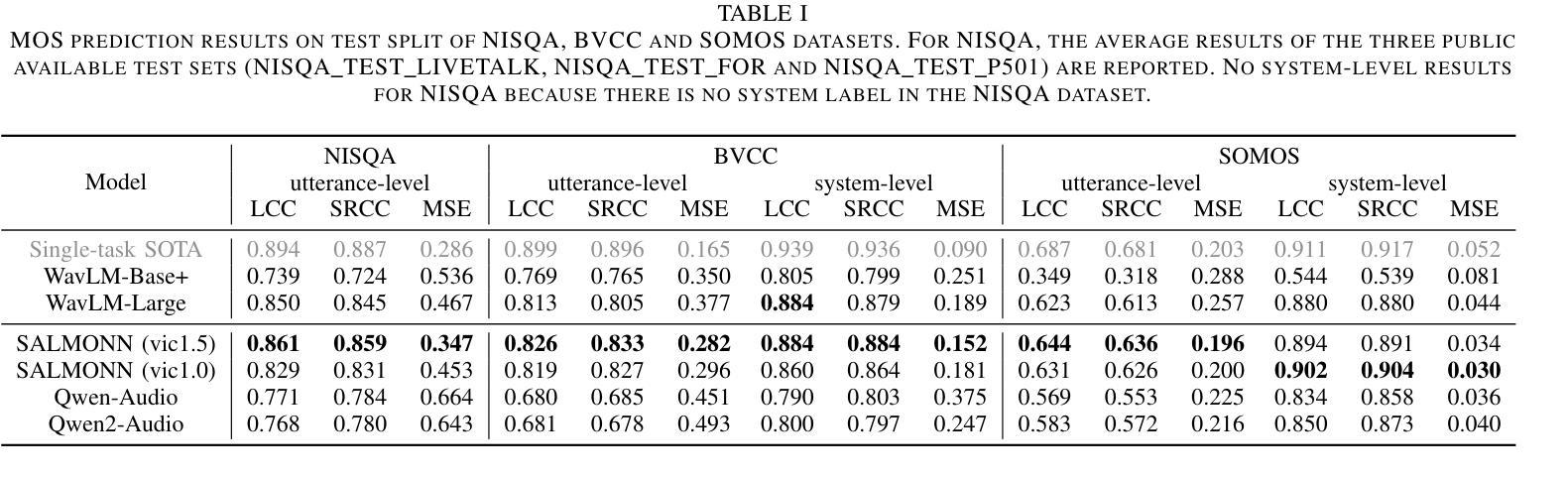
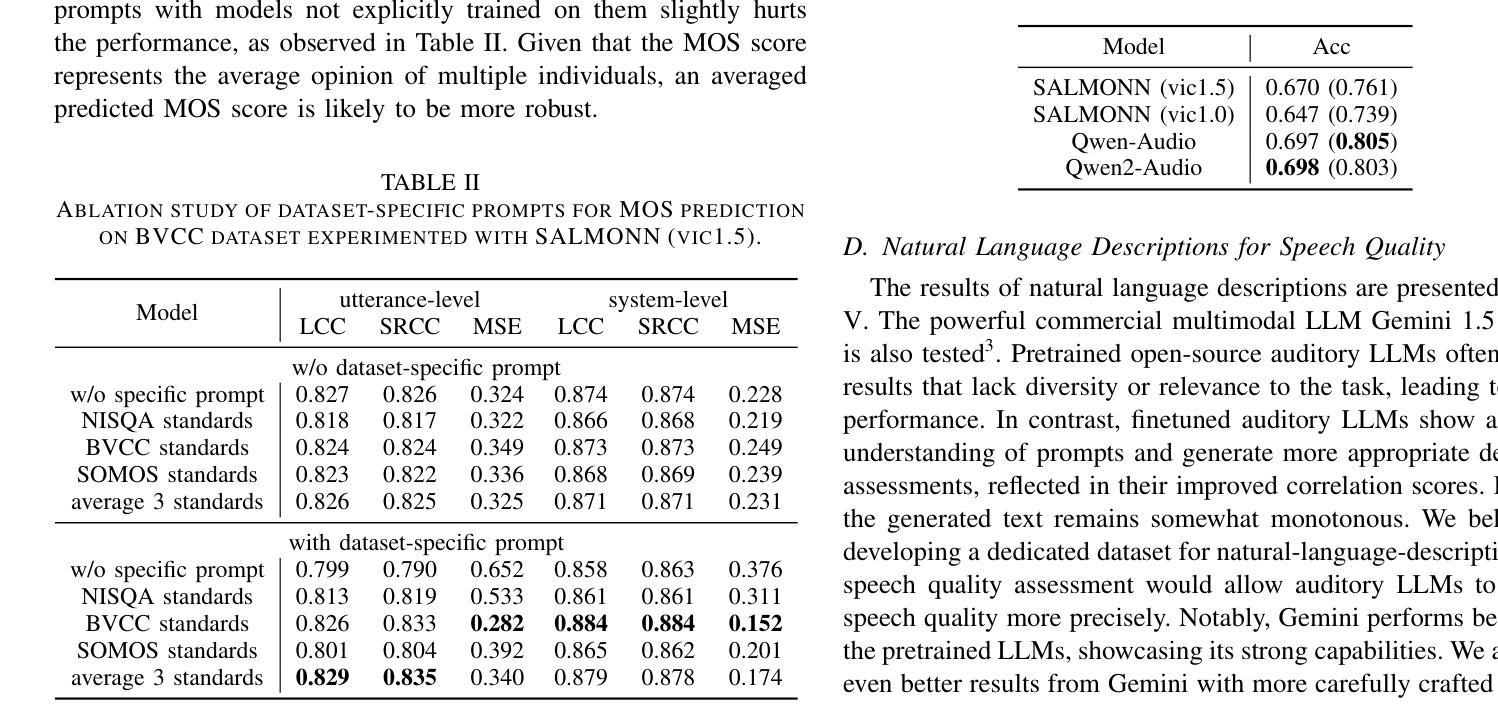
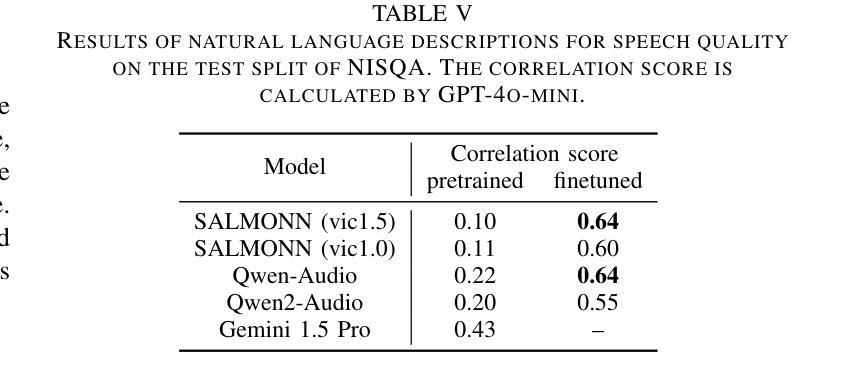
Enabling Auditory Large Language Models for Automatic Speech Quality Evaluation
Authors:Siyin Wang, Wenyi Yu, Yudong Yang, Changli Tang, Yixuan Li, Jimin Zhuang, Xianzhao Chen, Xiaohai Tian, Jun Zhang, Guangzhi Sun, Lu Lu, Yuxuan Wang, Chao Zhang
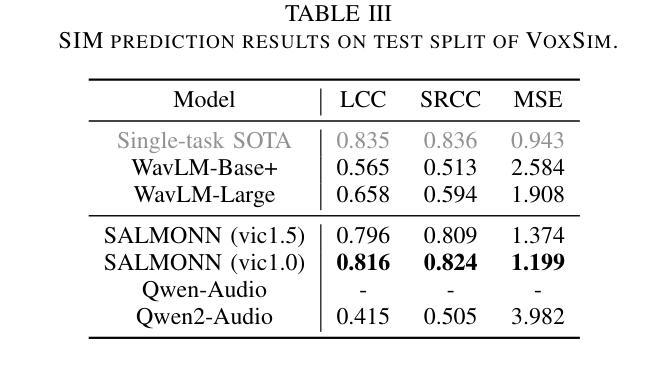
Speech quality assessment typically requires evaluating audio from multiple aspects, such as mean opinion score (MOS) and speaker similarity (SIM) \etc., which can be challenging to cover using one small model designed for a single task. In this paper, we propose leveraging recently introduced auditory large language models (LLMs) for automatic speech quality assessment. By employing task-specific prompts, auditory LLMs are finetuned to predict MOS, SIM and A/B testing results, which are commonly used for evaluating text-to-speech systems. Additionally, the finetuned auditory LLM is able to generate natural language descriptions assessing aspects like noisiness, distortion, discontinuity, and overall quality, providing more interpretable outputs. Extensive experiments have been performed on the NISQA, BVCC, SOMOS and VoxSim speech quality datasets, using open-source auditory LLMs such as SALMONN, Qwen-Audio, and Qwen2-Audio. For the natural language descriptions task, a commercial model Google Gemini 1.5 Pro is also evaluated. The results demonstrate that auditory LLMs achieve competitive performance compared to state-of-the-art task-specific small models in predicting MOS and SIM, while also delivering promising results in A/B testing and natural language descriptions. Our data processing scripts and finetuned model checkpoints can be found at https://github.com/bytedance/SALMONN.
语音质量评估通常需要从多个方面对音频进行评估,如平均意见得分(MOS)和说话人相似性(SIM)等。使用专为单一任务设计的小型模型来覆盖这些方面可能具有挑战性。在本文中,我们提议利用最近引入的听觉大型语言模型(LLM)进行自动语音质量评估。通过采用特定任务的提示,可以对听觉LLM进行微调,以预测MOS、SIM和A/B测试结果,这些结果通常用于评估文本到语音系统。此外,经过微调后的听觉LLM能够生成自然语言描述,评估噪声、失真、不连续性和总体质量等方面,提供更可解释的输出。我们在NISQA、BVCC、SOMOS和VoxSim语音质量数据集上进行了大量实验,使用了开源的听觉LLM,如SALMONN、Qwen-Audio和Qwen2-Audio。对于自然语言描述任务,还评估了商业模型Google Gemini 1.5 Pro。结果表明,听觉LLM在预测MOS和SIM方面与最新任务特定的小型模型相比具有竞争力,同时在A/B测试和自然语言描述方面也表现出有前景的结果。我们的数据处理脚本和微调后的模型检查点位于https://github.com/bytedance/SALMONN。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文提出利用新近引入的听觉大型语言模型(LLMs)进行自动语音质量评估。通过特定任务的提示,对听觉LLMs进行微调以预测平均意见得分(MOS)、说话人相似性(SIM)和A/B测试结果,这些常用于评估文本到语音系统。此外,微调后的听觉LLM能够生成评估噪音、失真、不连续性和总体质量等方面的自然语言描述,提供更可解释的输出。在多个语音质量数据集上的实验表明,听觉LLM的性能与最先进的特定任务小型模型相当,同时在A/B测试和自然语言描述方面表现出有希望的成果。
Key Takeaways
- 语音质量评估需要评估音频的多个方面,如平均意见得分(MOS)和说话人相似性(SIM)。
- 借助任务特定提示,听觉大型语言模型(LLMs)可以用于自动语音质量评估。
- 听觉LLM经过微调,可以预测MOS、SIM和A/B测试结果。
- 听觉LLM能够生成评估语音质量的自然语言描述,如噪音、失真、不连续性等。
- 听觉LLM在多个语音质量数据集上的表现与最新的小型模型相当。
- 提供了数据处理脚本和微调模型检查点供公众使用。
点此查看论文截图