⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-04 更新
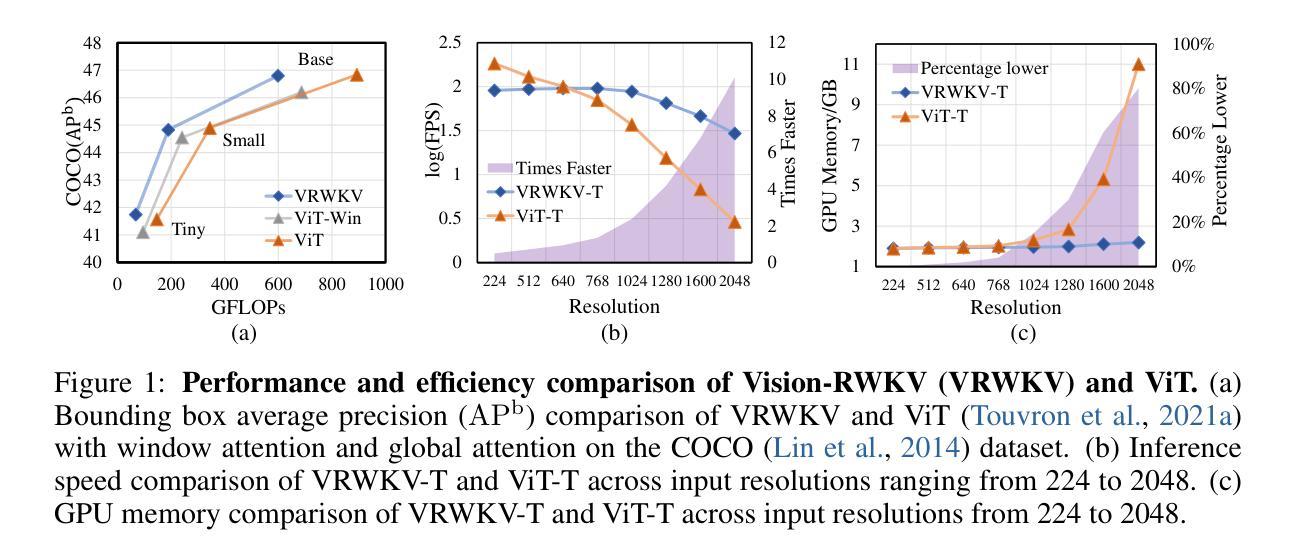
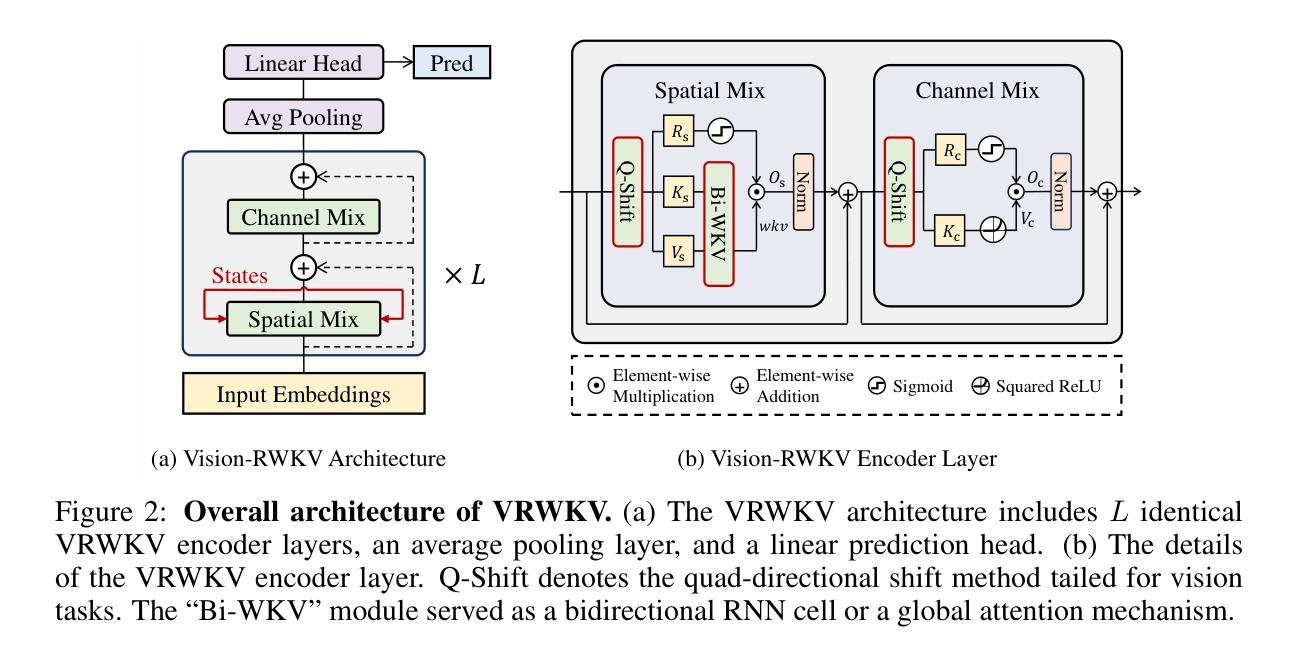
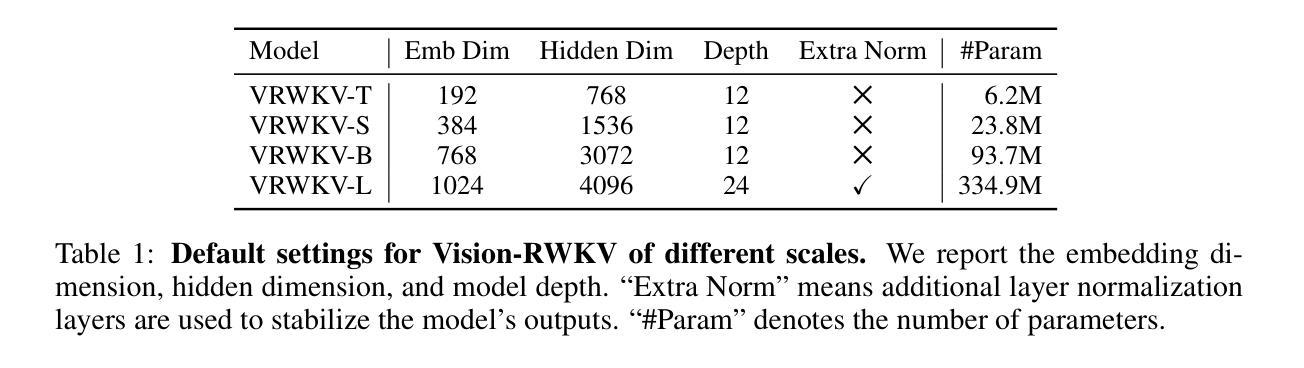
Vision-RWKV: Efficient and Scalable Visual Perception with RWKV-Like Architectures
Authors:Yuchen Duan, Weiyun Wang, Zhe Chen, Xizhou Zhu, Lewei Lu, Tong Lu, Yu Qiao, Hongsheng Li, Jifeng Dai, Wenhai Wang
Transformers have revolutionized computer vision and natural language processing, but their high computational complexity limits their application in high-resolution image processing and long-context analysis. This paper introduces Vision-RWKV (VRWKV), a model adapted from the RWKV model used in the NLP field with necessary modifications for vision tasks. Similar to the Vision Transformer (ViT), our model is designed to efficiently handle sparse inputs and demonstrate robust global processing capabilities, while also scaling up effectively, accommodating both large-scale parameters and extensive datasets. Its distinctive advantage lies in its reduced spatial aggregation complexity, which renders it exceptionally adept at processing high-resolution images seamlessly, eliminating the necessity for windowing operations. Our evaluations demonstrate that VRWKV surpasses ViT’s performance in image classification and has significantly faster speeds and lower memory usage processing high-resolution inputs. In dense prediction tasks, it outperforms window-based models, maintaining comparable speeds. These results highlight VRWKV’s potential as a more efficient alternative for visual perception tasks. Code is released at https://github.com/OpenGVLab/Vision-RWKV.
Transformer模型已经彻底改变了计算机视觉和自然语言处理的领域,但其较高的计算复杂度限制了其在高分辨率图像处理和长上下文分析中的应用。本文介绍了Vision-RWKV(VRWKV)模型,该模型是在NLP领域使用的RWKV模型的基础上进行了必要的修改以适应视觉任务。与Vision Transformer(ViT)类似,我们的模型旨在有效地处理稀疏输入,展现出强大的全局处理能力,同时可以有效地进行扩展,适应大规模参数和大规模数据集。其独特的优势在于降低了空间聚合复杂度,使其能够无缝处理高分辨率图像,无需窗口操作。我们的评估表明,VRWKV在图像分类方面的性能超过了ViT,处理高分辨率输入时速度更快、内存使用更低。在密集预测任务中,它超越了基于窗口的模型,并保持相当的速度。这些结果凸显了VRWKV作为视觉感知任务更高效替代方案的潜力。代码已发布在https://github.com/OpenGVLab/Vision-RWKV。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code is released at \url{https://github.com/OpenGVLab/Vision-RWKV}
Summary
本文介绍了Vision-RWKV(VRWKV)模型,它是基于RWKV模型的改进,专为计算机视觉任务设计。VRWKV模型能够高效处理稀疏输入,具有强大的全局处理能力,并可扩展以适应大规模参数和大量数据集。其优势在于降低空间聚合复杂性,可无缝处理高分辨率图像,无需窗口操作。在图像分类任务中,VRWKV性能优于Vision Transformer(ViT),并且处理高分辨率输入时速度更快、内存使用更低。在密集预测任务中,它也表现出超越基于窗口的模型的性能,同时保持相当的处理速度。
Key Takeaways
- Vision-RWKV (VRWKV) 是一个基于RWKV模型的改进,专为计算机视觉任务设计。
- VRWKV模型能够高效处理稀疏输入,展现强大的全局处理能力。
- VRWKV模型可降低空间聚合复杂性,实现高分辨率图像的无缝处理。
- 在图像分类任务中,VRWKV性能优于Vision Transformer(ViT)。
- VRWKV在处理高分辨率输入时,具有更快的速度和更低的内存使用。
- 在密集预测任务中,VRWKV表现优于基于窗口的模型,同时保持快速处理速度。
- 发布的代码位于https://github.com/OpenGVLab/Vision-RWKV。
点此查看论文截图

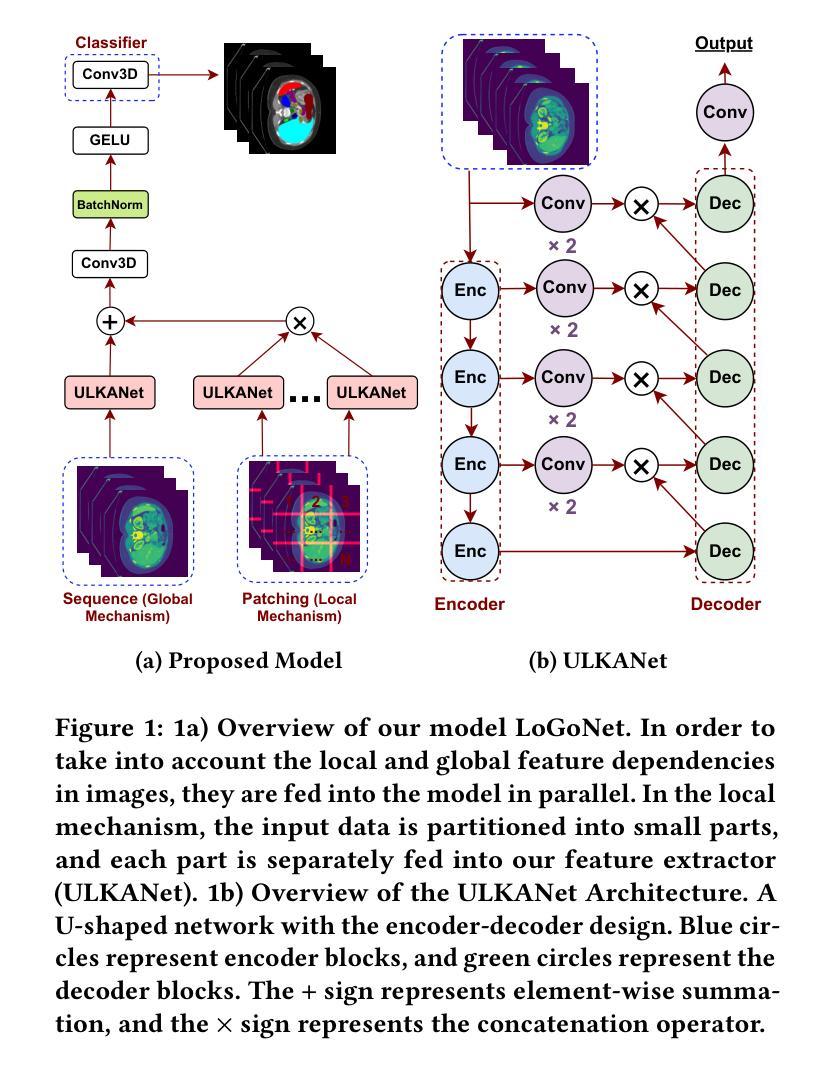
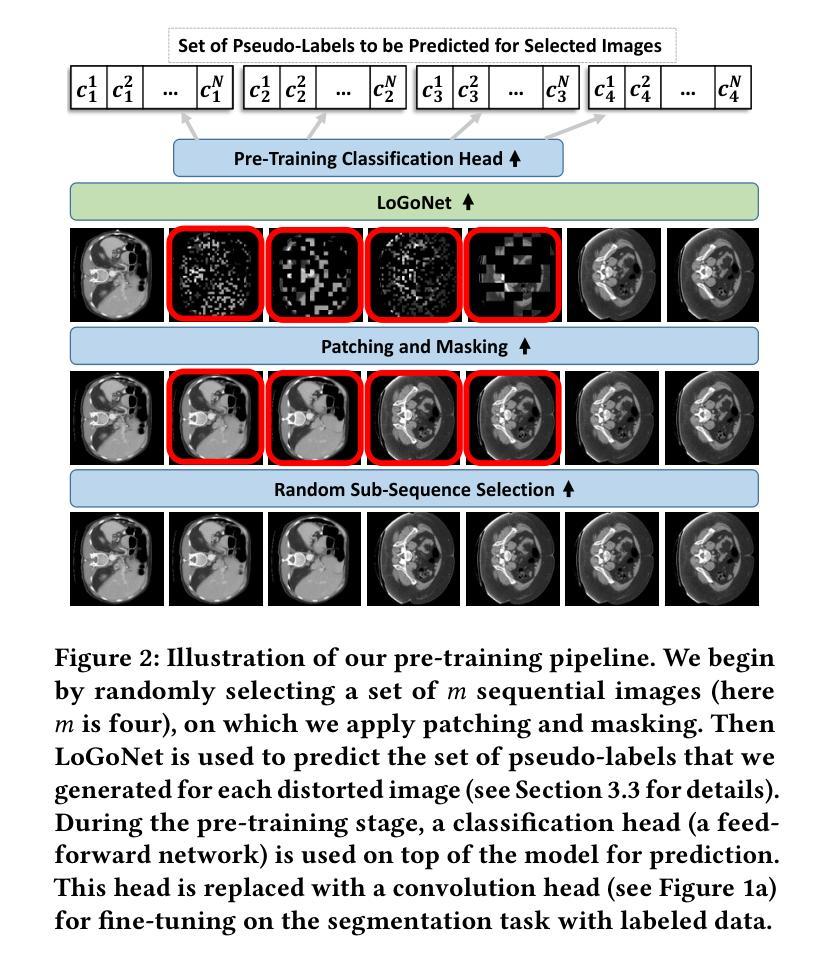
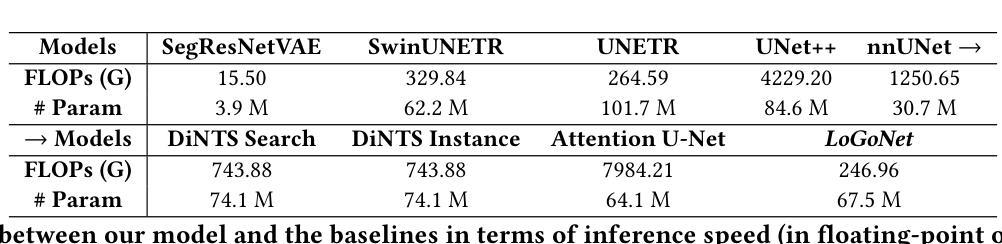
Masked LoGoNet: Fast and Accurate 3D Image Analysis for Medical Domain
Authors:Amin Karimi Monsefi, Payam Karisani, Mengxi Zhou, Stacey Choi, Nathan Doble, Heng Ji, Srinivasan Parthasarathy, Rajiv Ramnath
Standard modern machine-learning-based imaging methods have faced challenges in medical applications due to the high cost of dataset construction and, thereby, the limited labeled training data available. Additionally, upon deployment, these methods are usually used to process a large volume of data on a daily basis, imposing a high maintenance cost on medical facilities. In this paper, we introduce a new neural network architecture, termed LoGoNet, with a tailored self-supervised learning (SSL) method to mitigate such challenges. LoGoNet integrates a novel feature extractor within a U-shaped architecture, leveraging Large Kernel Attention (LKA) and a dual encoding strategy to capture both long-range and short-range feature dependencies adeptly. This is in contrast to existing methods that rely on increasing network capacity to enhance feature extraction. This combination of novel techniques in our model is especially beneficial in medical image segmentation, given the difficulty of learning intricate and often irregular body organ shapes, such as the spleen. Complementary, we propose a novel SSL method tailored for 3D images to compensate for the lack of large labeled datasets. The method combines masking and contrastive learning techniques within a multi-task learning framework and is compatible with both Vision Transformer (ViT) and CNN-based models. We demonstrate the efficacy of our methods in numerous tasks across two standard datasets (i.e., BTCV and MSD). Benchmark comparisons with eight state-of-the-art models highlight LoGoNet’s superior performance in both inference time and accuracy.
标准现代机器学习成像方法在面对医学应用时遇到了挑战,主要是由于数据集构建的成本高昂,导致可用的有标签训练数据有限。此外,这些方法部署后通常用于每日处理大量数据,给医疗机构带来了高昂的维护成本。在本文中,我们引入了一种新的神经网络架构,称为LoGoNet,它采用定制的自监督学习方法来缓解这些挑战。LoGoNet在U形架构内集成了一种新型特征提取器,利用大内核注意力(LKA)和双编码策略来巧妙地捕捉长短范围的特征依赖性。这与现有方法不同,后者依赖于增加网络容量来提高特征提取能力。我们模型中这种新技术的组合在医学图像分割中尤其有益,考虑到学习复杂且通常不规则的器官形状(如脾脏)的困难。作为补充,我们针对三维图像提出了一种新型自监督学习方法,以弥补缺乏大型标记数据集的不足。该方法在多任务学习框架内结合了掩蔽和对比学习技术,可与Vision Transformer(ViT)和CNN模型兼容。我们在两个标准数据集(即BTCV和MSD)的多个任务中展示了我们的方法的有效性。与八种最新模型的基准比较突显了LoGoNet在推理时间和准确性方面的卓越性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to KDD 2024
摘要
针对现代机器学习成像方法在医疗应用中面临的数据集构建成本高、标注训练数据有限的问题,本文提出了一种新型神经网络架构LoGoNet,并结合定制的自监督学习方法来缓解这些挑战。LoGoNet在U型架构内集成了一种新颖的特征提取器,利用大内核注意力(LKA)和双编码策略,擅长捕捉长程和短程特征依赖性。相较于现有方法,该模型尤其有利于医疗图像分割,能够学习复杂的、经常是不规则的器官形状。同时,针对缺乏大规模标注数据集的问题,我们提出了一种针对三维图像的新型自监督学习方法。该方法在多任务学习框架内结合了掩蔽和对比学习技术,可与Vision Transformer(ViT)和CNN模型兼容。在多个任务和两个标准数据集(BTCV和MSD)上的实验表明,与八种最新模型相比,LoGoNet在推理时间和准确性方面均表现出卓越性能。
关键见解
- LoGoNet是一种新型的神经网络架构,通过整合特征提取器、大内核注意力(LKA)和双编码策略,提高了医疗图像分割的准确性和效率。
- LoGoNet采用U型架构,相较于依赖增加网络容量来提升特征提取的现有方法,其表现更为出色。
- 针对医疗应用中标注数据集有限的问题,提出了一种新型自监督学习方法,结合掩蔽和对比学习技术,适用于三维图像。
- 该自监督学习方法可在多任务学习框架内实施,与Vision Transformer(ViT)和CNN模型兼容。
- 在多个任务和两个标准数据集上的实验表明,LoGoNet在推理时间和准确性方面均超越八种最新模型。
- LoGoNet特别适合于处理医疗图像中复杂的器官形状和不规则的边界。
点此查看论文截图