⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-05 更新
STING-BEE: Towards Vision-Language Model for Real-World X-ray Baggage Security Inspection
Authors:Divya Velayudhan, Abdelfatah Ahmed, Mohamad Alansari, Neha Gour, Abderaouf Behouch, Taimur Hassan, Syed Talal Wasim, Nabil Maalej, Muzammal Naseer, Juergen Gall, Mohammed Bennamoun, Ernesto Damiani, Naoufel Werghi
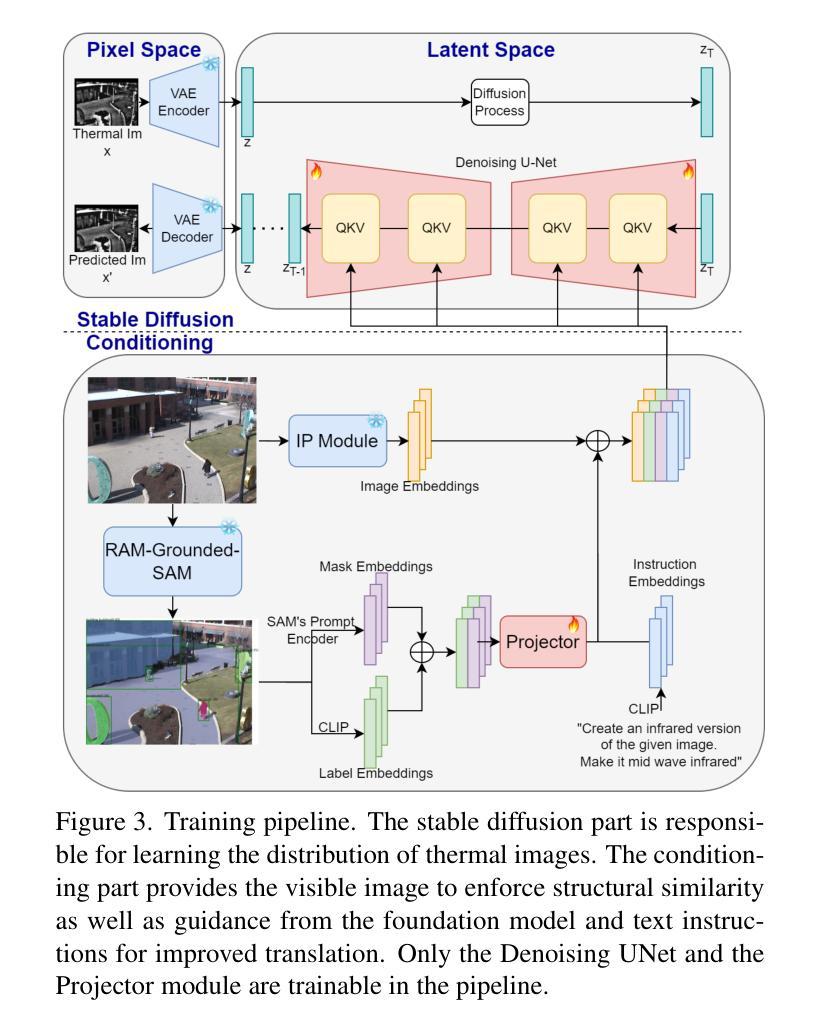
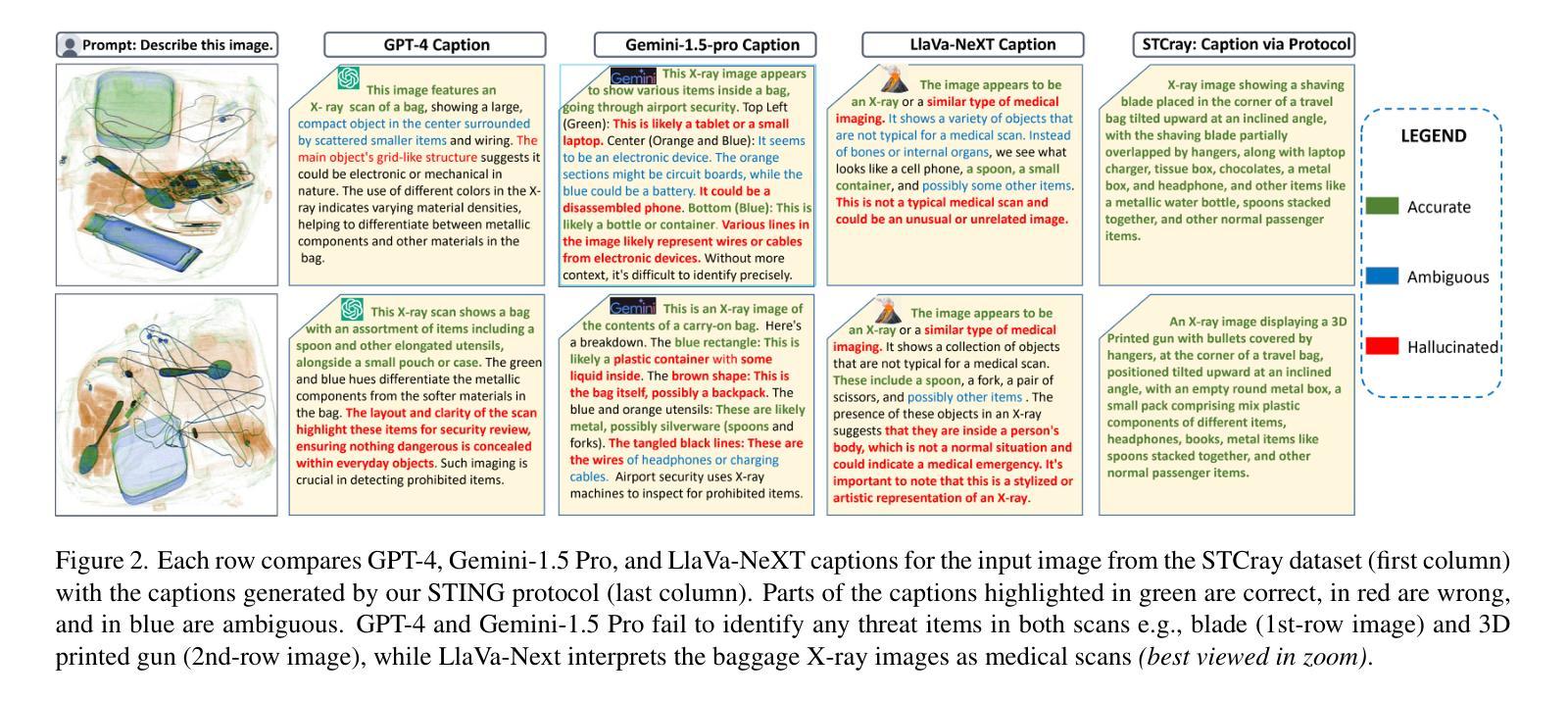
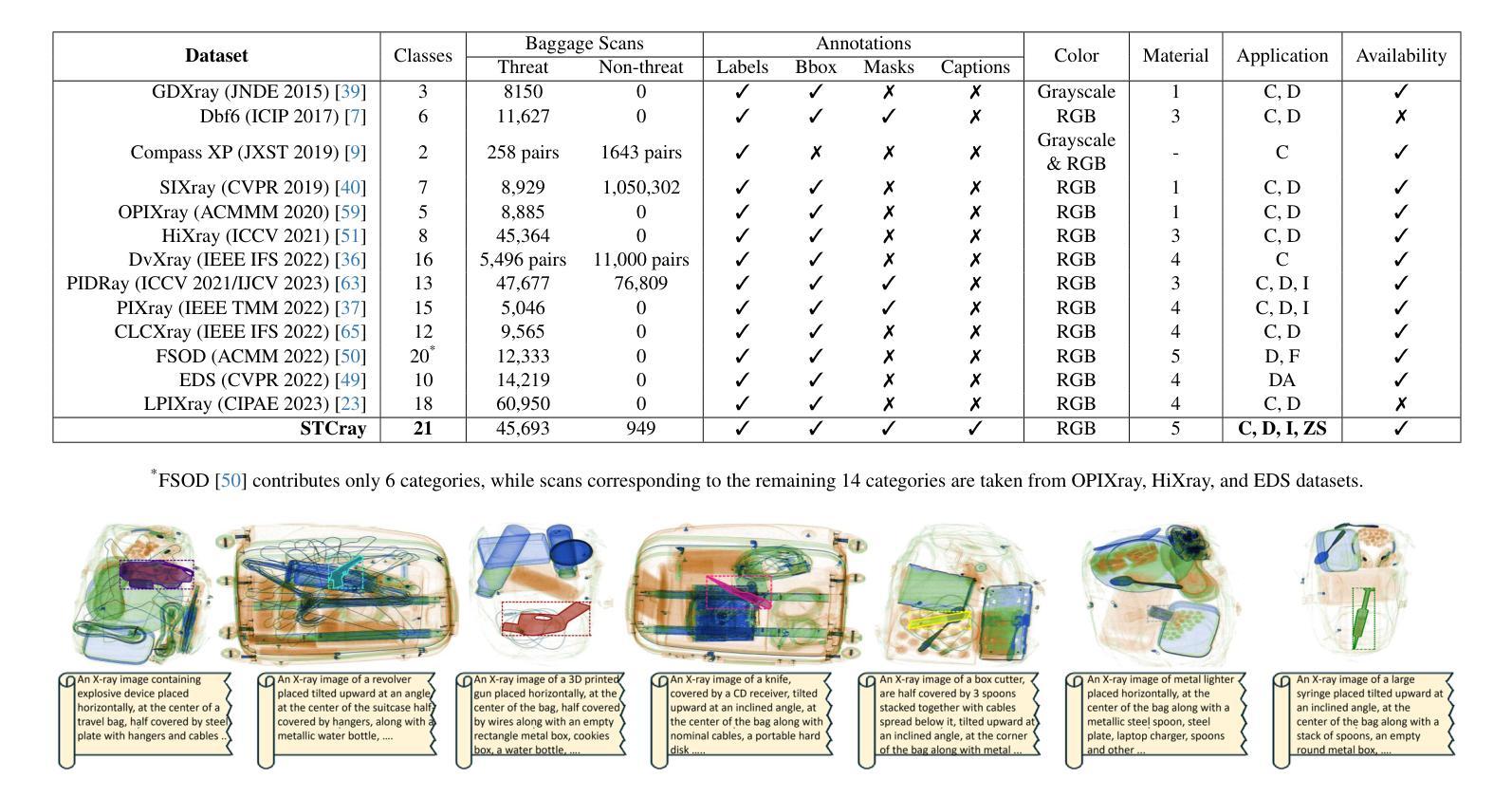
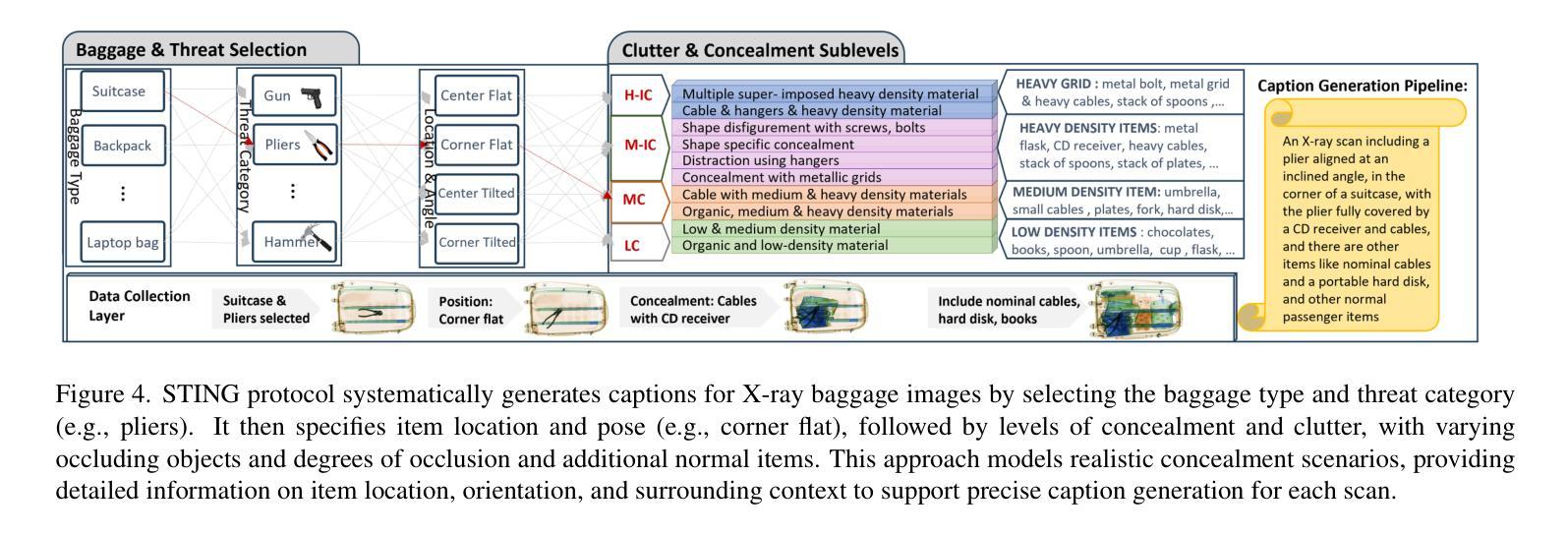
Advancements in Computer-Aided Screening (CAS) systems are essential for improving the detection of security threats in X-ray baggage scans. However, current datasets are limited in representing real-world, sophisticated threats and concealment tactics, and existing approaches are constrained by a closed-set paradigm with predefined labels. To address these challenges, we introduce STCray, the first multimodal X-ray baggage security dataset, comprising 46,642 image-caption paired scans across 21 threat categories, generated using an X-ray scanner for airport security. STCray is meticulously developed with our specialized protocol that ensures domain-aware, coherent captions, that lead to the multi-modal instruction following data in X-ray baggage security. This allows us to train a domain-aware visual AI assistant named STING-BEE that supports a range of vision-language tasks, including scene comprehension, referring threat localization, visual grounding, and visual question answering (VQA), establishing novel baselines for multi-modal learning in X-ray baggage security. Further, STING-BEE shows state-of-the-art generalization in cross-domain settings. Code, data, and models are available at https://divs1159.github.io/STING-BEE/.
计算机辅助筛查(CAS)系统的进步对于提高X光行李扫描中安全威胁的检测至关重要。然而,当前的数据集在表示现实世界中复杂威胁和隐蔽策略方面存在局限性,现有方法受到封闭集模式的约束,具有预定义标签。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了STCray,这是第一个多模态X光行李安全数据集,包含46642张图像和标题配对扫描,跨越21个威胁类别,使用X光扫描仪生成用于机场安全。STCray经过我们专门开发的协议精心开发,确保领域感知、连贯的标题,引导X光行李安全中的多模态指令跟随数据。这使我们能够训练一个名为STING-BEE的领域感知视觉人工智能助手,支持一系列视觉语言任务,包括场景理解、威胁定位、视觉定位和视觉问答(VQA),为X光行李安全中的多模态学习建立新的基准。此外,STING-BEE在跨域设置中显示出最先进的泛化能力。代码、数据和模型可在https://divs1159.github.io/STING-BEE/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CVPR 2025
Summary
新一代计算机辅助筛查系统对提升X光行李扫描中的安全威胁检测至关重要。当前数据集面临现实世界中复杂威胁和隐蔽藏匿方式的代表性不足的问题,且现有方法受限于预设标签的封闭集范式。为此,我们推出STCray——首个多模态X光行李安全数据集,包含46,642张图像和描述配对扫描,涵盖21类威胁,使用机场安全X光扫描仪生成。STCray采用专业协议确保领域感知、连贯的描述,支持X光行李安全中的多模态指令跟随数据。这使我们能够训练一个名为STING-BEE的领域感知视觉人工智能助理,支持场景理解、指代威胁定位、视觉接地和视觉问答等视觉语言任务,为X光行李安全中的多模态学习建立新基准。此外,STING-BEE在跨域设置中显示出最先进的泛化能力。相关代码、数据和模型可访问https://divs1159.github.io/STING-BEE/获取。
Key Takeaways
- 计算机辅助筛查系统对提升X光行李扫描中的安全威胁检测至关重要。
- 当前数据集面临代表性不足和封闭集范式的限制。
- 推出STCray多模态X光行李安全数据集,涵盖多种威胁类别,使用机场安全X光扫描仪生成。
- STCray采用专业协议确保领域感知、连贯的描述,支持多模态指令跟随数据。
- 训练出领域感知视觉人工智能助理STING-BEE,支持多种视觉语言任务。
- STING-BEE在跨域设置中具有先进的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

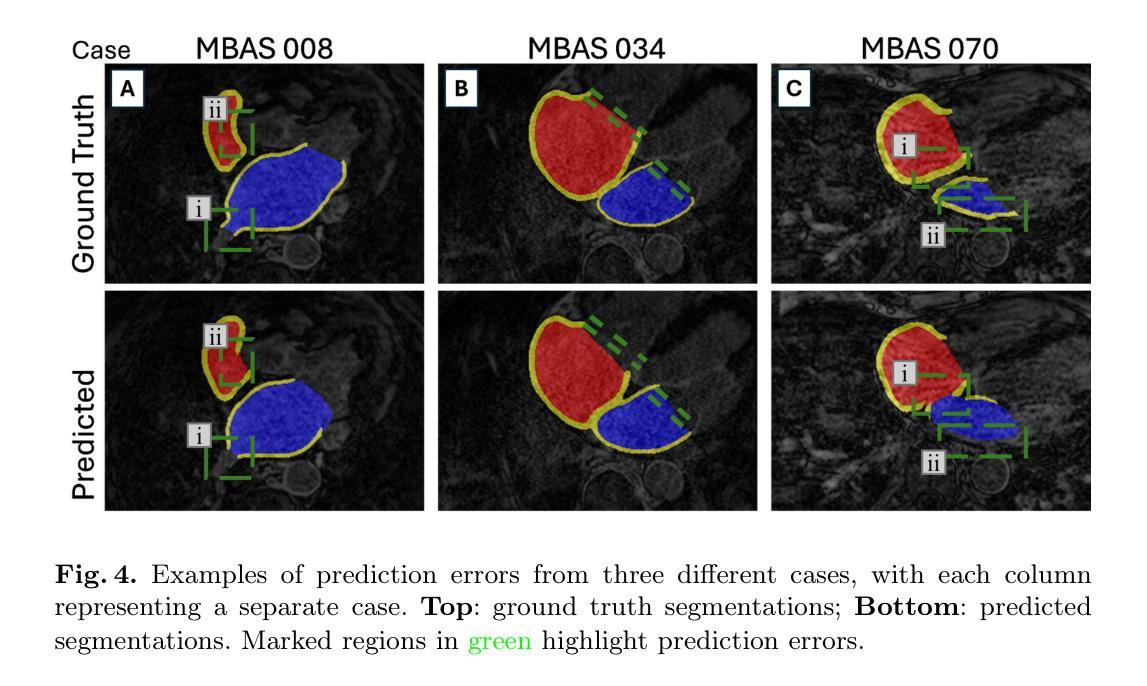
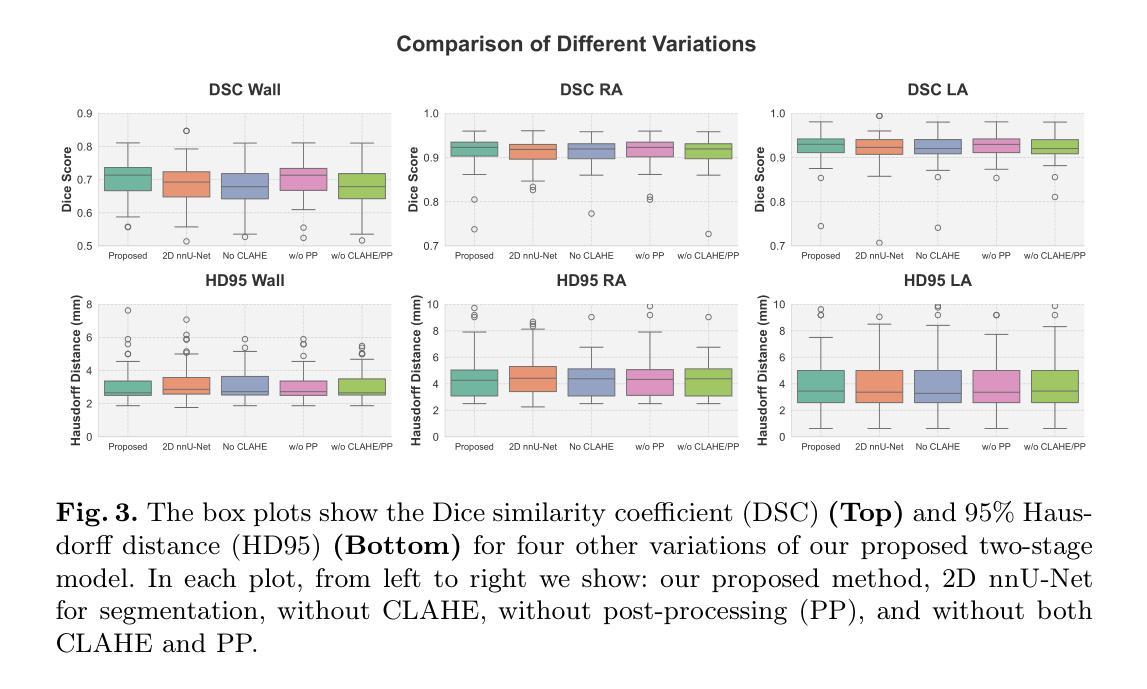
Two-Stage nnU-Net for Automatic Multi-class Bi-Atrial Segmentation from LGE-MRIs
Authors:Y. On, C. Galazis, C. Chiu, M. Varela
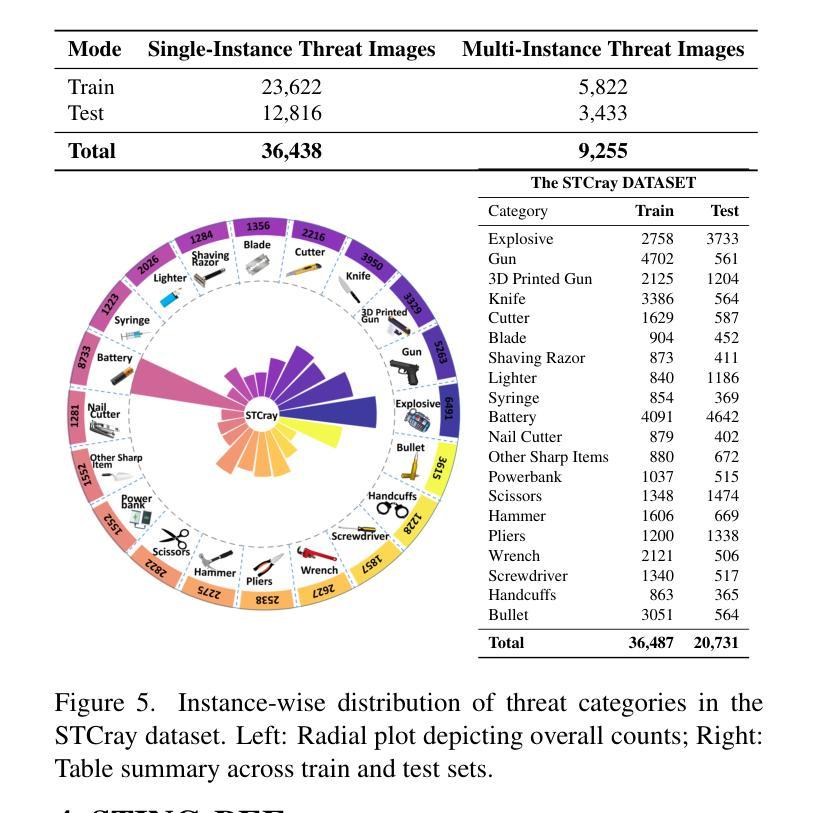
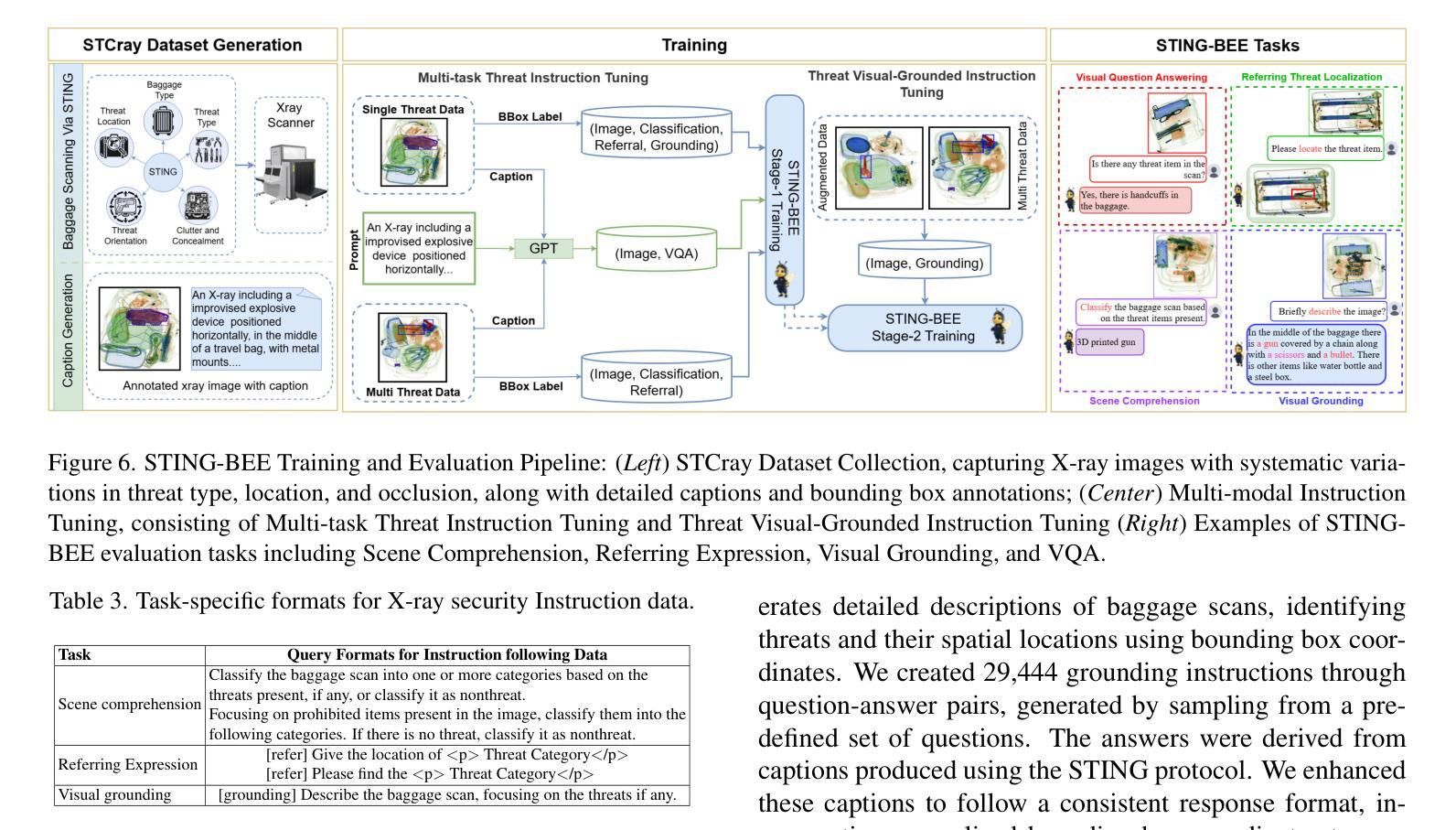
Late gadolinium enhancement magnetic resonance imaging (LGE-MRI) is used to visualise atrial fibrosis and scars, providing important information for personalised atrial fibrillation (AF) treatments. Since manual analysis and delineations of these images can be both labour-intensive and subject to variability, we develop an automatic pipeline to perform segmentation of the left atrial (LA) cavity, the right atrial (RA) cavity, and the wall of both atria on LGE-MRI. Our method is based on a two-stage nnU-Net architecture, combining 2D and 3D convolutional networks, and incorporates adaptive histogram equalisation to improve tissue contrast in the input images and morphological operations on the output segmentation maps. We achieve Dice similarity coefficients of 0.92 +/- 0.03, 0.93 +/- 0.03, 0.71 +/- 0.05 and 95% Hausdorff distances of (3.89 +/- 6.67) mm, (4.42 +/- 1.66) mm and (3.94 +/- 1.83) mm for LA, RA, and wall, respectively. The accurate delineation of the LA, RA and the myocardial wall is the first step in analysing atrial structure in cardiovascular patients, especially those with AF. This can allow clinicians to provide adequate and personalised treatment plans in a timely manner.
钆延迟增强磁共振成像(Late Gadolinium Enhancement MRI,简称 LGE-MRI)被用来可视化心房纤维化和瘢痕,为个性化治疗心房颤动(AF)提供重要信息。由于对这些图像的手动分析和轮廓描绘既耗时又存在差异性,我们开发了一个自动管道,用于对 LGE-MRI 上的左心房(LA)、右心房(RA)以及心房壁进行分割。我们的方法基于两阶段 nnU-Net 架构,结合二维和三维卷积网络,并融入自适应直方图均衡化,以提高输入图像中的组织对比度以及输出分割图上的形态操作。我们实现了狄克相似系数分别为 0.92 ± 0.03、0.93 ± 0.03、0.71 ± 0.05 以及 Hausdorff 距离的 95% 分别为 (3.89 ± 6.67) 毫米、(4.42 ± 1.66)毫米和(3.94 ± 1.83)毫米,分别对应 LA、RA 和心房壁。准确描绘 LA、RA 和心肌壁是分析心血管疾病患者心房结构的第一步,特别是对于那些患有心房颤动的患者。这可以使临床医生及时提供充足且个性化的治疗计划。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MBAS Challenge, STACOM, MICCAI 2024
Summary
基于LGE-MRI图像,研究团队开发了一种自动分割左心房(LA)、右心房(RA)以及心房壁的两阶段nnU-Net架构方法。此方法结合了二维和三维卷积网络,并采用自适应直方均衡化提高图像组织的对比度,以及对输出分割图进行形态学操作。该方法的Dice相似系数达到高值,表明准确度高。准确分割心房结构有助于心血管病患者,尤其是房颤患者的临床诊断和治疗计划制定。
Key Takeaways
- LGE-MRI用于可视化心房纤维化和疤痕,为个性化治疗房颤提供重要信息。
- 自动化管道基于两阶段nnU-Net架构,结合二维和三维卷积网络进行心房及其壁的分割。
- 采用自适应直方均衡化改善图像组织对比度,形态学操作优化分割结果。
- 方法实现了高Dice相似系数和低Hausdorff距离,显示分割准确性高。
- 准确的心房结构分析有助于心血管疾病的诊断和治疗。
- 自动分割技术可减轻医生手动分析的工作量,提高分析一致性。
点此查看论文截图

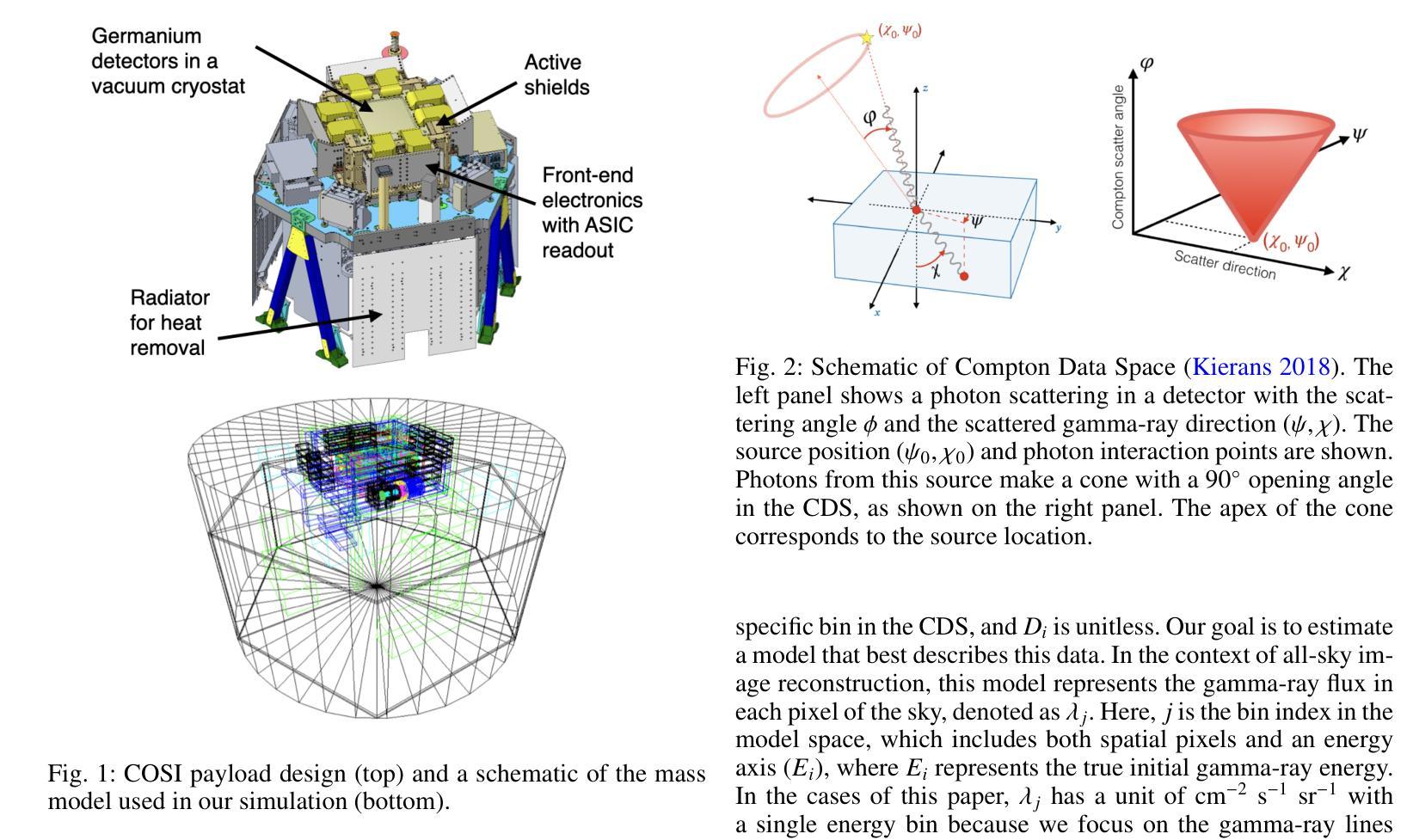
Enhancing Compton telescope imaging with maximum a posteriori estimation: a modified Richardson-Lucy algorithm for the Compton Spectrometer and Imager
Authors:Hiroki Yoneda, Thomas Siegert, Israel Martinez-Castellanos, Savitri Gallego, Chris Karwin, Hugh Bates, Steven E. Boggs, Chien-You Huang, Alyson Joens, Shigeki Matsumoto, Saurabh Mittal, Eliza Neights, Michela Negro, Uwe Oberlack, Keigo Okuma, Sean N. Pike, Jarred Roberts, Field Rogers, Yong Sheng, Tadayuki Takahashi, Anaya Valluvan, Yu Watanabe, Dieter Hartmann, Carolyn Kierans, John Tomsick, Andreas Zoglauer
We present a modified Richardson-Lucy (RL) algorithm tailored for image reconstruction in MeV gamma-ray observations, focusing on its application to the upcoming Compton Spectrometer and Imager (COSI) mission. Our method addresses key challenges in MeV gamma-ray astronomy by incorporating Bayesian priors for sparseness and smoothness while optimizing background components simultaneously. We introduce a novel sparsity term suitable for Poisson-sampled data in addition to a smoothness prior, allowing for flexible reconstruction of both point sources and extended emission. The performance of the algorithm is evaluated using simulated three-month COSI observations of gamma-ray lines of $^{44}$Ti (1.157 MeV), $^{26}$Al (1.809 MeV), and positron annihilation (0.511 MeV), respectively, representing various spatial features. Our results demonstrate significant improvements over conventional RL methods, particularly in suppressing artificial structures in point source reconstructions and retaining diffuse spatial structures. This work represents an important step towards establishing a robust data analysis for studying nucleosynthesis, positron annihilation, and other high-energy phenomena in our Galaxy.
我们提出了一种针对MeV伽马射线观测的图像重建的改进Richardson-Lucy(RL)算法,重点关注其在即将进行的康普顿光谱仪和成像器(COSI)任务中的应用。我们的方法通过融入贝叶斯先验来解决MeV伽马射线天文学领域的关键挑战,优化背景成分的同时兼顾稀疏性和平滑性。除了平滑先验之外,我们还引入了一种适用于Poisson采样数据的新稀疏项,能够实现点源和扩展发射的灵活重建。我们通过模拟三个月的COSI对$^{44}$Ti(1.157 MeV)、$^{26}$Al(1.809 MeV)和正电子退火(0.511 MeV)的伽马射线线观测来评估算法性能,分别代表不同的空间特征。我们的结果相较于传统的RL方法有明显的改进,特别是在抑制点源重建中的人工结构和保留扩散空间结构方面。这项工作对于建立稳健的数据分析来研究核合成、正电子退火以及我们银河系中的其他高能现象具有重要意义。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, accepted by Astronomy & Astrophysics
摘要
针对MeV伽马射线观测的图像重建,我们提出了一种改进的Richardson-Lucy(RL)算法,特别适用于即将发射的Compton光谱仪和成像仪(COSI)任务。该方法通过引入贝叶斯先验来实现稀疏性和平滑性,同时优化背景成分,解决了MeV伽马射线天文学中的关键挑战。除了平滑性先验外,我们还引入了一个适合Poisson采样数据的新稀疏性术语,可以实现点源和扩展发射的灵活重建。我们使用模拟的COSI对$^{44}$Ti(1.157 MeV)、$^{26}$Al(1.809 MeV)和正电子退火(0.511 MeV)的伽马射线线观测结果来评估算法性能,这些观测结果代表了不同的空间特征。结果表明,与传统RL方法相比,该算法在抑制点源重建中的人工结构以及保留扩散空间结构方面表现出显著改善。这项工作对于建立研究核合成、正电子退火以及银河系中其他高能现象的强大数据分析方法具有重要意义。
关键见解
- 改进Richardson-Lucy算法,适用于MeV伽马射线观测的图像重建。
- 引入贝叶斯先验实现稀疏性和平滑性,优化背景成分。
- 引入适合Poisson采样数据的新稀疏性术语,实现灵活重建点源和扩展发射。
- 通过模拟的COSI观测结果评估算法性能。
- 相较于传统RL方法,该算法在抑制人工结构保留扩散空间结构方面表现出显著改善。
- 对于研究核合成、正电子退火等高能现象具有强大的数据分析潜力。
点此查看论文截图

Benchmark of Segmentation Techniques for Pelvic Fracture in CT and X-ray: Summary of the PENGWIN 2024 Challenge
Authors:Yudi Sang, Yanzhen Liu, Sutuke Yibulayimu, Yunning Wang, Benjamin D. Killeen, Mingxu Liu, Ping-Cheng Ku, Ole Johannsen, Karol Gotkowski, Maximilian Zenk, Klaus Maier-Hein, Fabian Isensee, Peiyan Yue, Yi Wang, Haidong Yu, Zhaohong Pan, Yutong He, Xiaokun Liang, Daiqi Liu, Fuxin Fan, Artur Jurgas, Andrzej Skalski, Yuxi Ma, Jing Yang, Szymon Płotka, Rafał Litka, Gang Zhu, Yingchun Song, Mathias Unberath, Mehran Armand, Dan Ruan, S. Kevin Zhou, Qiyong Cao, Chunpeng Zhao, Xinbao Wu, Yu Wang
The segmentation of pelvic fracture fragments in CT and X-ray images is crucial for trauma diagnosis, surgical planning, and intraoperative guidance. However, accurately and efficiently delineating the bone fragments remains a significant challenge due to complex anatomy and imaging limitations. The PENGWIN challenge, organized as a MICCAI 2024 satellite event, aimed to advance automated fracture segmentation by benchmarking state-of-the-art algorithms on these complex tasks. A diverse dataset of 150 CT scans was collected from multiple clinical centers, and a large set of simulated X-ray images was generated using the DeepDRR method. Final submissions from 16 teams worldwide were evaluated under a rigorous multi-metric testing scheme. The top-performing CT algorithm achieved an average fragment-wise intersection over union (IoU) of 0.930, demonstrating satisfactory accuracy. However, in the X-ray task, the best algorithm attained an IoU of 0.774, highlighting the greater challenges posed by overlapping anatomical structures. Beyond the quantitative evaluation, the challenge revealed methodological diversity in algorithm design. Variations in instance representation, such as primary-secondary classification versus boundary-core separation, led to differing segmentation strategies. Despite promising results, the challenge also exposed inherent uncertainties in fragment definition, particularly in cases of incomplete fractures. These findings suggest that interactive segmentation approaches, integrating human decision-making with task-relevant information, may be essential for improving model reliability and clinical applicability.
骨盆骨折碎片在CT和X射线图像中的分割对于创伤诊断、手术规划和术中指导至关重要。然而,由于复杂的解剖结构和成像限制,准确高效地描绘骨碎片仍然是一个巨大的挑战。PENGWIN挑战作为MICCAI 2024的卫星活动,旨在通过最新算法在这些复杂任务上的基准测试,推动自动骨折分割的发展。从多个临床中心收集了150份CT扫描的多样数据集,并使用DeepDRR方法生成了大量模拟X射线图像。来自全球16个团队的最终提交作品在严格的多指标测试方案下进行了评估。表现最佳的CT算法平均片段级交并比(IoU)达到0.930,显示出令人满意的准确性。然而,在X射线任务中,最佳算法的IoU为0.774,这突出了由重叠的解剖结构带来的更大挑战。除了定量评估之外,该挑战还揭示了算法设计中的方法多样性。实例表示中的变化,如主次分类与边界核心分离,导致了不同的分割策略。尽管结果具有前景,但挑战也暴露了碎片定义中的固有不确定性,特别是在不完全骨折的情况下。这些发现表明,融合人类决策与任务相关信息的交互式分割方法可能对于提高模型可靠性和临床适用性至关重要。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF PENGWIN 2024 Challenge Report
Summary
本文介绍了盆腔骨折碎片在CT和X射线图像中的分割对于创伤诊断、手术规划和术中指导的重要性。然而,由于复杂的解剖结构和成像限制,准确高效地进行骨碎片分割仍是一项挑战。PENGWIN挑战作为MICCAI 2024的卫星活动,旨在通过评估最先进的算法在这些复杂任务上的性能来促进自动骨折分割的发展。使用从多个临床中心收集的150个CT扫描构建的多样化数据集,并使用DeepDRR方法生成了大量模拟X射线图像。来自全球16个团队的最终提交作品在严格的多指标测试方案下进行了评估。在CT任务中,顶级算法的平均片段级交并比(IoU)达到0.930,显示出令人满意的准确性。然而,在X射线任务中,最佳算法的IoU为0.774,突显出由重叠解剖结构带来的更大挑战。挑战还揭示了算法设计中的方法多样性,如主要次级分类与边界核心分离等不同实例表示之间的差异。尽管结果具有前景,但挑战也暴露了碎片定义中的固有不确定性,特别是在不完全骨折的情况下。
Key Takeaways
- 盆腔骨折碎片的分割对于创伤诊断、手术规划和术中指导至关重要。
- CT和X射线图像中的骨碎片分割是一项具有挑战性的任务,主要由于复杂的解剖结构和成像限制。
- PENGWIN挑战旨在通过评估最先进算法在CT和X射线图像中的骨折分割性能来促进该领域的发展。
- 在CT任务中,顶级算法表现出高准确性,平均片段级交并比(IoU)达到0.930。
- 在X射线任务中,最佳算法的IoU为0.774,表明存在更大的挑战,尤其是由于重叠解剖结构导致的。
- 挑战揭示了骨折分割算法设计中的方法多样性,包括不同的实例表示策略。
点此查看论文截图

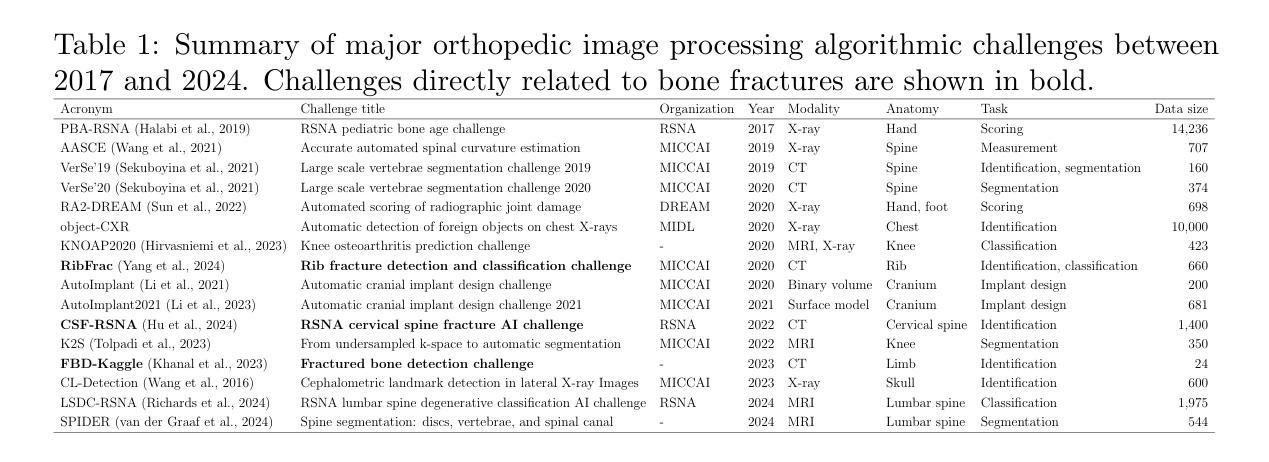
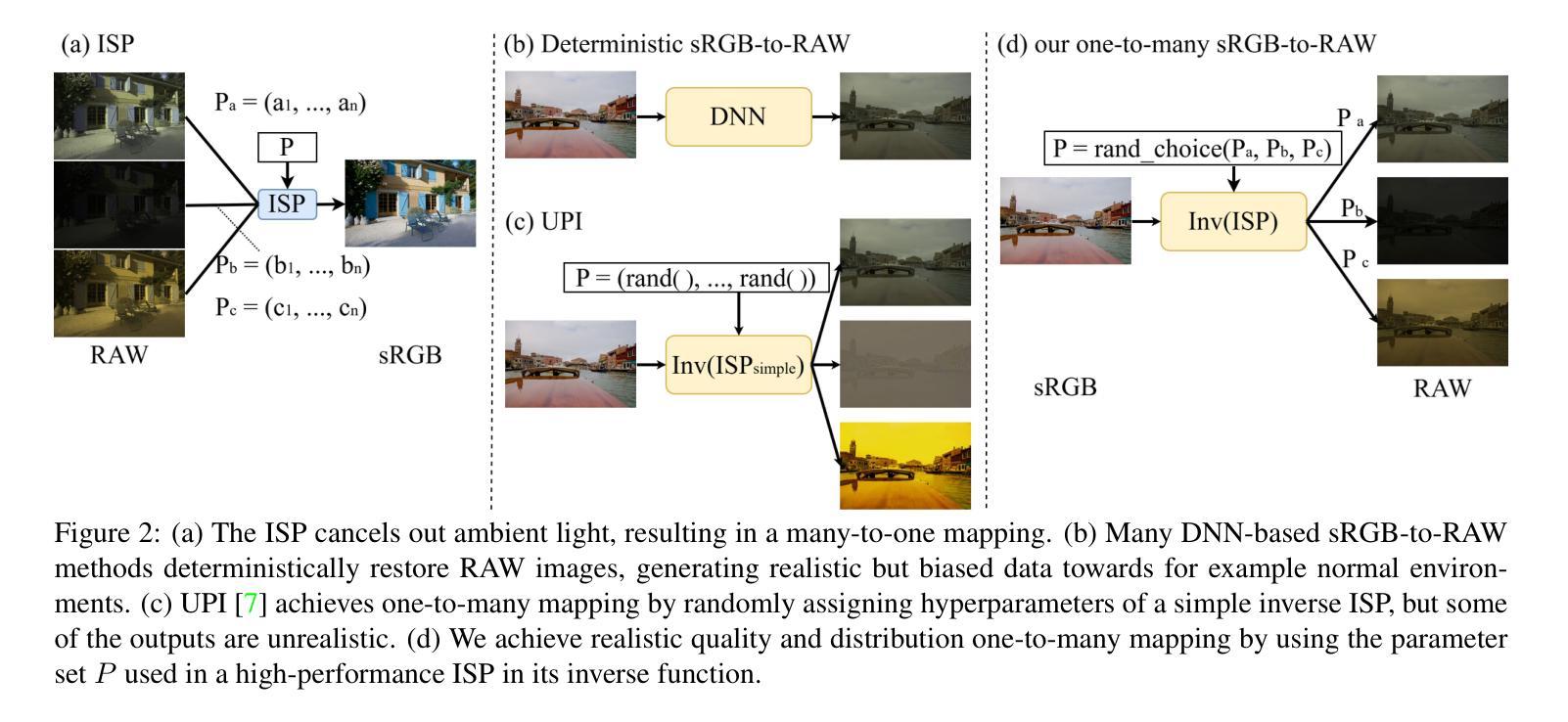
SemiISP/SemiIE: Semi-Supervised Image Signal Processor and Image Enhancement Leveraging One-to-Many Mapping sRGB-to-RAW
Authors:Masakazu Yoshimura, Junji Otsuka, Radu Berdan, Takeshi Ohashi
DNN-based methods have been successful in Image Signal Processor (ISP) and image enhancement (IE) tasks. However, the cost of creating training data for these tasks is considerably higher than for other tasks, making it difficult to prepare large-scale datasets. Also, creating personalized ISP and IE with minimal training data can lead to new value streams since preferred image quality varies depending on the person and use case. While semi-supervised learning could be a potential solution in such cases, it has rarely been utilized for these tasks. In this paper, we realize semi-supervised learning for ISP and IE leveraging a RAW image reconstruction (sRGB-to-RAW) method. Although existing sRGB-to-RAW methods can generate pseudo-RAW image datasets that improve the accuracy of RAW-based high-level computer vision tasks such as object detection, their quality is not sufficient for ISP and IE tasks that require precise image quality definition. Therefore, we also propose a sRGB-to-RAW method that can improve the image quality of these tasks. The proposed semi-supervised learning with the proposed sRGB-to-RAW method successfully improves the image quality of various models on various datasets.
基于深度神经网络(DNN)的方法在图像信号处理器(ISP)和图像增强(IE)任务中取得了成功。然而,这些任务的训练数据制作成本明显高于其他任务,难以准备大规模数据集。此外,使用少量训练数据创建个性化ISP和IE可以带来新价值流,因为偏好的图像质量会因人而异,取决于用例。虽然半监督学习可能是此类情况的潜在解决方案,但很少用于这些任务。在本文中,我们利用RAW图像重建(sRGB-to-RAW)方法实现ISP和IE的半监督学习。尽管现有的sRGB-to-RAW方法可以生成伪RAW图像数据集,提高了基于RAW的高级计算机视觉任务的准确性,如目标检测,但它们的质量对于需要精确图像质量定义的ISP和IE任务来说还不足以满足需求。因此,我们还提出了一种改进的sRGB-to-RAW方法,可以提高这些任务的图像质量。所提出的结合改进sRGB-to-RAW方法的半监督学习成功提高了各种数据集上各种模型的图像质量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于深度神经网络的方法在图像信号处理器(ISP)和图像增强(IE)任务中取得了成功。然而,这些任务创建训练数据的成本远高于其他任务,难以准备大规模数据集。本文通过结合RAW图像重建(sRGB-to-RAW)方法实现了ISP和IE的半监督学习,解决这一难题。提出的sRGB-to-RAW方法能够提升ISP和IE任务的图像质量,并结合半监督学习成功提高了不同模型在不同数据集上的图像质量。
Key Takeaways
- DNN方法在ISP和IE任务中表现良好,但训练数据成本高昂,难以构建大规模数据集。
- 个性化的ISP和IE需求因人和用例而异,对训练数据量有更高要求。
- 半监督学习在ISP和IE任务中有潜力,但应用较少。
- 存在sRGB-to-RAW方法生成伪RAW图像数据集,用于提高基于RAW的高级计算机视觉任务的准确性。
- 现有sRGB-to-RAW方法对于需要精确图像质量定义的ISP和IE任务效果不足。
- 本文提出了一种新的sRGB-to-RAW方法,能够提高ISP和IE任务的图像质量。
点此查看论文截图

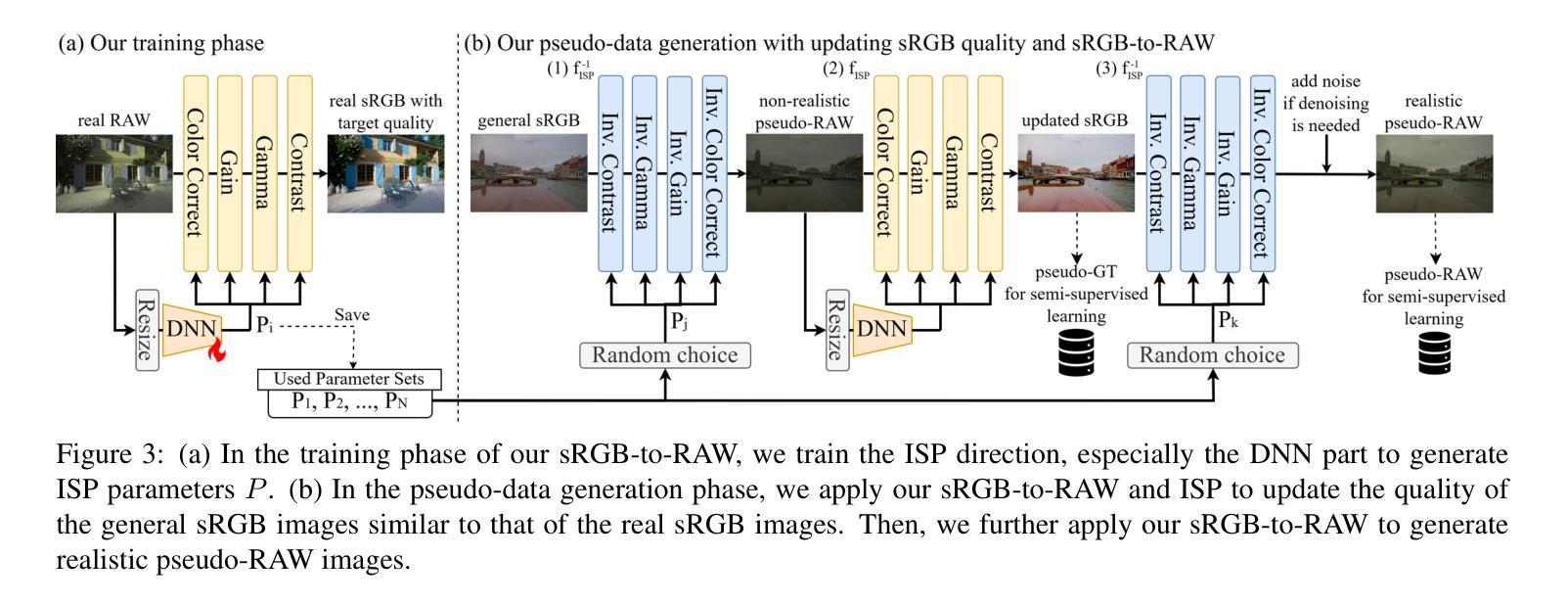
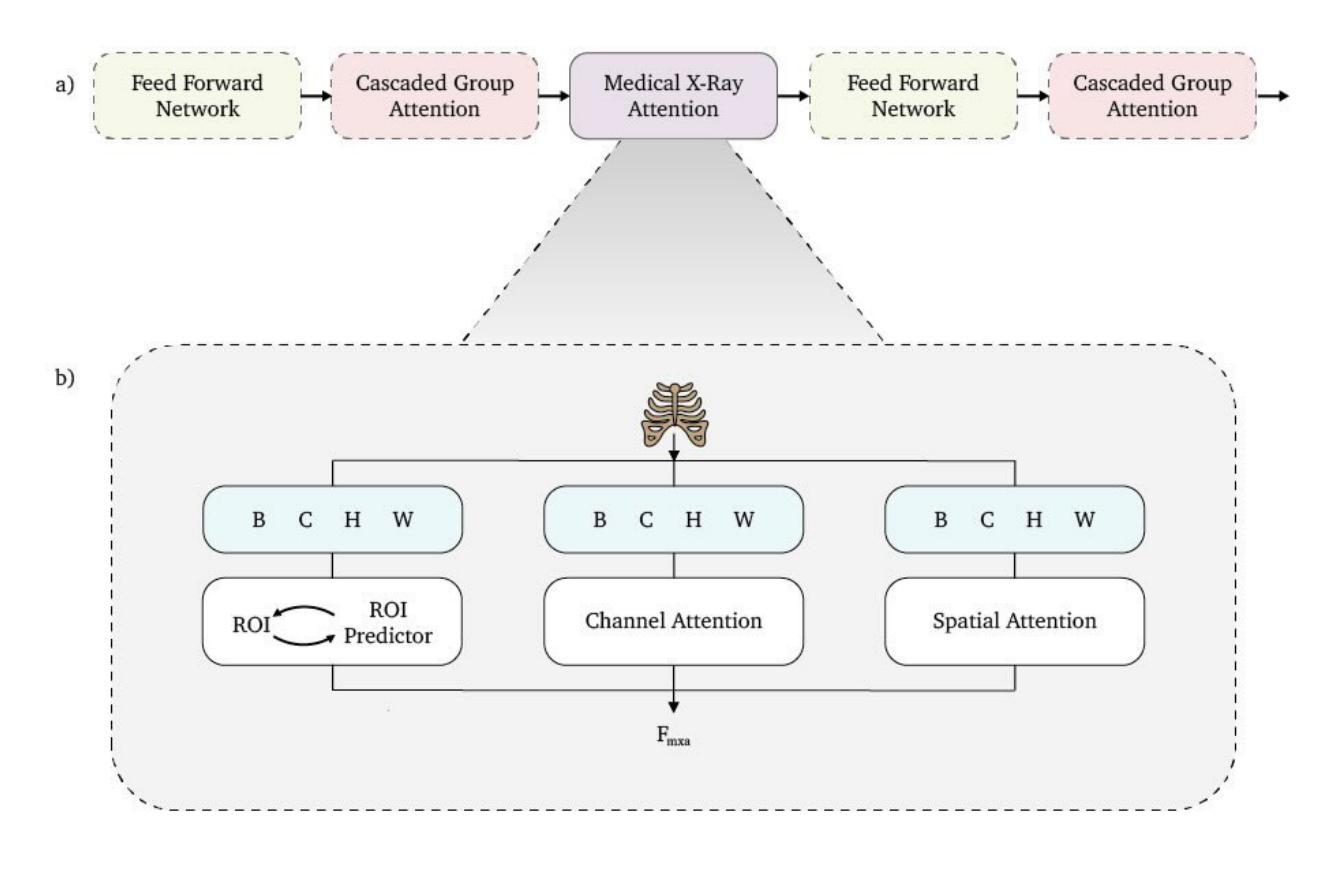
Beyond Conventional Transformers: The Medical X-ray Attention (MXA) Block for Improved Multi-Label Diagnosis Using Knowledge Distillation
Authors:Amit Rand, Hadi Ibrahim
Medical imaging, particularly X-ray analysis, often involves detecting multiple conditions simultaneously within a single scan, making multi-label classification crucial for real-world clinical applications. We present the Medical X-ray Attention (MXA) block, a novel attention mechanism tailored specifically to address the unique challenges of X-ray abnormality detection. The MXA block enhances traditional Multi-Head Self Attention (MHSA) by integrating a specialized module that efficiently captures both detailed local information and broader global context. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to propose a task-specific attention mechanism for diagnosing chest X-rays, as well as to attempt multi-label classification using an Efficient Vision Transformer (EfficientViT). By embedding the MXA block within the EfficientViT architecture and employing knowledge distillation, our proposed model significantly improves performance on the CheXpert dataset, a widely used benchmark for multi-label chest X-ray abnormality detection. Our approach achieves an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.85, an absolute improvement of 0.19 compared to our baseline model’s AUC of 0.66, corresponding to a substantial approximate 233% relative improvement over random guessing (AUC = 0.5).
医学成像,特别是X射线分析,经常需要在单次扫描中检测多种状况,这使得多标签分类在现实世界临床应用中至关重要。我们提出了医学X射线注意力(MXA)块,这是一种新型注意力机制,专门设计来解决X射线异常检测的独特挑战。MXA块通过集成一个专门模块来增强传统的多头自注意力(MHSA),该模块能够高效捕获详细的局部信息和更广泛的全局上下文。据我们所知,这是首次提出针对胸部X射线诊断的任务特定注意力机制的工作,也是首次尝试使用高效视觉转换器(EfficientViT)进行多标签分类。通过将MXA块嵌入EfficientViT架构并采用知识蒸馏,我们提出的模型在CheXpert数据集上显著提高了性能,CheXpert数据集是用于多标签胸部X射线异常检测的广泛使用的基准测试。我们的方法达到了曲线下面积(AUC)为0.85,与基线模型的AUC 0.66相比,绝对提高了0.19,这意味着相对于随机猜测有大约233%的相对改进(AUC = 0.5)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 4 figures, 5 tables. For supplementary material and code, see https://github.com/Hadi-M-Ibrahim/Beyond-Conventional-Transformers/
Summary
医学图像领域中的X射线分析经常需要同时检测多种疾病状况,为此多标签分类显得尤为重要。我们提出了Medical X-ray Attention(MXA)模块,这是一种针对X射线异常检测独特挑战的新型注意力机制。MXA模块通过集成一个专门设计的模块,增强了传统的多头自注意力(MHSA),以有效地捕获详细的局部信息和更广泛的全球上下文。据我们所知,这是首次提出用于诊断胸部X射线的特定任务注意力机制的工作,也是首次尝试使用高效视觉转换器(EfficientViT)进行多标签分类。通过在EfficientViT架构中嵌入MXA模块并采用知识蒸馏的方法,我们的模型在用于多标签胸部X射线异常检测的广泛使用的CheXpert数据集上取得了显著的性能提升。我们的方法达到了曲线下面积(AUC)为0.85,与基线模型的AUC相比,绝对提高了0.19,相对于随机猜测的AUC = 0.5,有大约233%的相对改善。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像领域中的X射线分析需要同时进行多标签分类以应对实际临床应用中的多种疾病检测挑战。
- 提出了全新的Medical X-ray Attention(MXA)模块,结合了MHSA和专门设计的模块以捕捉详细信息和全局上下文。
- MXA模块首次被应用于胸部X射线的诊断任务中,并且结合了EfficientViT进行多标签分类。
- 在CheXpert数据集上,嵌入MXA模块的模型显著提高了性能,AUC达到了0.85。
点此查看论文截图

Investigating the Recursive Short X-ray Burst Behavior of Magnetars Through Crustal Interactions
Authors:Ozge Keskin, Samuel K. Lander, Ersin Gogus
Energetic bursts from strongly magnetized neutron stars, known as magnetars, are typically detected in clusters. Once an active episode begins, anywhere from a few to thousands of hard X-ray bursts can occur over durations ranging from days to months. The temporal clustering of these recurrent bursts during an active episode suggests an underlying mechanism that triggers multiple bursts in rapid succession. These burst clusters are likely crucial for understanding the processes driving magnetar activity. In this study, we investigate the repetitive short X-ray burst behavior of magnetars through crustal interactions, employing the cellular automaton model for the magnetar crust proposed by Lander (2023). Our simulations, based on physically motivated criteria, successfully reproduce burst clustering. Additionally, the durations and energetics of active episodes in our simulations agree well with observational data. We discuss the potential physical mechanisms underlying burst clusters observed in numerous magnetars, as well as the reactivations of an individual magnetar.
来自强磁化中子星的能量爆发,被称为磁星,通常会在星群中被检测到。一旦活跃期开始,从几天到几个月的时间里,可能会爆发从几次到数千次的硬X射线。这些反复爆发的时序聚集表明存在一个潜在机制,触发连续多次爆发。这些爆发群对于理解驱动磁星活动的过程可能是至关重要的。在这项研究中,我们通过采用地壳相互作用来探究磁星的重复性短期X射线爆发行为,运用Lander(2023)为磁星地壳提出的元胞自动机模型。我们的模拟基于物理驱动标准,成功再现了爆发聚集现象。此外,我们的模拟中的活跃期时长和能量与观测数据非常吻合。我们讨论了众多磁星观测到的爆发群以及单个磁星重新活化背后的潜在物理机制。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in ApJ
Summary
此文本描述了强磁化中子星(也称为磁星)的能量爆发,这些爆发通常以集群的形式出现。活跃期开始后,可能产生数量不等的硬X射线爆发,持续时间从几天到几个月不等。爆发集群表明存在触发多次快速连续的爆发机制。对于理解磁星活动的驱动过程,这些爆发集群至关重要。本研究通过模拟磁星地壳相互作用来研究磁星的重复性短X射线爆发行为,采用Lander(2023)提出的磁星地壳的元胞自动机模型。基于物理驱动标准的模拟成功再现了爆发集群,并且模拟的活跃期持续时间与观测数据吻合良好。我们讨论了磁星中观察到的爆发集群以及单个磁星重新激活的潜在物理机制。
Key Takeaways
- 磁星的能量爆发通常以集群形式出现。
- 活跃期开始后,会有多次硬X射线爆发,持续时间不一。
- 爆发集群表明存在触发多次快速连续的爆发的机制。
- 爆发集群对于理解磁星活动的驱动过程至关重要。
- 采用元胞自动机模型模拟磁星地壳相互作用来研究其重复性短X射线爆发行为。
- 模拟成功再现了爆发集群,活跃期持续时间与观测数据吻合良好。
点此查看论文截图

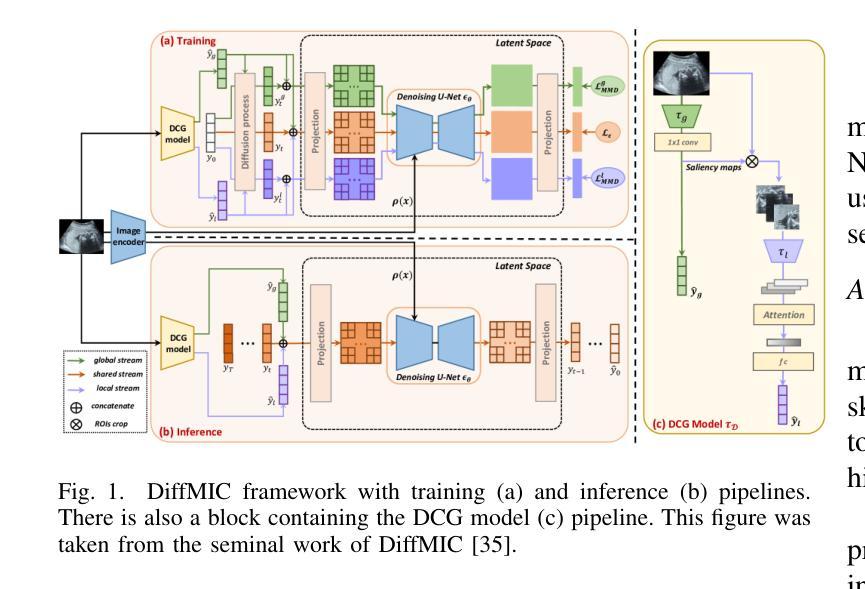
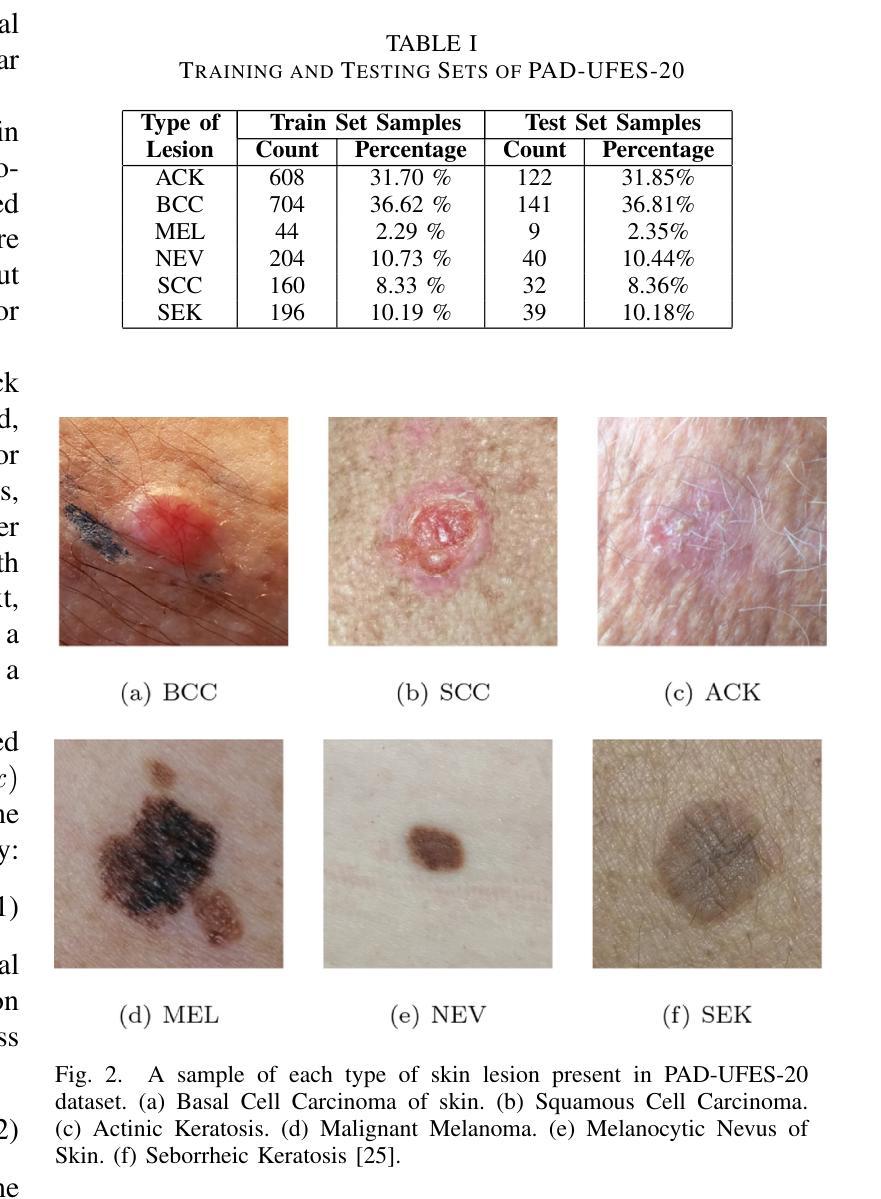
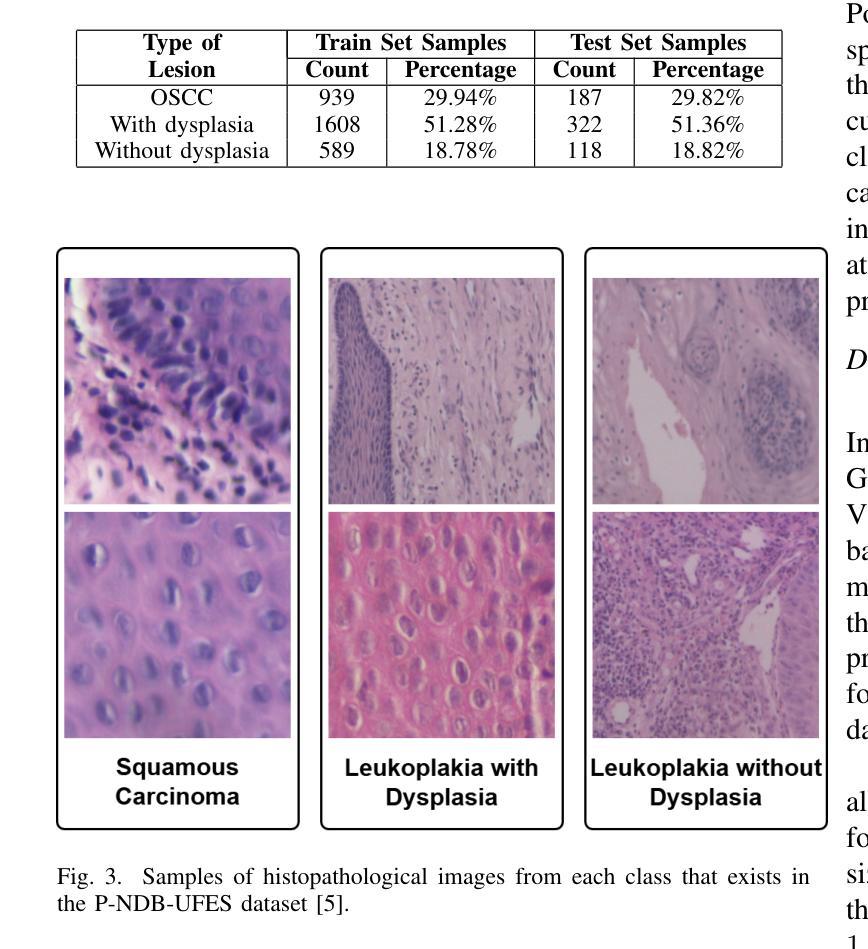
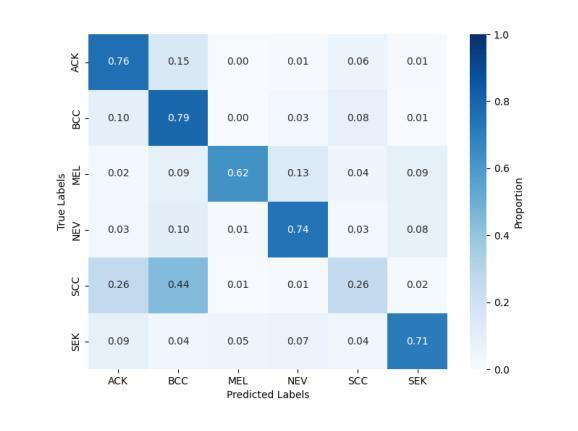
Diffusion models applied to skin and oral cancer classification
Authors:José J. M. Uliana, Renato A. Krohling
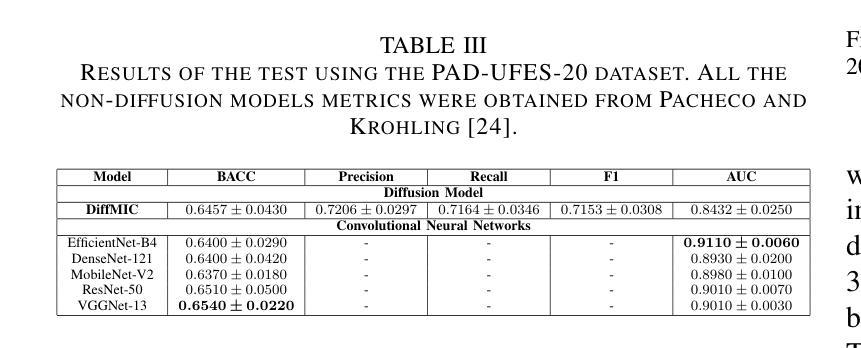
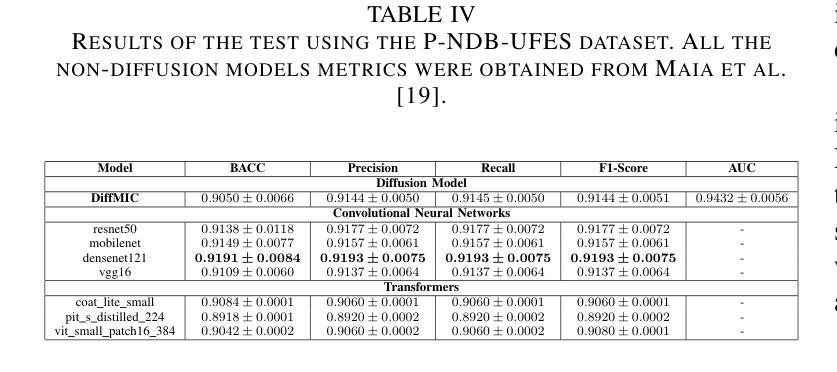
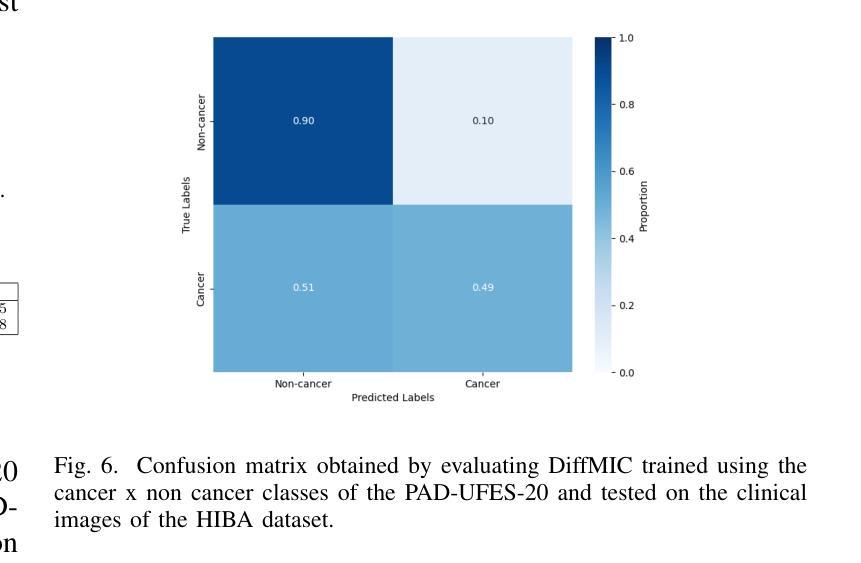
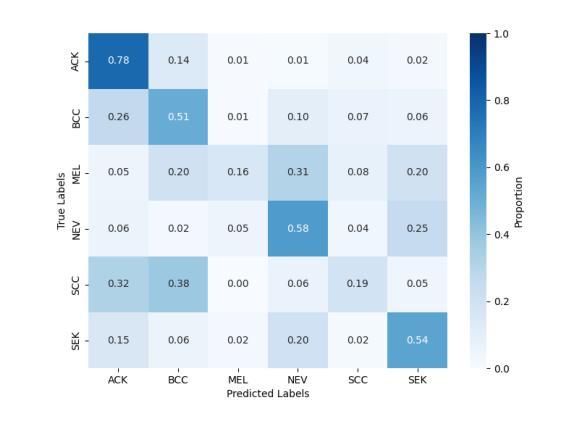
This study investigates the application of diffusion models in medical image classification (DiffMIC), focusing on skin and oral lesions. Utilizing the datasets PAD-UFES-20 for skin cancer and P-NDB-UFES for oral cancer, the diffusion model demonstrated competitive performance compared to state-of-the-art deep learning models like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Transformers. Specifically, for the PAD-UFES-20 dataset, the model achieved a balanced accuracy of 0.6457 for six-class classification and 0.8357 for binary classification (cancer vs. non-cancer). For the P-NDB-UFES dataset, it attained a balanced accuracy of 0.9050. These results suggest that diffusion models are viable models for classifying medical images of skin and oral lesions. In addition, we investigate the robustness of the model trained on PAD-UFES-20 for skin cancer but tested on the clinical images of the HIBA dataset.
本研究探讨了扩散模型在医学图像分类(DiffMIC)中的应用,重点关注皮肤和口腔病变。研究使用PAD-UFES-20数据集对皮肤癌进行研究,以及使用P-NDB-UFES数据集对口腔癌进行研究。扩散模型的性能表现与先进的深度学习模型(如卷积神经网络(CNN)和Transformer)相比具有竞争力。具体而言,对于PAD-UFES-20数据集,该模型在六类分类中实现了0.6457的平衡准确率,在二元分类(癌症与非癌症)中实现了0.8357的平衡准确率。对于P-NDB-UFES数据集,它达到了0.9050的平衡准确率。这些结果表明,扩散模型是分类皮肤和口腔病变医学图像的可行模型。此外,我们还研究了在PAD-UFES-20数据集上训练的模型对HIBA临床图像数据集的鲁棒性测试。该模型在临床图像上的表现证明了其在实际应用中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究探讨了扩散模型在医学图像分类(DiffMIC)中的应用,重点研究皮肤与口腔病灶。研究使用PAD-UFES-20皮肤癌数据集和P-NDB-UFES口腔癌数据集,扩散模型的性能与先进的深度学习模型(如卷积神经网络(CNNs)和Transformer)相比具有竞争力。对于PAD-UFES-20数据集,该模型在六类分类中达到0.6457的平衡准确率,在二元分类(癌症与非癌症)中达到0.8357的平衡准确率。对于P-NDB-UFES数据集,其平衡准确率为0.9050。这些结果表明扩散模型是分类皮肤和口腔病变医学图像的可行模型。此外,该研究还探讨了用PAD-UFES-20皮肤癌数据集训练的模型在HIBA临床图像上的稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究探讨了扩散模型在医学图像分类中的应用,特别是在皮肤和口腔病灶的分类上。
- 研究使用了PAD-UFES-20皮肤癌数据集和P-NDB-UFES口腔癌数据集进行扩散模型的训练和验证。
- 扩散模型在分类性能上展现出竞争力,与先进的深度学习模型如卷积神经网络(CNNs)和Transformer相比表现良好。
- 在PAD-UFES-20数据集上,扩散模型实现了较高的平衡准确率,特别是在二元分类任务中。
- 在P-NDB-UFES数据集上,扩散模型的平衡准确率达到了较高的水平。
- 研究表明扩散模型是分类医学图像的可行模型,特别是在皮肤和口腔病灶的分类上。
点此查看论文截图

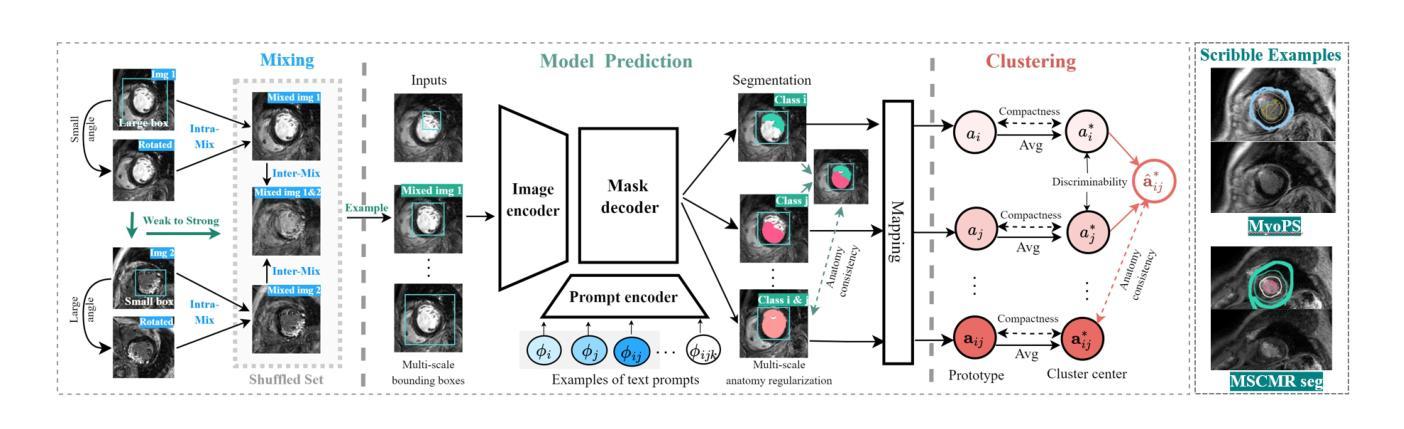
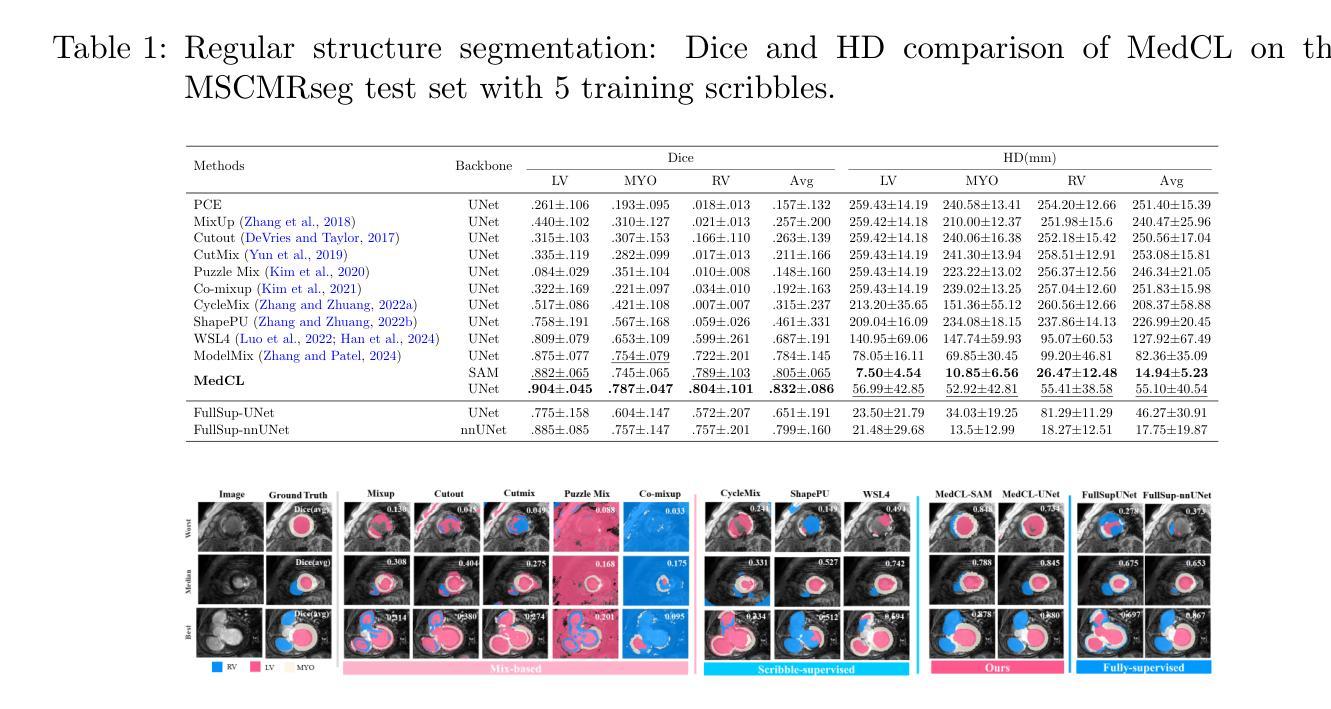
MedCL: Learning Consistent Anatomy Distribution for Scribble-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Ke Zhang, Vishal M. Patel
Curating large-scale fully annotated datasets is expensive, laborious, and cumbersome, especially for medical images. Several methods have been proposed in the literature that make use of weak annotations in the form of scribbles. However, these approaches require large amounts of scribble annotations, and are only applied to the segmentation of regular organs, which are often unavailable for the disease species that fall in the long-tailed distribution. Motivated by the fact that the medical labels have anatomy distribution priors, we propose a scribble-supervised clustering-based framework, called MedCL, to learn the inherent anatomy distribution of medical labels. Our approach consists of two steps: i) Mix the features with intra- and inter-image mix operations, and ii) Perform feature clustering and regularize the anatomy distribution at both local and global levels. Combined with a small amount of weak supervision, the proposed MedCL is able to segment both regular organs and challenging irregular pathologies. We implement MedCL based on SAM and UNet backbones, and evaluate the performance on three open datasets of regular structure (MSCMRseg), multiple organs (BTCV) and irregular pathology (MyoPS). It is shown that even with less scribble supervision, MedCL substantially outperforms the conventional segmentation methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/BWGZK/MedCL.
构建大规模全注释数据集既昂贵又耗时,特别是在医学图像领域。尽管文献中提出了几种利用涂鸦形式弱注释的方法,但这些方法需要大量涂鸦注释,并且仅应用于常规器官的分割,对于长尾分布中的疾病种类则无法适用。受到医学标签具有解剖学分布先验事实启发,我们提出了一种基于涂鸦监督聚类的框架,名为MedCL,用于学习医学标签的固有解剖学分布。我们的方法分为两步:i)通过图像内和图像间混合操作混合特征;ii)执行特征聚类并在局部和全局层面调整解剖学分布。结合少量的弱监督,所提出MedCL能够对常规器官和具有挑战性的不规则病理进行分割。我们基于SAM和UNet骨干网实现了MedCL,并在三个开放数据集(常规结构MSCMRseg、多器官BTCV和不规则病理MyoPS)上评估其性能。结果表明,即使使用较少的涂鸦监督,MedCL也大大优于传统分割方法。我们的代码位于https://github.com/BWGZK/MedCL。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于涂鸦监督的聚类方法(MedCL),用于学习医学标签的固有解剖分布。该方法混合图像内和图像间的特征,进行特征聚类,并在局部和全局层面调整解剖分布。结合少量弱监督,MedCL能够分割常规器官和具有挑战性的不规则病理。在三个公开数据集上的实验表明,即使使用较少的涂鸦监督,MedCL也能显著优于传统分割方法。
Key Takeaways
- MedCL是一种基于涂鸦监督的聚类方法,用于医学图像分割。
- MedCL利用医学标签的解剖分布先验进行学习。
- MedCL分为两步:特征混合和特征聚类。
- 特征混合包括图像内和图像间的操作。
- 聚类后进行局部和全局的解剖分布调整。
- 结合少量弱监督,MedCL能分割常规器官和不规则病理。
- 在三个公开数据集上的实验表明,MedCL性能优于传统方法。
点此查看论文截图

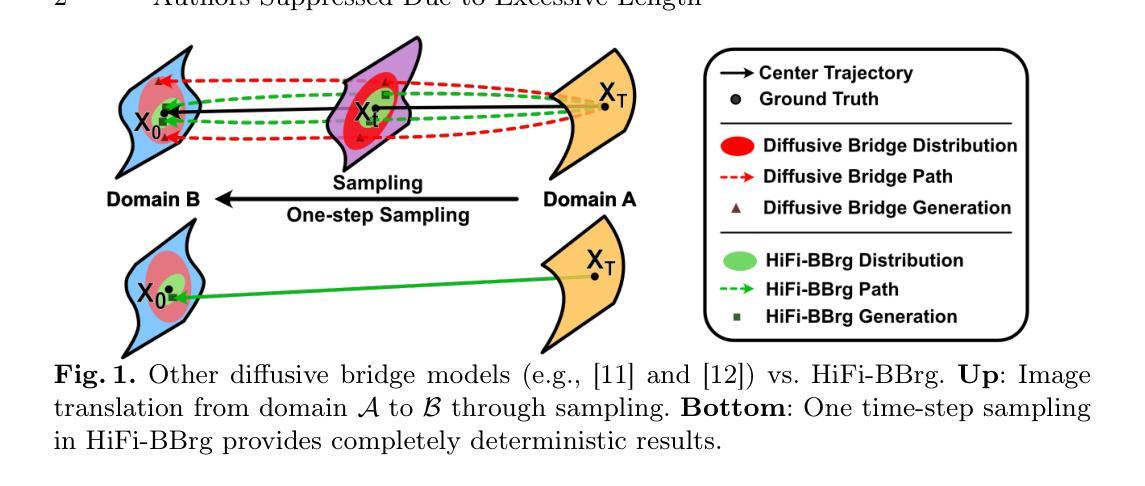
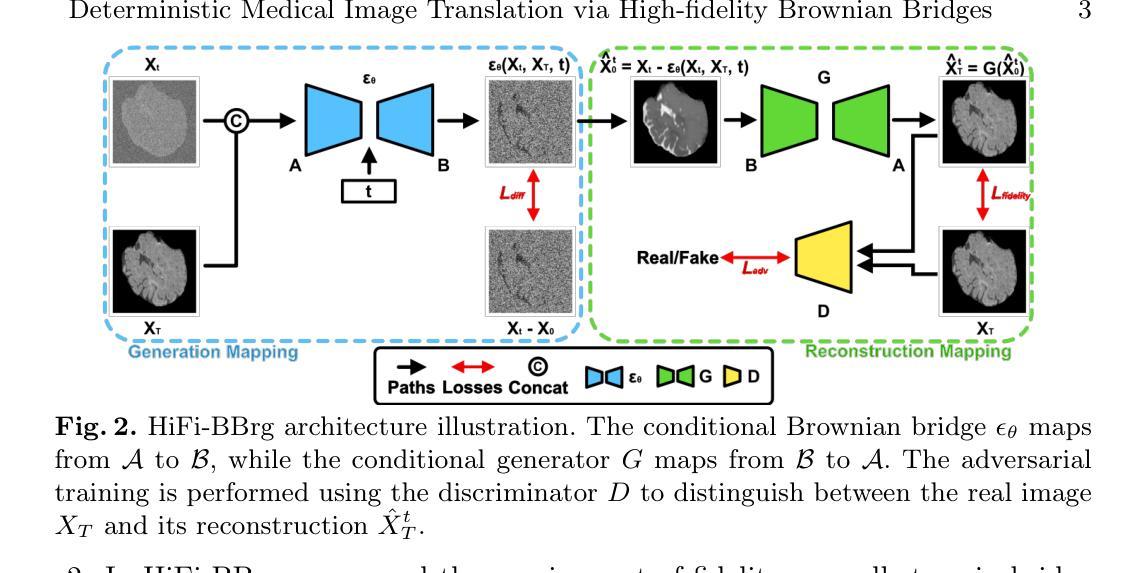
Deterministic Medical Image Translation via High-fidelity Brownian Bridges
Authors:Qisheng He, Nicholas Summerfield, Peiyong Wang, Carri Glide-Hurst, Ming Dong
Recent studies have shown that diffusion models produce superior synthetic images when compared to Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). However, their outputs are often non-deterministic and lack high fidelity to the ground truth due to the inherent randomness. In this paper, we propose a novel High-fidelity Brownian bridge model (HiFi-BBrg) for deterministic medical image translations. Our model comprises two distinct yet mutually beneficial mappings: a generation mapping and a reconstruction mapping. The Brownian bridge training process is guided by the fidelity loss and adversarial training in the reconstruction mapping. This ensures that translated images can be accurately reversed to their original forms, thereby achieving consistent translations with high fidelity to the ground truth. Our extensive experiments on multiple datasets show HiFi-BBrg outperforms state-of-the-art methods in multi-modal image translation and multi-image super-resolution.
最近的研究表明,与生成对抗网络(GANs)相比,扩散模型能够生成更优质的合成图像。然而,由于其固有的随机性,其输出通常是非确定的,并且与真实情况的高保真度有所缺失。在本文中,我们提出了一种用于确定性医学图像翻译的高保真布朗桥模型(HiFi-BBrg)。我们的模型包含两种不同但相互促进的映射:生成映射和重建映射。布朗桥训练过程由重建映射中的保真度损失和对抗训练引导,这确保了翻译后的图像可以准确地恢复到其原始形式,从而实现与真实情况高度一致的翻译。我们在多个数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,HiFi-BBrg在跨模态图像翻译和多图像超分辨率方面优于最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的确定性医学图像翻译模型——高保真布朗桥模型(HiFi-BBrg)。该模型通过生成映射和重建映射两个相互补充的过程,实现了医学图像的确定性翻译,并通过对重建映射中的保真度损失和对抗性训练进行引导,确保了翻译后的图像能够准确还原为原始形式,实现了高保真度的图像翻译。实验证明,HiFi-BBrg在多模态图像翻译和多图像超分辨率方面优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在生成合成图像方面表现出优越性,但输出常具有非确定性和低保真度。
- 提出了高保真布朗桥模型(HiFi-BBrg)用于确定性医学图像翻译。
- HiFi-BBrg模型包含生成映射和重建映射两个互补部分。
- 通过重建映射中的布朗桥训练过程,HiFi-BBrg确保了图像翻译的可逆性。
- HiFi-BBrg模型实现了高保真度的图像翻译,保持与原始图像的相似性。
- 广泛实验证明HiFi-BBrg在多模态图像翻译和多图像超分辨率方面优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

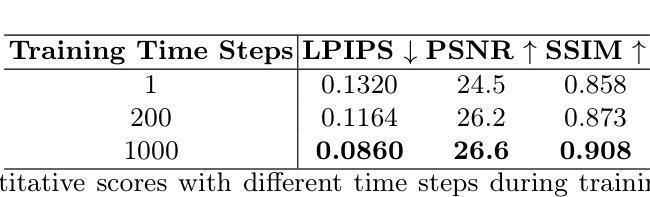
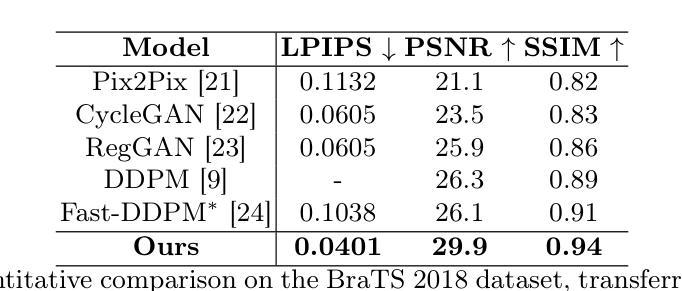
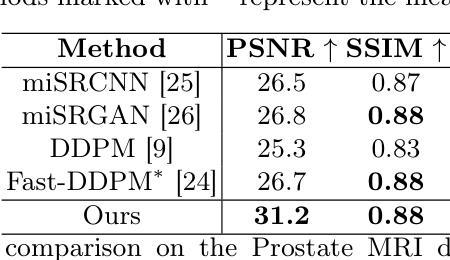
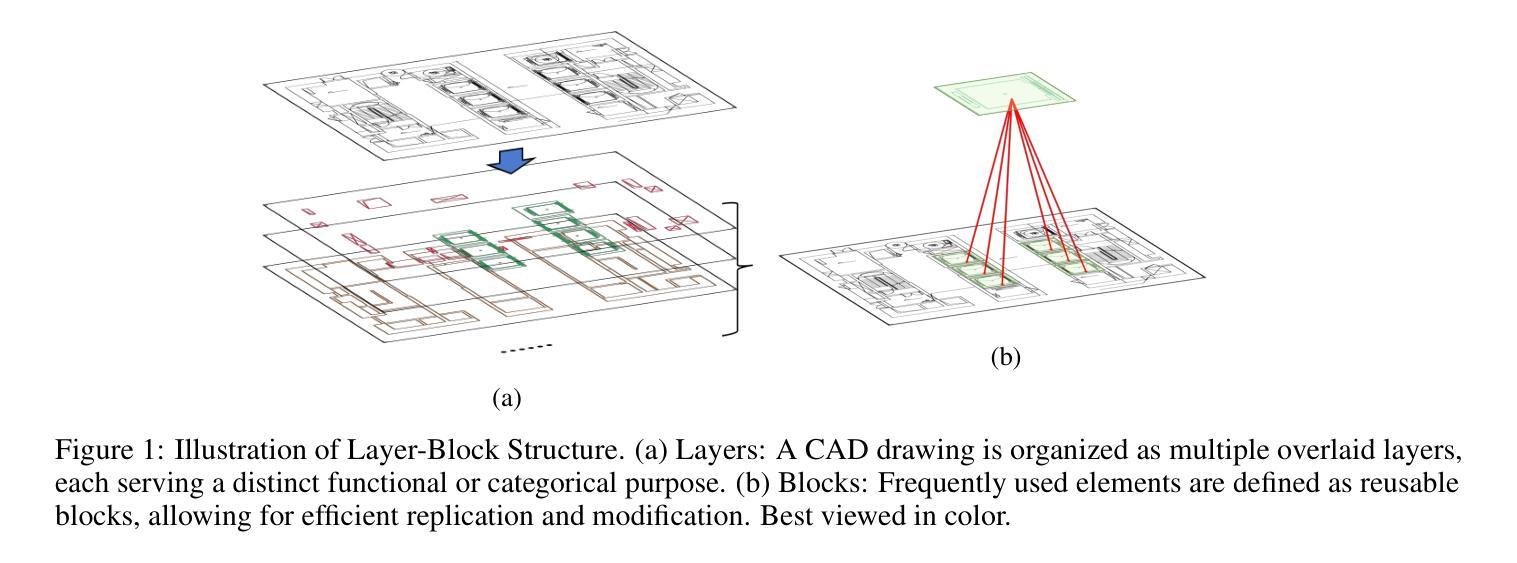
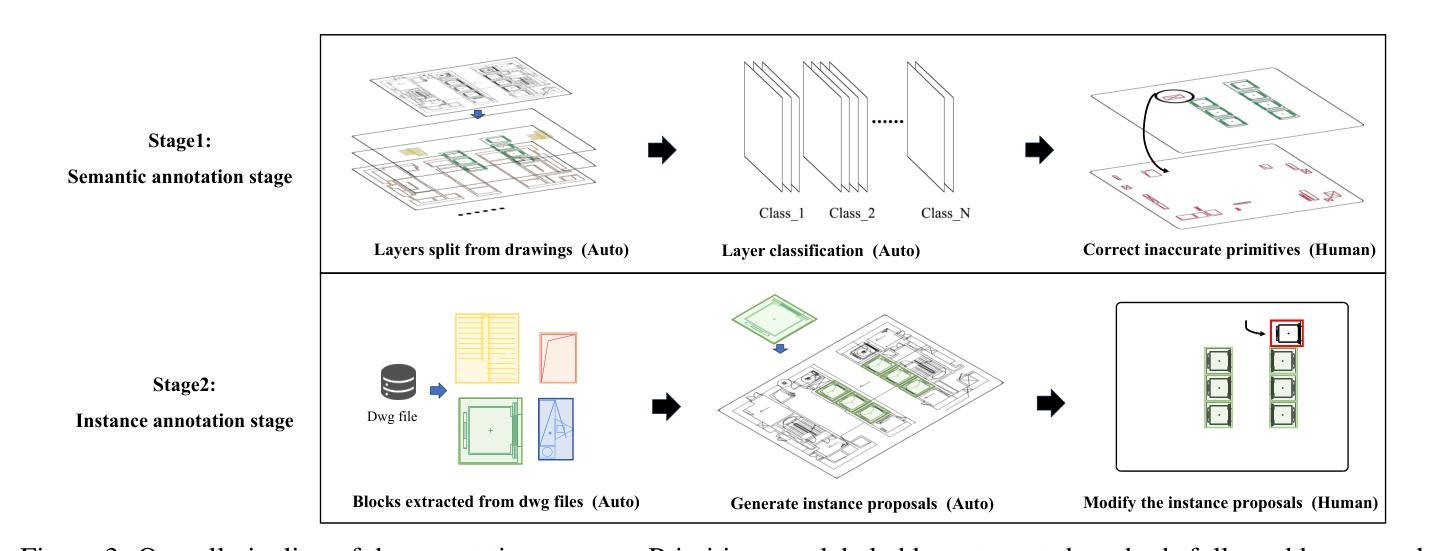
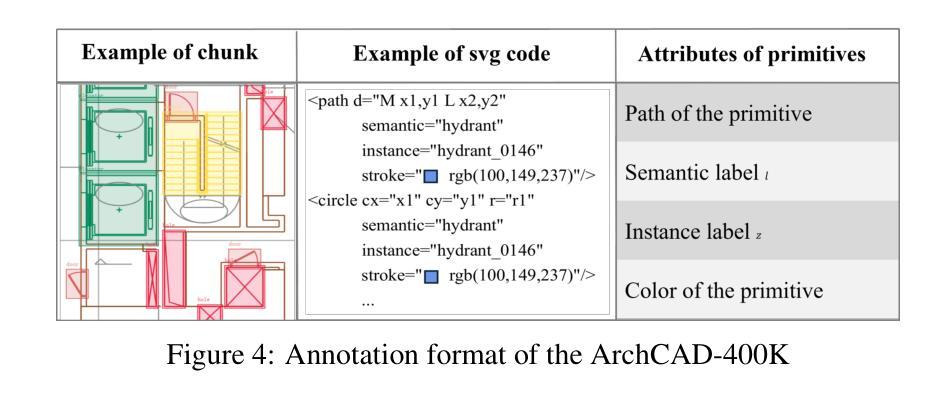
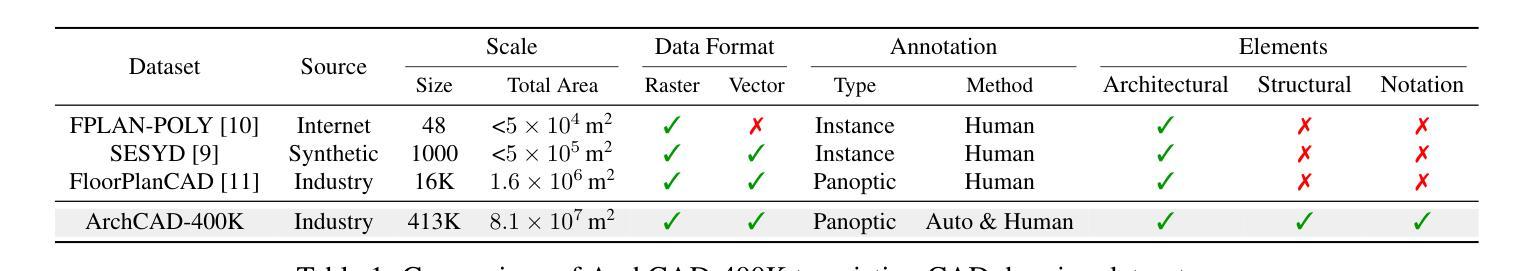
ArchCAD-400K: An Open Large-Scale Architectural CAD Dataset and New Baseline for Panoptic Symbol Spotting
Authors:Ruifeng Luo, Zhengjie Liu, Tianxiao Cheng, Jie Wang, Tongjie Wang, Xingguang Wei, Haomin Wang, YanPeng Li, Fu Chai, Fei Cheng, Shenglong Ye, Wenhai Wang, Yanting Zhang, Yu Qiao, Hongjie Zhang, Xianzhong Zhao
Recognizing symbols in architectural CAD drawings is critical for various advanced engineering applications. In this paper, we propose a novel CAD data annotation engine that leverages intrinsic attributes from systematically archived CAD drawings to automatically generate high-quality annotations, thus significantly reducing manual labeling efforts. Utilizing this engine, we construct ArchCAD-400K, a large-scale CAD dataset consisting of 413,062 chunks from 5538 highly standardized drawings, making it over 26 times larger than the largest existing CAD dataset. ArchCAD-400K boasts an extended drawing diversity and broader categories, offering line-grained annotations. Furthermore, we present a new baseline model for panoptic symbol spotting, termed Dual-Pathway Symbol Spotter (DPSS). It incorporates an adaptive fusion module to enhance primitive features with complementary image features, achieving state-of-the-art performance and enhanced robustness. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of DPSS, demonstrating the value of ArchCAD-400K and its potential to drive innovation in architectural design and construction.
识别建筑CAD图纸中的符号对于各种高级工程应用至关重要。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的CAD数据标注引擎,该引擎利用系统归档的CAD图纸中的内在属性,自动生成高质量标注,从而显著减少手动标注的工作量。利用此引擎,我们构建了ArchCAD-400K,这是一个大规模的CAD数据集,由5538张高度标准化的图纸中的413,062个数据块组成,是现有最大CAD数据集的26倍以上。ArchCAD-400K拥有扩展的绘图多样性和更广泛的类别,提供精细的线条标注。此外,我们为全景符号检测任务提出了一种新的基线模型,称为双路径符号检测器(DPSS)。它结合了一个自适应融合模块,以增强原始特征与互补图像特征的融合,实现了卓越的性能和增强的稳健性。大量实验验证了DPSS的有效性,证明了ArchCAD-400K的价值及其在建筑设计领域的潜力以及推动创新的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型的CAD数据标注引擎,该引擎利用系统归档的CAD图纸中的内在属性自动生成高质量标注,显著减少手动标注工作量。基于此引擎构建的大型CAD数据集ArchCAD-400K,包含从高度标准化的图纸中提取的413,062个数据块,较现有的最大CAD数据集大出逾26倍。ArchCAD-400K展现出的绘图多样性和更广泛的类别,提供了详细的标注。此外,本文提出了全新的全景符号识别基准模型——双路径符号识别器(DPSS),它通过自适应融合模块强化原始特征与互补图像特征的融合,实现了业界领先的性能和稳健性。多项实验验证了DPSS的有效性,展示了ArchCAD-400K的价值及其在建筑设计领域的创新潜力。
Key Takeaways
- CAD数据标注引擎能利用CAD图纸的内在属性自动生成高质量标注,降低手动标注工作量。
- ArchCAD-400K数据集是大型的CAD数据集,由高度标准化的图纸构成,比现有数据集规模更大。
- ArchCAD-400K提供多样的绘图和广泛的类别,具有详细的标注。
- 提出了全新的全景符号识别模型——双路径符号识别器(DPSS)。
- DPSS模型能融合原始特征和互补图像特征,增强识别性能。
- DPSS模型实现了业界领先的性能和稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

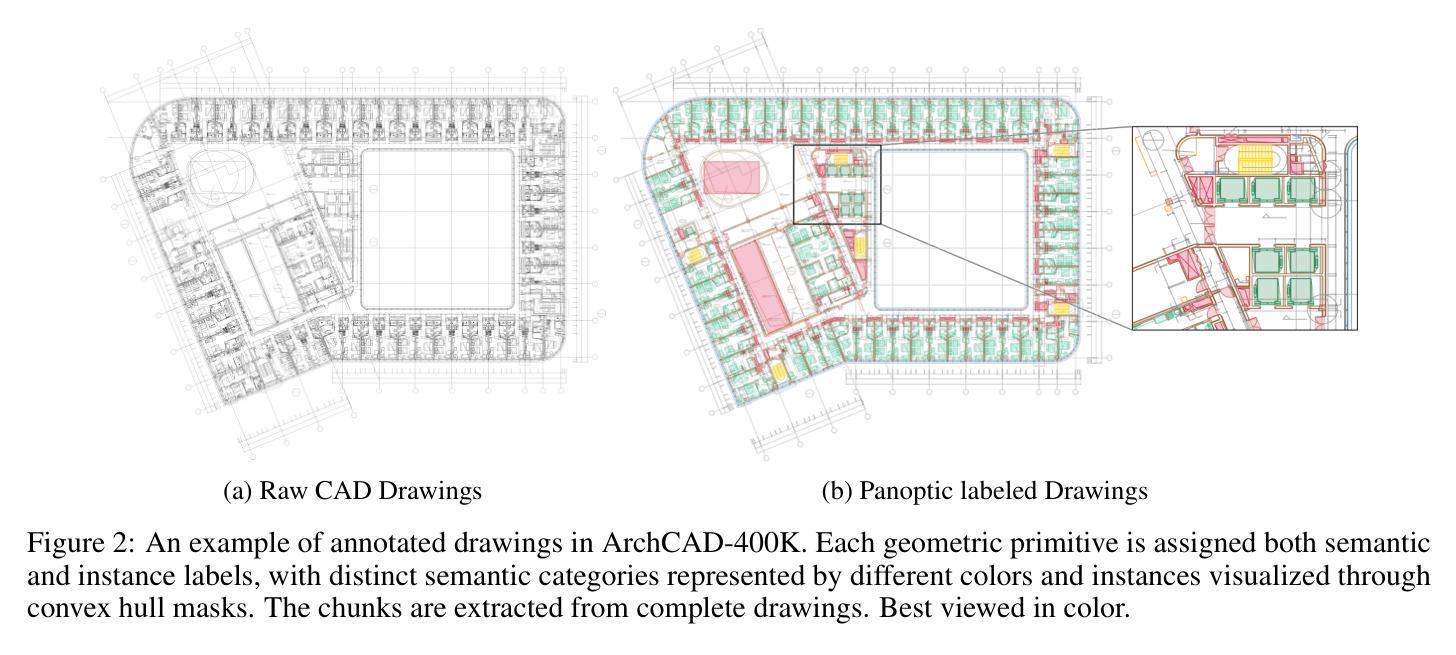
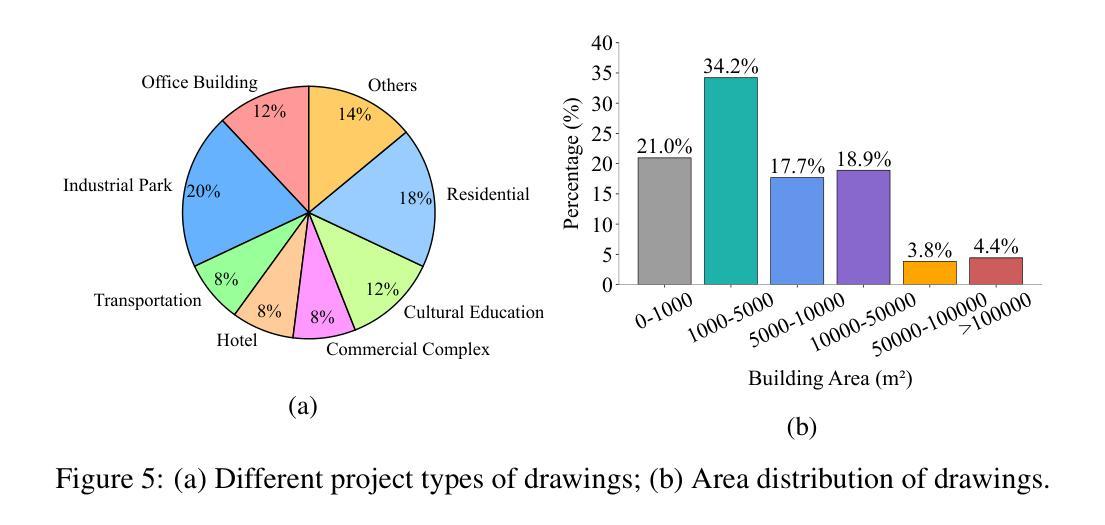
Eyes Tell the Truth: GazeVal Highlights Shortcomings of Generative AI in Medical Imaging
Authors:David Wong, Bin Wang, Gorkem Durak, Marouane Tliba, Akshay Chaudhari, Aladine Chetouani, Ahmet Enis Cetin, Cagdas Topel, Nicolo Gennaro, Camila Lopes Vendrami, Tugce Agirlar Trabzonlu, Amir Ali Rahsepar, Laetitia Perronne, Matthew Antalek, Onural Ozturk, Gokcan Okur, Andrew C. Gordon, Ayis Pyrros, Frank H. Miller, Amir Borhani, Hatice Savas, Eric Hart, Drew Torigian, Jayaram K. Udupa, Elizabeth Krupinski, Ulas Bagci
The demand for high-quality synthetic data for model training and augmentation has never been greater in medical imaging. However, current evaluations predominantly rely on computational metrics that fail to align with human expert recognition. This leads to synthetic images that may appear realistic numerically but lack clinical authenticity, posing significant challenges in ensuring the reliability and effectiveness of AI-driven medical tools. To address this gap, we introduce GazeVal, a practical framework that synergizes expert eye-tracking data with direct radiological evaluations to assess the quality of synthetic medical images. GazeVal leverages gaze patterns of radiologists as they provide a deeper understanding of how experts perceive and interact with synthetic data in different tasks (i.e., diagnostic or Turing tests). Experiments with sixteen radiologists revealed that 96.6% of the generated images (by the most recent state-of-the-art AI algorithm) were identified as fake, demonstrating the limitations of generative AI in producing clinically accurate images.
在医学成像领域,对于高质量合成数据用于模型训练和增强的需求从未如此之大。然而,当前的评估主要依赖于计算指标,这些指标与人类专家识别的匹配度很低。这导致合成图像虽然在数值上看起来很真实,但在临床真实性上却有所欠缺,从而在保证人工智能驱动的医疗工具的可靠性和有效性方面带来重大挑战。为了解决这一差距,我们引入了GazeVal,这是一个实用的框架,它将专家眼动数据与直接放射学评估相结合,以评估合成医学图像的质量。GazeVal利用放射科医生在评估合成数据时表现出的注视模式,以更深入地了解专家在不同任务(如诊断或图灵测试)中如何感知和与合成数据互动。有十六名放射科医生参与的实验显示,最新最先进的算法生成的图像中,有96.6%被识别为假的,这显示了生成式人工智能在生成临床准确图像方面的局限性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在医学成像领域,高质量合成数据的需求巨大,但现有评估主要依赖计算指标,与人类专家识别存在偏差。这导致合成图像虽然数值上看起来真实,但缺乏临床真实性,给人工智能驱动的医学工具带来可靠性和有效性挑战。为解决此问题,我们提出GazeVal框架,结合专家眼动追踪数据和直接放射学评估,评估合成医学图像的质量。实验显示,十六位放射科医生中,有九成以上认为最新人工智能算法生成的图像为假,表明生成式人工智能在临床准确性方面存在局限。
Key Takeaways
- 医学成像领域对高质量合成数据的需求巨大。
- 当前评估方法主要依赖计算指标,忽略了与人类专家识别的匹配程度。
- 合成图像可能在数值上看起来很真实,但在临床真实性方面存在缺陷。
- 提出GazeVal框架以评估合成医学图像质量,结合了专家眼动数据和直接放射学评估。
- GazeVal框架能更深入地了解专家如何感知和与合成数据互动。
- 实验显示,最新人工智能算法生成的医学图像被大多数放射科医生识别为假。
点此查看论文截图

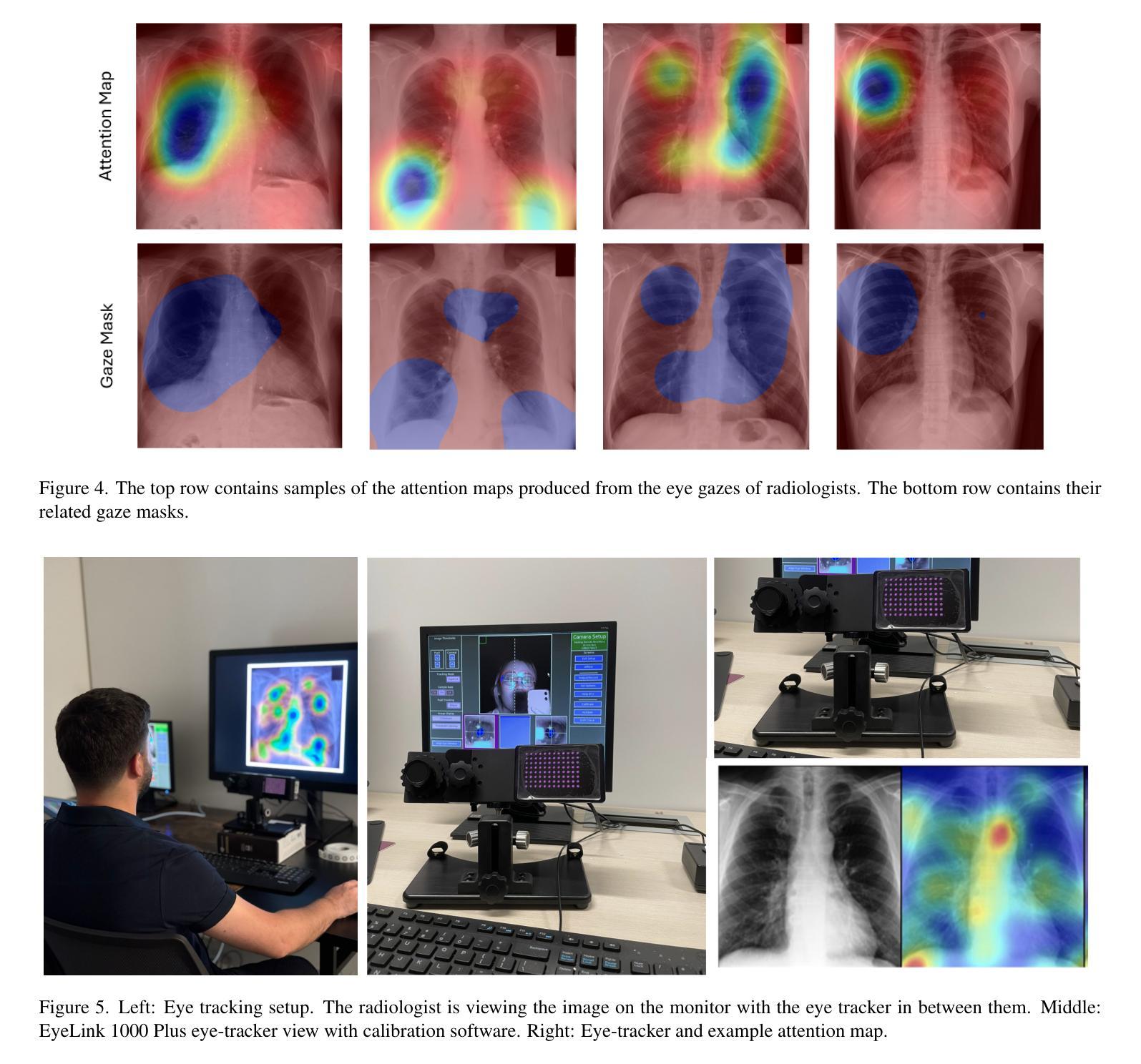
VGAT: A Cancer Survival Analysis Framework Transitioning from Generative Visual Question Answering to Genomic Reconstruction
Authors:Zizhi Chen, Minghao Han, Xukun Zhang, Shuwei Ma, Tao Liu, Xing Wei, Lihua Zhang
Multimodal learning combining pathology images and genomic sequences enhances cancer survival analysis but faces clinical implementation barriers due to limited access to genomic sequencing in under-resourced regions. To enable survival prediction using only whole-slide images (WSI), we propose the Visual-Genomic Answering-Guided Transformer (VGAT), a framework integrating Visual Question Answering (VQA) techniques for genomic modality reconstruction. By adapting VQA’s text feature extraction approach, we derive stable genomic representations that circumvent dimensionality challenges in raw genomic data. Simultaneously, a cluster-based visual prompt module selectively enhances discriminative WSI patches, addressing noise from unfiltered image regions. Evaluated across five TCGA datasets, VGAT outperforms existing WSI-only methods, demonstrating the viability of genomic-informed inference without sequencing. This approach bridges multimodal research and clinical feasibility in resource-constrained settings. The code link is https://github.com/CZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ/VGAT.
将病理图像与基因组序列相结合的多模态学习提高了癌症生存分析能力,但由于资源匮乏地区基因组测序的有限访问性,面临着临床实施障碍。为了仅使用全幻灯片图像(WSI)进行生存预测,我们提出了视觉基因组问答引导转换器(VGAT)框架,该框架集成了视觉问答(VQA)技术用于基因组模式重建。通过适应VQA的文本特征提取方法,我们得出稳定的基因组表示,这避免了原始基因组数据中的维度挑战。同时,基于集群的视觉提示模块会选择性增强判别WSI补丁,解决未过滤图像区域的噪声问题。在五个TCGA数据集上进行评估,VGAT在仅使用WSI的方法中表现出色,证明了在不需要测序的情况下进行基因组信息推断的可行性。这种方法在多模态研究和资源受限环境中的临床可行性之间搭建了桥梁。代码链接是https://github.com/CZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ/VGAT。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Acceppted by ICME2025
Summary
本文结合病理学图像和基因组序列的多模态学习提升了癌症生存分析的效果,但在资源匮乏地区由于基因组测序的有限访问而面临临床实施的障碍。为了仅使用全幻灯片图像(WSI)进行生存预测,我们提出了视觉基因组问答引导转换器(VGAT)框架,该框架整合了视觉问答(VQA)技术用于基因组模态重建。通过适应VQA的文本特征提取方法,我们得出了稳定的基因组表示,避免了原始基因组数据的维度挑战。同时,基于集群的视觉提示模块选择性地增强了鉴别性的WSI补丁,解决了未过滤图像区域的噪声问题。在五个TCGA数据集上的评估表明,VGAT在仅使用WSI的情况下表现出优越的性能,证明了无测序的基因组信息推断的可行性。这种方法在资源受限的环境中实现了多模态研究与临床可行性的结合。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态学习结合病理图像和基因组序列增强了癌症生存分析。
- 在资源有限地区,临床实施面临基因组测序有限访问的障碍。
- 提出了VGAT框架,利用视觉问答技术实现基因组模态重建。
- VQA的文本特征提取方法用于稳定基因组表示,降低维度挑战。
- 基于集群的视觉提示模块增强鉴别性WSI补丁,减少未过滤图像区域的噪声。
- VGAT在多个数据集上表现优越,证明了无测序的基因组信息推断的可行性。
点此查看论文截图
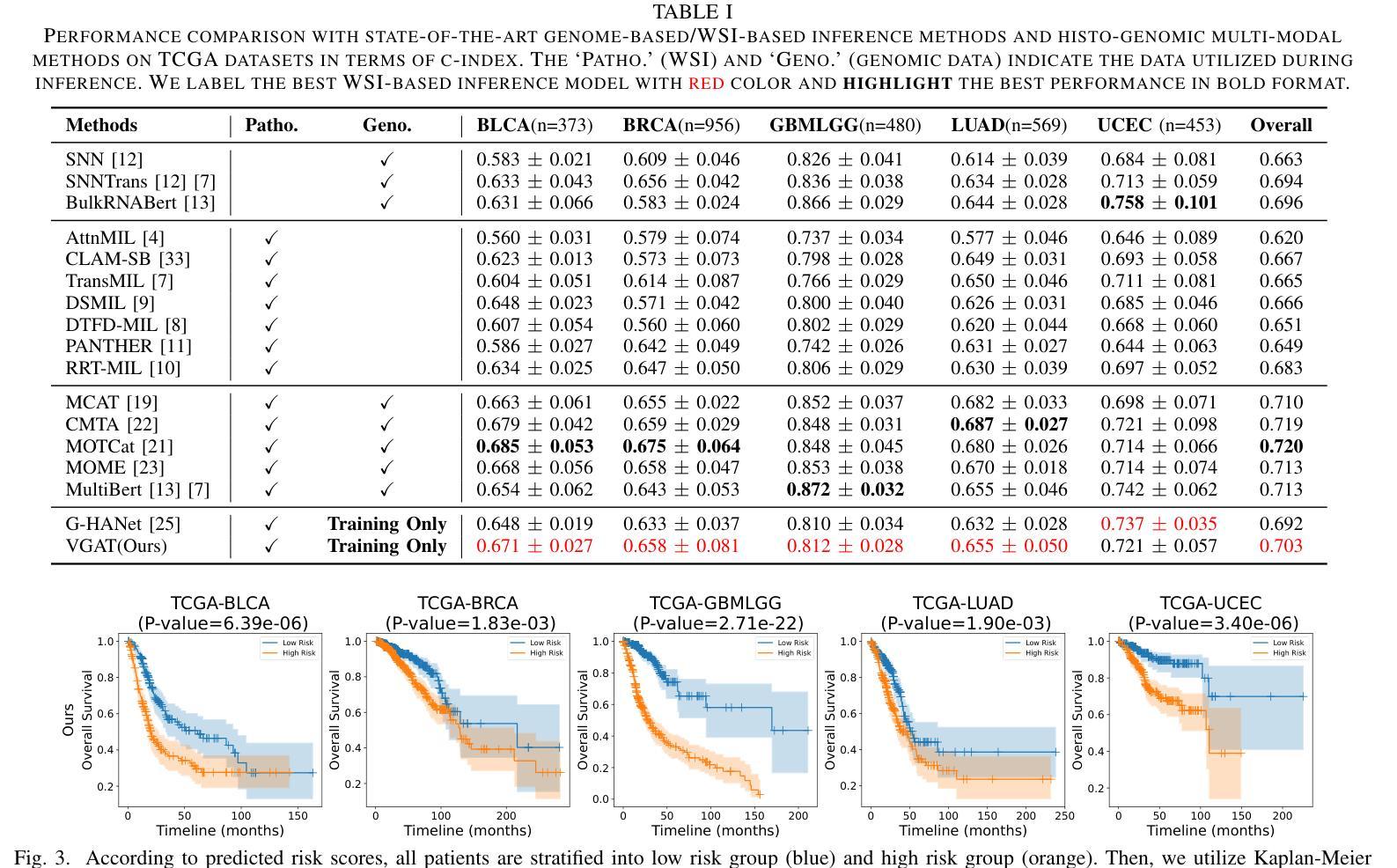
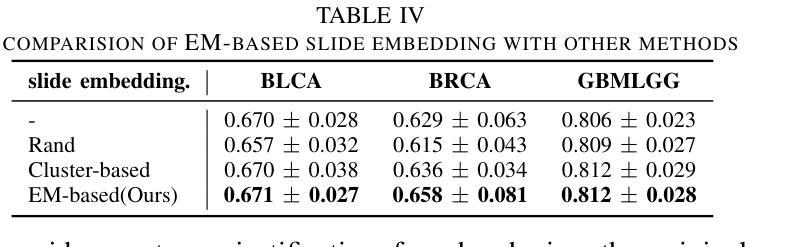
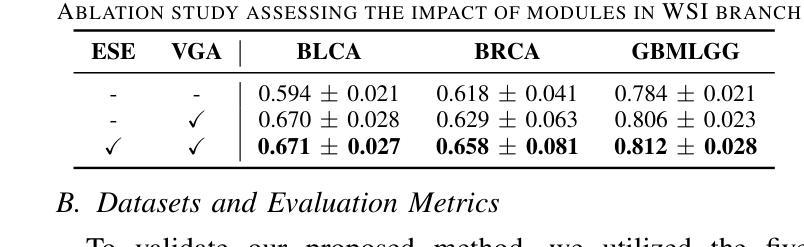
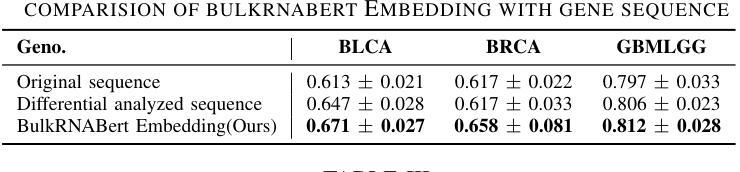
Imaging Ultrafast Dynamical Diffraction wavefronts of femtosecond laser-induced lattice distortions inside crystalline semiconductors
Authors:Angel Rodríguez-Fernández, Jan-Etienne Pudell, Roman Shayduk, Wonhyuk Jo, James Wrigley, Johannes Möller, Peter Zalden, Alexey Zozulya, Jörg Hallmann, Anders Madsen, Pablo Villanueva-Perez, Zdenek Matej, Thies J. Albert, Dominik Kaczmarek, Klaus Sokolowski-Tinten, Antonowicz Jerzy, Ryszard Sobierajski, Rahimi Mosafer, Oleksii I. Liubchenko, Javier Solis, Jan Siegel
Material processing with femtosecond lasers has attracted enormous attention because of its potential for technology and industry applications. In parallel, time-resolved x-ray diffraction has been successfully used to study ultrafast structural distortion dynamics in semiconductor thin films. Gracing incident x-ray geometry has been also used to look to distortion dynamics, but this technique is only sensitive to the surface of bulk materials with a limited temporal resolution. However, ‘real-world’ processing applications deal mostly with bulk materials, which prevent the use of such techniques. For processing applications, a fast and depth-sensitive probe is needed. To address this, we present a novel technique based on ultrafast dynamical diffraction (UDD) capable of imaging transient strain distributions inside bulk crystals upon single-pulse excitation. This pump-probe technique provides a complete picture of the temporal evolution of ultrafast distortion depth profiles. Our measurements were obtained in a thin crystalline Si wafer upon single pulse femtosecond optical excitation revealing that even below the melting threshold strong lattice distortions appear on ps time scales due to the formation and propagation of high-amplitude strain waves into the bulk.
材料通过飞秒激光进行处理已经引起了科技和工业应用领域的大量关注。同时,时间解析X射线衍射技术已成功应用于研究半导体薄膜中的超快结构畸变动力学。倾斜入射的X射线几何技术也被用来观察畸变动力学,但该技术仅对大块材料的表面敏感,且时间分辨率有限。然而,“现实世界”处理应用大多涉及大块材料,这使得这些技术的应用受到限制。针对处理应用,需要一个快速且对深度敏感的探针。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于超快动力学衍射(UDD)的新技术,能够在单脉冲激发下对晶体内部瞬时应变分布进行成像。这种泵浦探针技术提供了超快畸变深度分布的时间演化的完整图像。我们的测量是在单晶硅薄片上进行的,通过单脉冲飞秒光学激发后发现,即使在低于熔点阈值的条件下,由于高振幅应变波的形成和向内部的传播,皮秒时间尺度上也会出现强烈的晶格畸变。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
材料加工中的飞秒激光技术因其对技术和工业应用的潜力而备受关注。同时,时间分辨X射线衍射已成功应用于研究半导体薄膜中的超快结构畸变动力学。虽然倾斜入射X射线几何技术也可用于观察畸变动力学,但其仅对体材料表面敏感,且时间分辨率有限,无法适用于大多数现实世界中的加工应用,涉及的主要材料多为体材料。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于超快动力学衍射(UDD)的新技术,能够在单脉冲激发下成像晶体内部的瞬态应变分布。这种泵浦探针技术提供了超快畸变深度分布的暂时演化的完整图像。我们在单晶硅薄膜上的单次脉冲飞秒光学激发测量中发现,即使在低于熔化阈值的条件下,也会出现强晶格畸变,这是由于在皮秒时间尺度上形成了高振幅应变波并向体材料内部传播。
Key Takeaways
- 飞秒激光技术在材料加工领域受到广泛关注,具有广泛的应用前景。
- 时间分辨X射线衍射技术已成功应用于研究超快结构畸变动力学。
- 倾斜入射X射线几何技术虽然可用于观察畸变动力学,但主要局限于体材料表面的研究,且时间分辨率有限。
- 需要一种快速且对深度敏感的检测方法,以应对涉及体材料的实际加工应用。
- 基于超快动力学衍射(UDD)的新技术能够提供体材料内部的瞬态应变分布的图像。
- 这种新技术可以揭示超快畸变的深度分布和暂时演化。
点此查看论文截图

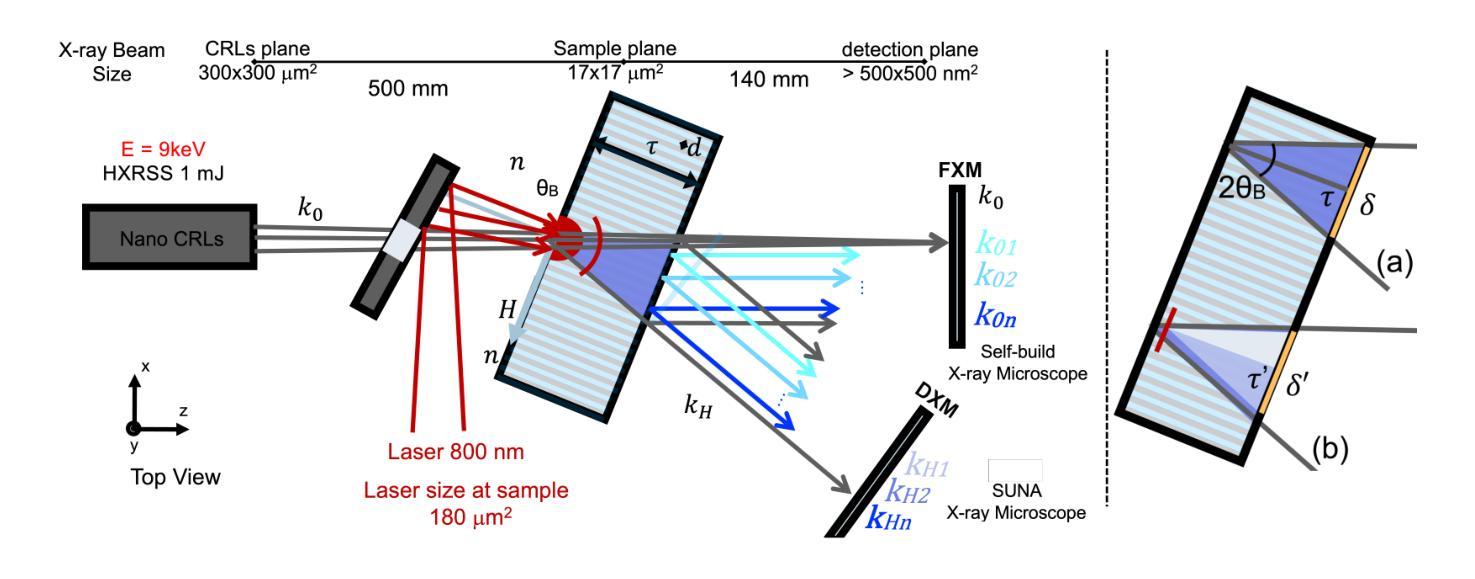
UnPuzzle: A Unified Framework for Pathology Image Analysis
Authors:Dankai Liao, Sicheng Chen, Nuwa Xi, Qiaochu Xue, Jieyu Li, Lingxuan Hou, Zeyu Liu, Chang Han Low, Yufeng Wu, Yiling Liu, Yanqin Jiang, Dandan Li, Shangqing Lyu
Pathology image analysis plays a pivotal role in medical diagnosis, with deep learning techniques significantly advancing diagnostic accuracy and research. While numerous studies have been conducted to address specific pathological tasks, the lack of standardization in pre-processing methods and model/database architectures complicates fair comparisons across different approaches. This highlights the need for a unified pipeline and comprehensive benchmarks to enable consistent evaluation and accelerate research progress. In this paper, we present UnPuzzle, a novel and unified framework for pathological AI research that covers a broad range of pathology tasks with benchmark results. From high-level to low-level, upstream to downstream tasks, UnPuzzle offers a modular pipeline that encompasses data pre-processing, model composition,taskconfiguration,andexperimentconduction.Specifically, it facilitates efficient benchmarking for both Whole Slide Images (WSIs) and Region of Interest (ROI) tasks. Moreover, the framework supports variouslearningparadigms,includingself-supervisedlearning,multi-task learning,andmulti-modallearning,enablingcomprehensivedevelopment of pathology AI models. Through extensive benchmarking across multiple datasets, we demonstrate the effectiveness of UnPuzzle in streamlining pathology AI research and promoting reproducibility. We envision UnPuzzle as a cornerstone for future advancements in pathology AI, providing a more accessible, transparent, and standardized approach to model evaluation. The UnPuzzle repository is publicly available at https://github.com/Puzzle-AI/UnPuzzle.
病理学图像分析在医学诊断中扮演着至关重要的角色,深度学习技术显著提高了诊断准确性和研究水平。虽然已进行了大量研究来解决特定的病理任务,但在预处理方法和模型/数据库架构方面缺乏标准化,使得不同方法之间的公平比较变得复杂。这突显了需要一个统一的流程和综合基准测试,以进行一致性的评估并加速研究进展。在本文中,我们提出了UnPuzzle,这是一个用于病理人工智能研究的新型统一框架,涵盖广泛的病理任务并提供基准结果。从高级到低级,从上游到下游任务,UnPuzzle提供了一个模块化流程,包括数据预处理、模型组合、任务配置和实验执行。具体来说,它有助于对整个幻灯片图像(WSIs)和感兴趣区域(ROI)任务进行高效的基准测试。此外,该框架支持多种学习范式,包括自我监督学习、多任务学习和多模式学习,从而全面开发病理人工智能模型。通过多个数据集的基准测试,我们证明了UnPuzzle在简化病理人工智能研究并促进可重复性方面的有效性。我们期望UnPuzzle能成为未来病理人工智能发展的基石,为模型评估提供更便捷、透明和标准化的方法。UnPuzzle仓库可在https://github.com/Puzzle-AI/UnPuzzle公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages,2 figures
Summary
病理学图像分析在医学诊断中扮演重要角色,深度学习技术显著提高了诊断准确性和研究水平。当前缺乏标准化预处理方法和模型/数据库架构,导致不同方法之间的公平比较变得复杂。本文提出UnPuzzle,一个针对病理学人工智能研究的新型统一框架,涵盖广泛病理学任务并提供基准结果。UnPuzzle提供模块化管道,涵盖从高级到低级、上游到下游任务的数据预处理、模型组合、任务配置和实验执行。它支持多种学习范式,包括自监督学习、多任务学习和多模态学习,促进病理学AI模型的全面发展。通过跨多个数据集的广泛基准测试,证明了UnPuzzle在简化病理学人工智能研究和促进可重复性方面的有效性。我们期望UnPuzzle成为未来病理学人工智能发展的基石,提供更易于访问、透明和标准化的模型评估方法。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习技术显著提高了病理学图像分析的准确性和研究水平。
- 缺乏标准化的预处理方法和模型架构阻碍了病理学研究的比较和进展。
- UnPuzzle提供了一个新型统一框架,旨在解决上述问题,并涵盖广泛的病理学任务。
- UnPuzzle提供模块化管道,包括数据预处理、模型组合、任务配置和实验执行。
- 该框架支持多种学习范式,促进了病理学AI模型的全面发展。
- UnPuzzle通过跨多个数据集的基准测试证明了其有效性。
点此查看论文截图

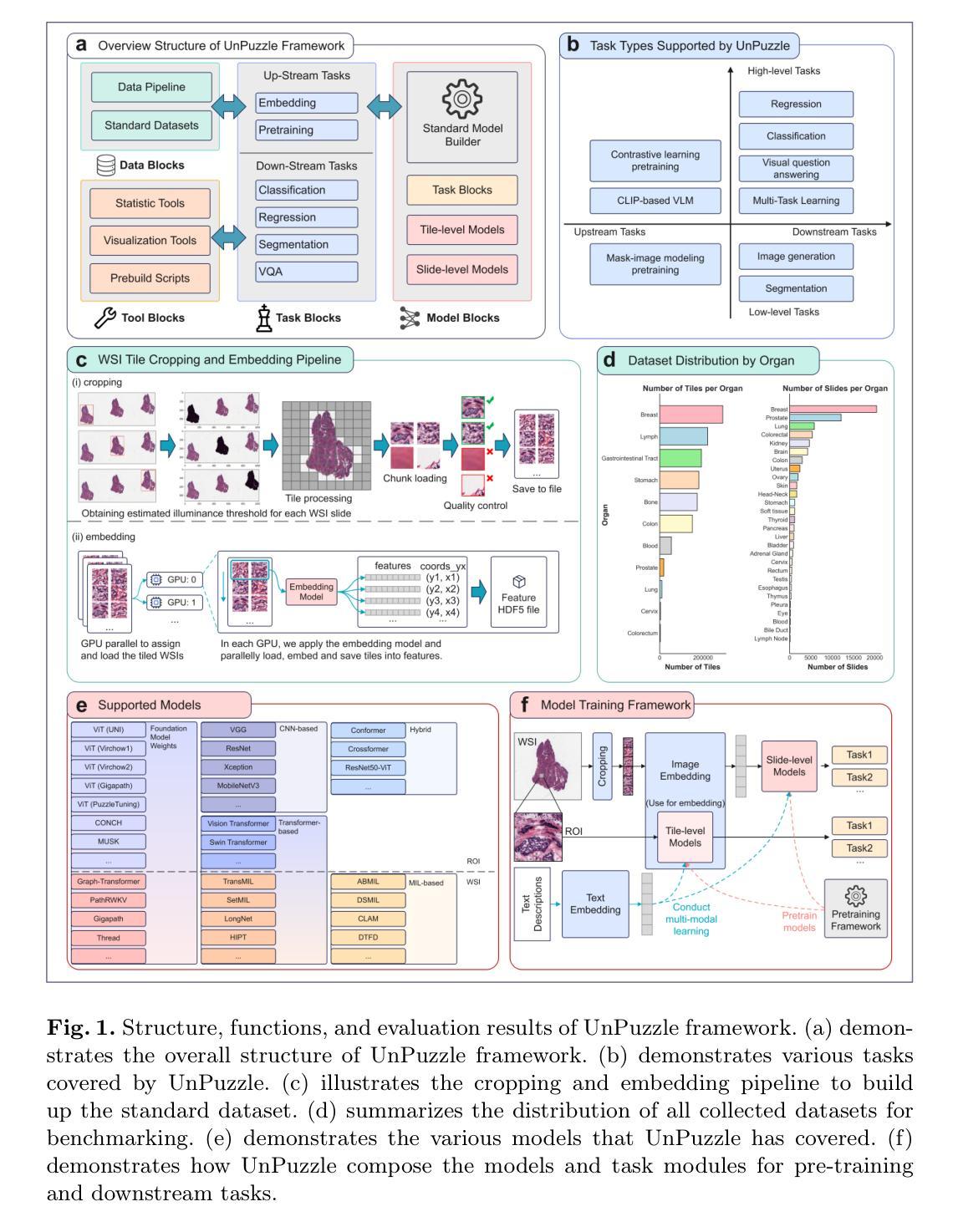
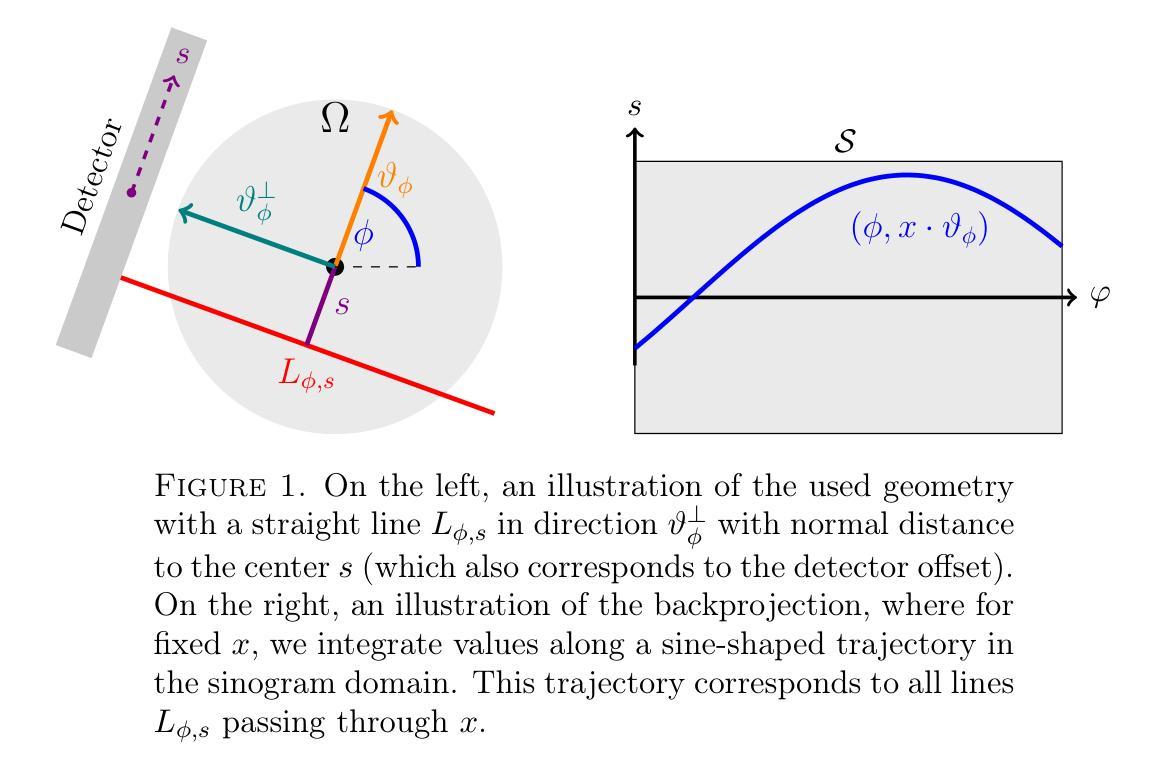
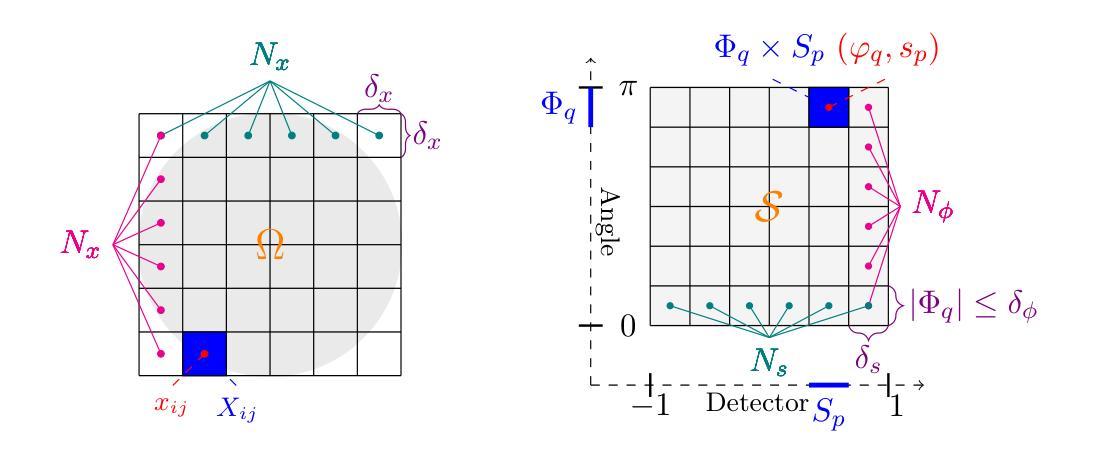
Convergence of Ray- and Pixel-Driven Discretization Frameworks in the Strong Operator Topology
Authors:Richard Huber
Tomography is a central tool in medical applications, allowing doctors to investigate patients’ interior features. The Radon transform (in two dimensions) is commonly used to model the measurement process in parallel-beam CT. Suitable discretization of the Radon transform and its adjoint (called the backprojection) is crucial. The most commonly used discretization approach combines the ray-driven Radon transform with the pixel-driven backprojection, as anecdotal reports describe these as showing the best approximation performance. However, there is little rigorous understanding of induced approximation errors. These methods involve three discretization parameters: the spatial-, detector-, and angular resolutions. Most commonly, balanced resolutions are used, i.e., the same (or similar) spatial- and detector resolutions are employed. We present a novel interpretation of ray- and pixel-driven discretizations as `convolutional methods’. This allows for a structured analysis that can explain observed behavior. In particular, we prove convergence in the strong operator topology of the ray-driven Radon transform and the pixel-driven backprojection under balanced resolutions, thus theoretically justifying this approach. In particular, with high enough resolutions one can approximate the Radon transform arbitrarily well.
断层扫描技术是医疗应用中的核心工具,它可以让医生检查患者的内部结构。拉东变换(二维)常用于平行束CT的测量过程建模。拉东变换及其伴随(称为反向投影)的适当离散化至关重要。最常用的离散化方法是将射线驱动的拉东变换与像素驱动的背投影相结合,正如个别报告所述,这些方法在近似性能上表现最佳。然而,对于诱导的近似误差,人们对其了解甚少。这些方法涉及三个离散化参数:空间分辨率、检测器分辨率和角度分辨率。通常使用的是平衡分辨率,即采用相同(或相似)的空间分辨率和检测器分辨率。我们将射线驱动和像素驱动的离散化作为一种新型的“卷积方法”进行解读。这允许进行结构化分析,从而解释观察到的行为。特别地,我们证明了在平衡分辨率下,射线驱动的拉东变换和像素驱动的背投影在强算子拓扑中会收敛,从而为这种方法提供了理论支持。特别是,分辨率足够高时,可以任意好地近似拉东变换。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 29 pages, 10 figures, Preprint was substantially updated with inclusion of section 4 concerning numerical experiments, as well as improvments in all sections
Summary
医学成像中,断层摄影是关键工具。拉冬变换常用于平行光束CT的测量过程建模。拉冬变换及其伴随变换(反向投影)的适当离散化非常重要。常用的离散化方法是结合射线驱动的拉冬变换和像素驱动的背投影,虽然这提供了最佳近似性能,但对近似误差的了解还不够深入。此方法涉及三个离散参数:空间分辨率、检测器分辨率和角度分辨率。采用平衡分辨率的方法最为常见。我们提出一种新的解释方法,将射线驱动和像素驱动的离散化视为卷积方法,这有助于进行结构化分析并解释观察到的行为。在平衡分辨率下,我们证明了射线驱动的拉冬变换和像素驱动的背投影在强算子拓扑中的收敛性,从而从理论上证实了这种方法。分辨率足够高时,可以任意逼近拉冬变换。
Key Takeaways
- 断层摄影是医学应用中的关键工具,允许医生研究患者的内部结构。
- 拉冬变换常用于平行光束CT的测量过程建模。
- 射线驱动和像素驱动的离散化是常用的拉冬变换处理方法。
- 目前的常用方法在理论上对近似误差的解释不足。
- 三个关键的离散参数包括空间分辨率、检测器分辨率和角度分辨率。
- 采用平衡分辨率的方法最为常见,即采用相同或相似的空间和检测器分辨率。
- 将射线驱动和像素驱动的离散化视为卷积方法是一种新的解释方法。
点此查看论文截图

Boltzmann Attention Sampling for Image Analysis with Small Objects
Authors:Theodore Zhao, Sid Kiblawi, Naoto Usuyama, Ho Hin Lee, Sam Preston, Hoifung Poon, Mu Wei
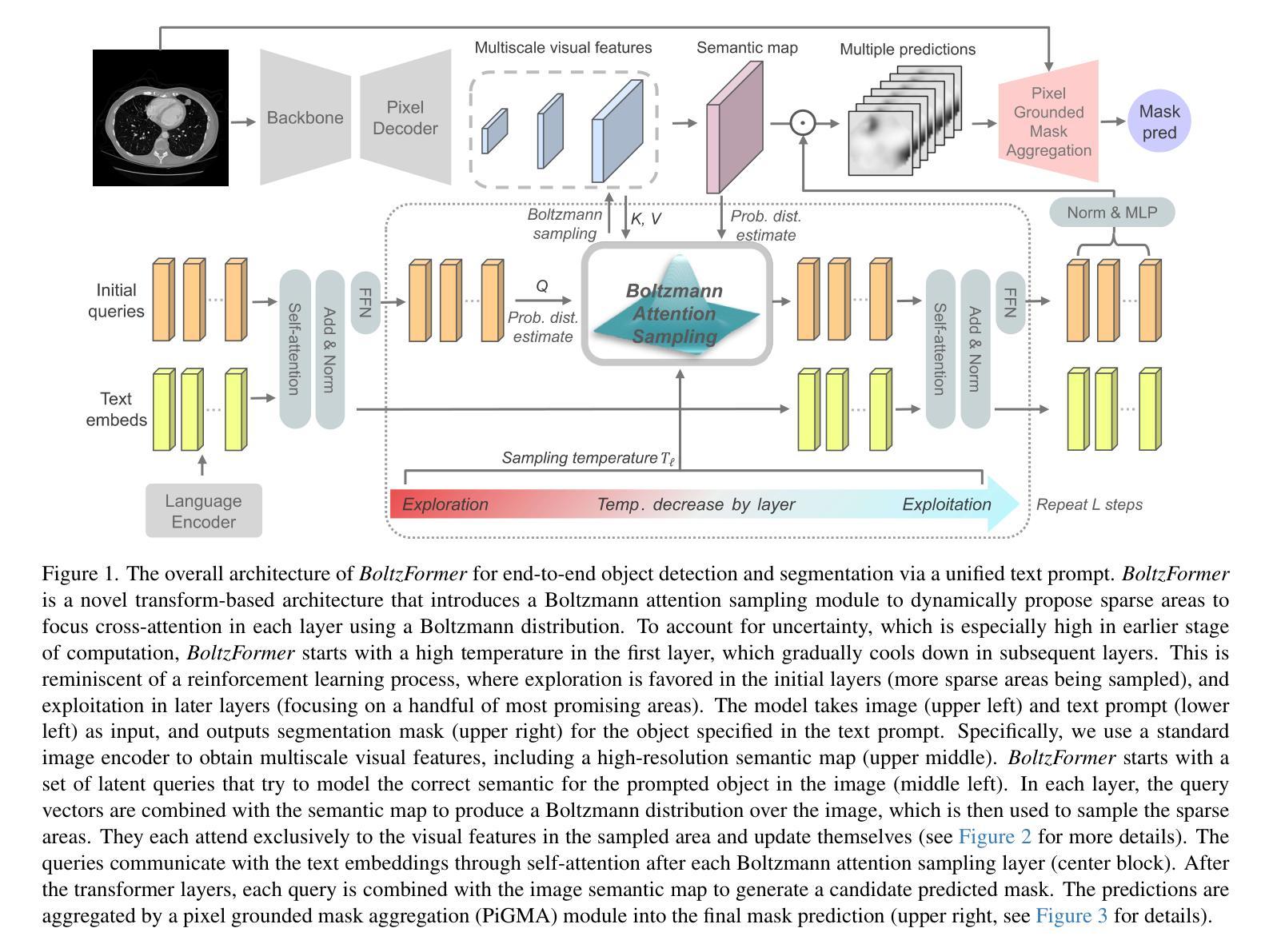
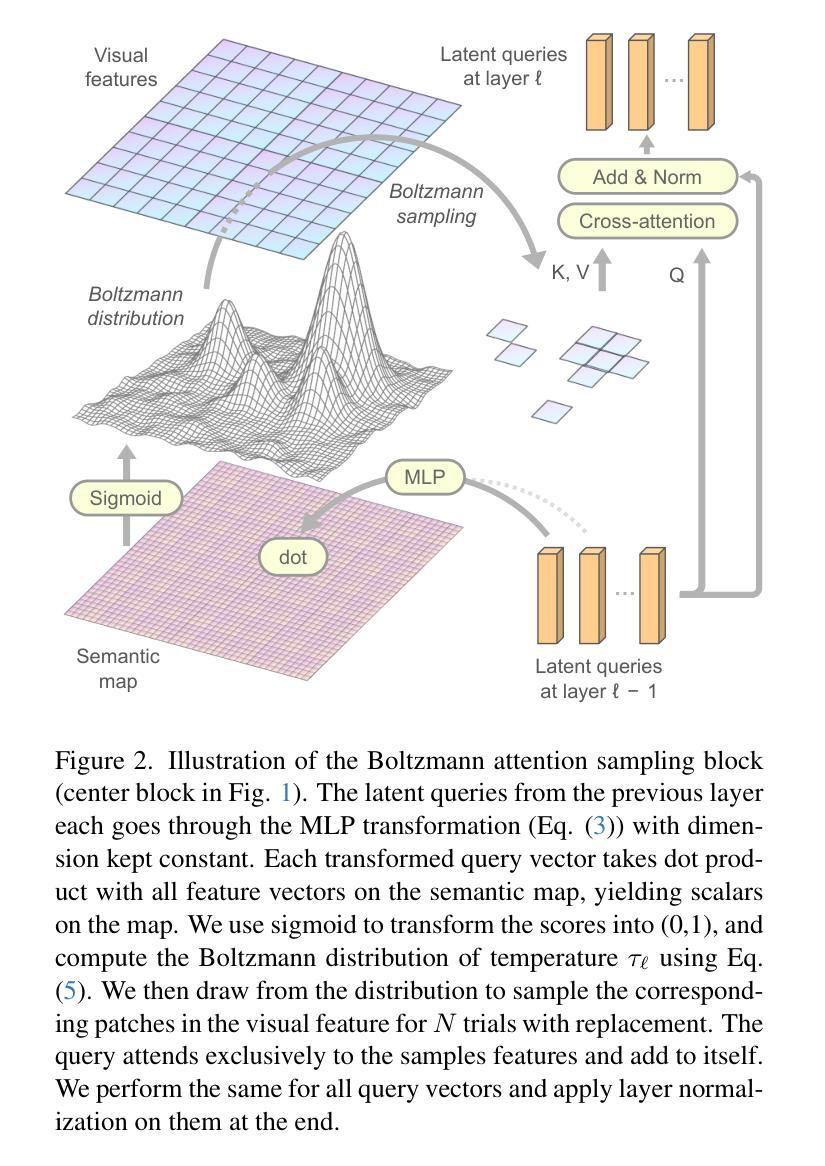
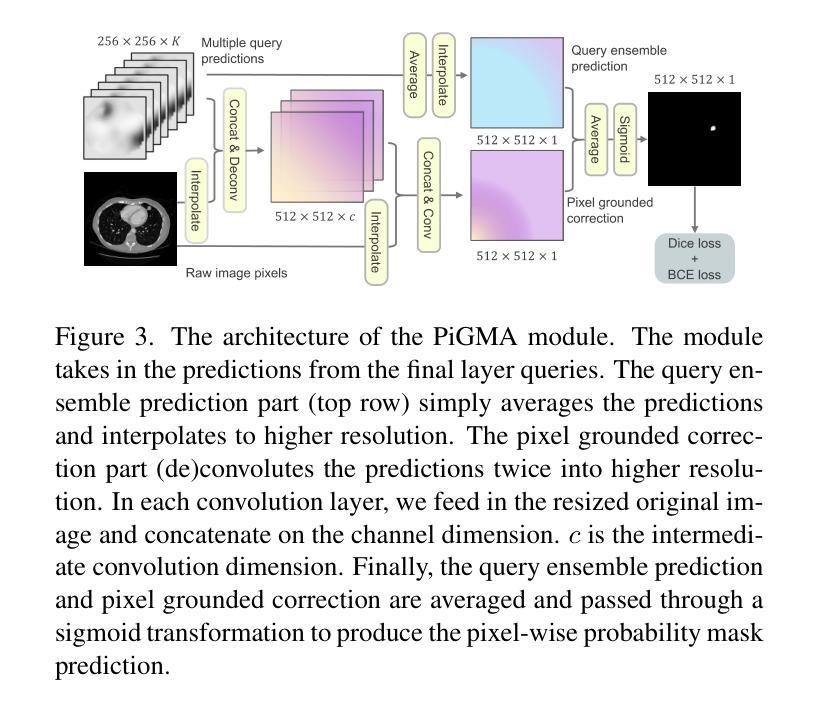
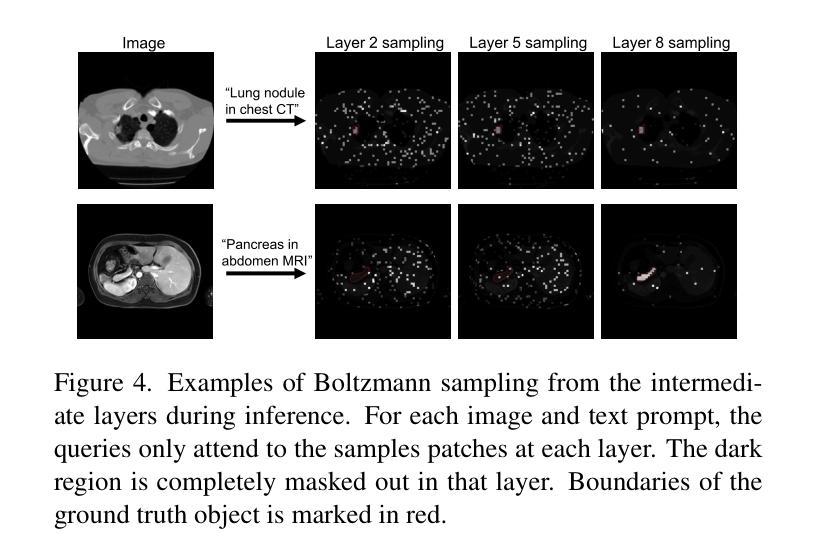
Detecting and segmenting small objects, such as lung nodules and tumor lesions, remains a critical challenge in image analysis. These objects often occupy less than 0.1% of an image, making traditional transformer architectures inefficient and prone to performance degradation due to redundant attention computations on irrelevant regions. Existing sparse attention mechanisms rely on rigid hierarchical structures, which are poorly suited for detecting small, variable, and uncertain object locations. In this paper, we propose BoltzFormer, a novel transformer-based architecture designed to address these challenges through dynamic sparse attention. BoltzFormer identifies and focuses attention on relevant areas by modeling uncertainty using a Boltzmann distribution with an annealing schedule. Initially, a higher temperature allows broader area sampling in early layers, when object location uncertainty is greatest. As the temperature decreases in later layers, attention becomes more focused, enhancing efficiency and accuracy. BoltzFormer seamlessly integrates into existing transformer architectures via a modular Boltzmann attention sampling mechanism. Comprehensive evaluations on benchmark datasets demonstrate that BoltzFormer significantly improves segmentation performance for small objects while reducing attention computation by an order of magnitude compared to previous state-of-the-art methods.
检测并分割图像中小目标物体(如肺结节和肿瘤病灶)仍然是图像分析中的一个重要挑战。这些目标物体往往仅占图像的不到0.1%,这使得传统的transformer架构因对无关紧要区域的冗余注意力计算而导致效率低下,并且容易发生性能下降。现有的稀疏注意力机制依赖于僵硬的层次结构,这对于检测位置小、多变且不确定的目标物体来说并不适合。在本文中,我们提出了BoltzFormer,这是一种基于transformer的新型架构,通过动态稀疏注意力来解决这些挑战。BoltzFormer通过利用带有退火计划的玻尔兹曼分布对不确定性进行建模来识别和集中关注相关区域。在对象位置不确定性最大的早期层中,较高的初始温度允许更大的区域采样。随着后续层中的温度降低,注意力变得更加集中,提高了效率和准确性。BoltzFormer通过模块化的玻尔兹曼注意力采样机制无缝集成到现有的transformer架构中。在基准数据集上的综合评估表明,BoltzFormer在分割小目标物体方面显著提高了性能,同时将注意力计算时间减少了数倍于现有先进技术方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于动态稀疏注意力机制的BoltzFormer模型,用于解决图像分析中检测与分割小对象(如肺结节和肿瘤病变)的挑战。该模型采用模块化设计,引入波尔兹曼注意力采样机制对图像中的小对象进行识别和定位,并在降低计算冗余的同时提高检测效率和准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 检测与分割图像中的小对象是当前图像分析领域的挑战。
- 传统transformer架构在处理小对象时存在性能下降的问题,主要原因是冗余的注意力计算和不关注区域的过度关注。
- 现有的稀疏注意力机制依赖于刚性的层次结构,难以适应检测小、可变和不确定的对象位置。
- BoltzFormer通过动态稀疏注意力机制解决这些问题,它使用波尔兹曼分布对不确定性进行建模并利用退火计划来调整关注度。
- BoltzFormer模型可以在早期层中采样更广泛的区域来应对更大的位置不确定性,随着温度降低,关注度变得更加集中以提高效率和准确性。
- BoltzFormer通过模块化设计无缝集成到现有transformer架构中。
点此查看论文截图

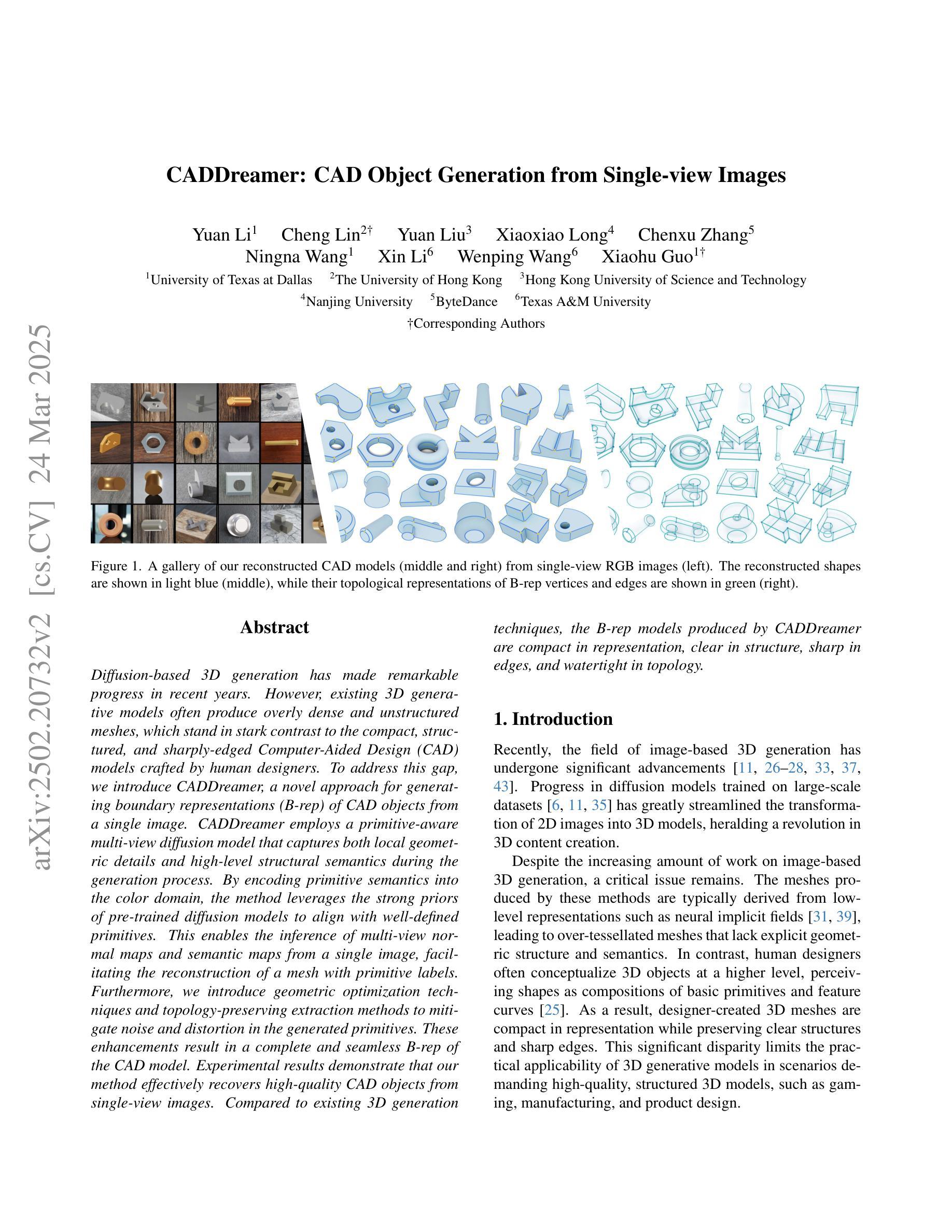
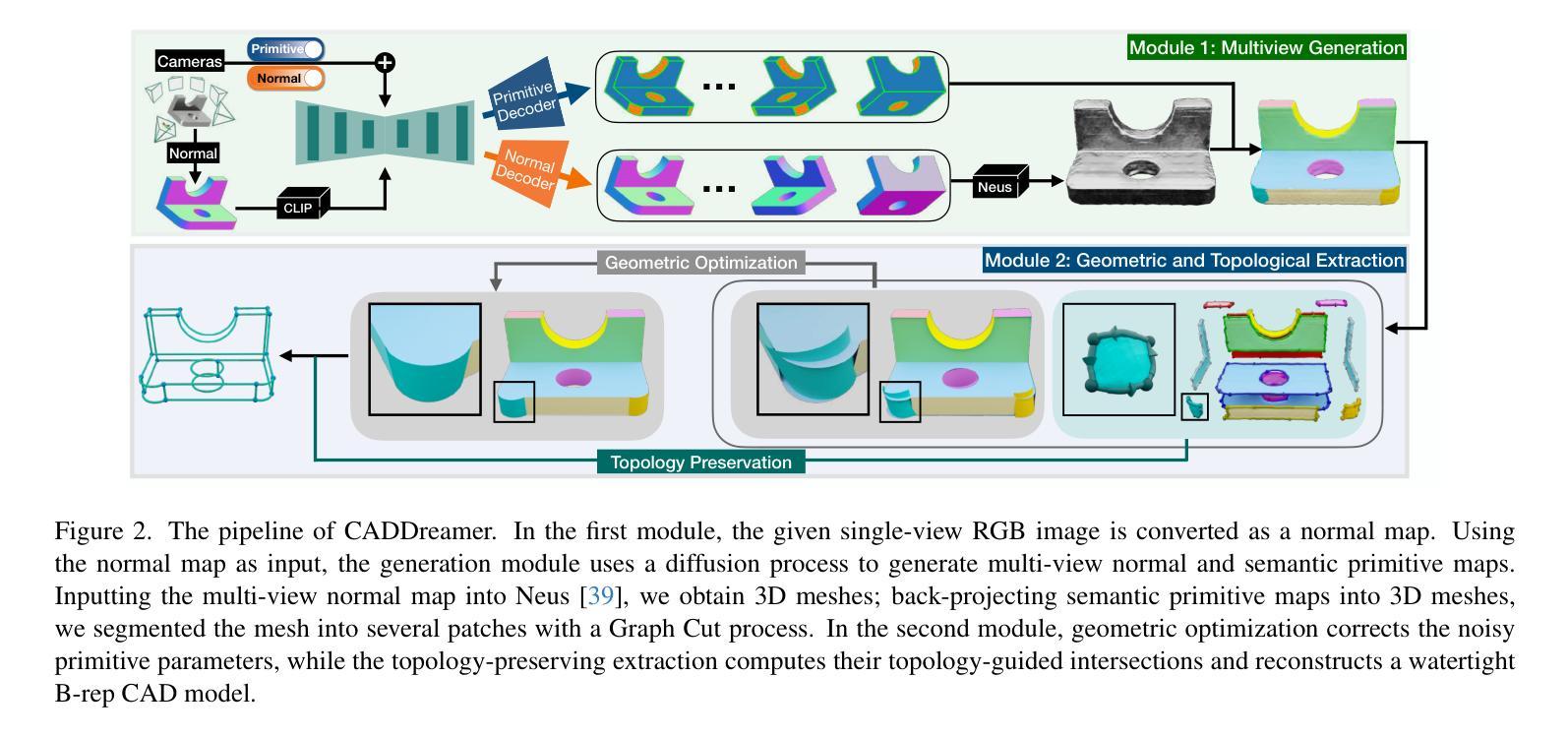
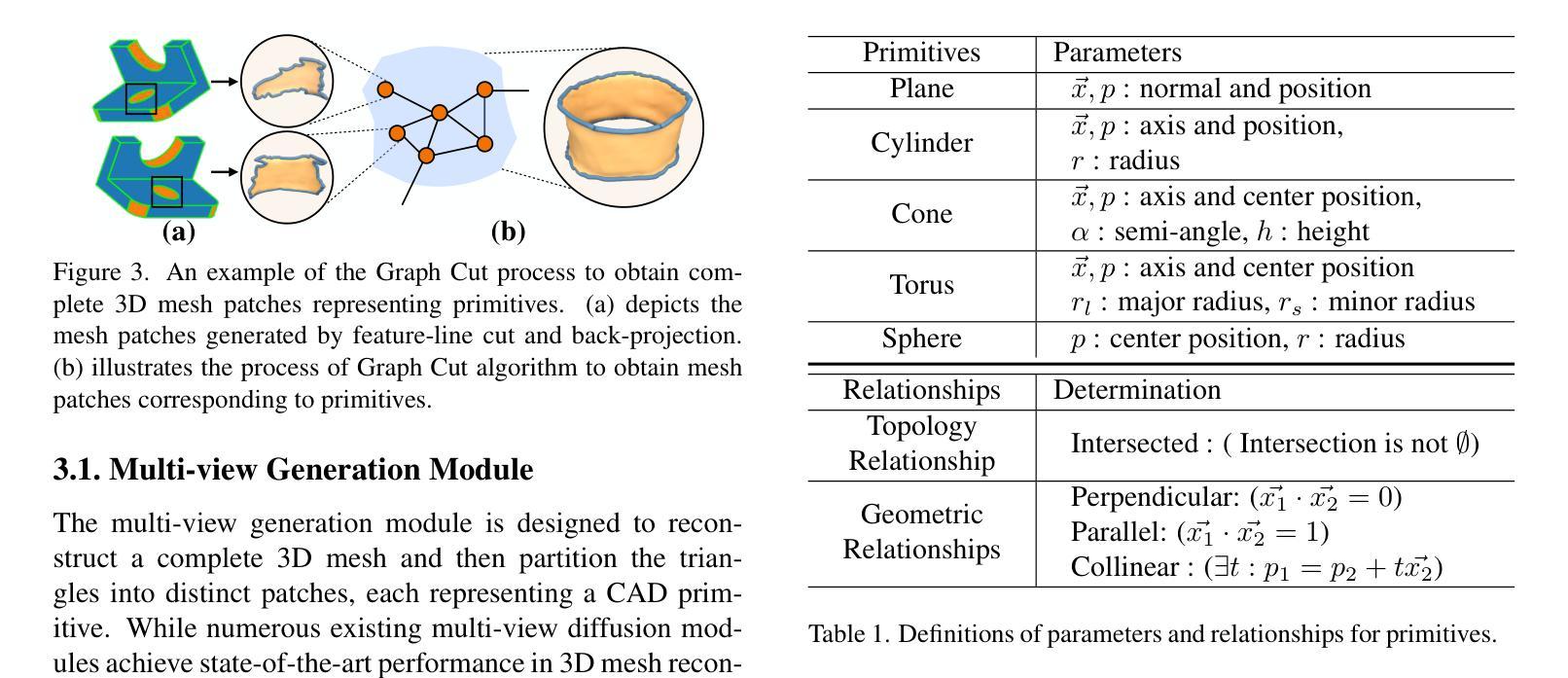
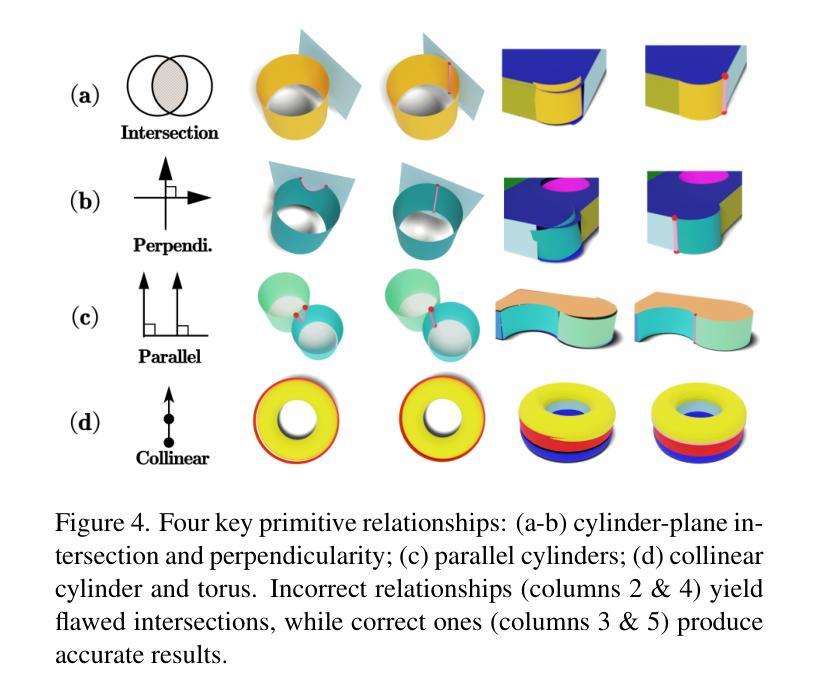
CADDreamer: CAD Object Generation from Single-view Images
Authors:Yuan Li, Cheng Lin, Yuan Liu, Xiaoxiao Long, Chenxu Zhang, Ningna Wang, Xin Li, Wenping Wang, Xiaohu Guo
Diffusion-based 3D generation has made remarkable progress in recent years. However, existing 3D generative models often produce overly dense and unstructured meshes, which stand in stark contrast to the compact, structured, and sharply-edged Computer-Aided Design (CAD) models crafted by human designers. To address this gap, we introduce CADDreamer, a novel approach for generating boundary representations (B-rep) of CAD objects from a single image. CADDreamer employs a primitive-aware multi-view diffusion model that captures both local geometric details and high-level structural semantics during the generation process. By encoding primitive semantics into the color domain, the method leverages the strong priors of pre-trained diffusion models to align with well-defined primitives. This enables the inference of multi-view normal maps and semantic maps from a single image, facilitating the reconstruction of a mesh with primitive labels. Furthermore, we introduce geometric optimization techniques and topology-preserving extraction methods to mitigate noise and distortion in the generated primitives. These enhancements result in a complete and seamless B-rep of the CAD model. Experimental results demonstrate that our method effectively recovers high-quality CAD objects from single-view images. Compared to existing 3D generation techniques, the B-rep models produced by CADDreamer are compact in representation, clear in structure, sharp in edges, and watertight in topology.
近年来,基于扩散的3D生成技术取得了显著进展。然而,现有的3D生成模型往往会产生过于密集且无结构的网格,这与人类设计师精心制作的紧凑、结构化、边缘清晰的计算机辅助设计(CAD)模型形成鲜明对比。为了解决这一差距,我们引入了CADDreamer,这是一种从单张图像生成计算机辅助设计(CAD)对象边界表示(B-rep)的新方法。CADDreamer采用了一种原始感知的多视角扩散模型,该模型在生成过程中能够捕捉局部几何细节和高级结构语义。通过将原始语义编码到颜色域中,该方法利用预训练扩散模型的强大先验知识与定义良好的原始数据对齐。这使得能够从单张图像推断多视角法线贴图和语义贴图,便于带有原始标签的网格重建。此外,我们引入了几何优化技术和拓扑保留提取方法,以减轻生成原始数据中的噪声和失真。这些增强功能导致了一个完整且无缝隙的CAD模型的B-rep。实验结果表明,我们的方法能够从单视图图像有效地恢复高质量的CAD对象。与现有的3D生成技术相比,CADDreamer产生的B-rep模型在表示上更紧凑、结构上更清晰、边缘更锋利、拓扑上更无渗漏。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
CADDreamer是一个从单张图像生成CAD对象边界表示(B-rep)的新型方法,通过采用具备原始感知能力的多视角扩散模型,结合了局部几何细节和高级结构语义。通过编码原始语义到色彩领域,并引入几何优化技术和拓扑保留提取方法,有效重建网格并带有原始标签。与现有3D生成技术相比,CADDreamer生成的B-rep模型在表示上更紧凑、结构上更清晰、边缘更锋利、拓扑更防水。
Key Takeaways
- CADDreamer是一种从单张图像生成CAD对象B-rep的新型方法。
- CADDreamer采用原始感知多视角扩散模型,结合局部几何细节和高级结构语义。
- 通过编码原始语义到色彩领域,利用预训练扩散模型的强先验知识与定义的原始相符合。
- 该方法可以推断出多视角法线和语义地图,便于从单张图像重建带有原始标签的网格。
- 引入几何优化技术和拓扑保留提取方法,减少生成原始噪声和失真。
- CADDreamer生成的B-rep模型在表示上更紧凑、结构上清晰、边缘锋利且拓扑防水。
点此查看论文截图
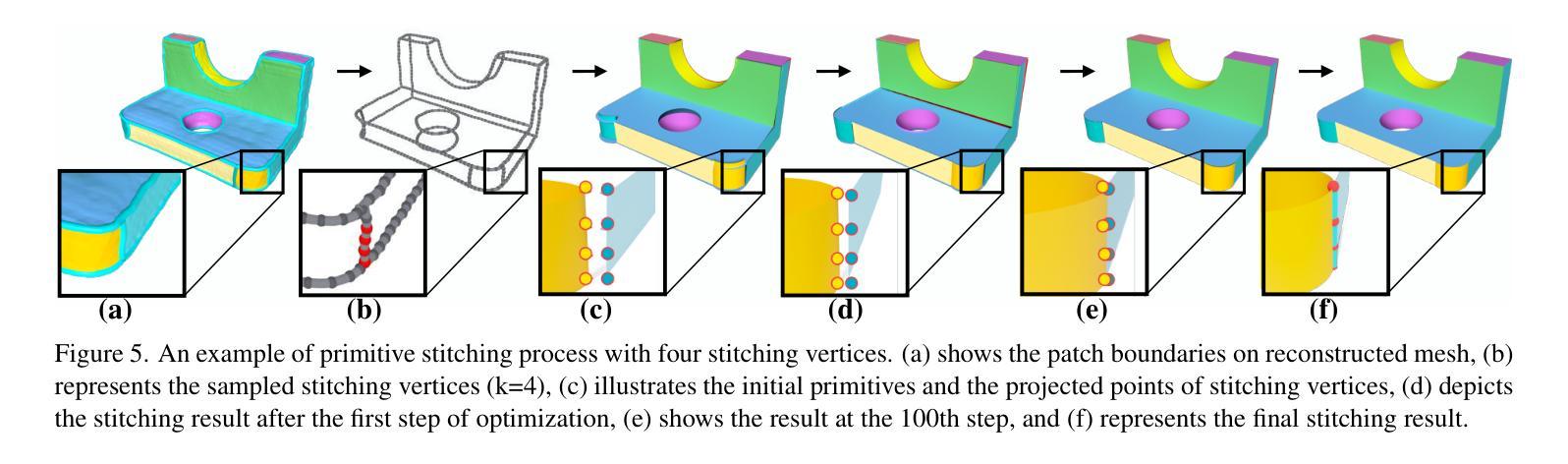
A Comparative Tutorial of the Histogram-based Image Segmentation Methods
Authors:ZhenZhou Wang
The histogram of an image is the accurate graphical representation of the numerical grayscale distribution and it is also an estimate of the probability distribution of image pixels. Therefore, histogram has been widely adopted to calculate the clustering means and partitioning thresholds for image segmentation. There have been many classical histogram-based image segmentation methods proposed and played important roles in both academics and industry. In this tutorial, the histories and recent advances of the histogram-based image segmentation techniques are first reviewed and then they are divided into four categories: (1) the means-based method, (2) the Gaussian-mixture-model-based method, (3) the entropy-based method and (4) the feature-points-based method. The purpose of this tutorial is threefold: 1) to teach the principles of the classical histogram-based image segmentation methods to the interested readers; 2) to evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of these classical histogram-based image segmentation methods objectively; 3) to compare the performances of these classical histogram-based image segmentation methods with state-of-the-art deep learning based methods objectively.
图像的直方图是数值灰度分布的准确图形表示,也是对图像像素概率分布的估计。因此,直方图已被广泛应用于计算图像分割的聚类均值和分区阈值。已有许多基于直方图的图像分割方法被提出,在学术界和工业界都发挥了重要作用。在本教程中,首先回顾了基于直方图的图像分割技术的历史和最新进展,然后将其分为四类:(1)基于均值的方法,(2)基于高斯混合模型的方法,(3)基于熵的方法和(4)基于特征点的方法。本教程的目的有三点:1)向感兴趣的读者传授基于直方图的经典图像分割方法的原理;2)客观地评估这些基于直方图的经典图像分割方法的优缺点;3)客观地比较这些基于直方图的经典图像分割方法与最新的基于深度学习的方法的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
图像直方图是灰度值分布的准确图形表示,也是图像像素概率分布的估计。直方图已被广泛应用于计算图像分割的聚类均值和分割阈值。本文首先回顾了基于直方图的图像分割技术的历史和最新进展,然后将其分为四类:(1)基于均值的方法、(2)基于高斯混合模型的方法、(3)基于熵的方法和(4)基于特征点的方法。本文的目的是:1)向感兴趣的读者传授基于直方图的经典图像分割方法的原理;2)客观地评估这些基于直方图的经典图像分割方法的优缺点;3)比较这些基于直方图的经典图像分割方法与最新的深度学习方法的效果。
Key Takeaways
- 图像直方图是灰度值分布的准确图形表示,也是图像像素概率分布的估计。
- 直方图已被广泛应用于计算图像分割的聚类均值和分割阈值。
- 基于直方图的图像分割方法分为四类:基于均值、基于高斯混合模型、基于熵和基于特征点的方法。
- 本文旨在传授基于直方图的经典图像分割方法的原理。
- 文章客观地评估了基于直方图的经典图像分割方法的优缺点。
- 本文比较了基于直方图的经典图像分割方法与深度学习方法的效果。
点此查看论文截图

Tool or Tutor? Experimental evidence from AI deployment in cancer diagnosis
Authors:Vivianna Fang He, Sihan Li, Phanish Puranam, Feng Lin
Professionals increasingly use Artificial Intelligence (AI) to enhance their capabilities and assist with task execution. While prior research has examined these uses separately, their potential interaction remains underexplored. We propose that AI-driven training (“tutor”) and AI-assisted task completion (“tool”) can have a joint effect on human capability and test this hypothesis in the context of lung cancer diagnosis. In a field experiment with 336 medical students, we manipulated AI deployment in training, in practice, and in both. Our findings reveal that while AI-integrated training and AI assistance independently improved diagnostic performance, their combination yielded the highest accuracy. These results underscore AI’s dual role in enhancing human performance through both learning and real-time support, offering insights into AI deployment in professional settings where human expertise remains essential.
专业人员越来越多地使用人工智能(AI)来增强自身能力并辅助执行任务。虽然之前的研究已经分别研究了这些用途,但它们之间的潜在交互仍然被忽视。我们提出人工智能驱动的训练(“导师”)和人工智能辅助的任务完成(“工具”)可以对人类能力产生联合效应,并在肺癌诊断的背景下测试这一假设。在一项由336名医学生参加的现场实验中,我们对培训、实践和两者都涉及的人工智能部署进行了操作。我们的研究发现,虽然人工智能集成培训和人工智能辅助独立提高了诊断性能,但它们的组合却获得了最高的准确率。这些结果强调了人工智能通过学习和实时支持增强人类性能的双重作用,为在仍需要人类专业知识的情况下在专业环境中部署人工智能提供了见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人工智能(AI)在医疗领域的应用日益广泛,本文探讨了AI驱动的培训(导师)和AI辅助任务完成(工具)的联合效应,特别是在肺癌诊断方面的应用。通过对336名医学专业的学生进行实地实验,发现AI集成培训和AI辅助支持能各自提高诊断性能,二者的结合使用能达到最高准确率。这表明AI在提升人类表现方面扮演着双重角色,既可以通过学习提升能力,也可以在实时支持方面发挥优势。在专业环境中部署AI时,应结合两者来发挥AI的最大效用。同时应继续利用人工智能技术不断提高诊断准确性,同时确保人类专家的作用得到充分发挥。
Key Takeaways
- AI在医疗领域的应用逐渐普及,尤其在肺癌诊断方面发挥了重要作用。
- AI驱动的培训(导师)和AI辅助任务完成(工具)在提高诊断性能方面具有联合效应。
- 通过实地实验发现,AI集成培训和AI辅助支持各自能够提高诊断性能,二者结合使用能达到最高准确率。
- AI在提高人类表现方面扮演着双重角色,既可以通过学习提升能力,也可以在实时支持方面发挥优势。
点此查看论文截图