⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-05 更新
Adaptive Frequency Enhancement Network for Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Feng Gao, Miao Fu, Jingchao Cao, Junyu Dong, Qian Du
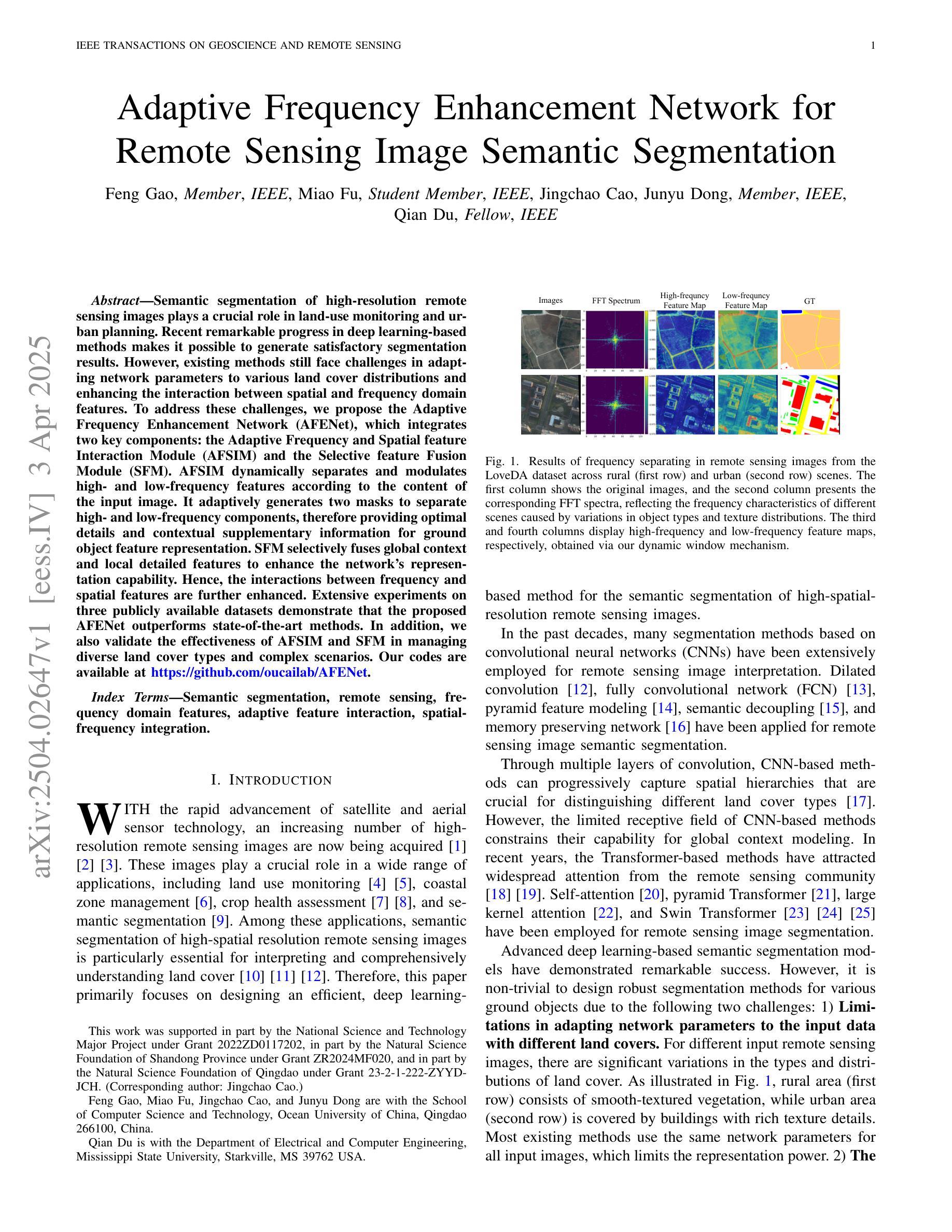
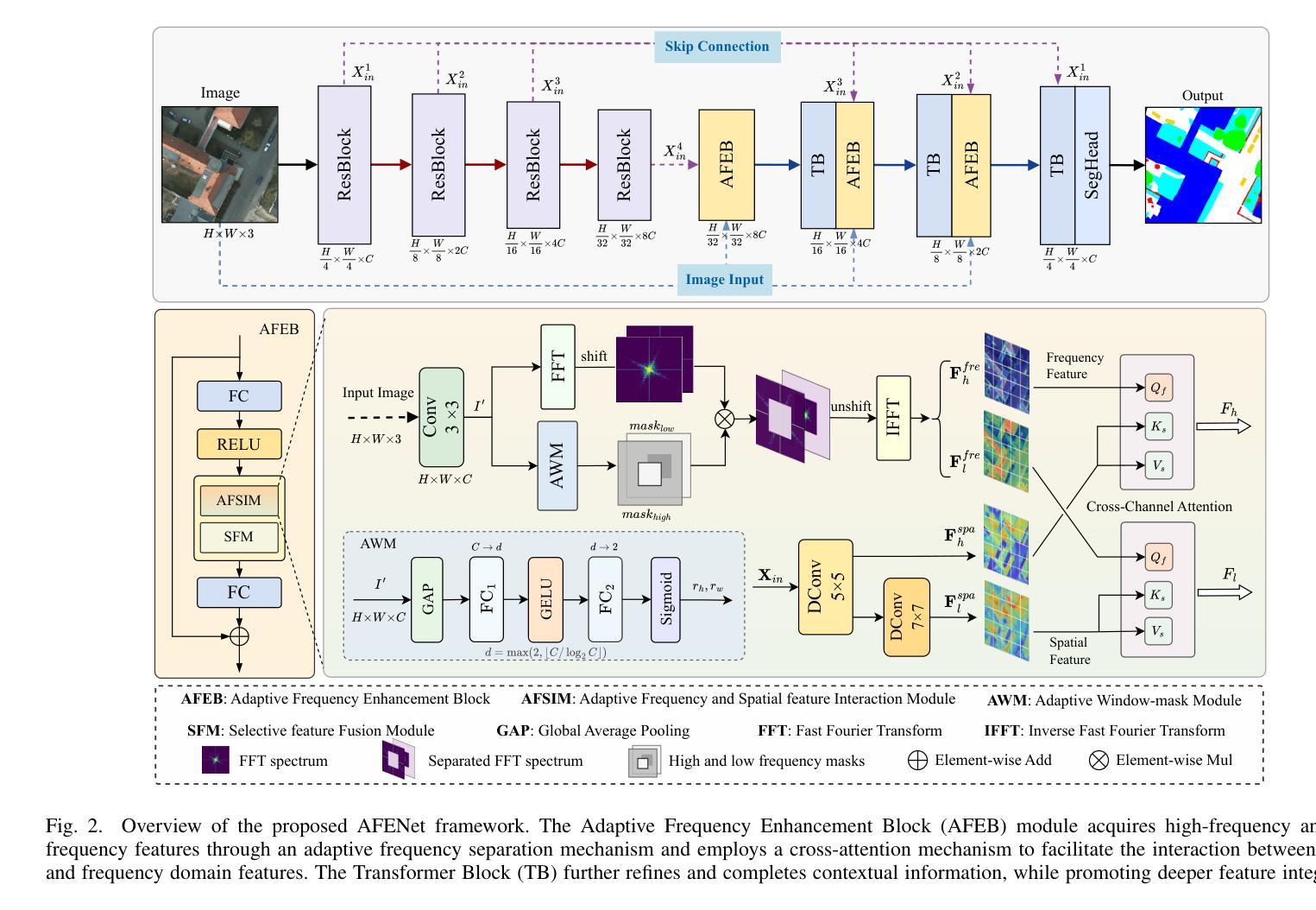
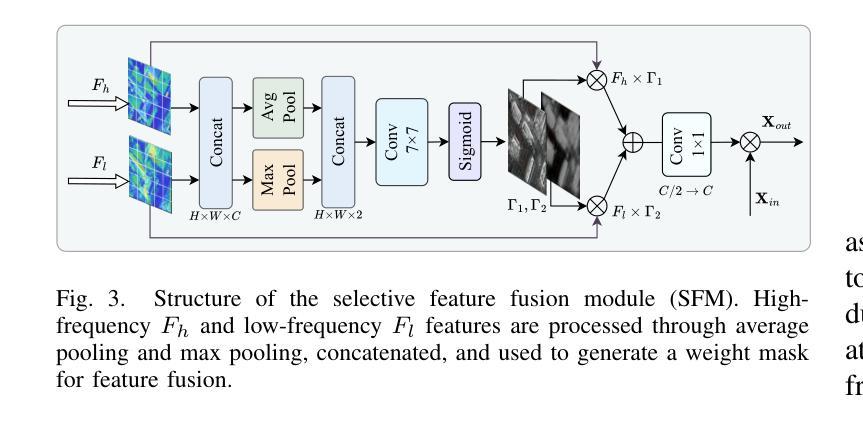
Semantic segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing images plays a crucial role in land-use monitoring and urban planning. Recent remarkable progress in deep learning-based methods makes it possible to generate satisfactory segmentation results. However, existing methods still face challenges in adapting network parameters to various land cover distributions and enhancing the interaction between spatial and frequency domain features. To address these challenges, we propose the Adaptive Frequency Enhancement Network (AFENet), which integrates two key components: the Adaptive Frequency and Spatial feature Interaction Module (AFSIM) and the Selective feature Fusion Module (SFM). AFSIM dynamically separates and modulates high- and low-frequency features according to the content of the input image. It adaptively generates two masks to separate high- and low-frequency components, therefore providing optimal details and contextual supplementary information for ground object feature representation. SFM selectively fuses global context and local detailed features to enhance the network’s representation capability. Hence, the interactions between frequency and spatial features are further enhanced. Extensive experiments on three publicly available datasets demonstrate that the proposed AFENet outperforms state-of-the-art methods. In addition, we also validate the effectiveness of AFSIM and SFM in managing diverse land cover types and complex scenarios. Our codes are available at https://github.com/oucailab/AFENet.
高分辨率遥感影像的语义分割在土地利用监测和城市规划中扮演着至关重要的角色。最近基于深度学习的方法的显著进步使得生成令人满意的分割结果成为可能。然而,现有方法仍然面临着适应网络参数以应对各种土地覆盖分布以及增强空间域和频域特征之间交互的挑战。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了自适应频率增强网络(AFENet),它集成了两个关键组件:自适应频率和空间特征交互模块(AFSIM)和选择性特征融合模块(SFM)。AFSIM根据输入图像的内容动态分离和调制高频和低频特征。它自适应地生成两个掩膜来分离高频和低频组件,从而为地面对象特征表示提供最佳细节和上下文补充信息。SFM选择性融合全局上下文和局部详细特征,以增强网络的表示能力。因此,频率和空间特征之间的交互得到了进一步增强。在三个公开数据集上的大量实验表明,所提出的AFENet优于最先进的方法。此外,我们还验证了AFSIM和SFM在处理多种土地覆盖类型和复杂场景方面的有效性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/oucailab/AFENet上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE TGRS 2025
Summary
基于深度学习的语义分割在高分辨率遥感图像中扮演重要角色,在土地监测和城市规划中发挥着关键作用。然而,现有方法在处理不同土地覆盖分布和增强空间与频域特征交互方面面临挑战。为解决这些问题,提出了自适应频率增强网络(AFENet),包括自适应频率和空间特征交互模块(AFSIM)和选择性特征融合模块(SFM)。AFSIM可根据输入图像内容动态分离和调制高低频特征,为地面目标特征表示提供最佳细节和上下文补充信息。SFM选择性融合全局上下文和局部详细特征,提高网络的表示能力。实验表明,AFENet在三个公开数据集上的性能优于现有先进方法。同时验证了AFSIM和SFM在处理不同土地覆盖类型和复杂场景中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 语义分割在高分辨率遥感图像中对土地监测和城市规划至关重要。
- 现有方法在处理不同土地覆盖分布时面临挑战,并需要增强特征与特征的交互。
- AFENet通过AFSIM和SFM两个关键组件来解决这些问题。
- AFSIM能自适应分离高低频特征,为地面目标特征表示提供最佳细节和上下文信息。
- SFM通过选择性融合全局和局部特征来增强网络表示能力。
- AFENet在多个公开数据集上的性能优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图
Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Images Salient Object Detection: The First Benchmark Dataset and Baseline
Authors:Peifu Liu, Huiyan Bai, Tingfa Xu, Jihui Wang, Huan Chen, Jianan Li
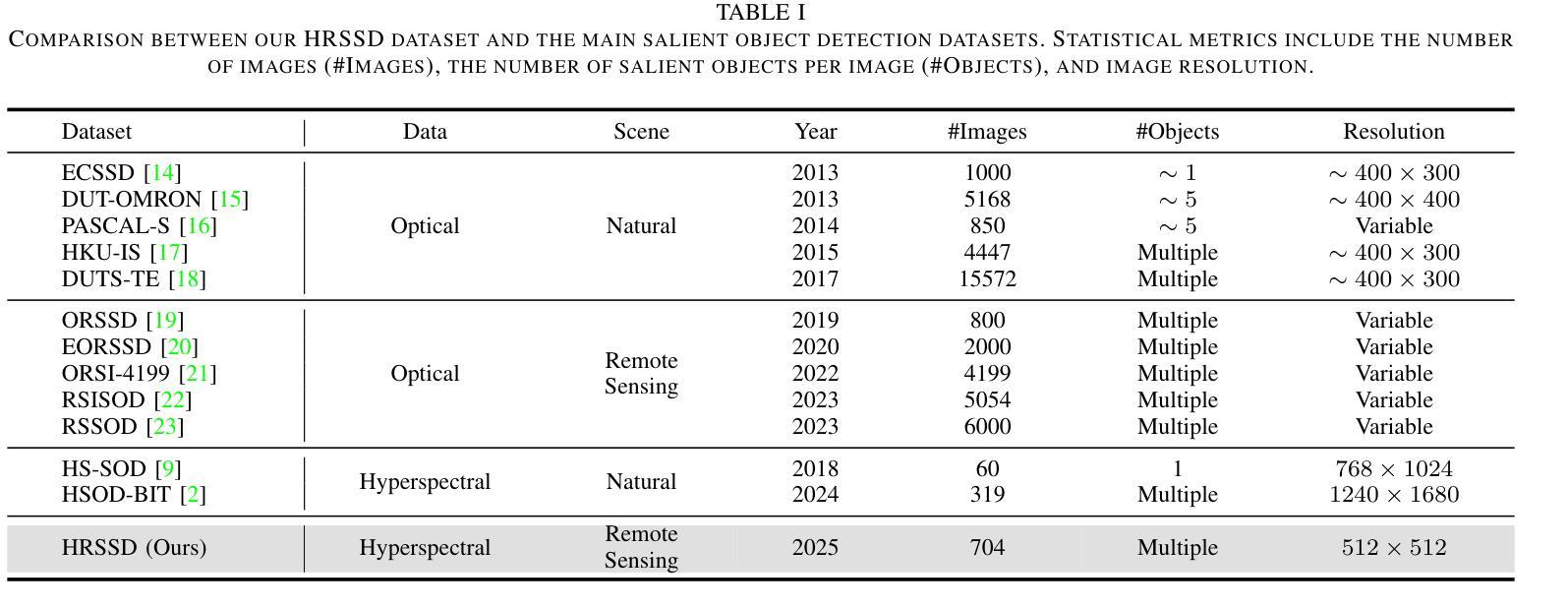
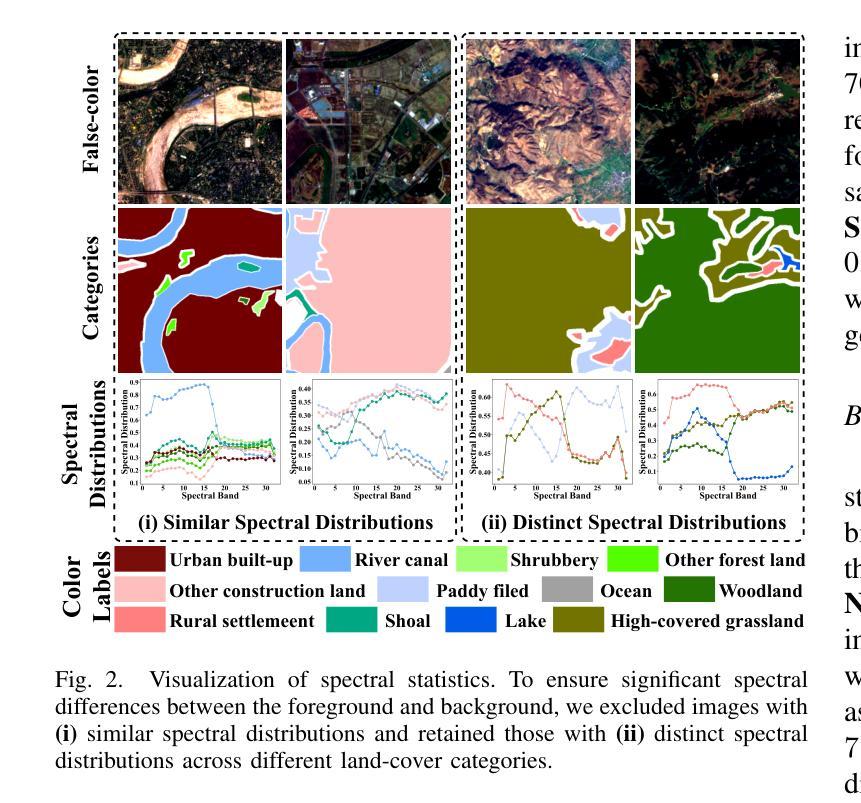
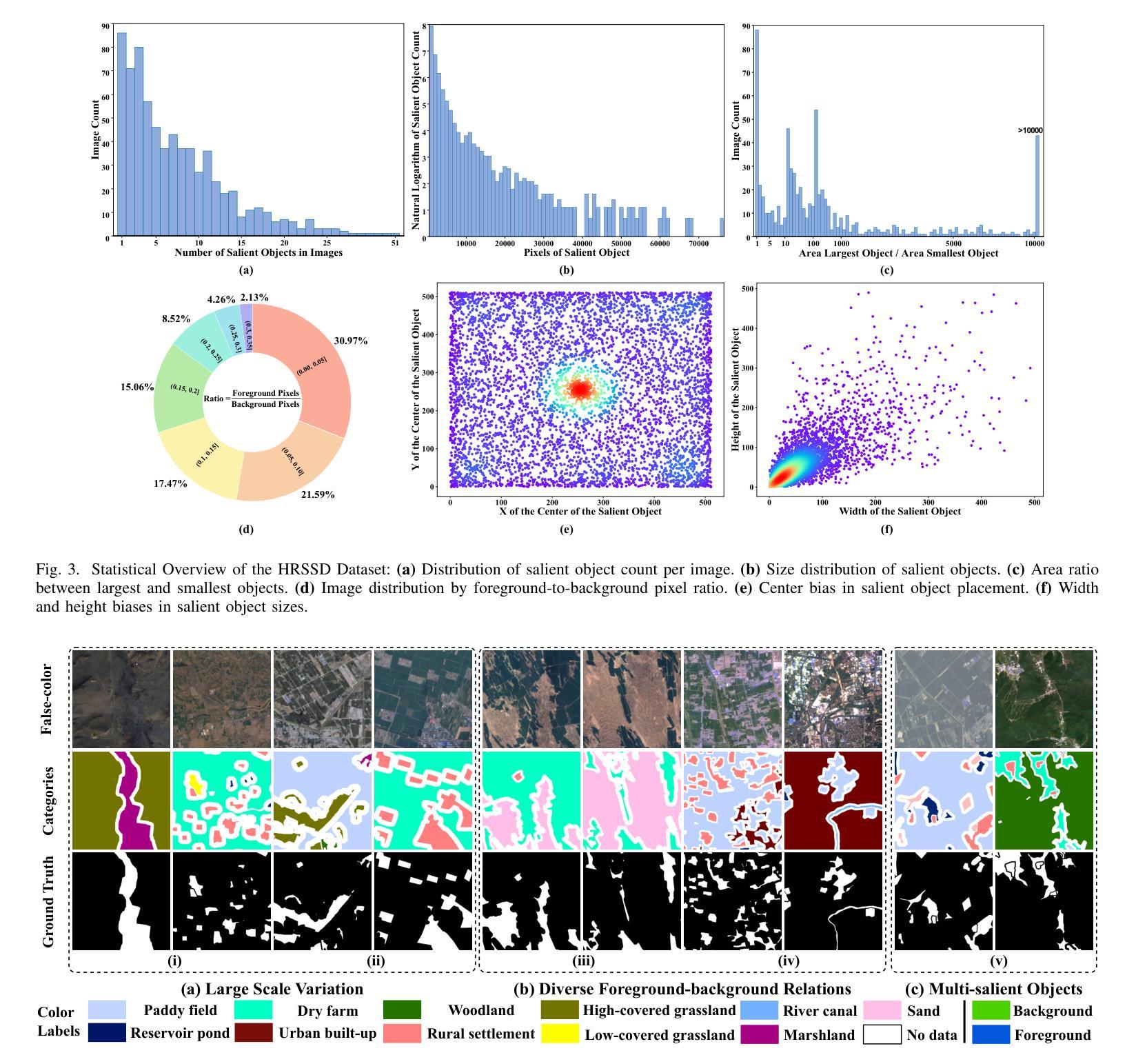
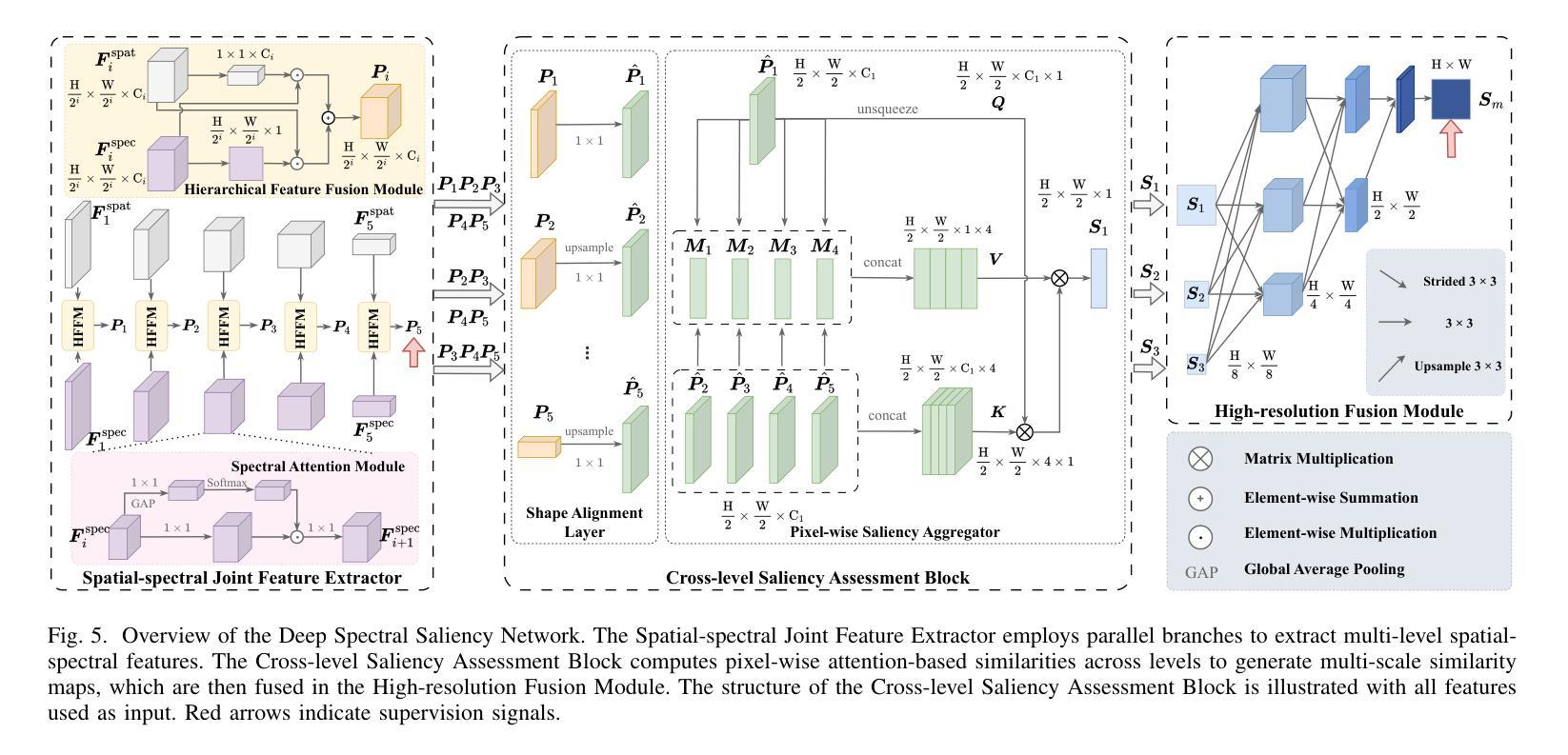
The objective of hyperspectral remote sensing image salient object detection (HRSI-SOD) is to identify objects or regions that exhibit distinct spectrum contrasts with the background. This area holds significant promise for practical applications; however, progress has been limited by a notable scarcity of dedicated datasets and methodologies. To bridge this gap and stimulate further research, we introduce the first HRSI-SOD dataset, termed HRSSD, which includes 704 hyperspectral images and 5327 pixel-level annotated salient objects. The HRSSD dataset poses substantial challenges for salient object detection algorithms due to large scale variation, diverse foreground-background relations, and multi-salient objects. Additionally, we propose an innovative and efficient baseline model for HRSI-SOD, termed the Deep Spectral Saliency Network (DSSN). The core of DSSN is the Cross-level Saliency Assessment Block, which performs pixel-wise attention and evaluates the contributions of multi-scale similarity maps at each spatial location, effectively reducing erroneous responses in cluttered regions and emphasizes salient regions across scales. Additionally, the High-resolution Fusion Module combines bottom-up fusion strategy and learned spatial upsampling to leverage the strengths of multi-scale saliency maps, ensuring accurate localization of small objects. Experiments on the HRSSD dataset robustly validate the superiority of DSSN, underscoring the critical need for specialized datasets and methodologies in this domain. Further evaluations on the HSOD-BIT and HS-SOD datasets demonstrate the generalizability of the proposed method. The dataset and source code are publicly available at https://github.com/laprf/HRSSD.
高光谱遥感图像显著目标检测(HRSI-SOD)的目标是识别与背景具有明显光谱对比的对象或区域。这个领域在实际应用方面前景广阔,然而由于专用数据集和方法论的匮乏,研究进展受到限制。为了弥补这一差距并促进进一步研究,我们引入了第一个HRSI-SOD数据集,称为HRSSD,其中包括704幅高光谱图像和5327个像素级注释的显著目标。HRSSD数据集为显著目标检测算法带来了重大挑战,由于大规模变异、多样化的前景背景关系和多个显著目标。此外,我们提出了一个用于HRSI-SOD的创新且高效的基线模型,称为深度谱显著性网络(DSSN)。DSSN的核心是跨级显著性评估块,它执行像素级注意,评估每个空间位置上多尺度相似图的贡献,有效地减少了杂乱区域的错误响应,并强调了跨尺度的显著区域。此外,高分辨率融合模块结合了自下而上的融合策略和学习的空间上采样,以利用多尺度显著性图的优势,确保小目标的准确定位。在HRSSD数据集上的实验稳健地验证了DSSN的优越性,突显了该领域对专用数据集和方法论的关键需求。在HSOD-BIT和HS-SOD数据集上的进一步评估证明了该方法的通用性。数据集和源代码可在https://github.com/laprf/HRSSD公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by TGRS 2025
Summary
推出首个针对高光谱遥感图像显著目标检测(HRSI-SOD)的专用数据集HRSSD,包含704张高光谱图像和5327个像素级标注的显著目标。同时,提出高效基线模型DSSN,包含跨级显著性评估模块与高分融合模块,可在复杂背景下有效识别显著目标。模型在HRSSD数据集上表现优越,且在HSOD-BIT与HS-SOD数据集上具有泛化性。数据集及源代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- HRSSD数据集是首个针对高光谱遥感图像显著目标检测(HRSI-SOD)的专用数据集。
- HRSSD包含704张高光谱图像和5327个像素级标注的显著目标。
- DSSN模型包含跨级显著性评估模块,能有效减少杂乱区域的误响应并强调跨尺度的显著区域。
- DSSN模型的高分辨率融合模块结合了自下而上的融合策略和学习的空间上采样,利用多尺度显著性地图的优势,确保小目标的准确定位。
- DSSN模型在HRSSD数据集上的表现经过实验验证优于其他方法。
- DSSN模型在HSOD-BIT和HS-OD数据集上具有泛化性。
点此查看论文截图

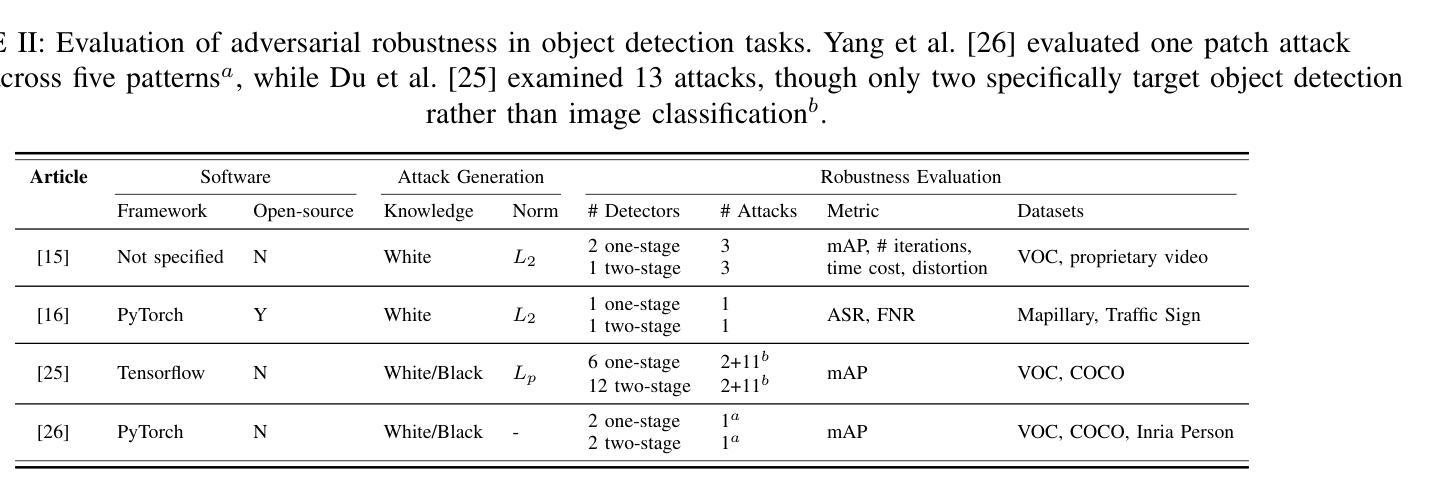
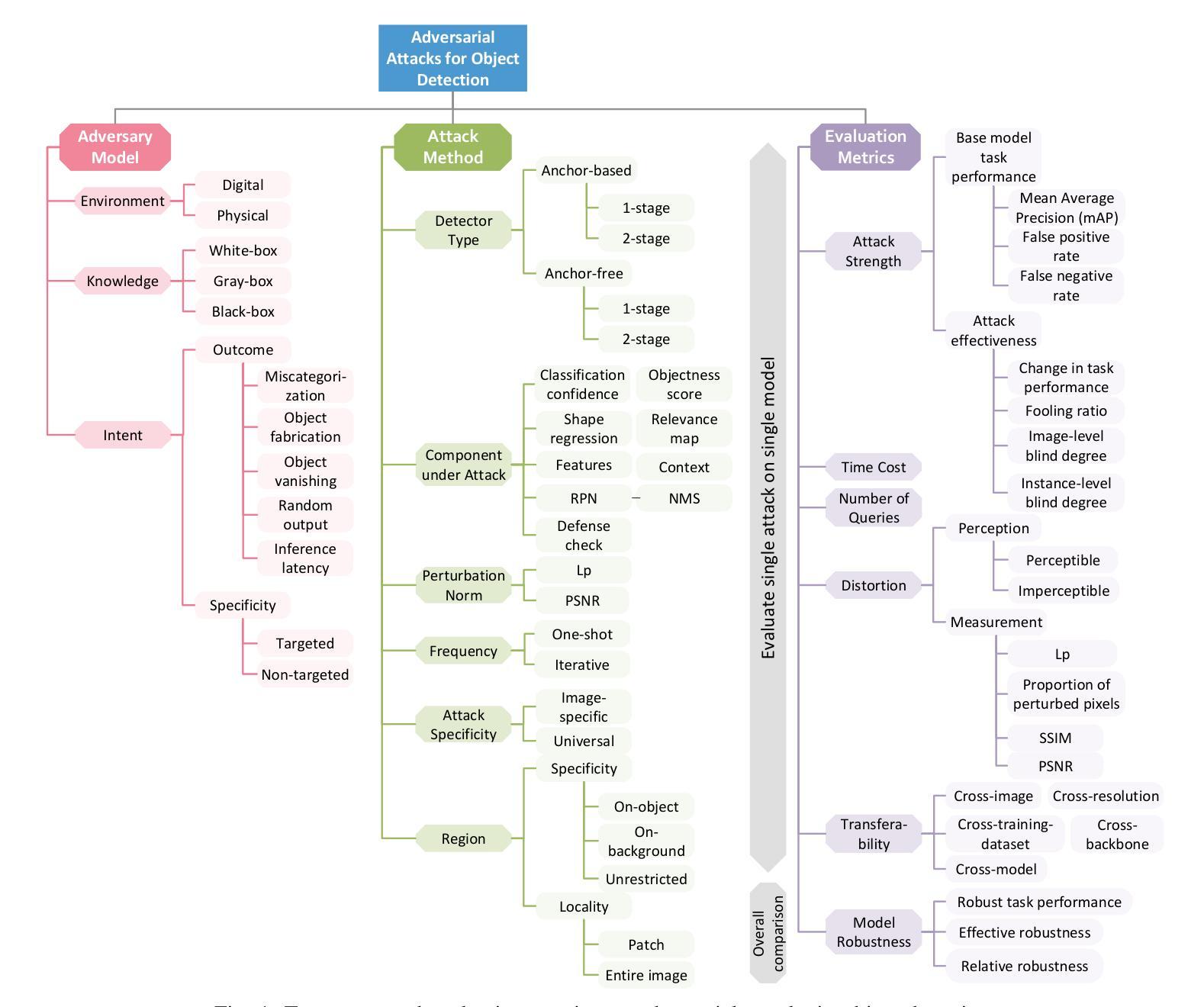
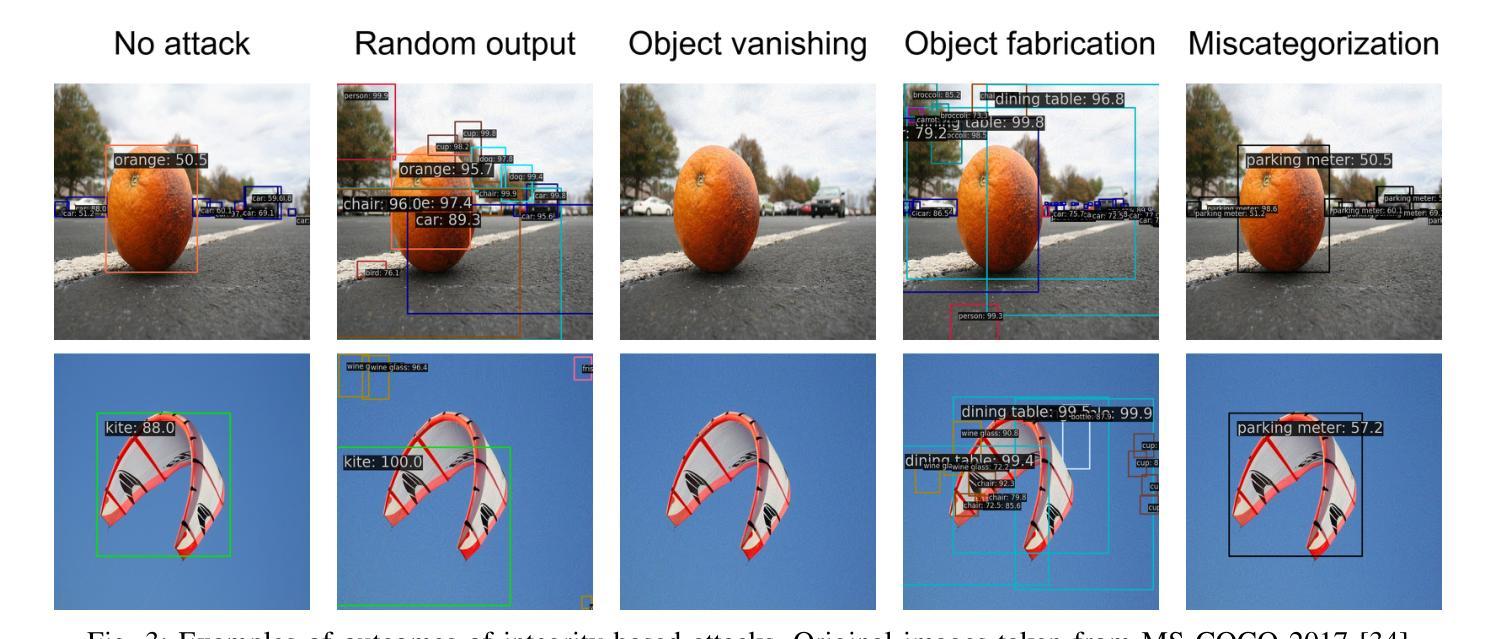
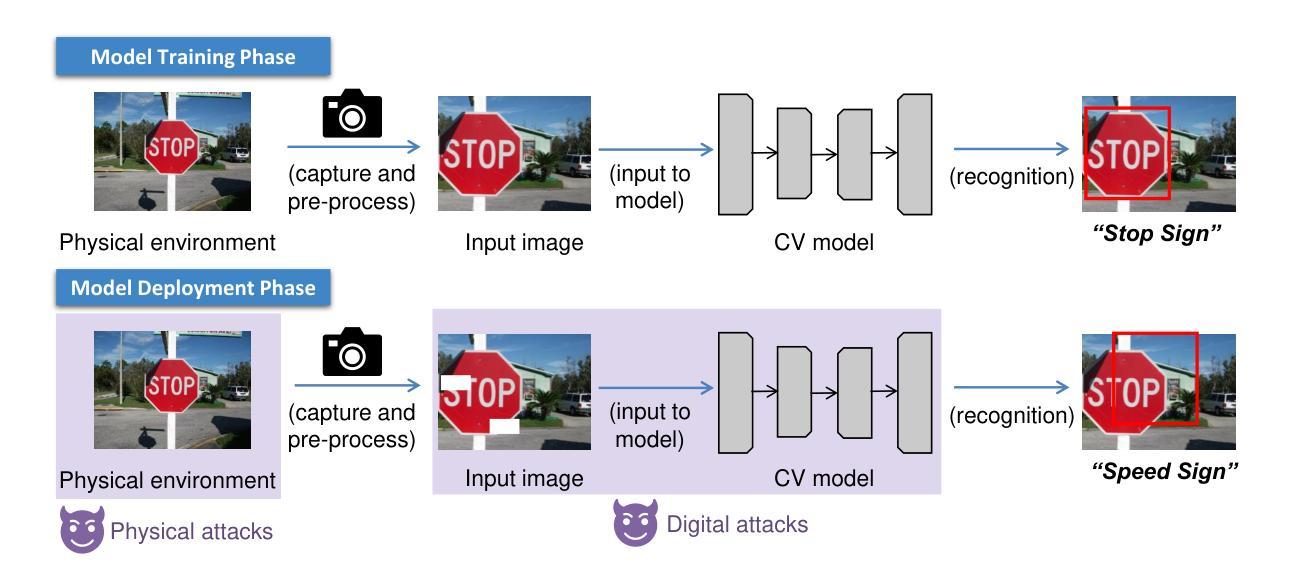
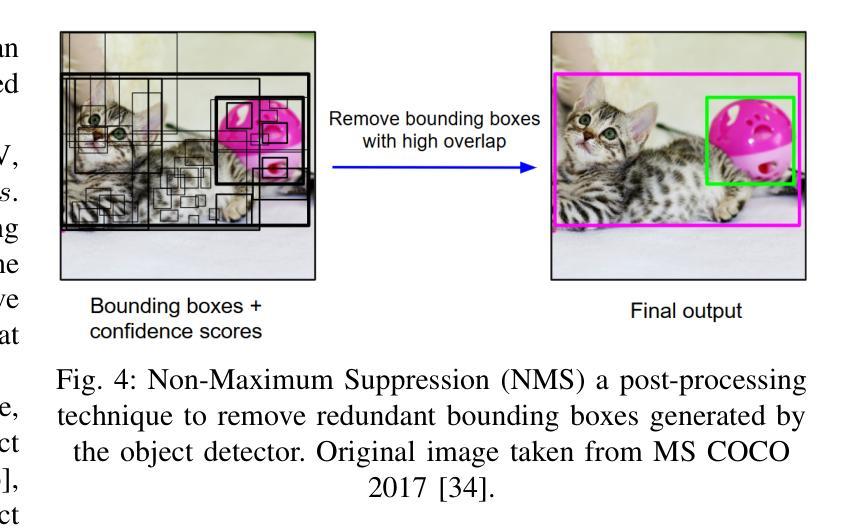
A Survey and Evaluation of Adversarial Attacks for Object Detection
Authors:Khoi Nguyen Tiet Nguyen, Wenyu Zhang, Kangkang Lu, Yuhuan Wu, Xingjian Zheng, Hui Li Tan, Liangli Zhen
Deep learning models achieve remarkable accuracy in computer vision tasks, yet remain vulnerable to adversarial examples–carefully crafted perturbations to input images that can deceive these models into making confident but incorrect predictions. This vulnerability pose significant risks in high-stakes applications such as autonomous vehicles, security surveillance, and safety-critical inspection systems. While the existing literature extensively covers adversarial attacks in image classification, comprehensive analyses of such attacks on object detection systems remain limited. This paper presents a novel taxonomic framework for categorizing adversarial attacks specific to object detection architectures, synthesizes existing robustness metrics, and provides a comprehensive empirical evaluation of state-of-the-art attack methodologies on popular object detection models, including both traditional detectors and modern detectors with vision-language pretraining. Through rigorous analysis of open-source attack implementations and their effectiveness across diverse detection architectures, we derive key insights into attack characteristics. Furthermore, we delineate critical research gaps and emerging challenges to guide future investigations in securing object detection systems against adversarial threats. Our findings establish a foundation for developing more robust detection models while highlighting the urgent need for standardized evaluation protocols in this rapidly evolving domain.
深度学习模型在计算机视觉任务中取得了令人瞩目的准确性,但仍然容易受到对抗样本的威胁。对抗样本是对输入图像进行精心制作的扰动,可以欺骗这些模型做出自信但错误的预测。这种脆弱性在高风险应用(如自动驾驶、安全监控和关键安全检测系统)中构成了重大风险。尽管现有文献广泛涵盖了图像分类中的对抗性攻击,但对目标检测系统中此类攻击的综合分析仍然有限。本文提出了一个针对目标检测架构的对抗性攻击的新型分类框架,综合了现有的稳健性指标,并对流行目标检测模型上的最新攻击方法进行了全面的实证评估,包括传统检测器和具有视觉语言预训练的现代检测器。通过对开源攻击实现及其在不同检测架构中的有效性进行严谨分析,我们获得了关于攻击特性的关键见解。此外,我们指出了关键的研究差距和新兴挑战,为未来的研究在保护目标检测系统免受对抗性威胁方面提供了指导。我们的研究为开发更稳健的检测模型奠定了基础,同时强调了在这一快速发展的领域中迫切需要标准化评估协议。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages
Summary
深度学习模型在计算机视觉任务中取得了令人瞩目的准确性,但仍易受到对抗性示例的威胁。对抗性示例是对输入图像进行精心设计的扰动,可以欺骗模型做出自信但错误的预测。这种脆弱性在高风险应用(如自动驾驶、安全监控和关键安全检查系统)中构成了重大风险。尽管现有文献广泛涵盖了图像分类中的对抗性攻击,但对于目标检测系统遭受的对抗性攻击的综合分析仍然有限。本文提出一个新的分类框架,专门针对目标检测架构的对抗性攻击进行分类,并总结了现有的稳健性度量指标。同时,我们对流行的目标检测模型进行了全面的实证评估,包括传统检测器以及具有视觉语言预训练的现代检测器。通过对开源攻击实现进行严谨分析,以及在多种检测架构上的有效性评估,我们获得了关于攻击特性的关键见解。此外,我们还指出了关键的研究空白和新兴挑战,为未来在保护目标检测系统免受对抗性威胁方面的调查提供了指导。我们的研究为开发更稳健的检测模型奠定了基础,同时强调了这一快速发展领域中标准化评估协议紧迫需求的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 对抗性示例可以欺骗深度学习模型做出错误预测。
- 目标检测系统面临对抗性攻击的风险,相关研究仍有限。
- 本文提出了针对目标检测架构的对抗性攻击的分类框架。
- 论文总结了现有的稳健性度量指标并进行了实证评估。
- 评估涉及多种目标检测模型,包括传统和现代模型。
- 研究指出了攻击特性的关键见解。
点此查看论文截图