⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-05 更新
CHARMS: Cognitive Hierarchical Agent with Reasoning and Motion Styles
Authors:Jingyi Wang, Duanfeng Chu, Zejian Deng, Liping Lu
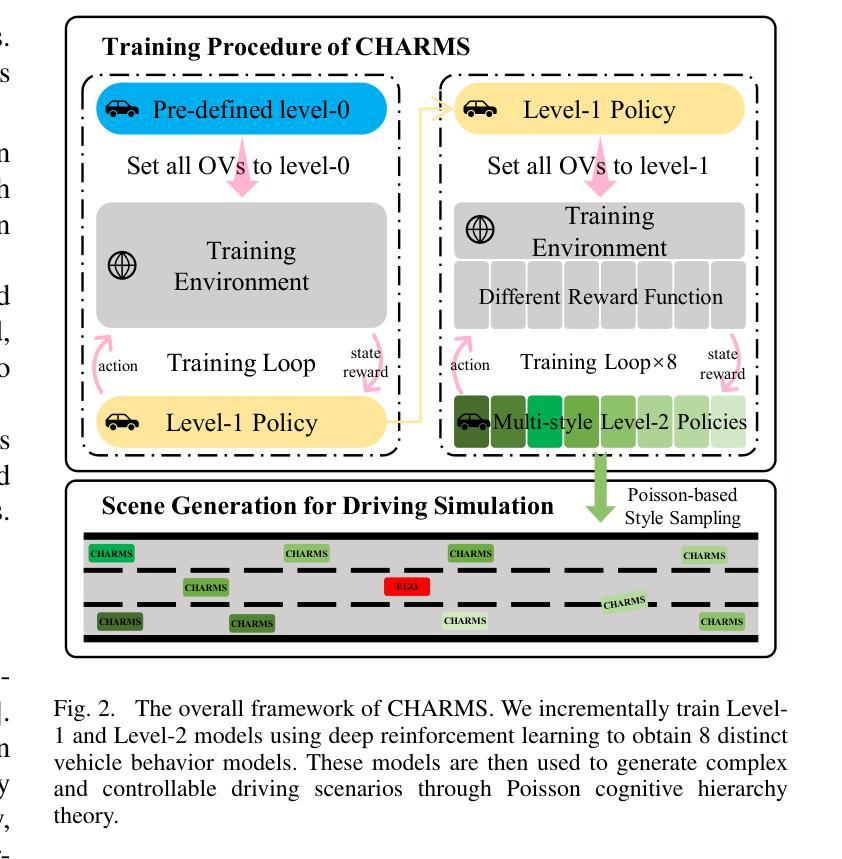
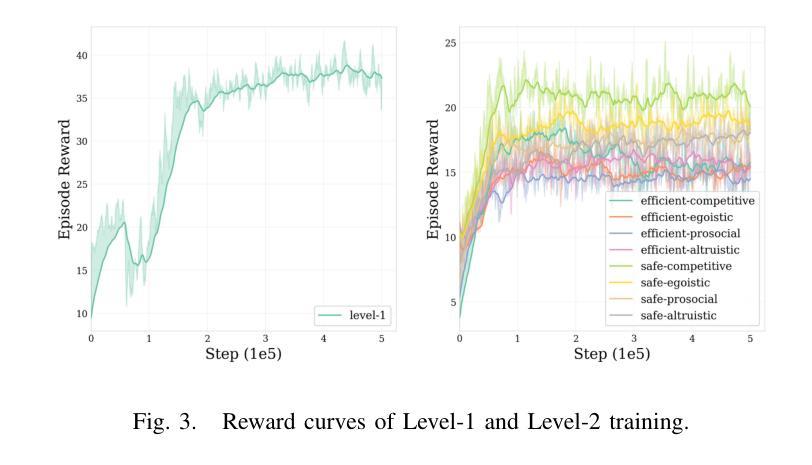
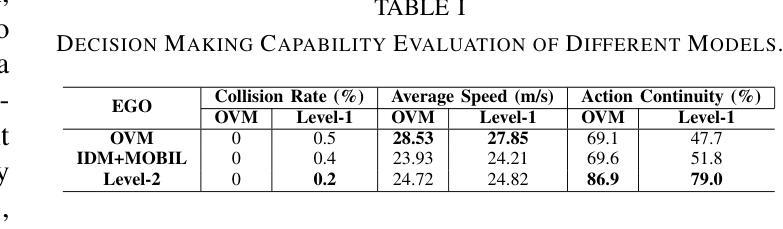
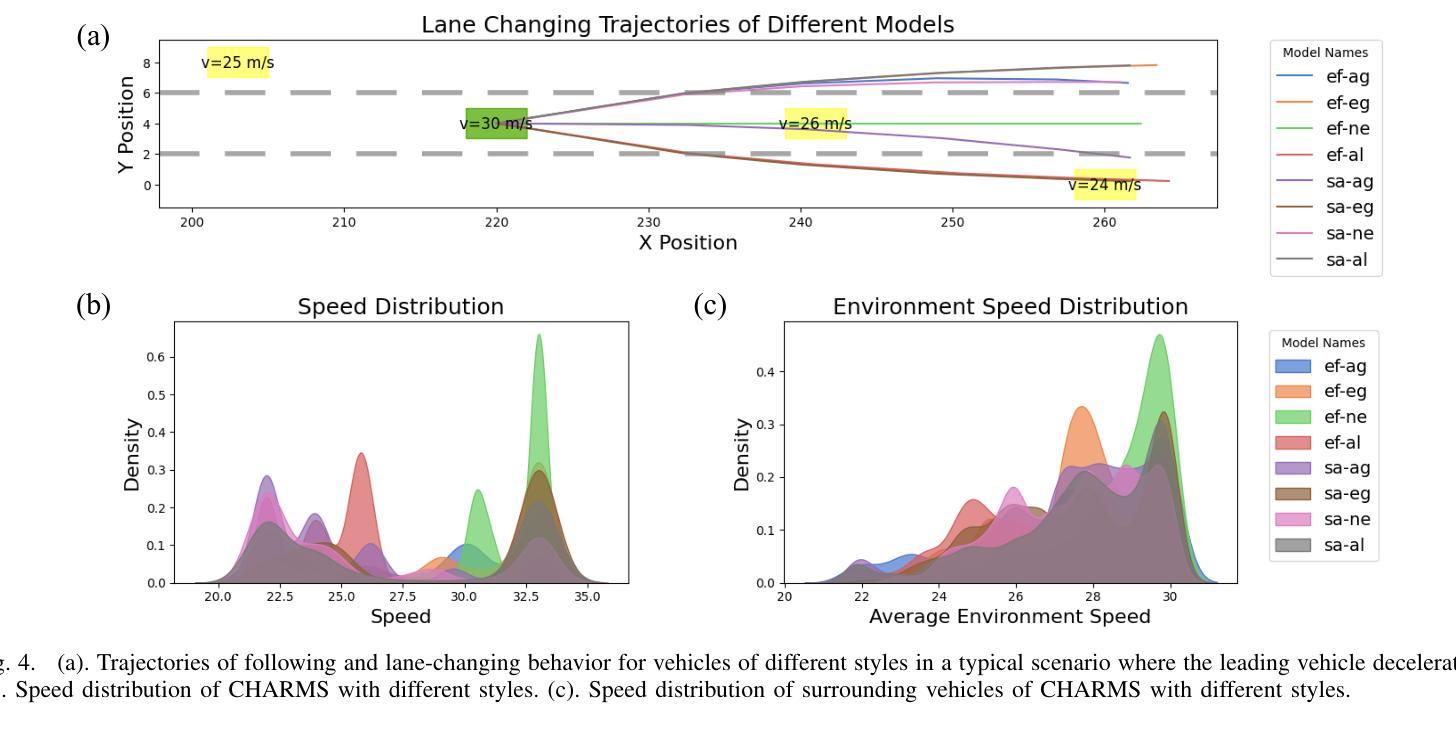
To address the current challenges of low intelligence and simplistic vehicle behavior modeling in autonomous driving simulation scenarios, this paper proposes the Cognitive Hierarchical Agent with Reasoning and Motion Styles (CHARMS). The model can reason about the behavior of other vehicles like a human driver and respond with different decision-making styles, thereby improving the intelligence and diversity of the surrounding vehicles in the driving scenario. By introducing the Level-k behavioral game theory, the paper models the decision-making process of human drivers and employs deep reinforcement learning to train the models with diverse decision styles, simulating different reasoning approaches and behavioral characteristics. Building on the Poisson cognitive hierarchy theory, this paper also presents a novel driving scenario generation method. The method controls the proportion of vehicles with different driving styles in the scenario using Poisson and binomial distributions, thus generating controllable and diverse driving environments. Experimental results demonstrate that CHARMS not only exhibits superior decision-making capabilities as ego vehicles, but also generates more complex and diverse driving scenarios as surrounding vehicles. We will release code for CHARMS at https://github.com/WUTAD-Wjy/CHARMS.
针对当前自动驾驶模拟场景中低智能和车辆行为建模过于简单的问题,本文提出了具有推理和运动风格认知分层代理(CHARMS)。该模型可以像人类驾驶员一样推理其他车辆的行为,并以不同的决策风格做出响应,从而提高了驾驶场景周围车辆的智能和多样性。通过引入Level-k行为博弈理论,论文对人类驾驶员的决策过程进行了建模,并采用深度强化学习来训练具有不同决策风格的模型,模拟不同的推理方法和行为特征。基于Poisson认知层次理论,本文还提出了一种新的驾驶场景生成方法。该方法使用Poisson和二项分布来控制场景中不同驾驶风格的车辆比例,从而生成可控且多样化的驾驶环境。实验结果表明,CHARMS不仅作为自动驾驶车辆表现出优越的决策能力,而且作为周围车辆生成了更复杂和多样化的驾驶场景。我们将在https://github.com/WUTAD-Wjy/CHARMS上发布CHARMS的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文为解决自动驾驶模拟场景中车辆行为智能化低及模型行为过于单一的问题,提出了认知层级化代理决策模型(CHARMS)。该模型可模拟其他车辆的行为如同人类驾驶员决策一样灵活多样,增强了驾驶场景的智能化与多元化。CHARMS结合层级博弈论,构建了人类驾驶员决策过程模型,并利用深度强化学习技术训练多种决策风格模型。此外,该论文还基于Poisson认知层次理论提出了一种新型驾驶场景生成方法,该方法通过控制不同驾驶风格车辆的比例生成可控且多样化的驾驶环境。实验证明,CHARMS不仅提升了自动驾驶车辆的决策能力,还能生成更复杂多变的驾驶场景。相关代码将公开在https://github.com/WUTAD-Wjy/CHARMS。
Key Takeaways
- CHARMS模型提高了自动驾驶模拟场景中车辆的智能化和行为的多样性。
- CHARMS模型能够模拟人类驾驶员的决策过程和行为特征。
- 通过结合层级博弈论和深度强化学习技术,CHARMS训练出多种决策风格的模型。
- 基于Poisson认知层次理论的新型驾驶场景生成方法使得场景更加可控和多样化。
- CHARMS模型不仅在自动驾驶车辆的决策能力上有所提升,还能生成复杂多变的驾驶场景。
- 代码将在公开平台共享以便研究人员进一步开发和使用。
点此查看论文截图

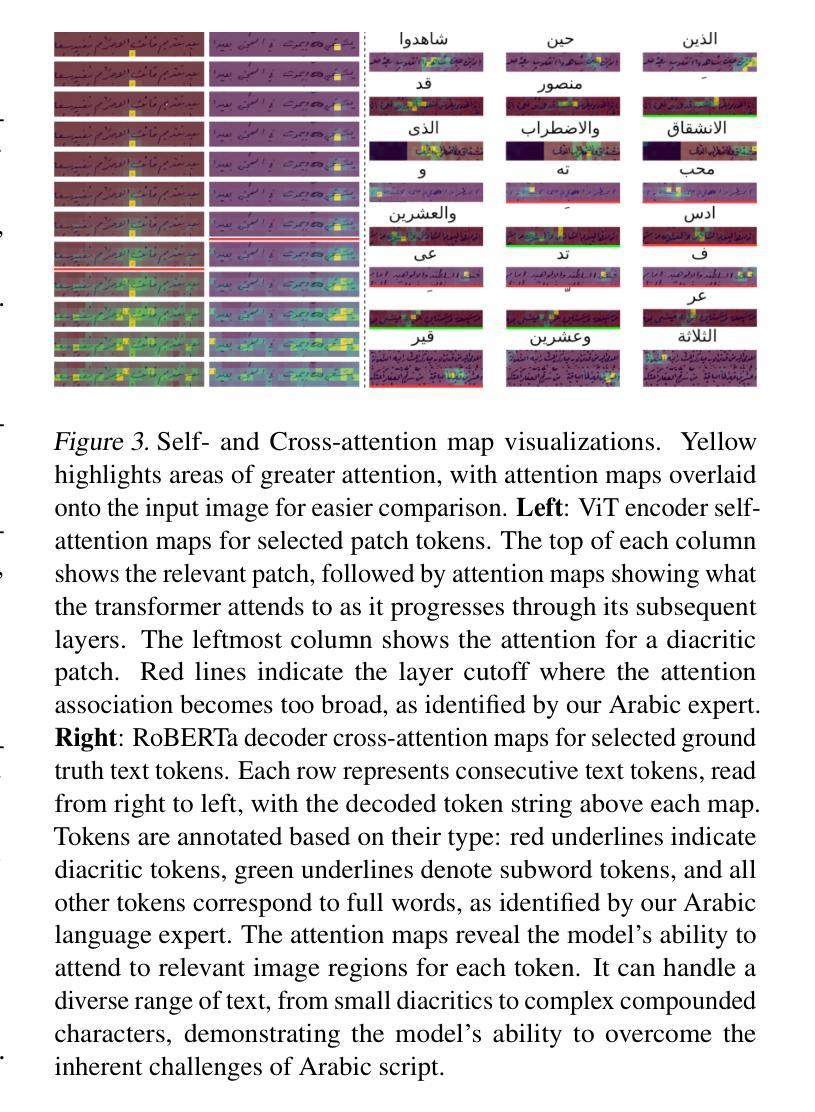
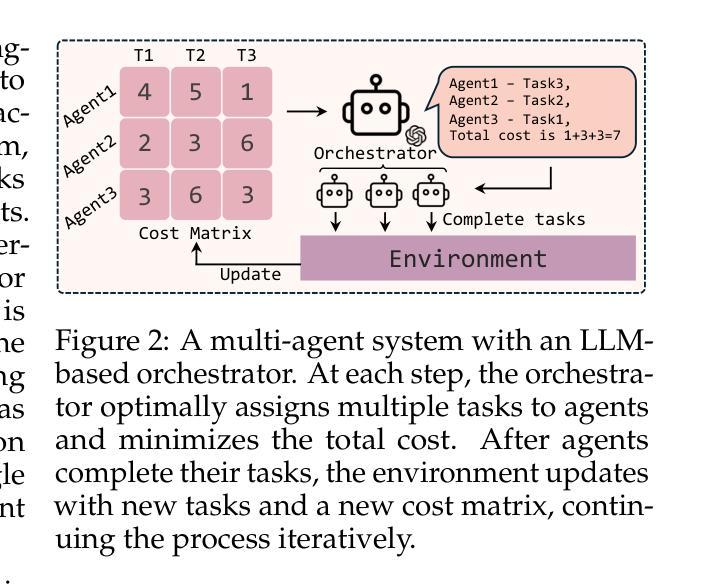
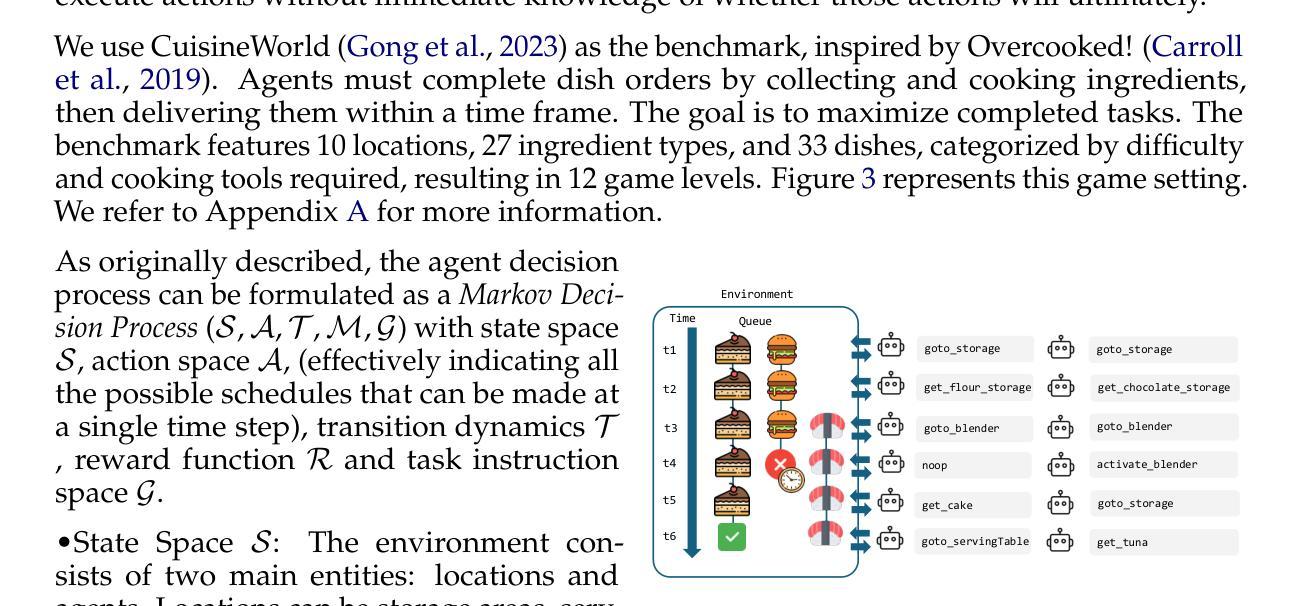
Self-Resource Allocation in Multi-Agent LLM Systems
Authors:Alfonso Amayuelas, Jingbo Yang, Saaket Agashe, Ashwin Nagarajan, Antonis Antoniades, Xin Eric Wang, William Wang
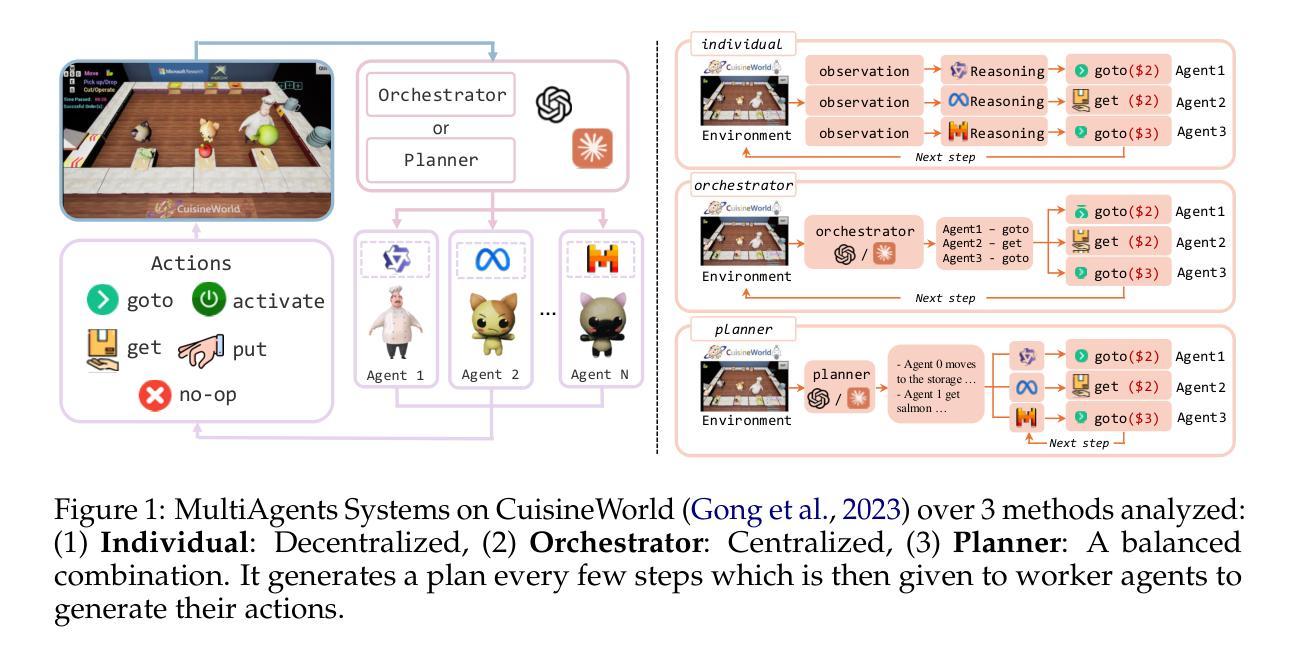
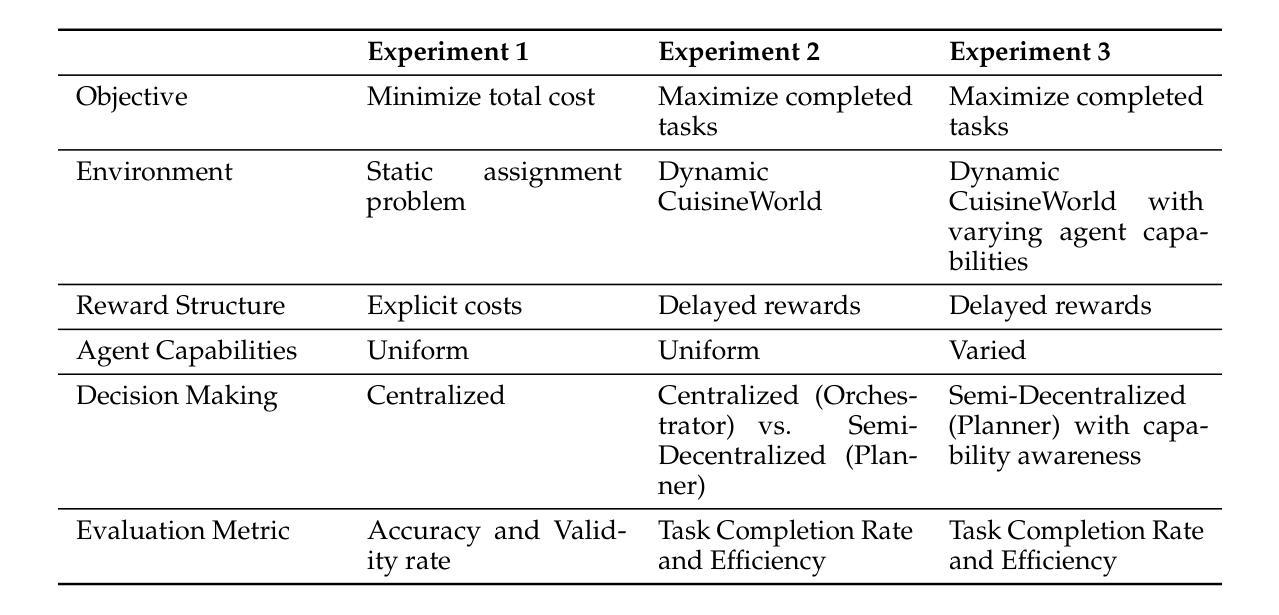
With the development of LLMs as agents, there is a growing interest in connecting multiple agents into multi-agent systems to solve tasks concurrently, focusing on their role in task assignment and coordination. This paper explores how LLMs can effectively allocate computational tasks among multiple agents, considering factors such as cost, efficiency, and performance. In this work, we address key questions, including the effectiveness of LLMs as orchestrators and planners, comparing their effectiveness in task assignment and coordination. Our experiments demonstrate that LLMs can achieve high validity and accuracy in resource allocation tasks. We find that the planner method outperforms the orchestrator method in handling concurrent actions, resulting in improved efficiency and better utilization of agents. Additionally, we show that providing explicit information about worker capabilities enhances the allocation strategies of planners, particularly when dealing with suboptimal workers.
随着作为代理的大型语言模型(LLMs)的发展,将多个代理连接到多代理系统以并行解决任务的兴趣不断增长,人们关注的重点是它们在任务分配和协调中的作用。本文探讨了大型语言模型如何在多个代理之间有效地分配计算任务,同时考虑成本、效率和性能等因素。在这项工作中,我们解决了关键问题,包括大型语言模型作为协调者和规划者的有效性,并比较了它们在任务分配和协调方面的有效性。我们的实验表明,大型语言模型在资源分配任务中可以取得很高的有效性和准确性。我们发现,在处理并发操作时,规划器方法的性能优于协调器方法,从而提高了效率并更好地利用了代理。此外,我们还表明,提供有关工作者能力的明确信息可以增强规划者的分配策略,特别是在处理非最优工作者时。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着大型语言模型(LLMs)作为代理人的发展,多代理人系统的构建日益受到关注,旨在同时解决多个任务。本文探讨了LLMs如何在多代理人系统中有效地分配计算任务,并考虑了成本、效率和性能等因素。实验表明,LLMs在资源分配任务中具有较高的有效性和准确性。在处理并发操作时,规划器方法优于编排器方法,提高了效率和对代理人的利用率。提供关于工作者能力的明确信息,能增强规划者的分配策略,特别是在处理非最优工作者时更是如此。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs在多代理人系统中扮演重要角色,可有效地分配计算任务。
- LLMs在资源分配任务中具有高有效性和准确性。
- 相较于编排器方法,规划器方法在处理并发操作时表现更佳。
- 规划器方法能提高效率和对代理人的利用率。
- 提供关于工作者能力的明确信息对增强规划者的分配策略至关重要。
- 在处理非最优工作者时,明确的工作者能力信息尤为重要。
点此查看论文截图

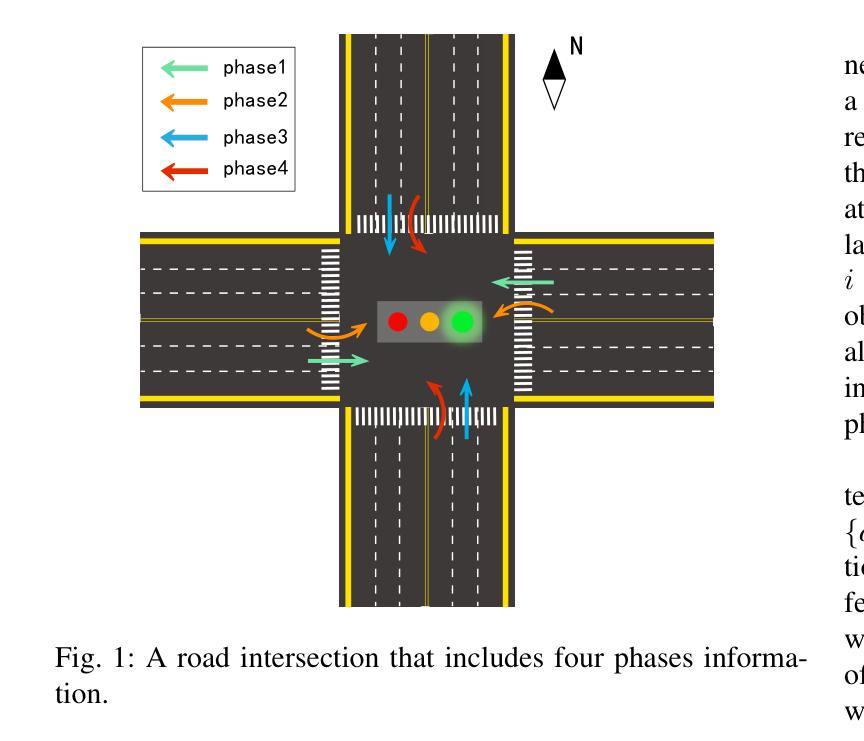
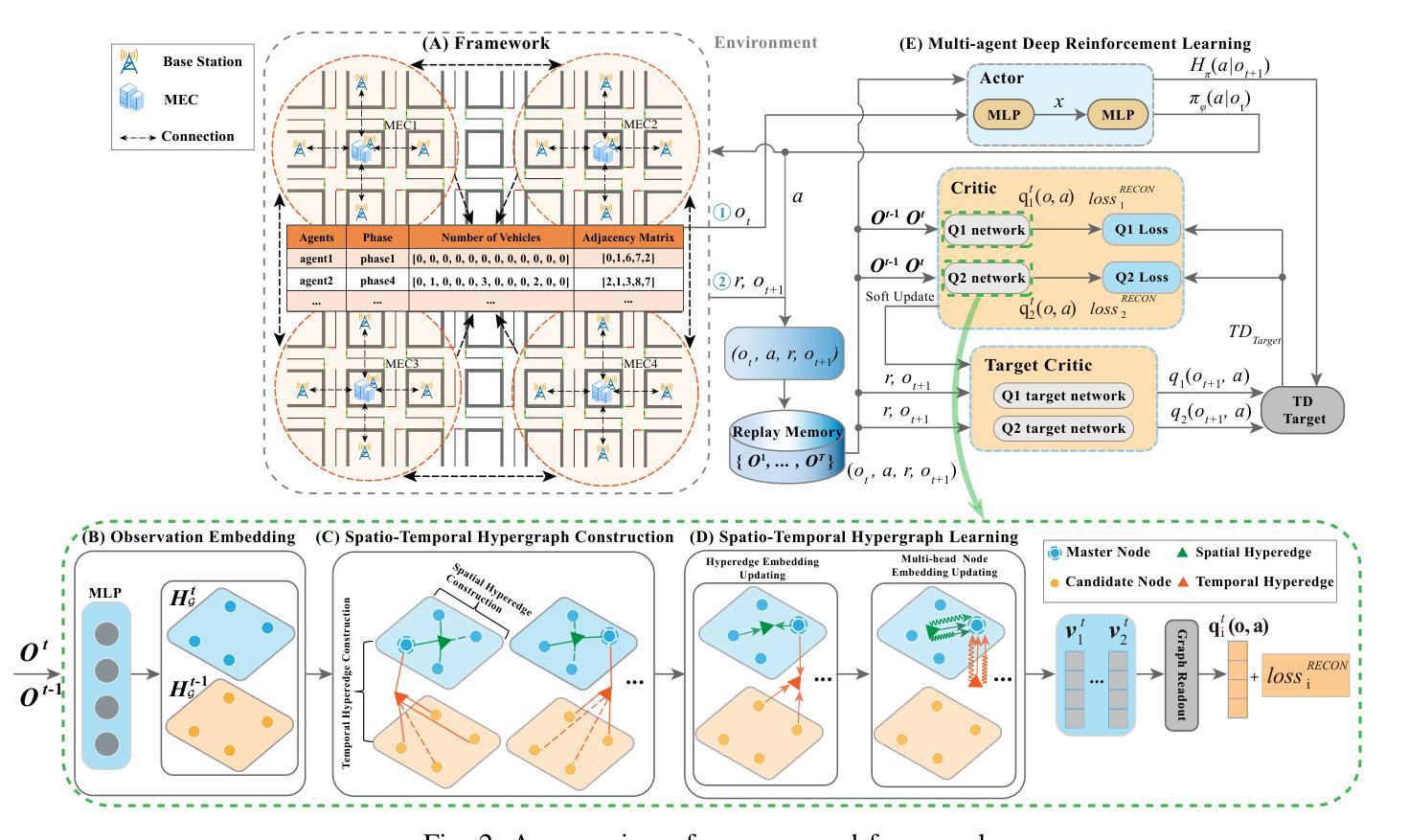
Towards Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning based Traffic Signal Control through Spatio-temporal Hypergraphs
Authors:Kang Wang, Zhishu Shen, Zhen Lei, Tiehua Zhang
Traffic signal control systems (TSCSs) are integral to intelligent traffic management, fostering efficient vehicle flow. Traditional approaches often simplify road networks into standard graphs, which results in a failure to consider the dynamic nature of traffic data at neighboring intersections, thereby neglecting higher-order interconnections necessary for real-time control. To address this, we propose a novel TSCS framework to realize intelligent traffic control. This framework collaborates with multiple neighboring edge computing servers to collect traffic information across the road network. To elevate the efficiency of traffic signal control, we have crafted a multi-agent soft actor-critic (MA-SAC) reinforcement learning algorithm. Within this algorithm, individual agents are deployed at each intersection with a mandate to optimize traffic flow across the road network collectively. Furthermore, we introduce hypergraph learning into the critic network of MA-SAC to enable the spatio-temporal interactions from multiple intersections in the road network. This method fuses hypergraph and spatio-temporal graph structures to encode traffic data and capture the complex spatio-temporal correlations between multiple intersections. Our empirical evaluation, tested on varied datasets, demonstrates the superiority of our framework in minimizing average vehicle travel times and sustaining high-throughput performance. This work facilitates the development of more intelligent urban traffic management solutions. We release the code to support the reproducibility of this work at https://github.com/Edun-Eyes/TSC
交通信号控制系统(TSCS)是智能交通管理的核心组成部分,能够促进车辆的高效流动。传统方法通常将道路网络简化为标准图形,这导致无法考虑相邻交叉口交通数据的动态特性,从而忽略了实时控制所需的高级互连。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新型的TSCS框架来实现智能交通控制。该框架与多个相邻的边缘计算服务器协作,以收集整个道路网上的交通信息。为了提高交通信号控制的效率,我们设计了一种基于多智能体软Actor-Critic(MA-SAC)的强化学习算法。在该算法中,个体智能体被部署在每个交叉口处,以集体优化整个道路网上的交通流量。此外,我们将超图学习引入到MA-SAC的批判网络中,以实现道路网上多个交叉口之间的时空交互。该方法融合了超图和时空图结构来编码交通数据,并捕捉多个交叉口之间复杂的时空相关性。我们的经验评估,在多种数据集上的测试表明,我们的框架在最小化平均车辆旅行时间和保持高吞吐量性能方面的优越性。这项工作促进了更智能的城市交通管理解决方案的开发。我们发布的代码支持该工作的可重复性,可在https://github.com/Edun-Eyes/TSC上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing
Summary
该文本介绍了一种新型的交通信号控制系统框架,它利用多智能体技术实现智能交通控制。该框架通过与多个邻近的边缘计算服务器协作,收集整个道路网络的交通信息,并采用基于强化学习的多智能体软演员评论家算法优化交通信号控制。此外,引入超图学习进入评论家网络,以捕捉多个交叉口的时空交互作用。经过实证评估,证明该框架能显著降低车辆平均旅行时间并保持高性能。此工作推动了智能交通管理解决方案的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 交通信号控制系统是智能交通管理的核心部分,需要实现高效车辆流动。
- 传统方法简化道路网络为标准图,无法考虑邻近交叉口交通数据的动态特性,忽略了实时控制所需的高阶互联。
- 新型交通信号控制系统框架利用多智能体技术实现智能交通控制,与多个邻近边缘计算服务器协作收集交通信息。
- 采用多智能体软演员评论家算法优化交通信号控制效率。
- 引入超图学习进入评论家网络,以捕捉多个交叉口的时空交互作用。
- 实证评估证明该框架能显著降低车辆平均旅行时间。
点此查看论文截图

Do LLM Agents Have Regret? A Case Study in Online Learning and Games
Authors:Chanwoo Park, Xiangyu Liu, Asuman Ozdaglar, Kaiqing Zhang
Large language models (LLMs) have been increasingly employed for (interactive) decision-making, via the development of LLM-based autonomous agents. Despite their emerging successes, the performance of LLM agents in decision-making has not been fully investigated through quantitative metrics, especially in the multi-agent setting when they interact with each other, a typical scenario in real-world LLM-agent applications. To better understand the limits of LLM agents in these interactive environments, we propose to study their interactions in benchmark decision-making settings in online learning and game theory, through the performance metric of \emph{regret}. We first empirically study the {no-regret} behaviors of LLMs in canonical (non-stationary) online learning problems, as well as the emergence of equilibria when LLM agents interact through playing repeated games. We then provide some theoretical insights into the no-regret behaviors of LLM agents, under certain assumptions on the supervised pre-training and the rationality model of human decision-makers who generate the data. Notably, we also identify (simple) cases where advanced LLMs such as GPT-4 fail to be no-regret. To promote the no-regret behaviors, we propose a novel \emph{unsupervised} training loss of \emph{regret-loss}, which, in contrast to the supervised pre-training loss, does not require the labels of (optimal) actions. We then establish the statistical guarantee of generalization bound for regret-loss minimization, followed by the optimization guarantee that minimizing such a loss may automatically lead to known no-regret learning algorithms. Our further experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our regret-loss, especially in addressing the above ``regrettable’’ cases.
大型语言模型(LLM)越来越多地被用于(交互)决策制定,这是通过开发基于LLM的自主代理来实现的。尽管它们取得了新兴的成功,但LLM代理在决策制定方面的表现尚未通过定量指标进行全面研究,特别是在多代理环境中它们相互交互时,这是现实世界LLM代理应用中的典型场景。为了更好地了解LLM代理在这些交互式环境中的局限性,我们提议研究它们在在线学习和博弈理论基准决策制定环境中的交互作用,通过“遗憾”这一性能指标进行评估。我们首先对LLM在典型(非稳态)在线学习问题中的无遗憾行为进行了实证研究,以及当LLM代理通过重复游戏进行交互时均衡状态的出现。然后,我们基于有关监督预训练和人类决策者理性模型的某些假设,对LLM代理的无遗憾行为提供了一些理论见解。这些人类决策者生成的数据。值得注意的是,我们还确定了高级LLM(如GPT-4)在特定情况下也会出现遗憾的情况。为了促进无遗憾行为,我们提出了一种新的无监督训练损失,即“遗憾损失”,与监督预训练损失相比,它不需要(最优)行动标签。然后我们建立了遗憾损失最小化的泛化界统计保证,以及优化保证,即最小化这种损失可能会自动导致已知的无遗憾学习算法。我们的进一步实验证明了我们的遗憾损失的有效性,尤其是在解决上述“遗憾”情况方面。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Camera ready version of ICLR 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)已广泛应用于基于自主代理的决策制定。然而,关于LLM代理在决策制定中的性能,特别是在多代理环境中相互交互时的性能,尚未通过定量指标进行全面研究。为了更好地理解LLM代理在交互式环境中的局限性,我们提出在在线学习和博弈理论的标准决策制定环境中研究其交互,通过后悔这一性能指标来评估。我们实证研究了LLM在非平稳在线学习问题中的无后悔行为,以及LLM代理在重复游戏中交互时均衡的出现。我们还从理论角度探讨了LLM代理的无后悔行为,并在某些假设下探讨了监督预训练和人类决策者理性模型对数据生成的影响。我们提出了一种新的无监督训练损失——后悔损失,以改善无后悔行为。最后,我们通过实验验证了后悔损失的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)已用于基于自主代理的决策制定。
- LLM在多代理环境中的决策制定性能尚未得到充分研究。
- 后悔是评估LLM代理在交互式环境中性能的重要指标。
- LLM在无监督的在线学习环境中可能会出现后悔的情况。
- 在某些假设下,LLM的无后悔行为受到监督预训练和人类决策者理性模型的影响。
- 提出了一种新的无监督训练损失——后悔损失,以改善无后悔行为。
点此查看论文截图