⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-05 更新
Concept Lancet: Image Editing with Compositional Representation Transplant
Authors:Jinqi Luo, Tianjiao Ding, Kwan Ho Ryan Chan, Hancheng Min, Chris Callison-Burch, René Vidal
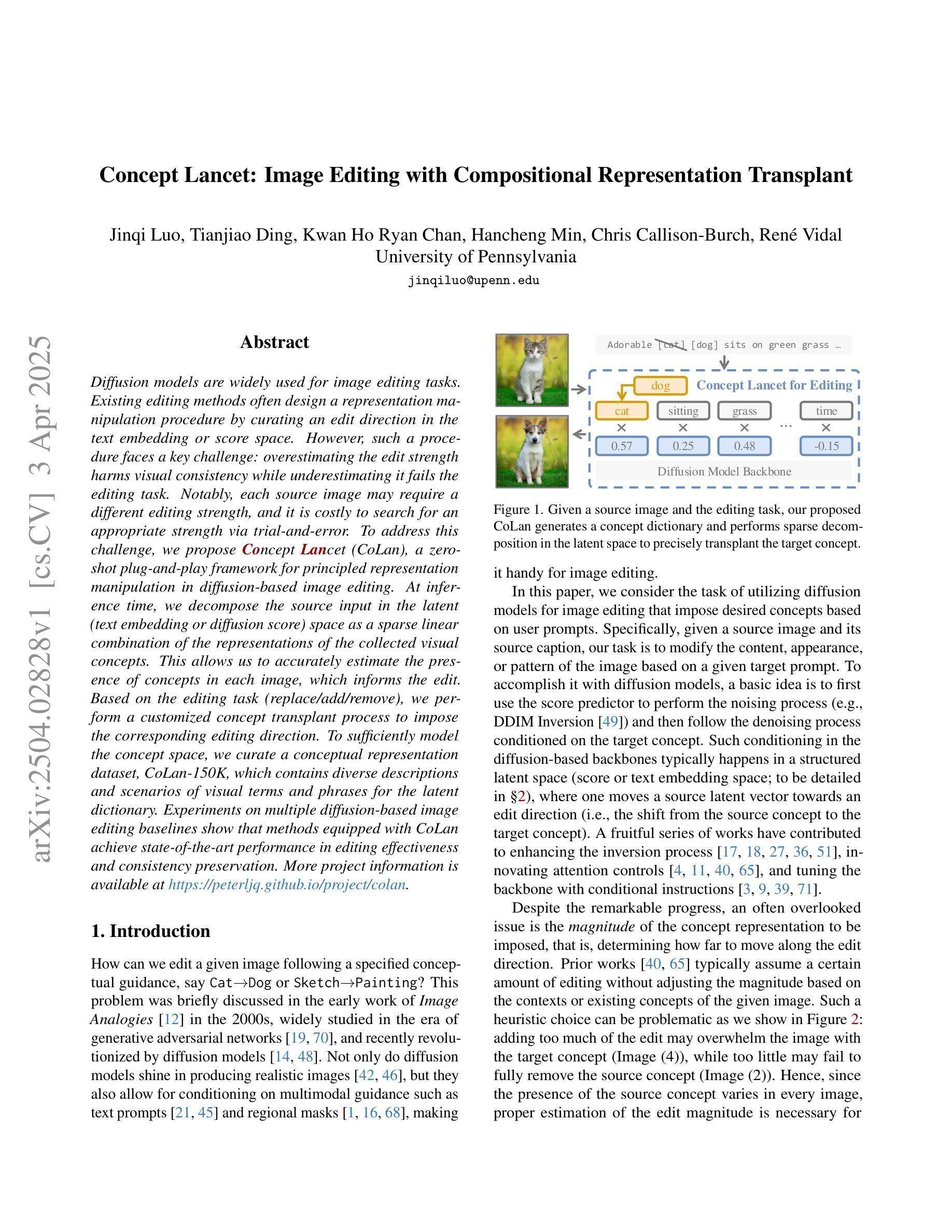
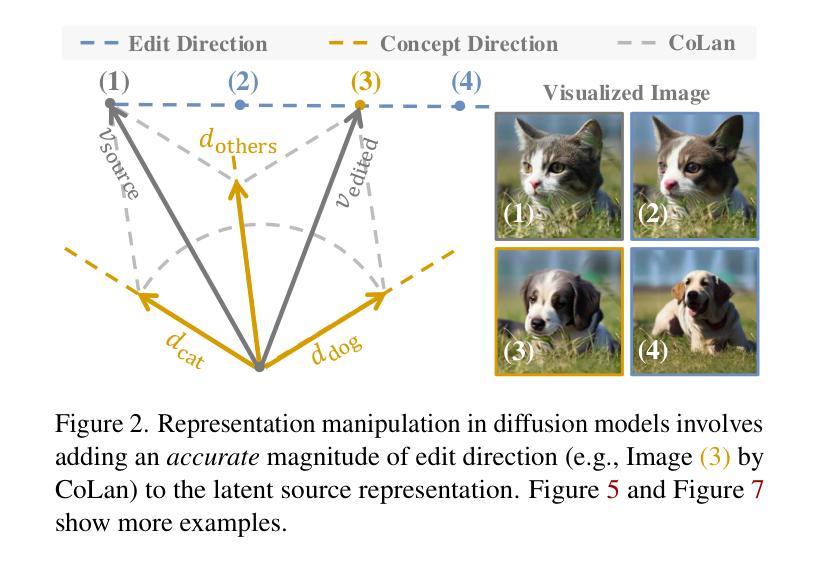
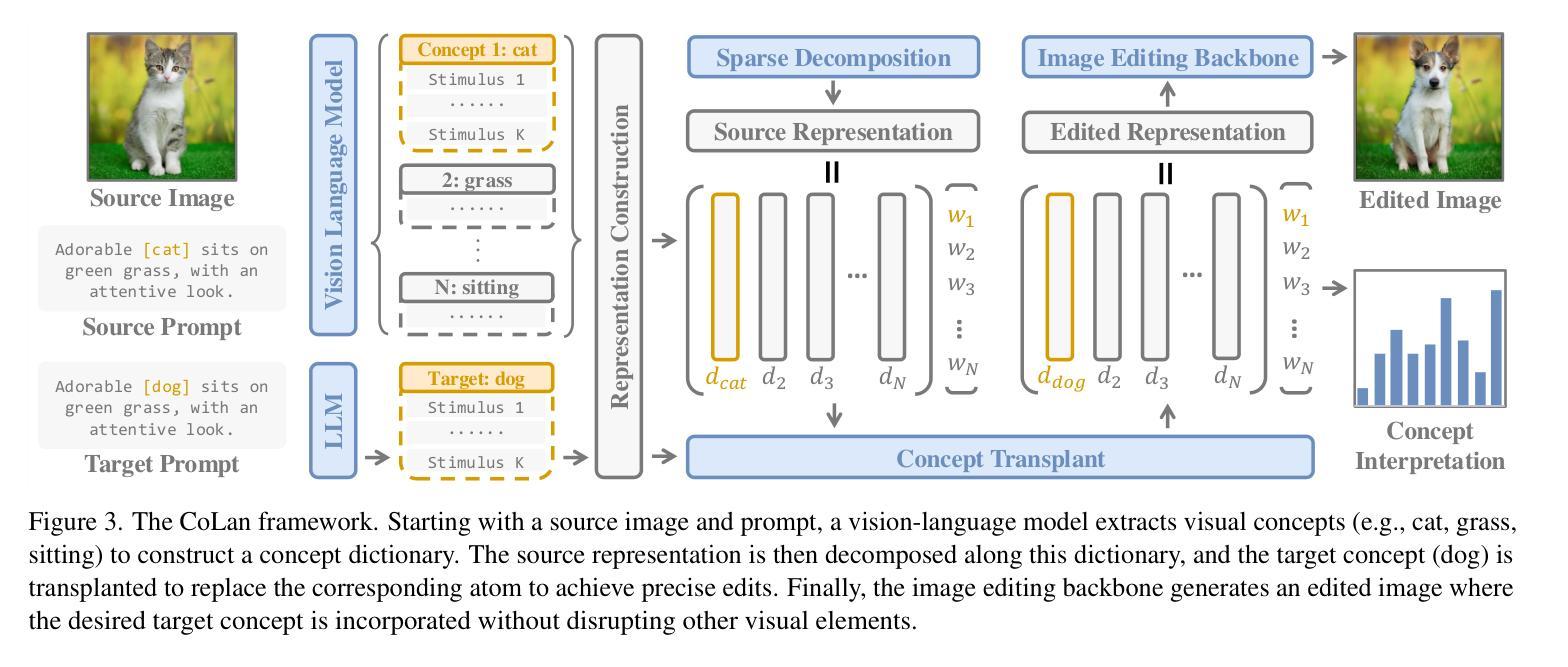
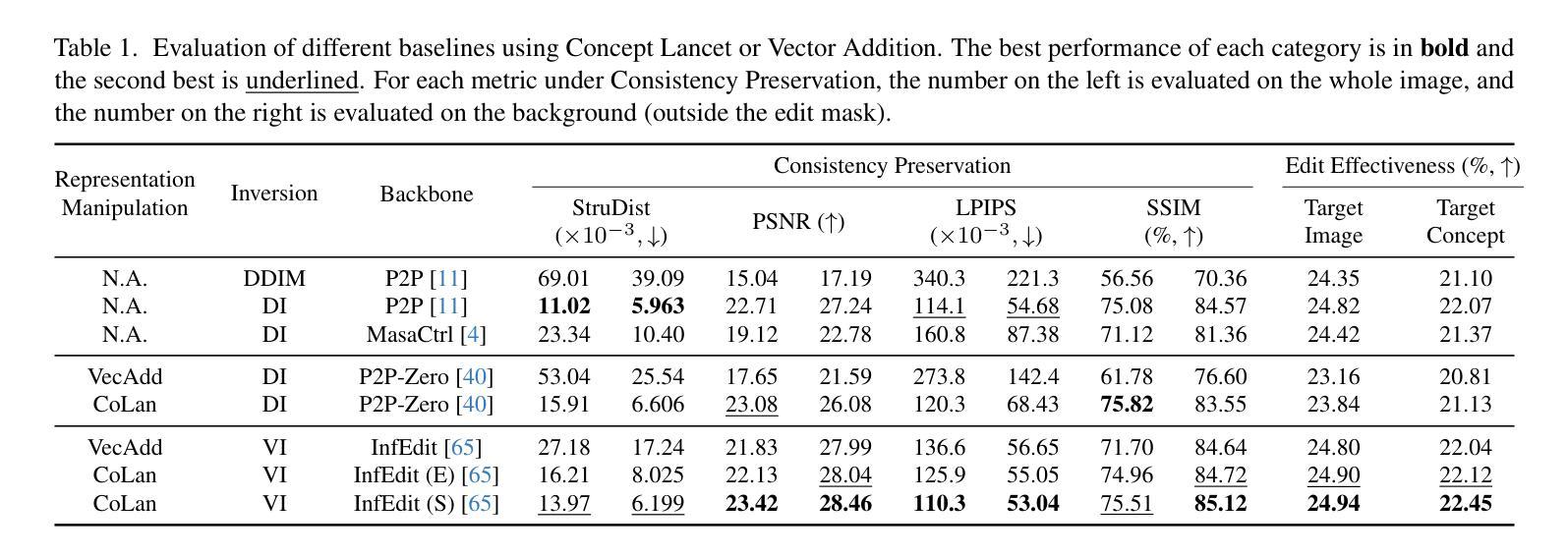
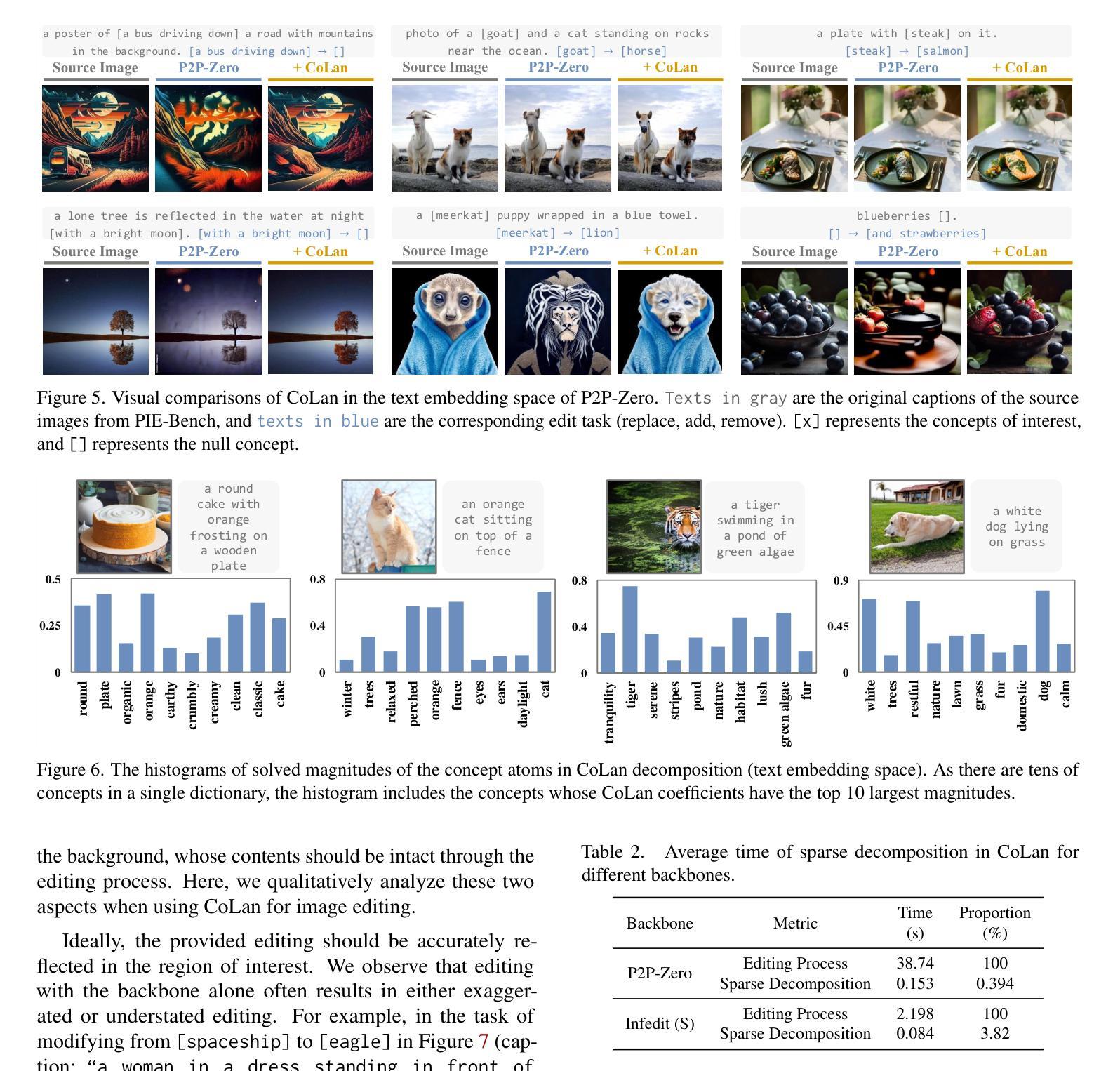
Diffusion models are widely used for image editing tasks. Existing editing methods often design a representation manipulation procedure by curating an edit direction in the text embedding or score space. However, such a procedure faces a key challenge: overestimating the edit strength harms visual consistency while underestimating it fails the editing task. Notably, each source image may require a different editing strength, and it is costly to search for an appropriate strength via trial-and-error. To address this challenge, we propose Concept Lancet (CoLan), a zero-shot plug-and-play framework for principled representation manipulation in diffusion-based image editing. At inference time, we decompose the source input in the latent (text embedding or diffusion score) space as a sparse linear combination of the representations of the collected visual concepts. This allows us to accurately estimate the presence of concepts in each image, which informs the edit. Based on the editing task (replace/add/remove), we perform a customized concept transplant process to impose the corresponding editing direction. To sufficiently model the concept space, we curate a conceptual representation dataset, CoLan-150K, which contains diverse descriptions and scenarios of visual terms and phrases for the latent dictionary. Experiments on multiple diffusion-based image editing baselines show that methods equipped with CoLan achieve state-of-the-art performance in editing effectiveness and consistency preservation.
扩散模型广泛应用于图像编辑任务。现有的编辑方法通常通过策划文本嵌入或分数空间中的编辑方向来设计一个表示操纵过程。然而,这一过程面临一个关键挑战:高估编辑强度会损害视觉一致性,而低估则无法完成编辑任务。值得注意的是,每个源图像可能需要不同的编辑强度,通过试错搜索适当的强度成本很高。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了Concept Lancet(CoLan),这是一种用于扩散式图像编辑中有原则表示操作的零样本即插即用框架。在推理时间,我们将源输入在潜在(文本嵌入或扩散分数)空间中分解为所收集的视觉概念表示的稀疏线性组合。这允许我们准确估计每个图像中概念的存在,从而为编辑提供信息。基于编辑任务(替换/添加/删除),我们执行定制的概念移植过程以强制执行相应的编辑方向。为了充分建模概念空间,我们整理了一个概念表示数据集CoLan-150K,其中包含视觉术语和短语的多样描述和场景,用于潜在字典。在多个基于扩散的图像编辑基准实验上表明,配备CoLan的方法在编辑效果和一致性保持方面达到最新技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in CVPR 2025. Project page at https://peterljq.github.io/project/colan
Summary
扩散模型广泛应用于图像编辑任务。现有编辑方法通过在文本嵌入或分数空间策划编辑方向来设计表示操纵程序,但面临估算编辑强度挑战:过度估计会损害视觉一致性,而低估则无法完成编辑任务。为此,我们提出Concept Lancet(CoLan)框架,用于扩散式图像编辑中的原则性表示操纵。在推理时,我们将源输入在潜在(文本嵌入或扩散分数)空间中分解为收集的视觉概念的表示的稀疏线性组合,准确估计图像中概念的存在,为编辑提供信息。基于编辑任务(替换/添加/删除),我们执行定制的概念移植过程以施加相应的编辑方向。通过构建概念表示数据集CoLan-150K,包含视觉术语和短语的多样描述和场景作为潜在字典,实验表明配备CoLan的方法在编辑效果和一致性保持方面达到最新技术水平。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型常用于图像编辑任务。
- 现有编辑方法设计表示操纵程序时面临估算编辑强度的挑战。
- Concept Lancet(CoLan)框架用于解决这一挑战,通过分解源输入在潜在空间中的表示来准确估计图像中的概念。
- CoLan基于编辑任务执行定制的概念移植过程。
- CoLan通过构建CoLan-150K数据集来充分建模概念空间。
- 配备CoLan的实验方法在多个扩散式图像编辑基准测试中达到最新技术水平。
点此查看论文截图

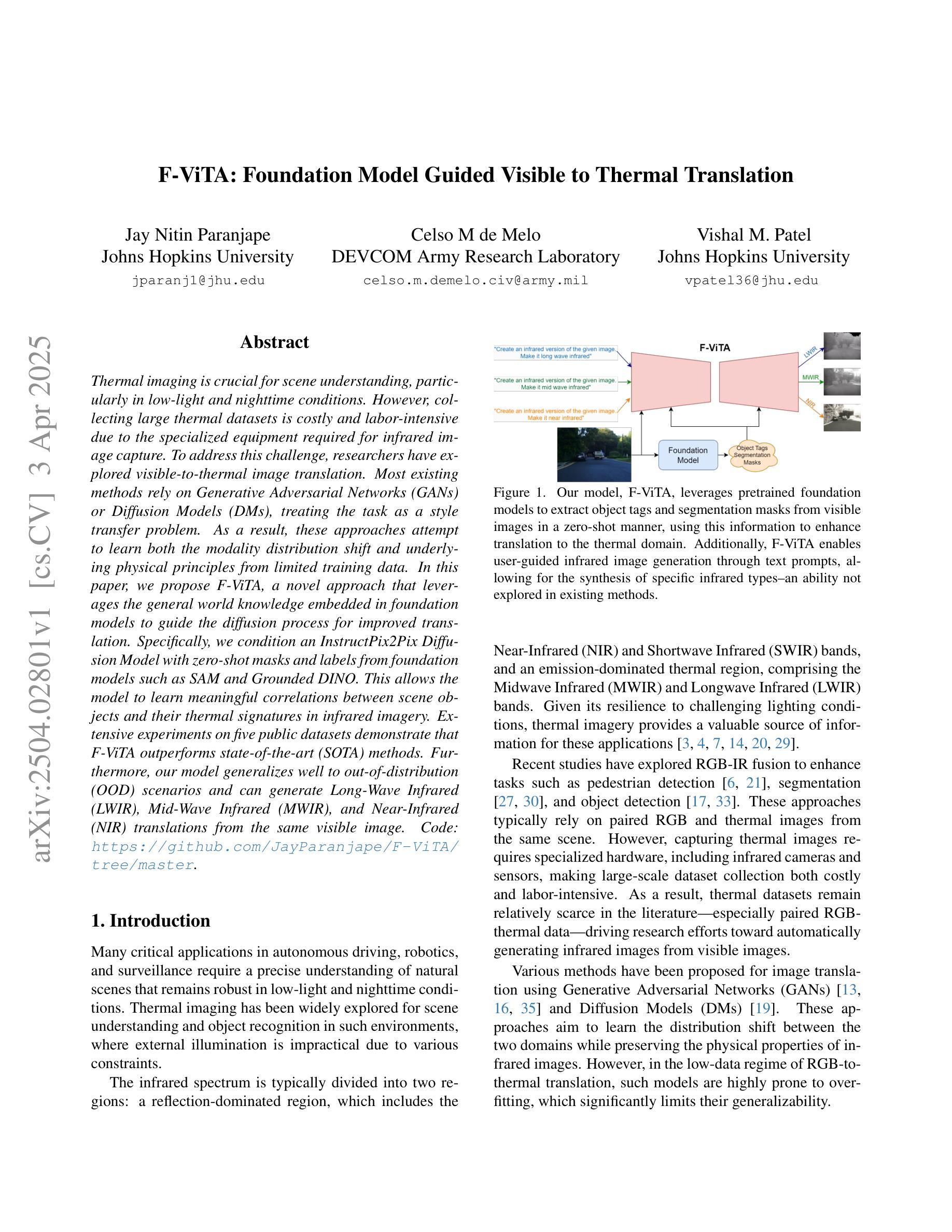
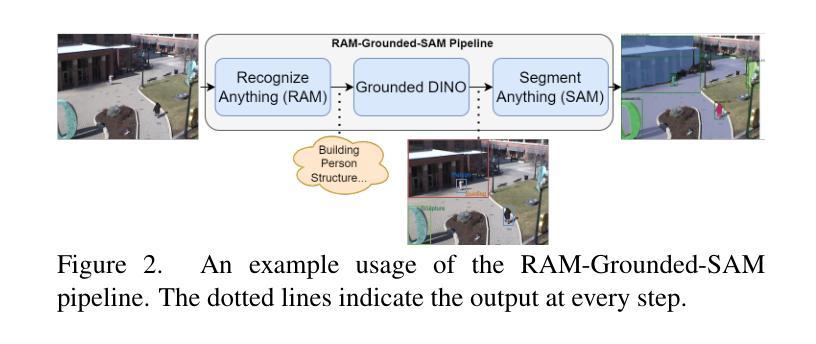
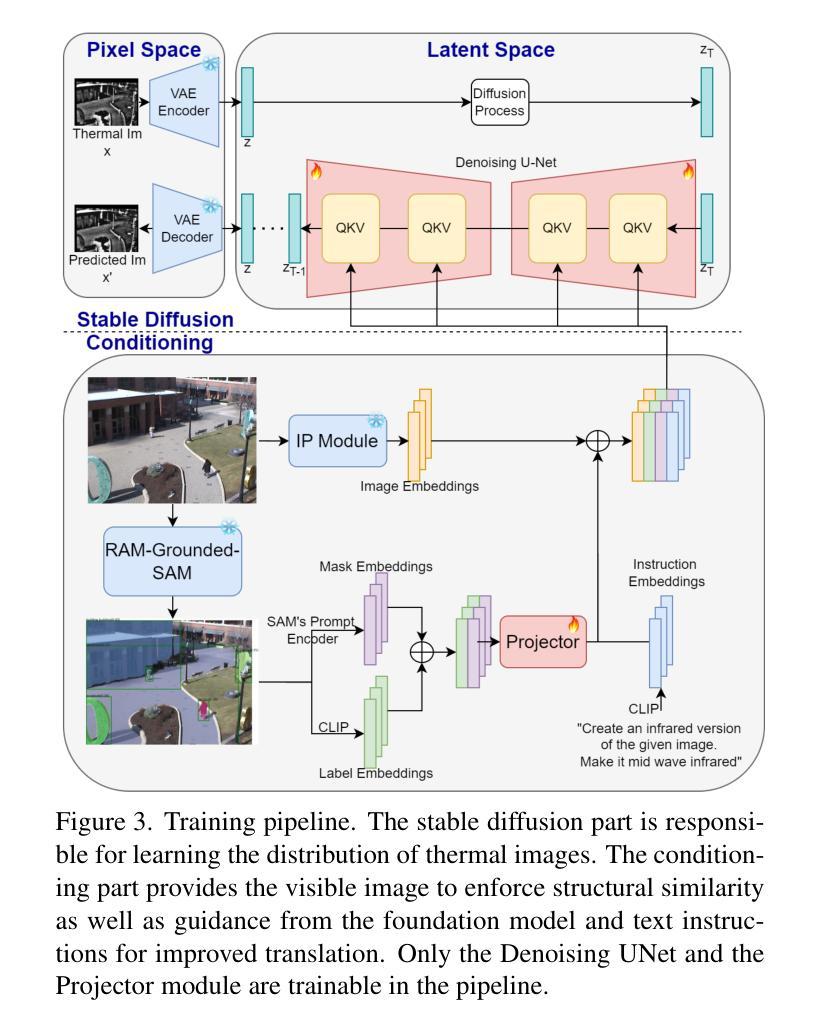
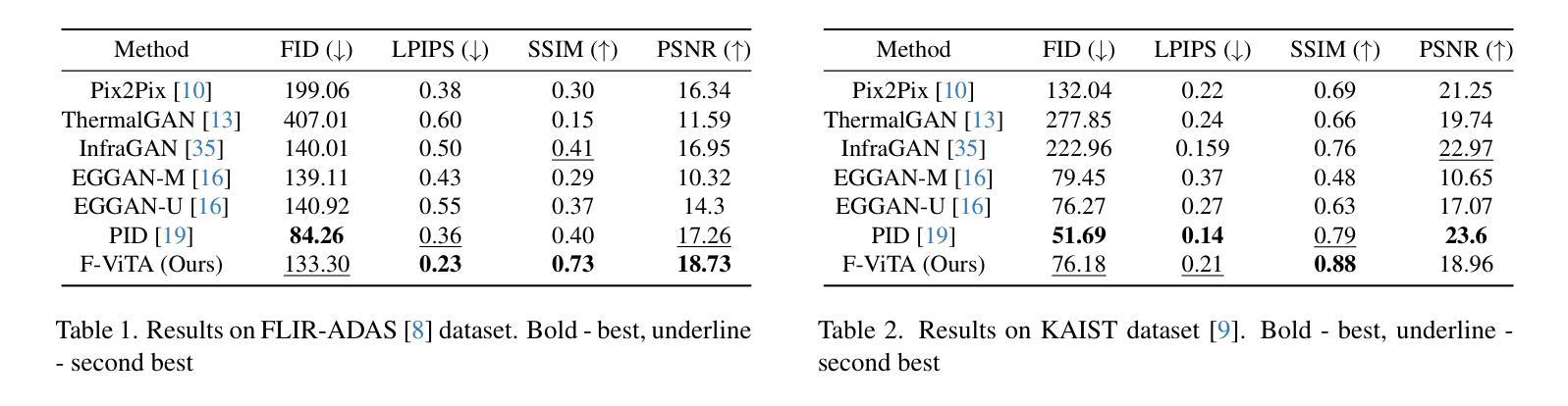
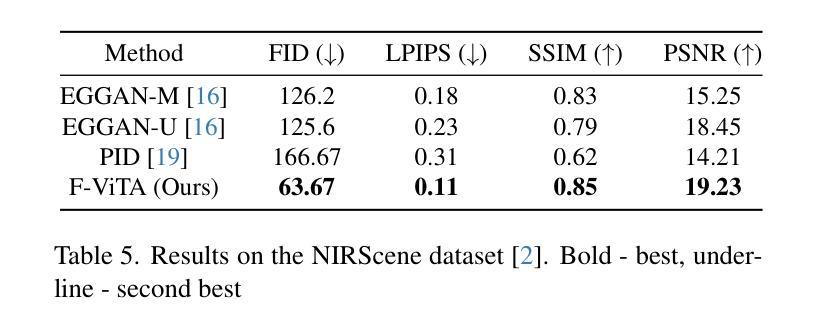
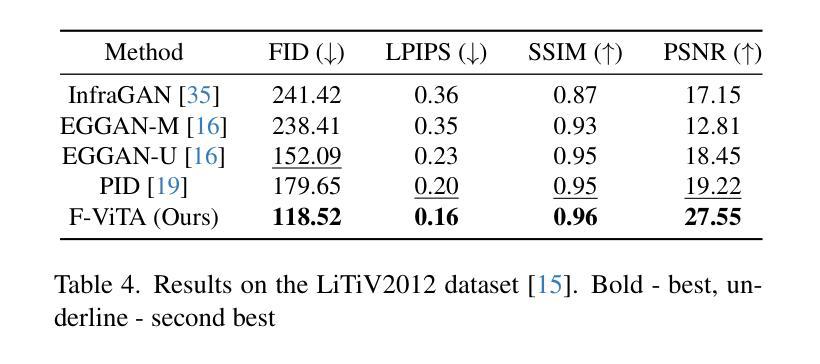
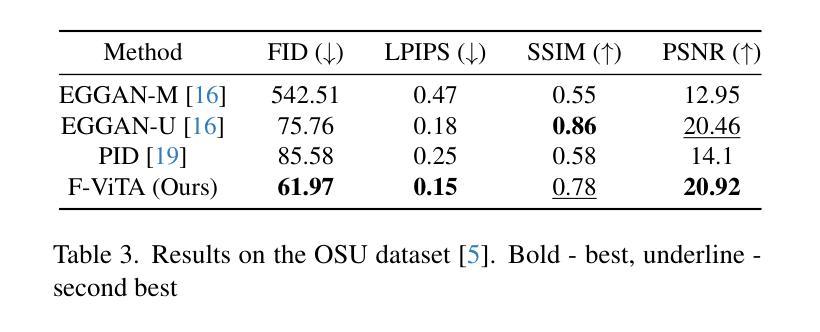
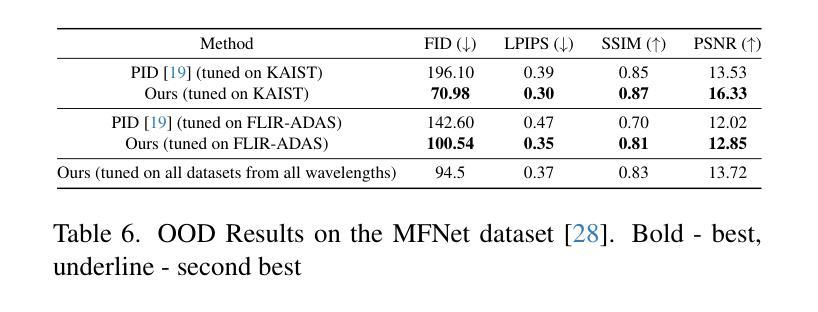
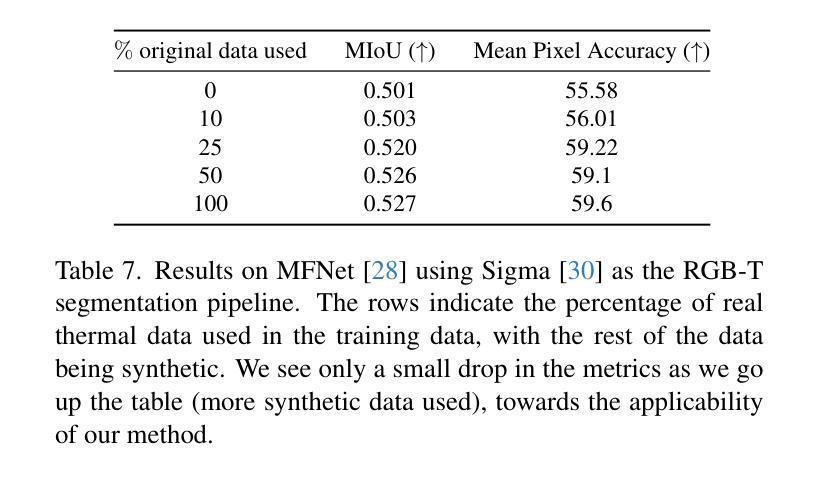
F-ViTA: Foundation Model Guided Visible to Thermal Translation
Authors:Jay N. Paranjape, Celso de Melo, Vishal M. Patel
Thermal imaging is crucial for scene understanding, particularly in low-light and nighttime conditions. However, collecting large thermal datasets is costly and labor-intensive due to the specialized equipment required for infrared image capture. To address this challenge, researchers have explored visible-to-thermal image translation. Most existing methods rely on Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) or Diffusion Models (DMs), treating the task as a style transfer problem. As a result, these approaches attempt to learn both the modality distribution shift and underlying physical principles from limited training data. In this paper, we propose F-ViTA, a novel approach that leverages the general world knowledge embedded in foundation models to guide the diffusion process for improved translation. Specifically, we condition an InstructPix2Pix Diffusion Model with zero-shot masks and labels from foundation models such as SAM and Grounded DINO. This allows the model to learn meaningful correlations between scene objects and their thermal signatures in infrared imagery. Extensive experiments on five public datasets demonstrate that F-ViTA outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. Furthermore, our model generalizes well to out-of-distribution (OOD) scenarios and can generate Long-Wave Infrared (LWIR), Mid-Wave Infrared (MWIR), and Near-Infrared (NIR) translations from the same visible image. Code: https://github.com/JayParanjape/F-ViTA/tree/master.
热成像对于场景理解至关重要,特别是在低光和夜间条件下。然而,由于红外图像捕获所需的专业设备,收集大量的热数据集成本高昂且劳动密集。为了应对这一挑战,研究人员已经探索了可见光到热成像的图像翻译技术。现有的大多数方法依赖于生成对抗网络(GANs)或扩散模型(DMs),将任务视为风格转换问题。因此,这些方法试图从有限的训练数据中学习模态分布变化和潜在的物理原理。在本文中,我们提出了一种新方法F-ViTA,它利用基础模型中嵌入的世界通用知识来指导扩散过程,以改进翻译效果。具体来说,我们使用InstructPix2Pix扩散模型,以基础模型(如SAM和Grounded DINO)的零样本遮罩和标签作为条件。这允许模型学习场景物体与其在红外图像中的热特征之间的有意义关联。在五个公共数据集上的广泛实验表明,F-ViTA优于最新技术方法。此外,我们的模型能够很好地泛化到域外场景,并且可以从同一可见图像生成长波红外(LWIR)、中波红外(MWIR)和近红外(NIR)翻译。代码:https://github.com/JayParanjape/F-ViTA/tree/master。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文提出一种利用基础模型中的通用世界知识来指导扩散过程的新型可见光到热成像翻译方法——F-ViTA。通过结合InstructPix2Pix扩散模型和基础模型(如SAM和Grounded DINO)的零样本掩码和标签,F-ViTA能在场景物体与它们在红外成像中的热特征之间建立有意义的关联。在五个公共数据集上的实验表明,F-ViTA优于现有技术,并具有良好的泛化能力,能从同一可见图像生成长波红外、中波红外和近红外翻译。
Key Takeaways:
- 可见光到热成像翻译是解决热成像数据收集成本高昂和劳动密集的有效方法。
- F-ViTA利用基础模型中的通用世界知识来指导扩散过程,实现更好的翻译效果。
- F-ViTA结合了InstructPix2Pix扩散模型和基础模型的零样本掩码和标签。
- F-ViTA能在场景物体与热特征之间建立有意义的关联。
- F-ViTA在多个公共数据集上的实验表现优于现有技术。
- F-ViTA具有良好的泛化能力,能生成不同红外波段的翻译。
点此查看论文截图
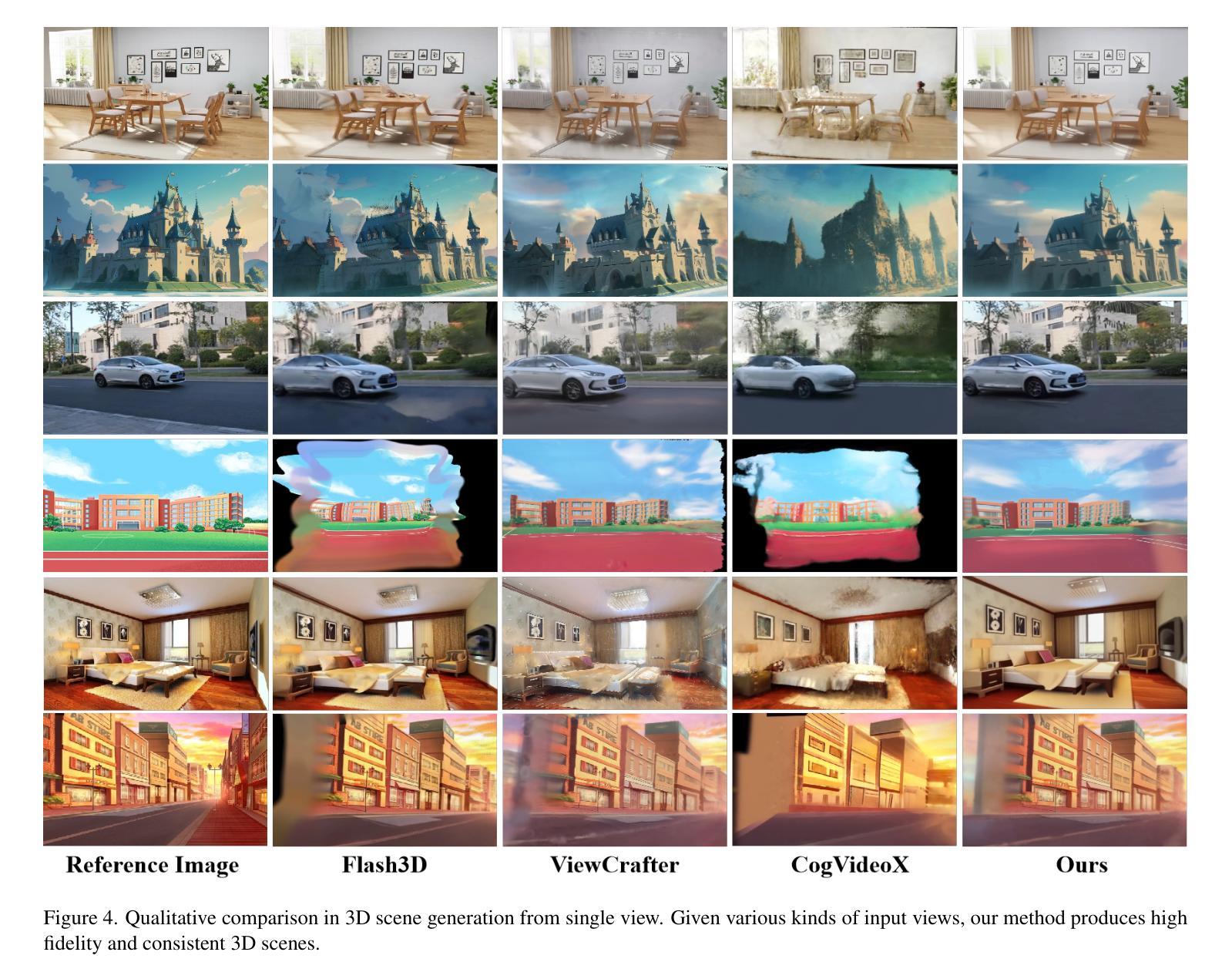
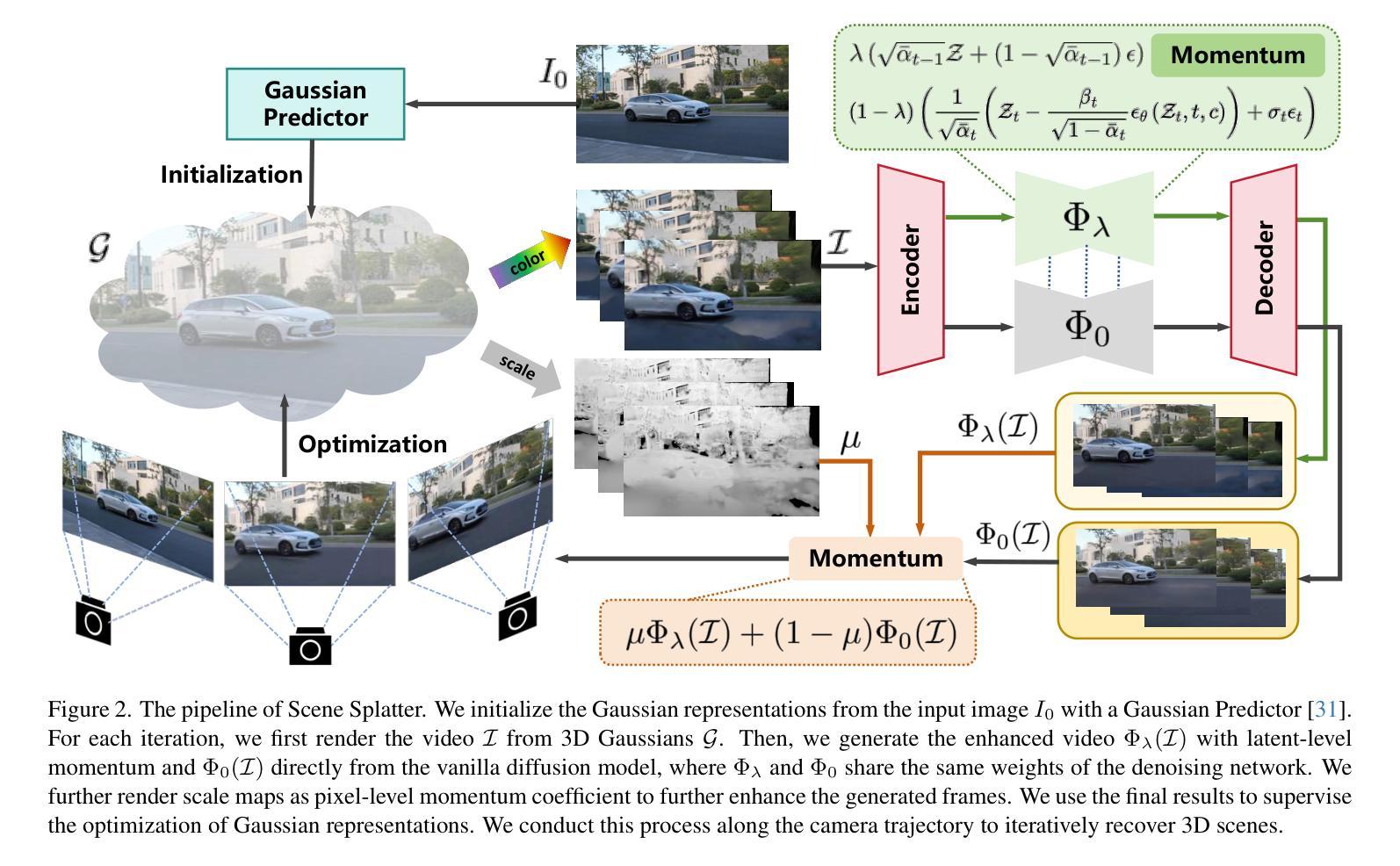
Scene Splatter: Momentum 3D Scene Generation from Single Image with Video Diffusion Model
Authors:Shengjun Zhang, Jinzhao Li, Xin Fei, Hao Liu, Yueqi Duan
In this paper, we propose Scene Splatter, a momentum-based paradigm for video diffusion to generate generic scenes from single image. Existing methods, which employ video generation models to synthesize novel views, suffer from limited video length and scene inconsistency, leading to artifacts and distortions during further reconstruction. To address this issue, we construct noisy samples from original features as momentum to enhance video details and maintain scene consistency. However, for latent features with the perception field that spans both known and unknown regions, such latent-level momentum restricts the generative ability of video diffusion in unknown regions. Therefore, we further introduce the aforementioned consistent video as a pixel-level momentum to a directly generated video without momentum for better recovery of unseen regions. Our cascaded momentum enables video diffusion models to generate both high-fidelity and consistent novel views. We further finetune the global Gaussian representations with enhanced frames and render new frames for momentum update in the next step. In this manner, we can iteratively recover a 3D scene, avoiding the limitation of video length. Extensive experiments demonstrate the generalization capability and superior performance of our method in high-fidelity and consistent scene generation.
本文提出了Scene Splatter,这是一种基于动量的视频扩散范式,用于从单幅图像生成通用场景。现有方法采用视频生成模型来合成新视角,存在视频长度有限和场景不一致的问题,导致在进一步重建时出现伪影和失真。为了解决这一问题,我们从原始特征中构建噪声样本作为动量,以增强视频细节并保持场景一致性。然而,对于感知场同时覆盖已知和未知区域的潜在特征,这种潜在层次的动量限制了视频扩散在未知区域的生成能力。因此,我们进一步引入了上述一致视频作为无动量的直接生成视频的像素级动量,以更好地恢复未见区域。我们的级联动量使视频扩散模型能够生成高保真且一致的全新视角。我们进一步使用增强帧微调全局高斯表示,并在下一步渲染新帧以进行动量更新。通过这种方式,我们可以迭代地恢复3D场景,避免视频长度的限制。大量实验表明,我们的方法在高保真和一致场景生成方面具有泛化能力和优越性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
本文提出了Scene Splatter方法,这是一种基于动量的视频扩散范式,能够从单幅图像生成通用场景。现有方法使用视频生成模型合成新视图时,存在视频长度有限和场景不一致的问题,导致进一步重建时出现伪影和失真。为解决这一问题,本文通过原始特征构建噪声样本作为动量,增强视频细节并保持场景一致性。然而,对于同时包含已知和未知区域的感知场域中的潜在特征,这种潜在层面的动量限制了视频扩散在未知区域的生成能力。因此,本文进一步引入了上述一致视频作为无动量的直接生成视频的像素级动量,以更好地恢复未见区域。级联动量使视频扩散模型能够生成高保真且一致的全新视图。通过微调全局高斯表示和增强帧进行渲染,为下一步更新动量提供新帧。通过这种方式,可以迭代恢复3D场景,避免视频长度的限制。
Key Takeaways
- Scene Splatter是一种基于动量的视频扩散方法,能够从单幅图像生成通用场景。
- 现有视频生成方法存在视频长度有限和场景不一致的问题。
- 通过构建噪声样本作为动量,Scene Splatter能增强视频细节并保持场景一致性。
- 潜在层面的动量在已知和未知区域的感知场域中限制了视频扩散的生成能力。
- Scene Splatter引入了像素级动量来恢复未见区域,并生成高保真且一致的全新视图。
- 通过微调全局高斯表示和增强帧进行渲染,可以迭代恢复3D场景。
点此查看论文截图


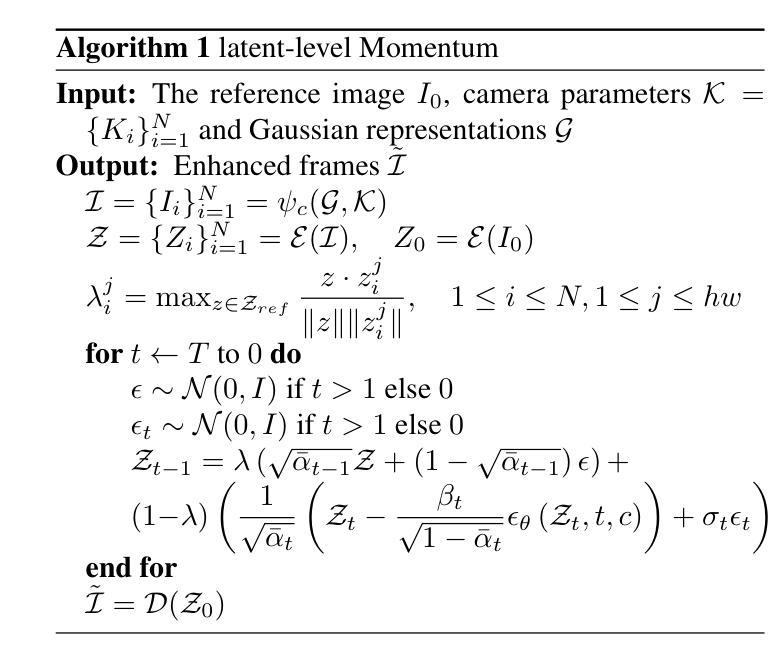

MD-ProjTex: Texturing 3D Shapes with Multi-Diffusion Projection
Authors:Ahmet Burak Yildirim, Mustafa Utku Aydogdu, Duygu Ceylan, Aysegul Dundar
We introduce MD-ProjTex, a method for fast and consistent text-guided texture generation for 3D shapes using pretrained text-to-image diffusion models. At the core of our approach is a multi-view consistency mechanism in UV space, which ensures coherent textures across different viewpoints. Specifically, MD-ProjTex fuses noise predictions from multiple views at each diffusion step and jointly updates the per-view denoising directions to maintain 3D consistency. In contrast to existing state-of-the-art methods that rely on optimization or sequential view synthesis, MD-ProjTex is computationally more efficient and achieves better quantitative and qualitative results.
我们介绍了MD-ProjTex方法,这是一种利用预训练的文本到图像扩散模型进行快速且一致的文本引导纹理生成的3D形状处理方法。我们的方法的核心在于UV空间中的多视角一致性机制,它能确保不同视角之间的纹理一致性。具体来说,MD-ProjTex在每个扩散步骤融合多个视角的噪声预测,并联合更新每个视角的去噪方向,以保持3D一致性。与现有的最先进方法相比,这些方法依赖于优化或顺序视图合成,MD-ProjTex计算效率更高,并且在数量和质量上都能实现更好的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
我们推出了MD-ProjTex方法,它利用预训练的文本到图像扩散模型,实现了快速且一致的文本引导纹理生成技术。该方法的核心在于UV空间的多视角一致性机制,确保不同视角的纹理连贯性。MD-ProjTex融合了多个视角的噪声预测,并在扩散过程中联合更新每个视角的去噪方向,以保持三维一致性。相较于依赖优化或顺序视角合成的现有方法,MD-ProjTex计算效率更高,且取得了更好的定量和定性结果。
Key Takeaways:
- MD-ProjTex是一种基于预训练的文本到图像扩散模型的快速且一致的文本引导纹理生成方法。
- 该方法采用多视角一致性机制,确保不同视角的纹理连贯性。
- MD-ProjTex融合了多个视角的噪声预测,并在扩散过程中更新去噪方向。
- MD-ProjTex相比现有方法,计算效率更高。
- MD-ProjTex在定量和定性评估中都取得了更好的结果。
- 该方法的核心贡献在于利用文本指导生成与文本内容相匹配的3D形状纹理。
点此查看论文截图


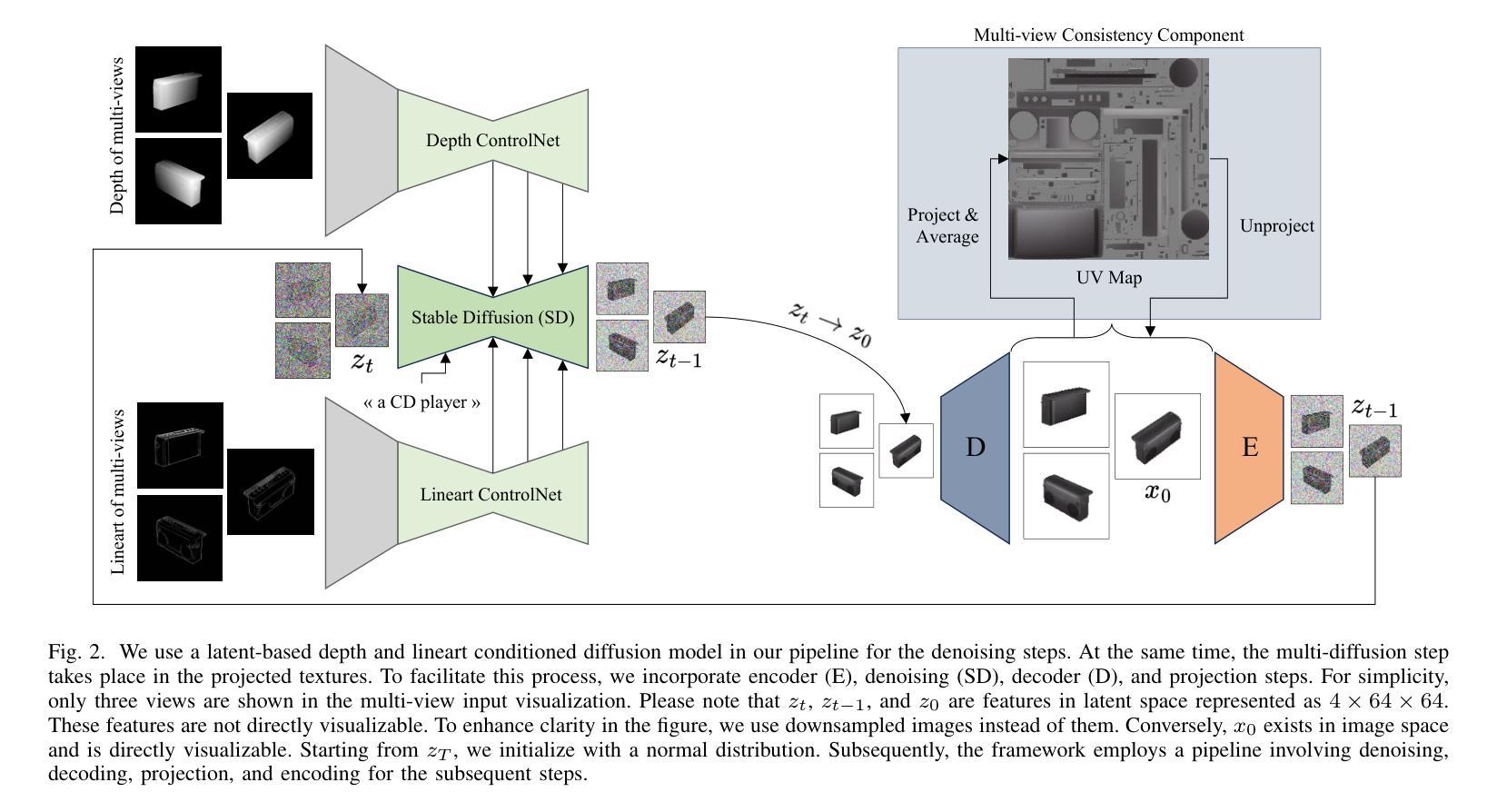

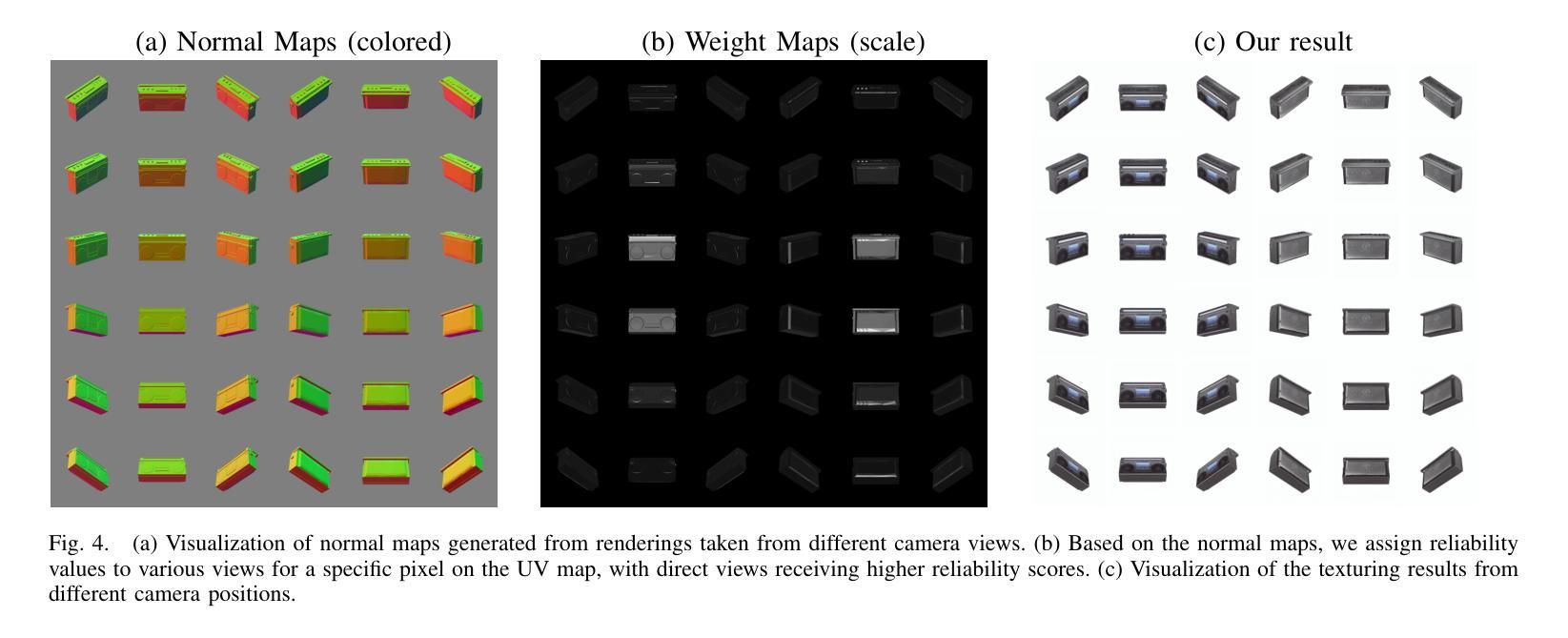
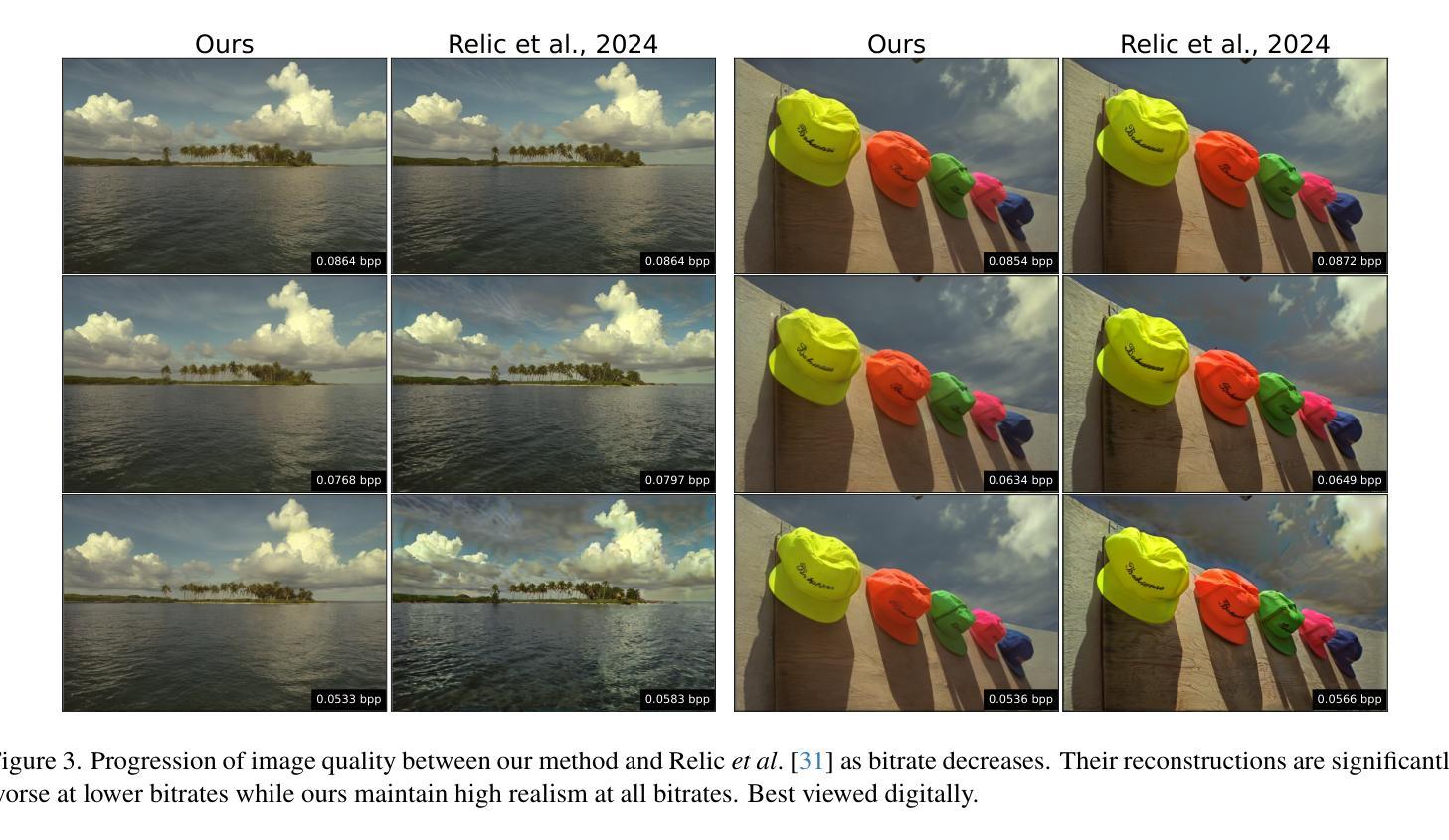
Bridging the Gap between Gaussian Diffusion Models and Universal Quantization for Image Compression
Authors:Lucas Relic, Roberto Azevedo, Yang Zhang, Markus Gross, Christopher Schroers
Generative neural image compression supports data representation at extremely low bitrate, synthesizing details at the client and consistently producing highly realistic images. By leveraging the similarities between quantization error and additive noise, diffusion-based generative image compression codecs can be built using a latent diffusion model to “denoise” the artifacts introduced by quantization. However, we identify three critical gaps in previous approaches following this paradigm (namely, the noise level, noise type, and discretization gaps) that result in the quantized data falling out of the data distribution known by the diffusion model. In this work, we propose a novel quantization-based forward diffusion process with theoretical foundations that tackles all three aforementioned gaps. We achieve this through universal quantization with a carefully tailored quantization schedule and a diffusion model trained with uniform noise. Compared to previous work, our proposal produces consistently realistic and detailed reconstructions, even at very low bitrates. In such a regime, we achieve the best rate-distortion-realism performance, outperforming previous related works.
生成式神经网络压缩支持以极低的比特率进行数据表示,可在客户端合成细节,并始终生成高度逼真的图像。通过利用量化误差和添加性噪声之间的相似性,可以使用潜在扩散模型构建基于扩散的生成式图像压缩编解码器,以“去噪”量化引起的伪影。然而,我们发现了遵循此模式(即噪声水平、噪声类型和离散化差距)的先前方法中的三个关键差距,导致量化数据脱离扩散模型所知道的数据分布。在本研究中,我们提出了一种基于量化理论基础的向前扩散过程新方案,解决了上述所有三个差距。我们通过使用通用量化以及精心定制的量化时间表,以及使用均匀噪声训练的扩散模型来实现这一点。与之前的工作相比,我们的方案即使在非常低的比特率下也能始终产生逼真的细节丰富的重建。在这种模式下,我们实现了最佳的速率失真逼真度性能,超越了以前的相关作品。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear at CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了基于扩散模型的生成式图像压缩技术。该技术能够在极低码率下支持数据表示,合成细节,并始终产生高度逼真的图像。文章指出先前的方法在噪声水平、噪声类型和离散化方面存在差距,导致量化数据脱离扩散模型所知的数据分布。为此,本文提出了一种基于量化的前向扩散过程,通过通用量化和精心定制的量化时间表以及使用均匀噪声训练的扩散模型,解决了上述问题。与以前的工作相比,该方案即使在码率极低的情况下也能始终产生逼真且详细的重建,实现了最佳的率失真现实性能。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式神经图像压缩利用扩散模型在极低码率下实现数据表示,能合成细节并生成高度逼真的图像。
- 指出先前方法在噪声水平、类型和离散化方面的差距,导致量化数据与扩散模型所知的数据分布不匹配。
- 提出一种基于量化的前向扩散过程,具有理论根基,解决了上述差距。
- 使用通用量化和精心定制的量化时间表。
- 扩散模型采用均匀噪声训练。
- 该方案在极低码率下仍能产生逼真且详细的重建。
点此查看论文截图

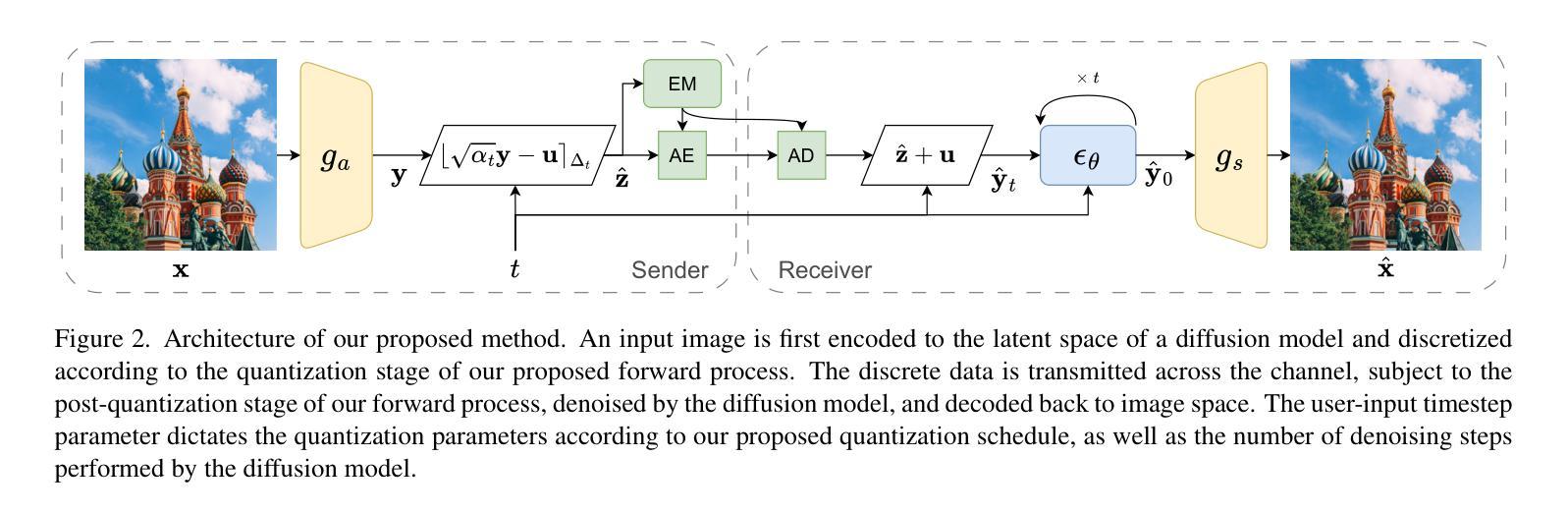

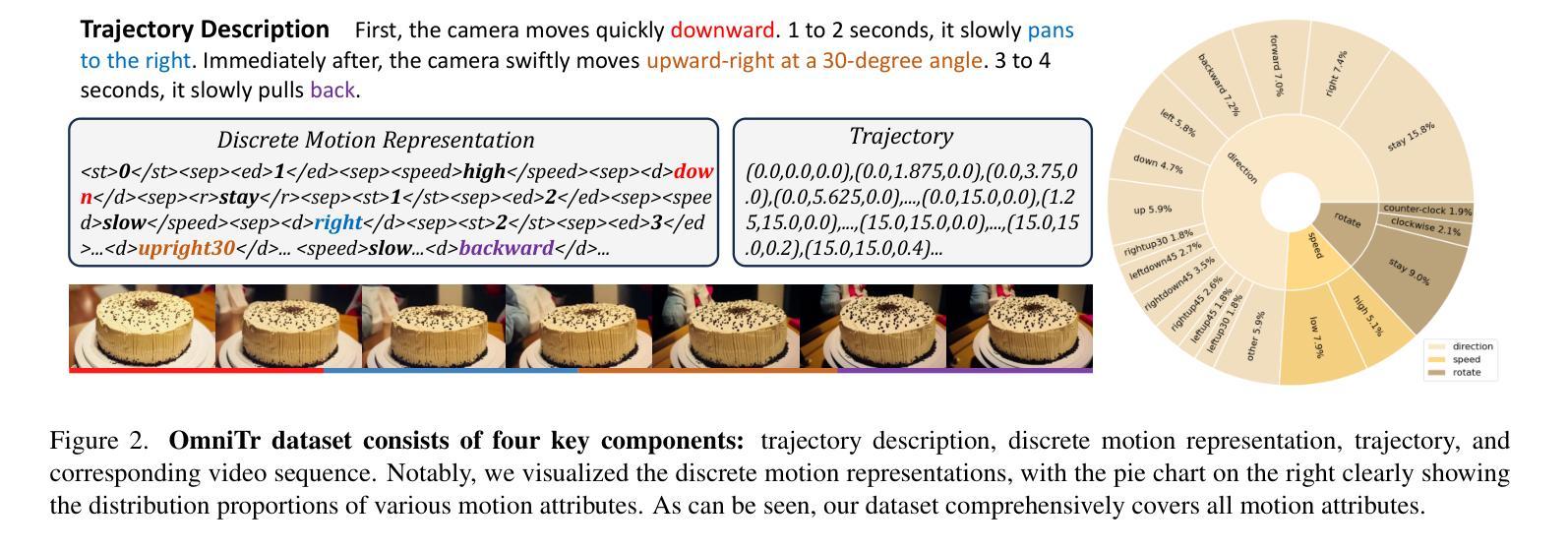
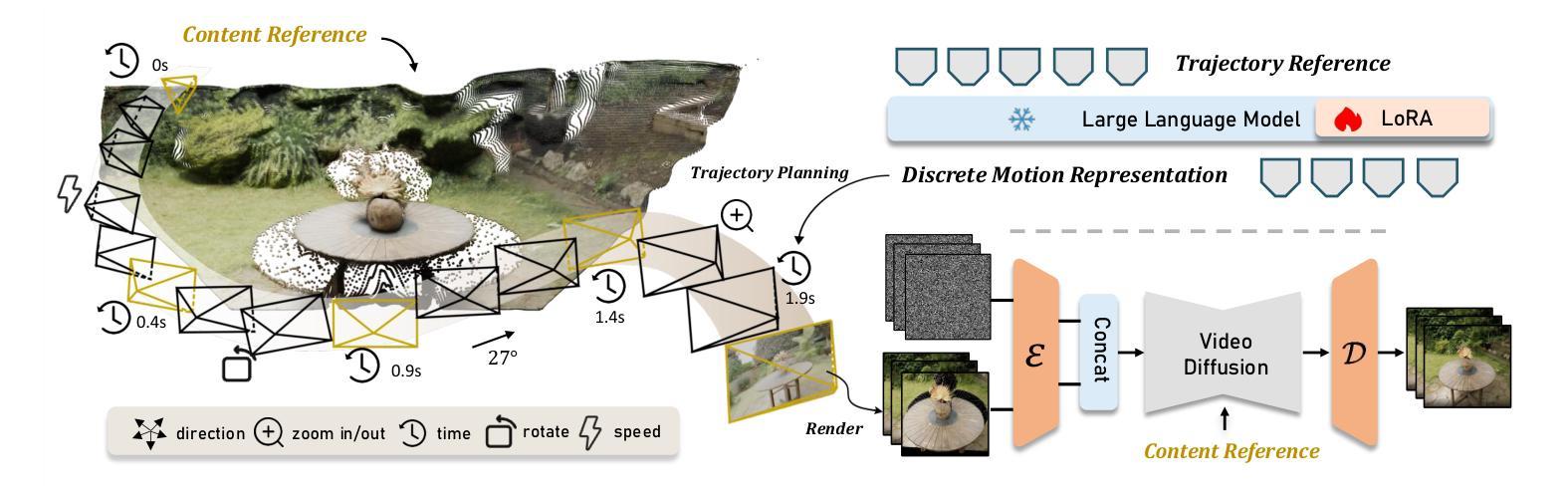
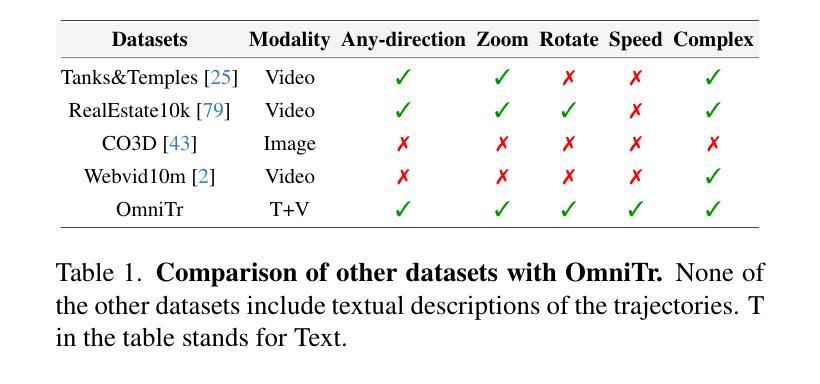
OmniCam: Unified Multimodal Video Generation via Camera Control
Authors:Xiaoda Yang, Jiayang Xu, Kaixuan Luan, Xinyu Zhan, Hongshun Qiu, Shijun Shi, Hao Li, Shuai Yang, Li Zhang, Checheng Yu, Cewu Lu, Lixin Yang
Camera control, which achieves diverse visual effects by changing camera position and pose, has attracted widespread attention. However, existing methods face challenges such as complex interaction and limited control capabilities. To address these issues, we present OmniCam, a unified multimodal camera control framework. Leveraging large language models and video diffusion models, OmniCam generates spatio-temporally consistent videos. It supports various combinations of input modalities: the user can provide text or video with expected trajectory as camera path guidance, and image or video as content reference, enabling precise control over camera motion. To facilitate the training of OmniCam, we introduce the OmniTr dataset, which contains a large collection of high-quality long-sequence trajectories, videos, and corresponding descriptions. Experimental results demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance in high-quality camera-controlled video generation across various metrics.
摄像机控制通过改变摄像机的位置和姿态来实现多种视觉效果,已经引起了广泛关注。然而,现有方法面临交互复杂和控制能力有限的挑战。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了OmniCam,一个统一的多模式摄像机控制框架。OmniCam利用大型语言模型和视频扩散模型,生成时空一致的视频。它支持各种输入模式的组合:用户可以提供文本或视频作为预期的轨迹作为摄像机路径指导,以及图像或视频作为内容参考,实现对摄像机运动的精确控制。为了促进OmniCam的训练,我们引入了OmniTr数据集,它包含大量高质量的长序列轨迹、视频和相应描述。实验结果表明,我们的模型在各种指标上实现了高质量的摄像机控制视频生成的前沿性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为OmniCam的多模态相机控制框架,它利用大型语言模型和视频扩散模型,通过改变相机位置和姿态实现多样化的视觉效果。OmniCam支持各种输入模态的组合,用户可以通过文本或视频提供预期的轨迹作为相机路径指导,图像或视频作为内容参考,实现对相机运动的精确控制。为训练OmniCam,引入了OmniTr数据集,包含大量高质量的长序列轨迹、视频和相应描述。实验结果表明,该模型在高质量相机控制视频生成方面实现了先进性能。
Key Takeaways
- OmniCam是一个多模态相机控制框架,利用大型语言模型和视频扩散模型。
- OmniCam可以通过改变相机位置和姿态实现多样化的视觉效果。
- OmniCam支持多种输入模态组合,包括文本或视频轨迹作为相机路径指导,图像或视频作为内容参考。
- OmniCam的引入解决了现有相机控制方法面临的复杂交互和有限控制能力的挑战。
- 为训练OmniCam,引入了OmniTr数据集,包含大量高质量的长序列轨迹、视频和相应描述。
- 实验结果表明,OmniCam在高质量相机控制视频生成方面达到了先进性能。
点此查看论文截图

Random Conditioning with Distillation for Data-Efficient Diffusion Model Compression
Authors:Dohyun Kim, Sehwan Park, Geonhee Han, Seung Wook Kim, Paul Hongsuck Seo
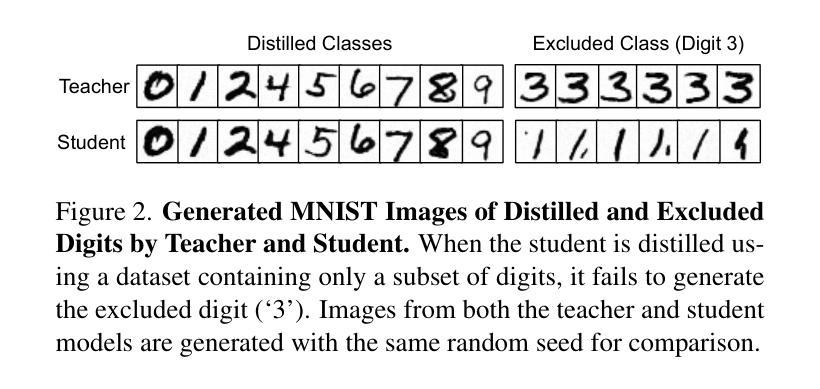
Diffusion models generate high-quality images through progressive denoising but are computationally intensive due to large model sizes and repeated sampling. Knowledge distillation, which transfers knowledge from a complex teacher to a simpler student model, has been widely studied in recognition tasks, particularly for transferring concepts unseen during student training. However, its application to diffusion models remains underexplored, especially in enabling student models to generate concepts not covered by the training images. In this work, we propose Random Conditioning, a novel approach that pairs noised images with randomly selected text conditions to enable efficient, image-free knowledge distillation. By leveraging this technique, we show that the student can generate concepts unseen in the training images. When applied to conditional diffusion model distillation, our method allows the student to explore the condition space without generating condition-specific images, resulting in notable improvements in both generation quality and efficiency. This promotes resource-efficient deployment of generative diffusion models, broadening their accessibility for both research and real-world applications. Code, models, and datasets are available at https://dohyun-as.github.io/Random-Conditioning .
扩散模型通过逐步去噪生成高质量图像,但由于模型体积庞大和重复采样,计算量较大。知识蒸馏是一种将知识从复杂的教师模型转移到简单的学模型的技术,在识别任务中已被广泛应用,特别是在学生训练期间未见的概念的转移方面。然而,其在扩散模型中的应用仍然被探索不足,特别是在使学生模型生成未涵盖在训练图像中的概念方面。在这项工作中,我们提出了随机条件化方法,这是一种将噪声图像与随机选择的文本条件配对的新方法,以实现高效的无图像知识蒸馏。通过利用这项技术,我们证明了学生模型可以生成在训练图像中未见的概念。当应用于条件扩散模型蒸馏时,我们的方法允许学生在不生成特定条件图像的情况下探索条件空间,导致生成质量和效率的显著提高。这促进了生成扩散模型的资源高效部署,扩大了其在研究和实际应用中的可及性。代码、模型和数据集可通过https://dohyun-as.github.io/Random-Conditioning获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025. 8 pages main paper + 4 pages references + 5 pages supplementary, 9 figures in total
Summary
扩散模型通过逐步去噪生成高质量图像,但由于模型规模庞大且涉及重复采样,计算量大。知识蒸馏在识别任务中广泛应用,可从复杂的教师模型向简单的模型转移知识,特别是在学生训练期间未见的概念转移方面。然而,其在扩散模型中的应用仍被较少探索,特别是在使学生模型生成训练图像未涵盖的概念方面。本研究提出一种名为Random Conditioning的新方法,它通过随机选择的文本条件配对噪声图像,实现了高效、无需图像的知识蒸馏。利用此技术,学生模型能够在训练图像中生成未见的概念。在应用于条件扩散模型蒸馏时,该方法使学生能够在无需生成特定条件图像的情况下探索条件空间,从而在生成质量和效率方面取得显著改善。这促进了生成扩散模型的资源高效部署,扩大了其在研究和实际应用中的可及性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型通过逐步去噪生成高质量图像,但计算量大。
- 知识蒸馏在识别任务中广泛应用,但在扩散模型中的应用仍被较少探索。
- Random Conditioning方法通过随机选择的文本条件配对噪声图像,实现了高效、无需图像的知识蒸馏。
- 学生模型能够在训练图像中生成未见的概念。
- 该方法提高了生成质量和效率。
- 该方法促进了生成扩散模型的资源高效部署。
点此查看论文截图


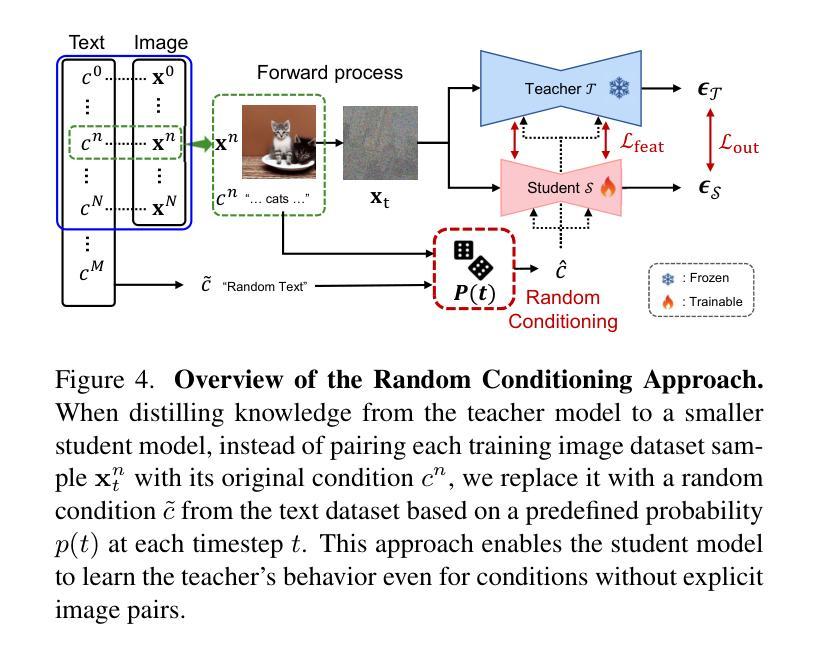
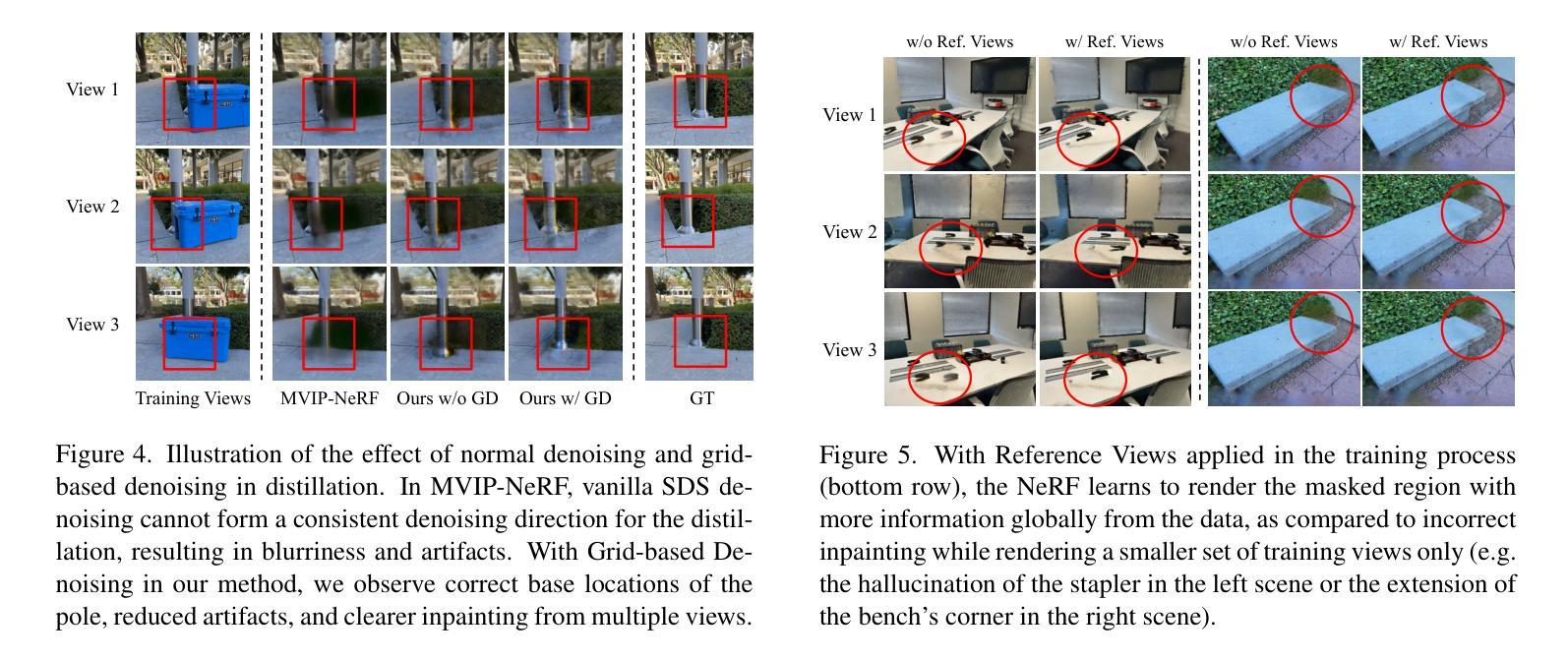
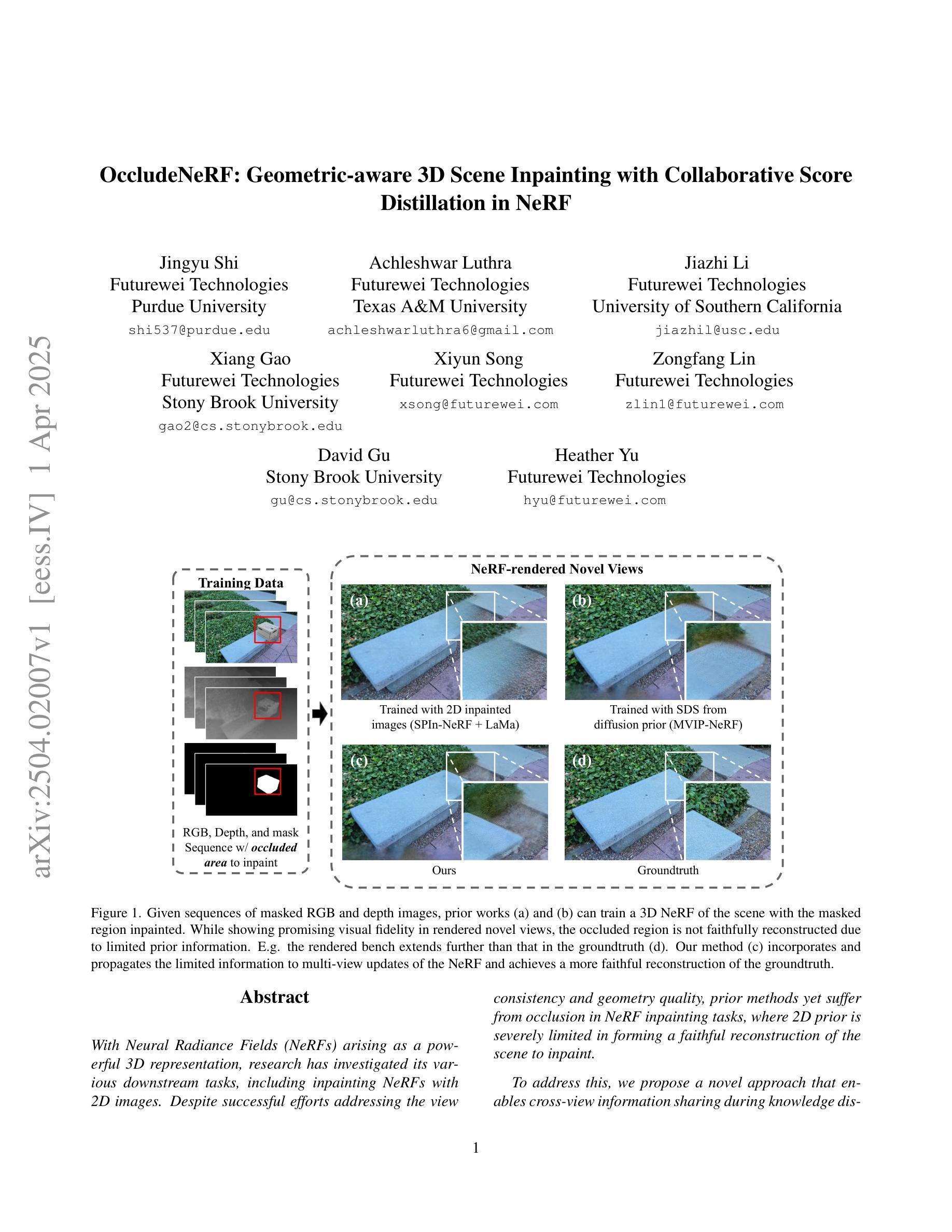
OccludeNeRF: Geometric-aware 3D Scene Inpainting with Collaborative Score Distillation in NeRF
Authors:Jingyu Shi, Achleshwar Luthra, Jiazhi Li, Xiang Gao, Xiyun Song, Zongfang Lin, David Gu, Heather Yu
With Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) arising as a powerful 3D representation, research has investigated its various downstream tasks, including inpainting NeRFs with 2D images. Despite successful efforts addressing the view consistency and geometry quality, prior methods yet suffer from occlusion in NeRF inpainting tasks, where 2D prior is severely limited in forming a faithful reconstruction of the scene to inpaint. To address this, we propose a novel approach that enables cross-view information sharing during knowledge distillation from a diffusion model, effectively propagating occluded information across limited views. Additionally, to align the distillation direction across multiple sampled views, we apply a grid-based denoising strategy and incorporate additional rendered views to enhance cross-view consistency. To assess our approach’s capability of handling occlusion cases, we construct a dataset consisting of challenging scenes with severe occlusion, in addition to existing datasets. Compared with baseline methods, our method demonstrates better performance in cross-view consistency and faithfulness in reconstruction, while preserving high rendering quality and fidelity.
随着神经辐射场(NeRFs)作为一种强大的3D表示方法的发展,研究已经探索了其各种下游任务,包括使用2D图像填充NeRFs。尽管已经出现了针对视图一致性和几何质量提升的成功尝试,先前的方法在NeRF填充任务中仍受到遮挡问题的困扰,其中由于二维先验的局限性,无法准确重建场景以进行填充。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新方法,通过扩散模型的知识蒸馏过程实现跨视图信息共享,有效地传播了有限的视图中的遮挡信息。此外,为了对齐多个采样视图中的蒸馏方向,我们采用基于网格的去噪策略并融入额外的渲染视图以增强跨视图一致性。为了评估我们的方法在处理遮挡案例方面的能力,除了现有的数据集外,我们还构建了一个包含具有严重遮挡的挑战性场景的数据集。与基准方法相比,我们的方法在跨视图一致性、重建的忠实性和保持高质量渲染方面表现出了更好的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025 CV4Metaverse
Summary
基于NeRF(神经辐射场)的强大3D表示能力,现有研究对其下游任务进行了深入探索,包括利用2D图像进行NeRF补全。尽管现有方法在保持视图一致性和几何质量方面取得了显著进展,但在NeRF补全任务中仍面临遮挡问题,2D先验信息在重建待补全场景时难以形成忠实表达。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新方法,利用扩散模型的知识蒸馏过程实现跨视图信息共享,有效传播跨有限视图的遮挡信息。此外,我们还采用基于网格的去噪策略,并通过添加额外渲染视图来对齐多个采样视图的蒸馏方向,以提高跨视图一致性。通过构建包含严重遮挡挑战场景的数据集,并与其他基准方法进行比较,我们的方法在跨视图一致性、重建忠实度、渲染质量和保真度方面表现出更佳的性能。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF作为一种强大的3D表示方法,在下游任务如NeRF补全中受到关注。
- 现有方法在解决NeRF补全任务中的遮挡问题时存在局限,2D先验信息难以形成对场景的忠实重建。
- 提出了一种利用扩散模型知识蒸馏的跨视图信息共享新方法,以解决遮挡问题。
- 通过基于网格的去噪策略和额外渲染视图,提高跨视图一致性。
- 构建了一个包含具有严重遮挡挑战场景的数据集,以评估方法性能。
- 与基准方法相比,该方法在跨视图一致性、重建忠实度、渲染质量和保真度方面表现更佳。
点此查看论文截图
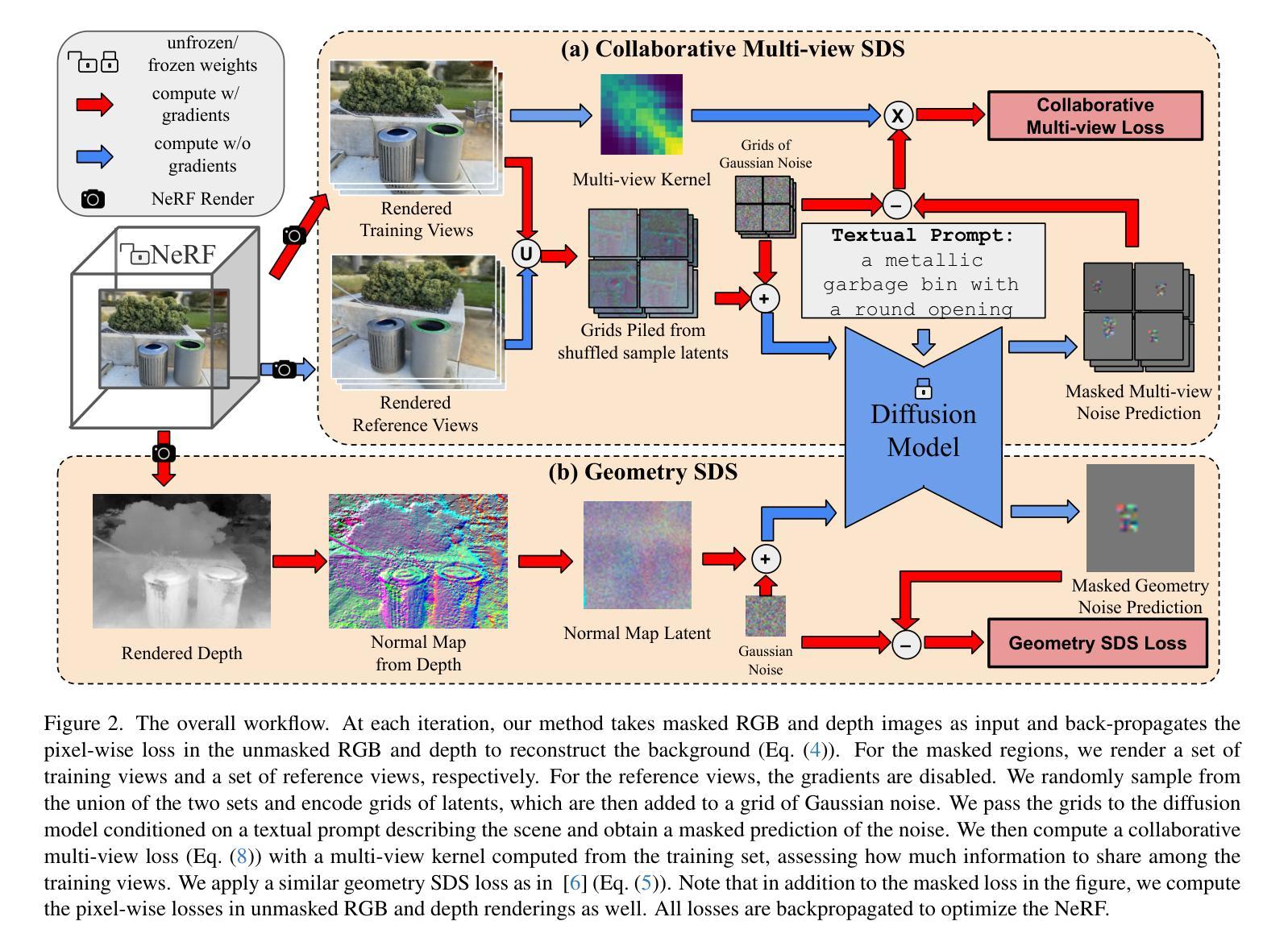


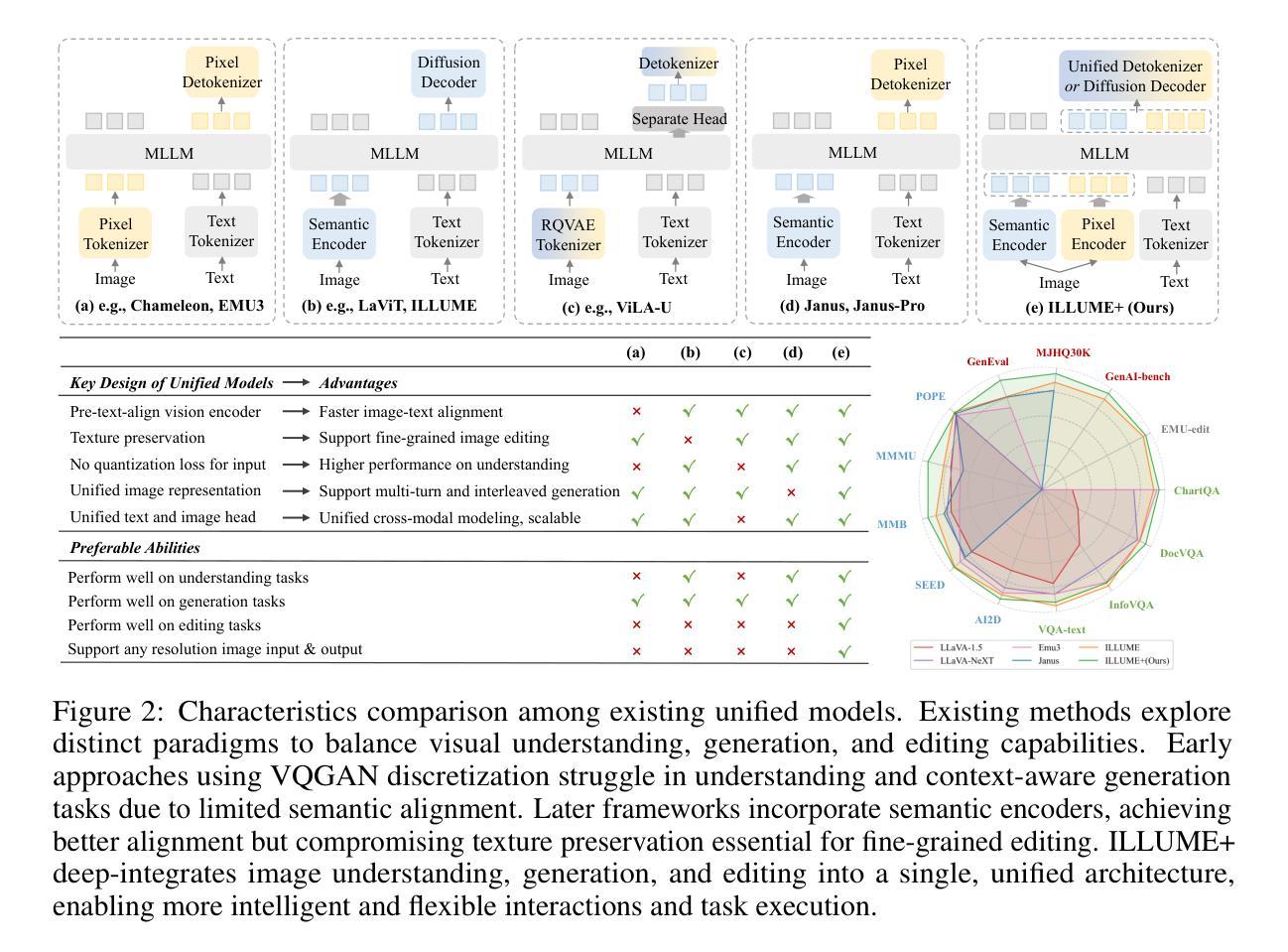
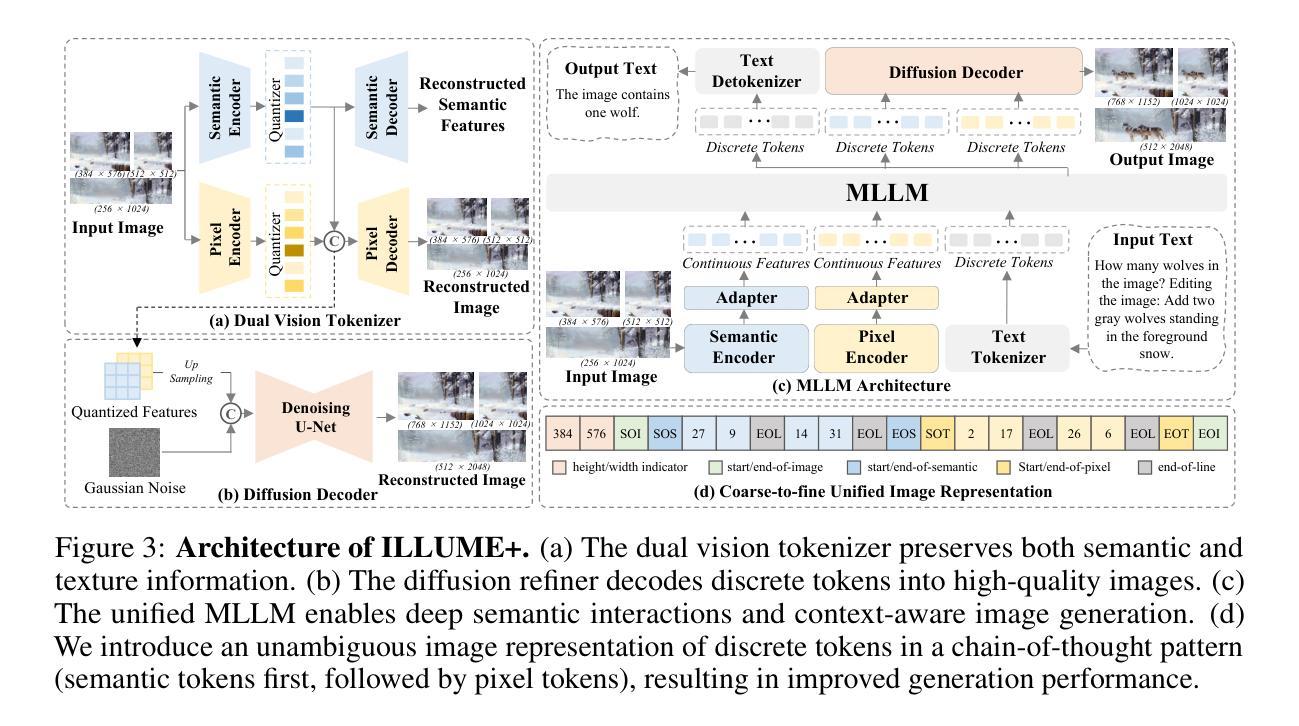
ILLUME+: Illuminating Unified MLLM with Dual Visual Tokenization and Diffusion Refinement
Authors:Runhui Huang, Chunwei Wang, Junwei Yang, Guansong Lu, Yunlong Yuan, Jianhua Han, Lu Hou, Wei Zhang, Lanqing Hong, Hengshuang Zhao, Hang Xu
We present ILLUME+ that leverages dual visual tokenization and a diffusion decoder to improve both deep semantic understanding and high-fidelity image generation. Existing unified models have struggled to simultaneously handle the three fundamental capabilities in a unified model: understanding, generation, and editing. Models like Chameleon and EMU3 utilize VQGAN for image discretization, due to the lack of deep semantic interaction, they lag behind specialist models like LLaVA in visual understanding tasks. To mitigate this, LaViT and ILLUME employ semantic encoders for tokenization, but they struggle with image editing due to poor texture preservation. Meanwhile, Janus series decouples the input and output image representation, limiting their abilities to seamlessly handle interleaved image-text understanding and generation. In contrast, ILLUME+ introduces a unified dual visual tokenizer, DualViTok, which preserves both fine-grained textures and text-aligned semantics while enabling a coarse-to-fine image representation strategy for multimodal understanding and generation. Additionally, we employ a diffusion model as the image detokenizer for enhanced generation quality and efficient super-resolution. ILLUME+ follows a continuous-input, discrete-output scheme within the unified MLLM and adopts a progressive training procedure that supports dynamic resolution across the vision tokenizer, MLLM, and diffusion decoder. This design allows for flexible and efficient context-aware image editing and generation across diverse tasks. ILLUME+ (3B) exhibits competitive performance against existing unified MLLMs and specialized models across multimodal understanding, generation, and editing benchmarks. With its strong performance, ILLUME+ provides a scalable and versatile foundation for future multimodal applications. Project Page: https://illume-unified-mllm.github.io/.
我们提出了ILLUME+,它利用双重视觉标记化和扩散解码器来提高深度语义理解和高保真图像生成能力。现有的统一模型在统一模型中同时处理三种基本能力(理解、生成和编辑)时遇到了困难。诸如变色龙和EMU3之类的模型使用VQGAN进行图像离散化,由于缺乏深度语义交互,它们在视觉理解任务上落后于LLaVA等专用模型。为了缓解这一问题,LaViT和ILLUME采用语义编码器进行标记化,但它们在进行图像编辑时由于纹理保存不佳而遇到困难。与此同时,Janus系列将输入和输出图像表示分离,限制了它们无缝处理交错式图像文本理解和生成的能力。相比之下,ILLUME+引入了一个统一的双重视觉标记器DualViTok,它既能保留精细纹理又能保持文本对齐语义,同时实现粗细结合的图像表示策略,用于多模态理解和生成。此外,我们采用扩散模型作为图像解标记器,以提高生成质量和高效超分辨率。ILLUME+在统一MLLM内采用连续输入、离散输出的方案,并采用渐进式训练程序,支持视觉标记器、MLLM和扩散解码器之间的动态分辨率调整。这种设计使得跨不同任务的灵活和高效上下文感知图像编辑和生成成为可能。ILLUME+(3B)在多模态理解、生成和编辑基准测试中表现出与现有统一MLLM和专用模型相竞争的性能。凭借强大的性能,ILLUME+为未来多模态应用提供了可扩展和多功能的基础。项目页面:https://illume-unified-mllm.github.io/.
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
ILUME+通过利用双重视觉标记化和扩散解码器,改进了深度语义理解和高保真图像生成。现有统一模型在三项基本能力上难以兼顾:理解、生成和编辑。ILLUME+引入统一双重视觉标记器DualViTok,保留精细纹理和文本对齐语义,采用由粗到细图像表示策略进行多模态理解和生成。此外,采用扩散模型作为图像解标记器,提高生成质量和超分辨率效率。ILLUME+采用连续输入、离散输出的统一MLLM方案,采用渐进式训练程序,支持视觉标记器、MLLM和扩散解码器之间的动态分辨率。这为跨不同任务的上下文感知图像编辑和生成提供了灵活和高效的方法。
关键见解
- ILLUME+结合了双重视觉标记化和扩散解码器,提升了深度语义理解和高保真图像生成。
- 现有模型如Chameleon和EMU3在视觉理解任务上落后于专家模型,如LLaVA。
- LaViT和ILLUME使用语义编码器进行标记化,但在图像编辑方面因纹理保留不足而遇到困难。
- Janus系列将输入和输出图像表示解耦,限制了他们处理交织的图像-文本理解和生成的能力。
- ILLUME+的DualViTok保留了精细纹理和文本对齐语义,并实现了粗到细的图像表示策略。
- 采用扩散模型作为图像解标记器,提高了生成质量和超分辨率效率。
- ILLUME+的渐进式训练程序支持动态分辨率调整,为跨任务上下文感知图像编辑和生成提供了灵活性。
点此查看论文截图

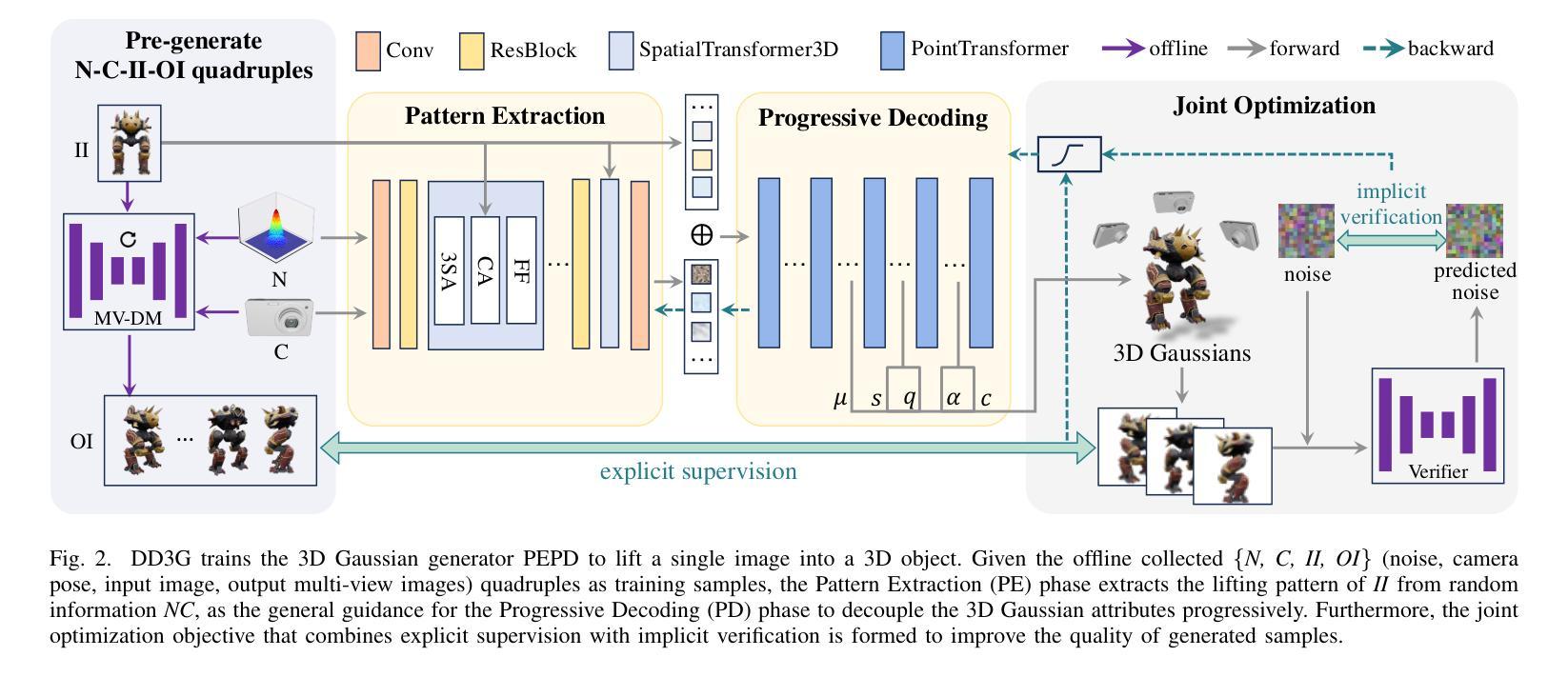
Distilling Multi-view Diffusion Models into 3D Generators
Authors:Hao Qin, Luyuan Chen, Ming Kong, Mengxu Lu, Qiang Zhu
We introduce DD3G, a formulation that Distills a multi-view Diffusion model (MV-DM) into a 3D Generator using gaussian splatting. DD3G compresses and integrates extensive visual and spatial geometric knowledge from the MV-DM by simulating its ordinary differential equation (ODE) trajectory, ensuring the distilled generator generalizes better than those trained solely on 3D data. Unlike previous amortized optimization approaches, we align the MV-DM and 3D generator representation spaces to transfer the teacher’s probabilistic flow to the student, thus avoiding inconsistencies in optimization objectives caused by probabilistic sampling. The introduction of probabilistic flow and the coupling of various attributes in 3D Gaussians introduce challenges in the generation process. To tackle this, we propose PEPD, a generator consisting of Pattern Extraction and Progressive Decoding phases, which enables efficient fusion of probabilistic flow and converts a single image into 3D Gaussians within 0.06 seconds. Furthermore, to reduce knowledge loss and overcome sparse-view supervision, we design a joint optimization objective that ensures the quality of generated samples through explicit supervision and implicit verification. Leveraging existing 2D generation models, we compile 120k high-quality RGBA images for distillation. Experiments on synthetic and public datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. Our project is available at: https://qinbaigao.github.io/DD3G_project/
我们介绍了DD3G,这是一种通过高斯拼贴法将多视角扩散模型(MV-DM)蒸馏到3D生成器的方法。DD3G通过模拟MV-DM的常微分方程(ODE)轨迹,压缩并集成了广泛的视觉和空间几何知识,确保蒸馏出的生成器比仅基于3D数据训练的生成器具有更好的泛化性能。与前期的摊销优化方法不同,我们将MV-DM和3D生成器的表示空间对齐,以将教师的概率流传输给学生,从而避免由概率采样引起的优化目标不一致。概率流的引入和3D高斯中各种属性的耦合给生成过程带来了挑战。为此,我们提出了PEPD生成器,包括模式提取和渐进解码两个阶段,能够实现概率流的有效融合,并在0.06秒内将单幅图像转换为3D高斯。此外,为了减少知识损失并克服稀疏视图监督,我们设计了一个联合优化目标,通过明确监督和隐式验证确保生成样本的质量。我们利用现有的2D生成模型,编译了12万张高质量RGBA图像用于蒸馏。在合成和公开数据集上的实验证明了我们的方法的有效性。我们的项目可在以下网址找到:https://qinbaigao.github.io/DD3G_project/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
DD3G是一个将多视图扩散模型(MV-DM)蒸馏到3D生成器的模型。它通过模拟MV-DM的常微分方程(ODE)轨迹,压缩并整合视觉和几何空间知识。DD3G采用概率流对齐的方式,避免优化目标的不一致性。为应对生成过程中的挑战,引入PEPD生成器,实现概率流的融合和高效转换。通过联合优化目标,减少知识损失并克服稀疏监督问题。实验证明该方法在合成和公开数据集上的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- DD3G是一个多视图扩散模型的蒸馏版本,被蒸馏成一个3D生成器。
- 通过模拟MV-DM的ODE轨迹,DD3G整合了视觉和几何空间知识。
- 采用概率流对齐方式,确保学生模型能够学习教师的概率流,避免了优化目标的不一致性。
- PEPD生成器的引入解决了生成过程中的挑战,实现了概率流的融合和高效转换。
- 通过联合优化目标,减少知识损失并克服稀疏监督问题,确保了生成样本的质量。
- 该方法在合成和公开数据集上的实验证明了其有效性。
点此查看论文截图

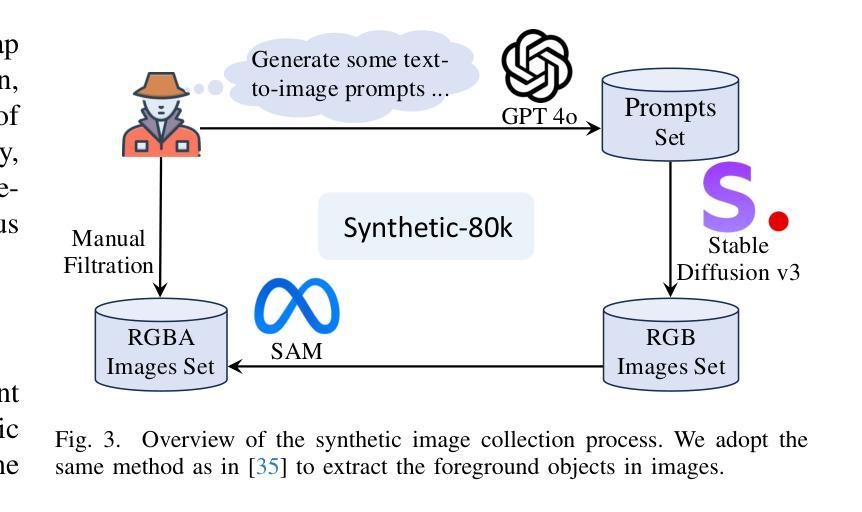

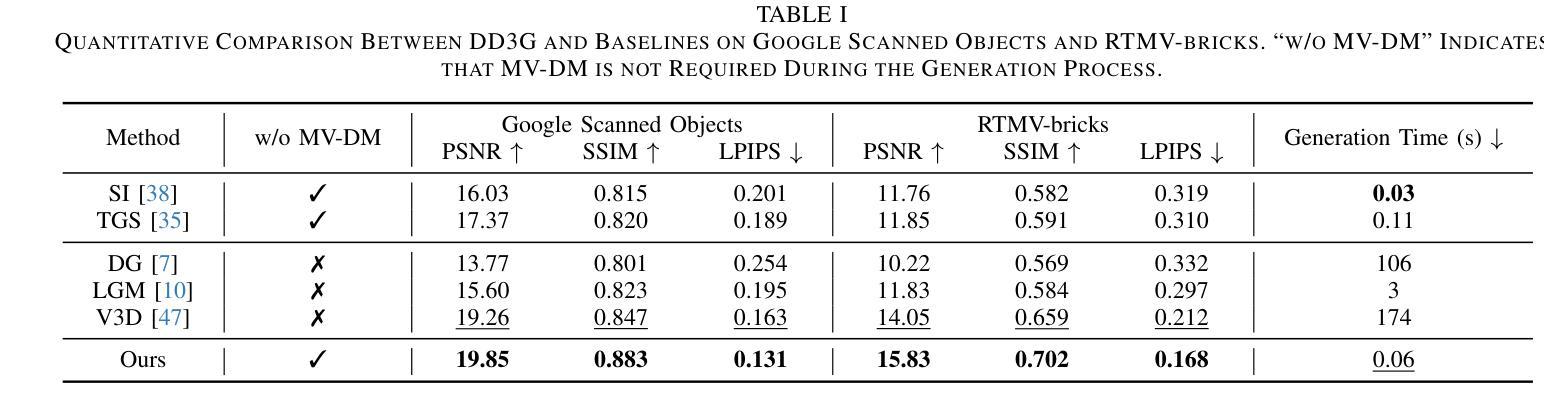
Flow to the Mode: Mode-Seeking Diffusion Autoencoders for State-of-the-Art Image Tokenization
Authors:Kyle Sargent, Kyle Hsu, Justin Johnson, Li Fei-Fei, Jiajun Wu
Since the advent of popular visual generation frameworks like VQGAN and latent diffusion models, state-of-the-art image generation systems have generally been two-stage systems that first tokenize or compress visual data into a lower-dimensional latent space before learning a generative model. Tokenizer training typically follows a standard recipe in which images are compressed and reconstructed subject to a combination of MSE, perceptual, and adversarial losses. Diffusion autoencoders have been proposed in prior work as a way to learn end-to-end perceptually-oriented image compression, but have not yet shown state-of-the-art performance on the competitive task of ImageNet-1K reconstruction. We propose FlowMo, a transformer-based diffusion autoencoder that achieves a new state-of-the-art for image tokenization at multiple compression rates without using convolutions, adversarial losses, spatially-aligned two-dimensional latent codes, or distilling from other tokenizers. Our key insight is that FlowMo training should be broken into a mode-matching pre-training stage and a mode-seeking post-training stage. In addition, we conduct extensive analyses and explore the training of generative models atop the FlowMo tokenizer. Our code and models will be available at http://kylesargent.github.io/flowmo .
自从出现了VQGAN和潜在扩散模型等流行的视觉生成框架以来,最先进的图像生成系统通常是一个两阶段系统,它首先会将视觉数据标记化或压缩到低维潜在空间,然后学习生成模型。标记器训练通常遵循一个标准流程,图像被压缩和重建,同时受到均方误差、感知和对抗损失的制约。先前的工作已经提出了扩散自编码器作为学习端到端感知导向的图像压缩的一种方法,但在ImageNet-1K重建的竞赛任务中尚未表现出最佳性能。我们提出了FlowMo,这是一个基于转换器的扩散自编码器,它实现了图像标记化的新最佳性能,支持多种压缩率,无需使用卷积、对抗性损失、空间对齐的二维潜在代码或其他标记器进行提炼。我们的关键见解是FlowMo训练应该分为模式匹配的预训练阶段和模式搜索的后训练阶段。此外,我们还进行了广泛的分析和探索了基于FlowMo标记器的生成模型的训练。我们的代码和模型将在http://kylesargent.github.io/flowmo上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 13 figures
Summary
基于VQGAN和潜在扩散模型等流行视觉生成框架的出现,目前先进的图像生成系统通常采用两阶段系统,第一阶段将视觉数据令牌化或压缩到低维潜在空间,然后学习生成模型。本文提出FlowMo,一种基于转换器的扩散自动编码器,无需卷积、对抗性损失、空间对齐的二维潜在代码或蒸馏,即可在多个压缩率下实现图像令牌化的新最先进的性能。关键见解是FlowMo训练应分为模式匹配的预训练阶段和模式搜索的后训练阶段。
Key Takeaways
- 当前图像生成系统多采用两阶段系统,包括数据令牌化或压缩到潜在空间以及生成模型的学习。
- FlowMo是一种新型的扩散自动编码器,能够在不使用卷积、对抗性损失等技术的情况下实现图像令牌化的先进性能。
- FlowMo训练分为模式匹配的预训练阶段和模式搜索的后训练阶段。
- FlowMo在多个压缩率下均表现出优秀的性能。
- 该研究提出了一种创新的图像压缩方法,旨在提高图像生成系统的效率和性能。
- 研究者还进行了广泛的实验和分析,探讨了基于FlowMo令牌器的生成模型的训练。
点此查看论文截图

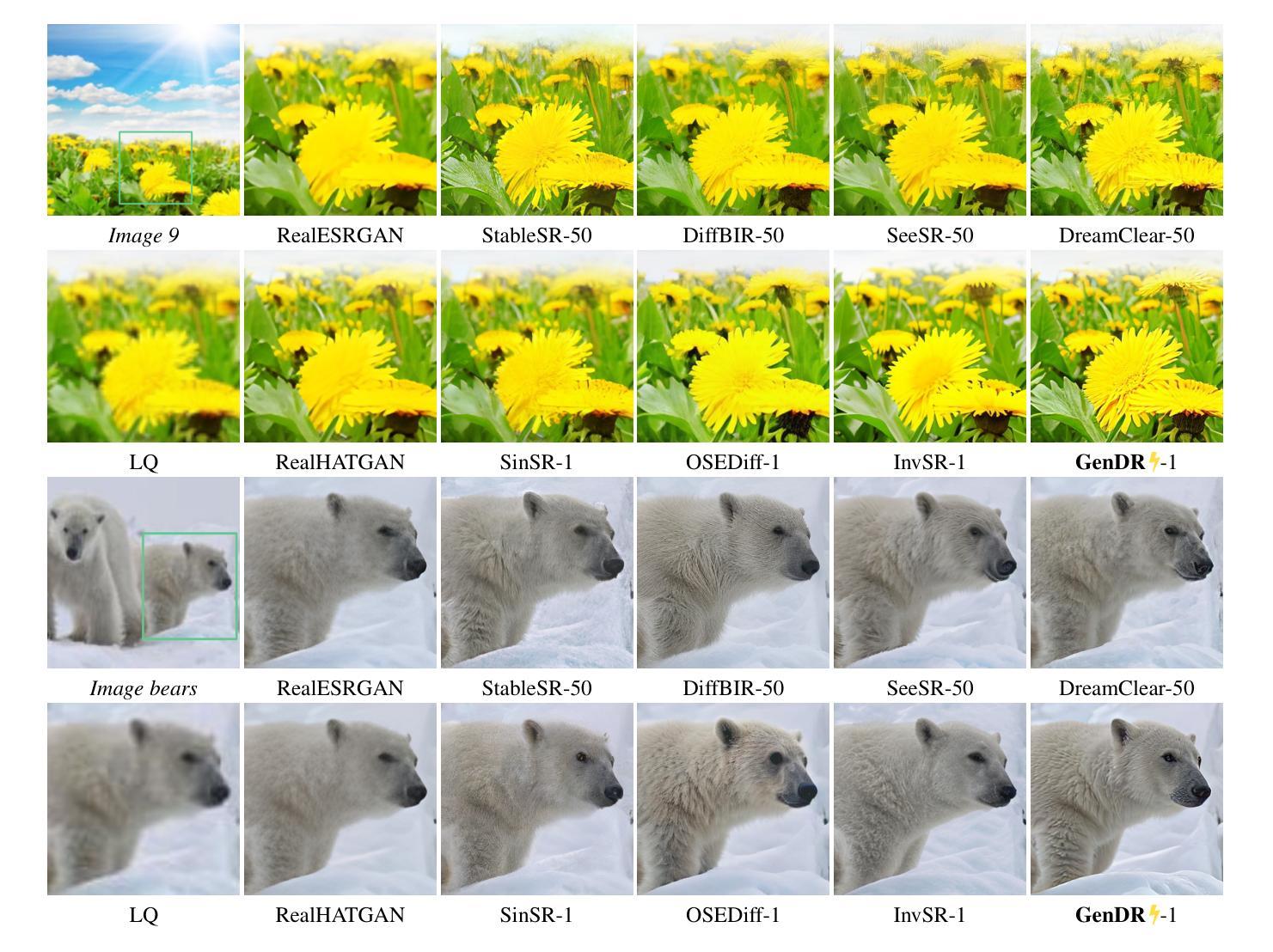
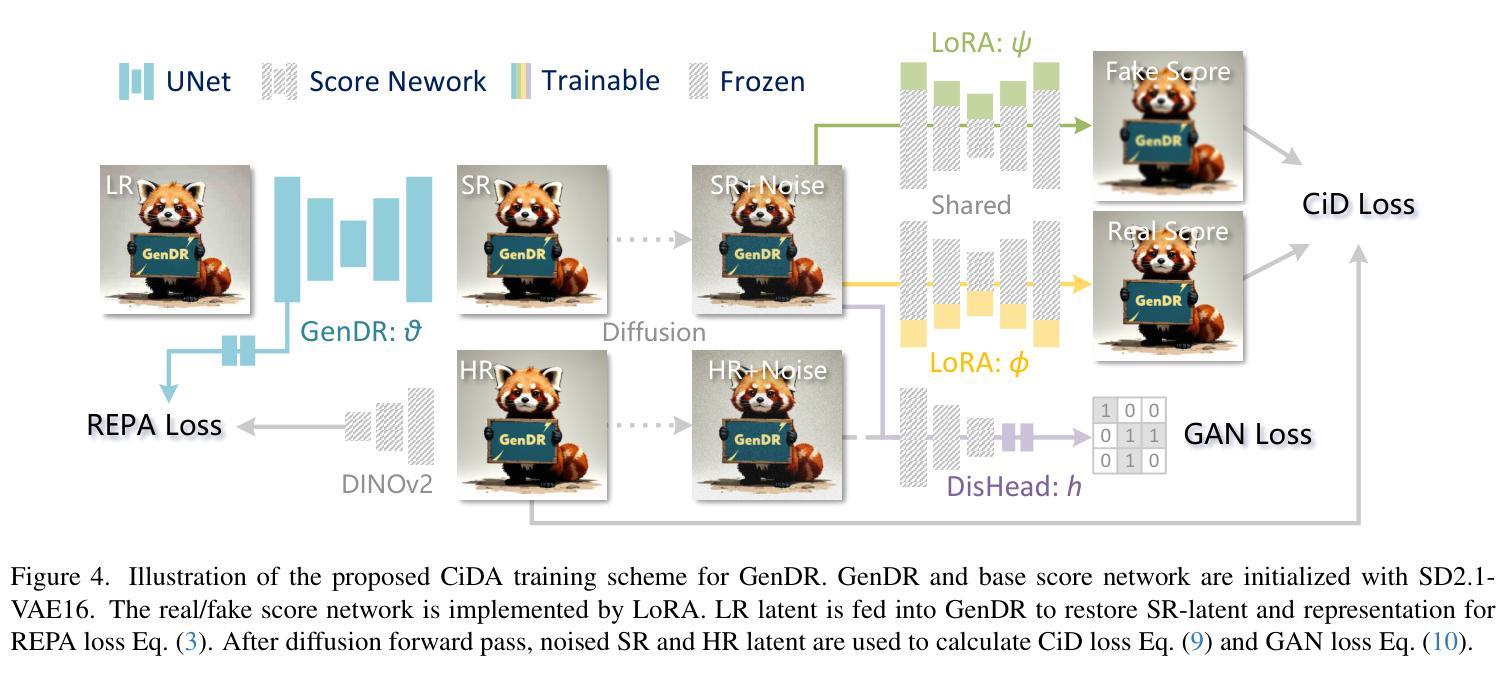
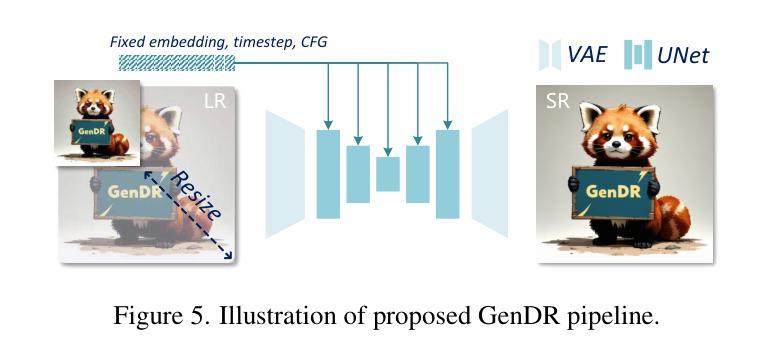
GenDR: Lightning Generative Detail Restorator
Authors:Yan Wang, Shijie Zhao, Kai Chen, Kexin Zhang, Junlin Li, Li Zhang
Recent research applying text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models to real-world super-resolution (SR) has achieved remarkable success. However, fundamental misalignments between T2I and SR targets result in a dilemma between inference speed and detail fidelity. Specifically, T2I tasks prioritize multi-step inversion to synthesize coherent outputs aligned with textual prompts and shrink the latent space to reduce generating complexity. Contrariwise, SR tasks preserve most information from low-resolution input while solely restoring high-frequency details, thus necessitating sufficient latent space and fewer inference steps. To bridge the gap, we present a one-step diffusion model for generative detail restoration, GenDR, distilled from a tailored diffusion model with larger latent space. In detail, we train a new SD2.1-VAE16 (0.9B) via representation alignment to expand latent space without enlarging the model size. Regarding step-distillation, we propose consistent score identity distillation (CiD) that incorporates SR task-specific loss into score distillation to leverage more SR priors and align the training target. Furthermore, we extend CiD with adversarial learning and representation alignment (CiDA) to enhance perceptual quality and accelerate training. We also polish the pipeline to achieve a more efficient inference. Experimental results demonstrate that GenDR achieves state-of-the-art performance in both quantitative metrics and visual fidelity.
近期将文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型应用于现实世界的超分辨率(SR)研究取得了显著的成功。然而,T2I和SR目标之间的基本不对齐导致了推理速度与细节保真度之间的困境。具体来说,T2I任务优先进行多步反转,以合成与文本提示对齐的输出,并缩小潜在空间以减少生成复杂性。相反,SR任务保留来自低分辨率输入的最多信息,同时仅恢复高频细节,因此需要足够的潜在空间和较少的推理步骤。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了一种用于生成细节恢复的扩散模型(GenDR),它是从一个具有更大潜在空间的定制扩散模型中提炼出来的一步模型。具体来说,我们通过表示对齐训练了一个新的SD2.1-VAE16(0.9B)来扩展潜在空间,而无需扩大模型大小。关于步骤蒸馏,我们提出了基于一致评分身份蒸馏(CiD)的方法,该方法将SR任务特定损失纳入评分蒸馏中,以利用更多的SR先验知识并调整训练目标。此外,我们将对抗性学习与表示对齐扩展到CiDA,以提高感知质量和加速训练。我们还优化了管道,以实现更有效的推理。实验结果表明,GenDR在定量指标和视觉保真度方面都达到了最新技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在真实世界超分辨率(SR)应用上取得了显著成功,但T2I和SR目标之间的基本不匹配导致推理速度与细节保真度之间的困境。为弥补这一差距,提出了一种用于生成细节恢复的一次性扩散模型GenDR,它由一个具有更大潜在空间的定制扩散模型提炼而成。通过新的SD2.1-VAE16(0.9B)模型和一致分数身份蒸馏(CiD)等技术,提高感知质量并加速训练。GenDR在定量指标和视觉保真度上都达到了最新水平。
Key Takeaways
- T2I扩散模型在SR应用上表现卓越,但存在推理速度与细节保真度的困境。
- GenDR是一个用于生成细节恢复的一次性扩散模型,解决了T2I和SR目标之间的不匹配问题。
- GenDR通过扩大潜在空间来提高性能,采用新的SD2.1-VAE16(0.9B)模型。
- 一致分数身份蒸馏(CiD)技术被提出,结合SR任务特定损失进行分数蒸馏,利用更多SR先验并调整训练目标。
- CiD与对抗性学习及表示对齐相结合,增强了感知质量和加速了训练。
- GenDR的实验结果达到了在定量指标和视觉保真度上的最新水平。
点此查看论文截图



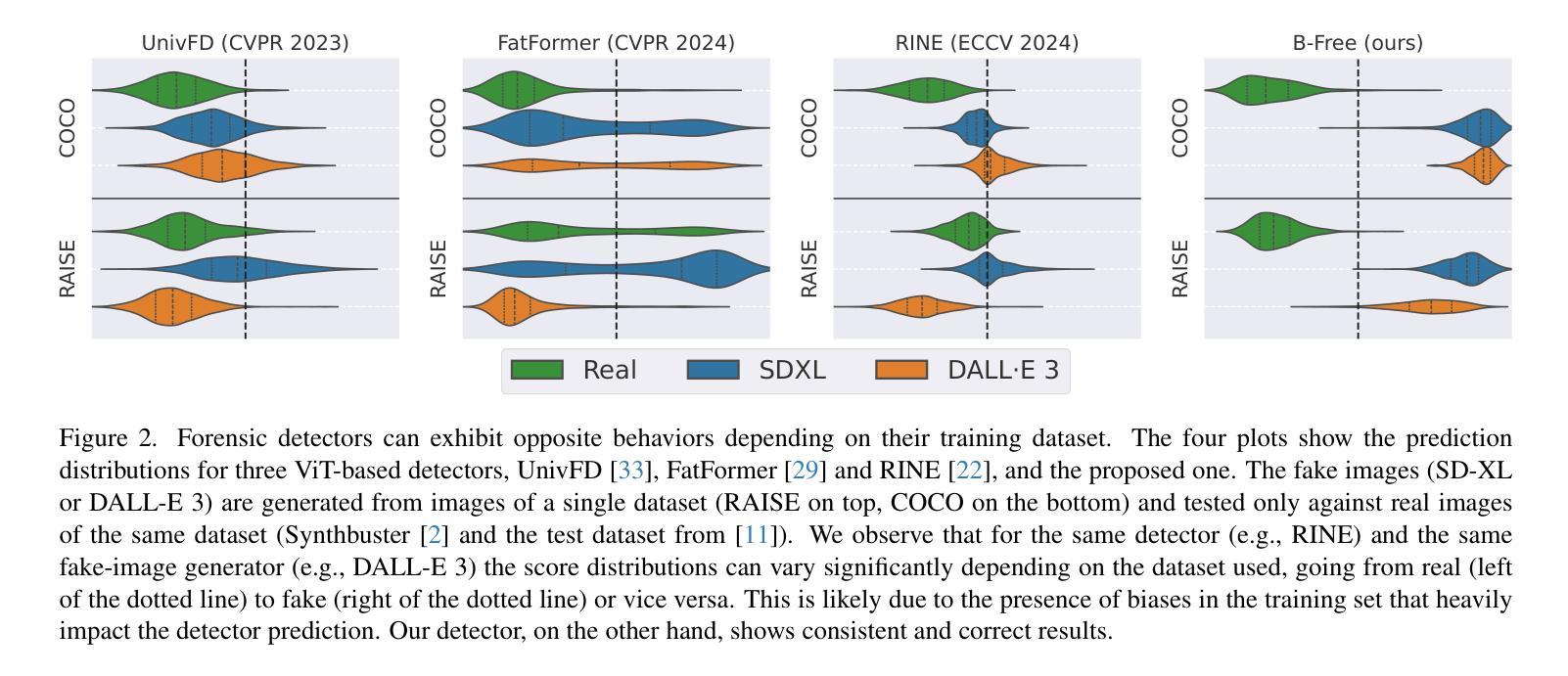
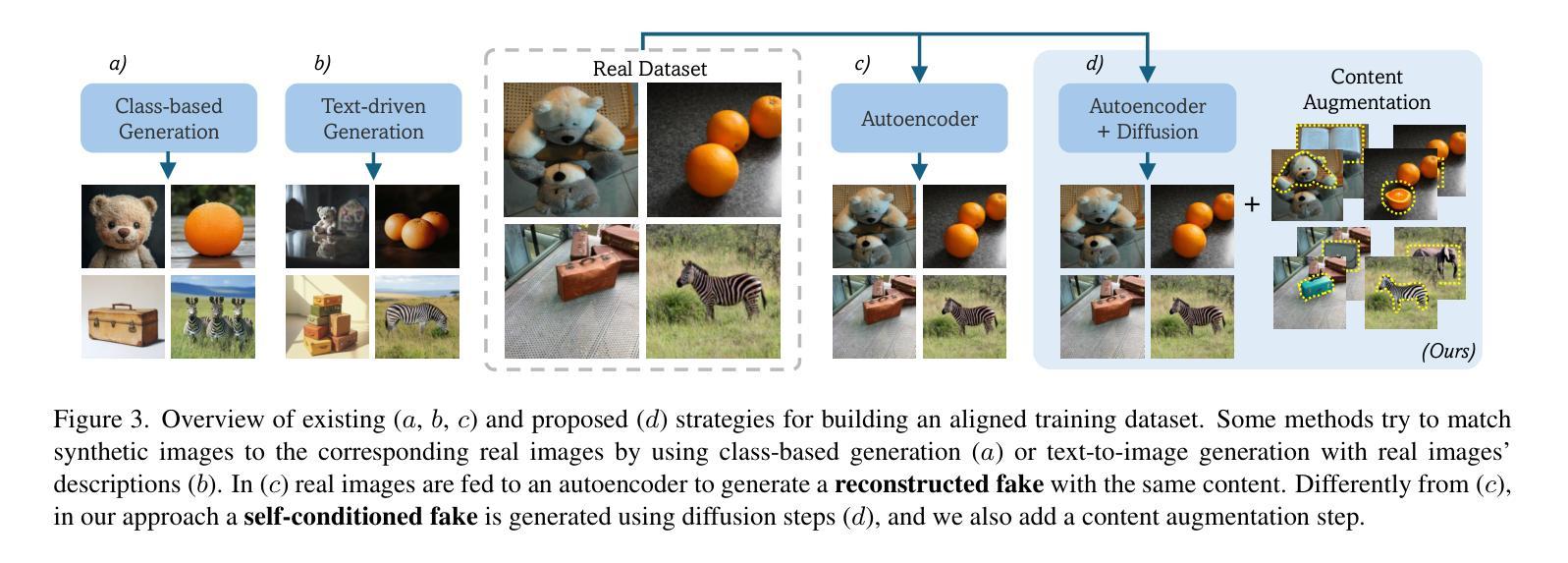
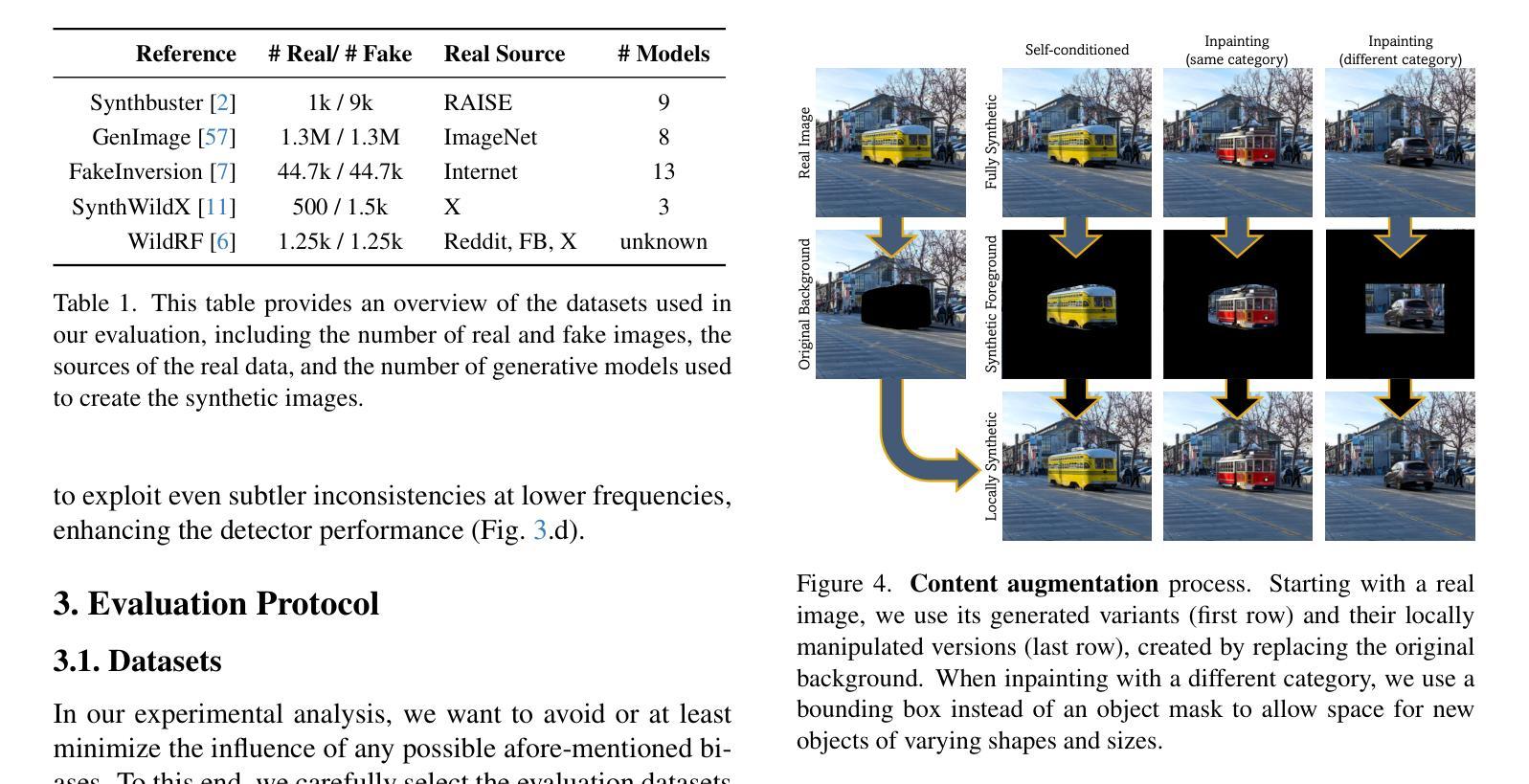
A Bias-Free Training Paradigm for More General AI-generated Image Detection
Authors:Fabrizio Guillaro, Giada Zingarini, Ben Usman, Avneesh Sud, Davide Cozzolino, Luisa Verdoliva
Successful forensic detectors can produce excellent results in supervised learning benchmarks but struggle to transfer to real-world applications. We believe this limitation is largely due to inadequate training data quality. While most research focuses on developing new algorithms, less attention is given to training data selection, despite evidence that performance can be strongly impacted by spurious correlations such as content, format, or resolution. A well-designed forensic detector should detect generator specific artifacts rather than reflect data biases. To this end, we propose B-Free, a bias-free training paradigm, where fake images are generated from real ones using the conditioning procedure of stable diffusion models. This ensures semantic alignment between real and fake images, allowing any differences to stem solely from the subtle artifacts introduced by AI generation. Through content-based augmentation, we show significant improvements in both generalization and robustness over state-of-the-art detectors and more calibrated results across 27 different generative models, including recent releases, like FLUX and Stable Diffusion 3.5. Our findings emphasize the importance of a careful dataset design, highlighting the need for further research on this topic. Code and data are publicly available at https://grip-unina.github.io/B-Free/.
在监督学习基准测试中,成功的法医检测器可以产生出色的结果,但在转移到现实世界应用时却遇到了困难。我们认为这种局限性很大程度上是由于训练数据质量不足。虽然大多数研究都集中在开发新算法上,但对于数据选择方面关注的却很少。尽管有证据表明,性能可能会受到内容、格式或分辨率等虚假关联因素的强烈影响。一个设计良好的法医检测器应该检测生成器特定的伪影,而不是反映数据偏见。为此,我们提出了无偏见训练范式B-Free,在该范式中,使用稳定扩散模型的调节程序从真实图像生成虚假图像。这确保了真实和虚假图像之间的语义对齐,使得任何差异都仅源于人工智能生成所引入的微妙伪影。通过基于内容的增强方法,我们显示出与最新检测器相比在通用性和稳健性方面的显著改进,并且在包括最新发布的FLUX和Stable Diffusion 3.5等27种不同的生成模型上获得了更精确的结果。我们的研究强调了精心设计数据集的重要性,并突出了对这一主题进行进一步研究的必要性。相关代码和数据公开在https://grip-unina.github.io/B-Free/上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
现有司法鉴定探测器在监督学习基准测试中表现优异,但在实际应用中却存在困难。这主要是因为训练数据质量不足。尽管大多数研究关注新算法的开发,但对训练数据选择的重要性却认识不足。数据中的虚假关联会影响性能。为此,我们提出了无偏训练范式B-Free,通过真实图像生成虚假图像,确保真实与虚假图像之间的语义对齐,仅通过AI生成引入细微差异。通过基于内容的增强技术,我们显示出相较于最新鉴定器在泛化和稳健性方面的显著改善,并在包括最新发布的FLUX和Stable Diffusion 3.5在内的27种生成模型上获得更准确的校准结果。我们强调了精心构建数据集的重要性,并突显对这方面的研究的必要。更多详细信息可通过https://grip-unina.github.io/B-Free/访问。
Key Takeaways
- 当前司法鉴定探测器面临从监督学习测试转移到实际应用时的挑战,主要原因是训练数据质量不足。
- 研究过于关注新算法开发,忽视了训练数据选择的重要性。
- 数据中的虚假关联会影响鉴定性能。
- 提出了一种名为B-Free的无偏训练范式,利用稳定扩散模型的条件程序从真实图像生成虚假图像。
- 该方法确保了真实和虚假图像之间的语义对齐,差异仅源于AI生成的细微特征。
- 通过基于内容的增强技术,在泛化和稳健性方面显示出显著改进,并在多种生成模型上获得更准确的校准结果。
点此查看论文截图

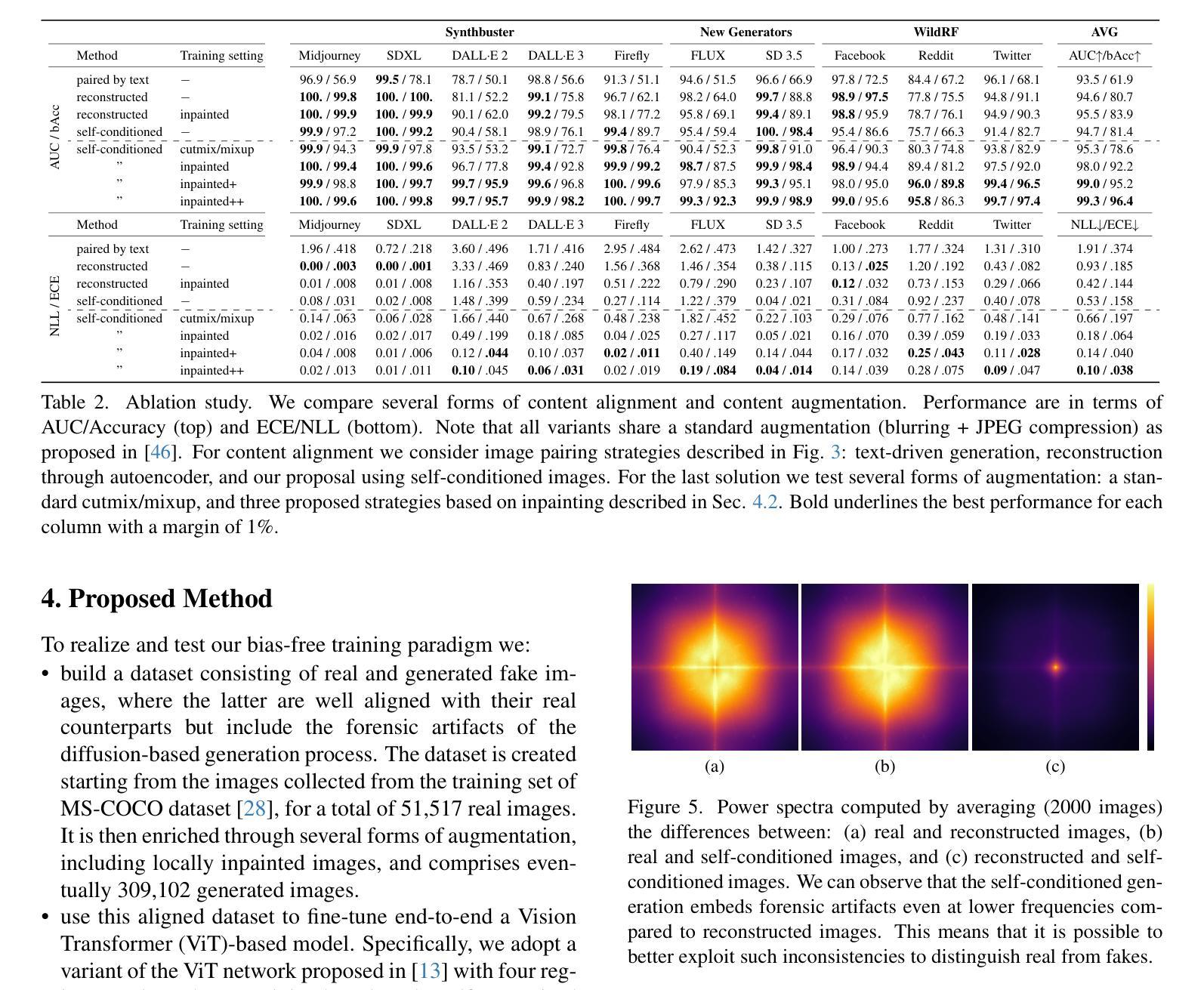
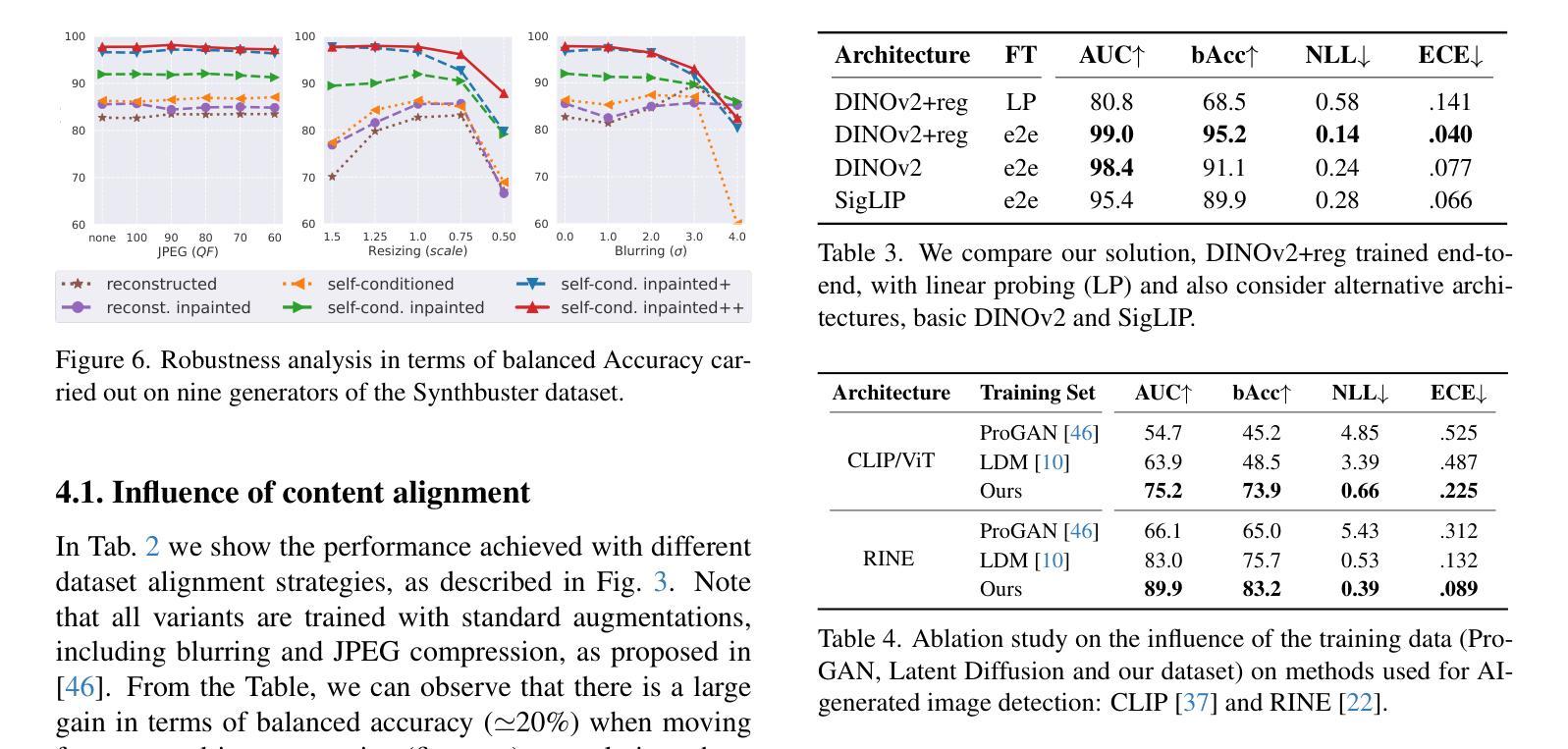
ROBIN: Robust and Invisible Watermarks for Diffusion Models with Adversarial Optimization
Authors:Huayang Huang, Yu Wu, Qian Wang
Watermarking generative content serves as a vital tool for authentication, ownership protection, and mitigation of potential misuse. Existing watermarking methods face the challenge of balancing robustness and concealment. They empirically inject a watermark that is both invisible and robust and passively achieve concealment by limiting the strength of the watermark, thus reducing the robustness. In this paper, we propose to explicitly introduce a watermark hiding process to actively achieve concealment, thus allowing the embedding of stronger watermarks. To be specific, we implant a robust watermark in an intermediate diffusion state and then guide the model to hide the watermark in the final generated image. We employ an adversarial optimization algorithm to produce the optimal hiding prompt guiding signal for each watermark. The prompt embedding is optimized to minimize artifacts in the generated image, while the watermark is optimized to achieve maximum strength. The watermark can be verified by reversing the generation process. Experiments on various diffusion models demonstrate the watermark remains verifiable even under significant image tampering and shows superior invisibility compared to other state-of-the-art robust watermarking methods. Code is available at https://github.com/Hannah1102/ROBIN.
水印作为生成内容认证、版权保护以及潜在误用缓解的重要工具,现有的水印方法面临平衡稳健性和隐蔽性的挑战。他们通过经验注入既不可见又稳健的水印,并通过限制水印强度被动地实现隐蔽性,从而降低了稳健性。在本文中,我们提议明确地引入一个水印隐藏过程来主动实现隐蔽性,从而允许嵌入更强的水印。具体来说,我们在中间扩散状态植入稳健的水印,然后引导模型将水印隐藏在最终生成的图像中。我们采用对抗优化算法为每个水印生成最佳隐藏提示引导信号。提示嵌入的优化旨在减少生成图像中的伪影,而水印的优化则为了实现最大强度。通过反转生成过程可以验证水印。在多种扩散模型上的实验表明,即使在图像遭到重大篡改的情况下,水印仍然可验证,并且与其他最先进的稳健水印方法相比具有出色的隐蔽性。代码可在https://github.com/Hannah1102/ROBIN找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accept to NeurIPS 2024
摘要
生成内容的水印技术对于验证、版权保护和潜在误用的缓解至关重要。当前的水印方法面临平衡稳健性和隐匿性的挑战。本文通过主动引入水印隐藏过程,允许嵌入更强大的水印,解决了以往通过限制水印强度实现隐匿的问题。具体来说,我们在中间扩散状态植入稳健水印,然后引导模型将水印隐藏在最终生成的图像中。我们使用对抗优化算法为每个水印生成最佳隐藏提示引导信号。提示嵌入的优化旨在减少生成图像中的伪影,而水印的优化则旨在实现最大强度。通过反转生成过程可以验证水印。在各种扩散模型上的实验表明,即使在重大图像篡改下,该水印仍然可验证,且相比其他先进的水印方法具有更好的隐蔽性。代码可通过https://github.com/Hannah1102/ROBIN获取。
关键见解
- 水印在生成内容中用于验证、版权保护和潜在误用缓解至关重要。
- 当前水印方法面临稳健性和隐匿性之间的平衡挑战。
- 本文通过主动引入水印隐藏过程解决了这个问题,允许嵌入更强健的水印。
- 在中间扩散状态植入水印,然后引导模型隐藏水印在最终生成的图像中。
- 使用对抗优化算法为每个水印生成最佳的隐藏提示引导信号。
- 该方法通过优化提示嵌入和水印强度,实现了在生成图像中减少伪影和最大化水印强度。
点此查看论文截图

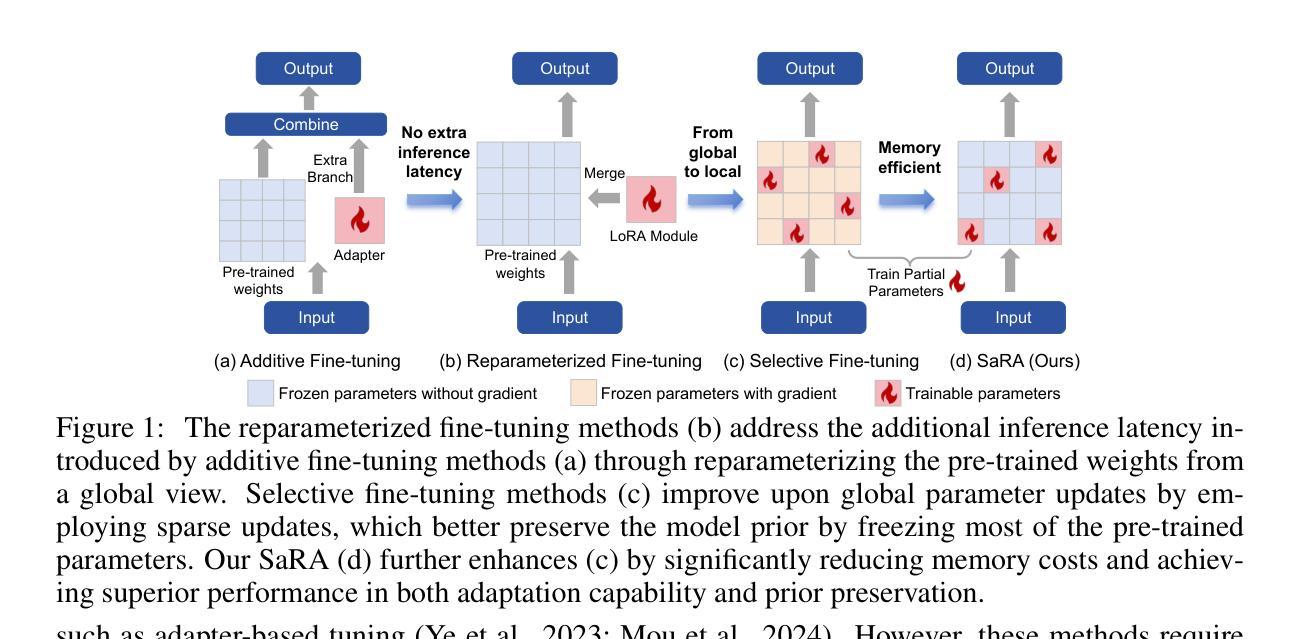
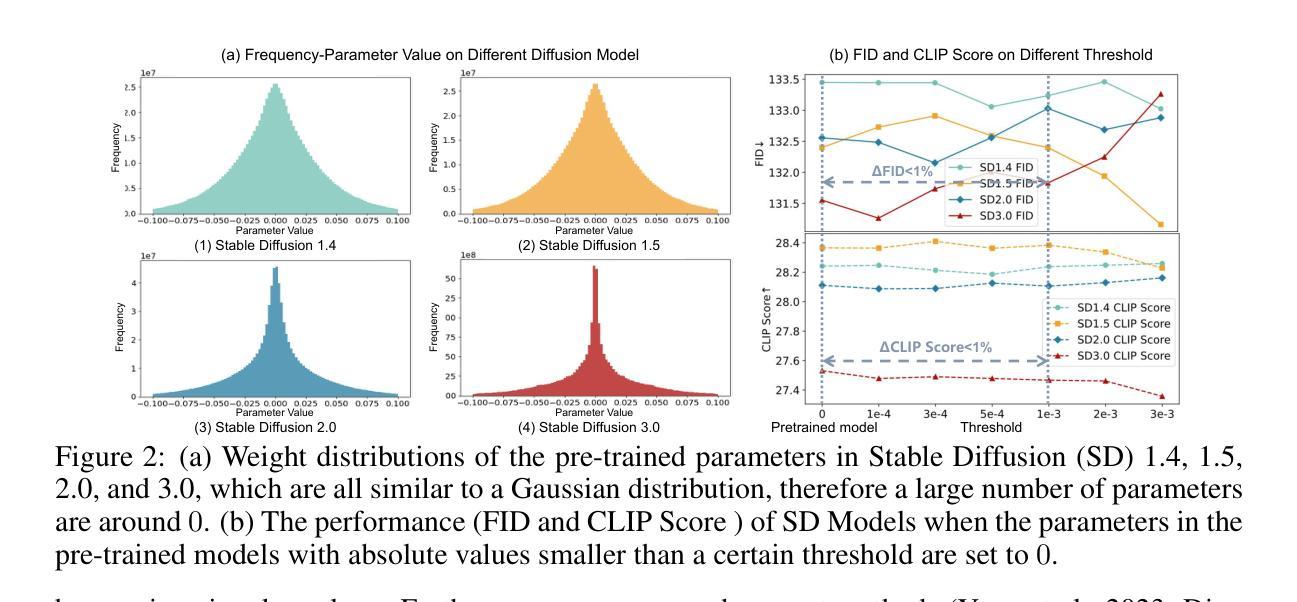
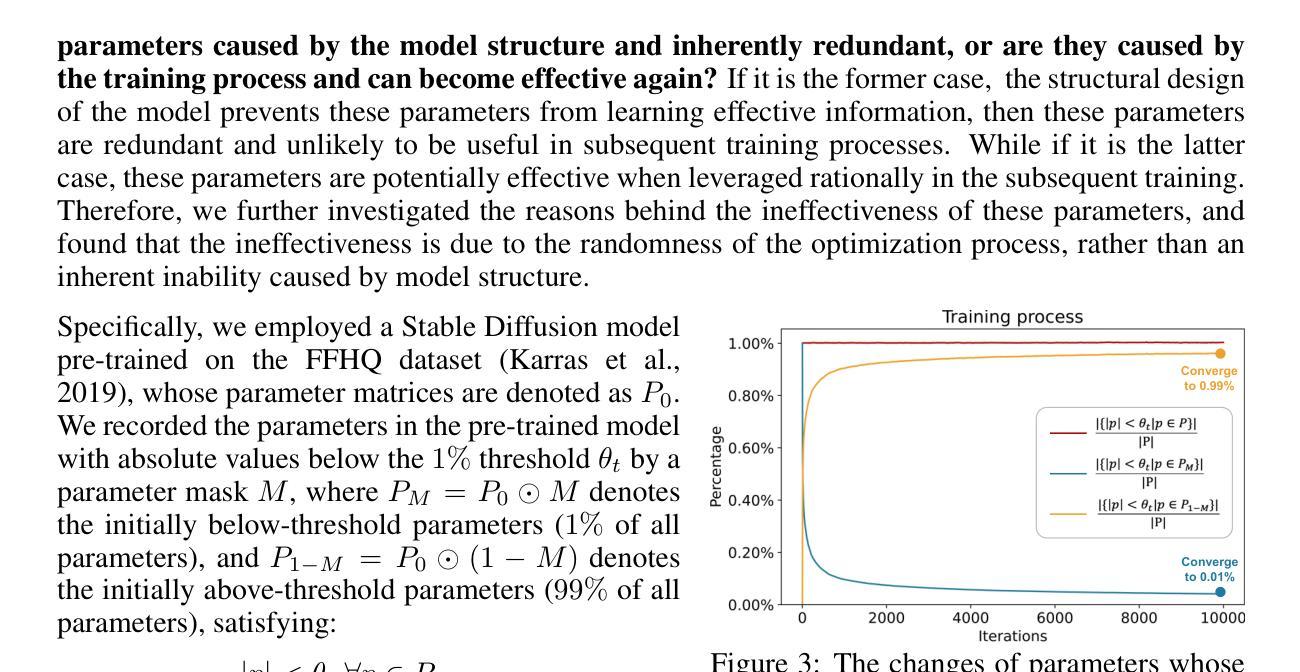
SaRA: High-Efficient Diffusion Model Fine-tuning with Progressive Sparse Low-Rank Adaptation
Authors:Teng Hu, Jiangning Zhang, Ran Yi, Hongrui Huang, Yabiao Wang, Lizhuang Ma
In recent years, the development of diffusion models has led to significant progress in image and video generation tasks, with pre-trained models like the Stable Diffusion series playing a crucial role. Inspired by model pruning which lightens large pre-trained models by removing unimportant parameters, we propose a novel model fine-tuning method to make full use of these ineffective parameters and enable the pre-trained model with new task-specified capabilities. In this work, we first investigate the importance of parameters in pre-trained diffusion models, and discover that the smallest 10% to 20% of parameters by absolute values do not contribute to the generation process. Based on this observation, we propose a method termed SaRA that re-utilizes these temporarily ineffective parameters, equating to optimizing a sparse weight matrix to learn the task-specific knowledge. To mitigate overfitting, we propose a nuclear-norm-based low-rank sparse training scheme for efficient fine-tuning. Furthermore, we design a new progressive parameter adjustment strategy to make full use of the re-trained/finetuned parameters. Finally, we propose a novel unstructural backpropagation strategy, which significantly reduces memory costs during fine-tuning. Our method enhances the generative capabilities of pre-trained models in downstream applications and outperforms traditional fine-tuning methods like LoRA in maintaining model’s generalization ability. We validate our approach through fine-tuning experiments on SD models, demonstrating significant improvements. SaRA also offers a practical advantage that requires only a single line of code modification for efficient implementation and is seamlessly compatible with existing methods.
近年来,扩散模型的发展在图像和视频生成任务中取得了显著进展,预训练模型如Stable Diffusion系列起到了关键作用。受模型修剪的启发,即通过移除不重要参数来减轻大型预训练模型的负担,我们提出了一种新型模型微调方法,该方法能够充分利用这些无效参数,并为预训练模型赋予新的任务特定功能。在这项工作中,我们首先研究了预训练扩散模型中参数的重要性,并发现绝对值最小的10%至20%的参数对生成过程没有贡献。基于此观察,我们提出了一种名为SaRA的方法,该方法重新利用这些暂时无效的参数,相当于优化稀疏权重矩阵来学习任务特定知识。为了减少过拟合,我们提出了一种基于核范数的低秩稀疏训练方案,以实现高效的微调。此外,我们设计了一种新的渐进参数调整策略,以充分利用重新训练/微调的参数。最后,我们提出了一种新型的非结构反向传播策略,在微调过程中显著减少了内存成本。我们的方法提高了预训练模型在下游应用中的生成能力,并且在保持模型的泛化能力方面优于传统的微调方法,如LoRA。我们通过SD模型的微调实验验证了我们的方法,并展示了显著的改进。SaRA还提供了一个实际优势,即只需一行代码修改即可实现高效实施,并且与现有方法无缝兼容。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICLR 2025
Summary
本文研究了扩散模型在图像和视频生成任务中的应用,并探讨了如何对预训练模型进行微调以提高其性能。文章提出了一种名为SaRA的新方法,该方法利用预训练模型中暂时不起作用的参数进行微调,从而提高模型在下游应用中的生成能力。通过核范数低秩稀疏训练方案和渐进参数调整策略,SaRA方法在保持模型泛化能力的同时,优化了模型的性能。此外,本文还提出了一种新型的非结构化反向传播策略,显著降低了微调过程中的内存成本。实验证明,SaRA方法显著提高了预训练模型的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像和视频生成任务中取得了显著进展,预训练模型如Stable Diffusion系列起到了关键作用。
- 提出了一种新型的模型微调方法SaRA,能够利用预训练模型中暂时不起作用的参数。
- SaRA方法通过优化稀疏权重矩阵来学习特定任务的知识,并通过核范数低秩稀疏训练方案进行高效微调。
- 渐进参数调整策略和新型非结构化反向传播策略被设计来充分利用重新训练或微调后的参数,并降低内存成本。
- SaRA方法提高了预训练模型在下游应用中的生成能力,并优于传统的微调方法如LoRA。
- SaRA方法具有实用性优势,只需对代码进行一行修改即可实现高效实施,并与现有方法无缝兼容。
点此查看论文截图

DreamScape: 3D Scene Creation via Gaussian Splatting joint Correlation Modeling
Authors:Yueming Zhao, Xuening Yuan, Hongyu Yang, Di Huang
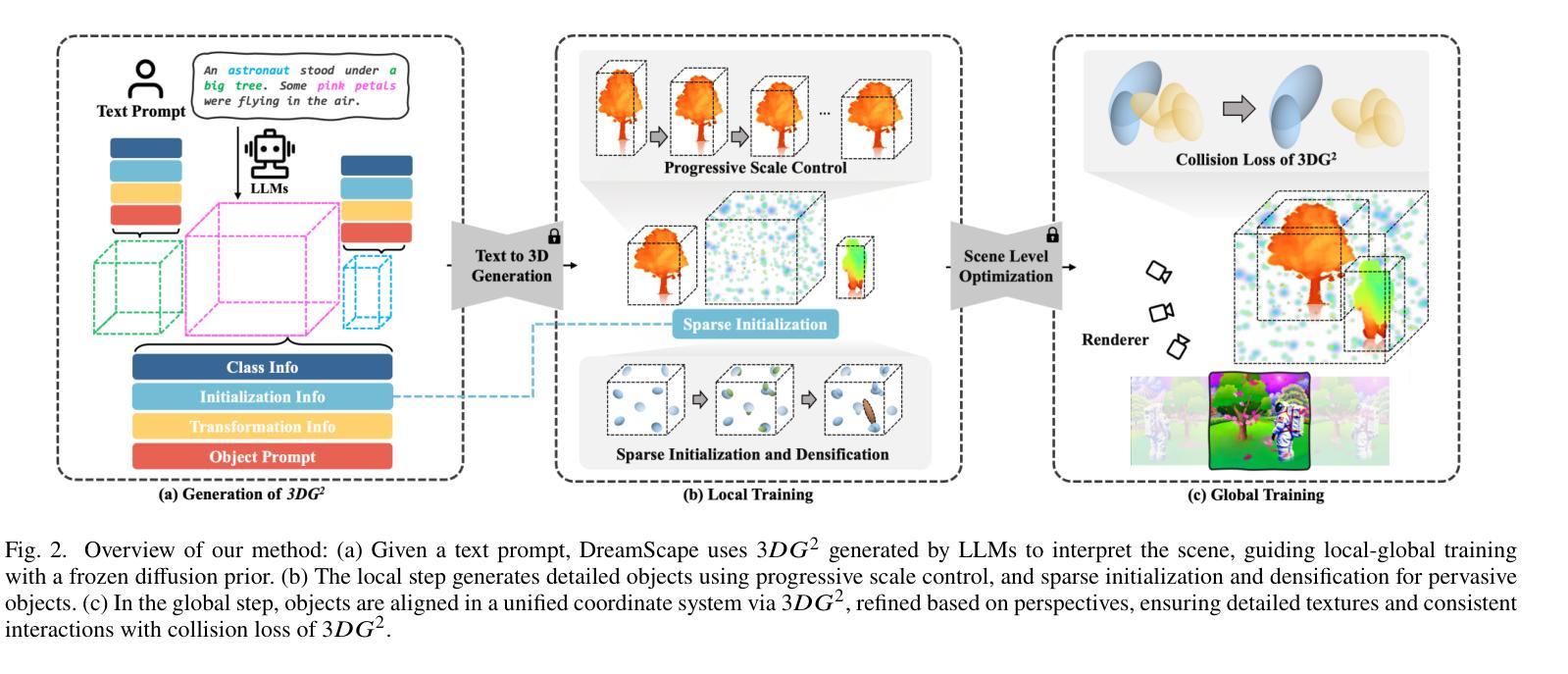
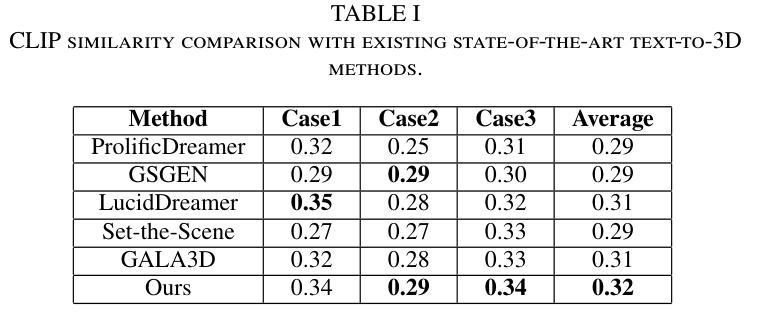
Recent advances in text-to-3D creation integrate the potent prior of Diffusion Models from text-to-image generation into 3D domain. Nevertheless, generating 3D scenes with multiple objects remains challenging. Therefore, we present DreamScape, a method for generating 3D scenes from text. Utilizing Gaussian Splatting for 3D representation, DreamScape introduces 3D Gaussian Guide that encodes semantic primitives, spatial transformations and relationships from text using LLMs, enabling local-to-global optimization. Progressive scale control is tailored during local object generation, addressing training instability issue arising from simple blending in the global optimization stage. Collision relationships between objects are modeled at the global level to mitigate biases in LLMs priors, ensuring physical correctness. Additionally, to generate pervasive objects like rain and snow distributed extensively across the scene, we design specialized sparse initialization and densification strategy. Experiments demonstrate that DreamScape achieves state-of-the-art performance, enabling high-fidelity, controllable 3D scene generation.
近期文本到3D创作的进展将文本到图像生成的Diffusion Models的强大先验知识整合到3D领域。然而,在3D场景中生成多个对象仍然具有挑战性。因此,我们提出了DreamScape方法,一种从文本生成3D场景的方法。利用高斯贴图进行3D表示,DreamScape引入了3D高斯指南,该指南使用大型语言模型(LLMs)从文本编码语义原始信息、空间变换和关系,实现局部到全局的优化。局部对象生成过程中进行了渐进的尺度控制,解决了全局优化阶段简单混合引起的训练不稳定问题。在全局层面建立了物体间的碰撞关系,以减轻LLMs先验中的偏见,确保物理正确性。此外,为了生成如雨雪等广泛分布在场景中的普遍物体,我们设计了专门的稀疏初始化和密集化策略。实验表明,DreamScape达到了最先进的性能,能够实现高保真、可控的3D场景生成。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于Diffusion Models的最新技术,将文本转化为三维场景。通过引入Gaussian Splatting进行三维表示和3D Gaussian Guide技术,该技术能够从文本中生成三维场景,并处理多物体之间的相互作用。DreamScape方法实现了局部到全局的优化,通过渐进式尺度控制和碰撞关系建模等技术,解决了训练不稳定和物体间物理正确性的问题。实验证明,DreamScape在生成高保真、可控的三维场景方面达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- DreamScape将Diffusion Models从文本到图像生成的潜力应用于三维领域。
- 利用Gaussian Splatting进行三维表示。
- 引入3D Gaussian Guide,通过大型语言模型(LLMs)从文本中编码语义原始信息、空间变换和关系。
- 实现局部到全局的优化,包括渐进式尺度控制和物体间碰撞关系的建模。
- 针对全局优化阶段出现的训练不稳定问题,采取了有效措施。
- 开发了专门的技术来生成场景中的普遍物体,如雨和雪。
点此查看论文截图