⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-05 更新
F-ViTA: Foundation Model Guided Visible to Thermal Translation
Authors:Jay N. Paranjape, Celso de Melo, Vishal M. Patel
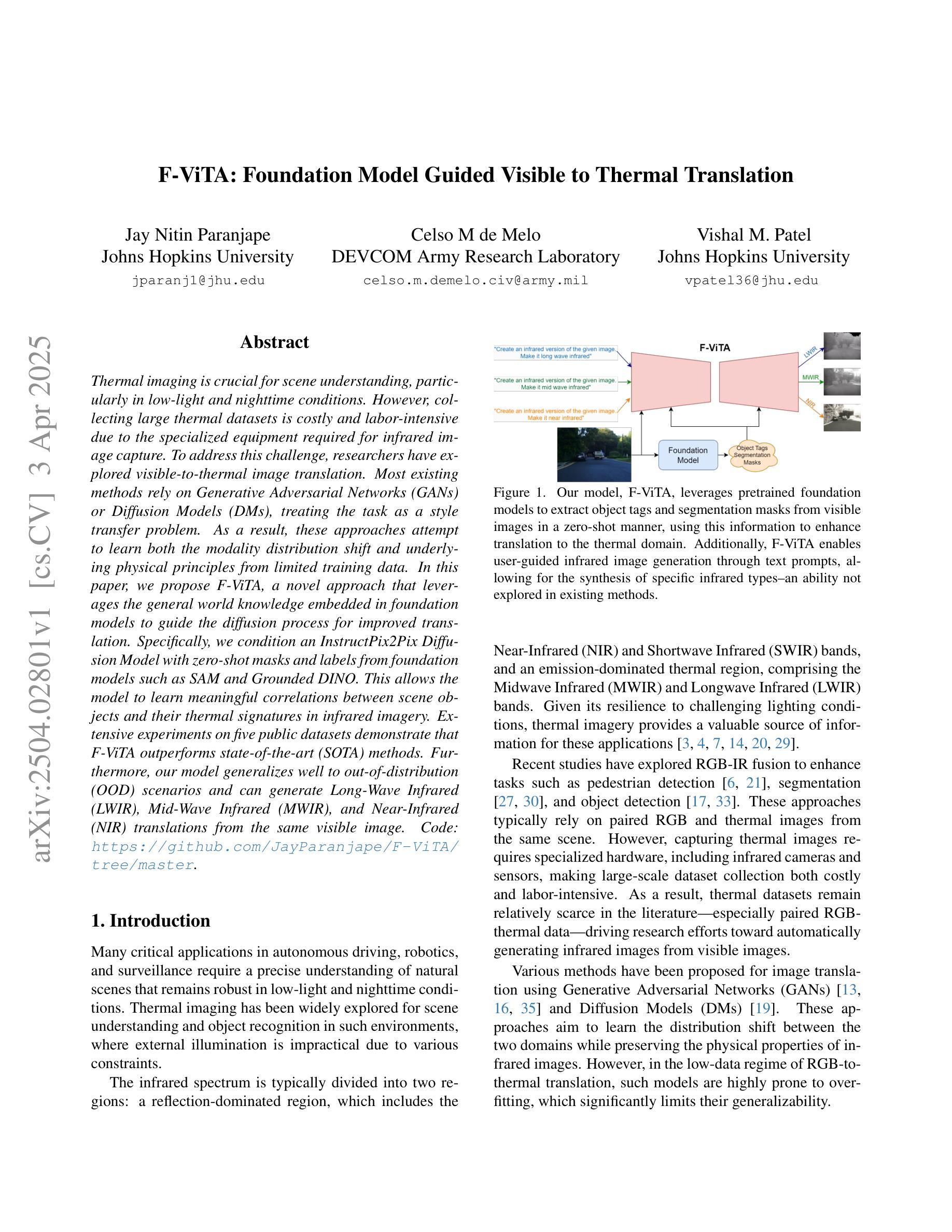
Thermal imaging is crucial for scene understanding, particularly in low-light and nighttime conditions. However, collecting large thermal datasets is costly and labor-intensive due to the specialized equipment required for infrared image capture. To address this challenge, researchers have explored visible-to-thermal image translation. Most existing methods rely on Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) or Diffusion Models (DMs), treating the task as a style transfer problem. As a result, these approaches attempt to learn both the modality distribution shift and underlying physical principles from limited training data. In this paper, we propose F-ViTA, a novel approach that leverages the general world knowledge embedded in foundation models to guide the diffusion process for improved translation. Specifically, we condition an InstructPix2Pix Diffusion Model with zero-shot masks and labels from foundation models such as SAM and Grounded DINO. This allows the model to learn meaningful correlations between scene objects and their thermal signatures in infrared imagery. Extensive experiments on five public datasets demonstrate that F-ViTA outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. Furthermore, our model generalizes well to out-of-distribution (OOD) scenarios and can generate Long-Wave Infrared (LWIR), Mid-Wave Infrared (MWIR), and Near-Infrared (NIR) translations from the same visible image. Code: https://github.com/JayParanjape/F-ViTA/tree/master.
热成像对于场景理解至关重要,特别是在低光和夜间条件下。然而,由于红外图像捕获所需的专业设备,收集大量的热数据集成本高昂且劳力密集。为了应对这一挑战,研究人员已经探索了可见光到热成像的图像翻译方法。现有的大多数方法依赖于生成对抗网络(GANs)或扩散模型(DMs),将任务视为风格转移问题。因此,这些方法试图从有限的训练数据中学习模态分布变化和潜在的物理原理。在本文中,我们提出了F-ViTA,一种利用基础模型中嵌入的世界通用知识来指导扩散过程,以改进翻译的新型方法。具体来说,我们用基础模型(如SAM和Grounded DINO)的零样本掩码和标签来条件指令Pix2Pix扩散模型。这使得模型能够学习场景物体与其在红外图像中的热特征之间的有意义关联。在五个公共数据集上的广泛实验表明,F-ViTA优于最新技术方法。此外,我们的模型能够很好地推广到超出分布的场景,并且可以从同一可见图像生成长波红外(LWIR)、中波红外(MWIR)和近红外(NIR)翻译。代码:https://github.com/JayParanjape/F-ViTA/tree/master。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于生成对抗网络(GAN)和扩散模型(DM)的新方法F-ViTA,用于可见光到热成像的图像翻译。该方法利用基础模型中的通用世界知识来指导扩散过程,从而提高翻译质量。通过条件化InstructPix2Pix扩散模型与基础模型的零样本掩膜和标签,模型能够学习场景物体与其在红外图像中的热特征之间的有意义关联。实验表明,F-ViTA在多个公共数据集上的表现优于现有方法,且具有良好的泛化能力,能够生成长波红外(LWIR)、中波红外(MWIR)和近红外(NIR)翻译自同一可见图像。
Key Takeaways
- F-ViTA是一种新的可见光到热成像图像翻译方法,结合了生成对抗网络和扩散模型。
- 该方法利用基础模型中的通用世界知识来指导扩散过程,提高翻译质量。
- F-ViTA通过条件化InstructPix2Pix扩散模型,学习场景物体与热特征之间的关联。
- 实验表明,F-ViTA在多个公共数据集上的表现优于现有方法。
- F-ViTA具有良好的泛化能力,能够生成不同波段的红外图像翻译。
- F-ViTA通过利用零样本掩膜和标签,提高了模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图
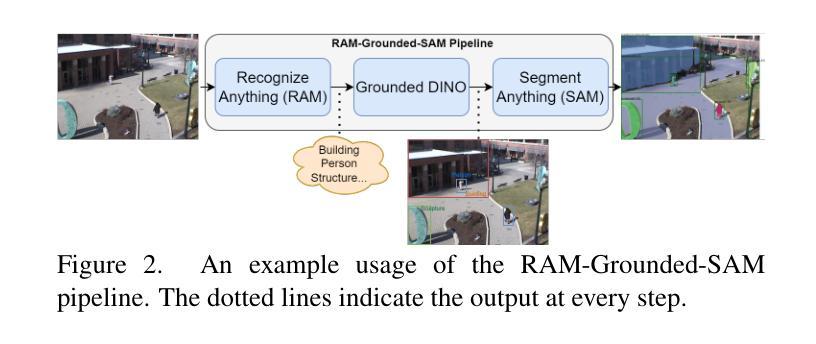
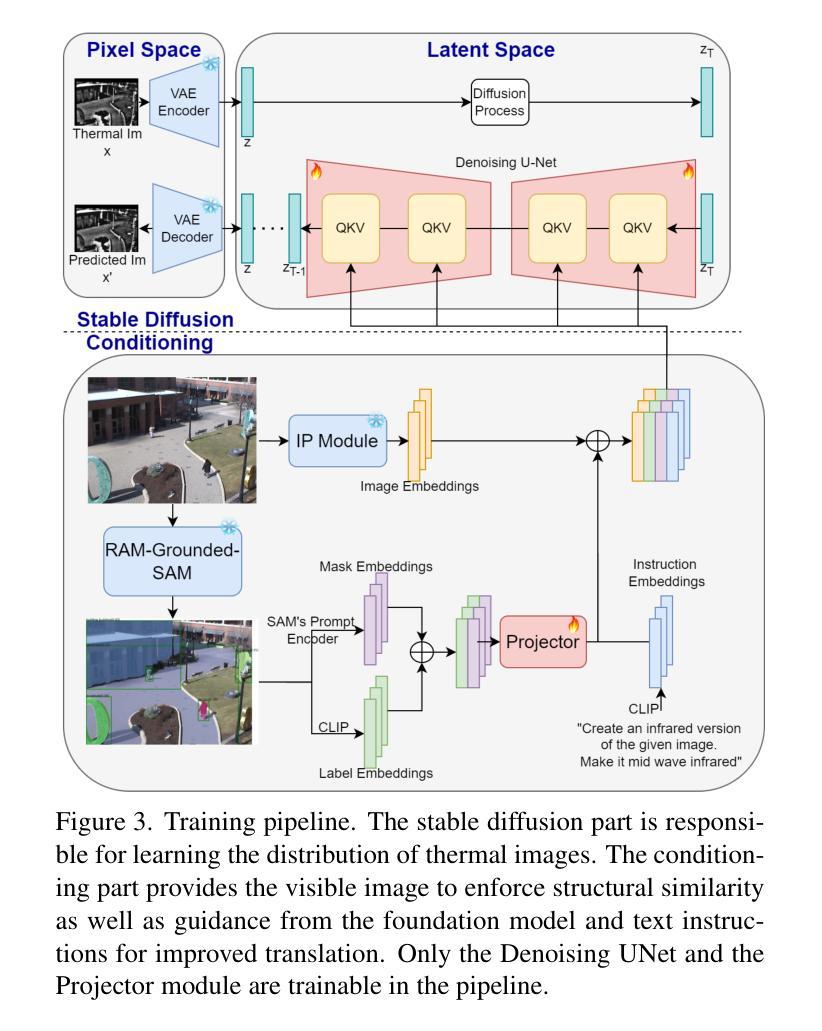
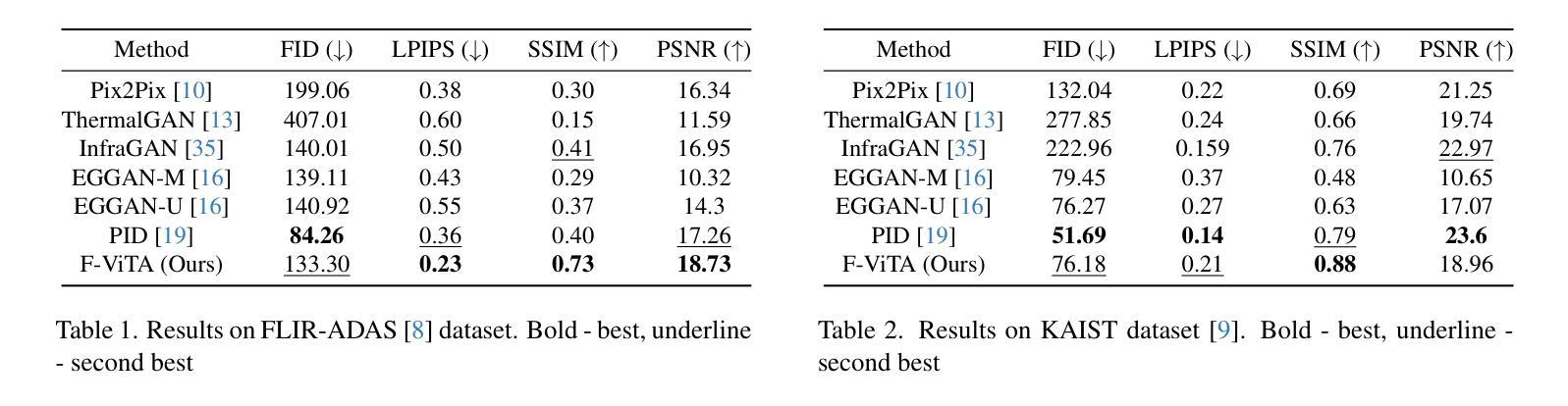
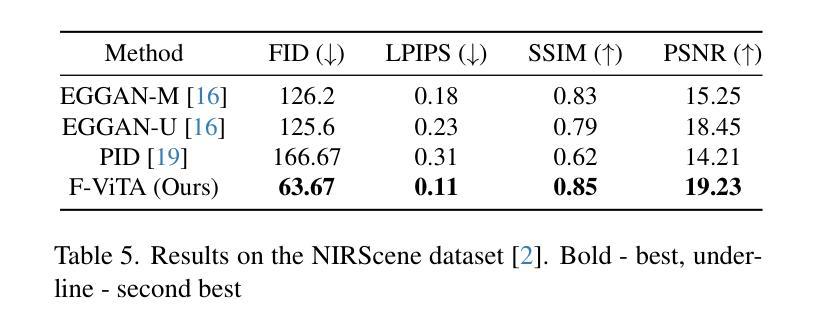
A GAN-Enhanced Deep Learning Framework for Rooftop Detection from Historical Aerial Imagery
Authors:Pengyu Chen, Sicheng Wang, Cuizhen Wang, Senrong Wang, Beiao Huang, Lu Huang, Zhe Zang
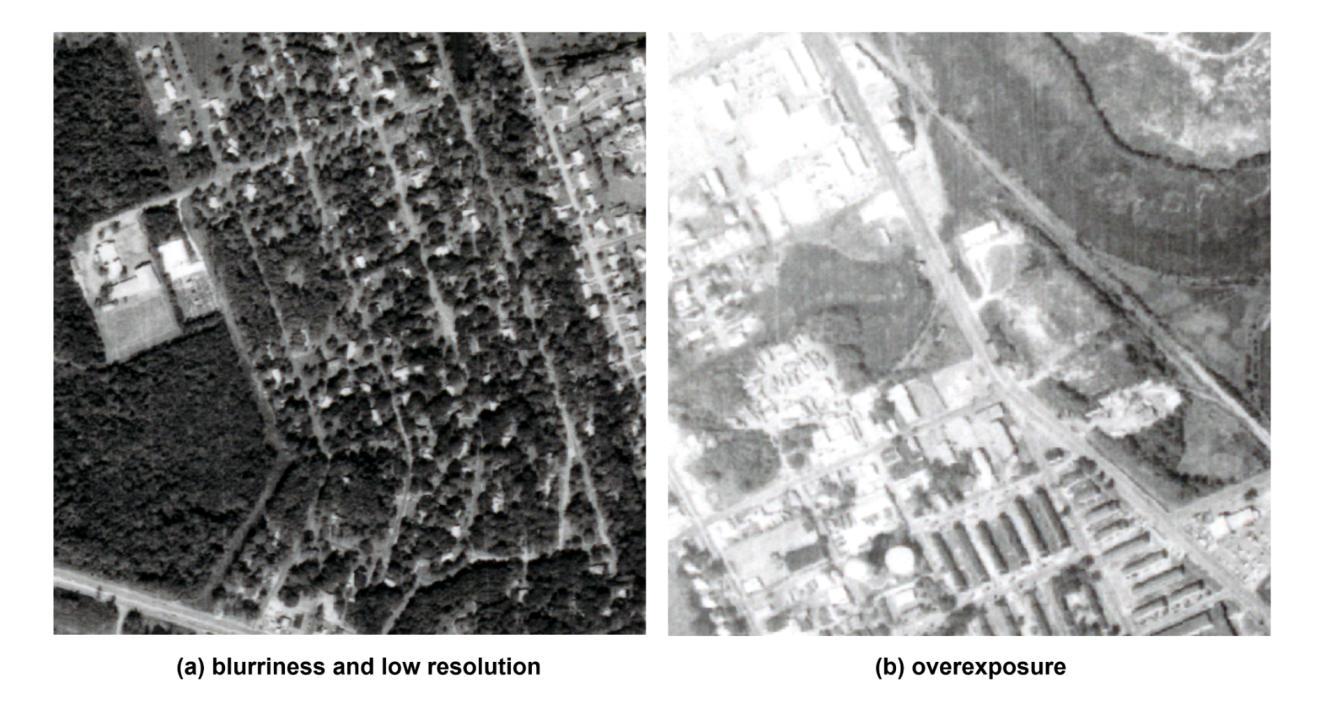
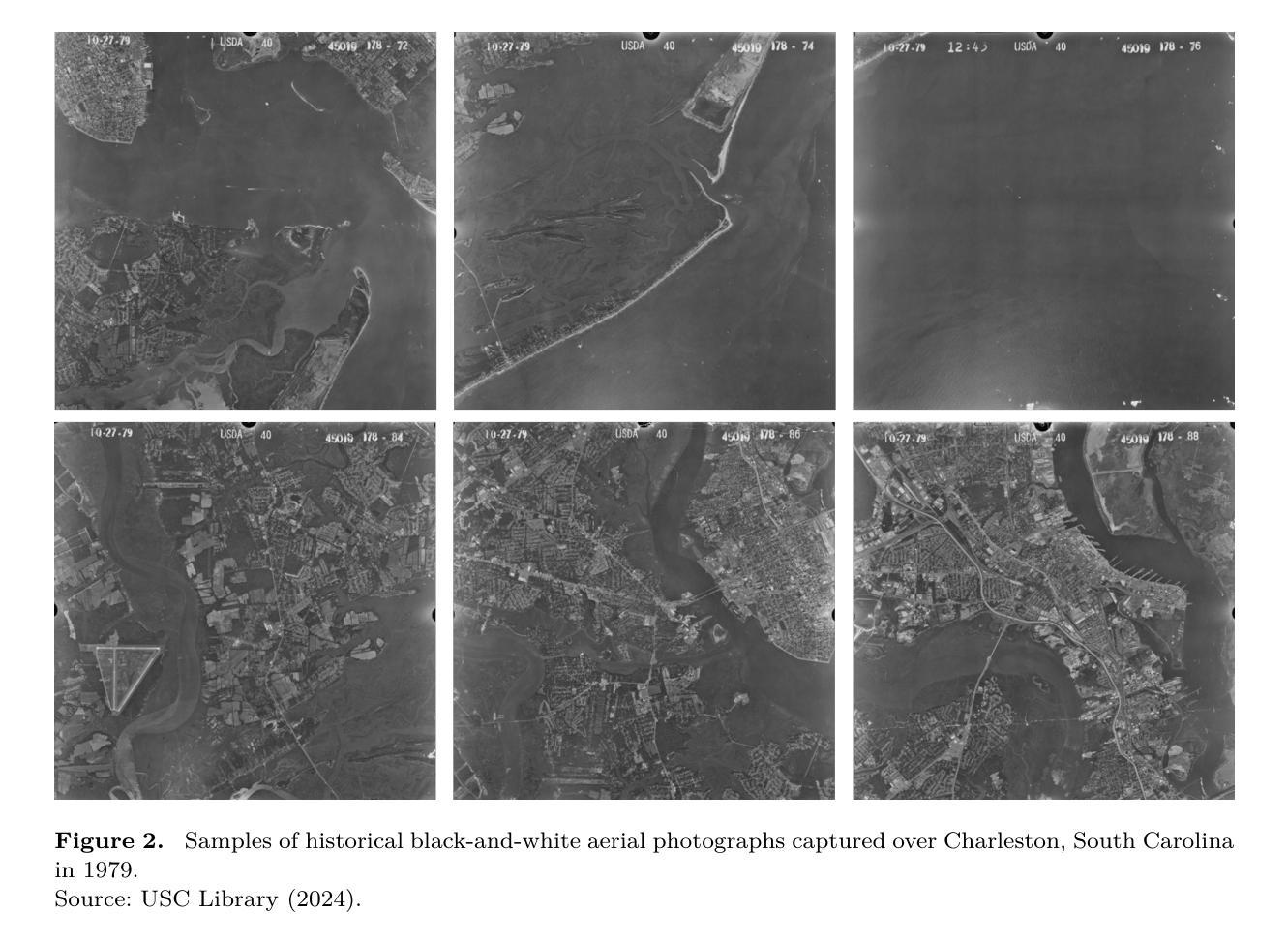
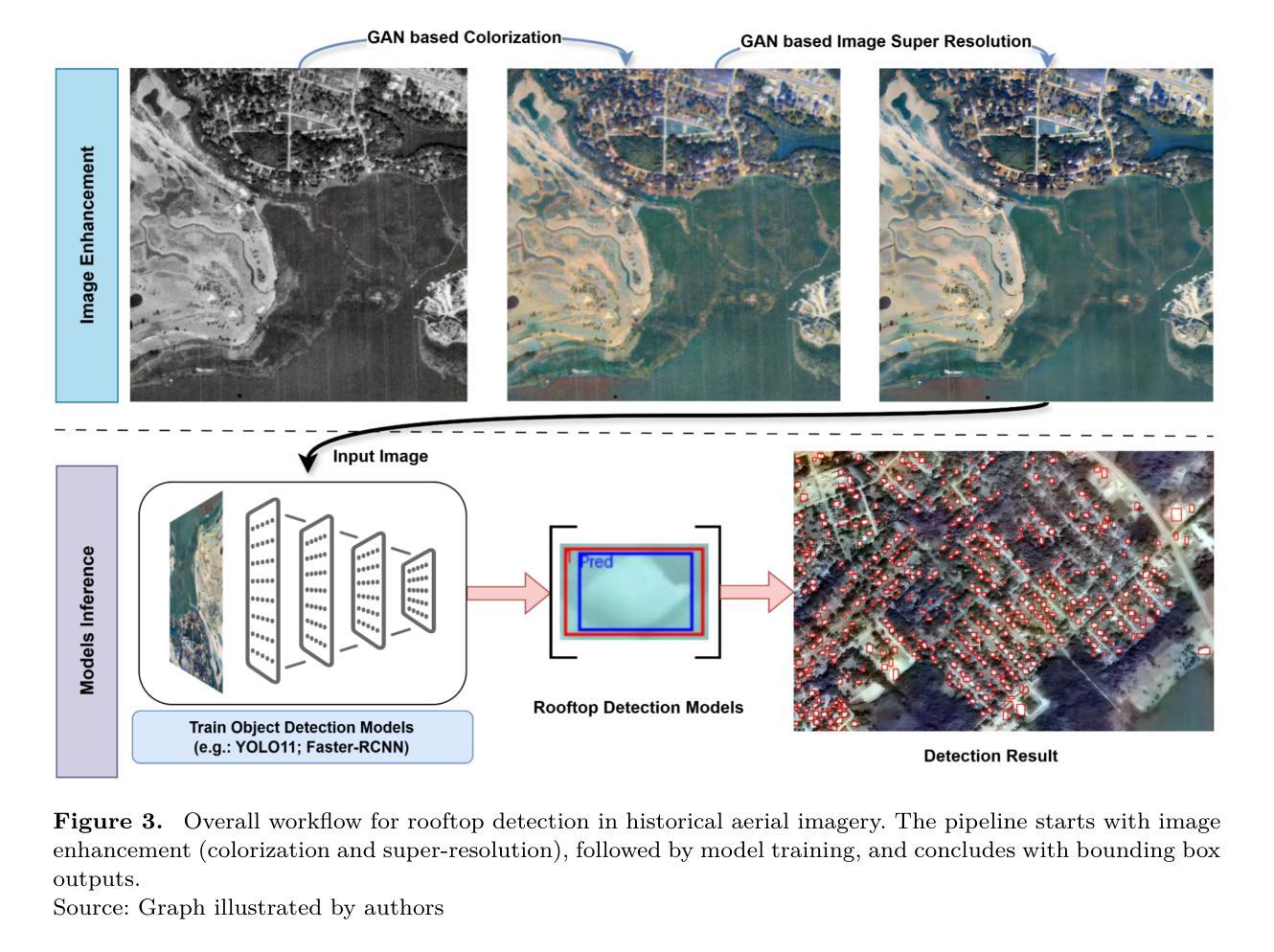
Precise detection of rooftops from historical aerial imagery is essential for analyzing long-term urban development and human settlement patterns. Nonetheless, black-and-white analog photographs present considerable challenges for modern object detection frameworks due to their limited spatial resolution, absence of color information, and archival degradation. To address these challenges, this research introduces a two-stage image enhancement pipeline based on Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): image colorization utilizing DeOldify, followed by super-resolution enhancement with Real-ESRGAN. The enhanced images were subsequently employed to train and evaluate rooftop detection models, including Faster R-CNN, DETReg, and YOLOv11n. The results demonstrate that the combination of colorization with super-resolution significantly enhances detection performance, with YOLOv11n achieving a mean Average Precision (mAP) exceeding 85%. This signifies an enhancement of approximately 40% over the original black-and-white images and 20% over images enhanced solely through colorization. The proposed method effectively bridges the gap between archival imagery and contemporary deep learning techniques, facilitating more reliable extraction of building footprints from historical aerial photographs. Code and resources for reproducing our results are publicly available at \href{https://github.com/Pengyu-gis/Historical-Aerial-Photos}{github.com/Pengyu-gis/Historical-Aerial-Photos}.
从历史航空影像中精确检测屋顶对于分析长期城市发展和人类定居模式至关重要。然而,黑白模拟照片为现代目标检测框架带来了相当大的挑战,因为它们具有空间分辨率有限、缺乏颜色信息和存档退化的特点。为了解决这些挑战,本研究引入了一种基于生成对抗网络(GANs)的两阶段图像增强流程:利用DeOldify进行图像上色,然后使用Real-ESRGAN进行超分辨率增强。增强后的图像随后被用于训练和评估屋顶检测模型,包括Faster R-CNN、DETReg和YOLOv11n。结果表明,上色与超分辨率的结合显著提高了检测性能,YOLOv11n的平均精度(mAP)超过85%。这标志着与原始黑白图像相比增强了约40%,与仅通过上色的图像相比增强了约20%。所提出的方法有效地架起了存档图像和当前深度学习技术之间的桥梁,促进了从历史航空照片中更可靠地提取建筑足迹。重现我们结果的代码和资源可在github.com/Pengyu-gis/Historical-Aerial-Photos获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本研究利用生成对抗网络(GANs)的两阶段图像增强管道,对黑白模拟照片进行彩色化和超分辨率增强,以解决从历史航空影像中精确检测屋顶的难题。增强后的图像被用于训练和评估屋顶检测模型,包括Faster R-CNN、DETReg和YOLOv11n。结果显示,彩色化与超分辨率结合能显著提高检测性能,YOLOv11n的平均精度(mAP)超过85%。该方法有效弥合了档案图像与当代深度学习技术之间的鸿沟,能更可靠地从历史航空照片中提取建筑足迹。
Key Takeaways:
- 历史航空影像的屋顶检测对于分析长期城市发展和人类定居模式至关重要。
- 黑白模拟照片对现代目标检测框架构成了挑战,因其空间分辨率有限、缺乏颜色信息和档案退化。
- 研究提出了基于GANs的两阶段图像增强流程,包括使用DeOldify进行彩色化,以及使用Real-ESRGAN进行超分辨率增强。
- 增强后的图像用于训练和评估屋顶检测模型,包括Faster R-CNN、DETReg和YOLOv11n。
- 结合彩色化和超分辨率增强能显著提高检测性能。
- YOLOv11n模型在增强图像上的mAP超过85%,相比原始黑白图像提升了约40%,相比仅进行彩色化增强的图像提升了约20%。
点此查看论文截图