⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-05 更新
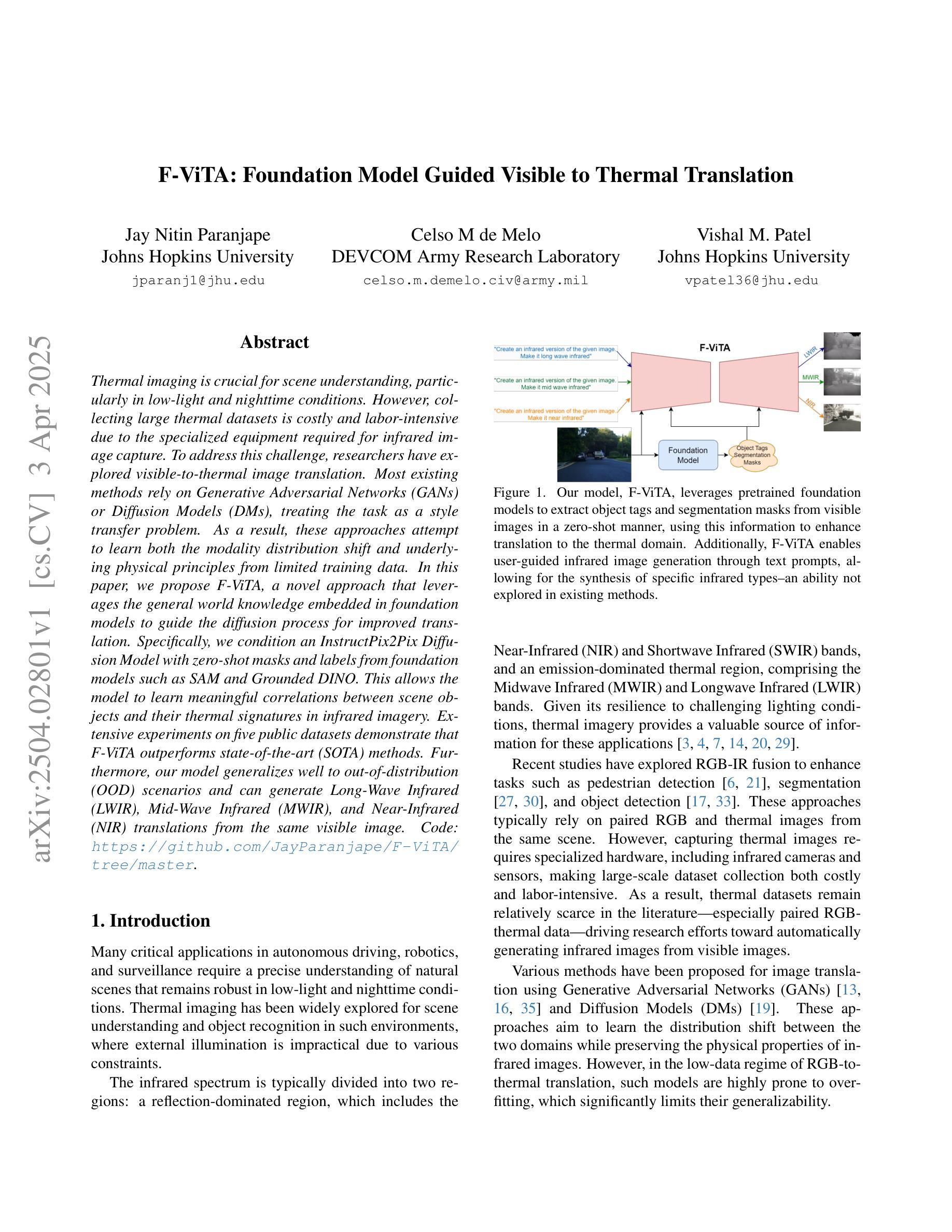
F-ViTA: Foundation Model Guided Visible to Thermal Translation
Authors:Jay N. Paranjape, Celso de Melo, Vishal M. Patel
Thermal imaging is crucial for scene understanding, particularly in low-light and nighttime conditions. However, collecting large thermal datasets is costly and labor-intensive due to the specialized equipment required for infrared image capture. To address this challenge, researchers have explored visible-to-thermal image translation. Most existing methods rely on Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) or Diffusion Models (DMs), treating the task as a style transfer problem. As a result, these approaches attempt to learn both the modality distribution shift and underlying physical principles from limited training data. In this paper, we propose F-ViTA, a novel approach that leverages the general world knowledge embedded in foundation models to guide the diffusion process for improved translation. Specifically, we condition an InstructPix2Pix Diffusion Model with zero-shot masks and labels from foundation models such as SAM and Grounded DINO. This allows the model to learn meaningful correlations between scene objects and their thermal signatures in infrared imagery. Extensive experiments on five public datasets demonstrate that F-ViTA outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. Furthermore, our model generalizes well to out-of-distribution (OOD) scenarios and can generate Long-Wave Infrared (LWIR), Mid-Wave Infrared (MWIR), and Near-Infrared (NIR) translations from the same visible image. Code: https://github.com/JayParanjape/F-ViTA/tree/master.
热成像对于场景理解至关重要,特别是在低光和夜间条件下。然而,由于红外图像捕获需要专用设备,收集大量的热数据集成本高昂且劳动密集。为了应对这一挑战,研究人员已经探索了可见光到热成像的翻译。现有的大多数方法依赖于生成对抗网络(GANs)或扩散模型(DMs),将任务视为风格转换问题。因此,这些方法试图从有限的训练数据中学习模态分布变化和潜在的物理原理。在本文中,我们提出了F-ViTA,一种利用基础模型中嵌入的世界通用知识来指导扩散过程,以改进翻译的新型方法。具体来说,我们使用InstructPix2Pix扩散模型,以基础模型(如SAM和Grounded DINO)的零样本蒙版和标签为条件。这使得模型能够学习场景物体与其在红外图像中的热特征之间的有意义关联。在五个公共数据集上的广泛实验表明,F-ViTA优于最新技术方法。此外,我们的模型在超出分布的场景中具有良好的通用性,并且可以从同一可见图像生成长波红外(LWIR)、中波红外(MWIR)和近红外(NIR)翻译。代码:https://github.com/JayParanjape/F-ViTA/tree/master。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型可见光到热成像图像翻译方法F-ViTA,利用基础模型中的通用世界知识来指导扩散过程,从而提高翻译效果。通过条件化InstructPix2Pix扩散模型,结合零样本掩膜和标签,模型能学习场景物体与红外图像中的热特征之间的有意义关联。在五个公共数据集上的实验表明,F-ViTA优于现有最佳方法,并能良好地推广到不同分布场景,可从同一可见图像生成长波红外、中波红外和近红外翻译图像。
Key Takeaways
- F-ViTA是一种新型的可见光到热成像图像翻译方法,旨在解决收集大规模热数据集的挑战。
- 该方法利用基础模型中的通用世界知识来指导扩散过程,提高翻译效果。
- F-ViTA使用条件化的InstructPix2Pix扩散模型,结合零样本掩膜和标签,学习场景物体与热特征之间的关联。
- 在多个公共数据集上,F-ViTA表现出优异的性能,优于现有最佳方法。
- F-ViTA具有良好的泛化能力,能够处理不同分布场景,生成不同波段的红外图像翻译。
- F-ViTA方法具有潜力在夜间和低光照条件下的场景理解中发挥重要作用。
点此查看论文截图
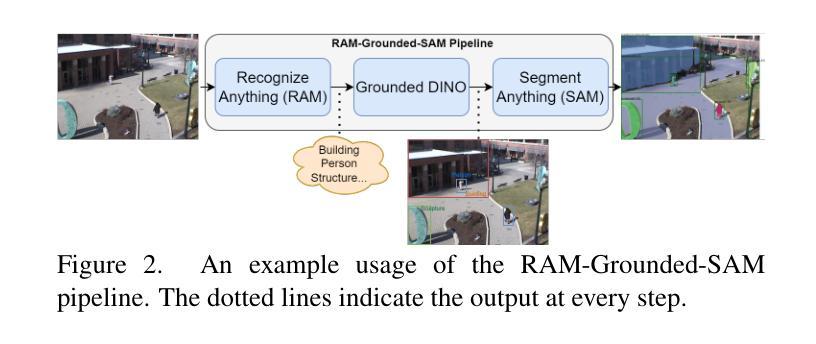
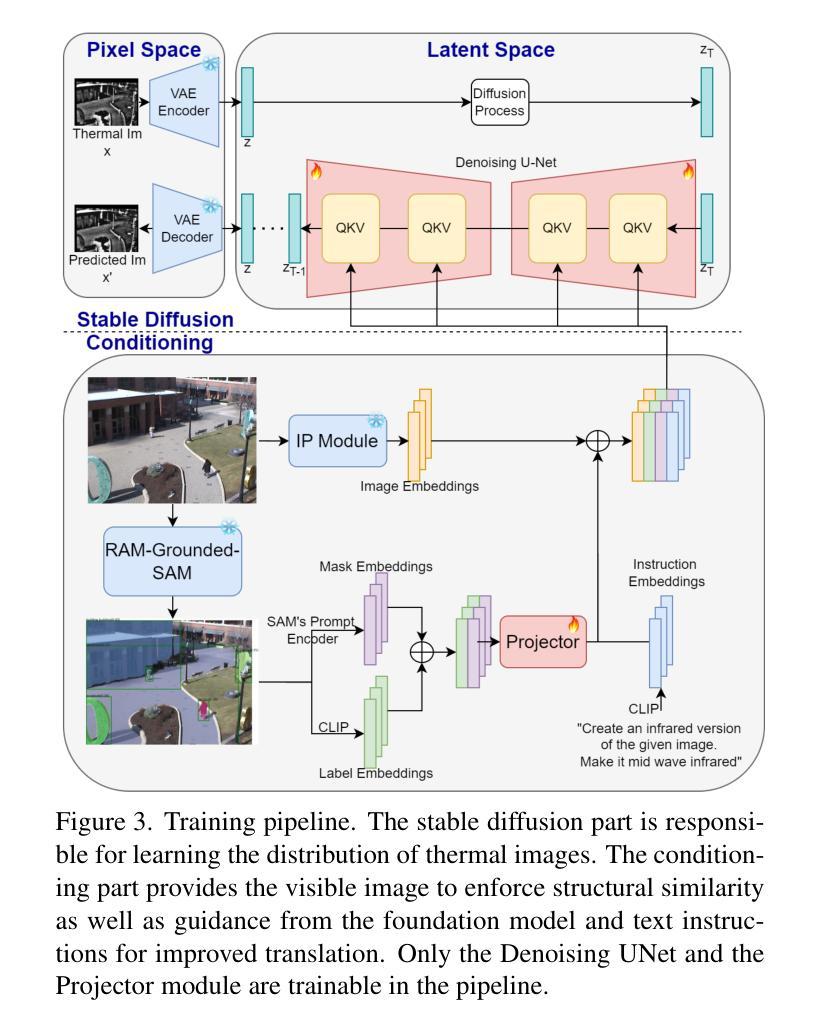
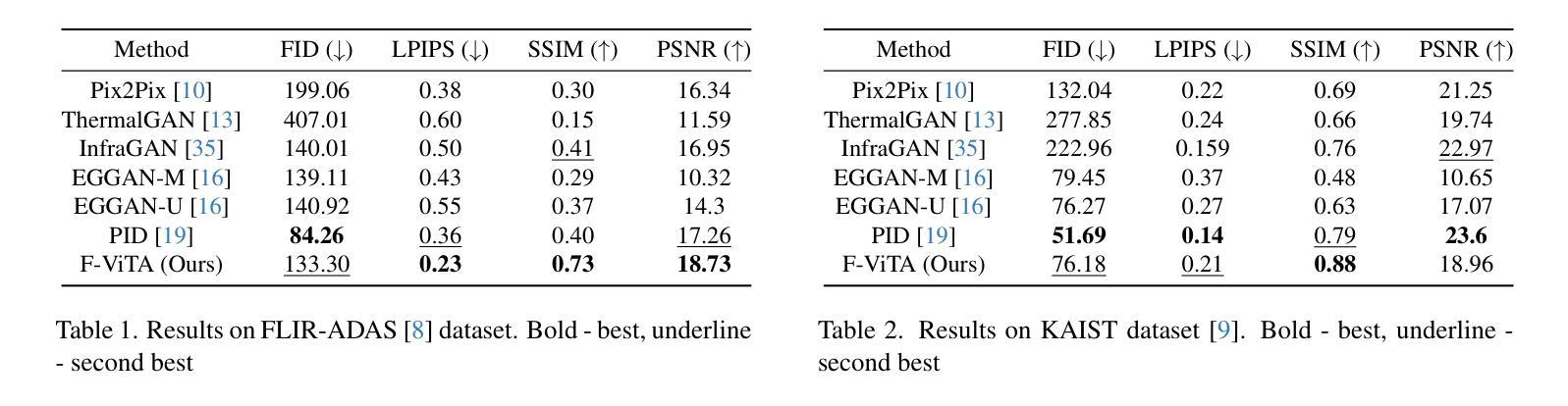
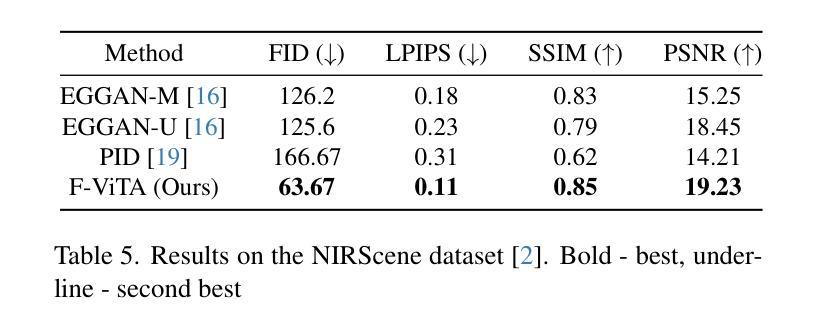
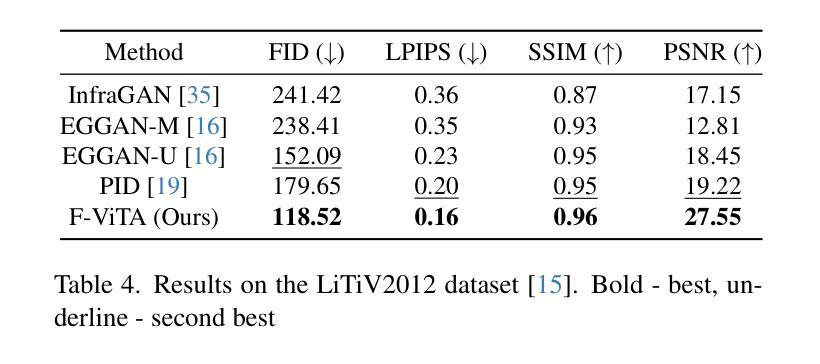
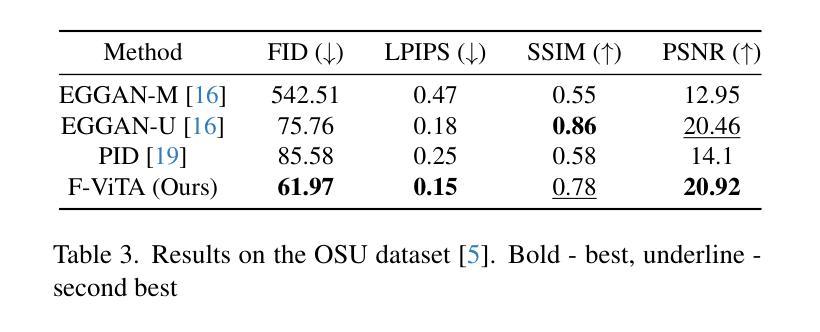
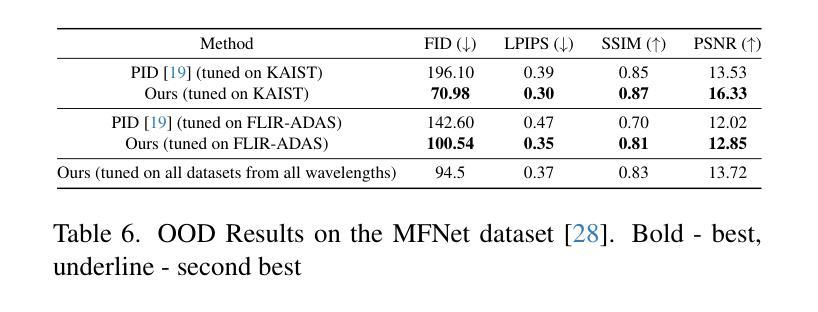
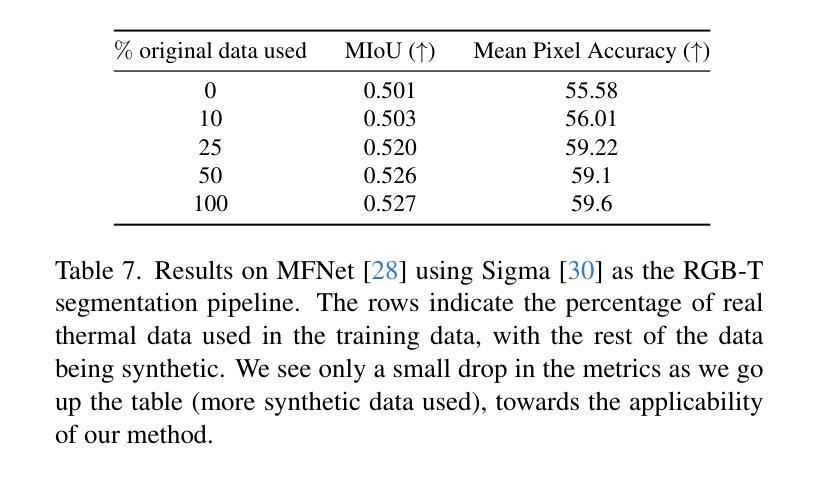
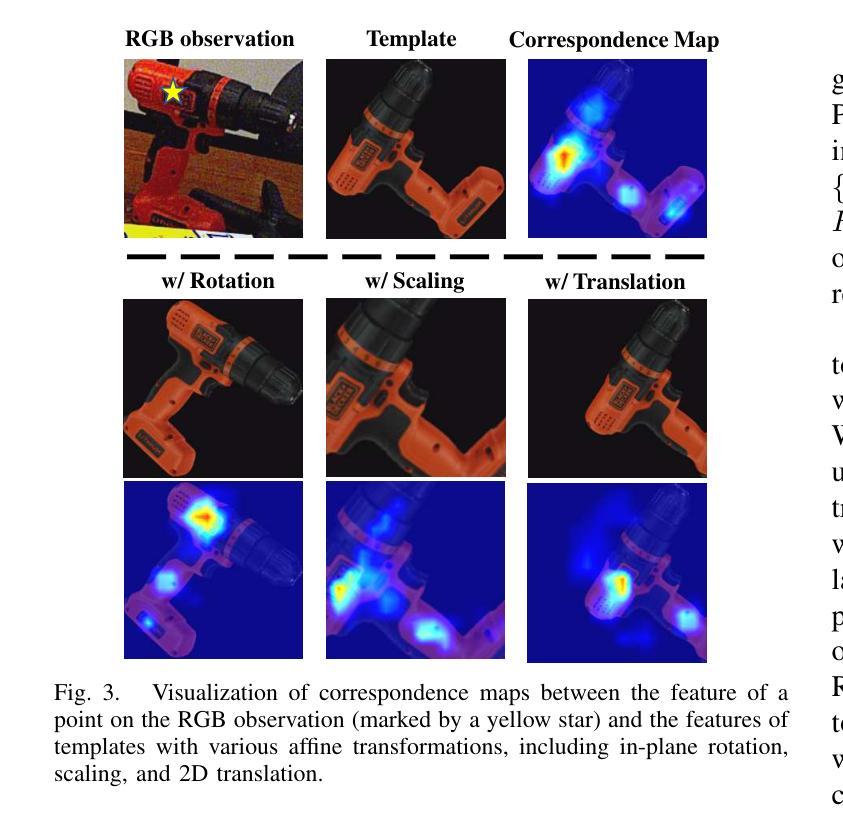
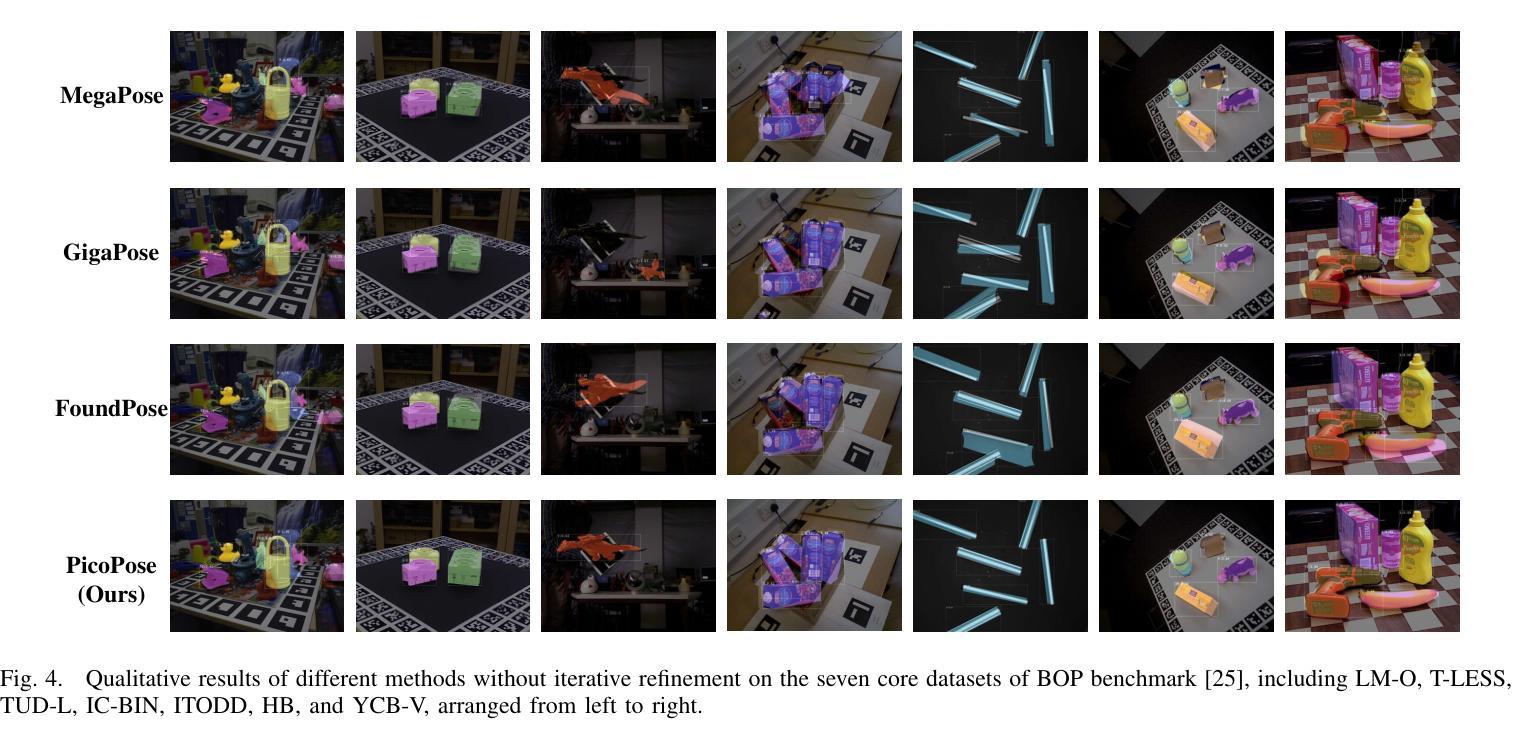
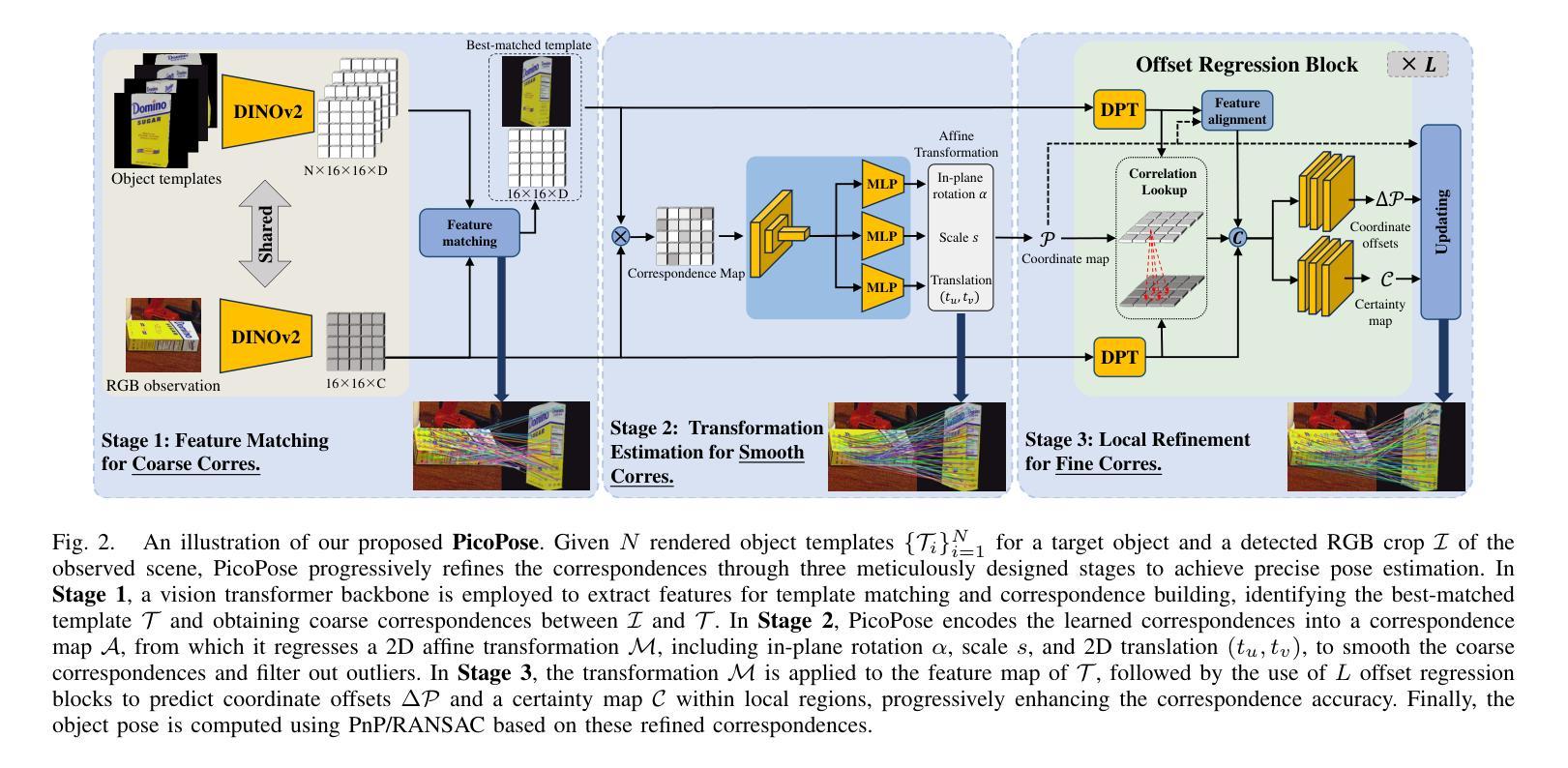
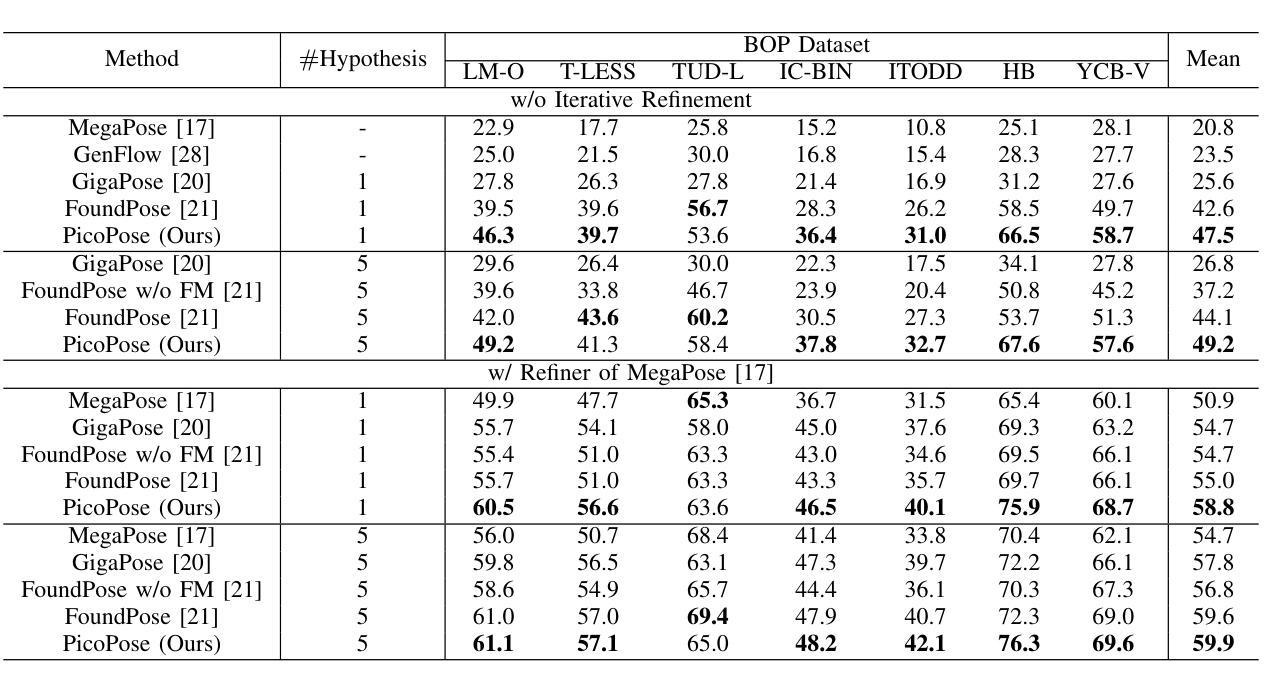
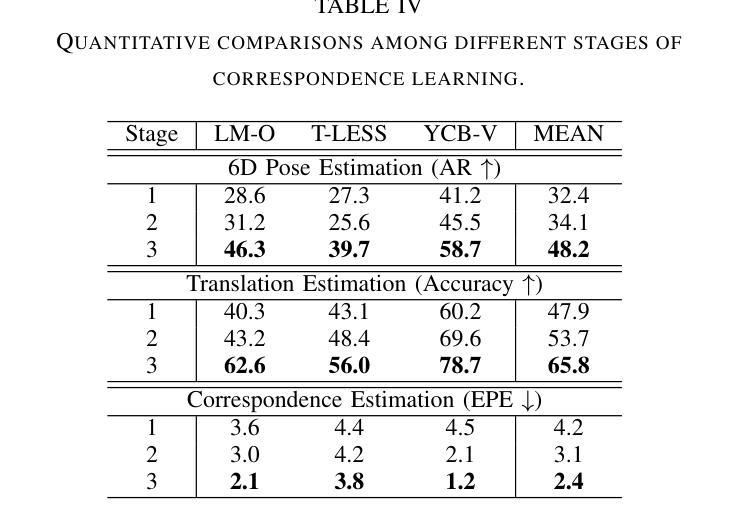
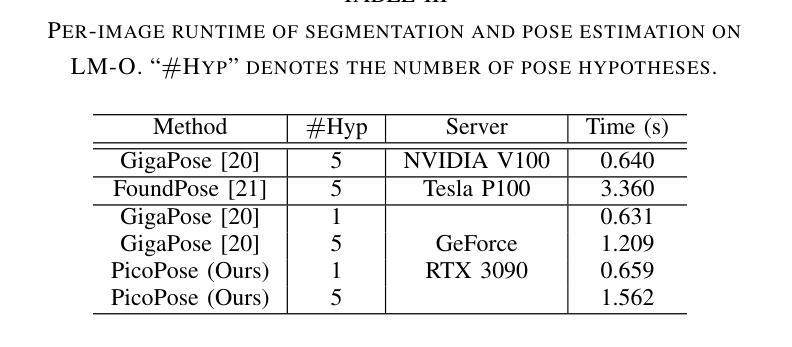
PicoPose: Progressive Pixel-to-Pixel Correspondence Learning for Novel Object Pose Estimation
Authors:Lihua Liu, Jiehong Lin, Zhenxin Liu, Kui Jia
Novel object pose estimation from RGB images presents a significant challenge for zero-shot generalization, as it involves estimating the relative 6D transformation between an RGB observation and a CAD model of an object that was not seen during training. In this paper, we introduce PicoPose, a novel framework designed to tackle this task using a three-stage pixel-to-pixel correspondence learning process. Firstly, PicoPose matches features from the RGB observation with those from rendered object templates, identifying the best-matched template and establishing coarse correspondences. Secondly, PicoPose smooths the correspondences by globally regressing a 2D affine transformation, including in-plane rotation, scale, and 2D translation, from the coarse correspondence map. Thirdly, PicoPose applies the affine transformation to the feature map of the best-matched template and learns correspondence offsets within local regions to achieve fine-grained correspondences. By progressively refining the correspondences, PicoPose significantly improves the accuracy of object poses computed via PnP/RANSAC. PicoPose achieves state-of-the-art performance on the seven core datasets of the BOP benchmark, demonstrating exceptional generalization to novel objects represented by CAD models or object reference images. Code and models are available at https://github.com/foollh/PicoPose.
从RGB图像进行新型物体姿态估计对于零样本泛化来说是一个重大挑战,因为这涉及到在训练期间未见过的RGB观测和CAD模型之间相对6D转变的估计。在本文中,我们介绍了PicoPose,这是一个专门设计用来解决此任务的新型框架,采用分阶段像素对应学习过程。首先,PicoPose将RGB观测的特征与渲染出的物体模板进行匹配,找出最佳匹配的模板,并建立粗略的对应关系。其次,PicoPose通过对粗略对应地图进行全局回归,平滑对应物,回归包括平面内旋转、缩放和2D平移的2D仿射变换。第三,PicoPose将仿射变换应用于最佳匹配模板的特征图,并在局部区域内学习对应偏移,以实现精细的对应关系。通过逐步优化对应关系,PicoPose能显著提高通过PnP/RANSAC计算出的物体姿态的准确度。PicoPose在BOP基准测试的七个核心数据集上达到了最先进的性能,显示出对由CAD模型或物体参考图像表示的新型物体的出色泛化能力。代码和模型可在https://github.com/foollh/PicoPose获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于RGB图像的新型物体姿态估计对于零样本泛化是一个挑战,因为需要估计RGB观测与CAD模型之间的相对6D转换。本文介绍了一种新型框架PicoPose,通过像素到像素的对应关系学习过程来解决此任务。该框架通过三个阶段逐步优化对应关系,从而提高通过PnP/RANSAC计算的物体姿态的准确性。PicoPose在BOP基准测试的七个核心数据集上取得了最先进的性能,显示出对新型物体的出色泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- PicoPose是一种用于解决从RGB图像进行新型物体姿态估计的挑战的新型框架。
- PicoPose采用像素到像素的对应关系学习过程,分为三个主要阶段。
- 第一阶段通过匹配RGB观测与渲染物体模板的特征来建立粗略对应关系。
- 第二阶段通过全局回归2D仿射变换平滑对应关系。
- 第三阶段通过应用仿射变换并学习局部区域内的对应偏移来实现精细的对应关系。
- PicoPose显著提高了通过PnP/RANSAC计算的物体姿态的准确性。
点此查看论文截图



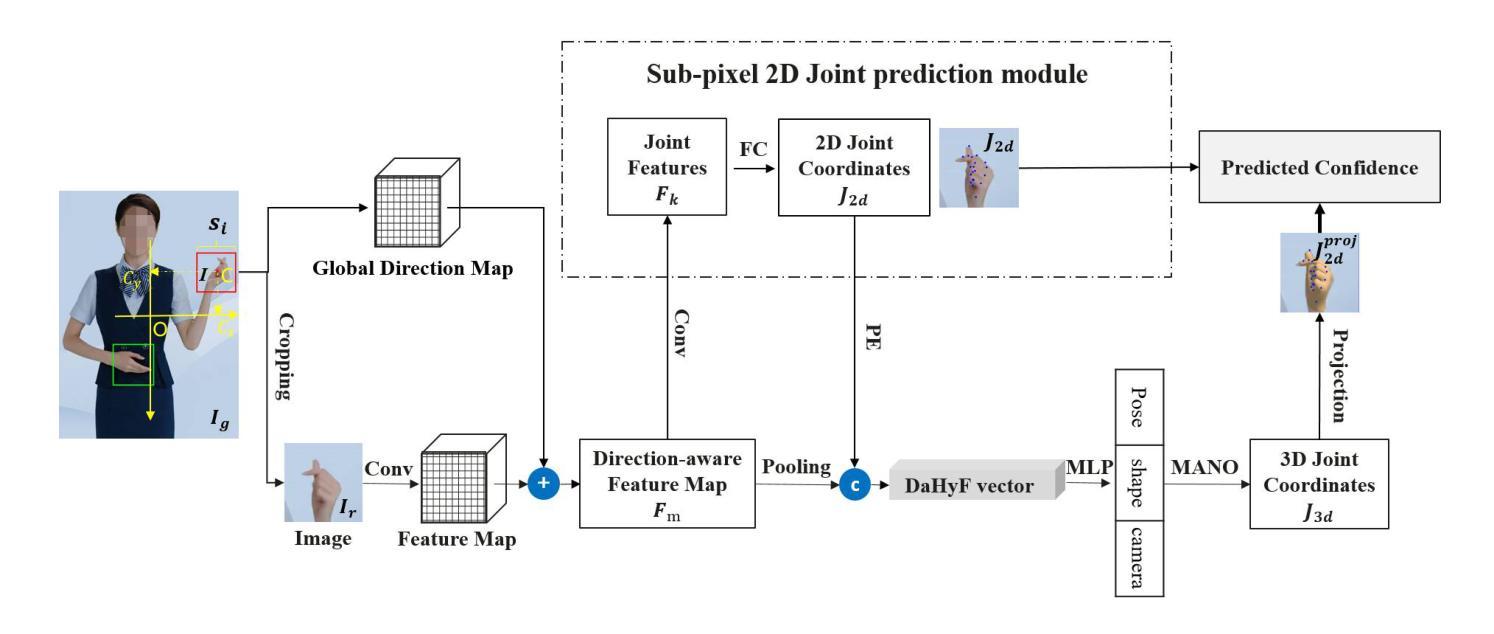
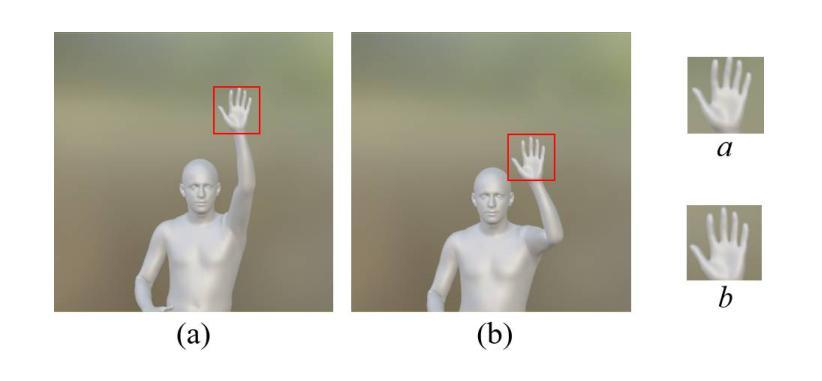
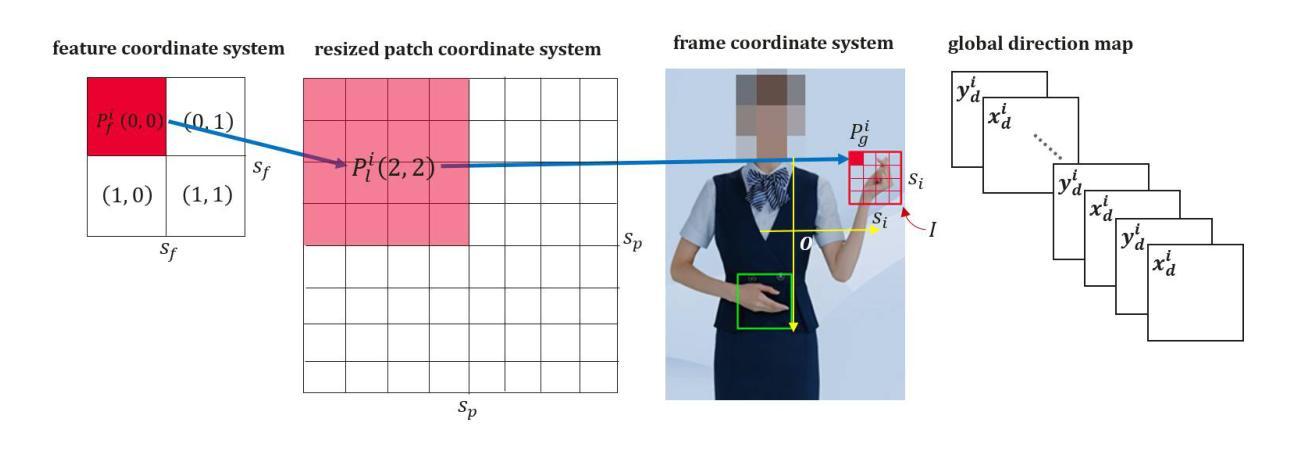
Direction-Aware Hybrid Representation Learning for 3D Hand Pose and Shape Estimation
Authors:Shiyong Liu, Zhihao Li, Xiao Tang, Jianzhuang Liu
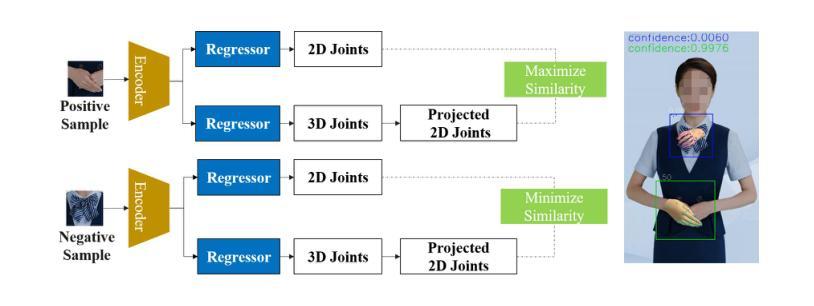
Most model-based 3D hand pose and shape estimation methods directly regress the parametric model parameters from an image to obtain 3D joints under weak supervision. However, these methods involve solving a complex optimization problem with many local minima, making training difficult. To address this challenge, we propose learning direction-aware hybrid features (DaHyF) that fuse implicit image features and explicit 2D joint coordinate features. This fusion is enhanced by the pixel direction information in the camera coordinate system to estimate pose, shape, and camera viewpoint. Our method directly predicts 3D hand poses with DaHyF representation and reduces jittering during motion capture using prediction confidence based on contrastive learning. We evaluate our method on the FreiHAND dataset and show that it outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods by more than 33% in accuracy. DaHyF also achieves the top ranking on both the HO3Dv2 and HO3Dv3 leaderboards for the metric of Mean Joint Error (after scale and translation alignment). Compared to the second-best results, the largest improvement observed is 10%. We also demonstrate its effectiveness in real-time motion capture scenarios with hand position variability, occlusion, and motion blur.
基于模型的3D手势姿态和形状估计方法大多直接从图像回归参数模型参数,以在弱监督下获得3D关节。然而,这些方法需要解决具有多个局部最小值的复杂优化问题,使得训练变得困难。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了学习方向感知混合特征(DaHyF),它融合了隐式图像特征和显式的2D关节坐标特征。这种融合通过相机坐标系中的像素方向信息来增强,以估计姿态、形状和相机视点。我们的方法直接使用DaHyF表示预测3D手势姿态,并利用基于对比学习的预测置信度减少运动捕捉过程中的抖动。我们在FreiHAND数据集上评估了我们的方法,并显示出它比现有最先进的方法的准确性高出33%以上。DaHyF在HO3Dv2和HO3Dv3排行榜上的平均关节误差指标方面也获得了排名第一。与第二好的结果相比,观察到的最大改进是10%。我们还证明了它在具有手势位置变化、遮挡和运动模糊的实时运动捕捉场景中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025 workshop
Summary
本文提出一种基于学习方向感知混合特征(DaHyF)的3D手姿势与形状估计方法。该方法融合了隐性图像特征与显性2D关节坐标特征,借助相机坐标系中的像素方向信息来估计姿势、形状和相机视角。DaHyF直接预测3D手姿势,通过对比学习减少运动捕捉中的抖动,并在FreiHAND数据集上实现了超过现有先进方法33%的准确性提升。同时,在HO3Dv2和HO3Dv3排行榜上,DaHyF在平均关节误差指标上获得排名第一,相较于第二名结果,其最大提升为10%。此外,该方法在具有手位置变化、遮挡和运动模糊的实时运动捕捉场景中表现出有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出学习方向感知混合特征(DaHyF)以解决模型基于的3D手姿势和形状估计方法的训练难题。
- DaHyF融合隐性图像特征与显性2D关节坐标特征,增强估计姿势、形状和相机视角的准确性。
- 通过引入像素方向信息,提高手姿势和形状的估计精度。
- DaHyF直接预测3D手姿势并减少运动捕捉中的抖动。
- 在FreiHAND数据集上的实验表明,DaHyF的准确性超过现有方法33%以上。
- DaHyF在HO3Dv2和HO3Dv3排行榜上获得排名第一,平均关节误差指标显著优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

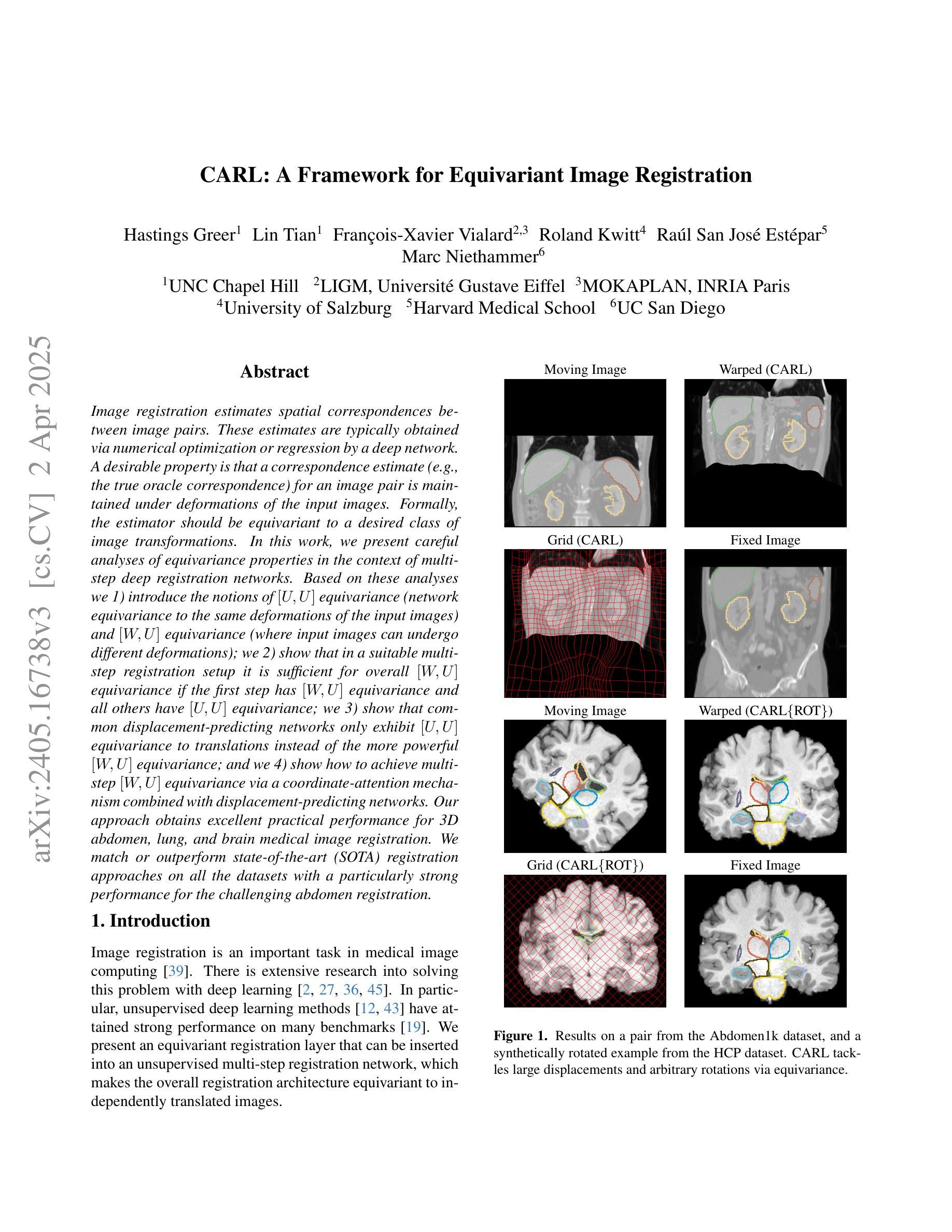
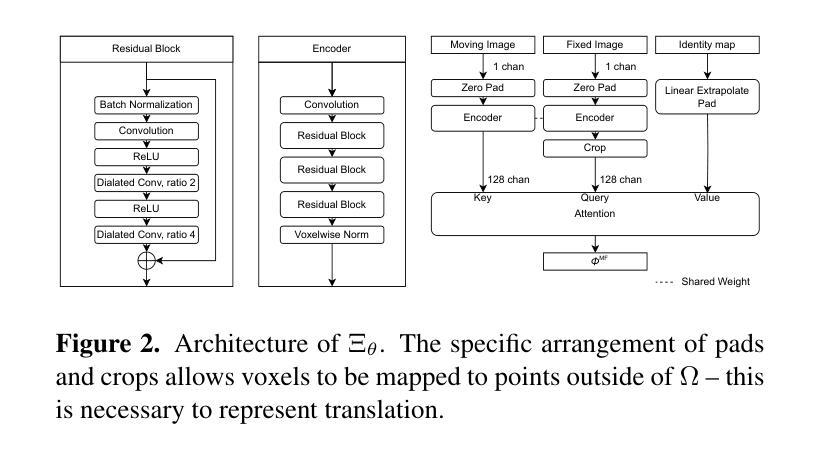
CARL: A Framework for Equivariant Image Registration
Authors:Hastings Greer, Lin Tian, Francois-Xavier Vialard, Roland Kwitt, Raul San Jose Estepar, Marc Niethammer
Image registration estimates spatial correspondences between a pair of images. These estimates are typically obtained via numerical optimization or regression by a deep network. A desirable property of such estimators is that a correspondence estimate (e.g., the true oracle correspondence) for an image pair is maintained under deformations of the input images. Formally, the estimator should be equivariant to a desired class of image transformations. In this work, we present careful analyses of the desired equivariance properties in the context of multi-step deep registration networks. Based on these analyses we 1) introduce the notions of $[U,U]$ equivariance (network equivariance to the same deformations of the input images) and $[W,U]$ equivariance (where input images can undergo different deformations); we 2) show that in a suitable multi-step registration setup it is sufficient for overall $[W,U]$ equivariance if the first step has $[W,U]$ equivariance and all others have $[U,U]$ equivariance; we 3) show that common displacement-predicting networks only exhibit $[U,U]$ equivariance to translations instead of the more powerful $[W,U]$ equivariance; and we 4) show how to achieve multi-step $[W,U]$ equivariance via a coordinate-attention mechanism combined with displacement-predicting refinement layers (CARL). Overall, our approach obtains excellent practical registration performance on several 3D medical image registration tasks and outperforms existing unsupervised approaches for the challenging problem of abdomen registration.
图像注册(Image registration)是估算一对图像之间的空间对应关系。这些估计通常通过数值优化或深度学习网络中的回归得到。对于这种估计器,理想的属性是,在输入图像发生变形时,仍然保持图像对之间的对应关系估计(例如真实对应关系)。在形式上,估计器应对期望的图像变换类别具有等变性。在这项工作中,我们对多步深度注册网络的期望等变性属性进行了仔细分析。基于这些分析,我们1)引入了$[U,U]$等变性(网络对输入图像的相同变形具有等变性)和$[W,U]$等变性(输入图像可以经历不同的变形)的概念;我们2)表明,在适当的多步注册设置中,如果第一步具有$[W,U]$等变性,而其他所有步骤都具有$[U,U]$等变性,那么对于整体而言就足够达到$[W,U]$等变性;我们3)表明,常见的位移预测网络仅对平移具有$[U,U]$等变性,而无法达到更强大的$[W,U]$等变性;我们4)展示了如何通过结合坐标注意机制和位移预测细化层(CARL)来实现多步$[W,U]$等变性。总体而言,我们的方法在多个3D医学图像注册任务上取得了出色的实际注册性能,并且在具有挑战性的腹部注册问题上优于现有的无监督方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
图像配准估算一对图像之间的空间对应关系,通常通过数值优化或深度网络的回归获得。本文在多部深配对网络上下文中,对所需的等变属性进行了深入分析。基于这些分析,我们介绍了[U,U]等变性和[W,U]等变性的概念,并在适当的多步配准设置中展示了整体[W,U]等变性的足够性。我们的方法通过坐标注意机制与位移预测修正层(CARL)相结合,实现了多步[W,U]等变性,并在多个3D医学图像配准任务上取得了优异的实际配准性能,并在腹部配准的挑战性问题上优于现有的无监督方法。
Key Takeaways
- 图像配准用于估算图像间的空间对应关系,可通过数值优化或深度网络回归得到。
- 深度注册网络所需的等变性进行了分析,区分了[U,U]等变性和[W,U]等变性。
- 在多步配准设置中,如果第一步具有[W,U]等变性且其余步骤具有[U,U]等变性,则足以实现整体[W,U]等变性。
- 常见的位移预测网络仅表现出对平移的[U,U]等变性,而非更强大的[W,U]等变性。
- 通过坐标注意机制与位移预测修正层(CARL)的结合,实现了多步[W,U]等变性。
- 该方法在多个3D医学图像配准任务上取得了优异的性能。
点此查看论文截图