⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-05 更新
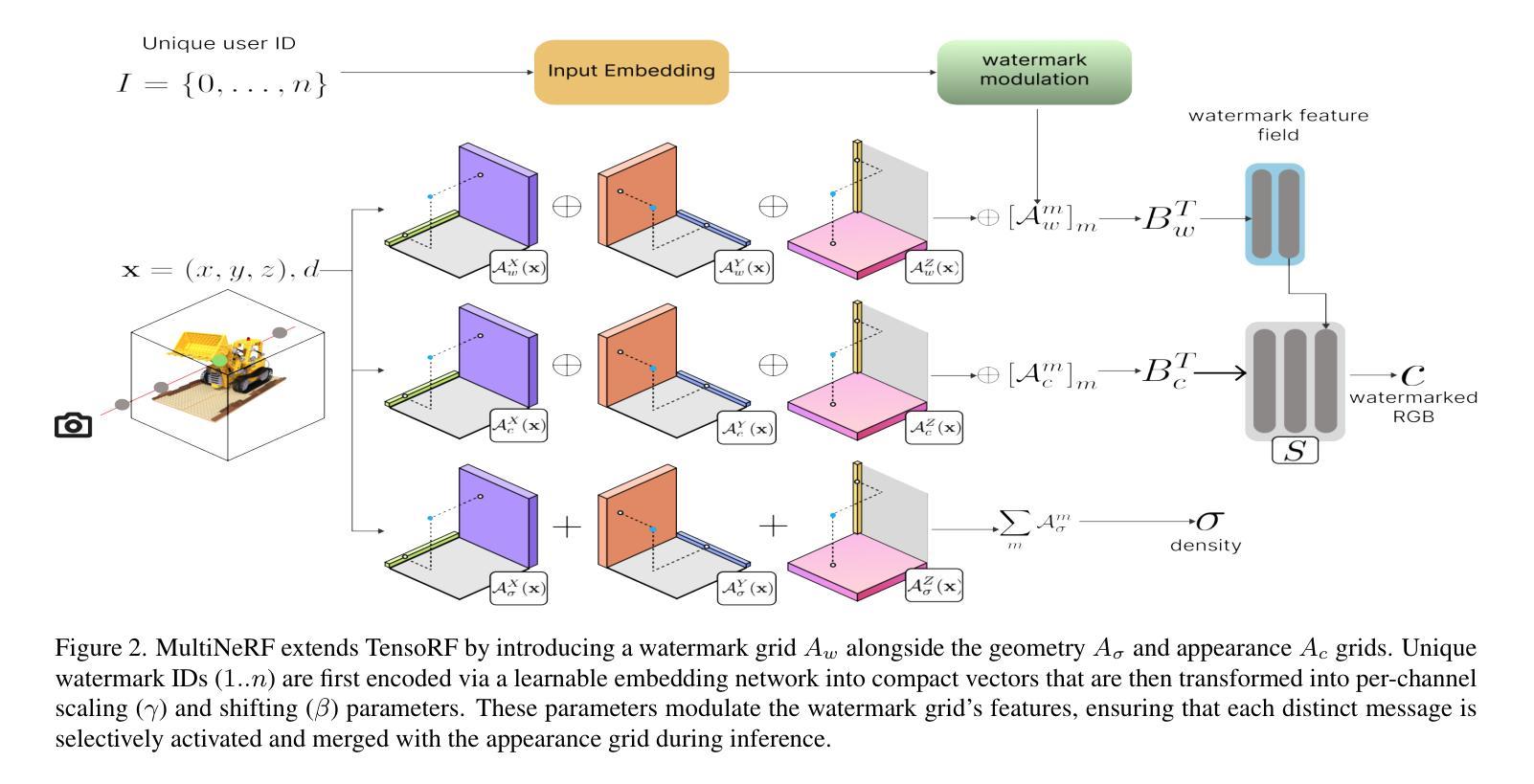
MultiNeRF: Multiple Watermark Embedding for Neural Radiance Fields
Authors:Yash Kulthe, Andrew Gilbert, John Collomosse
We present MultiNeRF, a 3D watermarking method that embeds multiple uniquely keyed watermarks within images rendered by a single Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) model, whilst maintaining high visual quality. Our approach extends the TensoRF NeRF model by incorporating a dedicated watermark grid alongside the existing geometry and appearance grids. This extension ensures higher watermark capacity without entangling watermark signals with scene content. We propose a FiLM-based conditional modulation mechanism that dynamically activates watermarks based on input identifiers, allowing multiple independent watermarks to be embedded and extracted without requiring model retraining. MultiNeRF is validated on the NeRF-Synthetic and LLFF datasets, with statistically significant improvements in robust capacity without compromising rendering quality. By generalizing single-watermark NeRF methods into a flexible multi-watermarking framework, MultiNeRF provides a scalable solution for 3D content. attribution.
我们提出了MultiNeRF,这是一种3D水印方法,能够在由单个神经辐射场(NeRF)模型渲染的图像中嵌入多个具有唯一密钥的水印,同时保持高视觉质量。我们的方法通过结合现有的几何和外观网格,扩展了TensoRF的NeRF模型,并加入了一个专门的水印网格。这一扩展确保了更高的水印容量,同时不会将水印信号与场景内容混淆。我们提出了一种基于FiLM的条件调制机制,该机制根据输入标识符动态激活水印,允许嵌入和提取多个独立水印,而无需重新训练模型。MultiNeRF在NeRF-Synthetic和LLFF数据集上进行了验证,在不影响渲染质量的情况下,稳健的容量得到了显著的提升。通过将单水印NeRF方法推广为灵活的多水印框架,MultiNeRF为3D内容的归属提供了可扩展的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
NeRF模型引入了一种名为MultiNeRF的多水印技术,该技术能够在渲染的图像中嵌入多个独特密钥的水印,同时保持高质量视觉效果。它通过扩展TensoRF模型,增加了一个专门的水印网格,确保更高的水印容量,并且不会将水印信号与场景内容混淆。此外,MultiNeRF还提出了一种基于FiLM的条件调制机制,根据输入标识符动态激活水印,允许嵌入和提取多个独立水印,无需重新训练模型。在NeRF-Synthetic和LLFF数据集上验证了MultiNeRF的有效性,其在提高稳健容量的同时,不损害渲染质量。它为3D内容提供可扩展的多水印解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- MultiNeRF成功将多个水印嵌入到NeRF模型中,提高了水印容量。
- 通过增加一个专门的水印网格,确保水印信号与场景内容分离。
- 基于FiLM的条件调制机制允许根据输入标识符动态激活水印。
- MultiNeRF支持在不重新训练模型的情况下嵌入和提取多个独立水印。
- 在NeRF-Synthetic和LLFF数据集上的验证显示,MultiNeRF提高了稳健容量,同时保持高质量的渲染。
- MultiNeRF提供了一种可扩展的多水印解决方案,适用于3D内容保护。
点此查看论文截图

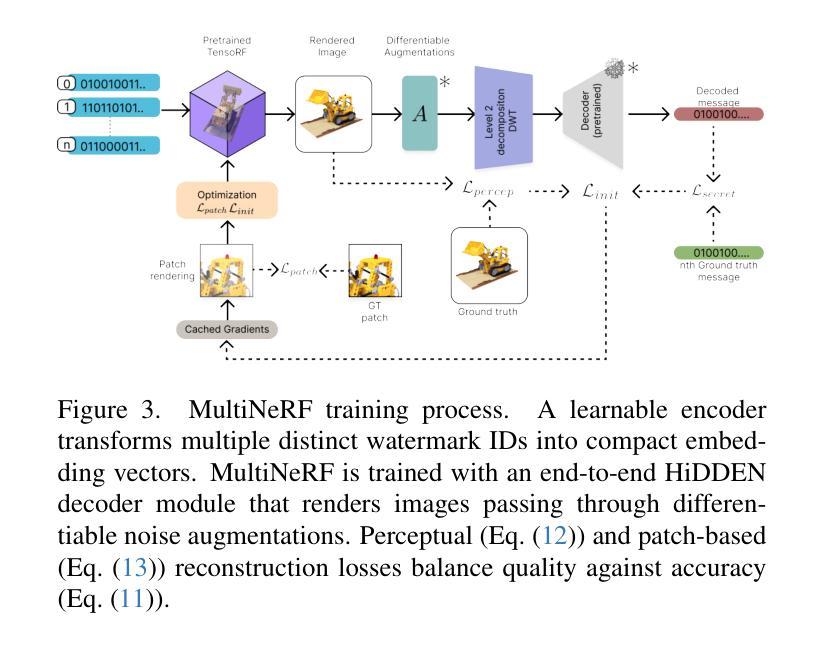
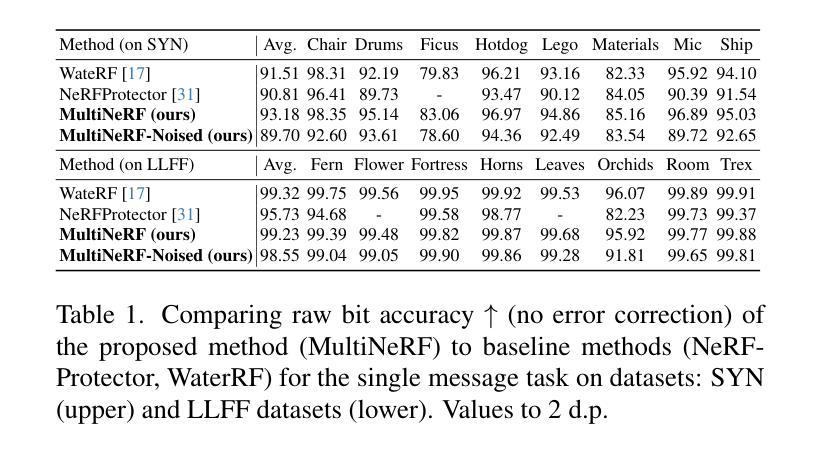
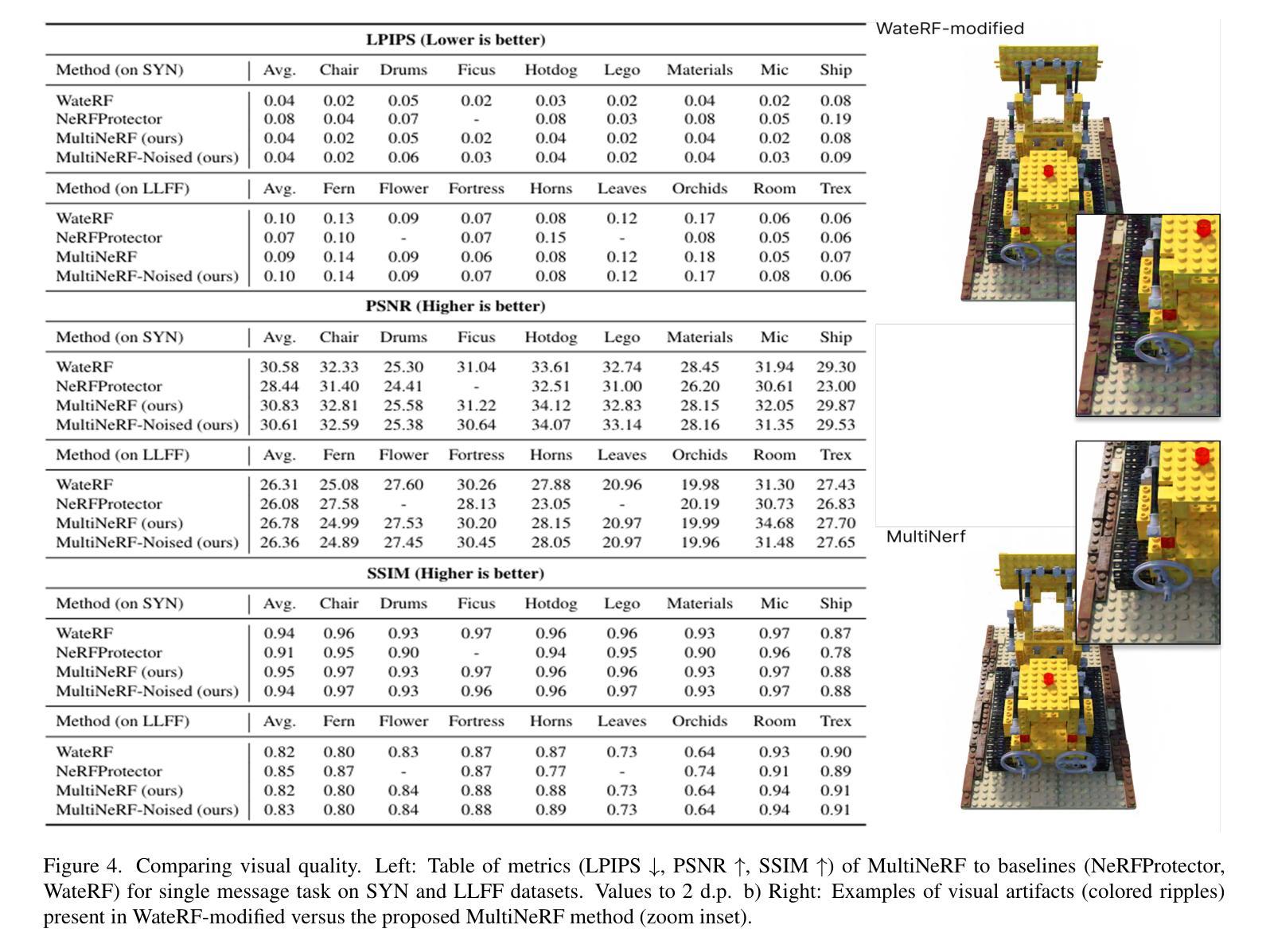
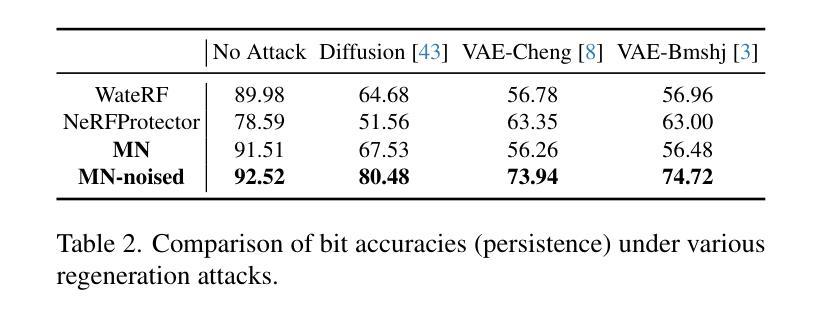
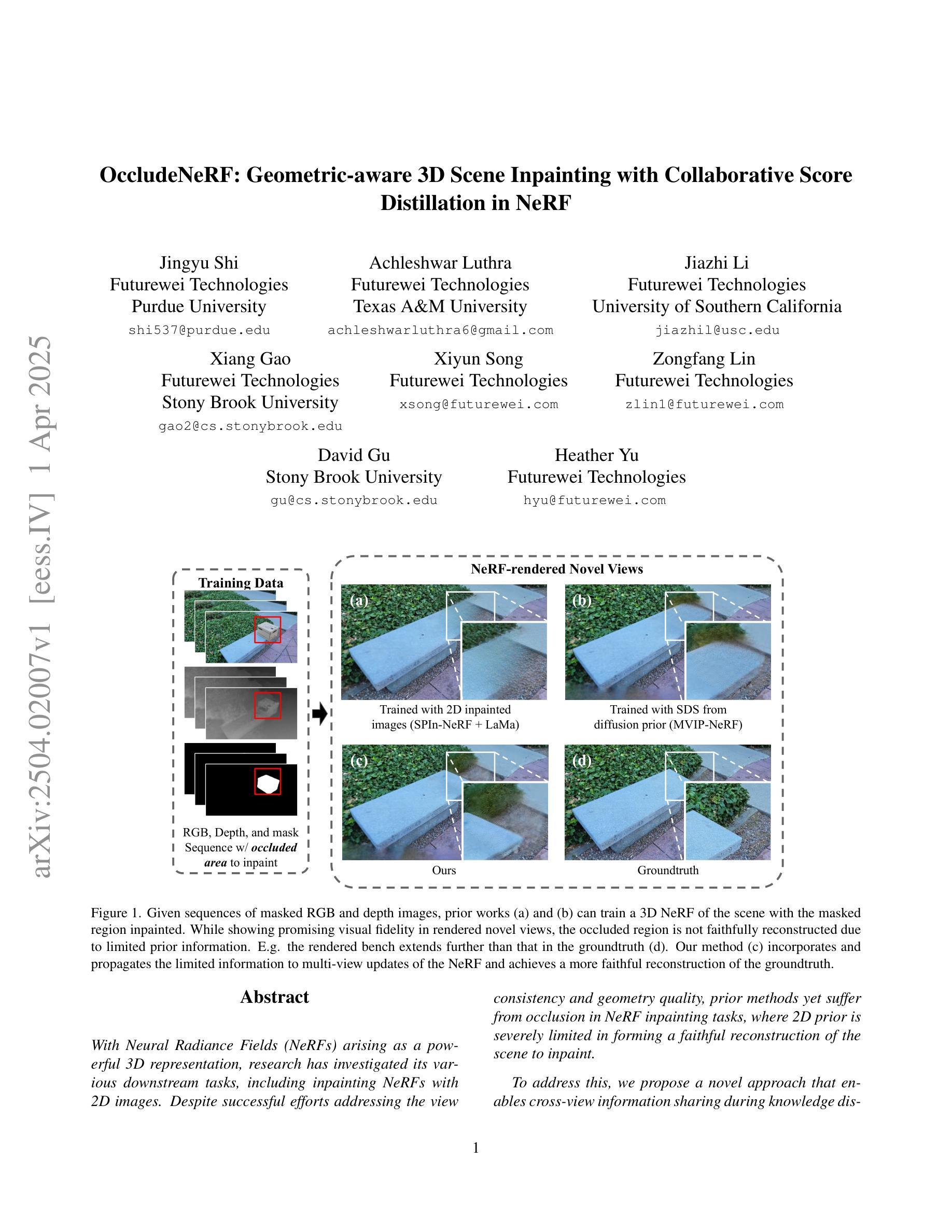
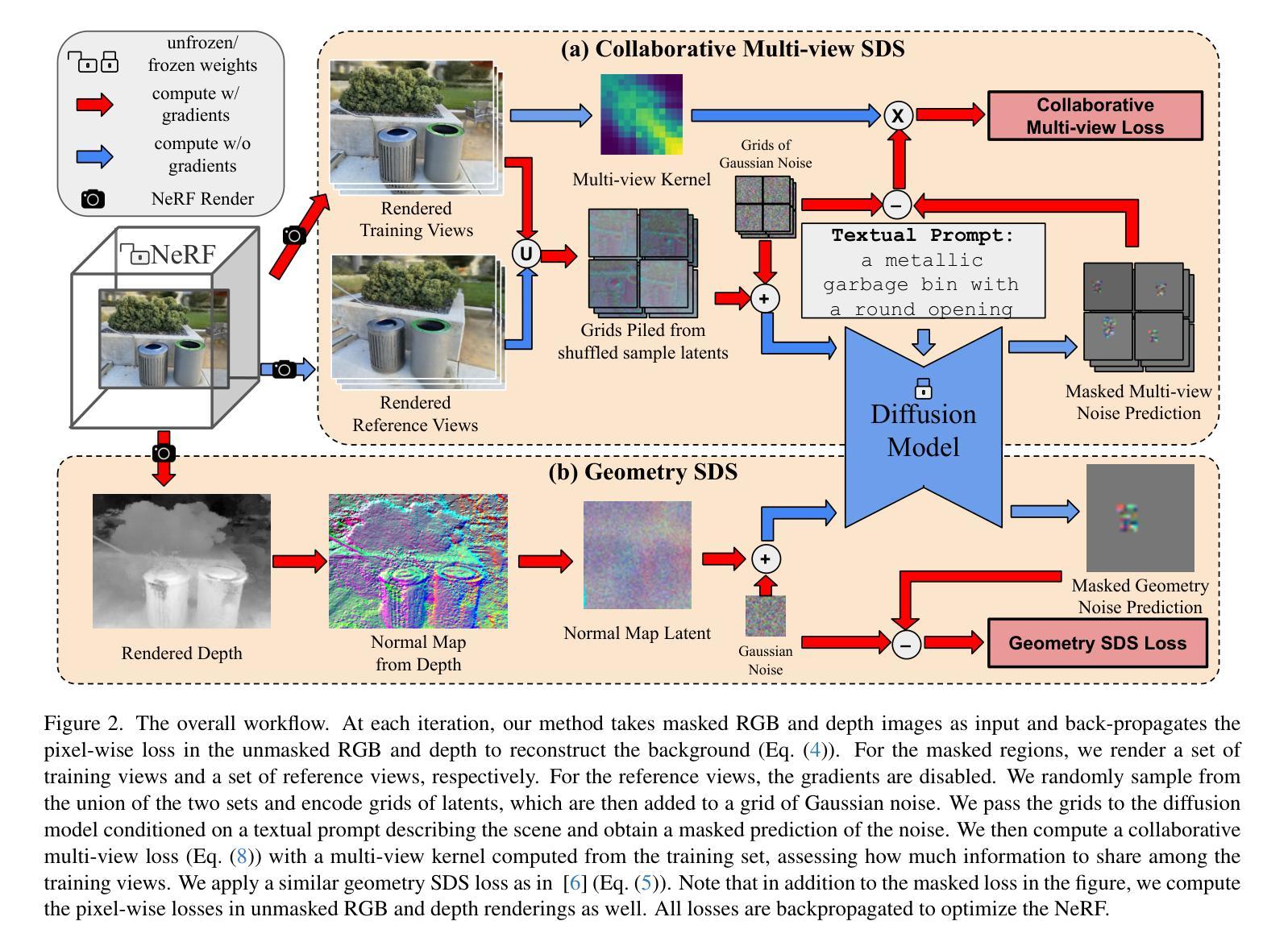
OccludeNeRF: Geometric-aware 3D Scene Inpainting with Collaborative Score Distillation in NeRF
Authors:Jingyu Shi, Achleshwar Luthra, Jiazhi Li, Xiang Gao, Xiyun Song, Zongfang Lin, David Gu, Heather Yu
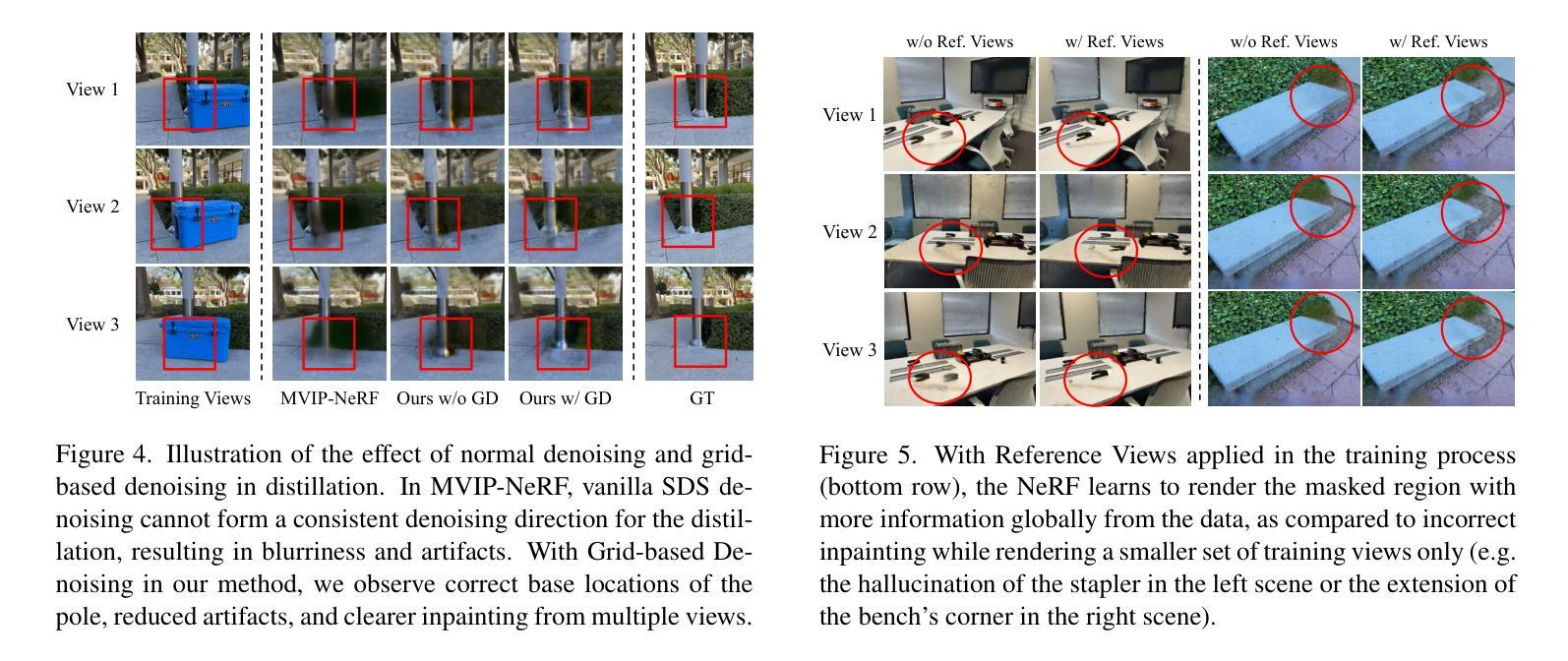
With Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) arising as a powerful 3D representation, research has investigated its various downstream tasks, including inpainting NeRFs with 2D images. Despite successful efforts addressing the view consistency and geometry quality, prior methods yet suffer from occlusion in NeRF inpainting tasks, where 2D prior is severely limited in forming a faithful reconstruction of the scene to inpaint. To address this, we propose a novel approach that enables cross-view information sharing during knowledge distillation from a diffusion model, effectively propagating occluded information across limited views. Additionally, to align the distillation direction across multiple sampled views, we apply a grid-based denoising strategy and incorporate additional rendered views to enhance cross-view consistency. To assess our approach’s capability of handling occlusion cases, we construct a dataset consisting of challenging scenes with severe occlusion, in addition to existing datasets. Compared with baseline methods, our method demonstrates better performance in cross-view consistency and faithfulness in reconstruction, while preserving high rendering quality and fidelity.
随着神经辐射场(NeRF)作为一种强大的3D表示方法的出现,研究已经探索了其各种下游任务,包括使用2D图像填充NeRF。尽管已有成功努力解决了视图一致性和几何质量的问题,但先前的方法在NeRF填充任务中仍受到遮挡的困扰,其中2D先验在形成待填充场景的忠实重建时受到严重限制。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新方法,通过在扩散模型的知识蒸馏过程中实现跨视图信息共享,有效地传播了有限视图中的遮挡信息。此外,为了对齐多个采样视图之间的蒸馏方向,我们采用了基于网格的去噪策略,并融入了额外的渲染视图,以提高跨视图的一致性。为了评估我们处理遮挡情况的能力,我们构建了一个由具有严重遮挡的挑战性场景组成的数据集,除此之外还有现有的数据集。与基准方法相比,我们的方法在跨视图一致性以及重建的忠实度方面表现出更好的性能,同时保持了高渲染质量和保真度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025 CV4Metaverse
Summary
NeRF的下游任务之一为NeRF补全任务,即利用二维图像进行补全。现有方法在处理NeRF补全任务时仍面临遮挡问题,缺乏处理不同视角信息的共享能力。本研究提出一种利用扩散模型的知识蒸馏过程中的跨视图信息共享的新方法,结合网格去噪策略和额外的渲染视图以增强跨视图一致性。相较于现有方法,本研究在构建的新数据集上展现出更好的处理遮挡情况的能力,同时保持高渲染质量和保真度。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF补全任务面临遮挡问题,现有方法受限于二维先验信息,难以形成场景的真实重建。
- 提出一种利用扩散模型进行知识蒸馏的方法,实现了跨视图的信息共享。
- 通过网格去噪策略和多视角渲染增强跨视图一致性。
- 构建包含复杂场景的新数据集以评估处理遮挡情况的能力。
- 与基线方法相比,在跨视图一致性和重建真实性方面表现更优。
- 保持高渲染质量和保真度。
点此查看论文截图


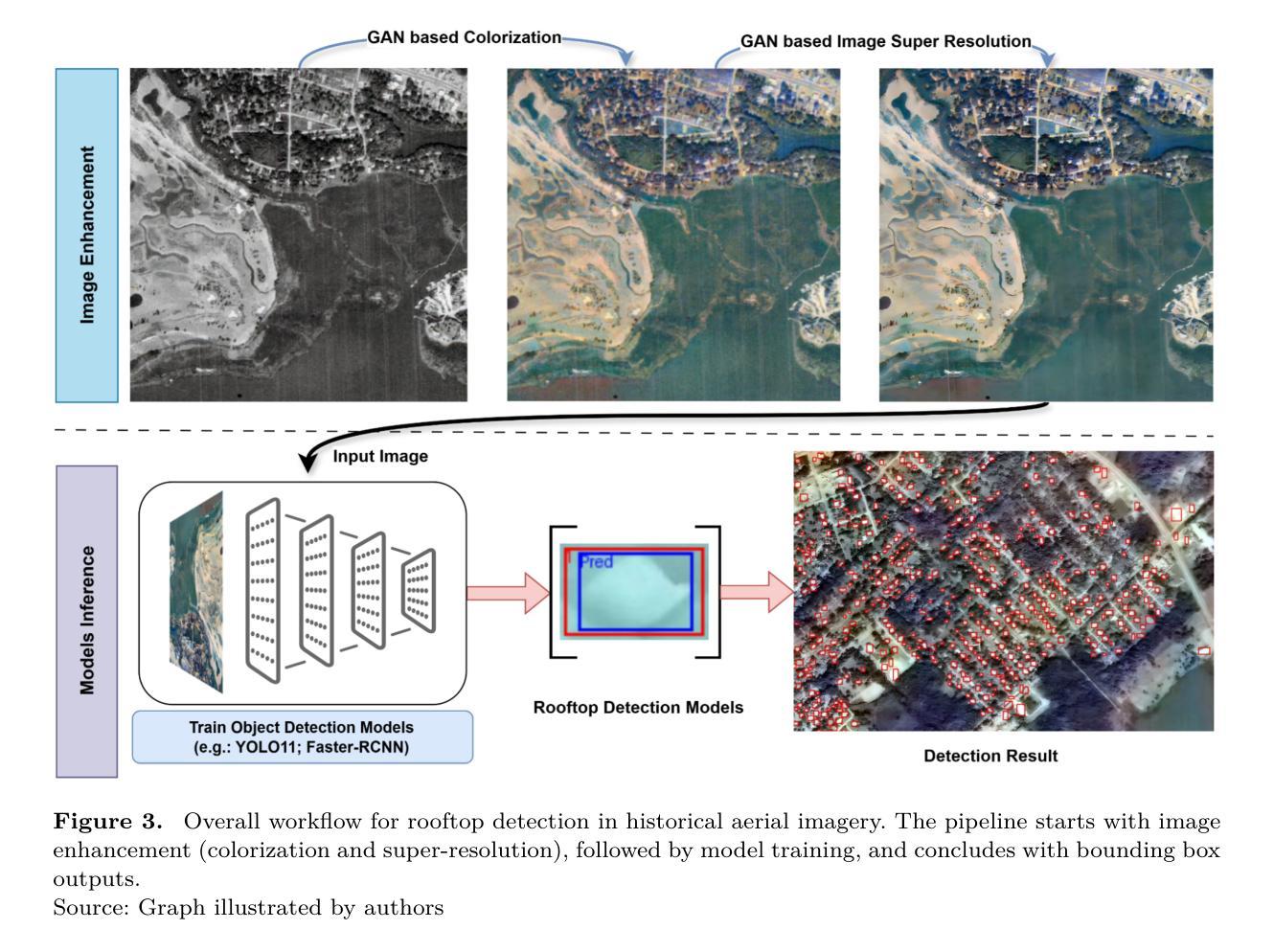
A GAN-Enhanced Deep Learning Framework for Rooftop Detection from Historical Aerial Imagery
Authors:Pengyu Chen, Sicheng Wang, Cuizhen Wang, Senrong Wang, Beiao Huang, Lu Huang, Zhe Zang
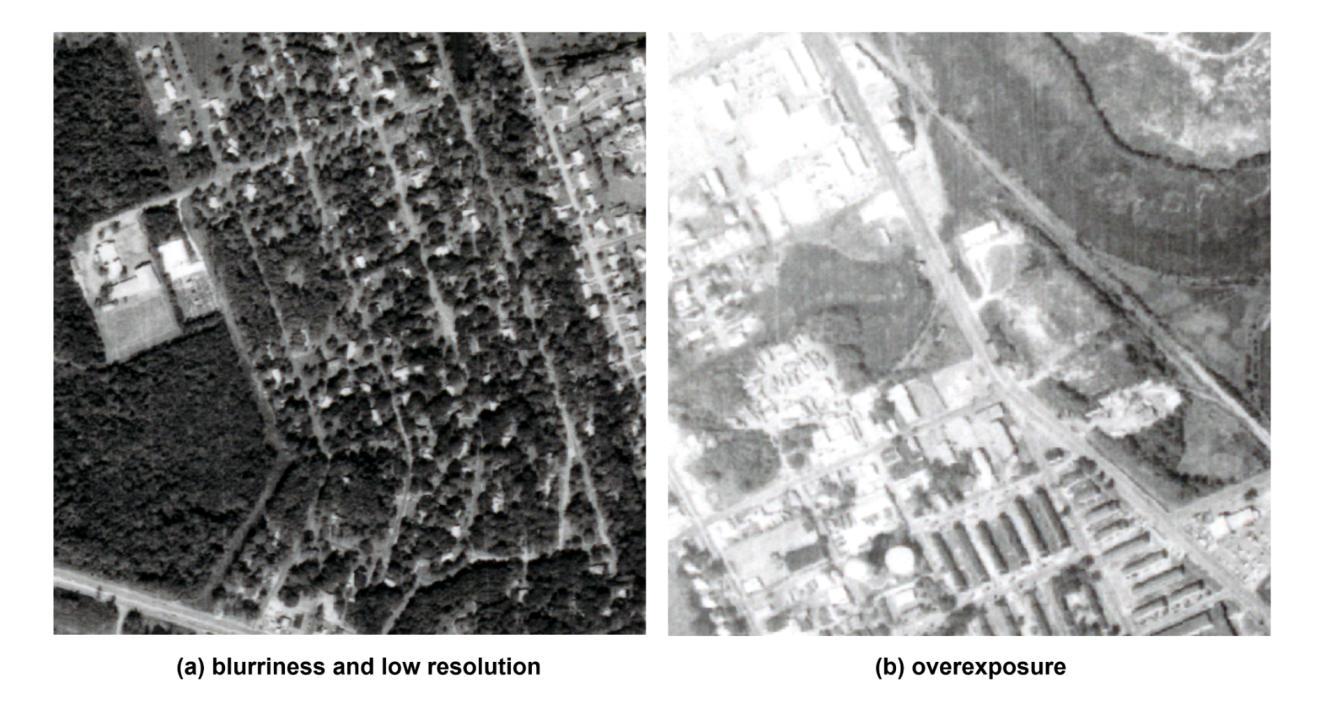
Precise detection of rooftops from historical aerial imagery is essential for analyzing long-term urban development and human settlement patterns. Nonetheless, black-and-white analog photographs present considerable challenges for modern object detection frameworks due to their limited spatial resolution, absence of color information, and archival degradation. To address these challenges, this research introduces a two-stage image enhancement pipeline based on Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): image colorization utilizing DeOldify, followed by super-resolution enhancement with Real-ESRGAN. The enhanced images were subsequently employed to train and evaluate rooftop detection models, including Faster R-CNN, DETReg, and YOLOv11n. The results demonstrate that the combination of colorization with super-resolution significantly enhances detection performance, with YOLOv11n achieving a mean Average Precision (mAP) exceeding 85%. This signifies an enhancement of approximately 40% over the original black-and-white images and 20% over images enhanced solely through colorization. The proposed method effectively bridges the gap between archival imagery and contemporary deep learning techniques, facilitating more reliable extraction of building footprints from historical aerial photographs. Code and resources for reproducing our results are publicly available at \href{https://github.com/Pengyu-gis/Historical-Aerial-Photos}{github.com/Pengyu-gis/Historical-Aerial-Photos}.
从历史航空影像中精确检测屋顶对于分析长期城市发展和人类定居模式至关重要。然而,黑白模拟照片为现代目标检测框架带来了巨大的挑战,因为它们空间分辨率有限、缺少颜色信息,并且存在档案退化问题。为了应对这些挑战,本研究引入了一种基于生成对抗网络(GANs)的两阶段图像增强管道:利用DeOldify进行图像上色,然后使用Real-ESRGAN进行超分辨率增强。增强后的图像随后被用于训练和评估屋顶检测模型,包括Faster R-CNN、DETReg和YOLOv11n。结果表明,上色与超分辨率的结合显著提高了检测性能,YOLOv11n的平均精度(mAP)超过85%。这意味着与原始黑白图像相比,性能提高了约40%,与仅通过上色的图像相比,性能提高了约20%。所提出的方法有效地架起了档案图像和当代深度学习技术之间的桥梁,促进了从旧航空照片中提取更可靠的建筑足迹。关于如何复制我们结果的代码和资源可在github.com/Pengyu-gis/Historical-Aerial-Photos上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于历史航空照片进行屋顶精准检测是分析长期城市发展和人类定居模式的关键。本研究采用基于生成对抗网络(GANs)的两阶段图像增强流程,利用DeOldify进行图像彩色化,然后使用Real-ESRGAN进行超分辨率增强。增强后的图像被用于训练和评估屋顶检测模型,包括Faster R-CNN、DETReg和YOLOv11n。结果显示,彩色化与超分辨率的结合显著提高了检测性能,YOLOv11n的平均精度(mAP)超过85%。相较于原始黑白图像,其性能提升约40%,相较于仅进行彩色化处理的图像,性能提升约20%。此方法有效地架起了档案图像与现代深度学习技术之间的桥梁,更可靠地提取了历史航空照片中的建筑足迹。相关代码和资源已公开在github上提供。
Key Takeaways
- 历史航空摄影中的屋顶检测对分析长期城市发展和人类定居模式至关重要。
- 采用两阶段GANs图像增强流程应对黑白历史照片的局限。
- 图像彩色化与超分辨率增强结合显著提高了屋顶检测性能。
- YOLOv11n模型表现出较高的检测性能,mAP超过85%。
- 与原始黑白图像相比,性能提升约40%,与仅彩色化图像相比,性能提升约20%。
- 此方法促进了档案图像与现代深度学习技术的结合。
点此查看论文截图


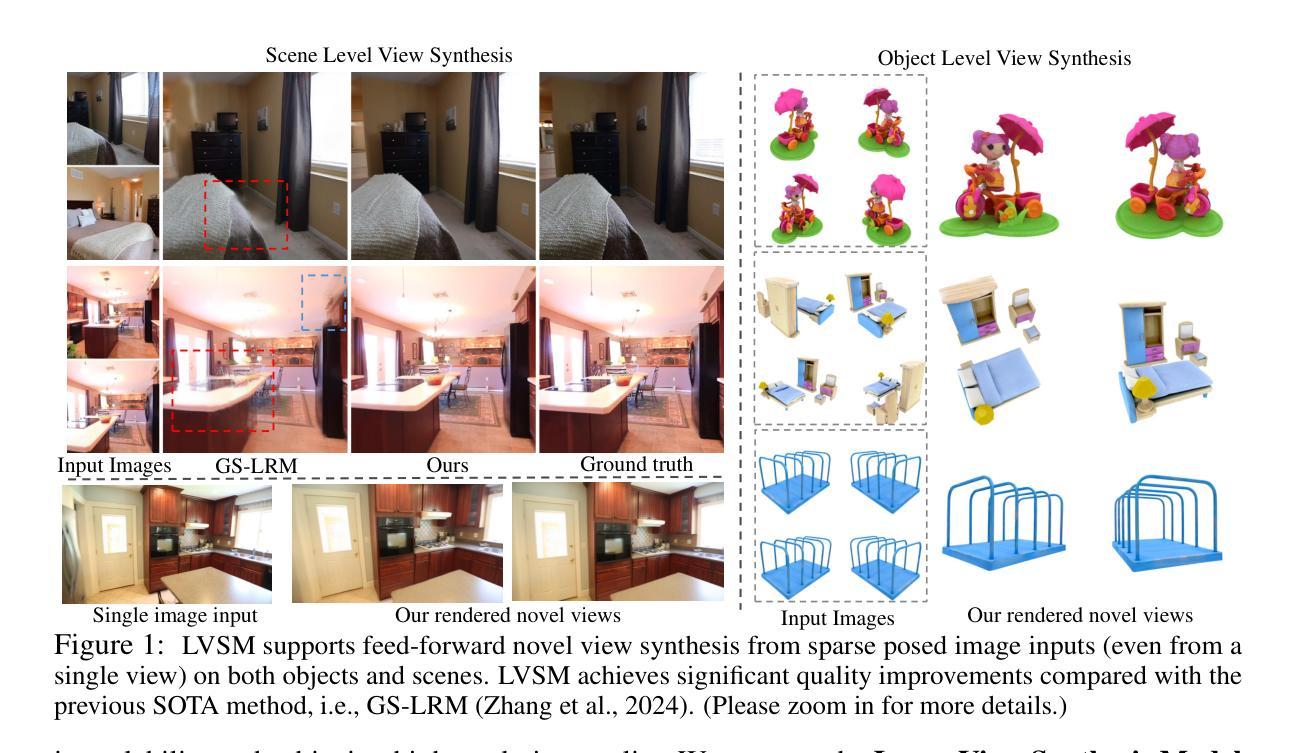
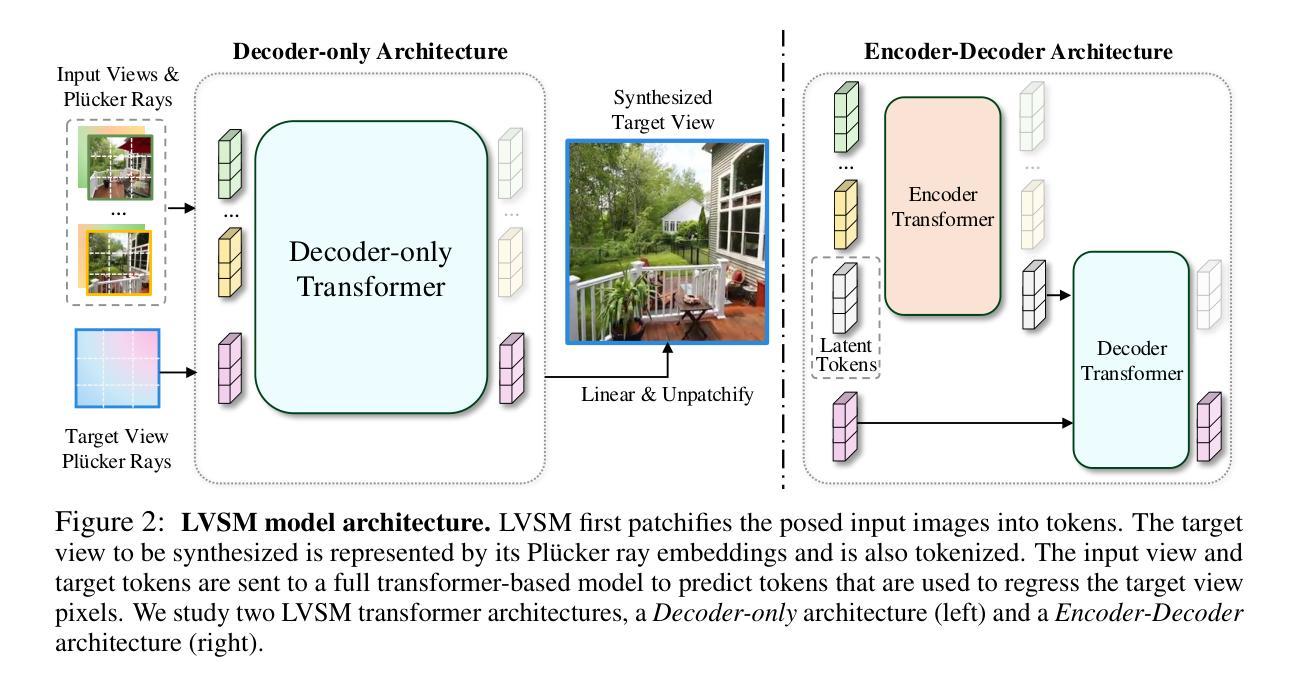
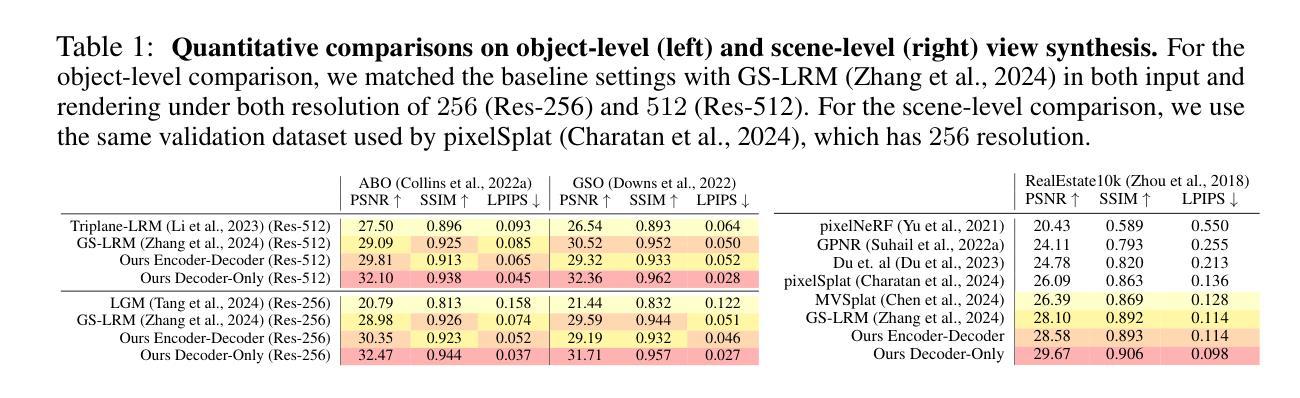
LVSM: A Large View Synthesis Model with Minimal 3D Inductive Bias
Authors:Haian Jin, Hanwen Jiang, Hao Tan, Kai Zhang, Sai Bi, Tianyuan Zhang, Fujun Luan, Noah Snavely, Zexiang Xu
We propose the Large View Synthesis Model (LVSM), a novel transformer-based approach for scalable and generalizable novel view synthesis from sparse-view inputs. We introduce two architectures: (1) an encoder-decoder LVSM, which encodes input image tokens into a fixed number of 1D latent tokens, functioning as a fully learned scene representation, and decodes novel-view images from them; and (2) a decoder-only LVSM, which directly maps input images to novel-view outputs, completely eliminating intermediate scene representations. Both models bypass the 3D inductive biases used in previous methods – from 3D representations (e.g., NeRF, 3DGS) to network designs (e.g., epipolar projections, plane sweeps) – addressing novel view synthesis with a fully data-driven approach. While the encoder-decoder model offers faster inference due to its independent latent representation, the decoder-only LVSM achieves superior quality, scalability, and zero-shot generalization, outperforming previous state-of-the-art methods by 1.5 to 3.5 dB PSNR. Comprehensive evaluations across multiple datasets demonstrate that both LVSM variants achieve state-of-the-art novel view synthesis quality. Notably, our models surpass all previous methods even with reduced computational resources (1-2 GPUs). Please see our website for more details: https://haian-jin.github.io/projects/LVSM/ .
我们提出了Large View Synthesis Model(LVSM)这一全新基于Transformer的方法,用于从稀疏视角输入实现可扩展且可泛化的新颖视角合成。我们介绍了两种架构:(1)编码器-解码器LVSM,它将输入图像标记编码为固定数量的1D潜在标记,作为完全学习的场景表示,并从中解码出新颖视角的图像;(2)仅解码器LVSM,它直接将输入图像映射到新颖视角的输出,完全消除了中间场景表示。这两种模型都绕过了以前方法使用的3D归纳偏见,从3D表示(例如NeRF、3DGS)到网络设计(例如极投影、平面扫描),采用全数据驱动的方法解决新颖视角合成问题。由于编码器-解码器模型的独立潜在表示,它提供了更快的推理速度,而仅解码器LVSM在质量、可扩展性和零射击泛化方面更胜一筹,比现有先进技术高出1.5至3.5 dB PSNR。在多个数据集上的综合评估表明,两种LVSM变体都达到了最新颖视角合成质量。值得注意的是,我们的模型即使在减少的计算资源(1-2个GPU)的情况下也超过了所有之前的方法。更多详细信息请参见我们的网站:https://haian-jin.github.io/projects/LVSM/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF project page: https://haian-jin.github.io/projects/LVSM/
Summary
本文提出了Large View Synthesis Model(LVSM),这是一种基于transformer的新型方法,用于从稀疏视角输入中进行可扩展和通用的新颖视角合成。该研究介绍了两种架构:一种是编码器-解码器LVSM,它将输入图像标记编码为固定数量的1D潜在标记,作为完全学习的场景表示,并从中解码出新的视角图像;另一种是仅解码器LVSM,它直接将输入图像映射到新视角输出,完全消除了中间场景表示。这两种模型都绕过了以前方法使用的3D归纳偏见,采用一种全新的数据驱动方法进行新颖视角合成。编码器-解码器模型由于其独立的潜在表示而提供更快的推理速度,而仅解码器LVSM在质量、可扩展性和零射击泛化方面表现更优,比现有技术领先1.5至3.5 dB PSNR。在多个数据集上的综合评估表明,两种LVSM变体均实现了最新颖的视角合成质量。
Key Takeaways
- LVSM是一个基于transformer的新型方法,用于新颖视角合成。
- LVSM提出了两种架构:编码器-解码器架构和仅解码器架构。
- LVSM绕过传统方法的3D归纳偏见,采用数据驱动方法。
- 编码器-解码器模型推理速度快,而仅解码器模型在质量、可扩展性和泛化性能上表现更优。
- LVSM在多个数据集上实现了最新颖的视角合成质量,并显著减少了计算资源需求。
- LVSM通过独立潜在表示和直接映射实现高效合成。
点此查看论文截图

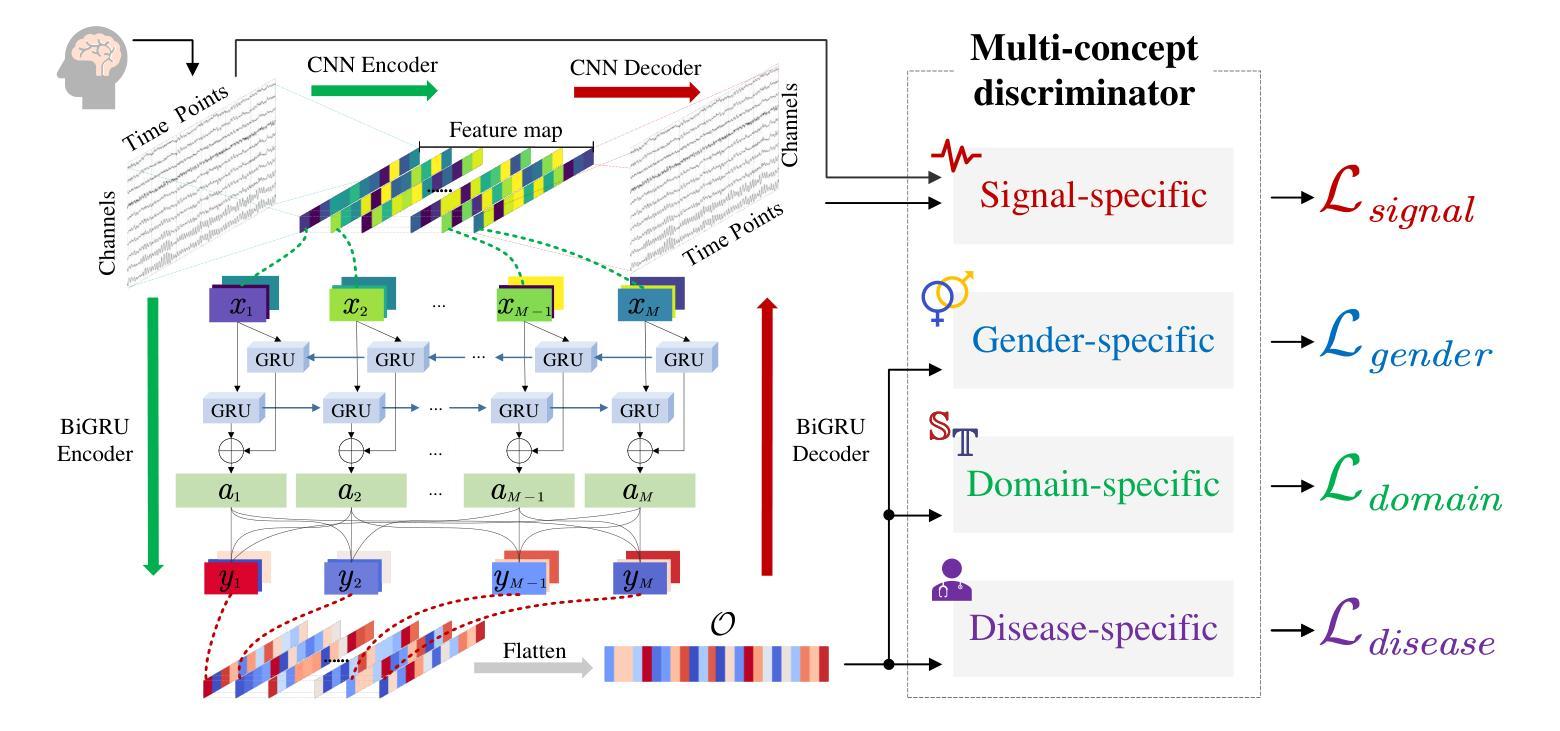
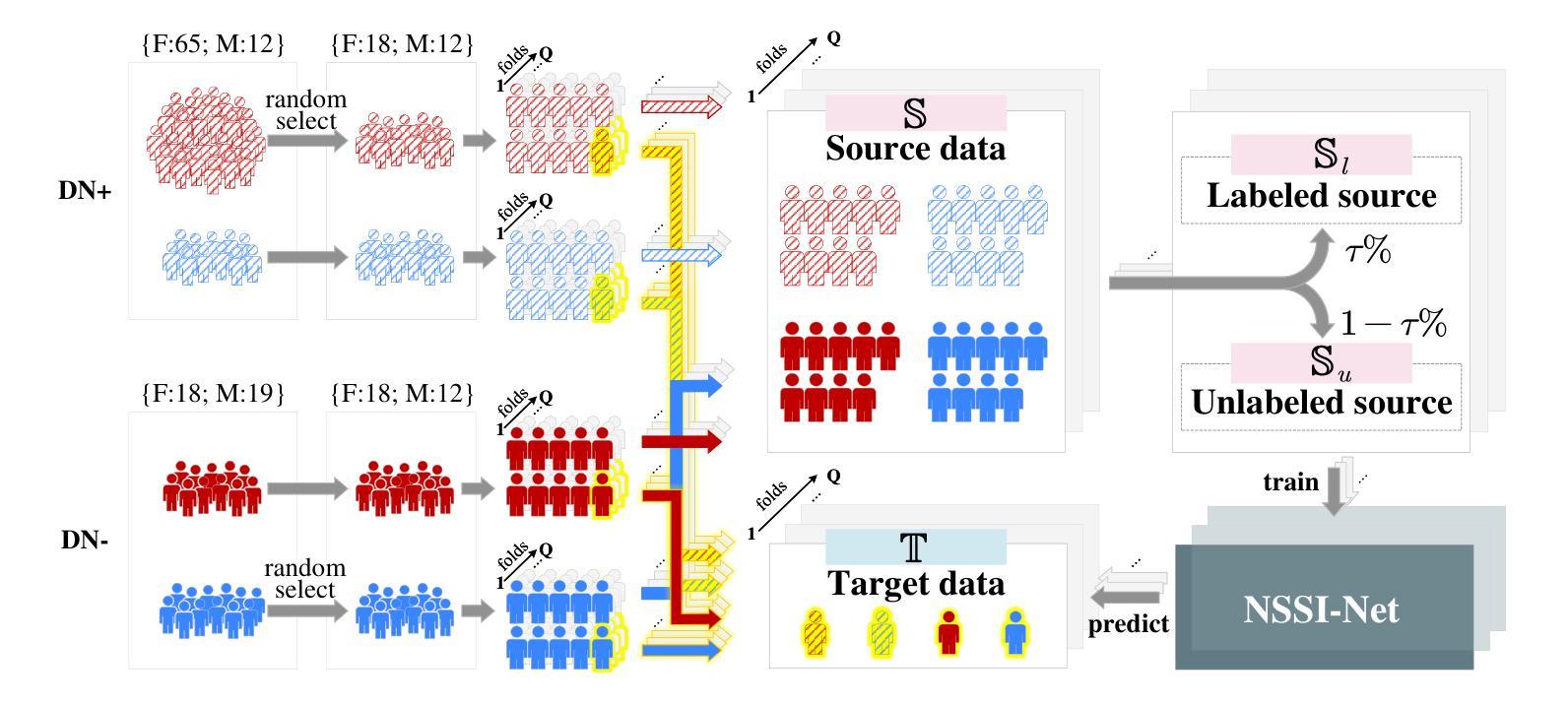
NSSI-Net: A Multi-Concept GAN for Non-Suicidal Self-Injury Detection Using High-Dimensional EEG in a Semi-Supervised Framework
Authors:Zhen Liang, Weishan Ye, Qile Liu, Li Zhang, Gan Huang, Yongjie Zhou
Non-suicidal self-injury (NSSI) is a serious threat to the physical and mental health of adolescents, significantly increasing the risk of suicide and attracting widespread public concern. Electroencephalography (EEG), as an objective tool for identifying brain disorders, holds great promise. However, extracting meaningful and reliable features from high-dimensional EEG data, especially by integrating spatiotemporal brain dynamics into informative representations, remains a major challenge. In this study, we introduce an advanced semi-supervised adversarial network, NSSI-Net, to effectively model EEG features related to NSSI. NSSI-Net consists of two key modules: a spatial-temporal feature extraction module and a multi-concept discriminator. In the spatial-temporal feature extraction module, an integrated 2D convolutional neural network (2D-CNN) and a bi-directional Gated Recurrent Unit (BiGRU) are used to capture both spatial and temporal dynamics in EEG data. In the multi-concept discriminator, signal, gender, domain, and disease levels are fully explored to extract meaningful EEG features, considering individual, demographic, disease variations across a diverse population. Based on self-collected NSSI data (n=114), the model’s effectiveness and reliability are demonstrated, with a 5.44% improvement in performance compared to existing machine learning and deep learning methods. This study advances the understanding and early diagnosis of NSSI in adolescents with depression, enabling timely intervention. The source code is available at https://github.com/Vesan-yws/NSSINet.
非自杀性自伤(NSSI)对青少年的身心健康构成严重威胁,大大增加自杀风险,引发社会广泛关注。脑电图(EEG)作为识别大脑疾病的客观工具,具有巨大潜力。然而,从高维EEG数据中提取有意义且可靠的特征,特别是将时空大脑动态整合到信息表示中,仍然是一个主要挑战。本研究引入了一种先进的半监督对抗网络NSSI-Net,以有效建模与NSSI相关的EEG特征。NSSI-Net由两个关键模块组成:时空特征提取模块和多概念鉴别器。在时空特征提取模块中,集成了二维卷积神经网络(2D-CNN)和双向门控循环单元(BiGRU),以捕获EEG数据中的空间和时间动态。在多概念鉴别器中,充分考虑信号、性别、领域和疾病水平,以提取有意义的EEG特征,同时考虑不同人群中的个体差异、人口统计特征和疾病变化。基于自我收集的NSSI数据(n=114),证明了该模型的有效性和可靠性,与现有的机器学习和深度学习方法相比,性能提高了5.44%。本研究有助于加深对青少年抑郁症患者NSSI行为的了解,实现早期诊断,为及时干预提供支持。源代码可访问https://github.com/Vesan-yws/NSSINet。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究引入了一种先进的半监督对抗网络NSSI-Net,用于有效建模与NSSI相关的EEG特征。该网络包括时空特征提取模块和多概念判别器两部分,能捕捉EEG数据中的时空动态,并充分考虑个体、人口统计学、疾病变化等因素,提取有意义的EEG特征。基于自收集的NSSI数据,该模型的有效性和可靠性得到了验证,与现有的机器学习和深度学习方法相比,性能提高了5.44%。
Key Takeaways
- NSSI(非自杀性自伤)对青少年身心健康构成严重威胁,增加自杀风险,引发社会广泛关注。
- EEG作为识别脑疾病的客观工具,在NSSI研究中有巨大潜力。
- NSSI-Net模型包括时空特征提取模块和多概念判别器两部分。
- 时空特征提取模块利用2D-CNN和BiGRU捕捉EEG数据的时空动态。
- 多概念判别器考虑信号、性别、领域和疾病水平等因素,提取有意义的EEG特征。
- 基于自收集的NSSI数据,NSSI-Net模型性能较现有机器学习和深度学习方法提高5.44%。
点此查看论文截图