⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-06 更新
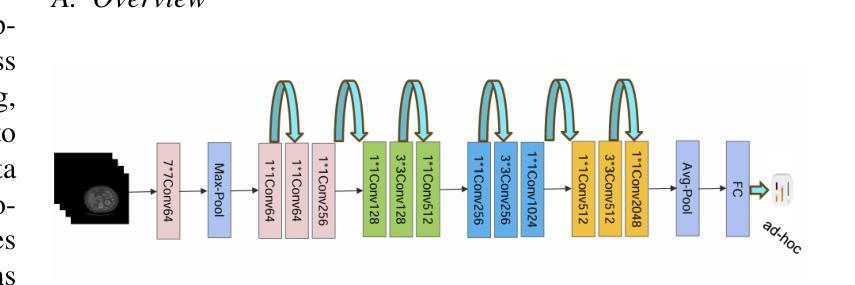
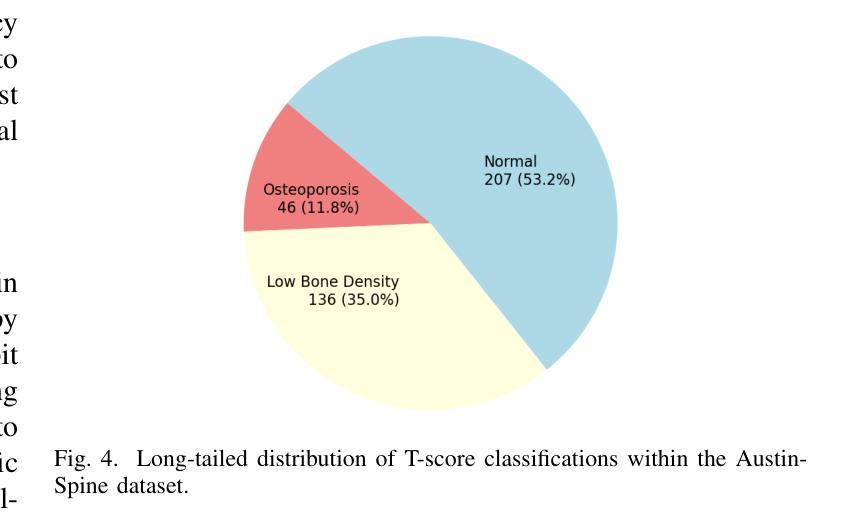
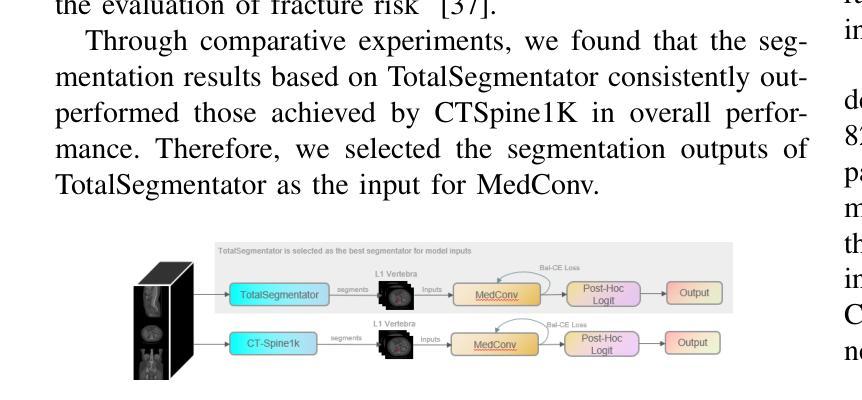
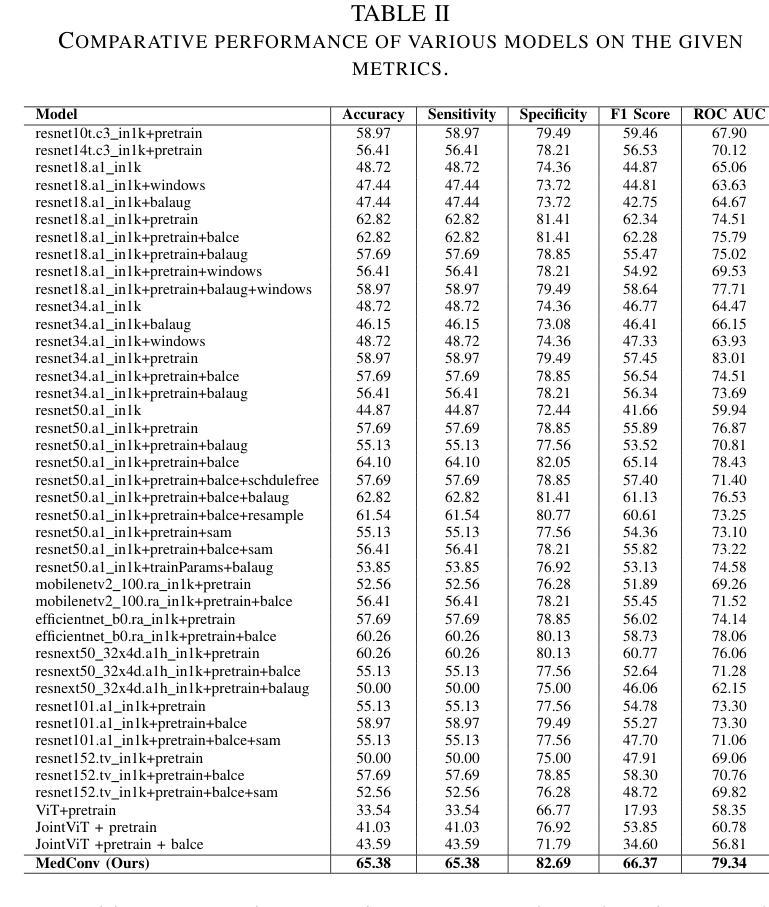
MedConv: Convolutions Beat Transformers on Long-Tailed Bone Density Prediction
Authors:Xuyin Qi, Zeyu Zhang, Huazhan Zheng, Mingxi Chen, Numan Kutaiba, Ruth Lim, Cherie Chiang, Zi En Tham, Xuan Ren, Wenxin Zhang, Lei Zhang, Hao Zhang, Wenbing Lv, Guangzhen Yao, Renda Han, Kangsheng Wang, Mingyuan Li, Hongtao Mao, Yu Li, Zhibin Liao, Yang Zhao, Minh-Son To
Bone density prediction via CT scans to estimate T-scores is crucial, providing a more precise assessment of bone health compared to traditional methods like X-ray bone density tests, which lack spatial resolution and the ability to detect localized changes. However, CT-based prediction faces two major challenges: the high computational complexity of transformer-based architectures, which limits their deployment in portable and clinical settings, and the imbalanced, long-tailed distribution of real-world hospital data that skews predictions. To address these issues, we introduce MedConv, a convolutional model for bone density prediction that outperforms transformer models with lower computational demands. We also adapt Bal-CE loss and post-hoc logit adjustment to improve class balance. Extensive experiments on our AustinSpine dataset shows that our approach achieves up to 21% improvement in accuracy and 20% in ROC AUC over previous state-of-the-art methods.
通过CT扫描预测骨密度以估算T值非常重要。与传统的X射线骨密度测试相比,这种方法提供了更精确的骨骼健康评估,因为传统的X射线测试缺乏空间分辨率和检测局部变化的能力。然而,基于CT的预测面临两大挑战:一是基于变压器的架构具有极高的计算复杂性,限制了其在便携和临床环境中的应用;二是现实世界医院数据存在不平衡的长尾分布,导致预测结果出现偏差。为了应对这些问题,我们引入了MedConv,这是一个用于骨密度预测的卷积模型,它以更低的计算需求超越了变压器模型的表现。我们还适应了Bal-CE损失和事后逻辑调整来改善类别平衡。在我们AustinSpine数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法相比之前的最先进方法,在准确性和ROC AUC方面分别提高了高达21%和20%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IJCNN 2025
Summary
利用CT扫描进行骨密度预测以估算T值,对于评估骨健康至关重要,相较于缺乏空间分辨率和检测局部变化能力的传统X射线骨密度测试方法更为精确。然而,CT预测面临两大挑战:基于变压器架构的高计算复杂度和现实世界医院数据不平衡、长尾分布导致的预测偏差。为解决这些问题,我们提出MedConv模型,即用于骨密度预测的卷积模型,在降低计算需求的同时超越变压器模型性能。此外,我们还通过采用Bal-CE损失和事后逻辑调整改善类别平衡问题。在AustinSpine数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法较以往先进方法准确度和ROC AUC值分别提高了高达21%和20%。
Key Takeaways
- CT扫描用于骨密度预测比传统方法更精确。
- CT预测面临两大挑战:高计算复杂度和数据不平衡问题。
- MedConv模型是一种用于骨密度预测的卷积模型,性能优于基于变压器的模型且计算需求较低。
- 采用Bal-CE损失和事后逻辑调整改善类别平衡问题。
- 在AustinSpine数据集上的实验表明,新方法较以往技术有显著提高。
点此查看论文截图


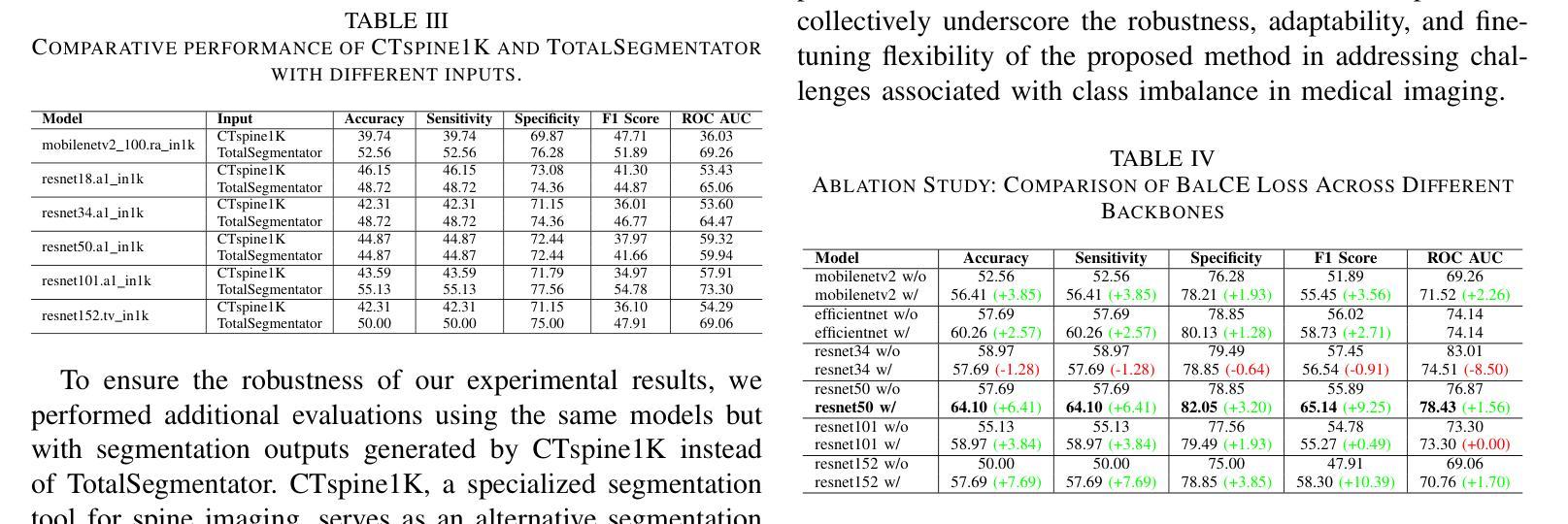
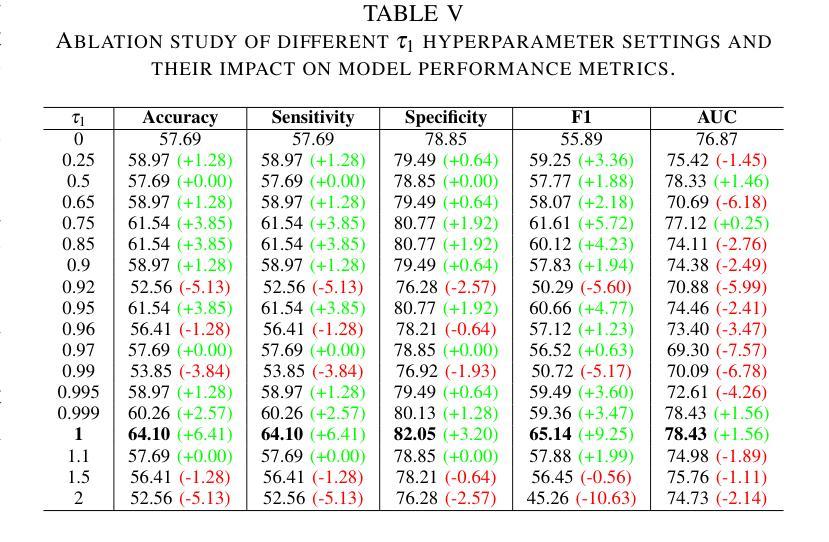
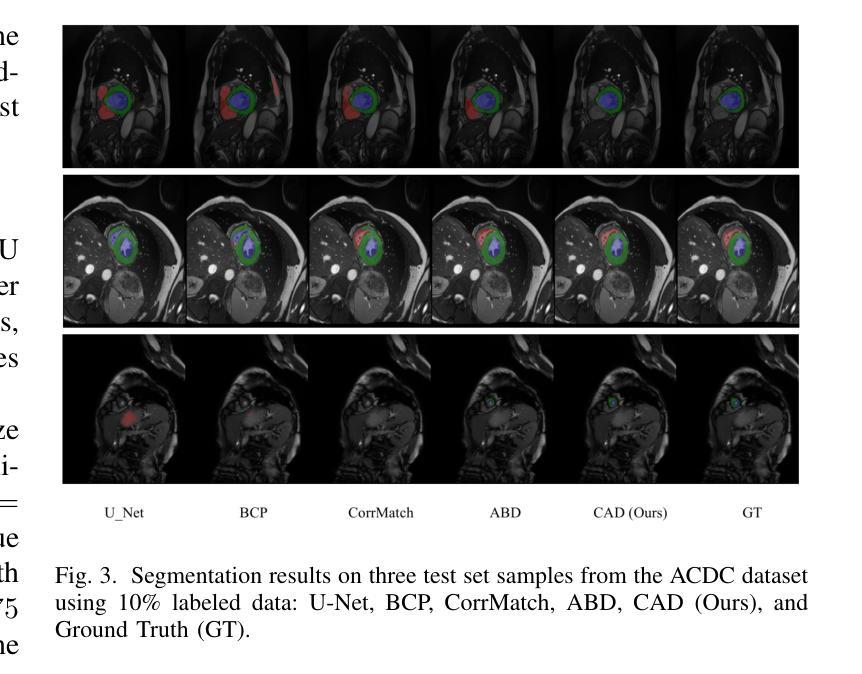
CAD: Confidence-Aware Adaptive Displacement for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Wenbo Xiao, Zhihao Xu, Guiping Liang, Yangjun Deng, Yi Xiao
Semi-supervised medical image segmentation aims to leverage minimal expert annotations, yet remains confronted by challenges in maintaining high-quality consistency learning. Excessive perturbations can degrade alignment and hinder precise decision boundaries, especially in regions with uncertain predictions. In this paper, we introduce Confidence-Aware Adaptive Displacement (CAD), a framework that selectively identifies and replaces the largest low-confidence regions with high-confidence patches. By dynamically adjusting both the maximum allowable replacement size and the confidence threshold throughout training, CAD progressively refines the segmentation quality without overwhelming the learning process. Experimental results on public medical datasets demonstrate that CAD effectively enhances segmentation quality, establishing new state-of-the-art accuracy in this field. The source code will be released after the paper is published.
半监督医学图像分割旨在利用最少的专家注释,但面临着如何保持高质量一致性学习的挑战。过度的扰动可能会破坏对齐并阻碍精确的决策边界,特别是在预测不确定的区域。本文介绍了信心感知自适应位移(CAD)框架,该框架能够有选择地识别和用高信心补丁替换最大低信心区域。通过动态调整最大允许替换大小和置信阈值,CAD能够在训练过程中逐步改进分割质量,而不会使学习过程过于复杂。在公共医学数据集上的实验结果表明,CAD能有效提高分割质量,在该领域建立了一个新的最先进的精度。论文发表后将公布源代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 3 figures, 4 tables
Summary
医学图像分割中的半监督学习旨在利用少量的专家标注数据,但面临着如何保持高质量一致性学习的挑战。为解决这一问题,本文提出一种名为Confidence-Aware Adaptive Displacement(CAD)的框架,它能自动识别并替换最大低置信度区域的高置信度补丁。通过动态调整最大允许替换大小和置信阈值,CAD能够在训练过程中逐步提高分割质量,而不会使学习过程过于复杂。在公共医学数据集上的实验结果表明,CAD能有效提高分割质量,达到该领域的新水平。源代码将在论文发表后发布。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督医学图像分割面临保持高质量一致性学习的挑战。
- CAD框架通过识别并替换低置信度区域,提高医学图像分割质量。
- CAD能动态调整最大允许替换大小和置信阈值,实现精细的分割质量改进。
- CAD在公共医学数据集上表现出优秀的性能,达到该领域的新水平。
- 该方法强调了自适应和灵活性在解决不确定性问题中的重要性。
- 通过引入CAD框架,本文提供了一种解决半监督医学图像分割中挑战的有效方法。
点此查看论文截图

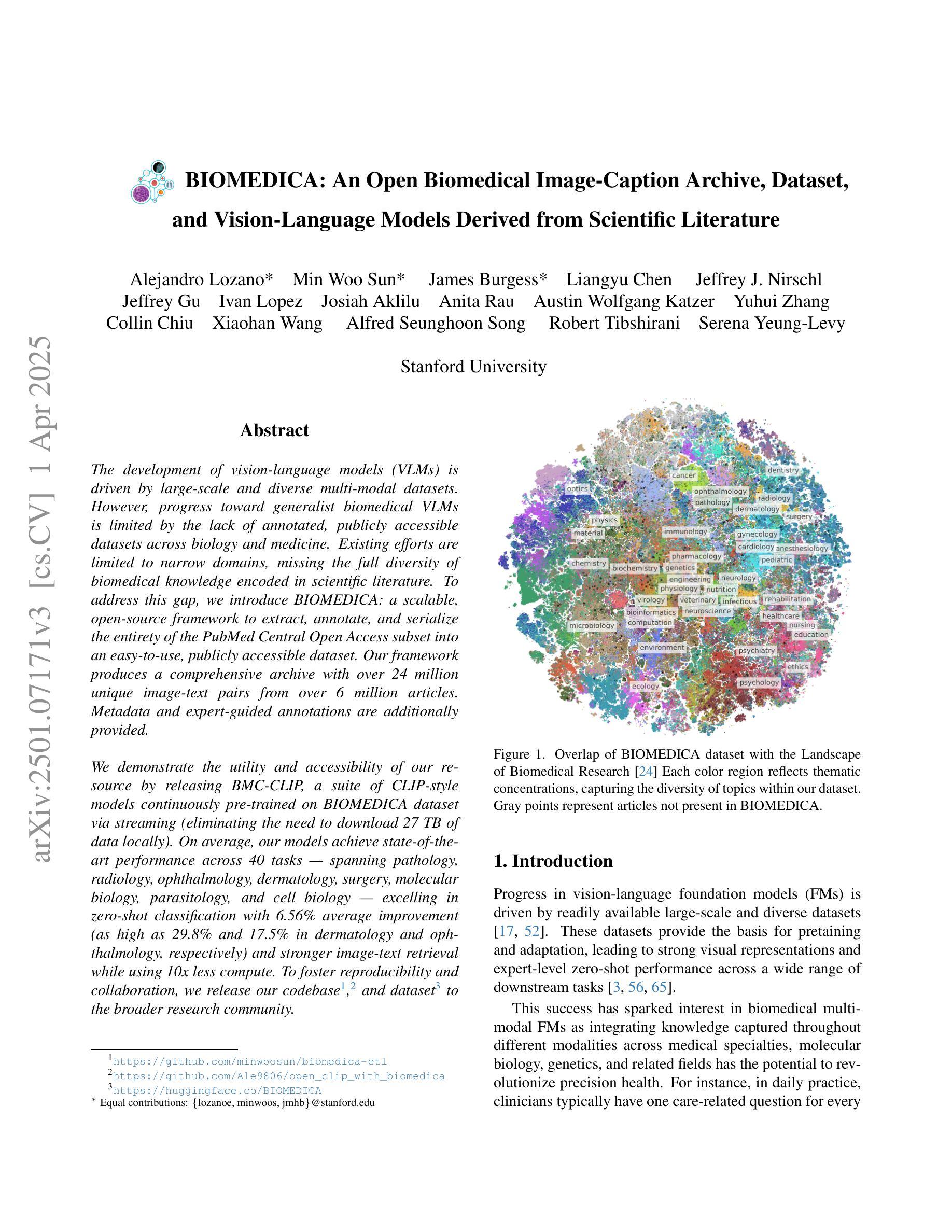
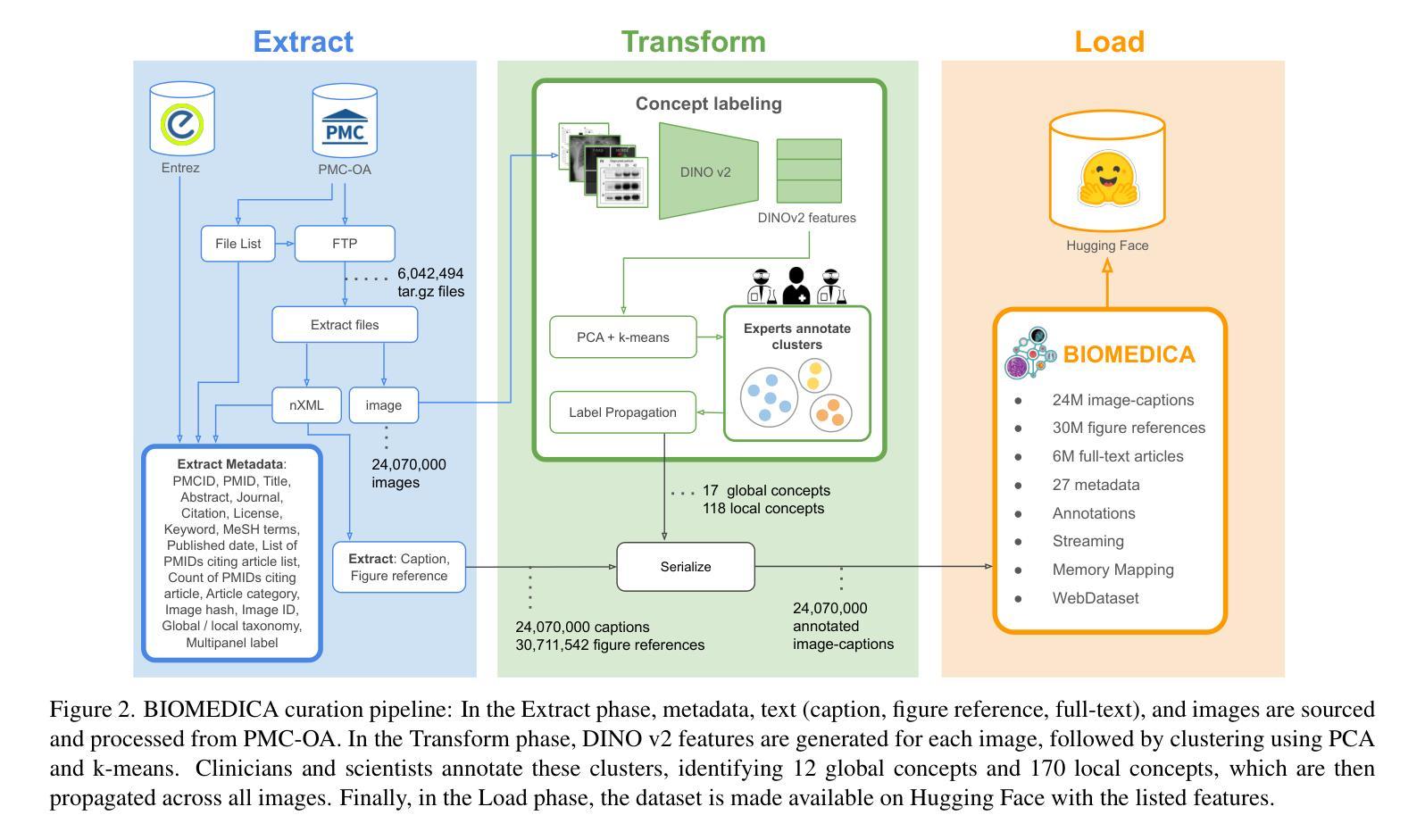
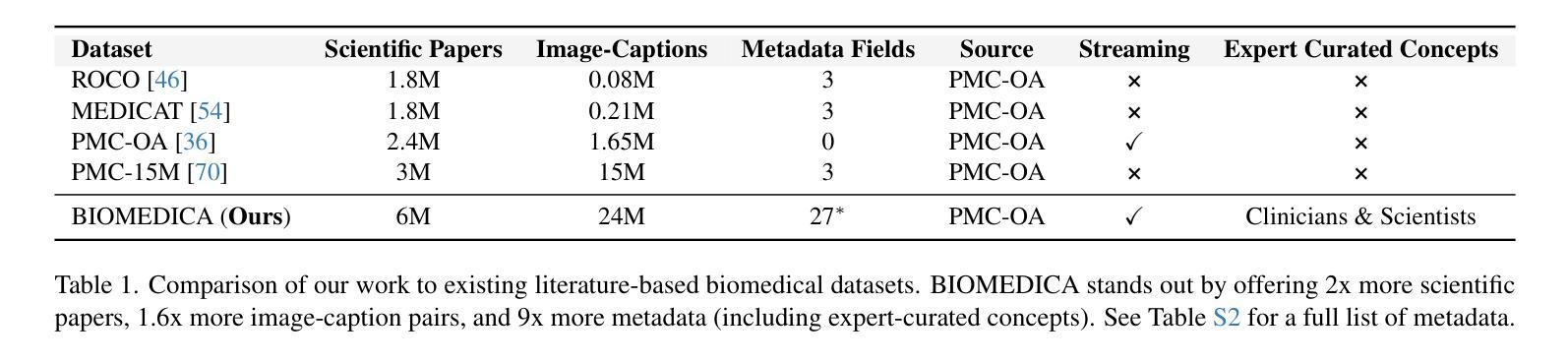
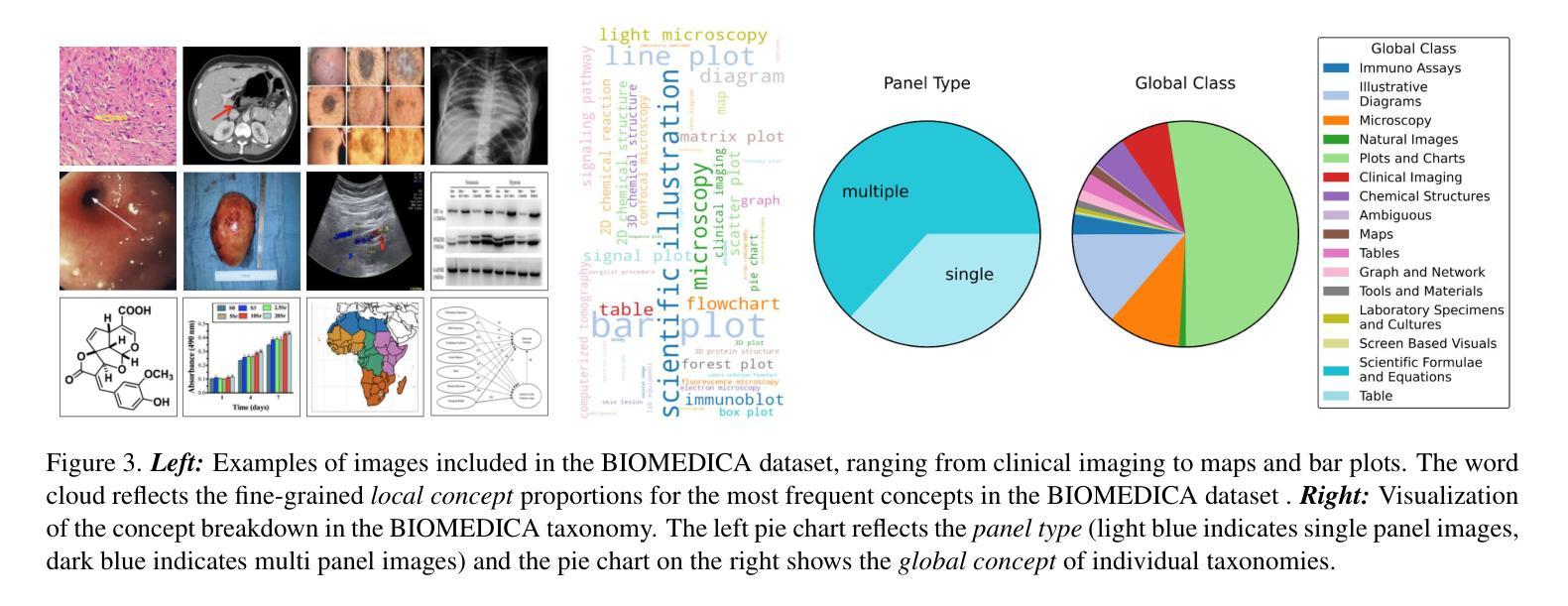
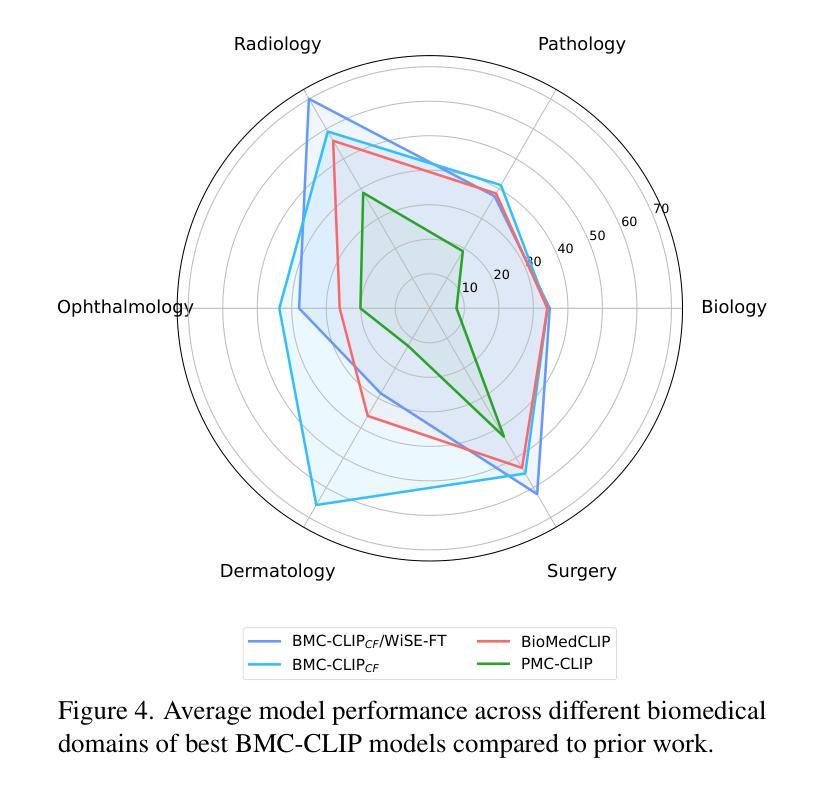
BIOMEDICA: An Open Biomedical Image-Caption Archive, Dataset, and Vision-Language Models Derived from Scientific Literature
Authors:Alejandro Lozano, Min Woo Sun, James Burgess, Liangyu Chen, Jeffrey J Nirschl, Jeffrey Gu, Ivan Lopez, Josiah Aklilu, Austin Wolfgang Katzer, Collin Chiu, Anita Rau, Xiaohan Wang, Yuhui Zhang, Alfred Seunghoon Song, Robert Tibshirani, Serena Yeung-Levy
The development of vision-language models (VLMs) is driven by large-scale and diverse multimodal datasets. However, progress toward generalist biomedical VLMs is limited by the lack of annotated, publicly accessible datasets across biology and medicine. Existing efforts are restricted to narrow domains, missing the full diversity of biomedical knowledge encoded in scientific literature. To address this gap, we introduce BIOMEDICA, a scalable, open-source framework to extract, annotate, and serialize the entirety of the PubMed Central Open Access subset into an easy-to-use, publicly accessible dataset. Our framework produces a comprehensive archive with over 24 million unique image-text pairs from over 6 million articles. Metadata and expert-guided annotations are also provided. We demonstrate the utility and accessibility of our resource by releasing BMCA-CLIP, a suite of CLIP-style models continuously pre-trained on the BIOMEDICA dataset via streaming, eliminating the need to download 27 TB of data locally. On average, our models achieve state-of-the-art performance across 40 tasks - spanning pathology, radiology, ophthalmology, dermatology, surgery, molecular biology, parasitology, and cell biology - excelling in zero-shot classification with a 6.56% average improvement (as high as 29.8% and 17.5% in dermatology and ophthalmology, respectively), and stronger image-text retrieval, all while using 10x less compute. To foster reproducibility and collaboration, we release our codebase and dataset for the broader research community.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)的发展是由大规模和多样化的多模态数据集驱动的。然而,通用生物医学VLMs的进展受限于生物学和医学领域缺乏公开访问的注释数据集。现有的努力仅限于狭窄的领域,错过了科学文献中编码的完整生物医学知识多样性。为了解决这一差距,我们引入了BIOMEDICA,这是一个可扩展的开放源代码框架,用于提取、注释和序列化PubMed Central Open Access子集的完整内容,使其成为一个易于使用、可公开访问的数据集。我们的框架产生了包含超过24万个唯一图像文本对的综合档案,涵盖超过6万篇文章。我们还提供了元数据和专业指导的注释。我们通过发布BMCA-CLIP来证明我们资源的实用性和可访问性,这是一套CLIP风格的模型,在BIOMEDICA数据集上连续进行预训练流处理,无需下载本地高达27TB的数据。平均而言,我们的模型在涵盖病理学、放射学、眼科、皮肤科、外科、分子生物学、寄生虫学和细胞生物学等领域的四十多项任务上取得了最先进的性能,特别是在零样本分类方面表现出色,平均改进率为6.56%(皮肤科和眼科高达29.8%和17.5%),并且在图像文本检索方面更强,同时使用计算机的计算能力减少十倍。为了促进可复制性和合作,我们向更广泛的研究社区发布我们的代码和数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本摘要介绍了一个名为BIOMEDICA的开源框架,该框架旨在解决生物医学领域中视觉语言模型(VLMs)缺乏大规模、多样化的多模态数据集的问题。通过提取、标注和序列化PubMed Central Open Access子集的全部内容,该框架建立了一个包含超过2.4亿个独特的图像文本对的综合档案库。同时,通过连续训练基于BIOMEDICA数据集的CLIP风格模型BMCA-CLIP,证明了其资源的实用性和可及性。该模型在多个生物医学任务上取得了最先进的性能,包括病理学、放射学、眼科等。为了促进再现性和合作,研究团队将公开数据集和代码库供更广泛的研究群体使用。
Key Takeaways
- BIOMEDICA框架解决了生物医学视觉语言模型(VLMs)缺乏大规模、多样化的多模态数据集的问题。
- BIOMEDICA框架提取并标注了PubMed Central Open Access子集的全部内容,建立了包含超过2.4亿个图像文本对的综合档案库。
- BMCA-CLIP模型是第一个在BIOMEDICA数据集上连续训练的CLIP风格模型,无需下载大量数据即可使用。
- BMCA-CLIP模型在多个生物医学任务上取得了最先进的性能,平均提高了6.56%,在皮肤科和眼科领域分别提高了高达29.8%和17.5%。
- BMCA-CLIP模型展现出强大的图像文本检索能力。
- BIOMEDICA框架和BMCA-CLIP模型的代码和数据集已公开,供更广泛的研究群体使用。
- BIOMEDICA框架具有可扩展性,能够支持更多的生物医学领域的数据集整合和标注。
点此查看论文截图
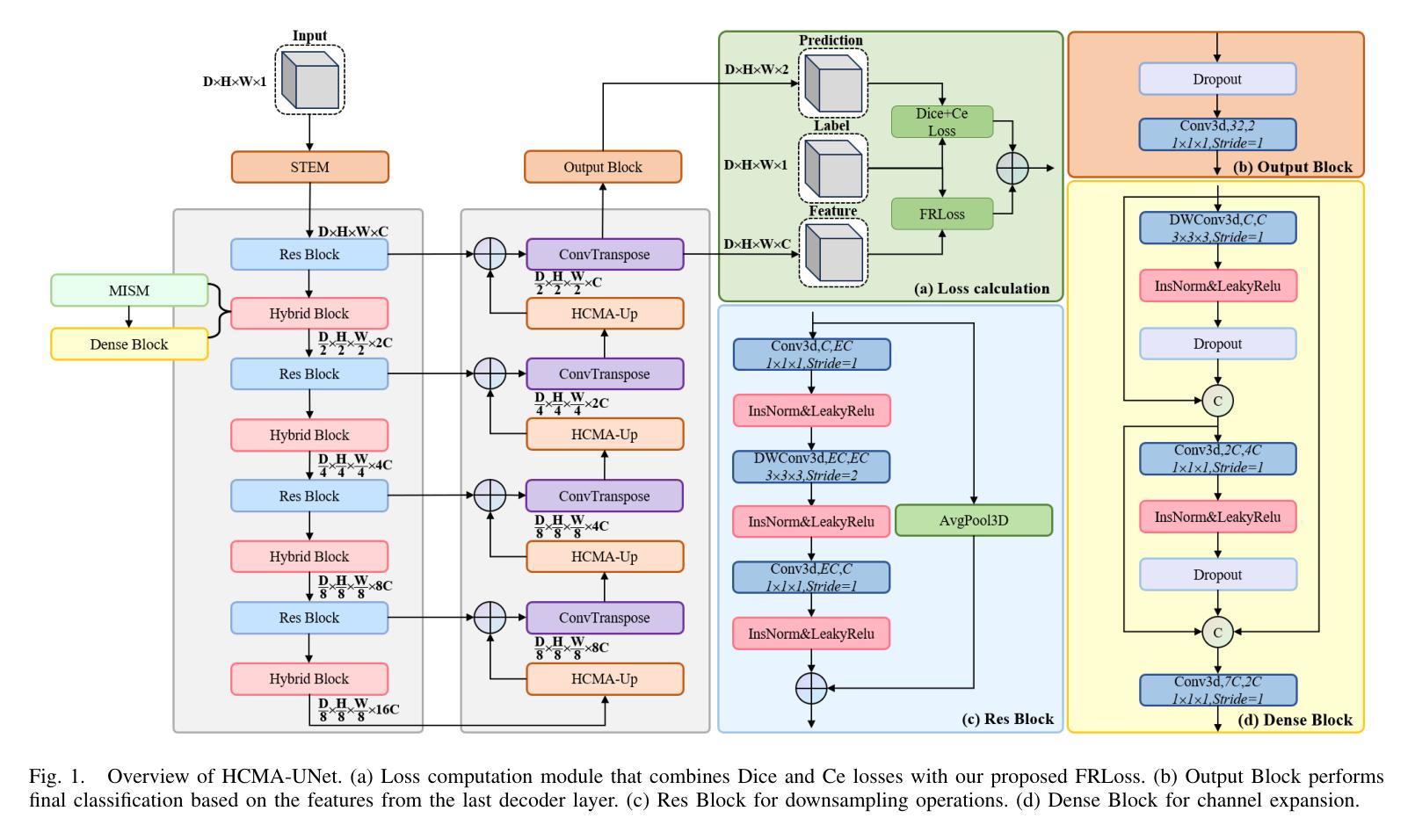
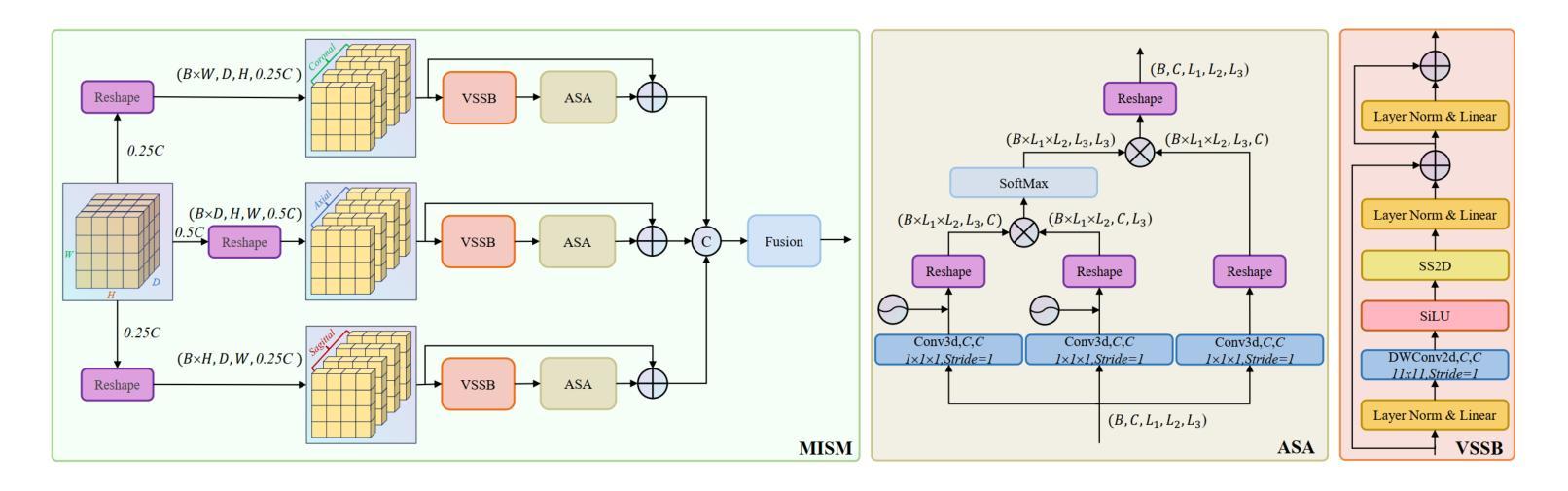
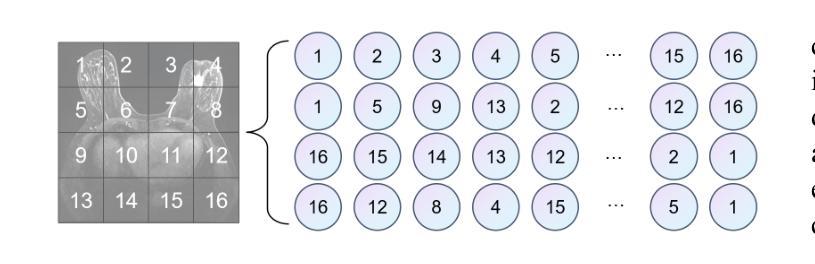
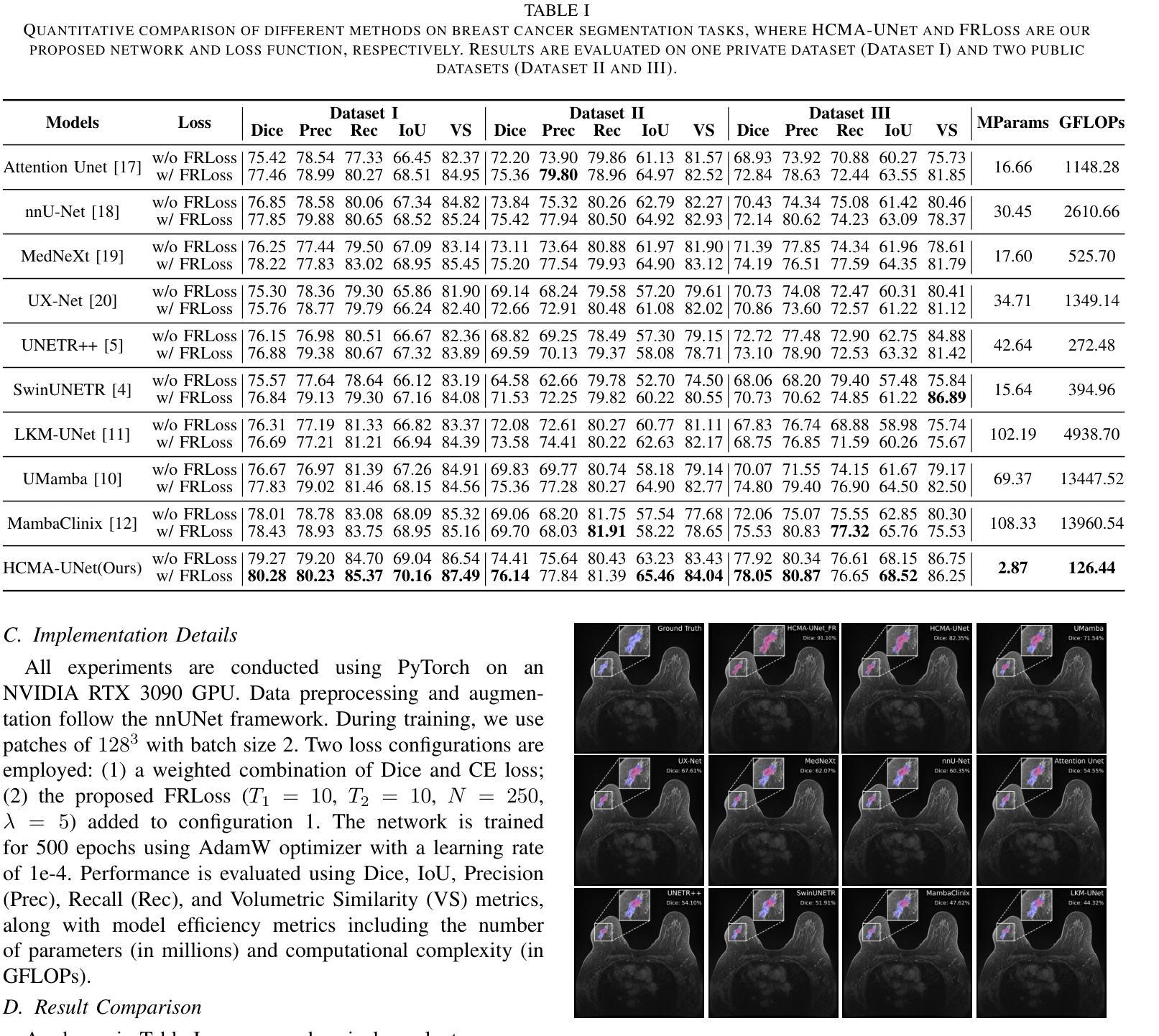
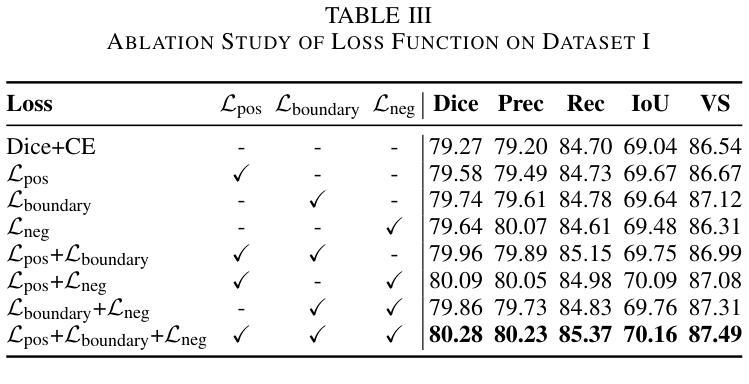
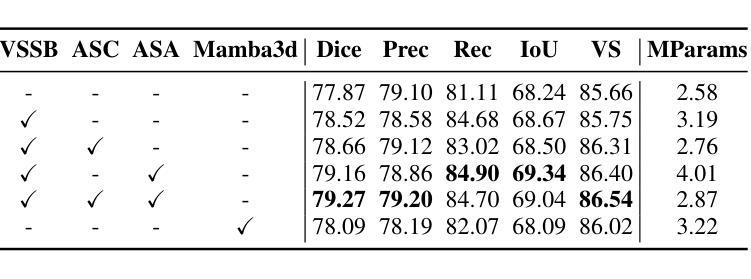
HCMA-UNet: A Hybrid CNN-Mamba UNet with Axial Self-Attention for Efficient Breast Cancer Segmentation
Authors:Haoxuan Li, Wei song, Peiwu Qin, Xi Yuan, Zhenglin Chen
Breast cancer lesion segmentation in DCE-MRI remains challenging due to heterogeneous tumor morphology and indistinct boundaries. To address these challenges, this study proposes a novel hybrid segmentation network, HCMA-UNet, for lesion segmentation of breast cancer. Our network consists of a lightweight CNN backbone and a Multi-view Axial Self-Attention Mamba (MISM) module. The MISM module integrates Visual State Space Block (VSSB) and Axial Self-Attention (ASA) mechanism, effectively reducing parameters through Asymmetric Split Channel (ASC) strategy to achieve efficient tri-directional feature extraction. Our lightweight model achieves superior performance with 2.87M parameters and 126.44 GFLOPs. A Feature-guided Region-aware loss function (FRLoss) is proposed to enhance segmentation accuracy. Extensive experiments on one private and two public DCE-MRI breast cancer datasets demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance while maintaining computational efficiency. FRLoss also exhibits good cross-architecture generalization capabilities. The source code is available at https://github.com/Haoxuanli-Thu/HCMA-UNet.
乳腺癌病灶在DCE-MRI中的分割仍然是一个挑战,因为肿瘤形态多样且边界不清。本研究提出了一种新型混合分割网络HCMA-UNet,用于乳腺癌病灶的分割。我们的网络由轻量级CNN骨干网和多视图轴向自注意力Mamba(MISM)模块组成。MISM模块结合了视觉状态空间块(VSSB)和轴向自注意力(ASA)机制,通过不对称分裂通道(ASC)策略有效地减少了参数,实现了高效的三向特征提取。我们的轻量级模型实现了卓越的性能,具有287万参数和每秒浮点运算量达每秒浮点运算量达每秒浮点运算量达每秒浮点运算量达每秒浮点运算量计算次数达到一百万浮点操作每妙级别性能优良其拥有领先的计算效率为最高达到亿级运算次以上;并提出了一种特征引导区域感知损失函数(FRLoss)来提高分割精度。在一套私有数据集和两个公开DCE-MRI乳腺癌数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的性能水平,同时保持了计算效率。FRLoss还表现出良好的跨架构泛化能力。源代码可在https://github.com/Haoxuanli-Thu/HCMA-UNet找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对乳腺癌DCE-MRI影像的病灶分割仍面临挑战,本文提出一种新型混合分割网络HCMA-UNet。该网络包括轻量级CNN骨干和多视角轴向自注意力Mamba(MISM)模块。MISM模块结合视觉状态空间块(VSSB)和轴向自注意力(ASA)机制,通过不对称分裂通道(ASC)策略实现高效的三向特征提取。该轻量级模型参数为2.87M,计算复杂度为126.44 GFLOPs,实现了卓越的性能。此外,还提出了一种特征引导区域感知损失函数(FRLoss)以提高分割精度。在私人及两个公共DCE-MRI乳腺癌数据集上的实验表明,该方法达到了先进的性能,同时保持了计算效率。FRLoss还具有良好的跨架构泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺癌DCE-MRI影像的病灶分割面临挑战,主要由于肿瘤形态异质性和边界不清晰。
- HCMA-UNet是一个新型的混合分割网络,包括轻量级CNN骨干和MISM模块。
- MISM模块结合了VSSB和ASA机制,通过ASC策略实现高效三向特征提取。
- HCMA-UNet模型具有优越性能,参数少(2.87M)且计算效率高(126.44 GFLOPs)。
- 提出了特征引导区域感知损失函数(FRLoss)以提高分割精度。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明HCMA-UNet达到了先进性能,且FRLoss具有良好的跨架构泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

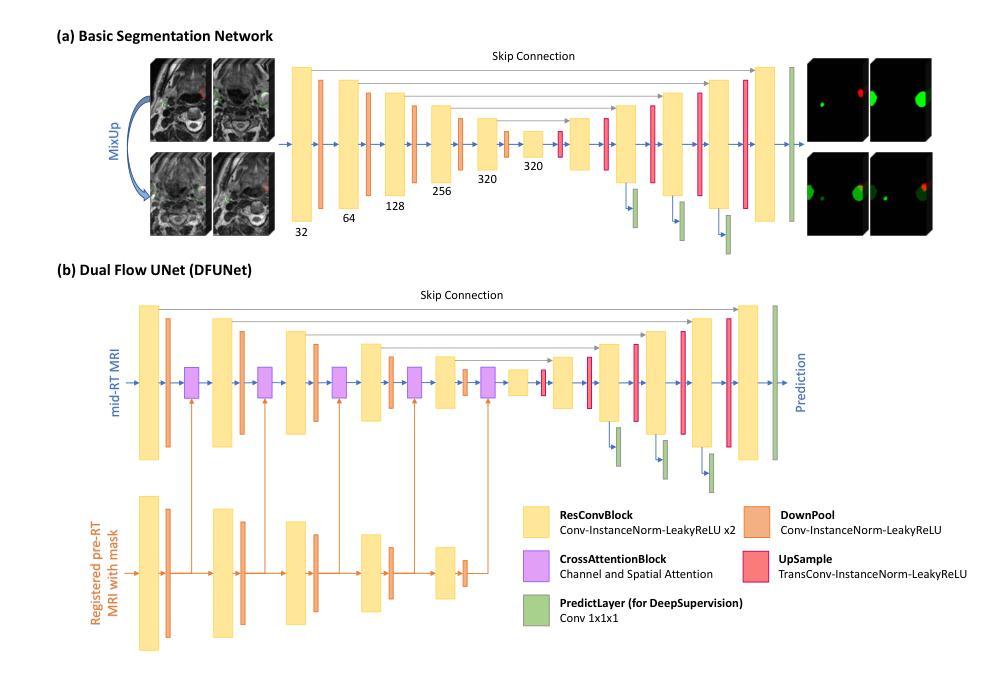
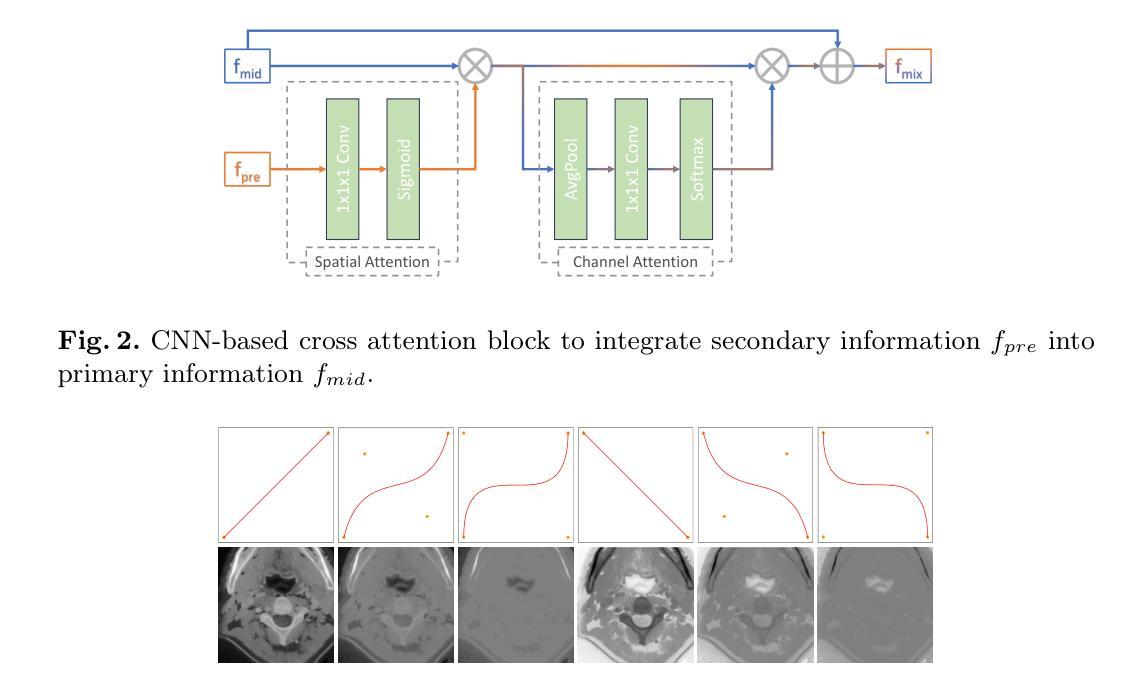
Head and Neck Tumor Segmentation of MRI from Pre- and Mid-radiotherapy with Pre-training, Data Augmentation and Dual Flow UNet
Authors:Litingyu Wang, Wenjun Liao, Shichuan Zhang, Guotai Wang
Head and neck tumors and metastatic lymph nodes are crucial for treatment planning and prognostic analysis. Accurate segmentation and quantitative analysis of these structures require pixel-level annotation, making automated segmentation techniques essential for the diagnosis and treatment of head and neck cancer. In this study, we investigated the effects of multiple strategies on the segmentation of pre-radiotherapy (pre-RT) and mid-radiotherapy (mid-RT) images. For the segmentation of pre-RT images, we utilized: 1) a fully supervised learning approach, and 2) the same approach enhanced with pre-trained weights and the MixUp data augmentation technique. For mid-RT images, we introduced a novel computational-friendly network architecture that features separate encoders for mid-RT images and registered pre-RT images with their labels. The mid-RT encoder branch integrates information from pre-RT images and labels progressively during the forward propagation. We selected the highest-performing model from each fold and used their predictions to create an ensemble average for inference. In the final test, our models achieved a segmentation performance of 82.38% for pre-RT and 72.53% for mid-RT on aggregated Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) as HiLab. Our code is available at https://github.com/WltyBY/HNTS-MRG2024_train_code.
头部和颈部肿瘤以及转移性淋巴结对治疗计划和预后分析至关重要。这些结构的精确分割和定量分析需要像素级注释,因此自动分割技术在头部和颈部癌症的诊断和治疗中至关重要。在这项研究中,我们研究了多种策略对放疗前(pre-RT)和放疗中(mid-RT)图像分割的影响。对于放疗前图像的分割,我们采用了:1)全监督学习方法;2)使用预训练权重和MixUp数据增强技术增强同一方法。对于放疗中图像,我们引入了一种计算友好的新型网络架构,该架构具有针对放疗中图像和已注册放疗前图像的单独编码器,并带有其标签。放疗中编码器分支在正向传播过程中逐步整合来自放疗前图像和标签的信息。我们从每一折中选择表现最佳的模型,并使用其预测结果创建集成平均值以进行推断。在最终测试中,我们的模型在HiLab的聚合Dice相似系数(DSC)上达到了放疗前分割性能为82.38%,放疗中分割性能为72.53%。我们的代码可通过https://github.com/WltyBY/HNTS-MRG2024_train_code访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了头颈部肿瘤和转移淋巴结的分割技术,对预放疗(pre-RT)和中期放疗(mid-RT)图像的分割策略进行了调查。采用全监督学习方法和增强预训练权重及MixUp数据增强技术的组合对预放疗图像进行分割。对于中期放疗图像,提出了一种计算友好的网络架构,该架构具有针对中期放疗图像和已注册预放疗图像的单独编码器,并在前向传播过程中逐步整合信息。最终测试结果显示,模型在HiLab上的分割性能达到预放疗的Dice相似系数(DSC)为82.38%,中期放疗的为72.53%。
Key Takeaways
- 头颈部肿瘤和转移淋巴结的精确分割对治疗计划和预后分析至关重要,需要像素级别的注释,因此自动化分割技术对于头颈部癌症的诊断和治疗至关重要。
- 研究中调查了预放疗和中期放疗图像的分割策略。
- 对于预放疗图像的分割,采用了全监督学习方法和增强预训练权重及MixUp数据增强技术的组合。
- 对于中期放疗图像,提出了一种新型的计算友好网络架构,该架构可以整合预放疗图像和标签的信息。
- 模型在分割头颈部肿瘤和转移淋巴结方面表现出良好的性能,预放疗图像的分割性能达到82.38%,中期放疗图像的分割性能为72.53%。
- 模型的代码已公开,便于其他研究者使用和改进。
点此查看论文截图

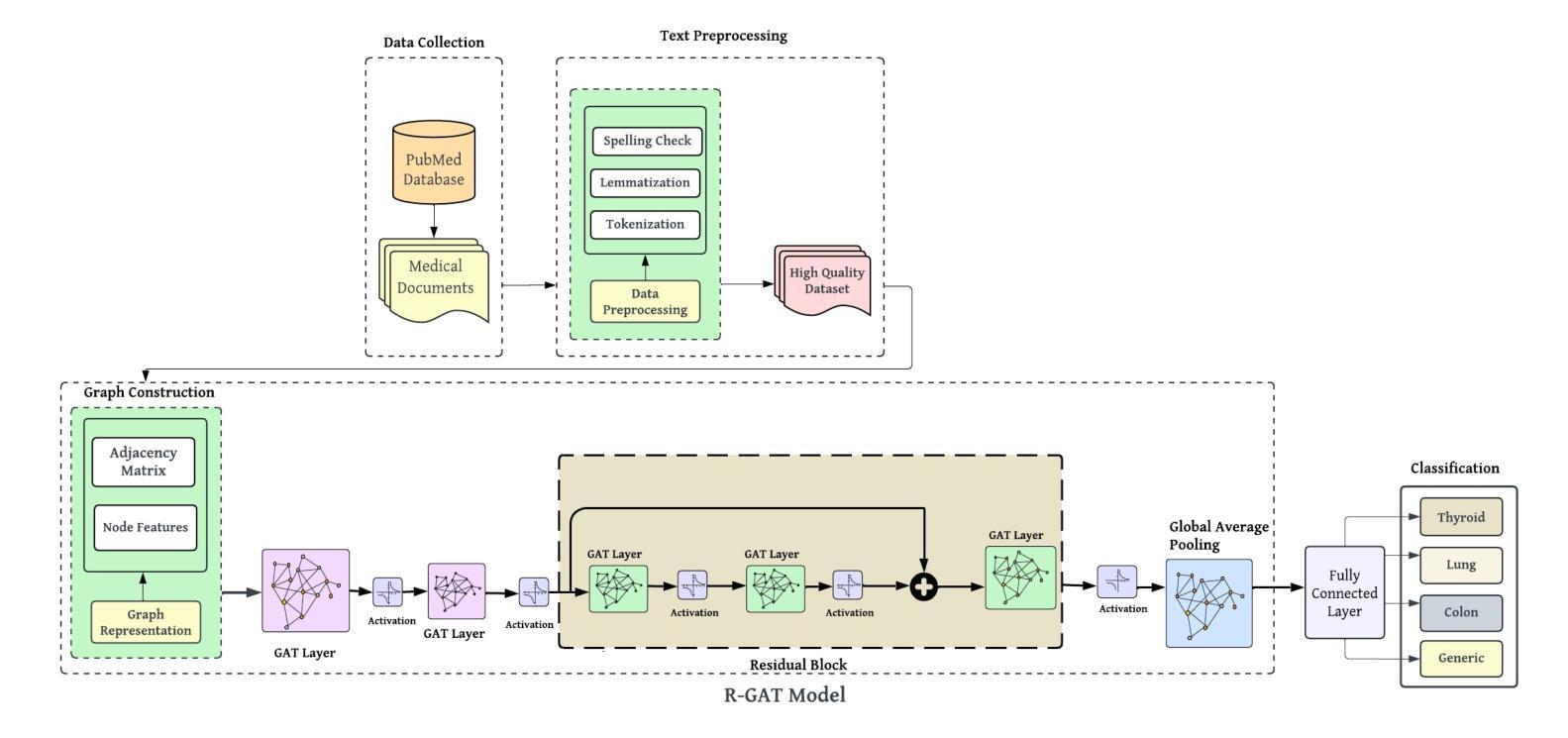
Medical-GAT: Cancer Document Classification Leveraging Graph-Based Residual Network for Scenarios with Limited Data
Authors:Elias Hossain, Tasfia Nuzhat, Shamsul Masum, Shahram Rahimi, Noorbakhsh Amiri Golilarz
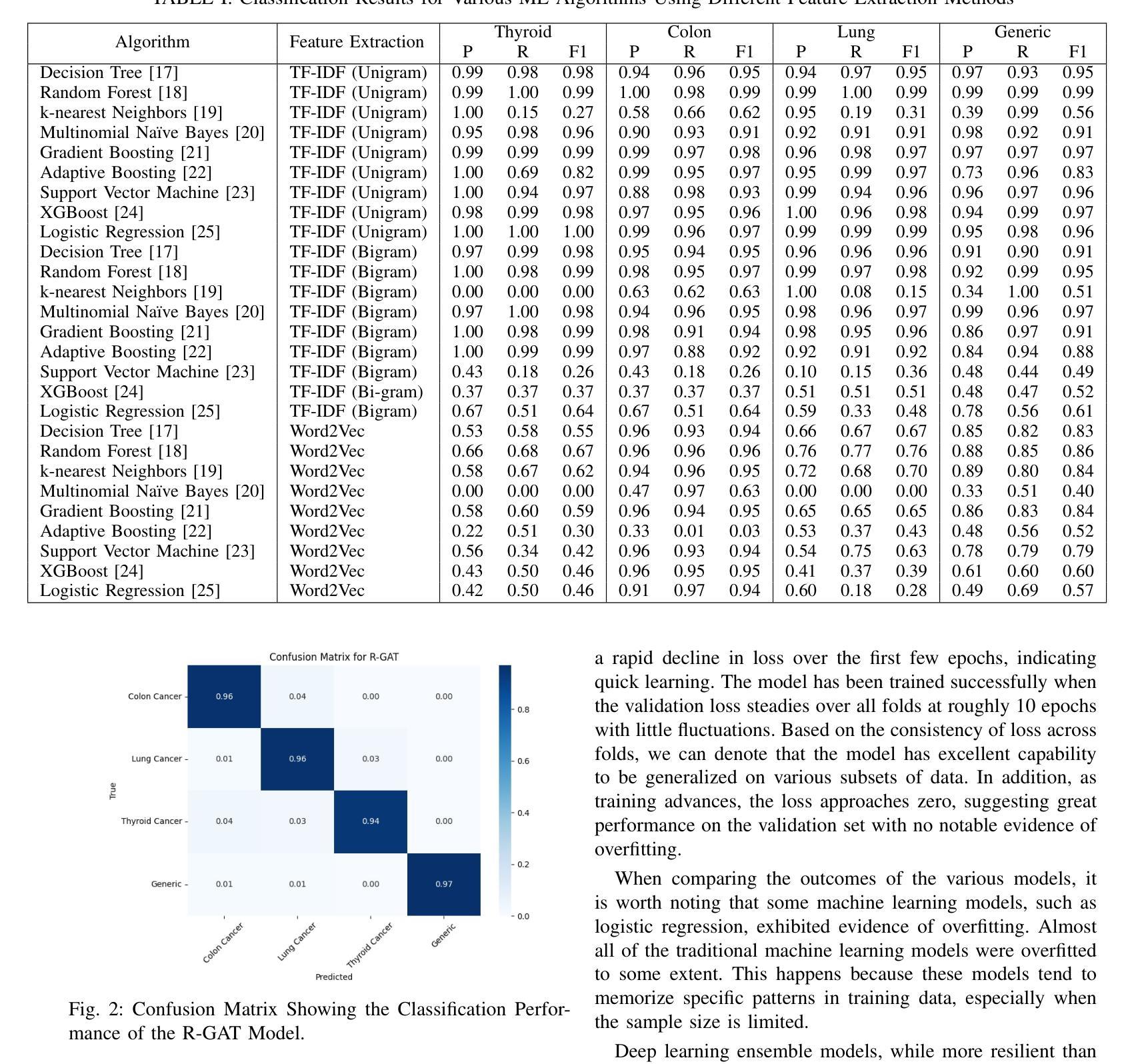
Accurate classification of cancer-related medical abstracts is crucial for healthcare management and research. However, obtaining large, labeled datasets in the medical domain is challenging due to privacy concerns and the complexity of clinical data. This scarcity of annotated data impedes the development of effective machine learning models for cancer document classification. To address this challenge, we present a curated dataset of 1,874 biomedical abstracts, categorized into thyroid cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer, and generic topics. Our research focuses on leveraging this dataset to improve classification performance, particularly in data-scarce scenarios. We introduce a Residual Graph Attention Network (R-GAT) with multiple graph attention layers that capture the semantic information and structural relationships within cancer-related documents. Our R-GAT model is compared with various techniques, including transformer-based models such as Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT), RoBERTa, and domain-specific models like BioBERT and Bio+ClinicalBERT. We also evaluated deep learning models (CNNs, LSTMs) and traditional machine learning models (Logistic Regression, SVM). Additionally, we explore ensemble approaches that combine deep learning models to enhance classification. Various feature extraction methods are assessed, including Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF) with unigrams and bigrams, Word2Vec, and tokenizers from BERT and RoBERTa. The R-GAT model outperforms other techniques, achieving precision, recall, and F1 scores of 0.99, 0.97, and 0.98 for thyroid cancer; 0.96, 0.94, and 0.95 for colon cancer; 0.96, 0.99, and 0.97 for lung cancer; and 0.95, 0.96, and 0.95 for generic topics.
癌症相关医学摘要的精确分类对医疗管理和研究至关重要。然而,由于隐私问题和临床数据的复杂性,在医学领域获得大量有标签的数据集具有挑战性。这种标注数据的稀缺性阻碍了癌症文档分类的有效机器学习模型的发展。为了应对这一挑战,我们呈现了一个包含1874篇生物医学摘要的数据集,这些摘要被分类为甲状腺癌、结肠癌、肺癌和通用主题。我们的研究重点是利用此数据集来改善分类性能,特别是在数据稀缺的情况下。我们引入了一种带有多个图注意力层的残差图注意力网络(R-GAT),能够捕捉癌症相关文档中的语义信息和结构关系。我们将R-GAT模型与各种技术进行了比较,包括基于变压器的模型,如来自变压器的双向编码器表示(BERT)、RoBERTa,以及特定领域的模型,如BioBERT和Bio+ClinicalBERT。我们还评估了深度学习模型(卷积神经网络、长短时记忆网络)和传统机器学习模型(逻辑回归、支持向量机)。此外,我们还探索了结合深度学习模型以增强分类的集成方法。还评估了各种特征提取方法,包括使用一元词和二元词的词频-逆文档频率(TF-IDF)、Word2Vec以及来自BERT和RoBERTa的标记器。R-GAT模型的性能优于其他技术,在甲状腺癌方面达到精确度、召回率和F1分数分别为0.99、0.97和0.98;结肠癌分别为0.96、0.94和0.95;肺癌分别为0.96、0.99和0.97;通用主题分别为0.95、0.96和0.95。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了癌症相关医学摘要的分类对于医疗管理和研究的重要性。针对医学领域标注数据集的缺乏问题,提出了一种基于Residual Graph Attention Network(R-GAT)的解决方案。该模型能够捕捉癌症相关文档中的语义信息和结构关系,与其他技术相比表现出优异的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 癌症相关医学摘要的分类对医疗管理和研究至关重要。
- 医学领域标注数据集的缺乏是开发有效机器学习模型的主要挑战。
- 提出了Residual Graph Attention Network(R-GAT)模型,用于改善分类性能,特别是在数据稀缺的情况下。
- R-GAT模型通过捕捉癌症相关文档中的语义信息和结构关系,实现了高性能分类。
- R-GAT模型与其他技术(包括BERT、RoBERTa、BioBERT、Bio+ClinicalBERT等)进行了比较,表现出优越性。
点此查看论文截图
First image-guided treatment of a mouse tumor with radioactive ion beams
Authors:Daria Boscolo, Giulio Lovatti, Olga Sokol, Tamara Vitacchio, Francesco Evangelista, Emma Haettner, Walter Tinganelli, Christian Graeff, Uli Weber, Christoph Schuy, Munetaka Nitta, Martina Moglioni, Daria Kostyleva, Sivaji Purushothaman, Peter G. Thirolf, Jonathan Bortfeldt, Christoph Scheidenberger, Katia Parodi, Marco Durante
Radioactive ion beams (RIB) are a key focus of current research in nuclear physics. Already long ago it was proposed that they could have applications in cancer therapy. In fact, while charged particle therapy is potentially the most effective radiotherapy technique available, it is highly susceptible to uncertainties in the beam range. RIB are well-suited for image-guided particle therapy, as isotopes that undergo \b{eta}+-decay can be precisely visualized using positron emission tomography (PET), enabling accurate real-time monitoring of the beam range. We successfully treated a mouse osteosarcoma using a radioactive 11C-ion beam. The tumor was located in the neck, in close proximity to the spinal cord, increasing the risk of radiation-induced myelopathy from even slight variations in the beam range caused by anatomical changes or incorrect calibration of the planning CT. We managed to completely control the tumor with the highest dose while minimizing toxicity. Low-grade neurological side effects were correlated to the positron activity measured in the spine. The biological washout of the activity from the tumor volume was dependent on the dose, indicating a potential component of vascular damage at high doses. This experiment marks the first instance of tumor treatment using RIB and paves the way for future clinical applications.
放射性离子束(RIB)是当前核物理研究的关键焦点。其实很早以前就有人提出它们可能在癌症治疗中有应用。实际上,虽然带电粒子疗法可能是目前可用的最有效的放射治疗技术,但它对光束范围的不确定性非常敏感。放射性离子束非常适合于图像引导粒子疗法,因为可以通过正电子发射断层扫描(PET)精确可视化发生正电子衰变的同位素,从而实现对光束范围的实时准确监测。我们使用放射性碳离子束成功治疗了一只患有骨肉瘤的小鼠。肿瘤位于颈部,靠近脊髓,即使由解剖结构变化或计划CT的校准不正确引起的光束范围轻微变化,也会增加辐射诱导脊髓病的风险。我们设法以最高剂量完全控制肿瘤,同时尽量减少毒性。低级别的神经副作用与脊柱中测量的正电子活性有关。肿瘤体积内的活性生物清除依赖于剂量,这表明在高剂量时可能存在血管损伤成分。这个实验标志着使用RIB进行肿瘤治疗的首例,为未来的临床应用铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 56 pages, 13 figures, supplements. Video supplements available on request
Summary
放射性离子束(RIB)是当前核物理研究的重要方向之一,具有应用于癌症治疗的潜力。尽管离子束疗法在放疗领域可能最有效,但它高度依赖束流的准确度。然而,通过利用放射性同位素发生eta衰变的特性,借助正电子发射断层扫描技术(PET)进行可视化,RIB在图像引导下治疗肿瘤方面具有优势。研究团队成功使用放射性碳离子束治疗了一只患有颈部骨肿瘤的鼠模型,在治疗过程中精准控制剂量以降低毒性并防止因束流误差引起的辐射损伤脊髓风险。实验首次展示了RIB在肿瘤治疗中的应用,为未来的临床应用铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 放射性离子束(RIB)是核物理领域的重要研究方向之一。
- RIB在癌症治疗中有潜在应用价值。
- RIB适用于图像引导下的粒子疗法。
- RIB通过PET可视化同位素衰变有助于精准监测束流范围。
- 成功使用放射性碳离子束治疗鼠颈部骨肿瘤案例。
- 治疗过程中需精准控制剂量以降低毒性并避免辐射损伤脊髓风险。
点此查看论文截图

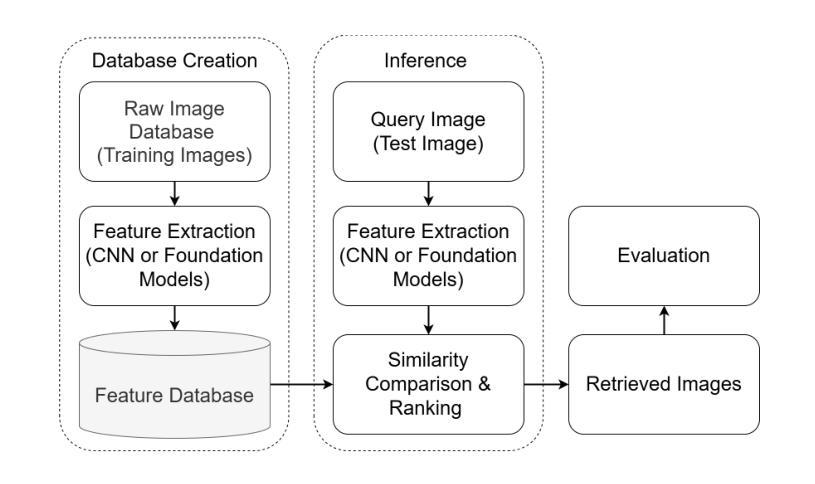
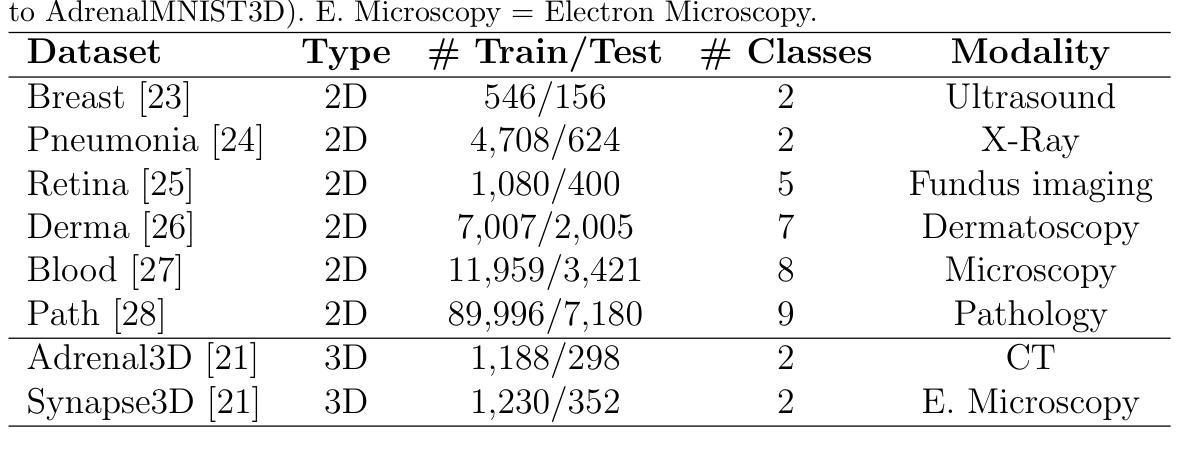
Evaluating Pre-trained Convolutional Neural Networks and Foundation Models as Feature Extractors for Content-based Medical Image Retrieval
Authors:Amirreza Mahbod, Nematollah Saeidi, Sepideh Hatamikia, Ramona Woitek
Medical image retrieval refers to the task of finding similar images for given query images in a database, with applications such as diagnosis support. While traditional medical image retrieval relied on clinical metadata, content-based medical image retrieval (CBMIR) depends on image features, which can be extracted automatically or semi-automatically. Many approaches have been proposed for CBMIR, and among them, using pre-trained convolutional neural networks (CNNs) is a widely utilized approach. However, considering the recent advances in the development of foundation models for various computer vision tasks, their application for CBMIR can also be investigated. In this study, we used several pre-trained feature extractors from well-known pre-trained CNNs and pre-trained foundation models and investigated the CBMIR performance on eight types of two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) medical images. Furthermore, we investigated the effect of image size on the CBMIR performance. Our results show that, overall, for the 2D datasets, foundation models deliver superior performance by a large margin compared to CNNs, with the general-purpose self-supervised model for computational pathology (UNI) providing the best overall performance across all datasets and image sizes. For 3D datasets, CNNs and foundation models deliver more competitive performance, with contrastive learning from captions for histopathology model (CONCH) achieving the best overall performance. Moreover, our findings confirm that while using larger image sizes (especially for 2D datasets) yields slightly better performance, competitive CBMIR performance can still be achieved even with smaller image sizes. Our codes to reproduce the results are available at: https://github.com/masih4/MedImageRetrieval.
医学图像检索是指在数据库中找到与给定查询图像相似的图像的任务,其应用场景如诊断支持。传统的医学图像检索依赖于临床元数据,而基于内容的医学图像检索(CBMIR)则依赖于图像特征,这些特征可以自动或半自动提取。已经提出了许多CBMIR的方法,其中使用预训练的卷积神经网络(CNN)是一种广泛应用的方法。然而,考虑到最近针对各种计算机视觉任务的基础模型开发方面的进展,也可以研究它们对CBMIR的应用。在本研究中,我们使用了来自著名预训练CNN和预训练基础模型的几个预训练特征提取器,并研究了它们在二维(2D)和三维(3D)医学图像上的CBMIR性能。此外,我们还研究了图像大小对CBMIR性能的影响。我们的结果表明,总体而言,对于二维数据集,基础模型在很大程度上表现出优于CNN的性能,其中用于计算病理学的通用自监督模型(UNI)在所有数据集和图像大小上表现出最佳的整体性能。对于三维数据集,CNN和基础模型表现出更具竞争力的性能,其中基于对比学习的组织病理学模型(CONCH)取得了最佳的整体性能。此外,我们的研究结果表明,虽然使用较大的图像大小(尤其是二维数据集)略微提高了性能,但即使使用较小的图像大小也可以实现具有竞争力的CBMIR性能。我们的代码可在https://github.com/masih4/MedImageRetrieval上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 37 pages
摘要
本研究使用预训练的CNN和预训练的Foundation模型进行基于内容的医学图像检索(CBMIR),并在二维和三维医学图像上评估其性能。发现对于二维数据集,Foundation模型相较于CNN具有显著优势,其中计算病理学通用自监督模型(UNI)表现最佳。对于三维数据集,CNN和Foundation模型表现更竞争,基于病理组织学模型(CONCH)对比学习实现最佳性能。增大图像尺寸能提高性能,但即使使用较小的图像尺寸也能实现竞争性的CBMIR性能。
关键见解
- 基于内容的医学图像检索(CBMIR)依赖于图像特征,可自动或半自动提取。
- 预训练的卷积神经网络(CNNs)广泛应用于CBMIR。
- 在二维数据集上,Foundation模型相较于CNN具有显著优势,特别是计算病理学通用自监督模型(UNI)。
- 对于三维数据集,卷积神经网络(CNN)和Foundation模型表现更具竞争力,对比学习模型(CONCH)表现最佳。
- 增大图像尺寸可以提高CBMIR的性能,但使用较小的图像尺寸也能实现竞争性结果。
- 本研究的结果表明Foundation模型在医学图像检索中的潜力与应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

DetailCLIP: Detail-Oriented CLIP for Fine-Grained Tasks
Authors:Amin Karimi Monsefi, Kishore Prakash Sailaja, Ali Alilooee, Ser-Nam Lim, Rajiv Ramnath
In this paper, we introduce DetailCLIP: A Detail-Oriented CLIP to address the limitations of contrastive learning-based vision-language models, particularly CLIP, in handling detail-oriented and fine-grained tasks like segmentation. While CLIP and its variants excel in the global alignment of image and text representations, they often struggle to capture the fine-grained details necessary for precise segmentation. To overcome these challenges, we propose a novel framework that employs patch-level comparison of self-distillation and pixel-level reconstruction losses, enhanced with an attention-based token removal mechanism. This approach selectively retains semantically relevant tokens, enabling the model to focus on the image’s critical regions aligned with the specific functions of our model, including textual information processing, patch comparison, and image reconstruction, ensuring that the model learns high-level semantics and detailed visual features. Our experiments demonstrate that DetailCLIP surpasses existing CLIP-based and traditional self-supervised learning (SSL) models in segmentation accuracy and exhibits superior generalization across diverse datasets. DetailCLIP represents a significant advancement in vision-language modeling, offering a robust solution for tasks that demand high-level semantic understanding and detailed feature extraction. https://github.com/KishoreP1/DetailCLIP.
本文介绍了DetailCLIP:一种面向细节的CLIP,旨在解决基于对比学习的视觉语言模型的局限性,特别是CLIP在处理面向细节和精细粒度任务(如分割)时的局限性。虽然CLIP及其变体在图像和文本表示的全局对齐方面表现出色,但它们往往难以捕捉精确分割所需的精细细节。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了一种新型框架,采用自蒸馏的补丁级比较和像素级重建损失,辅以基于注意力的令牌移除机制。此方法有选择地保留语义相关令牌,使模型能够关注与模型特定功能相对应的图形的关键区域,包括文本信息处理、补丁比较和图像重建,确保模型学习高级语义和详细的视觉特征。我们的实验表明,DetailCLIP在分割精度上超越了现有的CLIP和传统自监督学习(SSL)模型,并在各种数据集上表现出优越的泛化能力。DetailCLIP在视觉语言建模方面取得了重大进展,为需要高级语义理解和详细特征提取的任务提供了稳健的解决方案。详情请访问https://github.com/KishoreP1/DetailCLIP。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in SSI-FM Workshop of ICLR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了DetailCLIP:一种面向细节的CLIP,旨在解决基于对比学习的视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在处理细节导向和精细任务(如分割)时的局限性。DetailCLIP采用补丁级别的自我蒸馏和像素级别的重建损失的对比,结合基于注意力的令牌移除机制,以选择性保留语义相关的令牌,使模型能够关注与特定功能对齐的图像关键区域。实验表明,DetailCLIP在分割精度上超越了现有的CLIP和传统自监督学习模型,并在各种数据集上表现出良好的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- DetailCLIP旨在解决CLIP在处理细节导向和精细任务(如分割)时的局限性。
- DetailCLIP通过补丁级别的自我蒸馏和像素级别的重建损失的对比来解决这个问题。
- 该方法结合了基于注意力的令牌移除机制,以保留语义相关的关键信息。
- DetailCLIP使模型关注与特定任务对齐的图像关键区域。
- 实验结果显示,DetailCLIP在分割精度上超越了现有的CLIP和传统自监督学习模型。
- DetailCLIP在各种数据集上具有良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

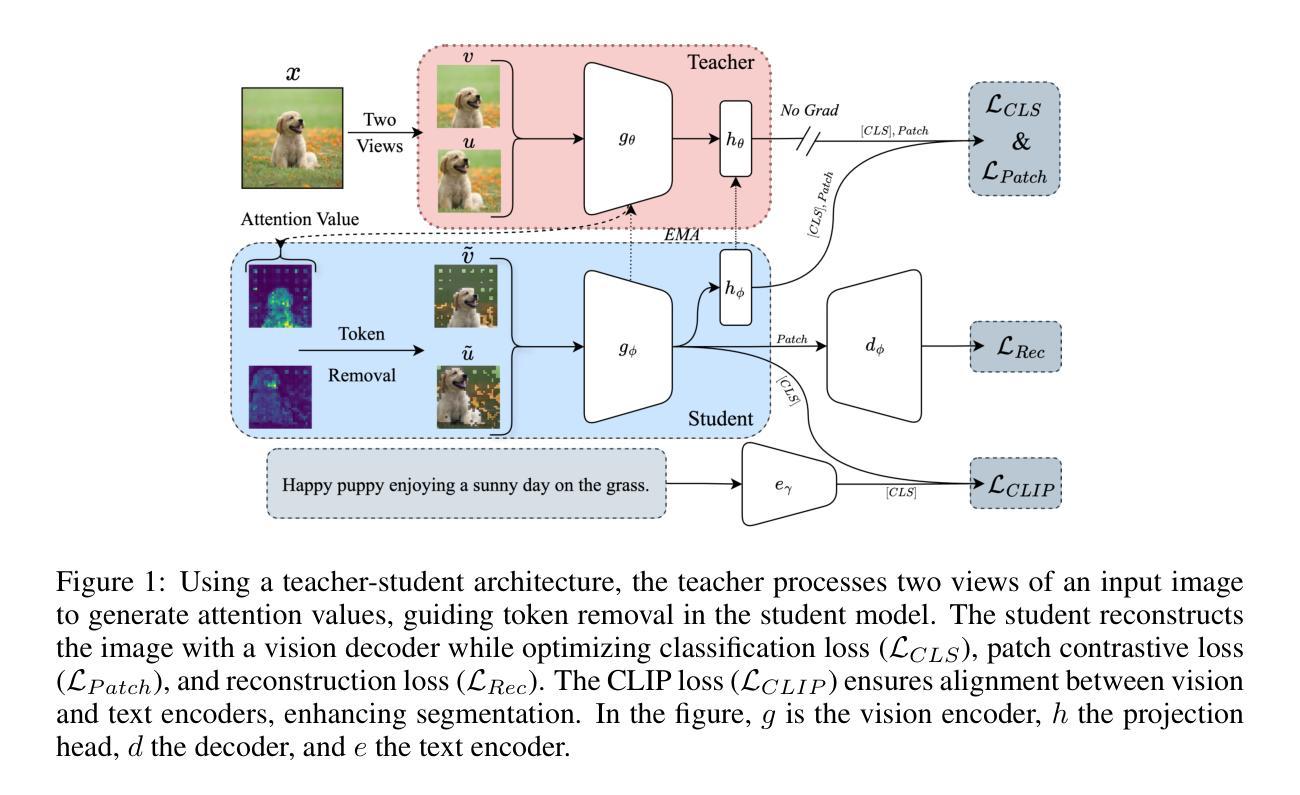
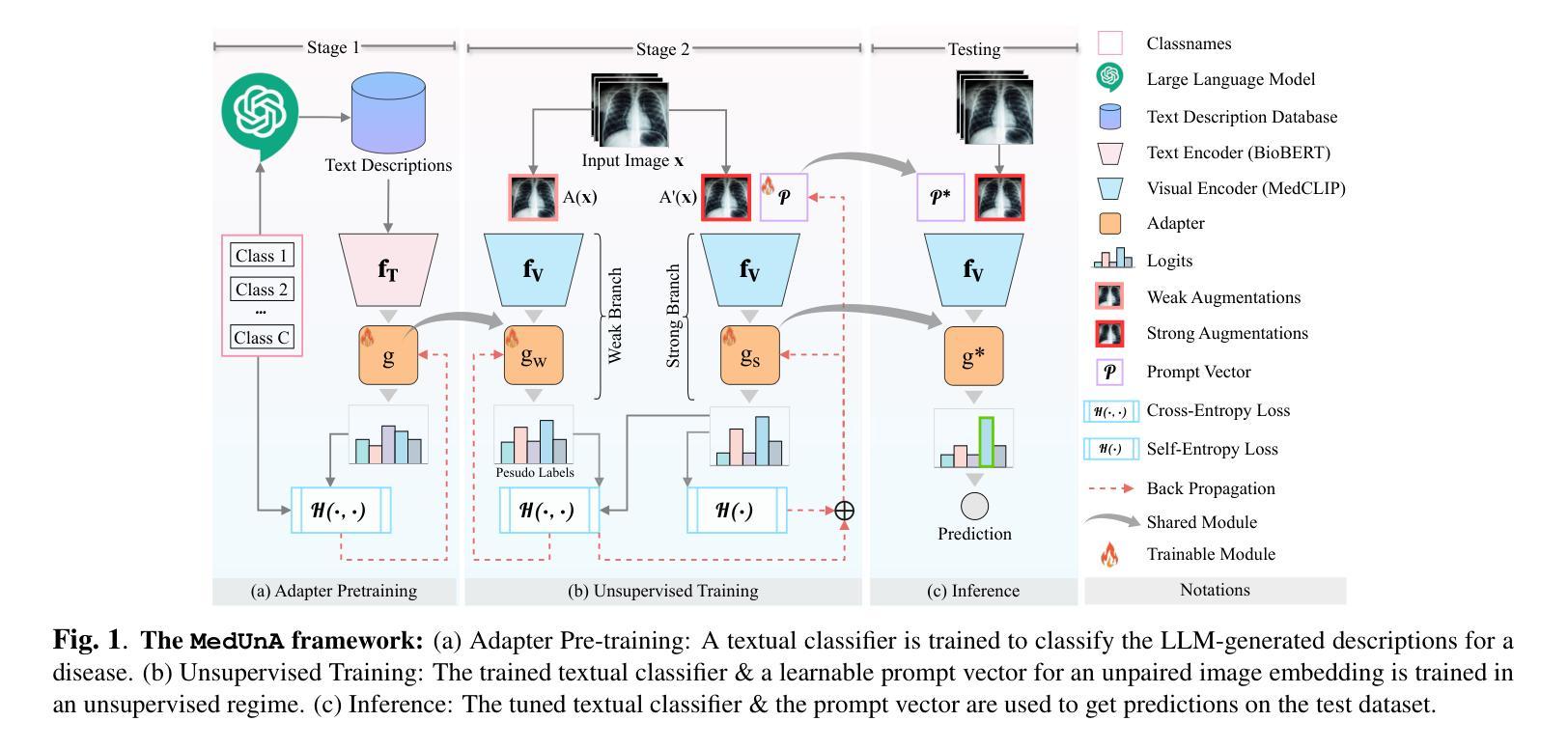
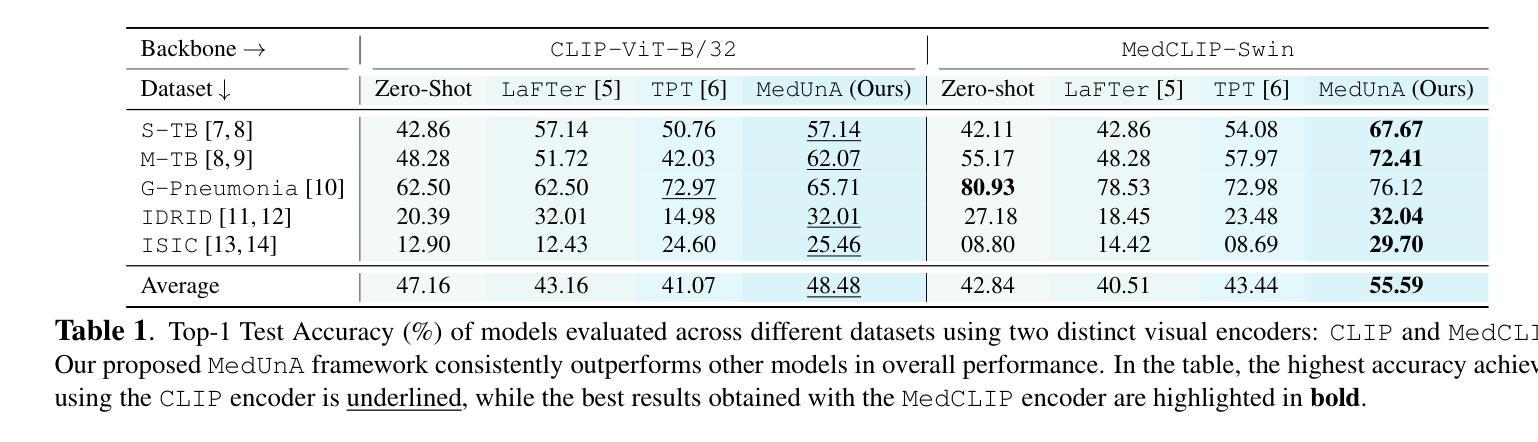
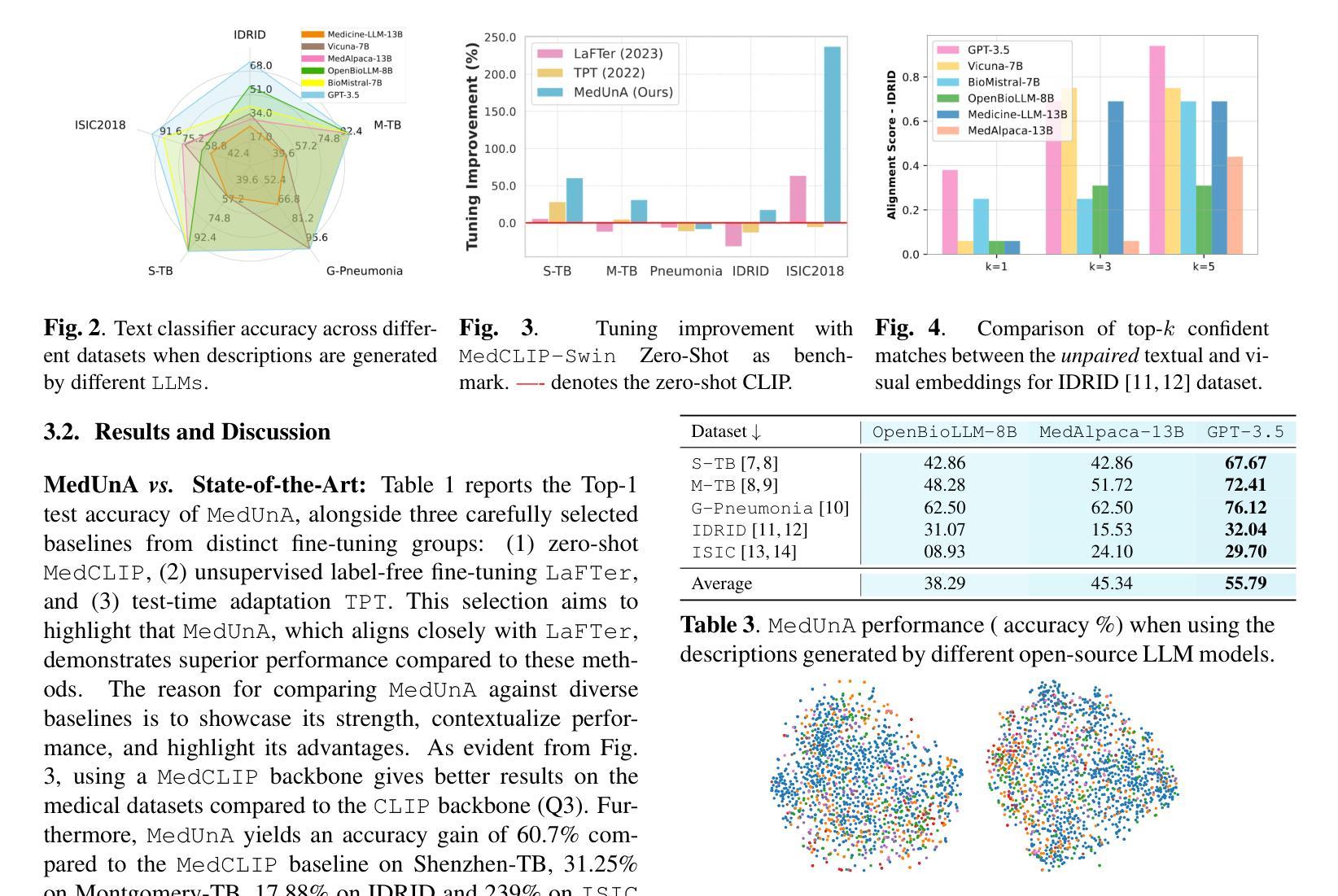
Can language-guided unsupervised adaptation improve medical image classification using unpaired images and texts?
Authors:Umaima Rahman, Raza Imam, Mohammad Yaqub, Boulbaba Ben Amor, Dwarikanath Mahapatra
In medical image classification, supervised learning is challenging due to the scarcity of labeled medical images. To address this, we leverage the visual-textual alignment within Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to enable unsupervised learning of a medical image classifier. In this work, we propose \underline{Med}ical \underline{Un}supervised \underline{A}daptation (\texttt{MedUnA}) of VLMs, where the LLM-generated descriptions for each class are encoded into text embeddings and matched with class labels via a cross-modal adapter. This adapter attaches to a visual encoder of \texttt{MedCLIP} and aligns the visual embeddings through unsupervised learning, driven by a contrastive entropy-based loss and prompt tuning. Thereby, improving performance in scenarios where textual information is more abundant than labeled images, particularly in the healthcare domain. Unlike traditional VLMs, \texttt{MedUnA} uses \textbf{unpaired images and text} for learning representations and enhances the potential of VLMs beyond traditional constraints. We evaluate the performance on three chest X-ray datasets and two multi-class datasets (diabetic retinopathy and skin lesions), showing significant accuracy gains over the zero-shot baseline. Our code is available at https://github.com/rumaima/meduna.
在医学图像分类中,由于缺少标记的医学图像,监督学习面临挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)中的视觉文本对齐功能,实现医学图像分类器的无监督学习。在这项工作中,我们提出了医学无监督适配(MedUnA)的VLMs方法,其中大型语言模型为每个类别生成的描述被编码为文本嵌入,并通过跨模态适配器与类别标签进行匹配。该适配器附加到MedCLIP的视觉编码器上,通过对无监督学习产生的视觉嵌入进行对齐,由基于对比熵的损失和提示调整驱动。因此,在文本信息比标记图像丰富的情况下,特别是在医疗领域,提高了性能。与传统的VLMs不同,MedUnA使用非配对图像和文本来学习表示,并超越了传统约束的VLMs的潜力。我们在三个胸部X射线数据集和两个多类数据集(糖尿病视网膜病变和皮肤病变)上评估了性能,与零样本基线相比,显示出显著的准确性提高。我们的代码可在https://github.com/rumaima/meduna找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Conference paper at International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2025
Summary
医学图像分类中监督学习因缺乏标注图像而面临挑战。研究提出利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)的视觉文本对齐特性,实现医疗图像分类器的无监督学习。本研究提出医疗无监督适应(MedUnA)方法,通过大型语言模型生成的各类描述,编码成文本嵌入,并通过跨模态适配器与类标签匹配。适配器连接MedCLIP的视觉编码器,通过对无监督学习驱动的对齐视觉嵌入,减少对比熵损失并调整提示,提高在文本信息丰富于标注图像的场景下的性能,特别是在医疗领域。不同于传统VLMs,MedUnA利用非配对图像和文本学习表征,突破了传统约束,提高了VLMs的潜力。在三个胸部X光数据集和两个多类数据集(糖尿病视网膜病变和皮肤病变)上评估性能,相较于零样本基线有显著精度提升。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分类面临监督学习挑战,因缺乏标注图像。
- 提出利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)的视觉文本对齐特性以实现无监督学习。
- 引入医疗无监督适应(MedUnA)方法,结合大型语言模型和跨模态适配器。
- MedUnA通过编码类描述生成文本嵌入,并与类标签匹配。
- MedUnA适配器连接至MedCLIP的视觉编码器以实现视觉嵌入对齐。
- 无监督学习通过减少对比熵损失和调整提示来提高性能。
- MedUnA在多种医学图像数据集上表现出显著性能提升,特别是在文本信息丰富的场景中。
点此查看论文截图

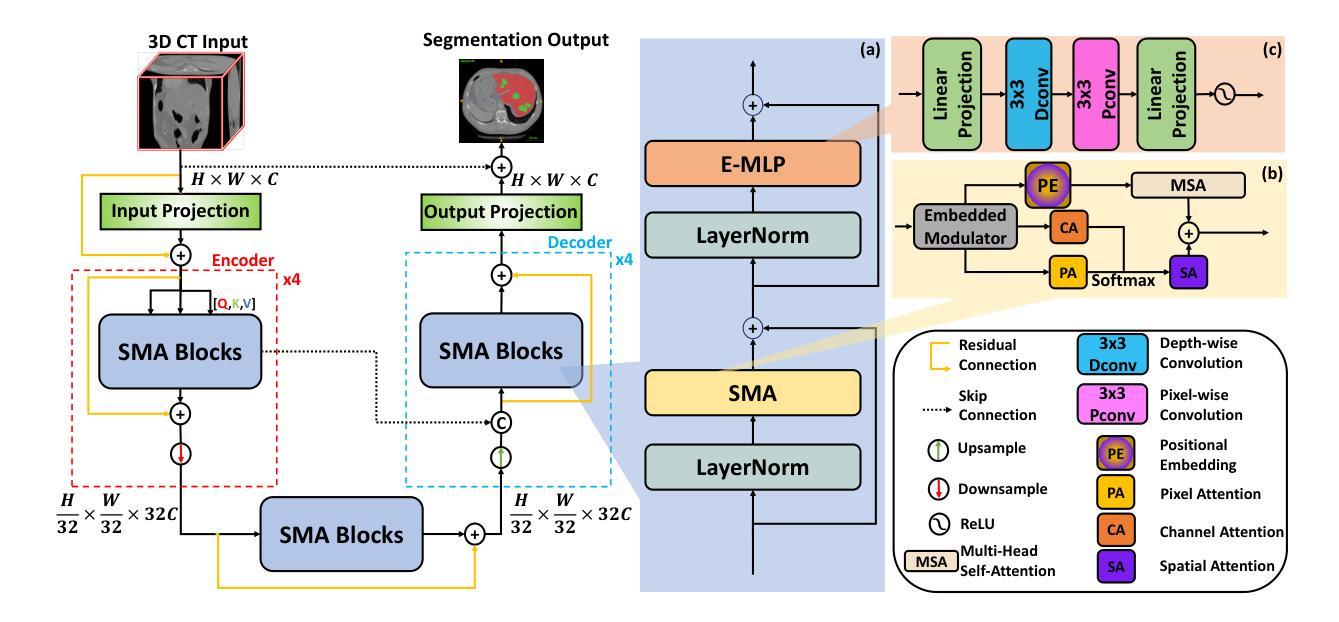
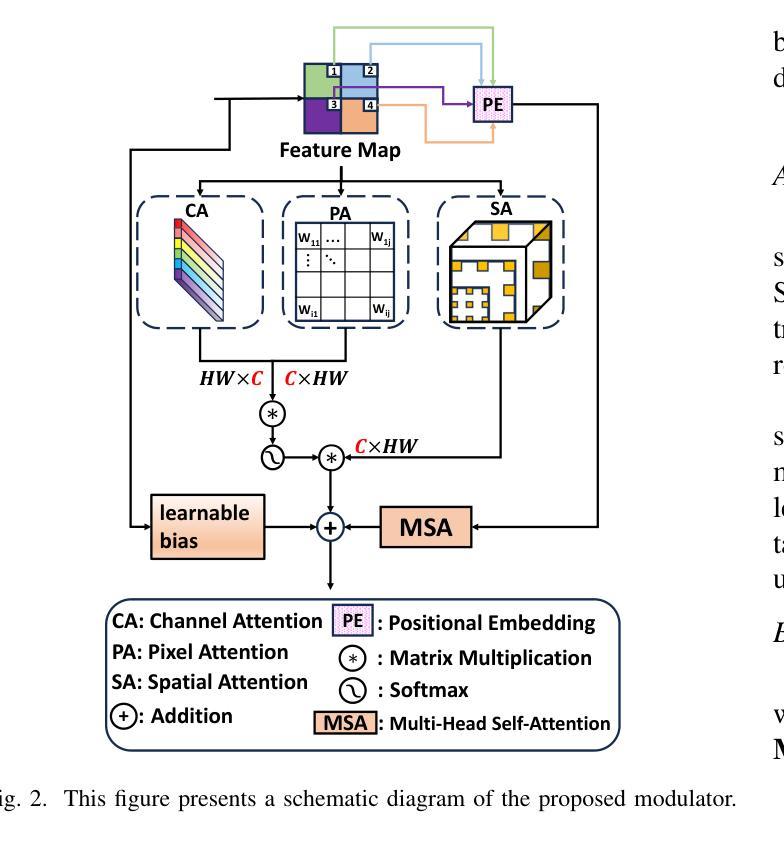
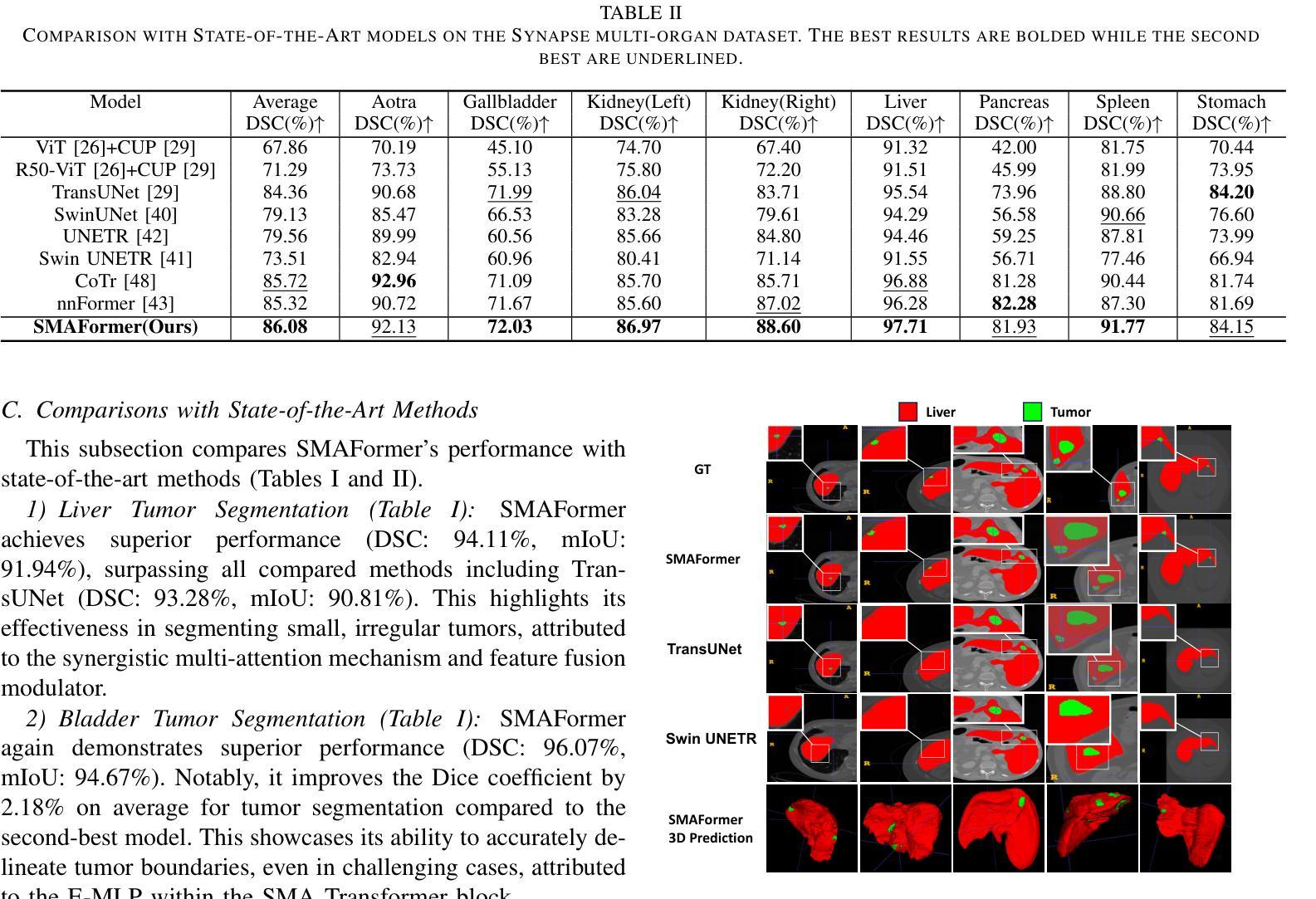
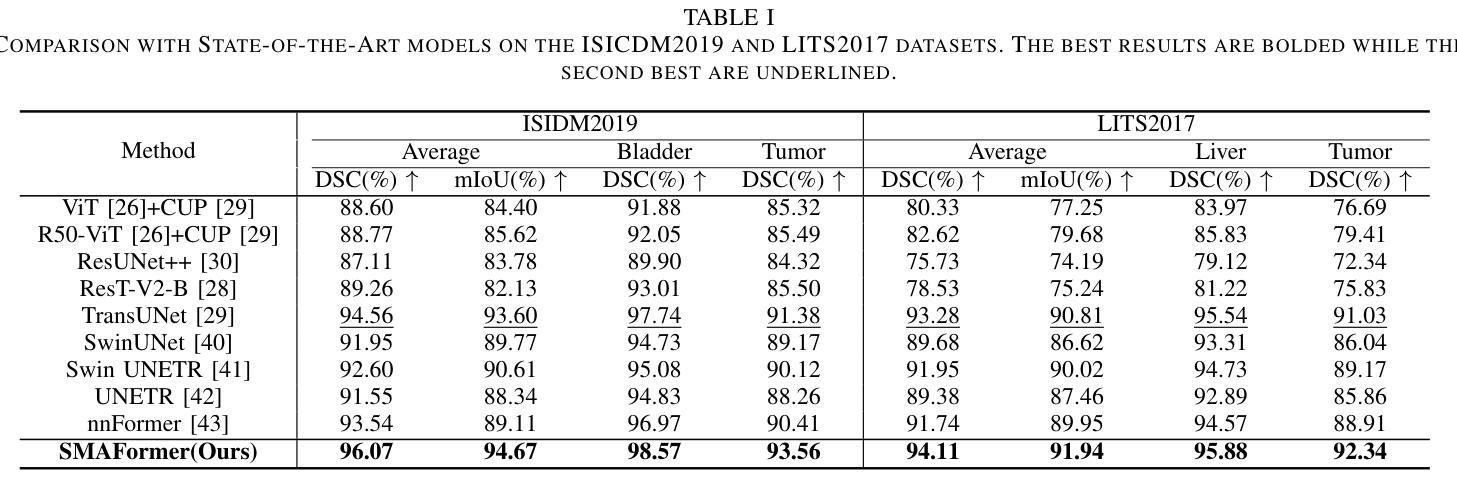
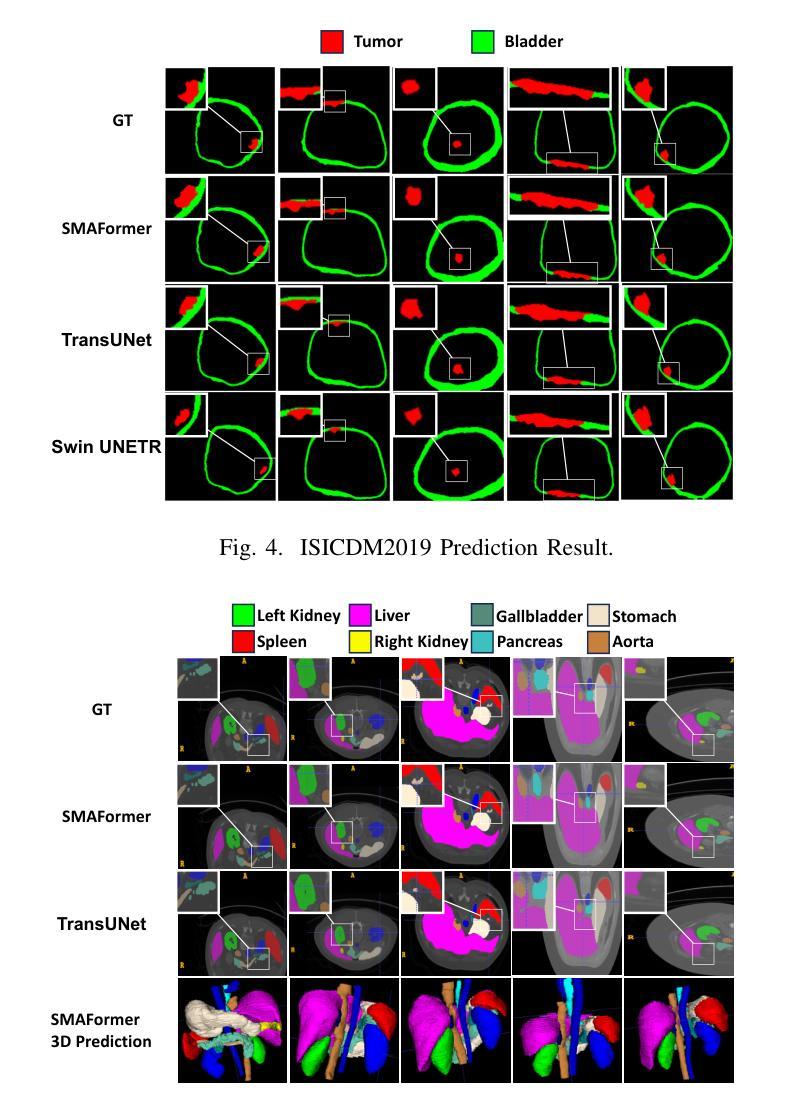
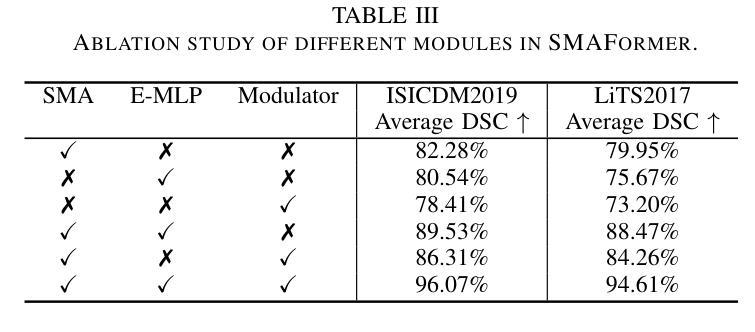
SMAFormer: Synergistic Multi-Attention Transformer for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Fuchen Zheng, Xuhang Chen, Weihuang Liu, Haolun Li, Yingtie Lei, Jiahui He, Chi-Man Pun, Shounjun Zhou
In medical image segmentation, specialized computer vision techniques, notably transformers grounded in attention mechanisms and residual networks employing skip connections, have been instrumental in advancing performance. Nonetheless, previous models often falter when segmenting small, irregularly shaped tumors. To this end, we introduce SMAFormer, an efficient, Transformer-based architecture that fuses multiple attention mechanisms for enhanced segmentation of small tumors and organs. SMAFormer can capture both local and global features for medical image segmentation. The architecture comprises two pivotal components. First, a Synergistic Multi-Attention (SMA) Transformer block is proposed, which has the benefits of Pixel Attention, Channel Attention, and Spatial Attention for feature enrichment. Second, addressing the challenge of information loss incurred during attention mechanism transitions and feature fusion, we design a Feature Fusion Modulator. This module bolsters the integration between the channel and spatial attention by mitigating reshaping-induced information attrition. To evaluate our method, we conduct extensive experiments on various medical image segmentation tasks, including multi-organ, liver tumor, and bladder tumor segmentation, achieving state-of-the-art results. Code and models are available at: https://github.com/CXH-Research/SMAFormer.
在医学图像分割领域,特定的计算机视觉技术,特别是基于注意力机制的变压器(transformer)和采用跳跃连接的残差网络(residual networks),在提升性能上发挥了重要作用。然而,以前的模型在分割小型、形状不规则的肿瘤时经常会遇到困难。为此,我们引入了SMAFormer,这是一种高效的基于变压器的架构,融合了多种注意力机制,用于改进小型肿瘤和器官的分割。SMAFormer可以捕获医学图像分割的局部和全局特征。该架构包含两个关键组件。首先,我们提出了协同多注意力(SMA)变压器块,该块具有像素注意力、通道注意力和空间注意力的优点,以实现特征丰富。其次,为了解决注意力机制转换和特征融合过程中信息损失的问题,我们设计了一个特征融合调制器。该模块通过减轻重塑引起的信息衰减,加强了通道和空间注意力之间的集成。为了评估我们的方法,我们在各种医学图像分割任务上进行了大量实验,包括多器官、肝脏肿瘤和膀胱肿瘤分割,取得了最新结果。代码和模型可在:https://github.com/CXH-Research/SMAFormer获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE BIBM 2024
Summary
基于注意力机制和残差网络的计算机视觉技术对于医学图像分割的性能提升起到了重要作用。然而,对于小型、形状不规则的肿瘤的分割,先前模型常常存在缺陷。我们提出了SMAFormer,这是一种高效的基于Transformer的架构,融合了多种注意力机制,用于改进小型肿瘤和器官的分割。SMAFormer能够捕捉医学图像分割的局部和全局特征。该架构包括两个关键组件:一是协同多注意力(SMA)Transformer块,具有像素注意力、通道注意力和空间注意力的优点,用于特征增强;二是解决注意力机制转换和特征融合过程中信息损失的问题,我们设计了一个特征融合调制器。该模块通过减轻重塑引起的信息衰减,加强了通道和空间注意力之间的集成。我们的方法在多项医学图像分割任务上进行了广泛实验,包括多器官、肝脏肿瘤和膀胱肿瘤分割,取得了最新结果。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割中,基于注意力机制和残差网络的计算机视觉技术展现了显著性能提升。
- 现有模型在分割小型、形状不规则的肿瘤时遇到困难。
- 提出SMAFormer架构,融合多种注意力机制以改进小型肿瘤和器官的分割。
- SMAFormer包含两个关键组件:协同多注意力(SMA)Transformer块和特征融合调制器。
- SMATransformer块能捕捉医学图像的局部和全局特征。
- 特征融合调制器解决了注意力机制转换和特征融合中的信息损失问题。
- 在多器官、肝脏肿瘤和膀胱肿瘤分割等任务上取得最新成果。
点此查看论文截图

AI in radiological imaging of soft-tissue and bone tumours: a systematic review evaluating against CLAIM and FUTURE-AI guidelines
Authors:Douwe J. Spaanderman, Matthew Marzetti, Xinyi Wan, Andrew F. Scarsbrook, Philip Robinson, Edwin H. G. Oei, Jacob J. Visser, Robert Hemke, Kirsten van Langevelde, David F. Hanff, Geert J. L. H. van Leenders, Cornelis Verhoef, Dirk J. Gruühagen, Wiro J. Niessen, Stefan Klein, Martijn P. A. Starmans
Soft-tissue and bone tumours (STBT) are rare, diagnostically challenging lesions with variable clinical behaviours and treatment approaches. This systematic review provides an overview of Artificial Intelligence (AI) methods using radiological imaging for diagnosis and prognosis of these tumours, highlighting challenges in clinical translation, and evaluating study alignment with the Checklist for AI in Medical Imaging (CLAIM) and the FUTURE-AI international consensus guidelines for trustworthy and deployable AI to promote the clinical translation of AI methods. The review covered literature from several bibliographic databases, including papers published before 17/07/2024. Original research in peer-reviewed journals focused on radiology-based AI for diagnosing or prognosing primary STBT was included. Exclusion criteria were animal, cadaveric, or laboratory studies, and non-English papers. Abstracts were screened by two of three independent reviewers for eligibility. Eligible papers were assessed against guidelines by one of three independent reviewers. The search identified 15,015 abstracts, from which 325 articles were included for evaluation. Most studies performed moderately on CLAIM, averaging a score of 28.9$\pm$7.5 out of 53, but poorly on FUTURE-AI, averaging 5.1$\pm$2.1 out of 30. Imaging-AI tools for STBT remain at the proof-of-concept stage, indicating significant room for improvement. Future efforts by AI developers should focus on design (e.g. define unmet clinical need, intended clinical setting and how AI would be integrated in clinical workflow), development (e.g. build on previous work, explainability), evaluation (e.g. evaluating and addressing biases, evaluating AI against best practices), and data reproducibility and availability (making documented code and data publicly available). Following these recommendations could improve clinical translation of AI methods.
软组织与骨肿瘤(STBT)是罕见且诊断困难的病变,其临床行为和治疗方式各异。这篇系统性综述概述了使用放射影像学进行诊断与预后预测的人工智能(AI)方法,强调了这些肿瘤在临床翻译中的挑战,并评估了研究是否符合医学影像人工智能核查表(CLAIM)以及可信且可部署的人工智能的FUTURE-AI国际共识指南,以促进AI方法的临床翻译。综述涵盖了来自多个文献数据库的文献,包括在2024年7月17日之前发表的文章。纳入的是经过同行评审的原创研究,这些研究侧重于基于放射学的AI用于原发性STBT的诊断或预后预测。排除标准是动物、尸体或实验室研究,以及非英文文章。摘要由三名独立评审员中的两名进行资格筛选。符合资格的论文由三名独立评审员中的一名根据指南进行评估。搜索共确定了15,015篇摘要,其中325篇文章被纳入评估。大多数研究在CLAIM上的表现中等,平均得分为28.9±7.5(满分53分),但在FUTURE-AI上的表现较差,平均得分为5.1±2.1(满分30分)。针对STBT的成像AI工具仍处于概念验证阶段,表明还有很大的改进空间。未来人工智能开发者的努力应集中在设计(例如确定未满足的临床需求、预期的临床环境以及AI如何融入临床工作流程)、开发(例如在之前的工作基础上进行建设、解释性)、评估(例如评估和解决偏见、按照最佳实践评估AI),以及数据可重复性和可用性(公开提供有记录的代码和数据)。遵循这些建议可能会改善AI方法的临床翻译。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages, 6 figures, 8 supplementary figures
摘要
本文系统综述了使用放射影像学进行软组织与骨肿瘤(STBT)诊断与预后的AI方法。文章概述了AI在STBT诊断与预后方面的应用,强调了临床翻译中的挑战,并评估了研究是否符合医学成像人工智能(CLAIM)清单和未来人工智能(FUTURE-AI)国际共识指南。文章涵盖了多个文献数据库的文献,包括至XXXX年XX月XX日前发表的论文。研究中,经过筛选,最终有XX篇文章符合条件。大部分研究在CLAIM上的表现是中等的,平均得分为XX±X分(满分XX分),但在FUTURE-AI上的表现较差,平均得分为X±X分(满分XX分)。对于STBT的成像人工智能工具仍处于概念验证阶段,仍有很大的改进空间。未来人工智能开发者应在设计、开发、评估和数据可重复性等方面加大投入,以促进人工智能在临床实践中的应用。总之,通过遵循这些建议,人工智能方法的临床转化将得到改进。
关键见解
- AI在STBT诊断和治疗中的应用得到了系统综述,强调了其在临床翻译中的挑战。
- 研究符合医学成像人工智能(CLAIM)清单和未来人工智能(FUTURE-AI)国际共识指南的评价标准。
- 大部分研究在CLAIM上的表现中等,但在FUTURE-AI上的表现较差,显示出AI工具在STBT领域的改进空间。
- 人工智能工具目前仍处于概念验证阶段,需要进一步提高其在临床实践中的适用性。
- AI开发者需要在设计、开发、评估和数据可重复性方面加大投入,以促进人工智能的临床转化。
- 定义未满足的临床需求、预期的临床环境以及AI如何融入临床工作流程对于AI的设计至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

Real-Time Image Analysis Software Suitable for Resource-Constrained Computing
Authors:Alexandre Matov
Methods: We have developed a software suite (DataSet Tracker) for real-time analysis designed to run on computers, smartphones, and smart glasses hardware and suitable for resource-constrained, on-the-fly computing in microscopes without internet connectivity; a demo is available for viewing at datasetanalysis.com. Our objective is to present the community with an integrated, easy to use by all, tool for resolving the complex dynamics of the cytoskeletal meshworks, intracytoplasmic membranous networks, and vesicle trafficking. Our software is optimized for resource-constrained computing and can be installed even on microscopes without internet connectivity. Results: Our computational platform can provide high-content analyses and functional secondary screening of novel compounds that are in the process of approval, or at a pre-clinical stage of development, and putative combination therapies based on FDA-approved drugs. Importantly, dissecting the mechanisms of drug action with quantitative detail will allow the design of drugs that impede relapse and optimal dose regimens with minimal harmful side effects by carefully exploiting disease-specific aberrations. Conclusions: DataSet Tracker, the real-time optical flow feature tracking software presented in this contribution, can serve as the base module of an integrated platform of existing and future algorithms for real-time cellular analysis. The computational assay we propose could successfully be applied to evaluate treatment strategies for any human organ. It is our goal to have this integrated tool approved for use in the clinical practice.
方法:我们开发了一套实时分析软件套件(DataSet Tracker),可在计算机、智能手机和智能眼镜等硬件上运行,适用于无网络连接显微镜下的资源受限、即时计算。可以在datasetanalysis.com上查看演示版。我们的目标是向研究群体提供一个集成工具,解决细胞骨架网格、胞质内膜网络和囊泡转运的复杂动态问题,该工具易于所有人使用。我们的软件针对资源受限计算进行了优化,甚至可以在没有互联网连接的显微镜上安装使用。
结果:我们的计算平台可以提供高内容分析和新型化合物的功能性二次筛选,这些化合物可能处于批准过程中或处于开发预临床阶段,以及基于FDA批准药物的潜在联合疗法。重要的是,以定量详细的方式分析药物作用机制,将有助于设计能够阻碍复发的药物,并借助对特定疾病异常的精细利用,制定具有最小有害副作用的最佳给药方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
数据集追踪器是一款为实时分析而开发的软件套件,适用于计算机、智能手机和智能眼镜等硬件资源受限的显微镜环境。该软件旨在解决细胞骨架网格、细胞内膜网络和囊泡运输的复杂动态问题,并可作为现有和未来算法的集成平台,用于实时细胞分析。该计算平台可以对处于批准过程中或处于开发预临床阶段的新型化合物进行高内容分析和功能二次筛选,并通过定量详细研究药物作用机制来设计能够阻止复发的药物,以及制定具有最少有害副作用的最佳剂量方案。数据集追踪器最终目标是获得批准用于临床实践。
Key Takeaways
- 软件套件DataSet Tracker用于实时分析,可在计算机、智能手机和智能眼镜等硬件上运行。
- 该软件适用于资源受限的显微镜环境,无需互联网连接。
- DataSet Tracker旨在解决细胞骨架网格、细胞内膜网络和囊泡运输的复杂动态问题。
- 该计算平台可以进行高内容分析和功能二次筛选,包括对新型化合物的分析。
- 通过定量详细研究药物作用机制,可设计阻止复发的药物并制定最佳剂量方案。
- DataSet Tracker可以作为集成现有和未来算法的实时细胞分析的基础模块。
点此查看论文截图

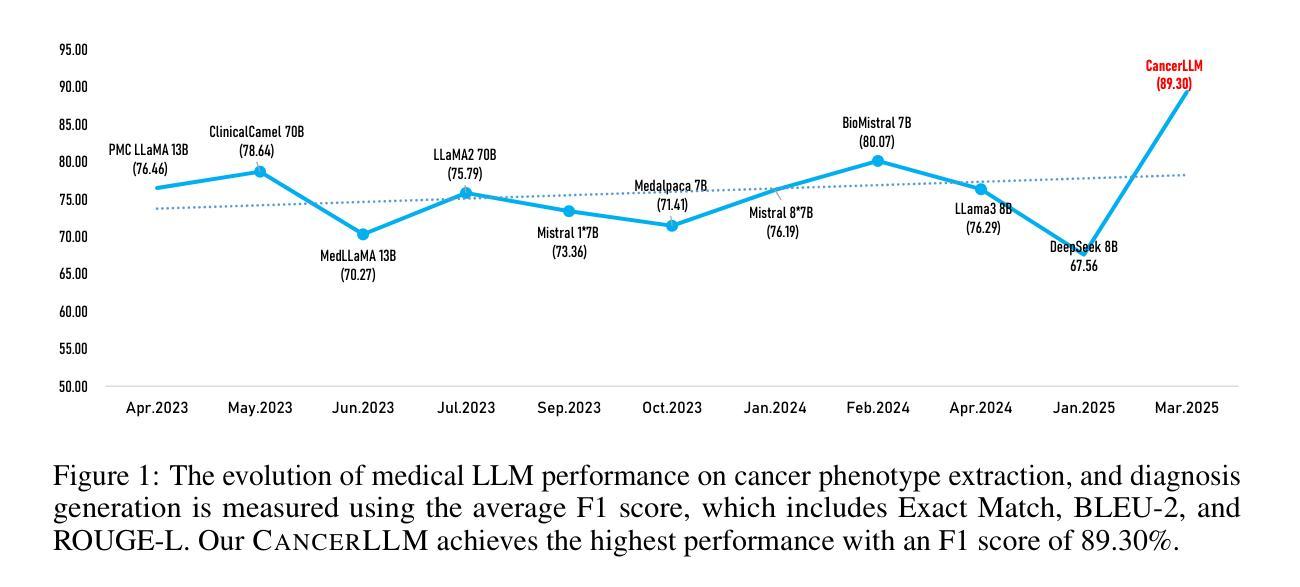
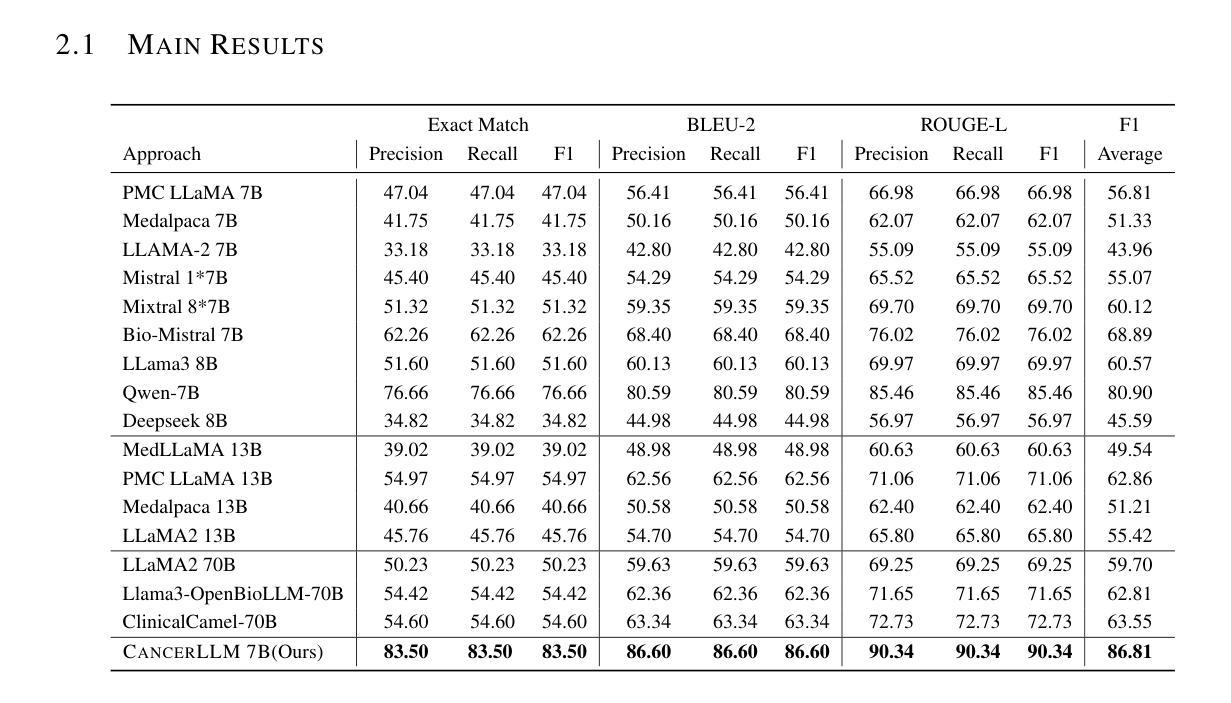
CancerLLM: A Large Language Model in Cancer Domain
Authors:Mingchen Li, Jiatan Huang, Jeremy Yeung, Anne Blaes, Steven Johnson, Hongfang Liu, Hua Xu, Rui Zhang
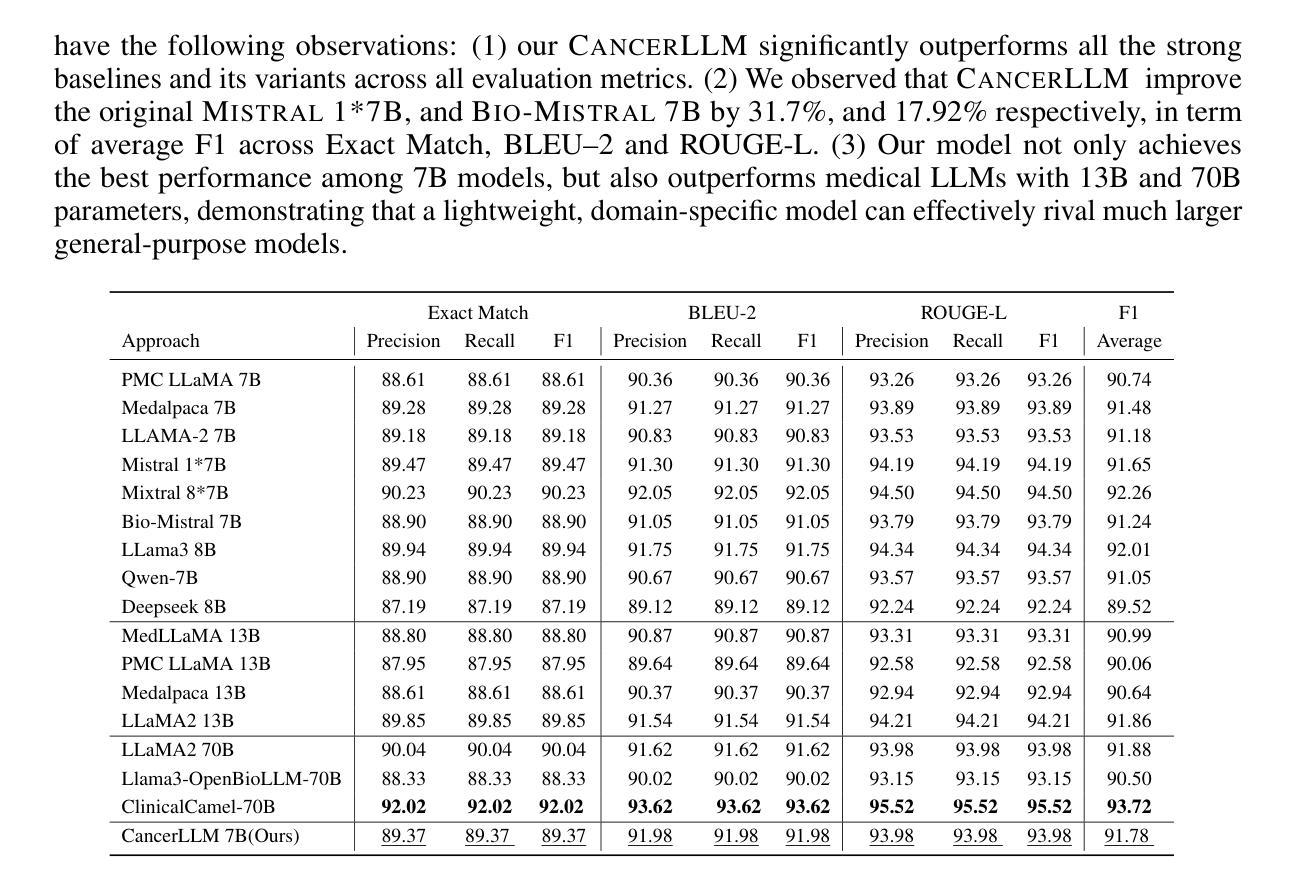
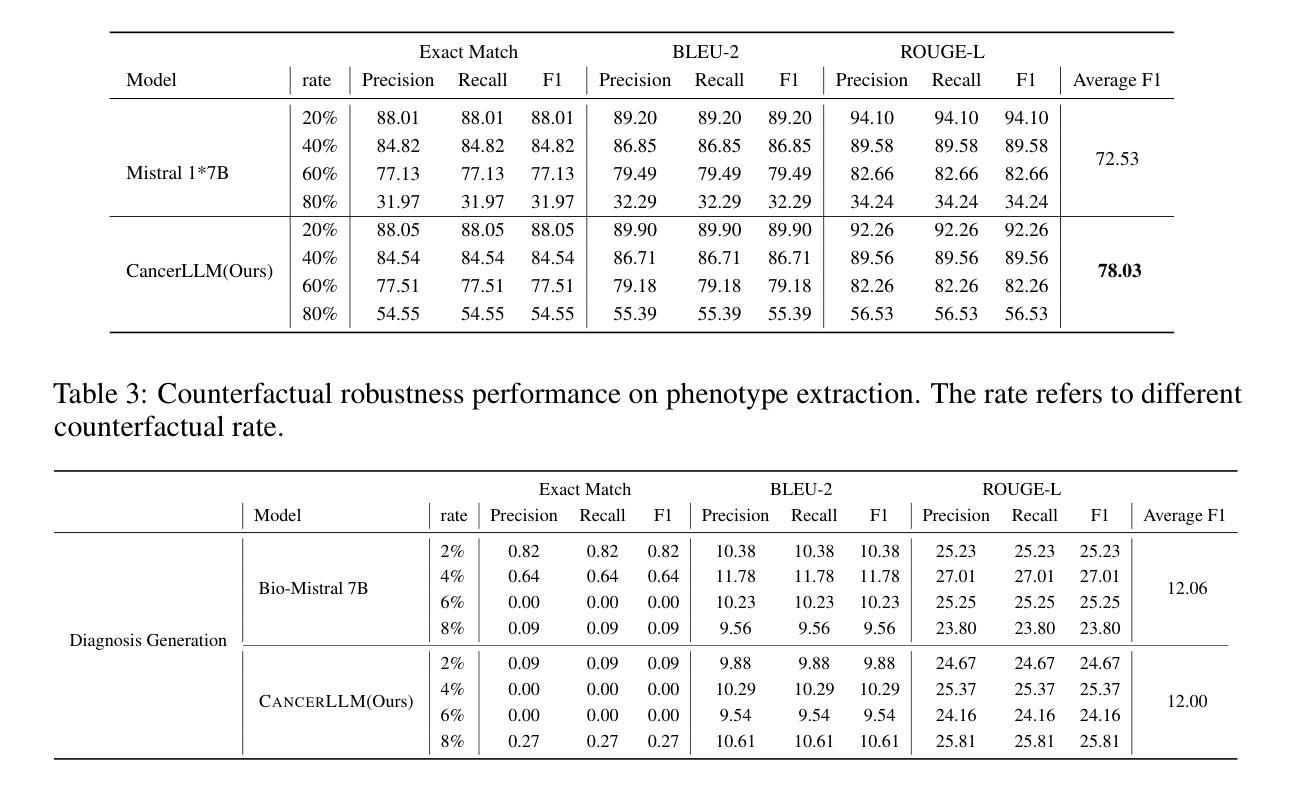
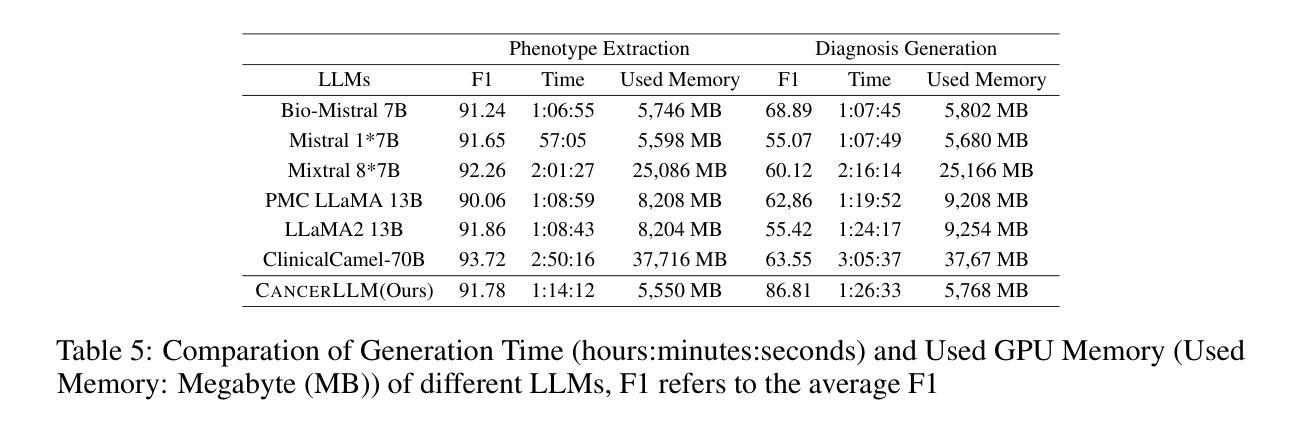
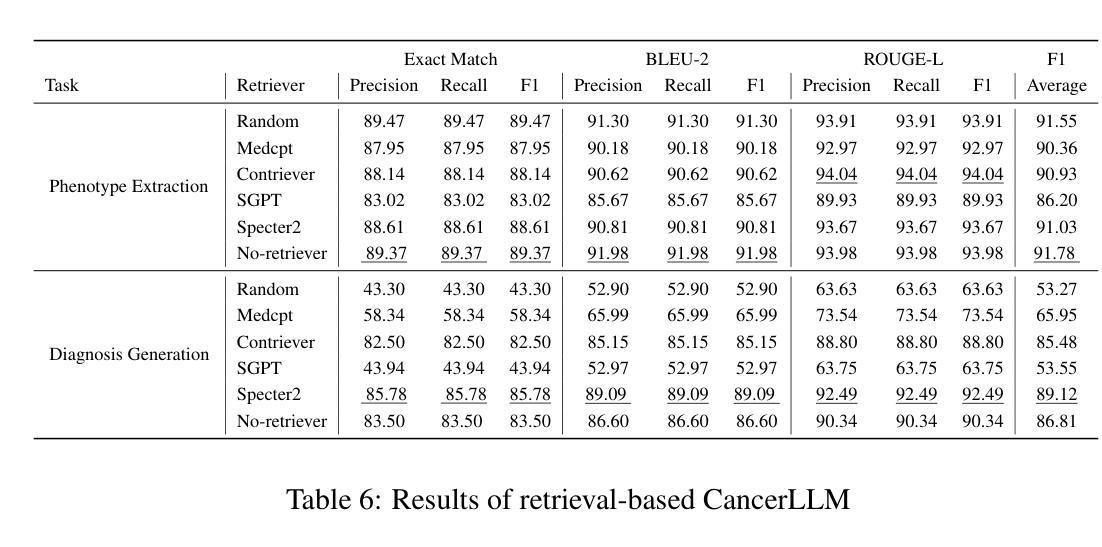
Medical Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance on a wide variety of medical NLP tasks; however, there still lacks a LLM specifically designed for phenotyping identification and diagnosis in cancer domain. Moreover, these LLMs typically have several billions of parameters, making them computationally expensive for healthcare systems. Thus, in this study, we propose CancerLLM, a model with 7 billion parameters and a Mistral-style architecture, pre-trained on nearly 2.7M clinical notes and over 515K pathology reports covering 17 cancer types, followed by fine-tuning on two cancer-relevant tasks, including cancer phenotypes extraction and cancer diagnosis generation. Our evaluation demonstrated that the CancerLLM achieves state-of-the-art results with F1 score of 91.78% on phenotyping extraction and 86.81% on disganois generation. It outperformed existing LLMs, with an average F1 score improvement of 9.23%. Additionally, the CancerLLM demonstrated its efficiency on time and GPU usage, and robustness comparing with other LLMs. We demonstrated that CancerLLM can potentially provide an effective and robust solution to advance clinical research and practice in cancer domain
医疗大型语言模型(LLM)在多种医疗NLP任务中表现出了令人印象深刻的性能;然而,针对癌症领域的表型识别和诊断设计的LLM仍然缺乏。此外,这些LLM通常有数十亿个参数,使得它们在医疗保健系统中的计算成本较高。因此,本研究提出了CancerLLM,这是一个拥有7亿个参数和Mistral风格架构的模型,它在近270万个临床笔记和超过51.5万个涵盖17种癌症类型的病理报告上进行预训练,随后对癌症相关的两个任务进行微调,包括癌症表型提取和癌症诊断生成。我们的评估表明,CancerLLM在表型提取方面达到了91.78%的F1分数,在诊断生成方面达到了86.81%的准确率,取得了最新结果。它优于现有的LLM,平均F1分数提高了9.23%。此外,CancerLLM在时间和GPU使用方面表现出了其效率,并且与其他LLM相比具有稳健性。我们证明,CancerLLM有望为癌症领域的临床研究和实践提供有效且稳健的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF new version, add the RAG version of cancerLLM
Summary
本文介绍了针对癌症领域专门设计的Medical Large Language Model(LLM)——CancerLLM。该模型具有7亿参数和Mistral风格架构,在约270万份临床笔记和超过51.5万份病理报告上进行预训练,涵盖17种癌症类型。通过微调两个与癌症相关的任务,包括癌症表型提取和癌症诊断生成,CancerLLM实现了先进的结果,在表型提取方面达到了91.78%的F1分数,在诊断生成方面达到了86.81%。相较于现有LLM,CancerLLM平均F1分数提高了9.23%,并在时间效率和GPU使用方面展现了优势,具有鲁棒性。该模型为癌症领域的临床研究和实践提供了有效且稳健的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- CancerLLM是专门为癌症领域设计的医疗大型语言模型(LLM)。
- 该模型具有7亿参数和Mistral风格架构。
- CancerLLM经过在大量临床笔记和病理报告上的预训练,涵盖17种癌症类型。
- 通过微调,CancerLLM在癌症表型提取和诊断生成任务上取得了先进结果。
- CancerLLM相较于现有LLM,F1分数平均提高了9.23%。
- CancerLLM在时间和GPU使用效率方面展现出优势。
点此查看论文截图

CARL: A Framework for Equivariant Image Registration
Authors:Hastings Greer, Lin Tian, Francois-Xavier Vialard, Roland Kwitt, Raul San Jose Estepar, Marc Niethammer
Image registration estimates spatial correspondences between a pair of images. These estimates are typically obtained via numerical optimization or regression by a deep network. A desirable property of such estimators is that a correspondence estimate (e.g., the true oracle correspondence) for an image pair is maintained under deformations of the input images. Formally, the estimator should be equivariant to a desired class of image transformations. In this work, we present careful analyses of the desired equivariance properties in the context of multi-step deep registration networks. Based on these analyses we 1) introduce the notions of $[U,U]$ equivariance (network equivariance to the same deformations of the input images) and $[W,U]$ equivariance (where input images can undergo different deformations); we 2) show that in a suitable multi-step registration setup it is sufficient for overall $[W,U]$ equivariance if the first step has $[W,U]$ equivariance and all others have $[U,U]$ equivariance; we 3) show that common displacement-predicting networks only exhibit $[U,U]$ equivariance to translations instead of the more powerful $[W,U]$ equivariance; and we 4) show how to achieve multi-step $[W,U]$ equivariance via a coordinate-attention mechanism combined with displacement-predicting refinement layers (CARL). Overall, our approach obtains excellent practical registration performance on several 3D medical image registration tasks and outperforms existing unsupervised approaches for the challenging problem of abdomen registration.
图像配准估计一对图像之间的空间对应关系。这些估计通常通过数值优化或深度网络的回归来获得。此类估计器的一个理想特性是,在输入图像变形的情况下,一对图像的对应估计(例如,真实对应)仍然保持不变。在形式上,估计器应对所需的图像转换类别具有等变性。在这项工作中,我们对多步深度配准网络的所需等变性属性进行了深入分析。基于这些分析,我们1)介绍了$[U,U]$等变性(网络对输入图像的相同变形的等变性)和$[W,U]$等变性(输入图像可以经历不同的变形)的概念;我们2)表明,在合适的多步配准设置中,如果第一步具有$[W,U]$等变性,而其他所有步骤都具有$[U,U]$等变性,那么对于整体而言,$[W,U]$等变性就足够了;我们3)表明,常见的位移预测网络仅对平移具有$[U,U]$等变性,而不是更强大的$[W,U]$等变性;我们4)展示了如何通过结合坐标注意机制与位移预测细化层(CARL)来实现多步$[W,U]$等变性。总体而言,我们的方法在多个3D医学图像配准任务上取得了出色的实际配准性能,并且在具有挑战性的腹部配准问题上优于现有的无监督方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
摘要
图像配准估计一对图像之间的空间对应关系。这些估计通常通过数值优化或深度网络的回归获得。理想情况下,这种估计器应能在输入图像变形的情况下保持一对图像之间的对应关系不变。具体来说,估计器应对期望的图像变换类具有等变性。在这项工作中,我们对多步深度配准网络的期望等变性属性进行了深入分析。基于这些分析,我们:1)引入了$[U,U]$等变性(网络对输入图像的相同变形的等变性)和$[W,U]$等变性(输入图像可以经历不同的变形)的概念;2)表明在合适的多步配准设置中,如果第一步具有$[W,U]$等变性,其余步骤具有$[U,U]$等变性,那么整体的$[W,U]$等变性就足够了;3)表明常见的位移预测网络仅对平移具有$[U,U]$等变性,而不是更强大的$[W,U]$等变性;4)展示了如何通过结合坐标注意机制与位移预测细化层(CARL)来实现多步$[W,U]$等变性。总体而言,我们的方法在多个三维医学图像配准任务上取得了出色的实际配准性能,并且在具有挑战性的腹部配准问题上优于现有的无监督方法。
要点提炼
- 图像配准估计图像间的空间对应关系,通常通过数值优化或深度网络实现。
- 理想情况下,配准估计器在输入图像变形的情况下应保持对应关系不变。这要求估计器对特定的图像变换具有等变性。
- 引入$[U,U]$等变性和$[W,U]$等变性的概念。
- 在多步配准中,若第一步具备$[W,U]$等变性且其余步骤具备$[U,U]$等变性,则足以实现整体的$[W,U]$等变性。
- 常见的位移预测网络仅对平移具有$[U,U]$等变性,缺乏更高级的$[W,U]$等变性。
- 提出结合坐标注意机制与位移预测细化层(CARL)的方法,实现多步$[W,U]$等变性。
点此查看论文截图
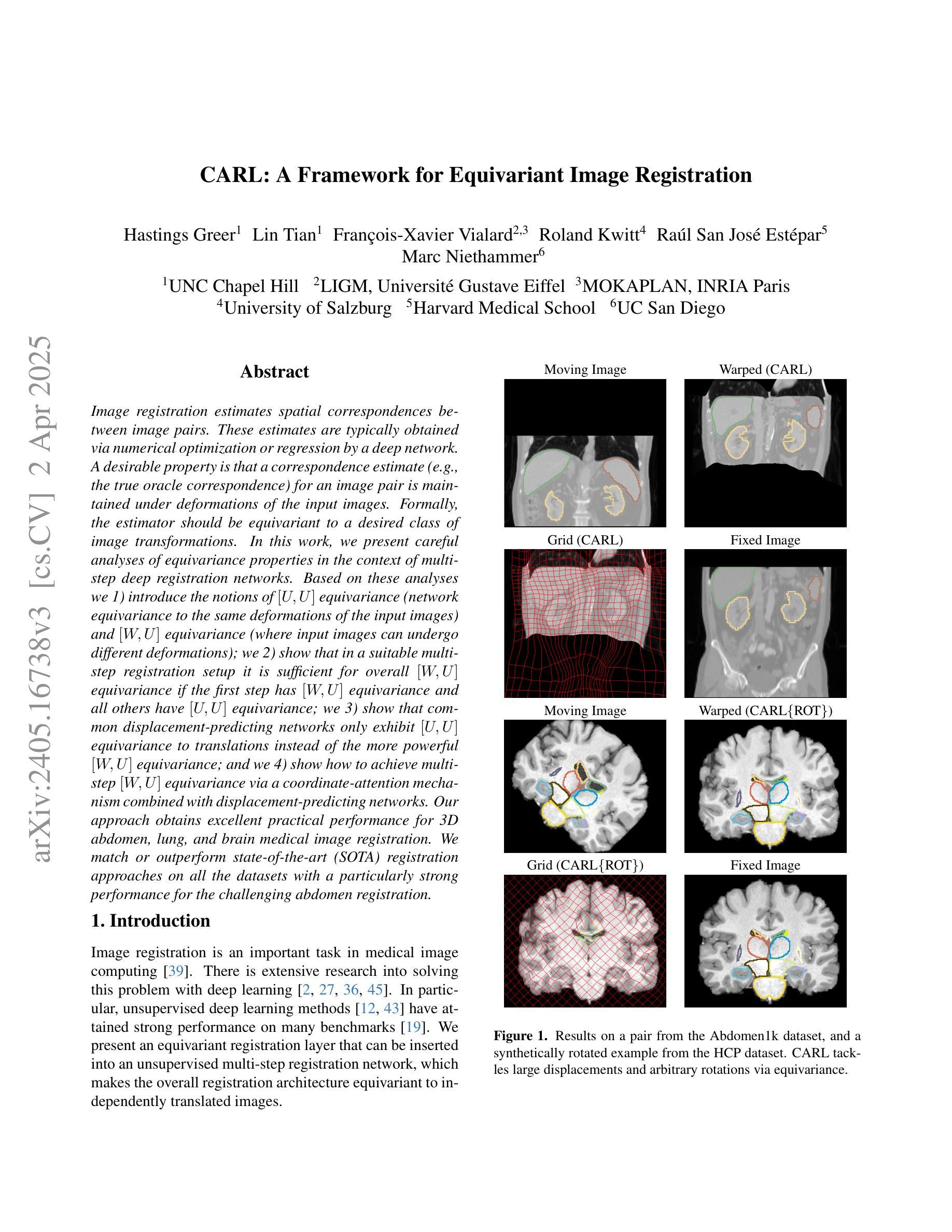
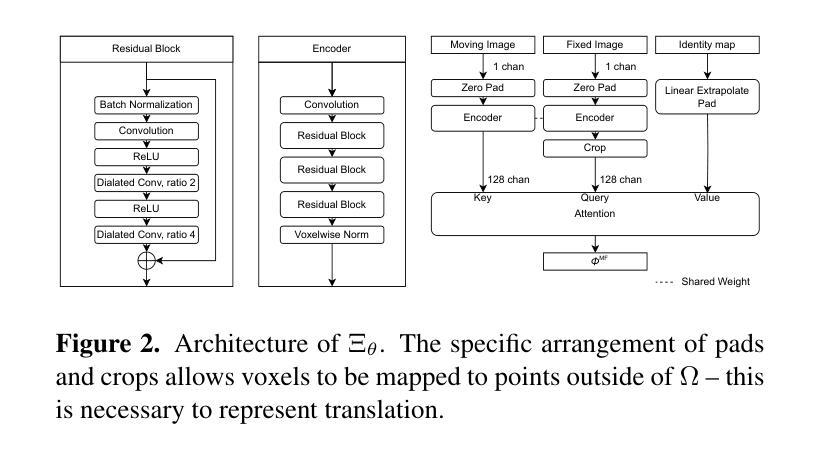
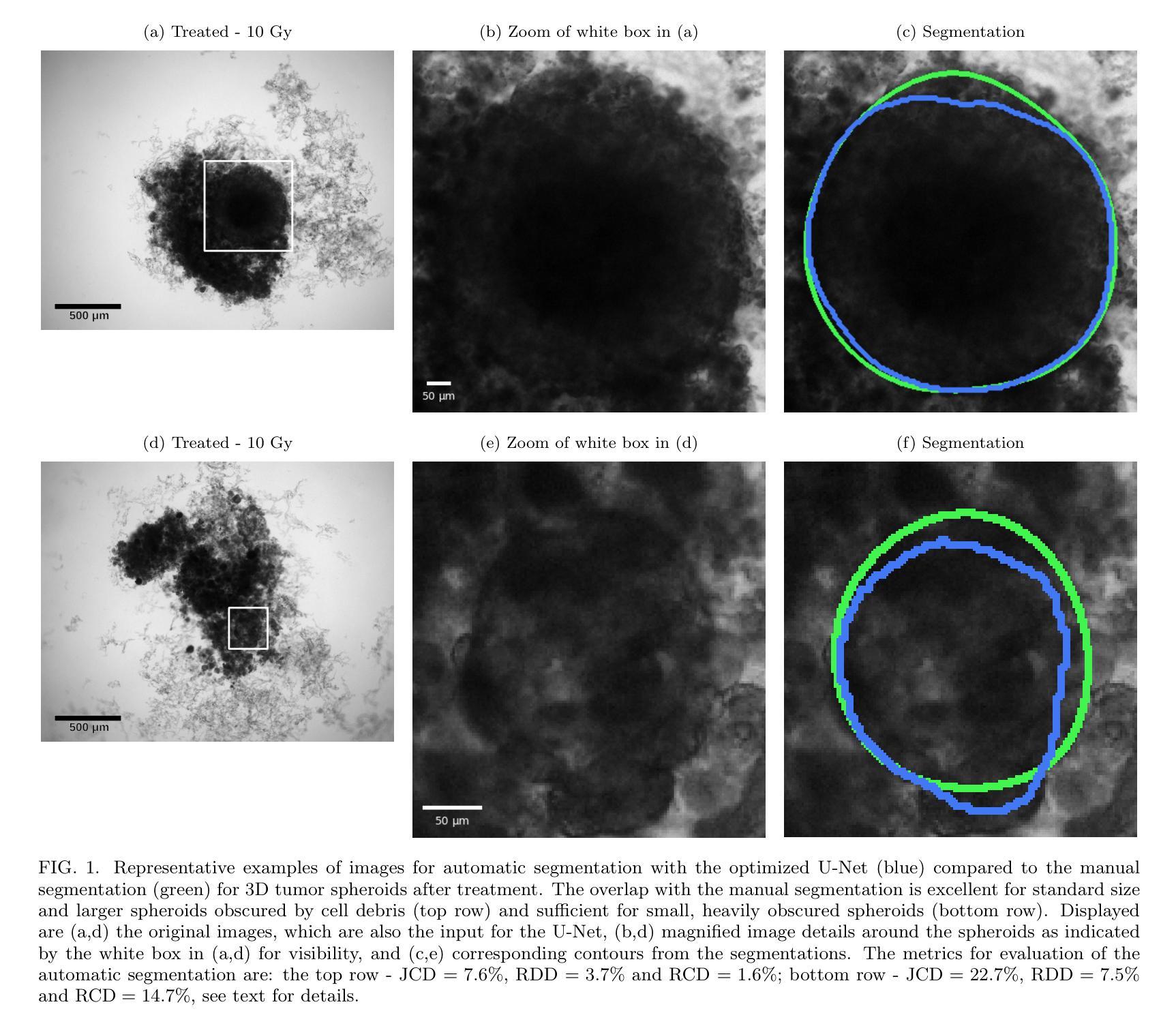
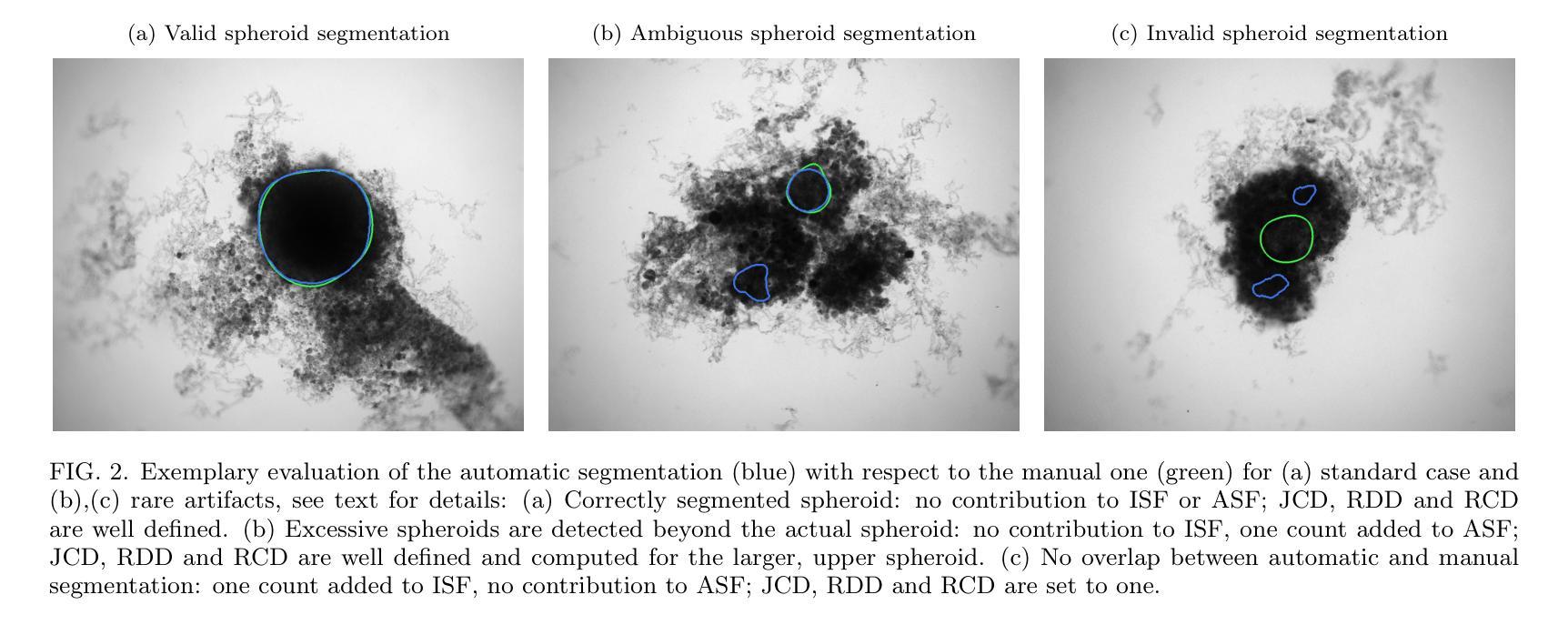
Image segmentation of treated and untreated tumor spheroids by Fully Convolutional Networks
Authors:Matthias Streller, Soňa Michlíková, Willy Ciecior, Katharina Lönnecke, Leoni A. Kunz-Schughart, Steffen Lange, Anja Voss-Böhme
Multicellular tumor spheroids (MCTS) are advanced cell culture systems for assessing the impact of combinatorial radio(chemo)therapy. They exhibit therapeutically relevant in-vivo-like characteristics from 3D cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions to radial pathophysiological gradients related to proliferative activity and nutrient/oxygen supply, altering cellular radioresponse. State-of-the-art assays quantify long-term curative endpoints based on collected brightfield image time series from large treated spheroid populations per irradiation dose and treatment arm. Here, spheroid control probabilities are documented analogous to in-vivo tumor control probabilities based on Kaplan-Meier curves. This analyses require laborious spheroid segmentation of up to 100.000 images per treatment arm to extract relevant structural information from the images, e.g., diameter, area, volume and circularity. While several image analysis algorithms are available for spheroid segmentation, they all focus on compact MCTS with clearly distinguishable outer rim throughout growth. However, treated MCTS may partly be detached and destroyed and are usually obscured by dead cell debris. We successfully train two Fully Convolutional Networks, UNet and HRNet, and optimize their hyperparameters to develop an automatic segmentation for both untreated and treated MCTS. We systematically validate the automatic segmentation on larger, independent data sets of spheroids derived from two human head-and-neck cancer cell lines. We find an excellent overlap between manual and automatic segmentation for most images, quantified by Jaccard indices at around 90%. For images with smaller overlap of the segmentations, we demonstrate that this error is comparable to the variations across segmentations from different biological experts, suggesting that these images represent biologically unclear or ambiguous cases.
多细胞肿瘤球体(MCTS)是评估组合放疗(化学疗法)影响的先进细胞培养系统。它们展现出与体内环境相关的治疗特性,从三维细胞与细胞外基质间的相互作用到与增殖活性、营养物/氧气供应相关的径向病理生理梯度变化,这些因素都影响细胞的放射反应。最新的实验方法基于从每个辐射剂量和治疗组收集的明视野图像时间序列,对长期治疗效果终点进行量化评估大型处理球体人群。在此,球体控制概率的记录方式与体内肿瘤控制概率类似,基于Kaplan-Meier曲线。这些分析需要繁琐的球体分割工作,每个治疗组可能需要处理高达10万张图像,以从图像中提取相关的结构信息,例如直径、面积、体积和圆度。虽然有几个图像分析算法可用于球体分割,但它们都侧重于紧凑的MCTS,在其生长过程中外围轮廓清晰可辨。然而,经过处理的MCTS可能会部分脱落和破坏,通常会被死细胞碎片遮蔽。我们成功训练了两个全卷积网络,即UNet和HRNet,并优化了其超参数,以实现对未处理和经过处理的MCTS的自动分割。我们对来自两个人头颈部癌细胞系的更大独立数据集的球体进行了自动分割的系统验证。我们发现大多数图像的自动分割与手动分割之间有着极好的重叠程度,Jaccard指数约为90%。对于分割重叠较少的图像,我们证明这种错误与不同生物学专家之间的分割差异相当,这表明这些图像代表了生物学上不明确或模糊的情况。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 30 pages, 23 figures
摘要
多细胞肿瘤球状体(MCTS)是评估组合放疗(化疗)影响的高级细胞培养系统。它们展现出从三维细胞间与细胞基质相互作用到与增殖活性、营养/氧气供应相关的径向病理生理梯度的治疗相关体内类似特性,这些特性改变了细胞的放射反应。基于从大型处理球状体群体收集的明视野图像时间序列,当前最先进的实验长期疗效评估端点记录类似于体内肿瘤控制概率的球状体控制概率。但这种分析需要繁琐的球状体分割,最多可达每个治疗手臂的10万张图像,以从图像中提取相关的结构信息,例如直径、面积、体积和圆度。虽然有多种图像分析算法可用于球状体分割,但它们主要针对紧凑的MCTS,生长过程中具有清晰可辨的外缘。然而,经过处理的MCTS可能会部分脱落和破坏,通常会被死细胞碎片遮蔽。我们成功训练了两个全卷积网络UNet和HRNet并优化了其超参数以实现对未处理和经过处理的MCTS的自动分割。我们对来自两种人头颈部癌细胞系的独立数据集上的球状体进行了系统验证。我们发现大多数图像的自动分割与手动分割之间有很好的重叠,雅卡尔指数约为90%。对于分割重叠较小的图像,我们证明这种误差与不同生物学专家之间的分割变化相当,这表明这些图像代表了生物学上不清楚或模糊的情况。
关键见解
- 多细胞肿瘤球状体(MCTS)是评估组合放疗和化疗效果的高级细胞培养系统,具有体内类似的特性。
- 当前分析需要繁琐的球状体分割以提取相关结构信息。
- 现有的图像分析算法主要针对具有清晰外缘的紧凑MCTS。
- 经过治疗的MCTS可能部分脱落和破坏,并被死细胞碎片遮蔽。
- 训练了UNet和HRNet两个全卷积网络进行自动分割。
- 在独立数据集上验证了自动分割的效果,发现大多数图像的自动分割与手动分割之间有很好的重叠。
点此查看论文截图

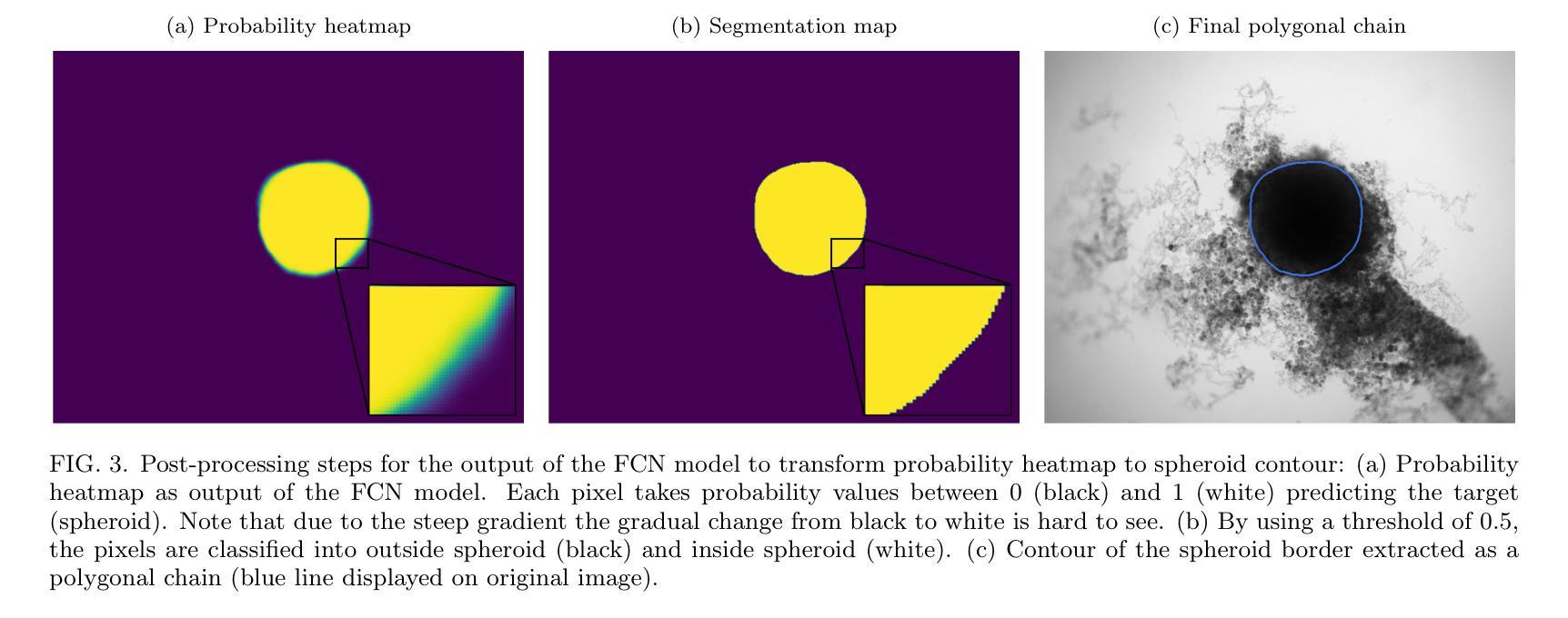
Masked LoGoNet: Fast and Accurate 3D Image Analysis for Medical Domain
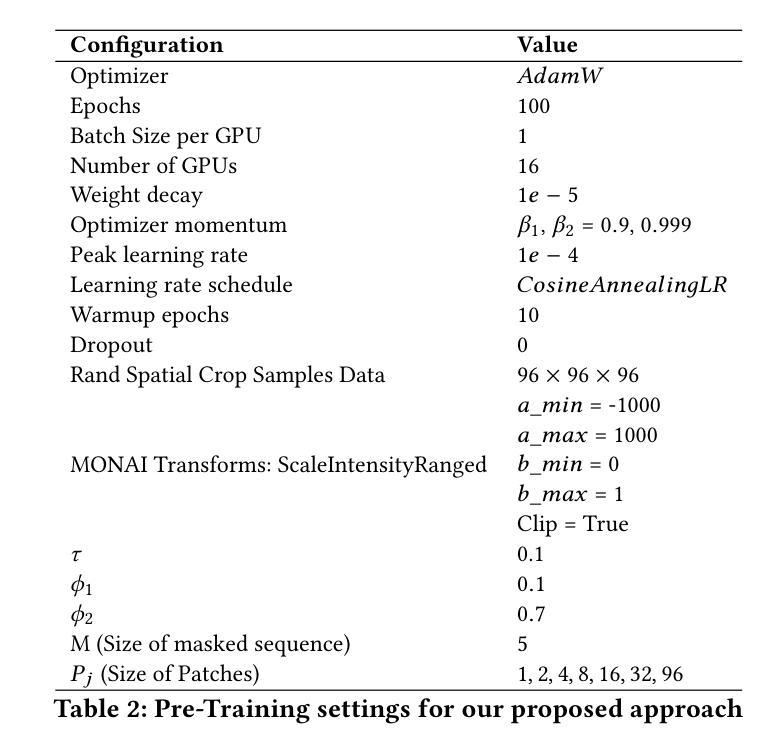
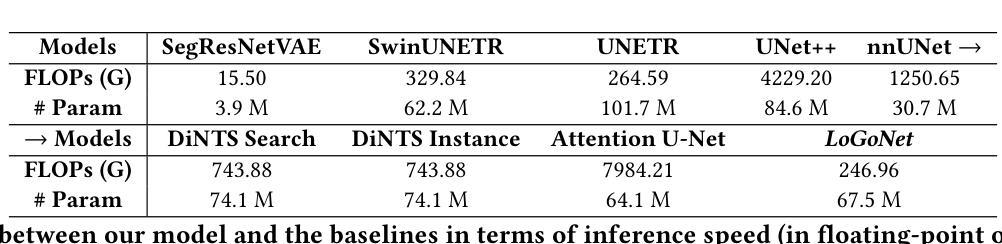
Authors:Amin Karimi Monsefi, Payam Karisani, Mengxi Zhou, Stacey Choi, Nathan Doble, Heng Ji, Srinivasan Parthasarathy, Rajiv Ramnath
Standard modern machine-learning-based imaging methods have faced challenges in medical applications due to the high cost of dataset construction and, thereby, the limited labeled training data available. Additionally, upon deployment, these methods are usually used to process a large volume of data on a daily basis, imposing a high maintenance cost on medical facilities. In this paper, we introduce a new neural network architecture, termed LoGoNet, with a tailored self-supervised learning (SSL) method to mitigate such challenges. LoGoNet integrates a novel feature extractor within a U-shaped architecture, leveraging Large Kernel Attention (LKA) and a dual encoding strategy to capture both long-range and short-range feature dependencies adeptly. This is in contrast to existing methods that rely on increasing network capacity to enhance feature extraction. This combination of novel techniques in our model is especially beneficial in medical image segmentation, given the difficulty of learning intricate and often irregular body organ shapes, such as the spleen. Complementary, we propose a novel SSL method tailored for 3D images to compensate for the lack of large labeled datasets. The method combines masking and contrastive learning techniques within a multi-task learning framework and is compatible with both Vision Transformer (ViT) and CNN-based models. We demonstrate the efficacy of our methods in numerous tasks across two standard datasets (i.e., BTCV and MSD). Benchmark comparisons with eight state-of-the-art models highlight LoGoNet’s superior performance in both inference time and accuracy.
标准现代机器学习成像方法在面对医疗应用时遇到了挑战,主要是由于数据集构建的成本高昂,因此可用的标记训练数据有限。此外,在部署后,这些方法通常用于处理每天的大量数据,给医疗机构带来了高昂的维护成本。在本文中,我们介绍了一种新的神经网络架构,称为LoGoNet,并配备了一种量身定制的自我监督学习(SSL)方法来缓解这些挑战。LoGoNet在一个U形架构内集成了一种新型特征提取器,利用大内核注意力(LKA)和双编码策略来巧妙地捕捉长短范围的特征依赖关系。这与现有方法不同,后者依赖于增加网络容量来增强特征提取能力。模型中结合的新技术对于医学图像分割特别有益,考虑到学习复杂且通常不规则的器官形状(如脾脏)的困难性。此外,我们提出了一种针对3D图像的新型SSL方法,以弥补大型标记数据集的缺乏。该方法结合多任务学习框架内的屏蔽和对比学习技术,可与Vision Transformer(ViT)和CNN模型兼容。我们在两个标准数据集(即BTCV和MSD)的多个任务中证明了我们的方法的有效性。与八种最新模型的基准比较突显了LoGoNet在推理时间和准确性方面的卓越性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to KDD 2024
Summary
本文介绍了一种新的神经网络架构LoGoNet,结合自监督学习方法,用于解决医疗图像分析中数据集构建成本高、训练数据有限及部署后维护成本高等问题。LoGoNet采用U型架构结合大型内核注意力机制与双编码策略,能灵活捕捉长短距离特征依赖关系,特别适合医学图像分割。同时,针对三维图像提出新型自监督学习方法,以弥补缺乏大量标记数据集的不足。该方法结合掩码和对比学习技术,在多任务学习框架内兼容ViT和CNN模型。在两项标准数据集上的实验表明,LoGoNet在推理时间和准确性方面均表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- LoGoNet是一种新型的神经网络架构,用于解决医疗图像分析中的挑战。
- 该架构结合了自监督学习方法,以应对数据集构建成本高和训练数据有限的问题。
- LoGoNet采用U型架构、大型内核注意力机制和双编码策略,能有效捕捉特征依赖关系。
- 提出了一种新型自监督学习方法,适用于三维图像,以弥补缺乏标记数据集的不足。
- 该方法结合了掩码和对比学习技术,并在多任务学习框架内实施。
- LoGoNet在医学图像分割方面表现出卓越性能,特别是在学习复杂和不规则器官形状方面。
点此查看论文截图

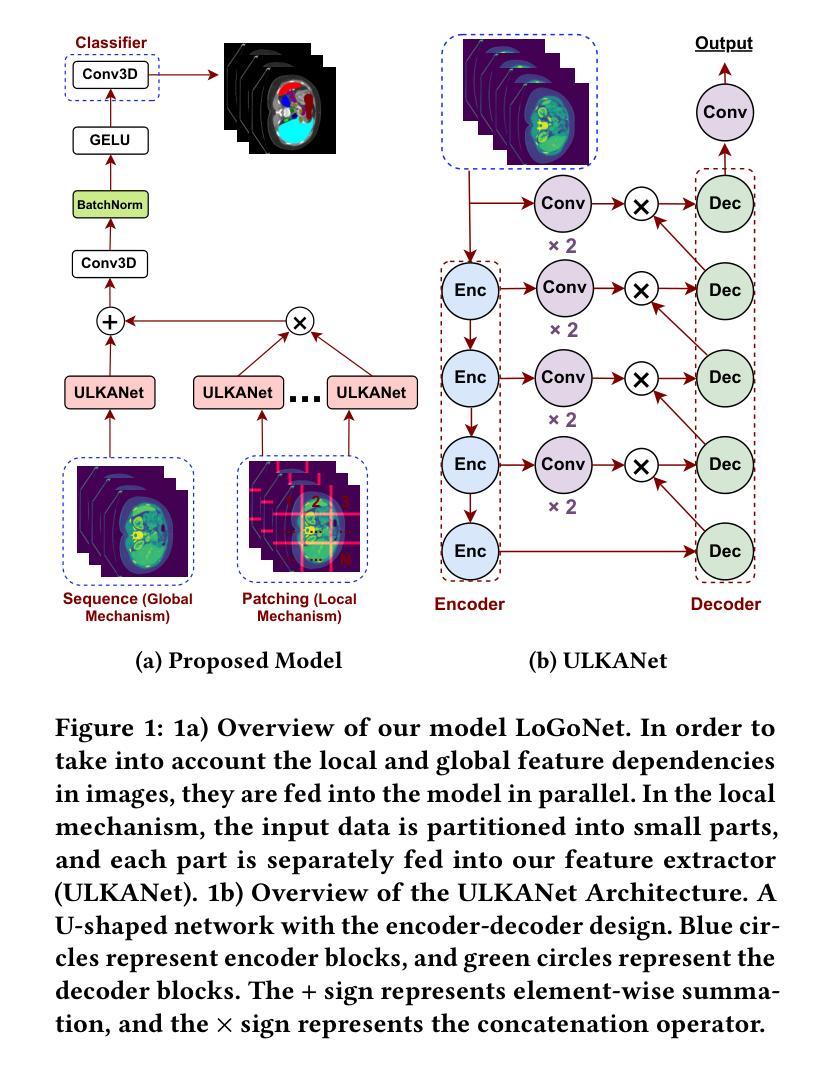
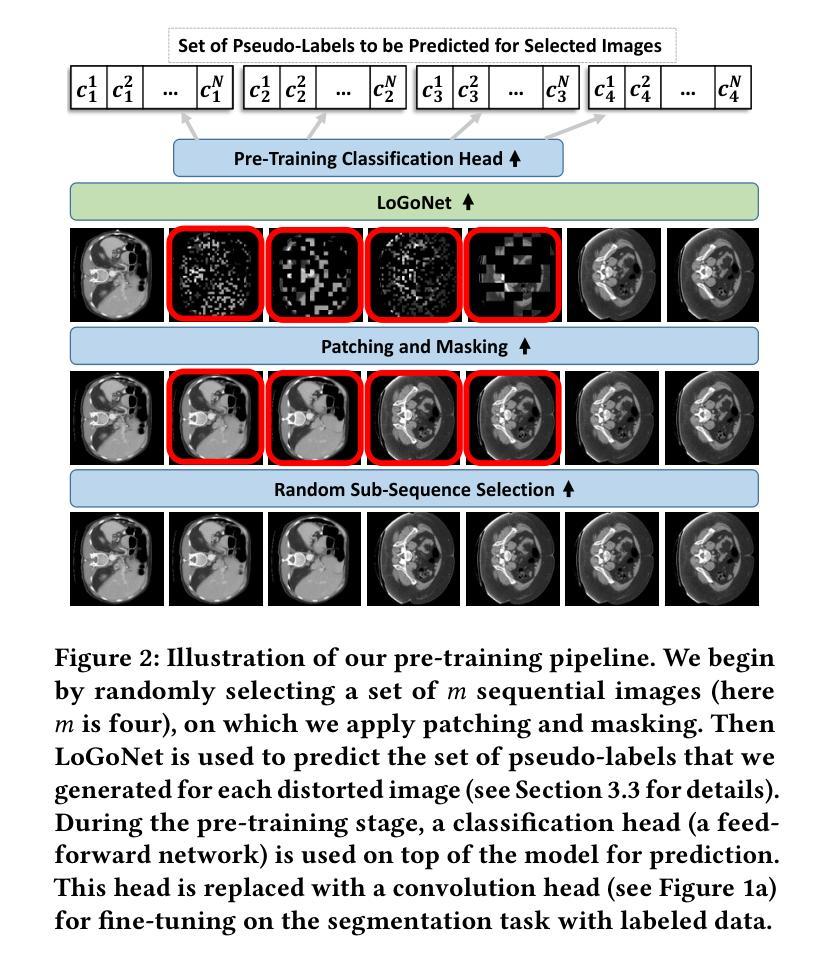
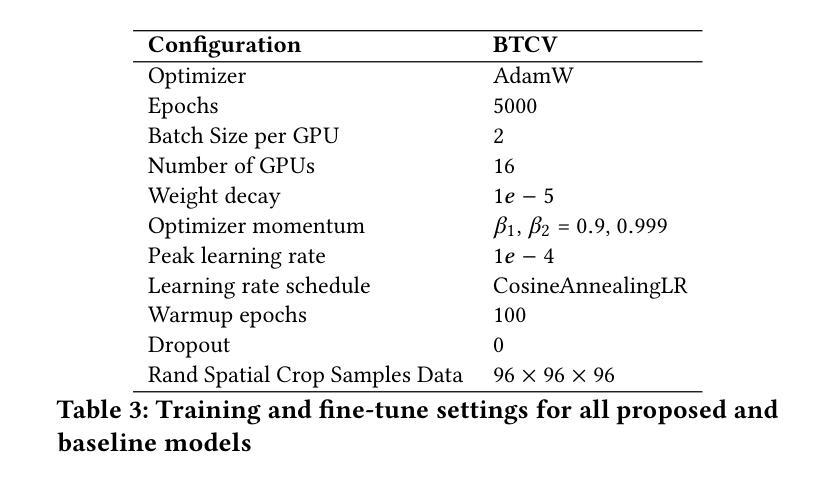
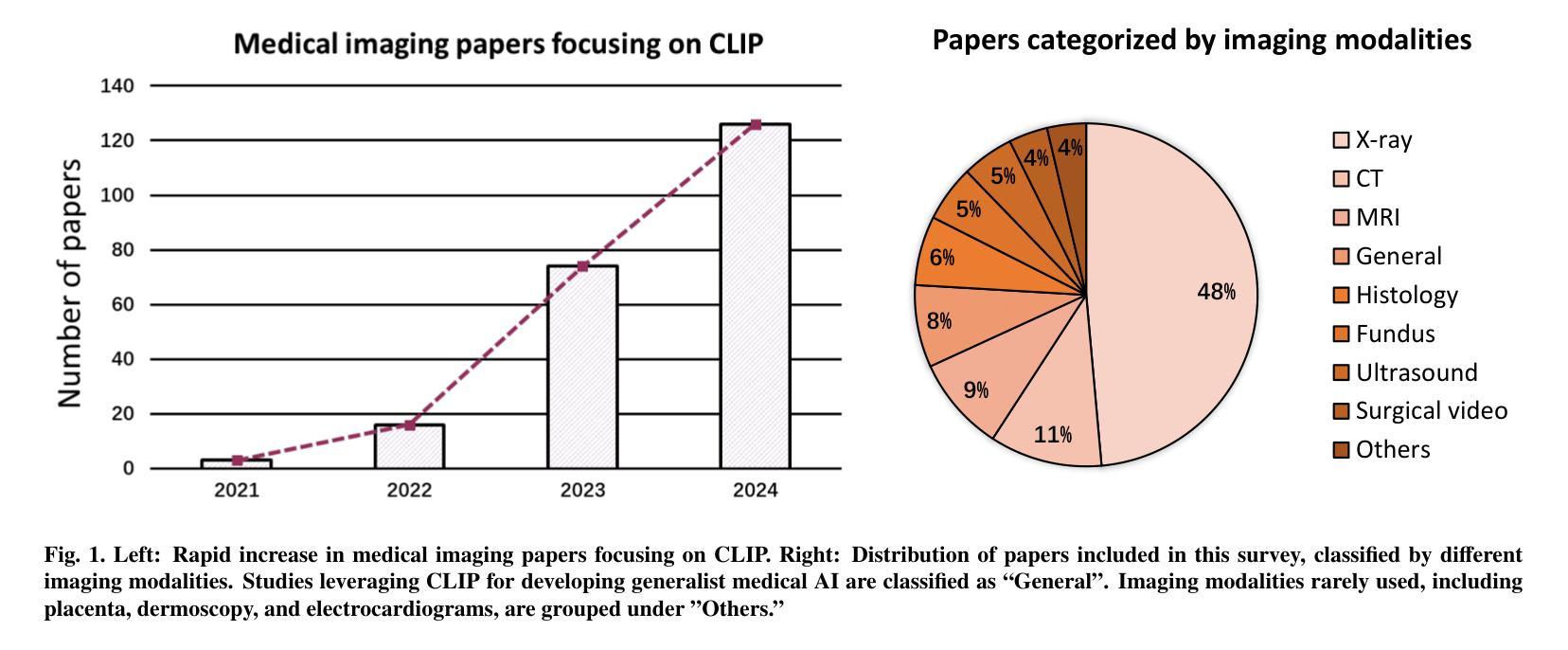
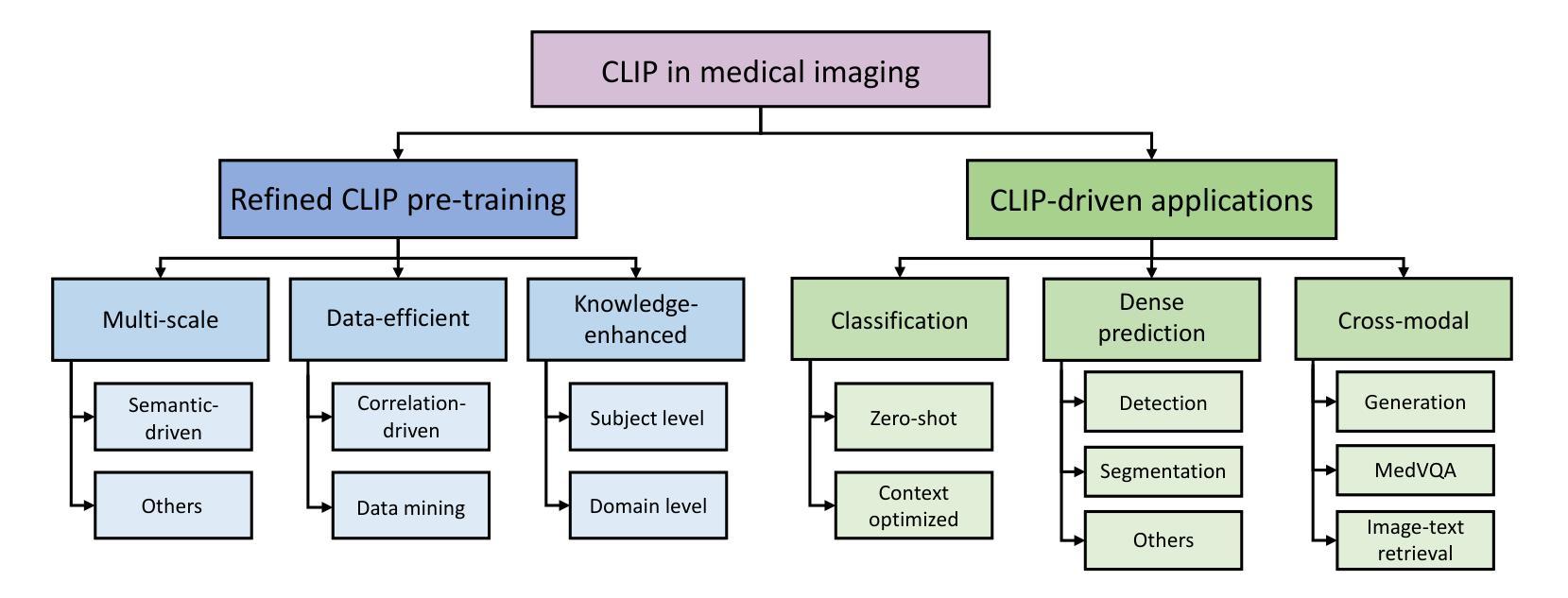
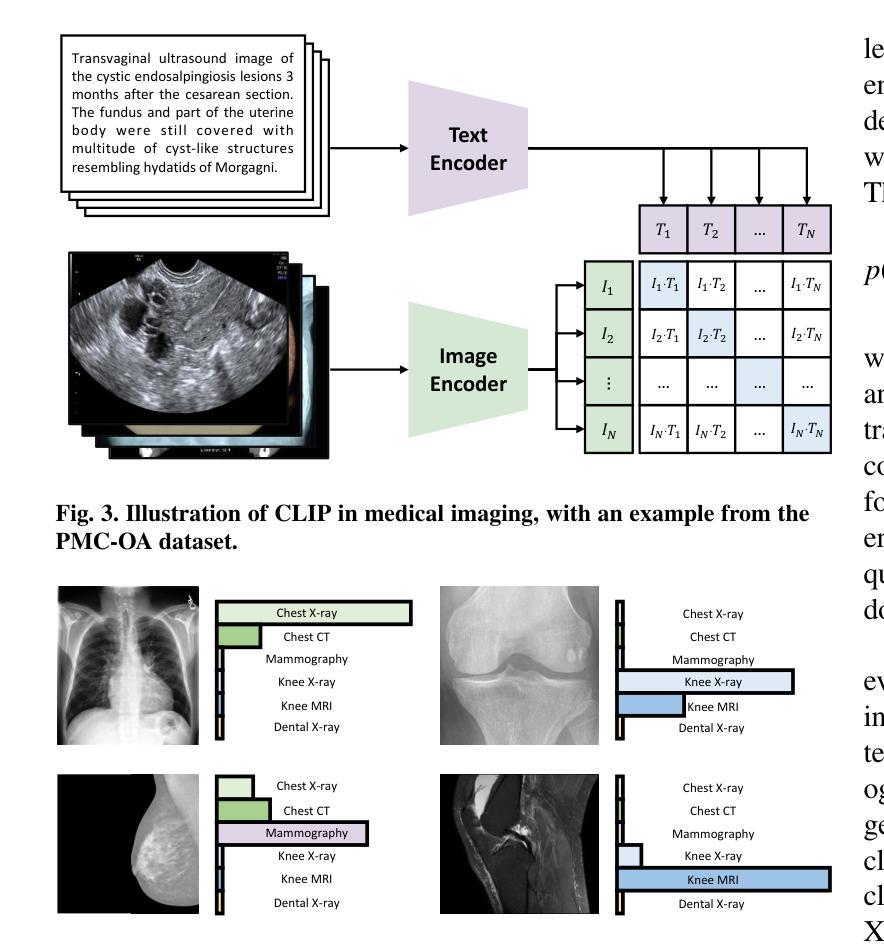
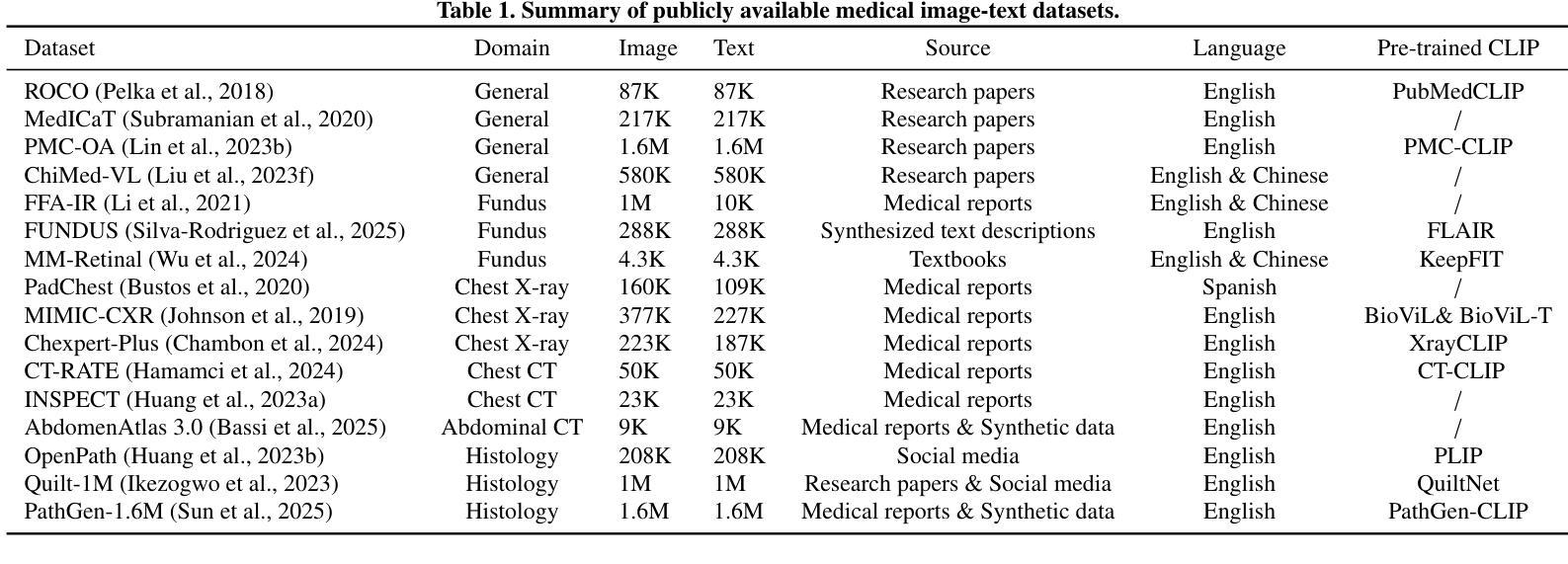
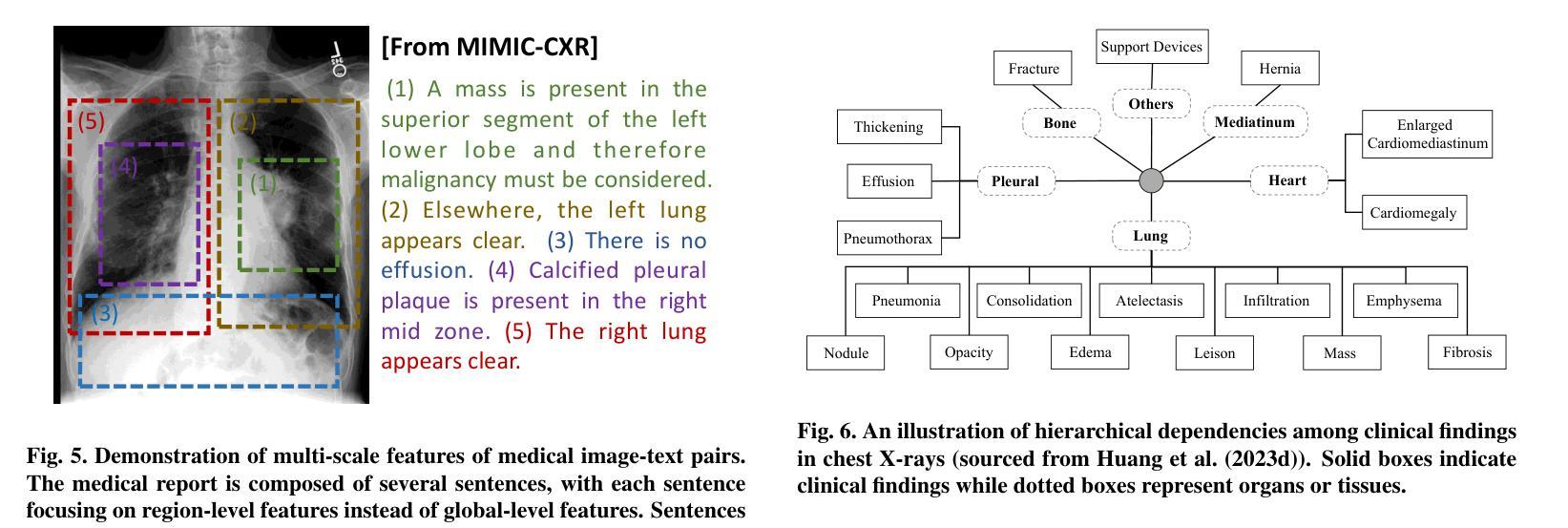
CLIP in Medical Imaging: A Survey
Authors:Zihao Zhao, Yuxiao Liu, Han Wu, Mei Wang, Yonghao Li, Sheng Wang, Lin Teng, Disheng Liu, Zhiming Cui, Qian Wang, Dinggang Shen
Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP), a simple yet effective pre-training paradigm, successfully introduces text supervision to vision models. It has shown promising results across various tasks due to its generalizability and interpretability. The use of CLIP has recently gained increasing interest in the medical imaging domain, serving as a pre-training paradigm for image-text alignment, or a critical component in diverse clinical tasks. With the aim of facilitating a deeper understanding of this promising direction, this survey offers an in-depth exploration of the CLIP within the domain of medical imaging, regarding both refined CLIP pre-training and CLIP-driven applications. In this paper, we (1) first start with a brief introduction to the fundamentals of CLIP methodology; (2) then investigate the adaptation of CLIP pre-training in the medical imaging domain, focusing on how to optimize CLIP given characteristics of medical images and reports; (3) further explore practical utilization of CLIP pre-trained models in various tasks, including classification, dense prediction, and cross-modal tasks; and (4) finally discuss existing limitations of CLIP in the context of medical imaging, and propose forward-looking directions to address the demands of medical imaging domain. Studies featuring technical and practical value are both investigated. We expect this survey will provide researchers with a holistic understanding of the CLIP paradigm and its potential implications. The project page of this survey can also be found on https://github.com/zhaozh10/Awesome-CLIP-in-Medical-Imaging.
对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)是一种简单有效的预训练范式,成功地将文本监督引入视觉模型。由于其通用性和可解释性,它在各种任务中显示出有前途的结果。CLIP在医学成像领域的使用日益受到关注,既作为图像文本对齐的预训练范式,也是多种临床任务的关键组件。为了加深对这一有前途方向的深入理解,本调查对医学成像领域的CLIP进行了深入研究,涉及精细的CLIP预训练和CLIP驱动的应用程序。在本文中,我们(1)首先从CLIP方法的基本原理开始简要介绍;(2)然后研究CLIP预训练在医学成像领域的应用,重点关注如何根据医学图像和报告的特性优化CLIP;(3)进一步探索CLIP预训练模型在各种任务中的实际应用,包括分类、密集预测和跨模态任务;(4)最后讨论CLIP在医学成像方面的现有局限性,并提出前瞻性的方向以满足医学成像领域的需求。我们调查了具有技术和实用价值的项目。我们希望此次调查能为研究人员提供对CLIP范式及其潜在影响的全面了解。本调查的项目页面也可在https://github.com/zhaozh10/Awesome-CLIP-in-Medical-Imaging找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page available at https://github.com/zhaozh10/Awesome-CLIP-in-Medical-Imaging
Summary
本文详细介绍了Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training(CLIP)在医学成像领域的应用。文章首先简要介绍了CLIP方法的基本原理,然后探讨了CLIP在医学成像领域的适应性预训练,并深入探索了CLIP在分类、密集预测和跨模态任务等实际应用中的表现。文章还讨论了CLIP在医学成像方面的现有局限性,并提出了未来研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP是一种简单有效的预训练方法,成功地将文本监督引入到视觉模型中。
- CLIP在多个任务中展现出良好的通用性和可解释性。
- 在医学成像领域,CLIP被用作图像文本对齐的预训练或临床任务的关键组件。
- 文章介绍了CLIP在医学成像领域的精细化预训练。
- CLIP在分类、密集预测和跨模态任务等医学成像任务中有实际应用。
- 文章讨论了CLIP在医学成像方面的局限性。
点此查看论文截图

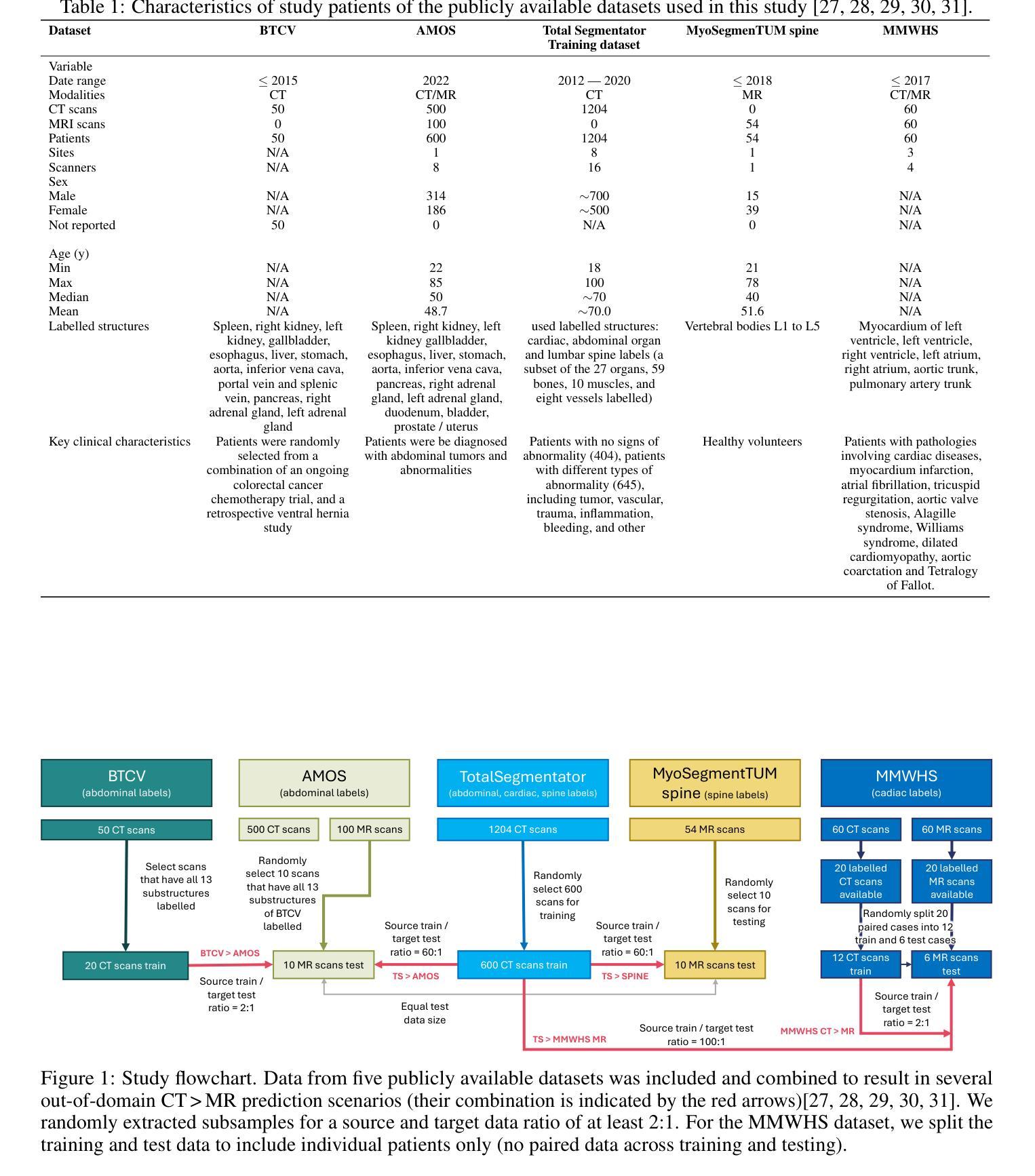
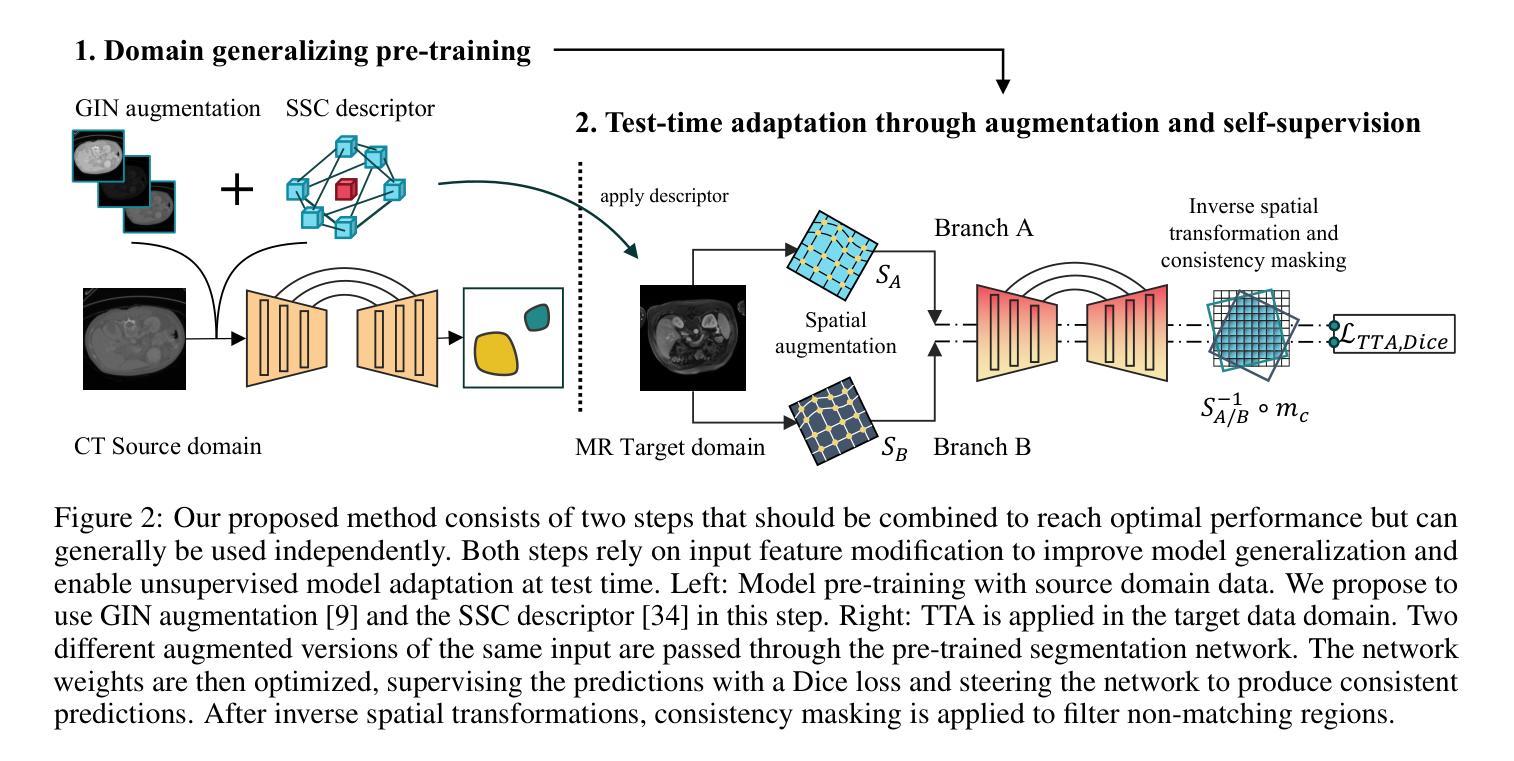
DG-TTA: Out-of-domain Medical Image Segmentation through Augmentation and Descriptor-driven Domain Generalization and Test-Time Adaptation
Authors:Christian Weihsbach, Christian N. Kruse, Alexander Bigalke, Mattias P. Heinrich
Purpose: Applying pre-trained medical deep learning segmentation models on out-of-domain images often yields predictions of insufficient quality. In this study, we propose to use a powerful generalizing descriptor along with augmentation to enable domain-generalized pre-training and test-time adaptation, achieving high-quality segmentation in unseen domains. Materials and Methods: In this retrospective study five different publicly available datasets (2012 to 2022) including 3D CT and MRI images are used to evaluate segmentation performance in out-of-domain scenarios. The settings include abdominal, spine, and cardiac imaging. The data is randomly split into training and test samples. Domain-generalized pre-training on source data is used to obtain the best initial performance in the target domain. We introduce the combination of the generalizing SSC descriptor and GIN intensity augmentation for optimal generalization. Segmentation results are subsequently optimized at test time, where we propose to adapt the pre-trained models for every unseen scan with a consistency scheme using the same augmentation-descriptor combination. The segmentation is evaluated using Dice similarity and Hausdorff distance and the significance of improvements is tested with the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Results: The proposed generalized pre-training and subsequent test-time adaptation improves model performance significantly in CT to MRI cross-domain prediction for abdominal (+46.2% and +28.2% Dice), spine (+72.9%), and cardiac (+14.2% and +55.7% Dice) scenarios (p<0.001). Conclusion: Our method enables optimal, independent usage of medical image source and target data and bridges domain gaps successfully with a compact and efficient methodology. Open-source code available at: https://github.com/multimodallearning/DG-TTA
目的:将在特定领域预训练的医学深度学习分割模型应用于非领域图像通常会产生质量不足的预测结果。本研究中,我们提出使用强大的通用描述符和增强技术,以实现领域通用预训练和测试时间适应,从而在未见领域实现高质量分割。
材料与方法:本研究为一项回顾性研究,使用了五个不同公共数据集(2012年至2022年),包括3D CT和MRI图像,以评估非领域场景中分割性能。设置包括腹部、脊椎和心脏成像。数据被随机分割为训练样本和测试样本。在源数据上进行领域通用预训练,以获得目标领域的最佳初始性能。我们引入了通用SSC描述符和GIN强度增强的组合,以实现最佳通用性。随后在测试时间优化分割结果,我们提出用一致性方案,利用相同的增强-描述符组合,对每一次未见扫描进行预训练模型的适应。使用Dice相似度和Hausdorff距离对分割结果进行评估,并使用Wilcoxon符号秩检验来测试改进的重要性。
结果:所提出的通用预训练和随后的测试时间适应方法,显著提高了CT到MRI跨领域预测中的模型性能,在腹部(+46.2%和+28.2% Dice)、脊椎(+72.9%)和心脏(+14.2%和+55.7% Dice)场景中应用效果显著(p<0.001)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种使用通用描述符与数据增强方法实现跨域医学影像分割的预训练与测试时间自适应方法。该研究在多个公开数据集上进行回顾性实验验证,结果显示该方法在CT至MRI跨域预测中显著提高模型性能,特别是在腹部、脊椎和心脏影像场景中。
Key Takeaways
- 提出使用通用描述符与数据增强进行域泛化预训练,以提高在未见域中的分割质量。
- 实验采用五个公开数据集,涵盖3D CT和MRI图像,用于评估跨域场景中的分割性能。
- 通过随机分割数据为训练集和测试集,进行源数据的域泛化预训练,以获得目标域中的最佳初始性能。
- 引入结合SSC通用描述符和GIN强度增强的方法,实现最佳泛化。
- 在测试时优化分割结果,通过一致性方案适应每个未见扫描,同时使用相同的增强-描述符组合。
- 使用Dice相似度和Hausdorff距离评估分割效果,并通过Wilcoxon符号秩检验评估改进显著性。
点此查看论文截图

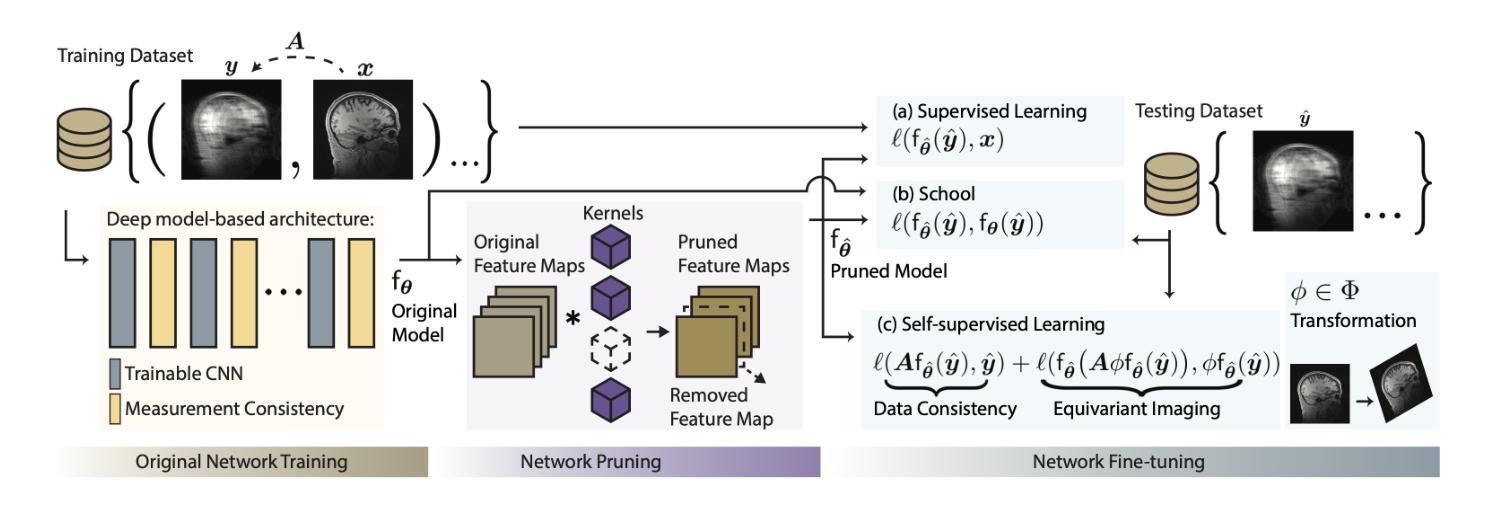
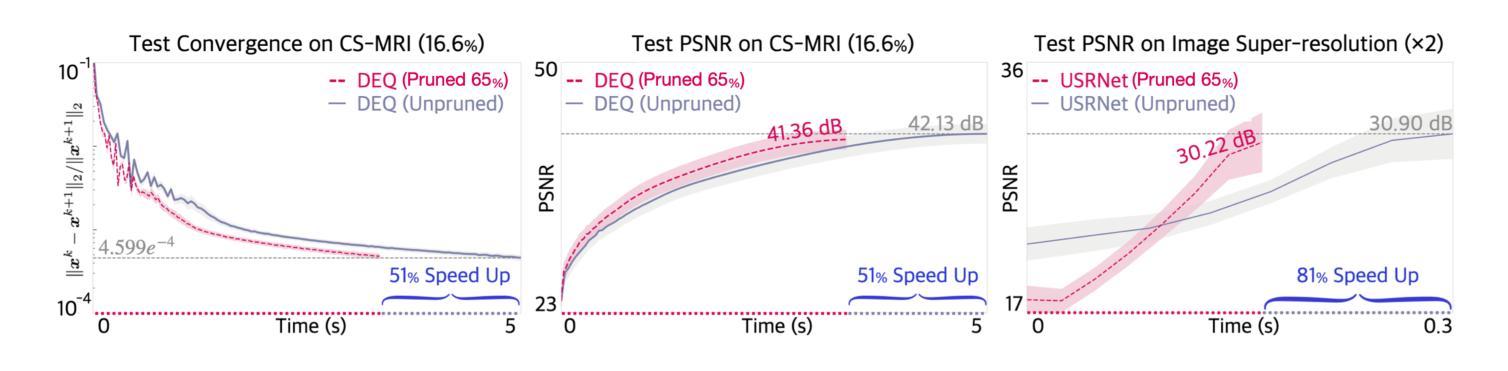
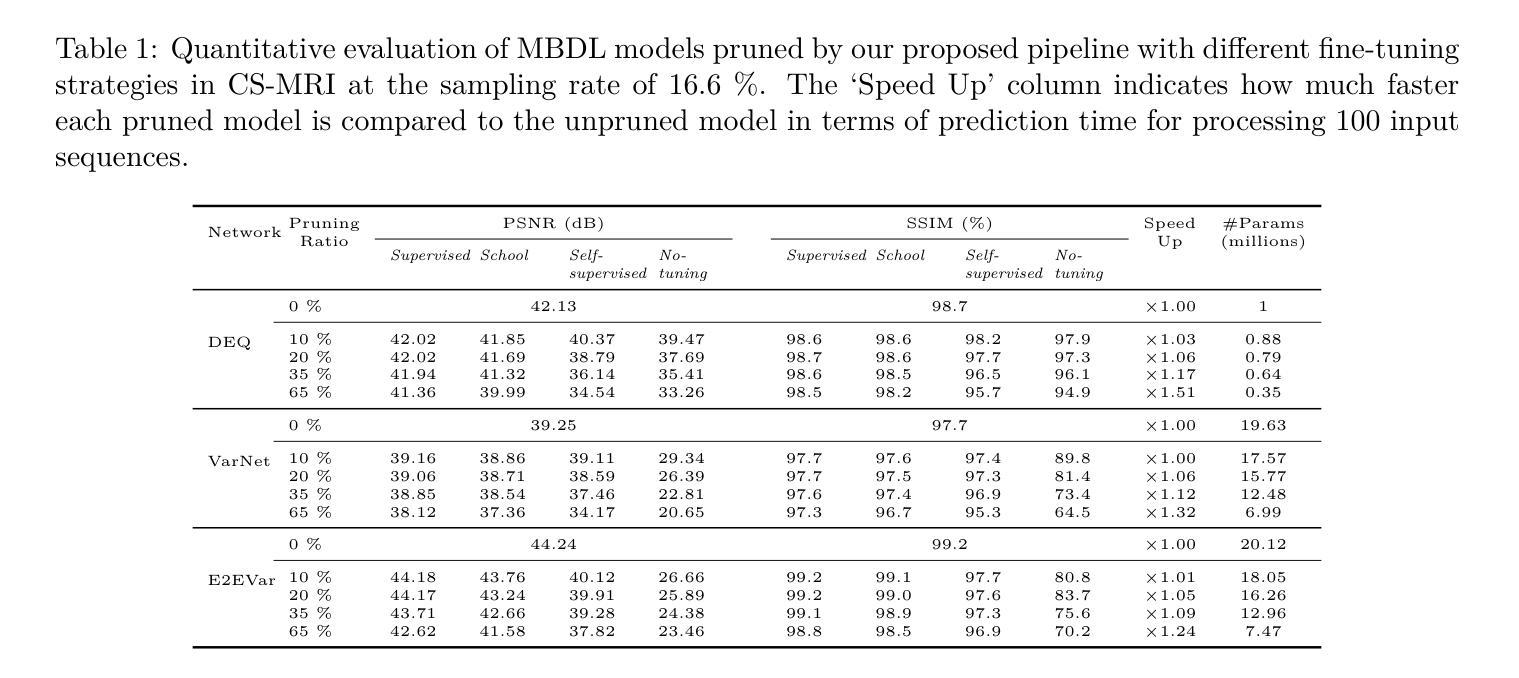
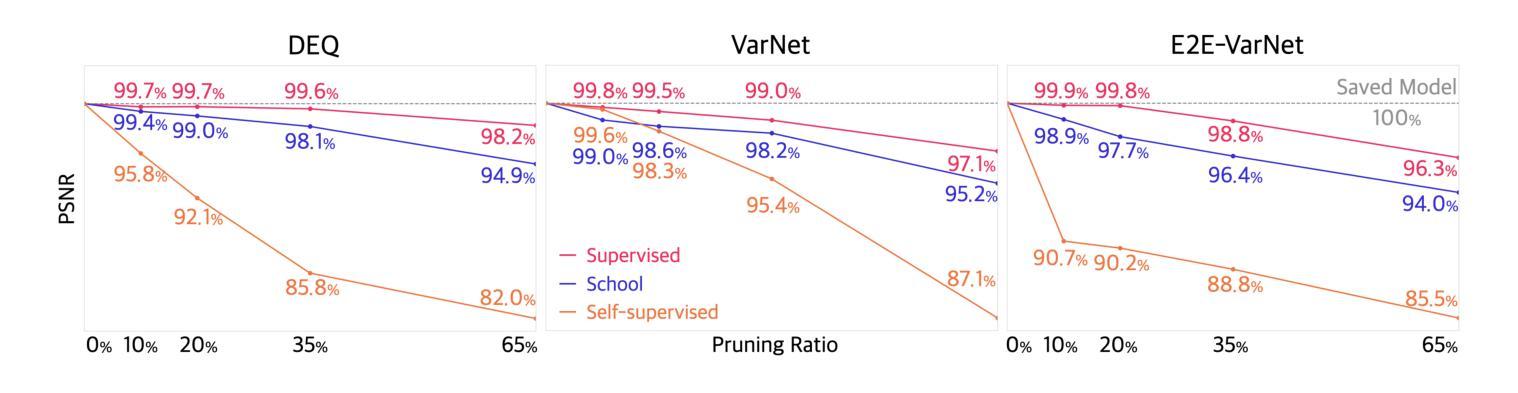
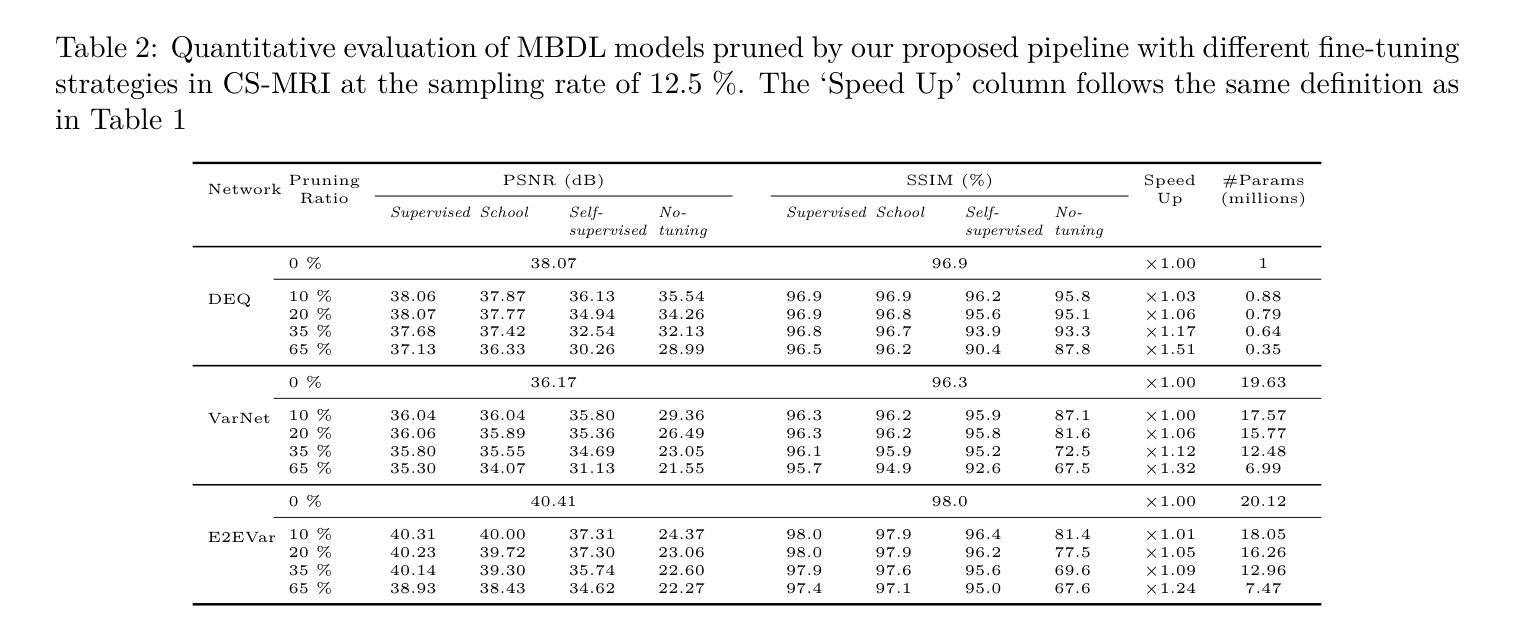
Efficient Model-Based Deep Learning via Network Pruning and Fine-Tuning
Authors:Chicago Y. Park, Weijie Gan, Zihao Zou, Yuyang Hu, Zhixin Sun, Ulugbek S. Kamilov
Model-based deep learning (MBDL) is a powerful methodology for designing deep models to solve imaging inverse problems. MBDL networks can be seen as iterative algorithms that estimate the desired image using a physical measurement model and a learned image prior specified using a convolutional neural net (CNNs). The iterative nature of MBDL networks increases the test-time computational complexity, which limits their applicability in certain large-scale applications. Here we make two contributions to address this issue: First, we show how structured pruning can be adopted to reduce the number of parameters in MBDL networks. Second, we present three methods to fine-tune the pruned MBDL networks to mitigate potential performance loss. Each fine-tuning strategy has a unique benefit that depends on the presence of a pre-trained model and a high-quality ground truth. We show that our pruning and fine-tuning approach can accelerate image reconstruction using popular deep equilibrium learning (DEQ) and deep unfolding (DU) methods by 50% and 32%, respectively, with nearly no performance loss. This work thus offers a step forward for solving inverse problems by showing the potential of pruning to improve the scalability of MBDL. Code is available at https://github.com/wustl-cig/MBDL_Pruning .
基于模型的深度学习(MBDL)是一种强大的方法论,用于设计深度模型以解决成像反问题。MBDL网络可以看作是使用物理测量模型和通过卷积神经网络(CNN)指定的学习图像先验来估计所需图像的迭代算法。MBDL网络的迭代性质增加了测试时的计算复杂性,这限制了其在某些大规模应用中的适用性。在这里,我们对这个问题做出了两个贡献:首先,我们展示了如何采用结构化修剪来减少MBDL网络中的参数数量。其次,我们提出了三种方法来微调修剪过的MBDL网络,以减轻潜在的性能损失。每种微调策略都具有独特的优势,这取决于是否存在预训练模型和高质量的真实标签。我们展示了我们的修剪和微调方法可以通过近乎不损失性能的情况下,使用流行的深度均衡学习(DEQ)和深度展开(DU)方法分别将图像重建速度提高50%和32%。因此,这项工作通过展示修剪在提高MBDL可扩展性方面的潜力,为解决反问题提供了前进的一步。代码可通过https://github.com/wustl-cig/MBDL_Pruning获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
模型驱动的深度学习(MBDL)是解决成像反问题的强大方法。本文提出两项贡献以减轻MBDL网络的计算复杂性,首先是通过结构修剪减少其参数数量,然后提供三种方法来微调修剪后的MBDL网络以减少潜在的性能损失。研究发现,该方法能够在对流行深度平衡学习(DEQ)和深度展开(DU)方法进行图像重建时,分别提高约50%和32%的计算速度,同时几乎不损失性能。此研究展示了修剪在提升MBDL可扩展性方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 模型驱动的深度学习(MBDL)是解决成像反问题的有效方法。
- 结构修剪可以减少MBDL网络的参数数量。
- 通过三种微调方法,可以减轻修剪后MBDL网络的性能损失。
- 结构修剪和微调方法可以加速图像重建过程。
- 对深度平衡学习(DEQ)和深度展开(DU)方法的加速效果分别达到了约50%和32%。
- 修剪方法提高了MBDL的可扩展性。
点此查看论文截图