⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-08 更新
MedSAM2: Segment Anything in 3D Medical Images and Videos
Authors:Jun Ma, Zongxin Yang, Sumin Kim, Bihui Chen, Mohammed Baharoon, Adibvafa Fallahpour, Reza Asakereh, Hongwei Lyu, Bo Wang
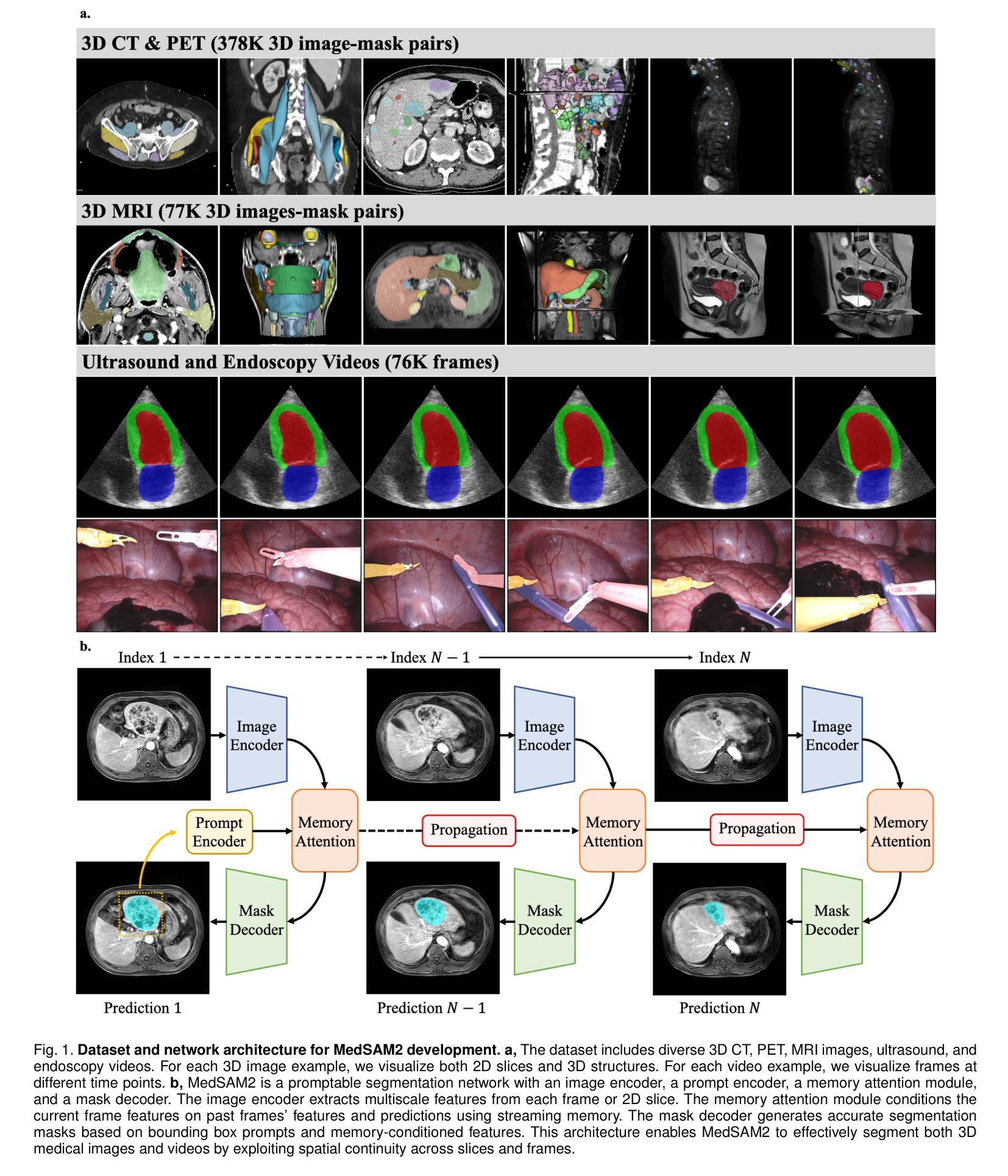
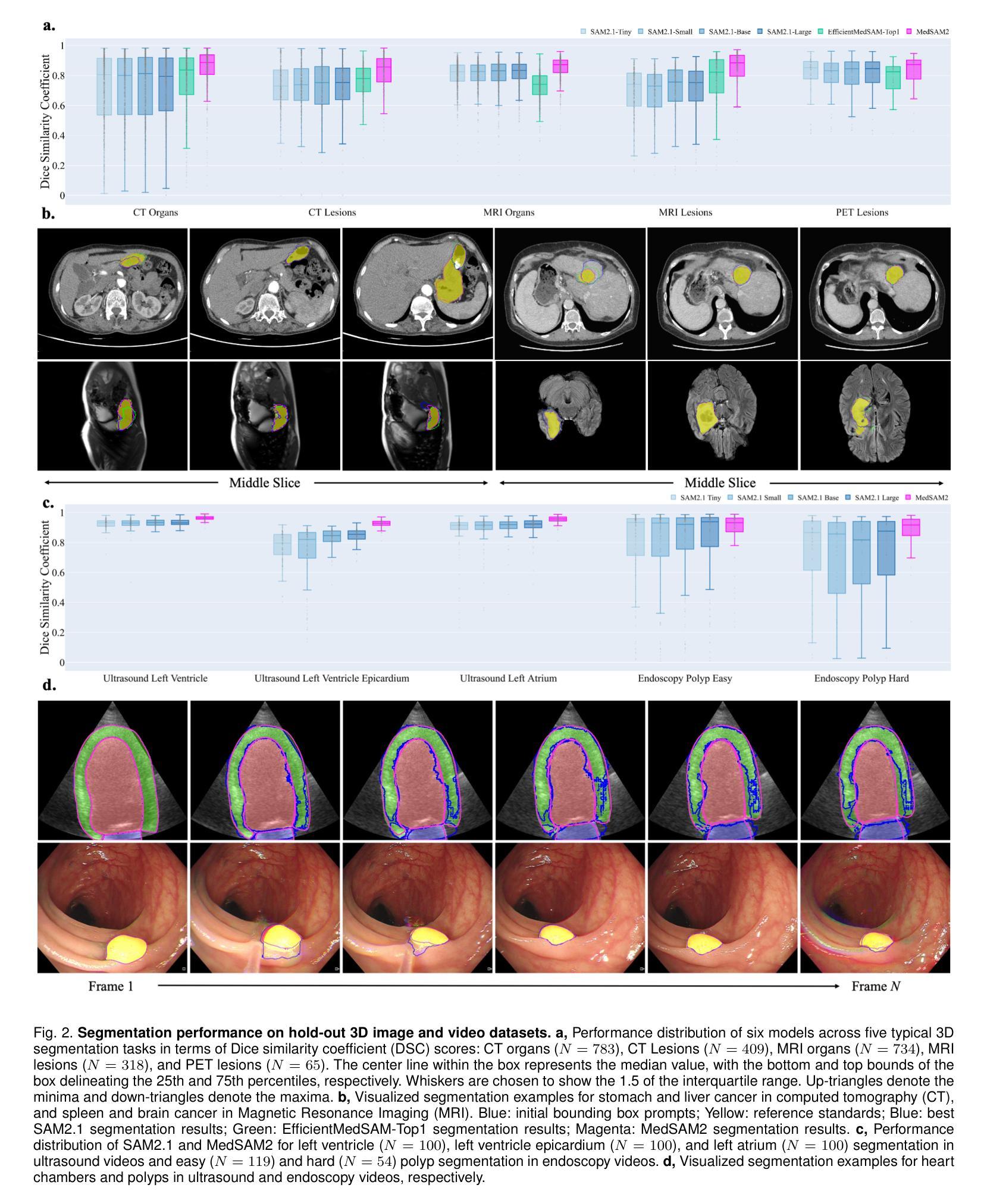
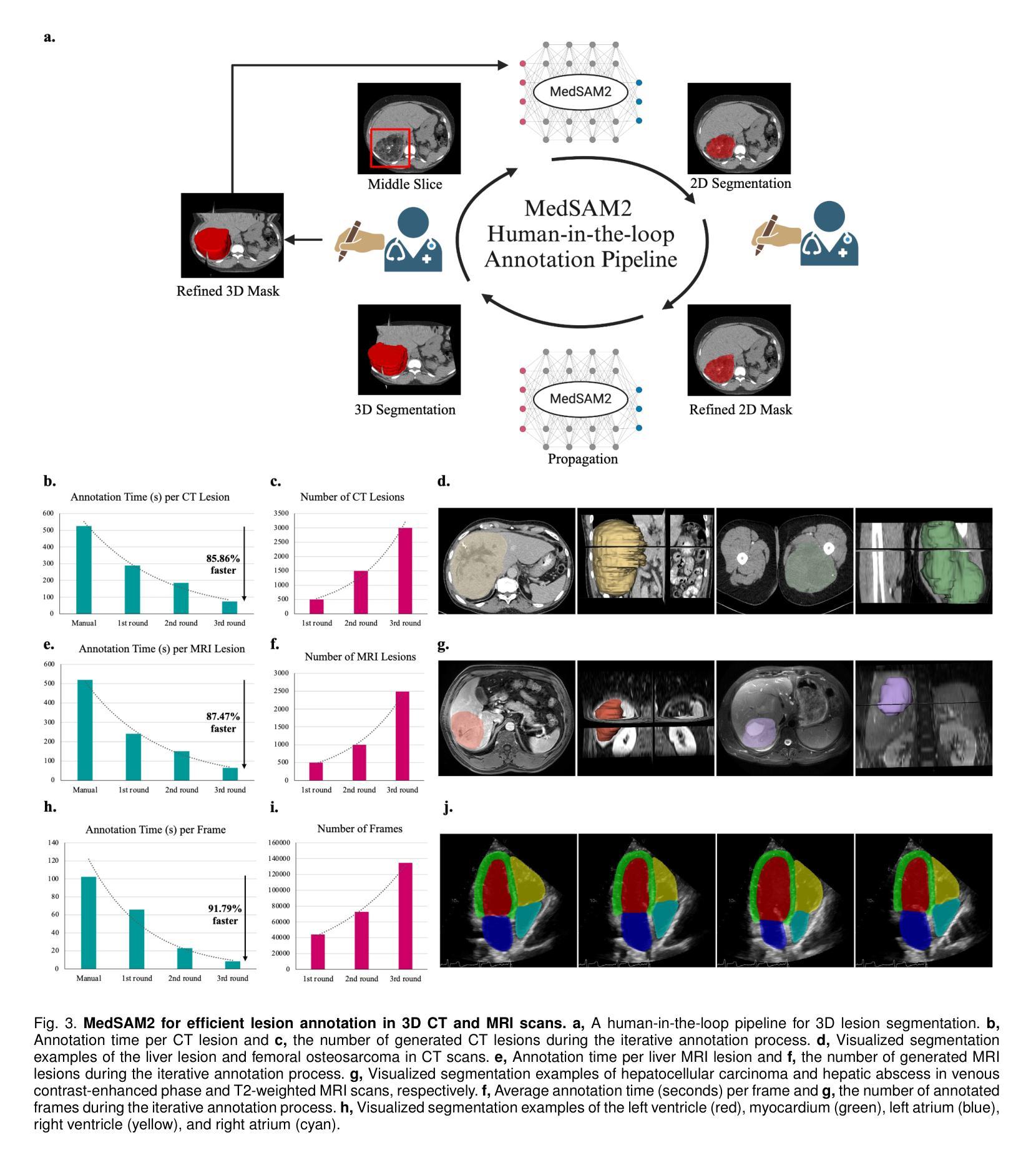
Medical image and video segmentation is a critical task for precision medicine, which has witnessed considerable progress in developing task or modality-specific and generalist models for 2D images. However, there have been limited studies on building general-purpose models for 3D images and videos with comprehensive user studies. Here, we present MedSAM2, a promptable segmentation foundation model for 3D image and video segmentation. The model is developed by fine-tuning the Segment Anything Model 2 on a large medical dataset with over 455,000 3D image-mask pairs and 76,000 frames, outperforming previous models across a wide range of organs, lesions, and imaging modalities. Furthermore, we implement a human-in-the-loop pipeline to facilitate the creation of large-scale datasets resulting in, to the best of our knowledge, the most extensive user study to date, involving the annotation of 5,000 CT lesions, 3,984 liver MRI lesions, and 251,550 echocardiogram video frames, demonstrating that MedSAM2 can reduce manual costs by more than 85%. MedSAM2 is also integrated into widely used platforms with user-friendly interfaces for local and cloud deployment, making it a practical tool for supporting efficient, scalable, and high-quality segmentation in both research and healthcare environments.
医学图像和视频分割是精准医学中的关键任务。针对二维图像的特定任务或通用模型已经取得了相当的进展。然而,关于构建用于三维图像和视频的通用模型的综合用户研究仍然有限。在这里,我们推出了MedSAM2,这是一个可用于三维图像和视频分割的提示分割基础模型。该模型是通过在包含超过45.5万张三维图像-掩膜对和7.6万帧的大型医疗数据集上对Segment Anything Model 2进行微调而开发出来的,在多种器官、病变和成像方式方面超越了以前的模型。此外,我们实现了一个人机循环管道,促进了大规模数据集的创建,据我们所知,这是迄今为止最广泛的用户研究,涉及对5000个CT病变、3984个肝脏MRI病变和251550个心电图视频帧的标注,证明了MedSAM2可以节省超过85%的人工成本。MedSAM2还集成到了广泛使用的本地和云平台用户友好型界面中,成为支持研究和医疗环境中高效、可扩展和高质量分割的实际工具。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://medsam2.github.io/
Summary
基于大规模医疗数据集训练的MedSAM2模型,能够对三维图像和视频进行精细分割,并在多种器官、病变和成像模式下表现出卓越性能。通过人类参与的循环管道,实现大规模数据集的创建,并显著降低手动成本。同时,该模型易于集成到本地和云端部署的平台上,为研究和医疗环境提供高效、可扩展和高质量的分割工具。
Key Takeaways
- MedSAM2模型可以对三维图像和视频进行分割,且性能卓越。
- 该模型在多种器官、病变和成像模式下都有出色表现。
- MedSAM2通过人类参与的循环管道实现大规模数据集的创建。
- MedSAM2能显著降低手动成本,减少超过85%。
- MedSAM2模型易于集成到广泛使用的平台上,支持本地和云端部署。
- 该模型为研究和医疗环境提供高效、可扩展和高质量的分割工具。
点此查看论文截图

Physics-informed 4D X-ray image reconstruction from ultra-sparse spatiotemporal data
Authors:Zisheng Yao, Yuhe Zhang, Zhe Hu, Robert Klöfkorn, Tobias Ritschel, Pablo Villanueva-Perez
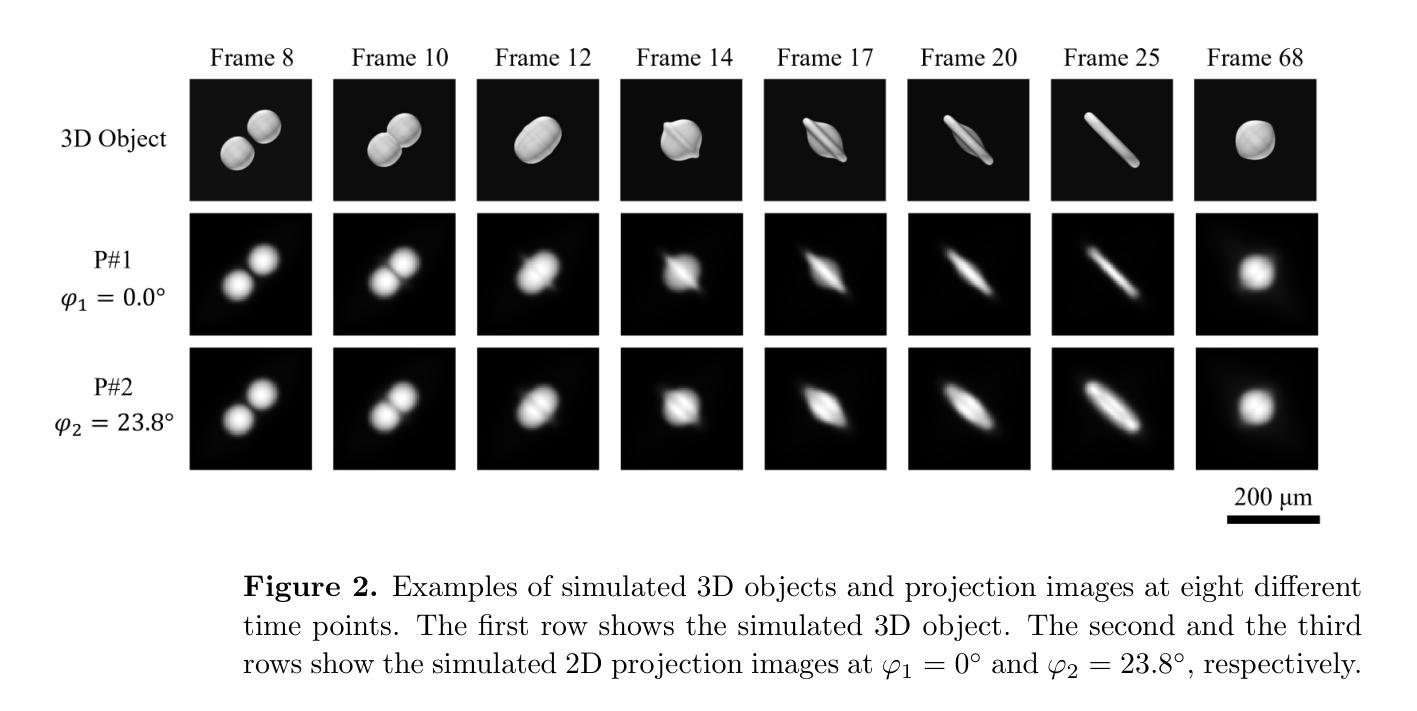
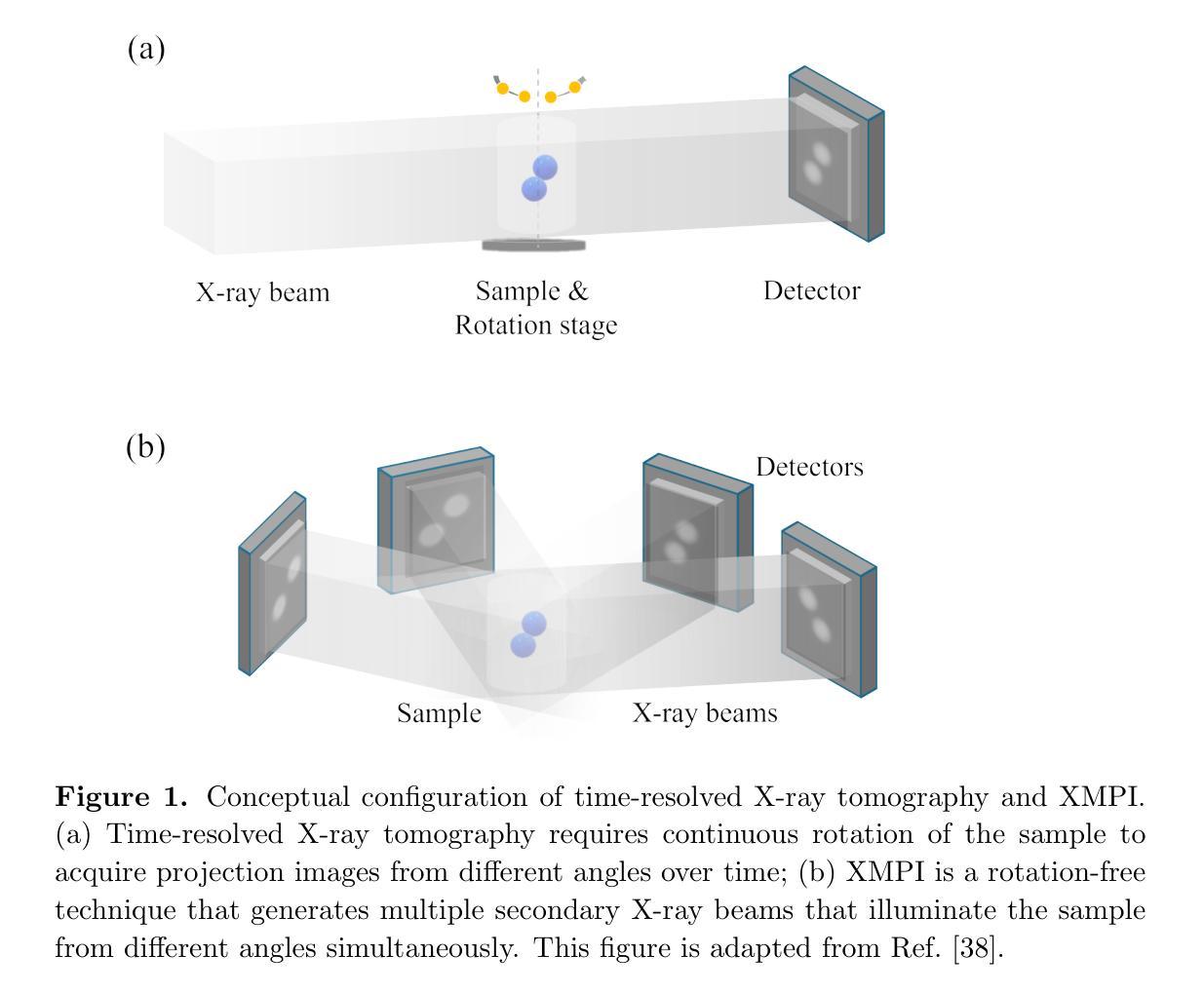
The unprecedented X-ray flux density provided by modern X-ray sources offers new spatiotemporal possibilities for X-ray imaging of fast dynamic processes. Approaches to exploit such possibilities often result in either i) a limited number of projections or spatial information due to limited scanning speed, as in time-resolved tomography, or ii) a limited number of time points, as in stroboscopic imaging, making the reconstruction problem ill-posed and unlikely to be solved by classical reconstruction approaches. 4D reconstruction from such data requires sample priors, which can be included via deep learning (DL). State-of-the-art 4D reconstruction methods for X-ray imaging combine the power of AI and the physics of X-ray propagation to tackle the challenge of sparse views. However, most approaches do not constrain the physics of the studied process, i.e., a full physical model. Here we present 4D physics-informed optimized neural implicit X-ray imaging (4D-PIONIX), a novel physics-informed 4D X-ray image reconstruction method combining the full physical model and a state-of-the-art DL-based reconstruction method for 4D X-ray imaging from sparse views. We demonstrate and evaluate the potential of our approach by retrieving 4D information from ultra-sparse spatiotemporal acquisitions of simulated binary droplet collisions, a relevant fluid dynamic process. We envision that this work will open new spatiotemporal possibilities for various 4D X-ray imaging modalities, such as time-resolved X-ray tomography and more novel sparse acquisition approaches like X-ray multi-projection imaging, which will pave the way for investigations of various rapid 4D dynamics, such as fluid dynamics and composite testing.
现代X射线源提供的前所未有的X射线流量密度,为快速动态过程的X射线成像提供了新的时空可能性。利用这些可能性的方法通常会导致(i)由于扫描速度有限,时间解析层析成像中的投影或空间信息数量有限,或者(ii)如闪光成像中的时间点数有限,这使得重建问题不适定,不太可能通过经典重建方法解决。从这些数据中进行4D重建需要样本先验,可以通过深度学习(DL)包含这些先验。最先进的X射线成像4D重建方法结合了人工智能和X射线传播物理学,以应对稀疏视角的挑战。然而,大多数方法并没有约束所研究过程的物理学,即一个完整的物理模型。在这里,我们提出了结合完整物理模型和基于最新技术的深度学习重建方法的4D物理信息优化神经隐式X射线成像(4D-PIONIX)。我们通过从模拟二进制液滴碰撞的超稀疏时空采集数据中恢复4D信息来展示和评估我们方法的潜力。我们预见,这项工作将为各种4D X射线成像模式开启新的时空可能性,如时间解析X射线层析成像和更新颖的稀疏采集方法,如X射线多投影成像,这将为各种快速4D动力学的研究,如流体力学和复合测试铺平道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
现代X射线源提供的前所未有的X射线流量密度,为快速动态过程的X射线成像提供了新的时空可能性。方法常导致投影数量或空间信息有限,重建问题成为病态的,无法用传统重建方法解决。4D重建需要样本先验,可通过深度学习(DL)实现。最先进的4D重建方法结合人工智能和X射线传播物理学来解决稀疏视图挑战。然而,大多数方法并不约束所研究过程的物理学模型。此处我们提出一种结合全物理模型和基于深度学习的重建方法的全新物理信息4D X射线成像技术——4D物理信息优化神经网络隐式射线成像(4D-PIONIX)。通过模拟二进制液滴碰撞等实验,验证了该方法从超稀疏时空采集数据中恢复4D信息的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 现代X射线源提供了更高的X射线流量密度,为快速动态过程的X射线成像提供了新时空可能性。
- 当前4D重建方法面临投影或时间点的限制,导致重建问题成为病态的。
- 深度学习被用于解决4D重建中的样本先验问题。
- 最先进的4D重建方法结合AI和X射线传播物理学处理稀疏视图挑战。
- 大多数现有方法缺乏物理过程的约束模型。
- 引入全新物理信息4D X射线成像技术——4D-PIONIX,结合了全物理模型和深度学习方法。
点此查看论文截图


FLAIRBrainSeg: Fine-grained brain segmentation using FLAIR MRI only
Authors:Edern Le Bot, Rémi Giraud, Boris Mansencal, Thomas Tourdias, Josè V. Manjon, Pierrick Coupé
This paper introduces a novel method for brain segmentation using only FLAIR MRIs, specifically targeting cases where access to other imaging modalities is limited. By leveraging existing automatic segmentation methods, we train a network to approximate segmentations, typically obtained from T1-weighted MRIs. Our method, called FLAIRBrainSeg, produces segmentations of 132 structures and is robust to multiple sclerosis lesions. Experiments on both in-domain and out-of-domain datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms modality-agnostic approaches based on image synthesis, the only currently available alternative for performing brain parcellation using FLAIR MRI alone. This technique holds promise for scenarios where T1-weighted MRIs are unavailable and offers a valuable alternative for clinicians and researchers in need of reliable anatomical segmentation.
本文介绍了一种仅使用FLAIR MRI进行大脑分割的新方法,特别适用于无法获得其他成像模式的情况。我们借助现有的自动分割方法,训练了一个网络来近似从T1加权MRI中获得的结果。我们的方法称为FLAIRBrainSeg,能够对132个结构进行分割,并且对于多发性硬化症病变具有很强的鲁棒性。在领域内的数据集和领域外的数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法在仅使用FLAIR MRI进行大脑分区的情况下,优于基于图像合成的模态无关方法,这是目前唯一可用的替代方法。对于无法使用T1加权MRI的场景,这项技术具有巨大的潜力,并为临床医生和研究人员提供了一个可靠的解剖分割的替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 6 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种仅使用FLAIR MRI进行脑分割的新方法,特别适用于无法获取其他成像模式的情况。该方法利用现有的自动分割方法,训练网络模拟通常从T1加权MRI获得的结果。实验证明,该方法在域内和域外数据集上的表现均优于基于图像合成的模态无关方法,为无法使用T1加权MRI的场景提供了可靠解剖分割的宝贵替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出了一种仅使用FLAIR MRIs进行脑分割的新方法。
- 该方法主要针对无法获取其他成像模式的情况。
- 该方法利用现有自动分割方法训练网络来模拟从T1加权MRI得到的结果。
- 论文介绍的方法被命名为FLAIRBrainSeg,能够分割132个结构。
- 该方法对多发性硬化病灶具有鲁棒性。
- 实验证明,该方法在域内和域外数据集上的表现均优于基于图像合成的模态无关方法。
点此查看论文截图

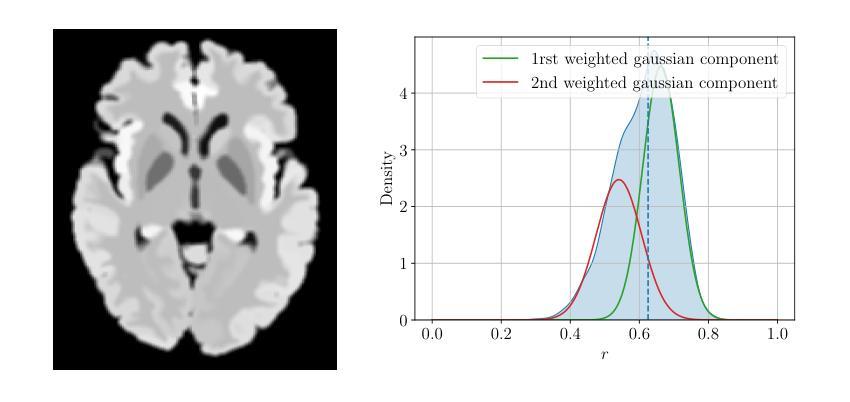
A Novel Optical Design for Wide-Field Imaging in X-ray Astronomy
Authors:Neeraj K. Tiwari, Santosh V. Vadawale, N. P. S. Mithun
Over the decades, astronomical X-ray telescopes have utilized the Wolter type-1 optical design, which provides stigmatic imaging in axial direction but suffers from coma and higher-order aberrations for off-axis sources. The Wolter-Schwarzschild design, with stigmatic imaging in the axial direction, while suffering from higher-order aberrations, is corrected for coma, thus performing better than the Wolter type-1. The Wolter type-1 and Wolter-Schwarzschild designs are optimized for on-axis but have reduced angular resolution when averaged over a wide field of view, with the averaging weighted by the area covered in the field of view. An optical design that maximizes angular resolution at the edge of the field of view rather than at the center is more suitable for wide-field X-ray telescopes required for deep-sky astronomical surveys or solar observations. A Hyperboloid-Hyperboloid optical design can compromise axial resolution to enhance field angle resolution, hence providing improved area-weighted average angular resolution over the Wolter-Schwarzschild design, but only for fields of view exceeding a specific size. Here, we introduce a new optical design that is free from coma aberration and capable of maximizing angular resolution at any desired field angle. This design consistently outperforms Wolter-1, Wolter-Schwarzschild, and Hyperboloid-Hyperboloid designs when averaged over any field of view size. The improvement in performance remains consistent across variations in other telescope parameters such as diameter, focal length, and mirror lengths. By utilizing this new optical design, we also present a design for a full-disk imaging solar X-ray telescope.
几十年来,天文X射线望远镜采用了Wolter 1型光学设计,该设计在轴向提供散光成像,但对于离轴源则存在彗星形和更高阶的像差问题。Wolter-Schwarzchild设计在轴向具有散光成像的优点,尽管存在高阶像差,但它经过修正以消除彗星形像差,因此性能优于Wolter 1型设计。Wolter 1型和Wolter-Schwarzchild设计以轴向优化为主,但在宽视场内的平均角分辨率会降低,平均结果由视场所覆盖的区域加权得出。对于深空天文普查或太阳观测所需的宽视场X射线望远镜而言,一种能在视场边缘而不是中心最大化角分辨率的光学设计更为合适。超椭圆体超椭圆光学设计可以妥协轴向分辨率以增强场角分辨率,从而在对Wolter-Schwarzchild设计进行改进时提高面积加权平均角分辨率,但这仅适用于超过特定大小的视场。在这里,我们介绍了一种新型光学设计,它无彗星形像差问题,能够在任何想要的视场角最大化角分辨率。在任何视场大小进行平均时,该设计始终优于Wolter 1型、Wolter-Schwarzchild和超椭圆体超椭圆光学设计。即使在其他望远镜参数(如直径、焦距和镜面长度)发生变化时,性能的提升也能保持一致。利用这种新型光学设计,我们还提出了一种全盘成像太阳X射线望远镜的设计方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been published in Experimental Astronomy
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型光学设计,该设计消除了彗星像差,可在任何期望的视场角上最大化角分辨率。这种设计在各种视场大小上均优于Wolter-1、Wolter-Schwarzchild和Hyperboloid-Hyperboloid设计,并且在望远镜参数如直径、焦距和镜长变化的情况下,性能改进保持一致。应用这种新光学设计,还提出了一种全盘成像太阳X射线望远镜的设计。
Key Takeaways
- 天文X射线望远镜几十年来一直使用Wolter type-1光学设计,它在轴向提供stigmatic成像,但对离轴源存在彗星像差和高阶像差。
- Wolter-Schwarzschild设计虽存在高阶像差,但已校正彗星像差,因此在某些方面优于Wolter type-1设计。
- 对于宽视场的深空天文观测或太阳观测,更适合一种能在视场边缘最大化角分辨率而不是在中心最大化的光学设计。
- Hyperboloid-Hyperboloid光学设计可通过牺牲轴向分辨率来提高视场角分辨率,但对于视野超过一定大小的领域效果更佳。
- 新型光学设计消除了彗星像差,可在任何视场角上最大化角分辨率,且性能改进在不同视场大小和其他望远镜参数变化时均保持一致。
- 这种新设计的优越性在于它能提供更为清晰、准确的图像,从而增强了望远镜的观测能力。
点此查看论文截图

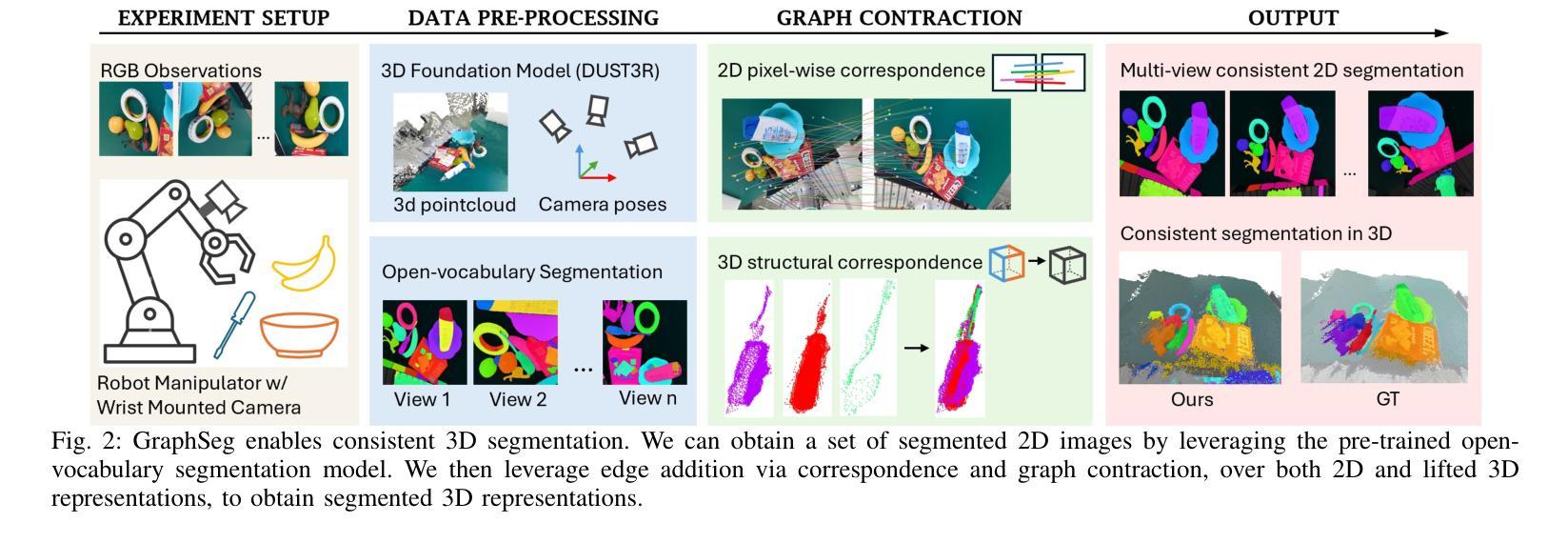
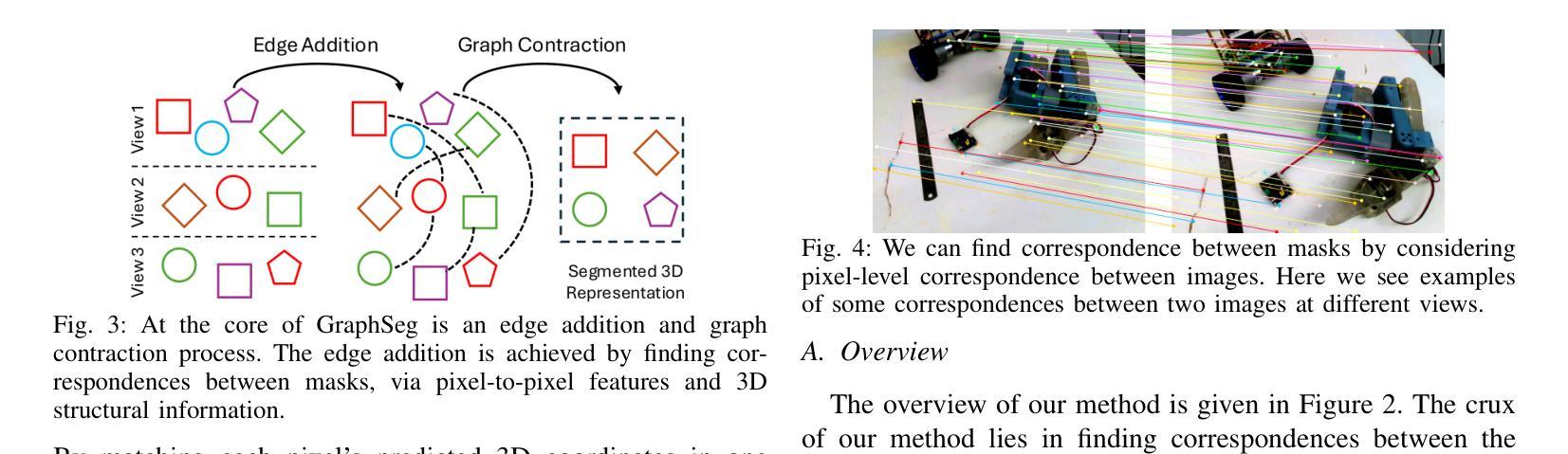
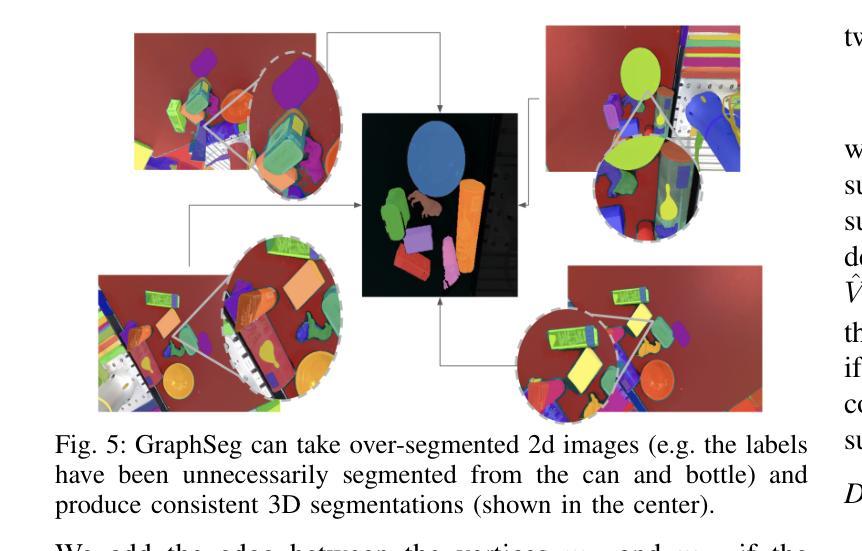
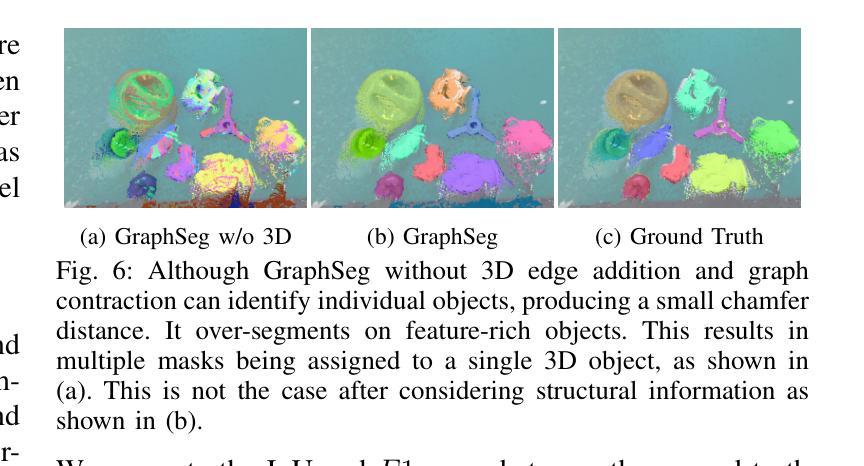
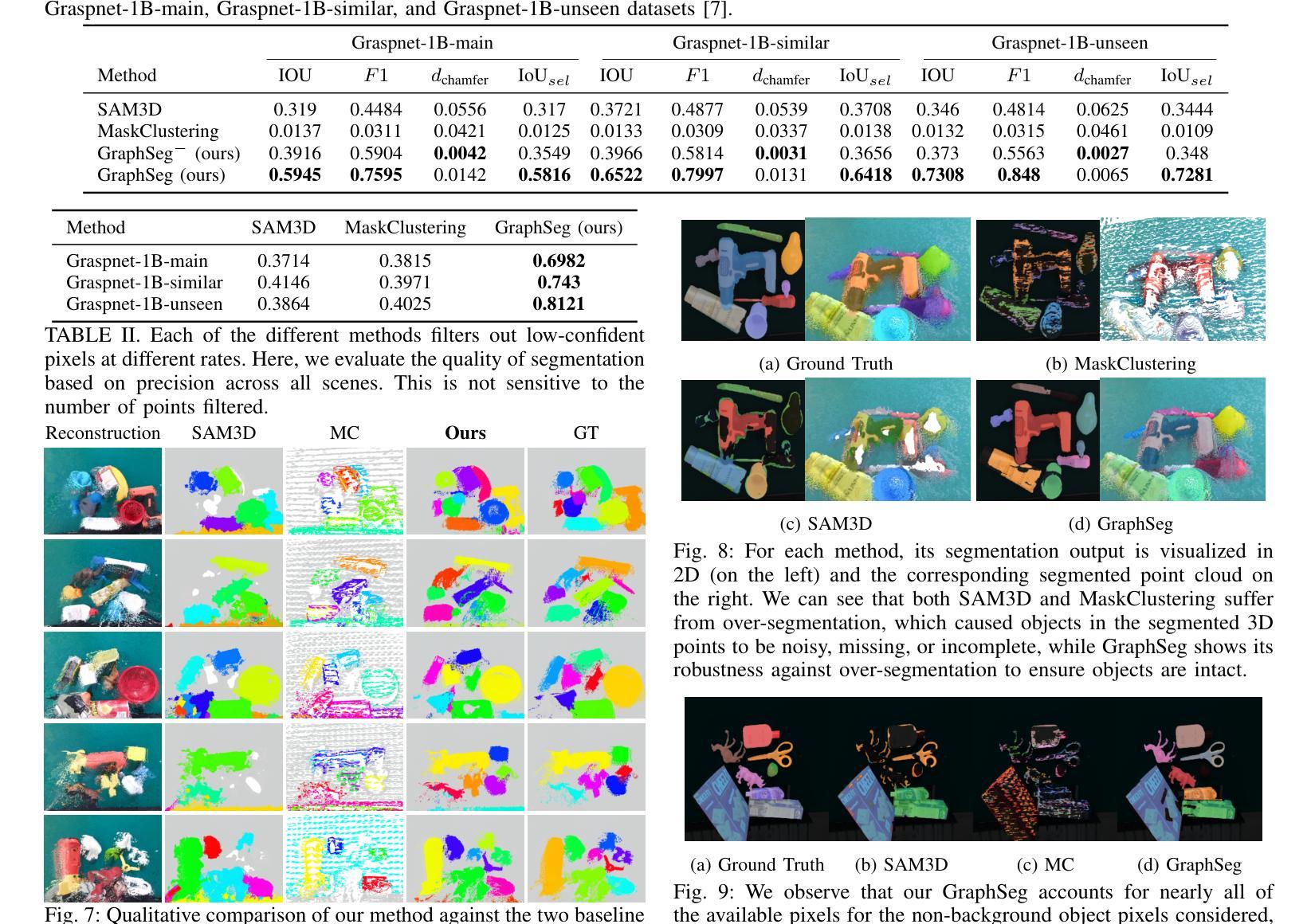
GraphSeg: Segmented 3D Representations via Graph Edge Addition and Contraction
Authors:Haozhan Tang, Tianyi Zhang, Oliver Kroemer, Matthew Johnson-Roberson, Weiming Zhi
Robots operating in unstructured environments often require accurate and consistent object-level representations. This typically requires segmenting individual objects from the robot’s surroundings. While recent large models such as Segment Anything (SAM) offer strong performance in 2D image segmentation. These advances do not translate directly to performance in the physical 3D world, where they often over-segment objects and fail to produce consistent mask correspondences across views. In this paper, we present GraphSeg, a framework for generating consistent 3D object segmentations from a sparse set of 2D images of the environment without any depth information. GraphSeg adds edges to graphs and constructs dual correspondence graphs: one from 2D pixel-level similarities and one from inferred 3D structure. We formulate segmentation as a problem of edge addition, then subsequent graph contraction, which merges multiple 2D masks into unified object-level segmentations. We can then leverage \emph{3D foundation models} to produce segmented 3D representations. GraphSeg achieves robust segmentation with significantly fewer images and greater accuracy than prior methods. We demonstrate state-of-the-art performance on tabletop scenes and show that GraphSeg enables improved performance on downstream robotic manipulation tasks. Code available at https://github.com/tomtang502/graphseg.git.
在结构化环境中操作的机器人通常需要准确且一致的对象级表示。这通常需要从机器人的周围环境中分割出单个物体。虽然最近的大型模型,如Anything分割(SAM)在2D图像分割方面表现出强大的性能。但这些进展并不能直接转化为在物理3D世界中的表现,它们在3D世界中经常过度分割物体,并且在不同视角之间无法产生一致的掩膜对应。在本文中,我们提出了GraphSeg,这是一个从环境的稀疏2D图像生成一致3D对象分割的框架,无需任何深度信息。GraphSeg向图中添加边并构建双对应图:一个基于2D像素级的相似性,另一个基于推断的3D结构。我们将分割制定为增边问题,然后进行图收缩,将多个2D掩膜合并为统一的对象级分割。然后我们可以利用3D基础模型来产生分割的3D表示。GraphSeg实现了稳健的分割,使用较少的图像并且具有比以前的方法更高的准确性。我们在桌面场景上展示了最先进的性能,并证明GraphSeg能改善下游机器人操作任务的性能。代码可在https://github.com/tomtang502/graphseg.git上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了GraphSeg框架,用于从稀疏的二维图像集中生成一致的3D对象分割,无需深度信息。GraphSeg通过添加边缘构建双重对应图,将像素级别的二维图像转化为物体级别的三维模型。分割被视为一个添加边缘的问题,再通过收缩图形实现不同二维遮罩的统一。该方法在桌面场景分割任务上取得了最先进的性能,提高了机器人操作任务的性能。
Key Takeaways
以下是本文的关键要点,以简练的列表形式呈现:
- GraphSeg是一个用于从稀疏的二维图像集生成一致的3D对象分割的框架。
- GraphSeg构建双重对应图:一个基于像素级别的二维相似性,另一个基于推断的三维结构。
点此查看论文截图

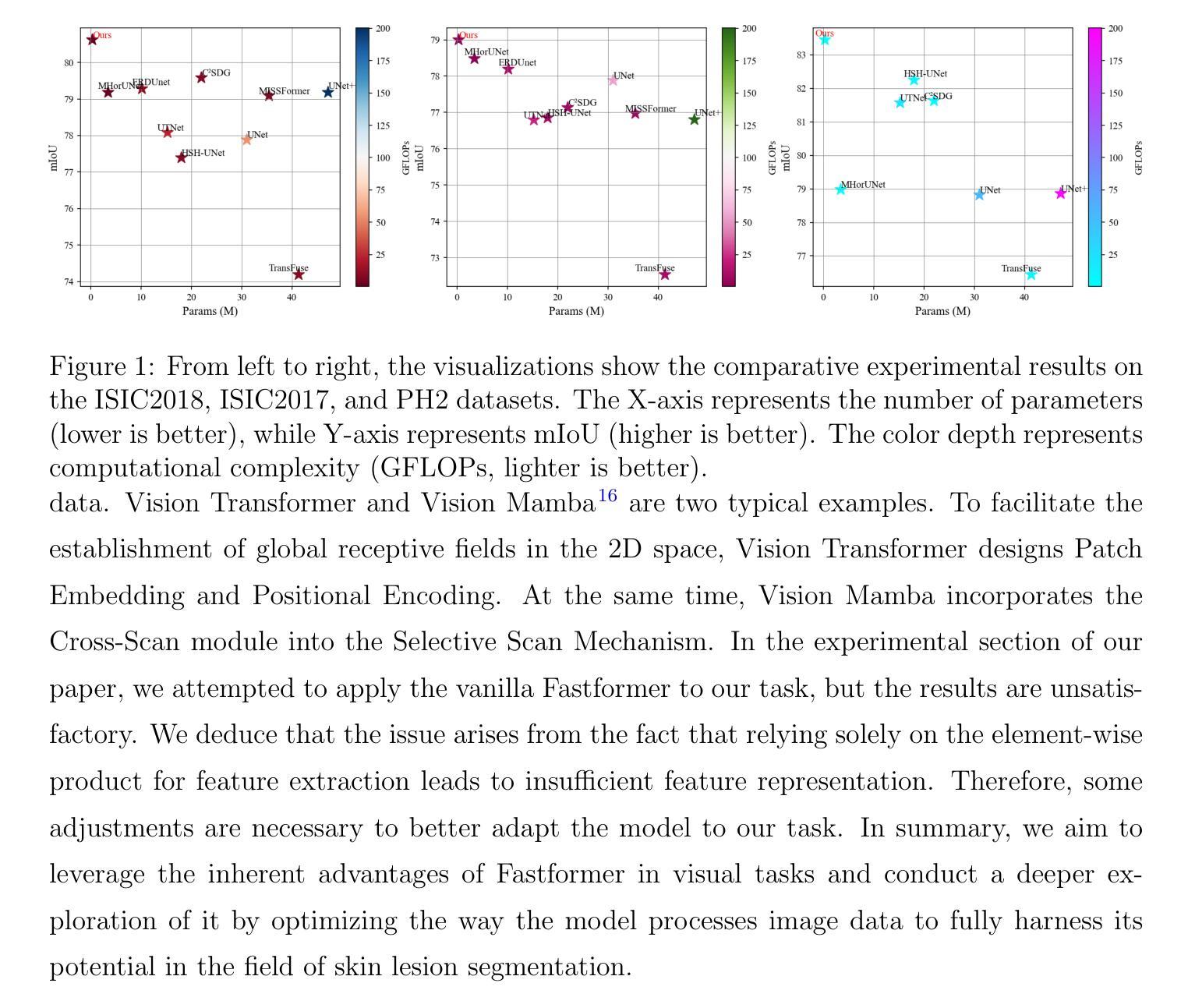
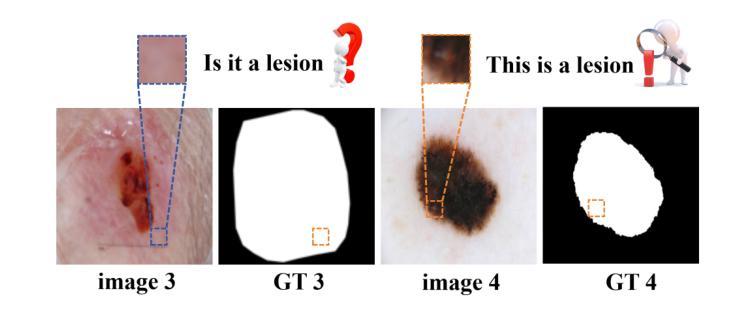
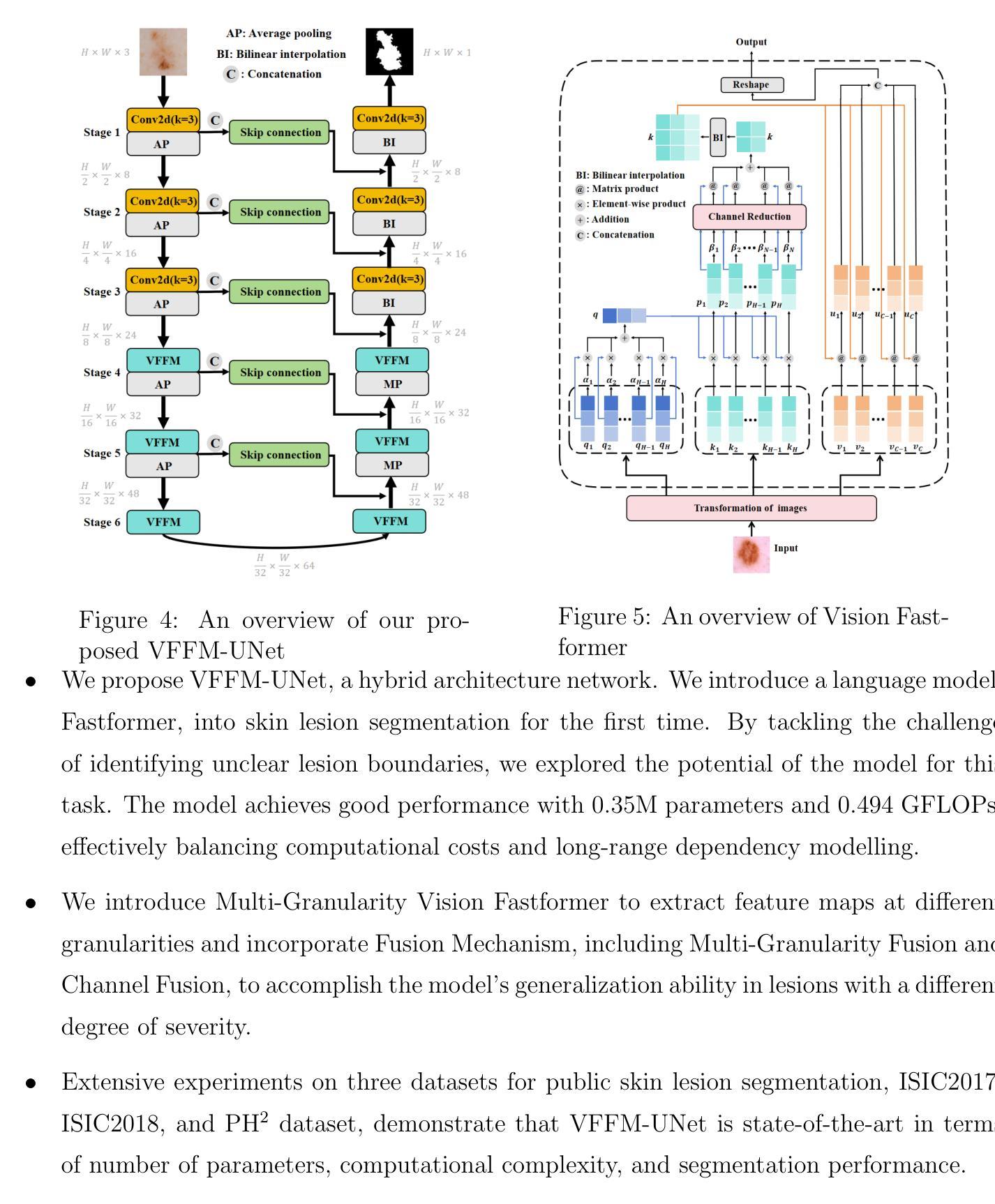
Multi-Granularity Vision Fastformer with Fusion Mechanism for Skin Lesion Segmentation
Authors:Xuanyu Liu, Huiyun Yao, Jinggui Gao, Zhongyi Guo, Xue Zhang, Yulin Dong
Background:Convolutional Neural Networks(CNN) and Vision Transformers(ViT) are the main techniques used in Medical image segmentation. However, CNN is limited to local contextual information, and ViT’s quadratic complexity results in significant computational costs. At the same time, equipping the model to distinguish lesion boundaries with varying degrees of severity is also a challenge encountered in skin lesion segmentation. Purpose:This research aims to optimize the balance between computational costs and long-range dependency modelling and achieve excellent generalization across lesions with different degrees of severity. Methods:we propose a lightweight U-shape network that utilizes Vision Fastformer with Fusion Mechanism (VFFM-UNet). We inherit the advantages of Fastformer’s additive attention mechanism, combining element-wise product and matrix product for comprehensive feature extraction and channel reduction to save computational costs. In order to accurately identify the lesion boundaries with varying degrees of severity, we designed Fusion Mechanism including Multi-Granularity Fusion and Channel Fusion, which can process the feature maps in the granularity and channel levels to obtain different contextual information. Results:Comprehensive experiments on the ISIC2017, ISIC2018 and PH2 datasets demonstrate that VFFM-UNet outperforms existing state-of-the-art models regarding parameter numbers, computational complexity and segmentation performance. In short, compared to MISSFormer, our model achieves superior segmentation performance while reducing parameter and computation costs by 101x and 15x, respectively. Conclusions:Both quantitative and qualitative analyses show that VFFM-UNet sets a new benchmark by reaching an ideal balance between parameter numbers, computational complexity, and segmentation performance compared to existing state-of-the-art models.
背景:卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)是医学图像分割中的主要技术。然而,CNN受限于局部上下文信息,而ViT的二次复杂性导致计算成本较高。同时,使模型能够区分不同程度严重性的病变边界也是皮肤病变分割中遇到的挑战。
目的:本研究旨在优化计算成本与长期依赖关系建模之间的平衡,并在不同严重程度病变之间实现出色的泛化能力。
方法:我们提出了一种轻量级的U形网络,该网络采用带有融合机制的视觉快速成形器(VFFM-UNet)。我们继承了Fastformer加法注意力机制的优势,结合元素乘积和矩阵乘积进行特征提取和综合通道缩减,以节省计算成本。为了准确识别不同程度严重性的病变边界,我们设计了融合机制,包括多粒度融合和通道融合,可以在粒度和通道级别处理特征映射以获得不同的上下文信息。
结果:在ISIC2017、ISIC2018和PH2数据集上的综合实验表明,VFFM-UNet在参数数量、计算复杂性和分割性能上优于现有最先进的模型。简而言之,与MISSFormer相比,我们的模型在减少参数和计算成本的同时实现了优越的分割性能,分别降低了101倍和15倍。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于轻量化U型网络与融合了快速形态注意力的优化机制用于医学图像分割。该方法结合了快速形态模型的优点,并采用多种融合机制来处理不同严重程度的病变边界。在多个数据集上的实验表明,该方法在参数数量、计算复杂度和分割性能上均优于现有技术模型。简而言之,新方法在降低成本的同时取得了良好的分割性能。
Key Takeaways
- 研究旨在优化计算成本与长距离依赖建模之间的平衡,并在不同严重程度病变中实现了出色的泛化性能。
- 采用了轻量级的U型网络结构,结合了快速形态模型的优点进行特征提取和通道缩减以降低计算成本。
- 设计了融合机制,包括多粒度融合和通道融合,可以在粒度和通道级别处理特征图以获取不同的上下文信息,从而准确识别不同严重程度病变的边界。
点此查看论文截图


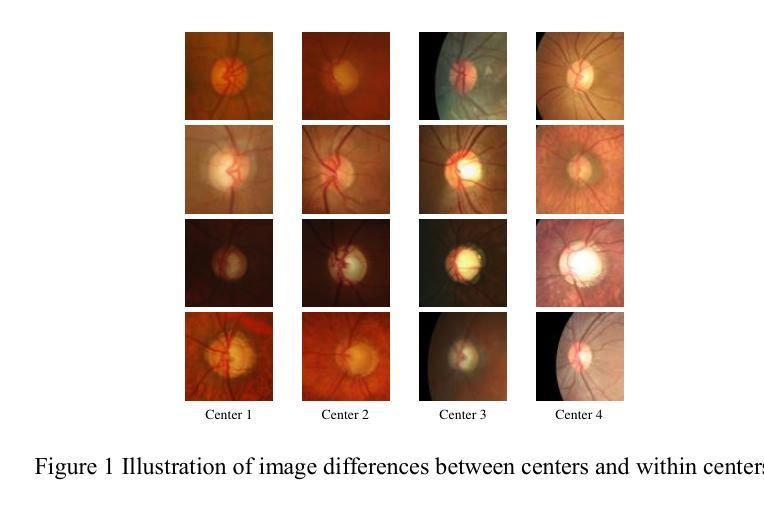
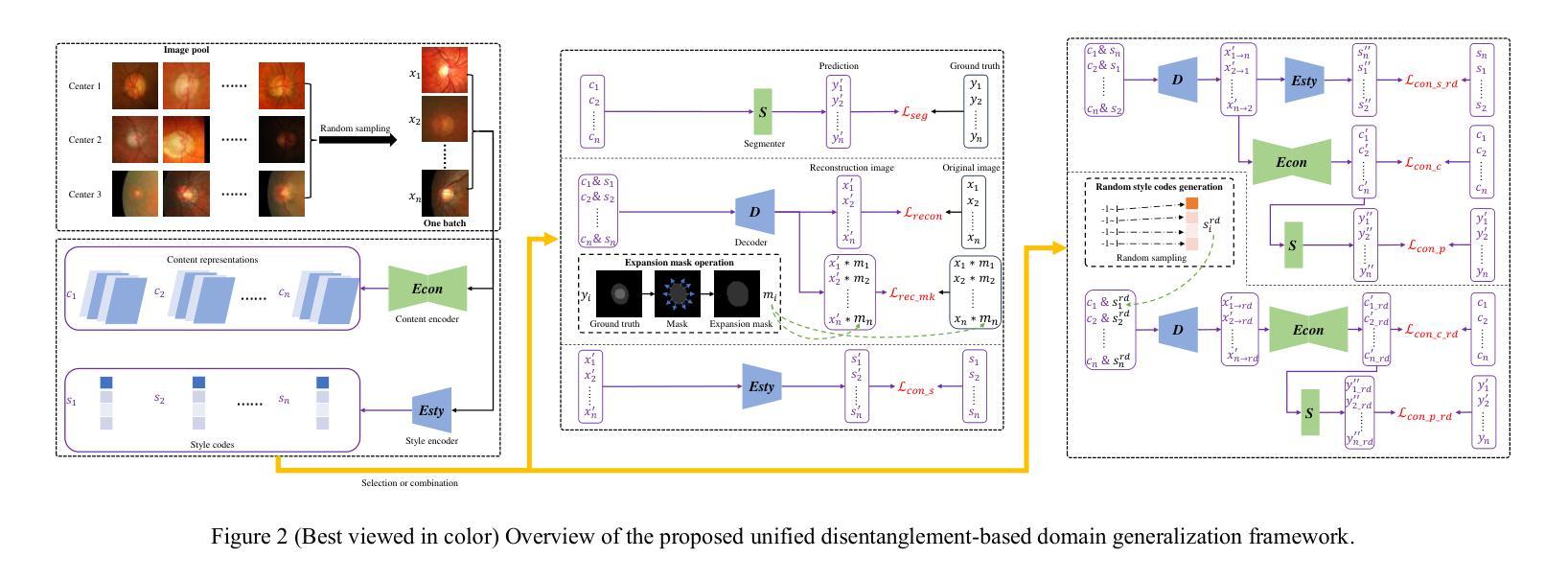
Rethinking domain generalization in medical image segmentation: One image as one domain
Authors:Jin Hong, Bo Liu, Guoli Long, Siyue Li, Khan Muhammad
Domain shifts in medical image segmentation, particularly when data comes from different centers, pose significant challenges. Intra-center variability, such as differences in scanner models or imaging protocols, can cause domain shifts as large as, or even larger than, those between centers. To address this, we propose the “one image as one domain” (OIOD) hypothesis, which treats each image as a unique domain, enabling flexible and robust domain generalization. Based on this hypothesis, we develop a unified disentanglement-based domain generalization (UniDDG) framework, which simultaneously handles both multi-source and single-source domain generalization without requiring explicit domain labels. This approach simplifies training with a fixed architecture, independent of the number of source domains, reducing complexity and enhancing scalability. We decouple each input image into content representation and style code, then exchange and combine these within the batch for segmentation, reconstruction, and further disentanglement. By maintaining distinct style codes for each image, our model ensures thorough decoupling of content representations and style codes, improving domain invariance of the content representations. Additionally, we enhance generalization with expansion mask attention (EMA) for boundary preservation and style augmentation (SA) to simulate diverse image styles, improving robustness to domain shifts. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves Dice scores of 84.43% and 88.91% for multi-source to single-center and single-center generalization in optic disc and optic cup segmentation, respectively, and 86.96% and 88.56% for prostate segmentation, outperforming current state-of-the-art domain generalization methods, offering superior performance and adaptability across clinical settings.
医学图像分割中的域偏移,尤其是当数据来自不同的中心时,会带来重大挑战。来自同一中心的内部数据变化,如扫描仪型号或成像协议的不同,可能会导致与跨中心一样甚至更大的域偏移。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了“一图一域”(OIOD)假设,将每张图像视为一个独特的域,以实现灵活和稳健的域泛化。基于这一假设,我们开发了一个统一的基于解纠缠的域泛化(UniDDG)框架,可以同时处理多源和单源域泛化,无需明确的域标签。这种方法简化了使用固定架构的训练过程,独立于源域的数量,降低了复杂性并增强了可扩展性。我们将每个输入图像解耦为内容表示和风格代码,然后在批次内交换并结合这些信息进行分割、重建和进一步的解纠缠。通过为每个图像保留独特的风格代码,我们的模型确保了内容表示和风格代码的彻底解耦,提高了内容表示的领域不变性。此外,我们通过扩展掩膜注意力(EMA)进行边界保留和风格增强(SA)来模拟各种图像风格,以增强对域偏移的稳健性。大量实验表明,我们的方法在视盘和视杯分割中,多源到单中心的泛化和单中心泛化分别实现了84.43%和88.91%的Dice得分;在前列腺分割中,我们方法的Dice得分为86.96%和88.56%,超越了当前最先进的域泛化方法,在临床环境中提供了卓越的性能和适应性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
医学图像分割领域面临来自不同中心数据的领域漂移挑战。为解决此问题,本文提出“一幅图像作为一个领域”(OIOD)假设,并基于此开发了一个统一解纠缠领域泛化(UniDDG)框架。该框架无需明确的领域标签即可同时处理多源和单源领域泛化问题。通过图像内容表示和风格代码的解耦,该框架提高了领域不变性。此外,本文还引入了扩展掩膜注意力(EMA)和风格增强(SA)技术以增强模型的鲁棒性。实验结果表明,该方法在医学图像分割任务中表现优异,如视盘和视杯分割以及前列腺分割等任务上的表现均优于当前最先进的领域泛化方法。
关键见解
- 领域漂移是医学图像分割中的重大挑战,尤其是当数据来自不同中心时。
- “一幅图像作为一个领域”(OIOD)假设解决了这一挑战,允许灵活的领域泛化。
- 提出的UniDDG框架能够同时处理多源和单源领域泛化问题,无需明确的领域标签。
- 通过解耦图像内容表示和风格代码,UniDDG框架提高了领域不变性。
- 扩展掩膜注意力(EMA)和风格增强(SA)技术增强了模型的鲁棒性。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在医学图像分割任务上表现优异,如视盘和视杯分割以及前列腺分割等任务上均优于当前最先进的领域泛化方法。
- 该方法简化了训练过程,提高了模型的适应性和可扩展性。
点此查看论文截图

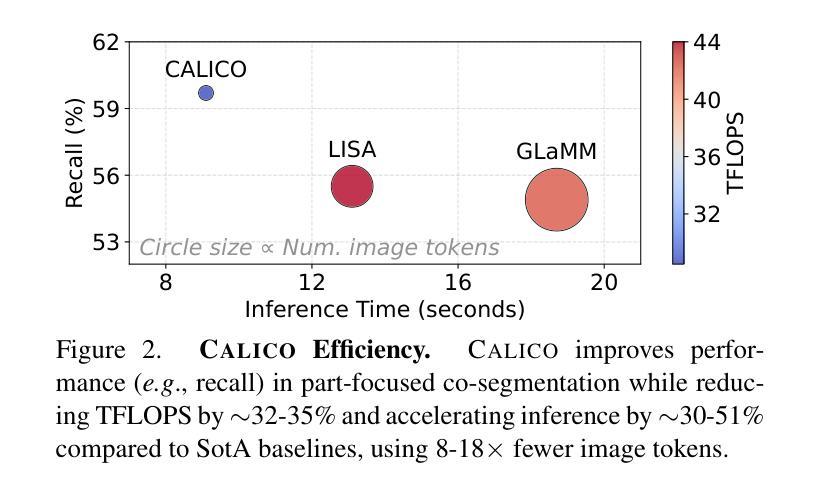
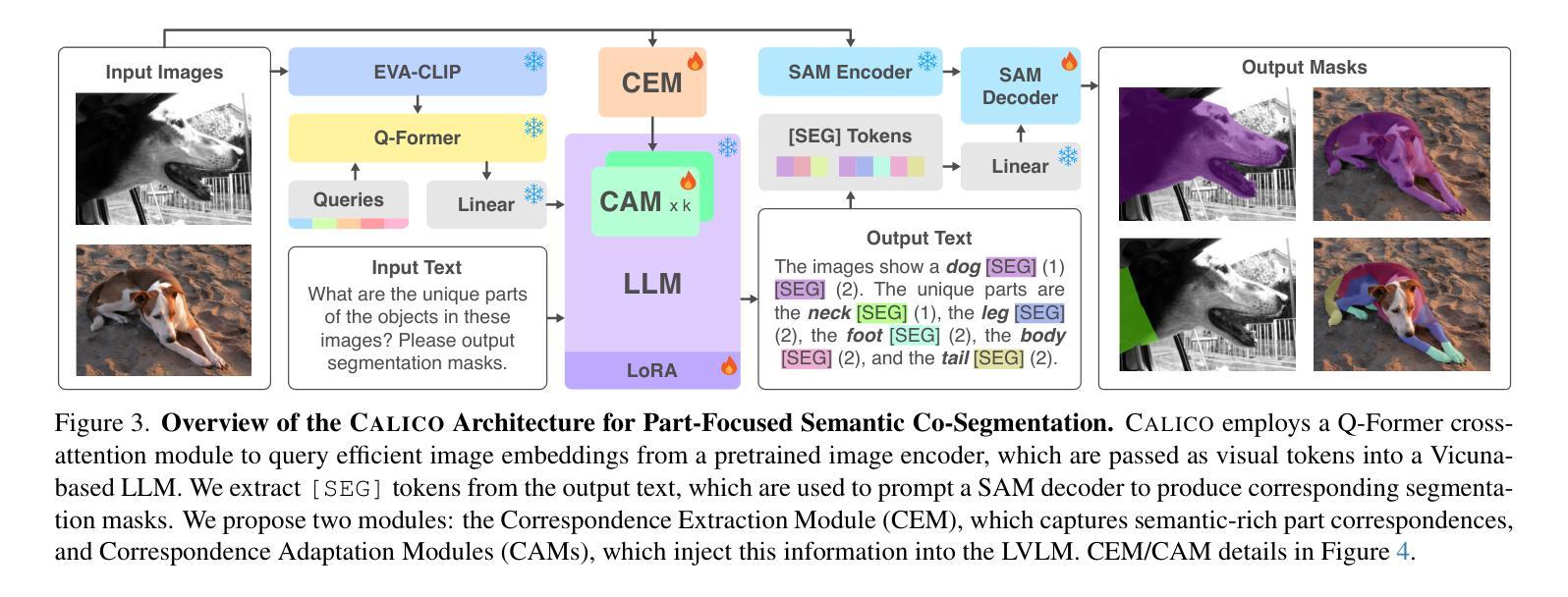
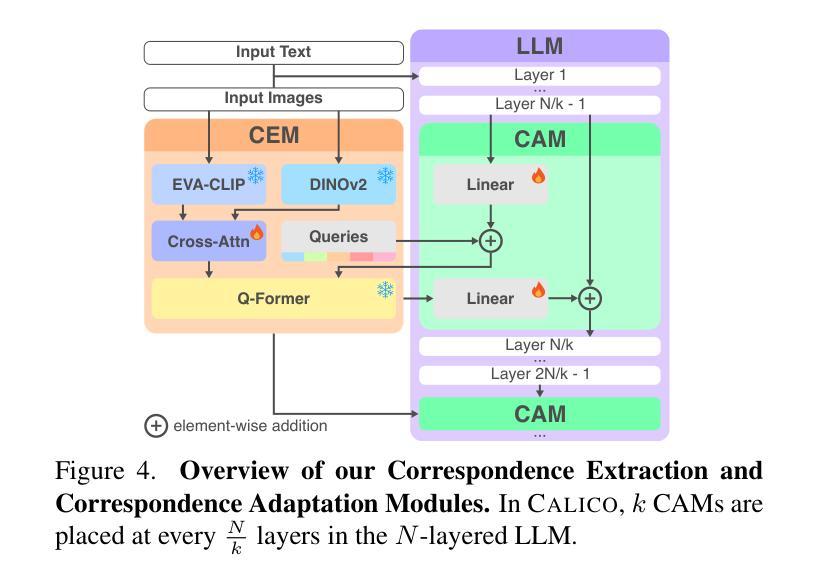
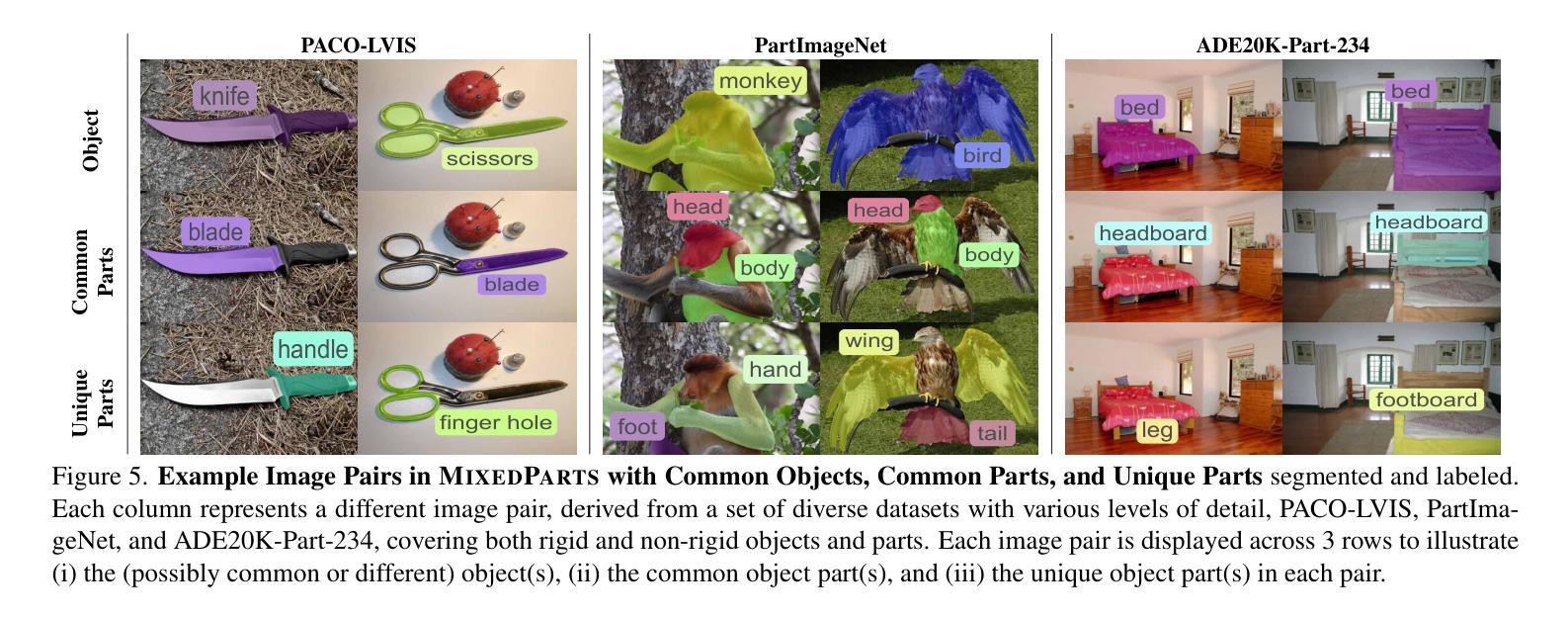
CALICO: Part-Focused Semantic Co-Segmentation with Large Vision-Language Models
Authors:Kiet A. Nguyen, Adheesh Juvekar, Tianjiao Yu, Muntasir Wahed, Ismini Lourentzou
Recent advances in Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have enabled general-purpose vision tasks through visual instruction tuning. While existing LVLMs can generate segmentation masks from text prompts for single images, they struggle with segmentation-grounded reasoning across images, especially at finer granularities such as object parts. In this paper, we introduce the new task of part-focused semantic co-segmentation, which involves identifying and segmenting common objects, as well as common and unique object parts across images. To address this task, we present CALICO, the first LVLM designed for multi-image part-level reasoning segmentation. CALICO features two key components, a novel Correspondence Extraction Module that identifies semantic part-level correspondences, and Correspondence Adaptation Modules that embed this information into the LVLM to facilitate multi-image understanding in a parameter-efficient manner. To support training and evaluation, we curate MixedParts, a large-scale multi-image segmentation dataset containing $\sim$2.4M samples across $\sim$44K images spanning diverse object and part categories. Experimental results demonstrate that CALICO, with just 0.3% of its parameters finetuned, achieves strong performance on this challenging task.
近期大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)的进步通过视觉指令调整实现了通用视觉任务。虽然现有的LVLMs可以为单张图片生成文本提示的分割掩膜,但它们在进行跨图像的分割推理时面临困难,尤其是在更精细的粒度(如物体部分)上。在本文中,我们引入了新的部分聚焦语义协同分割任务,该任务涉及识别和分割跨图像的常见对象和常见及独特的对象部分。为了应对这一任务,我们提出了CALICO,这是专为多图像部分级推理分割设计的首个LVLM。CALICO具有两个关键组件,一个是新颖的对应提取模块,用于识别语义部分级的对应,另一个是对应适应模块,用于将此信息嵌入LVLM中,以高效的方式促进多图像理解。为了支持训练和评估,我们创建了MixedParts数据集,这是一个大规模的多图像分割数据集,包含约4.4万张图像和约24万个样本,涵盖多种对象和部件类别。实验结果表明,在具有挑战性的任务中,只需微调CALICO的0.3%参数即可实现强大的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025. Project page: https://plan-lab.github.io/calico/
Summary
本文介绍了大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)的最新进展,通过视觉指令微调实现了通用视觉任务。针对现有LVLMs在跨图像分割推理方面的不足,特别是在更精细的粒度如物体部分上的挑战,本文引入了部分聚焦语义协同分割的新任务。为应对此任务,提出了专为多图像部分级推理分割设计的CALICO模型。CALICO包含两个关键组件:一种新型对应关系提取模块,用于识别语义部分级对应关系;以及对应关系适配模块,以参数有效的方式将此信息嵌入LVLM,促进多图像理解。为支持和评估模型训练,我们整理了MixedParts大型多图像分割数据集,包含约240万样本和约4万张涵盖多种对象和类别图像的图片。实验结果表明,在具有挑战性的任务中,仅需微调CALICO的0.3%参数即可实现强大性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)能够通过视觉指令微调完成通用视觉任务。
- 现有LVLMs在跨图像分割推理方面存在局限性,特别是在物体部分的精细粒度上。
- 引入了部分聚焦语义协同分割的新任务,旨在解决跨图像的物体和部分识别与分割问题。
- 提出了专为多图像部分级推理分割设计的CALICO模型。
- CALICO包含两个关键组件:对应关系提取模块和对应关系适配模块。
- 为了训练和评估CALICO模型,整理了一个大型多图像分割数据集MixedParts。
点此查看论文截图

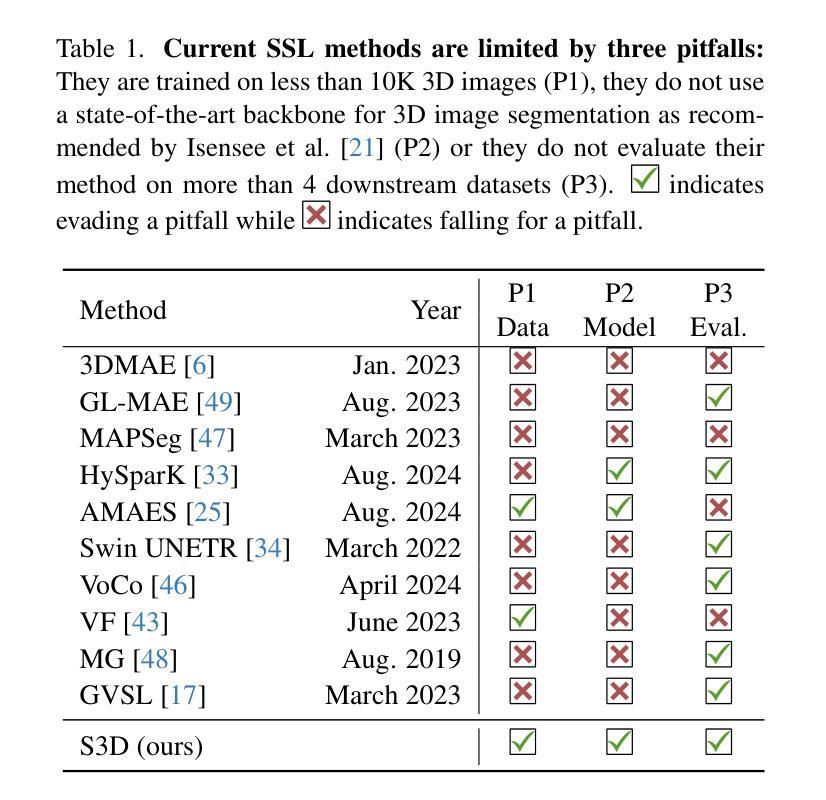
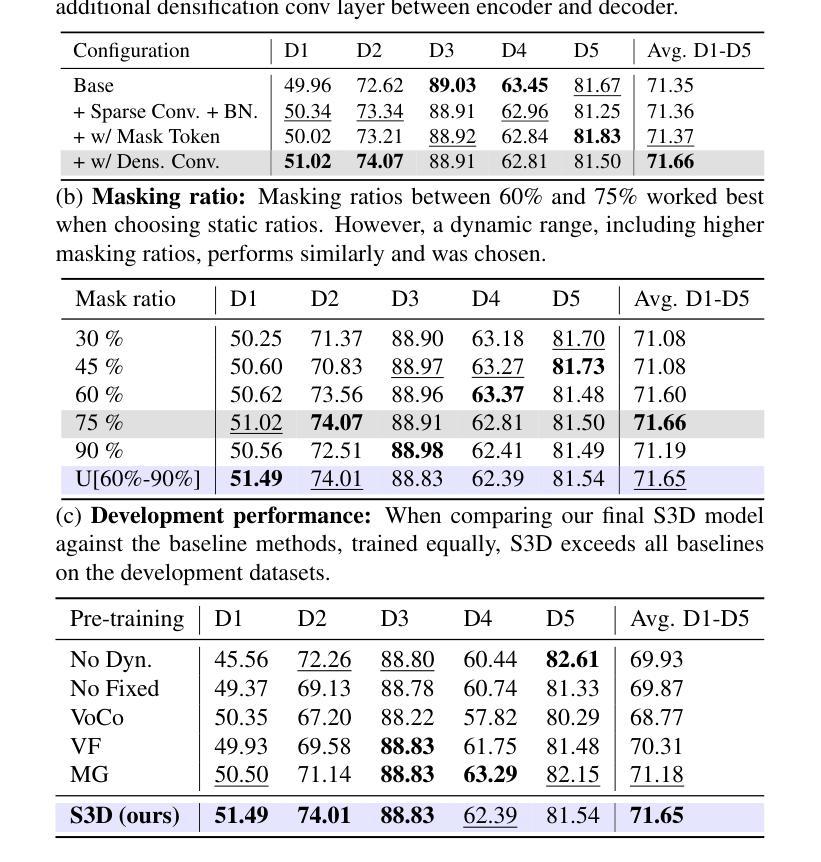
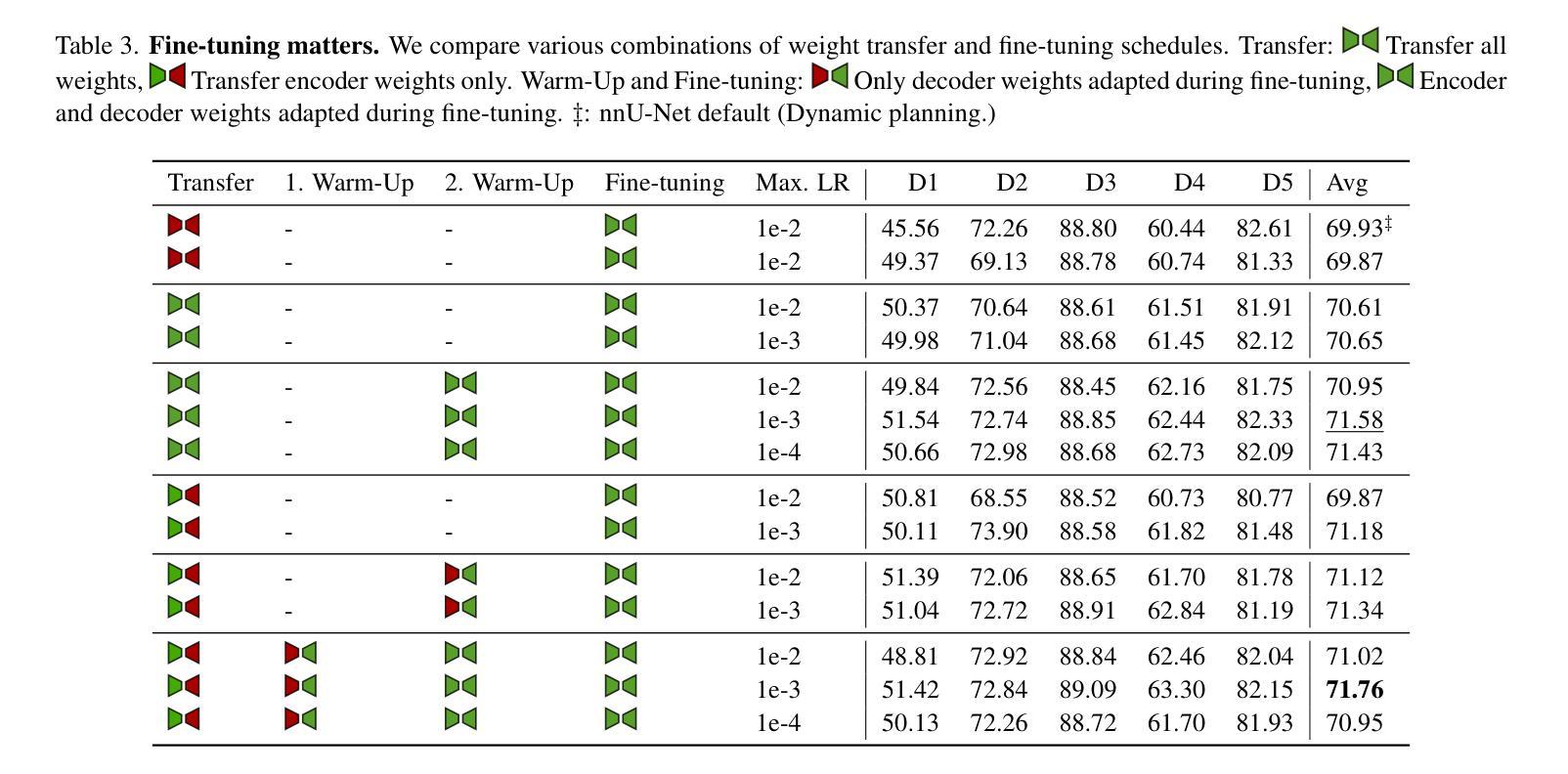
Revisiting MAE pre-training for 3D medical image segmentation
Authors:Tassilo Wald, Constantin Ulrich, Stanislav Lukyanenko, Andrei Goncharov, Alberto Paderno, Maximilian Miller, Leander Maerkisch, Paul F. Jäger, Klaus Maier-Hein
Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) presents an exciting opportunity to unlock the potential of vast, untapped clinical datasets, for various downstream applications that suffer from the scarcity of labeled data. While SSL has revolutionized fields like natural language processing and computer vision, its adoption in 3D medical image computing has been limited by three key pitfalls: Small pre-training dataset sizes, architectures inadequate for 3D medical image analysis, and insufficient evaluation practices. In this paper, we address these issues by i) leveraging a large-scale dataset of 39k 3D brain MRI volumes and ii) using a Residual Encoder U-Net architecture within the state-of-the-art nnU-Net framework. iii) A robust development framework, incorporating 5 development and 8 testing brain MRI segmentation datasets, allowed performance-driven design decisions to optimize the simple concept of Masked Auto Encoders (MAEs) for 3D CNNs. The resulting model not only surpasses previous SSL methods but also outperforms the strong nnU-Net baseline by an average of approximately 3 Dice points setting a new state-of-the-art. Our code and models are made available here.
自监督学习(SSL)为解锁大量未开发的临床数据集潜力提供了激动人心的机会,用于各种因缺乏标记数据而受影响的下游应用。虽然SSL已经彻底改变了自然语言处理和计算机视觉等领域,但其在3D医学图像计算中的应用受到三个主要问题的限制:预训练数据集规模小、用于3D医学图像分析的架构不足以及评估实践不充分。在本文中,我们通过以下方法解决这些问题:i)利用包含39k个3D大脑MRI体积的大规模数据集;ii)在最新nnU-Net框架内使用Residual Encoder U-Net架构;iii)一个稳健的开发框架,结合5个开发集和8个测试大脑MRI分割数据集,推动以性能为导向的设计决策,优化3D卷积神经网络的Masked Auto Encoders(MAEs)的简洁概念。由此产生的模型不仅超越了以前的SSL方法,而且还优于强大的nnU-Net基线,平均提高了大约3个Dice点,创造了新的最先进的水平。我们的代码和模型可在此处获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Update to Camera-Ready
Summary
本文探讨了自监督学习(SSL)在解决三维医学图像计算领域的问题中的潜力与应用。通过解决数据规模小、架构不足以及评估方法不完善三大挑战,采用大规模的三维医学图像数据集进行预训练、采用残差编码器U-Net架构并使用可靠的评估框架,成功实现了对自监督学习模型的优化。模型不仅在自监督学习方法上取得了突破,还超越了强大的nnU-Net基线模型,为三维医学图像分割提供了新的最佳实践。
Key Takeaways
- 自监督学习(SSL)对于解决三维医学图像计算问题有巨大潜力。
- 解决SSL在医学图像领域应用的三大挑战:小规模的预训练数据集、不适合三维医学图像分析的架构以及不足的评估方法。
- 利用大规模的三维医学图像数据集进行预训练,提高模型的性能。
- 采用残差编码器U-Net架构并结合nnU-Net框架进行优化。
- 通过采用Masked Auto Encoders(MAEs)的优化概念,显著提升了模型性能。
- 模型不仅在自监督学习方法上超越之前的模型,还超越了强大的基线模型nnU-Net,设置了一个新的性能基准。
点此查看论文截图

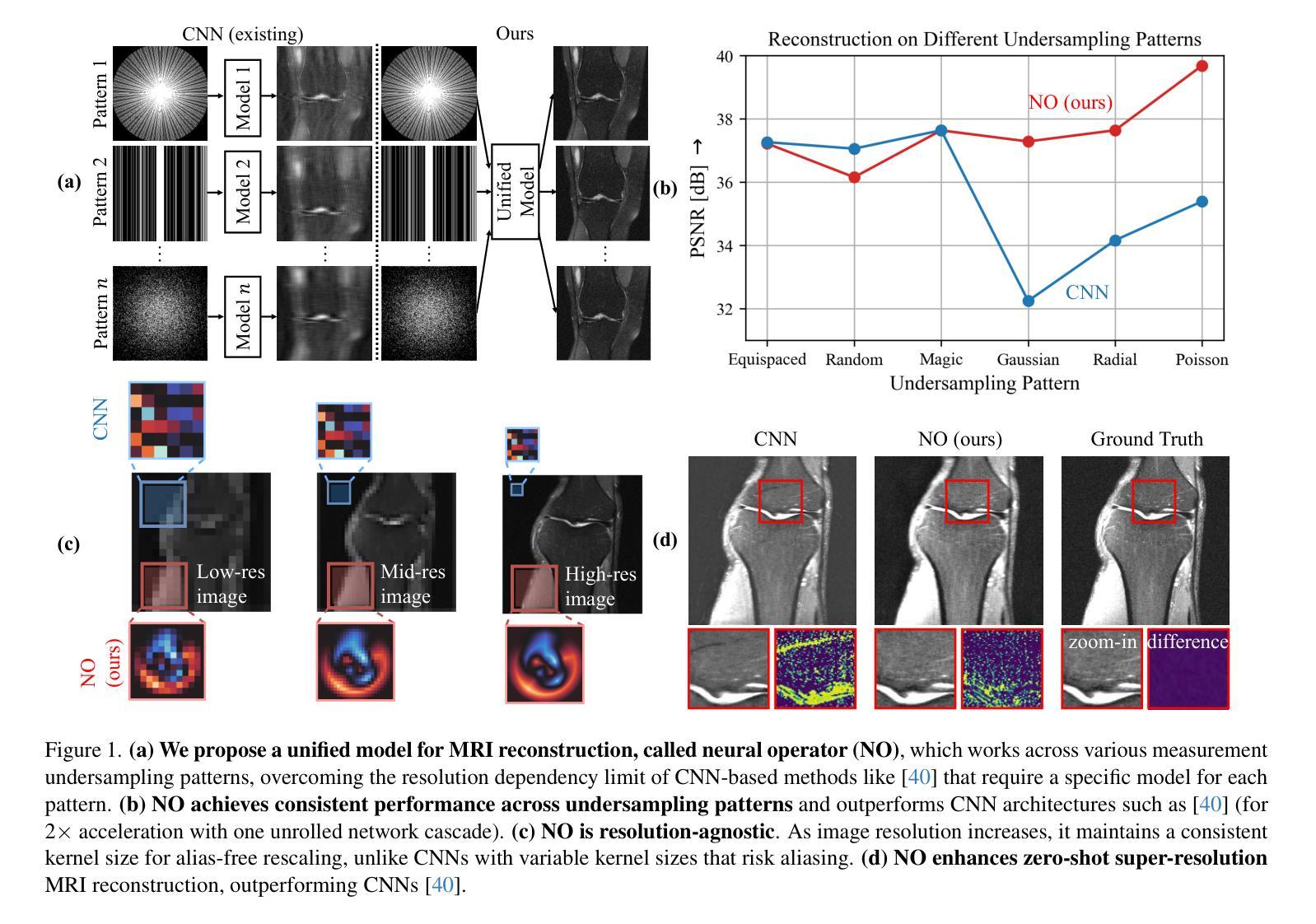
A Unified Model for Compressed Sensing MRI Across Undersampling Patterns
Authors:Armeet Singh Jatyani, Jiayun Wang, Aditi Chandrashekar, Zihui Wu, Miguel Liu-Schiaffini, Bahareh Tolooshams, Anima Anandkumar
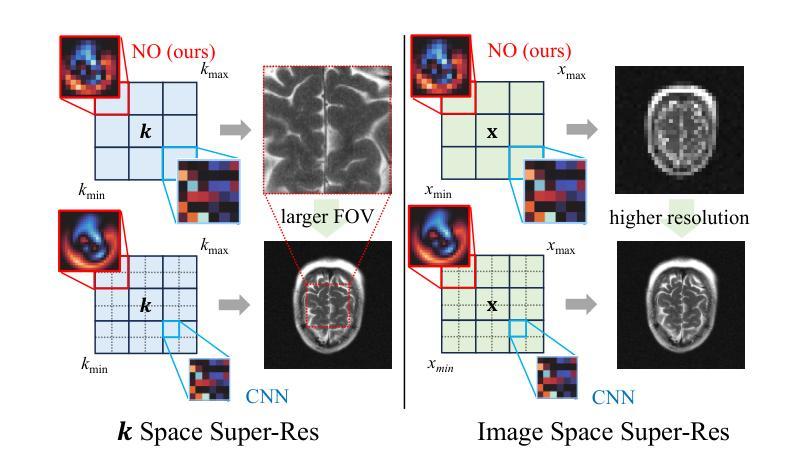
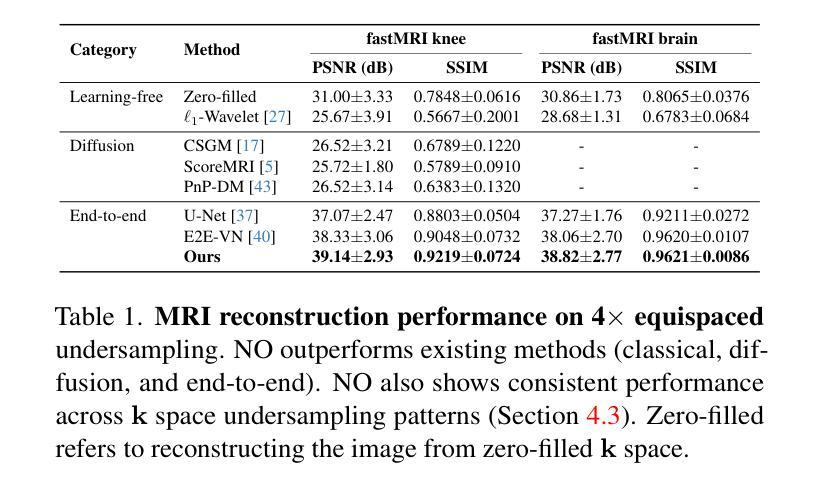
Compressed Sensing MRI reconstructs images of the body’s internal anatomy from undersampled measurements, thereby reducing scan time. Recently, deep learning has shown great potential for reconstructing high-fidelity images from highly undersampled measurements. However, one needs to train multiple models for different undersampling patterns and desired output image resolutions, since most networks operate on a fixed discretization. Such approaches are highly impractical in clinical settings, where undersampling patterns and image resolutions are frequently changed to accommodate different real-time imaging and diagnostic requirements. We propose a unified MRI reconstruction model robust to various measurement undersampling patterns and image resolutions. Our approach uses neural operators, a discretization-agnostic architecture applied in both image and measurement spaces, to capture local and global features. Empirically, our model improves SSIM by 11% and PSNR by 4 dB over a state-of-the-art CNN (End-to-End VarNet), with 600$\times$ faster inference than diffusion methods. The resolution-agnostic design also enables zero-shot super-resolution and extended field-of-view reconstruction, offering a versatile and efficient solution for clinical MR imaging. Our unified model offers a versatile solution for MRI, adapting seamlessly to various measurement undersampling and imaging resolutions, making it highly effective for flexible and reliable clinical imaging. Our code is available at https://armeet.ca/nomri.
压缩感知MRI通过欠采样的测量值重建身体内部解剖结构的图像,从而缩短扫描时间。最近,深度学习在从高度欠采样的测量值重建高保真图像方面显示出巨大潜力。然而,由于大多数网络在固定的离散化上操作,因此需要针对不同的欠采样模式和所需的输出图像分辨率训练多个模型。这种方法在临床环境中非常不实用,因为欠采样模式和图像分辨率经常根据不同的实时成像和诊断要求进行更改。我们提出了一种统一且对各种测量欠采样模式和图像分辨率具有鲁棒性的MRI重建模型。我们的方法使用神经算子,这是一种应用于图像和测量空间的离散化无关架构,以捕获局部和全局特征。经验上,我们的模型在最新CNN(端到端VarNet)的基础上提高了SSIM 11%和PSNR 4 dB,推理速度是扩散方法的600倍。分辨率无关的设计还实现了零快门超分辨率和扩展视野重建,为临床MR成像提供了通用且高效的解决方案。我们的统一模型为MRI提供了通用解决方案,无缝适应各种测量欠采样和成像分辨率,使其成为灵活可靠的临床成像中的高效工具。我们的代码可在https://armeet.ca/nomri找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at 2025 Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Summary
压缩感知MRI技术能从欠采样的测量值重建身体内部结构图像,从而缩短扫描时间。深度学习在从高度欠采样的测量值重建高保真图像方面展现出巨大潜力。然而,由于大多数网络在固定的离散化上操作,需要针对不同的欠采样模式和目标输出图像分辨率训练多个模型,这在临床环境中非常不实用。我们提出了一种统一的MRI重建模型,该模型对多种测量欠采样模式和图像分辨率具有鲁棒性。我们的方法使用神经算子,一种应用于图像和测量空间的离散化无关架构,来捕捉局部和全局特征。实验表明,我们的模型在SSIM上比最先进的CNN(端到端VarNet)提高了11%,PSNR提高了4分贝,并且推理速度比扩散方法快600倍。分辨率无关的设计还实现了零射击超分辨率和扩展视野重建,为临床MR成像提供了通用和高效的解决方案。我们的统一模型为MRI提供了一个通用解决方案,能够轻松适应各种测量欠采样和成像分辨率,对于灵活可靠的临床成像非常有效。我们的代码可在https://armeet.ca/nomri上找到。
Key Takeaways
- 压缩感知MRI能从欠采样测量值重建图像,缩短扫描时间。
- 深度学习在MRI重建中具有巨大潜力,尤其在处理高度欠采样数据方面。
- 当前方法需要针对多种欠采样模式和图像分辨率训练多个模型,不便于临床应用。
- 提出的统一MRI重建模型对各种欠采样模式和图像分辨率具有鲁棒性。
- 使用神经算子来捕捉局部和全局特征,实现更好的图像重建效果。
- 模型在SSIM和PSNR指标上表现优异,且推理速度较快。
点此查看论文截图


Developing Generalist Foundation Models from a Multimodal Dataset for 3D Computed Tomography
Authors:Ibrahim Ethem Hamamci, Sezgin Er, Chenyu Wang, Furkan Almas, Ayse Gulnihan Simsek, Sevval Nil Esirgun, Irem Doga, Omer Faruk Durugol, Weicheng Dai, Murong Xu, Muhammed Furkan Dasdelen, Bastian Wittmann, Tamaz Amiranashvili, Enis Simsar, Mehmet Simsar, Emine Bensu Erdemir, Abdullah Alanbay, Anjany Sekuboyina, Berkan Lafci, Christian Bluethgen, Kayhan Batmanghelich, Mehmet Kemal Ozdemir, Bjoern Menze
While computer vision has achieved tremendous success with multimodal encoding and direct textual interaction with images via chat-based large language models, similar advancements in medical imaging AI, particularly in 3D imaging, have been limited due to the scarcity of comprehensive datasets. To address this critical gap, we introduce CT-RATE, the first dataset that pairs 3D medical images with corresponding textual reports. CT-RATE comprises 25,692 non-contrast 3D chest CT scans from 21,304 unique patients. Through various reconstructions, these scans are expanded to 50,188 volumes, totaling over 14.3 million 2D slices. Each scan is accompanied by its corresponding radiology report. Leveraging CT-RATE, we develop CT-CLIP, a CT-focused contrastive language-image pretraining framework designed for broad applications without the need for task-specific training. We demonstrate how CT-CLIP can be used in two tasks: multi-abnormality detection and case retrieval. Remarkably, in multi-abnormality detection, CT-CLIP outperforms state-of-the-art fully supervised models across all key metrics, effectively eliminating the need for manual annotation. In case retrieval, it efficiently retrieves relevant cases using either image or textual queries, thereby enhancing knowledge dissemination. By combining CT-CLIP’s vision encoder with a pretrained large language model, we create CT-CHAT, a vision-language foundational chat model for 3D chest CT volumes. Finetuned on over 2.7 million question-answer pairs derived from the CT-RATE dataset, CT-CHAT surpasses other multimodal AI assistants, underscoring the necessity for specialized methods in 3D medical imaging. Collectively, the open-source release of CT-RATE, CT-CLIP, and CT-CHAT not only addresses critical challenges in 3D medical imaging, but also lays the groundwork for future innovations in medical AI and improved patient care.
虽然计算机视觉在多模态编码和基于聊天的大型语言模型的直接文本与图像交互方面取得了巨大的成功,但在医学影像人工智能领域,特别是在3D成像方面的进展却相对有限,这主要是由于缺乏综合数据集。为了弥补这一关键差距,我们推出了CT-RATE数据集,它是首个将3D医学图像与相应的文本报告配对的数据集。CT-RATE包含了来自21,304名独特患者的25,692个非对比剂3D胸部CT扫描。通过各种重建,这些扫描被扩展为超过5万个体积,总计超过一千四百万个二维切片。每个扫描都附有相应的放射学报告。借助CT-RATE,我们开发了CT-CLIP模型,这是一个专注于CT的对比语言图像预训练框架,适用于广泛的应用场景,无需特定任务训练。我们展示了如何在两个任务中使用CT-CLIP:多异常检测与案例检索。在多异常检测中,CT-CLIP在所有关键指标上都超越了最先进的全监督模型,有效地消除了对人工注释的需求。在案例检索中,它能够高效地使用图像或文本查询来检索相关案例,从而提高知识传播效率。通过将CT-CLIP的视觉编码器与预训练的的大型语言模型相结合,我们创建了用于三维胸部CT体积的CT-CHAT基础聊天模型。使用经过在超过千万问答案对进行训练的CT-CHAT超越其他多模态AI助手,凸显出在三维医学影像中采用专门方法的必要性。总之,CT-RATE、CT-CLIP和CT-CHAT的开源发布不仅解决了三维医学影像中的关键挑战,也为未来医疗人工智能的创新和患者护理的改善奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于计算机视觉技术在多模态编码和基于聊天的大型语言模型与图像直接交互方面的巨大成功,医疗影像人工智能(AI)在3D成像方面的进展却相对有限,主要由于缺乏全面的数据集。为解决这一关键空白,我们推出了CT-RATE数据集,它首次将3D医学图像与相应的文本报告配对。CT-RATE包含了来自21,304名独特患者的25,692个非对比性3D胸部CT扫描。通过这些扫描的多种重建,数据量扩展至超过千万个二维切片。每个扫描均附有相应的放射学报告。我们利用CT-RATE开发出了CT-CLIP,一个无需特定任务训练的通用对比语言图像预训练框架。在异常检测与案例检索两项任务中,CT-CLIP表现出了强大的性能。异常检测方面,CT-CLIP在所有关键指标上均超越了最先进的全监督模型,无需手动标注;案例检索方面,它能够高效地使用图像或文本查询检索相关案例,促进知识传播。通过结合CT-CLIP的视觉编码器和预训练的大型语言模型,我们创建了针对三维胸部CT体积的视语言基础聊天模型CT-CHAT。在由CT-RATE数据集派生的数百万问答对上微调后,CT-CHAT超越了其他多模态AI助手,突显了医学三维成像需要专业方法的重要性。总体而言,CT-RATE、CT-CLIP和CT-CHAT的开源发布不仅解决了医学三维成像的关键挑战,还为医疗人工智能的未来发展及患者护理的改善奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 缺乏全面的数据集限制了医疗影像AI在3D成像方面的进展。
- 引入CT-RATE数据集,实现3D医学图像与相应文本报告的配对。
- 开发CT-CLIP预训练框架,用于多模态语言图像对比任务,表现优异于多项关键任务指标。
- CT-CLIP在多异常检测方面超越先进模型,无需手动标注。
- CT-CLIP支持案例检索功能,促进知识传播。
- 结合视觉编码器和大型语言模型创建CT-CHAT聊天模型,针对三维胸部CT体积提供基础医疗服务。
点此查看论文截图