⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-08 更新
APIGen-MT: Agentic Pipeline for Multi-Turn Data Generation via Simulated Agent-Human Interplay
Authors:Akshara Prabhakar, Zuxin Liu, Weiran Yao, Jianguo Zhang, Ming Zhu, Shiyu Wang, Zhiwei Liu, Tulika Awalgaonkar, Haolin Chen, Thai Hoang, Juan Carlos Niebles, Shelby Heinecke, Huan Wang, Silvio Savarese, Caiming Xiong
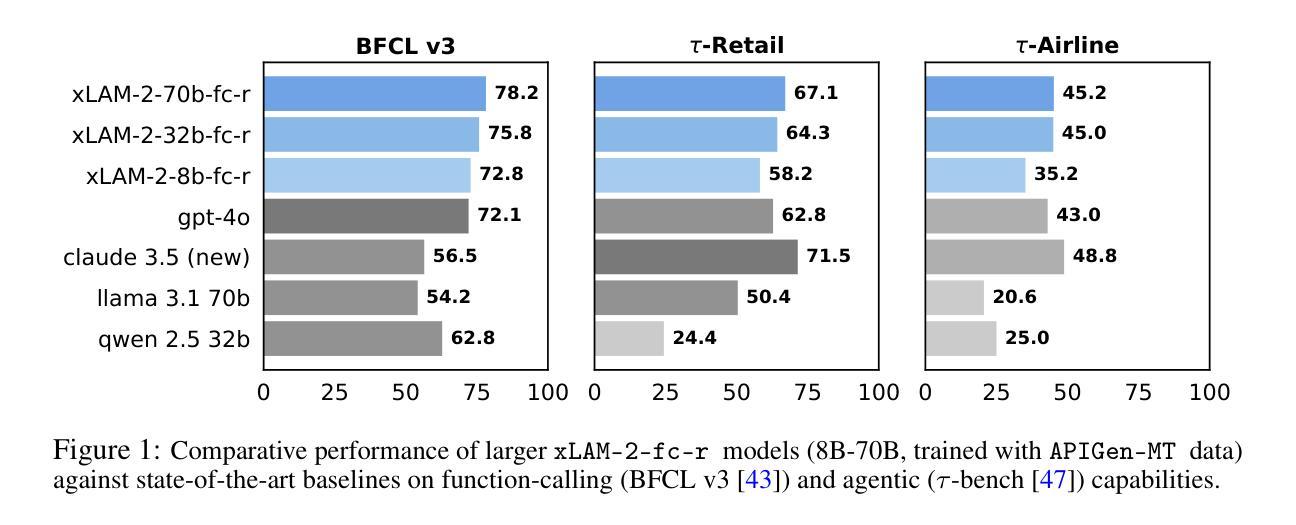
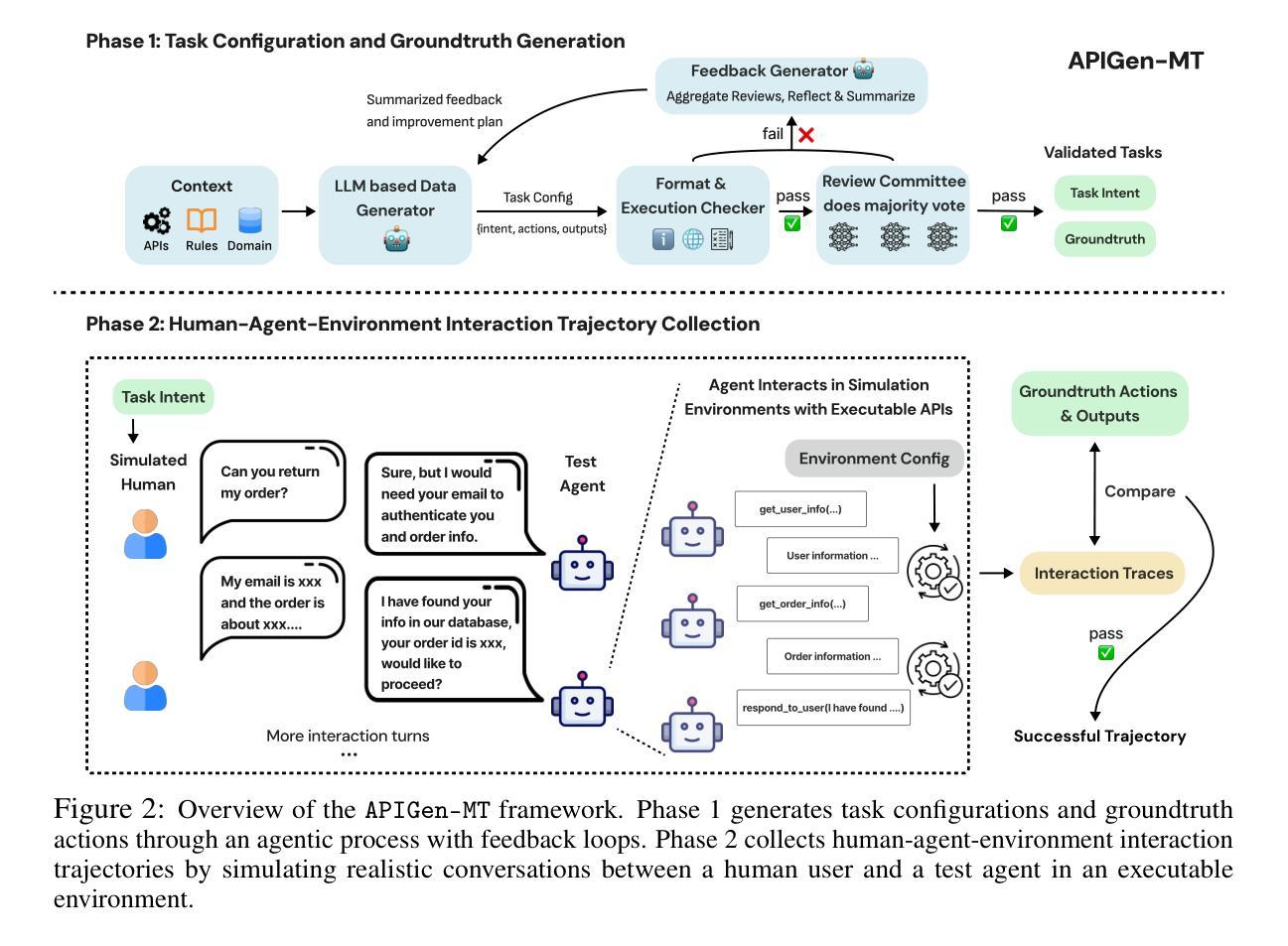
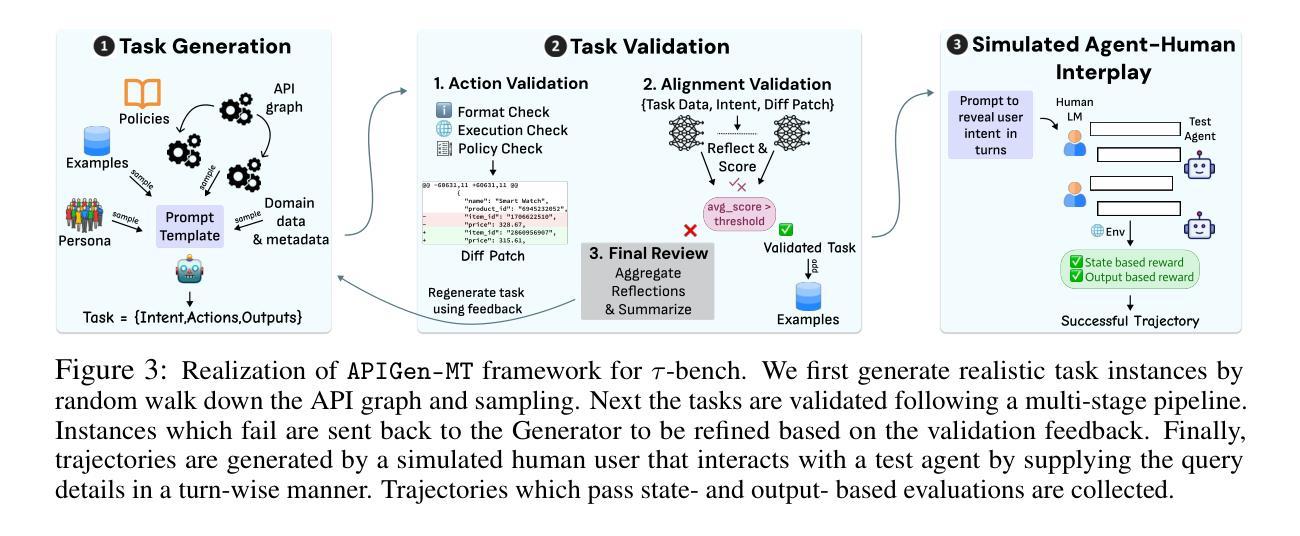
Training effective AI agents for multi-turn interactions requires high-quality data that captures realistic human-agent dynamics, yet such data is scarce and expensive to collect manually. We introduce APIGen-MT, a two-phase framework that generates verifiable and diverse multi-turn agent data. In the first phase, our agentic pipeline produces detailed task blueprints with ground-truth actions, leveraging a committee of LLM reviewers and iterative feedback loops. These blueprints are then transformed into complete interaction trajectories through simulated human-agent interplay. We train a family of models – the xLAM-2-fc-r series with sizes ranging from 1B to 70B parameters. Our models outperform frontier models such as GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 on $\tau$-bench and BFCL benchmarks, with the smaller models surpassing their larger counterparts, particularly in multi-turn settings, while maintaining superior consistency across multiple trials. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our verified blueprint-to-details approach yields high-quality training data, enabling the development of more reliable, efficient, and capable agents. We open-source both the synthetic data collected and the trained xLAM-2-fc-r models to advance research in AI agents. Models are available on HuggingFace at https://huggingface.co/collections/Salesforce/xlam-2-67ef5be12949d8dcdae354c4 and project website is https://apigen-mt.github.io
训练多轮互动的高效人工智能代理需要捕捉真实人类与代理动态的高质量数据,但这样的数据非常稀缺且难以手动收集。我们推出了APIGen-MT,这是一个两阶段框架,可生成可验证和多样化的多轮代理数据。在第一阶段,我们的代理管道会产生带有真实行动的任务蓝图,利用大型语言模型审查小组和迭代反馈循环。这些蓝图然后通过模拟人类与代理的互动转化为完整的交互轨迹。我们训练了一系列模型,即xLAM-2-fc-r系列,参数范围从1B到70B。我们的模型在τ基准测试和BFCL基准测试中超越了前沿模型,如GPT-4o和Claude 3.5。较小的模型在多轮设置中超越了较大的模型,同时在多次试验中保持了卓越的一致性。综合实验表明,我们的验证蓝图到细节的方法产生了高质量的训练数据,能够开发出更可靠、更高效、更强大的代理。我们开源收集的合成数据和训练的xLAM-2-fc-r模型,以促进人工智能代理的研究。模型可在HuggingFace上的Salesforce集合中找到:链接,项目网站为:链接。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages plus references and appendices
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为APIGen-MT的两阶段框架,用于生成可验证和多样化的多轮交互代理数据。该框架通过代理管道产生详细的带有真实动作的任务蓝图,并利用一组大型语言模型评审者和迭代反馈循环进行验证。蓝图进一步转化为模拟人机互动产生的完整交互轨迹。本文训练的xLAM-2-fc-r系列模型在τ基准测试和BFCL基准测试中表现出超越GPT-4o和Claude 3.5的性能,尤其是较小的模型在多轮设置中的表现超越较大模型的同时维持多次试验间的高度一致性。该项目公开了收集的合成数据和训练的模型,以推动人工智能代理研究的发展。
Key Takeaways
- APIGen-MT是一个用于生成多轮交互AI代理数据的两阶段框架。
- 该框架包括一个代理管道,用于生成详细的带有真实动作的任务蓝图。
- APIGen-MT利用大型语言模型评审者和迭代反馈循环验证蓝图的准确性。
- 通过模拟人机互动,将任务蓝图转化为完整的交互轨迹。
- xLAM-2-fc-r系列模型在多个基准测试中表现出卓越性能,尤其是多轮交互场景。
- 较小模型的性能超越了较大模型,同时保持了多次试验的一致性。
点此查看论文截图

SynWorld: Virtual Scenario Synthesis for Agentic Action Knowledge Refinement
Authors:Runnan Fang, Xiaobin Wang, Yuan Liang, Shuofei Qiao, Jialong Wu, Zekun Xi, Ningyu Zhang, Yong Jiang, Pengjun Xie, Fei Huang, Huajun Chen
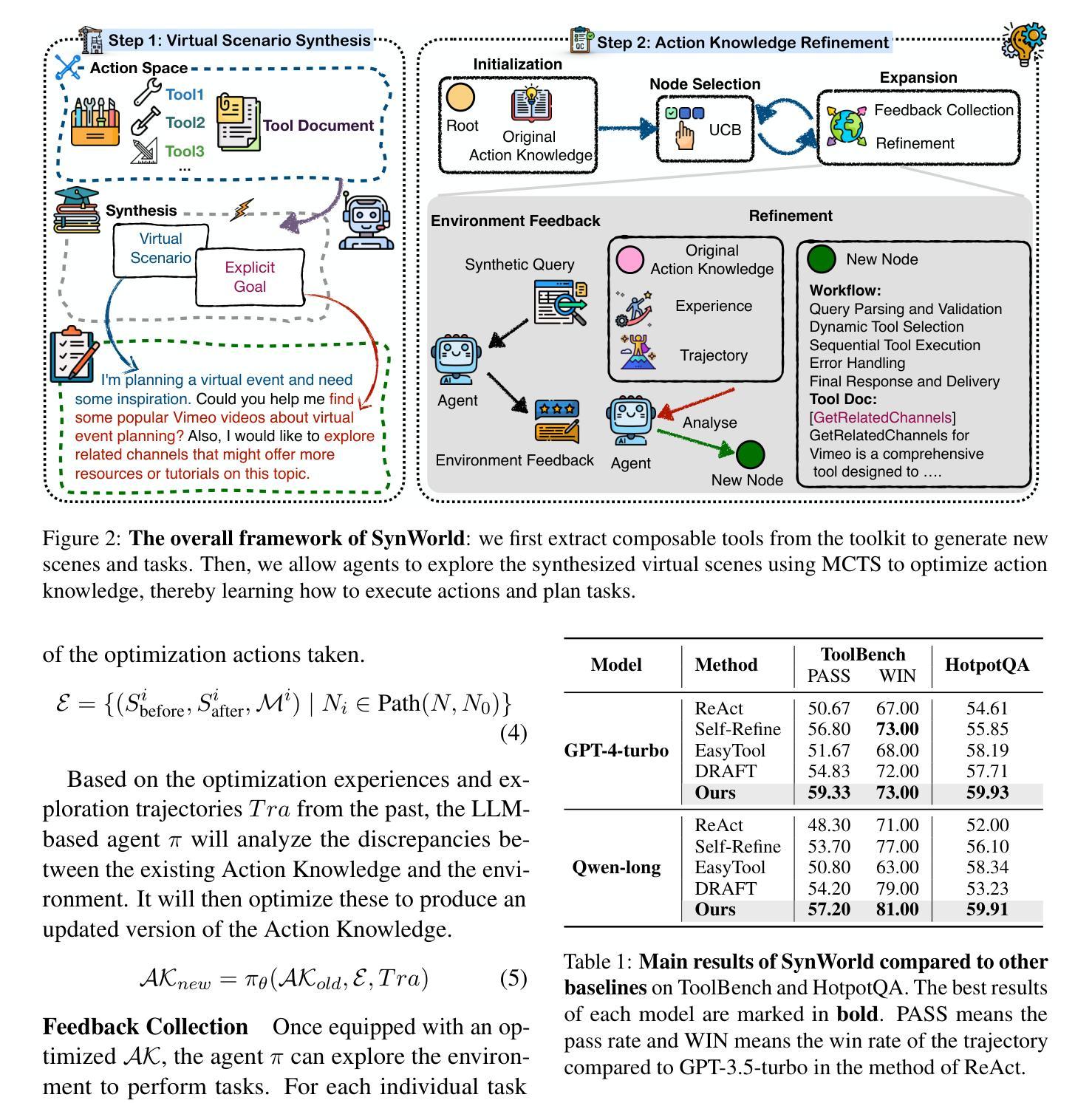
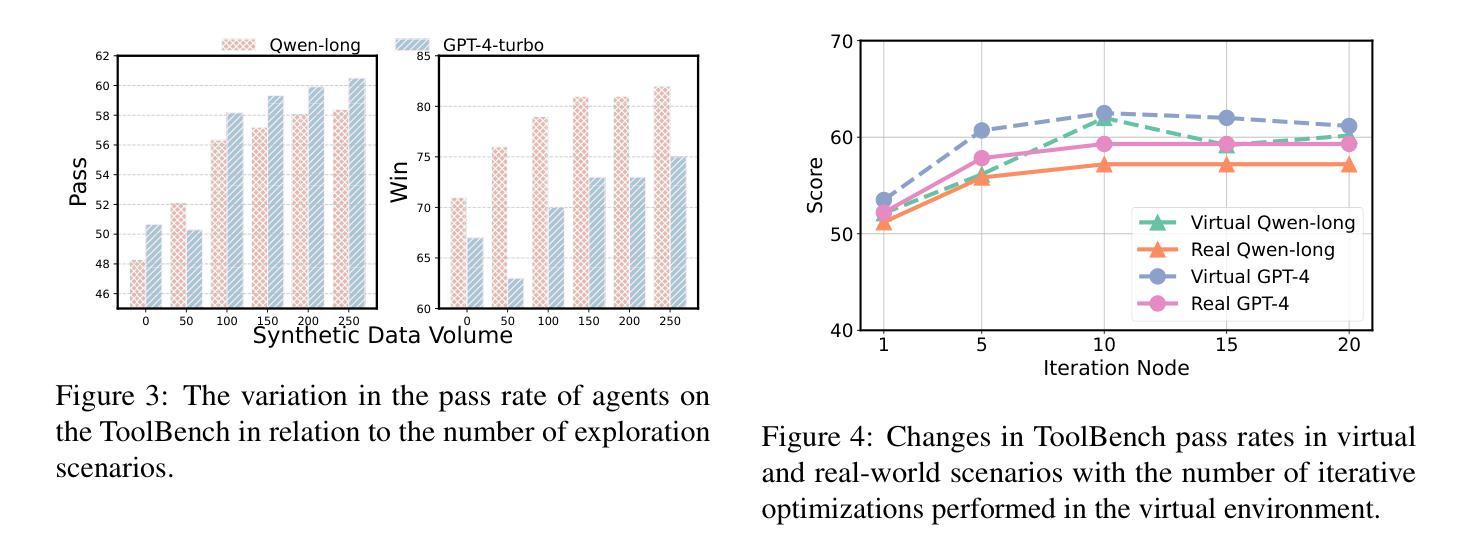
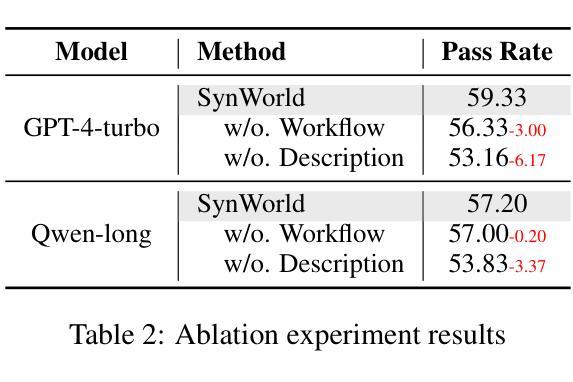
In the interaction between agents and their environments, agents expand their capabilities by planning and executing actions. However, LLM-based agents face substantial challenges when deployed in novel environments or required to navigate unconventional action spaces. To empower agents to autonomously explore environments, optimize workflows, and enhance their understanding of actions, we propose SynWorld, a framework that allows agents to synthesize possible scenarios with multi-step action invocation within the action space and perform Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) exploration to effectively refine their action knowledge in the current environment. Our experiments demonstrate that SynWorld is an effective and general approach to learning action knowledge in new environments. Code is available at https://github.com/zjunlp/SynWorld.
在智能体与其环境之间的交互中,智能体通过规划和执行行动来扩展其能力。然而,当部署在新型环境中或需要执行非常规动作时,基于大型语言模型的智能体会面临巨大的挑战。为了增强智能体自主探索环境、优化工作流程、增强对动作的理解能力,我们提出了SynWorld框架。该框架允许智能体在动作空间内通过多步动作调用合成可能的场景,并执行蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)探索,以有效地在当前环境中优化其动作知识。我们的实验表明,SynWorld是一种在新环境中学习动作知识的有效且通用的方法。代码可在https://github.com/zjunlp/SynWorld找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
Summary
在智能代理与其环境互动的过程中,通过规划与执行动作来扩展其能力。然而,基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理在部署于新环境或需要执行非传统动作时面临巨大挑战。为提升代理自主探索环境、优化工作流程和对动作的理解能力,我们提出SynWorld框架。该框架允许代理在动作空间内合成多种可能场景并执行多步骤动作调用,通过蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)探索来有效精进其在当前环境下的动作知识。实验证明,SynWorld是一种有效且通用的学习新环境下动作知识的方法。相关代码可在链接找到。
Key Takeaways
- 智能代理通过规划并执行动作来扩展其能力。
- 在新环境或执行非传统动作时,基于大型语言模型的代理面临挑战。
- SynWorld框架允许代理合成多种场景并在动作空间内执行多步骤动作。
- 通过蒙特卡洛树搜索探索,SynWorld框架帮助代理有效精进在当特环境下的动作知识。
- SynWorld是一个有效且通用的学习新环境下动作知识的方法。
- SynWorld框架提升代理自主探索环境、优化工作流程和对动作的理解能力。
点此查看论文截图

Agentic Knowledgeable Self-awareness
Authors:Shuofei Qiao, Zhisong Qiu, Baochang Ren, Xiaobin Wang, Xiangyuan Ru, Ningyu Zhang, Xiang Chen, Yong Jiang, Pengjun Xie, Fei Huang, Huajun Chen
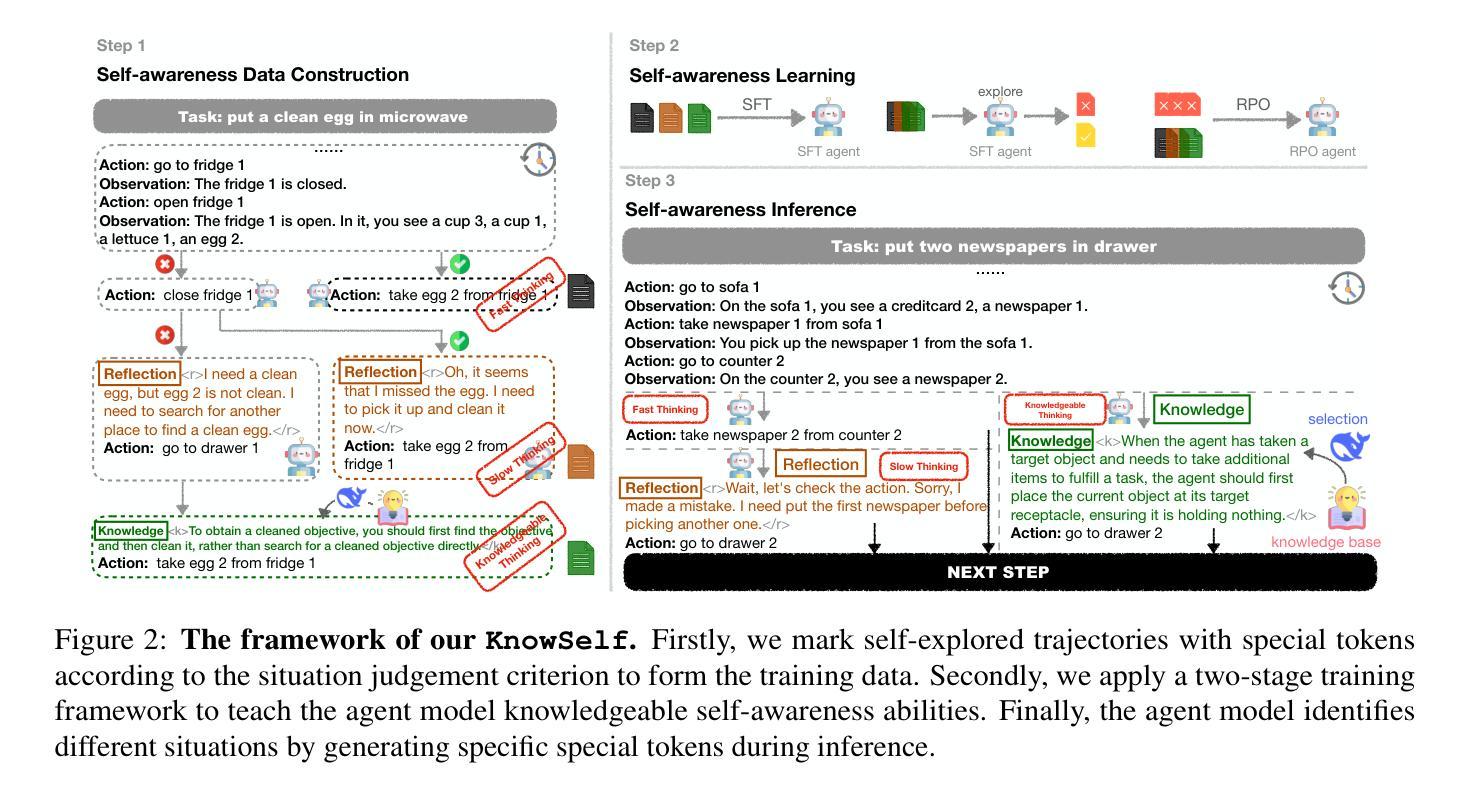
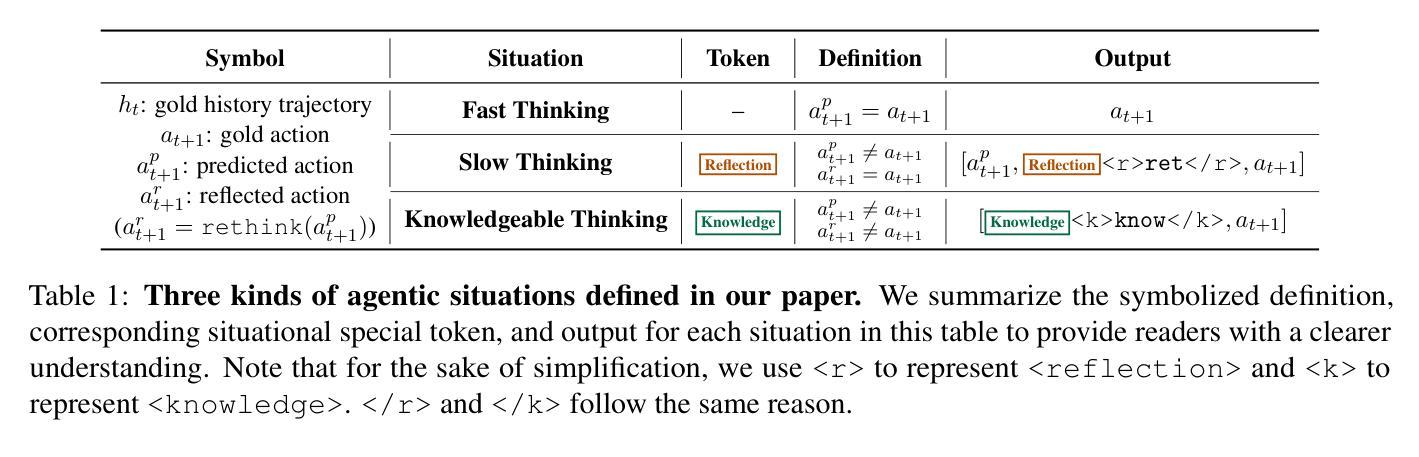
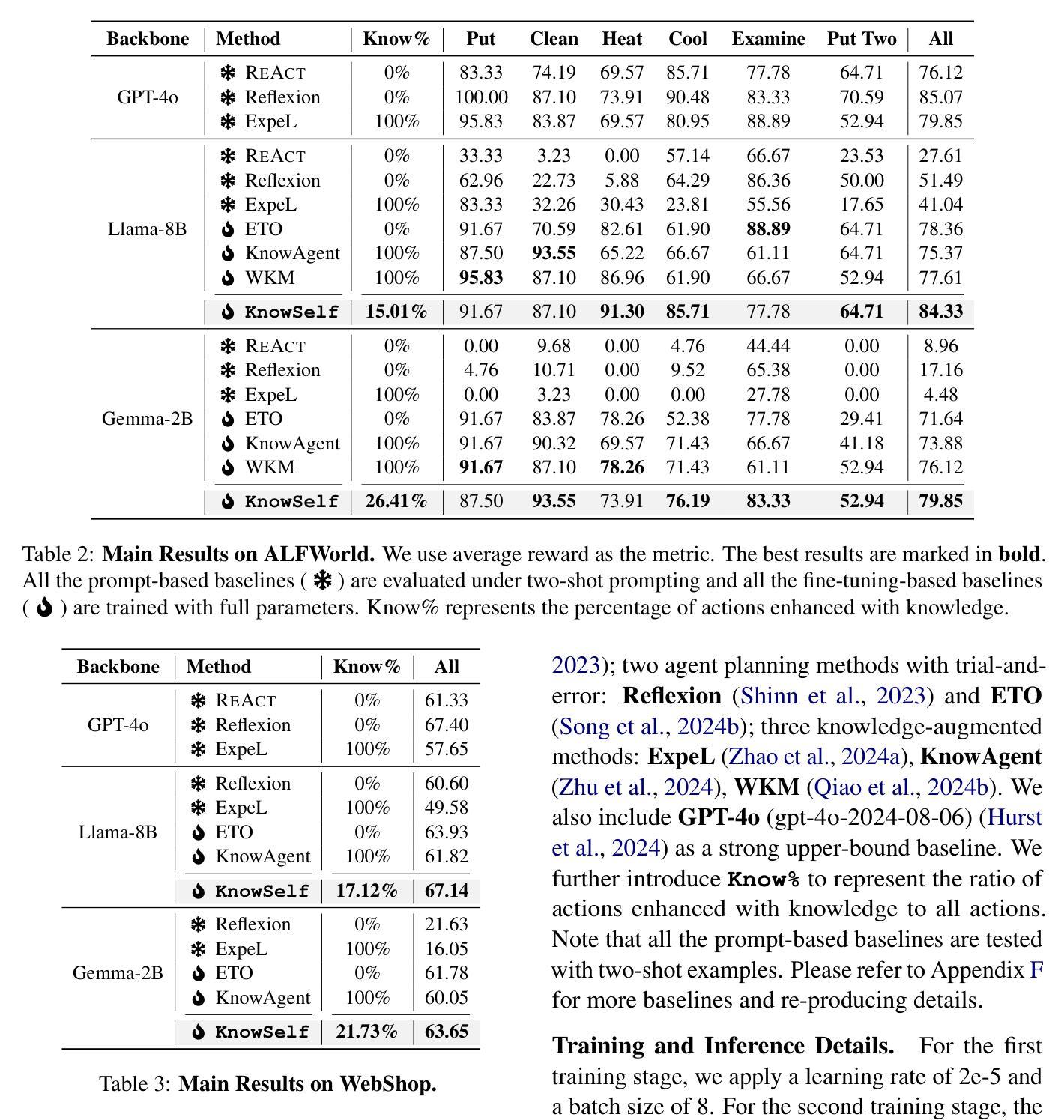
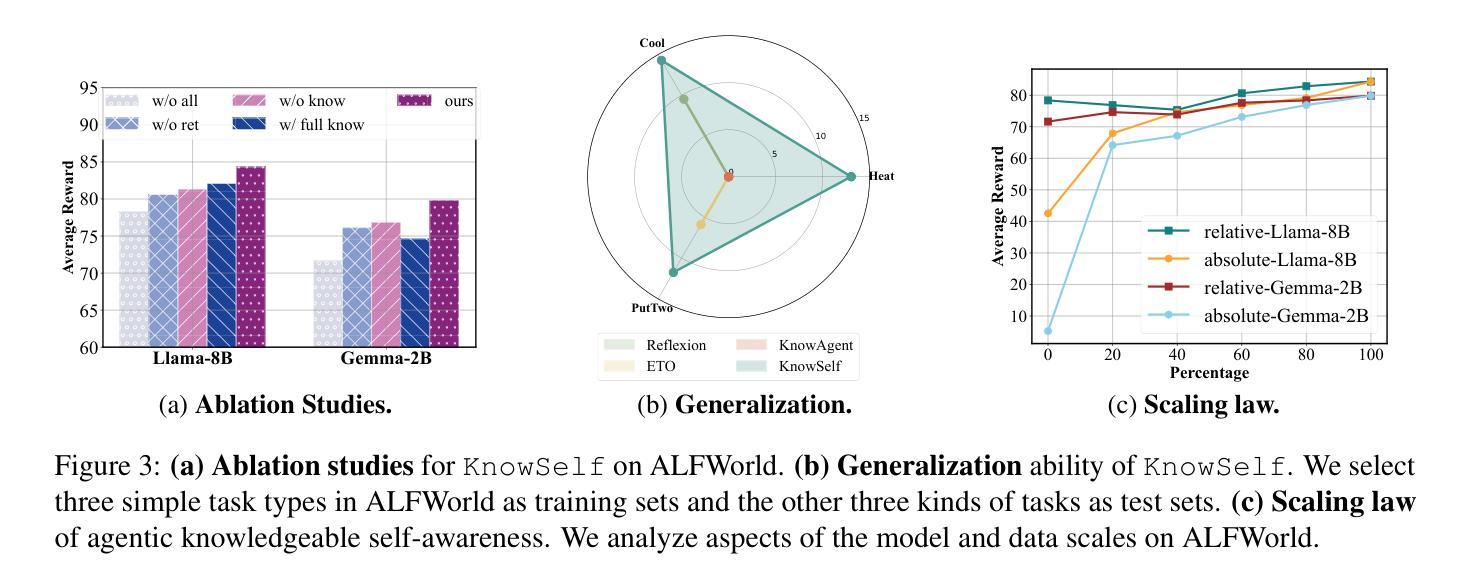
Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved considerable performance across various agentic planning tasks. However, traditional agent planning approaches adopt a “flood irrigation” methodology that indiscriminately injects gold trajectories, external feedback, and domain knowledge into agent models. This practice overlooks the fundamental human cognitive principle of situational self-awareness during decision-making-the ability to dynamically assess situational demands and strategically employ resources during decision-making. We propose agentic knowledgeable self-awareness to address this gap, a novel paradigm enabling LLM-based agents to autonomously regulate knowledge utilization. Specifically, we propose KnowSelf, a data-centric approach that applies agents with knowledgeable self-awareness like humans. Concretely, we devise a heuristic situation judgement criterion to mark special tokens on the agent’s self-explored trajectories for collecting training data. Through a two-stage training process, the agent model can switch between different situations by generating specific special tokens, achieving optimal planning effects with minimal costs. Our experiments demonstrate that KnowSelf can outperform various strong baselines on different tasks and models with minimal use of external knowledge. Code is available at https://github.com/zjunlp/KnowSelf.
大型语言模型(LLM)在各种智能规划任务中取得了显著的性能。然而,传统的智能规划方法采用“洪水灌溉”的方法,不加区别地将黄金轨迹、外部反馈和领域知识注入智能模型中。这种做法忽视了决策过程中情境自我意识这一基本的人类认知原则——即在决策过程中动态评估情境需求并战略性利用资源的能力。为了解决这一差距,我们提出了智能知识自我意识这一概念,这是一种新型范式,使基于LLM的智能体能够自主调节知识利用。具体来说,我们提出了KnowSelf方法,这是一种以数据为中心的方法,将智能知识自我意识应用于智能体,类似于人类的认知方式。我们设计了一种启发式情境判断标准,在智能体的自我探索轨迹上标记特殊令牌,以收集训练数据。通过两阶段训练过程,智能体模型可以通过生成特定的特殊令牌在不同情境之间切换,以最低的成本实现最佳的规划效果。我们的实验表明,在不同的任务和模型上,KnowSelf可以超越各种强大的基线,且对外部知识的使用最少。代码可在https://github.com/zjunlp/KnowSelf找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在多种智能规划任务中表现优异,但传统智能规划方法未考虑人类的认知原则,即情境自我感知能力。本文提出了知识自我感知的概念来解决这一问题,并介绍了一种数据驱动的方法KnowSelf,使LLM能够自主调节知识运用。通过两阶段训练过程,实现智能体在不同情境下生成特定标记,达到优化规划效果并降低成本。实验证明,KnowSelf在不同任务和模型上能超越多个强大的基线,且极少依赖外部知识。具体代码已公开于GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在智能规划任务中表现突出。
- 传统智能规划方法忽略了人类的情境自我感知能力。
- 知识自我感知概念的提出,旨在弥补这一缺陷。
- KnowSelf方法采用数据驱动的方式赋予LLM自主调节知识运用的能力。
- 通过两阶段训练过程,智能体能够在不同情境下生成特定标记以实现优化规划。
- KnowSelf在不同任务和模型上的表现超越了多个强大的基线。
点此查看论文截图

The AI Cosmologist I: An Agentic System for Automated Data Analysis
Authors:Adam Moss
We present the AI Cosmologist, an agentic system designed to automate cosmological/astronomical data analysis and machine learning research workflows. This implements a complete pipeline from idea generation to experimental evaluation and research dissemination, mimicking the scientific process typically performed by human researchers. The system employs specialized agents for planning, coding, execution, analysis, and synthesis that work together to develop novel approaches. Unlike traditional auto machine-learning systems, the AI Cosmologist generates diverse implementation strategies, writes complete code, handles execution errors, analyzes results, and synthesizes new approaches based on experimental outcomes. We demonstrate the AI Cosmologist capabilities across several machine learning tasks, showing how it can successfully explore solution spaces, iterate based on experimental results, and combine successful elements from different approaches. Our results indicate that agentic systems can automate portions of the research process, potentially accelerating scientific discovery. The code and experimental data used in this paper are available on GitHub at https://github.com/adammoss/aicosmologist. Example papers included in the appendix demonstrate the system’s capability to autonomously produce complete scientific publications, starting from only the dataset and task description
我们推出了AI宇宙学家(AI Cosmologist),这是一个旨在自动化宇宙学/天文学数据分析和机器学习研究流程的代理系统。这实现了从想法产生到实验评估和研究传播的全过程,模仿人类研究者通常进行的科学过程。该系统采用专门用于规划、编码、执行、分析和合成的智能代理,这些智能代理协同工作以开发新的方法。与传统自动机器学习系统不同,AI宇宙学家能够生成多样化的实现策略,编写完整的代码,处理执行错误,分析实验结果,并根据实验结果合成新的方法。我们在多个机器学习任务中展示了AI宇宙学家的能力,展示它在探索解决方案空间方面的成功,根据实验结果进行迭代,以及从不同方法中结合成功元素的能力。我们的结果表明,智能系统可以自动化研究过程的某些部分,从而可能加速科学发现。本论文中使用的代码和实验数据可在GitHub上找到:https://github.com/adammoss/aicosmologist。附录中包括的示例论文展示了系统自主完成科学论文的能力,仅从数据集和任务描述开始。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 45 pages
Summary
人工智能宇宙学家是一个自动化宇宙学/天文学数据分析和机器学习研究工作流程的系统。它模仿人类科学家的科学过程,实现从想法产生到实验评估和研究传播的一条龙服务。系统采用特殊代理进行规划、编码、执行、分析和综合,可生成多种实施策略、编写完整代码、处理执行错误、分析成果,并根据实验结果合成新方案。该系统可在多个机器学习任务中展示其能力,成功探索解空间、基于实验结果进行迭代,并整合不同方法中的成功元素。研究结果表明,智能系统可以自动化部分研究过程,从而加速科学发现。
Key Takeaways
- AI Cosmologist是一个自动化宇宙学/天文学数据分析和机器学习研究工作流程的系统。
- 该系统模仿人类科学家的科学过程,实现从想法产生到实验评估和研究传播的一条龙服务。
- AI Cosmologist采用特殊代理进行规划、编码、执行、分析和综合工作。
- 该系统可以生成多种实施策略,自动处理执行错误,并根据实验结果分析成果和合成新方案。
- AI Cosmologist在多个机器学习任务中表现出强大的能力,包括探索解空间、迭代和整合不同方法中的成功元素。
- 研究结果表明,智能系统可以自动化部分研究过程,提高研究效率。
- 该系统的代码和实验数据可在GitHub上获取。
点此查看论文截图

Inherent and emergent liability issues in LLM-based agentic systems: a principal-agent perspective
Authors:Garry A. Gabison, R. Patrick Xian
Agentic systems powered by large language models (LLMs) are becoming progressively more complex and capable. Their increasing agency and expanding deployment settings attract growing attention over effective governance policies, monitoring and control protocols. Based on emerging landscapes of the agentic market, we analyze the potential liability issues stemming from delegated use of LLM agents and their extended systems from a principal-agent perspective. Our analysis complements existing risk-based studies on artificial agency and covers the spectrum of important aspects of the principal-agent relationship and their potential consequences at deployment. Furthermore, we motivate method developments for technical governance along the directions of interpretability and behavior evaluations, reward and conflict management, and the mitigation of misalignment and misconduct through principled engineering of detection and fail-safe mechanisms. By illustrating the outstanding issues in AI liability for LLM-based agentic systems, we aim to inform the system design, auditing and monitoring approaches to enhancing transparency and accountability.
由大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的智能系统正变得越来越复杂和强大。其不断增长的代理能力和不断扩大的部署环境引起了人们对有效治理政策、监控和控制协议的日益关注。基于智能市场的新兴格局,我们从委托代理的角度分析了由LLM智能代理及其扩展系统引起的潜在责任问题。我们的分析补充了基于风险的人工智能代理研究,涵盖了委托代理关系的重要方面及其在部署过程中的潜在后果。此外,我们为推动技术治理方法的发展提供了动力,包括可解释性和行为评估、奖励和冲突管理以及通过原则工程检测和安全故障机制来缓解错位和不当行为的方向。通过阐明基于LLM的智能系统的AI责任突出问题,我们的目标是提供系统设计、审计和监控方法,以提高透明度和问责制。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages content (incl. appendix) + 12 pages references, comments welcome
Summary
基于大型语言模型的代理系统日益复杂且功能强大,其增长的应用场景引发了对有效治理政策、监控和控制协议的关注。本文通过分析主要用户代理的视角探讨基于大型语言模型代理系统的代理使用中可能出现的潜在责任问题。分析角度不仅包括人工智能领域基于风险的研究视角,也包含了关于主代关系中重要环节的部署潜在影响的分析视角。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型驱动的代理系统日益普及,引发对治理政策和监控的关注。
- 从主用户代理的角度分析了LLM代理系统的潜在责任问题。
- 分析了主代关系中重要环节的部署潜在影响。
- 强调了技术治理方法的发展,包括解释性、行为评估、奖励和冲突管理等方向。
- 提出了通过原则性工程检测机制和故障安全机制来缓解误操作和误配置问题的措施。
点此查看论文截图

Late Breaking Results: Breaking Symmetry- Unconventional Placement of Analog Circuits using Multi-Level Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Supriyo Maji, Linran Zhao, Souradip Poddar, David Z. Pan
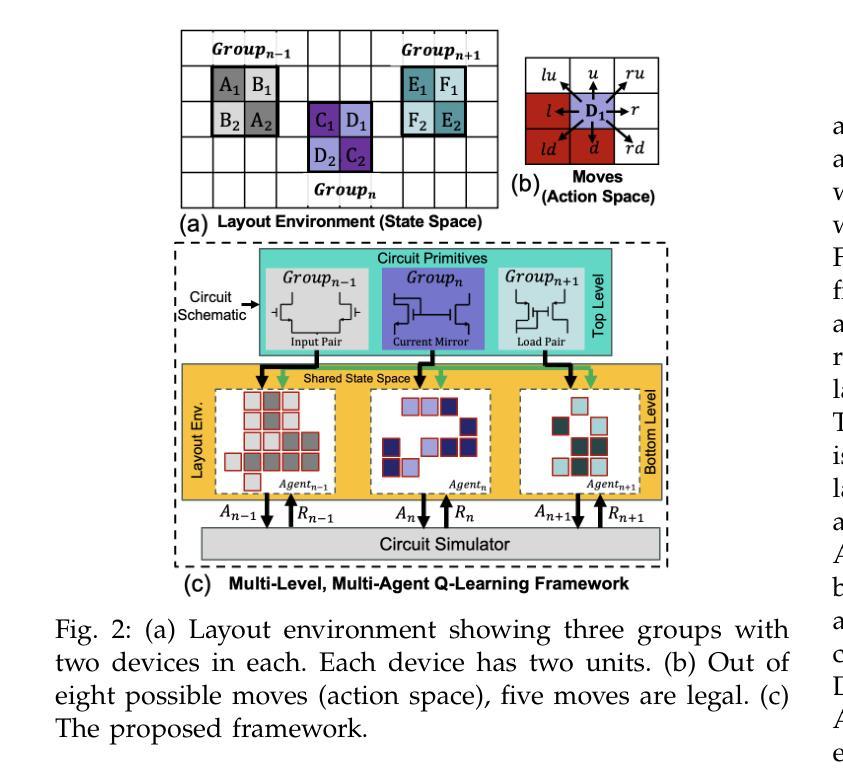
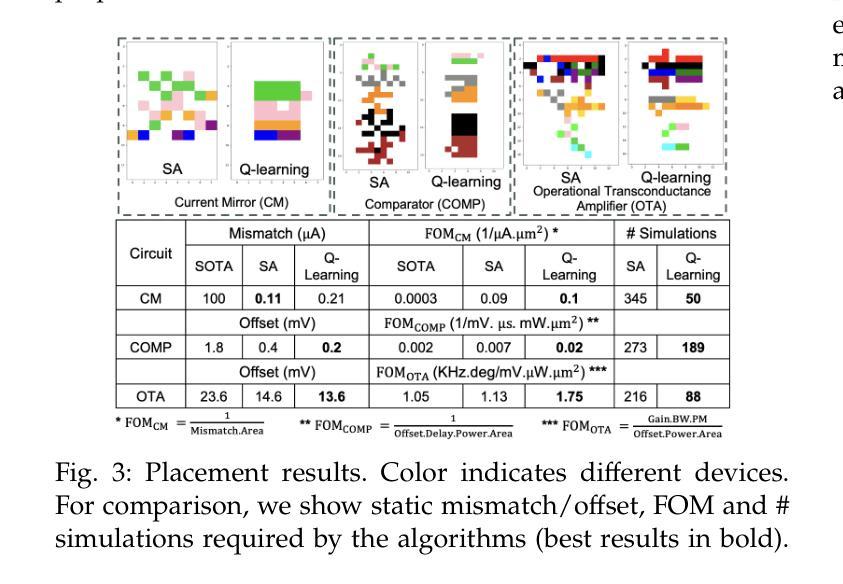
Layout-dependent effects (LDEs) significantly impact analog circuit performance. Traditionally, designers have relied on symmetric placement of circuit components to mitigate variations caused by LDEs. However, due to non-linear nature of these effects, conventional methods often fall short. We propose an objective-driven, multi-level, multi-agent Q-learning framework to explore unconventional design space of analog layout, opening new avenues for optimizing analog circuit performance. Our approach achieves better variation performance than the state-of-the-art layout techniques. Notably, this is the first application of multi-agent RL in analog layout automation. The proposed approach is compared with non-ML approach based on simulated annealing.
布局相关效应(LDEs)对模拟电路性能产生重大影响。传统上,设计者依靠电路组件的对称放置来减轻LDEs引起的变化。然而,由于这些影响的非线性性质,传统方法往往不足。我们提出了一种目标驱动的多层次多智能体Q学习框架,以探索模拟布局的非传统设计空间,为优化模拟电路性能开辟了新的途径。我们的方法实现了比当前最先进的布局技术更好的变化性能。值得注意的是,这是多智能体强化学习在模拟布局自动化中的首次应用。所提出的方法与基于模拟退火的非机器学习方法进行对比。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 2 pages, 3 figures, Proceedings of the 62nd ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), 2025
Summary
本文探讨了布局依赖效应(LDEs)对模拟电路性能的影响,并指出了传统设计方法在应对这种影响时的不足。为此,提出了一种以目标驱动的多层次多智能体Q学习框架,用于探索模拟布局的非传统设计空间,以优化模拟电路性能。该方法相较于现有的布局技术能更好地应对性能变化,并在模拟布局自动化领域首次应用了多智能体强化学习。与基于模拟退火的非机器学习方法进行对比,显示出其优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 模拟电路受到布局依赖效应(LDEs)的影响。
- 传统的设计方法依赖对称放置电路元件来减轻LDEs引起的变化,但效果有限。
- 提出了一种基于多智能体Q学习框架的新型设计方法,用于探索模拟布局的非传统设计空间。
- 该方法能优化模拟电路性能,比现有技术有更好的应对性能变化的能力。
- 这是首次将多智能体强化学习应用于模拟布局自动化。
- 该方法与基于模拟退火的非机器学习方法进行了对比,表现出优越性。
点此查看论文截图

RAIDER: Tool-Equipped Large Language Model Agent for Robotic Action Issue Detection, Explanation and Recovery
Authors:Silvia Izquierdo-Badiola, Carlos Rizzo, Guillem Alenyà
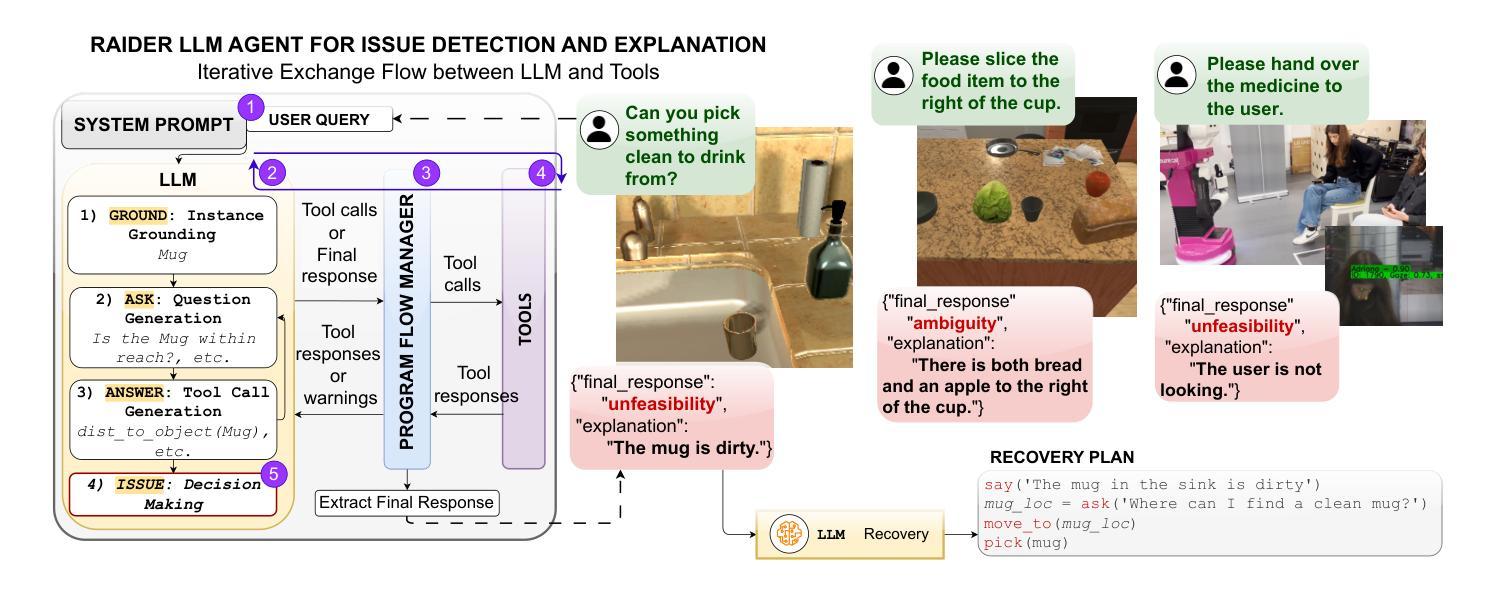
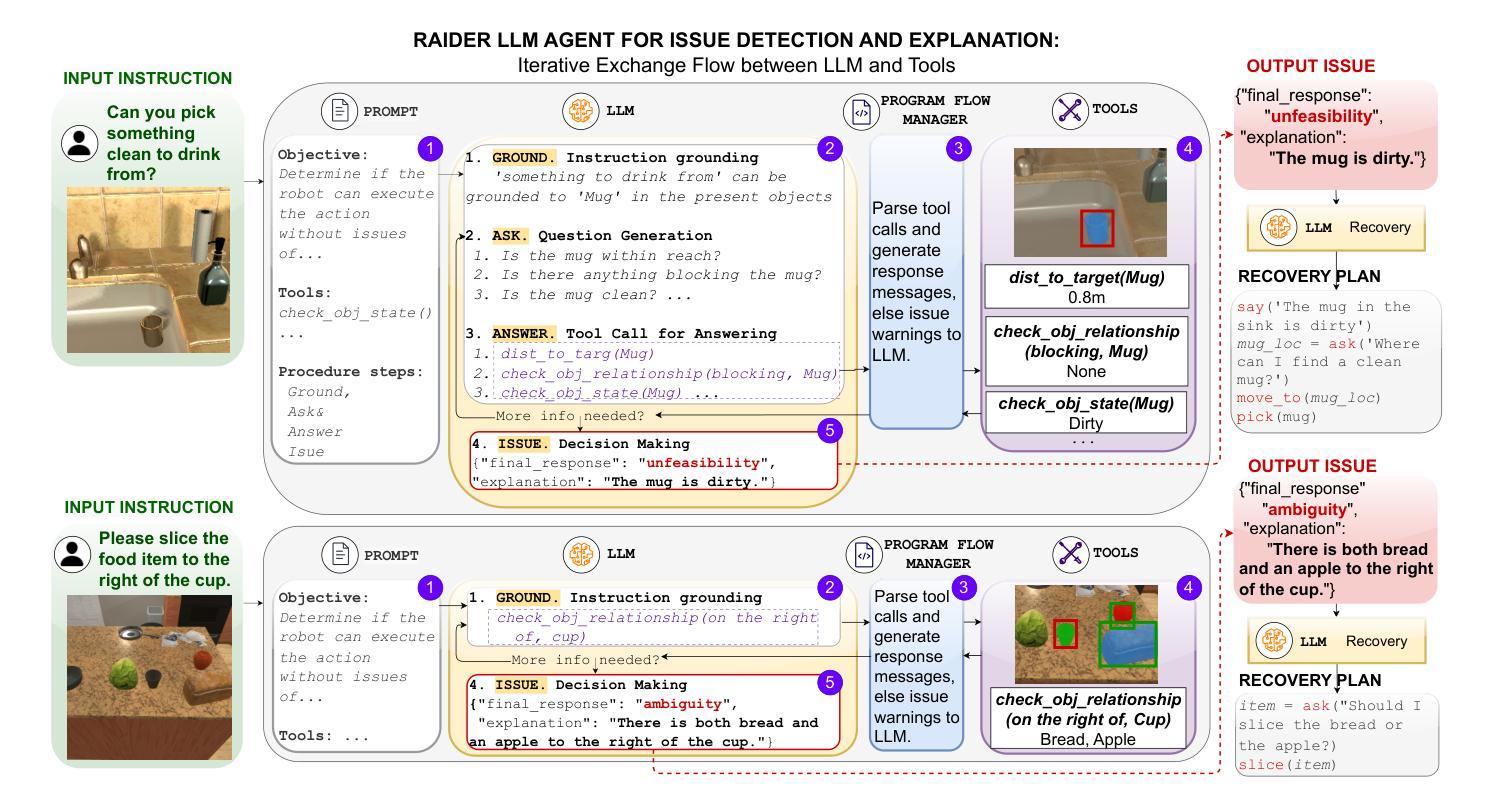
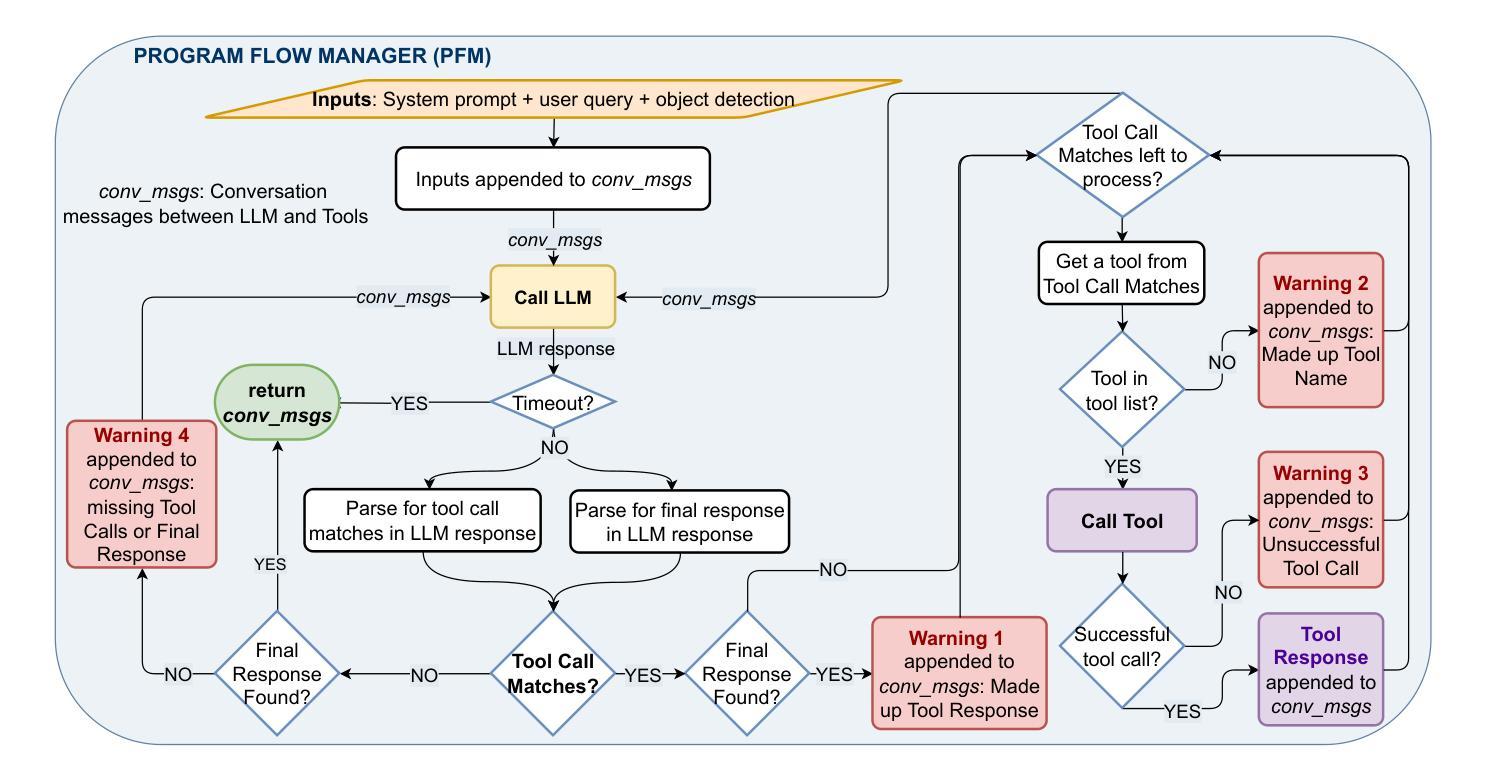
As robots increasingly operate in dynamic human-centric environments, improving their ability to detect, explain, and recover from action-related issues becomes crucial. Traditional model-based and data-driven techniques lack adaptability, while more flexible generative AI methods struggle with grounding extracted information to real-world constraints. We introduce RAIDER, a novel agent that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) with grounded tools for adaptable and efficient issue detection and explanation. Using a unique “Ground, Ask&Answer, Issue” procedure, RAIDER dynamically generates context-aware precondition questions and selects appropriate tools for resolution, achieving targeted information gathering. Our results within a simulated household environment surpass methods relying on predefined models, full scene descriptions, or standalone trained models. Additionally, RAIDER’s explanations enhance recovery success, including cases requiring human interaction. Its modular architecture, featuring self-correction mechanisms, enables straightforward adaptation to diverse scenarios, as demonstrated in a real-world human-assistive task. This showcases RAIDER’s potential as a versatile agentic AI solution for robotic issue detection and explanation, while addressing the problem of grounding generative AI for its effective application in embodied agents. Project website: https://eurecat.github.io/raider-llmagent/
随着机器人越来越多地在动态以人为中心的环境中运行,提高它们检测和解决与行动相关问题的能力变得至关重要。传统的基于模型和基于数据的技术缺乏适应性,而更灵活的生成式人工智能方法在将提取的信息与现实世界的约束相结合方面存在困难。我们引入了RAIDER,这是一个新型智能体,它结合了大型语言模型(LLM)和基于实际情境的工具,以实现灵活高效的问题检测和解释。通过独特的“接地、问答、问题”程序,RAIDER能够动态生成具有情境意识的先决条件问题,并选择合适的工具进行解答,从而实现有针对性的信息收集。在模拟家庭环境中的实验结果证明,RAIDER的表现超过了依赖预设模型、完整场景描述或独立训练模型的方法。此外,RAIDER的解释增强了恢复成功的可能性,包括需要人类互动的情况。其模块化架构配备了自我修正机制,能够轻松适应各种场景,如在现实世界中的人机辅助任务中所展示的那样。这展示了RAIDER作为通用智能体解决方案在机器人问题检测和解释方面的潜力,并解决了生成式人工智能在实体机器人中的应用中的接地问题。项目网站:https://eurecat.github.io/raider-llmagent/
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
机器人技术在动态以人为中心的环境中应用越来越广泛,因此提高机器人检测和解释行动相关问题的能力变得至关重要。传统的模型驱动和数据驱动技术缺乏适应性,而更灵活的生成式人工智能方法则难以将提取的信息与现实世界的约束相联系。本研究提出了一种新型智能体RAIDER,它结合了大型语言模型(LLM)和接地工具,用于实现灵活高效的故障检测和解释。采用独特的“接地、问答、故障处理”流程,RAIDER可动态生成上下文感知的先决条件问题并选择适当的工具进行解决,实现有针对性的信息收集。在模拟家庭环境中的表现优于依赖预设模型、全景描述或独立训练模型的方法。此外,RAIDER的解释功能提高了恢复成功率,包括需要人类互动的情况。其模块化架构具有自我校正机制,可轻松适应不同场景,在真实世界的人类辅助任务中得到了验证。这为RAIDER作为机器人故障检测和解释的通用智能体解决方案提供了潜力,并解决了生成式人工智能在实体机器人中的有效应用问题。
Key Takeaways
- 机器人的行动相关问题的检测、解释和恢复能力随着在动态以人为中心的环境中的操作越来越重要。
- 传统方法(模型驱动和数据驱动)和灵活的生成式AI方法存在局限性。
- RAIDER智能体通过结合大型语言模型和接地工具,实现了灵活高效的故障检测和解释。
- RAIDER采用独特的“接地、问答、故障处理”流程,能动态适应不同情境并选择适当的工具进行问题解决。
- 在模拟家庭环境中,RAIDER的表现优于其他方法。
- RAIDER的解释功能增强了恢复成功率,包括涉及人类互动的情况。
点此查看论文截图