⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-08 更新
Optimizing Specific and Shared Parameters for Efficient Parameter Tuning
Authors:Van-Anh Nguyen, Thanh-Toan Do, Mehrtash Harandi, Dinh Phung, Trung Le
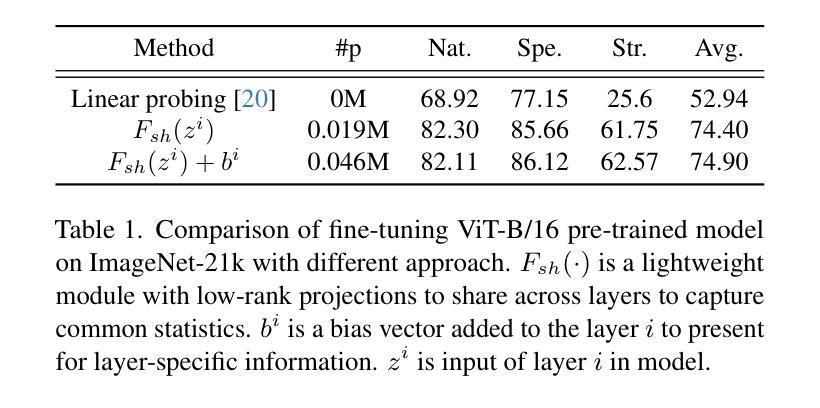
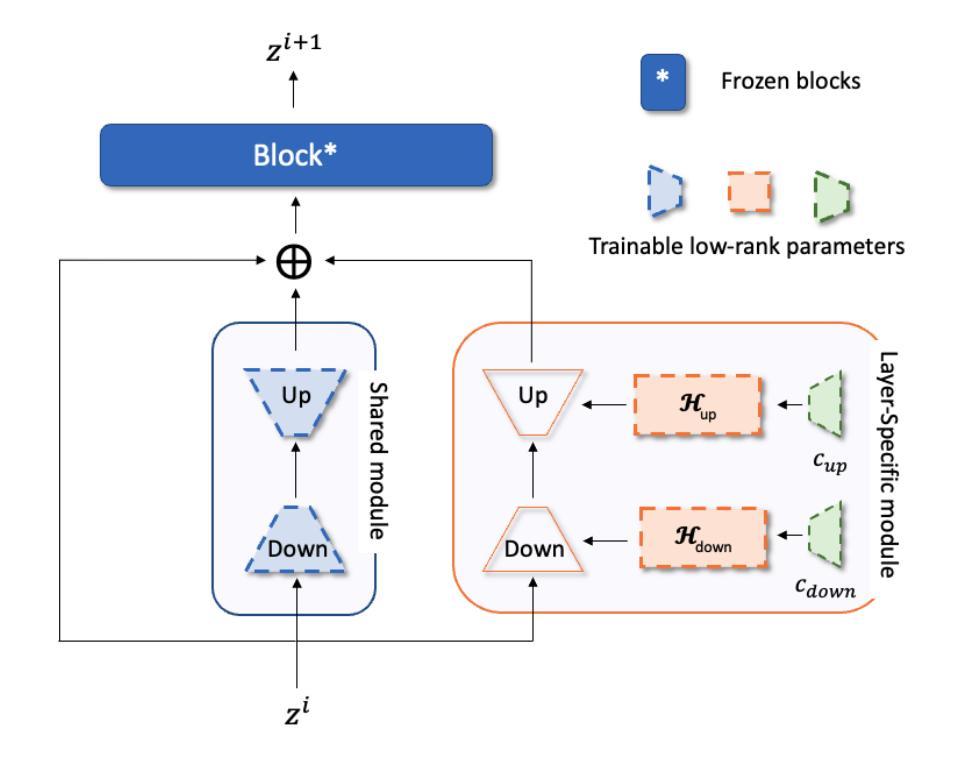
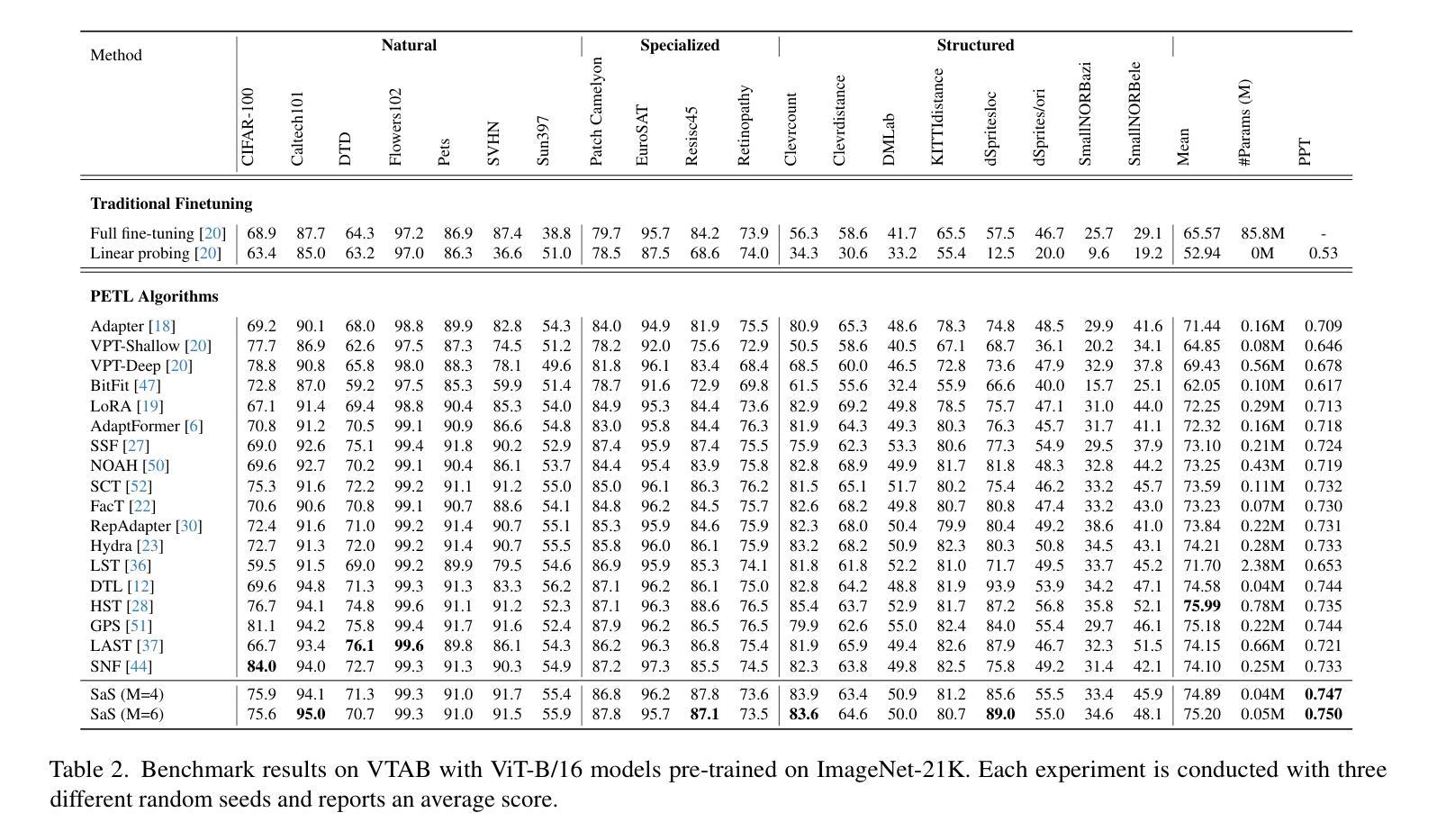
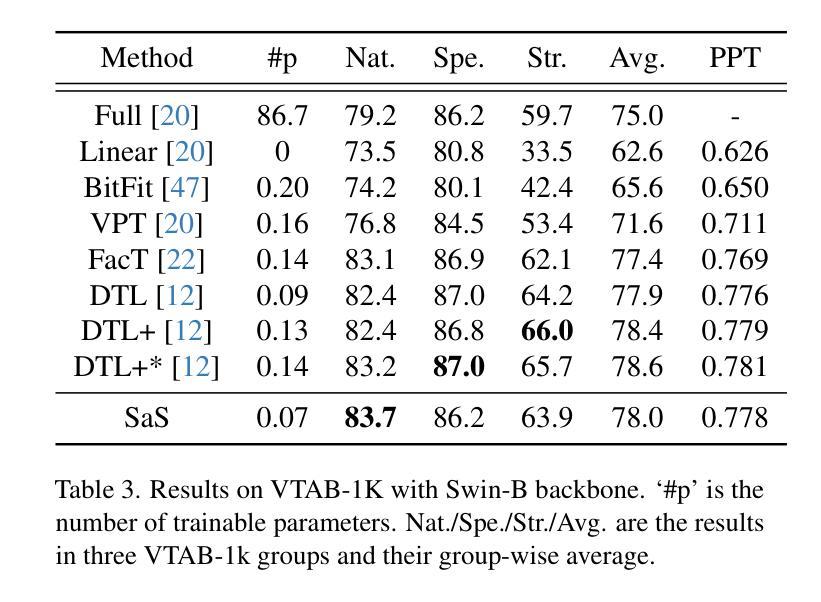
Foundation models, with a vast number of parameters and pretraining on massive datasets, achieve state-of-the-art performance across various applications. However, efficiently adapting them to downstream tasks with minimal computational overhead remains a challenge. Parameter-Efficient Transfer Learning (PETL) addresses this by fine-tuning only a small subset of parameters while preserving pre-trained knowledge. In this paper, we propose SaS, a novel PETL method that effectively mitigates distributional shifts during fine-tuning. SaS integrates (1) a shared module that captures common statistical characteristics across layers using low-rank projections and (2) a layer-specific module that employs hypernetworks to generate tailored parameters for each layer. This dual design ensures an optimal balance between performance and parameter efficiency while introducing less than 0.05% additional parameters, making it significantly more compact than existing methods. Extensive experiments on diverse downstream tasks, few-shot settings and domain generalization demonstrate that SaS significantly enhances performance while maintaining superior parameter efficiency compared to existing methods, highlighting the importance of capturing both shared and layer-specific information in transfer learning. Code and data are available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/SaS-PETL-3565.
基于大规模参数和大规模数据集预训练的模型在各种应用中实现了最先进的性能。然而,如何以最小的计算开销有效地将它们适应到下游任务仍然是一个挑战。参数高效迁移学习(PETL)通过仅微调一小部分参数同时保留预训练知识来解决这个问题。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的PETL方法SaS,它有效地缓解了微调过程中的分布转移问题。SaS集成了(1)一个共享模块,该模块使用低秩投影捕获跨层的通用统计特征;(2)一个针对特定层的模块,该模块采用超网络为每层生成定制参数。这种双重设计确保了性能与参数效率之间的最佳平衡,同时增加了不到0.05%的额外参数,使其比现有方法更加紧凑。在多种下游任务、小样本设置和领域泛化方面的广泛实验表明,SaS在保持优于现有方法的参数效率的同时,显著提高了性能,强调了捕获共享和特定层信息在迁移学习中的重要性。相关代码和数据可通过https://anonymous.4open.science/r/SaS-PETL-3565访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
预训练模型在多个应用上达到了最先进的性能水平,但其下游任务适应性和计算开销之间的平衡仍然是一个挑战。本文提出了一种新型的参数有效转移学习方法——SaS,它通过微调一小部分参数来保持预训练知识,同时有效缓解分布偏移问题。SaS包括一个共享模块和一层特定模块,前者通过低秩投影捕获跨层的统计特征,后者采用超网络为每层生成定制参数。该设计在确保高性能和参数效率之间达到了最佳平衡,仅增加了不到0.05%的参数。在多样的下游任务、小样本设置和领域泛化上的实验表明,SaS在维持出色的参数效率的同时,显著提高了性能,突显了在迁移学习中捕获共享和层特定信息的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练模型具有跨多个应用的先进性能,但下游任务适应性仍是挑战。
- SaS是一种参数有效转移学习方法,旨在通过微调小部分参数来保持预训练知识。
- SaS包括共享模块和层特定模块,分别用于捕获跨层的统计特征和为每层生成定制参数。
- SaS设计在保证高性能和参数效率之间达到了平衡,增加参数极少。
- 实验表明,SaS在多种下游任务、小样本设置和领域泛化上显著提高了性能。
- SaS方法的重要性在于它能够在迁移学习中同时捕获共享和层特定的信息。
点此查看论文截图

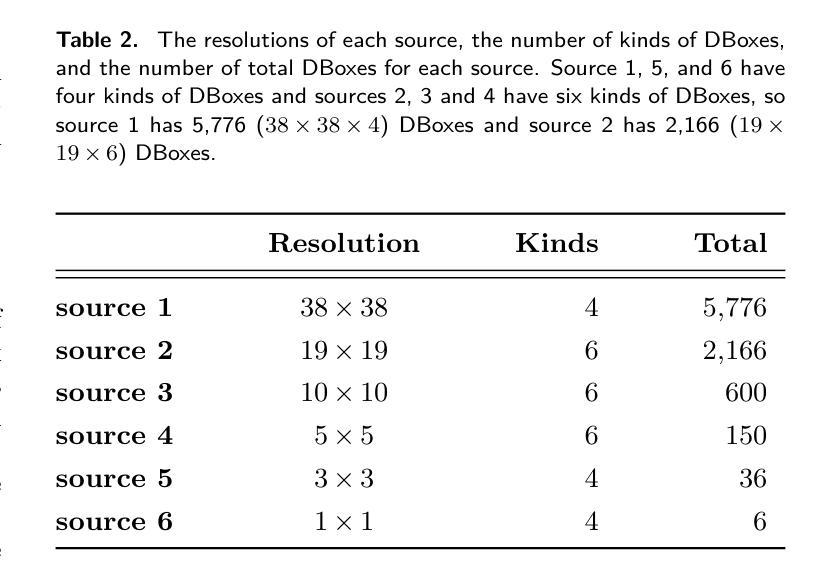
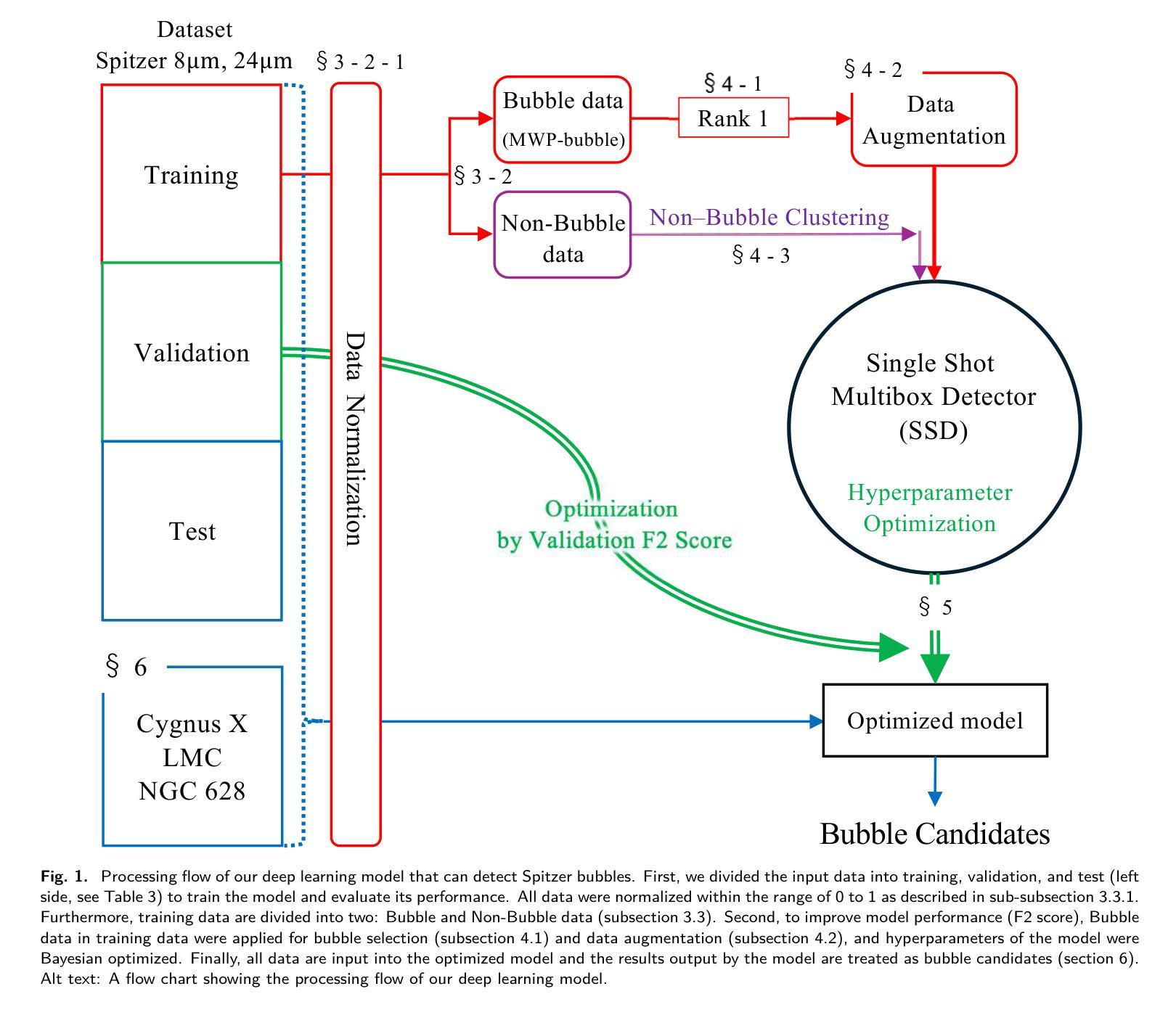
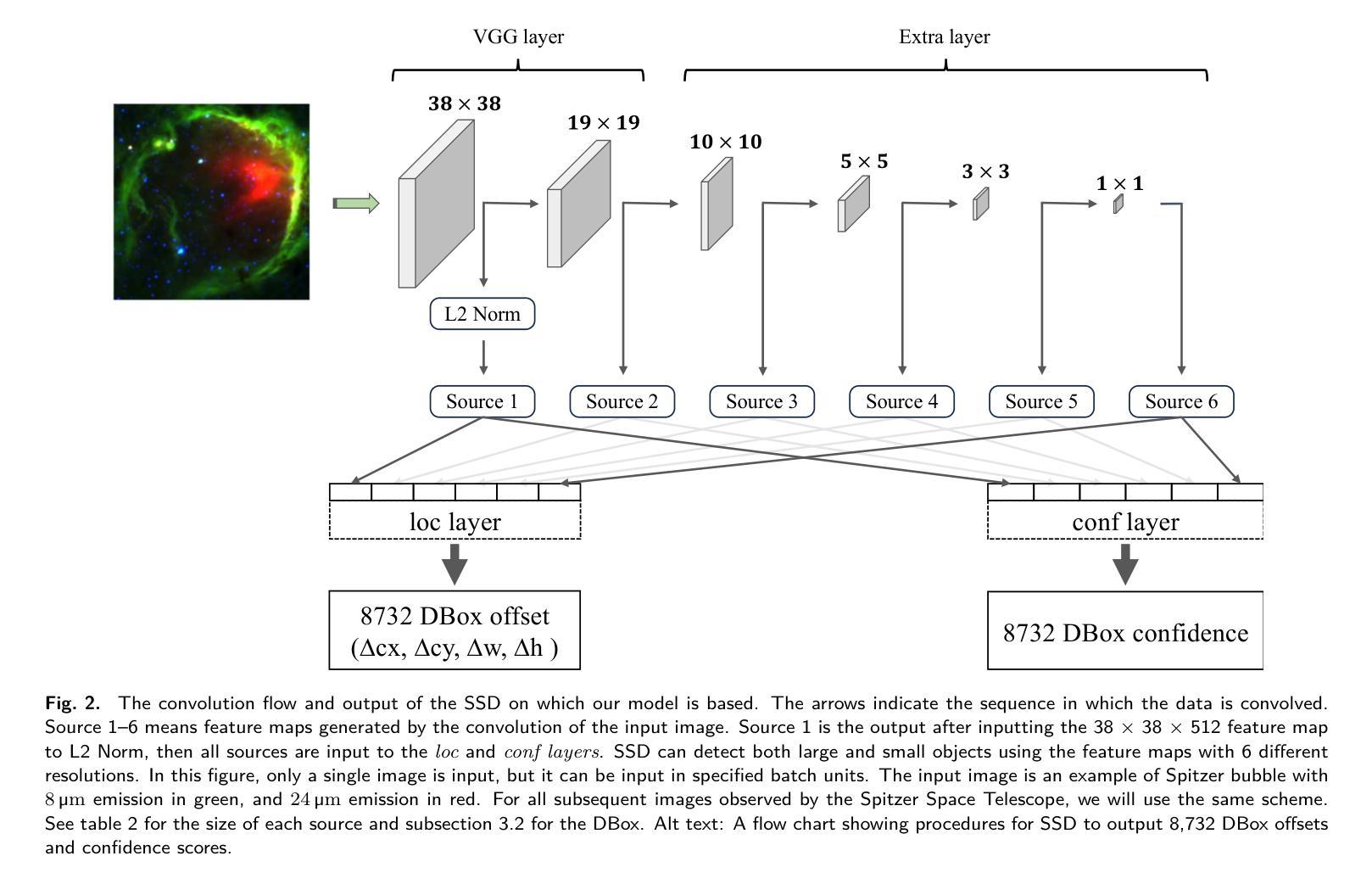
Infrared bubble recognition in the Milky Way and beyond using deep learning
Authors:Shimpei Nishimoto, Toshikazu Onishi, Atsushi Nishimura, Shinji Fujita, Yasutomo Kawanishi, Shuyo Nakatani, Kazuki Tokuda, Yoshito Shimajiri, Hiroyuki Kaneko, Yusuke Miyamoto, Tsuyoshi Inoue, Atsushi M Ito
We propose a deep learning model that can detect Spitzer bubbles accurately using two-wavelength near-infrared data acquired by the Spitzer Space Telescope and JWST. The model is based on the Single Shot MultiBox Detector as an object detection model, trained and validated using Spitzer bubbles identified by the Milky Way Project (MWP-Bubble). We found that using only MWP-Bubbles with clear structures, along with normalization and data augmentation, significantly improved performance. To reduce the dataset bias, we also use the data without bubbles in the dataset selected by combining two techniques: negative sampling and clustering. The model was optimized by hyperparameter tuning using Bayesian optimization. Applying this model to a test region of the Galactic plane resulted in a 98 $%$ detection rate for MWP-Bubbles with 8 $\mu$ m emission clearly encompassing 24 $\mu$ m emission. Additionally, we applied the model to a broader area of $1^\circ \leq |l| \leq 65^\circ$, $|b| \leq 1^\circ$, including both training and validation regions, and the model detected 3,006 bubbles, of which 1,413 were newly detected. We also attempted to detect bubbles in the high-mass star-forming region Cygnus $X$, as well as in the external galaxies Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) and NGC 628. The model successfully detected Spitzer bubbles in these external galaxies, though it also detected Mira-type variable stars and other compact sources that can be difficult to distinguish from Spitzer bubbles. The detection process takes only a few hours, demonstrating the efficiency in detecting bubble structures. Furthermore, the method used for detecting Spitzer bubbles was applied to detect shell-like structures observable only in the 8 $\mu$ m emission band, leading to the detection of 469 shell-like structures in the LMC and 143 in NGC 628.
我们提出了一种深度学习模型,能够利用斯皮策太空望远镜和JWST获取的双波长近红外数据准确检测斯皮策气泡。该模型以Single Shot MultiBox Detector为对象检测模型,利用银河系项目(MWP-Bubble)识别的斯皮策气泡进行训练和验证。我们发现,仅使用结构清晰的MWP-Bubbles,结合归一化和数据增强,可以显著提高性能。为了减少数据集偏差,我们还结合了两种技术:负采样和聚类,使用了数据集中没有气泡的数据。该模型通过贝叶斯优化进行超参数调整进行了优化。将该模型应用于银河平面测试区域,对MWP-Bubbles的检测率达到98%,其中8微米发射明显包含24微米发射。此外,我们将模型应用于$1^\circ \leq |l| \leq 65^\circ$,$|b| \leq 1^\circ$的更广泛区域,包括训练和验证区域,该模型检测到了3006个气泡,其中1413个是新检测到的。我们还尝试在高质量恒星形成区域天鹅X以及外部星系大麦哲伦云(LMC)和NGC 628中检测气泡。该模型成功检测到了这些外部星系中的斯皮策气泡,但也检测到了米拉型变星和其他与斯皮策气泡难以区分的致密源。检测过程只需几个小时,展示了检测气泡结构的效率。此外,用于检测斯皮策气泡的方法被应用于检测仅在8微米发射波段中可观察到的壳状结构,导致在LMC中检测到469个壳状结构,在NGC 628中检测到143个。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 26 figures
Summary
基于深度学习模型,利用斯皮策空间望远镜和JWST获取的双波长近红外数据,准确检测斯皮策气泡。模型以Single Shot MultiBox Detector为对象检测模型,利用银河系项目(MWP-Bubble)识别的斯皮策气泡进行训练和验证。通过数据增强和归一化提高了性能,并采用了两种技术结合的方式减少数据集偏差。模型在银河系平面测试区域的检测率高达98%,并在更广泛区域检测到3006个气泡,其中1413个为新检测。模型成功检测到外部星系中的斯皮策气泡及其他结构,如Cygnus X、大麦哲伦星系和NGC 628。检测过程仅需几小时,可高效检测气泡结构。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了基于深度学习的模型,用于利用双波长近红外数据准确检测斯皮策气泡。
- 模型以Single Shot MultiBox Detector为基础进行对象检测。
- 利用银河系项目(MWP-Bubble)识别的斯皮策气泡进行训练和验证。
- 通过数据增强和归一化提高了模型性能。
- 通过结合两种技术减少了数据集偏差。
- 模型在银河系平面测试区域有高达98%的检测率,并在更广泛区域检测到大量气泡,其中部分为新发现。
点此查看论文截图

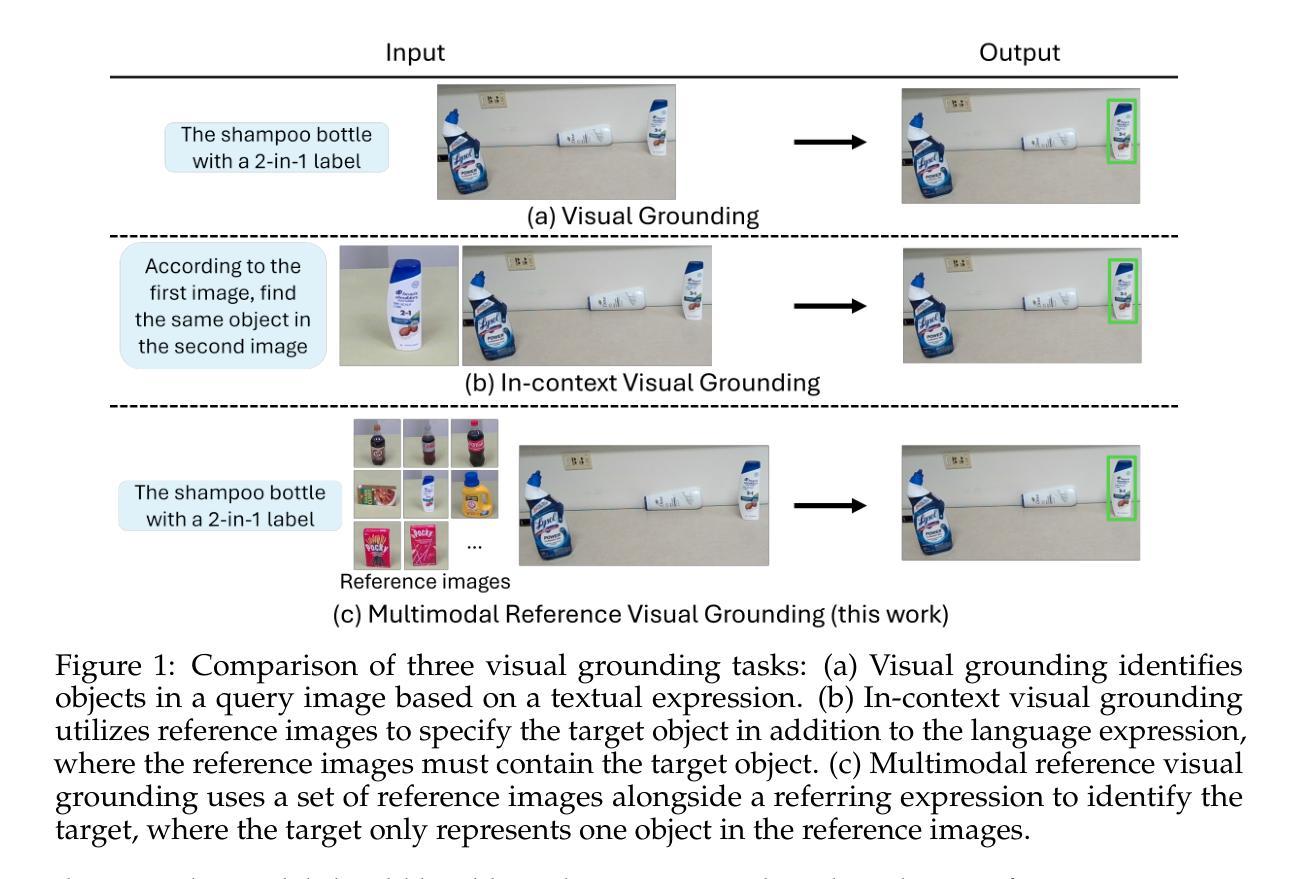
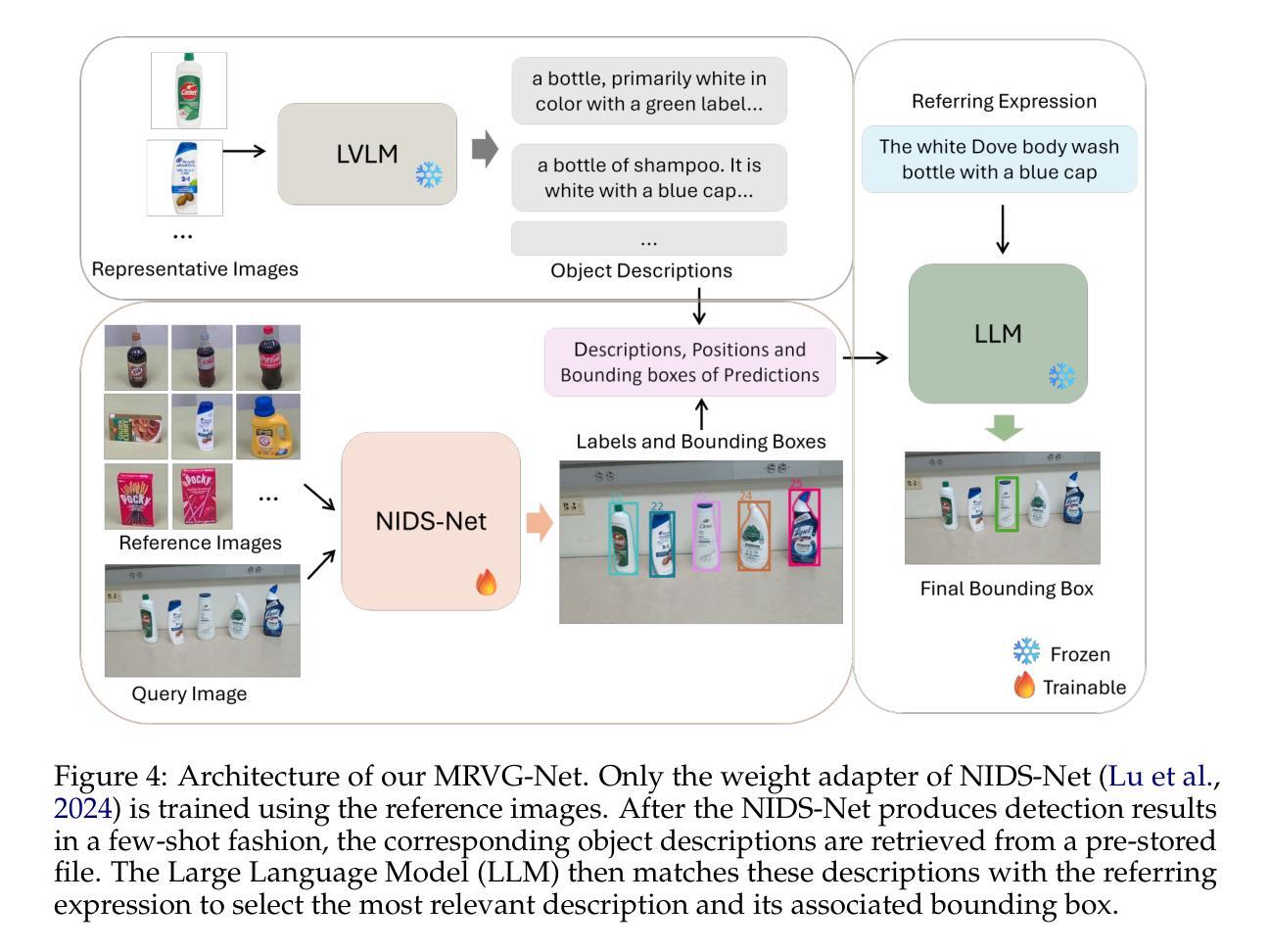
Multimodal Reference Visual Grounding
Authors:Yangxiao Lu, Ruosen Li, Liqiang Jing, Jikai Wang, Xinya Du, Yunhui Guo, Nicholas Ruozzi, Yu Xiang
Visual grounding focuses on detecting objects from images based on language expressions. Recent Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have significantly advanced visual grounding performance by training large models with large-scale datasets. However, the problem remains challenging, especially when similar objects appear in the input image. For example, an LVLM may not be able to differentiate Diet Coke and regular Coke in an image. In this case, if additional reference images of Diet Coke and regular Coke are available, it can help the visual grounding of similar objects. In this work, we introduce a new task named Multimodal Reference Visual Grounding (MRVG). In this task, a model has access to a set of reference images of objects in a database. Based on these reference images and a language expression, the model is required to detect a target object from a query image. We first introduce a new dataset to study the MRVG problem. Then we introduce a novel method, named MRVG-Net, to solve this visual grounding problem. We show that by efficiently using reference images with few-shot object detection and using Large Language Models (LLMs) for object matching, our method achieves superior visual grounding performance compared to the state-of-the-art LVLMs such as Qwen2.5-VL-7B. Our approach bridges the gap between few-shot detection and visual grounding, unlocking new capabilities for visual understanding. Project page with our code and dataset: https://irvlutd.github.io/MultiGrounding
视觉定位主要关注基于语言表达从图像中检测物体。最近的视觉语言大模型(LVLMs)通过大规模数据集训练大规模模型,显著提高了视觉定位的性能。然而,问题仍然存在挑战,特别是在输入图像中出现相似物体时。例如,LVLM可能无法区分图像中的无糖可乐和普通可乐。在这种情况下,如果有额外的无糖可乐和普通可乐的参考图像可用,它可以帮助对相似物体的视觉定位。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个名为多模态参考视觉定位(MRVG)的新任务。在此任务中,模型可以访问数据库中物体的参考图像集。基于这些参考图像和语言表达式,模型需要从查询图像中检测目标物体。我们首先引入一个新的数据集来研究MRVG问题。然后,我们介绍了一种名为MRVG-Net的新方法来解决这个视觉定位问题。我们展示了通过高效地使用参考图像进行少样本目标检测和利用大型语言模型进行目标匹配,我们的方法在视觉定位性能上超越了最先进的LVLMs,如Qwen2.5-VL-7B。我们的方法缩小了少样本检测和视觉定位之间的差距,为视觉理解解锁了新的能力。我们的代码和数据集项目页面:https://irvlutd.github.io/MultiGrounding
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page with our code and dataset: https://irvlutd.github.io/MultiGrounding
Summary
视觉定位是通过语言表达式来识别图像中的对象。最新的大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)通过大规模数据集训练大型模型,已经极大地提高了视觉定位的性能。然而,当输入图像中出现相似对象时,问题仍然具有挑战性。例如,LVLM可能无法区分图像中的无糖可乐和普通可乐。在这种情况下,如果有额外的无糖可乐和普通可乐的参考图像可用,可以帮助对相似对象的视觉定位。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个新的任务,称为多模态参考视觉定位(MRVG)。在此任务中,模型可以访问数据库中的一组参考图像对象。基于这些参考图像和语言表达式,模型需要从查询图像中检测目标对象。我们首先引入了一个新的数据集来研究MRVG问题。然后,我们介绍了一种名为MRVG-Net的新方法来解决这个视觉定位问题。我们展示了通过高效地使用参考图像进行少量目标检测和利用大型语言模型进行对象匹配,我们的方法实现了优于最新LVLMs的视觉定位性能。我们的方法缩小了few-shot检测和视觉定位之间的差距,为视觉理解解锁了新的能力。您可以访问我们的代码和数据集页面:链接。
Key Takeaways
- Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) 在视觉定位任务上有显著进展。
- 相似对象在视觉定位中造成挑战,需要区分度更高的方法。
- 引入多模态参考视觉定位(MRVG)任务,借助参考图像提高定位精度。
- 提出新的数据集以研究MRVG问题。
- 引入MRVG-Net方法,结合少量目标检测和大型语言模型进行视觉定位。
- MRVG-Net相较于现有LVLMs如Qwen2.5-VL-7B有更好的视觉定位性能。
点此查看论文截图


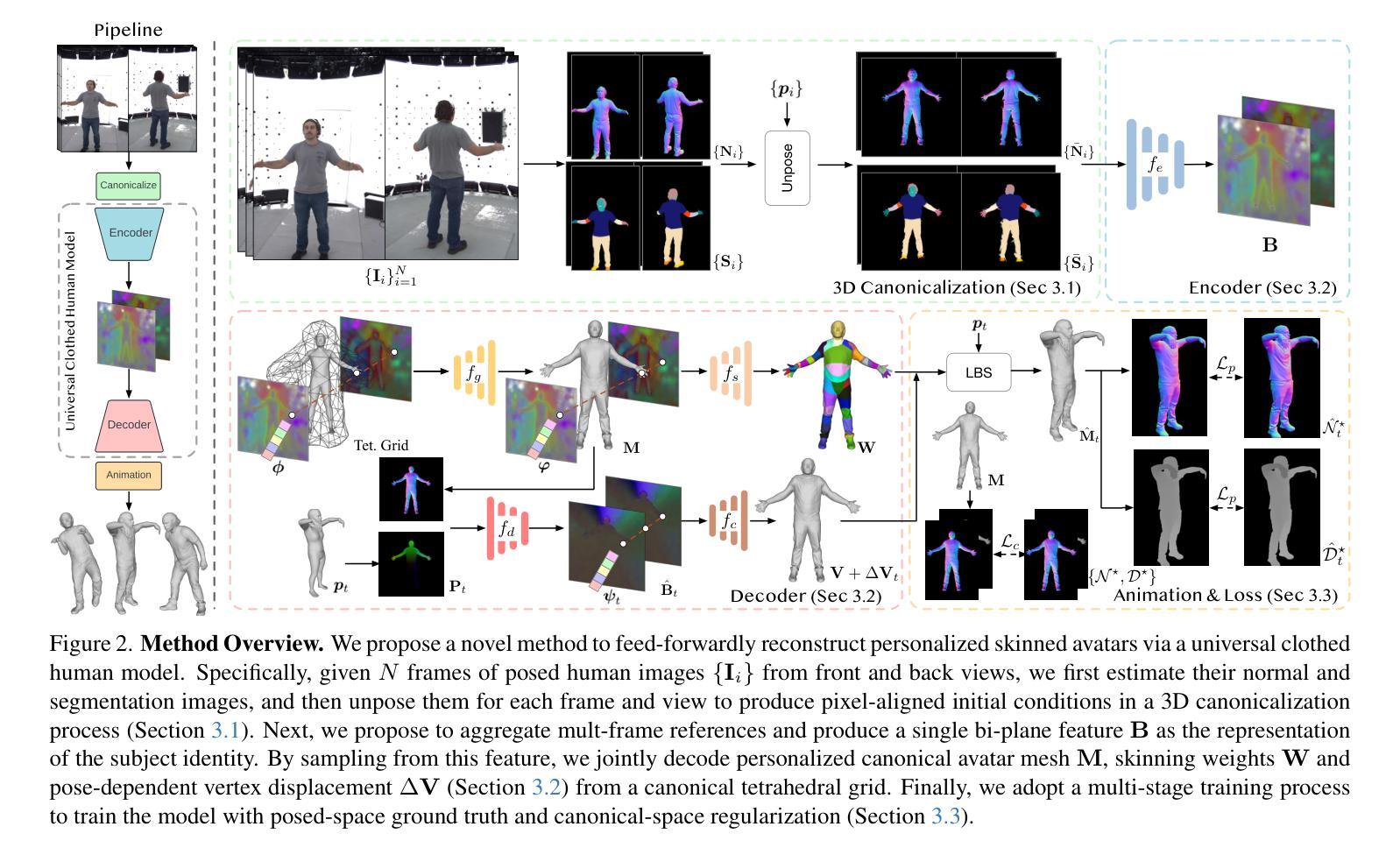
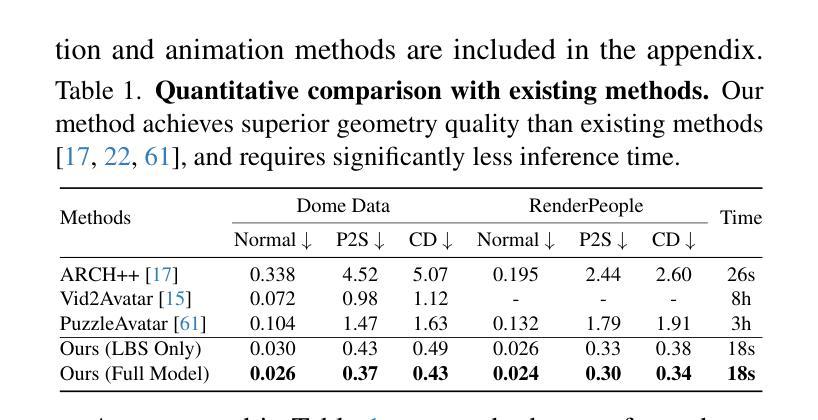
FRESA: Feedforward Reconstruction of Personalized Skinned Avatars from Few Images
Authors:Rong Wang, Fabian Prada, Ziyan Wang, Zhongshi Jiang, Chengxiang Yin, Junxuan Li, Shunsuke Saito, Igor Santesteban, Javier Romero, Rohan Joshi, Hongdong Li, Jason Saragih, Yaser Sheikh
We present a novel method for reconstructing personalized 3D human avatars with realistic animation from only a few images. Due to the large variations in body shapes, poses, and cloth types, existing methods mostly require hours of per-subject optimization during inference, which limits their practical applications. In contrast, we learn a universal prior from over a thousand clothed humans to achieve instant feedforward generation and zero-shot generalization. Specifically, instead of rigging the avatar with shared skinning weights, we jointly infer personalized avatar shape, skinning weights, and pose-dependent deformations, which effectively improves overall geometric fidelity and reduces deformation artifacts. Moreover, to normalize pose variations and resolve coupled ambiguity between canonical shapes and skinning weights, we design a 3D canonicalization process to produce pixel-aligned initial conditions, which helps to reconstruct fine-grained geometric details. We then propose a multi-frame feature aggregation to robustly reduce artifacts introduced in canonicalization and fuse a plausible avatar preserving person-specific identities. Finally, we train the model in an end-to-end framework on a large-scale capture dataset, which contains diverse human subjects paired with high-quality 3D scans. Extensive experiments show that our method generates more authentic reconstruction and animation than state-of-the-arts, and can be directly generalized to inputs from casually taken phone photos. Project page and code is available at https://github.com/rongakowang/FRESA.
我们提出了一种仅通过几张图片重建个性化3D人类角色并生成逼真动画的新方法。由于人体形状、姿势和衣物类型的巨大差异,现有方法大多需要在推理期间对每个主题进行数小时的优化,这限制了它们的实际应用。相比之下,我们从数千名穿衣人类身上学习通用先验知识,以实现即时前馈生成和零样本泛化。具体来说,我们没有使用通用的蒙皮权重来装配角色,而是联合推断个性化的角色形状、蒙皮权重和姿势相关的变形,这有效地提高了整体几何保真度并减少了变形伪影。此外,为了归一化姿势变化和解决规范形状与蒙皮权重之间的耦合模糊性,我们设计了一个3D规范化过程来生成像素对齐的初始条件,这有助于重建精细的几何细节。然后,我们提出了一种多帧特征聚合方法来稳健地减少规范化过程中产生的伪影,并融合保留个人特定身份的可行角色。最后,我们在大规模捕获数据集上以端到端的方式训练模型,该数据集包含与高质量3D扫描配对的多样化人类主题。大量实验表明,我们的方法比最先进的技术生成更真实的三维重建和动画,并且可以直接推广到来自随意拍摄的手机照片输入。项目页面和代码可通过https://github.com/rongakowang/FRESA获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in CVPR 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种仅通过少量图像即可重建个性化3D人类角色并实现逼真动画的新方法。该方法通过从数千名穿衣人类中学习通用先验知识,实现了即时前馈生成和零样本泛化。该方法联合推断个性化角色形状、蒙皮权重和姿态相关变形,提高了整体几何逼真度并减少了变形伪影。此外,设计了一个3D标准化流程以标准化姿态变化并解决标准形状和蒙皮权重之间的耦合歧义。在大型捕捉数据集上进行端到端框架训练,包含多种人类主体和高品质3D扫描配对。实验表明,该方法生成的角色动画更为真实且与当前技术相比更具优势,可直接应用于从手机照片等日常拍摄的图片中的输入。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于少量图像重建个性化3D人类角色的新方法,具有逼真动画效果。
- 通过学习数千名穿衣人类的通用先验知识,实现了即时前馈生成和零样本泛化。
- 联合推断个性化角色形状、蒙皮权重和姿态相关变形,提高了几何逼真度和减少了变形伪影。
- 设计了3D标准化流程以标准化姿态变化并解决标准形状和蒙皮权重之间的耦合歧义,有助于重建精细几何细节。
- 采用了多帧特征聚合技术,减少了标准化过程中的伪影,并融合了保留个人特征的可行角色。
- 在大型捕捉数据集上进行训练,包含多种人类主体和高品质3D扫描配对,增强了方法的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

Zero-Shot Image Restoration Using Few-Step Guidance of Consistency Models (and Beyond)
Authors:Tomer Garber, Tom Tirer
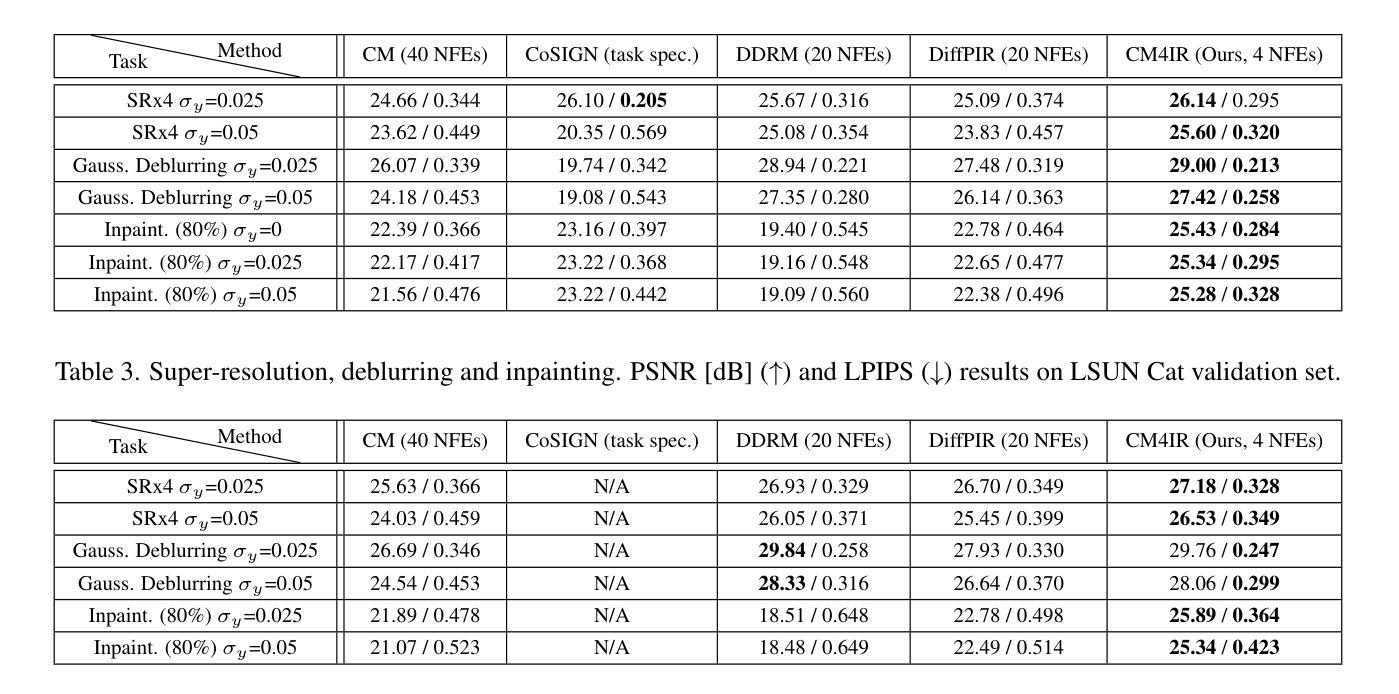
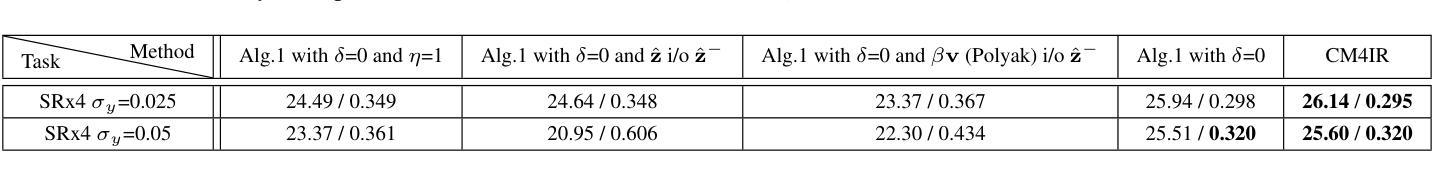
In recent years, it has become popular to tackle image restoration tasks with a single pretrained diffusion model (DM) and data-fidelity guidance, instead of training a dedicated deep neural network per task. However, such “zero-shot” restoration schemes currently require many Neural Function Evaluations (NFEs) for performing well, which may be attributed to the many NFEs needed in the original generative functionality of the DMs. Recently, faster variants of DMs have been explored for image generation. These include Consistency Models (CMs), which can generate samples via a couple of NFEs. However, existing works that use guided CMs for restoration still require tens of NFEs or fine-tuning of the model per task that leads to performance drop if the assumptions during the fine-tuning are not accurate. In this paper, we propose a zero-shot restoration scheme that uses CMs and operates well with as little as 4 NFEs. It is based on a wise combination of several ingredients: better initialization, back-projection guidance, and above all a novel noise injection mechanism. We demonstrate the advantages of our approach for image super-resolution, deblurring and inpainting. Interestingly, we show that the usefulness of our noise injection technique goes beyond CMs: it can also mitigate the performance degradation of existing guided DM methods when reducing their NFE count.
近年来,使用单个预训练的扩散模型(DM)和数据保真度指导来完成图像恢复任务变得非常流行,而不是针对每个任务训练一个专用的深度神经网络。然而,这样的“零射击”恢复方案目前需要许多神经功能评估(NFE)才能表现良好,这可能是由于DM的原始生成功能需要大量的NFE。最近,人们已经探索了用于图像生成的DM的更快变体。这包括一致性模型(CM),它可以通过几个NFE生成样本。然而,现有使用指导型CM进行恢复的工作仍然需要数十次NFE或对模型进行针对每项任务的微调,如果在微调期间假设不准确,会导致性能下降。在本文中,我们提出了一种使用CM的零射击恢复方案,它只需要很少的4个NFE就能很好地运行。它基于几种成分的明智组合:更好的初始化、反向投影指导和最重要的是一种新型噪声注入机制。我们展示了我们的方法在图像超分辨率、去模糊和图像修复方面的优势。有趣的是,我们证明了我们的噪声注入技术的实用性超越了CM:它还可以缓解现有指导型DM方法减少NFE计数时的性能下降。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025 (camera-ready). Code can be found at: https://github.com/tirer-lab/CM4IR
Summary
该论文提出了一种基于一致性模型(CMs)的零样本修复方案,使用更少(仅需4次)的神经功能评估(NFEs)即可实现图像超分辨率、去模糊和修复等任务。该方案结合了更好的初始化、反向投影指导和新颖的噪声注入机制。此外,该噪声注入技术不仅适用于CMs,还可以缓解现有引导扩散模型方法减少NFE计数时的性能下降问题。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出了一种新的零样本修复方案,基于一致性模型(CMs)实现图像超分辨率、去模糊和修复等任务。
- 该方案使用较少的神经功能评估(NFEs,仅需4次)即可完成这些任务。
- 论文结合了更好的初始化、反向投影指导和新颖的噪声注入机制来提高性能。
- 噪声注入技术不仅适用于一致性模型,还可以改善现有引导扩散模型在减少NFE计数时的性能下降问题。
- 该方案能够在不假定特定任务数据分布的情况下进行图像修复,具有一定的通用性。
- 与传统的深度神经网络相比,该方案使用单一预训练的扩散模型进行图像修复,简化了任务特定的训练过程。
点此查看论文截图

Memorization in In-Context Learning
Authors:Shahriar Golchin, Mihai Surdeanu, Steven Bethard, Eduardo Blanco, Ellen Riloff
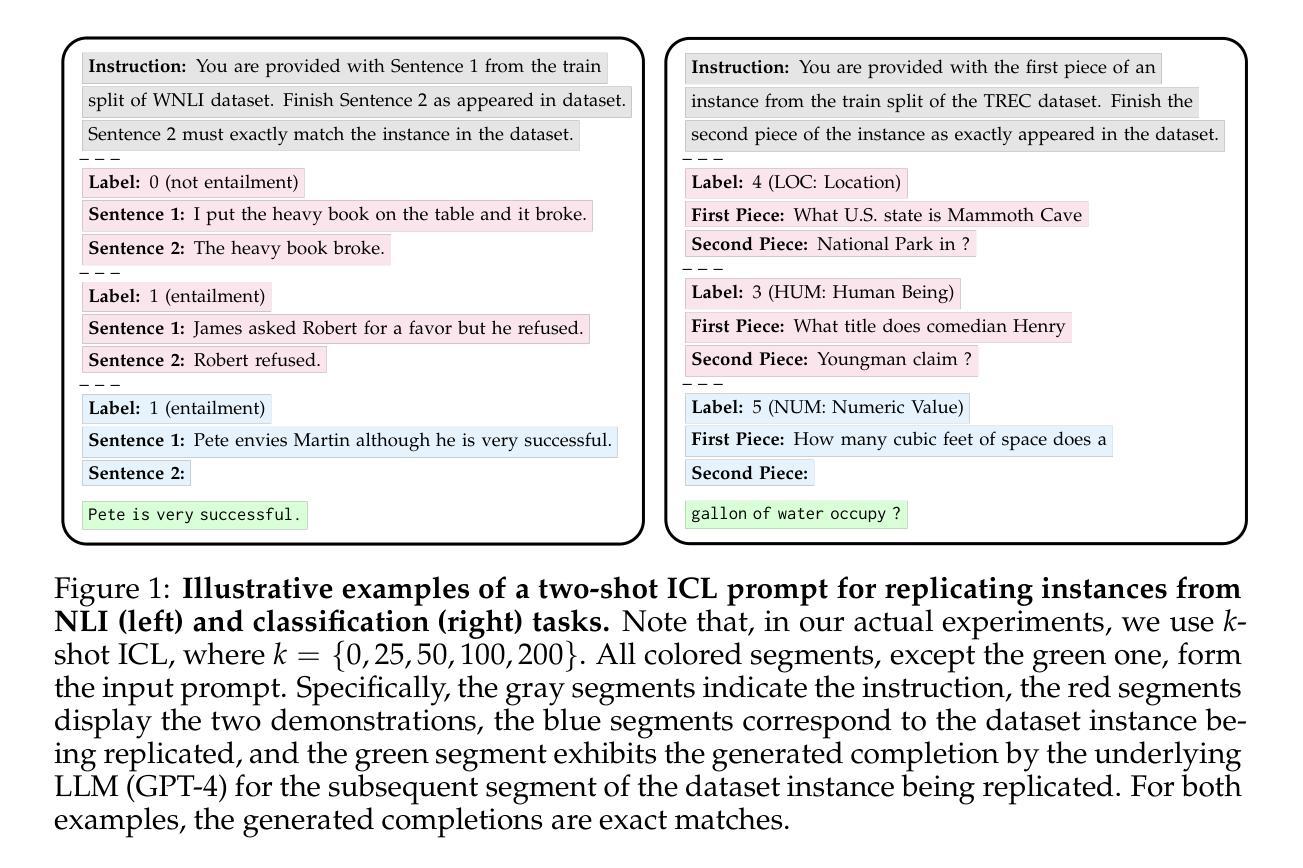
In-context learning (ICL) has proven to be an effective strategy for improving the performance of large language models (LLMs) with no additional training. However, the exact mechanism behind this performance improvement remains unclear. This study is the first to show how ICL surfaces memorized training data and to explore the correlation between this memorization and performance on downstream tasks across various ICL regimes: zero-shot, few-shot, and many-shot. Our most notable findings include: (1) ICL significantly surfaces memorization compared to zero-shot learning in most cases; (2) demonstrations, without their labels, are the most effective element in surfacing memorization; (3) ICL improves performance when the surfaced memorization in few-shot regimes reaches a high level (about 40%); and (4) there is a very strong correlation between performance and memorization in ICL when it outperforms zero-shot learning. Overall, our study uncovers memorization as a new factor impacting ICL, raising an important question: to what extent do LLMs truly generalize from demonstrations in ICL, and how much of their success is due to memorization?
上下文学习(ICL)已证明是一种无需额外训练即可提高大型语言模型(LLM)性能的有效策略。然而,这种性能提升背后的确切机制仍不清楚。本研究首次展示了ICL如何呈现记忆的训练数据,并探索了这种记忆与各种ICL机制(零样本、少样本和多样本)下游任务性能之间的相关性。我们的主要发现包括:(1)在大多数情况下,与零样本学习相比,ICL显著地呈现出记忆;(2)没有标签的演示是呈现记忆中最有效的元素;(3)当少样本制度中的呈现记忆达到高水平(约40%)时,ICL会提高性能;(4)当ICL优于零样本学习时,性能与记忆之间存在非常强烈的相关性。总体而言,我们的研究揭示了记忆作为影响ICL的一个新因素,提出了一个重要问题:LLM在多大程度上真正从ICL中的演示中泛化,它们的成功有多大程度是归因于记忆?
论文及项目相关链接
PDF v3
Summary
本研究首次展示了在无需额外训练的情况下,通过上下文学习(ICL)提升大型语言模型(LLM)性能的策略有效性。研究发现,在不同学习情境下(零样本、少样本和多样本),演示作为最有效元素显著显现记忆效果。总体上,记忆作为一种新的影响因在于起到了关键作用,引发关于LLM在多大程度上真正从演示中泛化的问题。
Key Takeaways
- ICL能有效提升大型语言模型的性能,无需额外训练。
- ICL能够显著显现记忆效果,特别是在少样本情境下。
- 演示(即使没有标签)是显现记忆效果的最有效元素。
- 在高水平的记忆显现情况下(大约达到百分之四十),ICL性能会提高。
- 当ICL表现优于零样本学习时,性能与记忆之间有着很强的相关性。
点此查看论文截图

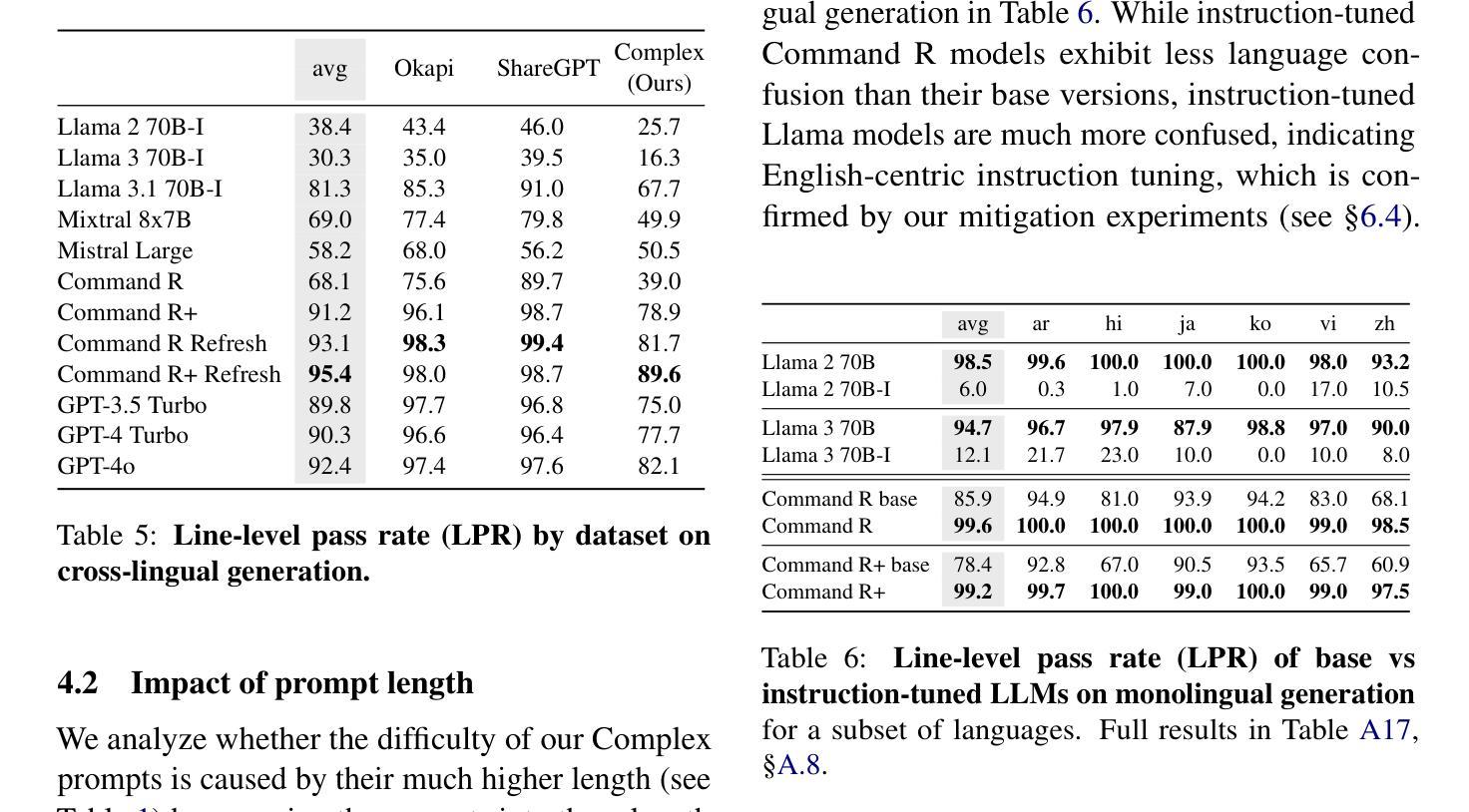
Understanding and Mitigating Language Confusion in LLMs
Authors:Kelly Marchisio, Wei-Yin Ko, Alexandre Bérard, Théo Dehaze, Sebastian Ruder
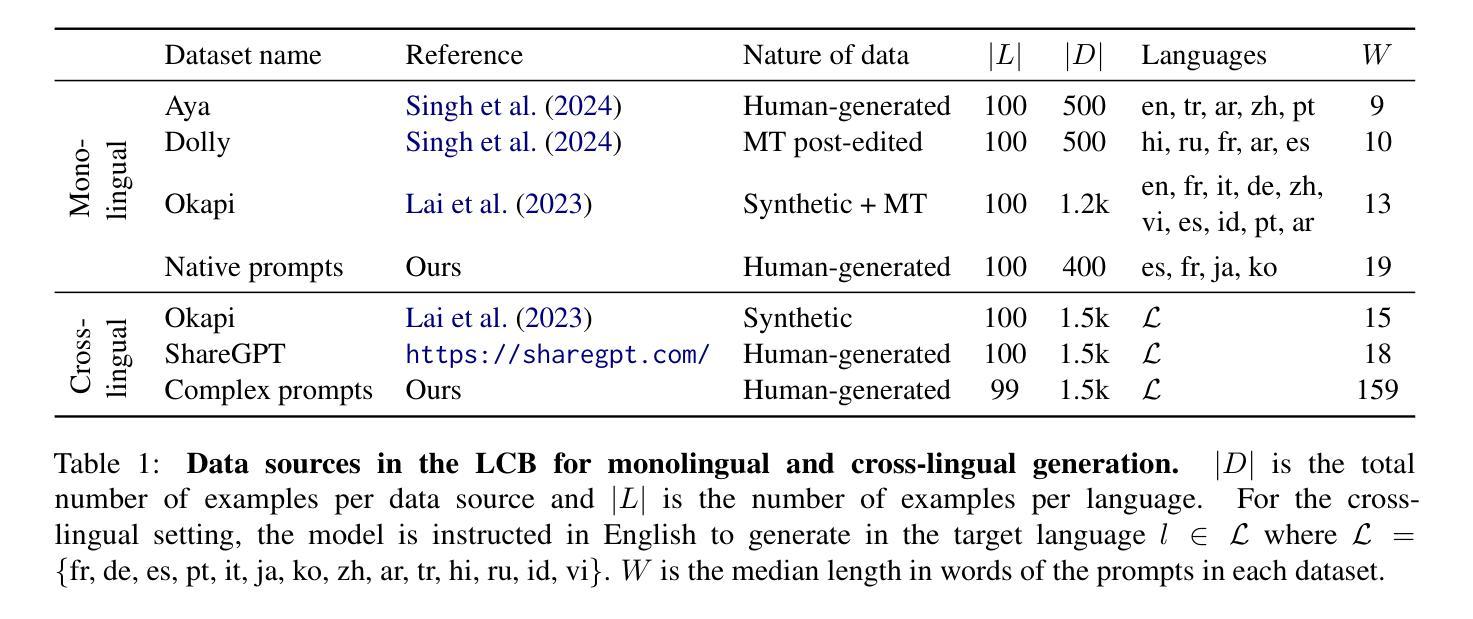
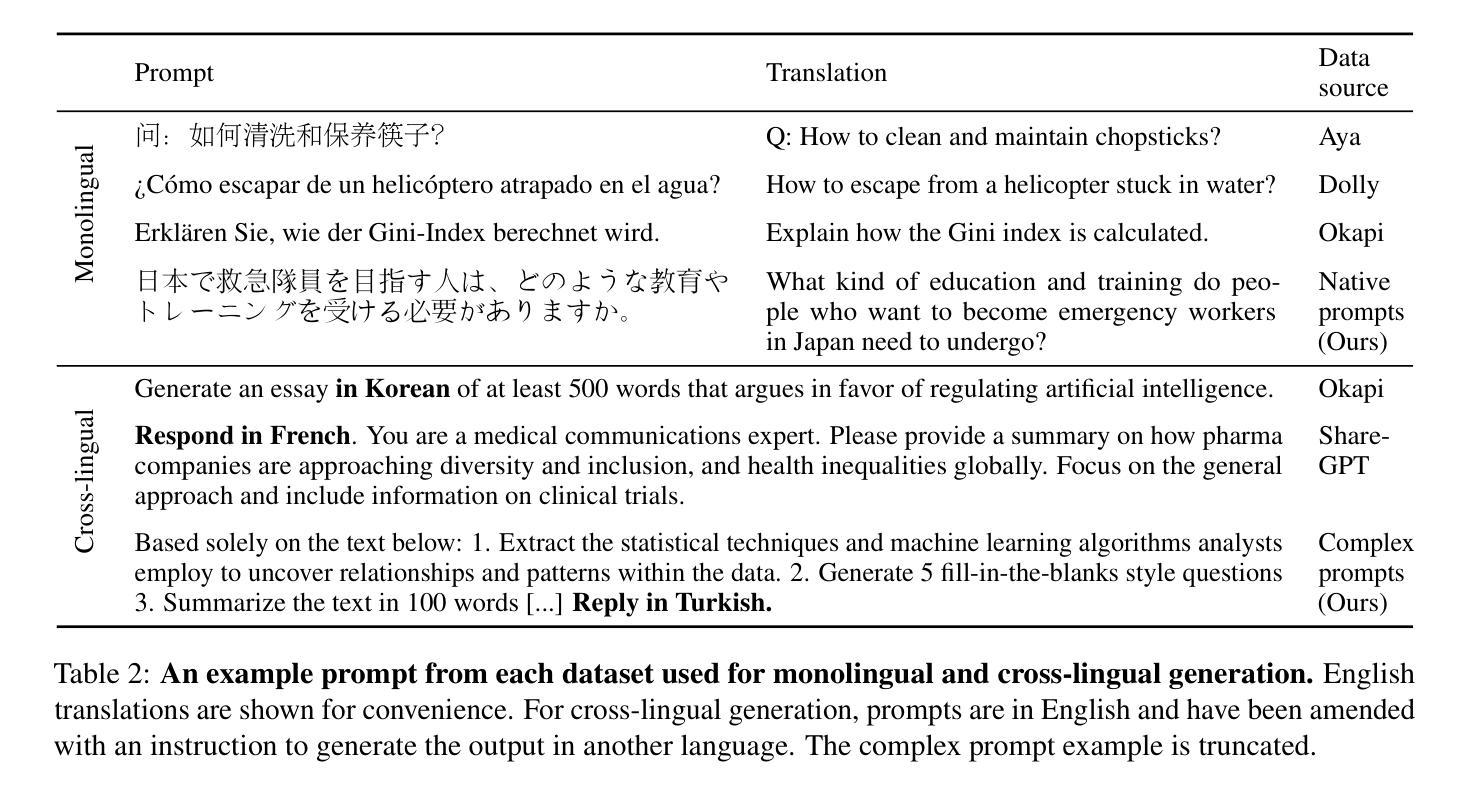
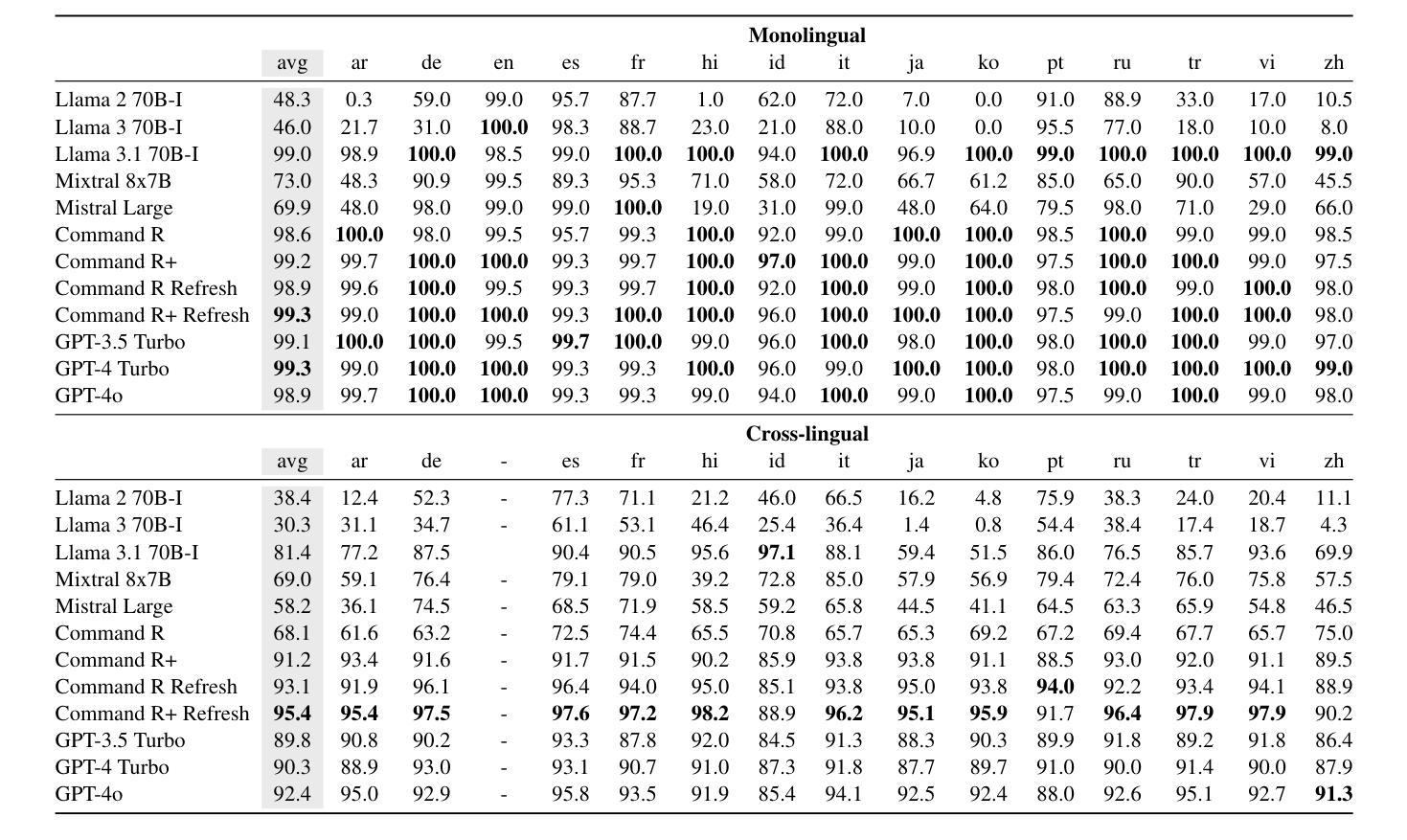
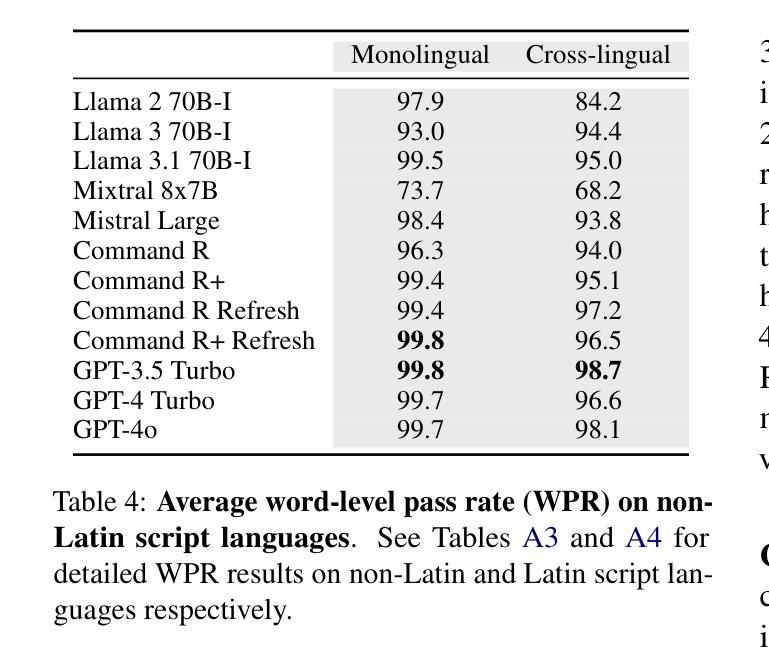
We investigate a surprising limitation of LLMs: their inability to consistently generate text in a user’s desired language. We create the Language Confusion Benchmark (LCB) to evaluate such failures, covering 15 typologically diverse languages with existing and newly-created English and multilingual prompts. We evaluate a range of LLMs on monolingual and cross-lingual generation reflecting practical use cases, finding that Llama Instruct and Mistral models exhibit high degrees of language confusion and even the strongest models fail to consistently respond in the correct language. We observe that base and English-centric instruct models are more prone to language confusion, which is aggravated by complex prompts and high sampling temperatures. We find that language confusion can be partially mitigated via few-shot prompting, multilingual SFT and preference tuning. We release our language confusion benchmark, which serves as a first layer of efficient, scalable multilingual evaluation at https://github.com/for-ai/language-confusion.
我们研究了大型语言模型(LLMs)的一个惊人局限:它们无法始终如一地生成用户所需语言的文本。为了评估这种失败,我们创建了语言混淆基准测试(LCB),涵盖15种类型多样的语言,包括现有的和新创建的英语和跨语言提示。我们对一系列LLMs进行了单语和跨语言生成的评估,反映了实际应用场景,发现Llama Instruct和Mistral模型存在高度的语言混淆现象,即使是最强大的模型也无法始终如一地以正确的语言做出回应。我们发现基础模型和以英语为中心的指令模型更容易出现语言混淆现象,复杂的提示和高采样温度会加剧这一现象。我们发现,通过少量提示、多语言场景优先调整和偏好微调,可以部分缓解语言混淆问题。我们在https://github.com/for-ai/language-confusion上发布了我们的语言混淆基准测试,作为高效、可扩展的多语言评估的第一层服务。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF EMNLP 2024 Main Conference Camera-ready. v3: hi, ru not run for monolingual Okapi
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)存在令人惊讶的局限性:无法始终如一地生成用户所需语言的文本。为此,我们创建了语言混淆基准测试(LCB)来评估这种失败,涵盖15种语言,包括现有的和新创建的英语和多语言提示。我们发现即使是表现最好的模型也无法始终在正确的语言下做出回应。基础模型和以英语为中心的指令模型更容易出现语言混淆,复杂的提示和高采样温度会加剧这一问题。通过少量提示、多语言预训练偏好调优可以部分缓解语言混淆问题。我们的语言混淆基准测试已在GitHub上发布,作为高效可扩展的多语言评估的第一层。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs存在无法始终生成用户所需语言的文本的局限性。
- 我们创建了语言混淆基准测试(LCB)来评估LLMs在这一方面的问题,涵盖多种语言。
- LLMs在复杂的提示和高采样温度下更容易出现语言混淆。
- 语言混淆问题可以通过少量提示、多语言预训练和偏好调优得到部分缓解。
- 我们发布的LCB基准测试是一个高效、可扩展的多语言评估工具。
- LCB有助于识别和改进LLMs在语言混淆方面的缺陷。
点此查看论文截图