⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-08 更新
MultiMed-ST: Large-scale Many-to-many Multilingual Medical Speech Translation
Authors:Khai Le-Duc, Tuyen Tran, Bach Phan Tat, Nguyen Kim Hai Bui, Quan Dang, Hung-Phong Tran, Thanh-Thuy Nguyen, Ly Nguyen, Tuan-Minh Phan, Thi Thu Phuong Tran, Chris Ngo, Nguyen X. Khanh, Thanh Nguyen-Tang
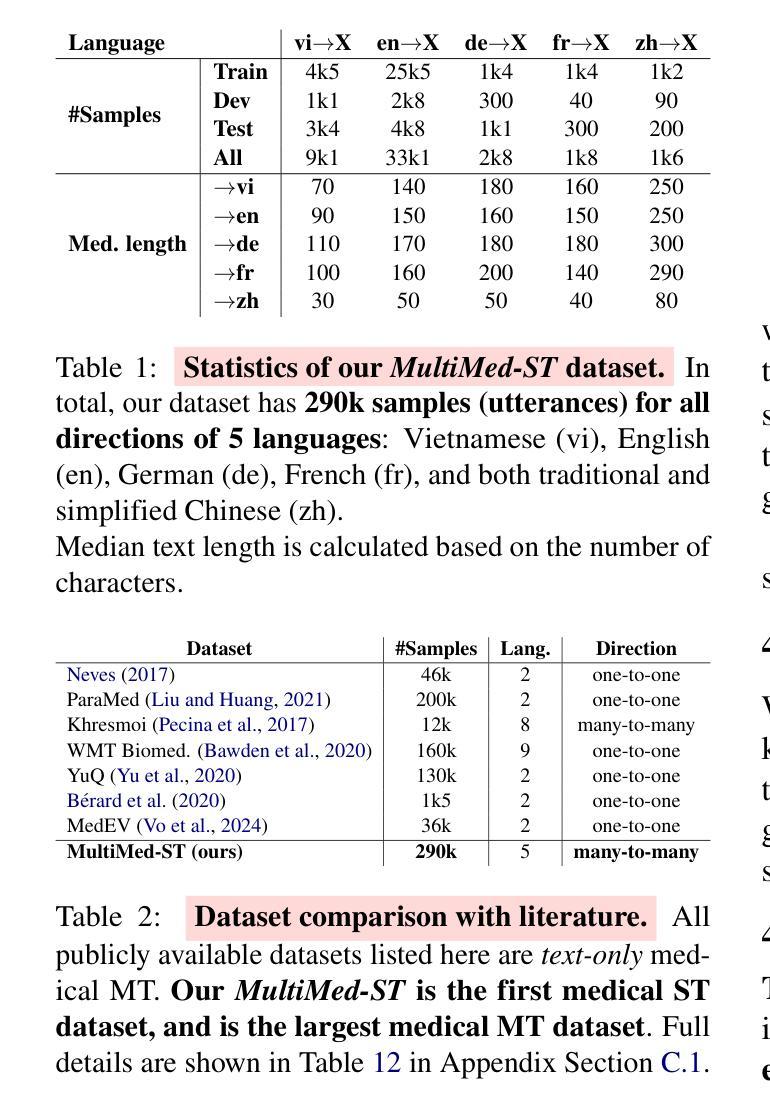
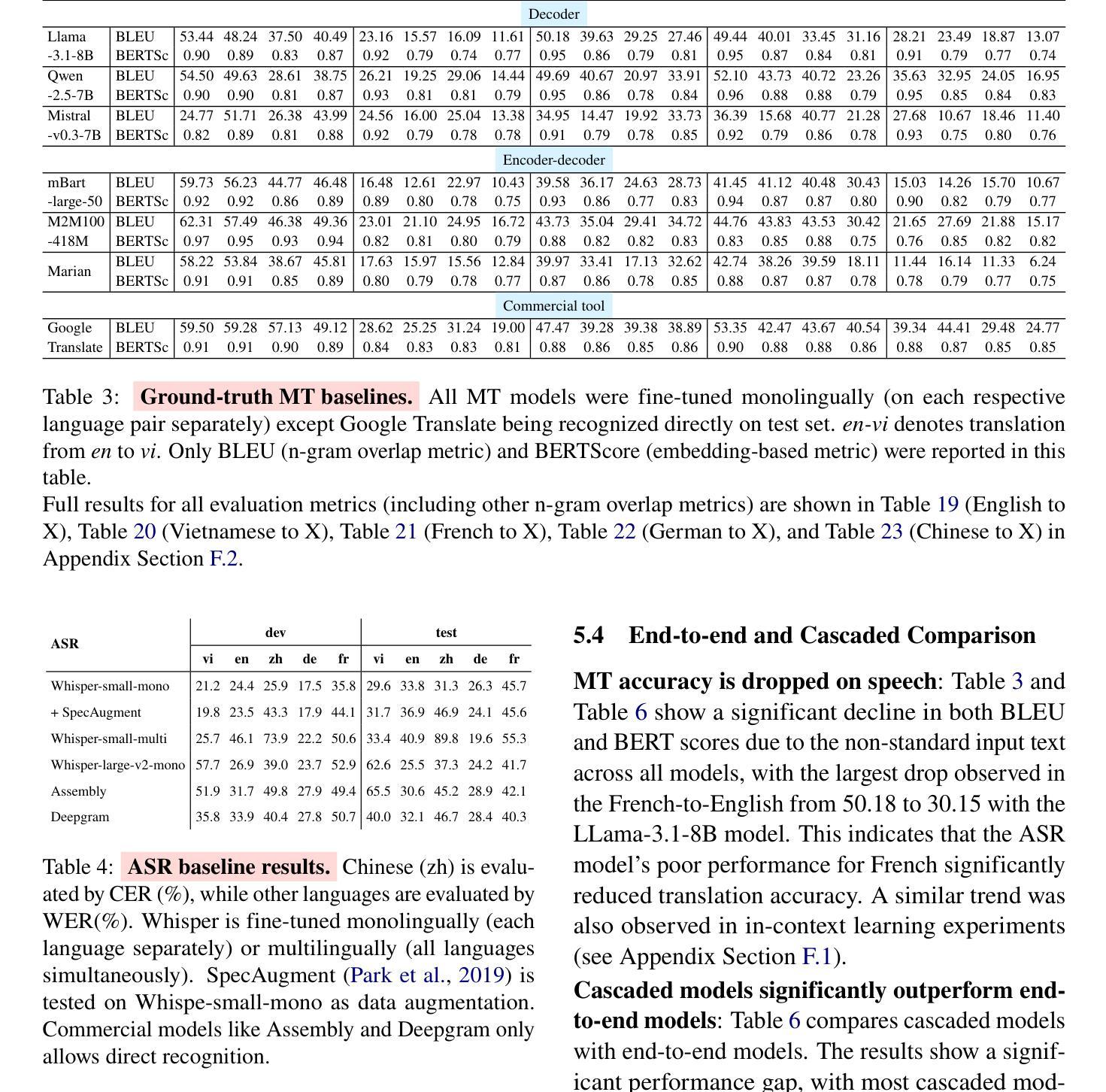
Multilingual speech translation (ST) in the medical domain enhances patient care by enabling efficient communication across language barriers, alleviating specialized workforce shortages, and facilitating improved diagnosis and treatment, particularly during pandemics. In this work, we present the first systematic study on medical ST, to our best knowledge, by releasing MultiMed-ST, a large-scale ST dataset for the medical domain, spanning all translation directions in five languages: Vietnamese, English, German, French, Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese, together with the models. With 290,000 samples, our dataset is the largest medical machine translation (MT) dataset and the largest many-to-many multilingual ST among all domains. Secondly, we present the most extensive analysis study in ST research to date, including: empirical baselines, bilingual-multilingual comparative study, end-to-end vs. cascaded comparative study, task-specific vs. multi-task sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq) comparative study, code-switch analysis, and quantitative-qualitative error analysis. All code, data, and models are available online: https://github.com/leduckhai/MultiMed-ST.
在医疗领域,多语言语音识别(ST)通过突破语言障碍实现高效沟通、缓解专业劳动力短缺、促进诊断和治疗的改进,特别是在疫情期间,提升了患者护理体验。在这项工作中,我们据我们所知,首次对医疗ST进行了系统研究,并发布了MultiMed-ST大规模医疗领域ST数据集。该数据集涵盖五个语种的全部翻译方向:越南语、英语、德语、法语、繁体中文和简体中文,并配备了模型。我们的数据集包含29万个样本,是迄今为止最大的医疗机器翻译(MT)数据集以及所有领域最大的多语种ST数据集。其次,我们目前进行了ST研究中最为广泛的分析研究,包括:实证基准线研究、双语-多语比较研究、端到端与级联比较研究、任务特定与多任务序列到序列(seq2seq)比较研究、代码切换分析和定量-定性误差分析。所有代码、数据和模型均可在网上找到:https://github.com/leduckhai/MultiMed-ST。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint, 122 pages
Summary
本文介绍了医疗领域中的多语言语音识别翻译(ST)技术,该技术通过消除语言障碍、缓解专业劳动力短缺以及促进诊断和治疗的改进,提高了患者护理的效率。文章首次系统性地研究了医疗ST,并发布了MultiMed-ST数据集,包含五种语言的大规模ST数据集,以及相应的模型。该数据集包含29万个样本,是医疗机器翻译(MT)领域最大的数据集,也是所有领域中最大的多对多语言ST数据集。此外,文章还进行了迄今为止最全面的ST研究分析,包括实证基准、双语-多语对比研究、端到端与级联对比研究、任务特定与多任务序列到序列(seq2seq)对比研究、代码切换分析和定量定性错误分析。所有代码、数据和模型均可在网上获取。
Key Takeaways
- 多语言语音识别翻译(ST)在医疗领域对提高患者护理效率至关重要,它能消除语言障碍、缓解专业劳动力短缺并促进诊断和治疗的改进。
- 首次系统性地研究了医疗ST,并发布了MultiMed-ST数据集,包含五种语言的大规模翻译数据集和模型。
- MultiMed-ST数据集包含29万个样本,是医疗机器翻译(MT)领域最大的数据集。
- 该研究进行了全面的ST分析,包括实证基准、双语-多语对比、端到端与级联对比等。
- 文章进行了任务特定与多任务序列到序列(seq2seq)对比研究,对于了解ST技术的发展和进步具有重要意义。
- 代码切换分析是本研究的一大亮点,有助于理解不同语言间的转换复杂性。
点此查看论文截图

Ichigo: Mixed-Modal Early-Fusion Realtime Voice Assistant
Authors:Alan Dao, Dinh Bach Vu, Huy Hoang Ha
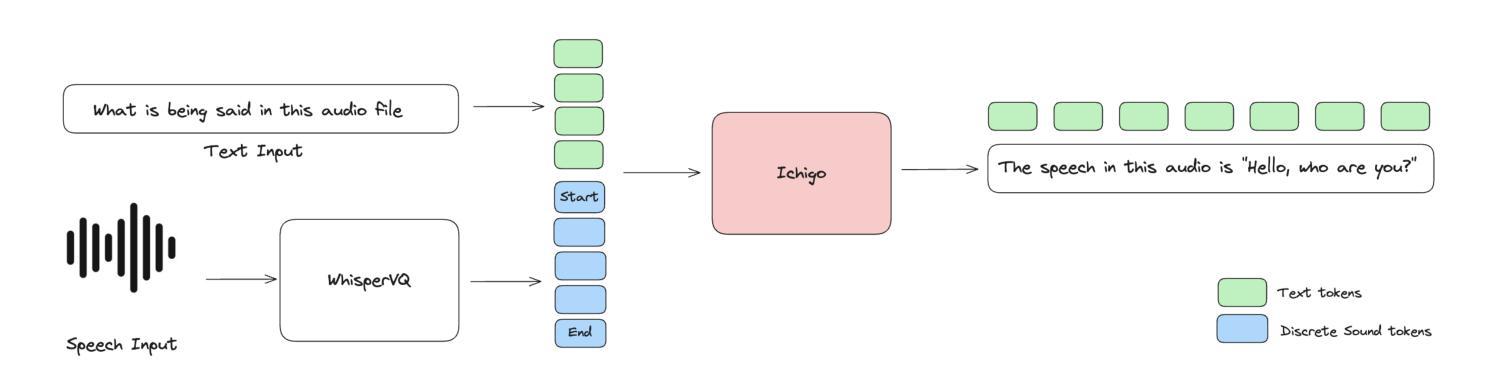
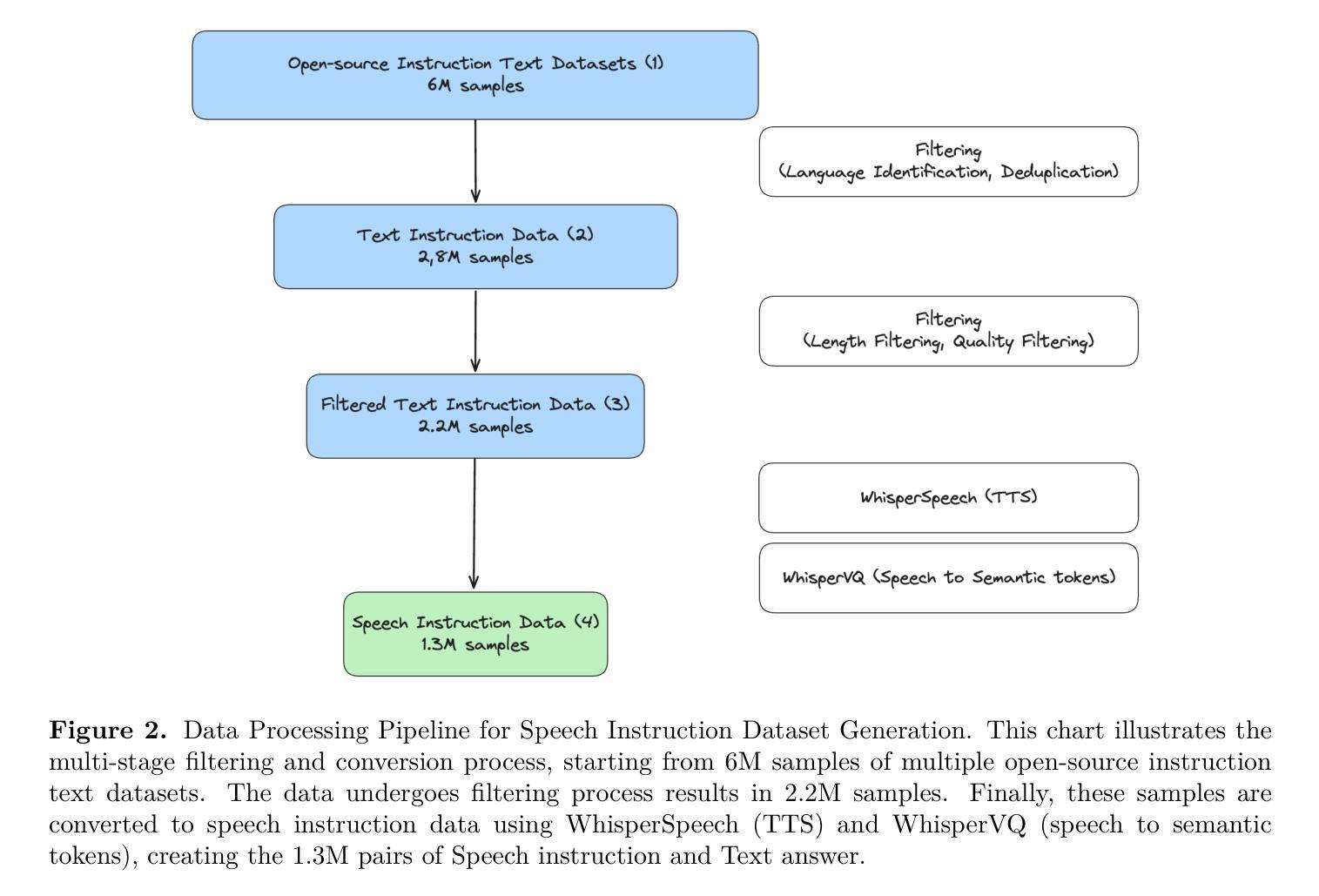
Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized natural language processing, but their application to speech-based tasks remains challenging due to the complexities of integrating audio and text modalities. This paper introduces Ichigo, a mixed-modal model that seamlessly processes interleaved sequences of speech and text. Utilizing a tokenized early-fusion approach, Ichigo quantizes speech into discrete tokens and employs a uniform transformer-based architecture for both speech and text modalities. This method enables joint reasoning and generation across modalities without the need for separate adapters. We present a comprehensive training methodology, including pre-training on multilingual speech recognition datasets and fine-tuning on a curated instruction dataset. Ichigo demonstrates state-of-the-art performance on speech question-answering benchmarks, outperforming existing open-source speech language models and achieving comparable results to cascaded systems. Notably, Ichigo exhibits a latency of just 111 ms to first token generation, significantly lower than current models. Our approach not only advances the field of multimodal AI but also provides a framework for smaller research teams to contribute effectively to open-source speech-language models.
大型语言模型(LLMs)已经彻底改变了自然语言处理的格局,但在基于语音的任务上应用这些模型仍然具有挑战性,原因是整合音频和文本模态的复杂性。本文介绍了一种名为Ichigo的混合模态模型,它能够无缝处理语音和文本交织的序列。Ichigo采用了一种早期融合令牌化的方法,将语音量化为离散令牌,并采用统一的基于转换器的架构来处理语音和文本两种模态。这种方法能够在无需单独适配器的情况下实现跨模态的联合推理和生成。我们提出了一种全面的训练方法,包括在多语言语音识别数据集上进行预训练以及在精选指令数据集上进行微调。Ichigo在语音问答基准测试中表现出了最先进的性能,超越了现有的开源语音语言模型,并取得了与级联系统相当的结果。值得注意的是,Ichigo的首个令牌生成的延迟时间仅为111毫秒,显著低于当前模型。我们的方法不仅推动了多模态人工智能领域的发展,而且为小型研究团队有效地为开源语音语言模型做出贡献提供了框架。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大语言模型在语音任务的应用中存在挑战,涉及语音和文字两种模态的集成。本文介绍了一种混合模态模型Ichigo,它能无缝处理语音和文字交织的序列。Ichigo采用早期融合方法,将语音量化成离散令牌,并使用统一的基于转换器的架构处理语音和文字模态。这种方法无需单独适配器即可实现跨模态推理和生成。Ichigo在多语种语音识别数据集上进行预训练,并在精选指令数据集上进行微调。在语音问答基准测试中,Ichigo表现出卓越性能,不仅优于现有开源语音语言模型,而且与级联系统结果相当。此外,Ichigo的首个令牌生成延迟仅为111毫秒,显著优于现有模型。这不仅推动了多模态人工智能领域的发展,也为小型研究团队有效参与开源语音语言模型提供了框架。
Key Takeaways
- Ichigo是一个混合模态模型,能够处理语音和文字交织的序列。
- 采用早期融合方法和令牌化语音处理。
- 使用统一的基于转换器的架构进行多模态处理。
- 通过预训练和微调,Ichigo在语音问答方面表现出卓越性能。
- Ichigo的生成延迟低于现有模型。
- Ichigo的框架有助于小型研究团队有效参与开源语音语言模型。
点此查看论文截图

Real-time Speech Summarization for Medical Conversations
Authors:Khai Le-Duc, Khai-Nguyen Nguyen, Long Vo-Dang, Truong-Son Hy
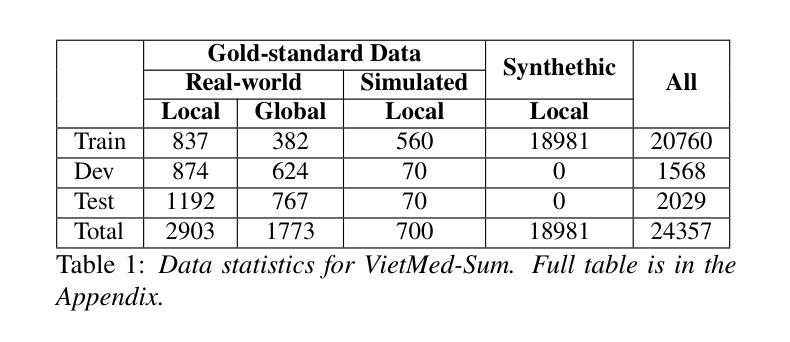
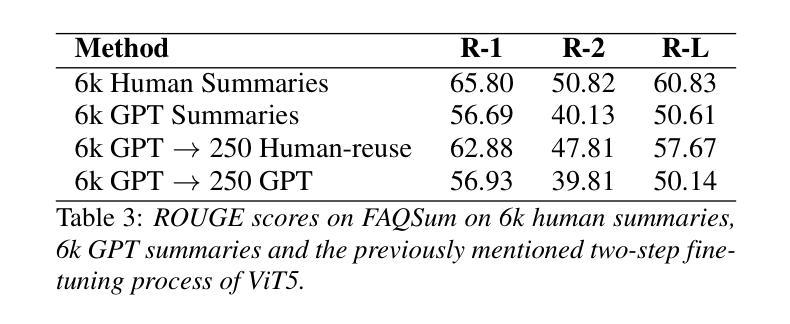
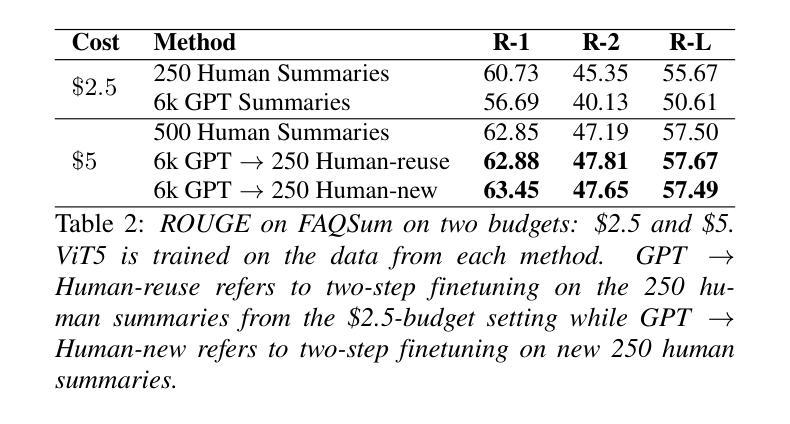
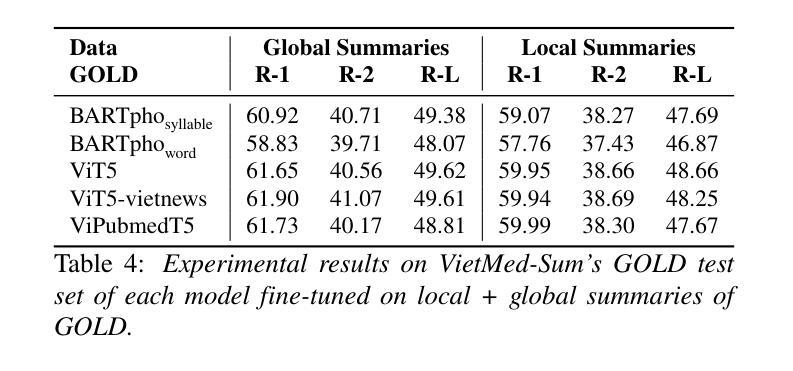
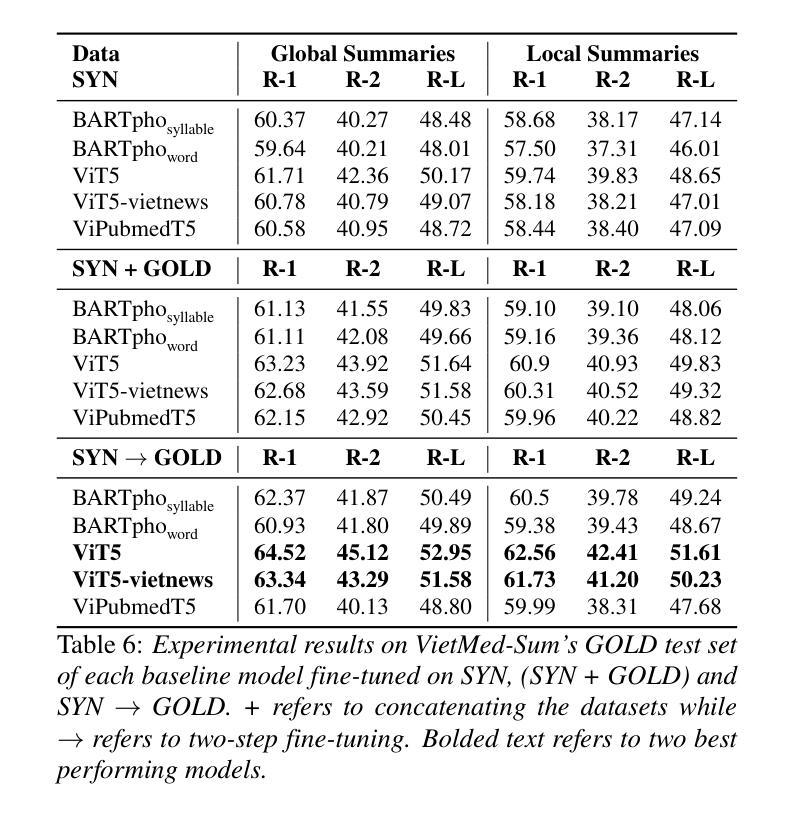
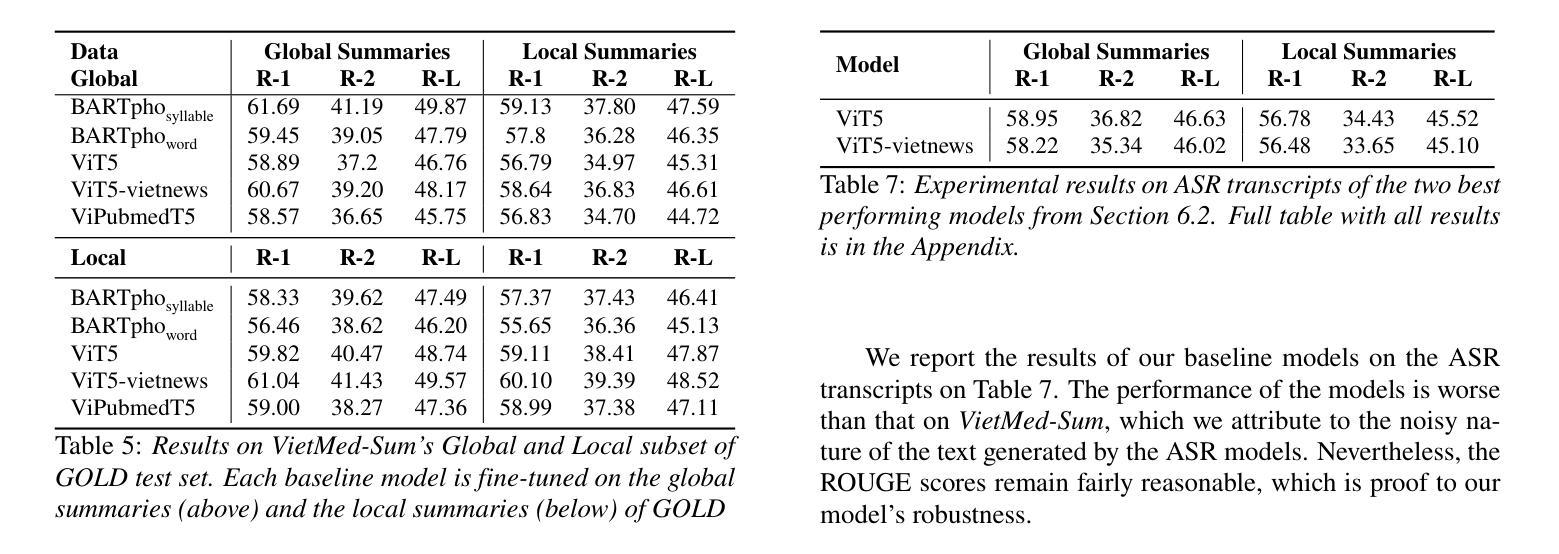
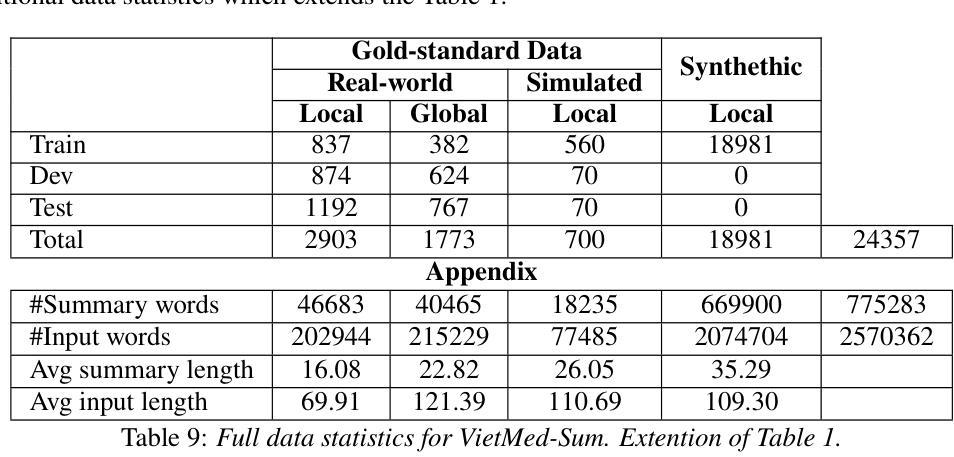
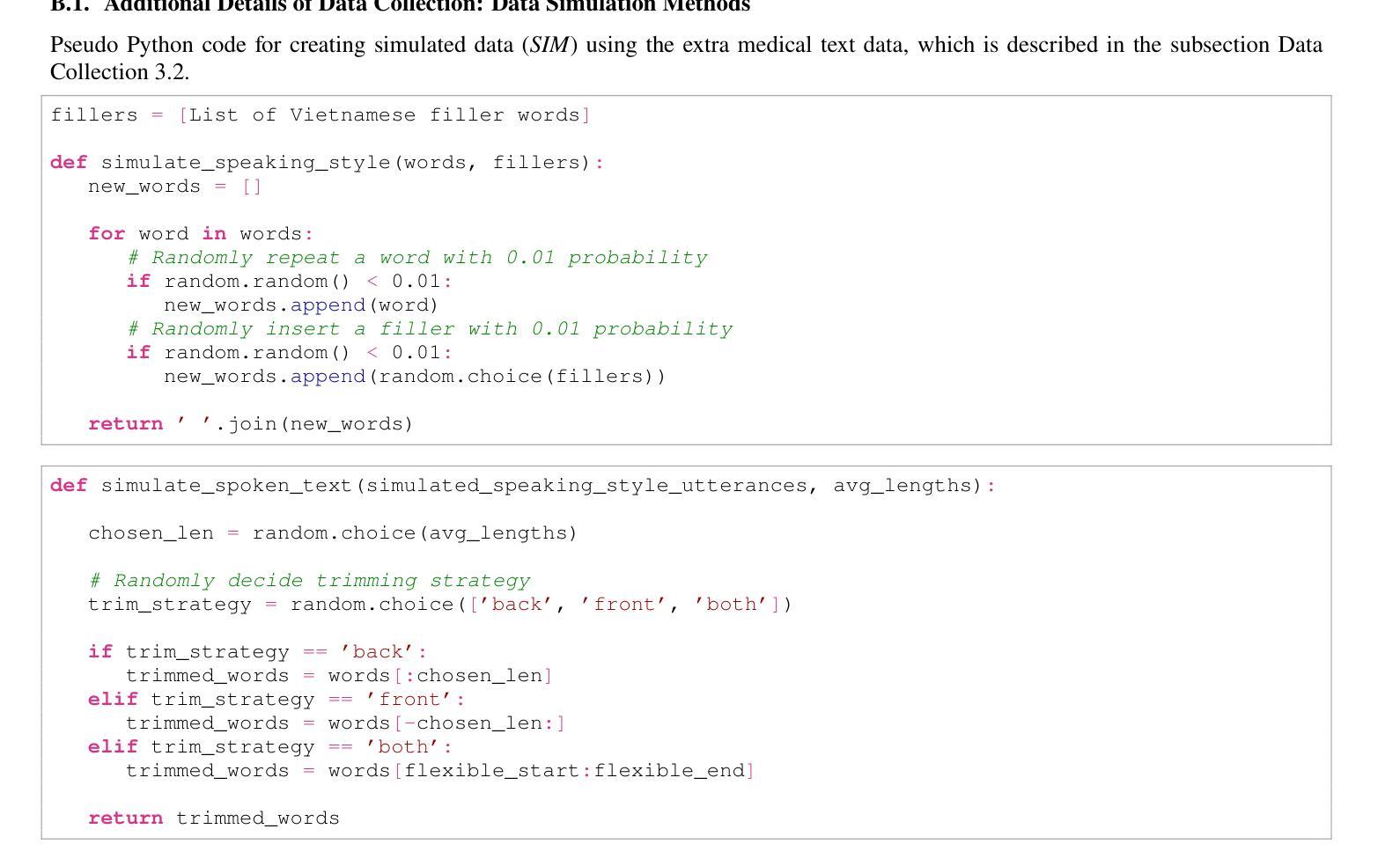
In doctor-patient conversations, identifying medically relevant information is crucial, posing the need for conversation summarization. In this work, we propose the first deployable real-time speech summarization system for real-world applications in industry, which generates a local summary after every N speech utterances within a conversation and a global summary after the end of a conversation. Our system could enhance user experience from a business standpoint, while also reducing computational costs from a technical perspective. Secondly, we present VietMed-Sum which, to our knowledge, is the first speech summarization dataset for medical conversations. Thirdly, we are the first to utilize LLM and human annotators collaboratively to create gold standard and synthetic summaries for medical conversation summarization. Finally, we present baseline results of state-of-the-art models on VietMed-Sum. All code, data (English-translated and Vietnamese) and models are available online: https://github.com/leduckhai/MultiMed/tree/master/VietMed-Sum
在医患对话中,识别医学相关信息至关重要,这提出了对话摘要的需求。在这项工作中,我们提出了首个可用于行业实际应用部署的实时语音摘要系统,该系统会在对话中的每N个语音片段后生成局部摘要,并在对话结束时生成全局摘要。从商业角度来看,我们的系统可以提升用户体验,从技术角度来看,还能降低计算成本。其次,我们推出了VietMed-Sum数据集,据我们所知,这是首个用于医疗对话的语音摘要数据集。此外,我们还是首次利用大型语言模型(LLM)和人类注释器进行合作,为医疗对话摘要创建金标准和合成摘要。最后,我们在VietMed-Sum上展示了最新模型的基线结果。所有代码、数据(英语翻译和越南语)和模型均可在网上找到:https://github.com/leduckhai/MultiMed/tree/master/VietMed-Sum
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Interspeech 2024 (Oral)
Summary
针对医患对话中的医学相关信息识别,提出首个可部署的实时语音摘要系统。该系统可在对话中的每个N个语音片段后生成局部摘要,并在对话结束时生成全局摘要。此系统从商业角度提升了用户体验,从技术角度降低了计算成本。此外,还推出了越南语医疗对话摘要数据集VietMed-Sum,并首次利用大型语言模型与人工标注师合作创建医疗对话摘要的金标准和合成摘要。最后,展示了先进模型在VietMed-Sum上的基线结果。
Key Takeaways
- 提出首个可部署的实时语音摘要系统,适用于医疗行业中的对话内容。
- 系统能够生成局部和全局两种摘要,提高用户体验并降低计算成本。
- 推出越南语医疗对话摘要数据集VietMed-Sum,为医疗行业提供数据支持。
- 首次结合大型语言模型与人工标注师,共同创建医疗对话摘要的标准数据。
- 利用协同工作的方式提高了数据集的多样性和准确性。
- 系统化的方法有助于解决医疗对话中的信息过载问题,提高沟通效率。
点此查看论文截图

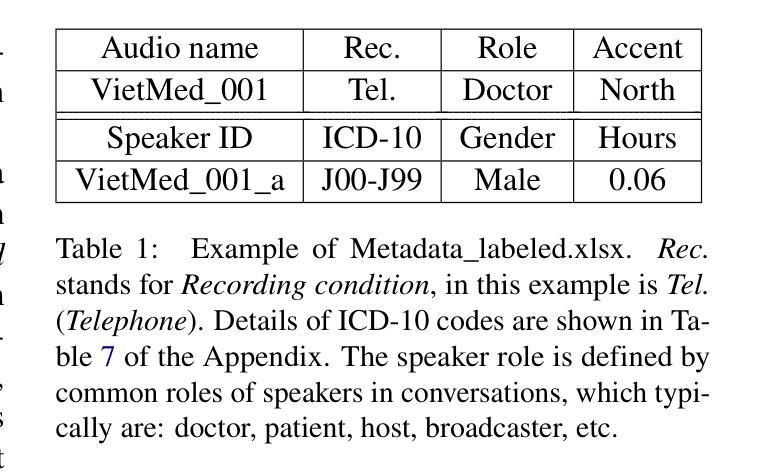
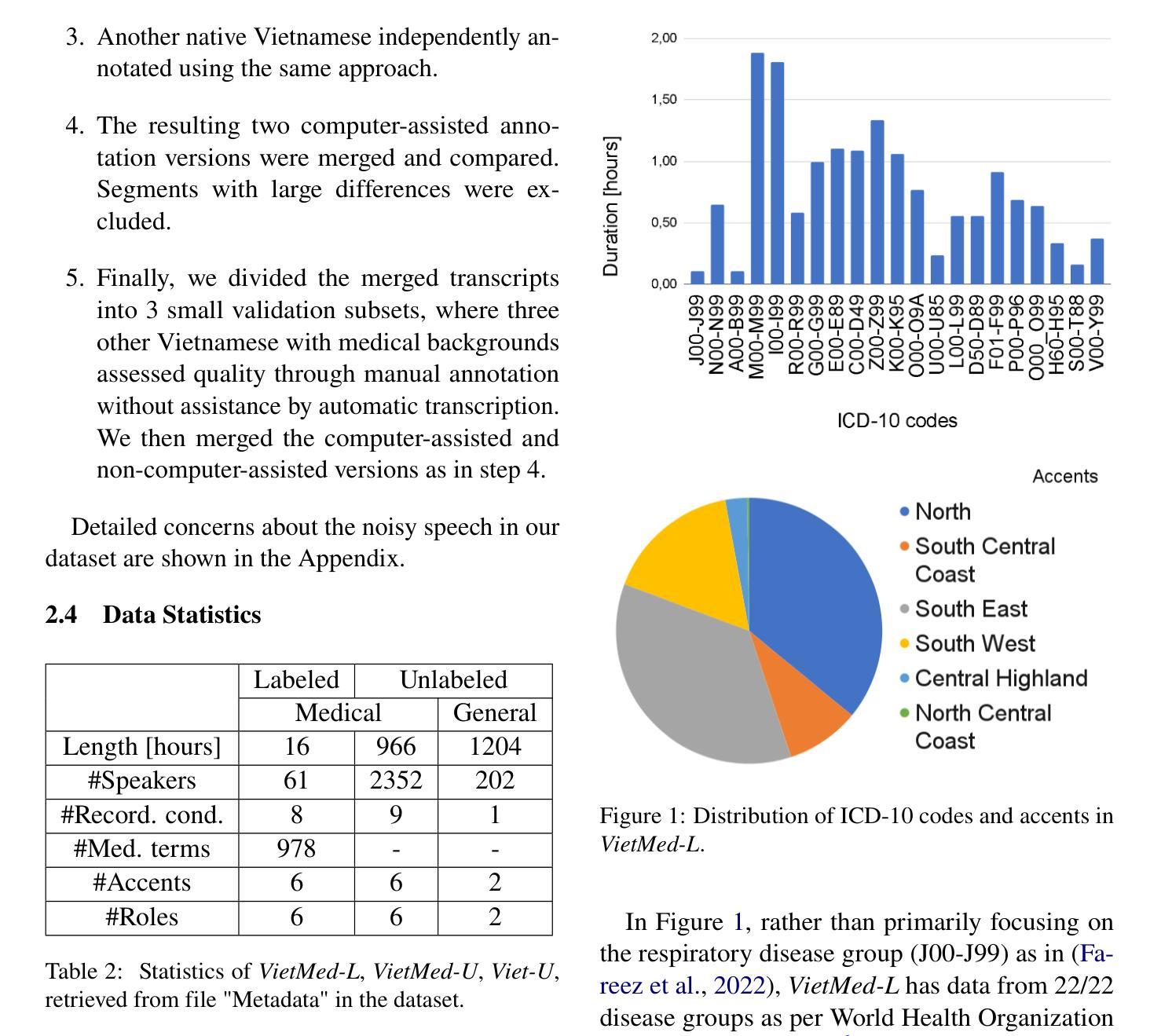
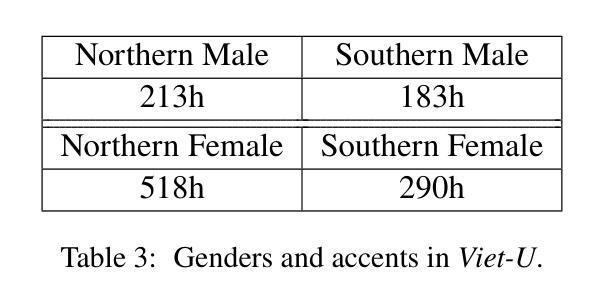
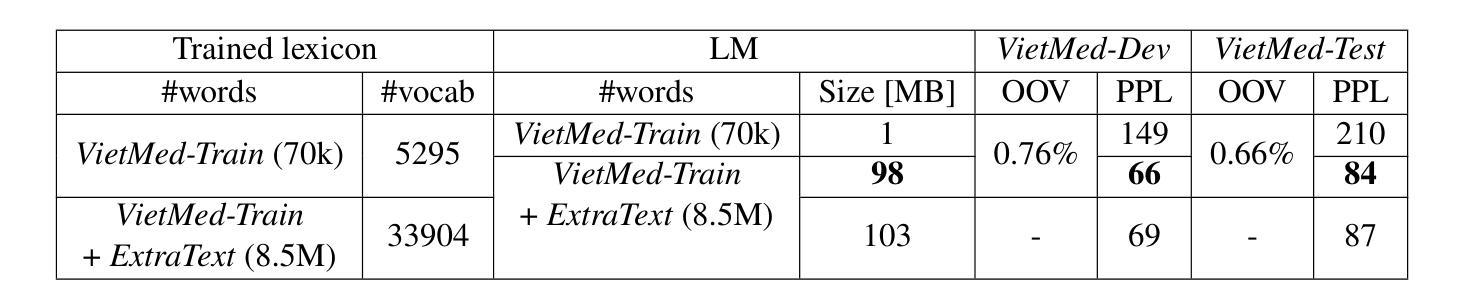
VietMed: A Dataset and Benchmark for Automatic Speech Recognition of Vietnamese in the Medical Domain
Authors:Khai Le-Duc
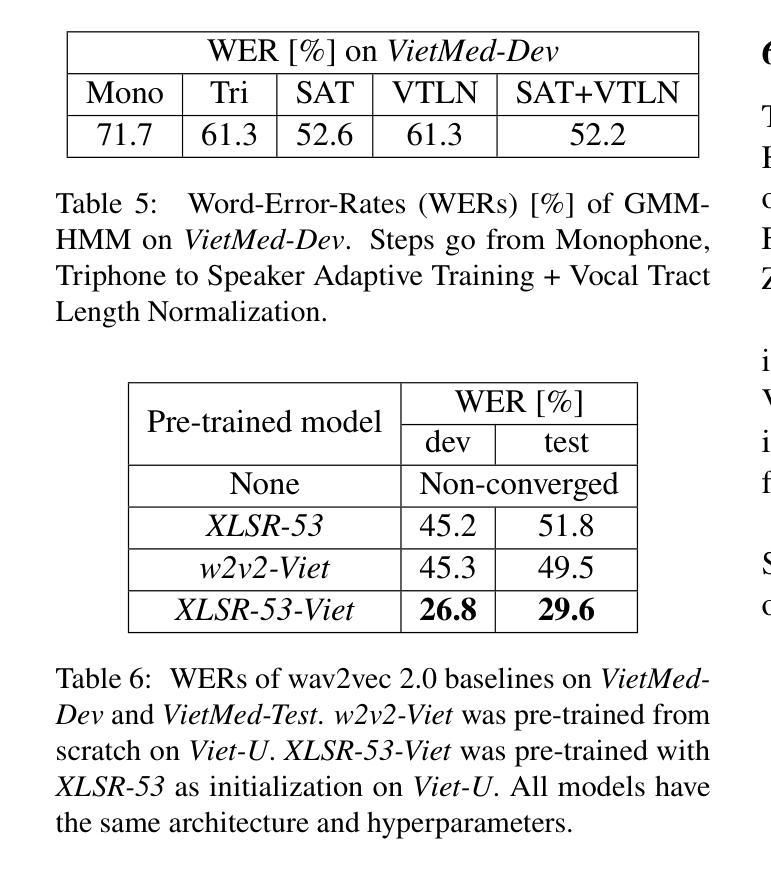
Due to privacy restrictions, there’s a shortage of publicly available speech recognition datasets in the medical domain. In this work, we present VietMed - a Vietnamese speech recognition dataset in the medical domain comprising 16h of labeled medical speech, 1000h of unlabeled medical speech and 1200h of unlabeled general-domain speech. To our best knowledge, VietMed is by far the world’s largest public medical speech recognition dataset in 7 aspects: total duration, number of speakers, diseases, recording conditions, speaker roles, unique medical terms and accents. VietMed is also by far the largest public Vietnamese speech dataset in terms of total duration. Additionally, we are the first to present a medical ASR dataset covering all ICD-10 disease groups and all accents within a country. Moreover, we release the first public large-scale pre-trained models for Vietnamese ASR, w2v2-Viet and XLSR-53-Viet, along with the first public large-scale fine-tuned models for medical ASR. Even without any medical data in unsupervised pre-training, our best pre-trained model XLSR-53-Viet generalizes very well to the medical domain by outperforming state-of-the-art XLSR-53, from 51.8% to 29.6% WER on test set (a relative reduction of more than 40%). All code, data and models are made publicly available: https://github.com/leduckhai/MultiMed/tree/master/VietMed.
由于隐私限制,医疗领域的公开语音识别数据集十分匮乏。在这项工作中,我们推出了VietMed——越南医疗领域的语音识别数据集,包含16小时的标注医疗语音、1000小时的无标签医疗语音和1200小时的无标签通用领域语音。据我们所知,VietMed迄今为止是世界上规模最大、涵盖7个方面的公开医疗语音识别数据集:总时长、发言人数量、疾病种类、录制条件、发言人角色、独特的医疗术语和口音。VietMed也是迄今为止公开越南语音数据集中总时长最长的。此外,我们是首次推出覆盖所有ICD-10疾病群体和一个国家内所有口音的医疗ASR数据集。而且,我们发布了首个公开的越南ASR大规模预训练模型w2v2-Viet和XLSR-53-Viet,以及首个公开的医疗ASR大规模微调模型。即使在没有医疗数据的无监督预训练中,我们最佳的预训练模型XLSR-53-Viet通过适应医疗领域,在测试集上的词错误率从XLSR-53的51.8%降低到29.6%(相对减少了40%以上)。所有代码、数据和模型均已公开提供:https://github.com/leduckhai/MultiMed/tree/master/VietMed。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF LREC-COLING 2024 (Oral), 24 pages
Summary
本文介绍了一个名为VietMed的越南语医疗领域语音识别数据集,包含16小时的标注医疗语音、1000小时的无标签医疗语音和1200小时的无标签通用领域语音。VietMed是目前世界上最大的公开医疗领域语音识别数据集,涵盖了总时长、说话人数、疾病种类、录制条件、说话人角色、独特医疗术语和口音等7个方面。此外,还首次发布了覆盖所有ICD-10疾病分组和越南境内所有口音的医疗ASR数据集。同时,本文还介绍了针对越南语ASR的预训练模型和首次公开发布的大型预训练模型w2v2-Viet和XLSR-53-Viet,以及针对医疗ASR的首次公开发布的大型微调模型。其中,XLSR-53-Viet模型在医疗领域的性能表现尤为出色,相较于当前最先进的XLSR-53模型,其在测试集上的词错误率降低了超过40%。
Key Takeaways
1.VietMed是首个大规模的公开医疗领域语音识别数据集,涵盖了16小时的标注医疗语音等数据。
2.VietMed在总时长、说话人数、疾病种类等方面是目前世界上最大的公开医疗语音识别数据集。
3.VietMed是首个覆盖所有ICD-10疾病分组和越南境内所有口音的医疗ASR数据集。
4.研究团队发布了针对越南语ASR的预训练模型w2v2-Viet和XLSR-53-Viet。
5.XLSR-53-Viet模型在医疗领域的性能显著,相较于当前最先进的XLSR-53模型,词错误率降低了超过40%。
6.该研究的代码、数据和模型均已公开提供,便于公众访问和使用。
点此查看论文截图

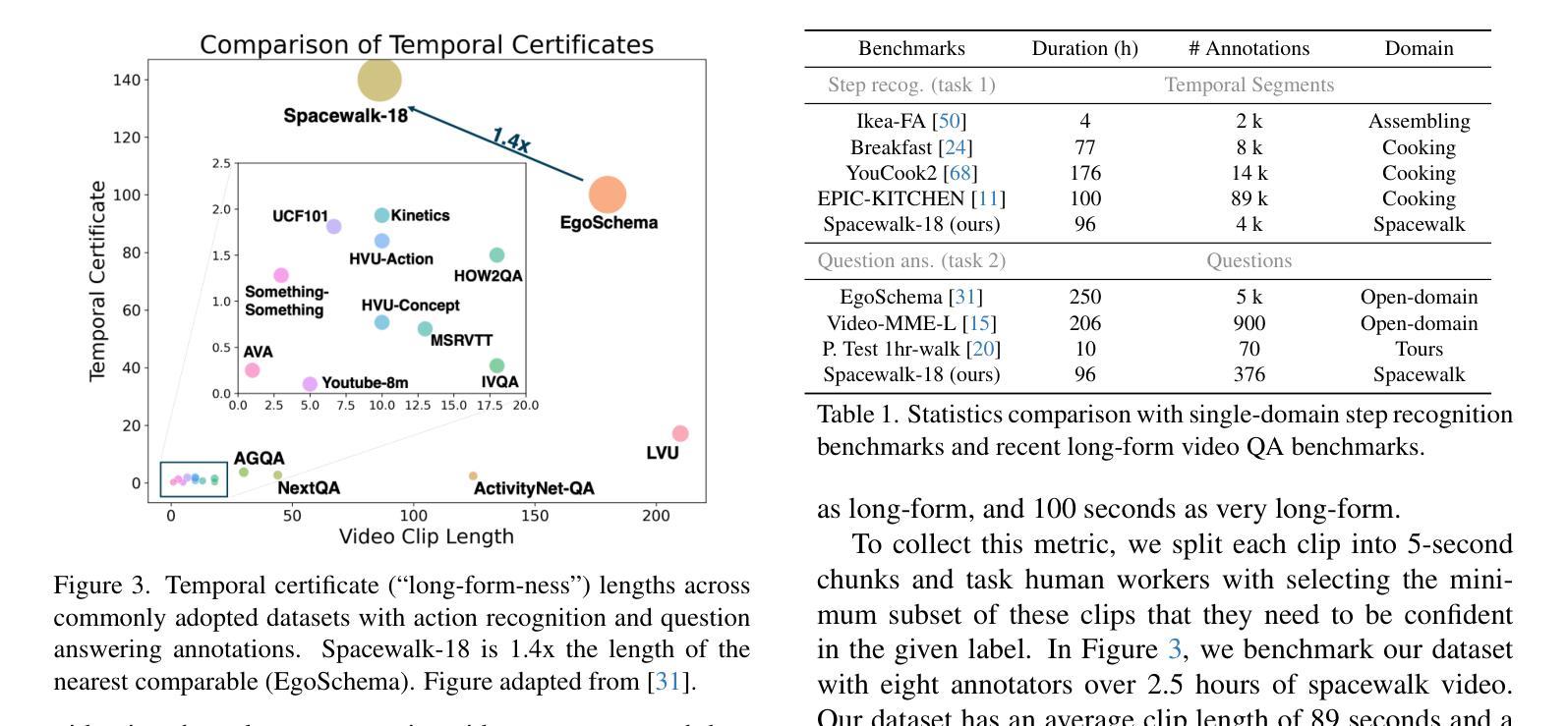
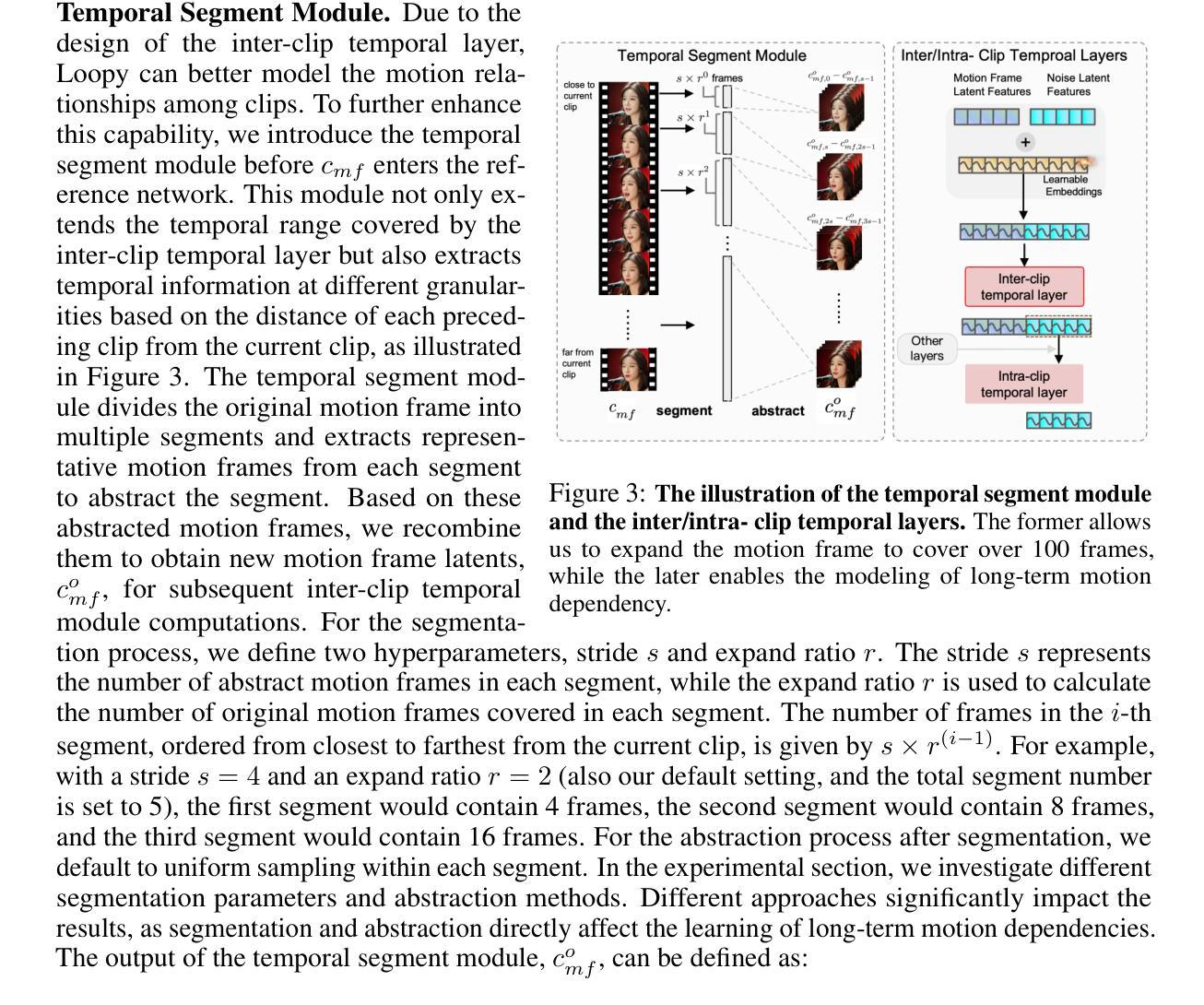
Spacewalk-18: A Benchmark for Multimodal and Long-form Procedural Video Understanding in Novel Domains
Authors:Zitian Tang, Rohan Myer Krishnan, Zhiqiu Yu, Chen Sun
Learning from (procedural) videos has increasingly served as a pathway for embodied agents to acquire skills from human demonstrations. To do this, video understanding models must be able to obtain structured understandings, such as the temporal segmentation of a demonstration into sequences of actions and skills, and to generalize the understandings to novel environments, tasks, and problem domains. In pursuit of this goal, we introduce Spacewalk-18, a benchmark containing two tasks: (1) step recognition and (2) video question answering, over a dataset of temporally segmented and labeled tasks in International Space Station spacewalk recordings. In tandem, the two tasks quantify a model’s ability to: (1) generalize to novel domains; (2) utilize long temporal context and multimodal (e.g. visual and speech) information. Our extensive experimental analysis highlights the challenges of Spacewalk-18, but also suggests best practices for domain generalization and long-form understanding. Notably, we discover a promising adaptation via summarization technique that leads to significant performance improvement without model fine-tuning. The Spacewalk-18 benchmark is released at https://brown-palm.github.io/Spacewalk-18/.
从(程序性)视频中学习已成为实体代理从人类演示中获取知识的一种途径。为此,视频理解模型必须能够获得结构化理解,例如将演示暂时分割成动作和技能的序列,并将理解推广至新环境、任务和领域。为实现这一目标,我们引入了Spacewalk-18基准测试,其中包含两个任务:(1)步骤识别;(2)视频问答,涉及国际空间站太空行走记录中暂时分割和标记的任务数据集。同时,这两个任务衡量模型的能力: (1)推广到全新领域;(2)利用长期的临时背景和多媒体(例如视觉和语音)信息。我们广泛的实验分析突出了Spacewalk-18的挑战,但也提出了领域推广和长形式理解的最佳实践。值得注意的是,我们发现了一种有前景的通过摘要技术进行适应的方法,该方法在无需对模型进行微调的情况下实现了显著的性能提升。Spacewalk-18基准测试发布在https://brown-palm.github.io/Spacewalk-18/上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under submission. Code and models will be released at https://brown-palm.github.io/Spacewalk-18/
Summary
从(程序性)视频中学习已成为实体代理人从人类演示中获取技能的重要途径。为此,视频理解模型必须获得结构化理解,如将演示内容在时间上分割成动作和技能序列,并能够将这些理解推广至新的环境、任务和领域。为实现这一目标,我们引入了Spacewalk-18基准测试,其中包含两项任务:(1)步骤识别;(2)视频问答。该数据集是对国际空间站太空行走记录中的任务进行时间分割和标注。同时进行的两项任务衡量模型的能力包括:(1)推广到新的领域;(2)利用长期时间背景和多媒体(如视觉和语音)信息。我们的实验分析突出了Spacewalk-18的挑战性,同时也提出了针对领域推广和长期理解的最佳实践。值得注意的是,我们发现了一种有前景的摘要技术改编方法,它在不微调模型的情况下实现了显著的性能提升。Spacewalk-18基准测试发布在https://brown-palm.github.io/Spacewalk-18/。
Key Takeaways
- 学习从视频中获得技能已成为实体代理人的重要途径,要求视频理解模型具备结构化理解能力。
- Spacewalk-18基准测试包含步骤识别和视频问答两项任务,衡量模型在推广至新环境、任务和领域的表现。
- 数据集涵盖国际空间站太空行走记录中的任务,并进行时间分割和标注。
- 模型需利用长期时间背景和多媒体信息,如视觉和语音。
- 实验分析突显了Spacewalk-18的挑战性,包括领域推广和长期理解方面的难题。
- 发现了一种通过摘要技术改编的适应方法,显著提高模型性能。
点此查看论文截图