⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-08 更新
Multi-Granularity Vision Fastformer with Fusion Mechanism for Skin Lesion Segmentation
Authors:Xuanyu Liu, Huiyun Yao, Jinggui Gao, Zhongyi Guo, Xue Zhang, Yulin Dong
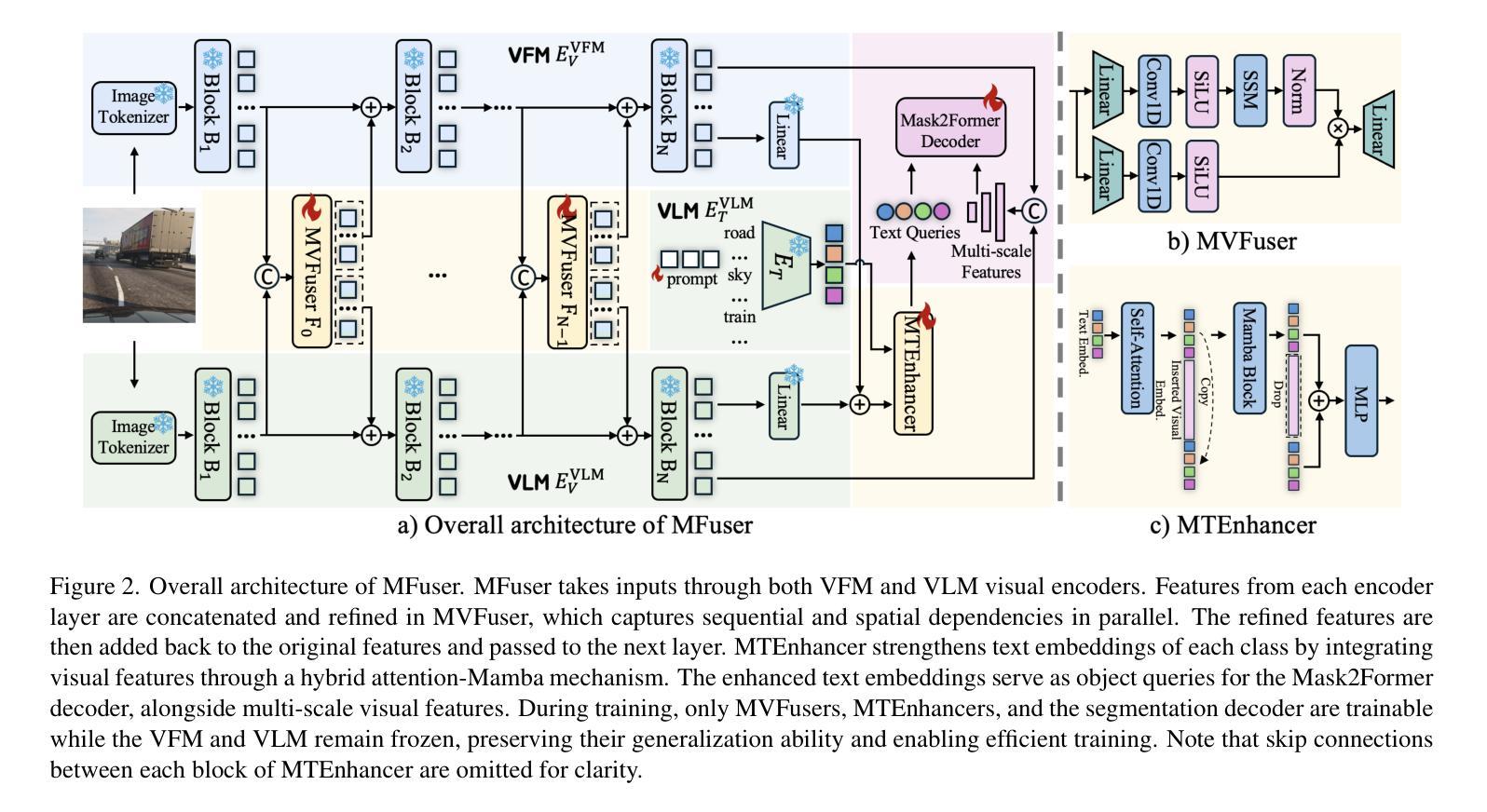
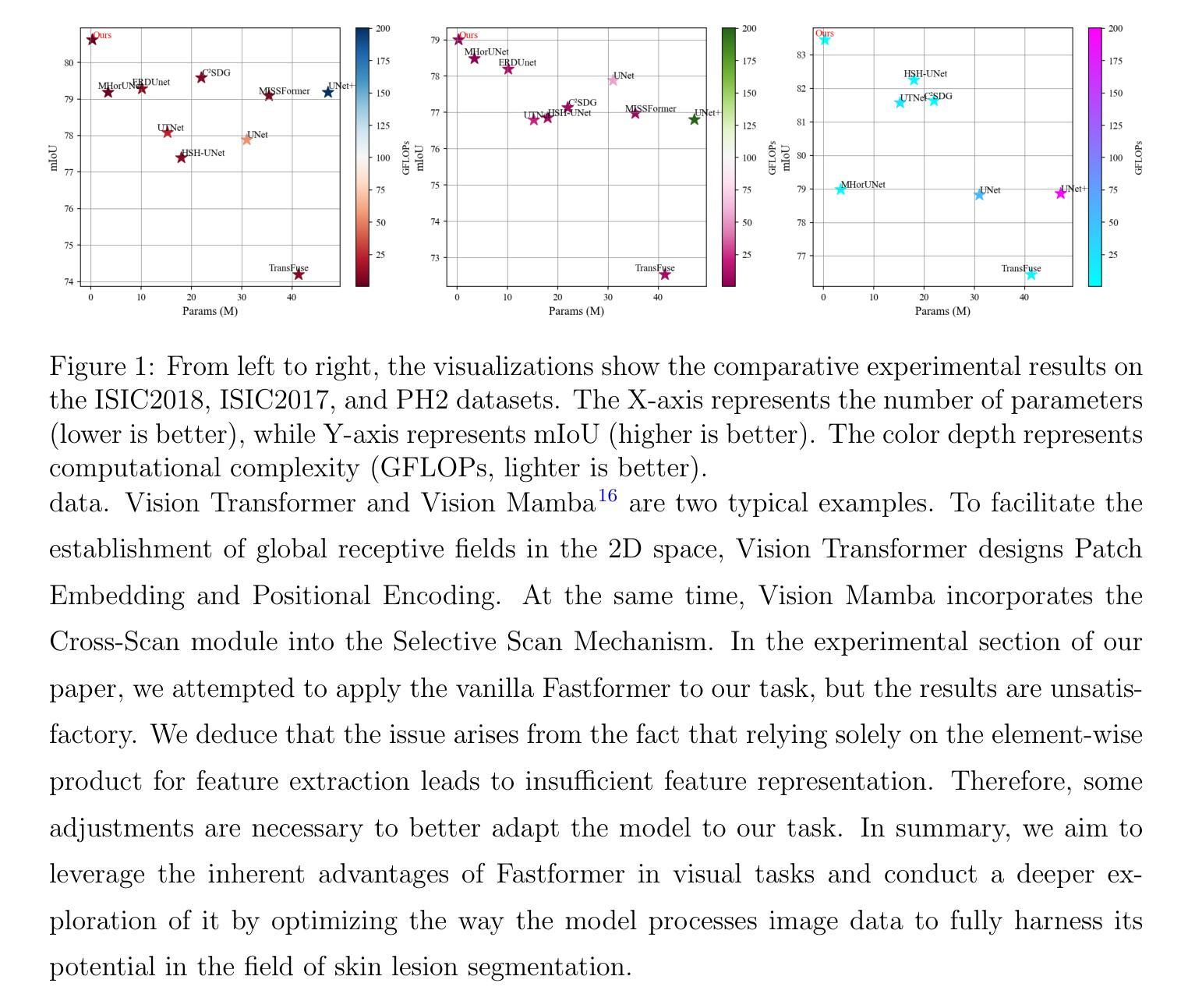
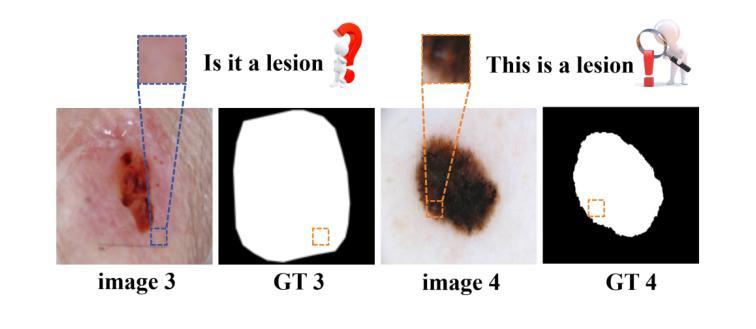
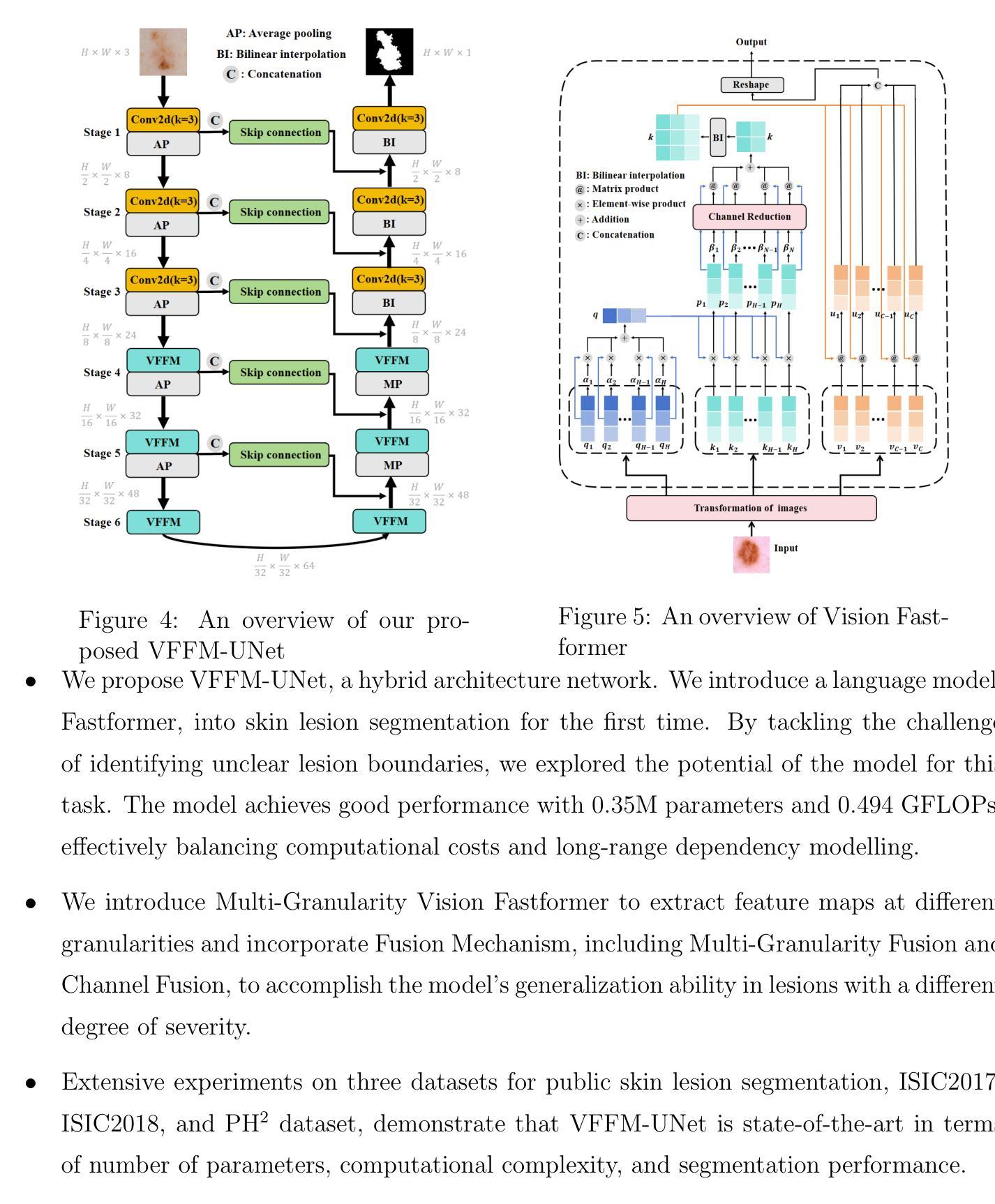
Background:Convolutional Neural Networks(CNN) and Vision Transformers(ViT) are the main techniques used in Medical image segmentation. However, CNN is limited to local contextual information, and ViT’s quadratic complexity results in significant computational costs. At the same time, equipping the model to distinguish lesion boundaries with varying degrees of severity is also a challenge encountered in skin lesion segmentation. Purpose:This research aims to optimize the balance between computational costs and long-range dependency modelling and achieve excellent generalization across lesions with different degrees of severity. Methods:we propose a lightweight U-shape network that utilizes Vision Fastformer with Fusion Mechanism (VFFM-UNet). We inherit the advantages of Fastformer’s additive attention mechanism, combining element-wise product and matrix product for comprehensive feature extraction and channel reduction to save computational costs. In order to accurately identify the lesion boundaries with varying degrees of severity, we designed Fusion Mechanism including Multi-Granularity Fusion and Channel Fusion, which can process the feature maps in the granularity and channel levels to obtain different contextual information. Results:Comprehensive experiments on the ISIC2017, ISIC2018 and PH2 datasets demonstrate that VFFM-UNet outperforms existing state-of-the-art models regarding parameter numbers, computational complexity and segmentation performance. In short, compared to MISSFormer, our model achieves superior segmentation performance while reducing parameter and computation costs by 101x and 15x, respectively. Conclusions:Both quantitative and qualitative analyses show that VFFM-UNet sets a new benchmark by reaching an ideal balance between parameter numbers, computational complexity, and segmentation performance compared to existing state-of-the-art models.
背景:卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)是医学图像分割中的主要技术。然而,CNN受限于局部上下文信息,而ViT的二次复杂性导致计算成本较高。同时,使模型能够区分不同程度严重性的病变边界,也是皮肤病变分割中所遇到的挑战。
目的:本研究旨在优化计算成本与长期依赖关系建模之间的平衡,并在不同严重程度病变上实现出色的泛化能力。
方法:我们提出了一种轻量级的U型网络,该网络利用具有融合机制(Fusion Mechanism)的视觉快速转换器(Vision Fastformer)(VFFM-UNet)。我们继承了快速转换器的附加注意力机制的优点,结合元素乘积和矩阵乘积进行特征提取和通道缩减,以节省计算成本。为了准确识别不同程度严重性的病变边界,我们设计了包括多粒度融合和通道融合的融合机制,可以在粒度和通道级别处理特征映射以获得不同的上下文信息。
结果:在ISIC2017、ISIC2018和PH2数据集上的综合实验表明,VFFM-UNet在参数数量、计算复杂度和分割性能上优于现有先进技术模型。简而言之,与MISSFormer相比,我们的模型在减少参数和计算成本的同时实现了更好的分割性能,分别减少了101倍和15倍。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种利用Vision Fastformer与融合机制(VFFM-UNet)的轻量级U型网络,旨在优化计算成本与长距离依赖建模之间的平衡,并实现在不同严重程度病变上的优秀泛化能力。通过综合特征提取和通道减少来节省计算成本,同时设计融合机制以准确识别不同严重程度病变的边界。在ISIC2017、ISIC2018和PH2数据集上的实验表明,VFFM-UNet在参数数量、计算复杂性和分割性能上超越了现有先进模型。
Key Takeaways
- 研究背景介绍了卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)在医学图像分割中的主要应用,但存在计算成本高和局部上下文信息限制的问题。
- 本文旨在优化计算成本与长距离依赖建模之间的平衡,并实现对不同严重程度病变的优异泛化。
- 提出一种轻量级的U型网络VFFM-UNet,结合Vision Fastformer的优点,通过综合特征提取和通道减少来降低计算成本。
- 设计了包括多粒度融合和通道融合的融合机制,以准确识别具有不同严重程度病变的边界。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,VFFM-UNet在参数数量、计算复杂性和分割性能上超越了现有先进模型。
- 与MISSFormer相比,VFFM-UNet在参数和计算成本上分别降低了101倍和15倍,同时实现了更好的分割性能。
点此查看论文截图


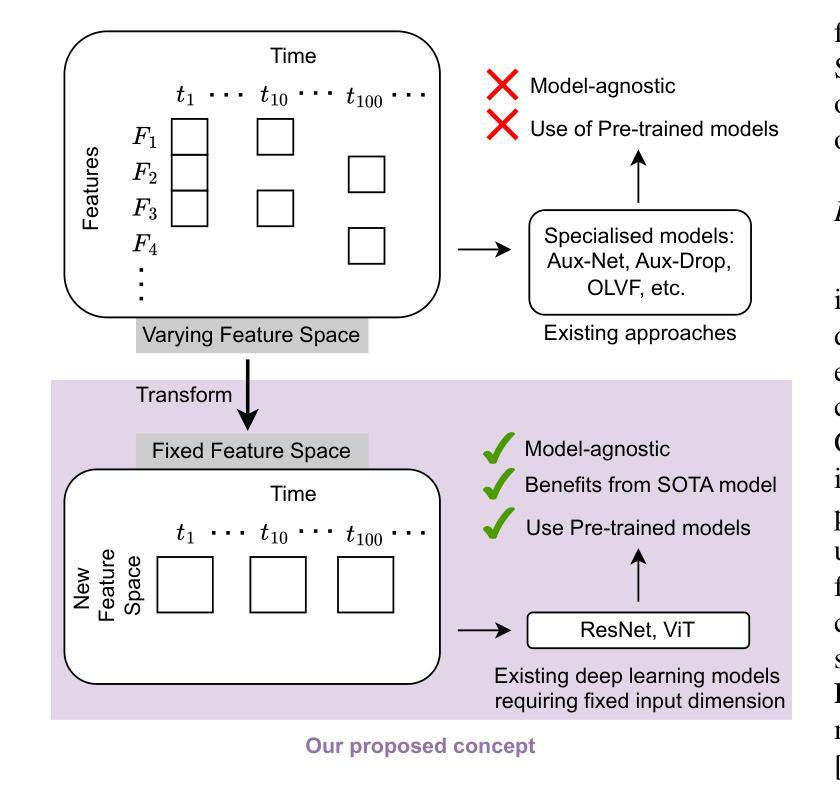
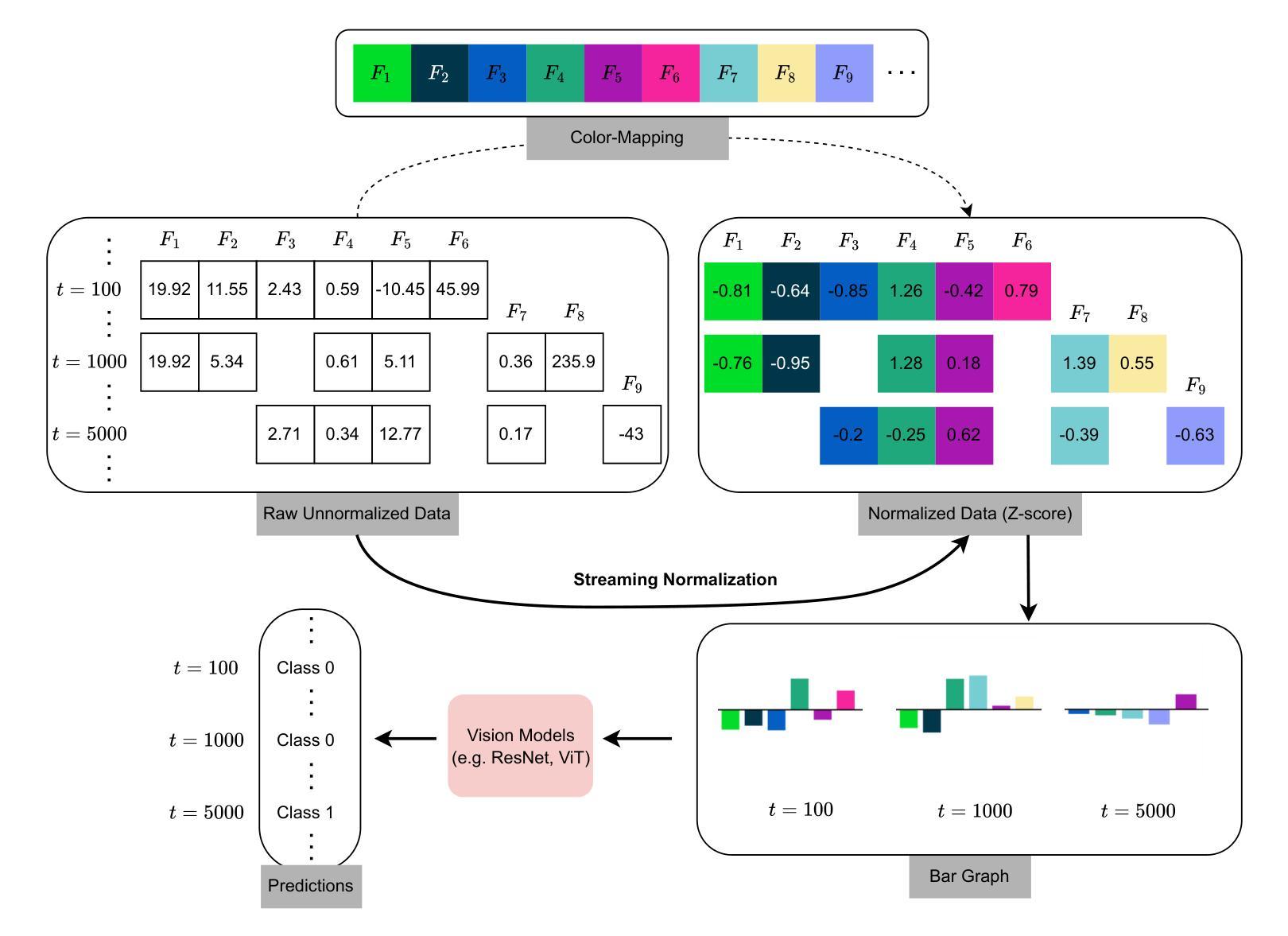
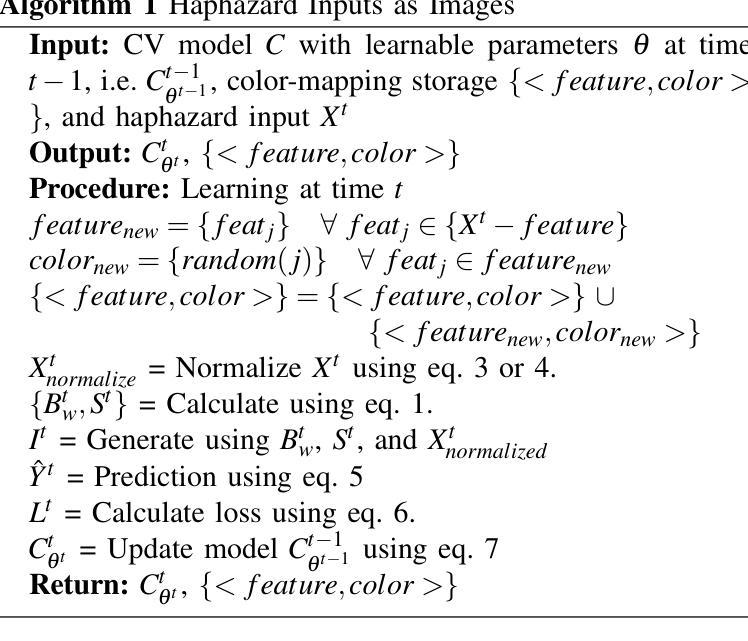
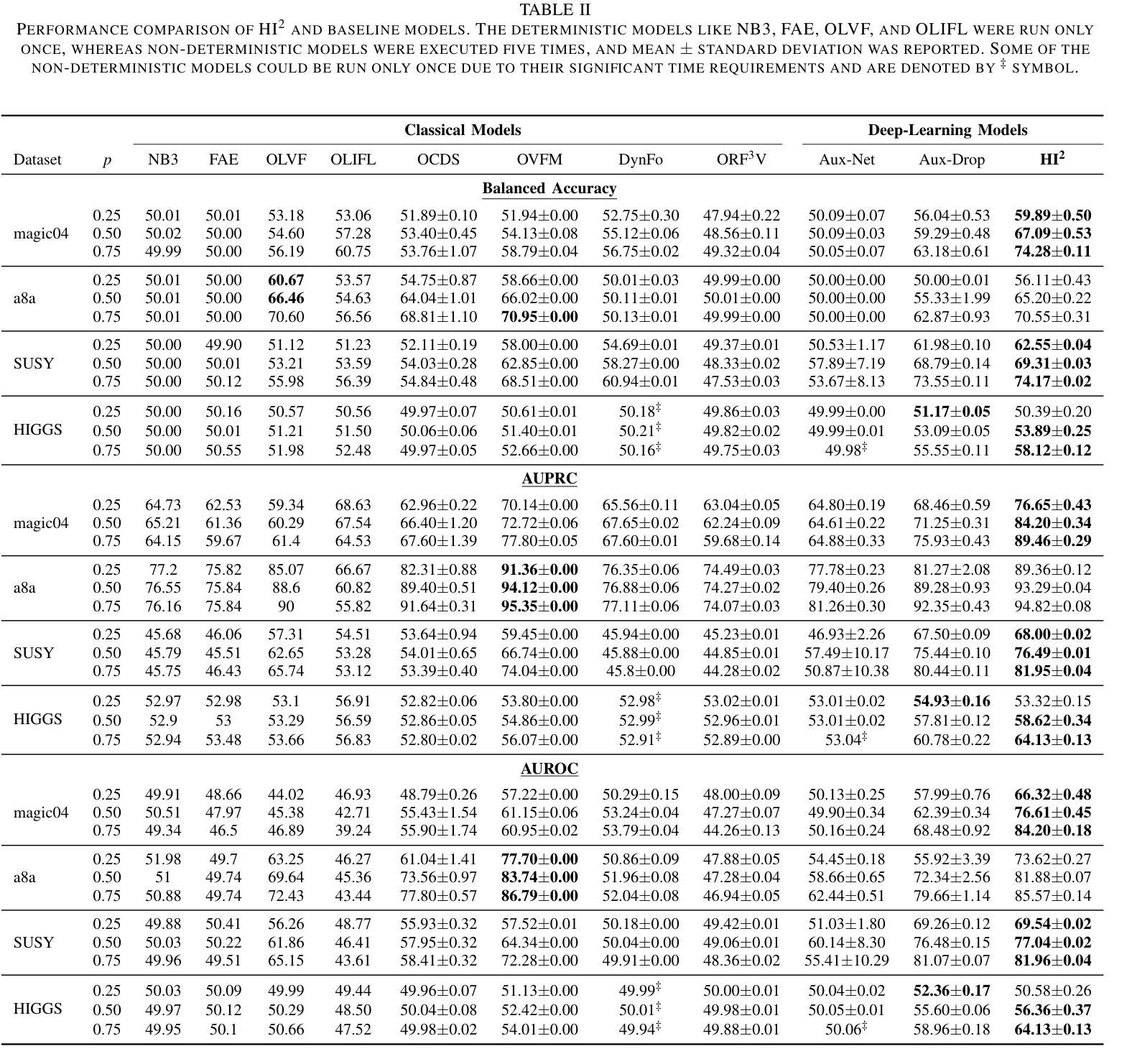
Haphazard Inputs as Images in Online Learning
Authors:Rohit Agarwal, Aryan Dessai, Arif Ahmed Sekh, Krishna Agarwal, Alexander Horsch, Dilip K. Prasad
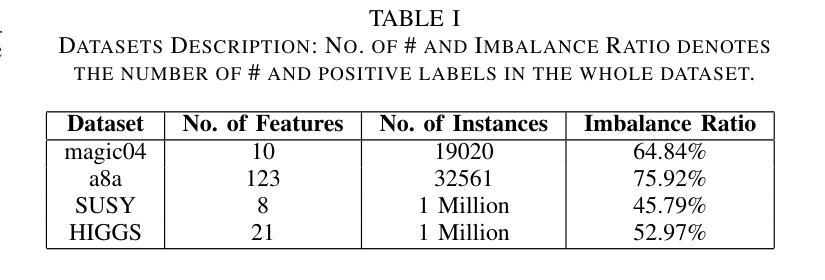
The field of varying feature space in online learning settings, also known as haphazard inputs, is very prominent nowadays due to its applicability in various fields. However, the current solutions to haphazard inputs are model-dependent and cannot benefit from the existing advanced deep-learning methods, which necessitate inputs of fixed dimensions. Therefore, we propose to transform the varying feature space in an online learning setting to a fixed-dimension image representation on the fly. This simple yet novel approach is model-agnostic, allowing any vision-based models to be applicable for haphazard inputs, as demonstrated using ResNet and ViT. The image representation handles the inconsistent input data seamlessly, making our proposed approach scalable and robust. We show the efficacy of our method on four publicly available datasets. The code is available at https://github.com/Rohit102497/HaphazardInputsAsImages.
在线学习环境中可变特征空间领域,也称为随机输入,如今非常突出,因为它在各种领域都有应用。然而,当前处理随机输入的解决方案依赖于模型,无法受益于现有的先进深度学习方法,这些方法需要固定维度的输入。因此,我们提出在在线学习环境中将可变特征空间实时转换为固定维度的图像表示。这种简单而新颖的方法是模型无关的,允许任何基于视觉的模型都适用于随机输入,如使用ResNet和ViT进行演示。图像表示可以无缝处理不一致的输入数据,使我们所提出的方法具有可扩展性和稳健性。我们在四个公开可用的数据集上展示了该方法的有效性。代码可在https://github.com/Rohit102497/HaphazardInputsAsImages找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IJCNN 2025
Summary
该文本介绍了在线学习环境中可变特征空间(也称为随机输入)的重要性及其现有解决方案的局限性。为此,提出了一种将可变特征空间实时转换为固定维度图像表示的方法,该方法模型无关,适用于任何基于视觉的模型,如ResNet和ViT。该图像表示能够无缝处理不一致的输入数据,使所提出的方法具有可扩展性和鲁棒性。在四个公开数据集上验证了该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 在线学习环境中的可变特征空间(随机输入)在现代非常普遍,且应用于各个领域。
- 现有解决方案对随机输入的处理依赖于特定模型,无法利用现有的深度学习技术。
- 提出了一种将可变特征空间实时转换为固定维度图像表示的方法,该方法适用于任何基于视觉的模型。
- 该图像表示可以无缝处理不一致的输入数据,增强了方法的鲁棒性和可扩展性。
- 在四个公开数据集上验证了该方法的有效性。
- 该方法的代码已公开提供,便于他人使用和研究。
点此查看论文截图