⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-09 更新
Federated Learning for Medical Image Classification: A Comprehensive Benchmark
Authors:Zhekai Zhou, Guibo Luo, Mingzhi Chen, Zhenyu Weng, Yuesheng Zhu
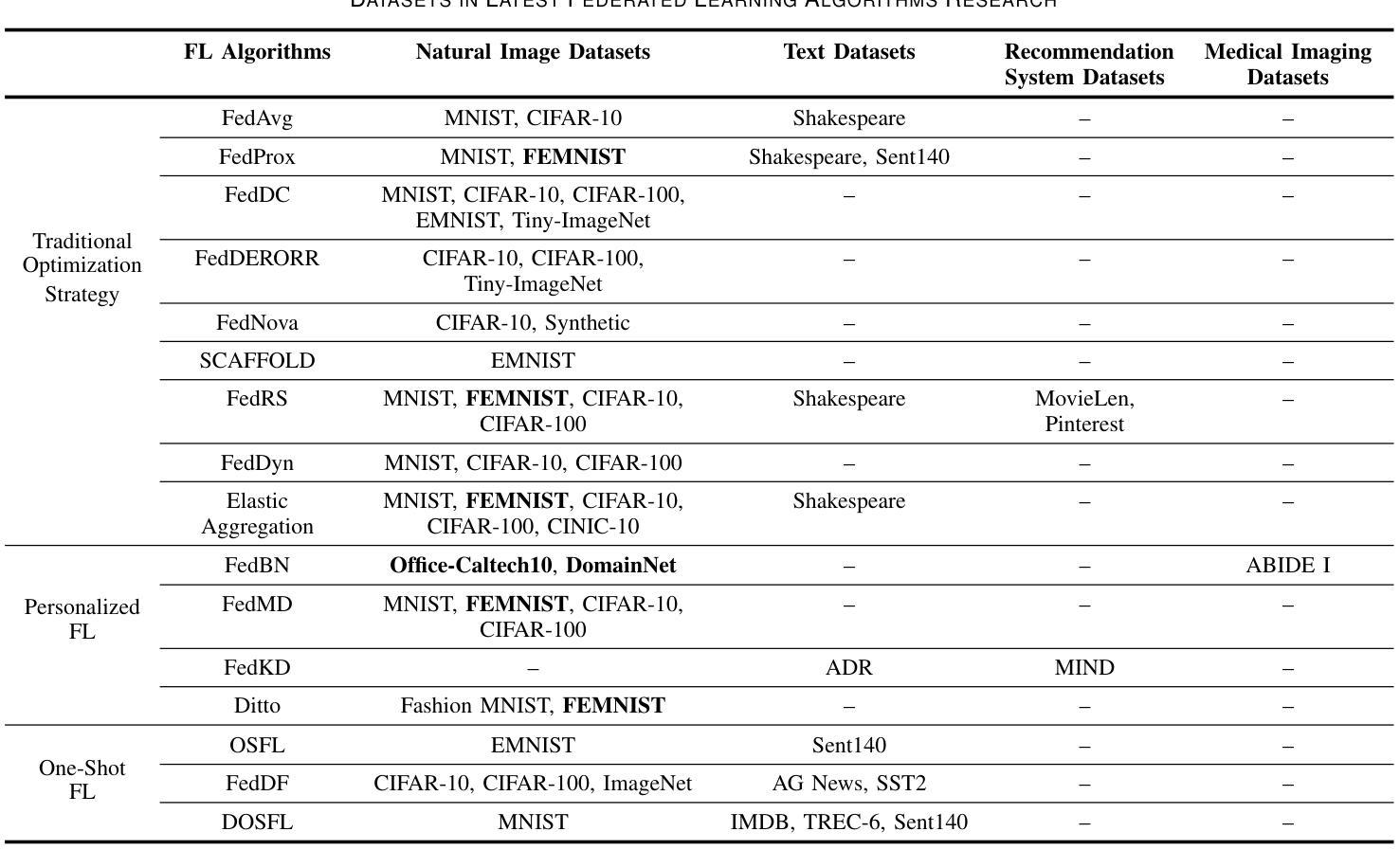
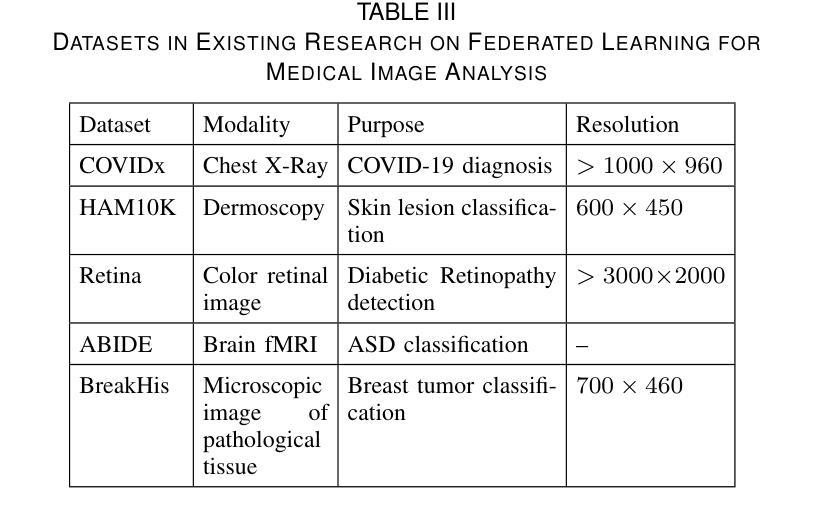
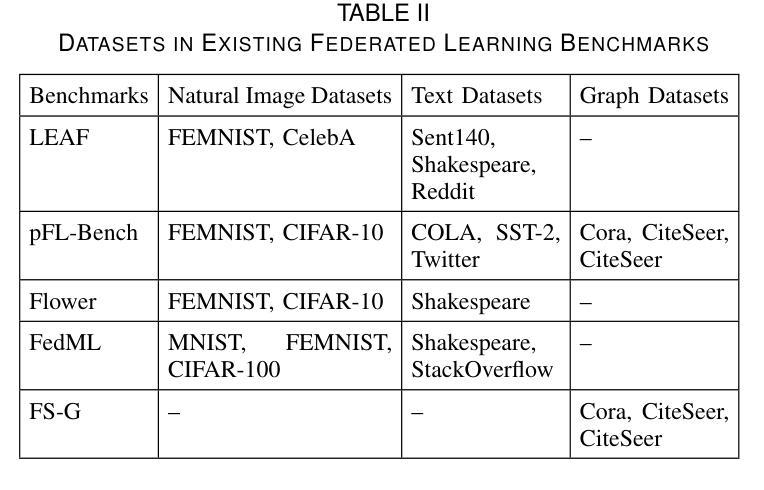
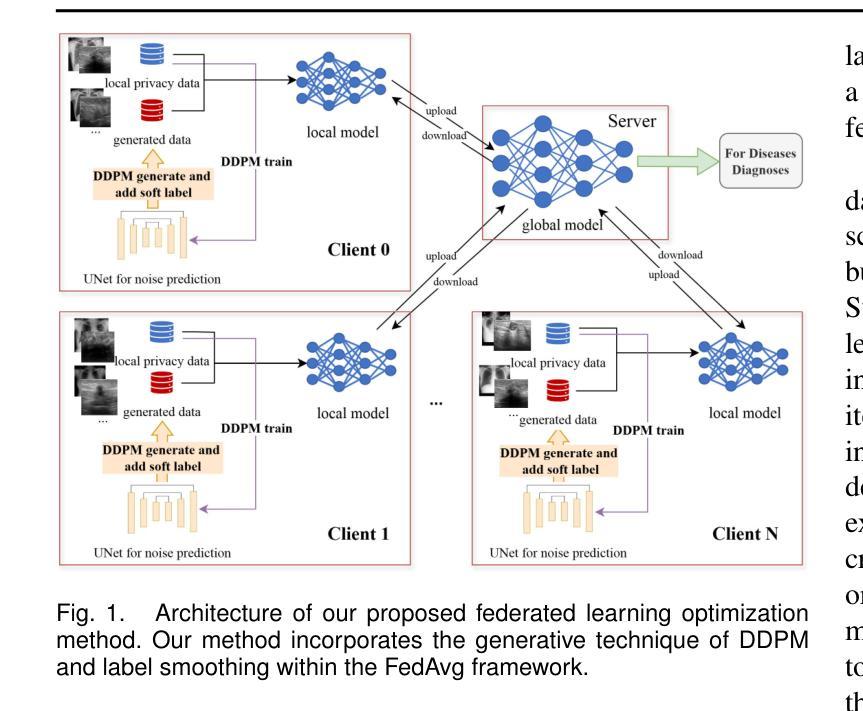
The federated learning paradigm is wellsuited for the field of medical image analysis, as it can effectively cope with machine learning on isolated multicenter data while protecting the privacy of participating parties. However, current research on optimization algorithms in federated learning often focuses on limited datasets and scenarios, primarily centered around natural images, with insufficient comparative experiments in medical contexts. In this work, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation of several state-of-the-art federated learning algorithms in the context of medical imaging. We conduct a fair comparison of classification models trained using various federated learning algorithms across multiple medical imaging datasets. Additionally, we evaluate system performance metrics, such as communication cost and computational efficiency, while considering different federated learning architectures. Our findings show that medical imaging datasets pose substantial challenges for current federated learning optimization algorithms. No single algorithm consistently delivers optimal performance across all medical federated learning scenarios, and many optimization algorithms may underperform when applied to these datasets. Our experiments provide a benchmark and guidance for future research and application of federated learning in medical imaging contexts. Furthermore, we propose an efficient and robust method that combines generative techniques using denoising diffusion probabilistic models with label smoothing to augment datasets, widely enhancing the performance of federated learning on classification tasks across various medical imaging datasets. Our code will be released on GitHub, offering a reliable and comprehensive benchmark for future federated learning studies in medical imaging.
联邦学习范式非常适合医学图像分析领域,因为它能够在保护参与方隐私的同时,有效应对孤立的多中心数据进行机器学习。然而,目前联邦学习中的优化算法研究主要集中在有限的数据集和场景上,主要围绕自然图像展开,在医疗环境下的对比实验不足。在这项工作中,我们对医疗成像背景下的几种最新联邦学习算法进行了全面评估。我们公平地比较了使用各种联邦学习算法在多个医学成像数据集上训练的分类模型。此外,我们还评估了系统性能指标,如通信成本和计算效率,同时考虑了不同的联邦学习架构。我们的研究发现,医学成像数据集对当前联邦学习优化算法构成了重大挑战。没有一种算法能在所有医学联邦学习场景中始终提供最佳性能,许多优化算法在这些数据集上的表现可能会不佳。我们的实验为联邦学习在医学成像领域未来的研究与应用提供了基准和指导。此外,我们提出了一种高效且稳健的方法,结合去噪扩散概率模型的生成技术与标签平滑来增强数据集,从而广泛提高了联邦学习在跨各种医学成像数据集的分类任务上的性能。我们的代码将在GitHub上发布,为医学成像中的联邦学习研究提供可靠和全面的基准。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了联邦学习算法在医学图像分析领域的表现,发现当前联邦学习优化算法在医学图像数据集上挑战较大,无单一算法能在所有场景中都表现最优。同时,提出了结合生成技术与标签平滑的方法,能有效增强数据集,提高联邦学习在医学图像分类任务上的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦学习范式适合医学图像分析领域,能有效处理多中心数据并保护隐私。
- 当前联邦学习优化算法在医学图像数据集上的表现面临挑战。
- 不同的联邦学习算法在不同医学图像数据集上的表现存在差异,无单一最优算法。
- 医学图像数据集的应用给现有联邦学习优化算法带来实质挑战。
- 结合生成技术与标签平滑的方法能广泛增强数据集,提高联邦学习在医学图像分类任务上的性能。
- 本文提供的实验为未来联邦学习在医学图像领域的研究与应用提供了基准和指引。
点此查看论文截图

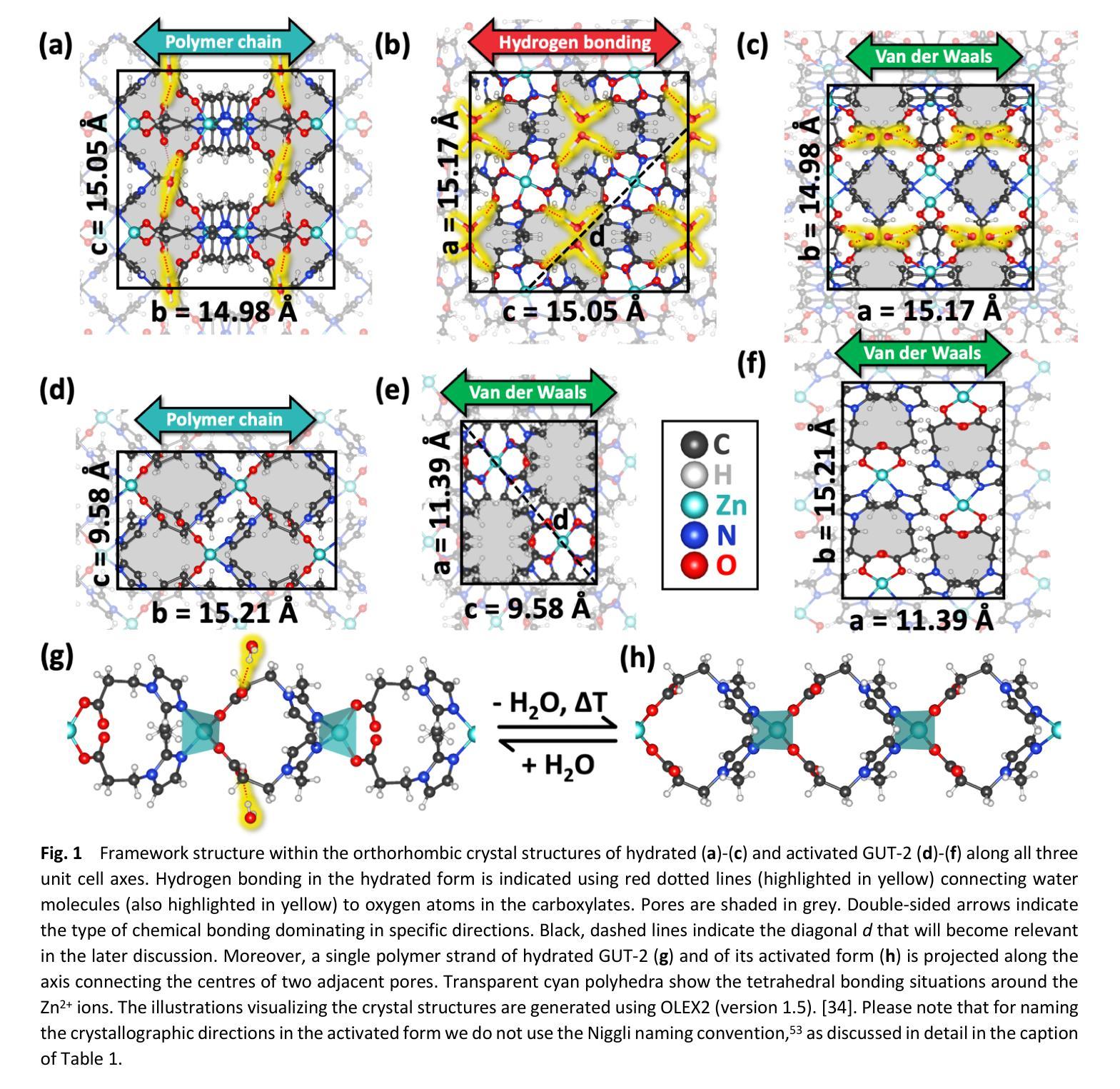
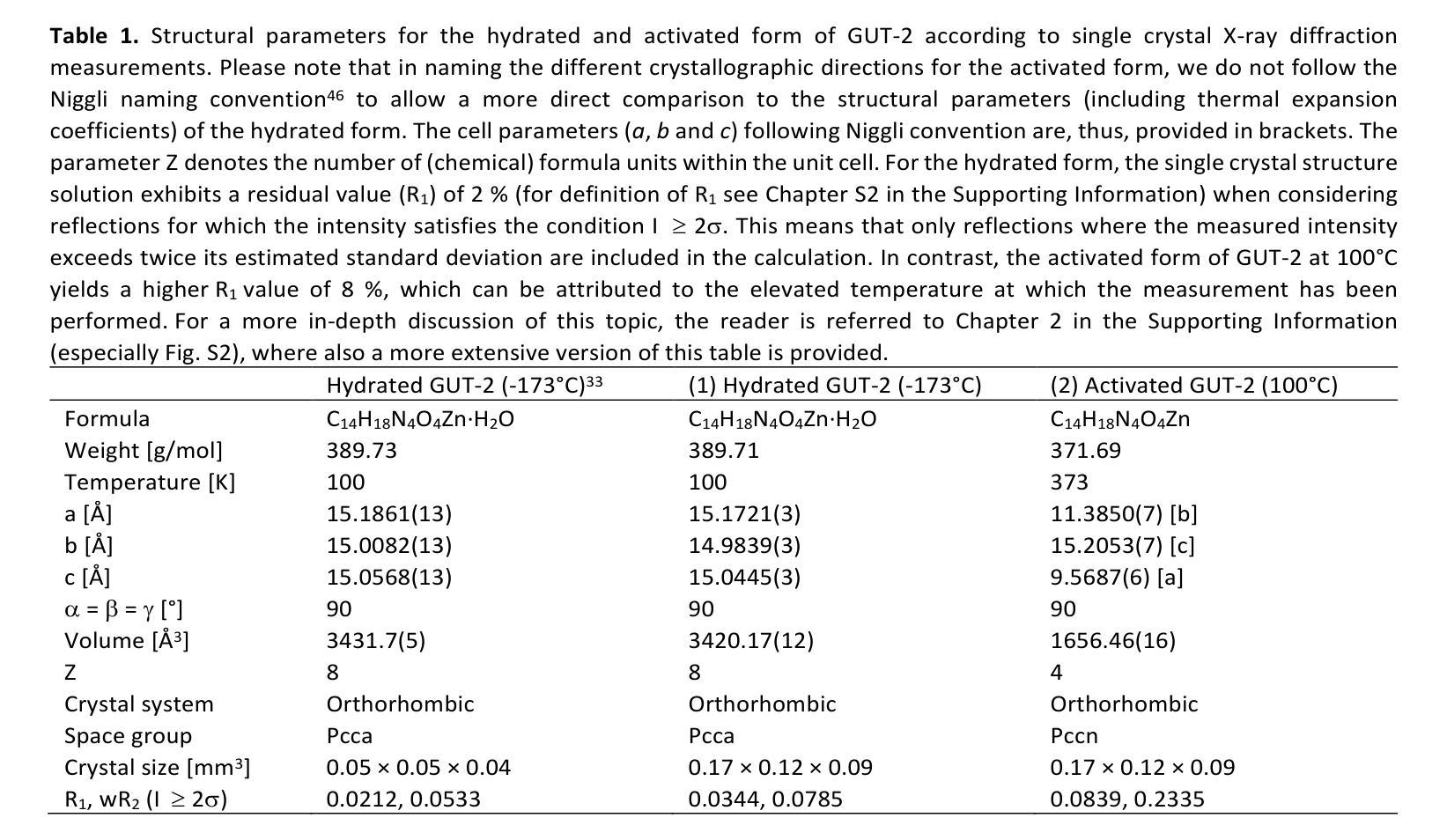
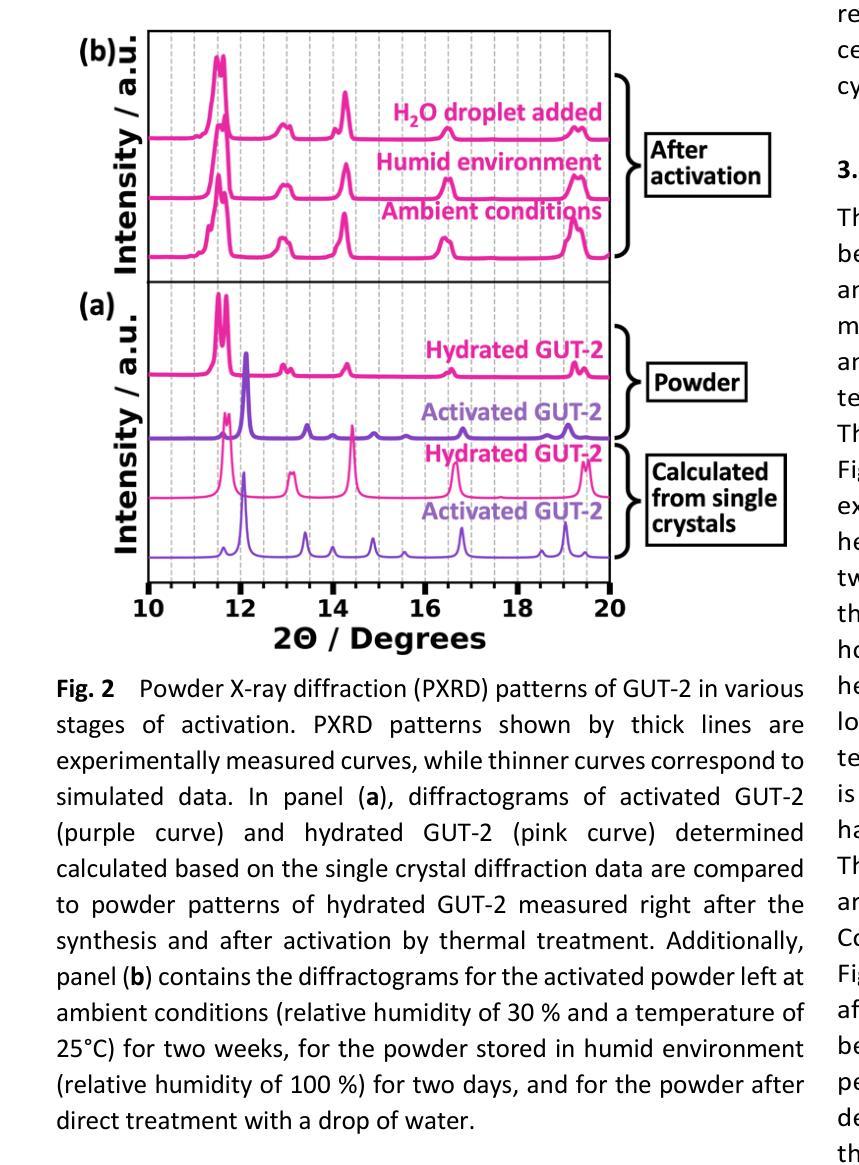
Influence of pore-confined water on the thermal expansion of a zinc-based metal-organic framework
Authors:Nina Strasser, Benedikt Schrode, Ana Torvisco, Sanjay John, Birgit Kunert, Brigitte Bitschnau, Florian Patrick Lindner, Christian Slugovc, Egbert Zojer, Roland Resel
Understanding the reversible intercalation of guest molecules into metal-organic frameworks is crucial for advancing their design for practical applications. In this work, we explore the impact of H${\mathrm{2}}!$O as a guest molecule on the thermal expansion of the zinc-based metal-organic framework GUT-2. Dehydration is achieved by thermal treatment of hydrated GUT-2. Rietveld refinement performed on temperature-dependent X-ray powder diffraction data confirms the reversible structural transformation. Additionally, it allows the determination of anisotropic thermal expansion coefficients for both phases. The hydrated form exhibits near-zero thermal expansion along the polymer chain direction, moderate expansion In the direction of predominantly hydrogen bonds, and the highest expansion in the direction with only Van der Waals bonding. Upon activation, the removal of H${\mathrm{2}}!$O molecules triggers a doubling of the thermal expansion coefficient in the direction, where the hydrogen bonds have been removed. Regarding the dynamics of the process, thermal activation in air occurs within 6 hours at a temperature of 50{\deg}C and takes only 30 minutes when heating to 90{\deg}C. In contrast, full rehydration under standard lab conditions (30 % relative humidity) requires two days. During the activation/dehydration processes no change of the widths of the X-ray diffraction peaks is observed, which shows that the underlying crystal structures remains fully intact during the transition processes. Fitting the transformations by the Avrami equation reveals a quasi one-dimensional evolution of the dehydrated areas for the activation process and a more intricate, predominantly two-dimensional mechanism for the rehydration.
了解客体分子可逆插入金属有机框架对于推动其在实际应用中的设计至关重要。在这项工作中,我们探索了水作为客体分子对锌基金属有机框架GUT-2热膨胀的影响。通过热处理水合GUT-2来实现脱水。里特维尔德(Rietveld)对温度依赖的X射线粉末衍射数据进行了修正,证实了可逆结构转变。此外,它还允许确定两个阶段的热膨胀系数。水合形式在聚合物链方向上表现出近零热膨胀,在主要由氢键方向上有中等膨胀,以及在仅通过范德华力结合的方向上有最高膨胀。活化后,H₂O分子的去除导致在氢键被移除的方向上热膨胀系数加倍。关于过程的动态,在空气中的热活化在50摄氏度的温度下在6小时内发生,当加热到90摄氏度时仅需30分钟。相比之下,在标准实验室条件下(30%相对湿度)完全重新水合需要两天。在活化/脱水过程中,观察到X射线衍射峰宽度没有变化,这表明在过渡过程中基础晶体结构保持完整。通过阿夫拉米方程(Avrami equation)拟合变形揭示,脱水区域的活化过程呈现准一维演变,而再水合过程则更为复杂,主要是二维机制。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
水分子作为客体分子对锌基金属有机框架GUT-2的热膨胀具有重要影响。通过热处理脱水,借助瑞特韦尔德修正法对温度依赖的X射线粉末衍射数据进行分析,证实了可逆结构转变的存在。各方向的热膨胀系数可由此确定。水合形式在某些方向表现出近零热膨胀,在氢键主导的方向上表现中等膨胀,而在仅存在范德华键的方向上膨胀最高。激活后去除水分子使得热膨胀系数加倍。激活过程在空气加热至50℃时可在6小时内完成,加热至90℃时仅需30分钟。相比之下,在标准实验室条件下(相对湿度30%)完全复水需要两天时间。活化脱水过程中观察到X射线衍射峰宽没有变化,表明晶体结构在转变过程中保持完整。通过阿夫拉米方程拟合揭示了脱水区域的准一维演化过程和复水过程的复杂二维机制。
关键见解
- 理解客体分子(如水)在金属有机框架中的可逆插层对于推动其实际应用设计至关重要。
- 通过热处理实现脱水状态,并利用瑞特韦尔德修正法分析温度依赖的X射线粉末衍射数据,揭示了可逆结构转变。
- 水合形式的GUT-2在不同方向上展现出不同的热膨胀特性,其中某些方向的热膨胀受水分子影响显著。
- 激活过程中去除水分子导致热膨胀系数增加。
- 加热至较高温度(如90℃)可显著缩短激活过程的时间。
- 复水过程需要较长时间,表明其与活化过程动力学机制不同。
- 晶体结构在活化脱水过程中保持完整,未观察到X射线衍射峰宽的变化。
点此查看论文截图

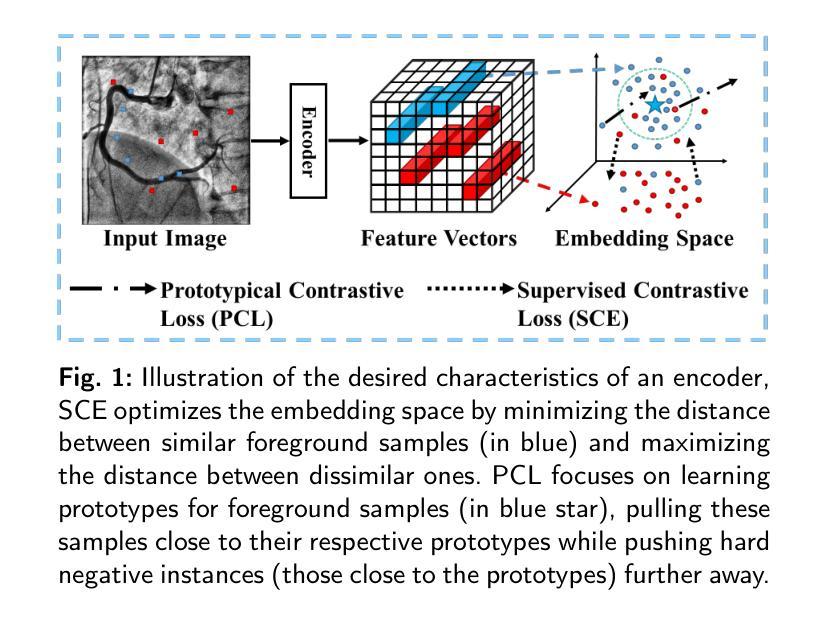
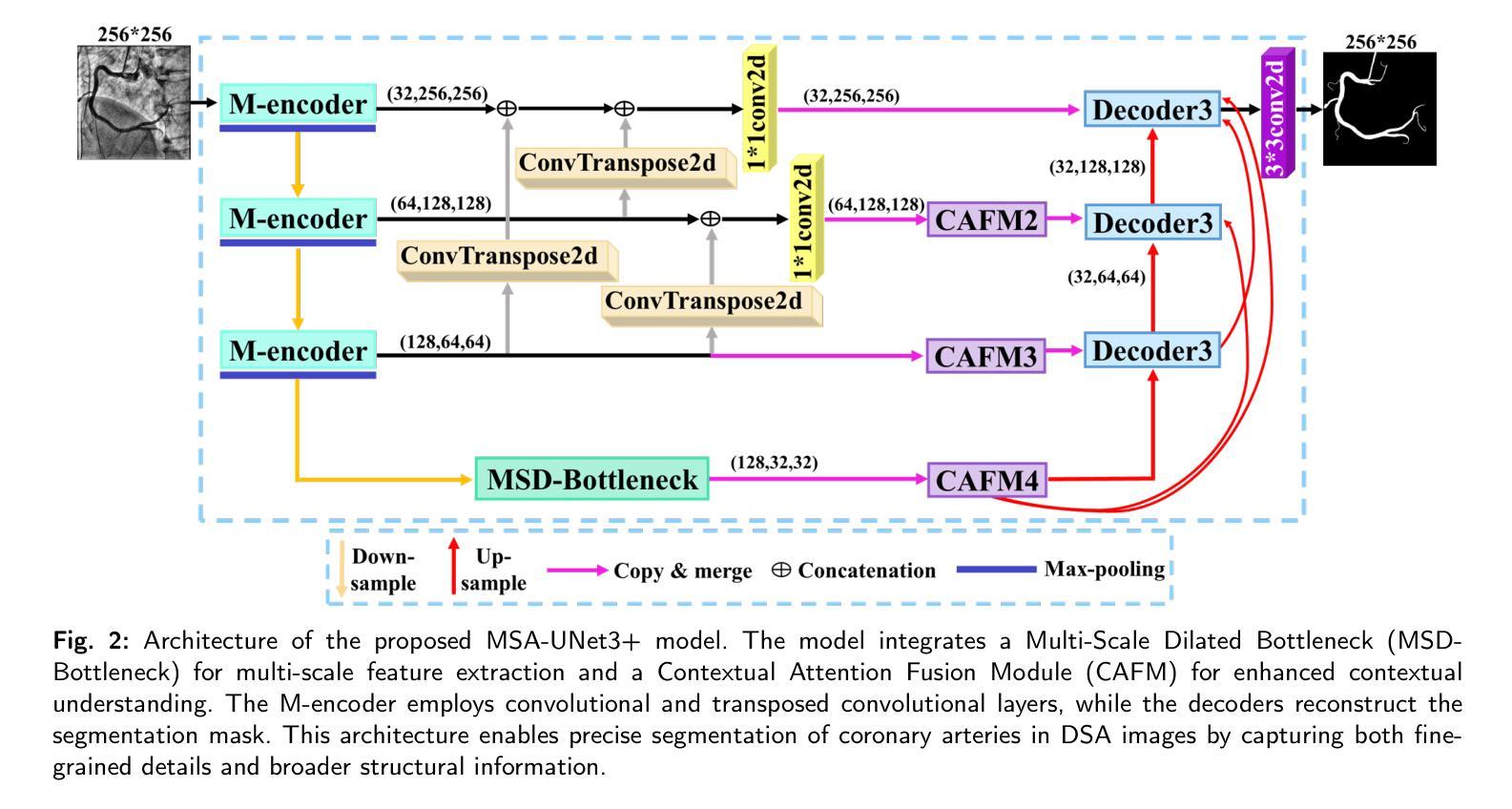
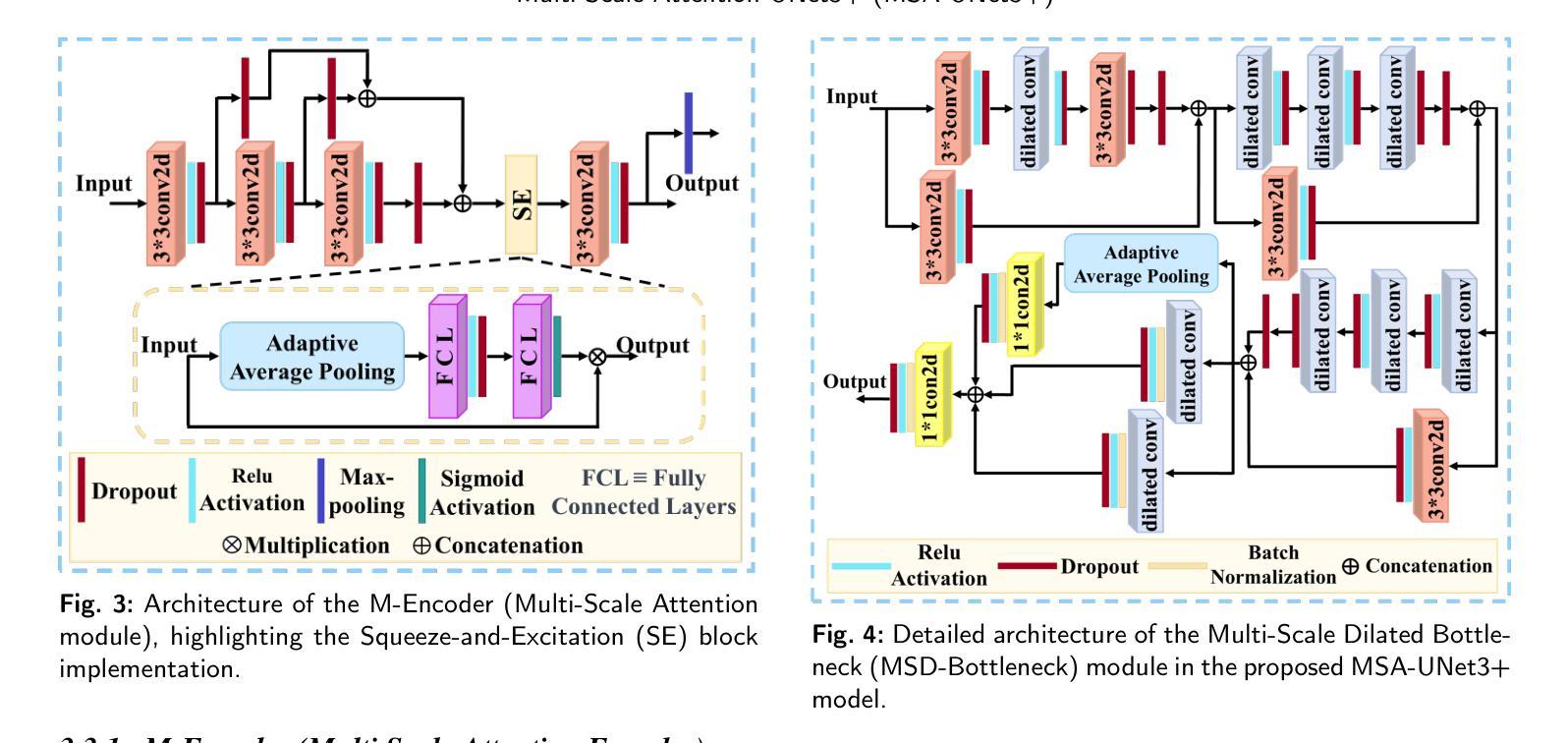
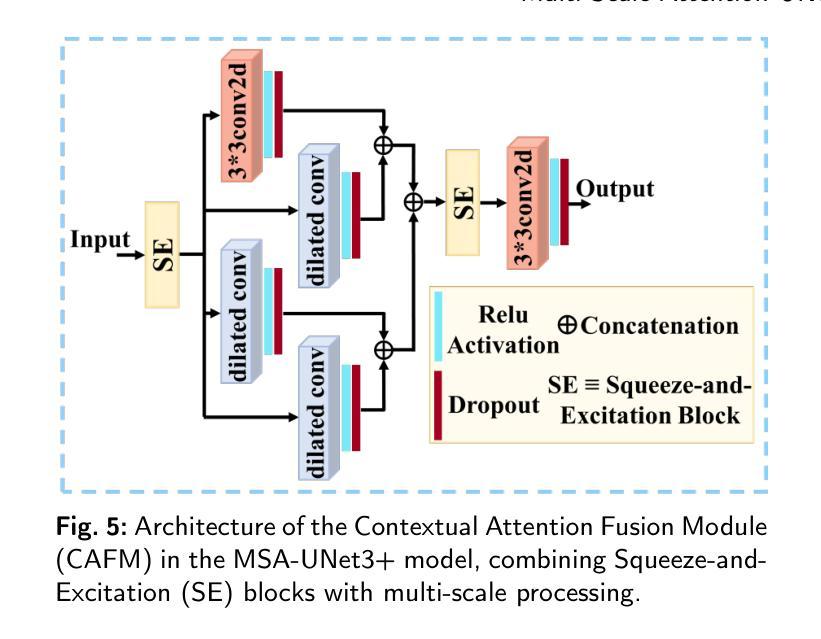
MSA-UNet3+: Multi-Scale Attention UNet3+ with New Supervised Prototypical Contrastive Loss for Coronary DSA Image Segmentation
Authors:Rayan Merghani Ahmed, Adnan Iltaf, Bin Li, Shoujun Zhou
The accurate segmentation of coronary Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) images is essential for diagnosing and treating coronary artery diseases. Despite advances in deep learning-based segmentation, challenges such as low contrast, noise, overlapping structures, high intra-class variance, and class imbalance limit precise vessel delineation. To overcome these limitations, we propose the MSA-UNet3+: a Multi-Scale Attention enhanced UNet3+ architecture for coronary DSA image segmentation. The framework combined Multi-Scale Dilated Bottleneck (MSD-Bottleneck) with Contextual Attention Fusion Module (CAFM), which not only enhances multi-scale feature extraction but also preserve fine-grained details, and improve contextual understanding. Furthermore, we propose a new Supervised Prototypical Contrastive Loss (SPCL), which combines supervised and prototypical contrastive learning to minimize class imbalance and high intra-class variance by focusing on hard-to-classified background samples. Experiments carried out on a private coronary DSA dataset demonstrate that MSA-UNet3+ outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving a Dice coefficient of 87.73%, an F1-score of 87.78%, and significantly reduced Average Surface Distance (ASD) and Average Contour Distance (ACD). The developed framework provides clinicians with precise vessel segmentation, enabling accurate identification of coronary stenosis and supporting informed diagnostic and therapeutic decisions. The code will be released at the following GitHub profile link https://github.com/rayanmerghani/MSA-UNet3plus.
冠状动脉数字减影血管造影(DSA)图像的准确分割对于冠状动脉疾病的诊断和治疗至关重要。尽管基于深度学习的分割技术有所进展,但低对比度、噪声、结构重叠、高类内方差和类不平衡等挑战仍然限制了血管精确勾勒。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了MSA-UNet3+:一种用于冠状动脉DSA图像分割的多尺度注意力增强UNet3+架构。该框架结合了多尺度膨胀瓶颈(MSD-Bottleneck)与上下文注意力融合模块(CAFM),这不仅可以增强多尺度特征提取,还可以保留细节并改进上下文理解。此外,我们提出了一种新的监督原型对比损失(SPCL),它将监督学习与原型对比学习相结合,通过关注难以分类的背景样本,最小化类不平衡和高类内方差问题。在私有冠状动脉DSA数据集上进行的实验表明,MSA-UNet3+优于最先进的方法,达到87.73%的Dice系数,87.78%的F1分数,以及显著降低的平均表面距离(ASD)和平均轮廓距离(ACD)。所开发的框架为临床医生提供了精确的血管分割,能够准确识别冠状动脉狭窄,为医生提供有根据的诊断和治疗决策支持。相关代码将发布在以下GitHub个人主页链接:链接地址。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
Summary
冠状动脉数字减影血管造影(DSA)图像的准确分割对于诊断和治疗冠状动脉疾病至关重要。面对低对比度、噪声、结构重叠、高类内方差和类别不平衡等挑战,我们提出了MSA-UNet3+架构,结合多尺度扩张瓶颈和上下文注意力融合模块,以提高多尺度特征提取和细节保留,并改善上下文理解。此外,我们还提出了一种新的监督原型对比损失(SPCL),通过关注难以分类的背景样本,最小化类别不平衡和高类内方差。实验表明,MSA-UNet3+优于现有方法,Dice系数为87.73%,F1分数为87.78%,平均表面距离(ASD)和平均轮廓距离(ACD)显著降低。该框架为临床医生提供精确的血管分割,有助于准确识别冠状动脉狭窄,支持诊断和治疗的决策制定。
Key Takeaways
- 冠状动脉DSA图像分割对诊断和治疗冠状动脉疾病至关重要。
- 存在低对比度、噪声、结构重叠等挑战,影响精确血管描绘。
- 提出了MSA-UNet3+架构,结合多尺度扩张瓶颈和上下文注意力融合模块,提高分割性能。
- 引入新的监督原型对比损失(SPCL),以处理类别不平衡和高类内方差问题。
- 实验证明MSA-UNet3+在冠状动脉DSA图像分割上表现优异。
- 该框架提供精确的血管分割,有助于识别冠状动脉狭窄。
点此查看论文截图

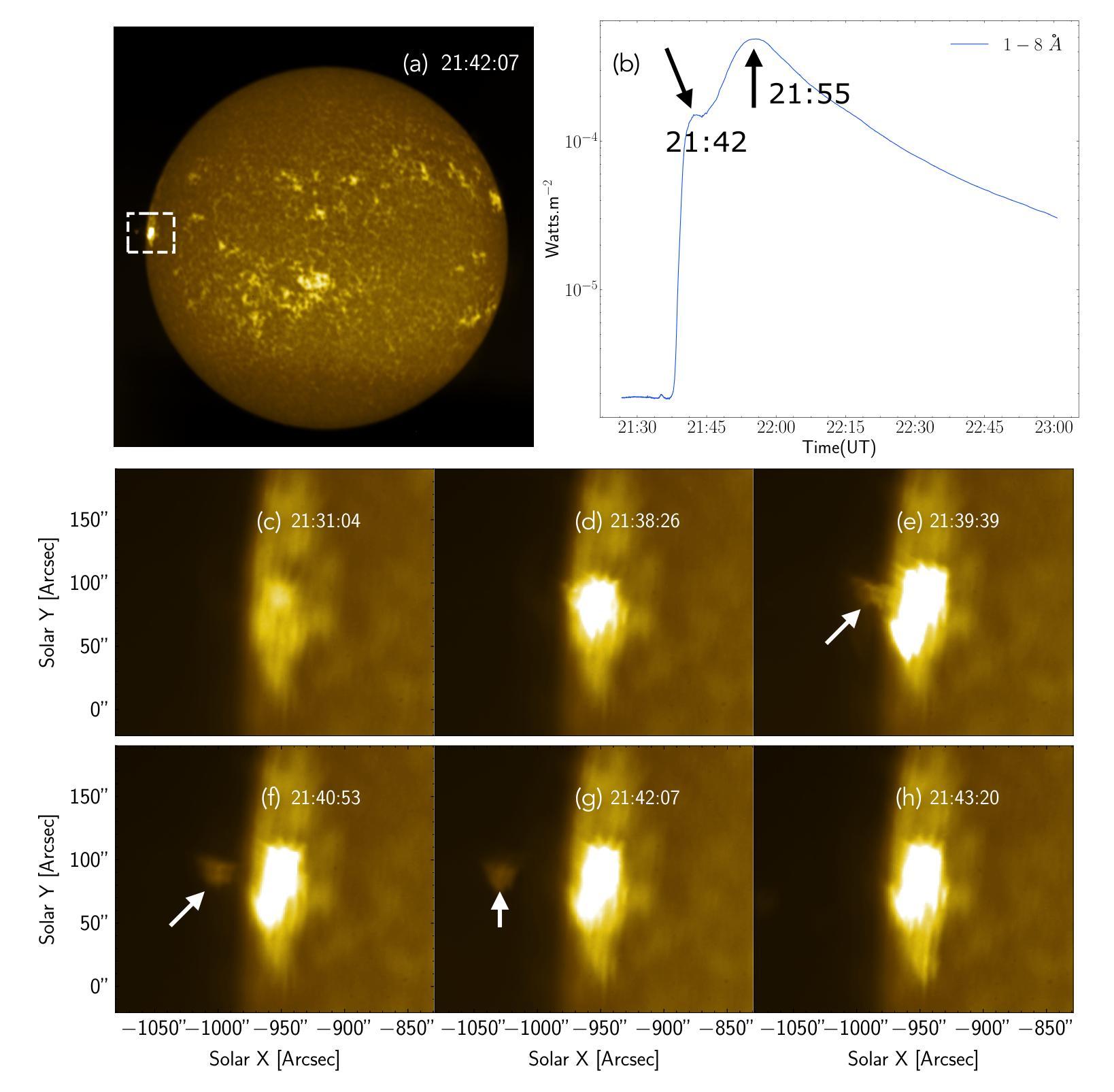
X-class flare on Dec 31, 2023, observed by the Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope on board Aditya-L1
Authors:Soumya Roy, Durgesh Tripathi, Vishal Upendran, Sreejith Padinhatteeri, A. N. Ramaprakash, Nived V. N., K. Sankarasubramanian, Sami K. Solanki, Janmejoy Sarkar, Rahul Gopalakrishnan, Rushikesh Deogaonkar, Dibyendu Nandy, Dipankar Banerjee
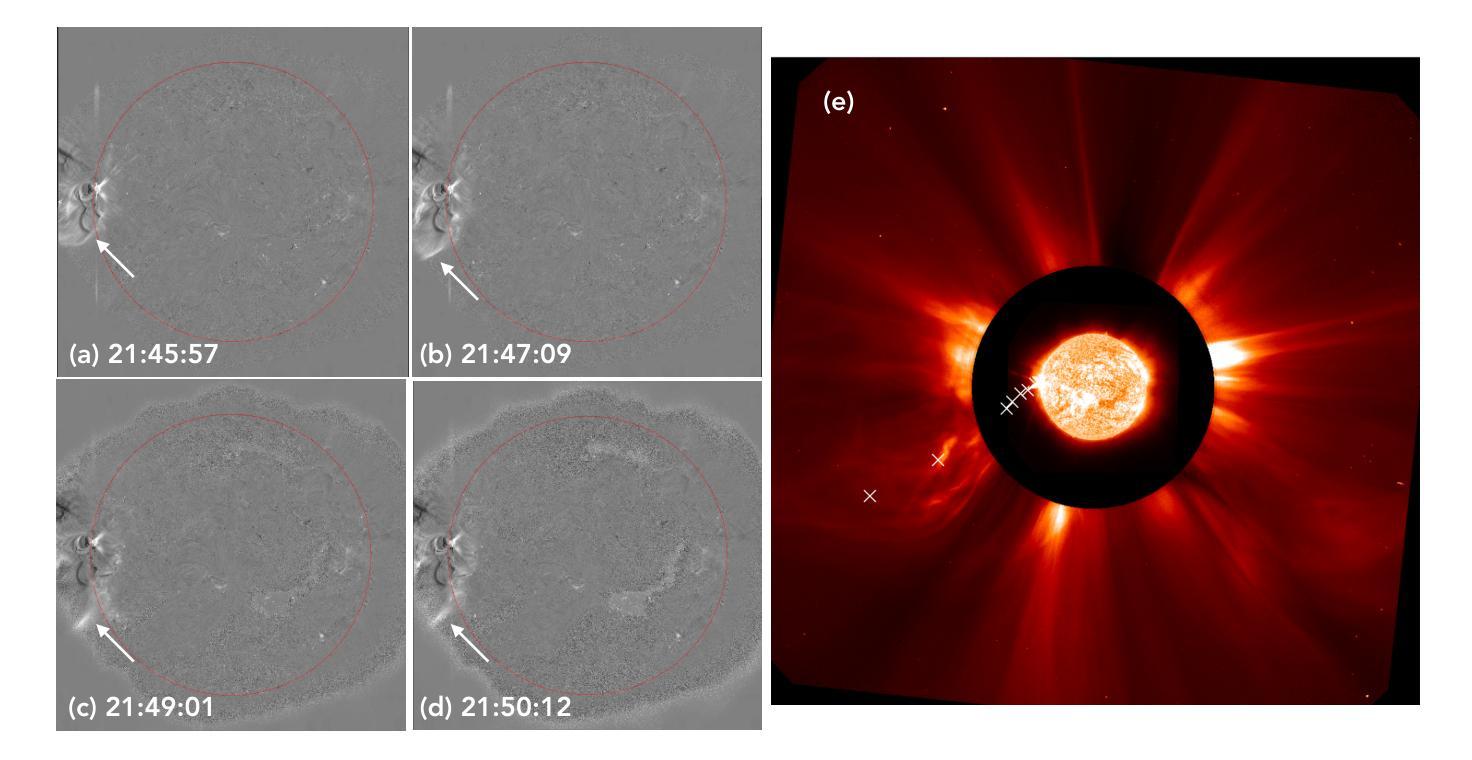
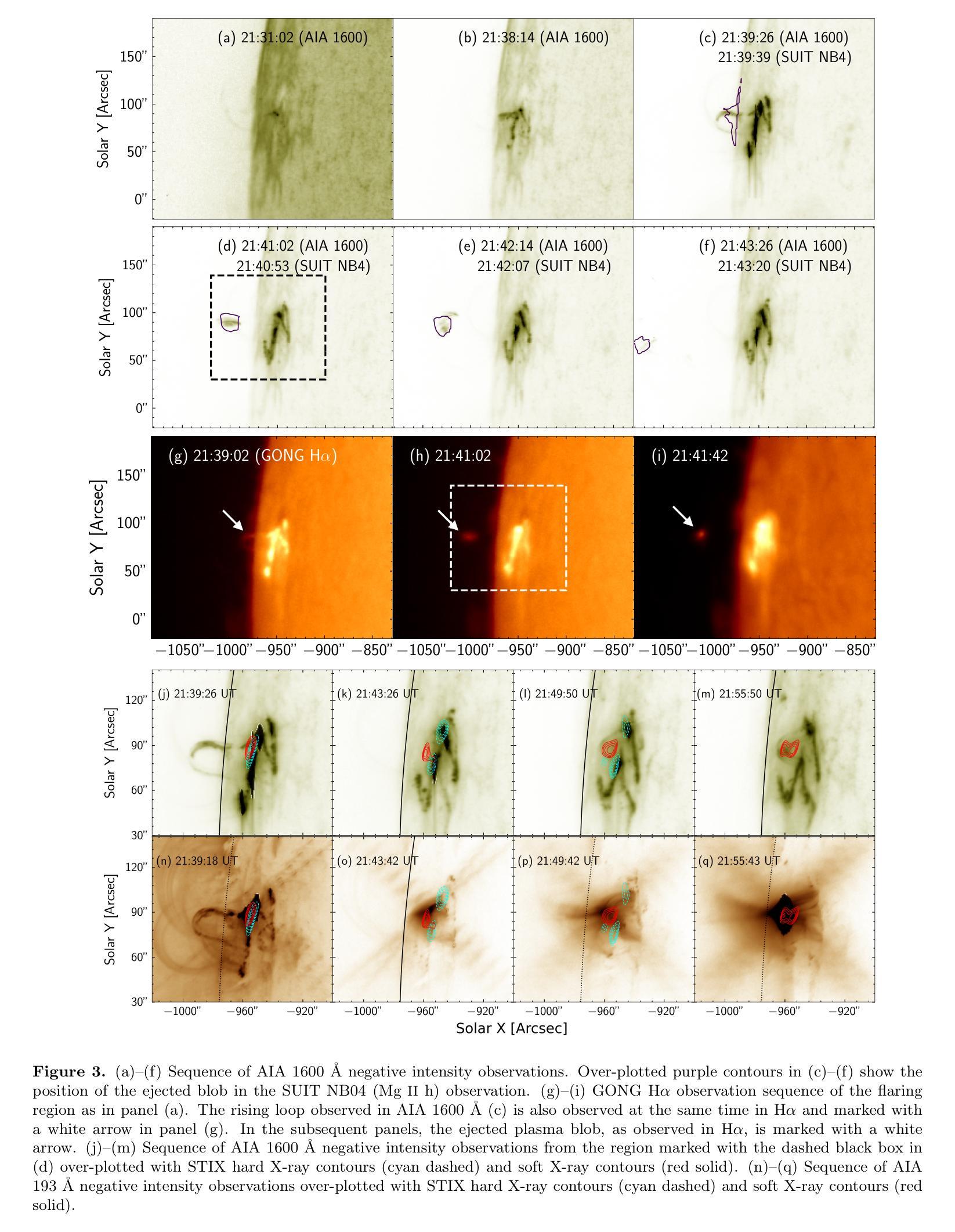
We present the multi-wavelength study of the ejection of a plasma blob from the limb flare SOL2023-12-31T21:36:00 from NOAA 13536 observed by the Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT) on board Aditya-L1. We use SUIT observations along with those from Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) on board SDO and Spectrometer/Telescope for Imaging X-rays (STIX) on board Solar Orbiter to infer the kinematics and thermal nature of the ejected blob and its connection to the associated flare. The observations show that the flare was comprised of two eruptions. The blob was ejected during the first eruption and later accelerated to velocities over 1500 km/s measured at a maximum projected height of ~ 178 Mm from the Sun’s surface. The acceleration of the ejected plasma blob is co-temporal with the bursty appearance of the hard X-ray light curve recorded by STIX. Radio spectrogram observations from STEREO-A/WAVES and RSTN reveal type III bursts at the same time, indicative of magnetic reconnection. DEM analysis using AIA observations suggests the plasma blob is comprised of cooler and denser plasma in comparison to the ambient corona. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first observation of such a plasma blob in the NUV, providing crucial measurements for eruption thermodynamics.
我们对来自NOAA 13536的等离子体团喷射进行了多波长研究,该喷射由Aditya-L1上的太阳紫外线成像望远镜(SUIT)观测到的SOL2023-12-31T21:36:00的边界耀斑引起。我们使用SUIT观测结果以及与SDO上的大气成像仪(AIA)和Solar Orbiter上的X射线成像光谱仪/望远镜(STIX)的观测结果,推断出喷射出的等离子体团的动态特性和热特性及其与相关耀斑的联系。观测结果显示,耀斑由两次爆发组成。等离子体团在第一次爆发时被喷射出去,之后在距离太阳表面最大投影高度约178 Mm处加速至超过1500 km/s的速度。喷射出的等离子体团加速的同时伴随着STIX记录的硬X射线光曲线的突发外观。来自STEREO-A/WAVES和RSTN的无线电频谱观测显示同时出现了Ⅲ型爆发,这标志着磁场重联。使用AIA观测结果进行DEM分析表明,该等离子体团与周围日冕相比,是由较冷且较密集的等离子体组成。据我们所知,这是首次在近紫外波段观察到这样的等离子体团,为爆发热力学提供了关键测量数据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 8 figures
Summary
采用多波长观测研究太阳等离子体团从边缘耀斑SOL2023-12-31T21:36:00的喷射现象,通过Aditya-L1上的SUIT望远镜、SDO上的AIA以及Solar Orbiter上的STIX仪器观测数据推断喷射体的运动学和热特性及其与耀斑的关联。观察到该耀斑由两次爆发组成,等离子体团在第一次爆发中被喷射出,之后在约离太阳表面最大高度为~ 178 Mm处加速至超过1500 km/s的速度。等离子体团的加速与STIX记录的硬X射线光曲线的突发外观相吻合。同时,从STEREO-A/WAVES和RSTN的无线电频谱观测显示出了Ⅲ型爆发,指示了磁重联的发生。使用AIA观测数据的DEM分析表明,等离子体团相对于周围日冕具有较冷和较密的等离子体特性。这是首次在紫外波段观察到此类等离子体团,为爆发热力学提供了关键测量数据。
Key Takeaways
- 文中研究了一次太阳边缘耀斑喷射等离子体团的多波长观测。
- 等离子体团在第一次爆发中被喷射,之后加速至超高速。
- 加速的等离子体团与硬X射线光曲线的突发活动同步。
- 无线电频谱观测显示磁重联的迹象。
- 通过DEM分析,发现等离子体团具有较冷和较密的特性,与周围日冕不同。
- 这是首次在紫外波段观察到此类等离子体团。
点此查看论文截图

Low-Count X-ray Polarimetry using the Bayesian Approach Reveals Fast Polarization Angle Variations
Authors:Hong Li, Qing-Chang Zhao, Hua Feng, Lian Tao, Sergey S. Tsygankov
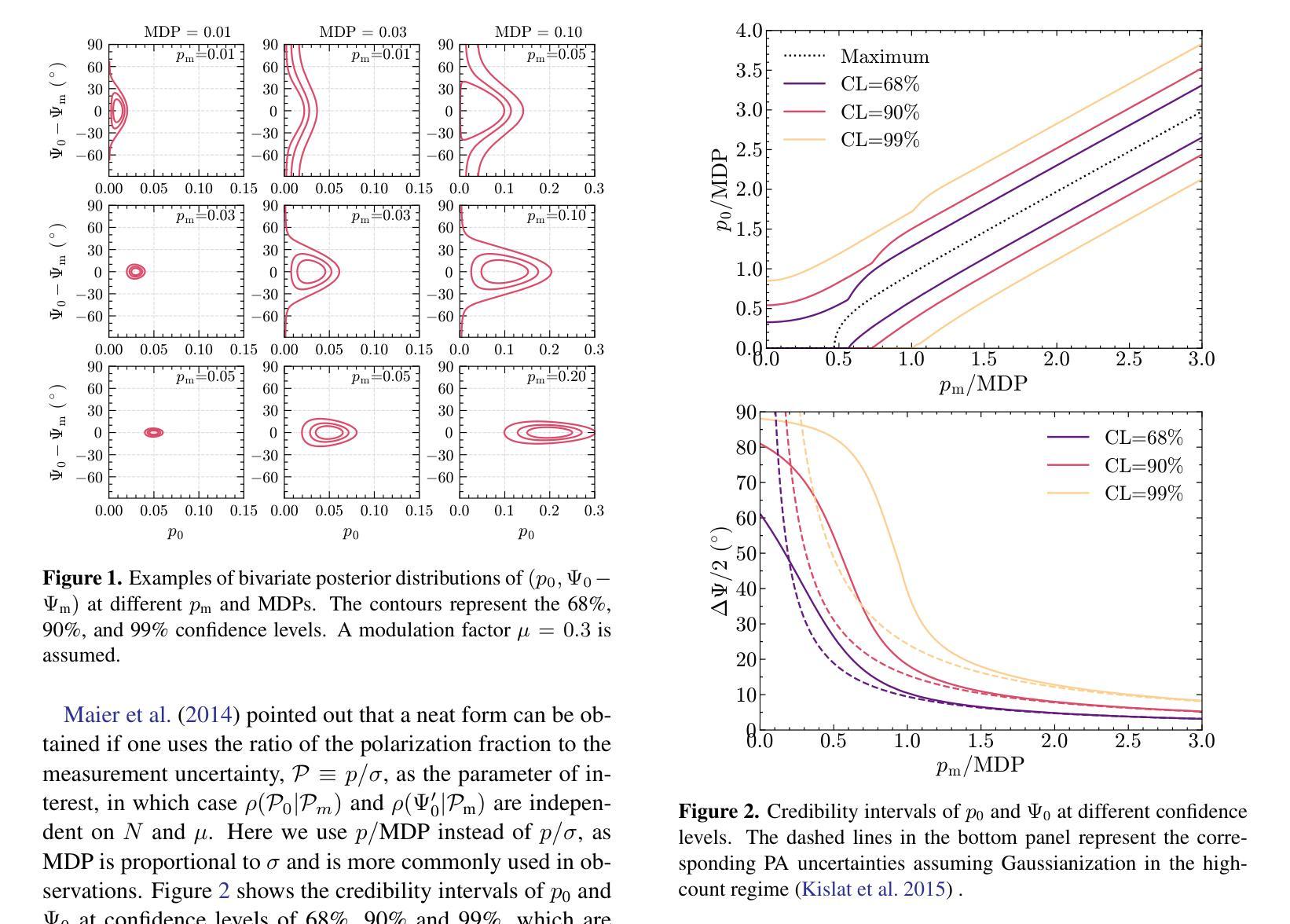
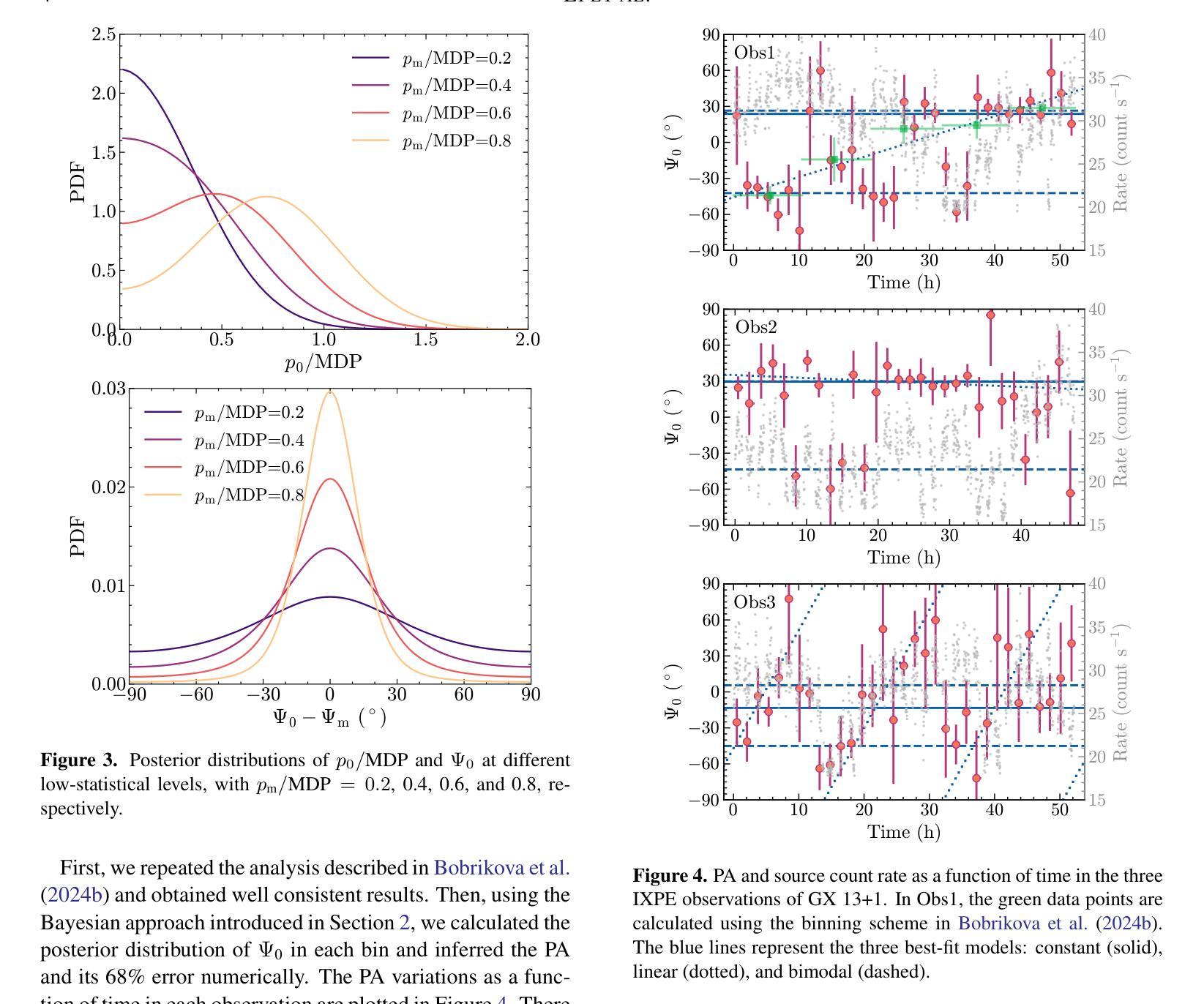
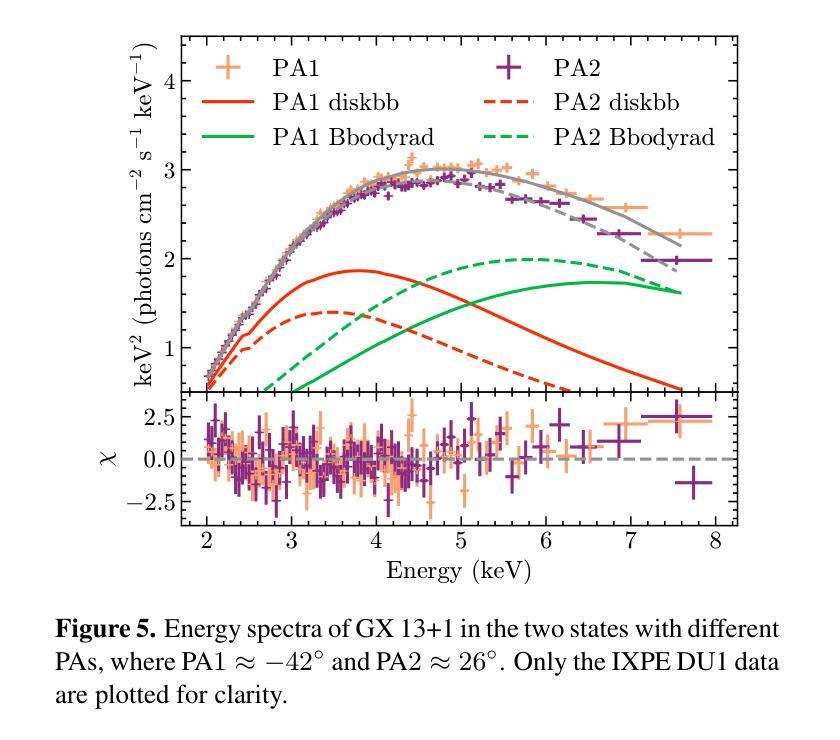
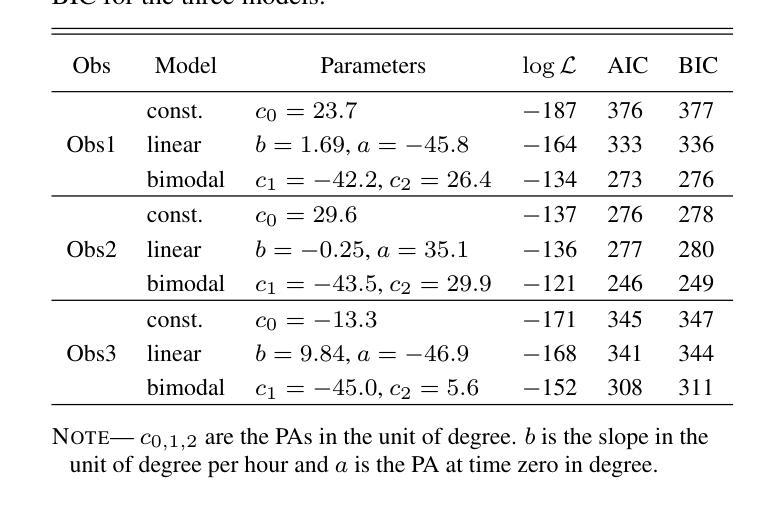
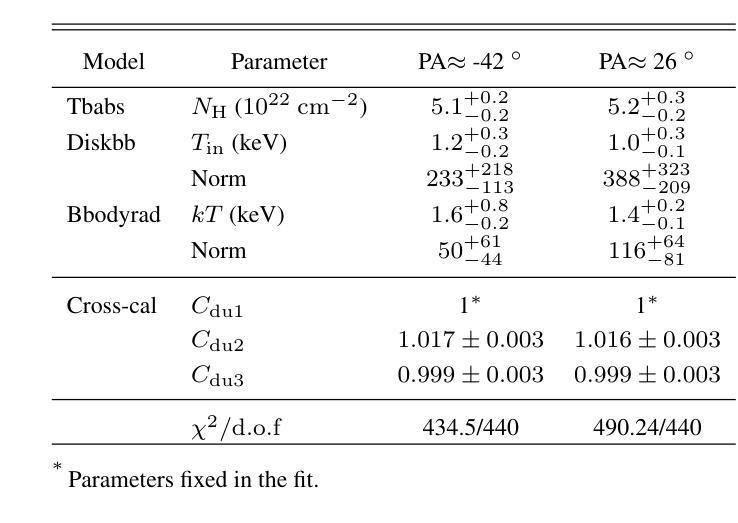
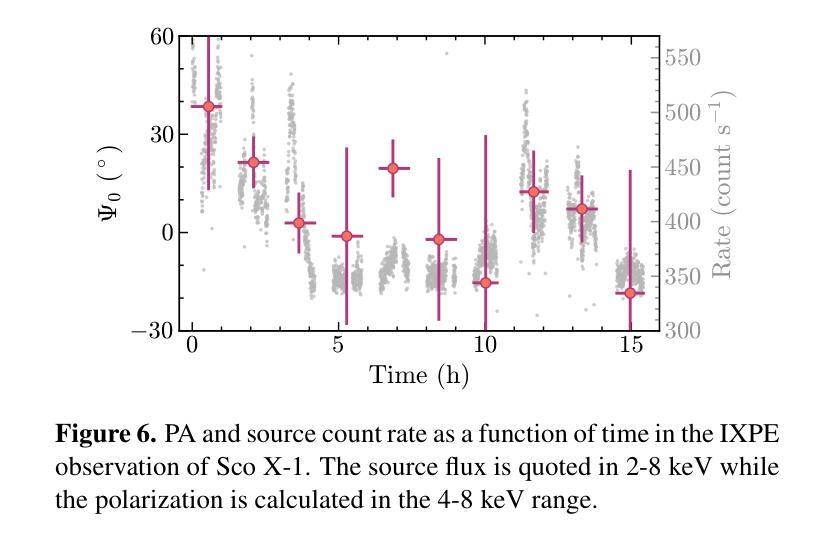
X-ray polarimetry of accreting compact object has revealed fast time variations in the polarization angle (PA), suggesting that the geometry and/or optical depth of the corona is changing rapidly. This prompts investigations into how fast such variability can be. Conventionally, the data are often binned to examine the time variability such that the measurement in each bin is above the minimum detectable polarization (MDP). Here we demonstrate that this is unnecessary, and even below the MDP, one can infer the posterior distribution of PA reliably using the Bayesian approach and still be able to place useful constraints on the physics in many cases. With this approach, we discovered that the PA variation in one of the Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) observations of GX 13+1 is not following a linear rotation mode as suggested previously. Instead, the PA swings between two discrete angles, suggesting that there are two emitting components, e.g., the boundary layer and the spreading layer, competing with each other. Also in one of the observations of GX 13+1 and Sco X-1, the PA is found to vary in correlation with the source count rate, indicating that the mass accretion rate is shaping the corona properties. Also, during the IXPE observation of Sco X-1, the PA in highest flux level seems to deviate from the averaged value and appear to be consistent with previous measurement results with PolarLight and OSO-8.
X射线偏振测量显示,吸积致密天体(accreting compact object)的偏振角(PA)存在快速时间变化,暗示着冕层的几何结构或光学深度正在快速变化。这促使研究者们研究这种变化能有多快。传统上,数据通常会被分组以检查时间变化,以确保每个分组中的测量值高于最小可检测偏振度(MDP)。在这里我们证明这是不必要的,即使低于MDP,我们也可以利用贝叶斯方法可靠地推断出偏振角的后验分布,并在许多情况下对物理过程施加有用的约束。使用这种方法,我们发现GX 13+1的一次成像X射线偏振仪观测中的偏振角变化并不像先前所建议的那样遵循线性旋转模式。相反,偏振角在两个离散角度之间摆动,这表明存在两个发射分量(例如边界层和扩散层)相互竞争。在GX 13+1和Sco X-1的一次观测中,还发现偏振角与源计数率相关变化,这表明物质吸积率正在塑造冕层特性。此外,在Sco X-1的一次IXPE观测中,最高流量水平的偏振角似乎偏离平均值,与之前的PolarLight和OSO-8的测量结果一致。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
X射线偏振成像观测显示,高光度源快速变化的光度变化可以通过贝叶斯分析揭示出其极化角度(PA)的偏振特性变化来探测出来,显示出内区磁层和增益区的交替分布对极化特征有影响,其中观测到的GX 13+1和Sco X-1的观测结果进一步证实了这一点。这些发现揭示了X射线光子的高度离散辐射性质和等离子结构效应的变化关系,也对吸积率和其他几何特征参数变化的建模提供了新的线索。通过对这些复杂源的偏振研究,可以更好地理解这些关键过程,对X射线天文学领域的研究具有重要影响。
Key Takeaways
- 高光度源的快速变化能够通过研究极化角度变化进行探测和分析。传统的分析方法通过将数据分组以超过最小可检测极化度(MDP)来检测时间变化,但新方法显示即使低于MDP,也能通过贝叶斯分析可靠地推断出PA的后验分布。
- 在GX 13+1的观测中,发现极化角度变化并不遵循先前认为的线性旋转模式,而是表现出在两个离散角度之间的摆动,暗示存在两个竞争发射组分,可能是边界层和扩展层。这为吸积盘中磁场效应的空间分布模型提供了线索。
点此查看论文截图

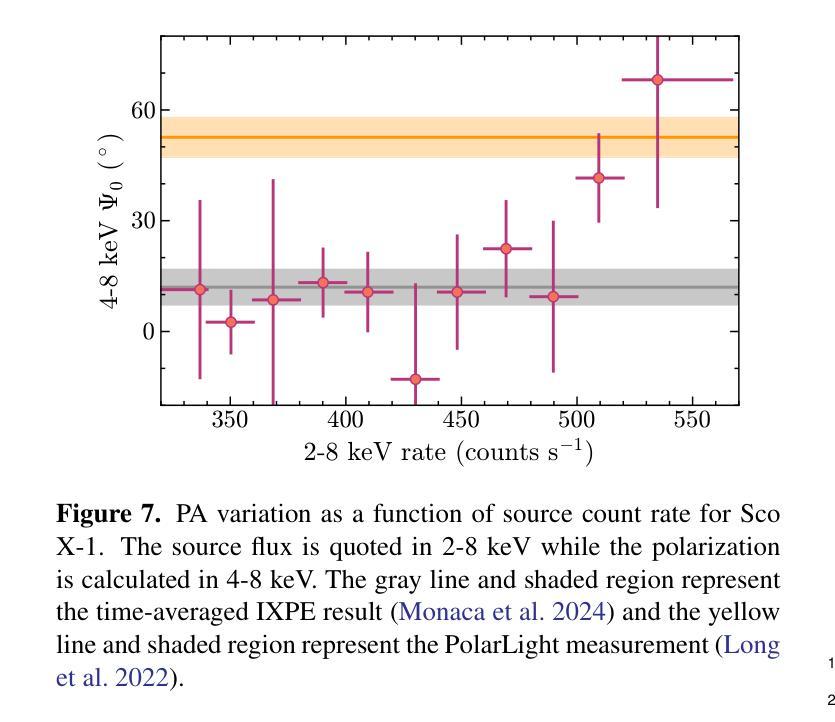
Here Comes the Explanation: A Shapley Perspective on Multi-contrast Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Tianyi Ren, Juampablo Heras Rivera, Hitender Oswal, Yutong Pan, Agamdeep Chopra, Jacob Ruzevick, Mehmet Kurt
Deep learning has been successfully applied to medical image segmentation, enabling accurate identification of regions of interest such as organs and lesions. This approach works effectively across diverse datasets, including those with single-image contrast, multi-contrast, and multimodal imaging data. To improve human understanding of these black-box models, there is a growing need for Explainable AI (XAI) techniques for model transparency and accountability. Previous research has primarily focused on post hoc pixel-level explanations, using methods gradient-based and perturbation-based apporaches. These methods rely on gradients or perturbations to explain model predictions. However, these pixel-level explanations often struggle with the complexity inherent in multi-contrast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) segmentation tasks, and the sparsely distributed explanations have limited clinical relevance. In this study, we propose using contrast-level Shapley values to explain state-of-the-art models trained on standard metrics used in brain tumor segmentation. Our results demonstrate that Shapley analysis provides valuable insights into different models’ behavior used for tumor segmentation. We demonstrated a bias for U-Net towards over-weighing T1-contrast and FLAIR, while Swin-UNETR provided a cross-contrast understanding with balanced Shapley distribution.
深度学习已成功应用于医学图像分割,能够准确识别感兴趣区域,如器官和病变。该方法在多种数据集上均有效,包括单图像对比度、多对比度和多模态成像数据。为了提高人们对这些黑箱模型的理解,对模型透明度和可解释性的可解释人工智能(XAI)技术的需求日益增长。以往的研究主要集中在事后像素级解释上,使用基于梯度和基于扰动的方法。这些方法依赖于梯度或扰动来解释模型预测。然而,这些像素级解释往往难以应对多对比度磁共振成像(MRI)分割任务的固有复杂性,稀疏分布的解释临床相关性有限。本研究中,我们提出使用对比度的Shapley值来解释在脑肿瘤分割中使用的标准指标训练的最新模型。结果表明,Shapley分析为不同模型在肿瘤分割中的行为提供了有价值的见解。我们展示了U-Net偏向于过度重视T1对比度和FLAIR,而Swin-UNETR提供了跨对比度的理解,Shapley分布均衡。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分割中深度学习应用广泛,能够通过精准识别感兴趣区域如器官和病灶等,实现跨多种数据集的有效分析。为提高对黑箱模型的理解,需要采用可解释人工智能(XAI)技术来提升模型的透明度和问责性。本研究采用基于对比度水平的沙普利值(Shapley values)分析方法,针对脑部肿瘤分割的先进模型进行解释。研究结果表明,沙普利分析为不同模型的肿瘤分割行为提供了宝贵见解。U-Net倾向于过度重视T1对比度和FLAIR,而Swin-UNETR则实现了跨对比度的均衡理解。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在医学图像分割中有广泛应用,能精准识别器官和病灶等感兴趣区域。
- 深度学习模型可跨多种数据集进行有效分析,包括单图像对比、多对比度和多模态成像数据。
- 为提高模型透明度与理解度,需要采用可解释人工智能(XAI)技术。
- 现有解释方法主要侧重于事后像素级解释,但它们在多对比度磁共振成像(MRI)分割任务中面临挑战。
- 沙普利值分析方法能够提供不同模型在肿瘤分割中的行为洞察。
- U-Net模型在T1对比度和FLAIR上存在过度重视的偏向。
点此查看论文截图

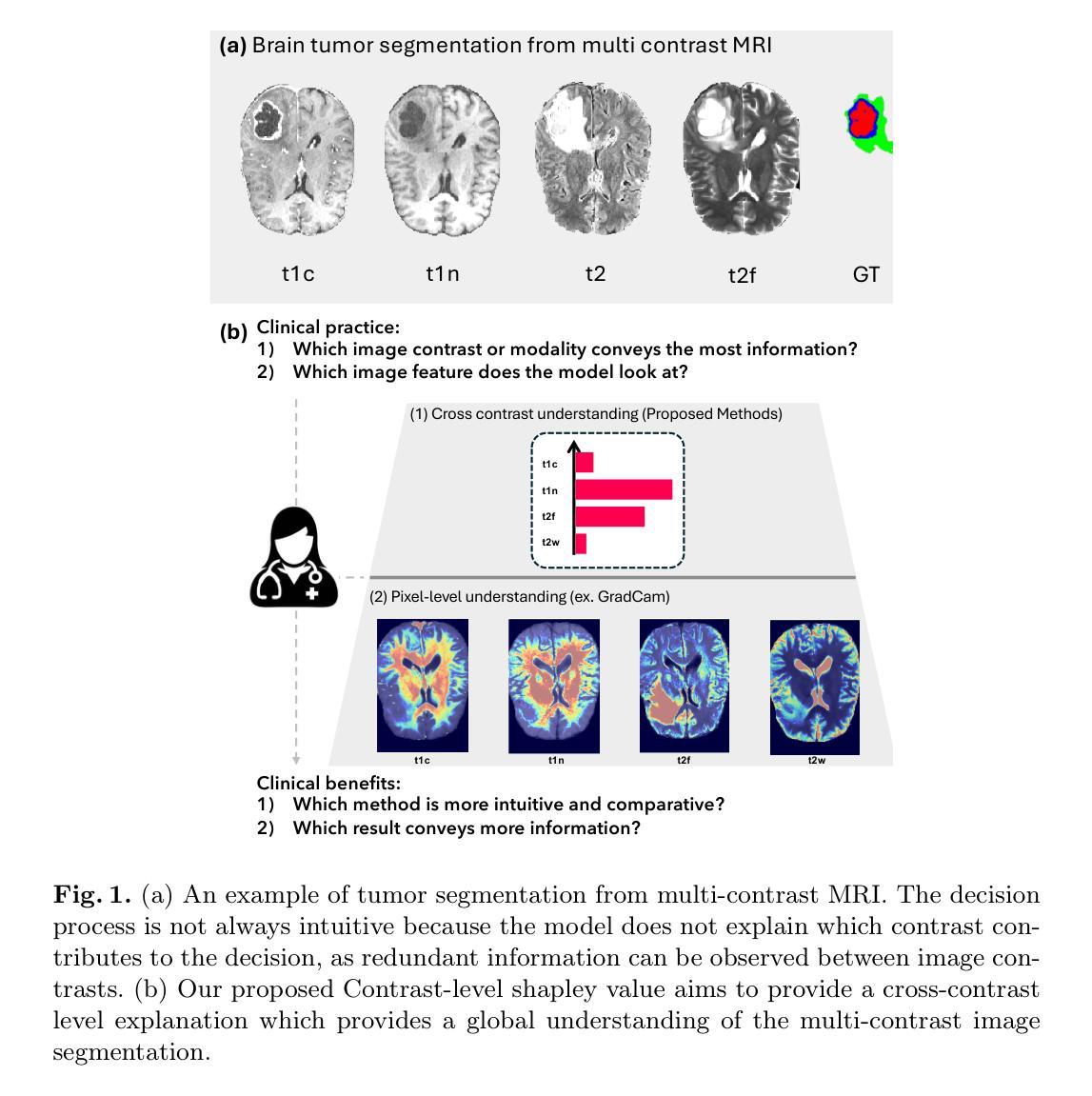
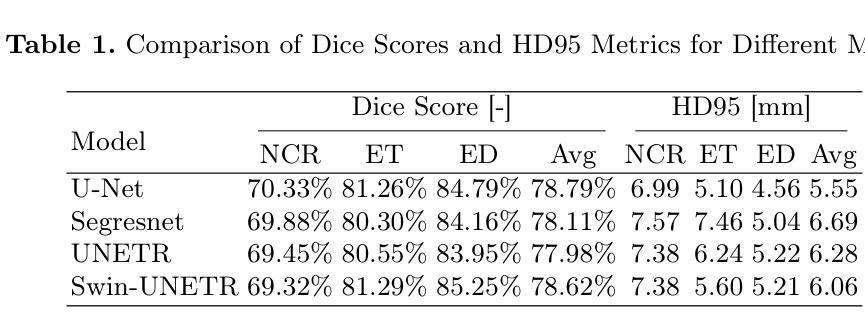
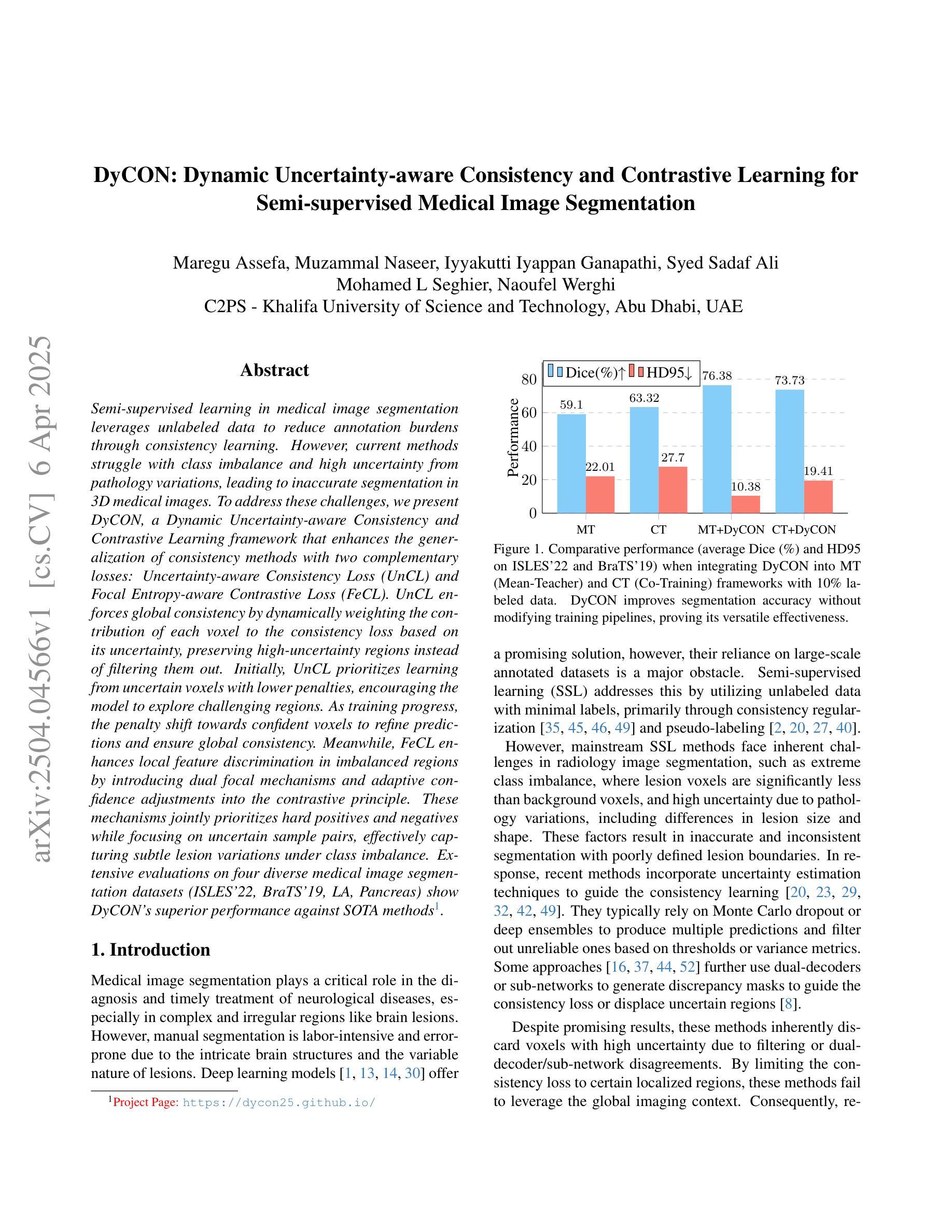
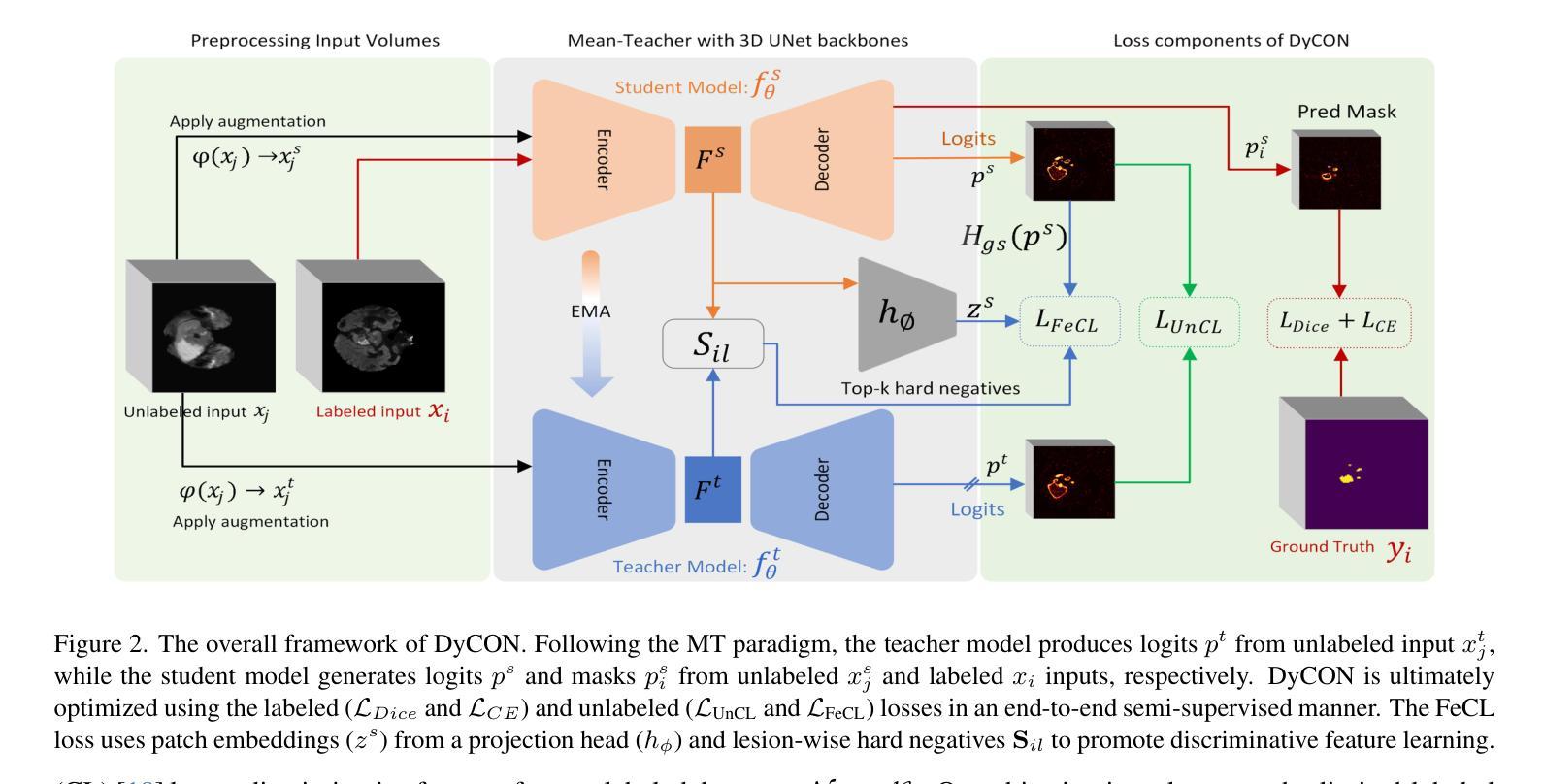
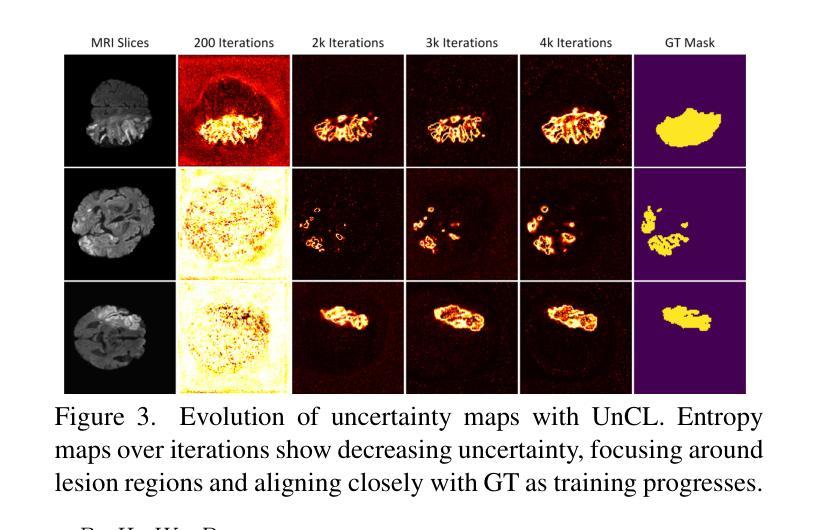
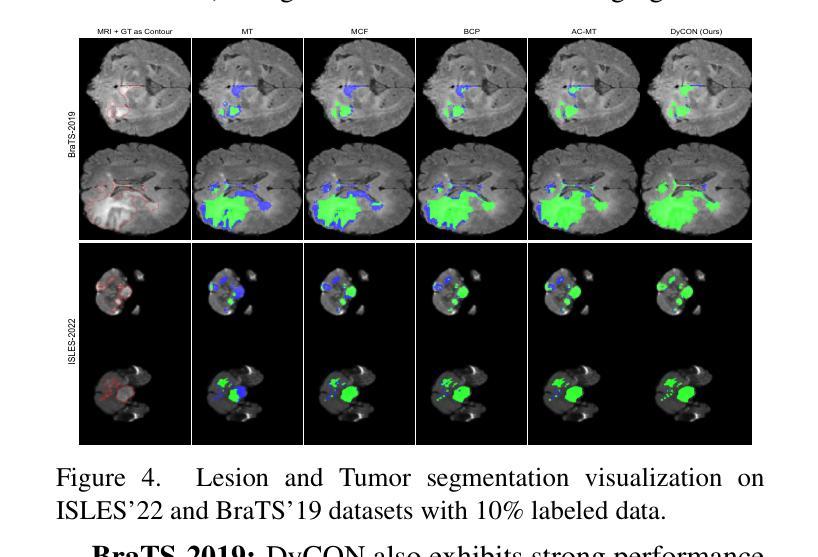
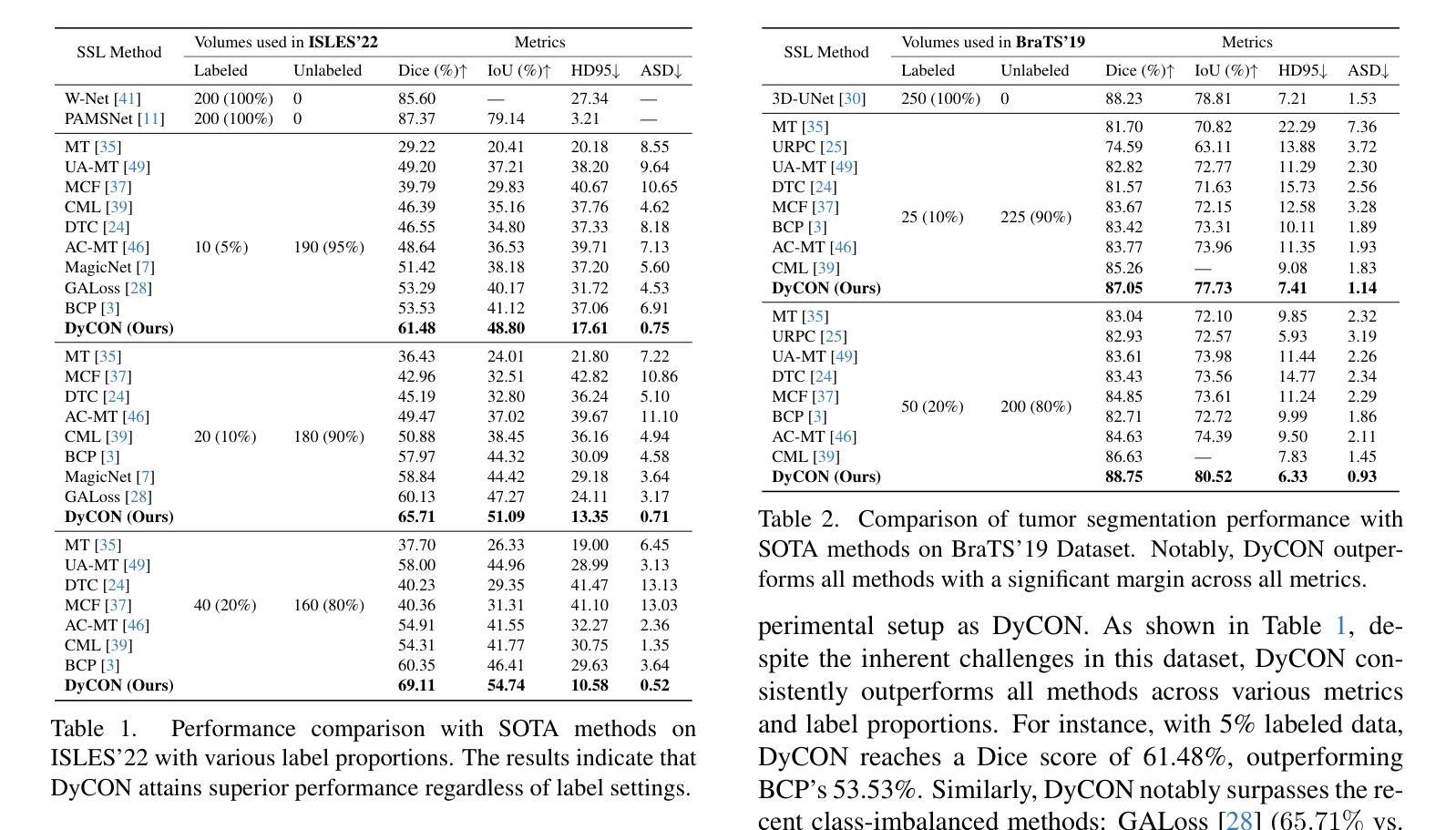
DyCON: Dynamic Uncertainty-aware Consistency and Contrastive Learning for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Maregu Assefa, Muzammal Naseer, Iyyakutti Iyappan Ganapathi, Syed Sadaf Ali, Mohamed L Seghier, Naoufel Werghi
Semi-supervised learning in medical image segmentation leverages unlabeled data to reduce annotation burdens through consistency learning. However, current methods struggle with class imbalance and high uncertainty from pathology variations, leading to inaccurate segmentation in 3D medical images. To address these challenges, we present DyCON, a Dynamic Uncertainty-aware Consistency and Contrastive Learning framework that enhances the generalization of consistency methods with two complementary losses: Uncertainty-aware Consistency Loss (UnCL) and Focal Entropy-aware Contrastive Loss (FeCL). UnCL enforces global consistency by dynamically weighting the contribution of each voxel to the consistency loss based on its uncertainty, preserving high-uncertainty regions instead of filtering them out. Initially, UnCL prioritizes learning from uncertain voxels with lower penalties, encouraging the model to explore challenging regions. As training progress, the penalty shift towards confident voxels to refine predictions and ensure global consistency. Meanwhile, FeCL enhances local feature discrimination in imbalanced regions by introducing dual focal mechanisms and adaptive confidence adjustments into the contrastive principle. These mechanisms jointly prioritizes hard positives and negatives while focusing on uncertain sample pairs, effectively capturing subtle lesion variations under class imbalance. Extensive evaluations on four diverse medical image segmentation datasets (ISLES’22, BraTS’19, LA, Pancreas) show DyCON’s superior performance against SOTA methods.
在医学图像分割中,半监督学习利用无标签数据通过一致性学习来减轻标注负担。然而,当前的方法在面临类别不平衡和高病理变化不确定性时,会出现对三维医学图像分割不准确的问题。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了DyCON,一个动态感知不确定性和对比学习框架,它通过两种互补的损失来增强一致性方法的泛化能力:感知不确定性一致性损失(UnCL)和焦点熵感知对比损失(FeCL)。UnCL通过动态权衡每个体素对一致性损失的贡献来实现全局一致性,这基于其不确定性,保留高不确定性区域而不是过滤掉它们。最初,UnCL优先从不确定性较高的体素中学习,采用较低的惩罚力度,鼓励模型探索具有挑战性的区域。随着训练的进行,惩罚力度转向确定性较高的体素,以完善预测并确保全局一致性。同时,FeCL通过在对比原则中引入双重焦点机制和自适应置信调整来增强不平衡区域的局部特征辨别能力。这些机制共同优先处理硬正样本和负样本,同时关注不确定的样本对,有效捕捉类别不平衡下的细微病变变化。在四个不同的医学图像分割数据集(ISLES’22、BraTS’19、LA、胰腺)上的广泛评估表明,DyCON的性能优于最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
医学图像分割中的半监督学习通过利用无标签数据减少标注负担,但面临类别不平衡和高不确定性等问题。为此,提出DyCON框架,结合动态不确定性感知的一致性损失和焦点熵感知对比损失,提高模型泛化能力。DyCON能动态权衡每个体素对一致性损失的不确定性贡献,同时强化局部特征判别能力,有效应对类别不平衡问题。在四个医学图像分割数据集上的评估显示,DyCON性能优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督学习在医学图像分割中利用无标签数据减少标注负担,但面临类别不平衡和高不确定性挑战。
- DyCON框架通过结合不确定性感知的一致性损失和焦点熵感知对比损失,提高模型泛化能力。
- DyCON能动态处理不确定性,在训练初期鼓励模型探索高不确定性区域,后期精细预测并确保全局一致性。
- FeCL损失通过引入双重焦点机制和自适应信心调整,增强局部特征判别能力,应对类别不平衡问题。
- DyCON框架在四个医学图像分割数据集上的性能评估表现优异。
- UnCL损失通过动态权衡每个体素的不确定性贡献,提高模型对高不确定性区域的保留能力。
点此查看论文截图
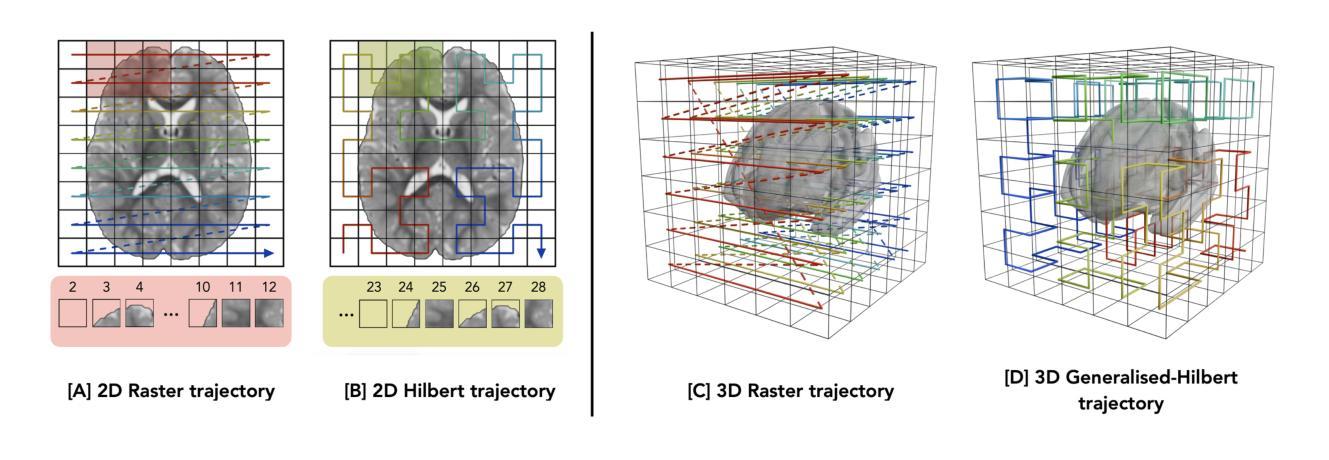
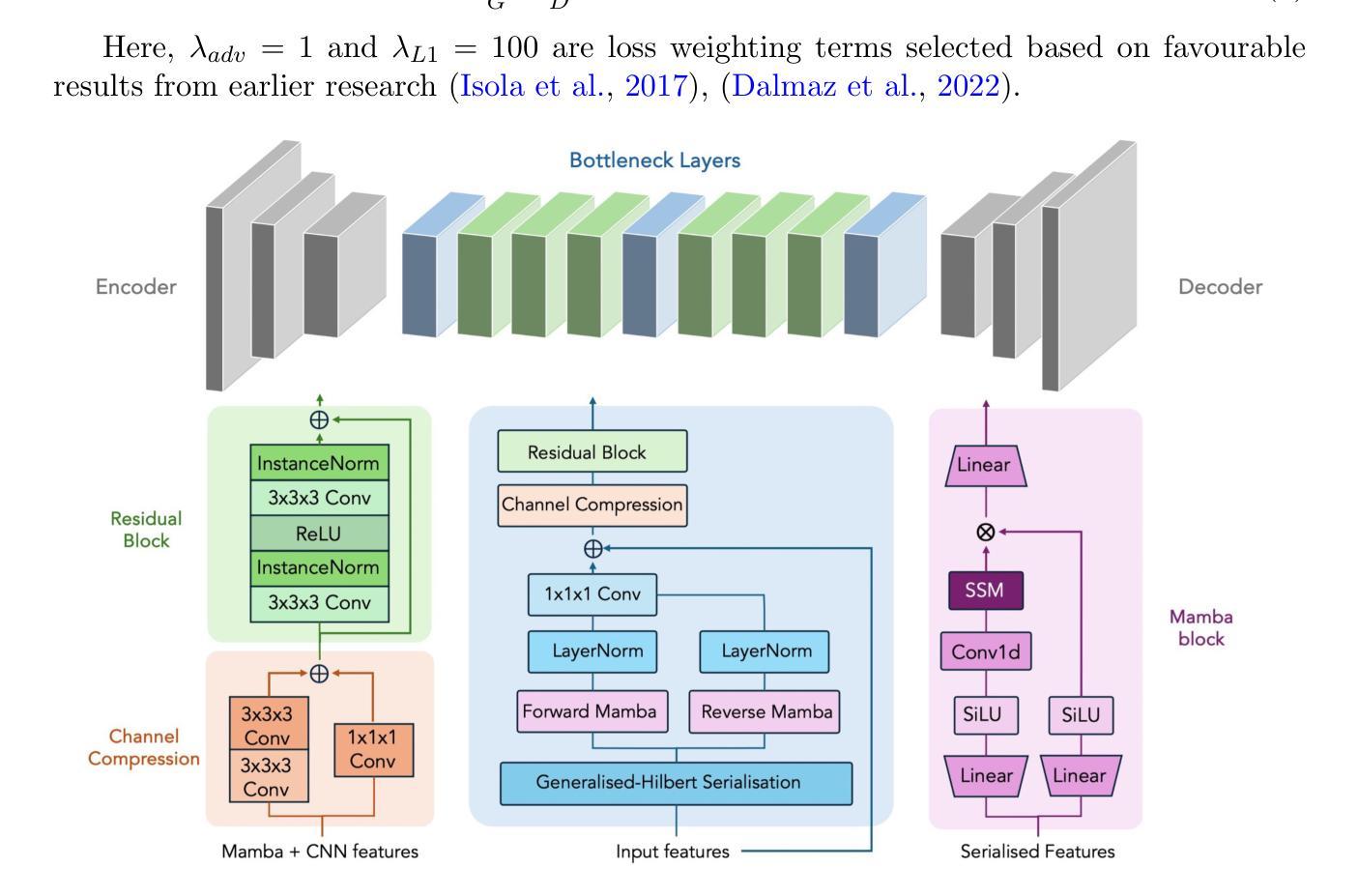
GAMBAS: Generalised-Hilbert Mamba for Super-resolution of Paediatric Ultra-Low-Field MRI
Authors:Levente Baljer, Ula Briski, Robert Leech, Niall J. Bourke, Kirsten A. Donald, Layla E. Bradford, Simone R. Williams, Sadia Parkar, Sidra Kaleem, Salman Osmani, Sean C. L. Deoni, Steven C. R. Williams, Rosalyn J. Moran, Emma C. Robinson, Frantisek Vasa
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is critical for neurodevelopmental research, however access to high-field (HF) systems in low- and middle-income countries is severely hindered by their cost. Ultra-low-field (ULF) systems mitigate such issues of access inequality, however their diminished signal-to-noise ratio limits their applicability for research and clinical use. Deep-learning approaches can enhance the quality of scans acquired at lower field strengths at no additional cost. For example, Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) fused with transformer modules have demonstrated a remarkable ability to capture both local information and long-range context. Unfortunately, the quadratic complexity of transformers leads to an undesirable trade-off between long-range sensitivity and local precision. We propose a hybrid CNN and state-space model (SSM) architecture featuring a novel 3D to 1D serialisation (GAMBAS), which learns long-range context without sacrificing spatial precision. We exhibit improved performance compared to other state-of-the-art medical image-to-image translation models.
磁共振成像(MRI)在神经发育研究中具有重要意义,但在低收入和中等收入国家,由于成本问题,获得高场(HF)系统的机会受到严重阻碍。超低场(ULF)系统缓解了获取不平等的问题,但其信噪比降低限制了其在研究和临床使用中的应用。深度学习的方法可以在不增加成本的情况下提高低场强扫描的质量。例如,与变压器模块融合的卷积神经网络(CNNs)表现出捕捉局部信息和远距离上下文的能力。然而,变压器二次复杂性导致远程敏感性和局部精度之间出现了不理想的权衡。我们提出了一种混合CNN和状态空间模型(SSM)架构,具有新型3D到1D序列化(GAMBAS),能够在不牺牲空间精度的情况下学习远距离上下文。与其他最先进的医学图像到图像翻译模型相比,我们展示了更好的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at MIDL 2025, 21 pages, 8 figures
Summary
深度学习技术能够提高低磁场强度MRI扫描图像的质量,从而实现神经发育研究的需求。提出一种融合卷积神经网络与状态空间模型的架构,具有创新性的3D转1D序列化方法(GAMBAS),能够兼顾远程上下文学习和空间精度。
Key Takeaways
- 磁共振成像在神经发育研究中非常重要,但高场系统在中低收入国家的普及受到成本限制。
- 超低场系统缓解了访问不平等问题,但其信噪比降低限制了其在研究和临床使用中的应用。
- 深度学习技术可以无额外费用地提高低磁场强度MRI扫描图像的质量。
- 卷积神经网络与转换器模块的融合展示了捕捉局部信息和远程上下文的能力。
- 转换器模块具有二次复杂性,在远程敏感性和局部精确性之间存在权衡。
- 提出了一种新型的混合CNN和SSM架构,结合了创新的GAMBAS方法,能够在不牺牲空间精度的情况下学习远程上下文。
点此查看论文截图

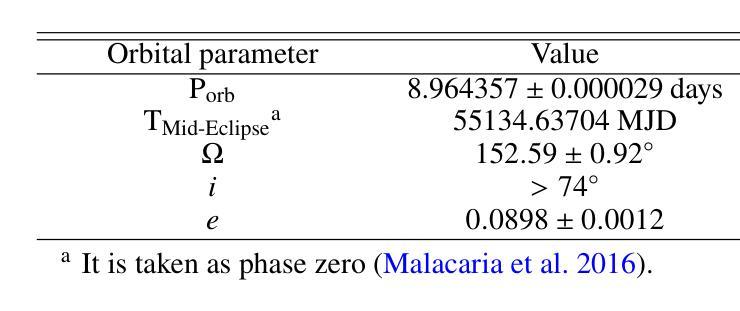
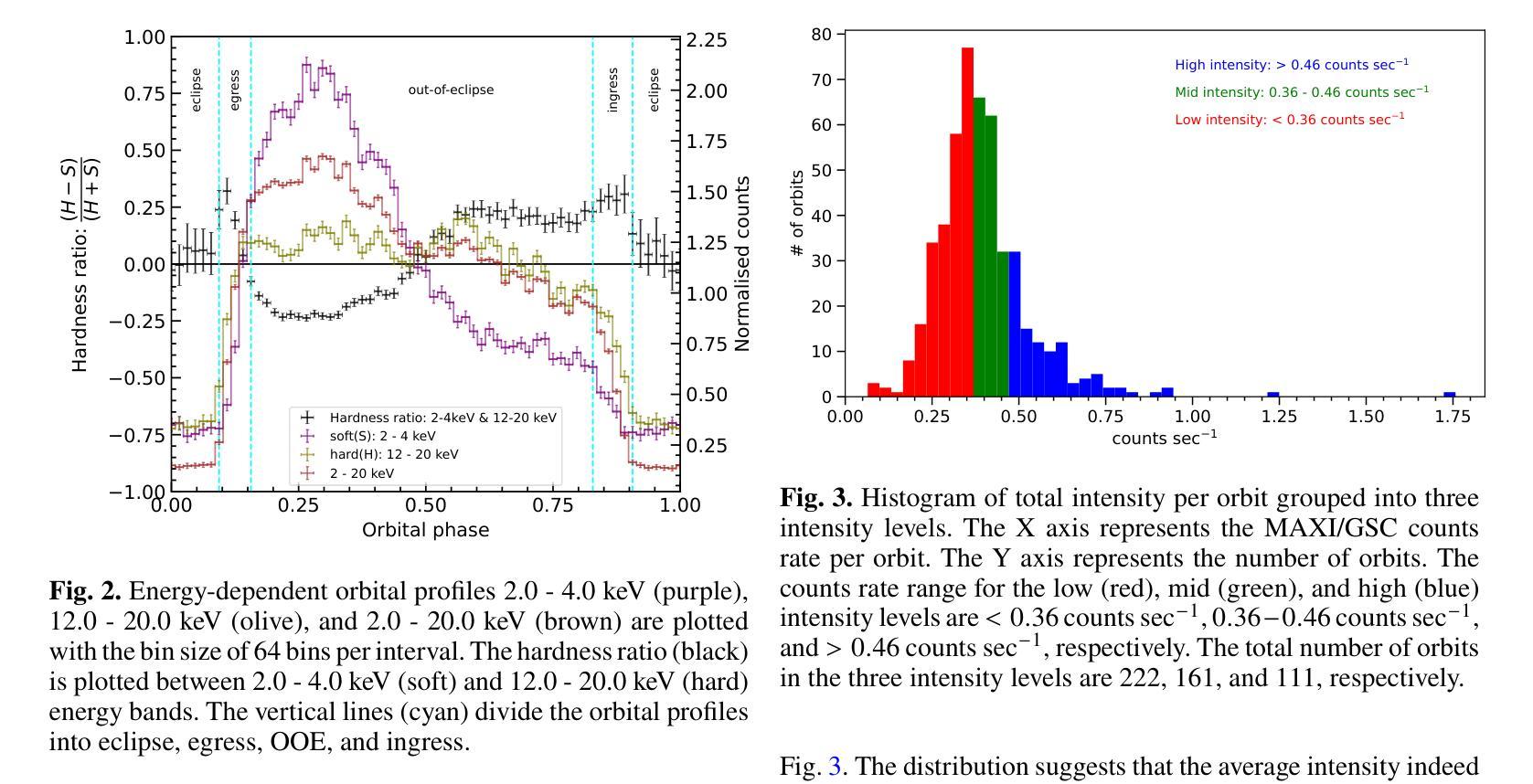
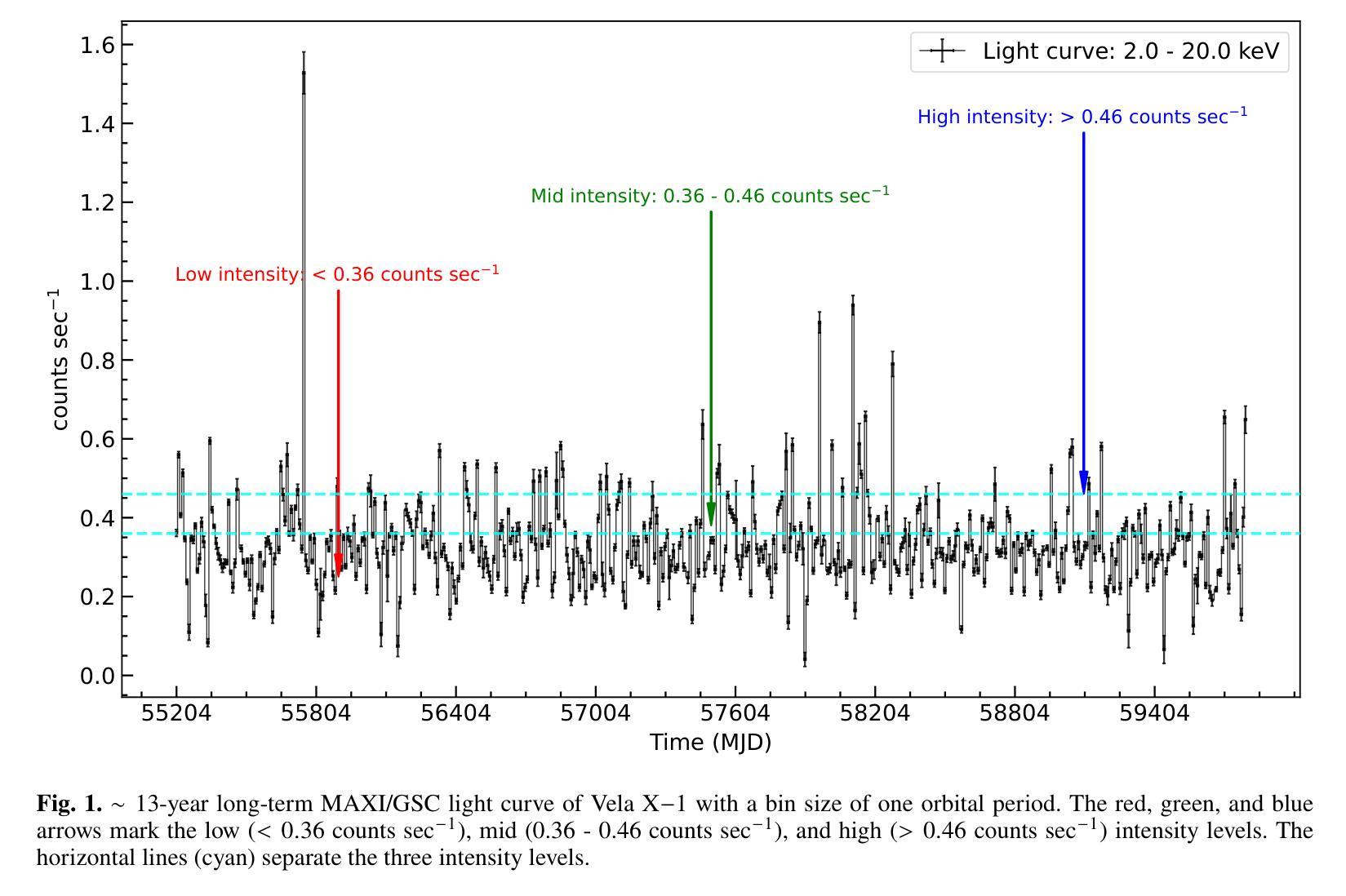
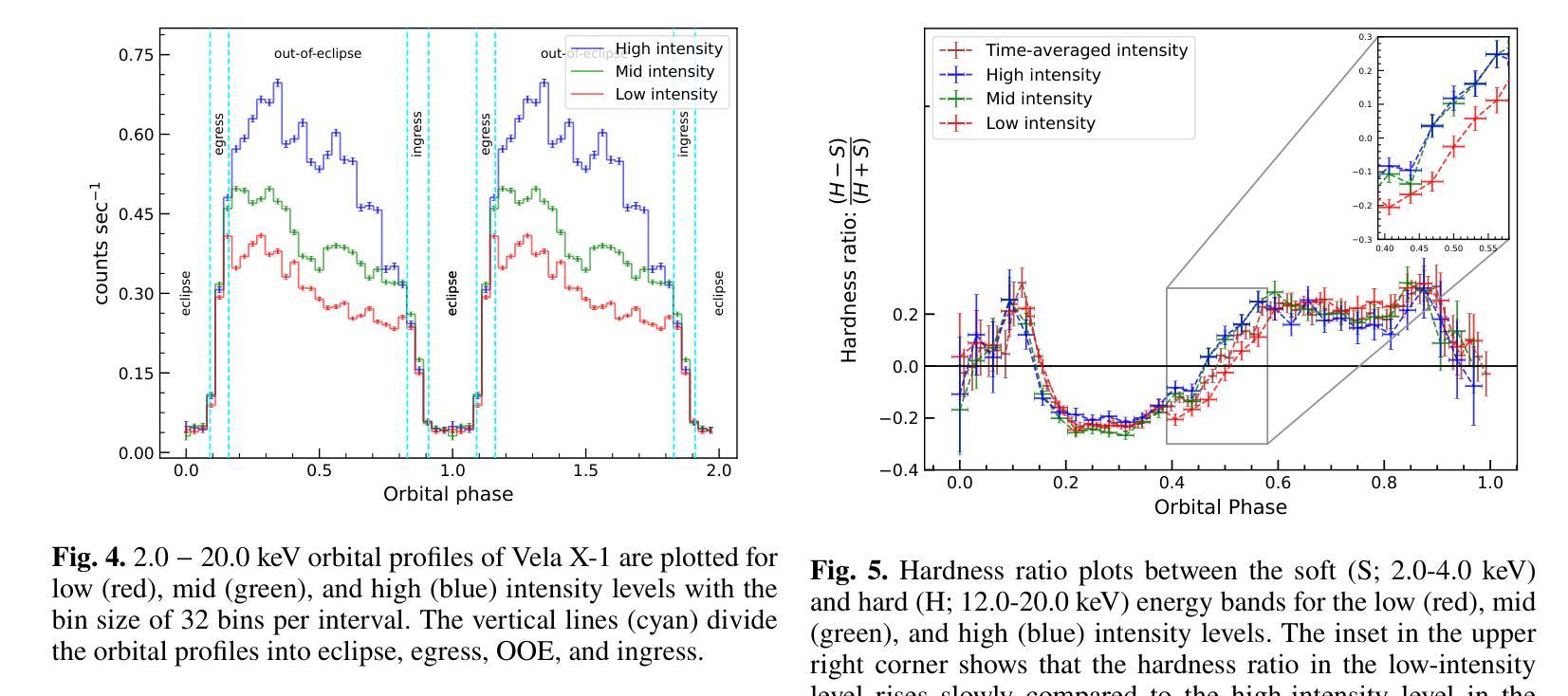
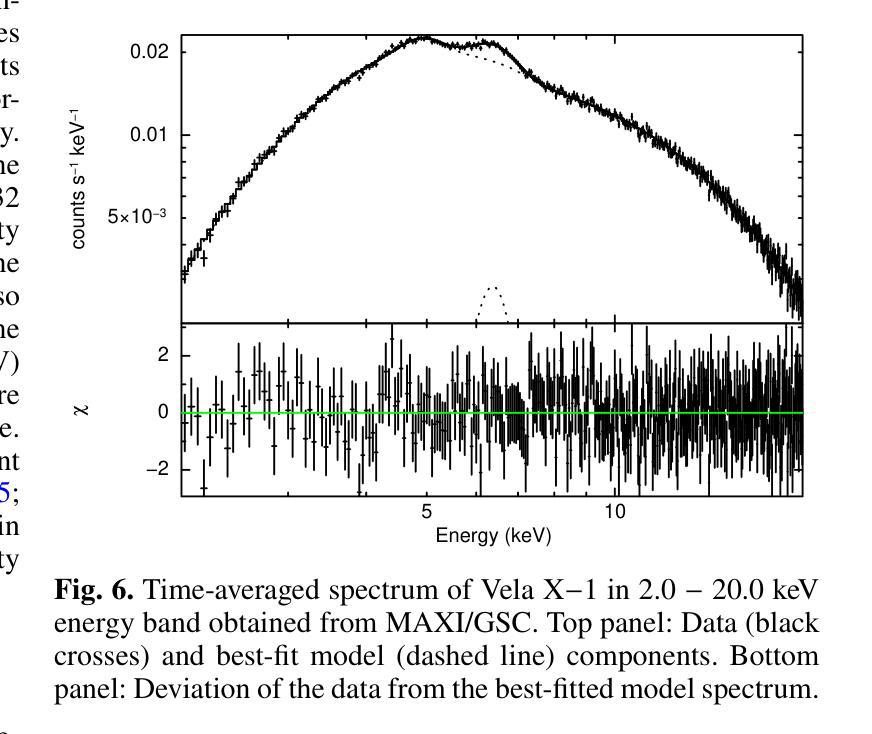
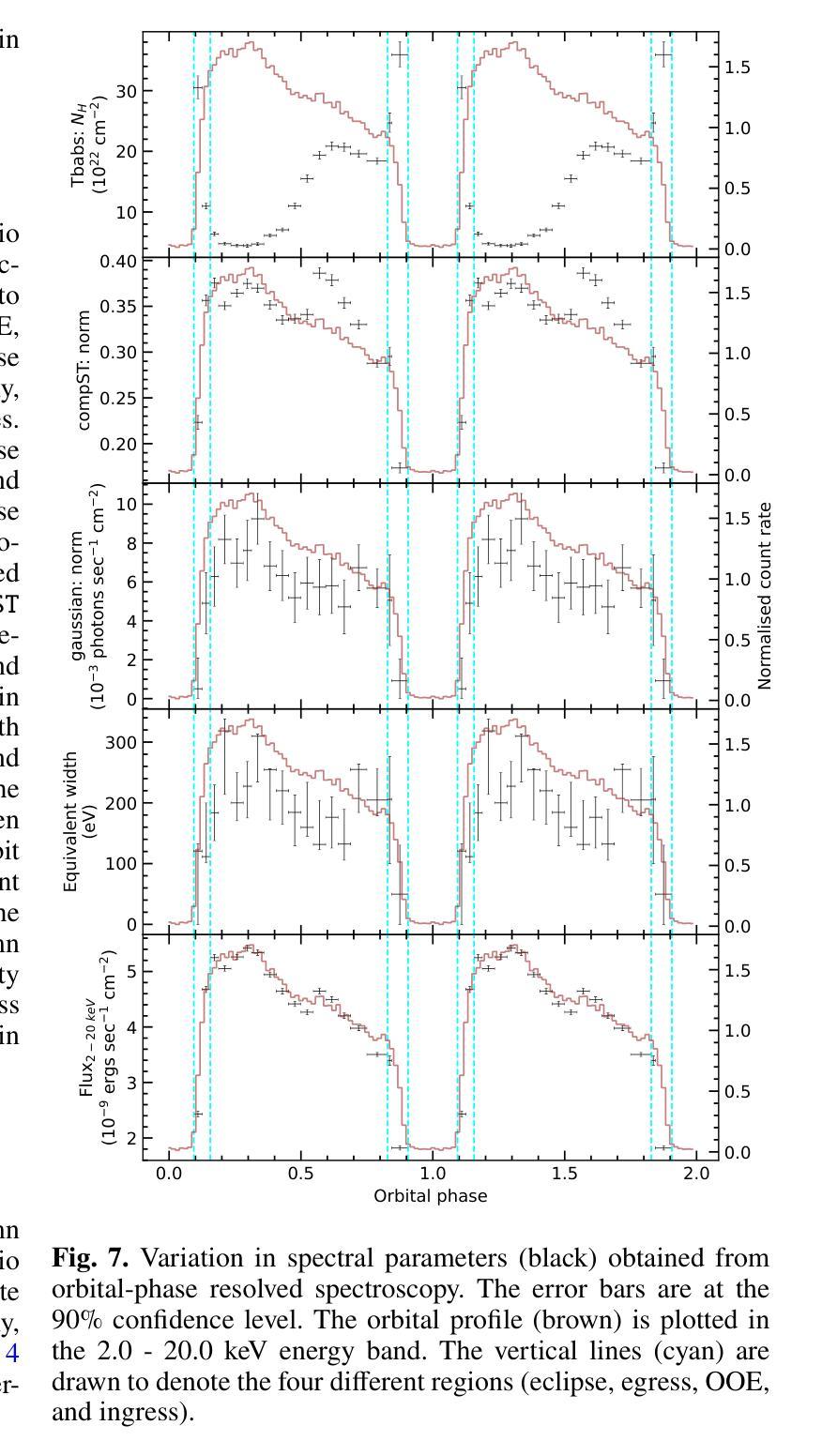
Unveiling the intensity-dependent wake structure of Vela X-1 using MAXI/GSC
Authors:Abhisek Tamang, Kinjal Roy, Hemanth Manikantan, Ajith Balu, Biswajit Paul
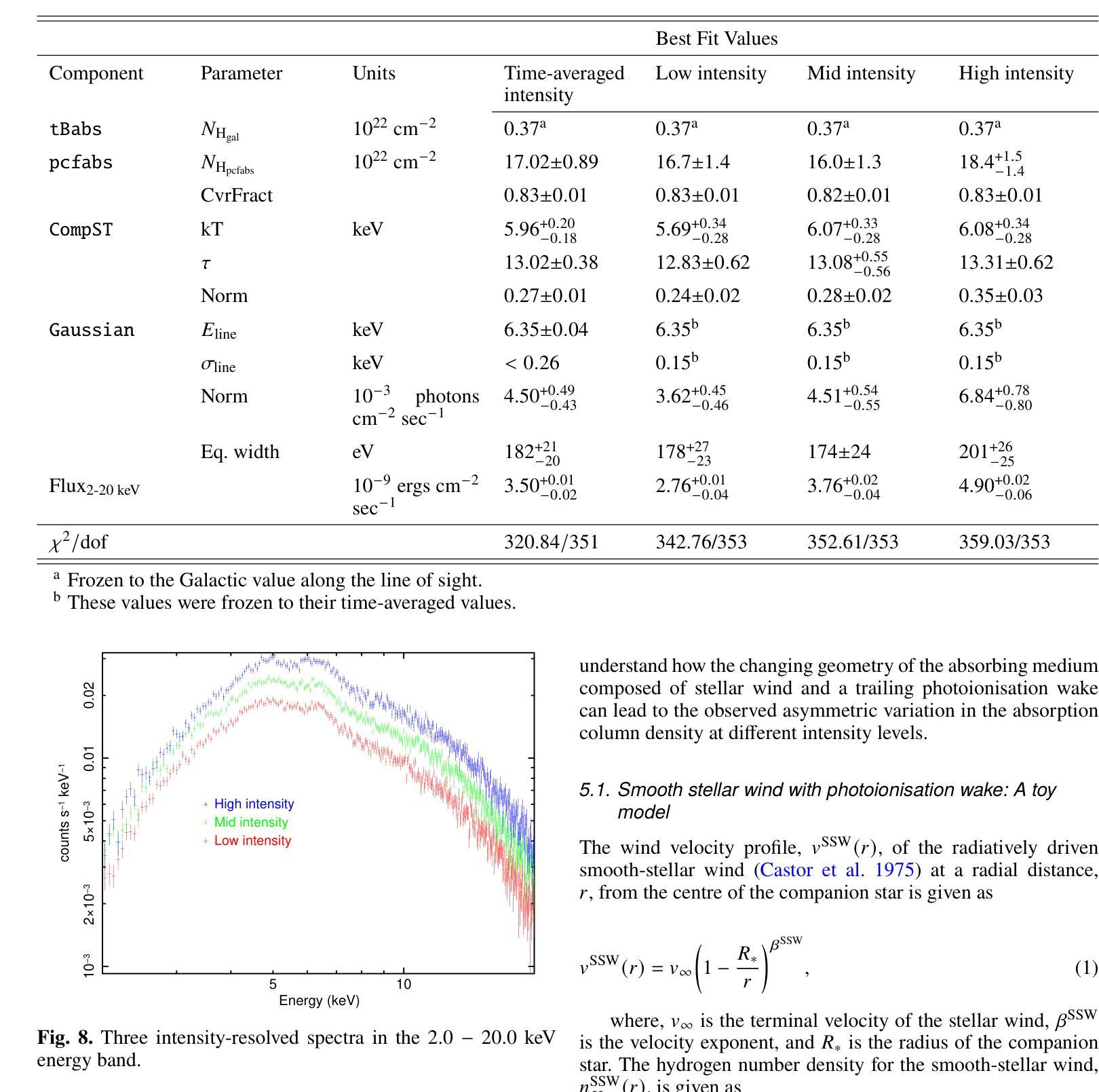
Context. Vela X-1 is among the earliest discovered high-mass X-ray binary (HMXB) pulsars. In such systems, the companion’s stellar wind is strongly affected by ionisation from X-rays emitted by the compact object. A smooth, isotropic stellar wind model cannot account for the observed orbital variation in absorption column density. A stream-like photoionisation wake trailing the neutron star has been proposed to explain this variation. Aims. We investigated the variability of the circumbinary environment at different intensity levels of the Vela X-1 and used a model similar to the above-mentioned stream-like photoionisation wake to explain the asymmetric absorption column density present in the source. Methods. The 2.0-20.0 keV MAXI/GSC spectrum was well modelled with a Comptonised continuum absorbed by local and interstellar material. Nearly 13 years of MAXI/GSC data was used to constrain the variations in absorption column density in Vela X-1 from orbital-phase and intensity-and-orbital-phase resolved spectroscopy. Results. The long-term light curve of Vela X-1 shows orbit-to-orbit intensity level variations without any apparent super-orbital periodicity. The orbital-phase resolved spectroscopy in multiple intensity levels reveals asymmetric variation in absorption column density changes across the intensity levels. Conclusions. We confirm that the orbital variation in absorption column density in Vela X-1 cannot be explained by a smooth stellar wind alone using long-term MAXI/GSC data. An additional component, such as a photoionisation or accretion wake, is required. The wake structure is present across intensity levels, with geometry varying by intensity. The long-term MAXI/GSC data enabled us to vary wake parameters and derive best-fit stellar wind parameters for the time-averaged intensity, reproducing observed absorption column density across intensity levels. (Abbreviated.)
背景。Vela X-1是最早发现的高质量X射线双星(HMXB)脉冲星之一。在这种系统中,伴星的恒星风受到来自紧凑物体发出的X射线的电离的强烈影响。平滑的、各向同性的恒星风模型无法解释观察到的轨道变化中的吸收柱密度。已经提出了类似于中子星后面的流状光离子化尾迹来解释这种变化。目标。我们研究了Vela X-1在不同强度水平的二元环境周围的变化,并使用类似于上述流状光离子化尾迹的模型来解释源中存在的不对称吸收柱密度。方法。2.0-20.0 keV的MAXI/GSC光谱被本地和星际物质吸收的康普顿连续谱很好地建模。使用近13年的MAXI/GSC数据,通过轨道相位和强度与轨道相位解析光谱来限制Vela X-1中吸收柱密度的变化。结果。Vela X-1的长期光变曲线显示出轨道到轨道的强度水平变化,没有明显的超轨道周期性。多强度水平的轨道相位解析光谱显示出吸收柱密度变化的不对称变化。结论。我们使用长期的MAXI/GSC数据确认,仅凭平滑的恒星风无法解释Vela X-1中吸收柱密度的轨道变化。需要额外的成分,例如光离子化或吸积尾迹。尾迹结构存在于各个强度水平,并且其几何形状随强度而变化。长期的MAXI/GSC数据使我们能够改变尾迹参数,并根据时间平均强度得出最佳的恒星风参数,从而再现了观察到的吸收柱密度变化。(摘要)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 15 figures, 3 tables, Accepted for publication in Astronomy & Astrophysics
摘要
Vela X-1是早期发现的高质量X射线双星(HMXB)脉冲星之一。在这种系统中,伴星的恒星风受到来自紧凑物体发出的X射线的电离影响。平滑的、各向同性的恒星风模型无法解释观察到的轨道变化中的吸收柱密度。已经提出类似流状的光电离尾迹来解释这种变化。通过调查不同强度水平的Vela X-1周围的二进制环境,并使用类似于上述流状光电离尾迹的模型来解释源中存在的不对称吸收柱密度,我们发现长期光曲线显示轨道到轨道的强度水平变化,没有明显的超轨道周期性。在多个强度水平上的轨道相位解析光谱显示不对称的吸收柱密度变化。我们确认,仅使用平滑的恒星风无法解释Vela X-1中的轨道吸收柱密度变化。需要额外的组件,例如光电离或积垢尾迹。尾迹结构存在于各个强度水平,其几何形状随强度而变化。长期MAXI/GSC数据使我们能够改变尾迹参数,并得出时间平均强度的最佳恒星风参数,以再现观察到的吸收柱密度变化。
要点
- Vela X-1是高质量X射线双星(HMXB)脉冲星,其伴随的恒星风受到X射线电离的影响。
- 轨道变化的吸收柱密度无法用平滑的恒星风模型解释。
- 提出流状光电离尾迹来解释这种变化。
- 通过分析长期MAXI/GSC数据,发现Vela X-1的轨道到轨道强度水平变化没有超轨道周期性。
- 在多个强度水平的轨道相位解析光谱显示不对称的吸收柱密度变化。
- 需要额外的组件(如光电离尾迹)来解释观察到的吸收柱密度变化,该尾迹结构存在于不同的强度水平。
点此查看论文截图

Generative Large Language Models Trained for Detecting Errors in Radiology Reports
Authors:Cong Sun, Kurt Teichman, Yiliang Zhou, Brian Critelli, David Nauheim, Graham Keir, Xindi Wang, Judy Zhong, Adam E Flanders, George Shih, Yifan Peng
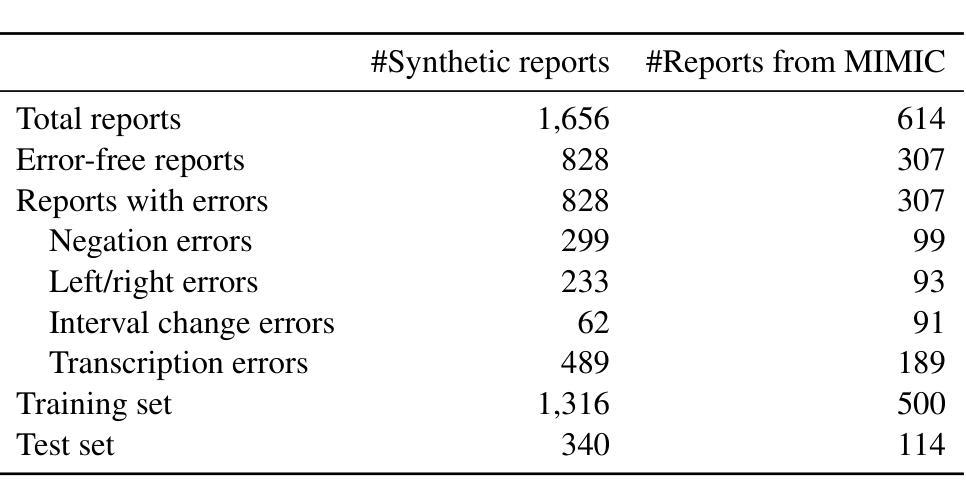
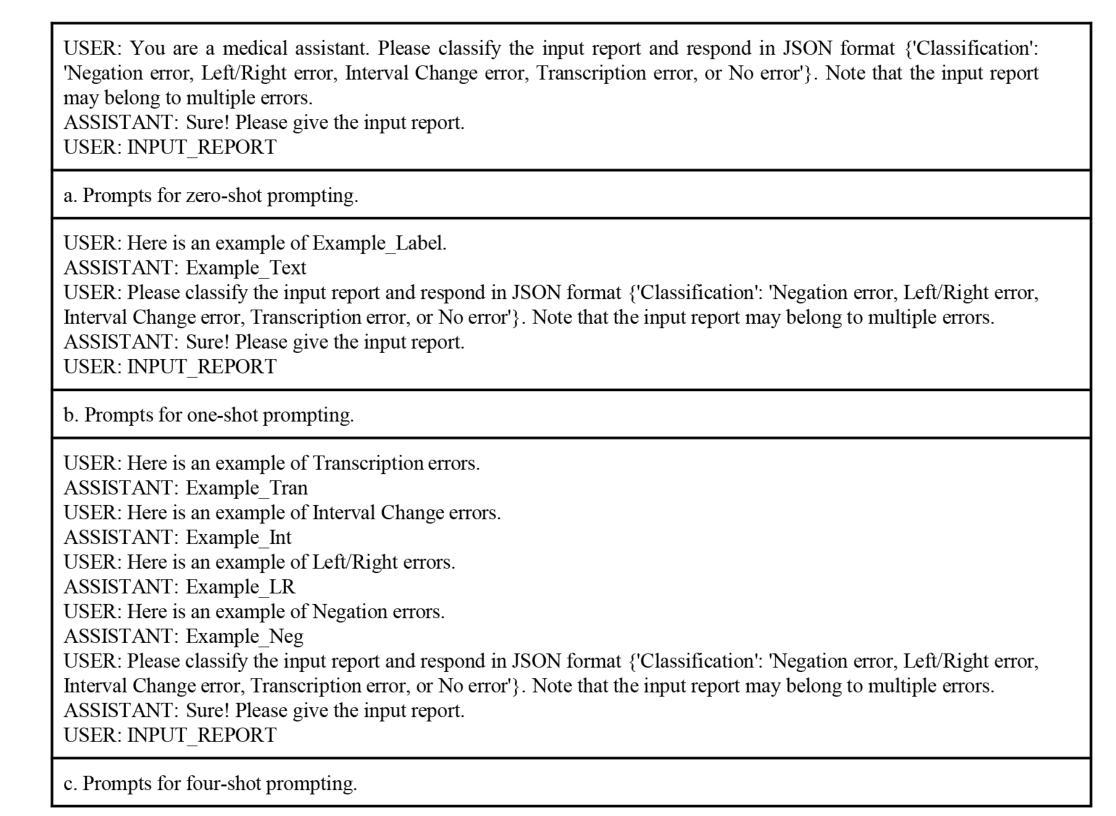
In this retrospective study, a dataset was constructed with two parts. The first part included 1,656 synthetic chest radiology reports generated by GPT-4 using specified prompts, with 828 being error-free synthetic reports and 828 containing errors. The second part included 614 reports: 307 error-free reports between 2011 and 2016 from the MIMIC-CXR database and 307 corresponding synthetic reports with errors generated by GPT-4 on the basis of these MIMIC-CXR reports and specified prompts. All errors were categorized into four types: negation, left/right, interval change, and transcription errors. Then, several models, including Llama-3, GPT-4, and BiomedBERT, were refined using zero-shot prompting, few-shot prompting, or fine-tuning strategies. Finally, the performance of these models was evaluated using the F1 score, 95% confidence interval (CI) and paired-sample t-tests on our constructed dataset, with the prediction results further assessed by radiologists. Using zero-shot prompting, the fine-tuned Llama-3-70B-Instruct model achieved the best performance with the following F1 scores: 0.769 for negation errors, 0.772 for left/right errors, 0.750 for interval change errors, 0.828 for transcription errors, and 0.780 overall. In the real-world evaluation phase, two radiologists reviewed 200 randomly selected reports output by the model. Of these, 99 were confirmed to contain errors detected by the models by both radiologists, and 163 were confirmed to contain model-detected errors by at least one radiologist. Generative LLMs, fine-tuned on synthetic and MIMIC-CXR radiology reports, greatly enhanced error detection in radiology reports.
在本次回顾性研究中,构建了包含两部分的数据集。第一部分包含由GPT-4根据指定提示生成的1656份合成胸部放射学报告,其中828份是无错误的合成报告,另外828份含有错误。第二部分包含614份报告,其中包括来自MIMIC-CXR数据库的2011年至2016年间的307份无错误报告,以及基于这些MIMIC-CXR报告和特定提示由GPT-4生成的307份相应的合成报告,其中含有错误。所有错误都被分为四种类型:否定、左右、间隔变化和转录错误。然后,使用零样本提示、少样本提示或微调策略对包括Llama-3、GPT-4和BiomedBERT在内的几个模型进行了改进。最后,使用F1得分、95%置信区间(CI)和配对样本t检验对我们构建的数据集上这些模型的表现进行了评估,预测结果还得到了放射科的进一步评估。在零样本提示下,经过微调的Llama-3-70B-Instruct模型在以下F1得分上表现最佳:否定错误为0.769,左右错误为0.772,间隔变化错误为0.750,转录错误为0.828,总体为0.780。在现实世界评估阶段,两名放射科医生审查了模型输出的200份随机选择的报告。其中,99份被模型和两位放射科医生都确认含有错误,163份被模型或至少一位放射科医生确认含有错误。在合成和MIMIC-CXR放射学报告上经过微调的生成式LLM极大地提高了放射学报告中的错误检测能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究利用合成报告和真实报告构建了数据集,对LLama-3、GPT-4和BiomedBERT等模型进行训练,并评估其在检测胸部放射学报告错误方面的性能。结果显示,经过微调的Llama-3模型在零样本提示下表现最佳,生成式LLM模型在合成报告和MIMIC-CXR数据库报告上的微调有助于增强报告错误的检测能力。
Key Takeaways
- 研究构建了一个包含合成和真实胸部放射学报告的数据集,用于模型训练。
- 数据集中的报告包含不同类型的错误,如否定、左右、间隔变化和转录错误。
- 研究评估了Llama-3、GPT-4和BiomedBERT等模型在报告错误检测方面的性能。
- 经过微调和零样本提示,Llama-3模型表现出最佳性能。
- 在真实世界评估阶段,模型检测到的错误得到了放射科医师的确认。
- 生成的LLM模型在合成和MIMIC-CXR放射学报告上的微调有助于增强报告错误的检测能力。
点此查看论文截图



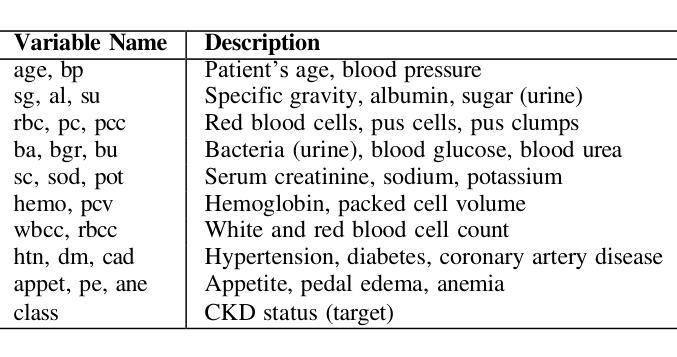
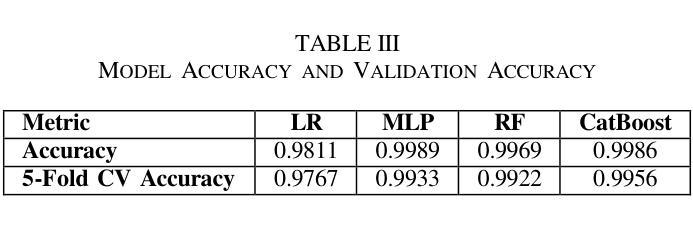
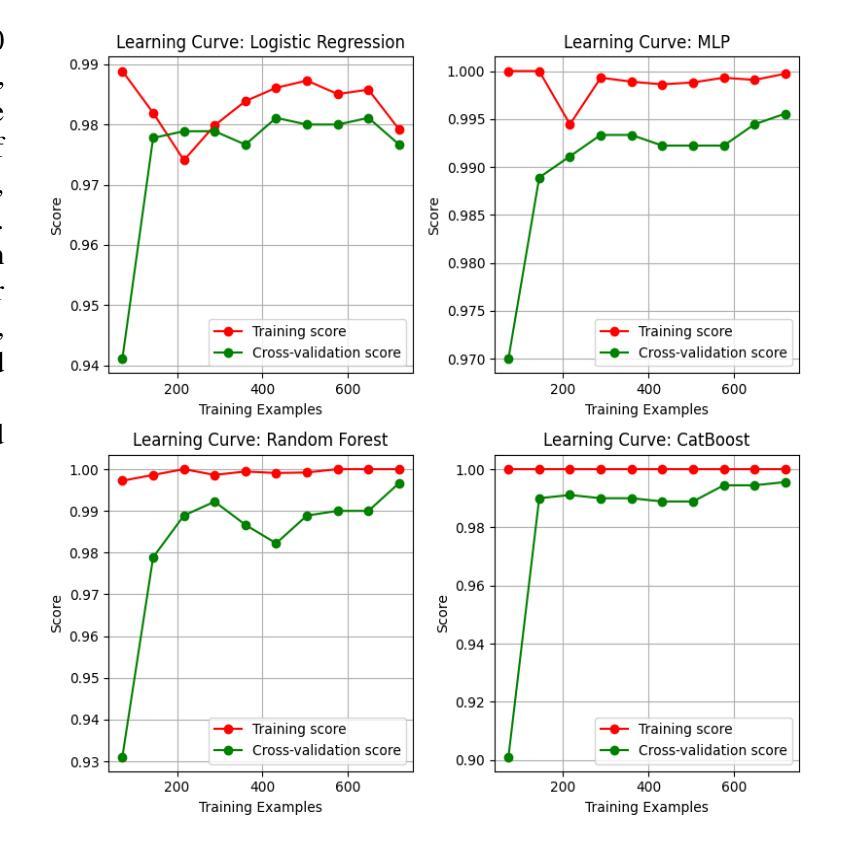
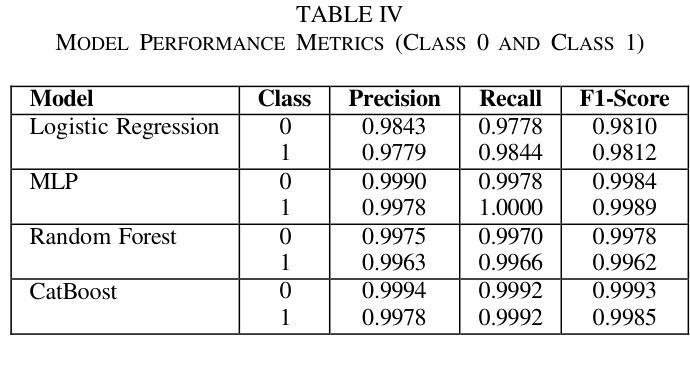
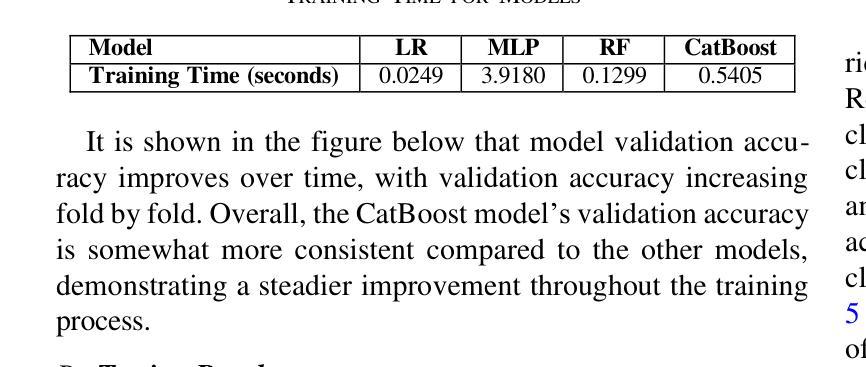
Improving Chronic Kidney Disease Detection Efficiency: Fine Tuned CatBoost and Nature-Inspired Algorithms with Explainable AI
Authors:Md. Ehsanul Haque, S. M. Jahidul Islam, Jeba Maliha, Md. Shakhauat Hossan Sumon, Rumana Sharmin, Sakib Rokoni
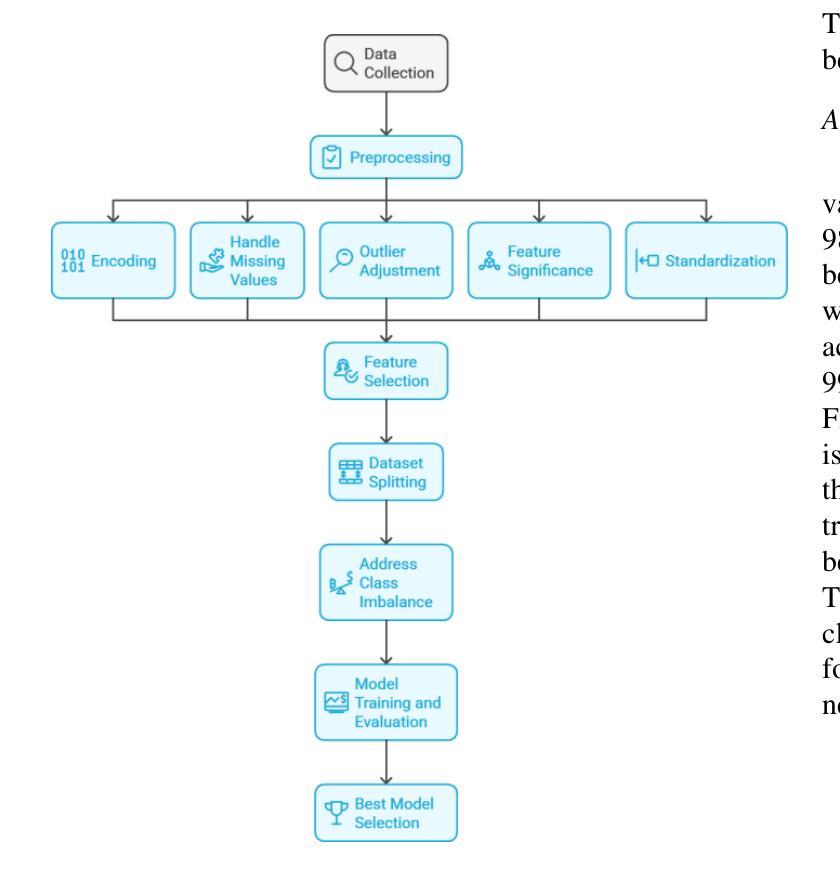
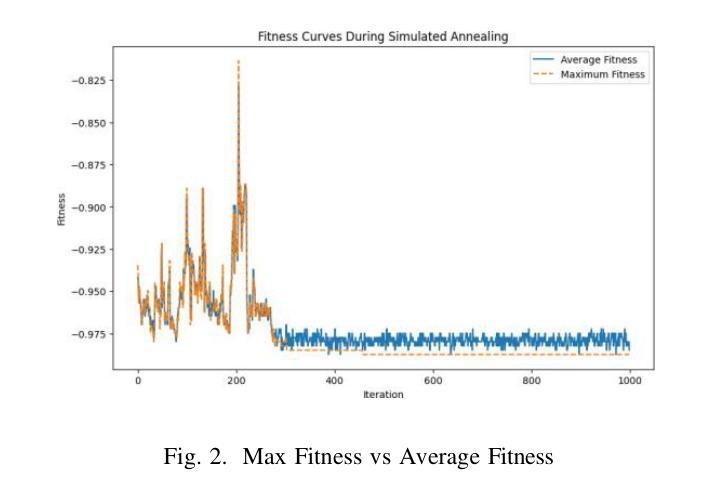
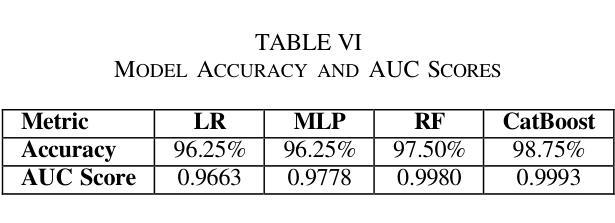
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a major global health issue which is affecting million people around the world and with increasing rate of mortality. Mitigation of progression of CKD and better patient outcomes requires early detection. Nevertheless, limitations lie in traditional diagnostic methods, especially in resource constrained settings. This study proposes an advanced machine learning approach to enhance CKD detection by evaluating four models: Random Forest (RF), Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP), Logistic Regression (LR), and a fine-tuned CatBoost algorithm. Specifically, among these, the fine-tuned CatBoost model demonstrated the best overall performance having an accuracy of 98.75%, an AUC of 0.9993 and a Kappa score of 97.35% of the studies. The proposed CatBoost model has used a nature inspired algorithm such as Simulated Annealing to select the most important features, Cuckoo Search to adjust outliers and grid search to fine tune its settings in such a way to achieve improved prediction accuracy. Features significance is explained by SHAP-a well-known XAI technique-for gaining transparency in the decision-making process of proposed model and bring up trust in diagnostic systems. Using SHAP, the significant clinical features were identified as specific gravity, serum creatinine, albumin, hemoglobin, and diabetes mellitus. The potential of advanced machine learning techniques in CKD detection is shown in this research, particularly for low income and middle-income healthcare settings where prompt and correct diagnoses are vital. This study seeks to provide a highly accurate, interpretable, and efficient diagnostic tool to add to efforts for early intervention and improved healthcare outcomes for all CKD patients.
慢性肾脏病(CKD)是一个全球性的重大健康问题,影响全球数千万人,且死亡率呈上升趋势。减缓CKD的进展并改善患者预后需要早期发现。然而,传统诊断方法存在局限性,特别是在资源受限的环境中。本研究提出了一种先进的机器学习方法来提高CKD的检测能力,评估了四种模型:随机森林(RF)、多层感知器(MLP)、逻辑回归(LR)和经过调优的CatBoost算法。特别是其中,经过调优的CatBoost模型表现出了最佳的总体性能,其准确度为98.75%,AUC为0.9993,Kappa得分为研究的97.35%。所提出的CatBoost模型使用了一种受自然启发的算法,如模拟退火算法来选择最重要的特征,利用布谷鸟搜索调整异常值,并使用网格搜索微调其设置,从而实现提高预测精度的目的。通过SHAP(一种众所周知的XAI技术)解释特征的重要性,以获得决策过程的透明度并对诊断系统建立信任。使用SHAP,确定的关键临床特征为特定比重、血清肌酐、白蛋白、血红蛋白和糖尿病。这项研究表明先进机器学习技术在CKD检测中的潜力,特别是在低收入和中收入医疗保健环境中,快速而正确的诊断至关重要。本研究旨在为所有CKD患者提供高度准确、可解释和高效的诊断工具,以支持早期干预和改善医疗保健结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 page, 8 figures , conference : 14th IEEE International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies (CSNT2025)
摘要
本研究采用先进的机器学习方法,对慢性肾病(CKD)进行早期检测。经过对比四种模型,发现经过精细调整的CatBoost模型表现最佳,准确度高达98.75%,AUC值为0.9993,Kappa得分为97.35%。该模型采用模拟退火等自然启发算法选择重要特征,采用布谷鸟搜索调整异常值,并采用网格搜索进行精细调整,以提高预测准确性。同时采用SHAP解释特征重要性,有助于建立诊断决策过程的透明度,并为诊断系统建立信任。本研究揭示了机器学习方法在慢性肾病检测中的潜力,特别是对收入较低和中等医疗环境的国家和地区具有重要影响。它为早期干预和所有慢性肾病患者的健康结果改善提供了一个准确、可解释和高效的诊断工具。
关键见解
1. 慢性肾病(CKD)是一个全球性的健康问题,影响着数百万人,且死亡率不断上升。
2. 传统诊断方法存在局限性,尤其是在资源受限的环境中。
3. 研究提出了一种基于机器学习的改进CKD检测方法,其中CatBoost模型表现最佳,准确度高。
4. CatBoost模型使用模拟退火等自然启发算法选择重要特征,并采用布谷鸟搜索和网格搜索进行优化。
5. SHAP被用来解释特征的重要性,以增加诊断过程的透明度并建立信任。
6. 研究识别了关键的临床特征,如特定比重、血清肌��.白蛋白、血红蛋白和糖尿病等。
点此查看论文截图

DocSAM: Unified Document Image Segmentation via Query Decomposition and Heterogeneous Mixed Learning
Authors:Xiao-Hui Li, Fei Yin, Cheng-Lin Liu
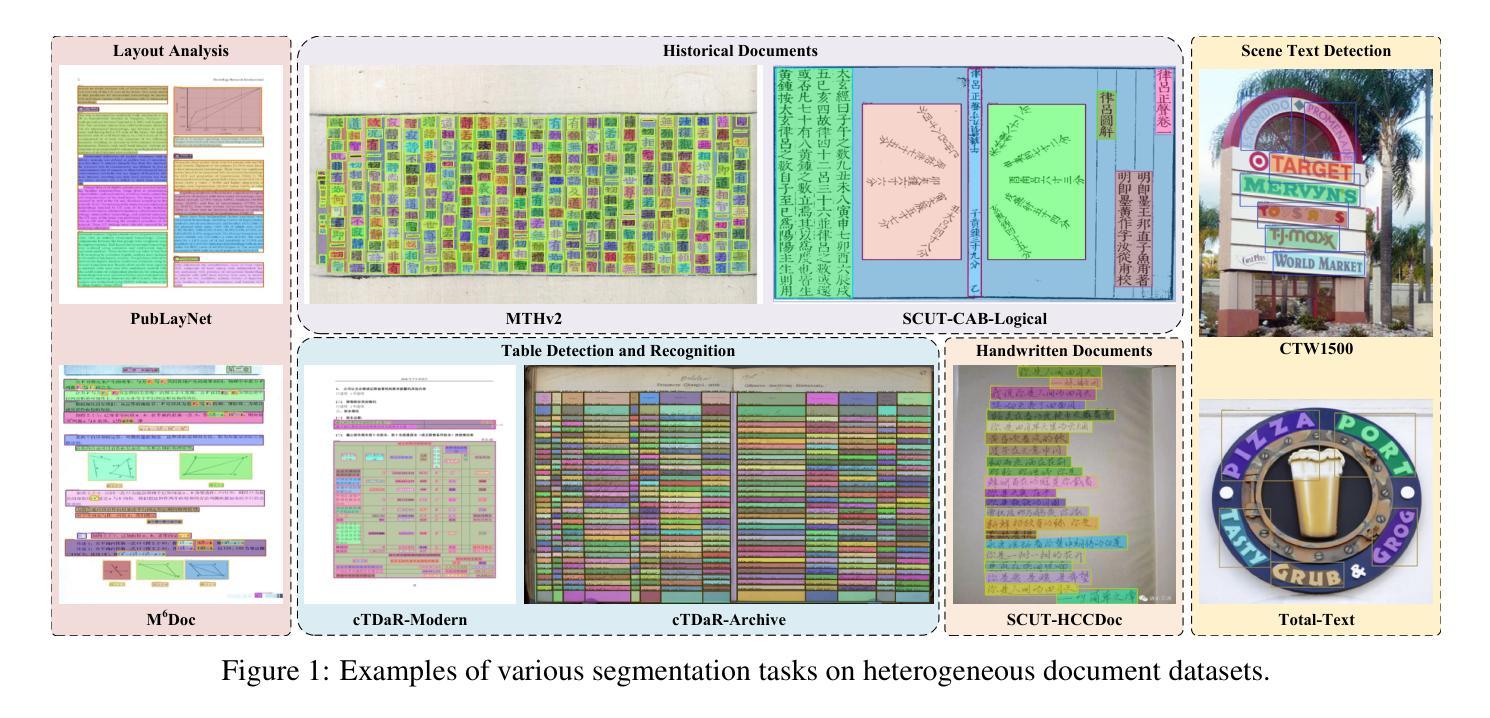
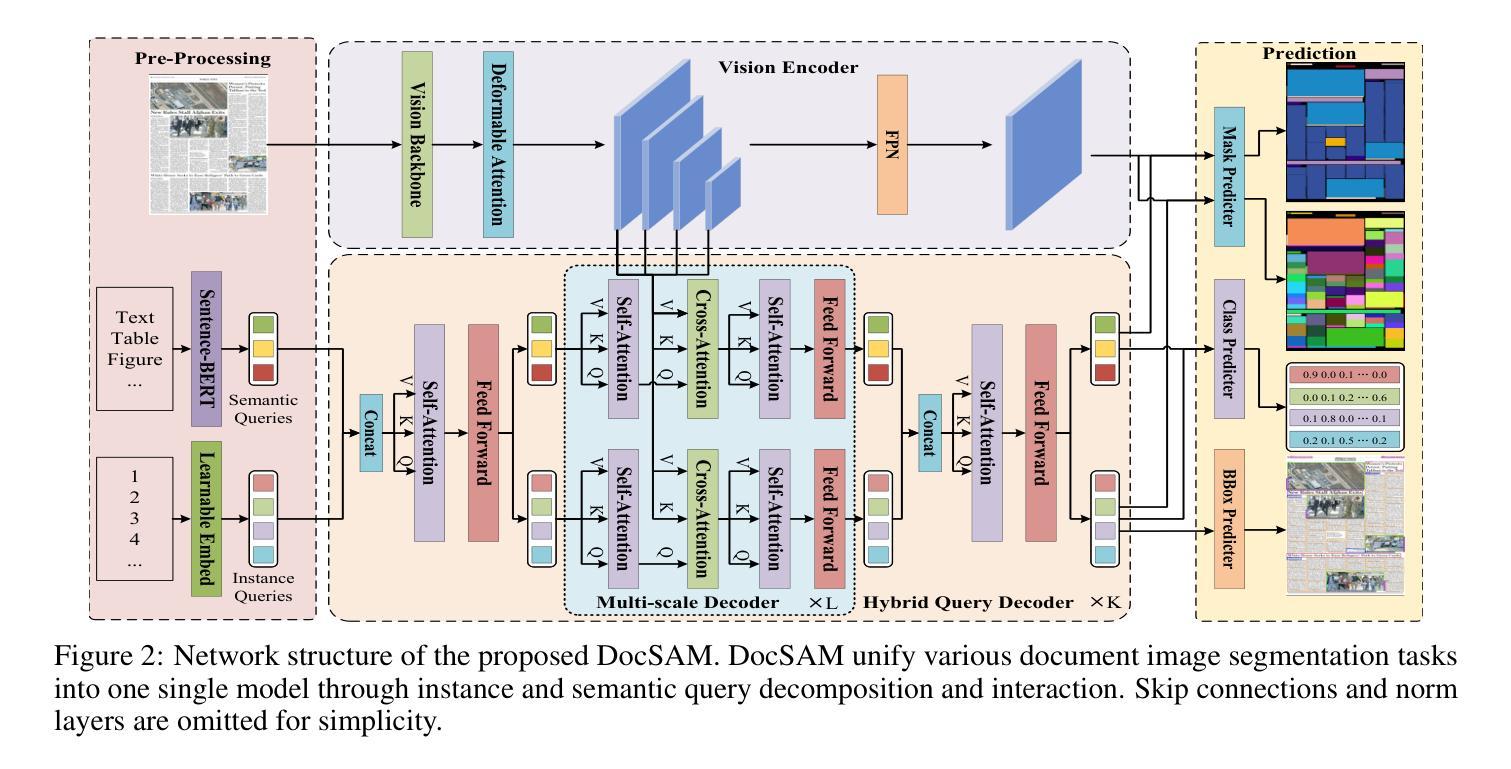
Document image segmentation is crucial for document analysis and recognition but remains challenging due to the diversity of document formats and segmentation tasks. Existing methods often address these tasks separately, resulting in limited generalization and resource wastage. This paper introduces DocSAM, a transformer-based unified framework designed for various document image segmentation tasks, such as document layout analysis, multi-granularity text segmentation, and table structure recognition, by modelling these tasks as a combination of instance and semantic segmentation. Specifically, DocSAM employs Sentence-BERT to map category names from each dataset into semantic queries that match the dimensionality of instance queries. These two sets of queries interact through an attention mechanism and are cross-attended with image features to predict instance and semantic segmentation masks. Instance categories are predicted by computing the dot product between instance and semantic queries, followed by softmax normalization of scores. Consequently, DocSAM can be jointly trained on heterogeneous datasets, enhancing robustness and generalization while reducing computational and storage resources. Comprehensive evaluations show that DocSAM surpasses existing methods in accuracy, efficiency, and adaptability, highlighting its potential for advancing document image understanding and segmentation across various applications. Codes are available at https://github.com/xhli-git/DocSAM.
文档图像分割对于文档分析和识别至关重要,但由于文档格式和分割任务的多样性,它仍然是一个挑战。现有方法通常将这些任务分别处理,导致泛化能力有限和资源浪费。本文介绍了DocSAM,这是一个基于变压器的统一框架,旨在为各种文档图像分割任务(如文档布局分析、多粒度文本分割和表格结构识别)而设计。它通过将这些任务建模为实例分割和语义分割的组合来实现这一目标。具体来说,DocSAM采用Sentence-BERT将每个数据集中的类别名称映射到语义查询上,这些查询与实例查询的维度相匹配。这两组查询通过注意力机制进行交互,并通过与图像特征的交叉注意力来预测实例和语义分割掩码。通过计算实例查询和语义查询之间的点积来预测实例类别,然后对分数进行softmax归一化。因此,DocSAM可以在异质数据集上进行联合训练,增强了稳健性和泛化能力,同时减少了计算和存储资源。全面评估表明,DocSAM在准确性、效率和适应性方面超越了现有方法,突显了其在推进各种应用中的文档图像理解和分割的潜力。代码可用在https://github.com/xhli-git/DocSAM。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
本文提出了DocSAM,这是一个基于转换器的统一框架,用于各种文档图像分割任务,如文档布局分析、多粒度文本分割和表格结构识别。它通过实例分割和语义分割的结合来建模这些任务,可以联合训练在异质数据集上,提高稳健性和泛化能力,同时减少计算和存储资源。DocSAM在准确性、效率和适应性方面超越了现有方法,有望推动文档图像理解和分割的广泛应用。
Key Takeaways
- DocSAM是一个统一框架,用于文档图像分割任务,包括文档布局分析、多粒度文本分割和表格结构识别。
- DocSAM结合实例分割和语义分割来建模任务。
- DocSAM使用Sentence-BERT将类别名称映射到语义查询,与实例查询匹配维度。
- 通过注意力机制,实例查询和语义查询相互交互,并与图像特征进行交叉注意力,以预测实例和语义分割掩膜。
- DocSAM可以通过计算实例和语义查询的点积来预测实例类别,并通过softmax归一化分数。
- DocSAM可以在异质数据集上进行联合训练,增强稳健性和泛化能力,同时减少计算和存储资源。
点此查看论文截图

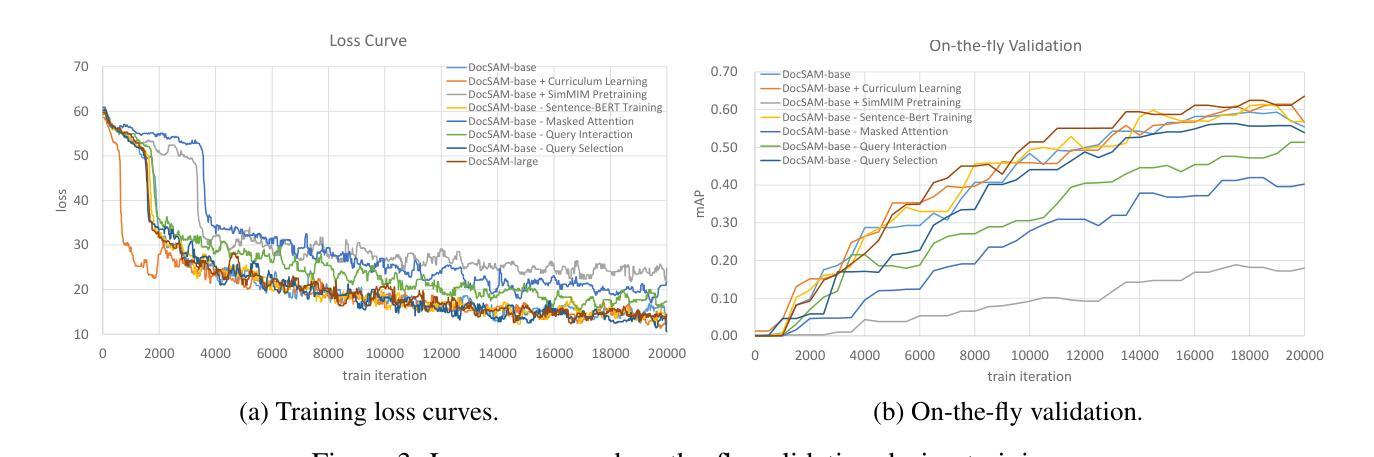
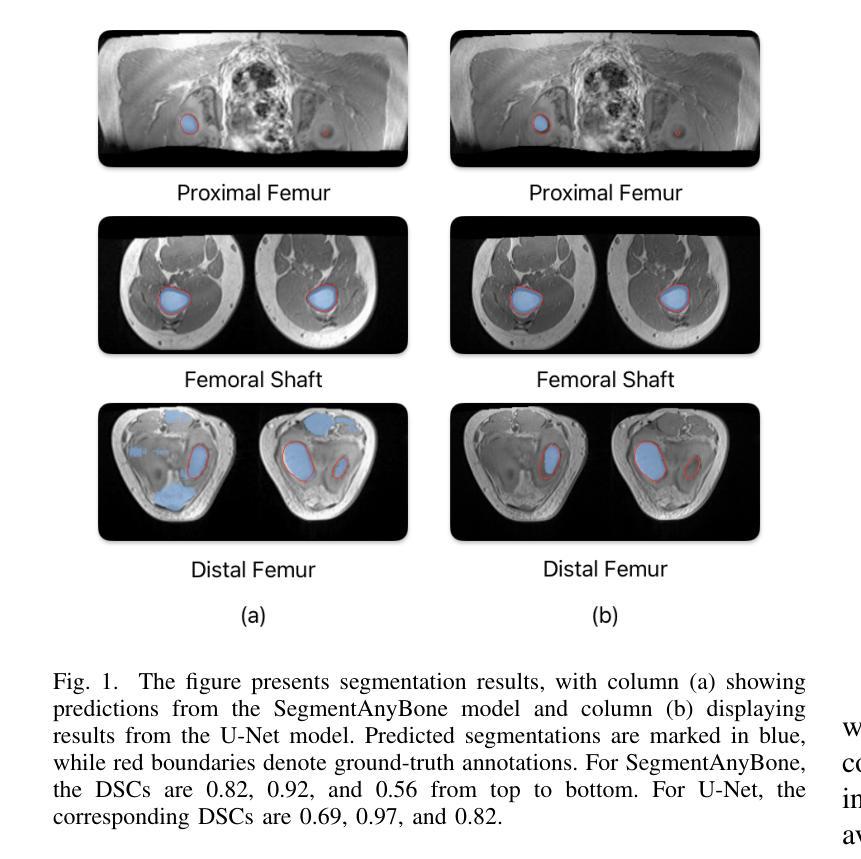
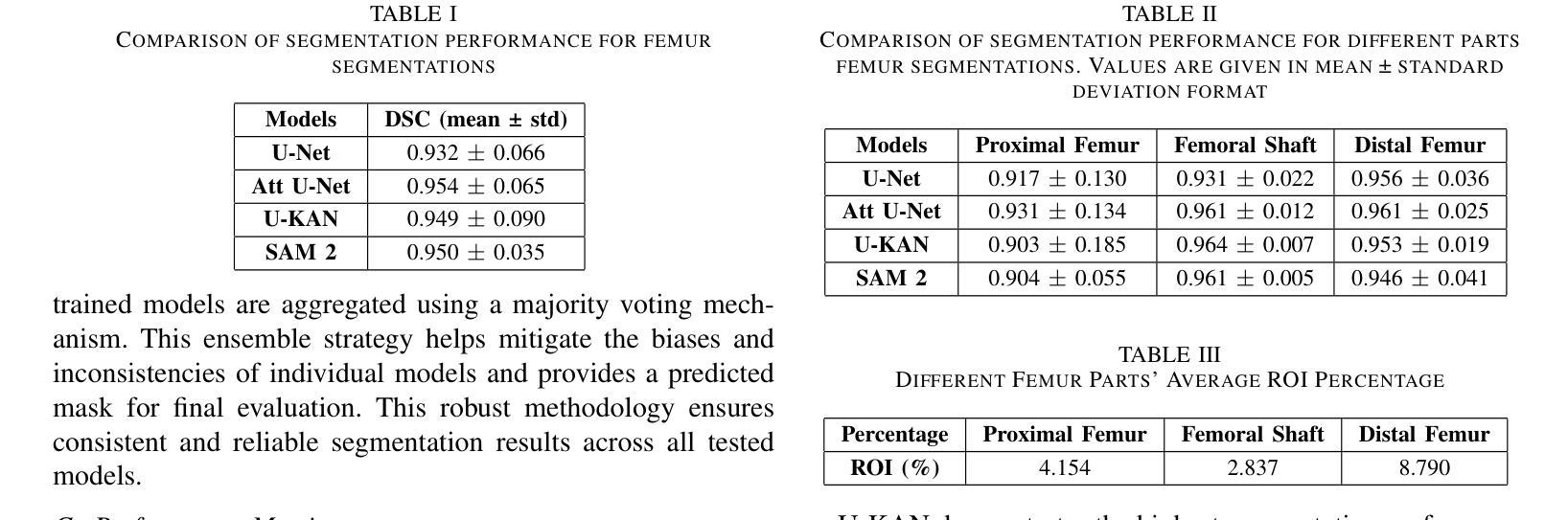
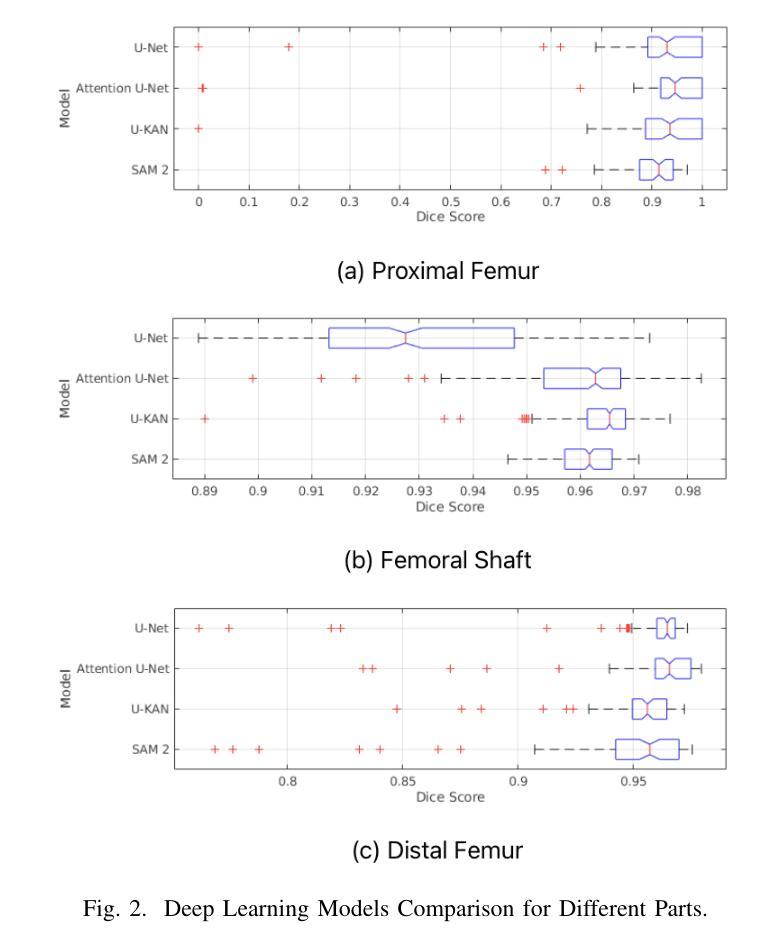
Performance Analysis of Deep Learning Models for Femur Segmentation in MRI Scan
Authors:Mengyuan Liu, Yixiao Chen, Anning Tian, Xinmeng Wu, Mozhi Shen, Tianchou Gong, Jeongkyu Lee
Convolutional neural networks like U-Net excel in medical image segmentation, while attention mechanisms and KAN enhance feature extraction. Meta’s SAM 2 uses Vision Transformers for prompt-based segmentation without fine-tuning. However, biases in these models impact generalization with limited data. In this study, we systematically evaluate and compare the performance of three CNN-based models, i.e., U-Net, Attention U-Net, and U-KAN, and one transformer-based model, i.e., SAM 2 for segmenting femur bone structures in MRI scan. The dataset comprises 11,164 MRI scans with detailed annotations of femoral regions. Performance is assessed using the Dice Similarity Coefficient, which ranges from 0.932 to 0.954. Attention U-Net achieves the highest overall scores, while U-KAN demonstrated superior performance in anatomical regions with a smaller region of interest, leveraging its enhanced learning capacity to improve segmentation accuracy.
卷积神经网络(如U-Net)在医学图像分割方面表现出色,而注意力机制和KAN则增强了特征提取的能力。Meta的SAM 2使用Vision Transformers进行基于提示的分割,无需微调。然而,这些模型中的偏见影响在有限数据下的泛化能力。在本研究中,我们系统地评估和比较了三种基于CNN的模型(即U-Net、Attention U-Net和U-KAN)和一种基于变压器的模型(即SAM 2)在MRI扫描中分割股骨结构的表现。数据集包含11,164份MRI扫描,详细标注了股骨区域。性能评估采用Dice相似系数,范围从0.932到0.954。Attention U-Net获得最高总分,而U-KAN在具有较小兴趣区域的解剖区域表现出卓越性能,利用其增强的学习能力提高分割精度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
卷积神经网络如U-Net在医学图像分割中表现出色,而注意力机制和KAN可增强特征提取功能。本研究对三种基于CNN的模型(U-Net、Attention U-Net和U-KAN)和一种基于变压器的模型(Meta的SAM 2)进行了系统评价比较,用于MRI扫描中的股骨结构分割。性能评估使用Dice相似系数,范围从0.932到0.954。Attention U-Net获得最高总体得分,U-KAN在较小的感兴趣区域展现出卓越性能,利用其增强学习能力提高分割准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 卷积神经网络(CNN)如U-Net在医学图像分割中表现优秀。
- 注意力机制和KAN机制能增强特征提取能力。
- Meta的SAM 2使用Vision Transformers进行基于提示的分割,无需微调。
- 模型的偏见会影响在有限数据上的泛化能力。
- 研究中对四种模型进行了系统评价,包括三种CNN模型(U-Net、Attention U-Net和U-KAN)和一种基于变压器的模型(SAM 2)。
- 在MRI扫描股骨结构分割的任务中,Attention U-Net获得最高总体得分。
点此查看论文截图

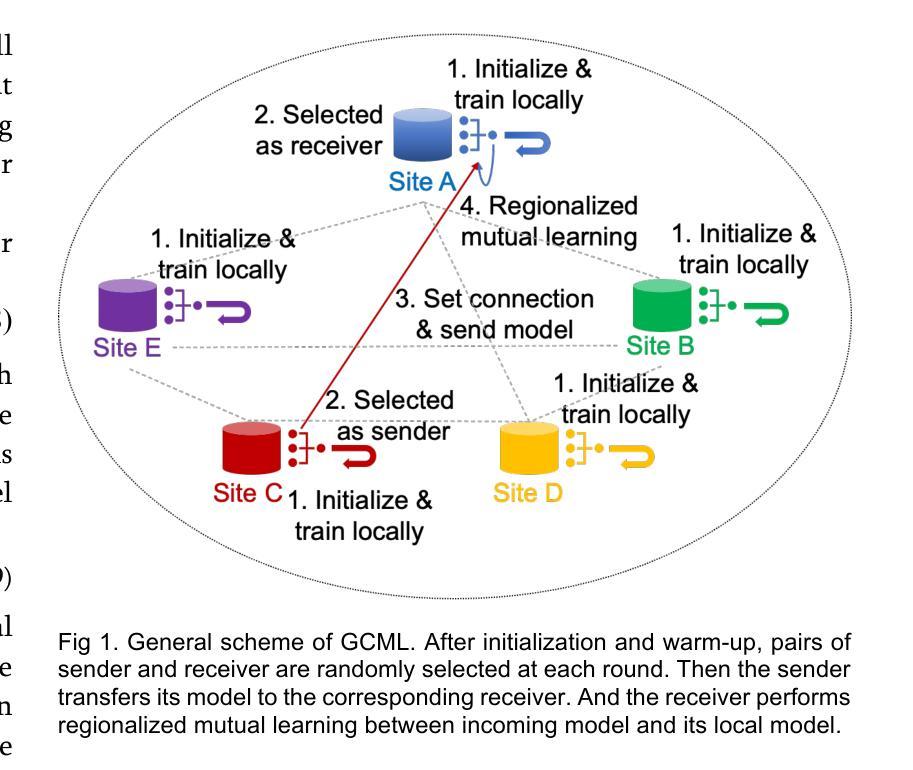
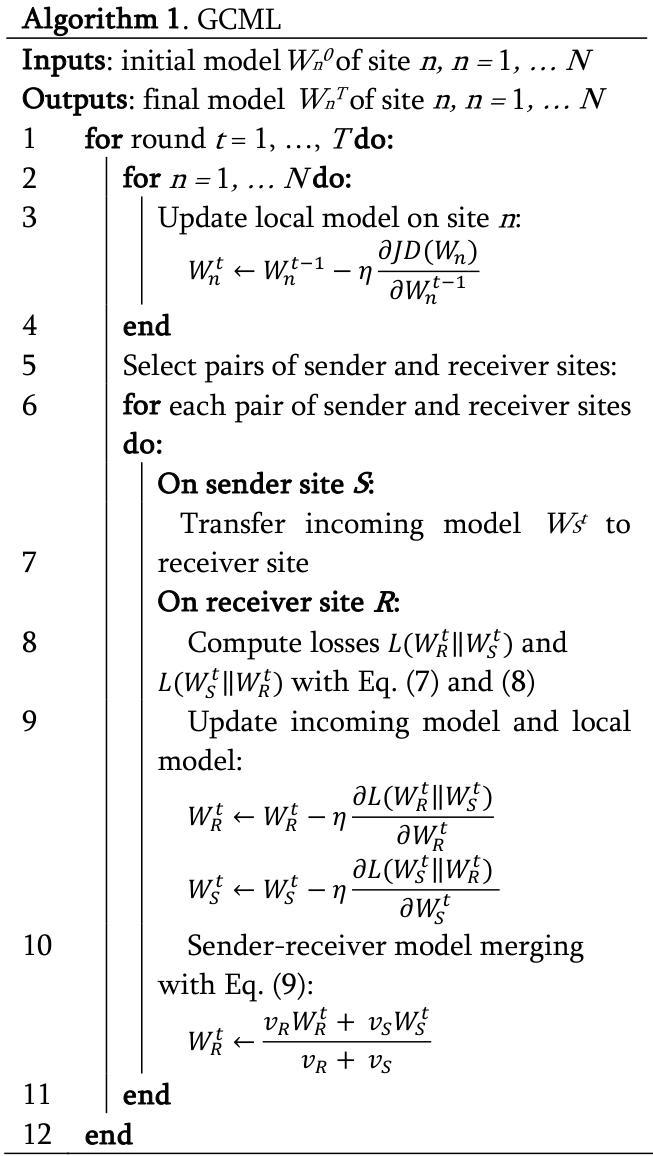
Decentralized Personalization for Federated Medical Image Segmentation via Gossip Contrastive Mutual Learning
Authors:Jingyun Chen, Yading Yuan
Federated Learning (FL) presents a promising avenue for collaborative model training among medical centers, facilitating knowledge exchange without compromising data privacy. However, vanilla FL is prone to server failures and rarely achieves optimal performance on all participating sites due to heterogeneous data distributions among them. To overcome these challenges, we propose Gossip Contrastive Mutual Learning (GCML), a unified framework to optimize personalized models in a decentralized environment, where Gossip Protocol is employed for flexible and robust peer-to-peer communication. To make efficient and reliable knowledge exchange in each communication without the global knowledge across all the sites, we introduce deep contrast mutual learning (DCML), a simple yet effective scheme to encourage knowledge transfer between the incoming and local models through collaborative training on local data. By integrating DCML with other efforts to optimize site-specific models by leveraging useful information from peers, we evaluated the performance and efficiency of the proposed method on three publicly available datasets with different segmentation tasks. Our extensive experimental results show that the proposed GCML framework outperformed both centralized and decentralized FL methods with significantly reduced communication overhead, indicating its potential for real-world deployment. Upon the acceptance of manuscript, the code will be available at: https://github.com/CUMC-Yuan-Lab/GCML.
联邦学习(FL)为医疗中心之间的协作模型训练提供了一个有前景的途径,促进了知识交换而不侵犯数据隐私。然而,原生的联邦学习容易受到服务器故障的影响,并且由于各参与方之间数据分布的异质性,很少在所有参与方上实现最佳性能。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了Gossip对比互学习(GCML)框架,这是一个在分布式环境中优化个性化模型的统一框架,采用Gossip协议进行灵活和稳健的点对点通信。为了在每次通信中进行高效可靠的知识交换,而不涉及所有站点的全局知识,我们引入了深度对比互学习(DCML)方案,这是一种简单有效的方案,通过本地数据的协作训练来鼓励传入模型和本地模型之间的知识转移。通过将DCML与其他努力相结合,以利用同行中的有用信息来优化特定站点的模型,我们在三个公开数据集上对所提出的方法进行了不同分割任务的性能和效率评估。我们的广泛实验结果表明,所提出的GCML框架在通信开销方面显著优于集中式和分布式联邦学习方法,显示出其在现实世界部署的潜力。手稿一旦被接受,代码将可通过以下链接获取:https://github.com/CUMC-Yuan-Lab/GCML。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, Open-source code at: https://github.com/CUMC-Yuan-Lab/GCML
Summary
联邦学习(FL)为医疗中心间的协作模型训练提供了有前景的途径,促进知识交换而不泄露数据隐私。然而,原始FL易受服务器故障影响,且由于数据分布不均很难在所有参与站点上实现最佳性能。为克服这些挑战,我们提出Gossip对比互学习(GCML)统一框架,用于在分布式环境中优化个性化模型。采用Gossip协议实现灵活稳健的点对点通信。通过引入深度对比互学习(DCML),在每次通信中进行高效可靠的知识交换,鼓励本地与传入模型间的知识转移,通过本地数据协作训练。将DCML与其他优化同行特定模型的策略相结合,我们在三个公开数据集上进行不同分割任务的评估。实验结果显示,GCML框架在通信开销显著降低的情况下,表现优于集中式和分布式联邦学习方法,具有现实部署潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦学习(FL)有助于医疗中心间的模型协作训练,促进知识交换而不泄露数据隐私。
- 原始联邦学习存在服务器故障和性能优化问题,特别是在数据分布不均的环境下。
- 提出Gossip对比互学习(GCML)框架,以优化分布式环境中的个性化模型。
- 采用Gossip协议实现灵活稳健的点对点通信,提高知识交换效率。
- 引入深度对比互学习(DCML),鼓励本地与传入模型间的知识转移。
- GCML框架通过结合多种策略,在多个公开数据集上表现优异,优于传统联邦学习方法。
- GCML框架降低了通信开销,具有现实部署的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

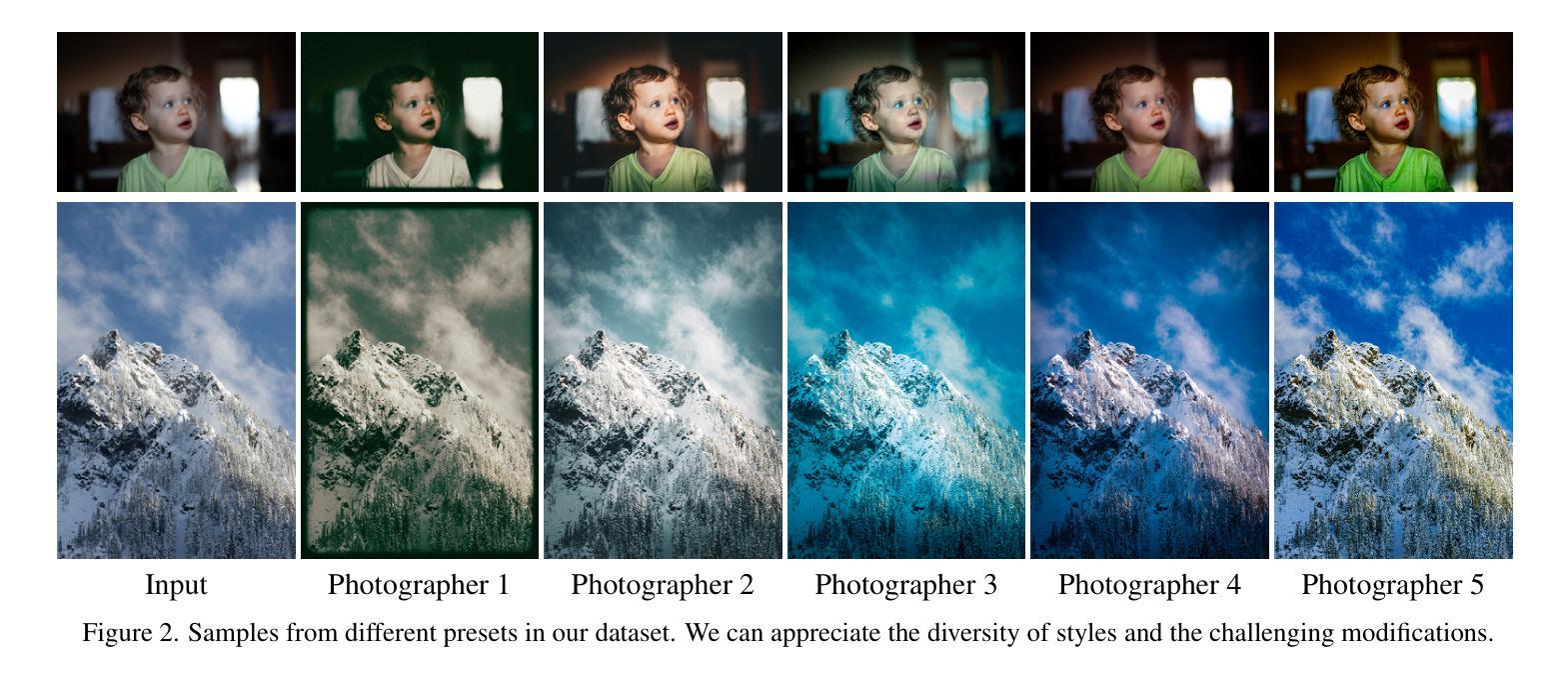
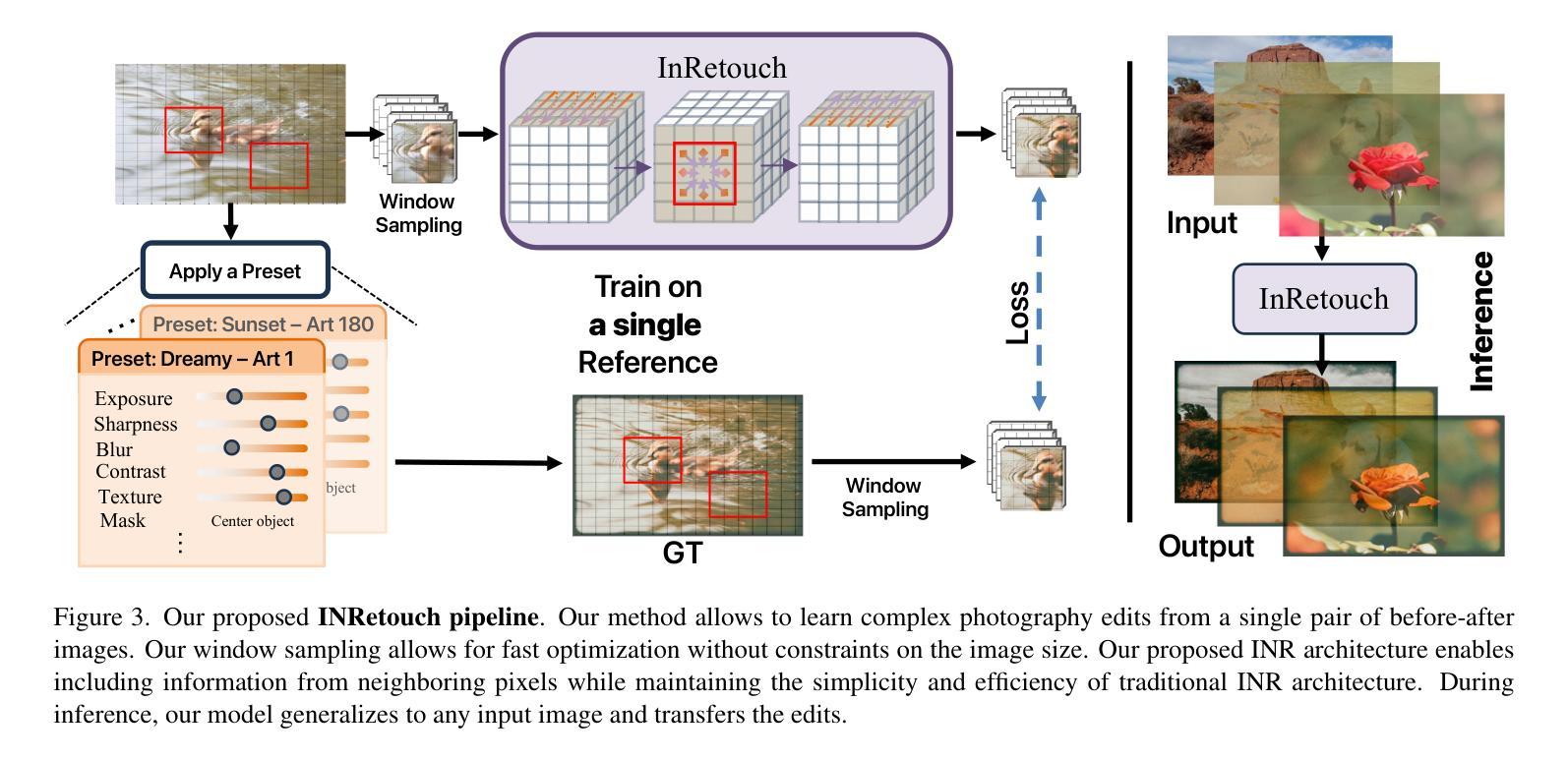
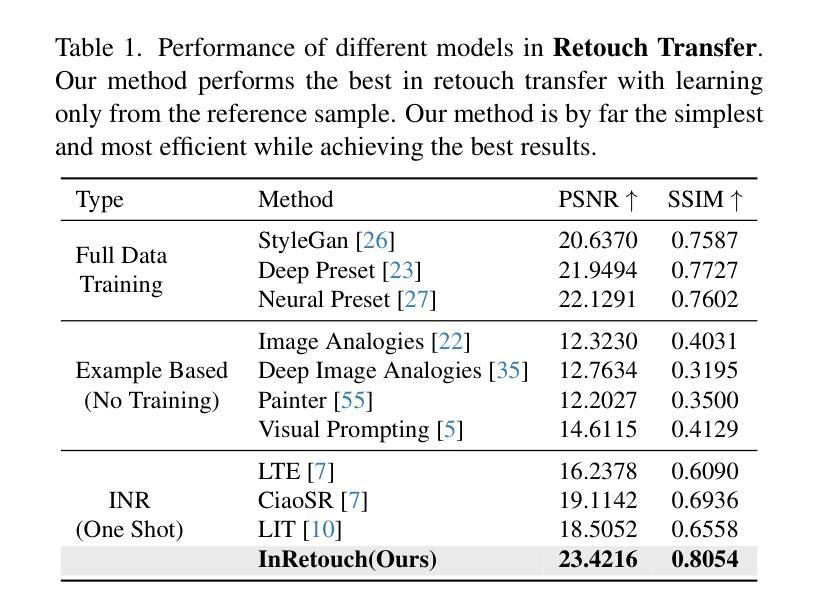
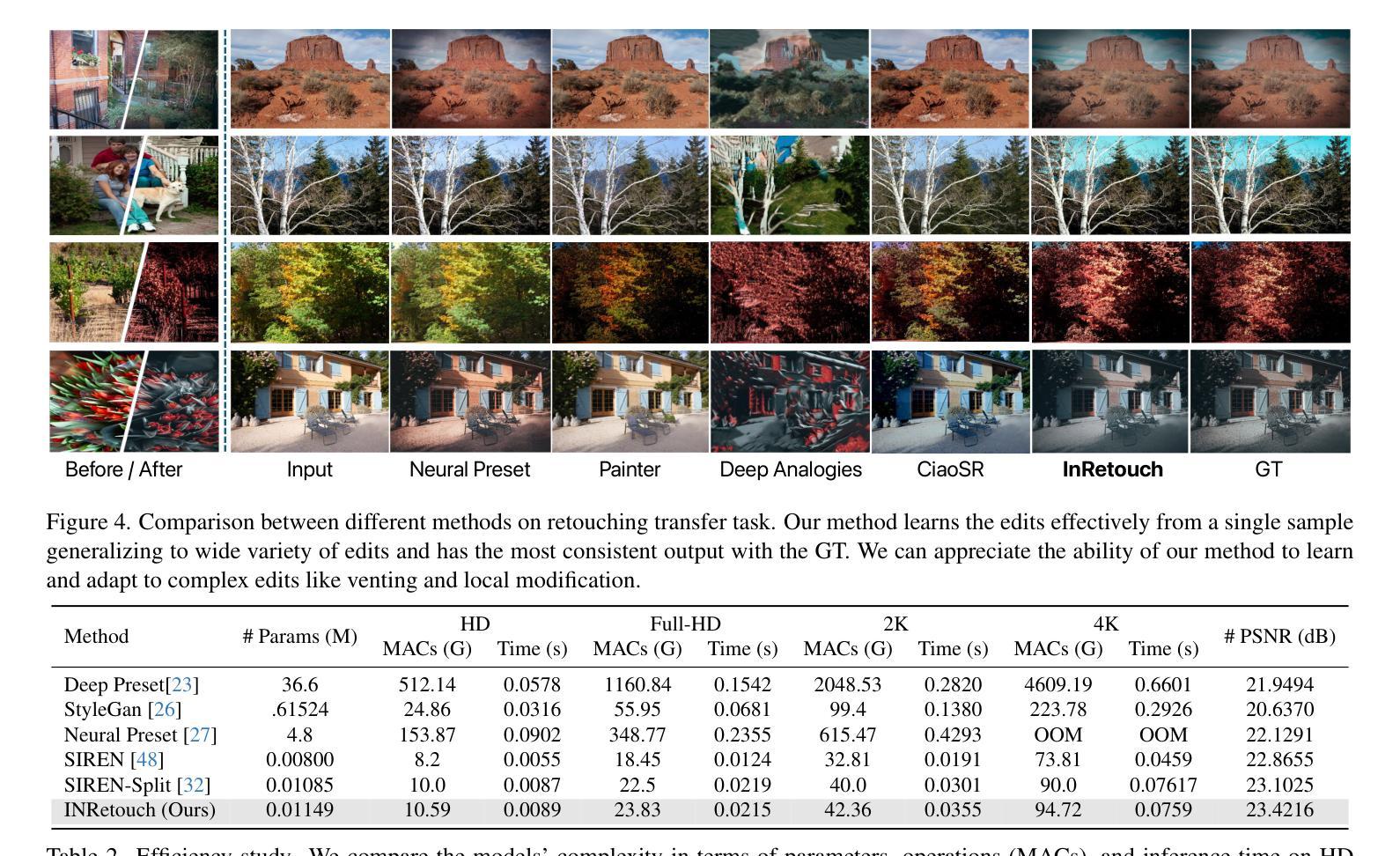
INRetouch: Context Aware Implicit Neural Representation for Photography Retouching
Authors:Omar Elezabi, Marcos V. Conde, Zongwei Wu, Radu Timofte
Professional photo editing remains challenging, requiring extensive knowledge of imaging pipelines and significant expertise. While recent deep learning approaches, particularly style transfer methods, have attempted to automate this process, they often struggle with output fidelity, editing control, and complex retouching capabilities. We propose a novel retouch transfer approach that learns from professional edits through before-after image pairs, enabling precise replication of complex editing operations. We develop a context-aware Implicit Neural Representation that learns to apply edits adaptively based on image content and context, and is capable of learning from a single example. Our method extracts implicit transformations from reference edits and adaptively applies them to new images. To facilitate this research direction, we introduce a comprehensive Photo Retouching Dataset comprising 100,000 high-quality images edited using over 170 professional Adobe Lightroom presets. Through extensive evaluation, we demonstrate that our approach not only surpasses existing methods in photo retouching but also enhances performance in related image reconstruction tasks like Gamut Mapping and Raw Reconstruction. By bridging the gap between professional editing capabilities and automated solutions, our work presents a significant step toward making sophisticated photo editing more accessible while maintaining high-fidelity results. Check the Project Page at https://omaralezaby.github.io/inretouch for more Results and information about Code and Dataset availability.
专业照片编辑仍然是一个挑战,需要深入了解成像管道和大量的专业知识。尽管最近的深度学习技术,尤其是风格转换方法,已经尝试自动完成此过程,但它们在输出保真度、编辑控制和复杂润饰功能方面往往面临困难。我们提出了一种新颖的润饰转换方法,它通过专业编辑前后的图像对进行学习,能够精确复制复杂的编辑操作。我们开发了一种上下文感知的隐式神经表示,它可以根据图像内容和上下文学习自适应应用编辑,并且能够从单个示例中学习。我们的方法从参考编辑中提取隐式转换,并自适应地应用于新图像。为了促进这一研究方向,我们引入了一个全面的照片润饰数据集,包含使用超过170种专业Adobe Lightroom预设编辑的10万张高质量图像。通过广泛评估,我们证明我们的方法不仅在照片润饰方面超越了现有方法,而且在相关图像重建任务(如色域映射和原始重建)方面也提高了性能。通过缩小专业编辑能力和自动化解决方案之间的差距,我们的工作在使复杂照片编辑更加易于访问的同时保持高保真结果方面迈出了重要一步。有关更多结果和关于代码和数据集可用性的信息,请访问项目页面:网站链接。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究提出一种新颖的照片修饰转换方法,通过专业修饰前后的图像对进行学习,能够精确复制复杂的编辑操作。开发了一种基于上下文内容的隐式神经表示方法,能根据图像内容和上下文自适应地应用编辑,并从单个示例中学习。为此研究方向引入包含10万张高质量图片的综合照片修饰数据集,涵盖使用超过170种专业Adobe Lightroom预设的编辑。研究结果表明,该方法不仅在照片修饰方面超越现有方法,还在相关图像重建任务如色域映射和原始重建中提高性能。该研究在缩短专业编辑与自动化解决方案之间的差距方面迈出重要一步,使高级照片编辑更加易于实现并保持高质量结果。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究解决了专业照片编辑的挑战,包括成像管道知识和专业技能的广泛需求。
- 通过对专业修饰前后的图像对进行学习,能够精确复制复杂的编辑操作。
- 开发了一种基于上下文内容的隐式神经表示方法,自适应地应用编辑。
- 方法能够从单个示例中学习并提取隐式转换。
- 研究引入了包含大量高质量图片的综合照片修饰数据集。
- 结果显示,该方法在照片修饰和图像重建任务上超越了现有方法。
点此查看论文截图


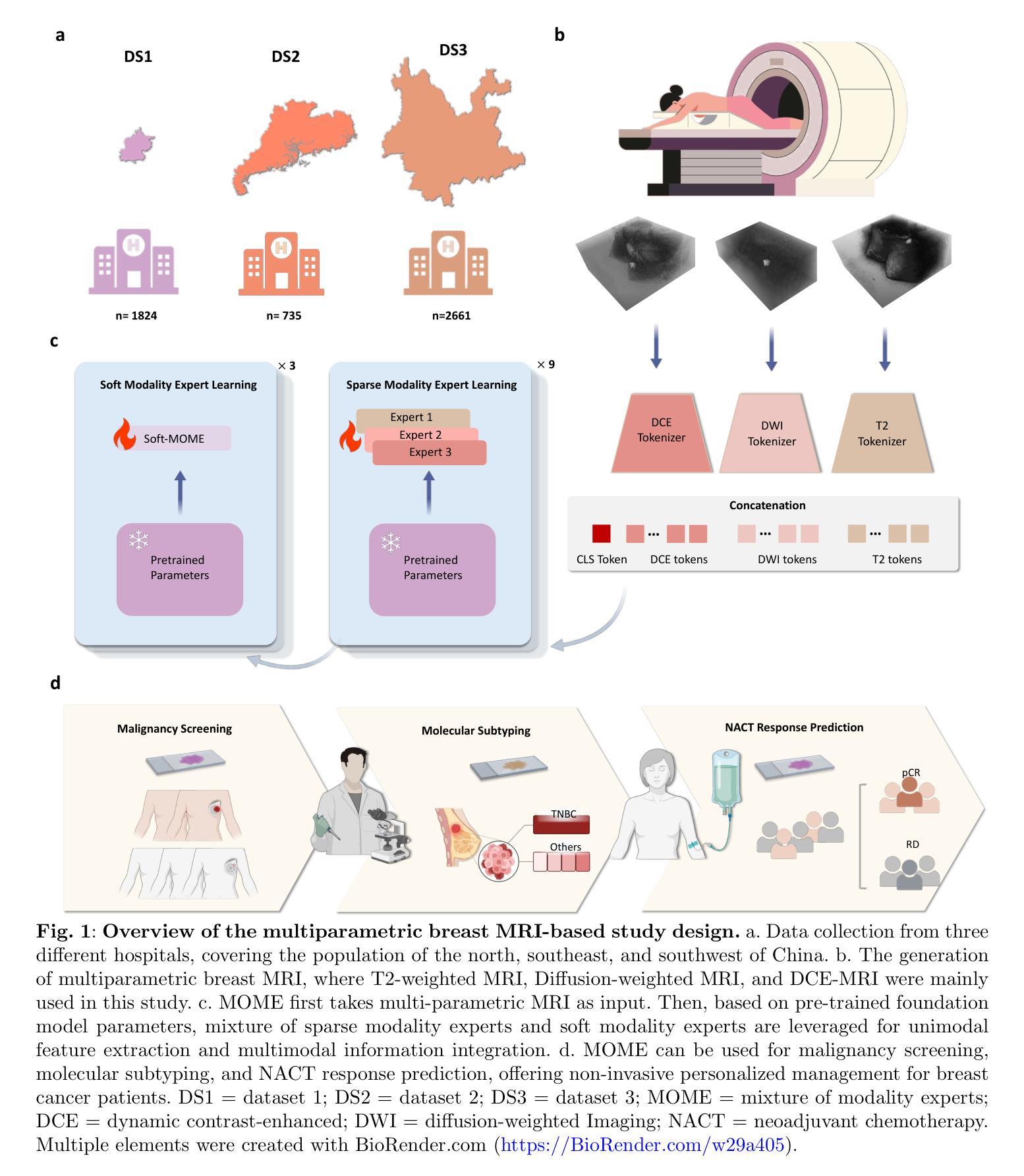
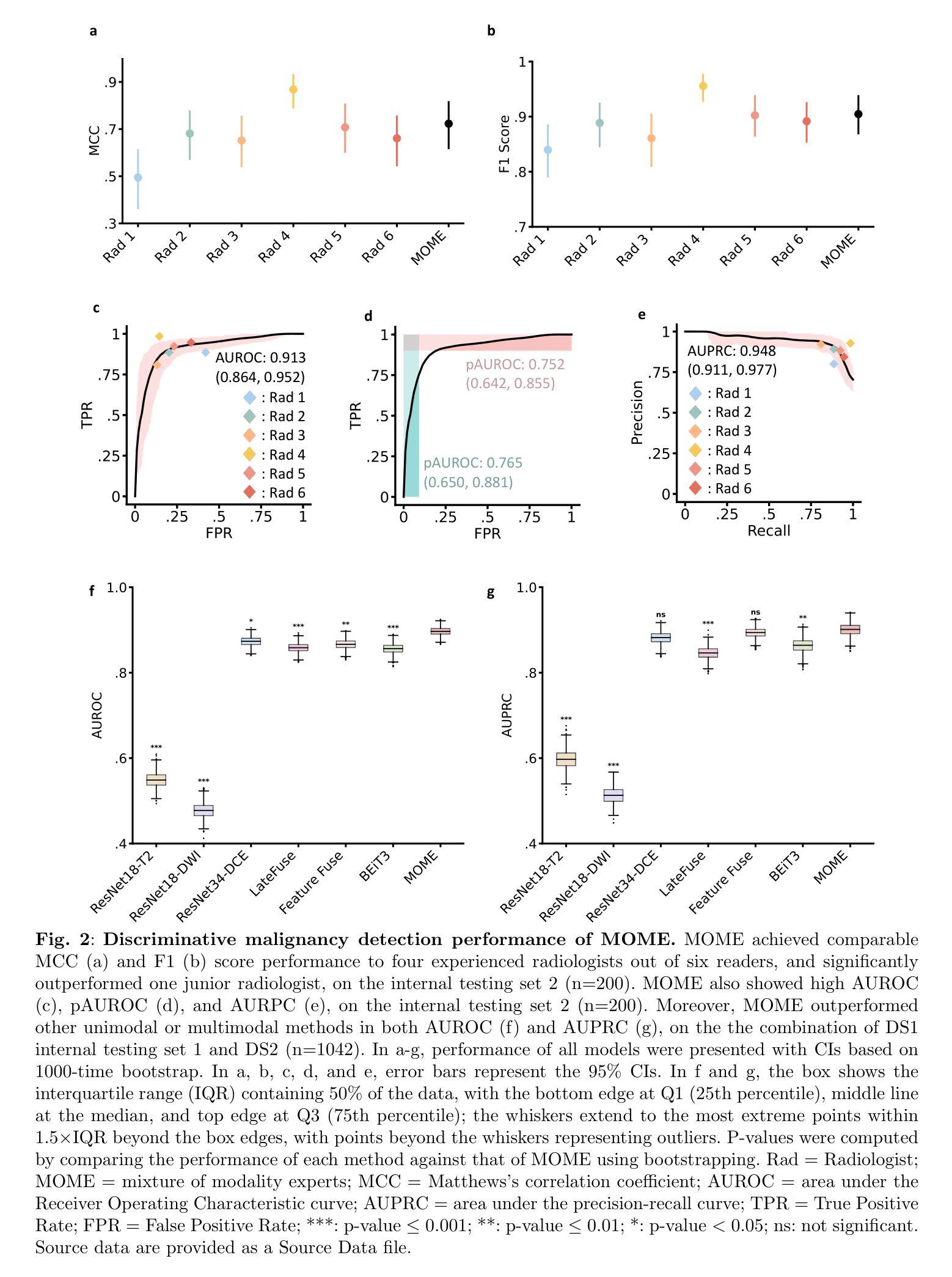
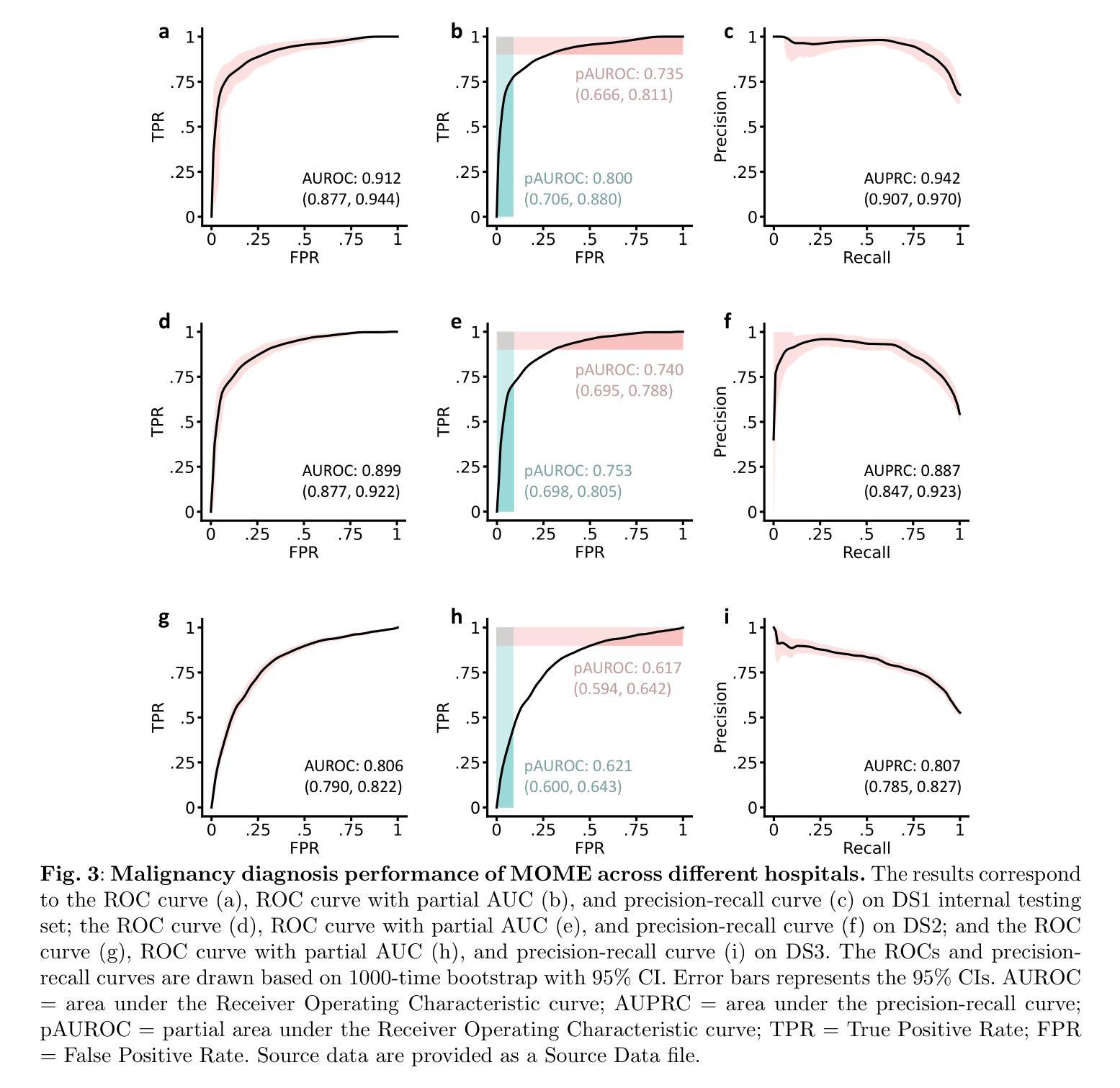
A Large Model for Non-invasive and Personalized Management of Breast Cancer from Multiparametric MRI
Authors:Luyang Luo, Mingxiang Wu, Mei Li, Yi Xin, Qiong Wang, Varut Vardhanabhuti, Winnie CW Chu, Zhenhui Li, Juan Zhou, Pranav Rajpurkar, Hao Chen
Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) demonstrates the highest sensitivity for breast cancer detection among imaging modalities and is standard practice for high-risk women. Interpreting the multi-sequence MRI is time-consuming and prone to subjective variation. We develop a large mixture-of-modality-experts model (MOME) that integrates multiparametric MRI information within a unified structure, leveraging breast MRI scans from 5,205 female patients in China for model development and validation. MOME matches four senior radiologists’ performance in identifying breast cancer and outperforms a junior radiologist. The model is able to reduce unnecessary biopsies in Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) 4 patients, classify triple-negative breast cancer, and predict pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. MOME further supports inference with missing modalities and provides decision explanations by highlighting lesions and measuring modality contributions. To summarize, MOME exemplifies an accurate and robust multimodal model for noninvasive, personalized management of breast cancer patients via multiparametric MRI. Code is available at https://github.com/LLYXC/MOME/tree/main.
乳腺磁共振成像(MRI)在成像模式中对乳腺癌检测具有最高的灵敏度,是高风险女性的标准实践。解释多序列MRI耗时且容易出现主观差异。我们开发了一种大型混合模式专家模型(MOME),该模型在统一结构中整合多参数MRI信息,利用中国5205名女性患者的乳腺MRI扫描进行模型开发和验证。MOME的乳腺癌识别性能与四名资深放射科医生相匹配,并优于初级放射科医生。该模型能够减少乳腺影像报告和数据系统(BI-RADS)4级患者的不必要活检,对三阴性乳腺癌进行分类,并预测新辅助化疗的病理完全反应。MOME还支持推断缺失的模式,并通过突出病变和测量模式贡献来提供决策解释。总之,MOME通过多参数MRI展示了准确且稳健的多模式模型,可用于非侵入式、个性化的乳腺癌患者管理。代码可在https://github.com/LLYXC/MOME/tree/main获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Nature Communications 2025
Summary
发展了一种大型混合模态专家模型(MOME),整合多参数MRI信息于统一结构内,用于乳腺癌检测。该模型性能与四位资深放射科医生相匹配,在识别乳腺癌方面优于初级放射科医生。MOME能减少不必要的活检,分类三阴性乳腺癌,预测新辅助化疗的病理完全反应。该模型支持推理缺失模态并提供决策解释,通过突出病变和测量模态贡献来支持。总之,MOME是一个准确、稳健的多模态模型,可通过多参数MRI实现乳腺癌患者的无创、个性化管理。
Key Takeaways
- MOME模型利用多参数MRI信息,展示了在乳腺癌检测方面的高敏感性。
- 模型开发使用了来自中国5,205名女性的乳腺MRI扫描数据。
- MOME与资深放射学家在识别乳腺癌方面的性能相匹配,并优于初级放射学家。
- MOME能够减少不必要的活检,特别是在BI-RADS 4患者中。
- 该模型能够分类三阴性乳腺癌,并预测新辅助化疗的病理完全反应。
- MOME支持在缺失模态的情况下进行推理,并提供决策解释。
点此查看论文截图

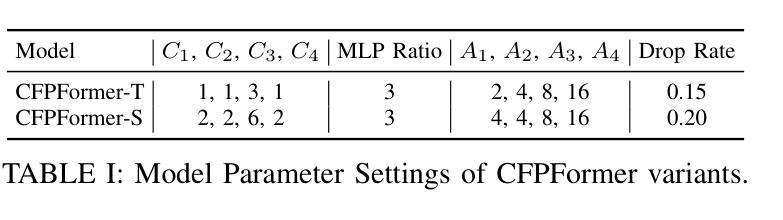
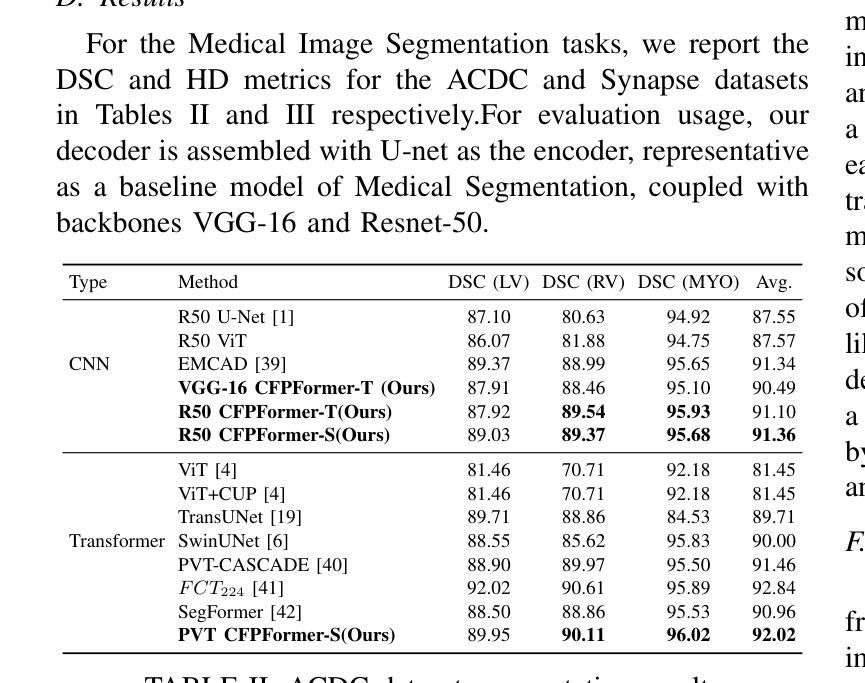
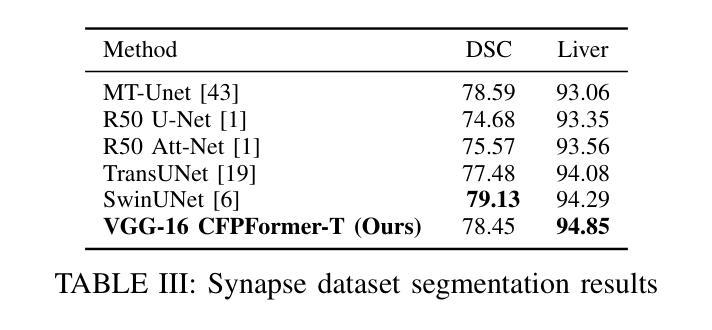
CFPFormer: Feature-pyramid like Transformer Decoder for Segmentation and Detection
Authors:Hongyi Cai, Mohammad Mahdinur Rahman, Wenzhen Dong, Jingyu Wu
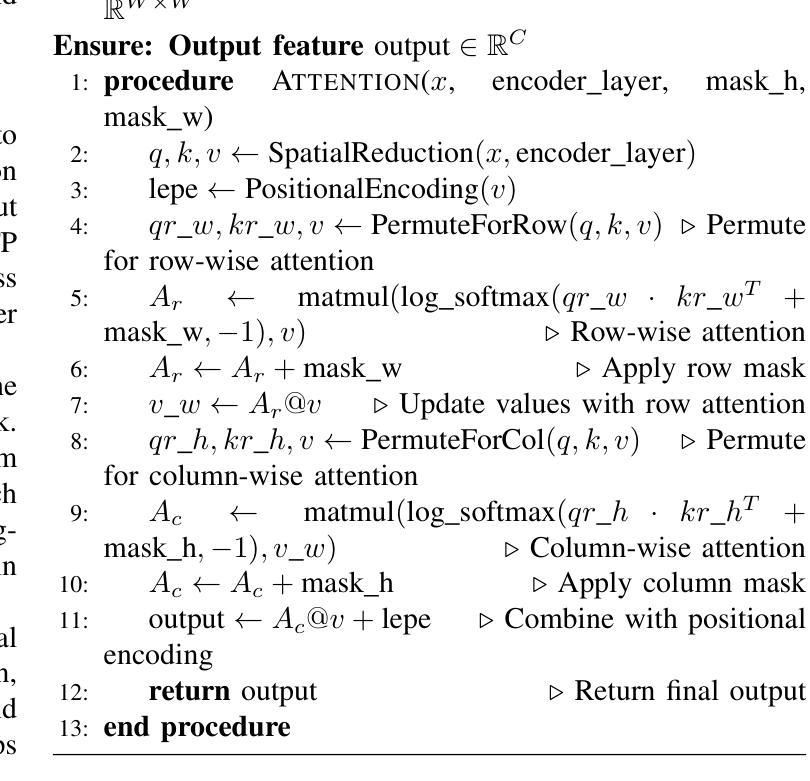
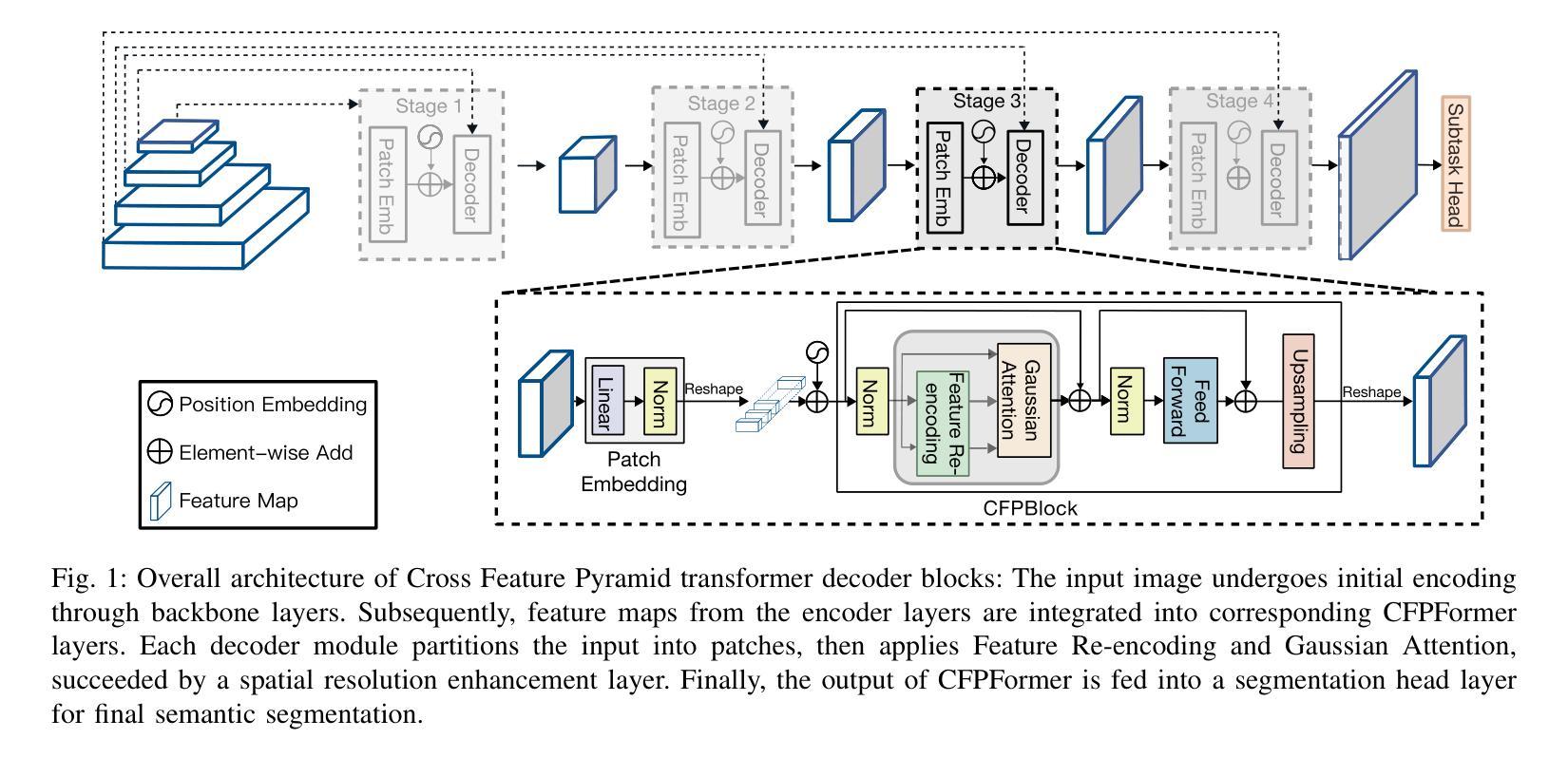
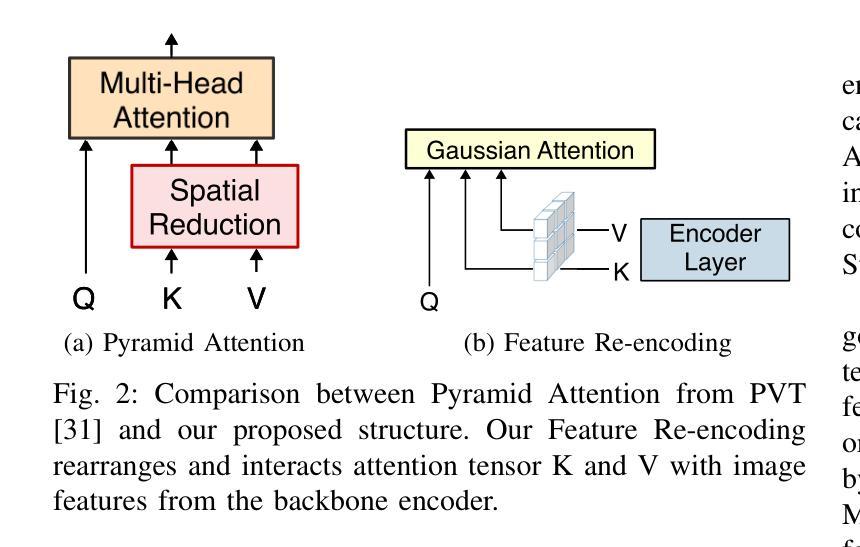
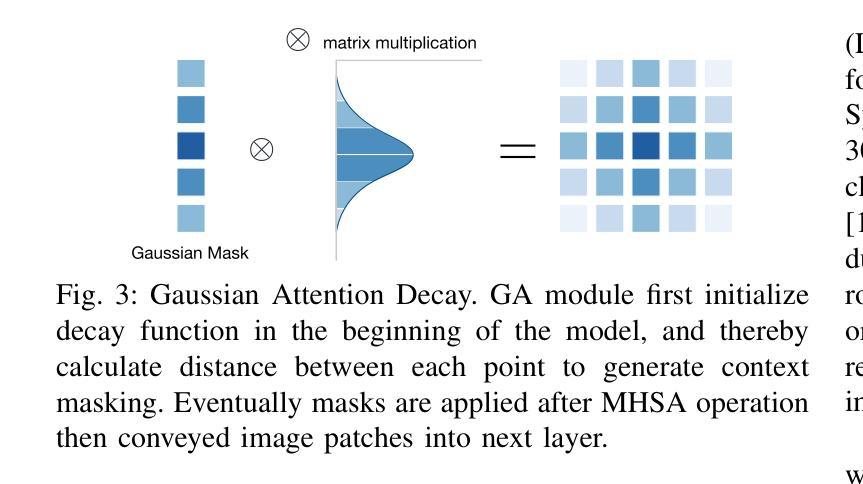
Feature pyramids have been widely adopted in convolutional neural networks and transformers for tasks in medical image segmentation. However, existing models generally focus on the Encoder-side Transformer for feature extraction. We further explore the potential in improving the feature decoder with a well-designed architecture. We propose Cross Feature Pyramid Transformer decoder (CFPFormer), a novel decoder block that integrates feature pyramids and transformers. Even though transformer-like architecture impress with outstanding performance in segmentation, the concerns to reduce the redundancy and training costs still exist. Specifically, by leveraging patch embedding, cross-layer feature concatenation mechanisms, CFPFormer enhances feature extraction capabilities while complexity issue is mitigated by our Gaussian Attention. Benefiting from Transformer structure and U-shaped connections, our work is capable of capturing long-range dependencies and effectively up-sample feature maps. Experimental results are provided to evaluate CFPFormer on medical image segmentation datasets, demonstrating the efficacy and effectiveness. With a ResNet50 backbone, our method achieves 92.02% Dice Score, highlighting the efficacy of our methods. Notably, our VGG-based model outperformed baselines with more complex ViT and Swin Transformer backbone.
特征金字塔已广泛应用于卷积神经网络和变压器中,用于医学图像分割任务。然而,现有模型通常专注于特征提取的编码器侧变压器。我们进一步探索了通过精心设计的架构改进特征解码器的潜力。我们提出了跨特征金字塔变压器解码器(CFPFormer),这是一种新的解码器块,它集成了特征金字塔和变压器。尽管变压器式的架构在分割方面表现出卓越的性能,但减少冗余和训练成本的担忧仍然存在。具体来说,通过利用补丁嵌入、跨层特征拼接机制,CFPFormer增强了特征提取能力,而复杂性问题则通过我们的高斯注意力得到了缓解。得益于变压器结构和U形连接,我们的工作能够捕捉长距离依赖关系并有效地上采样特征图。实验结果为CFPFormer在医学图像分割数据集上的评估提供了依据,证明了其有效性和有效性。使用ResNet50骨干网,我们的方法实现了92.02%的Dice得分,凸显了我们方法的有效性。值得注意的是,我们基于VGG的模型超越了具有更复杂ViT和Swin Transformer骨干网的基线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探索了在医学图像分割任务中,利用特征金字塔和变压器结构改进特征解码器的潜力。提出了一种新型的解码器块——Cross Feature Pyramid Transformer(CFPFormer),该解码器结合了特征金字塔和变压器的优点,能有效提升特征提取能力,并降低冗余和训练成本。实验结果表明,CFPFormer在医学图像分割数据集上表现出优异的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了Cross Feature Pyramid Transformer(CFPFormer)解码器,这是一种新型的解码器块,结合了特征金字塔和变压器的优点。
- CFPFormer通过利用补丁嵌入和跨层特征拼接机制,增强了特征提取能力。
- 与现有的模型相比,CFPFormer降低了模型的冗余和训练成本。
- 利用高斯注意力机制,CFPFormer缓解了复杂性问题。
- CFPFormer能够捕捉长距离依赖关系并有效地上采样特征图。
- 实验结果表明,CFPFormer在医学图像分割任务上具有良好的性能和效果。
点此查看论文截图