⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-09 更新
MSA-UNet3+: Multi-Scale Attention UNet3+ with New Supervised Prototypical Contrastive Loss for Coronary DSA Image Segmentation
Authors:Rayan Merghani Ahmed, Adnan Iltaf, Bin Li, Shoujun Zhou
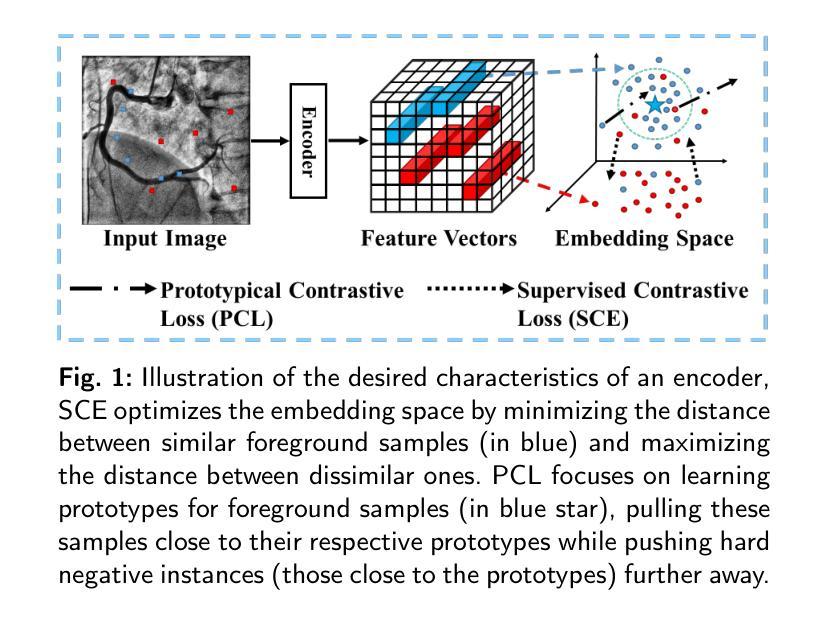
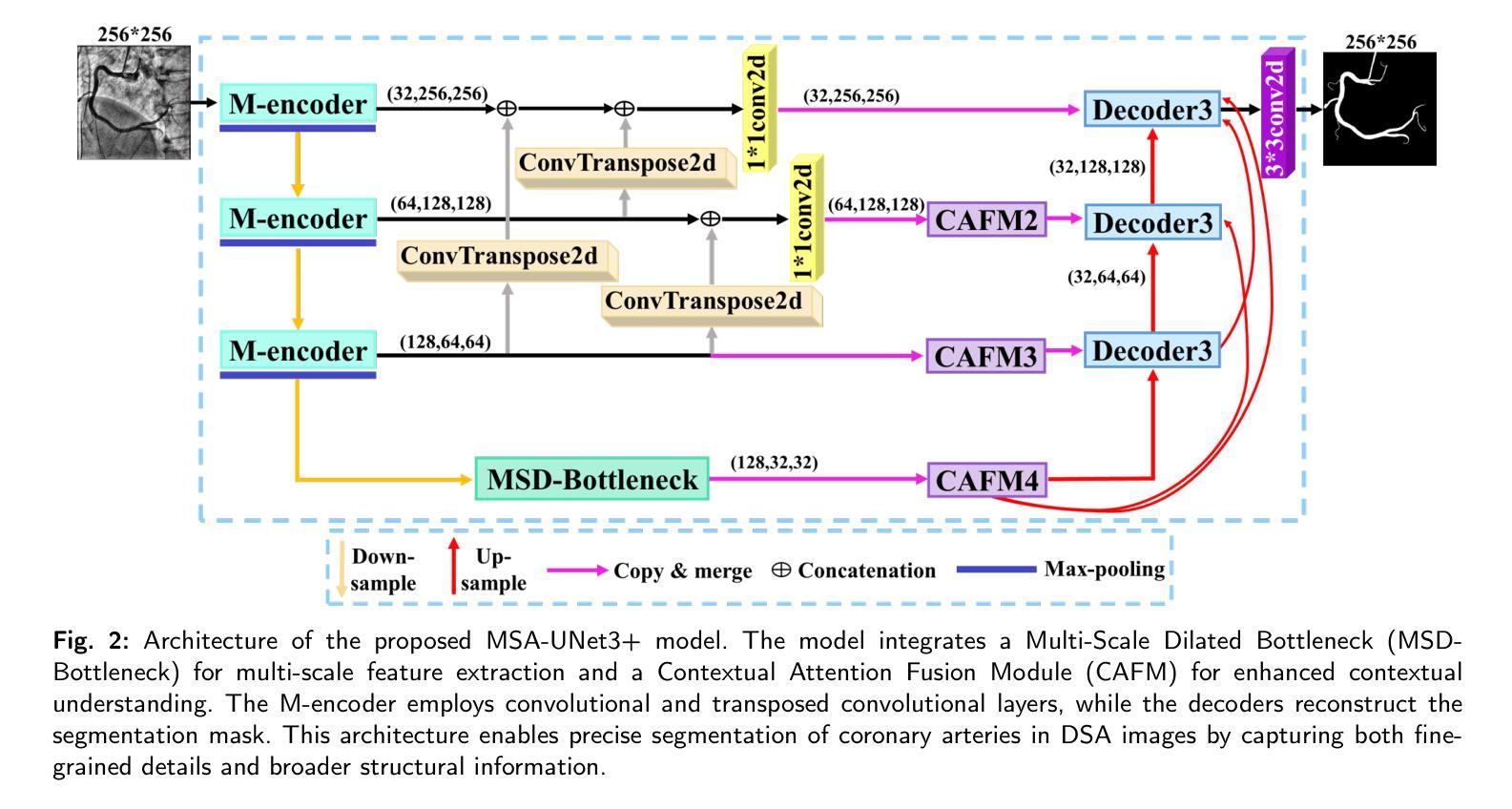
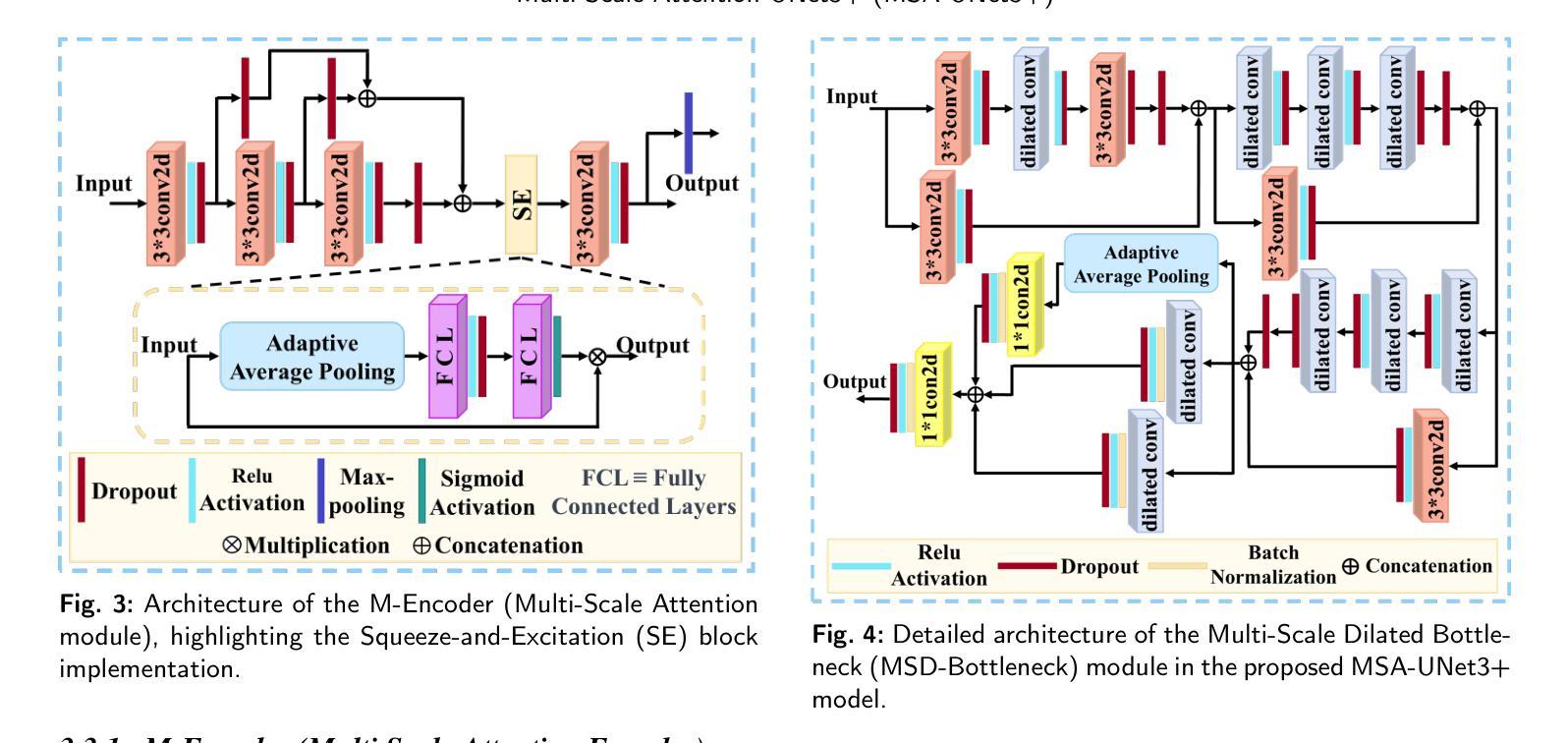
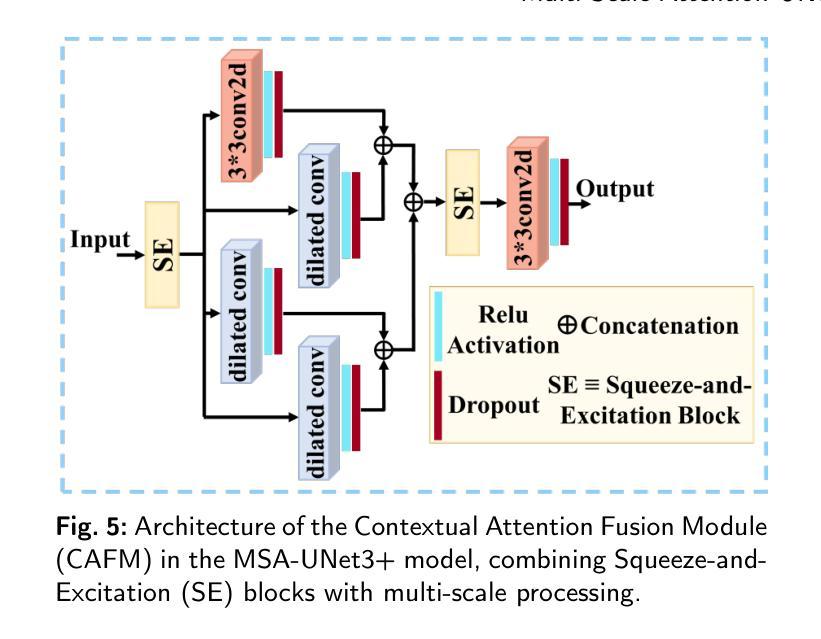
The accurate segmentation of coronary Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) images is essential for diagnosing and treating coronary artery diseases. Despite advances in deep learning-based segmentation, challenges such as low contrast, noise, overlapping structures, high intra-class variance, and class imbalance limit precise vessel delineation. To overcome these limitations, we propose the MSA-UNet3+: a Multi-Scale Attention enhanced UNet3+ architecture for coronary DSA image segmentation. The framework combined Multi-Scale Dilated Bottleneck (MSD-Bottleneck) with Contextual Attention Fusion Module (CAFM), which not only enhances multi-scale feature extraction but also preserve fine-grained details, and improve contextual understanding. Furthermore, we propose a new Supervised Prototypical Contrastive Loss (SPCL), which combines supervised and prototypical contrastive learning to minimize class imbalance and high intra-class variance by focusing on hard-to-classified background samples. Experiments carried out on a private coronary DSA dataset demonstrate that MSA-UNet3+ outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving a Dice coefficient of 87.73%, an F1-score of 87.78%, and significantly reduced Average Surface Distance (ASD) and Average Contour Distance (ACD). The developed framework provides clinicians with precise vessel segmentation, enabling accurate identification of coronary stenosis and supporting informed diagnostic and therapeutic decisions. The code will be released at the following GitHub profile link https://github.com/rayanmerghani/MSA-UNet3plus.
冠状动脉数字减影血管造影(DSA)图像的准确分割对于冠状动脉疾病的诊断和治疗至关重要。尽管基于深度学习的分割技术有所进展,但低对比度、噪声、结构重叠、高类内方差和类别不平衡等挑战仍然限制了精确血管勾勒的实现。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了MSA-UNet3+:一种用于冠状动脉DSA图像分割的多尺度注意力增强UNet3+架构。该框架结合了多尺度膨胀瓶颈(MSD-Bottleneck)与上下文注意力融合模块(CAFM),这不仅可以增强多尺度特征提取,还可以保留精细细节,并提高对上下文的理解。此外,我们提出了一种新的监督原型对比损失(SPCL),它将监督学习与原型对比学习相结合,通过关注难以分类的背景样本,最小化类别不平衡和高类内方差。在私有冠状动脉DSA数据集上进行的实验表明,MSA-UNet3+优于最新方法,达到87.73%的Dice系数,87.78%的F1分数,以及显著降低的平均表面距离(ASD)和平均轮廓距离(ACD)。所开发的框架为临床医生提供了精确的血管分割,能够准确识别冠状动脉狭窄,为诊断和治疗的决策提供有力支持。代码将在以下GitHub个人主页链接发布:GitHub链接。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
Summary
冠状动脉数字减影血管造影(DSA)图像的精准分割对于冠状动脉疾病的诊断与治疗至关重要。面对低对比、噪声、结构重叠、高类内方差和类别不平衡等挑战,我们提出了MSA-UNet3+架构,结合了多尺度扩张瓶颈(MSD-Bottleneck)与上下文注意力融合模块(CAFM),不仅提升了多尺度特征提取能力,还保留了精细的纹理细节并增强了上下文理解。此外,我们还提出了全新的监督原型对比损失(SPCL),结合监督学习和原型对比学习,通过关注难以分类的背景样本,来最小化类别不平衡和高类内方差问题。在私有冠状动脉DSA数据集上的实验表明,MSA-UNet3+较现有方法表现更优,达到了87.73%的Dice系数和87.78%的F1分数,平均表面距离(ASD)和平均轮廓距离(ACD)也显著降低。这为临床医生提供了精确的血管分割,有助于准确识别冠状动脉狭窄,支持医生做出准确的诊断和治疗方法选择。
Key Takeaways
- 冠状动脉DSA图像分割对诊断治疗至关重要。
- MSA-UNet3+架构结合了多尺度扩张瓶颈和上下文注意力融合模块,提升了特征提取和上下文理解。
- 新提出的监督原型对比损失(SPCL)有助于解决类别不平衡和高类内方差问题。
- MSA-UNet3+在私有冠状动脉DSA数据集上表现优异,Dice系数和F1分数较高。
- 该框架提供了精确的血管分割,有助于识别冠状动脉狭窄。
- 框架的开源代码将发布在GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图

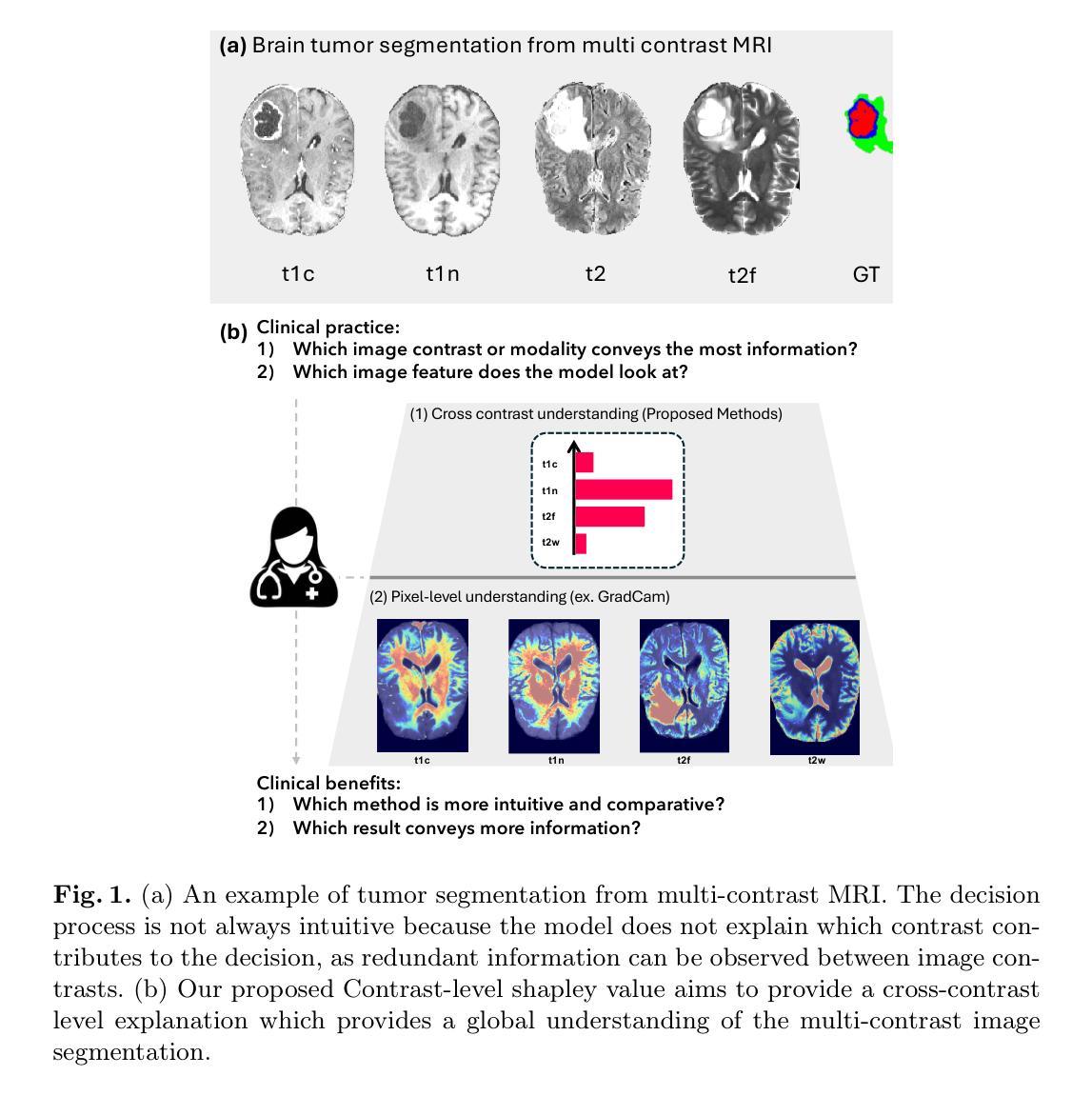
Here Comes the Explanation: A Shapley Perspective on Multi-contrast Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Tianyi Ren, Juampablo Heras Rivera, Hitender Oswal, Yutong Pan, Agamdeep Chopra, Jacob Ruzevick, Mehmet Kurt
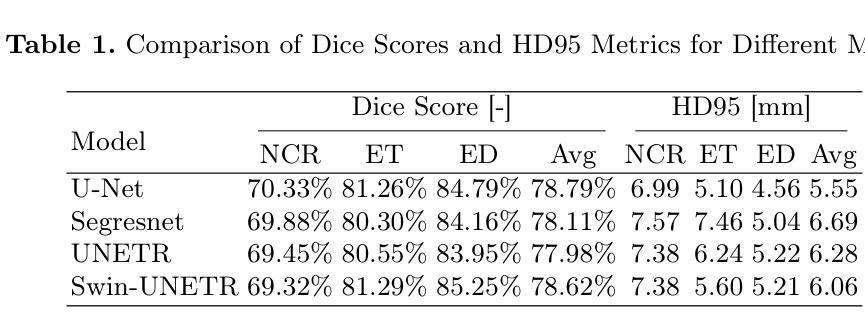
Deep learning has been successfully applied to medical image segmentation, enabling accurate identification of regions of interest such as organs and lesions. This approach works effectively across diverse datasets, including those with single-image contrast, multi-contrast, and multimodal imaging data. To improve human understanding of these black-box models, there is a growing need for Explainable AI (XAI) techniques for model transparency and accountability. Previous research has primarily focused on post hoc pixel-level explanations, using methods gradient-based and perturbation-based apporaches. These methods rely on gradients or perturbations to explain model predictions. However, these pixel-level explanations often struggle with the complexity inherent in multi-contrast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) segmentation tasks, and the sparsely distributed explanations have limited clinical relevance. In this study, we propose using contrast-level Shapley values to explain state-of-the-art models trained on standard metrics used in brain tumor segmentation. Our results demonstrate that Shapley analysis provides valuable insights into different models’ behavior used for tumor segmentation. We demonstrated a bias for U-Net towards over-weighing T1-contrast and FLAIR, while Swin-UNETR provided a cross-contrast understanding with balanced Shapley distribution.
深度学习已成功应用于医学图像分割,能够准确识别感兴趣区域,如器官和病变。该方法在多种数据集上均有效,包括单图像对比、多对比度和多模态成像数据。为了提高对这些黑盒模型的人类理解,对用于模型透明度和责任性的可解释人工智能(XAI)技术的需求日益增长。以往的研究主要集中在事后像素级解释上,使用基于梯度和基于扰动的方法。这些方法依赖于梯度或扰动来解释模型预测。然而,这些像素级解释往往难以应对多对比度磁共振成像(MRI)分割任务的固有复杂性,稀疏分布的解释临床相关性有限。本研究提出使用对比度级别的Shapley值来解释在脑肿瘤分割中使用的最新模型的标准指标训练结果。我们的结果表明,Shapley分析为不同模型的肿瘤分割行为提供了有价值的见解。我们证明了U-Net偏向于过度重视T1对比度和FLAIR,而Swin-UNETR提供了跨对比度的理解,具有平衡的Shapley分布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了深度学习在医学图像分割中的应用,特别是在多种数据集上的表现。为提高模型透明度和可解释性,采用可解释的AI(XAI)技术。研究使用对比水平的Shapley值来解释经过标准指标训练的模型在脑肿瘤分割中的行为。结果表明,Shapley分析有助于理解不同模型的肿瘤分割行为差异。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习成功应用于医学图像分割,能准确识别器官和病变等感兴趣区域。
- XAI技术用于提高模型的透明度和可解释性。
- 以往的解释方法主要基于像素级别,但在多对比度的磁共振成像(MRI)分割任务中存在局限性。
- Shapley分析提供了对不同模型行为的深入了解,特别是在肿瘤分割方面。
- U-Net模型偏向于过度重视T1对比和FLAIR,而Swin-UNETR提供了跨对比度的平衡理解。
点此查看论文截图

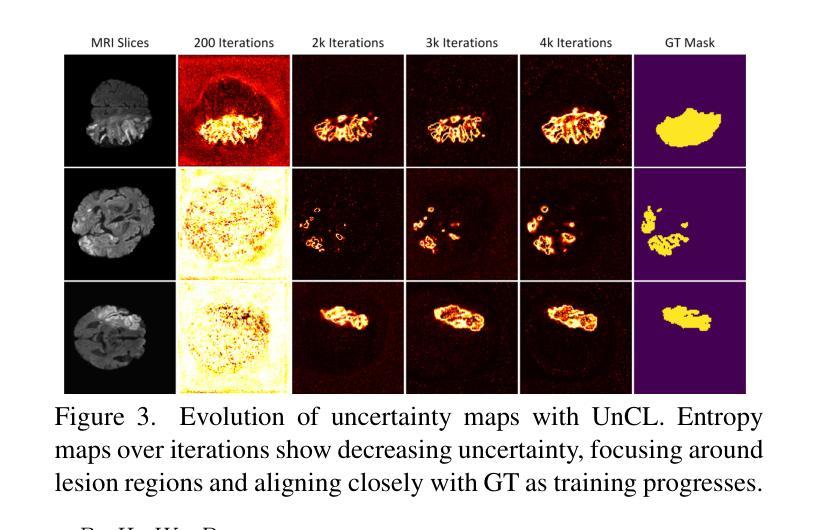
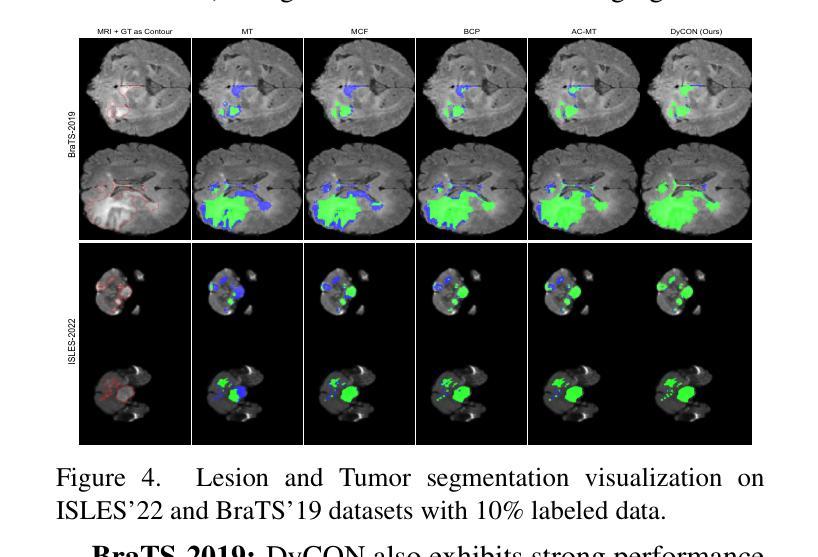
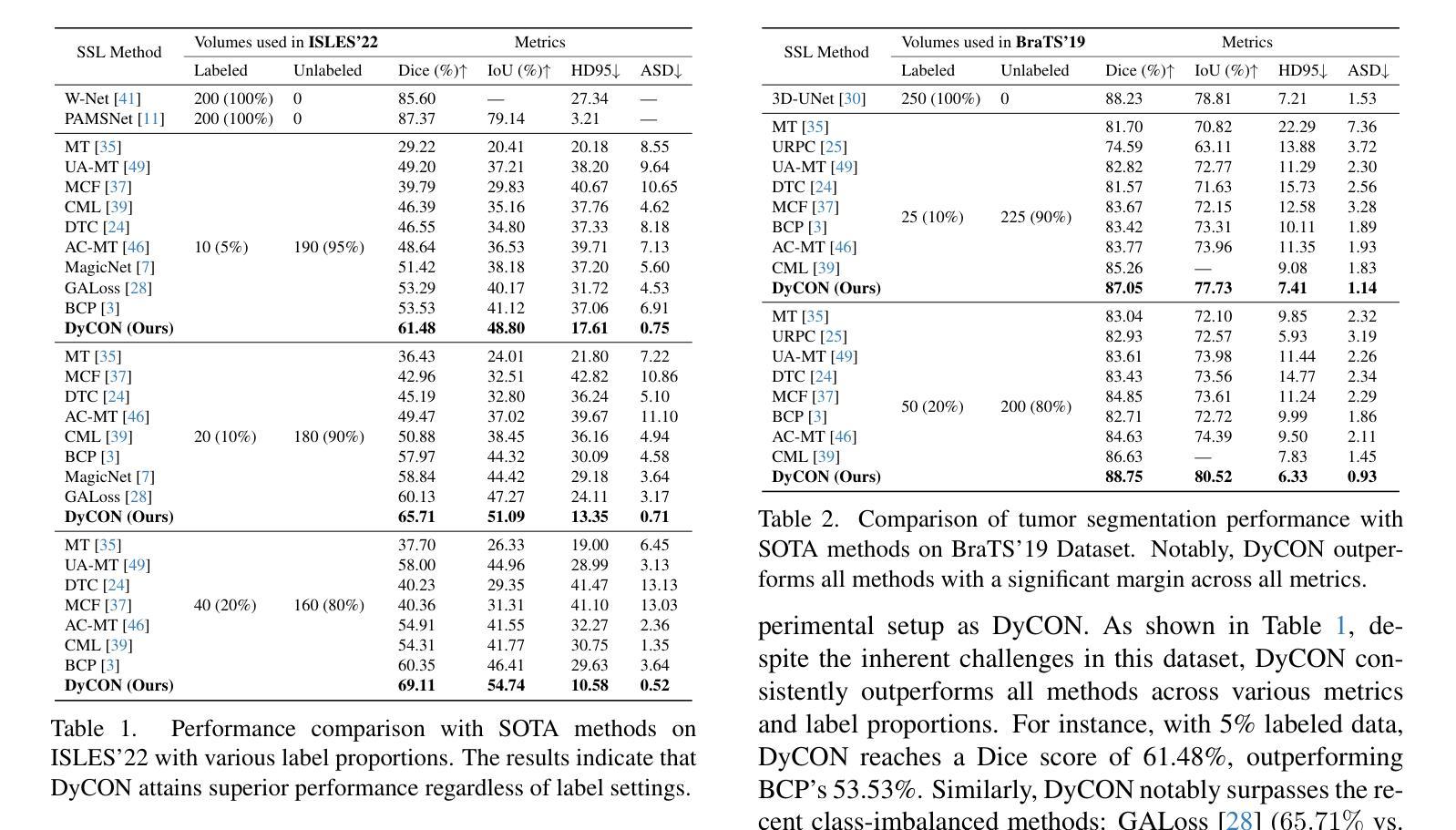
DyCON: Dynamic Uncertainty-aware Consistency and Contrastive Learning for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Maregu Assefa, Muzammal Naseer, Iyyakutti Iyappan Ganapathi, Syed Sadaf Ali, Mohamed L Seghier, Naoufel Werghi
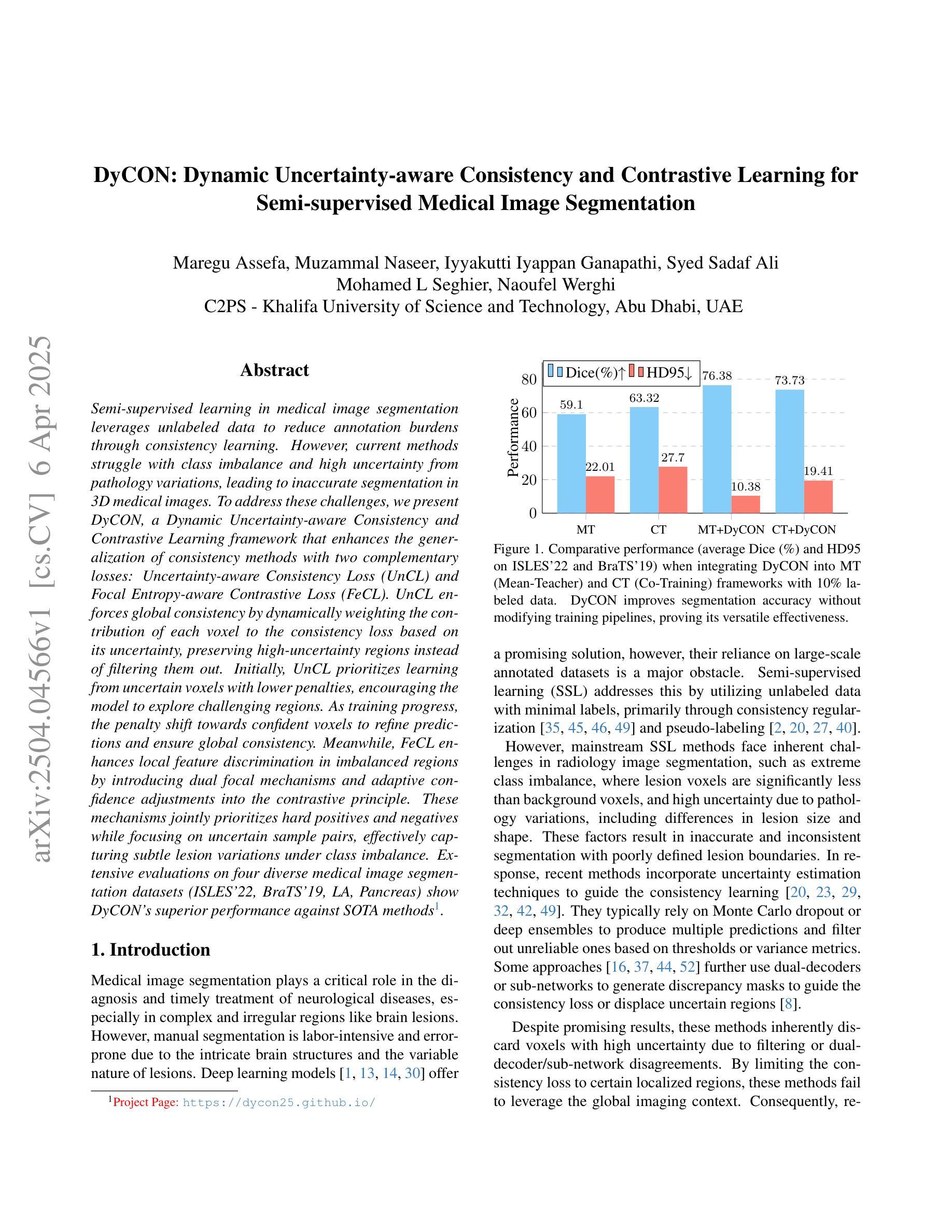
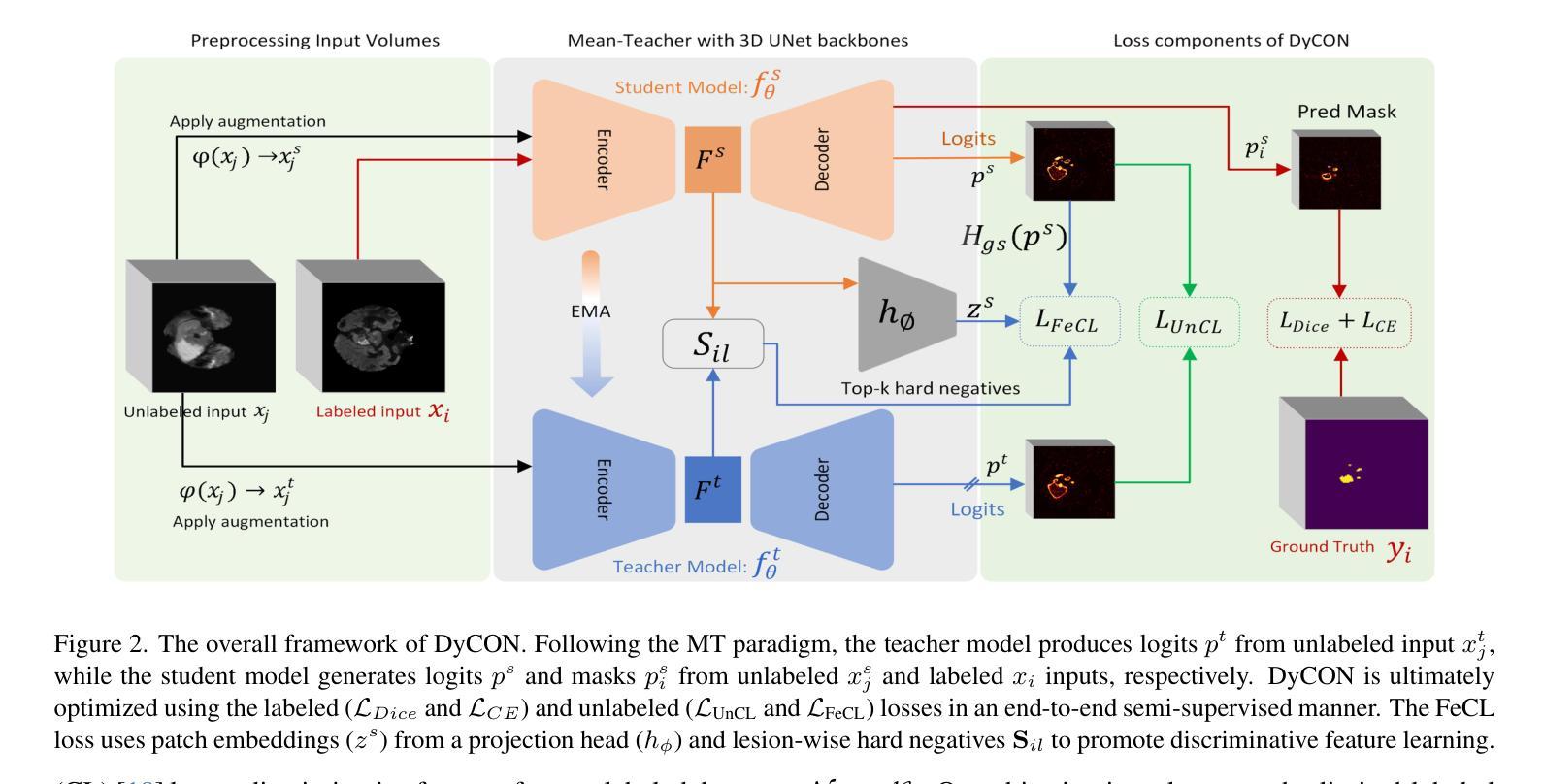
Semi-supervised learning in medical image segmentation leverages unlabeled data to reduce annotation burdens through consistency learning. However, current methods struggle with class imbalance and high uncertainty from pathology variations, leading to inaccurate segmentation in 3D medical images. To address these challenges, we present DyCON, a Dynamic Uncertainty-aware Consistency and Contrastive Learning framework that enhances the generalization of consistency methods with two complementary losses: Uncertainty-aware Consistency Loss (UnCL) and Focal Entropy-aware Contrastive Loss (FeCL). UnCL enforces global consistency by dynamically weighting the contribution of each voxel to the consistency loss based on its uncertainty, preserving high-uncertainty regions instead of filtering them out. Initially, UnCL prioritizes learning from uncertain voxels with lower penalties, encouraging the model to explore challenging regions. As training progress, the penalty shift towards confident voxels to refine predictions and ensure global consistency. Meanwhile, FeCL enhances local feature discrimination in imbalanced regions by introducing dual focal mechanisms and adaptive confidence adjustments into the contrastive principle. These mechanisms jointly prioritizes hard positives and negatives while focusing on uncertain sample pairs, effectively capturing subtle lesion variations under class imbalance. Extensive evaluations on four diverse medical image segmentation datasets (ISLES’22, BraTS’19, LA, Pancreas) show DyCON’s superior performance against SOTA methods.
医学图像分割中的半监督学习利用无标签数据通过一致性学习减少标注负担。然而,当前的方法在面临类别不平衡和高病理变化不确定性时,会在3D医学图像分割中产生不准确的分割结果。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了DyCON,一个动态感知不确定性的一致性对比学习框架,通过两种互补的损失增强了一致性方法的泛化能力:不确定性感知一致性损失(UnCL)和焦点熵感知对比损失(FeCL)。UnCL通过动态权衡每个体素对一致性损失的贡献来实现全局一致性,贡献大小取决于体素的不确定性,保留高不确定性区域而不是过滤掉它们。在训练初期,UnCL优先从不确定性较高的体素中学习并施加较低的惩罚,鼓励模型探索具有挑战性的区域。随着训练的进行,惩罚向确定性较高的体素转移,以优化预测并确保全局一致性。同时,FeCL通过引入双重焦点机制和自适应置信度调整来增强对比原则下的局部特征判别能力,特别是在类别不平衡的区域。这些机制共同优先处理难以区分的正样本和负样本,同时关注不确定的样本对,有效捕捉类别不平衡下的细微病变变化。在四个不同的医学图像分割数据集(ISLES’22、BraTS’19、LA、胰腺)上的广泛评估表明,DyCON的性能优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
本文主要介绍了针对半监督医学图像分割中面临的挑战(如类不平衡和高不确定性导致的病理变化),提出了一种名为DyCON的动态不确定性感知一致性对比学习框架。该框架结合了两种互补的损失:不确定性感知一致性损失(UnCL)和焦点熵感知对比损失(FeCL),旨在提高一致性方法的泛化能力。UnCL通过动态加权每个体素对一致性损失的贡献来保持全局一致性,同时优先学习不确定体素以鼓励模型探索困难区域。随着训练的进展,惩罚力度转向置信体素以改进预测并确保全局一致性。而FeCL通过引入双重焦点机制和自适应置信调整来增强不平衡区域的局部特征判别力。该框架在四个不同的医学图像分割数据集上的表现均优于当前最先进的方案。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督学习在医学图像分割中应用广泛,能够利用未标注数据减轻标注负担。
- 当前方法面临类不平衡和高不确定性导致的病理变化挑战,导致在三维医学图像分割中的准确性下降。
- DyCON框架结合了UnCL和FeCL两种互补损失,旨在提高一致性方法的泛化能力。
- UnCL通过动态加权每个体素对一致性损失的贡献来保持全局一致性,并优先学习不确定体素以鼓励模型探索困难区域。
- FeCL通过引入双重焦点机制和自适应置信调整来增强不平衡区域的局部特征判别力,能有效捕捉类不平衡下的细微病变差异。
点此查看论文截图
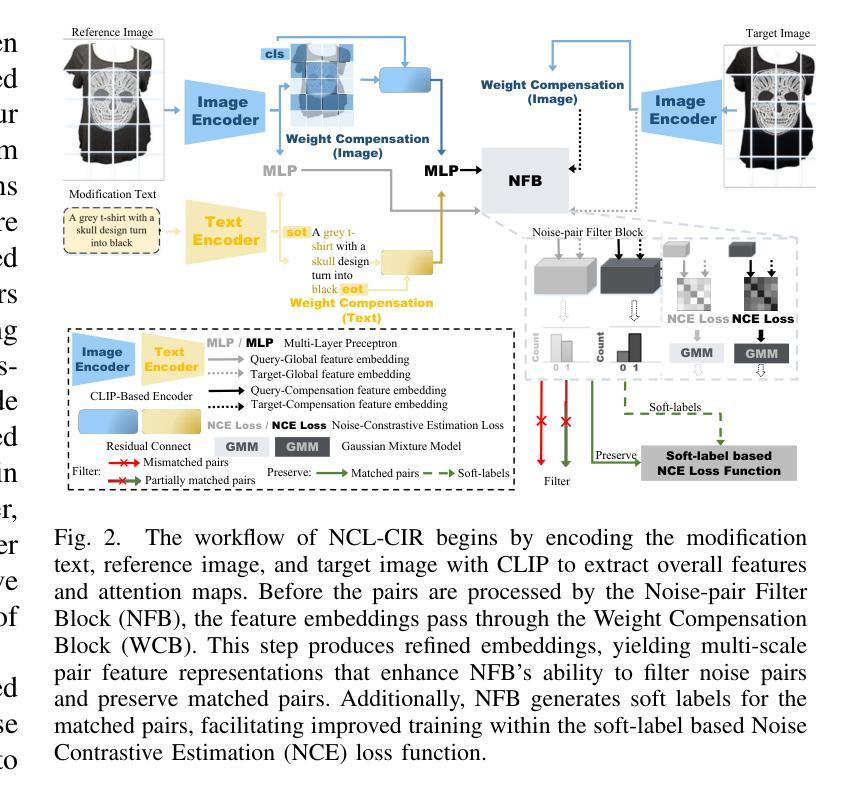
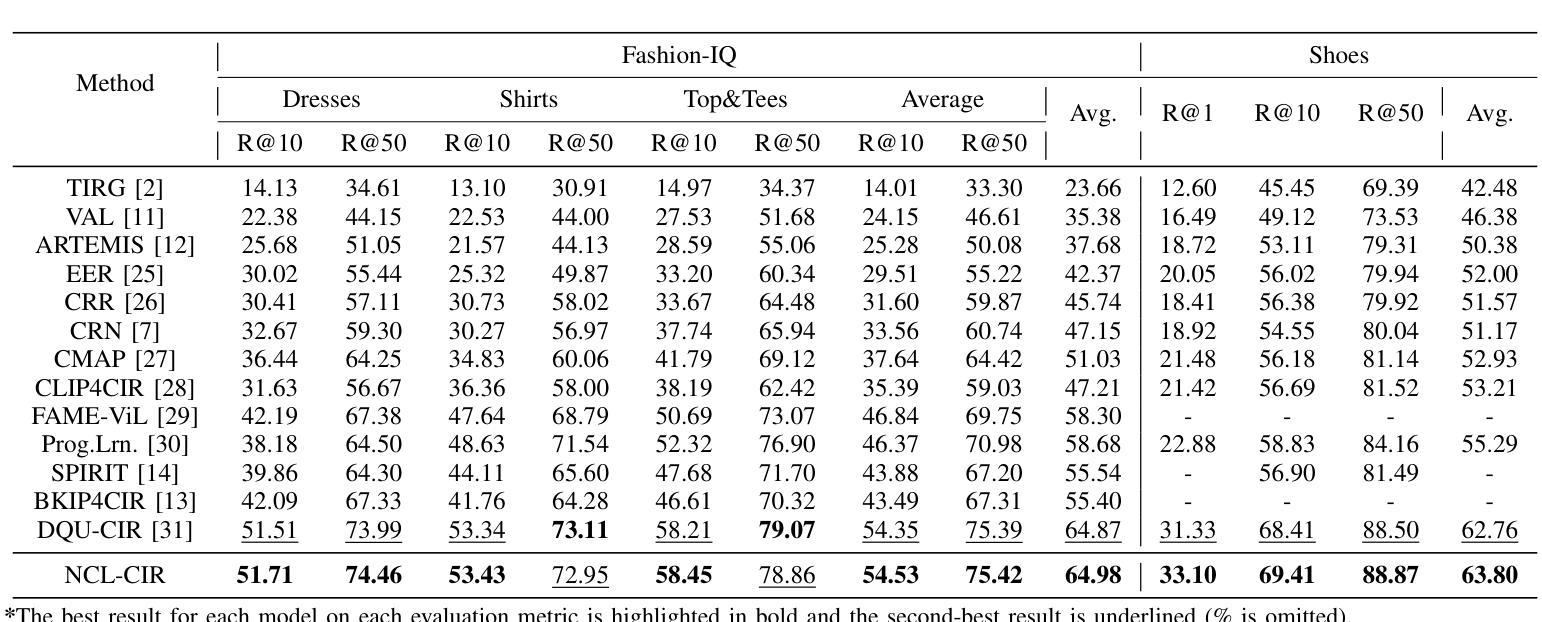
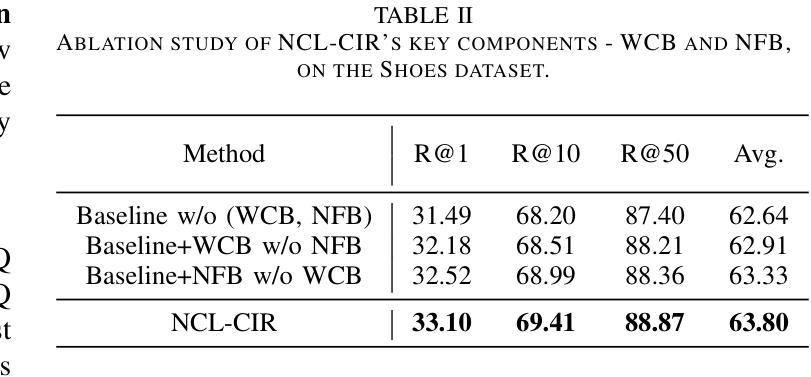
NCL-CIR: Noise-aware Contrastive Learning for Composed Image Retrieval
Authors:Peng Gao, Yujian Lee, Zailong Chen, Hui zhang, Xubo Liu, Yiyang Hu, Guquang Jing
Composed Image Retrieval (CIR) seeks to find a target image using a multi-modal query, which combines an image with modification text to pinpoint the target. While recent CIR methods have shown promise, they mainly focus on exploring relationships between the query pairs (image and text) through data augmentation or model design. These methods often assume perfect alignment between queries and target images, an idealized scenario rarely encountered in practice. In reality, pairs are often partially or completely mismatched due to issues like inaccurate modification texts, low-quality target images, and annotation errors. Ignoring these mismatches leads to numerous False Positive Pair (FFPs) denoted as noise pairs in the dataset, causing the model to overfit and ultimately reducing its performance. To address this problem, we propose the Noise-aware Contrastive Learning for CIR (NCL-CIR), comprising two key components: the Weight Compensation Block (WCB) and the Noise-pair Filter Block (NFB). The WCB coupled with diverse weight maps can ensure more stable token representations of multi-modal queries and target images. Meanwhile, the NFB, in conjunction with the Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) predicts noise pairs by evaluating loss distributions, and generates soft labels correspondingly, allowing for the design of the soft-label based Noise Contrastive Estimation (NCE) loss function. Consequently, the overall architecture helps to mitigate the influence of mismatched and partially matched samples, with experimental results demonstrating that NCL-CIR achieves exceptional performance on the benchmark datasets.
图像检索技术旨在使用多媒体查询找到目标图像,通过将图像与修改文本结合来精确定位目标。虽然最近的图像检索方法显示出潜力,但它们主要集中在通过数据增强或模型设计探索查询对(图像和文本)之间的关系。这些方法通常假设查询和目标图像之间的完美对齐,这在实践中很少遇到。实际上,由于不准确的修改文本、低质量的目标图像和注释错误等问题,配对通常部分或完全不匹配。忽略这些不匹配会导致数据集中的噪声对(False Positive Pair,FFP)增多,使模型过度拟合并最终降低其性能。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了用于图像检索的噪声感知对比学习(NCL-CIR),它包括两个关键组件:权重补偿块(WCB)和噪声配对滤波器块(NFB)。WCB与多种权重映射相结合,可以确保多媒体查询和目标图像的令牌表示更加稳定。同时,NFB结合高斯混合模型(GMM)通过评估损失分布来预测噪声对,并相应地生成软标签,从而设计基于软标签的噪声对比估计(NCE)损失函数。因此,整体架构有助于减轻不匹配和部分匹配样本的影响,实验结果表明,NCL-CIR在基准数据集上取得了出色的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Has been accepted by ICASSP2025
摘要
本文提出一种名为NCL-CIR的噪声感知对比学习方法,用于解决当前图像检索方法在处理实际应用中遇到的查询与图像不匹配问题。通过引入Weight Compensation Block(WCB)和Noise-pair Filter Block(NFB),提高了模型的稳健性和准确性。WCB结合多种权重映射,确保多模态查询和目标图像的令牌表示更加稳定。NFB结合高斯混合模型(GMM)预测噪声对,生成相应的软标签,用于设计基于软标签的噪声对比估计(NCE)损失函数。NCL-CIR整体架构能有效缓解不匹配和局部匹配样本的影响,在基准数据集上取得了卓越的性能表现。
关键见解
- Composed Image Retrieval (CIR) 使用多模态查询(结合图像和修改文本)来定位目标图像。
- 现有CIR方法主要关注查询对之间的关系,假设查询和目标图像完美对齐,但实践中常遇到不匹配问题。
- NCL-CIR 提出通过噪声感知对比学习来解决这一问题,包括Weight Compensation Block(WCB)和Noise-pair Filter Block(NFB)。
- WCB 结合不同权重映射,确保多模态查询和目标图像的令牌表示更稳定。
- NFB 利用高斯混合模型(GMM)预测噪声对,并生成软标签,为设计噪声对比估计损失函数奠定基础。
- NCL-CIR 架构有助于减轻不匹配和局部匹配样本的影响。
- 在基准数据集上的实验结果表明,NCL-CIR 实现了卓越的性能。
点此查看论文截图

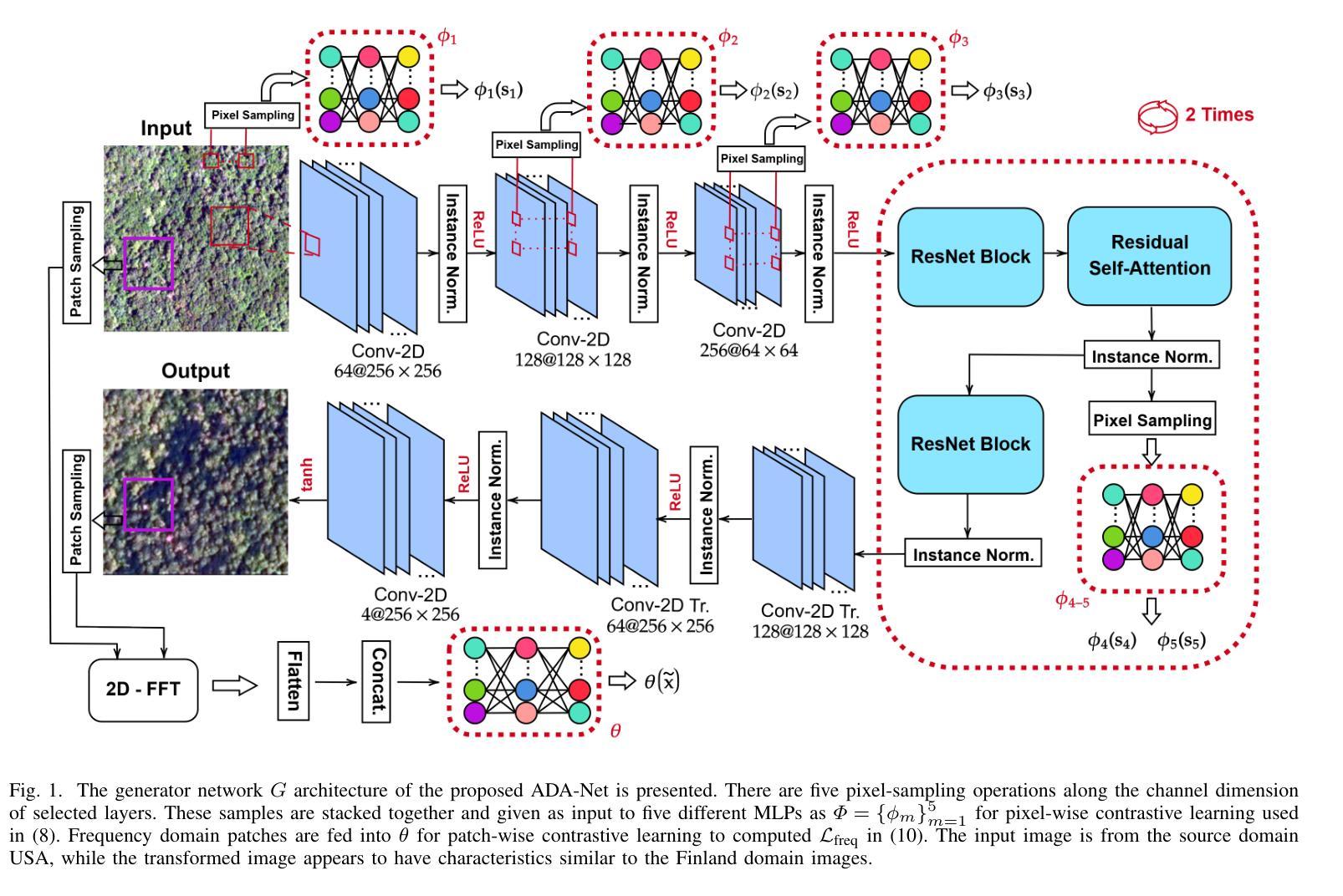
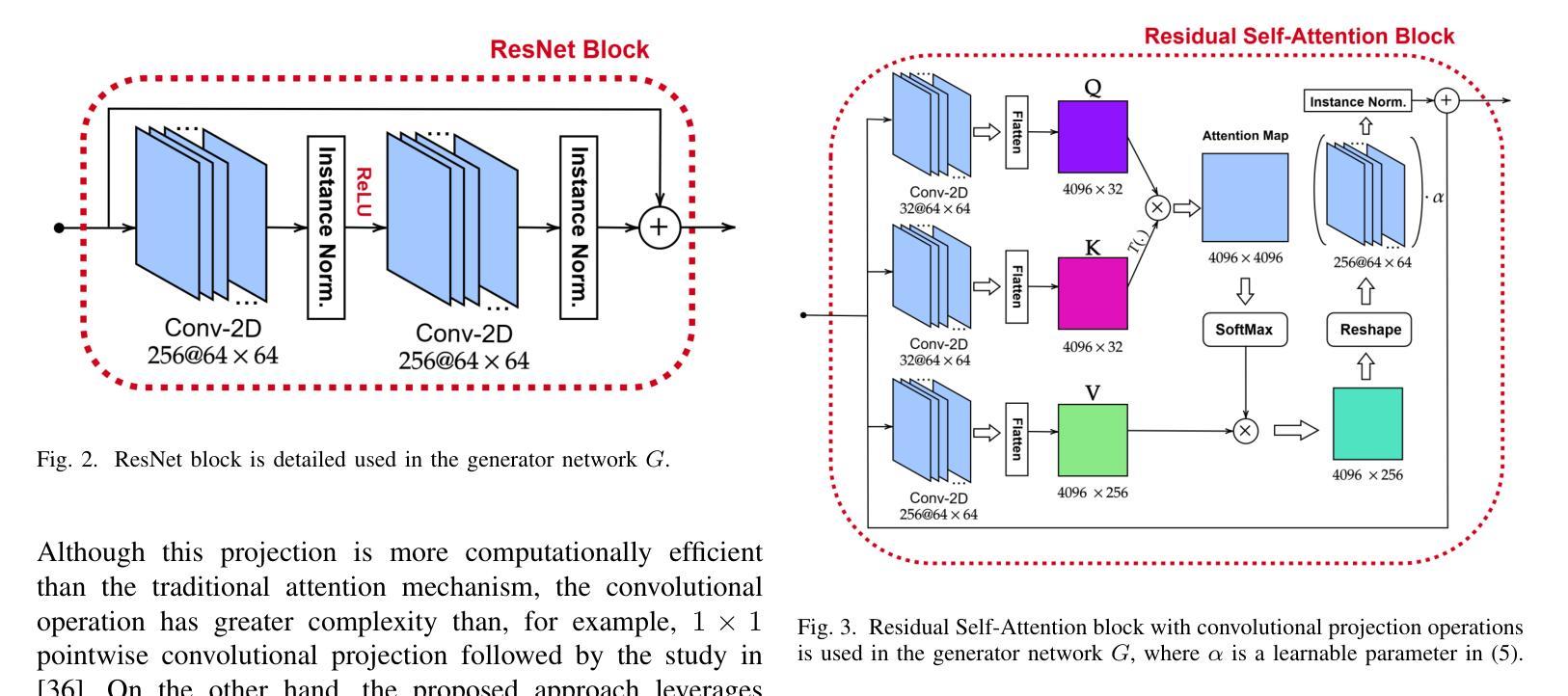
ADA-Net: Attention-Guided Domain Adaptation Network with Contrastive Learning for Standing Dead Tree Segmentation Using Aerial Imagery
Authors:Mete Ahishali, Anis Ur Rahman, Einari Heinaro, Samuli Junttila
Information on standing dead trees is important for understanding forest ecosystem functioning and resilience but has been lacking over large geographic regions. Climate change has caused large-scale tree mortality events that can remain undetected due to limited data. In this study, we propose a novel method for segmenting standing dead trees using aerial multispectral orthoimages. Because access to annotated datasets has been a significant problem in forest remote sensing due to the need for forest expertise, we introduce a method for domain transfer by leveraging domain adaptation to learn a transformation from a source domain X to target domain Y. In this Image-to-Image translation task, we aim to utilize available annotations in the target domain by pre-training a segmentation network. When images from a new study site without annotations are introduced (source domain X), these images are transformed into the target domain. Then, transfer learning is applied by inferring the pre-trained network on domain-adapted images. In addition to investigating the feasibility of current domain adaptation approaches for this objective, we propose a novel approach called the Attention-guided Domain Adaptation Network (ADA-Net) with enhanced contrastive learning. Accordingly, the ADA-Net approach provides new state-of-the-art domain adaptation performance levels outperforming existing approaches. We have evaluated the proposed approach using two datasets from Finland and the US. The USA images are converted to the Finland domain, and we show that the synthetic USA2Finland dataset exhibits similar characteristics to the Finland domain images. The software implementation is shared at https://github.com/meteahishali/ADA-Net. The data is publicly available at https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/meteahishali/aerial-imagery-for-standing-dead-tree-segmentation.
关于枯立木的信息对于理解森林生态系统的功能和恢复力非常重要,但在广大的地理区域一直缺乏这方面的信息。气候变化已引发大规模的树木死亡事件,由于数据有限,这些事件可能仍然未被探测到。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种利用航空多光谱正射影像分割枯立木的新方法。由于森林遥感中缺乏森林专业知识导致标注数据集难以获取,我们引入了一种通过领域适应进行领域迁移的方法,学习从源域X到目标域Y的转换。在这个图像到图像的翻译任务中,我们旨在通过预训练一个分割网络来利用目标域中的可用注释。当引入来自没有注释的新研究地点的图像(源域X)时,这些图像被转换为目标域。然后应用迁移学习,通过在领域适应的图像上推断预训练网络。除了探讨当前领域适应方法对此目标的可行性外,我们还提出了一种名为注意力引导领域适应网络(ADA-Net)的新方法,并增强了对比学习。因此,ADA-Net方法提供了新的最先进的领域适应性能水平,超越了现有方法。我们使用了芬兰和美国的两个数据集来评估所提出的方法。我们将美国图像转换为芬兰领域,并证明合成的USA2Finland数据集与芬兰领域图像具有相似的特征。软件实现共享在https://github.com/meteahishali/ADA-Net。数据在https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/meteahishali/aerial-imagery-for-standing-dead-tree-segmentation公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
一项研究提出了使用空中多光谱正射影像对枯立木进行分割的新方法。为解决森林遥感中缺乏注释数据集的问题,研究引入了域转移方法,通过域适应学习从源域X到目标域Y的转换。研究还提出了一种名为ADA-Net的注意力引导域适应网络新方法,并借助对比学习增强其性能。评估表明,该方法在芬兰和美国的数据集上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 枯立木信息对于理解森林生态系统的功能和恢复力至关重要,但在大地理区域上一直缺乏相关信息。
- 气候变化导致了大规模的树木死亡事件,但由于数据有限,这些事件可能会被忽略。
- 研究提出了一种使用空中多光谱正射影像对枯立木进行分割的新方法。
- 为解决森林遥感中缺乏注释数据集的问题,引入了域转移方法并成功实施。
- 研究提出了名为ADA-Net的注意力引导域适应网络新方法,该方法借助对比学习增强了性能。
- ADA-Net方法在芬兰和美国的数据集上表现出卓越的性能,超过了现有方法。
点此查看论文截图