⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-09 更新
SSLFusion: Scale & Space Aligned Latent Fusion Model for Multimodal 3D Object Detection
Authors:Bonan Ding, Jin Xie, Jing Nie, Jiale Cao
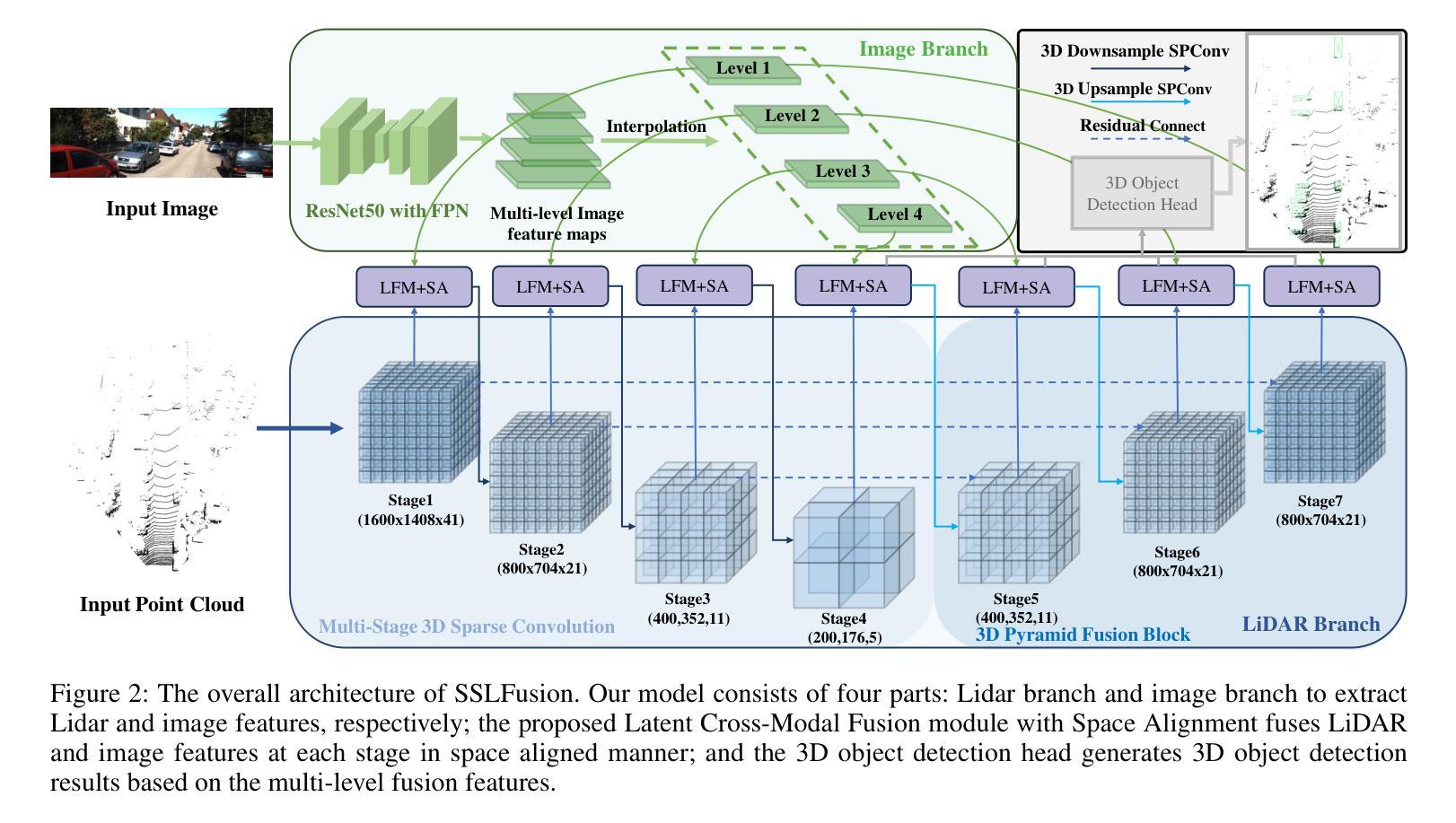
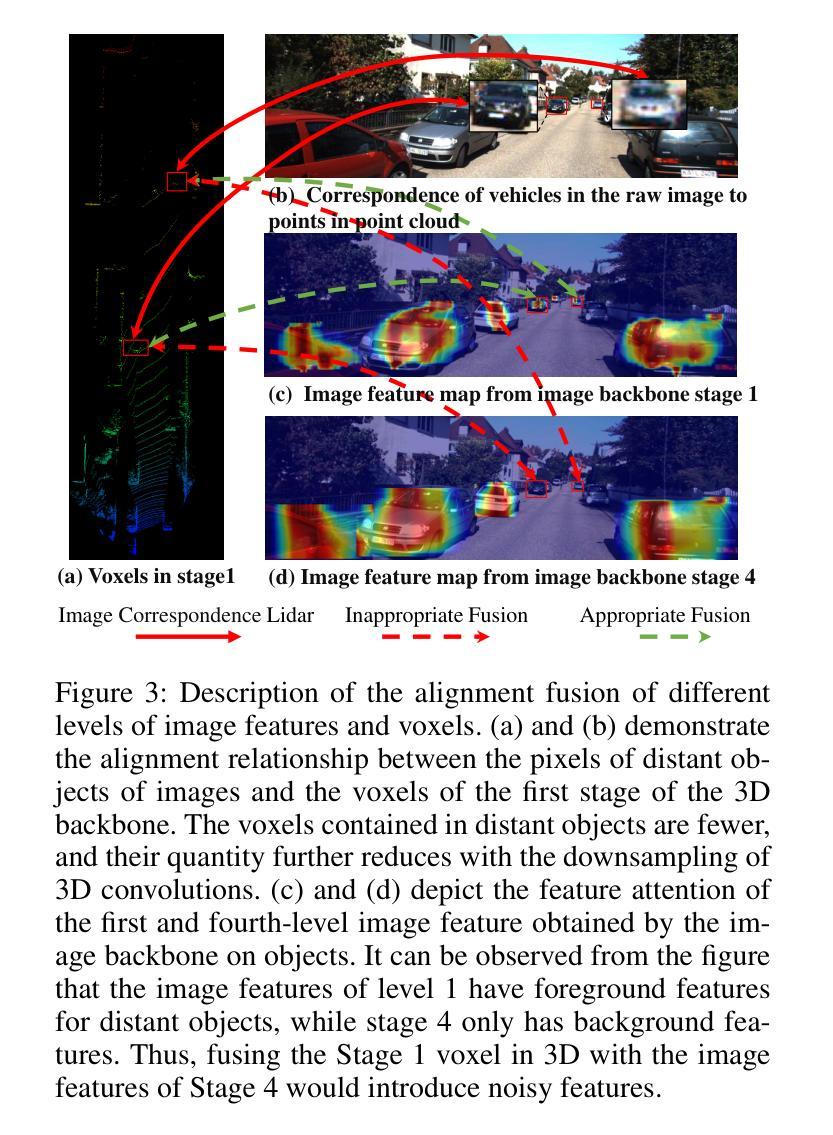
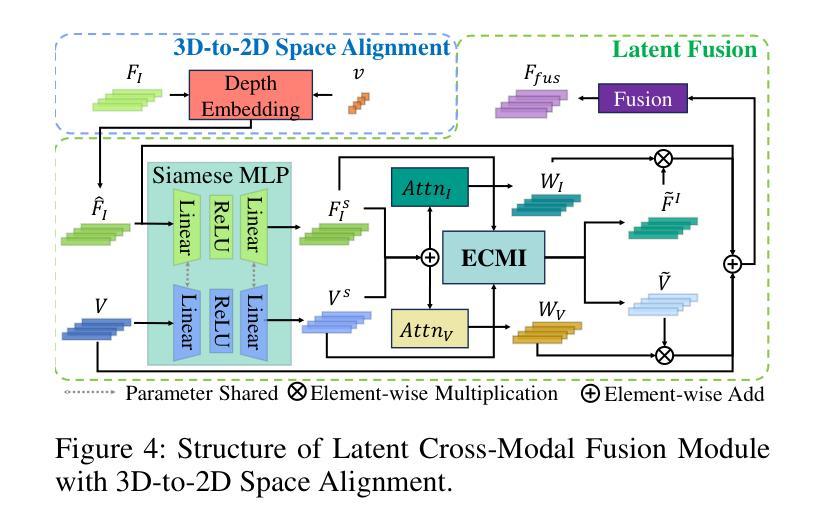
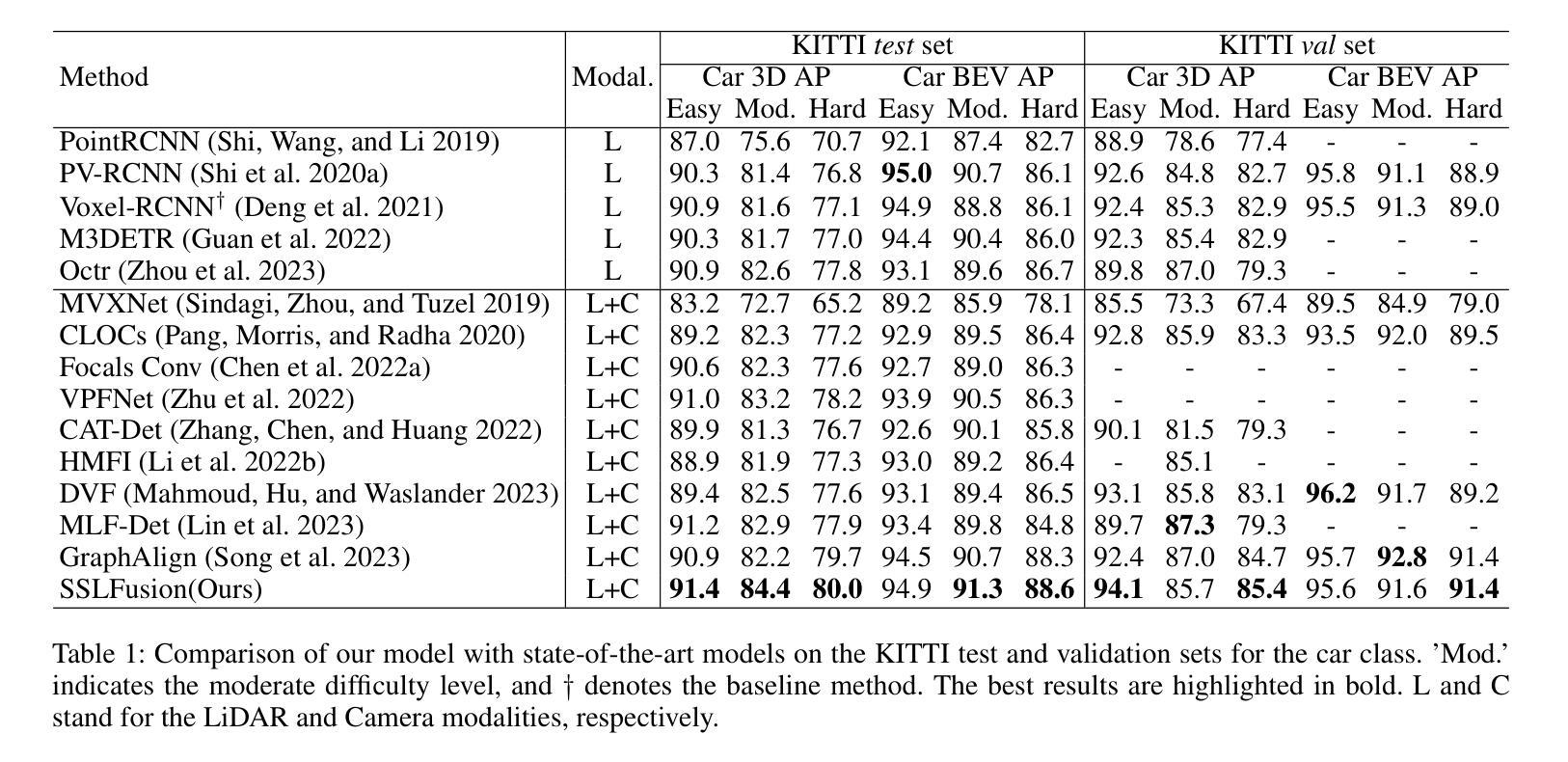
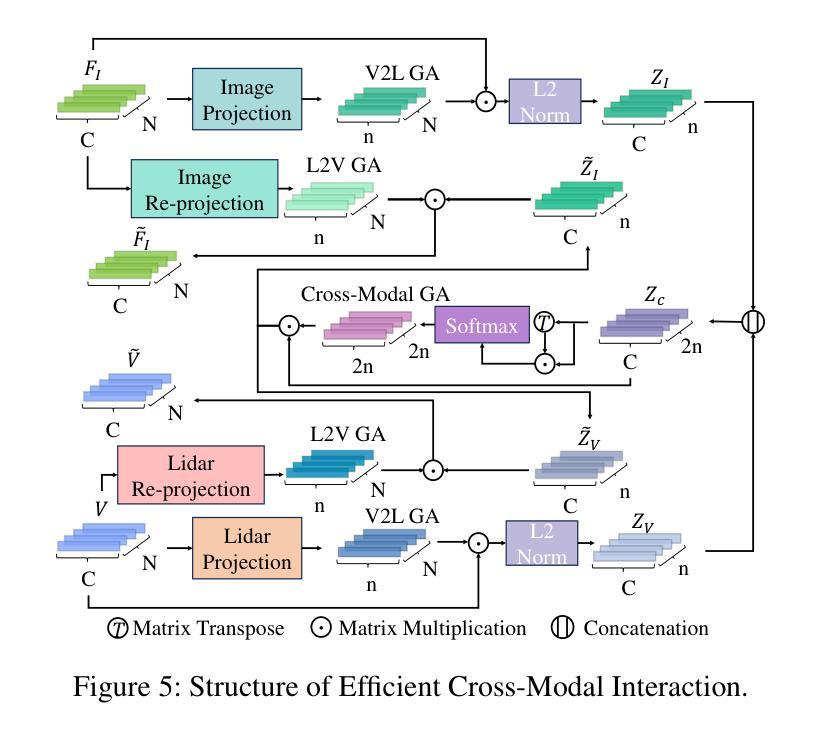
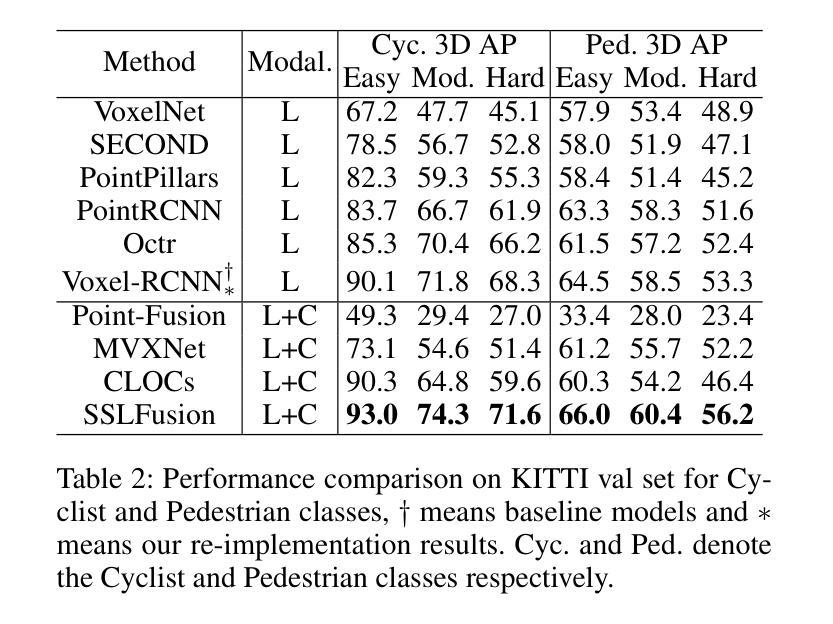
Multimodal 3D object detection based on deep neural networks has indeed made significant progress. However, it still faces challenges due to the misalignment of scale and spatial information between features extracted from 2D images and those derived from 3D point clouds. Existing methods usually aggregate multimodal features at a single stage. However, leveraging multi-stage cross-modal features is crucial for detecting objects of various scales. Therefore, these methods often struggle to integrate features across different scales and modalities effectively, thereby restricting the accuracy of detection. Additionally, the time-consuming Query-Key-Value-based (QKV-based) cross-attention operations often utilized in existing methods aid in reasoning the location and existence of objects by capturing non-local contexts. However, this approach tends to increase computational complexity. To address these challenges, we present SSLFusion, a novel Scale & Space Aligned Latent Fusion Model, consisting of a scale-aligned fusion strategy (SAF), a 3D-to-2D space alignment module (SAM), and a latent cross-modal fusion module (LFM). SAF mitigates scale misalignment between modalities by aggregating features from both images and point clouds across multiple levels. SAM is designed to reduce the inter-modal gap between features from images and point clouds by incorporating 3D coordinate information into 2D image features. Additionally, LFM captures cross-modal non-local contexts in the latent space without utilizing the QKV-based attention operations, thus mitigating computational complexity. Experiments on the KITTI and DENSE datasets demonstrate that our SSLFusion outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Our approach obtains an absolute gain of 2.15% in 3D AP, compared with the state-of-art method GraphAlign on the moderate level of the KITTI test set.
基于深度神经网络的多模态三维物体检测确实已经取得了显著的进展。然而,由于从二维图像提取的特征与从三维点云衍生的特征在规模和空间信息上的不匹配,它仍然面临挑战。现有方法通常在单一阶段聚合多模态特征。然而,利用多阶段的跨模态特征对于检测各种规模的目标至关重要。因此,这些方法在整合不同规模和模态的特征时往往面临困难,从而限制了检测精度。此外,现有方法中常用的基于查询-键-值(QKV)的跨注意力操作虽然有助于通过捕捉非局部上下文来推理物体的位置和存在,但这种方法往往会增加计算复杂性。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了SSLFusion,这是一种新的规模和空间对齐潜在融合模型,包括规模对齐融合策略(SAF)、3D到2D空间对齐模块(SAM)和潜在跨模态融合模块(LFM)。SAF通过在不同层级上聚合图像和点云的特征,缓解模态之间的规模不匹配问题。SAM通过融入3D坐标信息到2D图像特征中,旨在缩小图像和点云特征之间的跨模态差距。此外,LFM在潜在空间中捕捉跨模态的非局部上下文,而不使用QKV基于注意力的操作,从而缓解计算复杂性。在KITTI和DENSE数据集上的实验表明,我们的SSLFusion优于最新方法。我们的方法在KITTI测试集的适度水平上,与最新方法GraphAlign相比,3D AP绝对提升了2.15%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
基于深度神经网络的多模态三维物体检测技术已经取得显著进展,但仍面临二维图像和三维点云特征尺度与空间信息不对齐的挑战。现有方法通常在单一阶段进行多模态特征聚合,难以有效整合不同尺度和模态的特征,影响检测准确性。针对这些问题,我们提出了SSLFusion模型,包括尺度对齐融合策略(SAF)、三维到二维空间对齐模块(SAM)和潜在跨模态融合模块(LFM)。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态三维物体检测基于深度神经网络有显著的进步,但存在特征和尺度不对齐的问题。
- 现有方法通常在单一阶段进行多模态特征聚合,难以检测不同尺度的物体。
- SSLFusion模型包括尺度对齐融合策略(SAF),用于解决跨模态的尺度不对齐问题。
- 三维到二维空间对齐模块(SAM)通过融入三维坐标信息来缩小跨模态特征之间的差距。
- 潜在跨模态融合模块(LFM)能够在潜在空间中捕获跨模态的非局部上下文,同时不增加计算复杂性。
- SSLFusion模型在KITTI和DENSE数据集上的表现优于现有最先进的检测方法。
点此查看论文截图

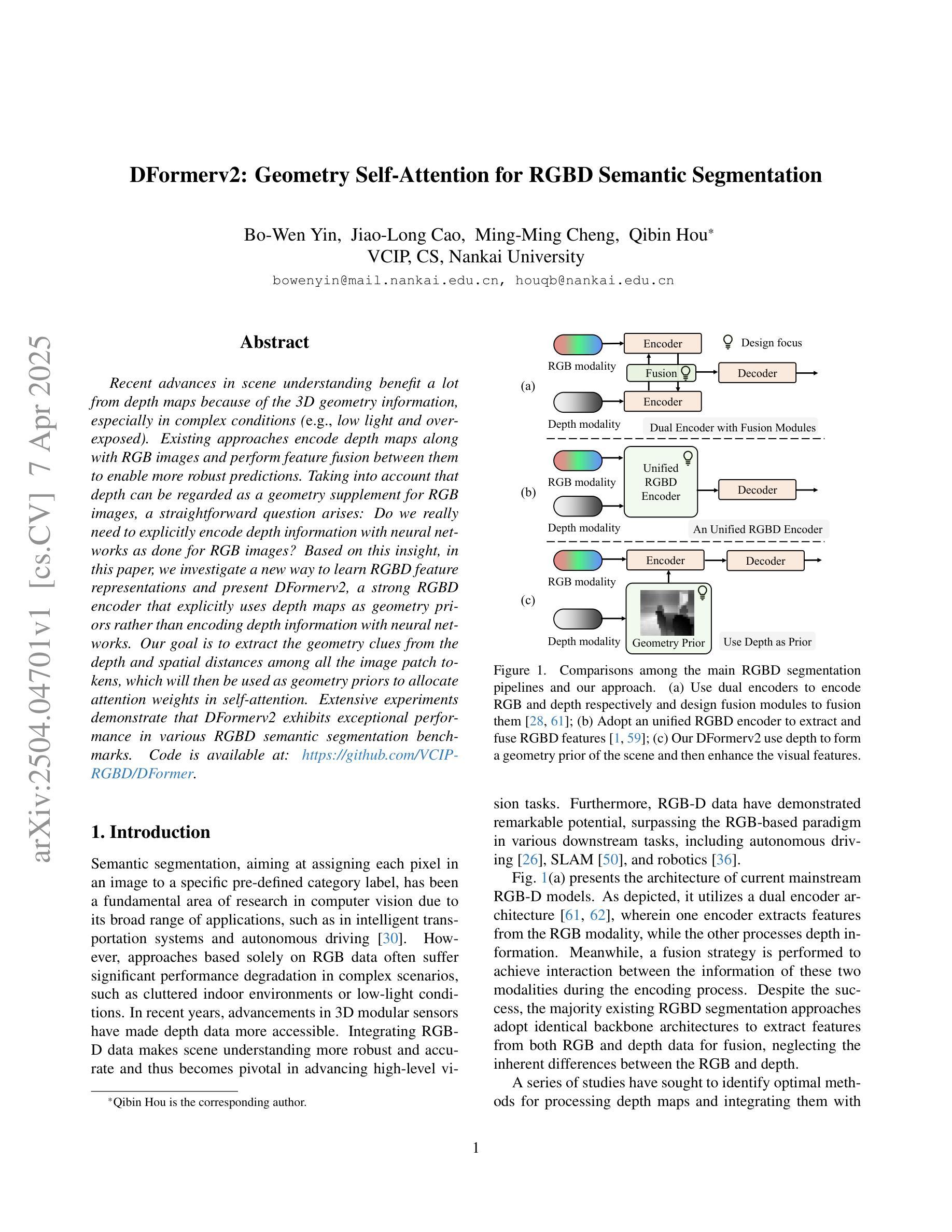
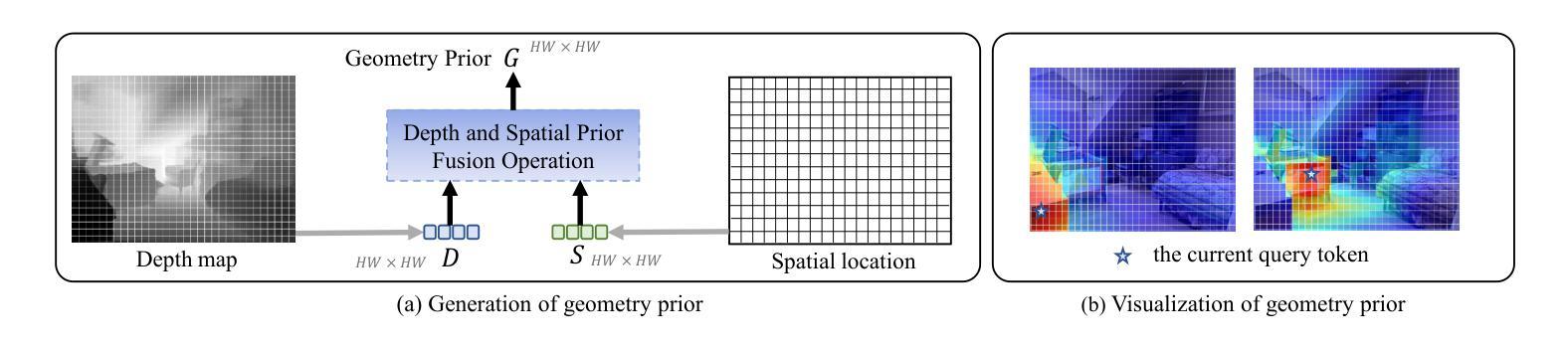
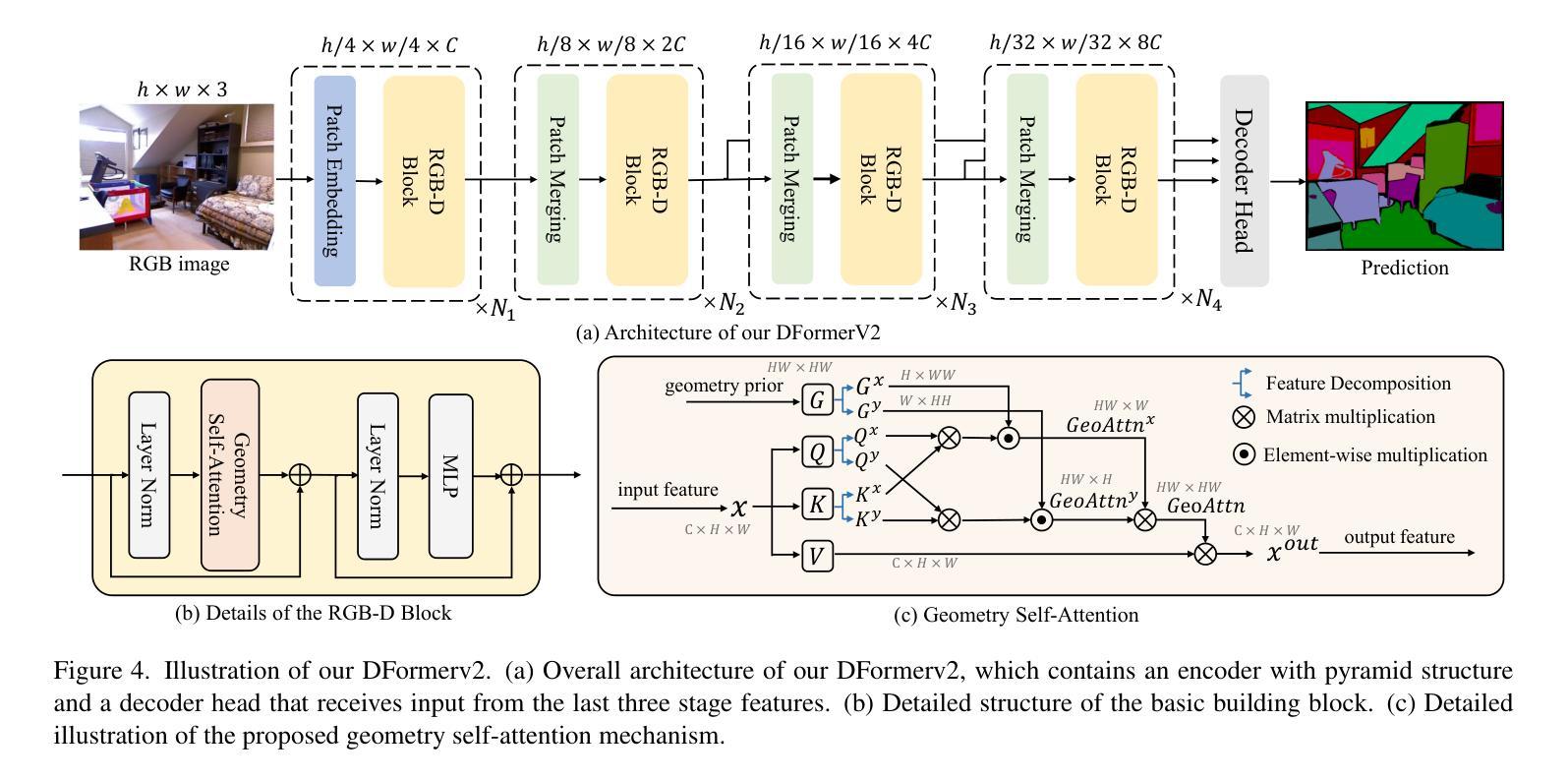
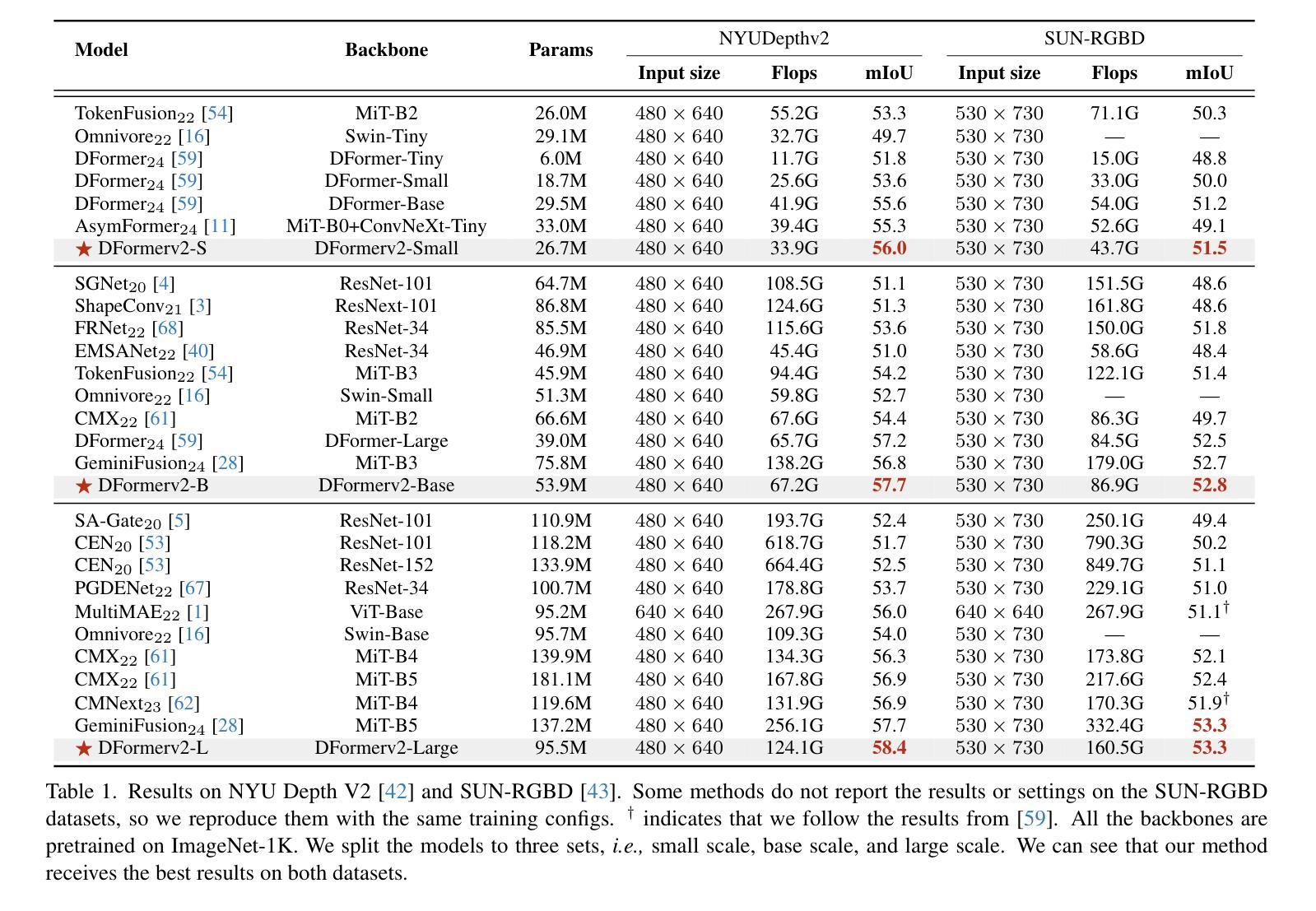
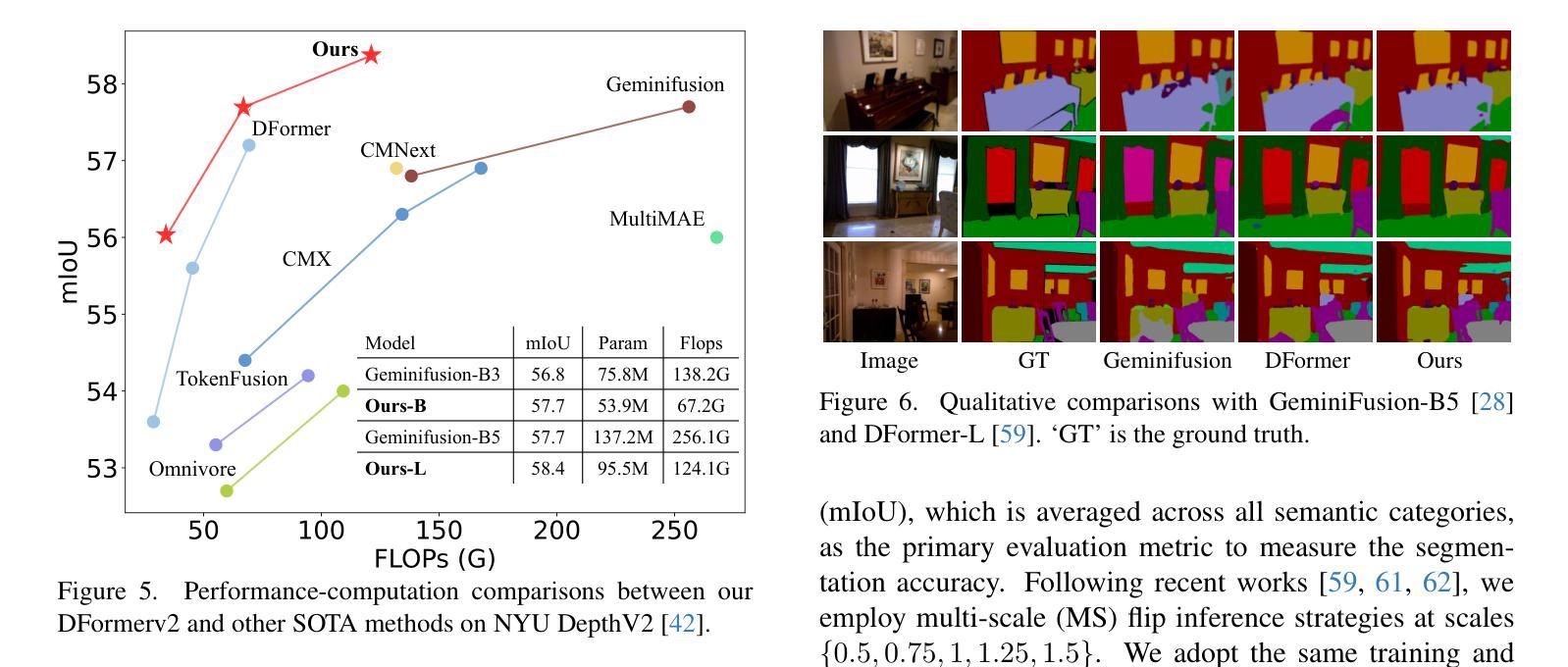
DFormerv2: Geometry Self-Attention for RGBD Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Bo-Wen Yin, Jiao-Long Cao, Ming-Ming Cheng, Qibin Hou
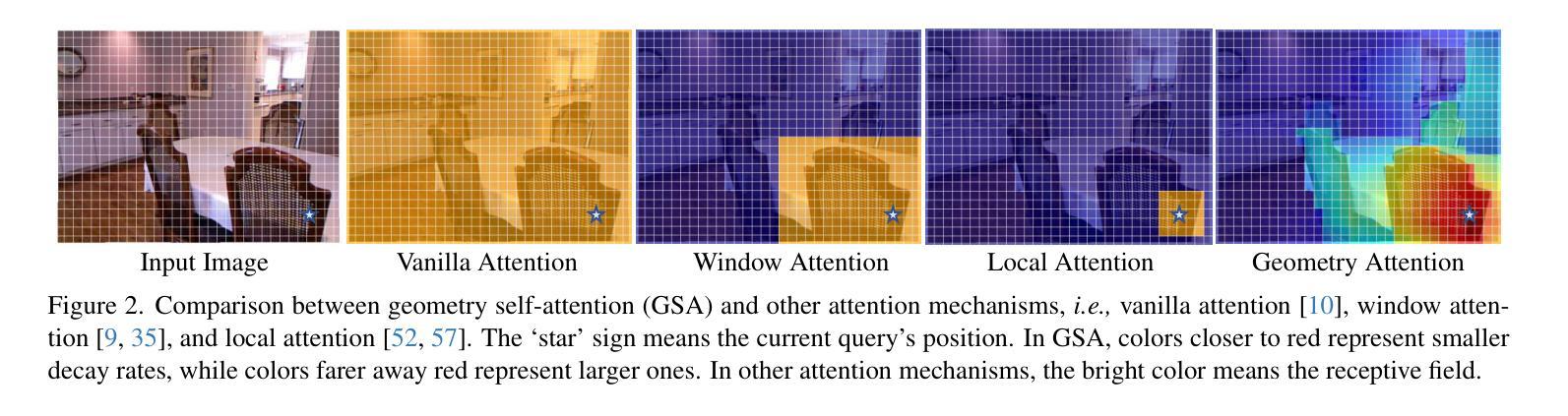
Recent advances in scene understanding benefit a lot from depth maps because of the 3D geometry information, especially in complex conditions (e.g., low light and overexposed). Existing approaches encode depth maps along with RGB images and perform feature fusion between them to enable more robust predictions. Taking into account that depth can be regarded as a geometry supplement for RGB images, a straightforward question arises: Do we really need to explicitly encode depth information with neural networks as done for RGB images? Based on this insight, in this paper, we investigate a new way to learn RGBD feature representations and present DFormerv2, a strong RGBD encoder that explicitly uses depth maps as geometry priors rather than encoding depth information with neural networks. Our goal is to extract the geometry clues from the depth and spatial distances among all the image patch tokens, which will then be used as geometry priors to allocate attention weights in self-attention. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DFormerv2 exhibits exceptional performance in various RGBD semantic segmentation benchmarks. Code is available at: https://github.com/VCIP-RGBD/DFormer.
最近,场景理解的进步在很大程度上得益于深度图所包含的3D几何信息,特别是在复杂条件下(例如低光和过度曝光)。现有方法将深度图与RGB图像进行编码,并在两者之间执行特征融合,以实现更稳健的预测。考虑到深度可被视为RGB图像的几何补充,一个直接的问题出现了:我们是否真的需要将深度信息像处理RGB图像那样显式地编码到神经网络中?基于这一见解,本文研究了一种新的RGBD特征表示学习方法,并推出了DFormerv2,这是一种强大的RGBD编码器,它显式地使用深度图作为几何先验,而不是通过神经网络编码深度信息。我们的目标是从深度和所有图像补丁标记之间的空间距离中提取几何线索,然后将这些线索用作几何先验来分配自注意力中的注意力权重。大量实验表明,DFormerv2在各种RGBD语义分割基准测试中表现出卓越的性能。代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/VCIP-RGBD/DFormer。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
本文探讨了RGBD特征表示的新学习方法,提出了一种名为DFormerv2的强RGBD编码器,它利用深度图作为几何先验信息,而不是通过神经网络对深度信息进行编码。该研究的目标是从深度图和图像块令牌间的空间距离中提取几何线索,将其作为几何先验信息用于分配自注意力中的注意力权重。实验表明,DFormerv2在多种RGBD语义分割基准测试中表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- DFormerv2利用深度图作为几何先验信息,提出了新的RGBD特征表示学习方法。
- 现有方法通常将深度图与RGB图像一起编码,并进行特征融合,而DFormerv2则将深度信息直接用于分配自注意力中的权重。
- 该方法从深度图和空间距离中提取几何线索,以增强图像理解。
- DFormerv2在多种RGBD语义分割基准测试中表现出卓越性能。
- 该研究强调了深度信息在复杂条件下的重要性,如低光和过曝光环境。
- DFormerv2的目标是通过利用深度图的几何信息来改进RGB图像的表示能力。
点此查看论文截图

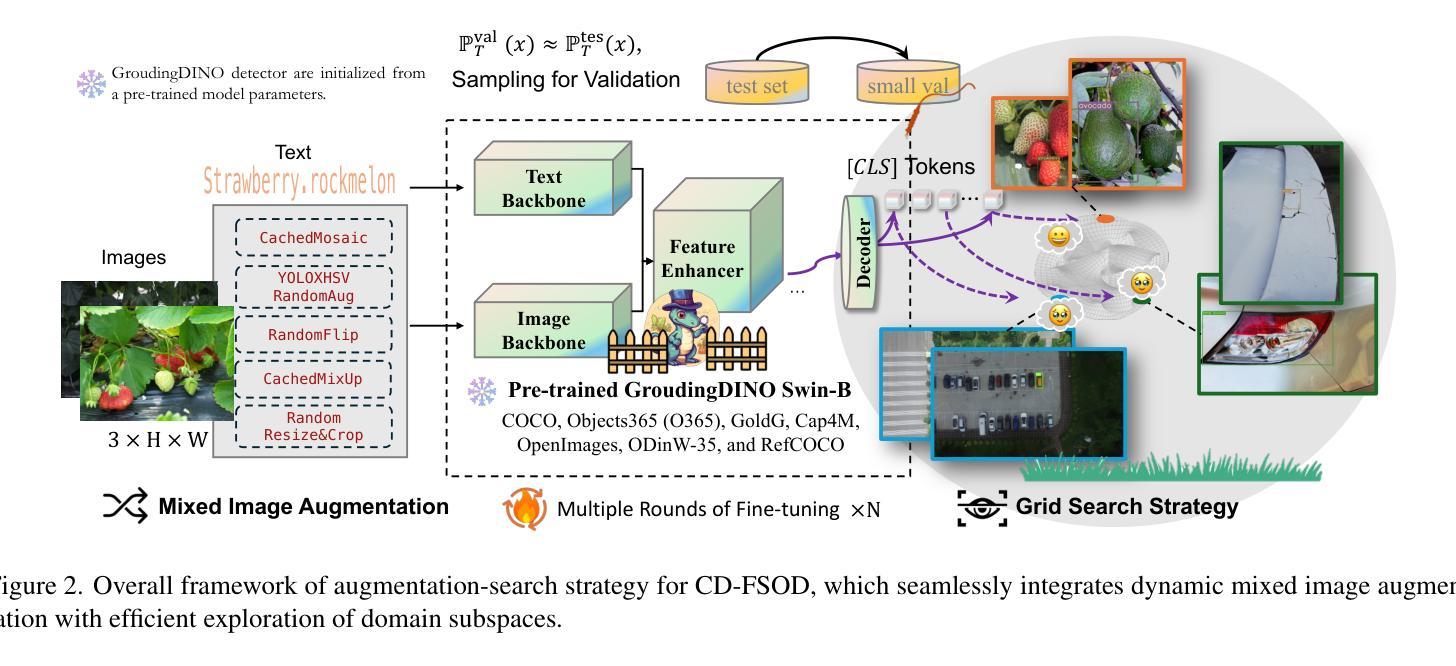
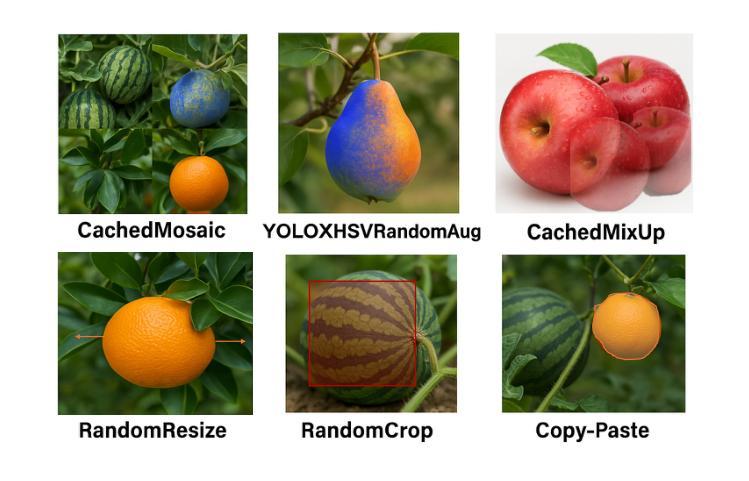
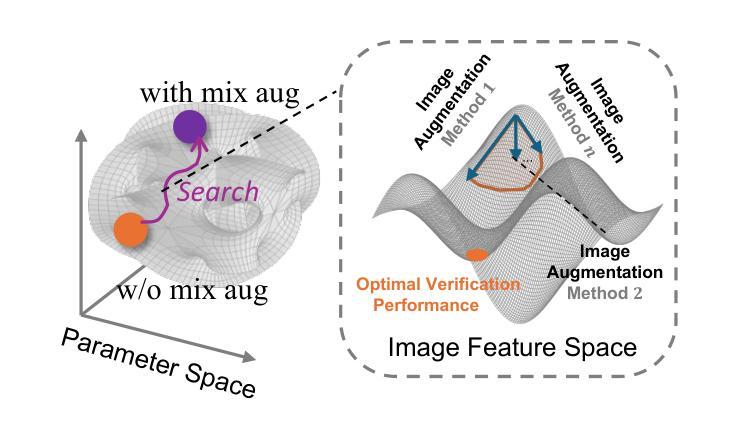
Enhance Then Search: An Augmentation-Search Strategy with Foundation Models for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Object Detection
Authors:Jiancheng Pan, Yanxing Liu, Xiao He, Long Peng, Jiahao Li, Yuze Sun, Xiaomeng Huang
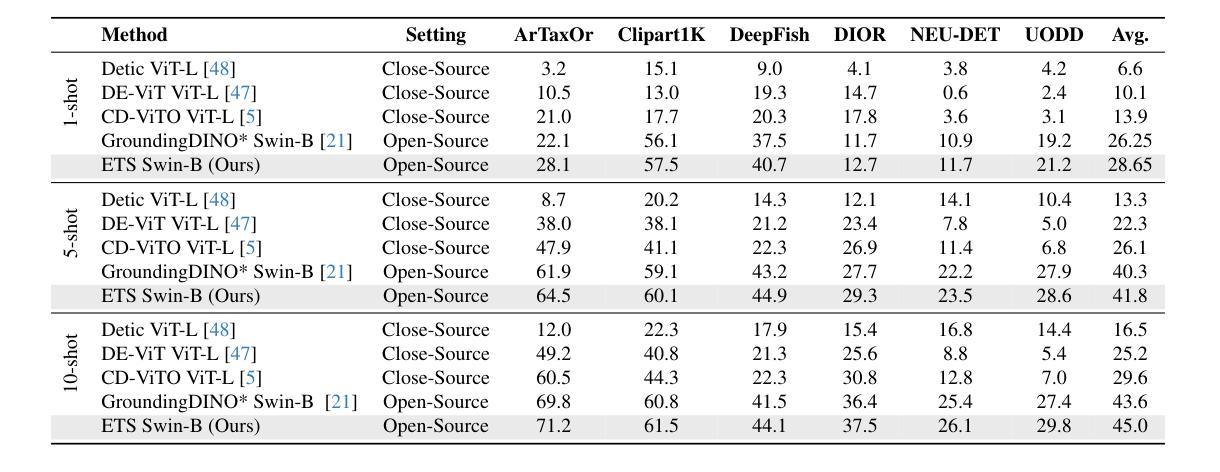
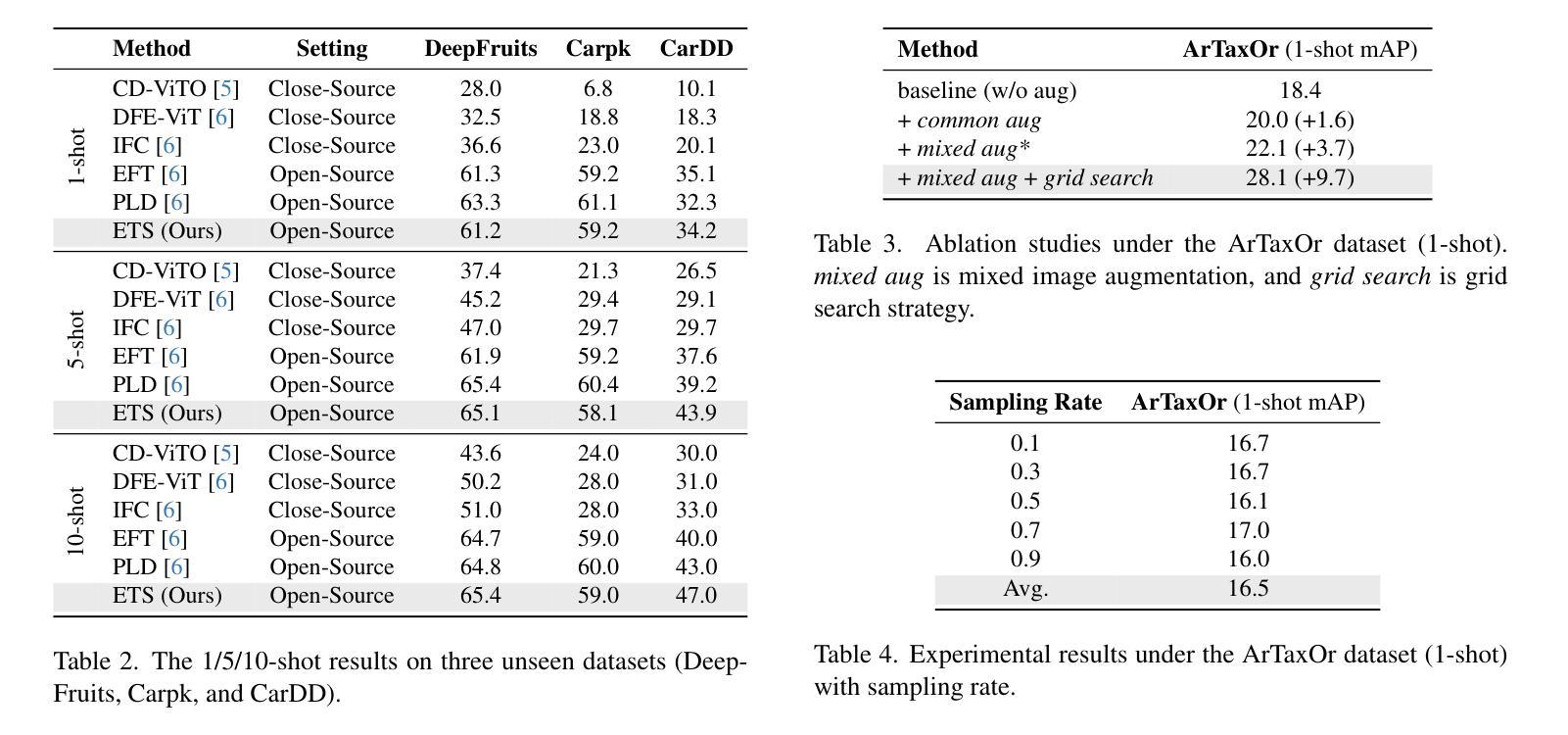
Foundation models pretrained on extensive datasets, such as GroundingDINO and LAE-DINO, have performed remarkably in the cross-domain few-shot object detection (CD-FSOD) task. Through rigorous few-shot training, we found that the integration of image-based data augmentation techniques and grid-based sub-domain search strategy significantly enhances the performance of these foundation models. Building upon GroundingDINO, we employed several widely used image augmentation methods and established optimization objectives to effectively navigate the expansive domain space in search of optimal sub-domains. This approach facilitates efficient few-shot object detection and introduces an approach to solving the CD-FSOD problem by efficiently searching for the optimal parameter configuration from the foundation model. Our findings substantially advance the practical deployment of vision-language models in data-scarce environments, offering critical insights into optimizing their cross-domain generalization capabilities without labor-intensive retraining. Code is available at https://github.com/jaychempan/ETS.
基于大规模数据集预训练的模型,如GroundingDINO和LAE-DINO,在跨域少样本目标检测(CD-FSOD)任务中表现突出。通过严格的少样本训练,我们发现结合基于图像的数据增强技术和基于网格的子域搜索策略,可以显著提高这些基础模型的性能。在GroundingDINO的基础上,我们采用了几种常用的图像增强方法,并建立了优化目标,以有效地遍历庞大的域空间,寻找最佳子域。这种方法促进了高效少样本目标检测,并通过从基础模型中有效搜索最佳参数配置来解决CD-FSOD问题。我们的研究为在数据稀缺环境中部署视觉语言模型提供了重大进展,并为在不进行劳动密集型再训练的情况下优化其跨域泛化能力提供了关键见解。代码可在https://github.com/jaychempan/ETS找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 6 figures
Summary
基于大规模数据集预训练的模型,如GroundingDINO和LAE-DINO,在跨域少样本目标检测任务中表现出卓越性能。研究通过严格少样本训练发现,图像数据增强技术与基于网格的子域搜索策略的结合,显著提升了这些预训练模型的性能。在GroundingDINO基础上,研究采用多种常用图像增强方法并建立优化目标,以有效遍历广阔域空间并寻找最佳子域,为解决CD-FSOD问题提供了一种方法。该研究有助于高效少样本目标检测,并为优化视觉语言模型在数据稀缺环境中的跨域泛化能力提供了关键见解。代码已公开于GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练的模型,如GroundingDINO和LAE-DINO,在跨域少样本目标检测中表现出优异性能。
- 图像数据增强技术结合基于网格的子域搜索策略显著提升了模型性能。
- 在GroundingDINO基础上,采用多种图像增强方法和优化目标,有效搜索最佳子域。
- 该方法为解决CD-FSOD问题提供了一种有效途径。
- 研究有助于提高少样本目标检测的效率和准确性。
- 研究为优化视觉语言模型在数据稀缺环境中的跨域泛化能力提供了关键见解。
点此查看论文截图

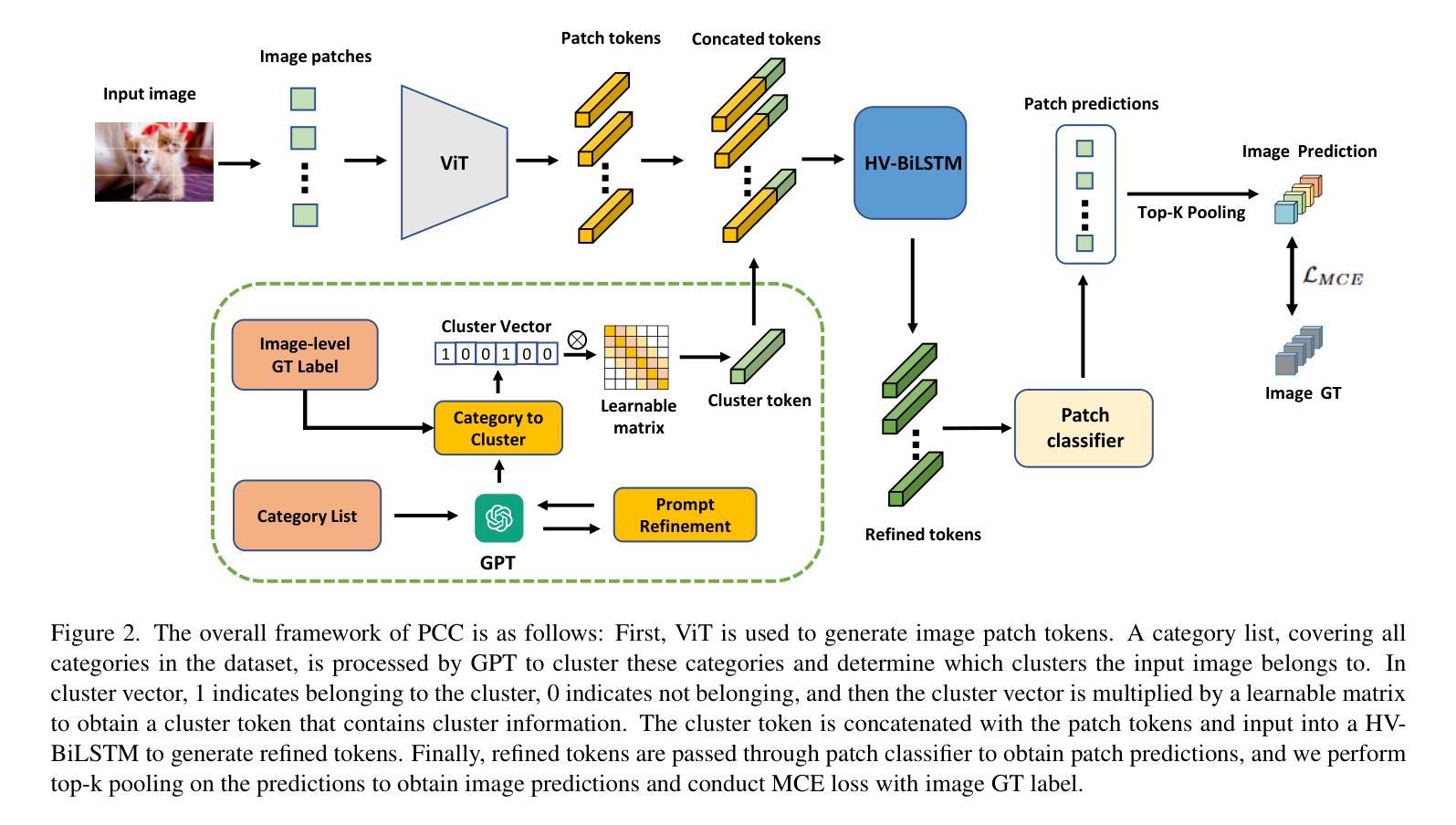
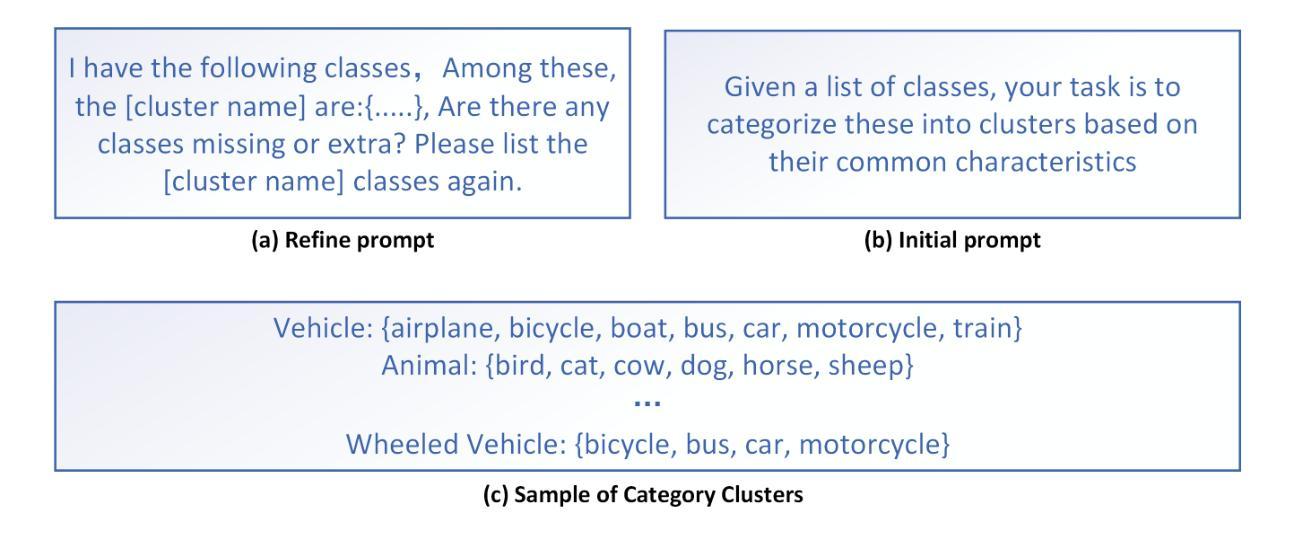
Prompt Categories Cluster for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Wangyu Wu, Xianglin Qiu, Siqi Song, Xiaowei Huang, Fei Ma, Jimin Xiao
Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS), which leverages image-level labels, has garnered significant attention due to its cost-effectiveness. The previous methods mainly strengthen the inter-class differences to avoid class semantic ambiguity which may lead to erroneous activation. However, they overlook the positive function of some shared information between similar classes. Categories within the same cluster share some similar features. Allowing the model to recognize these features can further relieve the semantic ambiguity between these classes. To effectively identify and utilize this shared information, in this paper, we introduce a novel WSSS framework called Prompt Categories Clustering (PCC). Specifically, we explore the ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to derive category clusters through prompts. These clusters effectively represent the intrinsic relationships between categories. By integrating this relational information into the training network, our model is able to better learn the hidden connections between categories. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, showing its ability to enhance performance on the PASCAL VOC 2012 dataset and surpass existing state-of-the-art methods in WSSS.
弱监督语义分割(WSSS)利用图像级别的标签,因其成本效益而备受关注。之前的方法主要强调类间差异,以避免可能导致错误激活的类语义模糊。然而,他们忽视了类似类别之间共享信息的积极作用。同一聚类中的类别共享一些相似特征。允许模型识别这些特征可以进一步缓解这些类别之间的语义模糊。为了有效识别和利用这些共享信息,本文引入了一种新型的WSSS框架,称为提示类别聚类(PCC)。具体来说,我们探索了大型语言模型(LLM)通过提示推导类别聚类的能力。这些聚类有效地代表了类别之间的内在关系。通过将这种关系信息集成到训练网络中,我们的模型能够更好地学习类别之间的隐藏连接。实验结果证明了我们的方法的有效性,表明其在PASCAL VOC 2012数据集上的性能有所提升,并超越了现有的WSSS先进方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CVPR 2025 ELVM
摘要
基于图像级标签的弱监督语义分割(WSSS)因其成本效益而受到广泛关注。以往的方法主要强化类间差异以避免语义模糊导致的错误激活,但忽略了相似类别间共享信息的积极作用。本文引入了一种名为Prompt Categories Clustering(PCC)的新型WSSS框架,能够识别并利用类别间的共享信息。通过大型语言模型(LLM)的提示能力,我们探索了类别聚类的形成,这些聚类有效地代表了类别之间的内在关系。通过将这种关系信息整合到训练网络中,我们的模型能够更好地学习类别之间的隐藏联系。实验结果表明,我们的方法在PASCAL VOC 2012数据集上的性能有所提升,并超越了现有的WSSS领域最先进的方法。
要点速览
- WSSS方法利用图像级标签,旨在解决语义模糊问题。
- 以往方法主要强化类间差异,但忽略了相似类别间共享信息的积极作用。
- 本研究引入了Prompt Categories Clustering(PCC)框架,利用大型语言模型识别类别间的共享信息。
- PCC通过形成类别聚类来代表类别间的内在关系。
- 将关系信息整合到训练网络中,提升模型学习类别间隐藏联系的能力。
点此查看论文截图

LUIEO: A Lightweight Model for Integrating Underwater Image Enhancement and Object Detection
Authors:Bin Li, Li Li, Zhenwei Zhang, Yuping Duan
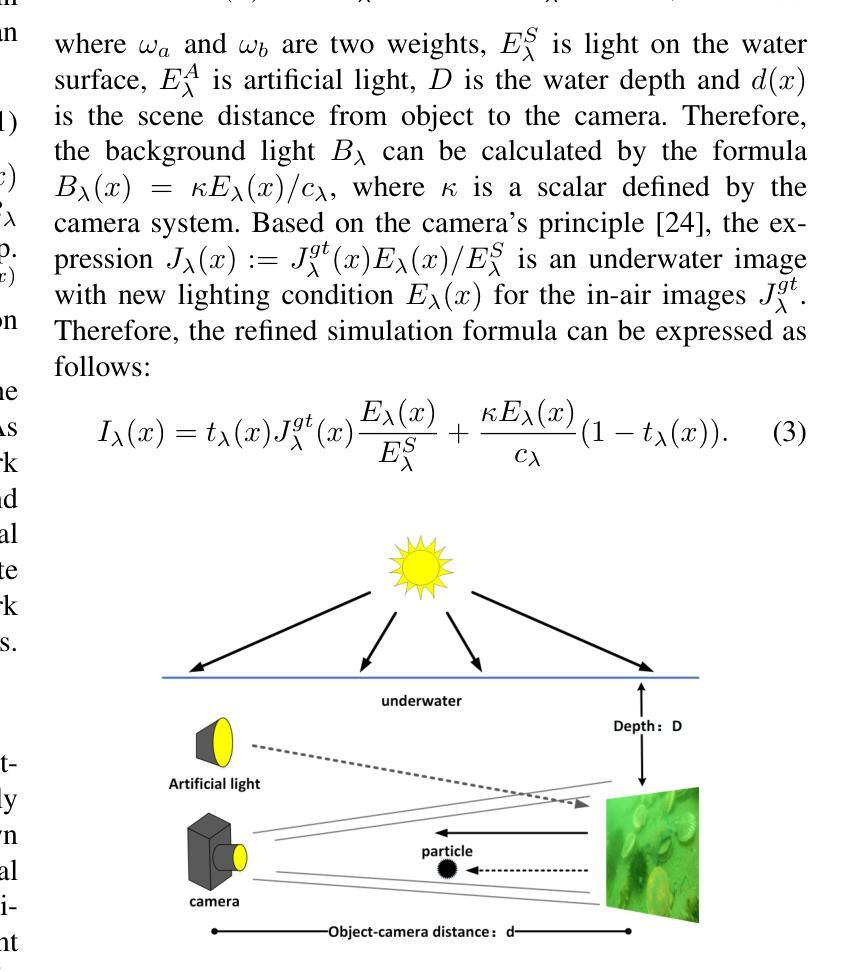
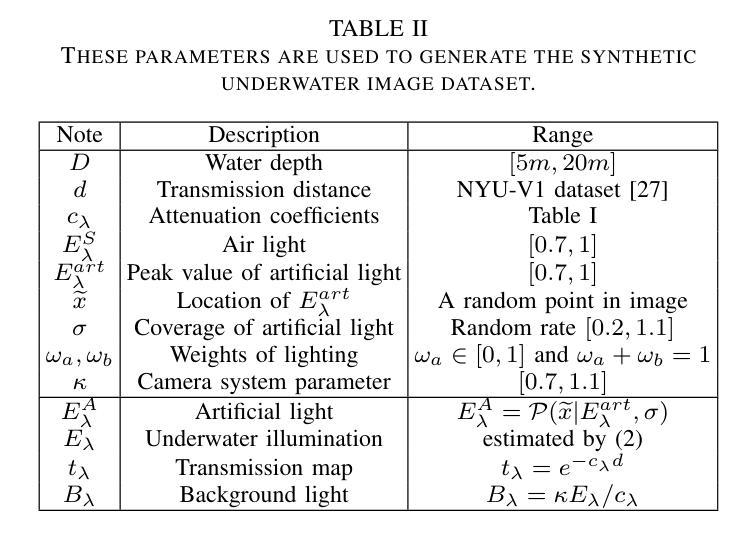
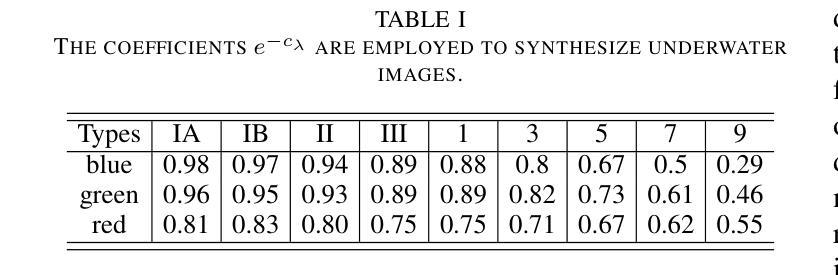
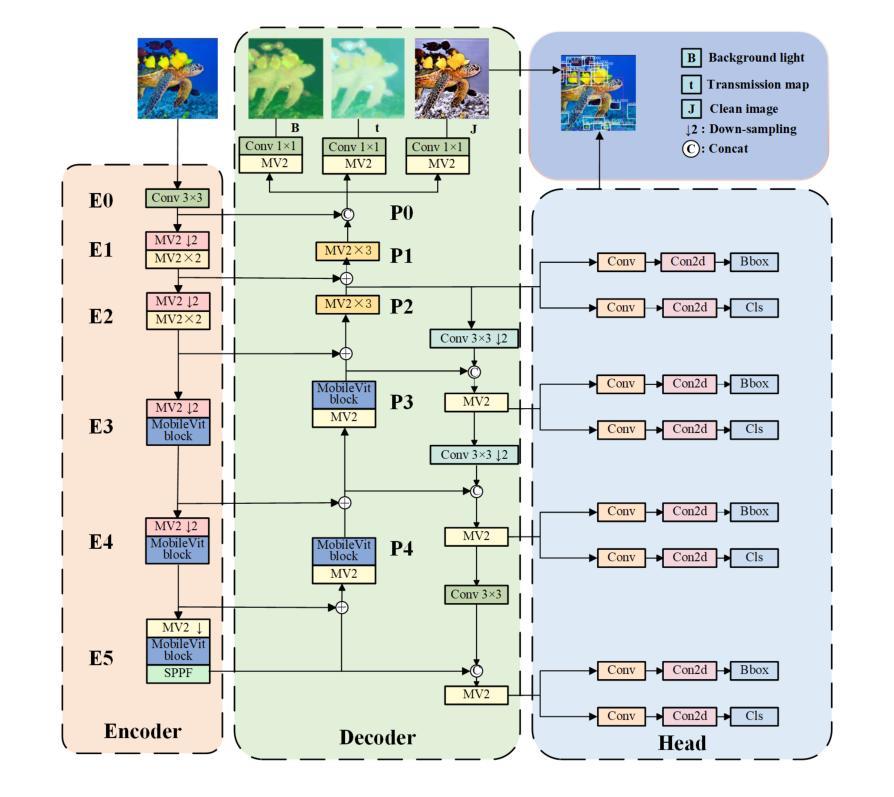
Underwater optical images inevitably suffer from various degradation factors such as blurring, low contrast, and color distortion, which hinder the accuracy of object detection tasks. Due to the lack of paired underwater/clean images, most research methods adopt a strategy of first enhancing and then detecting, resulting in a lack of feature communication between the two learning tasks. On the other hand, due to the contradiction between the diverse degradation factors of underwater images and the limited number of samples, existing underwater enhancement methods are difficult to effectively enhance degraded images of unknown water bodies, thereby limiting the improvement of object detection accuracy. Therefore, most underwater target detection results are still displayed on degraded images, making it difficult to visually judge the correctness of the detection results. To address the above issues, this paper proposes a multi-task learning method that simultaneously enhances underwater images and improves detection accuracy. Compared with single-task learning, the integrated model allows for the dynamic adjustment of information communication and sharing between different tasks. Due to the fact that real underwater images can only provide annotated object labels, this paper introduces physical constraints to ensure that object detection tasks do not interfere with image enhancement tasks. Therefore, this article introduces a physical module to decompose underwater images into clean images, background light, and transmission images and uses a physical model to calculate underwater images for self-supervision. Numerical experiments demonstrate that the proposed model achieves satisfactory results in visual performance, object detection accuracy, and detection efficiency compared to state-of-the-art comparative methods.
水下光学图像不可避免地受到模糊、低对比度和颜色失真等多种降质因素的影响,从而阻碍了目标检测任务的准确性。由于缺少配对的水下/清洁图像,大多数研究方法采用先增强后检测的策略,导致两个学习任务之间缺乏特征交流。另一方面,由于水下图像的各种降质因素与样本数量有限之间的矛盾,现有的水下增强方法难以有效增强未知水体的退化图像,从而限制了目标检测准确度的提高。因此,大多数水下目标检测结果仍显示在退化图像上,很难直观判断检测结果的正确性。为了解决上述问题,本文提出了一种多任务学习方法,同时增强水下图像并提高检测准确性。与单任务学习相比,集成模型允许不同任务之间动态调整信息通信和共享。由于真实水下图像只能提供注释的对象标签,本文引入物理约束以确保目标检测任务不会干扰图像增强任务。因此,本文引入了一个物理模块来将水下图像分解为清洁图像、背景光和传输图像,并使用物理模型计算水下图像进行自我监督。数值实验表明,与最先进的比较方法相比,所提模型在视觉性能、目标检测准确性和检测效率方面都取得了令人满意的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种多任务学习方法,旨在同时提升水下图像质量并提高其检测精度。面对水下图像模糊、对比度低、色彩失真等退化问题,以及缺乏配对的水下/清晰图像样本,该研究通过引入物理约束模块分解水下图像为清洁图像、背景光和透射图像,并利用物理模型计算水下图像进行自我监督,实现动态调整不同任务间的信息共享与交流。实验表明,该模型在视觉性能、目标检测精度和检测效率方面均取得满意结果。
Key Takeaways
- 水下图像退化问题如模糊、低对比度和色彩失真等,影响目标检测的准确性。
- 缺乏配对的水下/清晰图像样本,使得现有水下增强方法在未知水体中的图像增强效果有限。
- 提出一种多任务学习方法,同时增强水下图像并提升检测精度。
- 引入物理约束模块分解水下图像,便于自我监督和学习。
- 模型通过动态调整不同任务间的信息共享与交流,优化检测效果。
- 实验证明该模型在视觉性能、目标检测精度和检测效率上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

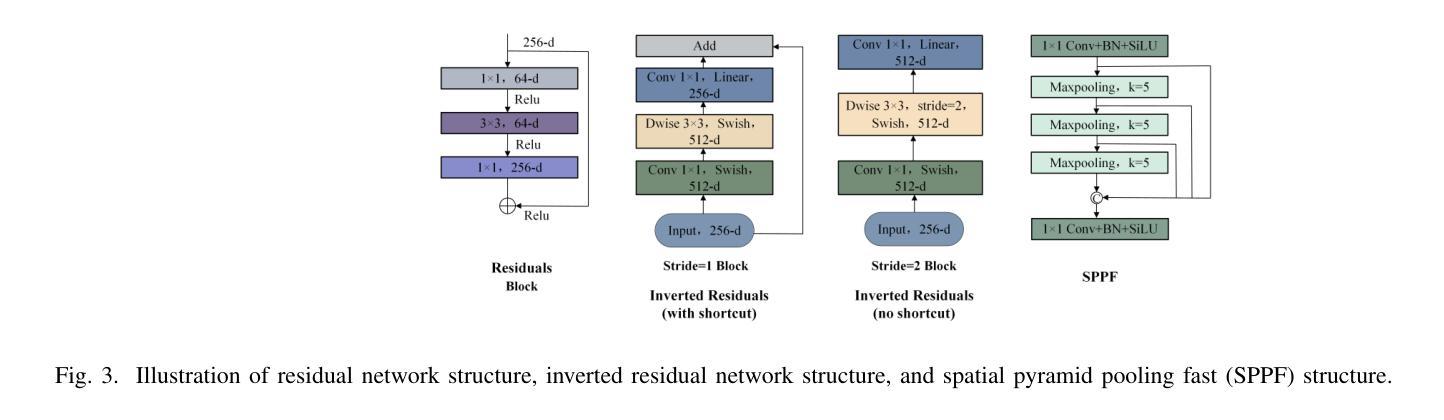
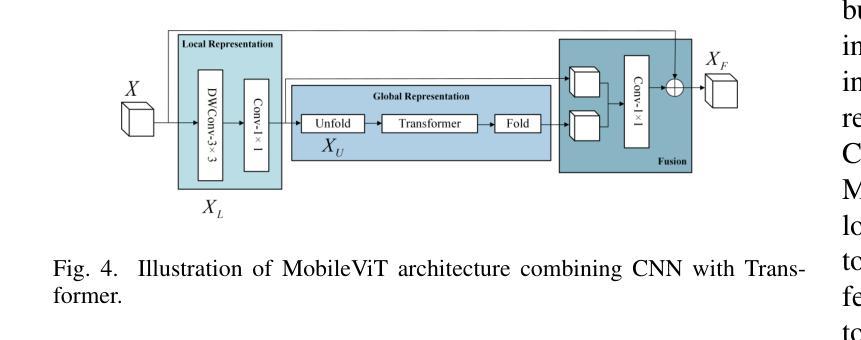
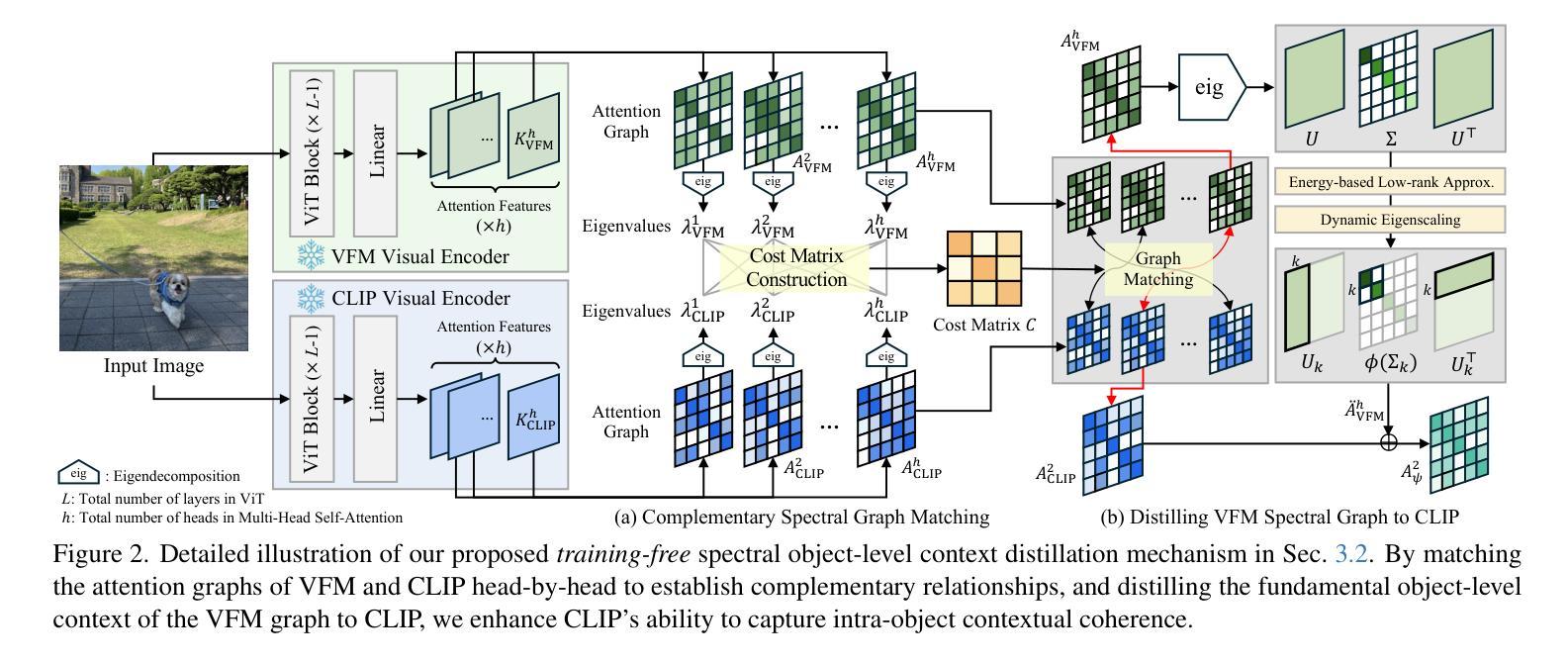
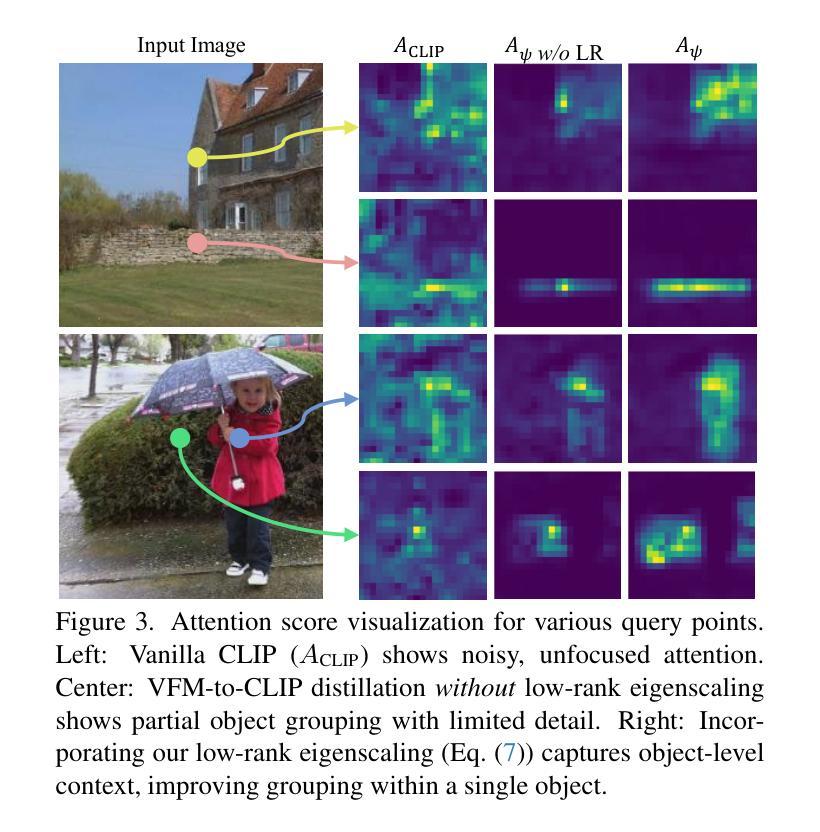
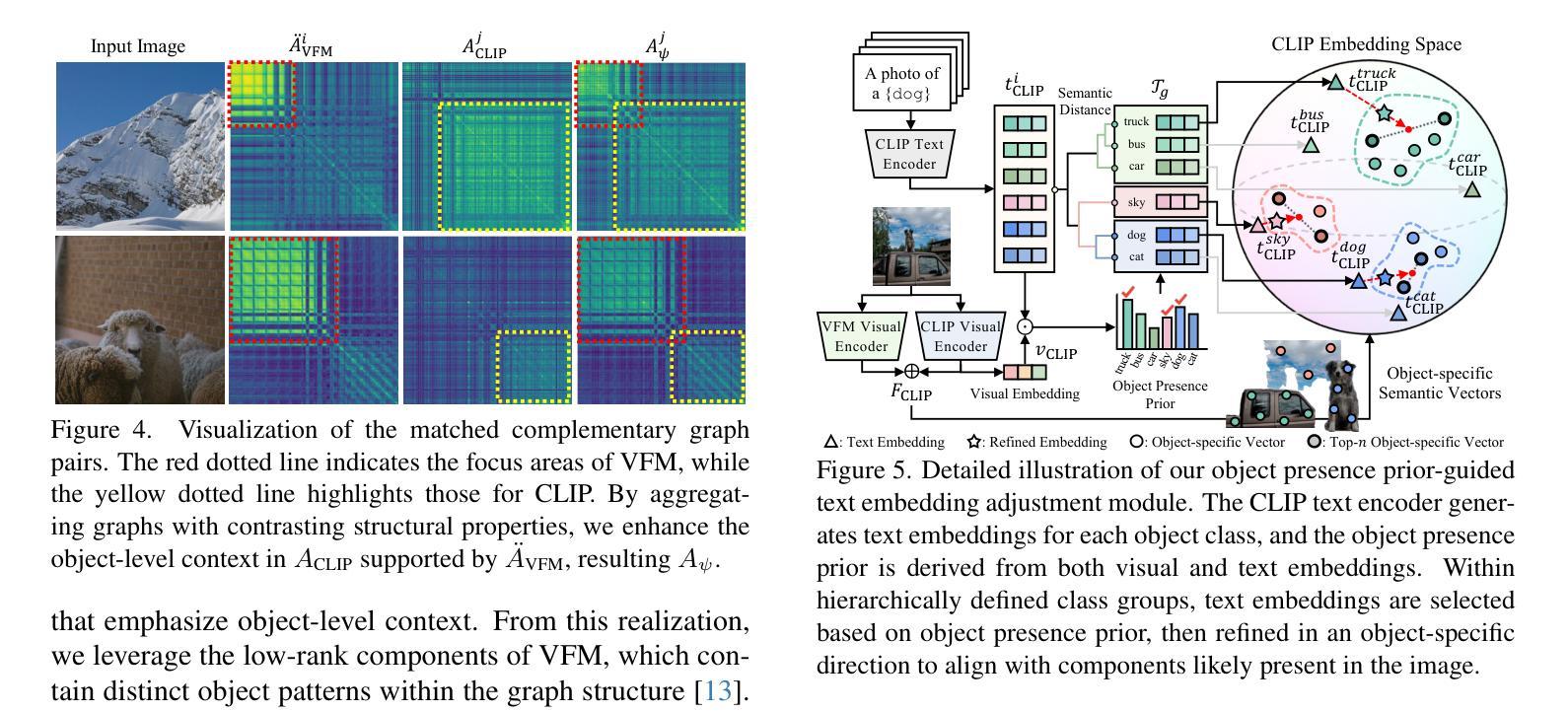
Distilling Spectral Graph for Object-Context Aware Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Chanyoung Kim, Dayun Ju, Woojung Han, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Seong Jae Hwang
Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation (OVSS) has advanced with recent vision-language models (VLMs), enabling segmentation beyond predefined categories through various learning schemes. Notably, training-free methods offer scalable, easily deployable solutions for handling unseen data, a key goal of OVSS. Yet, a critical issue persists: lack of object-level context consideration when segmenting complex objects in the challenging environment of OVSS based on arbitrary query prompts. This oversight limits models’ ability to group semantically consistent elements within object and map them precisely to user-defined arbitrary classes. In this work, we introduce a novel approach that overcomes this limitation by incorporating object-level contextual knowledge within images. Specifically, our model enhances intra-object consistency by distilling spectral-driven features from vision foundation models into the attention mechanism of the visual encoder, enabling semantically coherent components to form a single object mask. Additionally, we refine the text embeddings with zero-shot object presence likelihood to ensure accurate alignment with the specific objects represented in the images. By leveraging object-level contextual knowledge, our proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art performance with strong generalizability across diverse datasets.
开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)随着最近的视觉语言模型(VLMs)的发展而进步,通过各种学习方案实现了超出预定类别的分割。值得注意的是,无训练方法为处理未见数据提供了可扩展、易于部署的解决方案,这是OVSS的关键目标。然而,一个关键问题依然存在:在基于任意查询提示的OVSS的复杂环境中,对复杂对象进行分割时缺乏对象级别的上下文考虑。这种疏忽限制了模型在对象内组合语义一致元素的能力,并准确地将它们映射到用户定义的任意类别。在这项工作中,我们介绍了一种克服这一限制的新方法,该方法通过在图像中融入对象级别的上下文知识。具体来说,我们的模型通过从视觉基础模型中提炼光谱驱动特征并将其蒸馏到视觉编码器的注意力机制中,增强了对象内部的连贯性,使得语义一致的组件能够形成单个对象掩码。此外,我们还通过零样本对象存在概率对文本嵌入进行了精炼,以确保与图像中表示的特定对象的准确对齐。通过利用对象级别的上下文知识,我们提出的方法在多个数据集上实现了最先进的性能,并具有较强的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要介绍了开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)的最新进展,特别是如何利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)的先进技术实现超越预定类别的分割。文章重点介绍了一种新的方法,通过融入对象级别的上下文知识来解决在开放词汇语义分割中因任意查询提示而导致的复杂对象分割问题。该方法提高了模型的性能,使模型能够在各种数据集上实现最先进的性能并具有强大的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)借助视觉语言模型(VLMs)的先进技术,实现了超越预定类别的分割。
- 训练免费的方法为处理未见数据提供了可伸缩和易于部署的解决方案,这是OVSS的关键目标。
- 当前存在的问题是,在基于任意查询提示的开放词汇语义分割的复杂环境中,缺乏对象级别的上下文考虑。
- 新方法通过融入对象级别的上下文知识来解决此问题,提高了模型对对象内部一致性的表现。
- 该方法通过提炼视觉基础模型的频谱驱动特征并注入视觉编码器的注意力机制来实现。
- 对文本嵌入进行改进,使用零样本对象存在可能性来确保与图像中表示的特定对象的准确对齐。
点此查看论文截图

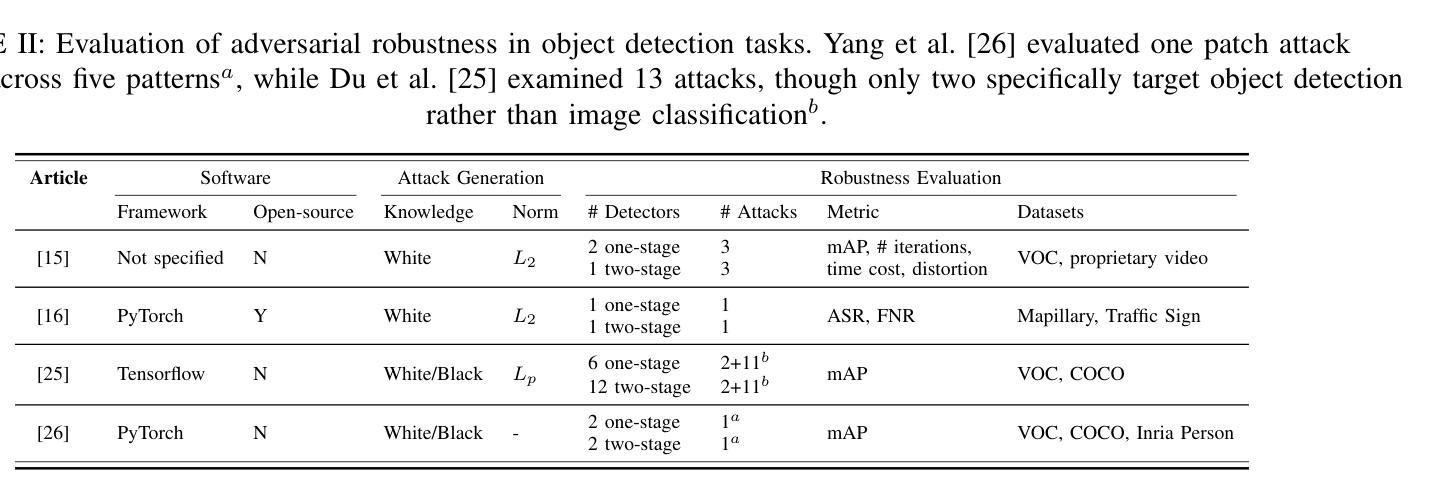
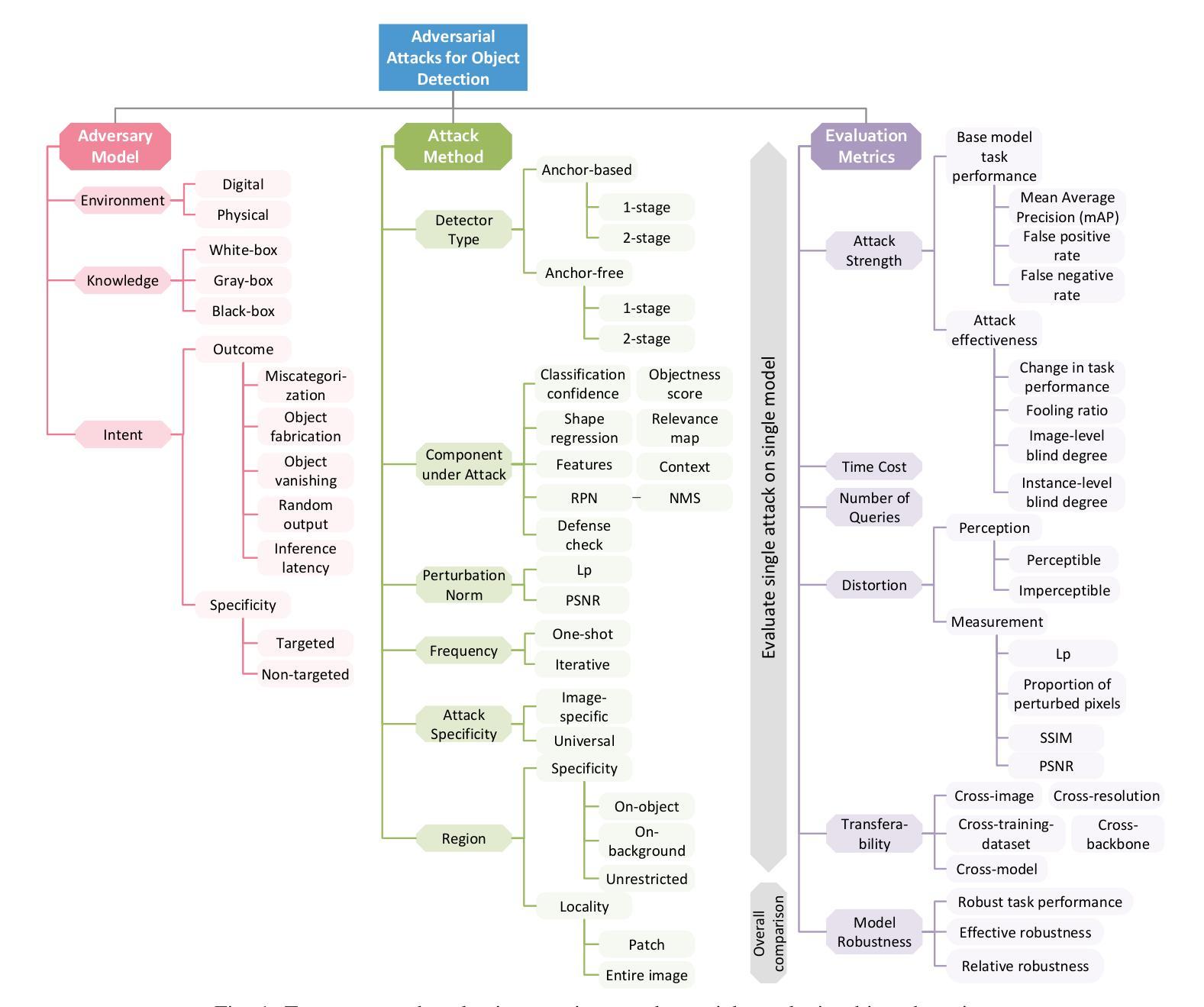
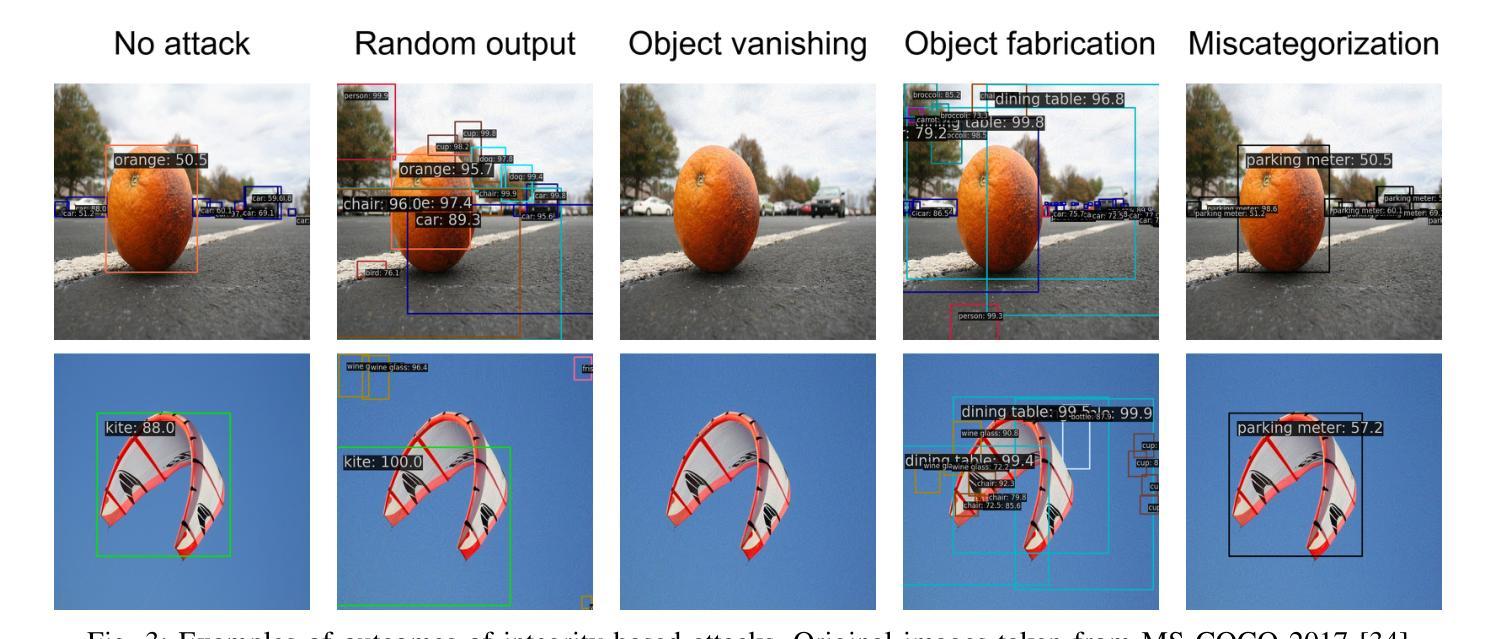
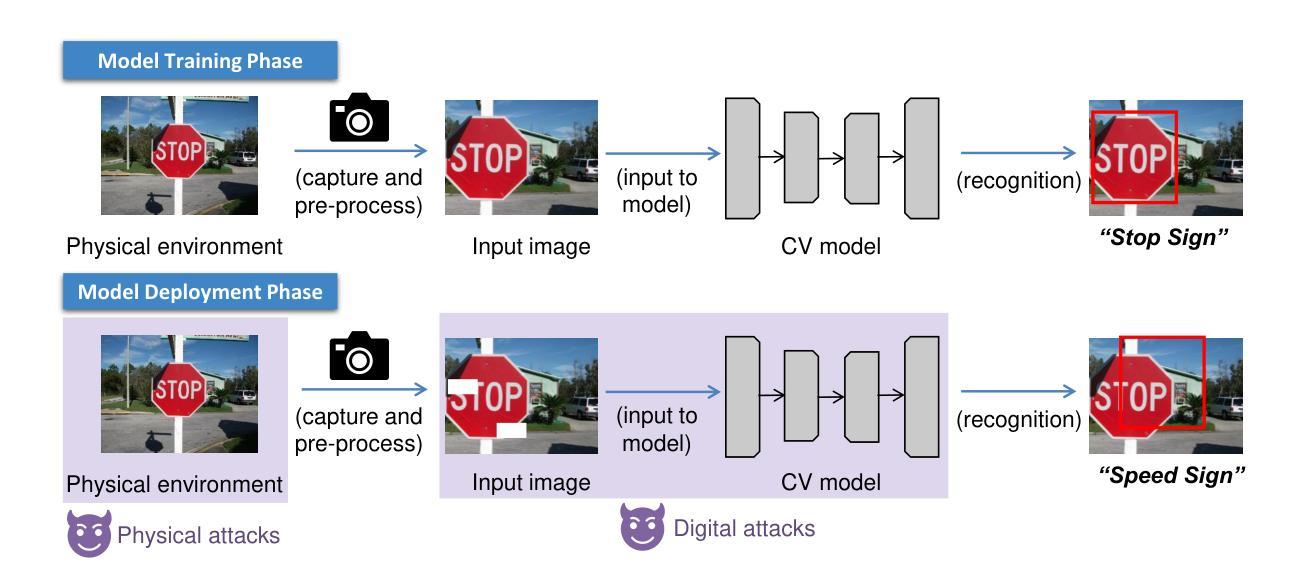
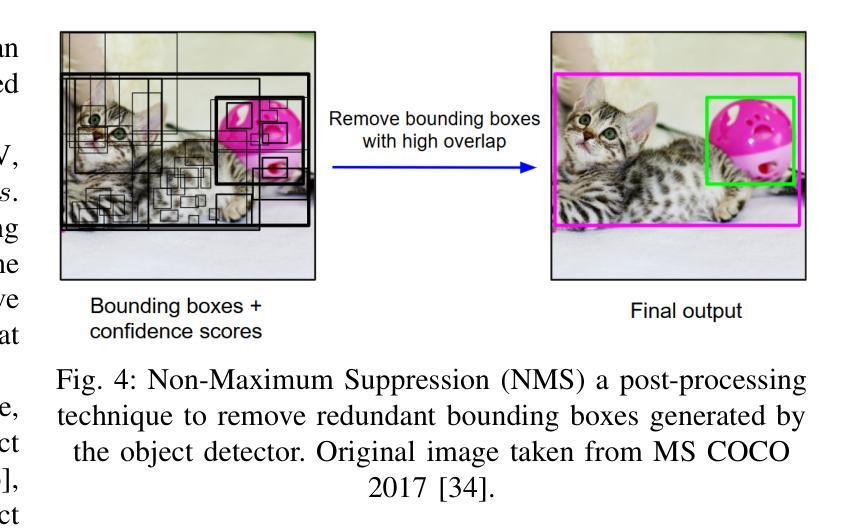
A Survey and Evaluation of Adversarial Attacks for Object Detection
Authors:Khoi Nguyen Tiet Nguyen, Wenyu Zhang, Kangkang Lu, Yuhuan Wu, Xingjian Zheng, Hui Li Tan, Liangli Zhen
Deep learning models achieve remarkable accuracy in computer vision tasks, yet remain vulnerable to adversarial examples–carefully crafted perturbations to input images that can deceive these models into making confident but incorrect predictions. This vulnerability pose significant risks in high-stakes applications such as autonomous vehicles, security surveillance, and safety-critical inspection systems. While the existing literature extensively covers adversarial attacks in image classification, comprehensive analyses of such attacks on object detection systems remain limited. This paper presents a novel taxonomic framework for categorizing adversarial attacks specific to object detection architectures, synthesizes existing robustness metrics, and provides a comprehensive empirical evaluation of state-of-the-art attack methodologies on popular object detection models, including both traditional detectors and modern detectors with vision-language pretraining. Through rigorous analysis of open-source attack implementations and their effectiveness across diverse detection architectures, we derive key insights into attack characteristics. Furthermore, we delineate critical research gaps and emerging challenges to guide future investigations in securing object detection systems against adversarial threats. Our findings establish a foundation for developing more robust detection models while highlighting the urgent need for standardized evaluation protocols in this rapidly evolving domain.
深度学习模型在计算机视觉任务中取得了令人瞩目的准确性,但仍然容易受到对抗样本的威胁。对抗样本是对输入图像进行精心制作的扰动,可以欺骗这些模型做出自信但错误的预测。这种脆弱性在高风险应用(如自动驾驶、安全监控和关键安全检测系统)中构成了重大风险。尽管现有文献广泛涵盖了图像分类中的对抗性攻击,但对目标检测系统中此类攻击的综合分析仍然有限。本文提出了一个针对目标检测架构的对抗性攻击的新型分类框架,对现有的稳健性指标进行了综合,对流行的目标检测模型上的最新攻击方法进行了全面的经验评估,包括传统检测器和使用视觉语言预训练的现代检测器。通过对开源攻击实现及其在不同检测架构中的有效性进行严谨分析,我们获得了关于攻击特性的关键见解。此外,我们指出了关键的研究空白和新兴挑战,为未来的研究提供了指导,以保护目标检测系统免受对抗性威胁。我们的研究为开发更稳健的检测模型奠定了基础,同时强调了在这一快速发展领域制定标准化评估协议的紧迫需求。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in the IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems (TNNLS)
Summary
深度学习模型在计算机视觉任务中取得了惊人的准确性,但在面临对抗样本时仍显得脆弱。对抗样本是精心制作的输入图像的扰动,可以欺骗模型做出自信但错误的预测。这一漏洞在高风险应用(如自动驾驶、安全监控和关键安全检查系统)中构成重大风险。本文提出了针对对象检测架构的对抗攻击的新型分类框架,综合了现有的稳健性指标,并对流行对象检测模型上的最新攻击方法进行了全面的实证评估,包括传统检测器和具有视觉语言预训练的现代检测器。通过对开源攻击实现的严格分析以及它们在各种检测架构中的有效性,我们获得了关于攻击特性的关键见解。我们的发现为开发更稳健的检测模型奠定了基础,同时强调了在这一快速发展领域中对标准化评估协议的迫切需求。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习模型在计算机视觉任务中表现出色,但在面对对抗样本时仍容易出错。
- 对抗样本可以欺骗模型做出自信但错误的预测,这在高风险应用中构成重大风险。
- 当前文献对图像分类中的对抗攻击进行了广泛覆盖,但对对象检测系统中的对抗攻击的综合分析仍然有限。
- 本文提出了针对对象检测架构的对抗攻击的新型分类框架。
- 综合了现有的稳健性指标,并对最新攻击方法在流行对象检测模型上的表现进行了全面评估。
- 通过对开源攻击实施的严格分析,获得了关于攻击特性的关键见解。
点此查看论文截图