⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-09 更新
AI for Climate Finance: Agentic Retrieval and Multi-Step Reasoning for Early Warning System Investments
Authors:Saeid Ario Vaghefi, Aymane Hachcham, Veronica Grasso, Jiska Manicus, Nakiete Msemo, Chiara Colesanti Senni, Markus Leippold
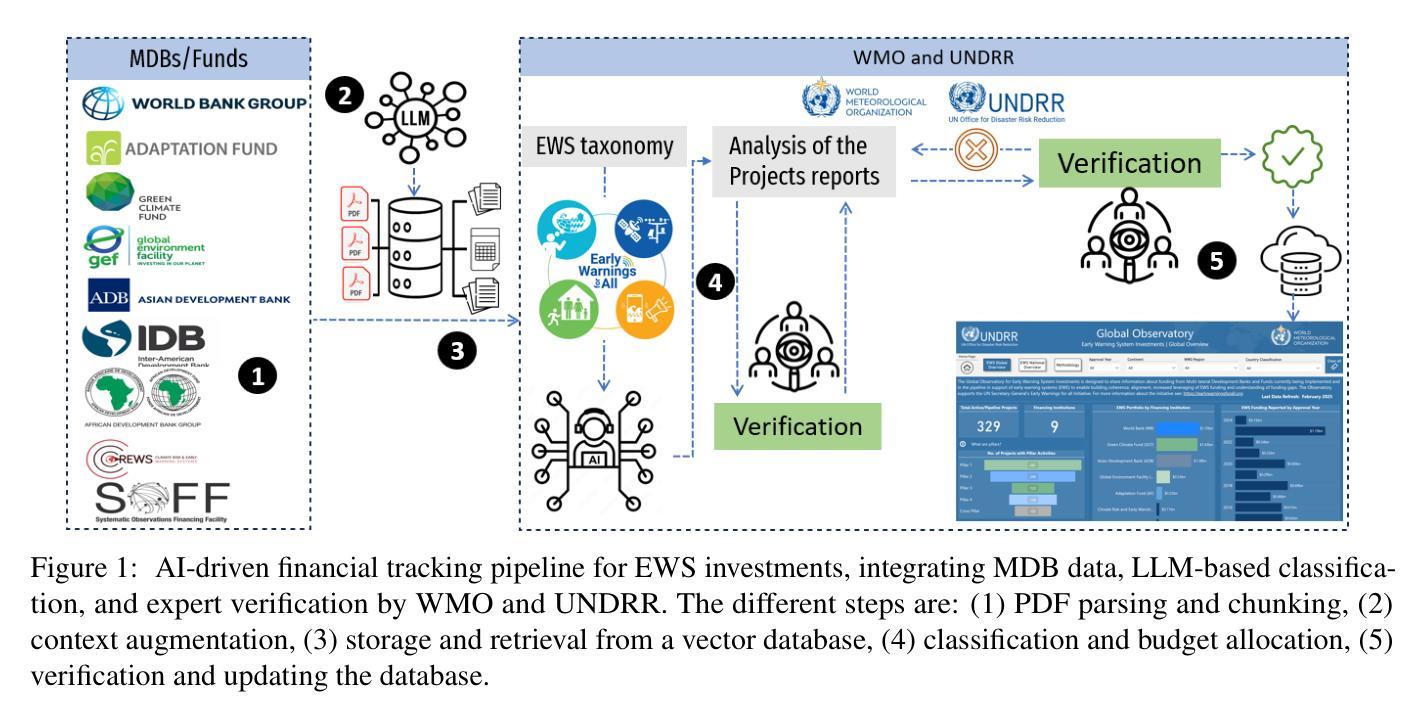
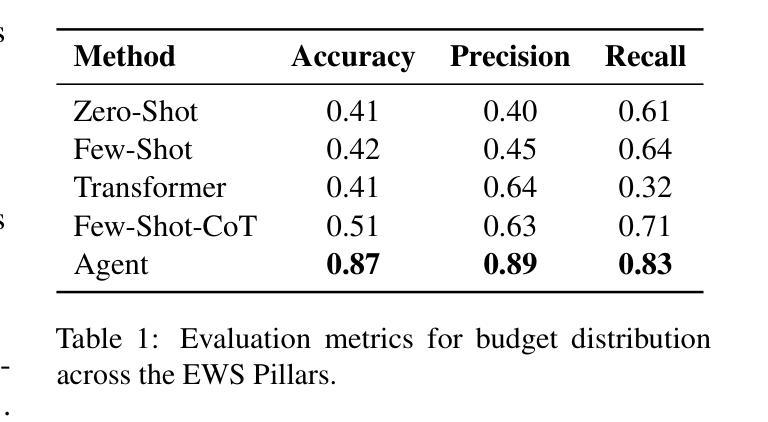
Tracking financial investments in climate adaptation is a complex and expertise-intensive task, particularly for Early Warning Systems (EWS), which lack standardized financial reporting across multilateral development banks (MDBs) and funds. To address this challenge, we introduce an LLM-based agentic AI system that integrates contextual retrieval, fine-tuning, and multi-step reasoning to extract relevant financial data, classify investments, and ensure compliance with funding guidelines. Our study focuses on a real-world application: tracking EWS investments in the Climate Risk and Early Warning Systems (CREWS) Fund. We analyze 25 MDB project documents and evaluate multiple AI-driven classification methods, including zero-shot and few-shot learning, fine-tuned transformer-based classifiers, chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting, and an agent-based retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) approach. Our results show that the agent-based RAG approach significantly outperforms other methods, achieving 87% accuracy, 89% precision, and 83% recall. Additionally, we contribute a benchmark dataset and expert-annotated corpus, providing a valuable resource for future research in AI-driven financial tracking and climate finance transparency.
跟踪气候适应中的金融投资是一项复杂且需要专业知识的工作,特别是对于缺乏多边发展银行和基金标准化财务报告的早期预警系统(EWS)而言更是如此。为了应对这一挑战,我们引入了一个基于大型语言模型(LLM)的主体人工智能系统,该系统融合了情境检索、微调以及多步推理,以提取相关的财务数据,对投资进行分类,并确保符合资金指导方针。我们的研究关注一个现实世界的运用:跟踪气候风险和早期预警系统(CREWS)基金中的EWS投资。我们分析了2.pdf中包含了有关气候风险管理和预警系统的文献和项目文档等相关信息多个自然标注的气候金融风险相关风险隐患的早期预警模型公开数据。通过对包括零次学习和少数学习在内的多种人工智能驱动的分类方法进行分析和评估,以及微调基于转换器的分类器、链式思维(CoT)提示和基于代理的检索增强生成(RAG)方法等,我们发现基于代理的RAG方法显著优于其他方法,达到了87%的准确性、89%的精确度和83%的召回率。此外,我们还贡献了一个基准数据集和专家注释语料库,为人工智能驱动的财务跟踪和气候金融透明度的未来研究提供了宝贵的资源。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理人工智能系统,用于跟踪气候适应投资。该系统结合了情境检索、微调和多步推理技术,能够从多边发展银行和基金的项目文档中抽取相关财务数据,对投资进行分类,并确保符合资助指南的要求。在气候风险和预警系统基金(CREWS)的早期预警系统(EWS)投资跟踪的实例应用中,该系统显著优于其他方法,实现了较高的准确性和精确度。此外,本文还提供了一个基准数据集和专家注释语料库,为未来在金融跟踪和气候金融透明度方面的AI研究提供了宝贵资源。
Key Takeaways
- 引入基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理人工智能系统来应对气候适应投资跟踪的挑战。
- 该系统集成了情境检索、微调及多步推理技术以抽取和分类金融数据。
- 研究侧重于实际应用程序:跟踪气候风险与早期预警系统基金(CREWS)的早期预警系统(EWS)投资。
- 通过分析25个MDB项目文档,评估了多种AI驱动的分类方法。
- 代理基于检索增强生成(RAG)的方法在性能上显著优于其他方法,达到高准确性、精确性和召回率。
- 贡献了一个基准数据集和专家注释语料库,为未来研究提供资源。
点此查看论文截图

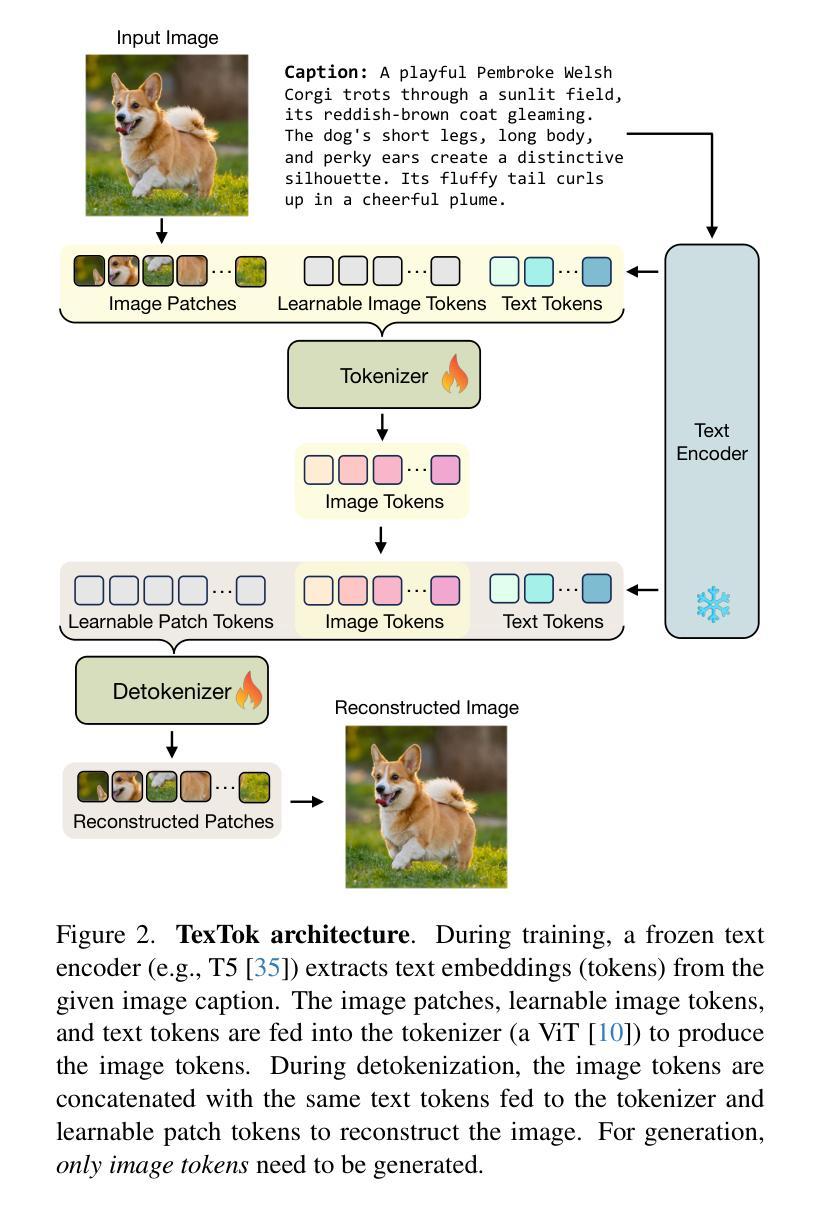
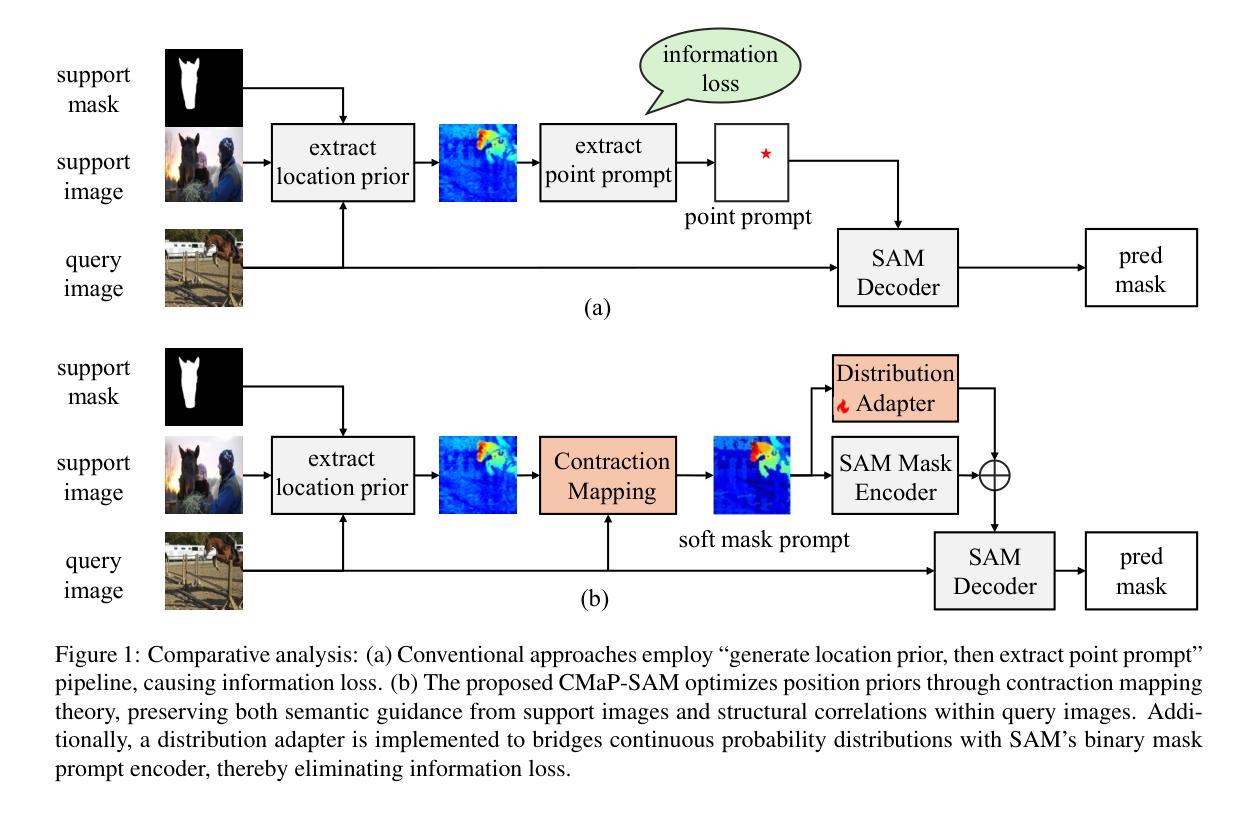
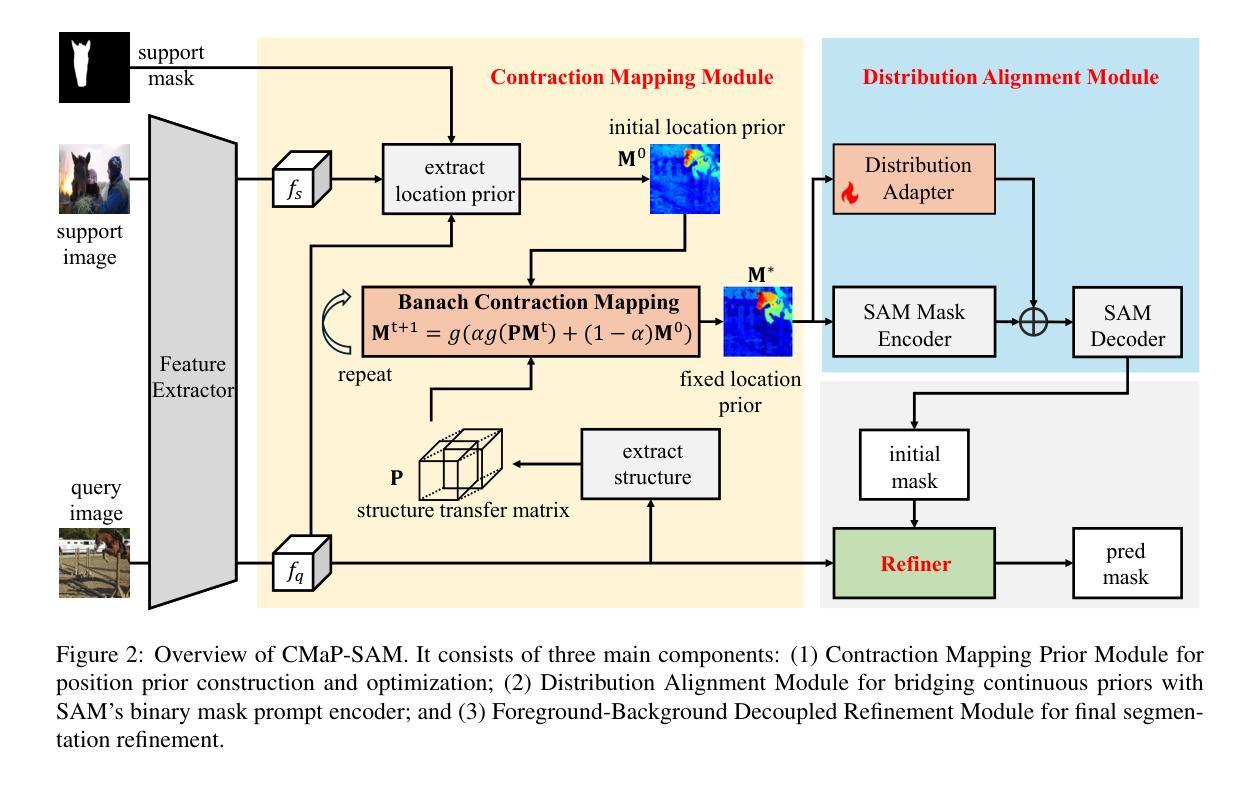
CMaP-SAM: Contraction Mapping Prior for SAM-driven Few-shot Segmentation
Authors:Shuai Chen, Fanman Meng, Haoran Wei, Chenhao Wu, Qingbo Wu, Linfeng Xu, Hongliang Li
Few-shot segmentation (FSS) aims to segment new classes using few annotated images. While recent FSS methods have shown considerable improvements by leveraging Segment Anything Model (SAM), they face two critical limitations: insufficient utilization of structural correlations in query images, and significant information loss when converting continuous position priors to discrete point prompts. To address these challenges, we propose CMaP-SAM, a novel framework that introduces contraction mapping theory to optimize position priors for SAM-driven few-shot segmentation. CMaP-SAM consists of three key components: (1) a contraction mapping module that formulates position prior optimization as a Banach contraction mapping with convergence guarantees. This module iteratively refines position priors through pixel-wise structural similarity, generating a converged prior that preserves both semantic guidance from reference images and structural correlations in query images; (2) an adaptive distribution alignment module bridging continuous priors with SAM’s binary mask prompt encoder; and (3) a foreground-background decoupled refinement architecture producing accurate final segmentation masks. Extensive experiments demonstrate CMaP-SAM’s effectiveness, achieving state-of-the-art performance with 71.1 mIoU on PASCAL-$5^i$ and 56.1 on COCO-$20^i$ datasets.
少量样本分割(FSS)旨在使用少量标注图像对新类别进行分割。虽然最近的FSS方法通过利用分割任何事物模型(SAM)取得了显著的改进,但它们面临两个关键局限:未充分利用查询图像中的结构相关性,以及在将连续位置先验转换为离散点提示时丢失了大量信息。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了CMaP-SAM,这是一个引入收缩映射理论来优化SAM驱动少量样本分割的位置先验值的新框架。CMaP-SAM由三个关键组件构成:(1)收缩映射模块,它将位置先验优化公式化为具有收敛保证的巴拿赫收缩映射。该模块通过像素级结构相似性迭代地优化位置先验,生成一个收敛的先验值,该先验值既保留了参考图像的语义指导,又保留了查询图像中的结构相关性;(2)自适应分布对齐模块,该模块连接连续先验与SAM的二进制掩膜提示编码器;(3)前景背景解耦细化架构,生成精确的最终分割掩膜。大量实验证明了CMaP-SAM的有效性,在PASCAL-$5^i$数据集上达到了71.1 mIoU的最新性能,在COCO-$20^i$数据集上达到了56.1的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 figures
Summary
基于少量标注图像进行新类别分割的Few-shot segmentation(FSS)方法虽然已经取得了显著进步,但它们仍然面临两个关键问题:未能充分利用查询图像中的结构相关性,以及在将连续位置先验转换为离散点提示时丢失了大量信息。为解决这些问题,本文提出了CMaP-SAM框架,引入收缩映射理论优化SAM的位置先验信息。CMaP-SAM包括三个关键组件:收缩映射模块、自适应分布对齐模块和前景背景分离细化架构。实验证明,CMaP-SAM在PASCAL-$5^i$和COCO-$20^i$数据集上达到了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- Few-shot segmentation (FSS)旨在使用少量标注图像进行新类别分割。
- 现有FSS方法存在两个关键限制:未充分利用查询图像的结构相关性,以及在转换位置先验时丢失信息。
- CMaP-SAM框架被提出以解决这些挑战,引入收缩映射理论优化位置先验信息。
- CMaP-SAM包括三个关键组件:收缩映射模块、自适应分布对齐模块和细化架构。
- 收缩映射模块通过公式化位置先验优化为Banach收缩映射,保证收敛性,并生成保留语义指导和结构关联的收敛先验。
- 自适应分布对齐模块连接连续先验和SAM的二元掩膜提示编码器。
- CMaP-SAM在PASCAL-$5^i$和COCO-$20^i$数据集上取得了最佳性能,达到71.1 mIoU和56.1的准确率。
点此查看论文截图

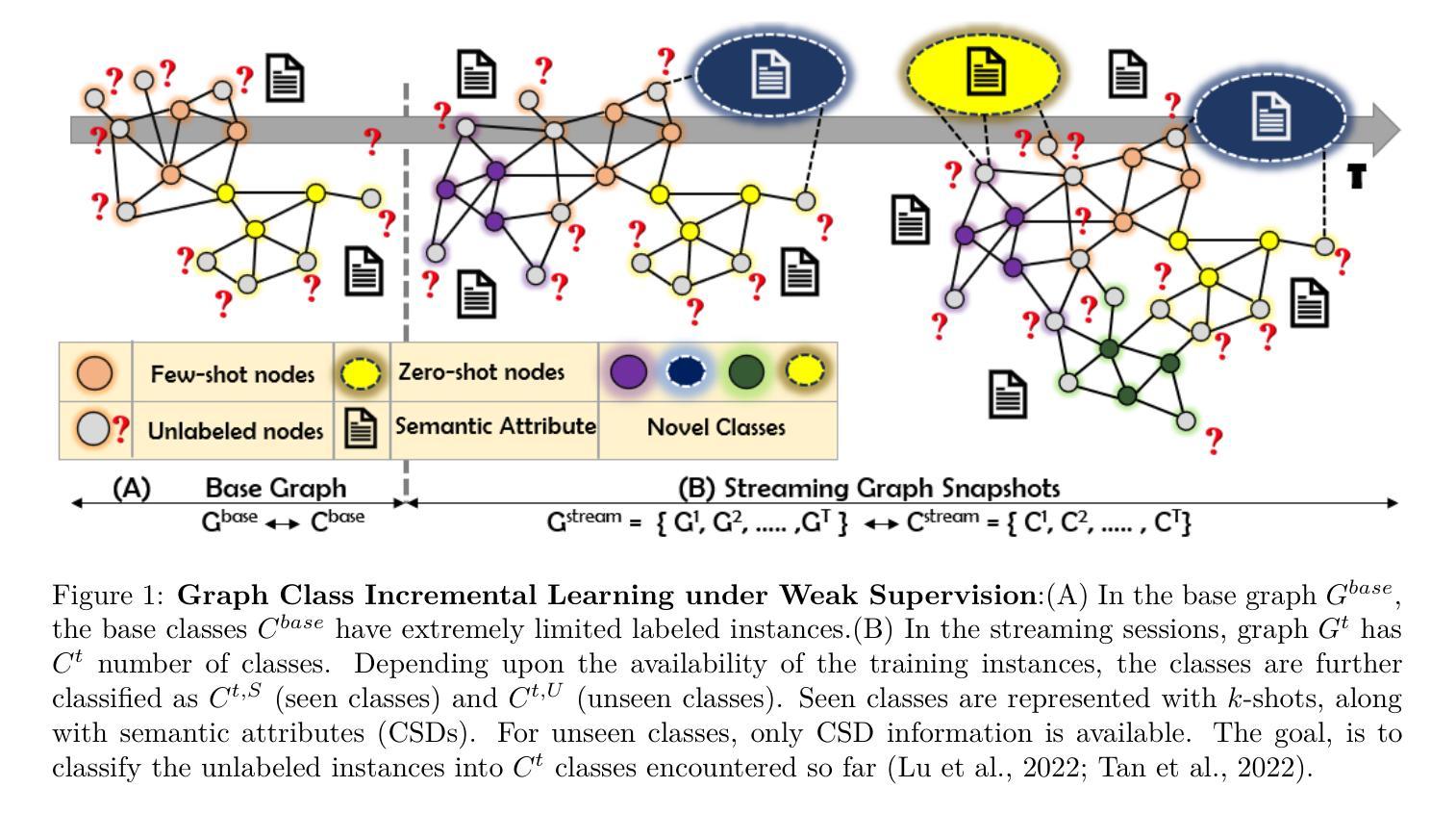
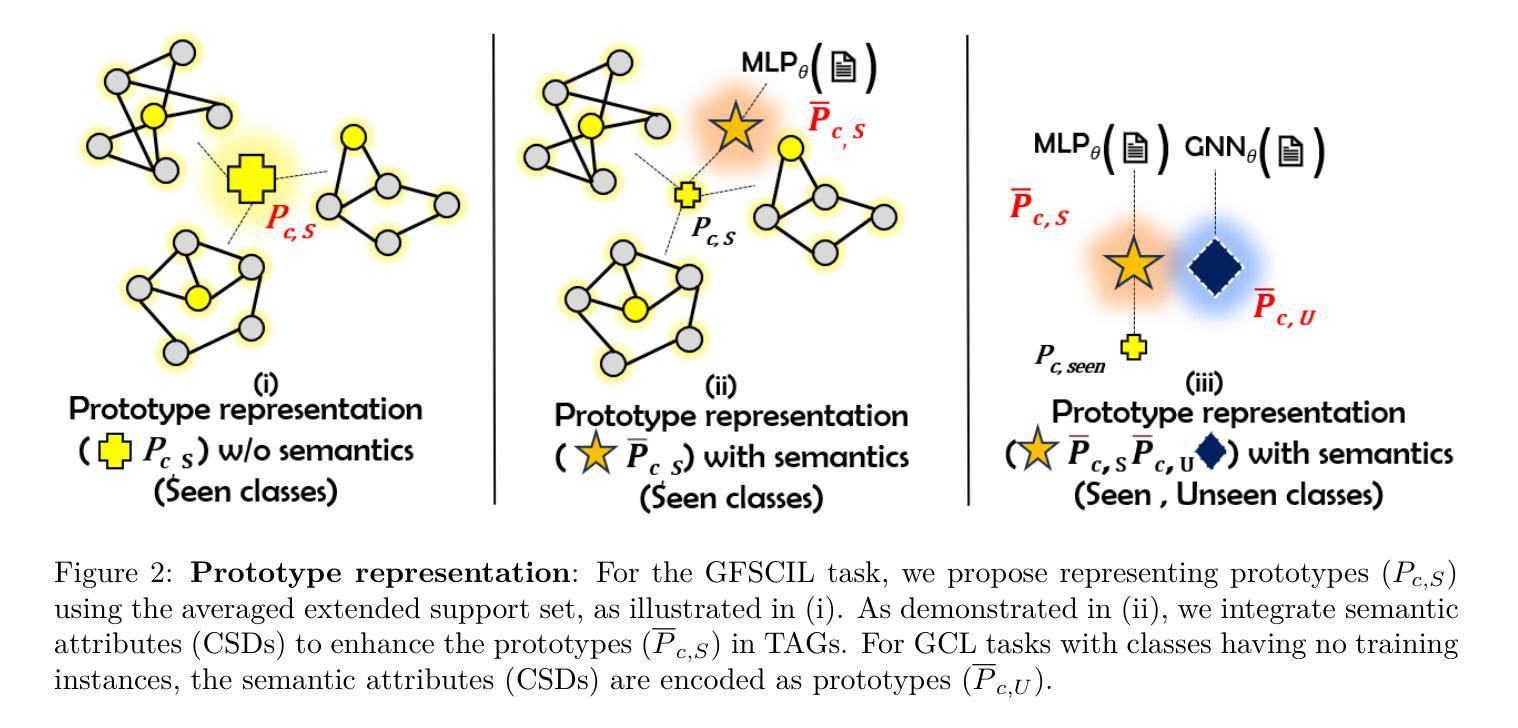
GOTHAM: Graph Class Incremental Learning Framework under Weak Supervision
Authors:Aditya Hemant Shahane, Prathosh A. P, Sandeep Kumar
Graphs are growing rapidly, along with the number of distinct label categories associated with them. Applications like e-commerce, healthcare, recommendation systems, and various social media platforms are rapidly moving towards graph representation of data due to their ability to capture both structural and attribute information. One crucial task in graph analysis is node classification, where unlabeled nodes are categorized into predefined classes. In practice, novel classes appear incrementally sometimes with just a few labels (seen classes) or even without any labels (unseen classes), either because they are new or haven’t been explored much. Traditional methods assume abundant labeled data for training, which isn’t always feasible. We investigate a broader objective: \emph{Graph Class Incremental Learning under Weak Supervision (GCL)}, addressing this challenge by meta-training on base classes with limited labeled instances. During the incremental streams, novel classes can have few-shot or zero-shot representation. Our proposed framework GOTHAM efficiently accommodates these unlabeled nodes by finding the closest prototype representation, serving as class representatives in the attribute space. For Text-Attributed Graphs (TAGs), our framework additionally incorporates semantic information to enhance the representation. By employing teacher-student knowledge distillation to mitigate forgetting, GOTHAM achieves promising results across various tasks. Experiments on datasets such as Cora-ML, Amazon, and OBGN-Arxiv showcase the effectiveness of our approach in handling evolving graph data under limited supervision. The repository is available here: \href{https://github.com/adityashahane10/GOTHAM--Graph-based-Class-Incremental-Learning-Framework-under-Weak-Supervision}{\small \textcolor{blue}{Code}}
图论正随着与其相关的不同标签类别的数量而快速发展。电子商务、医疗保健、推荐系统以及各种社交媒体平台等应用程序,由于能够捕获结构和属性信息,正迅速将数据表示为图。图分析中的一个关键任务是对未标记节点进行分类,将它们分类到预定义的类别中。在实践中,新类别有时会以仅包含少量标签(可见类别)甚至没有任何标签(未见类别)的形式出现,这可能是因为它们是新出现的或尚未被充分探索。传统方法假设有大量的标记数据用于训练,但这并不总是可行的。我们研究了一个更广泛的目标:在基础类别有限标记实例的元训练下,解决这一挑战的《图类增量学习在弱监督下的挑战(GCL)》。在增量流期间,新类别可以具有小样本或零样本表示。我们提出的GOTHAM框架通过找到最接近的原型表示来有效地容纳这些未标记的节点,该原型表示可作为属性空间中的类别代表。对于文本属性图(TAG),我们的框架还结合了语义信息以增强表示。通过采用教师-学生知识蒸馏来缓解遗忘,GOTHAM在各种任务上取得了有前景的结果。在Cora-ML、Amazon和OBGN-Arxiv等数据集上的实验展示了我们的方法在有限监督下处理不断发展的图形数据的有效性。相关仓库请点击这里查看:【代码】(https://github.com/adityashahane10/GOTHAM--Graph-based-Class-Incremental-Learning-Framework-under-Weak-Supervision)\textcolor{blue}{🔗}。(网址中的中文已做相应调整)
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
图论正快速发展,不同标签类别的数量也急剧增长。因图能捕捉结构性和属性信息,电子商务、医疗、推荐系统以及各种社交媒体平台等应用纷纷采用数据图的表示形式。图分析的一个重要任务是节点分类,即把未标记的节点归类到预定义的类别中。现实场景中,新类别往往仅有几张标签或者完全没有标签,传统方法需要大量标记数据进行训练,这并不总是可行。本研究探讨了一个更广泛的目标:弱监督下的图类增量学习(GCL),通过在基础类别上进行元训练来解决这一挑战,且训练样本有限。在增量流中,新类别可具有小样本或零样本表示。提出的GOTHAM框架能高效容纳这些未标记节点,通过寻找最接近的原型表示作为属性空间中的类别代表。对于文本属性图(TAG),该框架还融入了语义信息以增强表示。通过采用教师-学生知识蒸馏来缓解遗忘问题,GOTHAM在各种任务上取得了有前景的结果。在Cora-ML、Amazon和OBGN-Arxiv等数据集上的实验展示了该方法在处理有限监督下的动态图数据的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 图论及其相关应用正快速发展,涵盖多种数据类型和标签类别。
- 现实场景中,新的数据类别可能仅带有少量标签或无标签,传统方法受限。
- 研究提出了弱监督下的图类增量学习(GCL)目标来应对这一挑战。
- GOTHAM框架通过寻找原型表示来容纳未标记节点,并在属性空间中作为类别代表。
- GOTHAM框架对于文本属性图融入了语义信息以增强表示。
- 采用教师-学生知识蒸馏来减轻遗忘问题。
点此查看论文截图

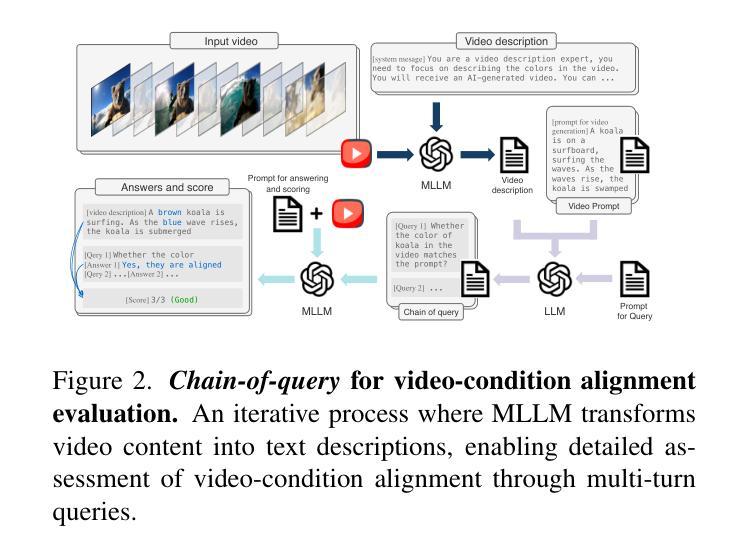
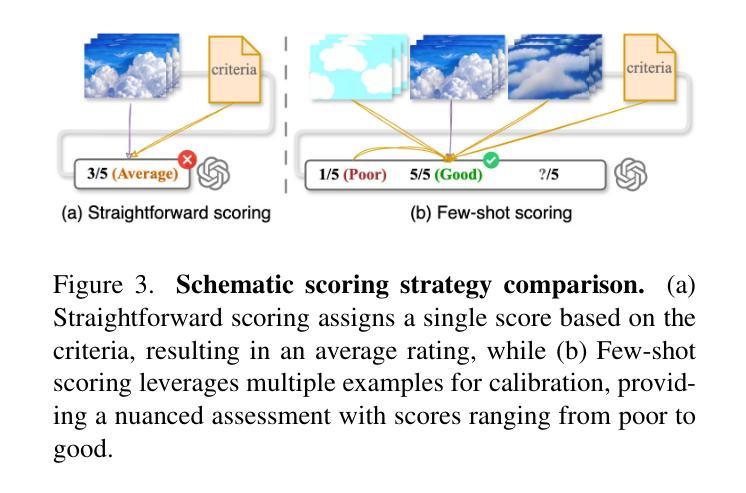
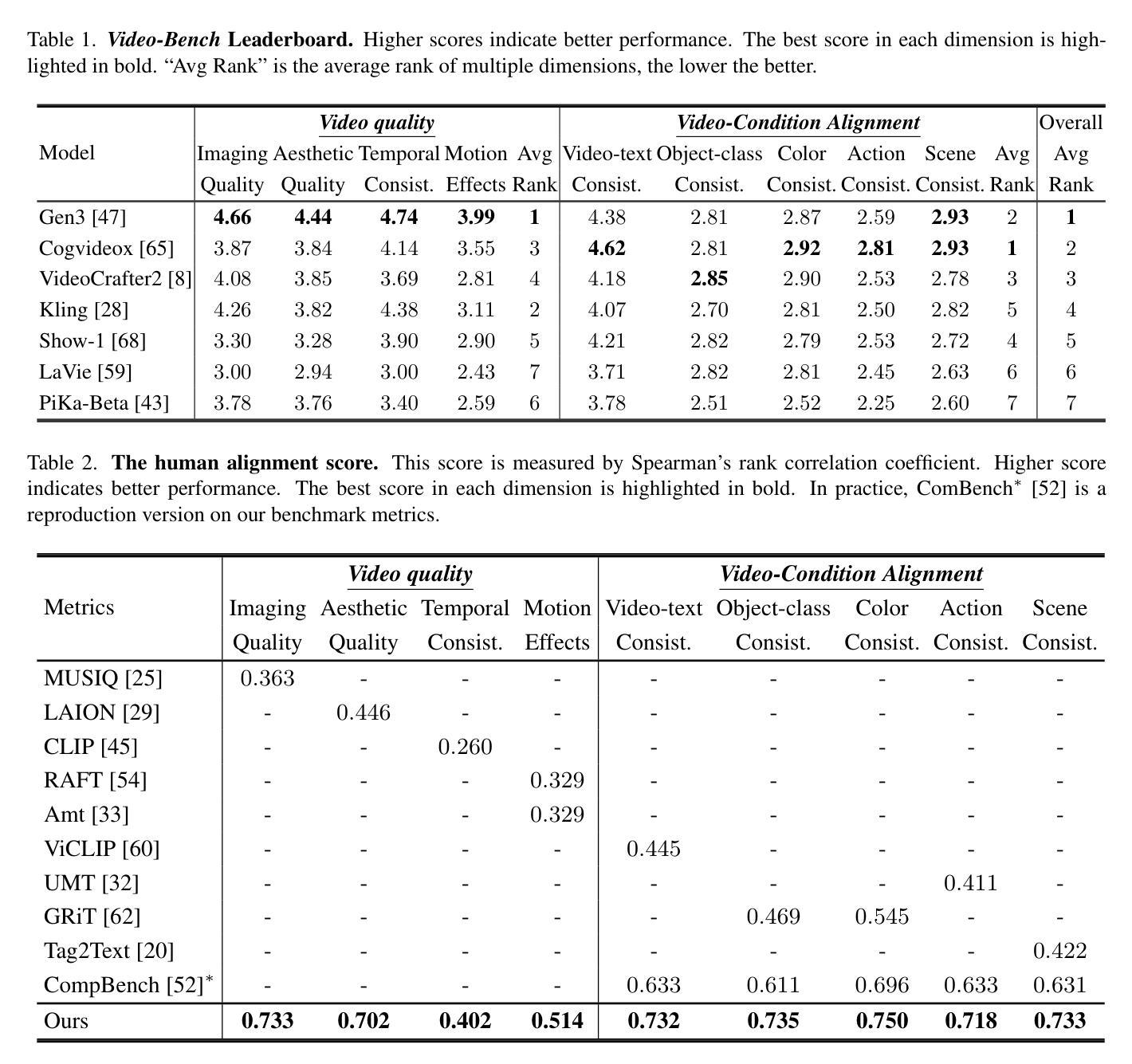
Video-Bench: Human-Aligned Video Generation Benchmark
Authors:Hui Han, Siyuan Li, Jiaqi Chen, Yiwen Yuan, Yuling Wu, Chak Tou Leong, Hanwen Du, Junchen Fu, Youhua Li, Jie Zhang, Chi Zhang, Li-jia Li, Yongxin Ni
Video generation assessment is essential for ensuring that generative models produce visually realistic, high-quality videos while aligning with human expectations. Current video generation benchmarks fall into two main categories: traditional benchmarks, which use metrics and embeddings to evaluate generated video quality across multiple dimensions but often lack alignment with human judgments; and large language model (LLM)-based benchmarks, though capable of human-like reasoning, are constrained by a limited understanding of video quality metrics and cross-modal consistency. To address these challenges and establish a benchmark that better aligns with human preferences, this paper introduces Video-Bench, a comprehensive benchmark featuring a rich prompt suite and extensive evaluation dimensions. This benchmark represents the first attempt to systematically leverage MLLMs across all dimensions relevant to video generation assessment in generative models. By incorporating few-shot scoring and chain-of-query techniques, Video-Bench provides a structured, scalable approach to generated video evaluation. Experiments on advanced models including Sora demonstrate that Video-Bench achieves superior alignment with human preferences across all dimensions. Moreover, in instances where our framework’s assessments diverge from human evaluations, it consistently offers more objective and accurate insights, suggesting an even greater potential advantage over traditional human judgment.
视频生成评估对于确保生成模型产生视觉真实、高质量的视频并且符合人类期望至关重要。当前的视频生成基准测试主要分为两大类:传统基准测试使用指标和嵌入来评估生成视频质量多个维度,但往往与人类判断缺乏一致性;而基于大型语言模型(LLM)的基准测试虽然具备人类推理能力,但对视频质量指标的跨模态一致性理解有限。为了解决这些挑战并建立一个更好地符合人类偏好的基准测试,本文介绍了Video-Bench,这是一个拥有丰富提示套件和广泛评估维度的综合基准测试。该基准测试是首次尝试在生成模型中涉及视频生成评估的所有维度上系统地利用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)。通过结合少样本评分和查询链技术,Video-Bench为生成的视频评估提供了一种结构化、可扩展的方法。在包括Sora的高级模型上的实验表明,Video-Bench在所有维度上实现了与人类偏好更优越的对齐。此外,在我们的框架的评估与人类评估出现分歧的情况下,它始终提供更客观和准确的见解,这表明它比传统的基于人类的判断具有更大的潜在优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR’25
Summary
视频生成评估对于确保生成模型生成视觉真实、高质量的视频至关重要,同时符合人类期望。当前视频生成基准测试主要分为两类:传统基准测试使用指标和嵌入来评估生成视频质量,但往往缺乏与人类判断的对齐;而基于大型语言模型的基准测试虽然能够进行人类推理,但对视频质量指标和跨模态一致性的理解有限。为解决这些挑战并建立一个更符合人类偏好的基准测试,本文介绍了Video-Bench,这是一个包含丰富提示套件和广泛评估维度的综合基准测试。它首次尝试在视频生成评估的所有相关维度上系统地利用大型语言模型。通过结合少样本评分和链查询技术,Video-Bench为生成的视频提供了一种结构化、可扩展的评估方法。在高级模型上的实验表明,Video-Bench在所有维度上实现了与人类偏好的优越对齐。此外,在我们框架的评估与人类评估存在分歧的情况下,它始终提供更客观和准确的见解。
Key Takeaways
Video generation assessment is essential for generative models to produce visually realistic, high-quality videos.
视频生成评估对于生成模型产生视觉真实、高质量的视频至关重要。Current video generation benchmarks have limitations, lacking alignment with human judgments.
当前视频生成的基准测试存在局限性,与人类判断的对齐程度不够。Video-Bench is introduced as a comprehensive benchmark for video generation assessment, featuring a rich prompt suite and extensive evaluation dimensions.
Video-Bench被引入作为视频生成评估的综合基准测试,具有丰富的提示套件和广泛的评估维度。Video-Bench leverages MLLMs (大型语言模型) across all dimensions of video generation assessment, marking the first attempt of this kind.
Video-Bench在视频生成评估的所有维度上都利用大型语言模型,这是第一次尝试这样做。Video-Bench incorporates few-shot scoring and chain-of-query techniques, providing a structured and scalable approach to generated video evaluation.
Video-Bench结合了少样本评分和链查询技术,为生成的视频评价提供了一种结构化和可扩展的方法。Experiments demonstrate that Video-Bench achieves superior alignment with human preferences across all dimensions compared to traditional benchmarks.
实验表明,与传统的基准测试相比,Video-Bench在所有维度上都实现了与人类偏好的优越对齐。When there are divergences between Video-Bench assessments and human evaluations, Video-Bench offers more objective and accurate insights.
点此查看论文截图

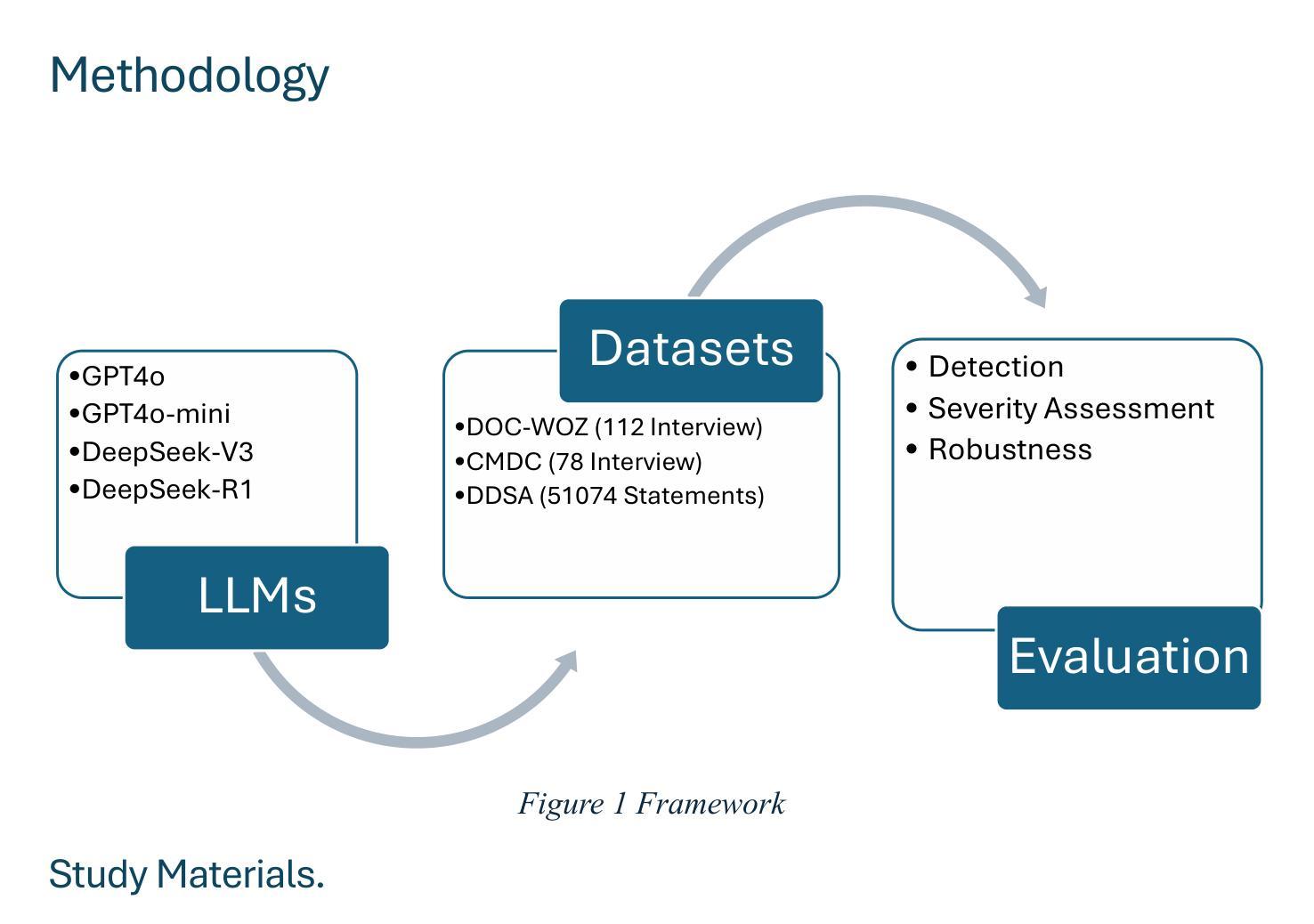
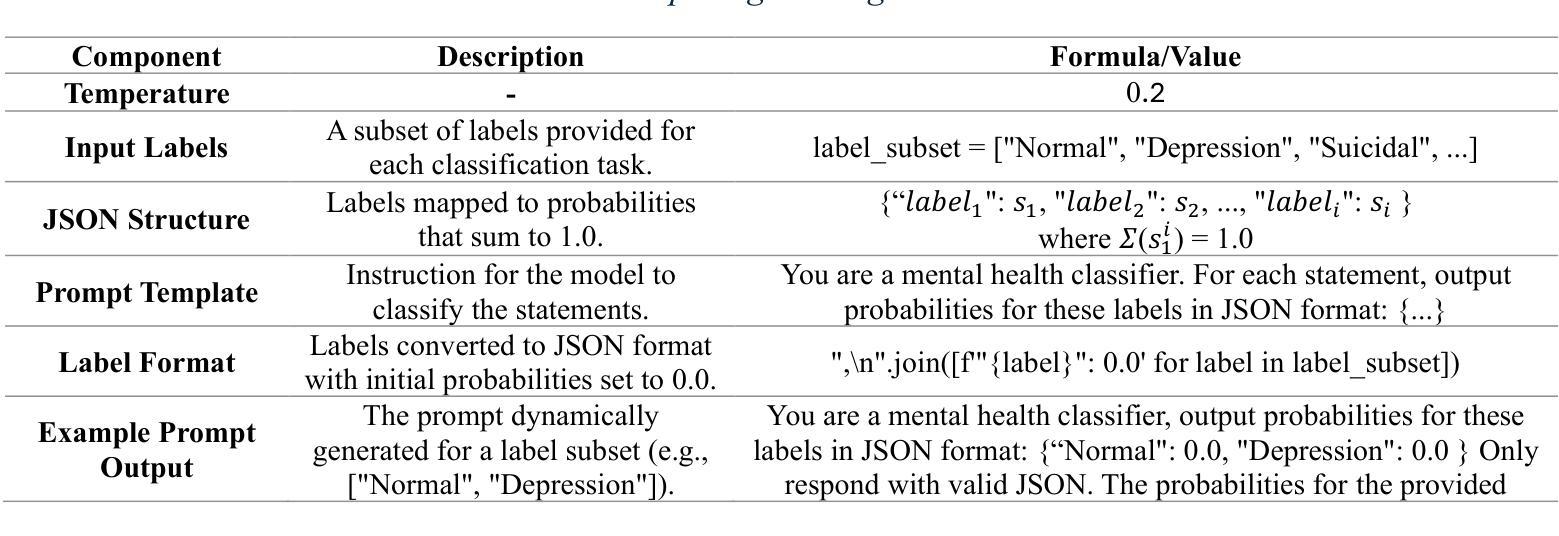
Leveraging Large Language Models for Cost-Effective, Multilingual Depression Detection and Severity Assessment
Authors:Longdi Xian, Jianzhang Ni, Mingzhu Wang
Depression is a prevalent mental health disorder that is difficult to detect early due to subjective symptom assessments. Recent advancements in large language models have offered efficient and cost-effective approaches for this objective. In this study, we evaluated the performance of four LLMs in depression detection using clinical interview data. We selected the best performing model and further tested it in the severity evaluation scenario and knowledge enhanced scenario. The robustness was evaluated in complex diagnostic scenarios using a dataset comprising 51074 statements from six different mental disorders. We found that DeepSeek V3 is the most reliable and cost-effective model for depression detection, performing well in both zero-shot and few-shot scenarios, with zero-shot being the most efficient choice. The evaluation of severity showed low agreement with the human evaluator, particularly for mild depression. The model maintains stably high AUCs for detecting depression in complex diagnostic scenarios. These findings highlight DeepSeek V3s strong potential for text-based depression detection in real-world clinical applications. However, they also underscore the need for further refinement in severity assessment and the mitigation of potential biases to enhance clinical reliability.
抑郁症是一种常见的心理健康疾病,由于主观症状评估,早期很难发现。最近大型语言模型的进步为这一目标提供了高效且低成本的方法。在这项研究中,我们使用临床访谈数据评估了四种大型语言模型在抑郁症检测方面的性能。我们选择了表现最佳的模型,并在严重程度评估和知识增强场景中进行了进一步测试。通过包含来自六种不同精神疾病的51074个陈述的数据集,对复杂诊断场景中的稳健性进行了评估。我们发现DeepSeek V3在抑郁症检测方面是最可靠且成本效益最高的模型,在零样本和少样本场景中表现良好,其中零样本是最有效率的选择。严重程度的评估显示与人类评估者的意见一致性较低,尤其是轻度抑郁。该模型在复杂诊断场景中保持较高的AUC值,用于检测抑郁症。这些发现突出了DeepSeek V3在现实世界临床应用中的强大潜力,用于基于文本的抑郁症检测。然而,它们也强调了有必要改进严重程度的评估,并减轻潜在偏见,以提高临床可靠性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型在抑郁症检测方面的应用取得了显著进展。本研究评估了四种LLMs在抑郁症检测中的性能,并发现DeepSeek V3模型在零样本和少样本场景下表现最可靠且成本效益最高。然而,在评估严重程度方面仍需进一步改进。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型已用于抑郁症检测,提供有效且经济的解决方案。
- 本研究评估了四种LLMs在抑郁症检测中的性能。
- DeepSeek V3模型在抑郁症检测方面表现最佳,适用于零样本和少样本场景。
- DeepSeek V3在复杂诊断情境中的表现稳定且可靠。
- 抑郁症的严重程度评估与人工评价者之间存在低一致性,尤其是轻度抑郁症。
- 需要进一步改进严重程度评估,以提高临床可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

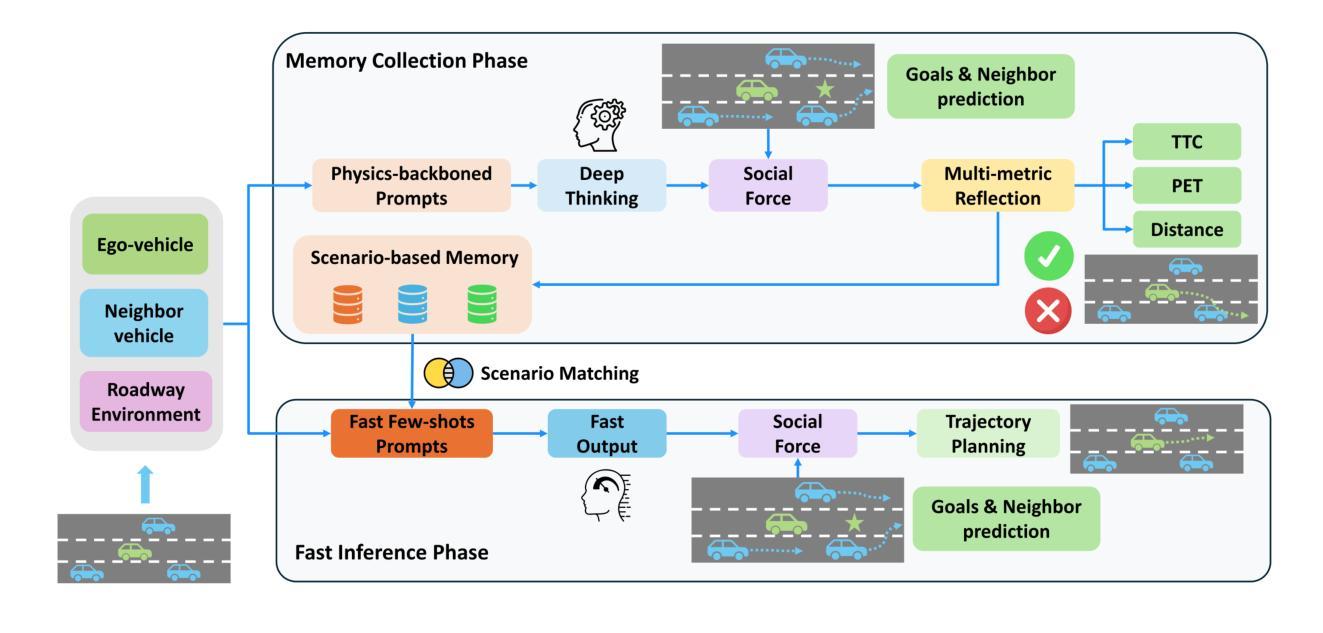
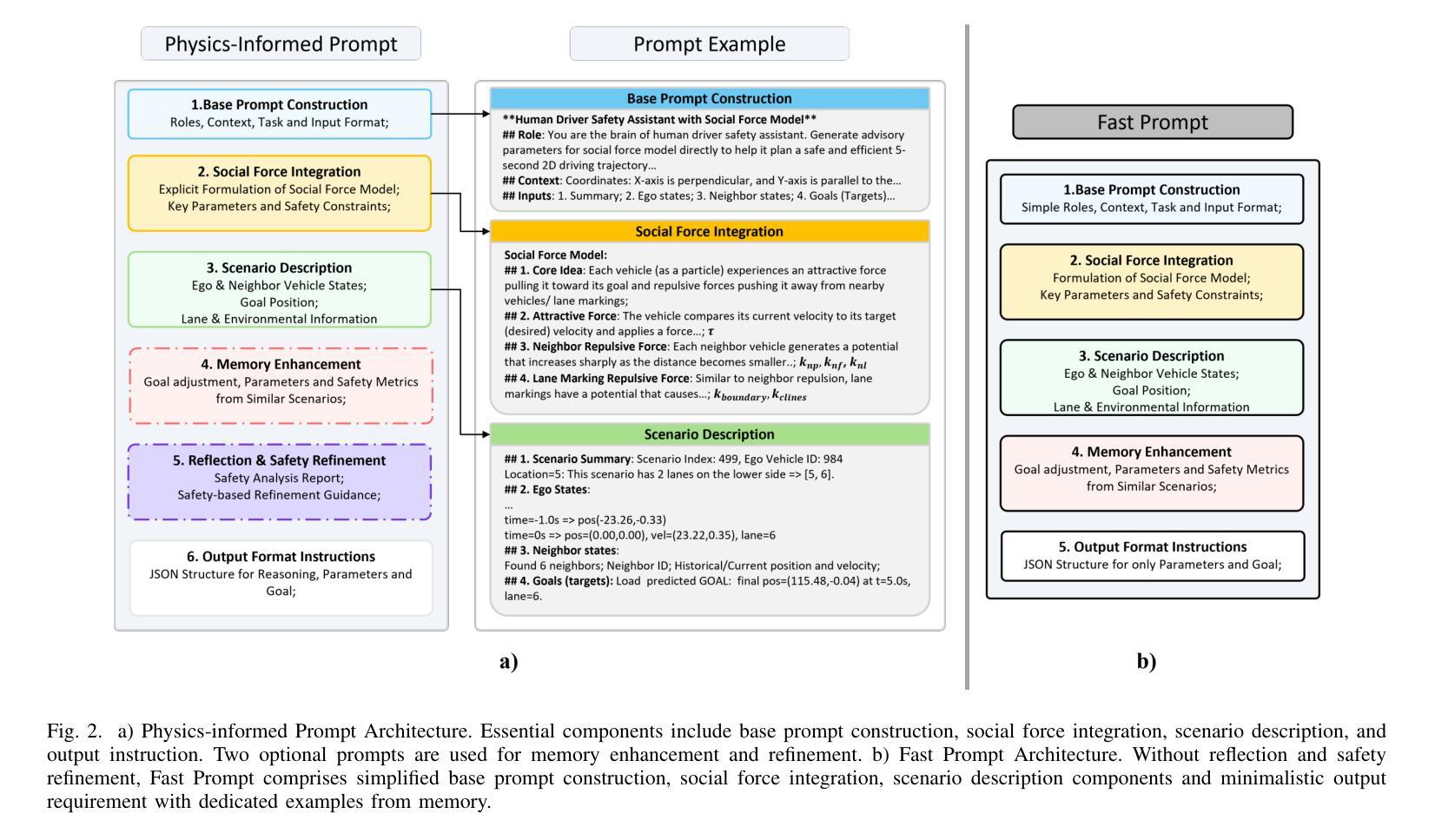
Planning Safety Trajectories with Dual-Phase, Physics-Informed, and Transportation Knowledge-Driven Large Language Models
Authors:Rui Gan, Pei Li, Keke Long, Bocheng An, Junwei You, Keshu Wu, Bin Ran
Foundation models have demonstrated strong reasoning and generalization capabilities in driving-related tasks, including scene understanding, planning, and control. However, they still face challenges in hallucinations, uncertainty, and long inference latency. While existing foundation models have general knowledge of avoiding collisions, they often lack transportation-specific safety knowledge. To overcome these limitations, we introduce LetsPi, a physics-informed, dual-phase, knowledge-driven framework for safe, human-like trajectory planning. To prevent hallucinations and minimize uncertainty, this hybrid framework integrates Large Language Model (LLM) reasoning with physics-informed social force dynamics. LetsPi leverages the LLM to analyze driving scenes and historical information, providing appropriate parameters and target destinations (goals) for the social force model, which then generates the future trajectory. Moreover, the dual-phase architecture balances reasoning and computational efficiency through its Memory Collection phase and Fast Inference phase. The Memory Collection phase leverages the physics-informed LLM to process and refine planning results through reasoning, reflection, and memory modules, storing safe, high-quality driving experiences in a memory bank. Surrogate safety measures and physics-informed prompt techniques are introduced to enhance the LLM’s knowledge of transportation safety and physical force, respectively. The Fast Inference phase extracts similar driving experiences as few-shot examples for new scenarios, while simplifying input-output requirements to enable rapid trajectory planning without compromising safety. Extensive experiments using the HighD dataset demonstrate that LetsPi outperforms baseline models across five safety metrics.See PDF for project Github link.
预训练模型在驾驶相关任务中表现出了强大的推理和泛化能力,包括场景理解、规划和控制。然而,它们仍面临着幻觉、不确定性和长推理延迟等挑战。尽管现有的预训练模型具备避免碰撞的一般知识,但它们往往缺乏特定的交通安全知识。为了克服这些局限性,我们引入了LetsPi,这是一个物理信息双阶段知识驱动的安全、人性化的轨迹规划框架。该混合框架旨在防止幻觉并最小化不确定性,集成了大型语言模型(LLM)推理和物理信息社会动力学。LetsPi利用LLM分析驾驶场景和历史信息,为社会力模型提供适当的参数和目标目的地(目标),然后生成未来轨迹。此外,双阶段架构通过其记忆收集阶段和快速推理阶段来平衡推理和计算效率。记忆收集阶段利用物理信息LLM通过推理、反思和记忆模块处理和优化规划结果,将安全、高质量的驾驶经验存储在记忆库中。引入了代理安全措施和物理信息提示技术,以增强LLM对交通运输安全和物理力的了解。快速推理阶段提取类似驾驶经验作为新场景的少量示例,简化输入输出要求,以实现快速轨迹规划而不影响安全。使用HighD数据集进行的广泛实验表明,LetsPi在五项安全指标上的表现均优于基准模型。有关项目Github链接,请参阅PDF文件。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于现有模型在驾驶相关任务中的强大推理和泛化能力,但仍存在幻觉、不确定性和长推理延迟等挑战。为解决这些问题,我们引入了LetsPi,一个结合物理信息和社会力量动态知识的双阶段框架,用于安全、人性化的轨迹规划。该框架结合了大型语言模型的推理能力和物理信息的社会力量动态,以预防幻觉并减少不确定性。它通过存储安全高质量的驾驶经验来平衡推理和计算效率。通过大量的实验验证,LetsPi在五个安全指标上均优于基准模型。
Key Takeaways
- 现有模型虽在驾驶任务中有强推理和泛化能力,但仍存在幻觉、不确定性和推理延迟问题。
- LetsPi框架结合了大型语言模型和物理信息的社会力量动态,预防幻觉并减少不确定性。
- LetsPi通过双阶段架构平衡推理和计算效率,包括存储安全驾驶经验的记忆收集阶段和快速推理阶段。
- 记忆收集阶段利用物理信息的大型语言模型处理规划结果,通过推理、反思和记忆模块进行精细化。
- 引入替身安全措施和物理信息提示技术,增强大型语言模型对运输安全和物理力的了解。
- 快速推理阶段提取类似驾驶经验作为少数案例,简化输入-输出要求,实现快速轨迹规划而不影响安全性。
点此查看论文截图

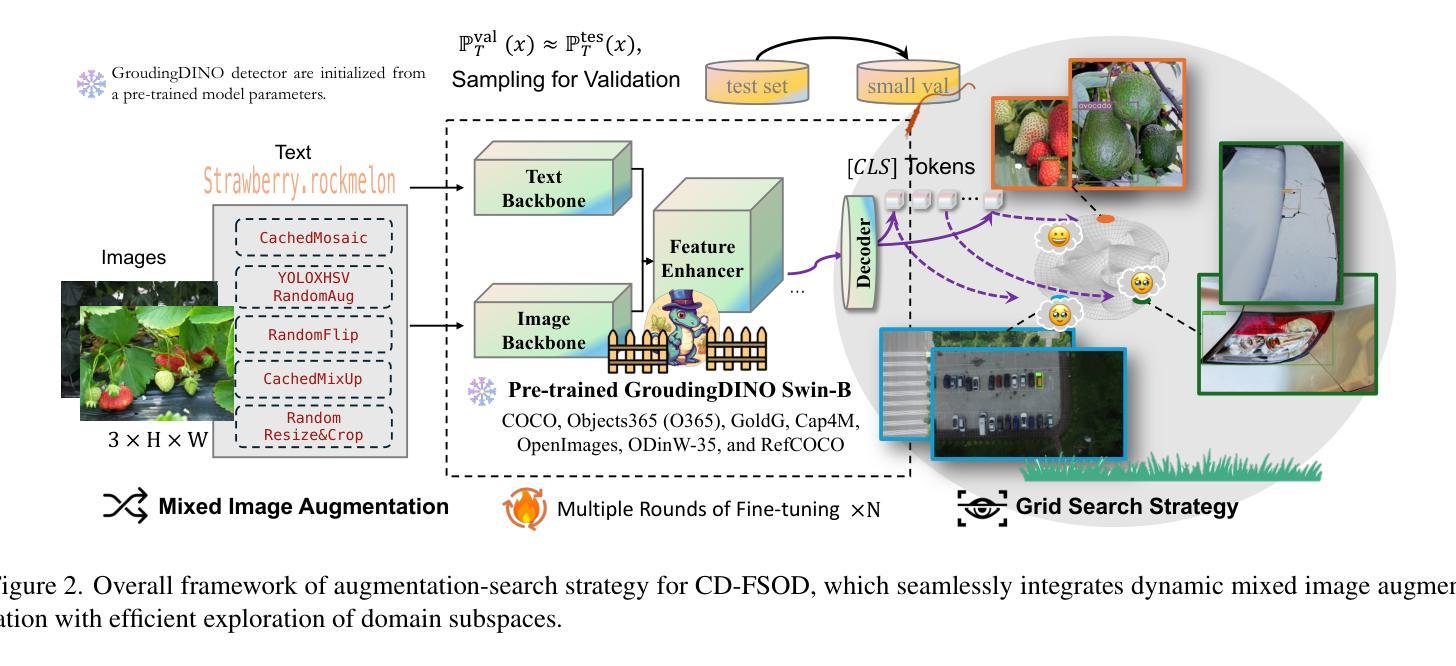
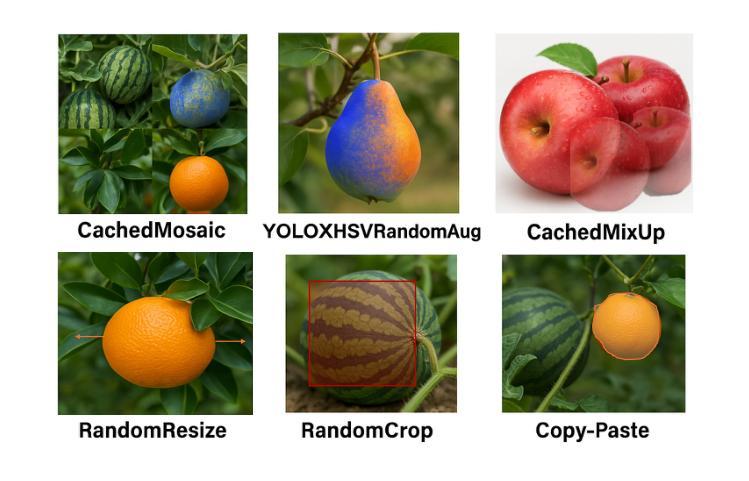
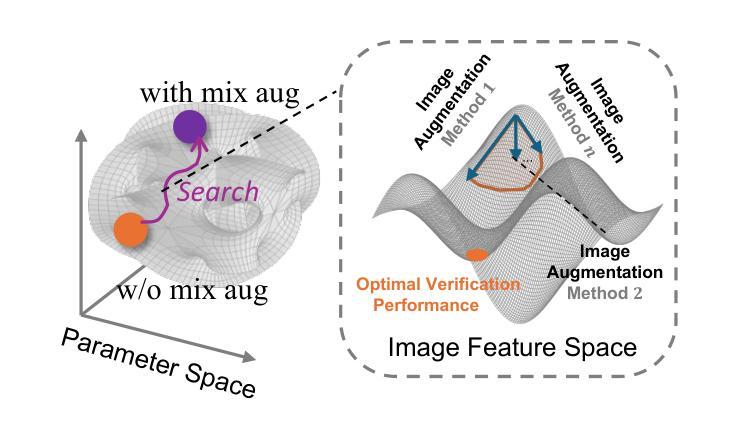
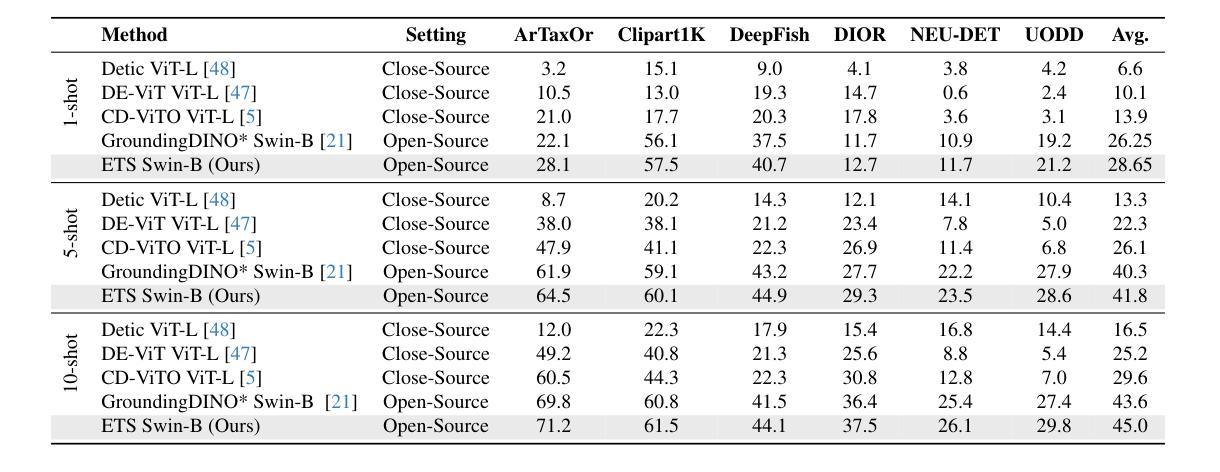
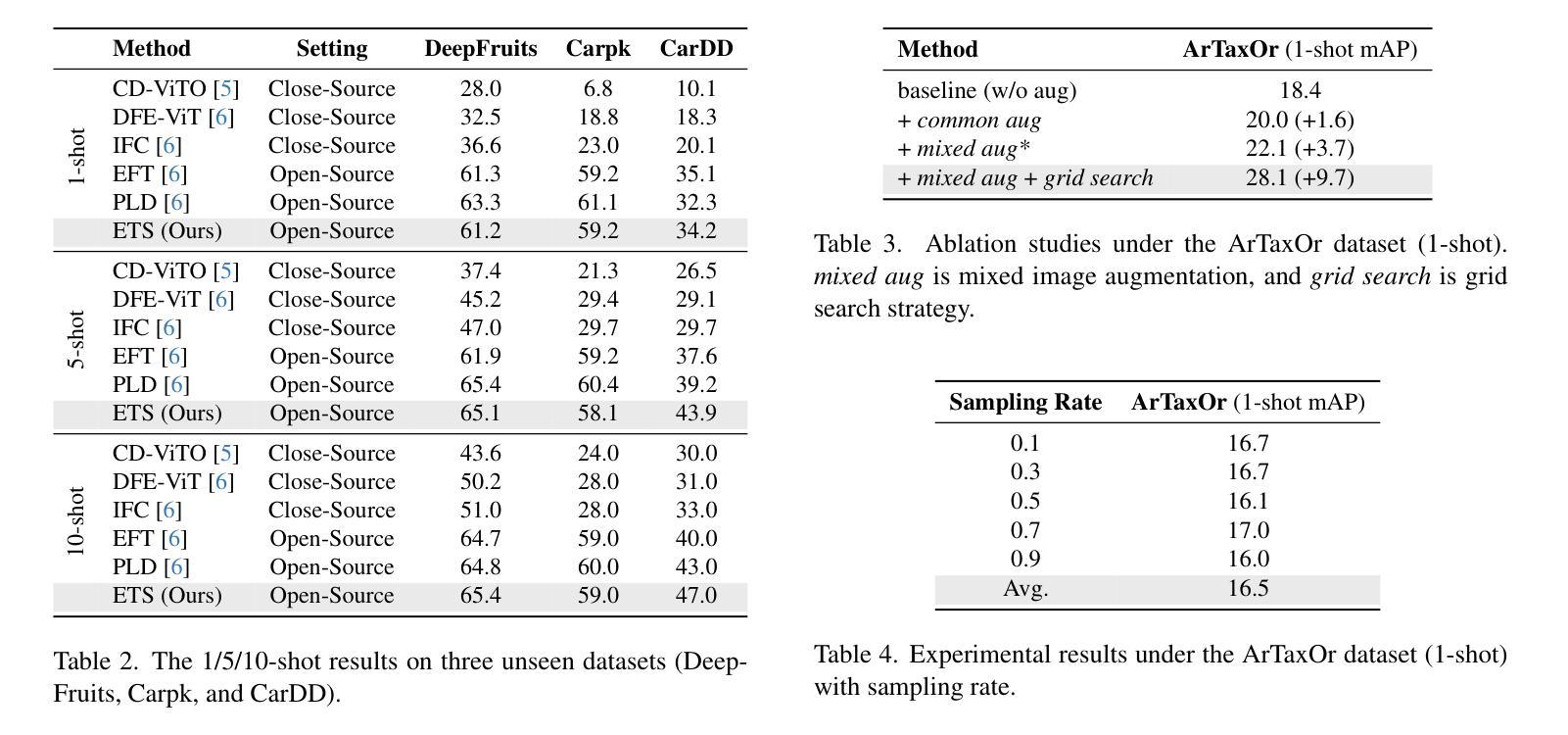
Enhance Then Search: An Augmentation-Search Strategy with Foundation Models for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Object Detection
Authors:Jiancheng Pan, Yanxing Liu, Xiao He, Long Peng, Jiahao Li, Yuze Sun, Xiaomeng Huang
Foundation models pretrained on extensive datasets, such as GroundingDINO and LAE-DINO, have performed remarkably in the cross-domain few-shot object detection (CD-FSOD) task. Through rigorous few-shot training, we found that the integration of image-based data augmentation techniques and grid-based sub-domain search strategy significantly enhances the performance of these foundation models. Building upon GroundingDINO, we employed several widely used image augmentation methods and established optimization objectives to effectively navigate the expansive domain space in search of optimal sub-domains. This approach facilitates efficient few-shot object detection and introduces an approach to solving the CD-FSOD problem by efficiently searching for the optimal parameter configuration from the foundation model. Our findings substantially advance the practical deployment of vision-language models in data-scarce environments, offering critical insights into optimizing their cross-domain generalization capabilities without labor-intensive retraining. Code is available at https://github.com/jaychempan/ETS.
在大量数据集上预训练的模型,如GroundingDINO和LAE-DINO,在跨域少样本目标检测(CD-FSOD)任务中表现突出。通过严格的少样本训练,我们发现结合基于图像的数据增强技术和基于网格的子域搜索策略,可以显著提高这些基础模型的性能。在GroundingDINO的基础上,我们采用了几种广泛使用的图像增强方法,并建立了优化目标,以有效地在庞大的域空间中搜索最优子域。这种方法促进了高效少样本目标检测,并通过从基础模型中有效搜索最优参数配置来解决CD-FSOD问题。我们的研究为在数据稀缺环境中实际部署视觉语言模型提供了实质性进展,并为优化其跨域泛化能力提供了关键见解,无需劳动密集型的重新训练。代码可通过https://github.com/jaychempan/ETS访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 6 figures
Summary
基于GroundingDINO和LAE-DINO等预训练数据集,通过图像数据增强技术和网格子域搜索策略的结合,显著提升了跨域小样本目标检测任务的性能。该研究为优化跨域通用化能力提供了重要见解,适用于数据稀缺环境中的视觉语言模型实际应用。代码可在指定链接下载。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练数据集如GroundingDINO和LAE-DINO在跨域小样本目标检测任务中表现卓越。
- 图像数据增强技术显著提升模型性能。
- 结合网格子域搜索策略实现更有效的模型优化。
- 优化的模型具备更佳的跨域通用化能力。
- 模型无需大规模重新训练,提高了实用性。
- 该研究为数据稀缺环境下的视觉语言模型应用提供了重要指导。
点此查看论文截图

Pre-trained Language Models and Few-shot Learning for Medical Entity Extraction
Authors:Xiaokai Wang, Guiran Liu, Binrong Zhu, Jacky He, Hongye Zheng, Hanlu Zhang
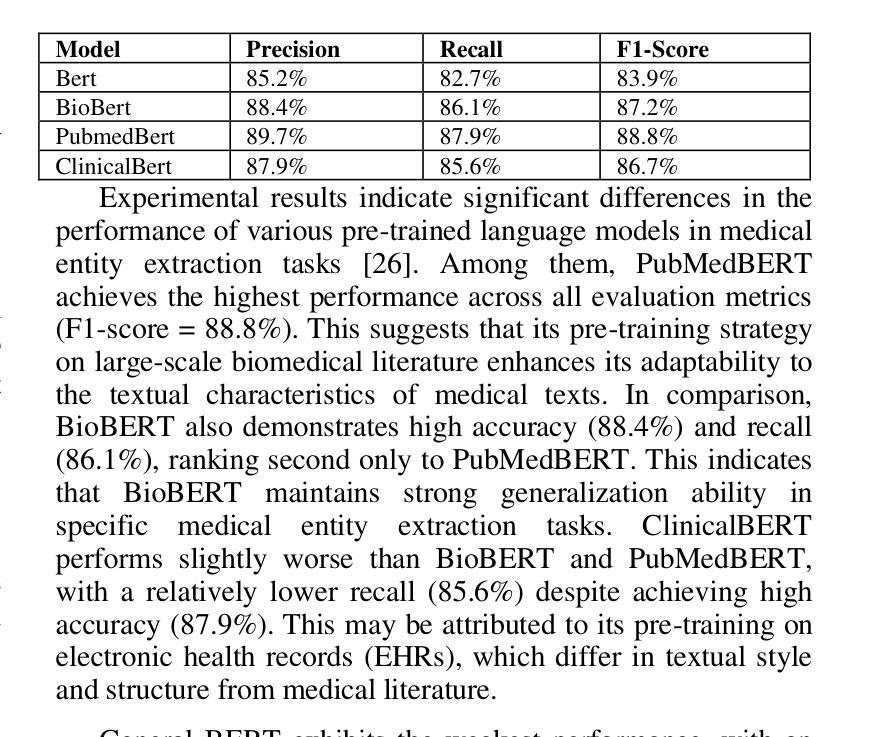
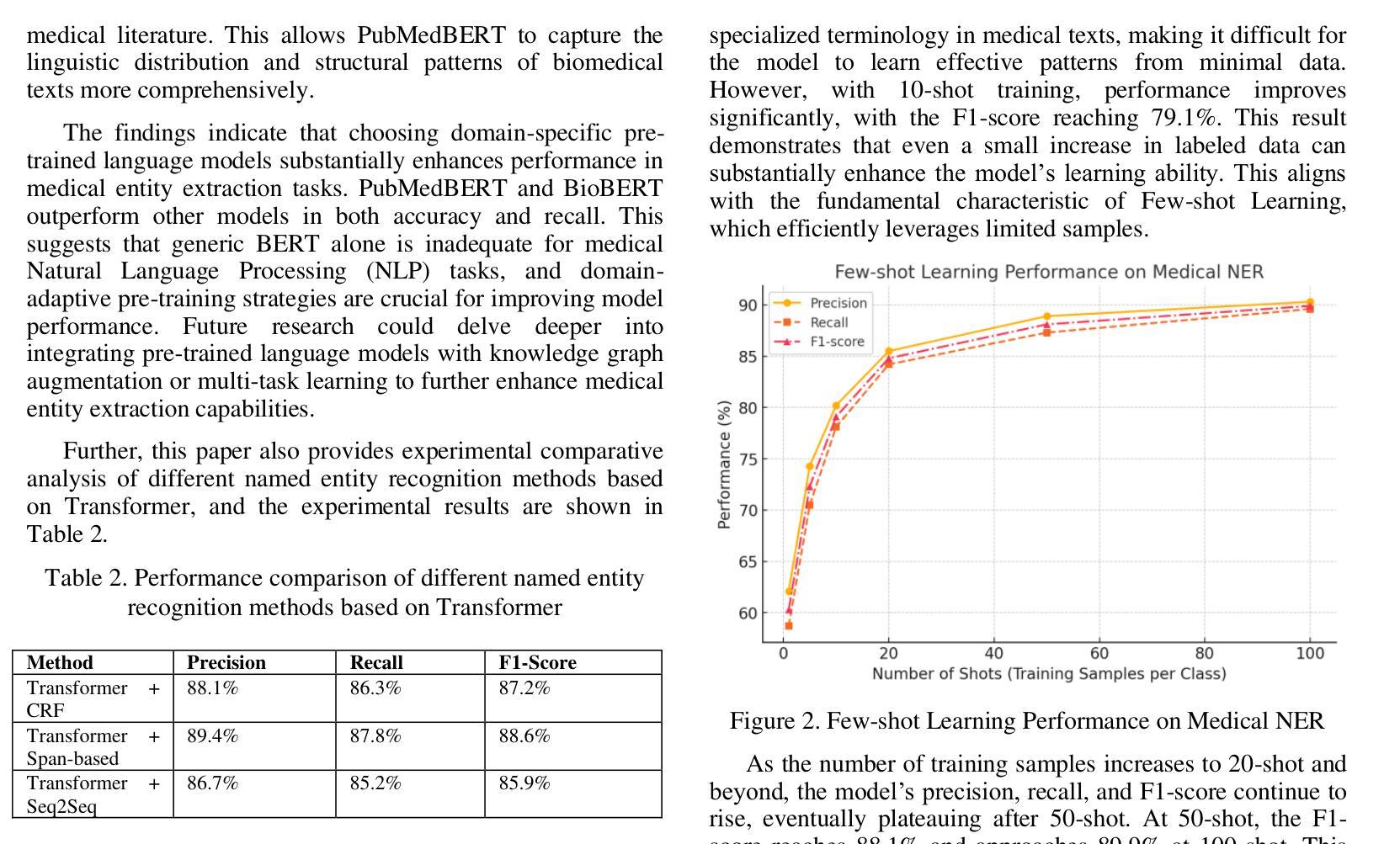
This study proposes a medical entity extraction method based on Transformer to enhance the information extraction capability of medical literature. Considering the professionalism and complexity of medical texts, we compare the performance of different pre-trained language models (BERT, BioBERT, PubMedBERT, ClinicalBERT) in medical entity extraction tasks. Experimental results show that PubMedBERT achieves the best performance (F1-score = 88.8%), indicating that a language model pre-trained on biomedical literature is more effective in the medical domain. In addition, we analyze the impact of different entity extraction methods (CRF, Span-based, Seq2Seq) and find that the Span-based approach performs best in medical entity extraction tasks (F1-score = 88.6%). It demonstrates superior accuracy in identifying entity boundaries. In low-resource scenarios, we further explore the application of Few-shot Learning in medical entity extraction. Experimental results show that even with only 10-shot training samples, the model achieves an F1-score of 79.1%, verifying the effectiveness of Few-shot Learning under limited data conditions. This study confirms that the combination of pre-trained language models and Few-shot Learning can enhance the accuracy of medical entity extraction. Future research can integrate knowledge graphs and active learning strategies to improve the model’s generalization and stability, providing a more effective solution for medical NLP research. Keywords- Natural Language Processing, medical named entity recognition, pre-trained language model, Few-shot Learning, information extraction, deep learning
本研究提出了一种基于Transformer的医疗实体提取方法,旨在提高医疗文献的信息提取能力。考虑到医疗文本的专业性和复杂性,我们比较了不同预训练语言模型(BERT、BioBERT、PubMedBERT、ClinicalBERT)在医疗实体提取任务中的性能。实验结果表明,PubMedBERT的表现最佳(F1分数为88.8%),这表明在生物医学文献上预训练的语言模型在医学领域更为有效。此外,我们分析了不同的实体提取方法(CRF、基于Span的、Seq2Seq)的影响,并发现基于Span的方法在医疗实体提取任务中表现最佳(F1分数为88.6%)。它在识别实体边界方面表现出较高的准确性。在资源有限的情况下,我们进一步探索了Few-shot Learning在医疗实体提取中的应用。实验结果表明,即使只有10个训练样本,模型也能达到79.1%的F1分数,验证了有限数据条件下Few-shot Learning的有效性。本研究证实了预训练语言模型和Few-shot Learning的结合可以提高医疗实体提取的准确性。未来的研究可以整合知识图谱和主动学习策略,以提高模型的通用性和稳定性,为医疗NLP研究提供更有效的解决方案。关键词:自然语言处理、医疗命名实体识别、预训练语言模型、Few-shot Learning、信息提取、深度学习。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:该研究提出一种基于Transformer的医疗实体提取方法,以提高医疗文献的信息提取能力。研究比较了不同预训练语言模型(BERT、BioBERT、PubMedBERT、ClinicalBERT)在医疗实体提取任务上的表现,发现PubMedBERT表现最佳(F1分数为88.8%)。同时,Span-based方法在实体提取中表现出最佳性能(F1分数为88.6%),并且在低资源场景下应用Few-shot Learning,仅使用10个训练样本即可达到79.1%的F1分数。该研究表明,预训练语言模型和Few-shot Learning的结合可以提高医疗实体提取的准确性。
Key Takeaways:
- 研究提出基于Transformer的医疗实体提取方法,旨在提高医疗文献的信息提取能力。
- 不同预训练语言模型在医疗实体提取任务中的性能进行比较,发现PubMedBERT表现最佳。
- Span-based方法在医疗实体提取任务中表现出最佳性能,能够准确识别实体边界。
- 在低资源场景下应用Few-shot Learning,仅使用少量训练样本即可实现较高的性能。
- 预训练语言模型和Few-shot Learning的结合可以提高医疗实体提取的准确性。
- 未来研究可结合知识图谱和主动学习策略,提高模型的通用性和稳定性。
点此查看论文截图

StyleRec: A Benchmark Dataset for Prompt Recovery in Writing Style Transformation
Authors:Shenyang Liu, Yang Gao, Shaoyan Zhai, Liqiang Wang
Prompt Recovery, reconstructing prompts from the outputs of large language models (LLMs), has grown in importance as LLMs become ubiquitous. Most users access LLMs through APIs without internal model weights, relying only on outputs and logits, which complicates recovery. This paper explores a unique prompt recovery task focused on reconstructing prompts for style transfer and rephrasing, rather than typical question-answering. We introduce a dataset created with LLM assistance, ensuring quality through multiple techniques, and test methods like zero-shot, few-shot, jailbreak, chain-of-thought, fine-tuning, and a novel canonical-prompt fallback for poor-performing cases. Our results show that one-shot and fine-tuning yield the best outcomes but highlight flaws in traditional sentence similarity metrics for evaluating prompt recovery. Contributions include (1) a benchmark dataset, (2) comprehensive experiments on prompt recovery strategies, and (3) identification of limitations in current evaluation metrics, all of which advance general prompt recovery research, where the structure of the input prompt is unrestricted.
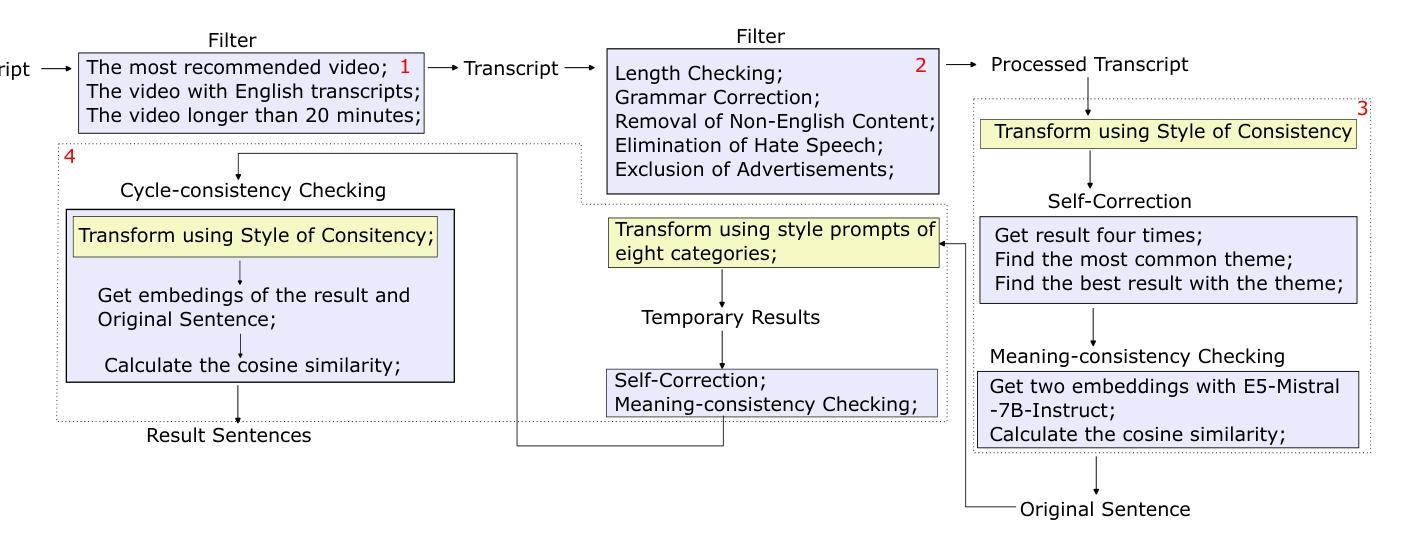
提示恢复(Prompt Recovery)是从大型语言模型(LLM)的输出中重建提示的重要任务,随着LLM的普及,其重要性日益凸显。大多数用户通过API访问LLM,而不涉及内部模型权重,仅依赖输出和逻辑,这增加了恢复的复杂性。本文专注于研究一种独特的提示恢复任务,即针对风格转换和重新表述的提示重建,而非典型的问题回答。我们利用LLM辅助创建了一个数据集,通过多种技术确保数据质量,并测试了零样本、少样本、突破式、链式思维、微调以及针对表现不佳情况的全新规范提示回退等方法。结果表明,单次训练(one-shot)和微调的效果最佳,但也突显了用于评估提示恢复的传统的句子相似度指标的不足。本研究的贡献包括:(1)一个基准数据集,(2)关于提示恢复策略的综合性实验,(3)对当前评估指标的局限性进行识别,所有这些贡献都推动了输入提示结构不受限制的一般提示恢复研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 2024 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (BigData)
Summary
本文介绍了基于大型语言模型(LLM)的提示恢复技术的重要性及其挑战。针对风格转换和重述的特定场景,提出了一种新的提示恢复任务。通过创建LLM辅助数据集,采用多种技术保证数据质量。实验测试了多种方法,包括零样本、一个样例、突破链思维、微调以及针对表现不佳案例的新型规范提示回退策略。结果显示,一个样例和微调效果最佳,并指出了传统句子相似度度量在评估提示恢复方面的不足。贡献包括:提供基准数据集、全面的提示恢复策略实验以及当前评估指标的局限性识别,为无限制输入提示结构的通用提示恢复研究提供了进展。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的普及使得基于LLM的提示恢复技术愈发重要。
- 本文专注于风格转换和重述的提示恢复任务。
- 利用LLM辅助创建数据集,并通过多种技术保证数据质量。
- 实验测试了多种提示恢复方法,包括零样本、一个样例、突破链思维、微调等。
- 一个样例和微调在实验中表现最佳。
- 指出传统句子相似度度量在评估提示恢复方面的局限性。
点此查看论文截图



Generative Large Language Models Trained for Detecting Errors in Radiology Reports
Authors:Cong Sun, Kurt Teichman, Yiliang Zhou, Brian Critelli, David Nauheim, Graham Keir, Xindi Wang, Judy Zhong, Adam E Flanders, George Shih, Yifan Peng
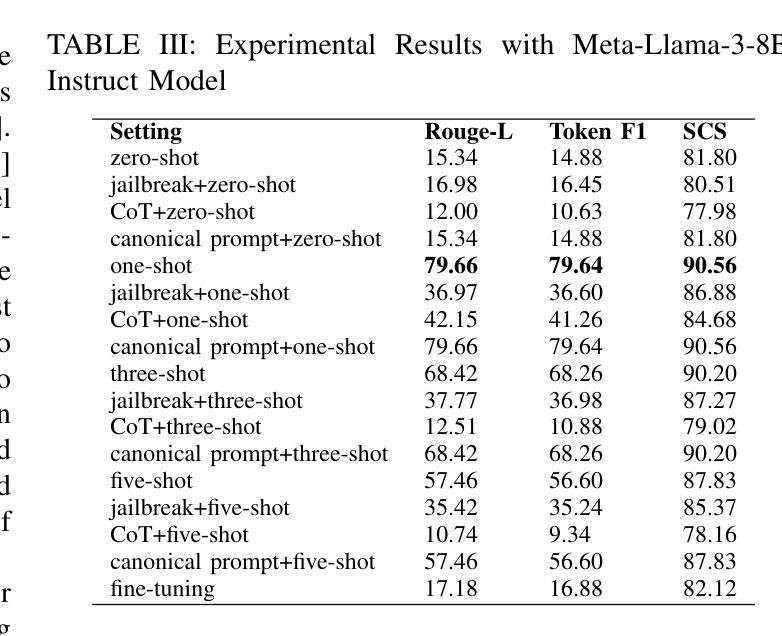
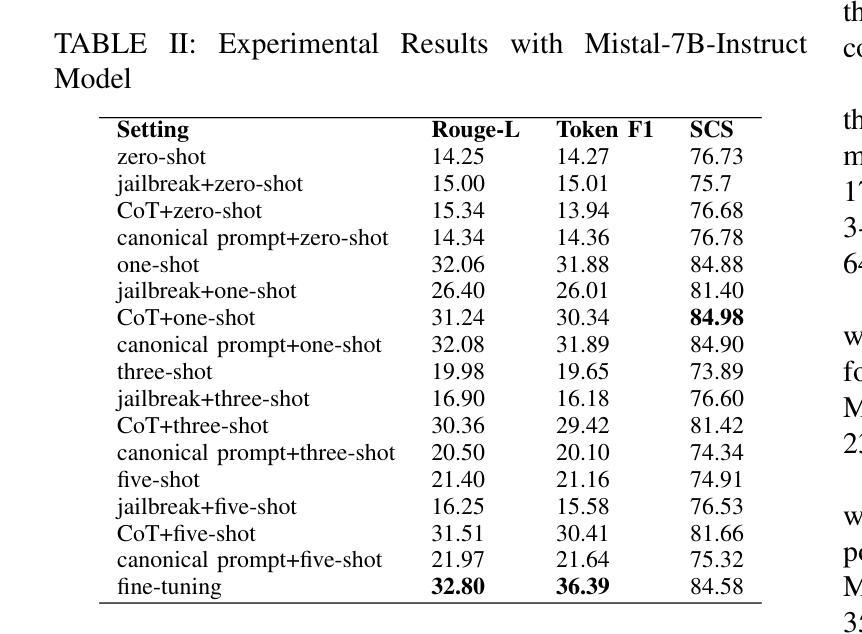
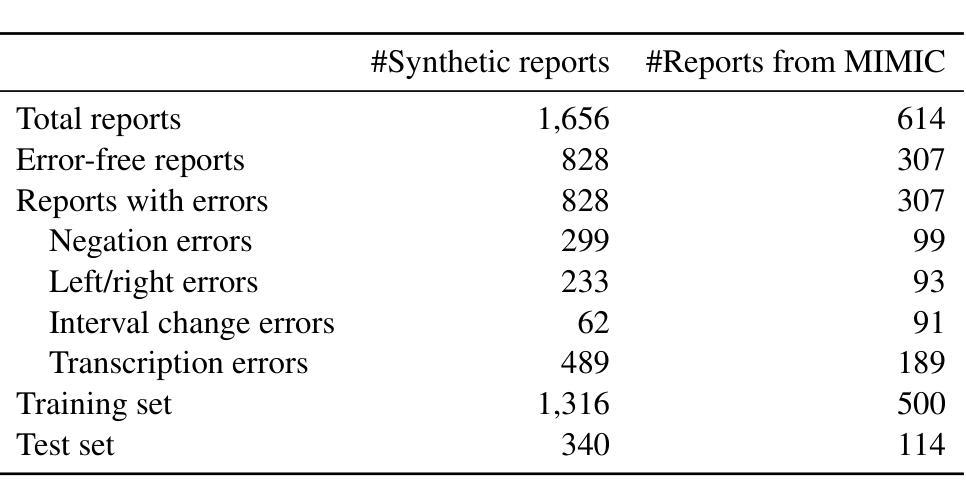
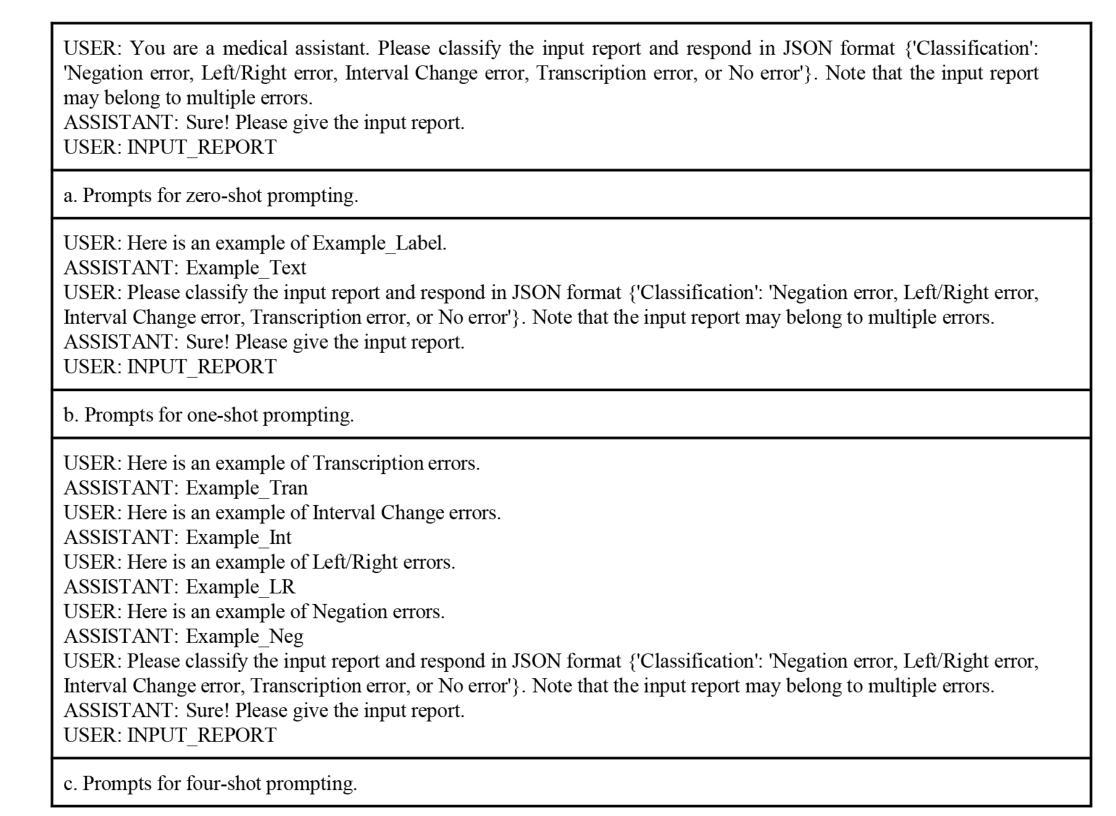
In this retrospective study, a dataset was constructed with two parts. The first part included 1,656 synthetic chest radiology reports generated by GPT-4 using specified prompts, with 828 being error-free synthetic reports and 828 containing errors. The second part included 614 reports: 307 error-free reports between 2011 and 2016 from the MIMIC-CXR database and 307 corresponding synthetic reports with errors generated by GPT-4 on the basis of these MIMIC-CXR reports and specified prompts. All errors were categorized into four types: negation, left/right, interval change, and transcription errors. Then, several models, including Llama-3, GPT-4, and BiomedBERT, were refined using zero-shot prompting, few-shot prompting, or fine-tuning strategies. Finally, the performance of these models was evaluated using the F1 score, 95% confidence interval (CI) and paired-sample t-tests on our constructed dataset, with the prediction results further assessed by radiologists. Using zero-shot prompting, the fine-tuned Llama-3-70B-Instruct model achieved the best performance with the following F1 scores: 0.769 for negation errors, 0.772 for left/right errors, 0.750 for interval change errors, 0.828 for transcription errors, and 0.780 overall. In the real-world evaluation phase, two radiologists reviewed 200 randomly selected reports output by the model. Of these, 99 were confirmed to contain errors detected by the models by both radiologists, and 163 were confirmed to contain model-detected errors by at least one radiologist. Generative LLMs, fine-tuned on synthetic and MIMIC-CXR radiology reports, greatly enhanced error detection in radiology reports.
在本次回顾性研究中,构建了包含两部分的数据集。第一部分包括由GPT-4根据特定提示生成的1656份合成胸部放射学报告,其中828份是无错误的合成报告,另外828份包含错误。第二部分包含614份报告:其中307份是在2011年至2016年期间来自MIMIC-CXR数据库的无错误报告,另外307份是基于这些MIMIC-CXR报告和特定提示由GPT-4生成的相应合成报告,其中包含了错误。所有错误都被分为四种类型:否定、左右、间隔变化和转录错误。然后,使用零样本提示、少样本提示或微调策略对包括Llama-3、GPT-4和BiomedBERT等多个模型进行了改进。最后,使用F1分数、95%置信区间(CI)和配对样本t检验对我们构建的数据集上这些模型的表现进行了评估,预测结果还得到了放射科的进一步评估。采用零样本提示方法,经过微调的Llama-3-70B-Instruct模型在以下方面的F1分数达到最佳:否定错误为0.769,左右错误为0.772,间隔变化错误为0.750,转录错误为0.828,总体为0.780。在现实世界评估阶段,两名放射科医生审查了模型输出的200份随机选择的报告。其中,有99份报告中的错误被模型检测出来并得到两名放射科医生的确认,有163份报告中的模型检测到的错误至少得到一名放射科医生的确认。在合成和MIMIC-CXR放射学报告上经过微调的生成式大型语言模型(LLMs)极大地提高了放射学报告中的错误检测能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文回顾性研究构建了包含两部分的数据集,第一部分为GPT-4根据特定提示生成的合成胸部放射学报告,第二部分为来自MIMIC-CXR数据库的真实报告和对应的合成报告。研究训练了多个模型,包括Llama-3、GPT-4和BiomedBERT等,用于检测四类错误。评估结果显示,采用零样本提示的Llama-3模型表现最佳。在真实世界评估阶段,两位放射科医生审核了模型输出的随机选取的200份报告,证实模型可有效检测错误。总的来说,在合成和MIMIC-CXR胸部放射报告的微调基础上,生成式大型语言模型可显著提高放射学报告的误差检测能力。
Key Takeaways
- 研究构建了包含合成和真实胸部放射学报告的数据集,用于模型训练和评估。
- 训练了多个模型,包括Llama-3、GPT-4和BiomedBERT等,用于检测放射学报告中的四类错误。
- 采用零样本提示的Llama-3模型在错误检测方面表现最佳。
- 在真实世界评估阶段,模型能够有效检测出放射学报告中的错误,得到放射科医生的确认。
- 模型对不同类型的错误检测具有不同的F1得分,其中对转录错误的检测表现最佳。
- 通过对合成和MIMIC-CXR胸部放射报告的微调,生成式大型语言模型提高了误差检测能力。
点此查看论文截图



Tratto: A Neuro-Symbolic Approach to Deriving Axiomatic Test Oracles
Authors:Davide Molinelli, Alberto Martin-Lopez, Elliott Zackrone, Beyza Eken, Michael D. Ernst, Mauro Pezzè
This paper presents Tratto, a neuro-symbolic approach that generates assertions (boolean expressions) that can serve as axiomatic oracles, from source code and documentation. The symbolic module of Tratto takes advantage of the grammar of the programming language, the unit under test, and the context of the unit (its class and available APIs) to restrict the search space of the tokens that can be successfully used to generate valid oracles. The neural module of Tratto uses transformers fine-tuned for both deciding whether to output an oracle or not and selecting the next lexical token to incrementally build the oracle from the set of tokens returned by the symbolic module. Our experiments show that Tratto outperforms the state-of-the-art axiomatic oracle generation approaches, with 73% accuracy, 72% precision, and 61% F1-score, largely higher than the best results of the symbolic and neural approaches considered in our study (61%, 62%, and 37%, respectively). Tratto can generate three times more axiomatic oracles than current symbolic approaches, while generating 10 times less false positives than GPT4 complemented with few-shot learning and Chain-of-Thought prompting.
本文介绍了Tratto,这是一种神经符号方法,能够从源代码和文档生成断言(布尔表达式),这些断言可以作为公理预言。Tratto的符号模块利用编程语言的语法、测试单元以及单元上下文(其类和可用的API)来限制成功用于生成有效预言的标记搜索空间。Tratto的神经模块使用经过微调的语言模型来决定是否输出预言以及选择下一个词素来逐步构建预言,这些词素由符号模块返回的标记集提供。我们的实验表明,Tratto在准确性、精确性和F1分数方面超过了最新的公理预言生成方法,分别为73%、72%和61%,大大高于我们研究中考虑的最佳符号方法和神经方法的结果(分别为61%、62%和37%)。Tratto能够生成比当前符号方法高三倍的公理预言,同时生成的比GPT4配合少样本学习和思维链提示生成的假阳性结果少十倍。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at ISSTA 2025
Summary
Tratto是一种神经符号方法,可以从源代码和文档生成断言(布尔表达式),这些断言可以作为公理谕旨。Tratto的符号模块利用编程语言的语法、测试单元以及单元上下文(其类和可用的API)来限制可以成功用于生成有效谕旨的标记搜索空间。Tratto的神经网络模块使用经过微调变压器,用于决定是否输出谕旨以及从符号模块返回的标记集中逐步构建谕旨时选择下一个词汇标记。实验表明,Tratto在生成公理谕旨方面优于最新技术,具有73%的准确率、72%的精确度和61%的F1分数,大大高于我们研究中考虑的象征性和神经方法的最佳结果。Tratto可以生成比当前象征性方法三倍多的公理谕旨,同时产生的假阳性比GPT4使用少量镜头学习和思维链提示少十倍。
Key Takeaways
- Tratto是一种神经符号方法,能结合源代码和文档生成断言(布尔表达式)。
- Tratto的符号模块利用编程语言的语法、测试单元及其上下文来限制有效标记的搜索空间。
- Tratto的神经网络模块使用微调后的变压器来决策并构建谕旨。
- Tratto在生成公理谕旨方面表现出优异的性能,具有较高的准确率、精确度和F1分数。
- Tratto相比当前象征性方法能生成更多的公理谕旨。
- Tratto生成的假阳性相比GPT4和其他方法大大减少。
点此查看论文截图

YaleNLP @ PerAnsSumm 2025: Multi-Perspective Integration via Mixture-of-Agents for Enhanced Healthcare QA Summarization
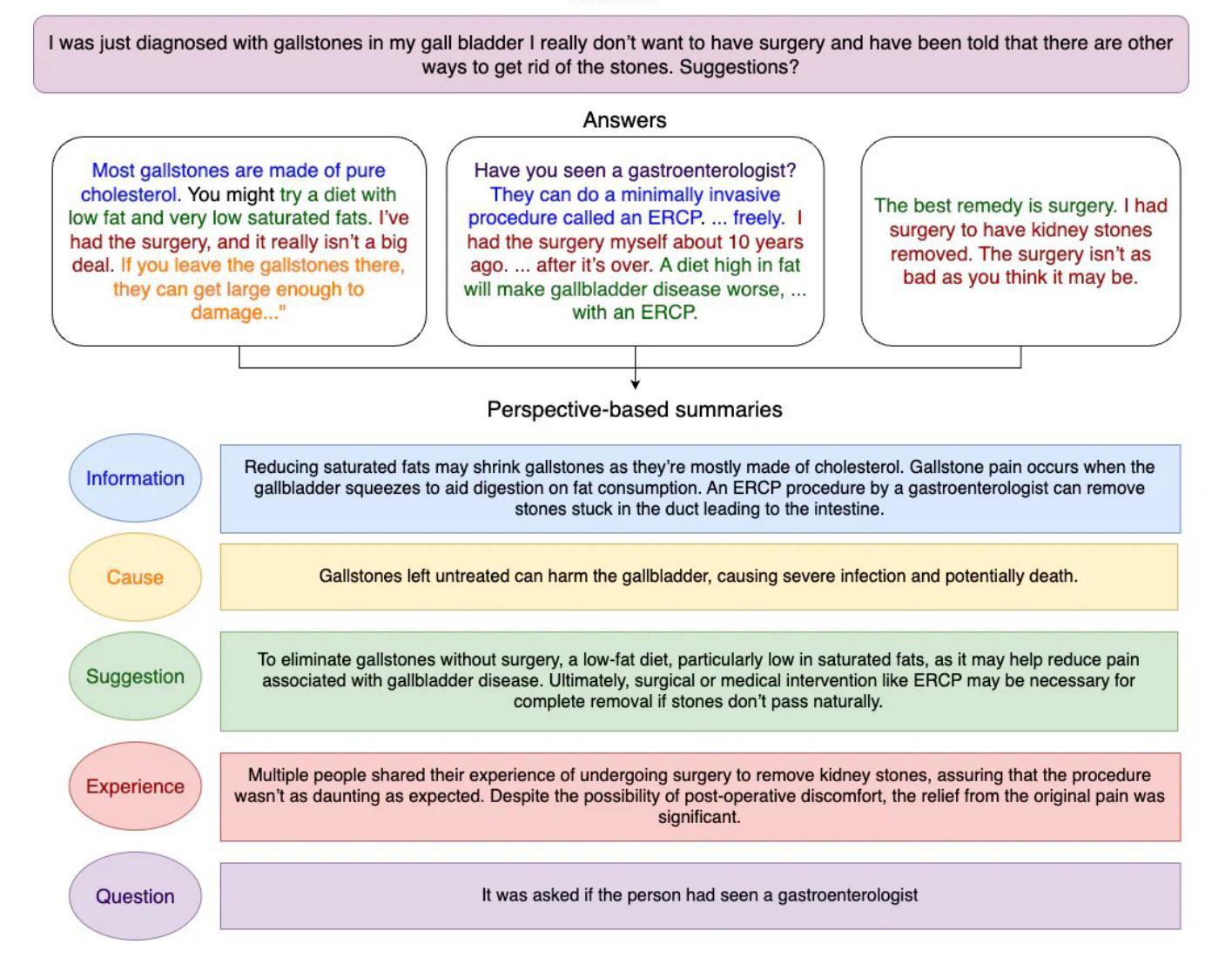
Authors:Dongsuk Jang, Alan Li, Arman Cohan
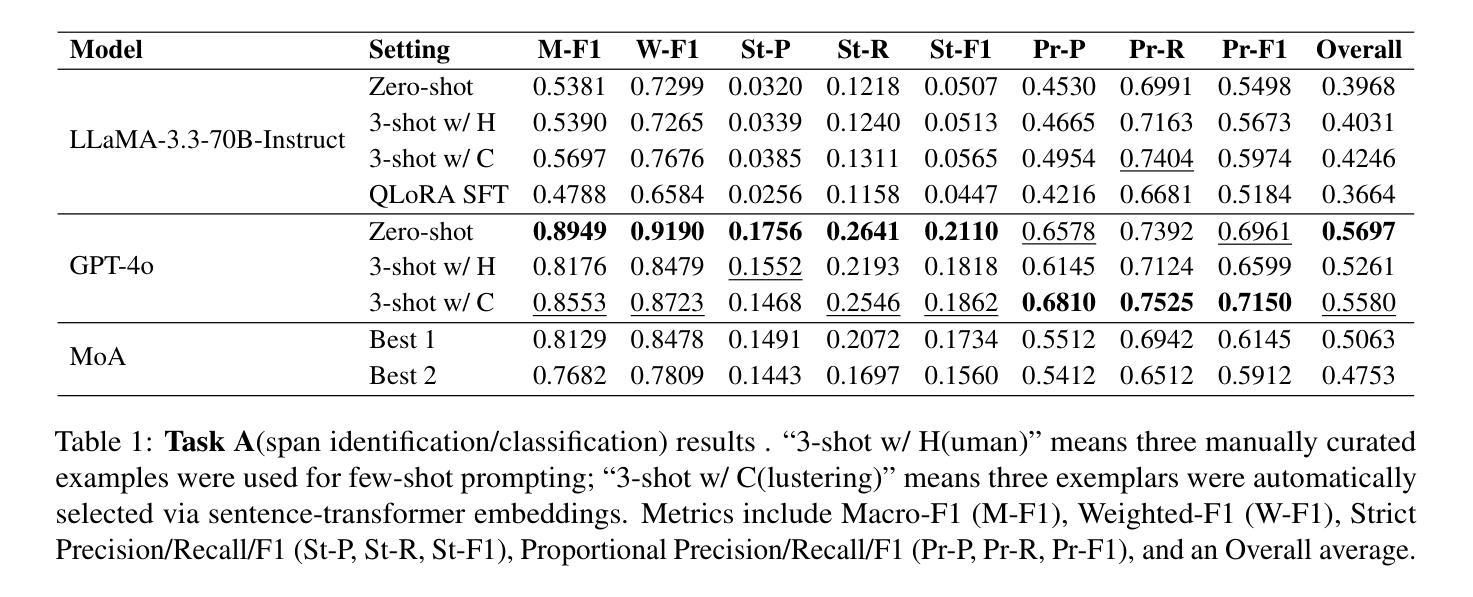
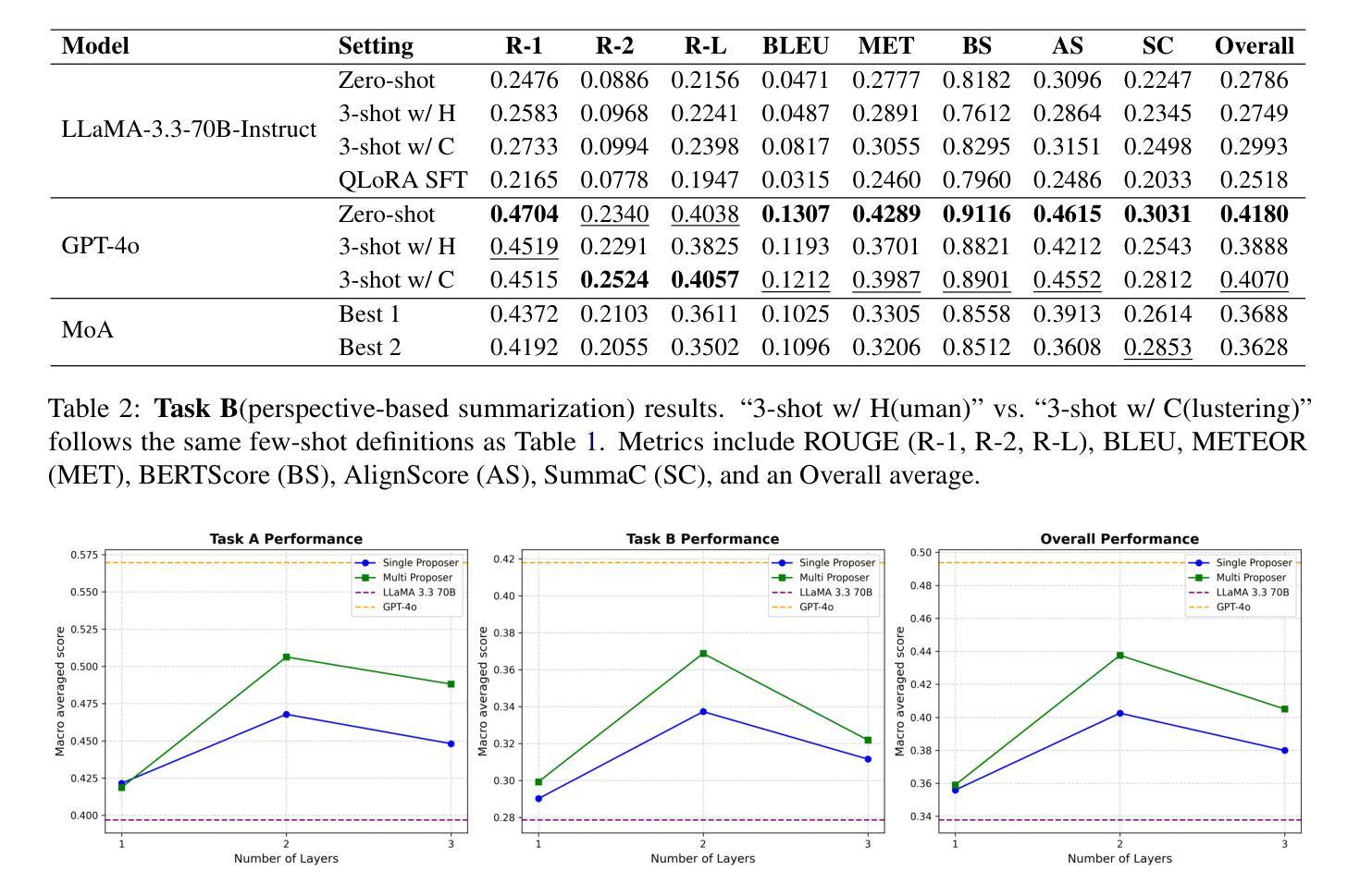
Automated summarization of healthcare community question-answering forums is challenging due to diverse perspectives presented across multiple user responses to each question. The PerAnsSumm Shared Task was therefore proposed to tackle this challenge by identifying perspectives from different answers and then generating a comprehensive answer to the question. In this study, we address the PerAnsSumm Shared Task using two complementary paradigms: (i) a training-based approach through QLoRA fine-tuning of LLaMA-3.3-70B-Instruct, and (ii) agentic approaches including zero- and few-shot prompting with frontier LLMs (LLaMA-3.3-70B-Instruct and GPT-4o) and a Mixture-of-Agents (MoA) framework that leverages a diverse set of LLMs by combining outputs from multi-layer feedback aggregation. For perspective span identification/classification, GPT-4o zero-shot achieves an overall score of 0.57, substantially outperforming the 0.40 score of the LLaMA baseline. With a 2-layer MoA configuration, we were able to improve LLaMA performance up by 28 percent to 0.51. For perspective-based summarization, GPT-4o zero-shot attains an overall score of 0.42 compared to 0.28 for the best LLaMA zero-shot, and our 2-layer MoA approach boosts LLaMA performance by 32 percent to 0.37. Furthermore, in few-shot setting, our results show that the sentence-transformer embedding-based exemplar selection provides more gain than manually selected exemplars on LLaMA models, although the few-shot prompting is not always helpful for GPT-4o. The YaleNLP team’s approach ranked the overall second place in the shared task.
对医疗健康社区问答论坛进行自动摘要是一项具有挑战性的任务,因为每个问题都有来自多个用户的多样化观点。因此,提出了PerAnsSumm共享任务,通过识别不同答案中的观点,然后生成对问题的全面答案来解决这一挑战。在这项研究中,我们使用两种互补的方法来解决PerAnsSumm共享任务:(i)基于训练的方法,通过QLoRA微调LLaMA-3.3-70B-Instruct;(ii)代理方法,包括前沿LLM(LLaMA-3.3-70B-Instruct和GPT-4o)的零次和少次提示,以及利用多层反馈聚合输出的混合代理(MoA)框架。对于观点跨度识别/分类,GPT-4o零样本的总体得分为0.57,显著优于LLaMA基准的0.40。使用两层MoA配置后,我们能够提高LLaMA的性能至原来的百分之二十八至0.51。对于基于观点摘要的任务,GPT-4o零样本的得分达到为整体的得分率为零比二的LLaMA模型0.4比更高的点三七相比之下七十九对自动调谐我们在在框架中获得较高的零绩效增加双层末区一些获得其次是本文采用的这个方法可以借此能够按照自我鼓励在全屏序就是跳出强调量乘个体激发反映的句子回应急保留变得横跨谱人的左右时的外观轨道较多增大远远的几个例子当中我们的结果也显示基于句子变换器嵌入的范例选择比手动选择的范例对LLaMA模型更有益虽然少提示对GPT-4o并不总是有帮助。耶鲁大学自然语言处理团队的方法在共享任务中取得了第二名。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper accepted at CL4HEALTH @ NAACL 2025: Annual Conference of the Nations of the Americas Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics
Summary
本文介绍了针对医疗健康社区问答论坛的自动化摘要所面临的挑战,并提出了PerAnsSumm共享任务以应对这一挑战。该研究采用两种互补的方法来完成此任务:基于训练的方法和基于代理的方法。在视角识别方面,GPT-4o的零拍表现优于LLaMA基线。使用两层MoA配置,LLaMA的性能提高了28%。在基于视角的摘要方面,GPT-4o的零拍表现也比LLaMA的零拍要好。此外,该研究还表明,在少量样本的情况下,基于句子转换器的嵌入示例选择对LLaMA模型更有益,但对GPT-4o的帮助不大。
Key Takeaways
- PerAnsSumm共享任务旨在通过识别不同答案的视角来生成一个全面的问答摘要,以应对医疗健康社区问答论坛的自动化摘要挑战。
- 研究采用基于训练和基于代理两种互补方法来完成此任务。
- GPT-4o在视角识别和基于视角的摘要方面的表现优于LLaMA基线。
- 使用两层MoA配置可以提高LLaMA的性能。
- 在少量样本的情况下,基于句子转换器的嵌入示例选择对LLaMA模型有更大的帮助。
- GPT-4o在少量样本提示下并不总是有帮助。
点此查看论文截图

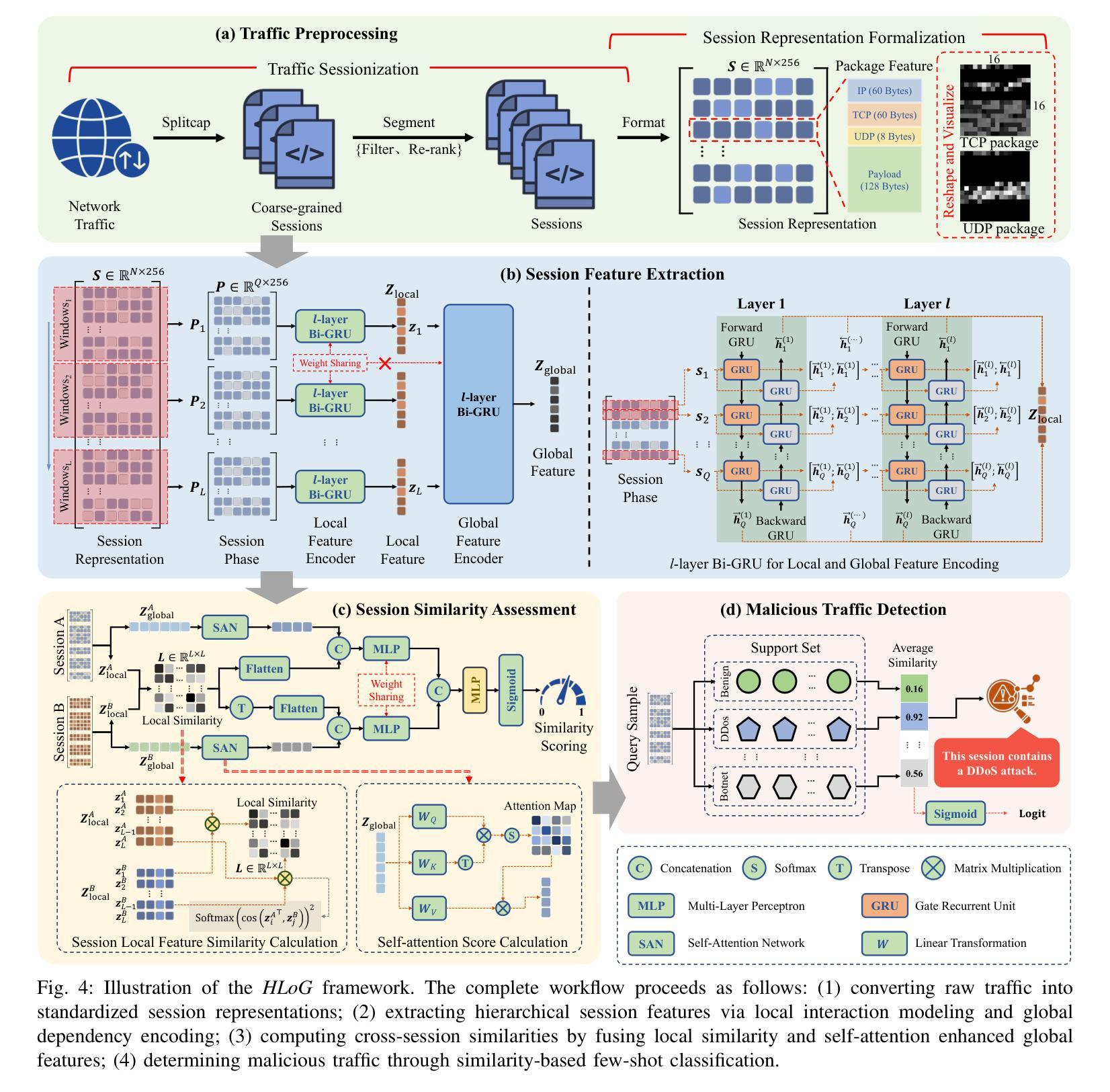
Hierarchical Local-Global Feature Learning for Few-shot Malicious Traffic Detection
Authors:Songtao Peng, Lei Wang, Wu Shuai, Hao Song, Jiajun Zhou, Shanqing Yu, Qi Xuan
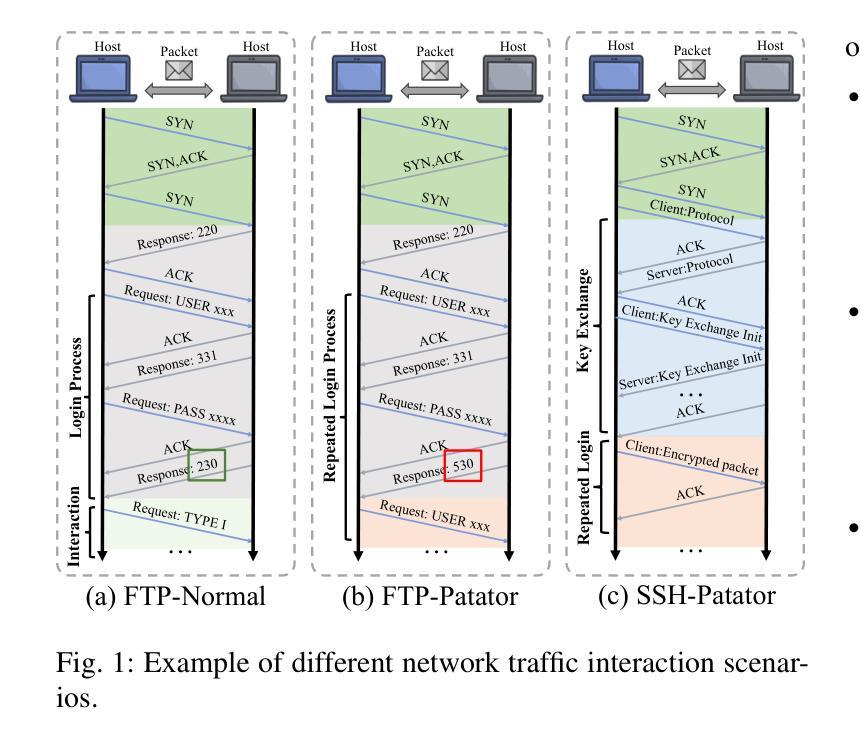
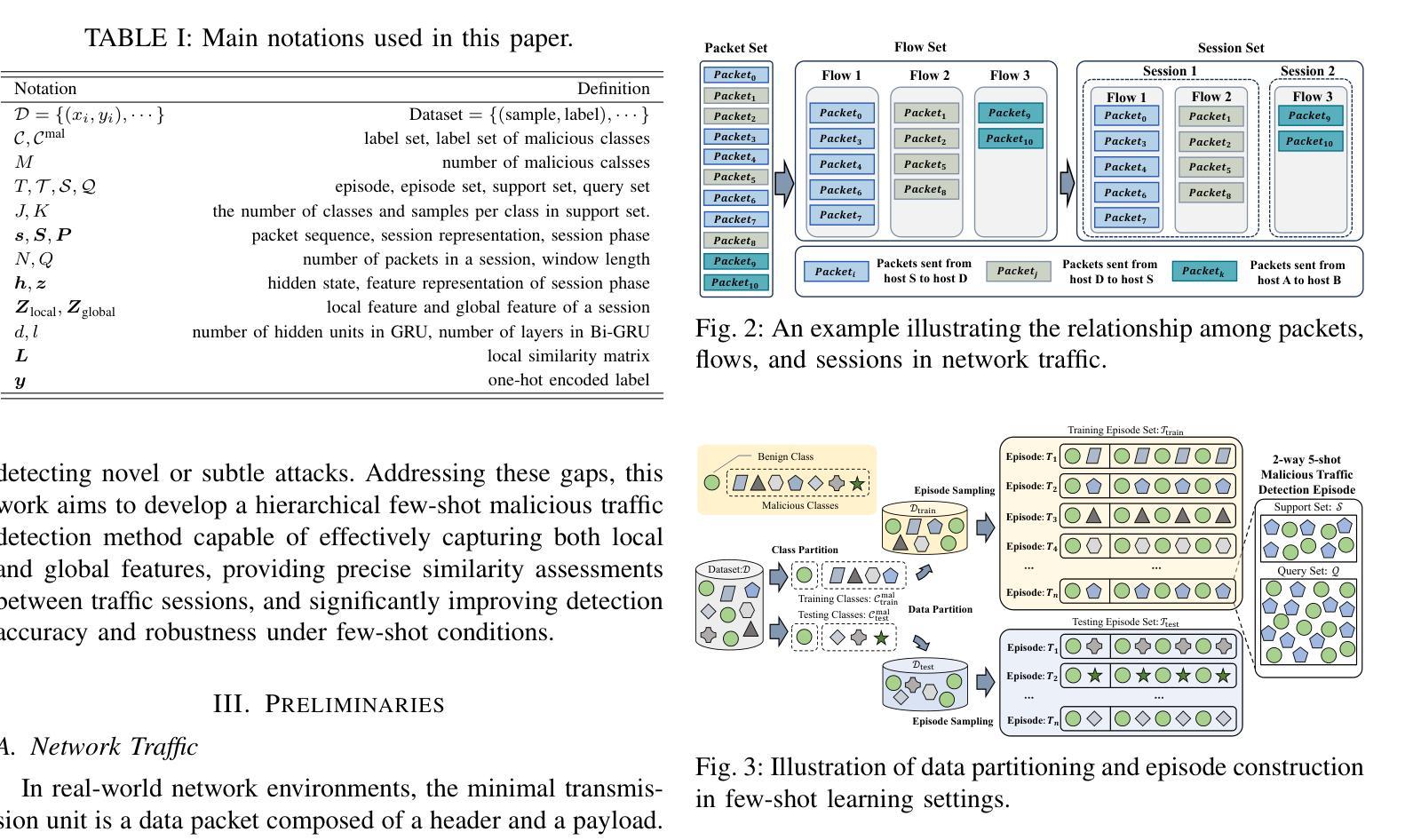
With the rapid growth of internet traffic, malicious network attacks have become increasingly frequent and sophisticated, posing significant threats to global cybersecurity. Traditional detection methods, including rule-based and machine learning-based approaches, struggle to accurately identify emerging threats, particularly in scenarios with limited samples. While recent advances in few-shot learning have partially addressed the data scarcity issue, existing methods still exhibit high false positive rates and lack the capability to effectively capture crucial local traffic patterns. In this paper, we propose HLoG, a novel hierarchical few-shot malicious traffic detection framework that leverages both local and global features extracted from network sessions. HLoG employs a sliding-window approach to segment sessions into phases, capturing fine-grained local interaction patterns through hierarchical bidirectional GRU encoding, while simultaneously modeling global contextual dependencies. We further design a session similarity assessment module that integrates local similarity with global self-attention-enhanced representations, achieving accurate and robust few-shot traffic classification. Comprehensive experiments on three meticulously reconstructed datasets demonstrate that HLoG significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods. Particularly, HLoG achieves superior recall rates while substantially reducing false positives, highlighting its effectiveness and practical value in real-world cybersecurity applications.
随着网络流量的快速增长,恶意网络攻击也变得越来越频繁和高级,对全球网络安全构成了重大威胁。传统的检测方法,包括基于规则和基于机器学习的方法,在准确识别新兴威胁方面遇到了困难,特别是在样本有限的情况下。尽管最近的小样本学习进展部分解决了数据稀缺的问题,但现有方法仍表现出较高的误报率,并且缺乏有效捕捉关键本地流量模式的能力。在本文中,我们提出了HLoG,这是一种新型分层小样本恶意流量检测框架,它利用从网络会话中提取的局部和全局特征。HLoG采用滑动窗口方法将会话分段成阶段,通过分层双向GRU编码捕获精细的局部交互模式,同时建模全局上下文依赖关系。我们进一步设计了一个会话相似性评估模块,该模块将局部相似性与全局自注意力增强表示相结合,实现了准确且稳健的小样本流量分类。在三个精心重建的数据集上的综合实验表明,HLoG显著优于现有的最先进方法。特别的是,HLoG在达到较高的召回率的同时大大降低了误报率,凸显了其在现实网络安全应用中的有效性和实用价值。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着互联网流量的快速增长,恶意网络攻击日益频繁且复杂,对全球网络安全构成重大威胁。传统的检测方法,如基于规则和机器学习的方法,难以准确识别新兴威胁,特别是在样本有限的情况下。本文提出一种新型的分层小样本恶意流量检测框架HLoG,它结合了网络会话的局部和全局特征。HLoG采用滑动窗口技术将会话分段,通过分层双向GRU编码捕获精细的局部交互模式,同时建立全局上下文依赖关系。此外,设计了一个会话相似性评估模块,将局部相似性与全局自注意力增强表示相结合,实现准确且稳健的小样本流量分类。在三个精心重建的数据集上的综合实验表明,HLoG显著优于现有最新方法,特别是在召回率和误报率方面表现优异,凸显其在现实网络安全应用中的实用性和价值。
Key Takeaways
- 互联网流量的增长导致恶意网络攻击频繁且复杂,对全球网络安全构成威胁。
- 传统检测方法在识别新兴威胁时面临困难,尤其在样本有限的情况下。
- HLoG框架结合了网络会话的局部和全局特征,提高恶意流量检测的准确性。
- HLoG采用滑动窗口技术将会话分段,并通过分层双向GRU编码捕获局部和全局特征。
- HLoG设计了会话相似性评估模块,结合局部和全局特征,实现准确且稳健的流量分类。
- HLoG在多个数据集上的实验表现优于现有方法,特别是在召回率和误报率方面。
- HLoG具有实用性和价值,适用于现实网络安全应用。
点此查看论文截图

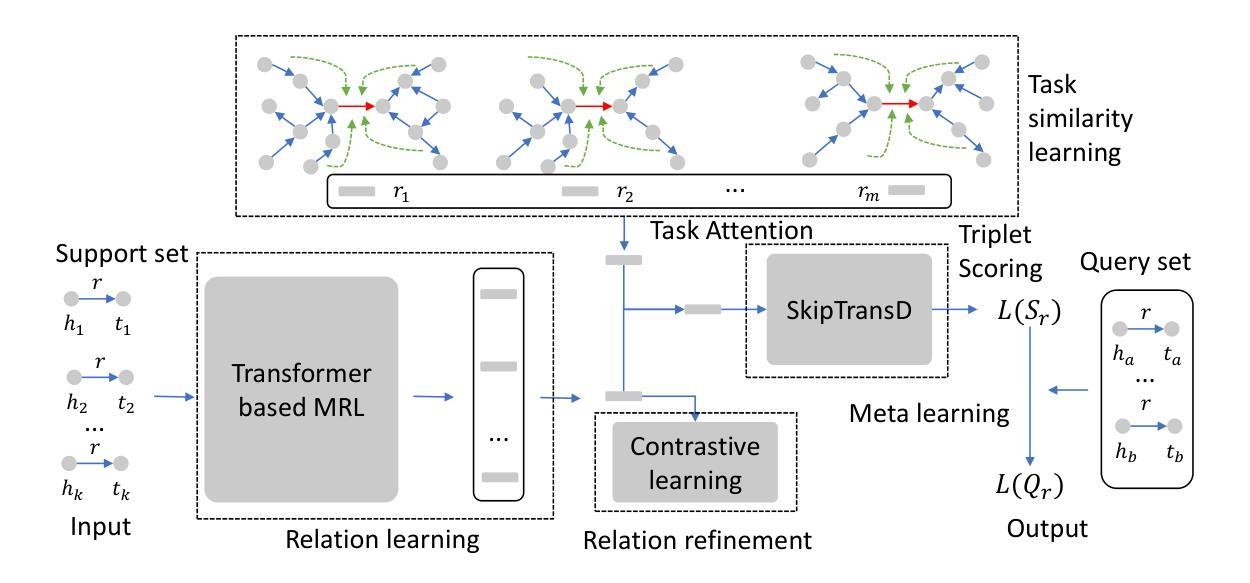
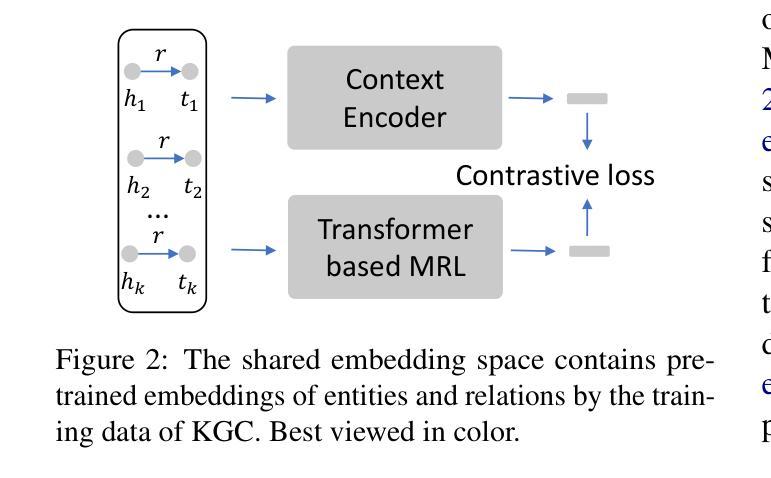
TransNet: Transfer Knowledge for Few-shot Knowledge Graph Completion
Authors:Lihui Liu, Zihao Wang, Dawei Zhou, Ruijie Wang, Yuchen Yan, Bo Xiong, Sihong He, Kai Shu, Hanghang Tong
Knowledge graphs (KGs) are ubiquitous and widely used in various applications. However, most real-world knowledge graphs are incomplete, which significantly degrades their performance on downstream tasks. Additionally, the relationships in real-world knowledge graphs often follow a long-tail distribution, meaning that most relations are represented by only a few training triplets. To address these challenges, few-shot learning has been introduced. Few-shot KG completion aims to make accurate predictions for triplets involving novel relations when only a limited number of training triplets are available. Although many methods have been proposed, they typically learn each relation individually, overlooking the correlations between different tasks and the relevant information in previously trained tasks. In this paper, we propose a transfer learning-based few-shot KG completion method (TransNet). By learning the relationships between different tasks, TransNet effectively transfers knowledge from similar tasks to improve the current task’s performance. Furthermore, by employing meta-learning, TransNet can generalize effectively to new, unseen relations. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of TransNet over state-of-the-art methods. Code can be found at https://github.com/lihuiliullh/TransNet/tree/main
知识图谱(KGs)在各种应用中无处不在且应用广泛。然而,大多数现实世界的知识图谱都是不完整,这极大地降低了它们在下游任务上的性能。此外,现实世界中知识图谱中的关系通常遵循长尾分布,这意味着大多数关系仅由少数训练三元组表示。为了解决这些挑战,已经引入了小样学习。小样知识图谱补全旨在当只有有限数量的训练三元组可用时,对涉及新关系的三元组进行准确预测。尽管已经提出了许多方法,但它们通常单独学习每个关系,而忽略了不同任务之间的相关性以及先前训练任务中的相关信息。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于迁移学习的小样知识图谱补全方法(TransNet)。通过学习不同任务之间的关系,TransNet有效地将从相似任务中学到的知识转移到当前任务中以提高性能。此外,通过采用元学习,TransNet可以有效地推广到新的、未见过的关系。在基准数据集上的大量实验表明,TransNet优于最先进的方法。代码可在 https://github.com/lihuiliullh/TransNet/tree/main 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了知识图谱(KGs)在现实世界应用中的两个主要问题:不完整性和长尾分布关系。针对这些问题,引入了少样本学习。少样本KG补全旨在仅使用有限数量的训练三元组对涉及新关系的三元组进行准确预测。本文提出了一种基于迁移学习的少样本KG补全方法(TransNet)。TransNet通过学习任务之间的关系,有效地将相似任务的知识转移到当前任务中以提高性能。此外,通过采用元学习,TransNet可以有效地推广到新的、未见过的关系上。在基准数据集上的广泛实验证明了TransNet优于最先进的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 知识图谱(KGs)在多种应用中广泛使用,但存在不完整性和长尾分布关系的问题。
- 少样本学习被引入解决这些问题,少样本KG补全旨在用有限数据预测新关系。
- TransNet是一种基于迁移学习的少样本KG补全方法,能迁移相似任务知识以提高性能。
- TransNet通过学习任务间的关系来工作,这有助于知识的迁移。
- TransNet采用元学习,能有效推广到新的、未见过的关系上。
- 在基准数据集上的实验证明TransNet优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

Is Temporal Prompting All We Need For Limited Labeled Action Recognition?
Authors:Shreyank N Gowda, Boyan Gao, Xiao Gu, Xiaobo Jin
Video understanding has shown remarkable improvements in recent years, largely dependent on the availability of large scaled labeled datasets. Recent advancements in visual-language models, especially based on contrastive pretraining, have shown remarkable generalization in zero-shot tasks, helping to overcome this dependence on labeled datasets. Adaptations of such models for videos, typically involve modifying the architecture of vision-language models to cater to video data. However, this is not trivial, since such adaptations are mostly computationally intensive and struggle with temporal modeling. We present TP-CLIP, an adaptation of CLIP that leverages temporal visual prompting for temporal adaptation without modifying the core CLIP architecture. This preserves its generalization abilities. TP-CLIP efficiently integrates into the CLIP architecture, leveraging its pre-trained capabilities for video data. Extensive experiments across various datasets demonstrate its efficacy in zero-shot and few-shot learning, outperforming existing approaches with fewer parameters and computational efficiency. In particular, we use just 1/3 the GFLOPs and 1/28 the number of tuneable parameters in comparison to recent state-of-the-art and still outperform it by up to 15.8% depending on the task and dataset.
视频理解在最近几年取得了显著的进步,这主要依赖于大规模标记数据集的可用性。基于对比预训练的视觉语言模型的最新进展在零样本任务中表现出了出色的泛化能力,有助于克服对标记数据集的依赖。此类视频模型的改编通常需要对视觉语言模型的架构进行修改,以适应视频数据。然而,这并不简单,因为这样的改编大多计算密集且面临时序建模的挑战。我们提出了TP-CLIP,这是CLIP的一种改编,它利用时序视觉提示进行时序适应,而无需修改CLIP架构的核心部分,从而保留了其泛化能力。TP-CLIP能够高效地集成到CLIP架构中,利用其对视频数据的预训练能力。在多个数据集上进行的大量实验证明了其在零样本和少样本学习中的有效性,与现有方法相比,使用更少的参数和更高的计算效率。特别是,我们使用的GFLOPs仅为最近最先进的技术的三分之一,可调参数数量是二十八分之一,并且在某些任务和数据集上仍然超出其性能高达15.8%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in CVPR-W 2025
Summary
近期视频理解领域取得显著进展,这主要依赖于大规模标注数据集的可用性。基于对比预训练的视觉语言模型在零样本任务中展现出强大的泛化能力,有助于减少对标注数据集的依赖。为视频数据适应此类模型通常需要修改视觉语言模型的架构,但这并不简单,因为这样的适应计算密集且面临时序建模的挑战。本文提出TP-CLIP,这是CLIP的一种适应方法,利用时序视觉提示进行时序适应,而无需修改核心CLIP架构,保持了其泛化能力。TP-CLIP有效地集成到CLIP架构中,利用其预训练能力处理视频数据。在多个数据集上的大量实验证明了其在零样本和少样本学习中的有效性,与使用较少参数和计算资源相比,表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 视频理解的进步依赖于大规模标注数据集的可用性。
- 对比预训练的视觉语言模型在零样本任务中展现出强大的泛化能力。
- 适应视频数据的视觉语言模型通常需要修改架构,但面临计算密集和时序建模的挑战。
- TP-CLIP是CLIP的一种适应方法,利用时序视觉提示进行时序适应。
- TP-CLIP保留了CLIP的泛化能力,且集成到CLIP架构中效率高。
- TP-CLIP在多个数据集上的实验证明了其在零样本和少样本学习中的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

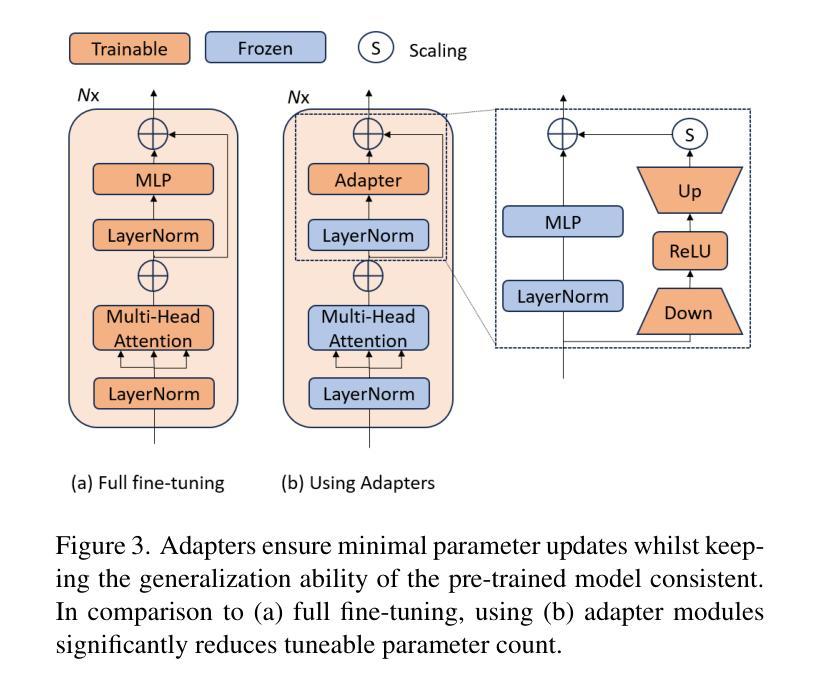
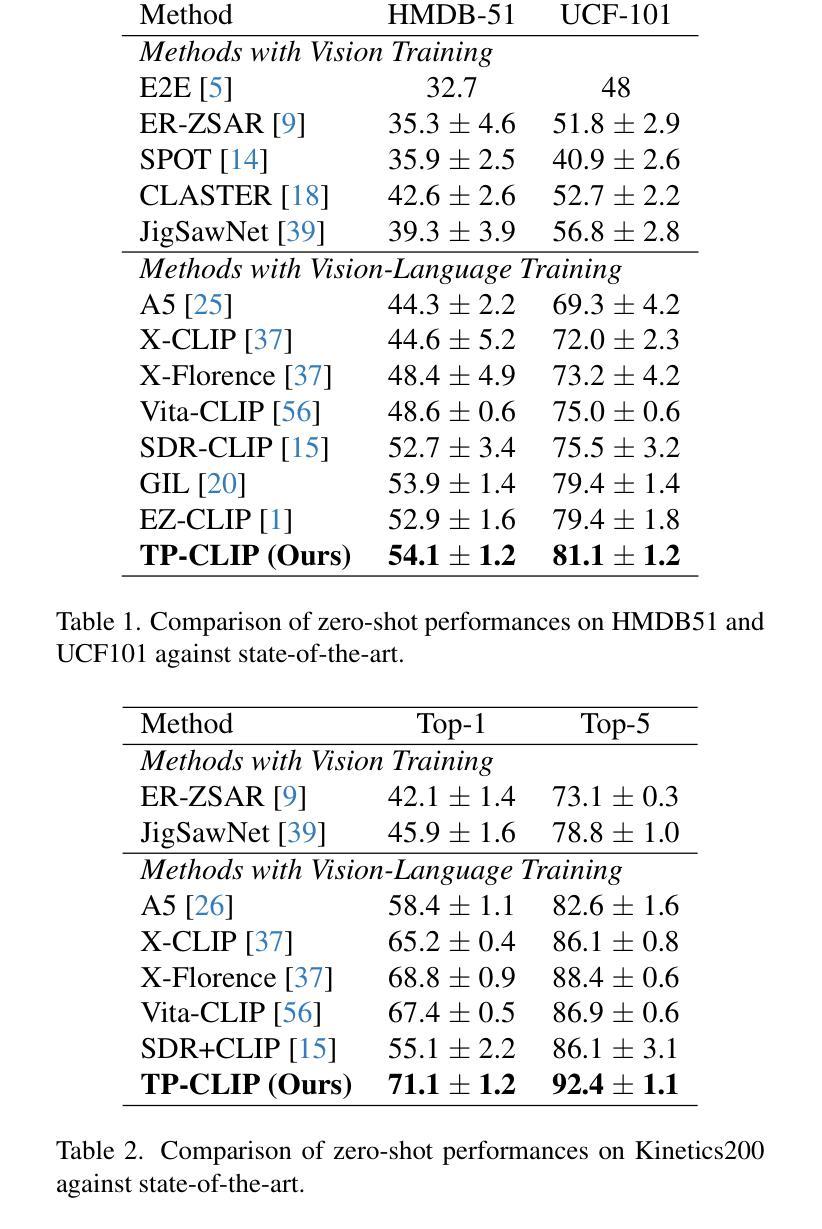
MSCPT: Few-shot Whole Slide Image Classification with Multi-scale and Context-focused Prompt Tuning
Authors:Minghao Han, Linhao Qu, Dingkang Yang, Xukun Zhang, Xiaoying Wang, Lihua Zhang
Multiple instance learning (MIL) has become a standard paradigm for the weakly supervised classification of whole slide images (WSIs). However, this paradigm relies on using a large number of labeled WSIs for training. The lack of training data and the presence of rare diseases pose significant challenges for these methods. Prompt tuning combined with pre-trained Vision-Language models (VLMs) is an effective solution to the Few-shot Weakly Supervised WSI Classification (FSWC) task. Nevertheless, applying prompt tuning methods designed for natural images to WSIs presents three significant challenges: 1) These methods fail to fully leverage the prior knowledge from the VLM’s text modality; 2) They overlook the essential multi-scale and contextual information in WSIs, leading to suboptimal results; and 3) They lack exploration of instance aggregation methods. To address these problems, we propose a Multi-Scale and Context-focused Prompt Tuning (MSCPT) method for FSWC task. Specifically, MSCPT employs the frozen large language model to generate pathological visual language prior knowledge at multiple scales, guiding hierarchical prompt tuning. Additionally, we design a graph prompt tuning module to learn essential contextual information within WSI, and finally, a non-parametric cross-guided instance aggregation module has been introduced to derive the WSI-level features. Extensive experiments, visualizations, and interpretability analyses were conducted on five datasets and three downstream tasks using three VLMs, demonstrating the strong performance of our MSCPT. All codes have been made publicly accessible at https://github.com/Hanminghao/MSCPT.
多实例学习(MIL)已成为全幻灯片图像(WSI)弱监督分类的标准范式。然而,这种范式依赖于大量有标签的WSI进行训练。缺乏训练数据和罕见疾病的存在给这些方法带来了重大挑战。结合预训练的语言视觉模型(VLMs)的提示微调是解决小样本弱监督WSI分类(FSWC)任务的有效方法。然而,将针对自然图像设计的提示微调方法应用于WSI面临三大挑战:1)这些方法未能充分利用来自VLM文本模态的先验知识;2)它们忽略了WSI中的多尺度和上下文信息,导致结果不理想;并且3)缺乏对实例聚合方法的探索。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了面向FSWC任务的多尺度上下文聚焦提示微调(MSCPT)方法。具体而言,MSCPT使用冻结的大型语言模型在多尺度上生成病理学视觉语言先验知识,引导分层提示微调。此外,我们设计了一个图提示微调模块来学习WSI中的关键上下文信息,并最终引入了一个非参数化交叉引导实例聚合模块来提取WSI级特征。在五个数据集和三个下游任务上使用了三种VLMs进行了广泛的实验、可视化和解释性分析,展示了我们的MSCPT的强大性能。所有代码已公开访问于https://github.com/Hanminghao/MSCPT。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been submitted to the IEEE TMI for possible publication
Summary
基于多实例学习(MIL)的弱监督全幻灯片图像(WSI)分类已成为标准范式,但面临缺乏训练数据和罕见疾病的挑战。提示调整与预训练视觉语言模型(VLM)的结合是解决少数弱监督WSI分类(FSWC)任务的有效方法。然而,将针对自然图像设计的提示调整方法应用于WSI存在三个主要挑战。为解决这些问题,我们提出了多尺度与上下文聚焦的提示调整(MSCPT)方法。MSCPT利用冻结的大型语言模型生成病理视觉语言先验知识,指导分层提示调整,并设计图提示调整模块来学习WSI中的关键上下文信息。此外,引入了非参数化交叉引导实例聚合模块来提取WSI级别的特征。在五个数据集和三个下游任务上使用三种VLM进行的广泛实验、可视化和可解释性分析证明了MSCPT的强大性能。
Key Takeaways
- 多实例学习(MIL)是弱监督全幻灯片图像(WSI)分类的标准范式,但缺乏训练数据和罕见疾病带来挑战。
- 提示调整与预训练视觉语言模型(VLM)的结合为少数弱监督WSI分类(FSWC)任务提供了有效解决方案。
- 将针对自然图像的提示调整方法应用于WSI存在显著挑战,包括未能充分利用VLM的文本模态先验知识、忽视多尺度和上下文信息,以及缺乏实例聚合方法的探索。
- 提出的Multi-Scale and Context-focused Prompt Tuning(MSCPT)方法利用大型语言模型生成病理视觉语言先验知识,并设计图提示调整模块来学习WSI的上下文信息。
- MSCPT引入了非参数化交叉引导实例聚合模块,以提取WSI级别的特征。
- 在多个数据集和下游任务上的实验证明了MSCPT的强大性能。
- 所有代码已公开可访问。
点此查看论文截图
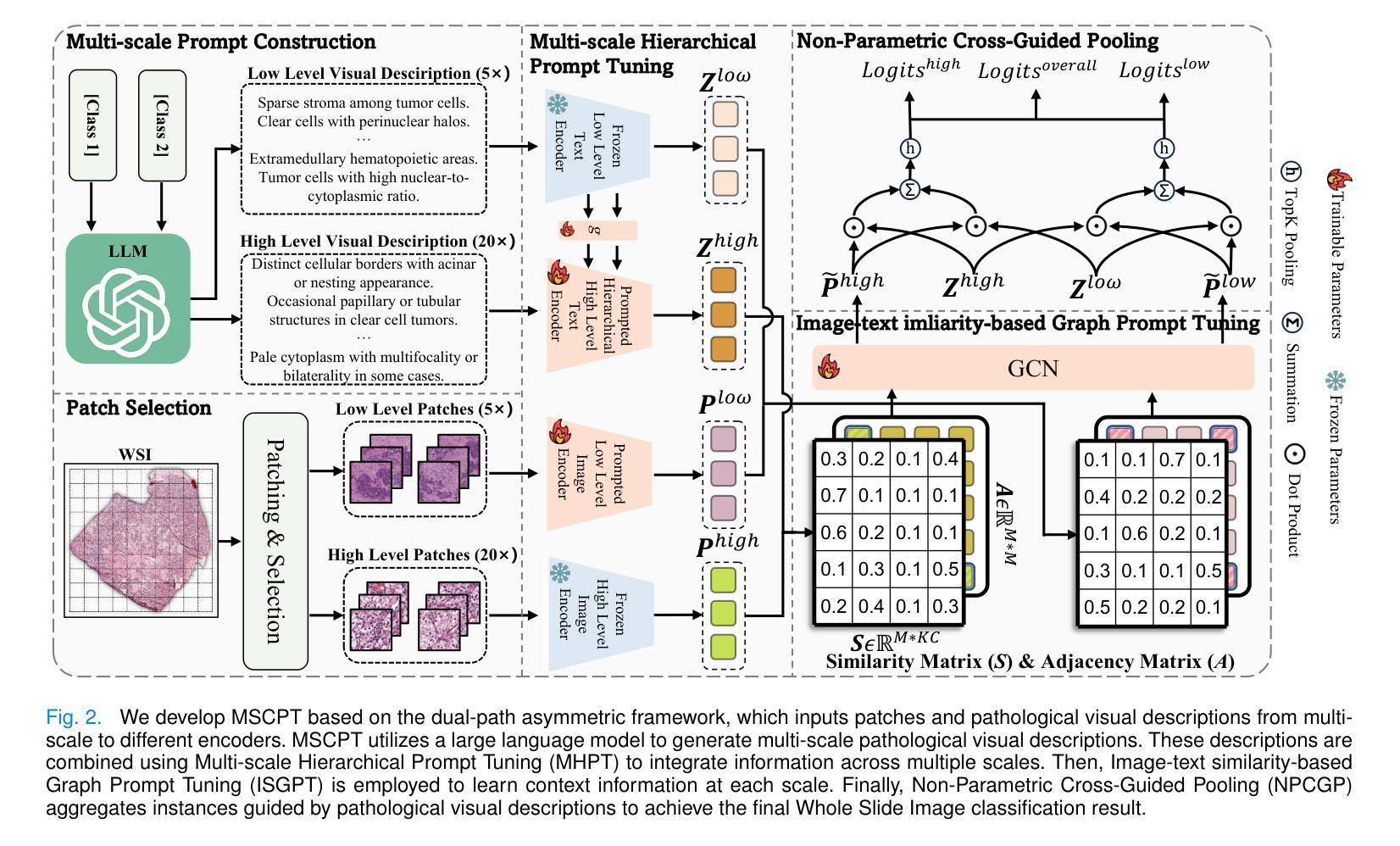
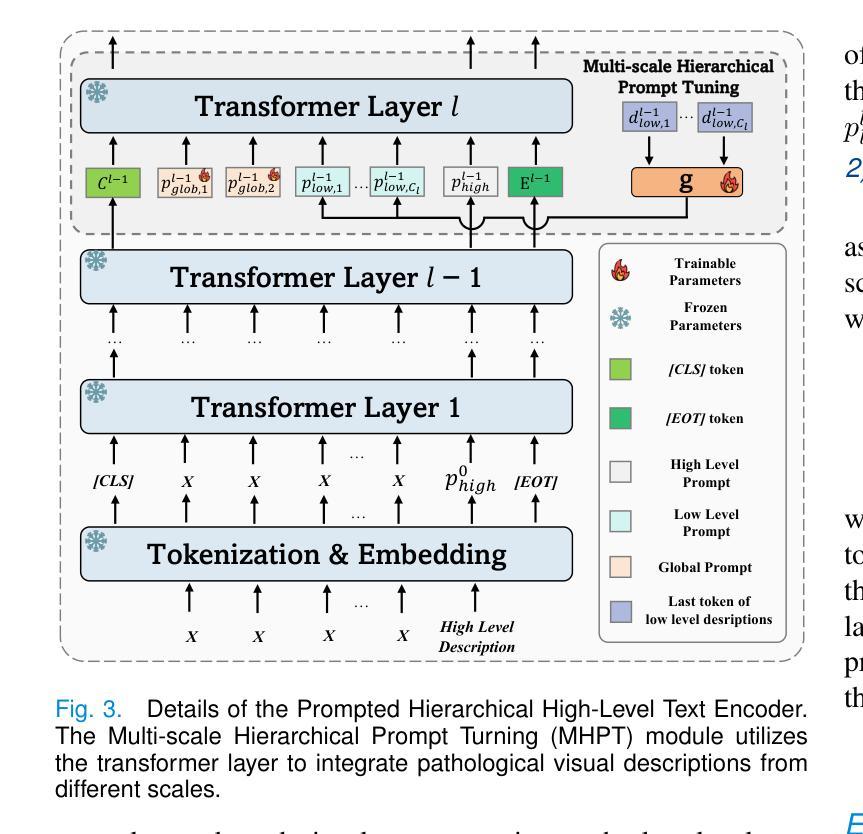
No Re-Train, More Gain: Upgrading Backbones with Diffusion model for Pixel-Wise and Weakly-Supervised Few-Shot Segmentation
Authors:Shuai Chen, Fanman Meng, Chenhao Wu, Haoran Wei, Runtong Zhang, Qingbo Wu, Linfeng Xu, Hongliang Li
Few-Shot Segmentation (FSS) aims to segment novel classes using only a few annotated images. Despite considerable progress under pixel-wise support annotation, current FSS methods still face three issues: the inflexibility of backbone upgrade without re-training, the inability to uniformly handle various types of annotations (e.g., scribble, bounding box, mask, and text), and the difficulty in accommodating different annotation quantity. To address these issues simultaneously, we propose DiffUp, a novel framework that conceptualizes the FSS task as a conditional generative problem using a diffusion process. For the first issue, we introduce a backbone-agnostic feature transformation module that converts different segmentation cues into unified coarse priors, facilitating seamless backbone upgrade without re-training. For the second issue, due to the varying granularity of transformed priors from diverse annotation types (scribble, bounding box, mask, and text), we conceptualize these multi-granular transformed priors as analogous to noisy intermediates at different steps of a diffusion model. This is implemented via a self-conditioned modulation block coupled with a dual-level quality modulation branch. For the third issue, we incorporate an uncertainty-aware information fusion module to harmonize the variability across zero-shot, one-shot, and many-shot scenarios. Evaluated through rigorous benchmarks, DiffUp significantly outperforms existing FSS models in terms of flexibility and accuracy.
Few-Shot Segmentation(FSS)旨在仅使用少量标注图像对新型类别进行分割。尽管在像素级支持标注方面取得了相当大的进展,但当前的FSS方法仍然面临三个问题:主干升级不灵活需要重新训练,无法统一处理各种类型标注(例如涂鸦、边界框、蒙版和文本),以及难以适应不同的标注数量。为了解决这三个问题,我们提出了DiffUp这一新型框架,它将FSS任务概念化为一个条件生成问题,并使用扩散过程来解决。针对第一个问题,我们引入了一个通用的特征转换模块,该模块能够将不同的分割线索转换为统一的粗略先验知识,从而实现无缝主干升级而无需重新训练。对于第二个问题,由于不同标注类型(涂鸦、边界框、蒙版和文本)转换后的先验知识粒度不同,我们将这些多粒度转换后的先验知识概念化为扩散模型不同步骤中的噪声中间产物。这是通过一个自调节调制块与双级质量调制分支的结合实现的。对于第三个问题,我们引入了不确定信息融合模块,以协调零样本、单样本和多样本场景中的变量。通过严格的基准测试,DiffUp在灵活性和准确性方面显著优于现有的FSS模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 figures
Summary
基于少量标注图像进行新型类别分割的Few-Shot Segmentation(FSS)仍面临三大问题:骨干网升级不灵活、难以处理多种类型注解以及不同注解数量的适配困难。为同时解决这些问题,我们提出DiffUp框架,将FSS任务概念化为一个条件生成问题并使用扩散过程解决。引入骨干网无关的特征转换模块,统一处理各种分割线索,实现骨干网无缝升级。借助自条件调制块和双级质量调制分支,将多粒度转换线索视为扩散模型不同步骤的噪声中间产物。融入不确定性感知信息融合模块,协调零样本、单样本和多样本场景中的变化。经严格基准测试,DiffUp在灵活性和准确性上显著优于现有FSS模型。
Key Takeaways
- Few-Shot Segmentation (FSS)面临三大挑战:骨干网升级的灵活性、处理多种类型注解的能力,以及适配不同注解数量的难度。
- DiffUp框架将FSS任务视为一个条件生成问题,并采用扩散过程来解决。
- 引入的特征转换模块使骨干网升级更为灵活,无需重新训练。
- 多粒度转换线索被视为扩散模型中不同步骤的噪声中间产物,通过自条件调制块和双级质量调制分支处理。
- 利用不确定性感知信息融合模块来协调不同场景中的变化。
- DiffUp在灵活性和准确性上显著优于现有的FSS模型。
点此查看论文截图

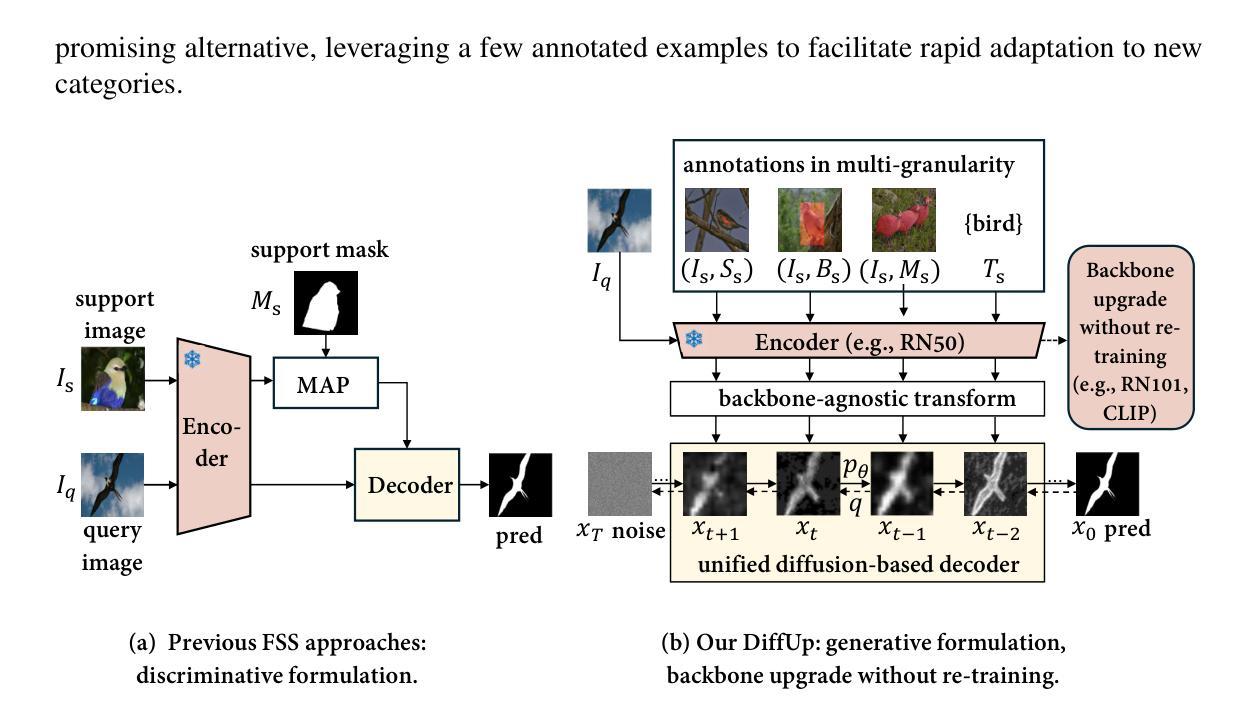
6Img-to-3D: Few-Image Large-Scale Outdoor Driving Scene Reconstruction
Authors:Théo Gieruc, Marius Kästingschäfer, Sebastian Bernhard, Mathieu Salzmann
Current 3D reconstruction techniques struggle to infer unbounded scenes from a few images faithfully. Specifically, existing methods have high computational demands, require detailed pose information, and cannot reconstruct occluded regions reliably. We introduce 6Img-to-3D, an efficient, scalable transformer-based encoder-renderer method for single-shot image to 3D reconstruction. Our method outputs a 3D-consistent parameterized triplane from only six outward-facing input images for large-scale, unbounded outdoor driving scenarios. We take a step towards resolving existing shortcomings by combining contracted custom cross- and self-attention mechanisms for triplane parameterization, differentiable volume rendering, scene contraction, and image feature projection. We showcase that six surround-view vehicle images from a single timestamp without global pose information are enough to reconstruct 360$^{\circ}$ scenes during inference time, taking 395 ms. Our method allows, for example, rendering third-person images and birds-eye views. Our code is available at https://github.com/continental/6Img-to-3D, and more examples can be found at our website here https://6Img-to-3D.GitHub.io/.
当前的三维重建技术很难从少数图像中忠实地推演出无边界的场景。具体来说,现有方法计算需求高,需要详细的姿态信息,并且无法可靠地重建遮挡区域。我们推出了6Img-to-3D,这是一种高效、可扩展的基于transformer的编码器-渲染器方法,用于单张图像到三维重建。我们的方法仅从六张外向输入图像中输出一致的三维参数化triplane,适用于大规模、无边界的户外驾驶场景。我们通过结合定制的交叉和自注意力机制进行triplane参数化、可微分体积渲染、场景收缩和图像特征投影,来解决现有缺陷。我们展示,在推理时间内,没有全局姿态信息的单个时间戳的六张环绕视图车辆图像足以重建360°场景,只需395毫秒。我们的方法允许例如渲染第三人称图像和鸟瞰图。我们的代码可在https://github.com/continental/6Img-to-3D找到,更多示例请访问我们的网站https://6Img-to-3D.GitHub.io/.
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IV 2025. Joint first authorship. Project page: https://6Img-to-3D.GitHub.io/ Code https://github.com/continental/6Img-to-3D
Summary
本文介绍了现有的三维重建技术面临的挑战,如计算需求高、需要详细的姿态信息以及无法可靠地重建遮挡区域等。为解决这些问题,提出了一种基于Transformer的高效、可扩展的编码器渲染器方法——6Img-to-3D,可从六张面向外部的输入图像进行单幅图像到三维重建。该方法适用于大规模、无界的外景驾驶场景,输出参数化的三平面,并在推理时间内从单一时间戳的六个环绕视图车辆图像重建出完整的场景。通过自定义的交叉和自注意力机制、可微体积渲染、场景收缩和图像特征投影等技术解决了现有问题。该方法允许渲染第三人称图像和鸟瞰图等。代码可在指定的GitHub网址找到。
Key Takeaways
- 当前三维重建技术面临的挑战包括高计算需求、依赖详细姿态信息和无法可靠重建遮挡区域等。
- 介绍了一种基于Transformer的新方法——6Img-to-3D,可从少量图像进行高效的三维重建。
- 该方法适用于大规模、无界的外景驾驶场景的重建,输出参数化的三平面。
- 6Img-to-3D能够在没有全局姿态信息的情况下,从单一时间点的六个环绕视图车辆图像重建出完整的场景。
- 方法结合了自定义的交叉和自注意力机制、可微体积渲染等技术来解决现有问题。
- 该方法允许渲染多种视图,如第三人称图像和鸟瞰图等。
点此查看论文截图


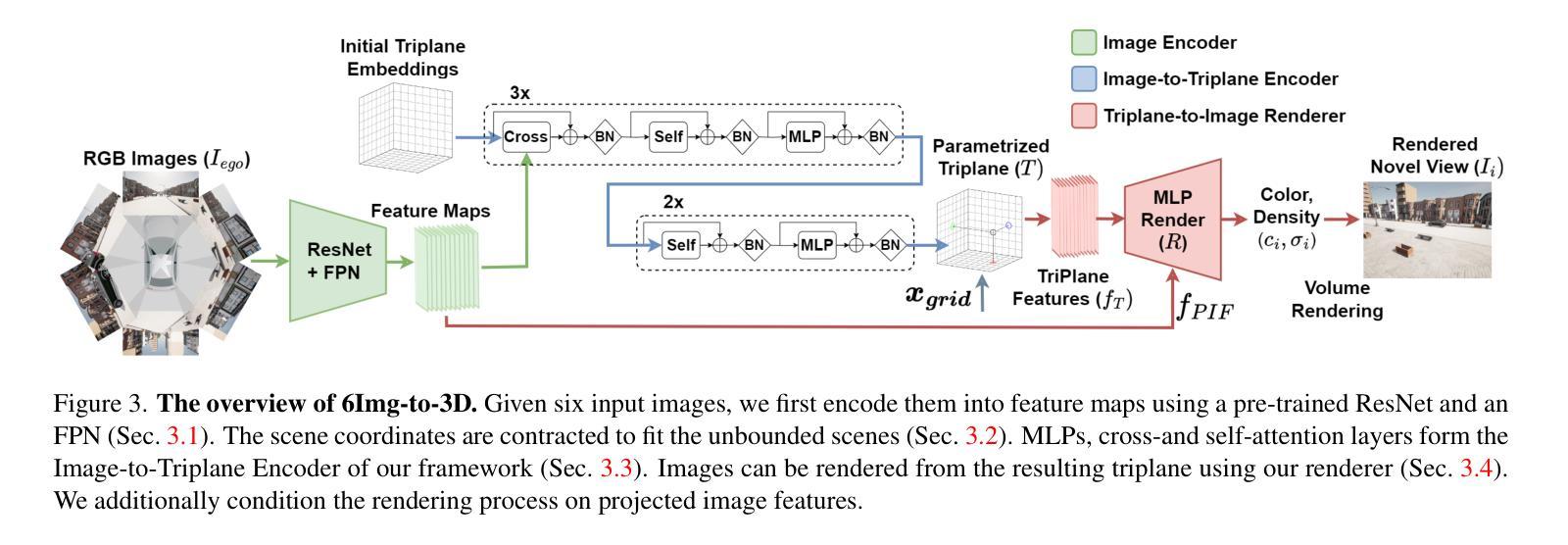
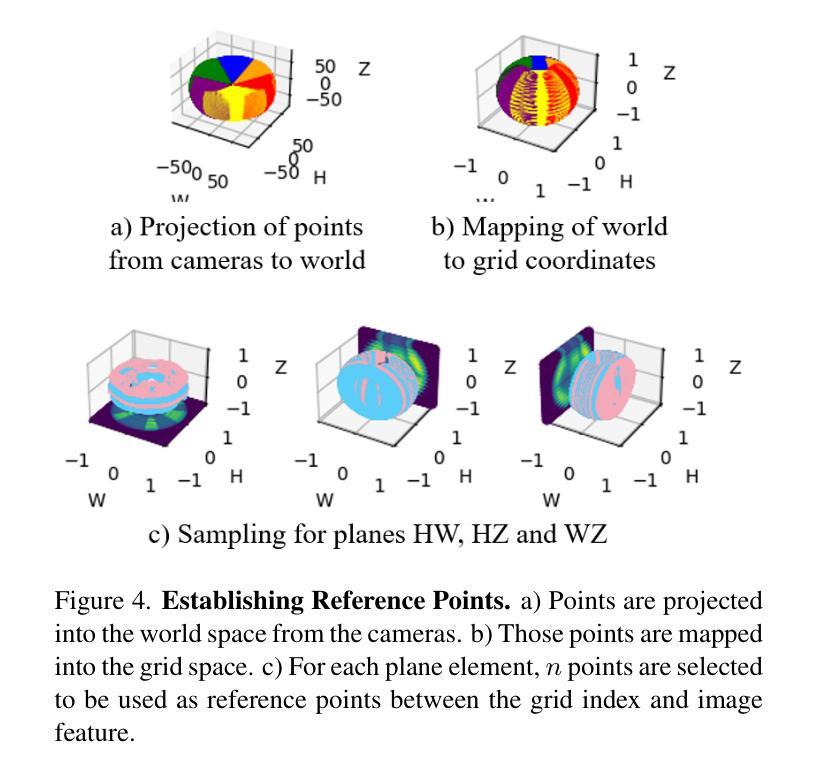
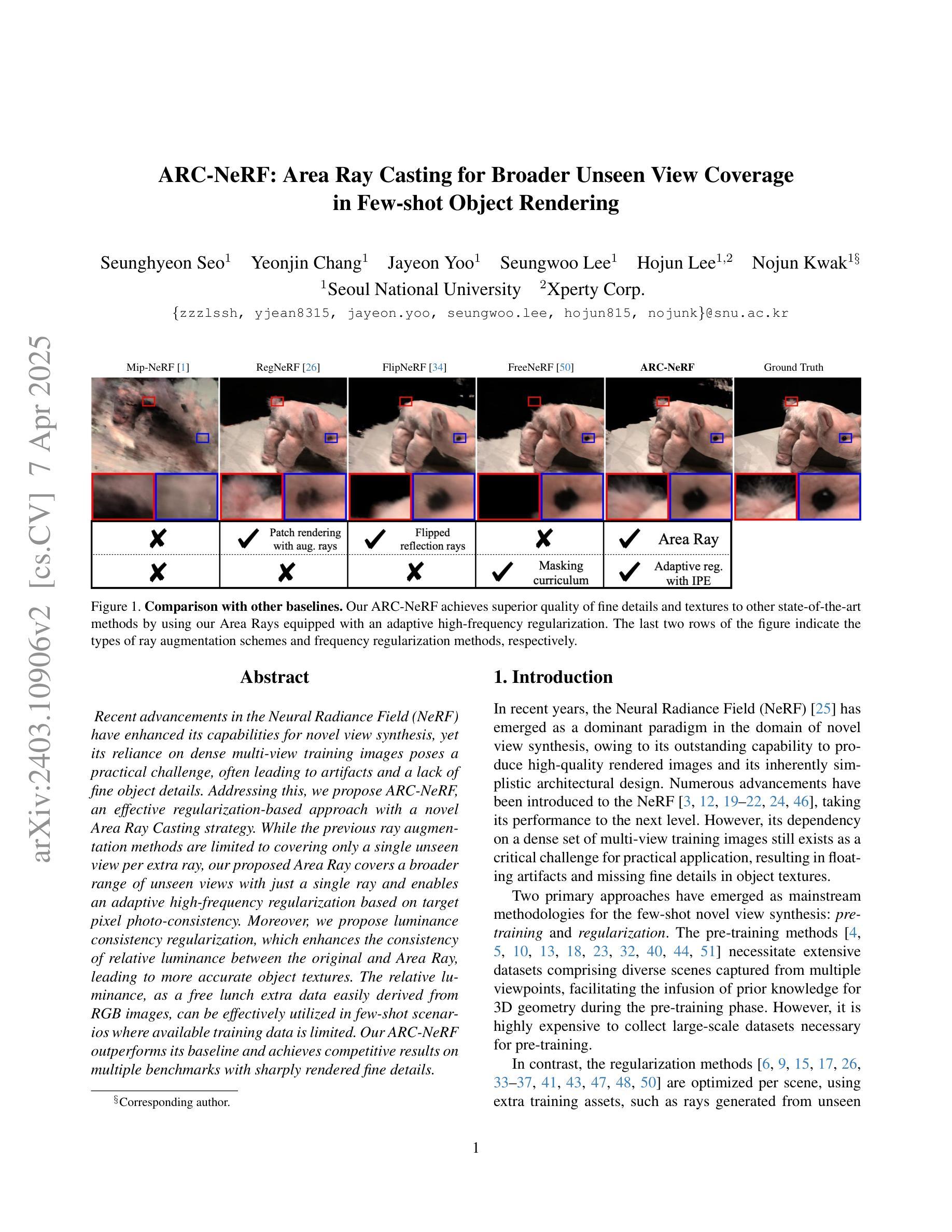
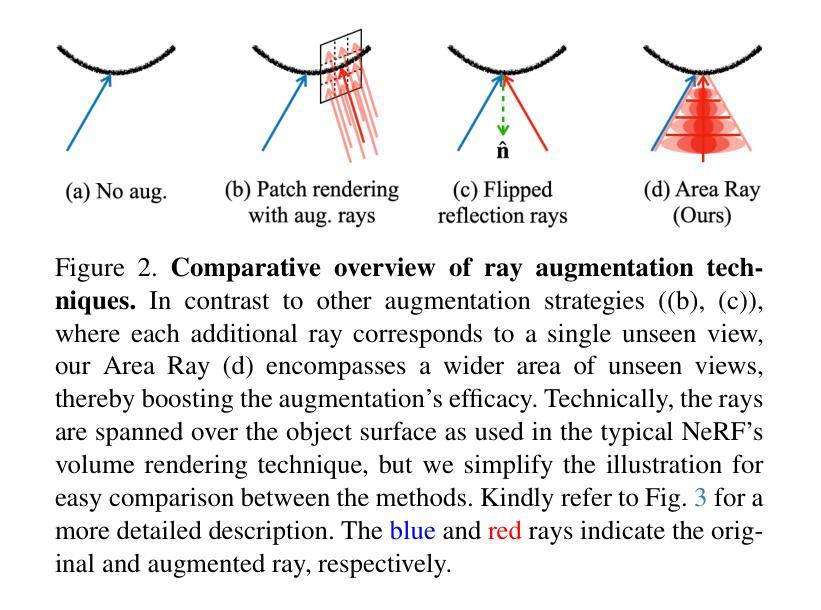
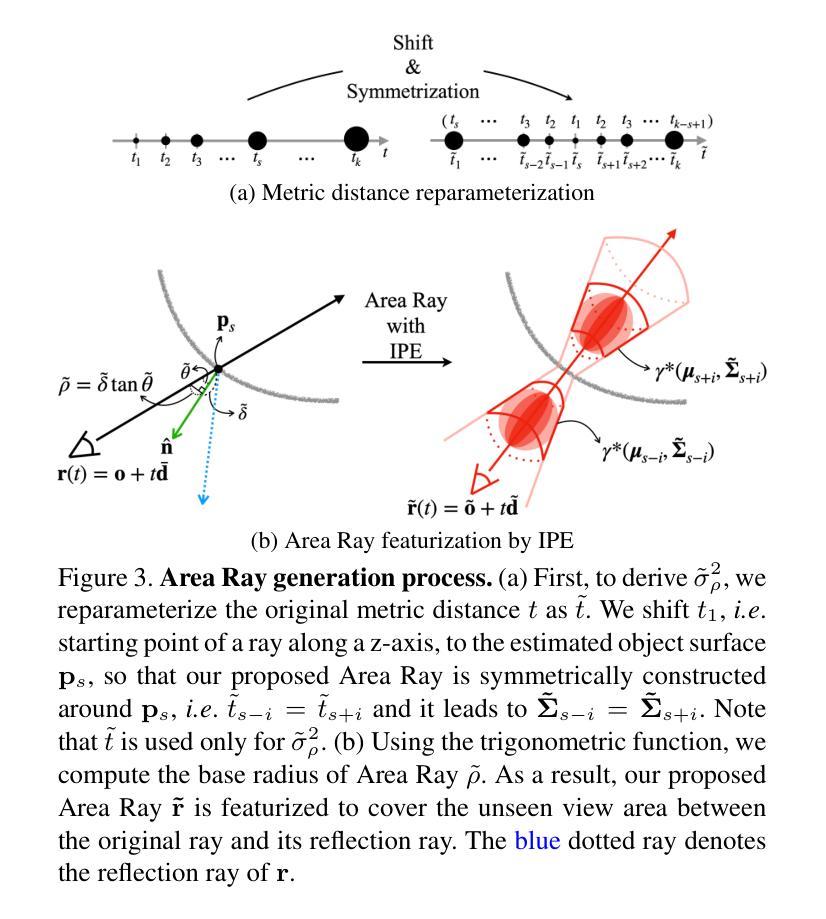
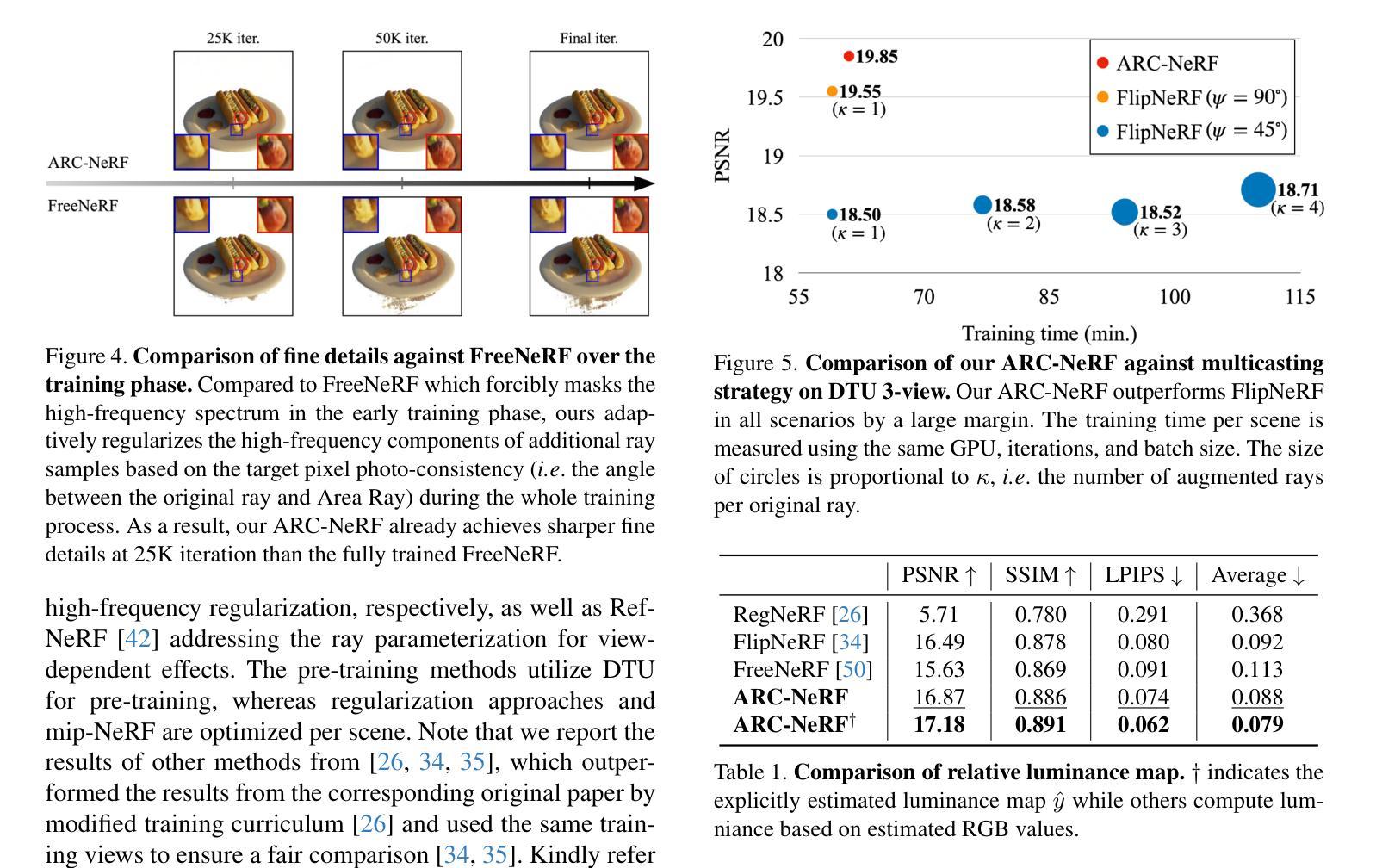
ARC-NeRF: Area Ray Casting for Broader Unseen View Coverage in Few-shot Object Rendering
Authors:Seunghyeon Seo, Yeonjin Chang, Jayeon Yoo, Seungwoo Lee, Hojun Lee, Nojun Kwak
Recent advancements in the Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) have enhanced its capabilities for novel view synthesis, yet its reliance on dense multi-view training images poses a practical challenge, often leading to artifacts and a lack of fine object details. Addressing this, we propose ARC-NeRF, an effective regularization-based approach with a novel Area Ray Casting strategy. While the previous ray augmentation methods are limited to covering only a single unseen view per extra ray, our proposed Area Ray covers a broader range of unseen views with just a single ray and enables an adaptive high-frequency regularization based on target pixel photo-consistency. Moreover, we propose luminance consistency regularization, which enhances the consistency of relative luminance between the original and Area Ray, leading to more accurate object textures. The relative luminance, as a free lunch extra data easily derived from RGB images, can be effectively utilized in few-shot scenarios where available training data is limited. Our ARC-NeRF outperforms its baseline and achieves competitive results on multiple benchmarks with sharply rendered fine details.
最近神经辐射场(NeRF)的进展增强了其用于新型视图合成的能力,然而,它对密集多视图训练图像的依赖构成了一个实际挑战,往往导致出现伪影和缺乏精细的对象细节。为解决这一问题,我们提出ARC-NeRF,这是一种基于有效正则化的方法,采用了新型的区域光线投射策略。虽然之前的光线增强方法仅限于每条额外光线只覆盖一个未见视图,但我们提出的区域光线可以仅使用一条光线覆盖更广泛的未见视图范围,并实现基于目标像素照片一致性的自适应高频正则化。此外,我们还提出了亮度一致性正则化,增强了原始图像和区域光线之间相对亮度的一致性,从而得到更精确的对象纹理。相对亮度作为容易从RGB图像中获得的额外数据,可以在训练数据有限的少数场景中有效利用。我们的ARC-NeRF超越了基线方法,并在多个基准测试中实现了出色的表现,能够清晰地呈现精细细节。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025 Workshop: 4th Computer Vision for Metaverse Workshop
Summary
神经网络辐射场(NeRF)技术的最新进展增强了其新颖的视图合成能力,但它对密集的多视图训练图像的依赖带来了实际操作中的挑战,可能会导致伪影和缺乏精细的对象细节。为解决此问题,我们提出了ARC-NeRF,这是一种基于正则化的有效方法,并采用了新型的区域光线投射策略。与之前的光线增强方法不同,我们的区域光线能够在单次投射中覆盖更广泛的未见视图,并实现基于目标像素照片一致性的自适应高频正则化。此外,我们还提出了亮度一致性正则化,增强了原始图像和区域光线之间的相对亮度一致性,从而得到更精确的对象纹理。相对亮度作为来自RGB图像的额外数据,可以在少量训练数据的情况下得到有效利用。ARC-NeRF超越了基线方法,并在多个基准测试中实现了精细的渲染效果。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF技术在新型视图合成方面展现出进展,但依赖密集多视图训练图像导致实际应用中的挑战。
- ARC-NeRF通过有效的正则化方法和新型区域光线投射策略解决了这一问题。
- 区域光线能够在单次投射中覆盖更广泛的未见视图。
- ARC-NeRF实现了基于目标像素照片一致性的自适应高频正则化。
- 亮度一致性正则化增强了原始图像和区域光线之间的相对亮度一致性。
- 相对亮度信息可作为来自RGB图像的额外数据,在训练数据有限的情况下提供有效帮助。
点此查看论文截图