⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-09 更新
GAMBAS: Generalised-Hilbert Mamba for Super-resolution of Paediatric Ultra-Low-Field MRI
Authors:Levente Baljer, Ula Briski, Robert Leech, Niall J. Bourke, Kirsten A. Donald, Layla E. Bradford, Simone R. Williams, Sadia Parkar, Sidra Kaleem, Salman Osmani, Sean C. L. Deoni, Steven C. R. Williams, Rosalyn J. Moran, Emma C. Robinson, Frantisek Vasa
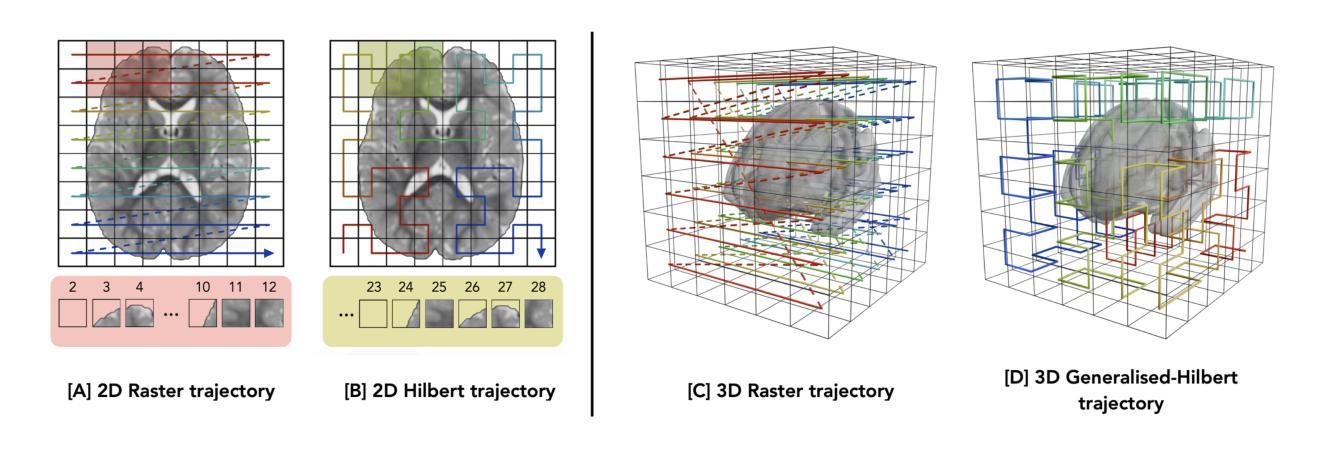
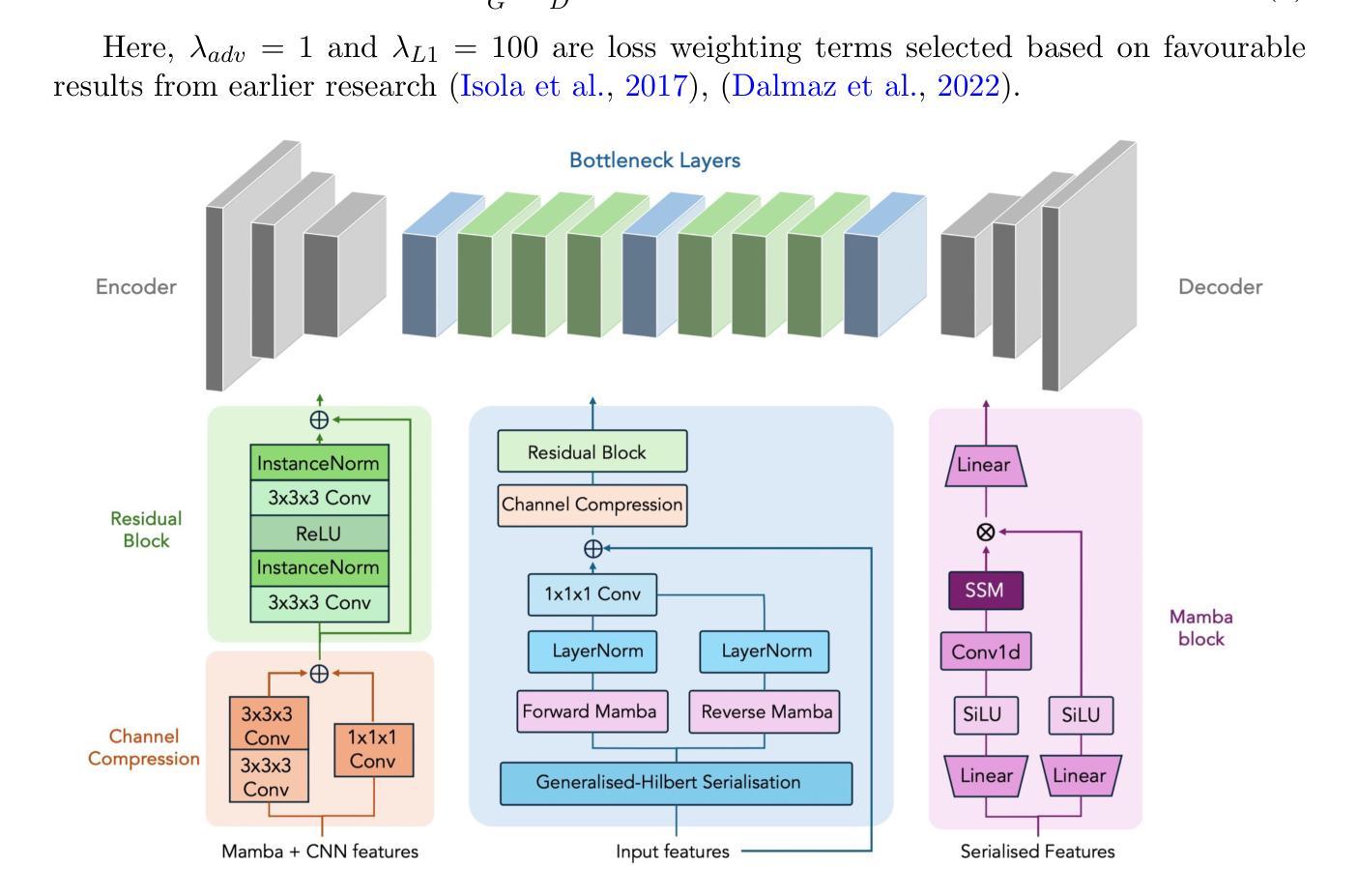
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is critical for neurodevelopmental research, however access to high-field (HF) systems in low- and middle-income countries is severely hindered by their cost. Ultra-low-field (ULF) systems mitigate such issues of access inequality, however their diminished signal-to-noise ratio limits their applicability for research and clinical use. Deep-learning approaches can enhance the quality of scans acquired at lower field strengths at no additional cost. For example, Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) fused with transformer modules have demonstrated a remarkable ability to capture both local information and long-range context. Unfortunately, the quadratic complexity of transformers leads to an undesirable trade-off between long-range sensitivity and local precision. We propose a hybrid CNN and state-space model (SSM) architecture featuring a novel 3D to 1D serialisation (GAMBAS), which learns long-range context without sacrificing spatial precision. We exhibit improved performance compared to other state-of-the-art medical image-to-image translation models.
磁共振成像(MRI)在神经发育研究中至关重要,但在中低收入国家,由于成本高昂,高场(HF)系统的使用受到严重阻碍。超低场(ULF)系统缓解了获取不平等的问题,但其信噪比降低限制了其在研究和临床使用中的应用。深度学习的方法可以在不增加额外成本的情况下提高低场强扫描的质量。例如,卷积神经网络(CNN)与变压器模块的融合已经显示出捕捉局部信息和长距离上下文信息的显著能力。然而,变压器二次复杂性导致长距离敏感度和局部精度之间出现了令人不快的权衡。我们提出了一种混合CNN和状态空间模型(SSM)架构,具有新型3D到1D序列化(GAMBAS),能在不牺牲空间精度的情况下学习长距离上下文。与其他最先进的医学图像到图像翻译模型相比,我们展现了更好的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at MIDL 2025, 21 pages, 8 figures
Summary
深度学习技术可以提高低磁场MRI扫描的质量,通过混合卷积神经网络(CNN)与状态空间模型(SSM)架构,实现高低磁场MRI图像之间的转换,为解决医疗资源分配不均问题提供新的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习技术可用于增强低磁场MRI扫描的质量。
- 卷积神经网络(CNN)与状态空间模型(SSM)的融合架构可以提高MRI图像的质量。
- 提出的架构实现了长程上下文学习与空间精度的平衡。
- 通过采用名为GAMBAS的3D到1D序列化技术,新型架构展现了改进的性能。
- 该技术相较于其他先进的医疗图像到图像翻译模型具有更好的表现。
- 低成本、高质量的医疗成像技术对于解决医疗资源分配不均问题具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

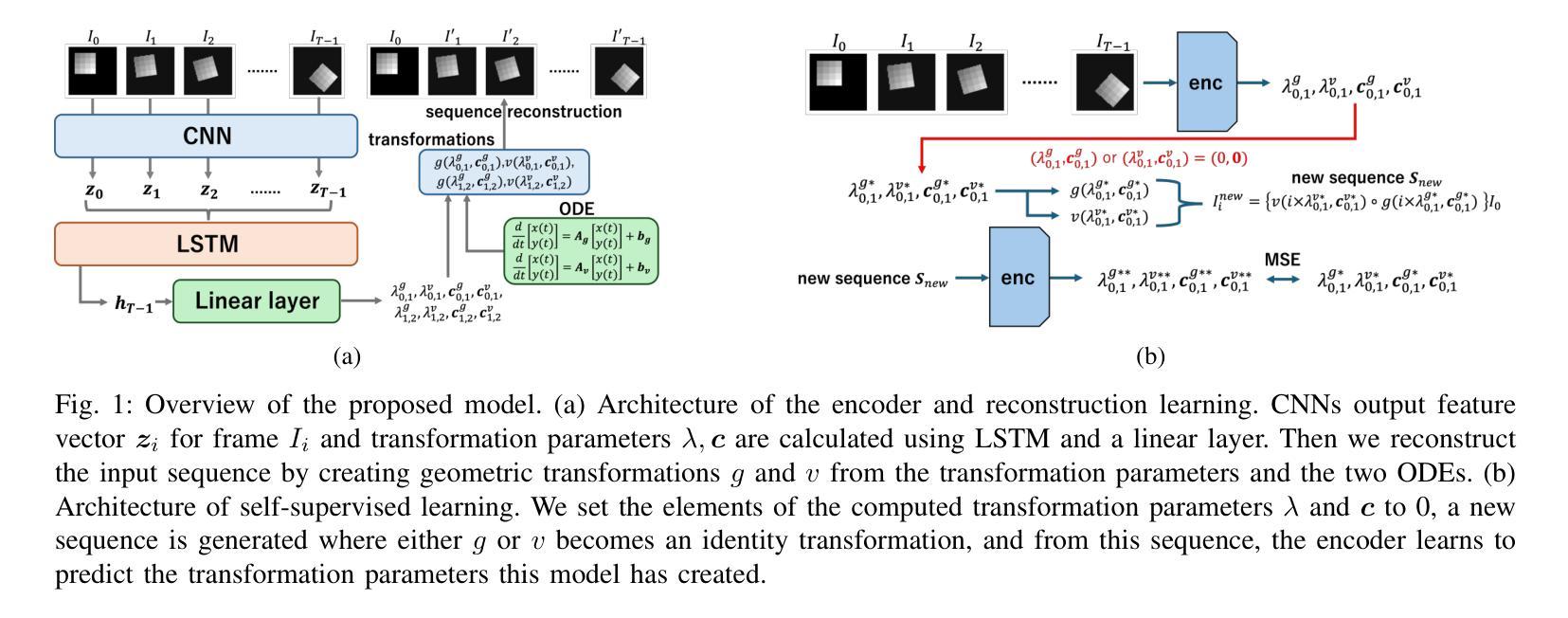
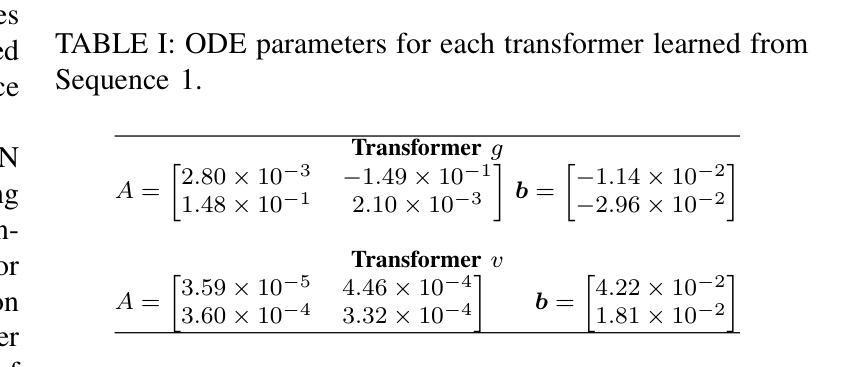
Learning Conditionally Independent Transformations using Normal Subgroups in Group Theory
Authors:Kayato Nishitsunoi, Yoshiyuki Ohmura, Takayuki Komatsu, Yasuo Kuniyoshi
Humans develop certain cognitive abilities to recognize objects and their transformations without explicit supervision, highlighting the importance of unsupervised representation learning. A fundamental challenge in unsupervised representation learning is to separate different transformations in learned feature representations. Although algebraic approaches have been explored, a comprehensive theoretical framework remains underdeveloped. Existing methods decompose transformations based on algebraic independence, but these methods primarily focus on commutative transformations and do not extend to cases where transformations are conditionally independent but noncommutative. To extend current representation learning frameworks, we draw inspiration from Galois theory, where the decomposition of groups through normal subgroups provides an approach for the analysis of structured transformations. Normal subgroups naturally extend commutativity under certain conditions and offer a foundation for the categorization of transformations, even when they do not commute. In this paper, we propose a novel approach that leverages normal subgroups to enable the separation of conditionally independent transformations, even in the absence of commutativity. Through experiments on geometric transformations in images, we show that our method successfully categorizes conditionally independent transformations, such as rotation and translation, in an unsupervised manner, suggesting a close link between group decomposition via normal subgroups and transformation categorization in representation learning.
人类发展出某些认知能力,能够识别物体及其转换,而无需明确的监督,这突出了无监督表示学习的重要性。无监督表示学习的一个基本挑战在于在学习的特征表示中分离不同的转换。虽然已探索了代数方法,但综合理论框架仍不够完善。现有方法基于代数独立性分解转换,但这些方法主要关注交换式转换,并不扩展到转换条件独立但非交换的情况。为了扩展当前的表示学习框架,我们从伽罗瓦理论(Galois theory)中汲取灵感,该理论通过正规子群对群组进行分解,为分析结构化转换提供了一种方法。正规子群在某些条件下自然地扩展了交换性,并为转换的分类提供了基础,即使它们不交换也是如此。在本文中,我们提出了一种利用正规子群分离条件独立转换的新方法,即使在缺乏交换性的情况下也是如此。通过图像中几何转换的实验,我们证明了我们的方法能够成功地对条件独立的转换进行分类,如旋转和平移,这是一种无监督的方式,这表明通过正规子群进行群组分解与表示学习中的转换分类之间存在密切联系。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 10 figures, conference paper
Summary
本文探讨人类在无明确监督下识别物体及其转换的认知能力,指出无监督表示学习的重要性。文章提出一种利用正规子群理论的新方法,实现对条件独立转换的分离,即使在不具备可交换性的情况下也是如此。通过图像几何转换的实验,证明该方法在无监督情况下成功地对旋转和翻译等条件独立转换进行分类,显示正规子群分解与表示学习中的转换分类之间的密切联系。
Key Takeaways
- 无监督表示学习在识别物体及其转换方面具有重要意义。
- 当前方法主要关注基于代数独立性的转换分解,但不适用于条件独立但不可交换的转换。
- 正规子群理论为结构化转换的分解提供了一种方法,即使在转换不可交换的情况下也能进行分类。
- 利用正规子群的理论框架,能够在无监督的情况下分离条件独立的转换,如旋转和翻译。
- 实验证明,该方法可有效处理图像中的几何转换。
- 此研究揭示了正规子群分解与表示学习中的转换分类之间的紧密联系。
点此查看论文截图

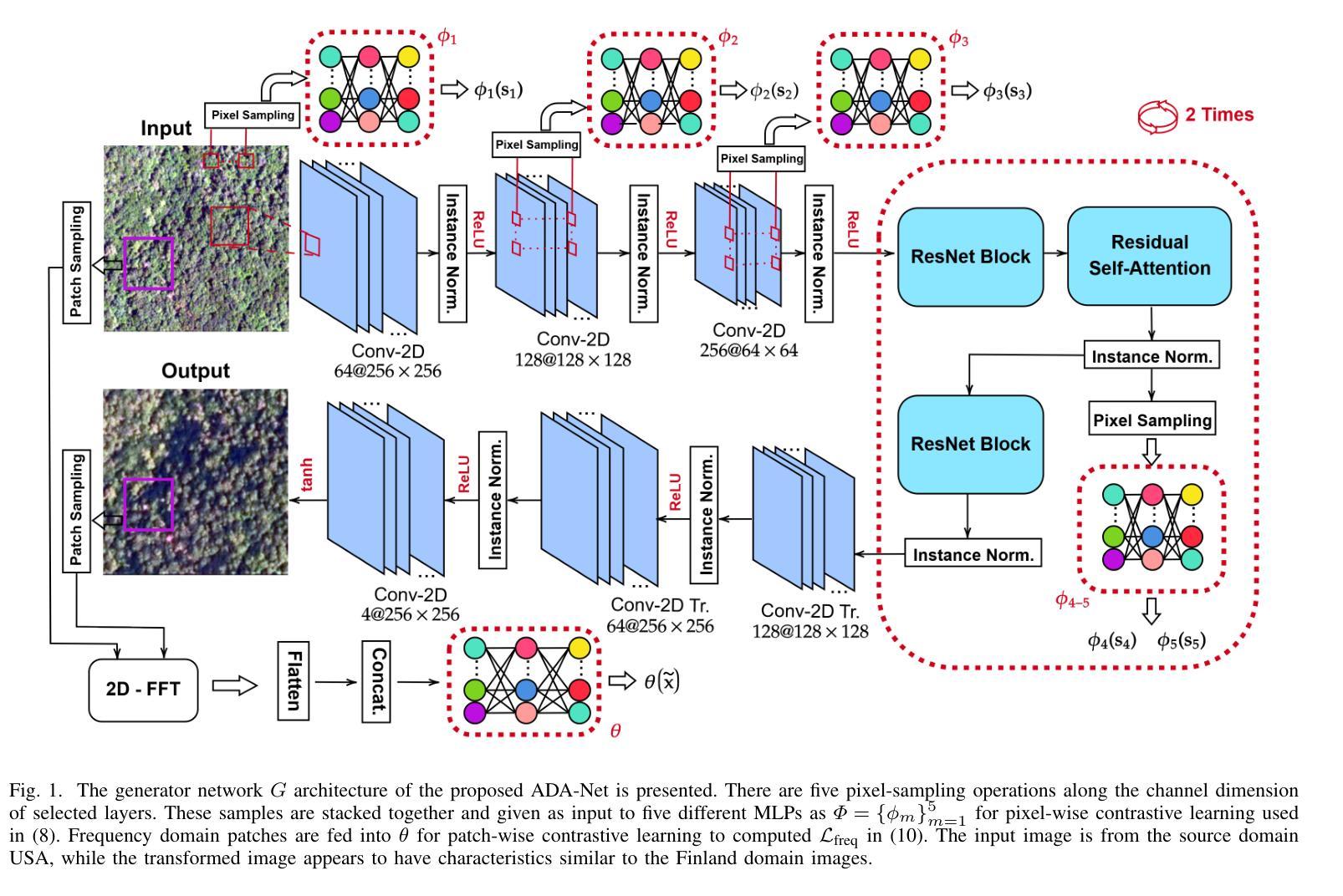
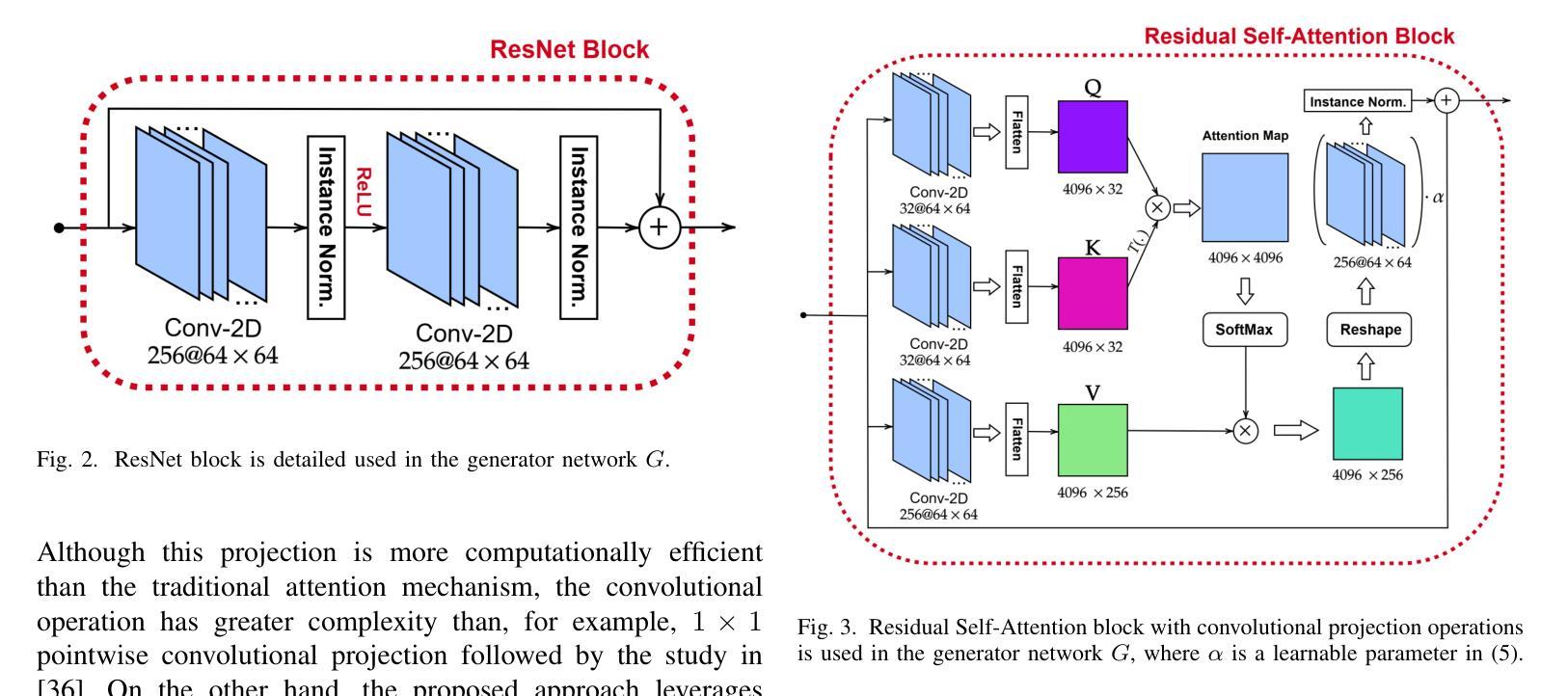
ADA-Net: Attention-Guided Domain Adaptation Network with Contrastive Learning for Standing Dead Tree Segmentation Using Aerial Imagery
Authors:Mete Ahishali, Anis Ur Rahman, Einari Heinaro, Samuli Junttila
Information on standing dead trees is important for understanding forest ecosystem functioning and resilience but has been lacking over large geographic regions. Climate change has caused large-scale tree mortality events that can remain undetected due to limited data. In this study, we propose a novel method for segmenting standing dead trees using aerial multispectral orthoimages. Because access to annotated datasets has been a significant problem in forest remote sensing due to the need for forest expertise, we introduce a method for domain transfer by leveraging domain adaptation to learn a transformation from a source domain X to target domain Y. In this Image-to-Image translation task, we aim to utilize available annotations in the target domain by pre-training a segmentation network. When images from a new study site without annotations are introduced (source domain X), these images are transformed into the target domain. Then, transfer learning is applied by inferring the pre-trained network on domain-adapted images. In addition to investigating the feasibility of current domain adaptation approaches for this objective, we propose a novel approach called the Attention-guided Domain Adaptation Network (ADA-Net) with enhanced contrastive learning. Accordingly, the ADA-Net approach provides new state-of-the-art domain adaptation performance levels outperforming existing approaches. We have evaluated the proposed approach using two datasets from Finland and the US. The USA images are converted to the Finland domain, and we show that the synthetic USA2Finland dataset exhibits similar characteristics to the Finland domain images. The software implementation is shared at https://github.com/meteahishali/ADA-Net. The data is publicly available at https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/meteahishali/aerial-imagery-for-standing-dead-tree-segmentation.
关于枯立木的信息对于了解森林生态系统的功能和恢复力至关重要,但在较大的地理区域一直缺失。气候变化已经引起大规模的树木死亡事件,由于数据有限,这些事件可能无法被检测到。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种利用航空多光谱正射影像分割枯立木的新方法。由于森林遥感中缺乏专家,访问标注数据集一直是一个重大问题,我们引入了一种通过领域适应进行领域转移的方法,学习从源域X到目标域Y的转换。在这个图像到图像的翻译任务中,我们旨在通过预训练一个分割网络来利用目标域中的可用注释。当引入来自没有注释的新研究地点的图像(源域X)时,这些图像被转换为目标域。然后,通过推断对域适应图像进行预训练的网络来应用迁移学习。除了研究当前领域适应方法对此目标的可行性外,我们还提出了一种名为注意力引导领域适应网络(ADA-Net)的新方法,并增强了对比学习。因此,ADA-Net方法提供了新的最先进的领域适应性能水平,超越了现有方法。我们已经使用芬兰和美国的两个数据集评估了所提出的方法。将美国图像转换为芬兰领域,我们证明合成USA2Finland数据集与芬兰领域图像具有相似的特性。软件实现共享在https://github.com/meteahishali/ADA-Net。数据在https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/meteahishali/aerial-imagery-for-standing-dead-tree-segmentation公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究提出一种利用空中多光谱正射图像分割立木死亡的新方法。为克服森林遥感中对标注数据集的需求瓶颈问题,引入域适应技术进行领域转换学习。本研究目标是利用目标域中的现有标注对分割网络进行预训练,并通过转化源域图像为匹配目标域来应用迁移学习。此外,研究还提出了一种名为ADA-Net的注意力引导域适应网络新方法,实现了卓越的性能水平。使用芬兰和美国的数据集进行了评估验证。
Key Takeaways
- 研究强调了立木死亡信息对理解森林生态系统和气候变化的巨大重要性。
- 提出使用空中多光谱正射图像分割立木死亡的新方法。
- 为解决森林遥感中标注数据集缺乏的问题,引入域适应技术进行领域转换学习。
- 提出一种名为ADA-Net的注意力引导域适应网络方法,具有增强的对比学习能力,实现最佳性能水平。
点此查看论文截图

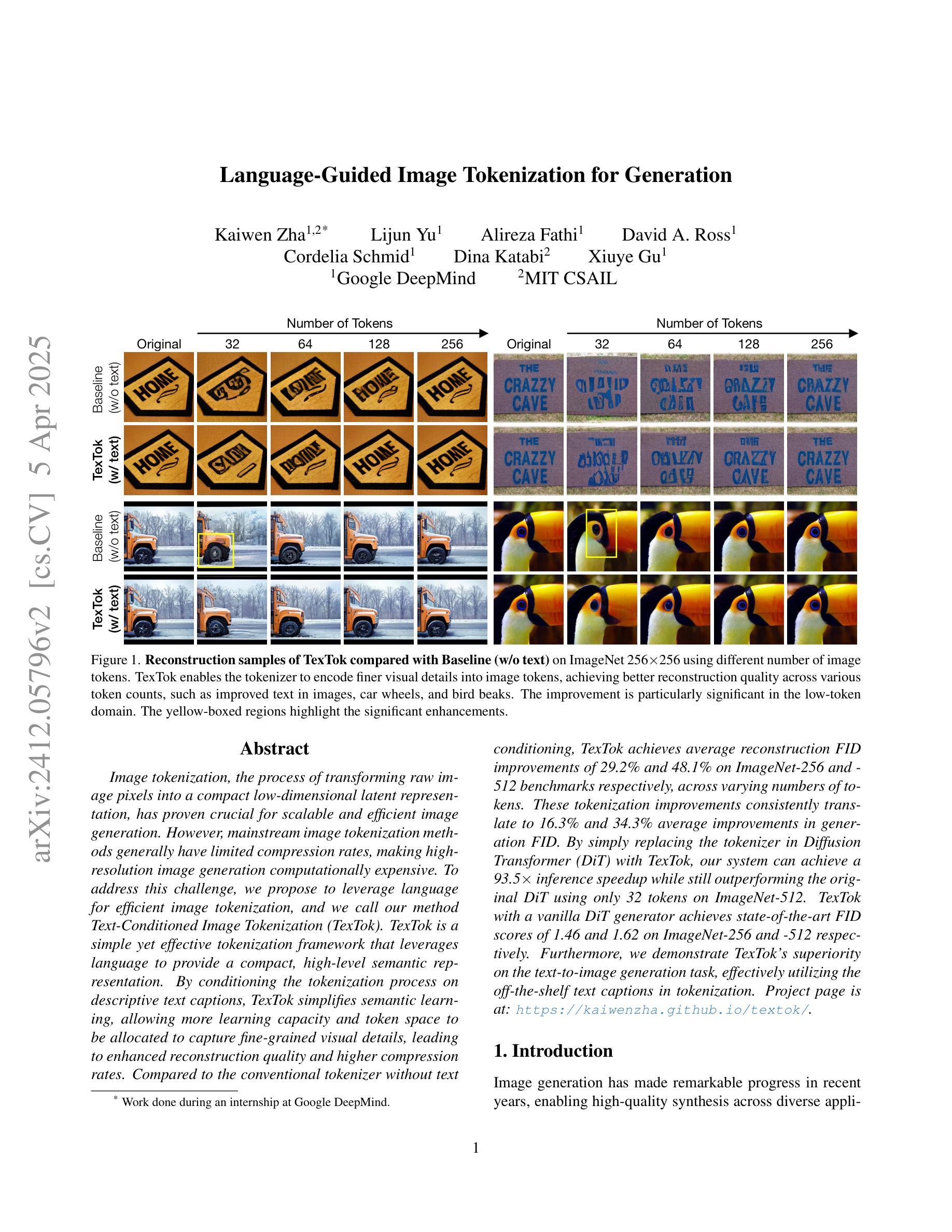
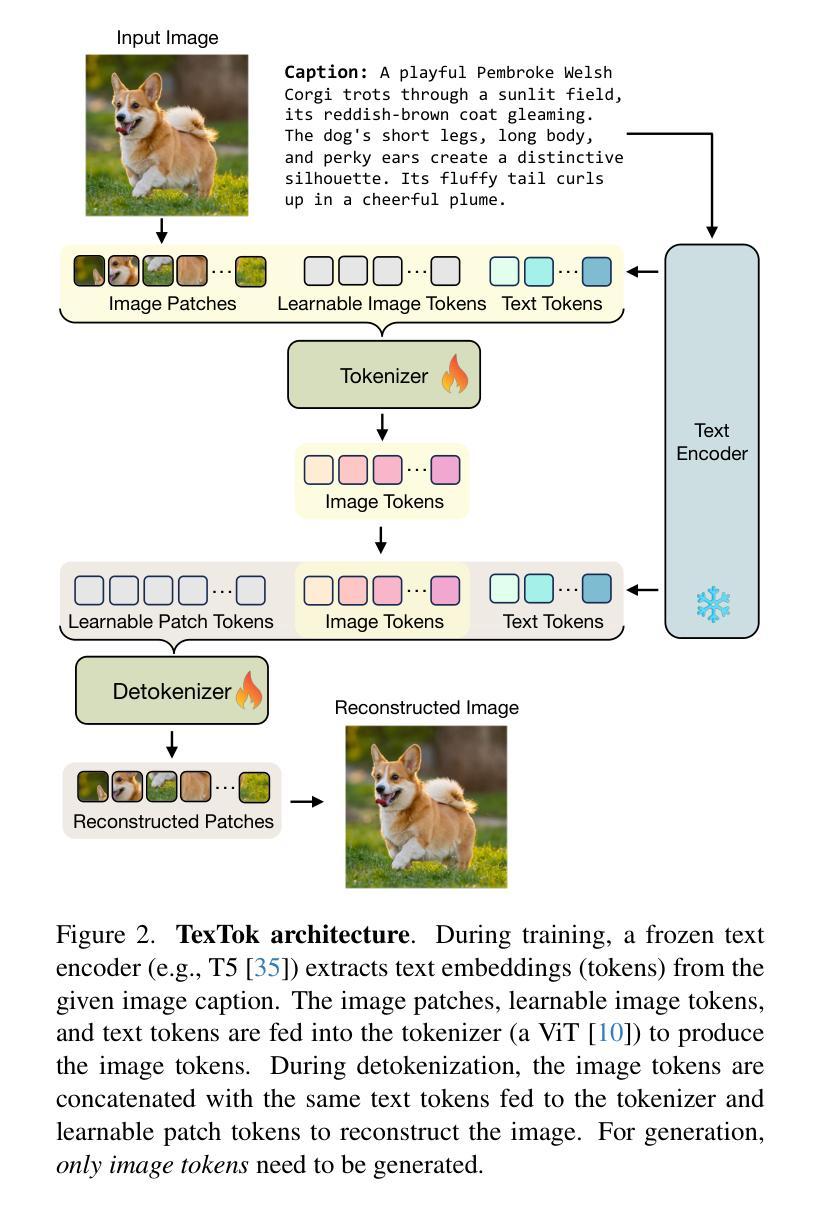
Language-Guided Image Tokenization for Generation
Authors:Kaiwen Zha, Lijun Yu, Alireza Fathi, David A. Ross, Cordelia Schmid, Dina Katabi, Xiuye Gu
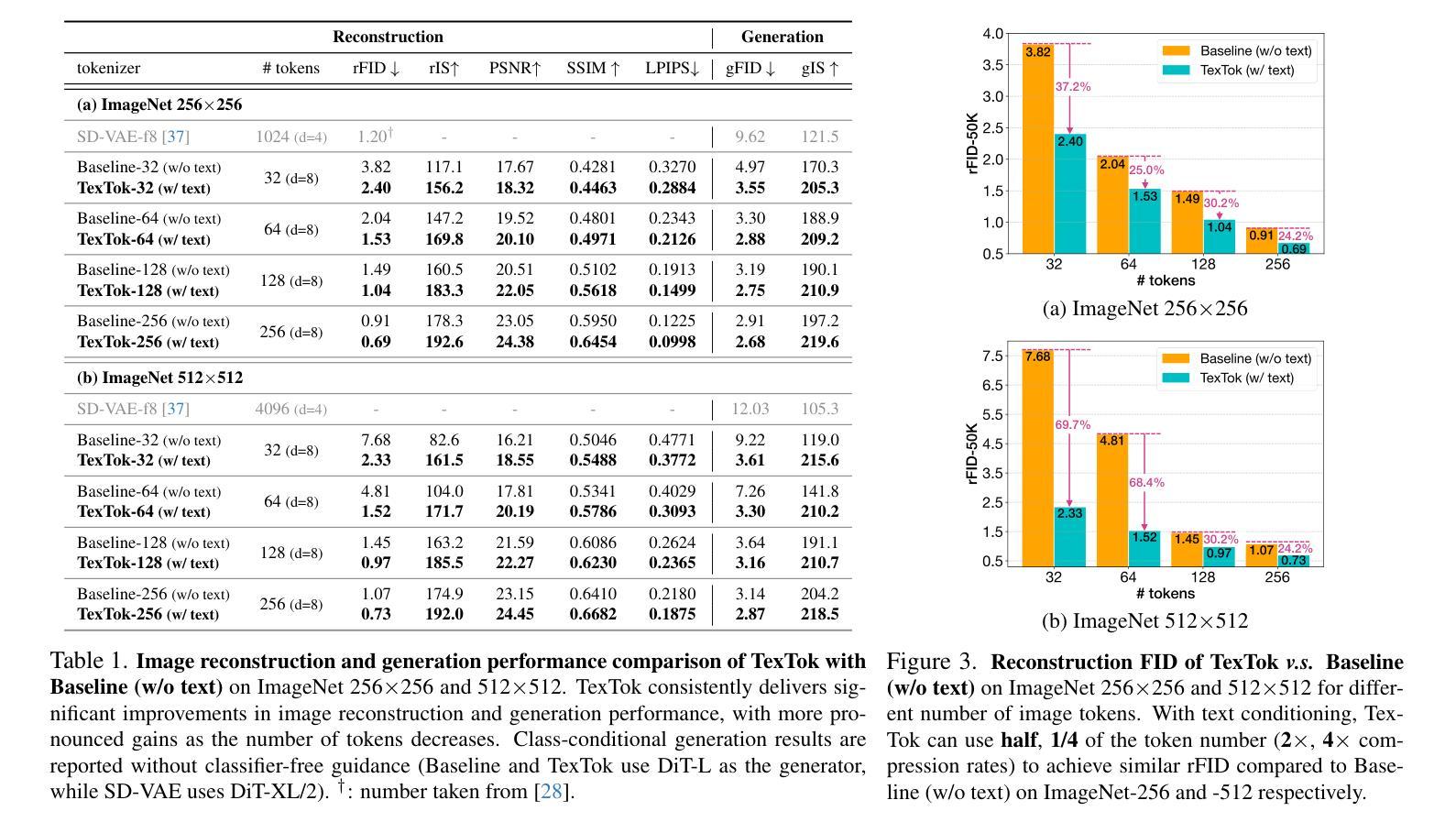
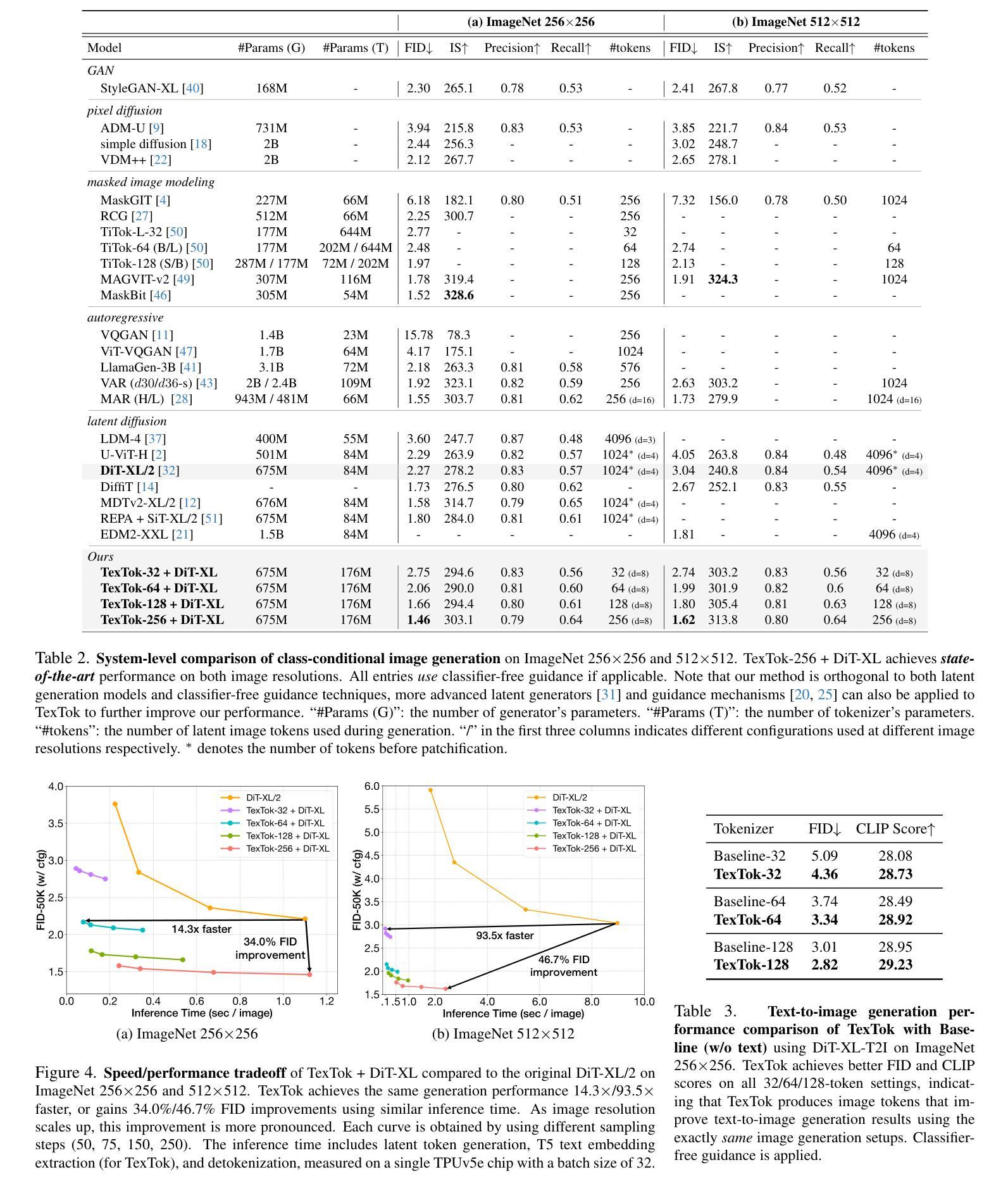
Image tokenization, the process of transforming raw image pixels into a compact low-dimensional latent representation, has proven crucial for scalable and efficient image generation. However, mainstream image tokenization methods generally have limited compression rates, making high-resolution image generation computationally expensive. To address this challenge, we propose to leverage language for efficient image tokenization, and we call our method Text-Conditioned Image Tokenization (TexTok). TexTok is a simple yet effective tokenization framework that leverages language to provide a compact, high-level semantic representation. By conditioning the tokenization process on descriptive text captions, TexTok simplifies semantic learning, allowing more learning capacity and token space to be allocated to capture fine-grained visual details, leading to enhanced reconstruction quality and higher compression rates. Compared to the conventional tokenizer without text conditioning, TexTok achieves average reconstruction FID improvements of 29.2% and 48.1% on ImageNet-256 and -512 benchmarks respectively, across varying numbers of tokens. These tokenization improvements consistently translate to 16.3% and 34.3% average improvements in generation FID. By simply replacing the tokenizer in Diffusion Transformer (DiT) with TexTok, our system can achieve a 93.5x inference speedup while still outperforming the original DiT using only 32 tokens on ImageNet-512. TexTok with a vanilla DiT generator achieves state-of-the-art FID scores of 1.46 and 1.62 on ImageNet-256 and -512 respectively. Furthermore, we demonstrate TexTok’s superiority on the text-to-image generation task, effectively utilizing the off-the-shelf text captions in tokenization. Project page is at: https://kaiwenzha.github.io/textok/.
图像令牌化是将原始图像像素转换为紧凑的低维潜在表示的过程,已被证明对于可扩展和高效的图像生成至关重要。然而,主流的图像令牌化方法通常压缩率有限,使得高分辨率图像生成计算成本高昂。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出利用语言进行高效的图像令牌化,并将我们的方法称为文本条件图像令牌化(TexTok)。TexTok是一个简单而有效的令牌化框架,它利用语言提供紧凑的高级语义表示。通过以描述性文本标题为条件,TexTok简化了语义学习,使得更多的学习容量和令牌空间能够分配给捕获精细的视觉细节,从而提高重建质量和压缩率。与没有文本条件的传统令牌化器相比,TexTok在ImageNet-256和-512基准测试上分别实现了平均重建FID改进率为29.2%和48.1%,跨越各种令牌数量。这些令牌化改进始终转化为生成FID的16.3%和34.3%的平均改进。通过简单地用TexTok替换扩散变压器(DiT)中的令牌化器,我们的系统在使用只有32个令牌时,仍能在ImageNet-512上超越原始的DiT,实现93.5倍的推理速度提升。TexTok与简单的DiT生成器在ImageNet-256和-512上实现了最先进的FID分数分别为1.46和1.62。此外,我们证明了TexTok在文本到图像生成任务上的优越性,有效地利用现成的文本标题进行令牌化。项目页面为:https://kaiwenzha.github.io/textok/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025 Oral. Project page: https://kaiwenzha.github.io/textok/
Summary
本文介绍了图像标记化的重要性以及当前主流方法的局限性。为了解决这个问题,提出了一种利用语言进行高效图像标记化的新方法,称为Text-Conditioned Image Tokenization(TexTok)。TexTok通过利用描述性的文本标题来简化语义学习,允许更多的学习容量和标记空间分配给捕捉精细的视觉细节,从而提高重建质量和压缩率。在ImageNet-256和-512基准测试中,TexTok相比常规的非文本条件标记器,平均重建FID分别提高了29.2%和48.1%。这些标记化改进始终转化为生成FID的16.3%和34.3%平均改进。通过简单地用TexTok替换扩散变压器(DiT)中的标记器,我们的系统可以在使用只有32个标记的ImageNet-512的情况下,实现93.5倍的推理速度提升,同时仍优于原始DiT。TexTok与简单的DiT生成器一起实现了ImageNet-256和-512上的最佳FID分数。此外,我们展示了TexTok在文本到图像生成任务上的优越性,有效地利用现成的文本标题进行标记化。
Key Takeaways
- TexTok是一种基于语言的图像标记化方法,通过结合描述性文本标题提供紧凑、高级语义表示来实现高效图像标记化。
- TexTok简化了语义学习,允许更多的学习容量和标记空间用于捕捉图像的精细视觉细节。
- TexTok在ImageNet基准测试中实现了显著的重建FID改进,表明其在提高图像生成质量方面的有效性。
- TexTok通过优化现有扩散变压器(DiT)模型的标记器,实现了显著的性能提升,包括推理速度的提升和生成质量的改进。
- TexTok与简单的DiT生成器结合,实现了在ImageNet上的最佳FID分数,表明其在图像生成领域的优越性。
- TexTok在文本到图像生成任务上表现出卓越性能,能够利用现成的文本标题进行标记化。
点此查看论文截图