⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-09 更新
Anisotropic space-time goal-oriented error control and mesh adaptivity for convection-diffusion-reaction equations
Authors:M. Bause, M. Bruchhäuser, B. Endtmayer, N. Margenberg, I. Toloupolous, T. Wick
We present an anisotropic goal-oriented error estimator based on the Dual Weighted Residual (DWR) method for time-dependent convection-diffusion-reaction (CDR) equations. Using anisotropic interpolation operators the estimator is elementwise separated with respect to the single directions in space and time leading to adaptive, anisotropic mesh refinement in a natural way. To prevent spurious oscillations the streamline upwind Petrov-Galerkin (SUPG) method is applied to stabilize the underlying system in the case of high P'{e}clet numbers. Efficiency and robustness of the underlying algorithm are demonstrated for different goal functionals. The directional error indicators quantify anisotropy of the solution with respect to the goal, and produce meshes that efficiently capture sharp layers. Numerical examples show the superiority of the proposed approach over isotropic adaptive and global mesh refinement using established benchmarks for convection-dominated transport.
我们提出了一种基于双权重残差(DWR)方法的面向目标的各向异性误差估计器,用于解决时间相关的对流扩散反应(CDR)方程。使用各向异性插值算子,估计器在空间和时间上的单个方向上进行元素分离,导致自然适应性的各向异性网格细化。为了防止虚假振荡,采用流线迎风Petrov-Galerkin(SUPG)方法对高Peclet数情况下的基础系统进行稳定处理。对于不同的目标函数,展示了基础算法的效率和稳健性。方向误差指标量化了解决方案相对于目标的各向异性,并产生能够高效捕获尖锐层的网格。数值例子表明,与针对对流主导传输建立的基准相比,该方法优于各向同性自适应和全局网格细化。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于双权残差(DWR)方法,我们提出了一种针对时间依赖对流扩散反应(CDR)方程的各向异性目标导向误差估计器。通过使用各向异性插值算子,估计器在空间和时间上的单个方向进行了元素分离,从而自然地实现了自适应的各向异性网格细化。为防止高P’eclet数下的虚假振荡,采用了流线迎风Petrov-Galerkin(SUPG)方法对基础系统进行稳定处理。对于不同的目标函数,该基础算法的效率和稳健性得到了验证。方向误差指标量化了解决方案相对于目标的各向异性,并产生了能够高效捕捉锐利层的网格。数值例子表明,该方法相对于各向同性自适应和全局网格细化方法具有优越性,已成为对流主导的运输过程的公认基准。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了基于DWR方法的各向异性目标导向误差估计器,用于解决时间依赖的CDR方程。
- 利用各向异性插值算子进行元素分离,实现自适应的各向异性网格细化。
- 采用SUPG方法稳定基础系统,防止高P’eclet数下的虚假振荡。
- 对不同目标函数的算法效率和稳健性进行了验证。
- 方向误差指标能量化解决方案的各向异性。
- 生成的网格能高效捕捉锐利层。
点此查看论文截图

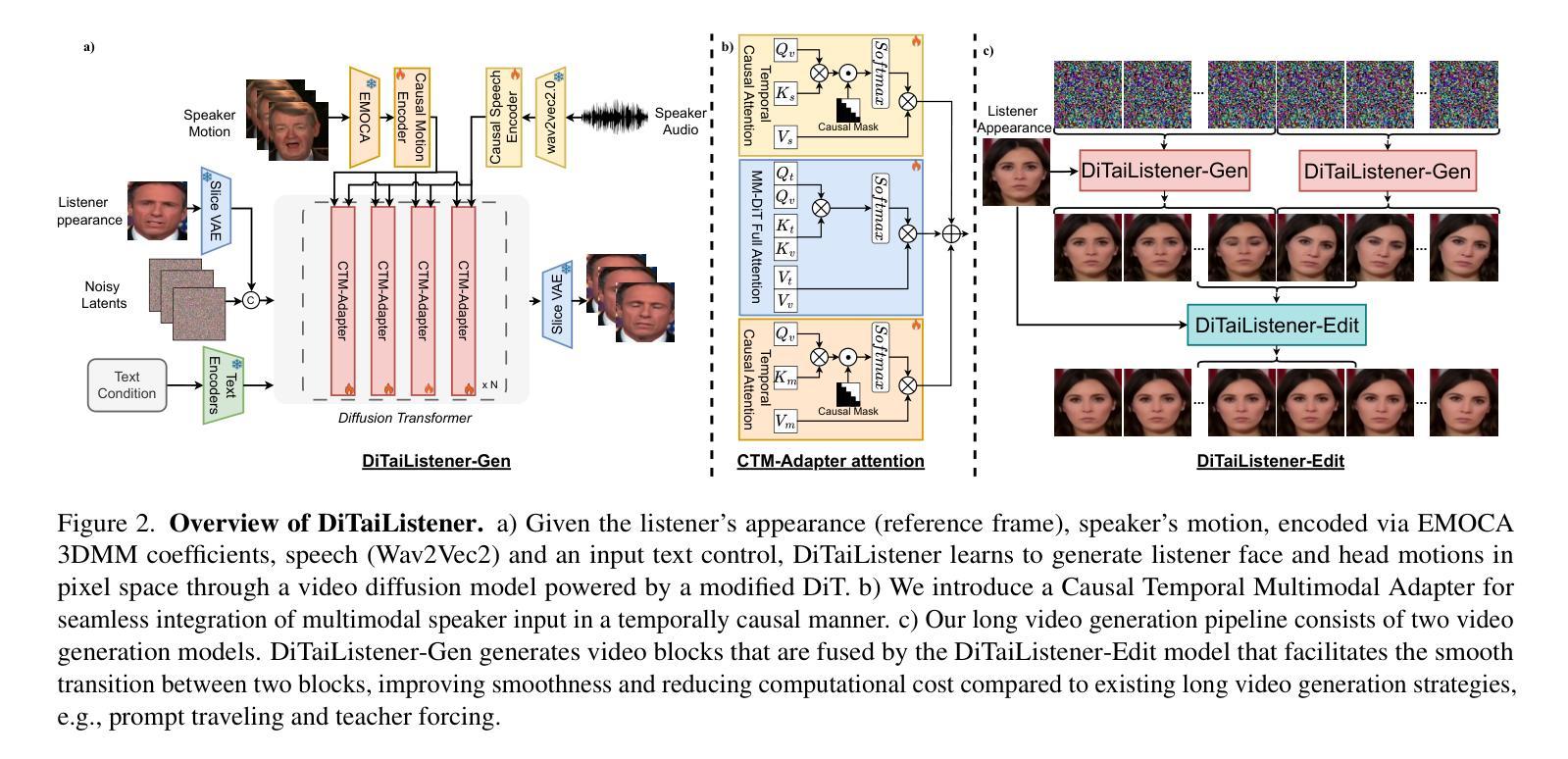
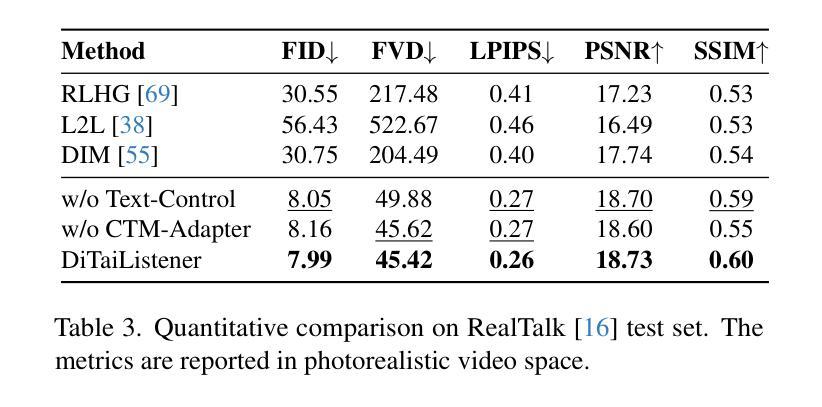
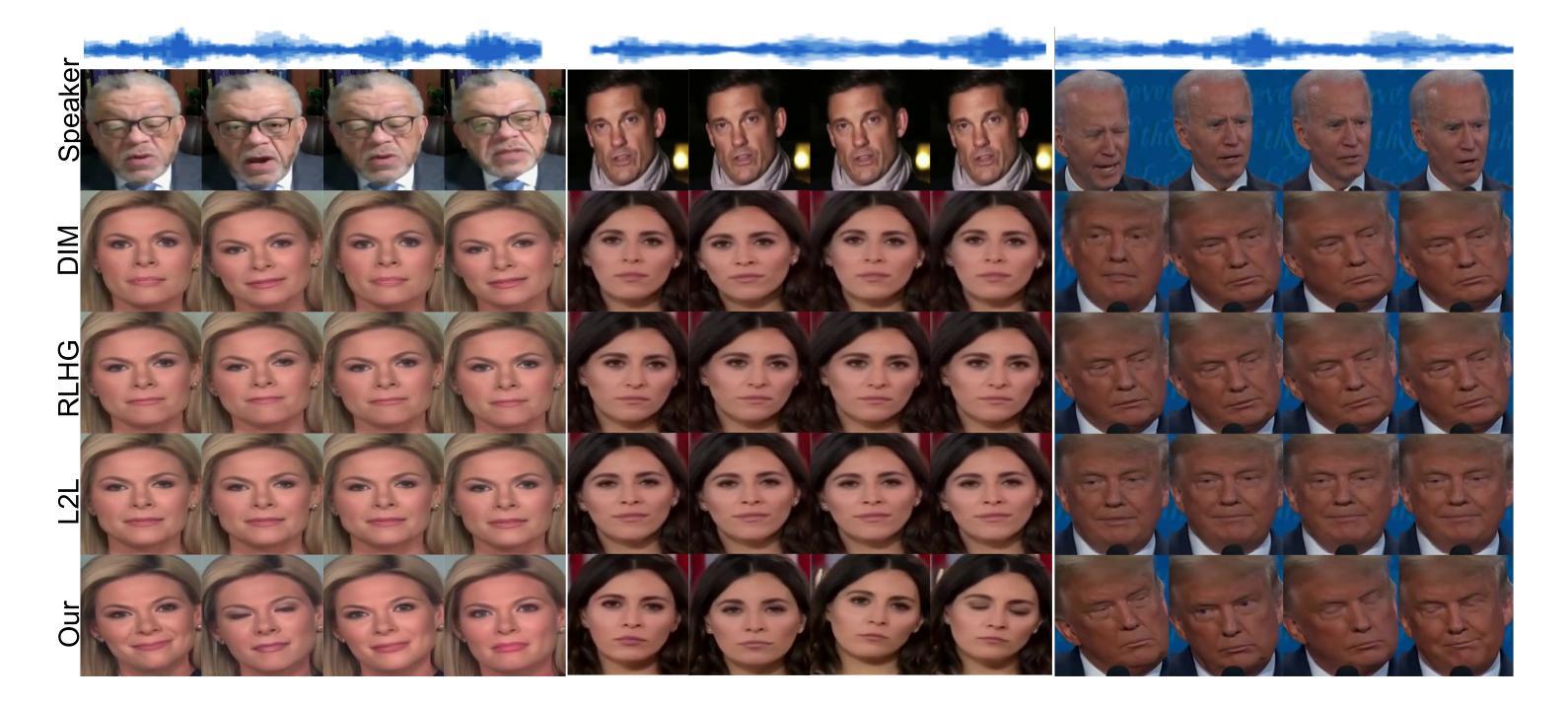
DiTaiListener: Controllable High Fidelity Listener Video Generation with Diffusion
Authors:Maksim Siniukov, Di Chang, Minh Tran, Hongkun Gong, Ashutosh Chaubey, Mohammad Soleymani
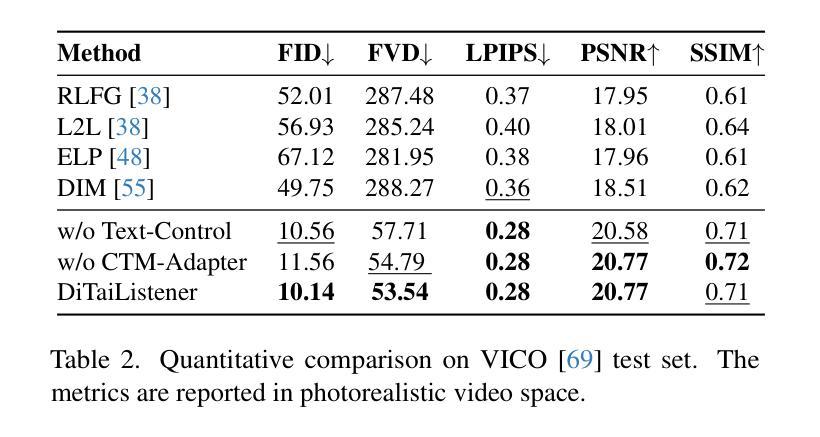
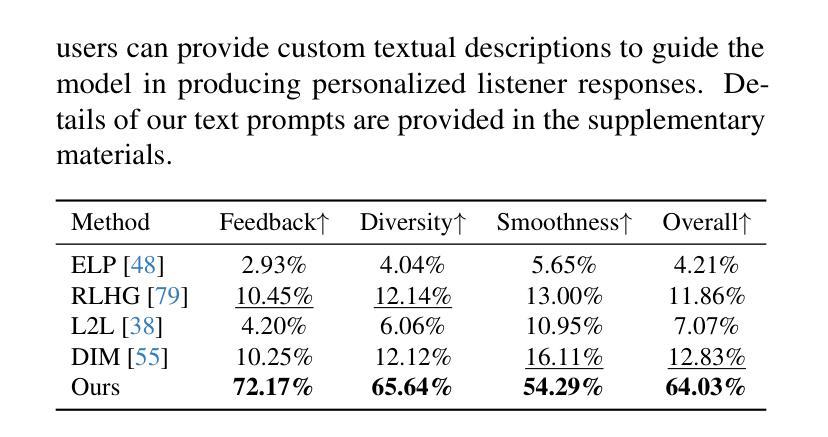
Generating naturalistic and nuanced listener motions for extended interactions remains an open problem. Existing methods often rely on low-dimensional motion codes for facial behavior generation followed by photorealistic rendering, limiting both visual fidelity and expressive richness. To address these challenges, we introduce DiTaiListener, powered by a video diffusion model with multimodal conditions. Our approach first generates short segments of listener responses conditioned on the speaker’s speech and facial motions with DiTaiListener-Gen. It then refines the transitional frames via DiTaiListener-Edit for a seamless transition. Specifically, DiTaiListener-Gen adapts a Diffusion Transformer (DiT) for the task of listener head portrait generation by introducing a Causal Temporal Multimodal Adapter (CTM-Adapter) to process speakers’ auditory and visual cues. CTM-Adapter integrates speakers’ input in a causal manner into the video generation process to ensure temporally coherent listener responses. For long-form video generation, we introduce DiTaiListener-Edit, a transition refinement video-to-video diffusion model. The model fuses video segments into smooth and continuous videos, ensuring temporal consistency in facial expressions and image quality when merging short video segments produced by DiTaiListener-Gen. Quantitatively, DiTaiListener achieves the state-of-the-art performance on benchmark datasets in both photorealism (+73.8% in FID on RealTalk) and motion representation (+6.1% in FD metric on VICO) spaces. User studies confirm the superior performance of DiTaiListener, with the model being the clear preference in terms of feedback, diversity, and smoothness, outperforming competitors by a significant margin.
生成自然且细微的听者动作以进行扩展交互仍然是一个开放性问题。现有方法通常依赖于低维运动代码进行面部行为生成,然后进行逼真的渲染,这限制了视觉保真度和表达丰富性。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了DiTaiListener,它由一个具有多模态条件约束的视频扩散模型提供支持。我们的方法首先使用DiTaiListener-Gen根据说话者的语音和面部动作生成简短的响应片段。然后,它使用DiTaiListener-Edit对过渡帧进行精细化处理,以实现无缝过渡。具体来说,DiTaiListener-Gen采用扩散转换器(DiT)来完成听者头部肖像生成的任务,并通过引入因果时序多模态适配器(CTM-Adapter)来处理说话者的听觉和视觉线索。CTM-Adapter以因果方式将说话者的输入集成到视频生成过程中,以确保听者响应的时间连贯性。对于长格式视频生成,我们引入了DiTaiListener-Edit,这是一种过渡细化视频到视频扩散模型。该模型将视频片段融合成流畅且连续的视频,确保在合并由DiTaiListener-Gen产生的短片时,面部表情和图像质量的时间一致性。从定量评估来看,DiTaiListener在基准数据集上实现了先进的表现,无论是在逼真度(RealTalk上的FID增加73.8%)还是运动表示(VICO上的FD指标增加6.1%)方面都表现出色。用户研究证实了DiTaiListener的优越性能,该模型在反馈、多样性和平滑度方面表现出明显的优势,明显优于竞争对手。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://havent-invented.github.io/DiTaiListener
Summary
针对自然和细微的听者动作生成问题,现有方法常依赖低维运动代码生成面部行为,随后进行逼真的渲染,这限制了视觉保真度和表达丰富性。为解决此挑战,我们推出DiTaiListener,它采用多模态条件的视频扩散模型。DiTaiListener首先根据说话者的语音和面部动作生成听者响应片段,再通过DiTaiListener-Edit优化过渡帧,实现无缝过渡。具体来说,DiTaiListener-Gen通过引入因果时间多模态适配器(CTM-Adapter)适应扩散变压器(DiT)用于听者头部肖像生成任务,处理说话者的听觉和视觉线索。对于长视频生成,我们引入DiTaiListener-Edit,一个用于优化过渡的视频到视频扩散模型,确保面部表达和图像质量在合并由DiTaiListener-Gen产生的短视频片段时的时空一致性。定量评估显示,DiTaiListener在基准数据集上实现了先进性能,用户研究也证实了其优越性。
Key Takeaways
- DiTaiListener解决了自然和细微的听者动作生成的问题。
- 现有方法依赖低维运动代码和逼真的渲染技术,存在视觉保真度和表达丰富性的限制。
- DiTaiListener采用视频扩散模型,结合多模态条件处理。
- DiTaiListener包括两个主要部分:DiTaiListener-Gen用于生成听者响应片段,DiTaiListener-Edit用于优化过渡帧。
- CTM-Adapter集成说话者的听觉和视觉线索,确保听者响应的时间连贯性。
- DiTaiListener-Edit通过合并短视频片段生成流畅、连续的视频。
点此查看论文截图


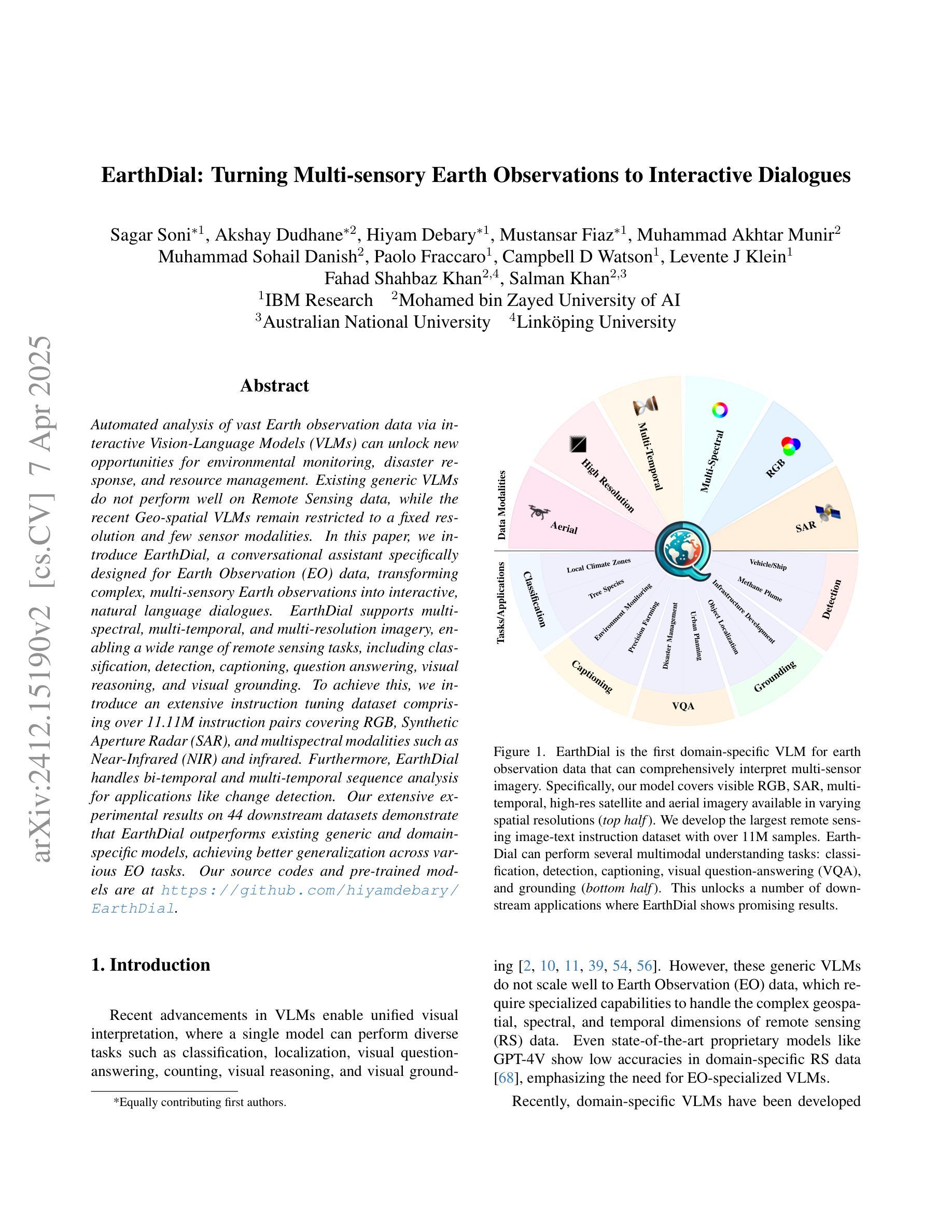
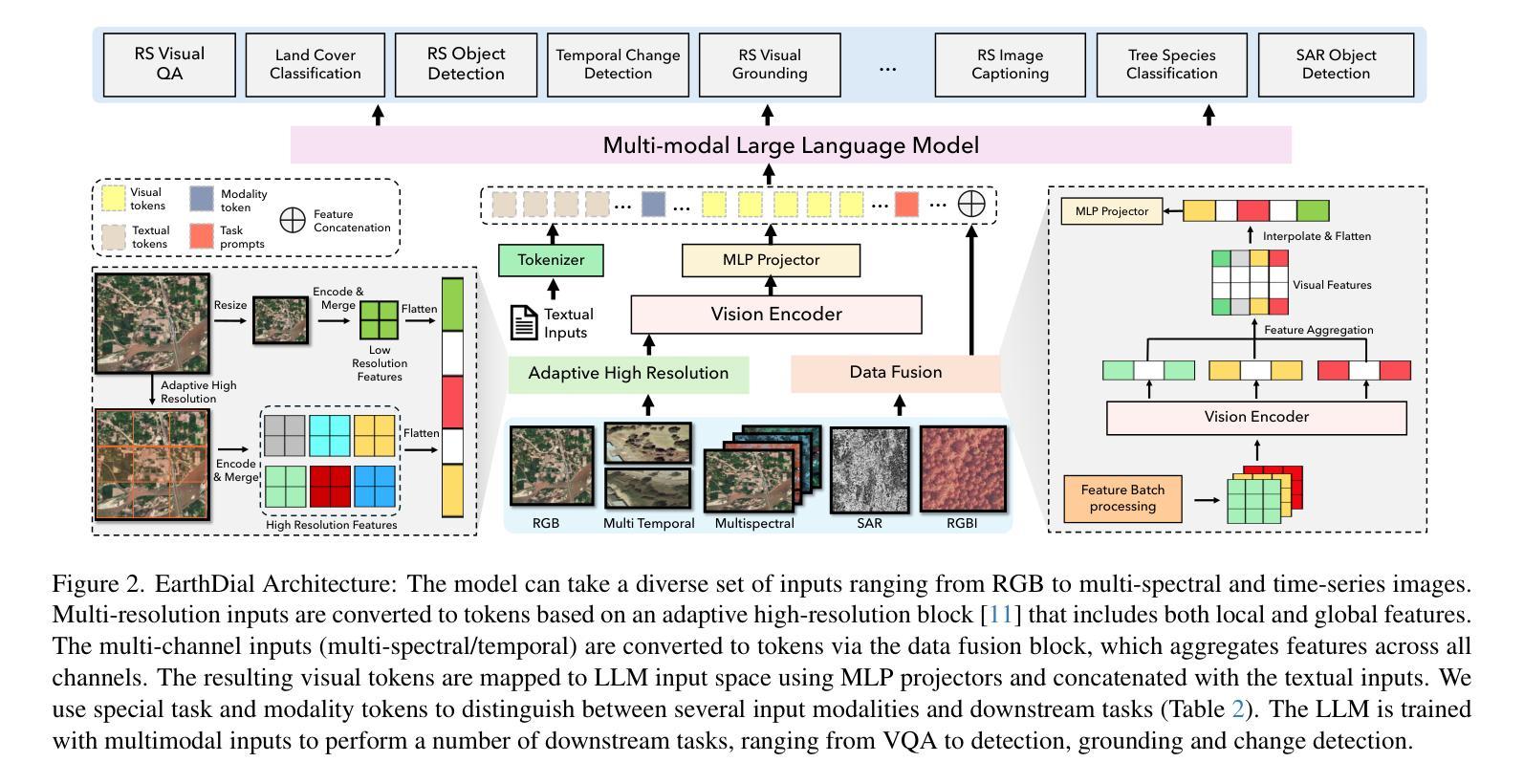
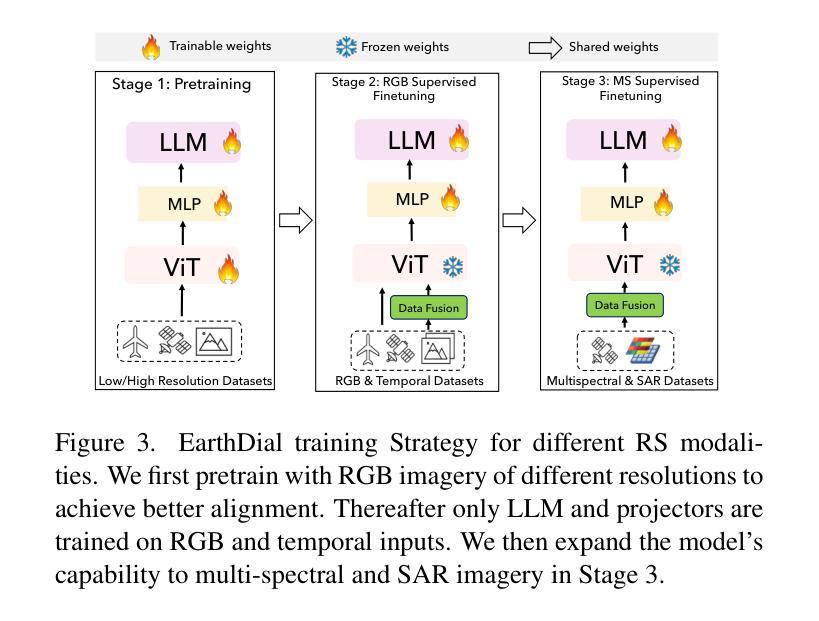
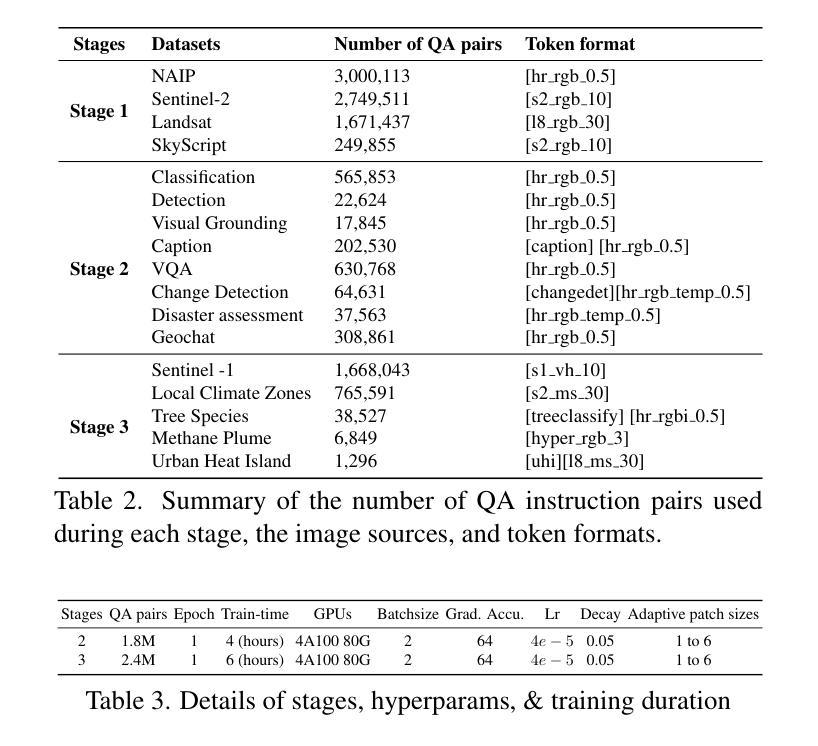
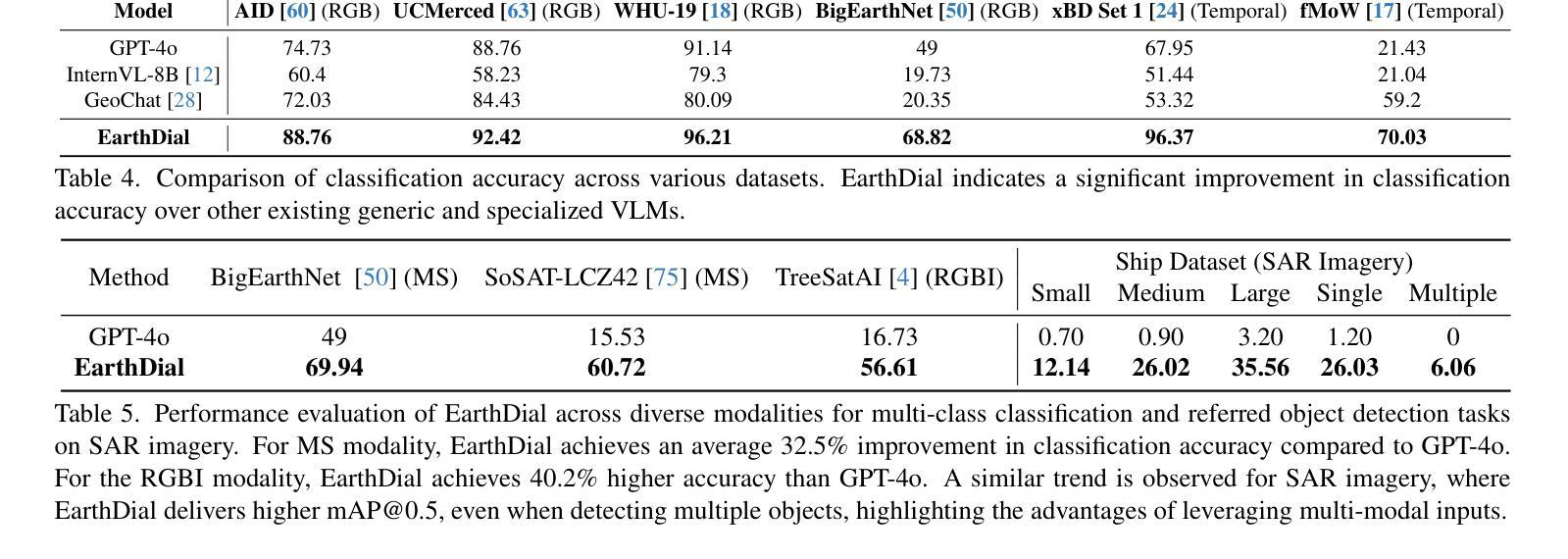
EarthDial: Turning Multi-sensory Earth Observations to Interactive Dialogues
Authors:Sagar Soni, Akshay Dudhane, Hiyam Debary, Mustansar Fiaz, Muhammad Akhtar Munir, Muhammad Sohail Danish, Paolo Fraccaro, Campbell D Watson, Levente J Klein, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Salman Khan
Automated analysis of vast Earth observation data via interactive Vision-Language Models (VLMs) can unlock new opportunities for environmental monitoring, disaster response, and {resource management}. Existing generic VLMs do not perform well on Remote Sensing data, while the recent Geo-spatial VLMs remain restricted to a fixed resolution and few sensor modalities. In this paper, we introduce EarthDial, a conversational assistant specifically designed for Earth Observation (EO) data, transforming complex, multi-sensory Earth observations into interactive, natural language dialogues. EarthDial supports multi-spectral, multi-temporal, and multi-resolution imagery, enabling a wide range of remote sensing tasks, including classification, detection, captioning, question answering, visual reasoning, and visual grounding. To achieve this, we introduce an extensive instruction tuning dataset comprising over 11.11M instruction pairs covering RGB, Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), and multispectral modalities such as Near-Infrared (NIR) and infrared. Furthermore, EarthDial handles bi-temporal and multi-temporal sequence analysis for applications like change detection. Our extensive experimental results on 44 downstream datasets demonstrate that EarthDial outperforms existing generic and domain-specific models, achieving better generalization across various EO tasks. Our source codes and pre-trained models are at https://github.com/hiyamdebary/EarthDial.
通过交互式的视觉语言模型(VLMs)对大量的地球观测数据进行自动化分析,可以为环境监测、灾害响应和{资源管理}带来新的机遇。现有的通用VLMs在遥感数据上的表现并不理想,而最近的地理空间VLMs仍然局限于固定的分辨率和少量的传感器模式。在本文中,我们介绍了EarthDial,这是一款专门为地球观测(EO)数据设计的对话助手,将复杂的多感官地球观测转化为交互式的自然语言对话。EarthDial支持多光谱、多时相和多分辨率的影像,能够完成广泛的遥感任务,包括分类、检测、标题生成、问答、视觉推理和视觉定位等。为了实现这一目标,我们引入了一个包含超过1111万个指令对的指令调整数据集,涵盖RGB、合成孔径雷达(SAR)以及近红外(NIR)和红外等多光谱模式。此外,EarthDial还处理双时相和多时相序列分析,适用于变化检测等应用。我们在44个下游数据集上进行的大量实验表明,EarthDial优于现有的通用和特定领域模型,在各种EO任务中实现了更好的泛化能力。我们的源代码和预训练模型位于https://github.com/hiyamdebary/EarthDial。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
自动化分析海量的地球观测数据,通过交互式的视觉语言模型(VLMs)为环境监测、灾害响应和{资源管理}带来新的机遇。现有通用VLMs在遥感数据上表现不佳,而最新的地理空间VLMs受限于固定分辨率和有限的传感器模式。本文介绍EarthDial,一个专为地球观测(EO)数据设计的对话助理,将复杂的多感官地球观测转化为交互式自然语言对话。EarthDial支持多光谱、多时相和多分辨率图像,可完成各种遥感任务,包括分类、检测、描述、问答、视觉推理和视觉定位。为达到此目的,我们引入了包含超过111万条指令对的庞大指令调整数据集,涵盖RGB、合成孔径雷达(SAR)和多光谱模式等近红外和红外数据。此外,EarthDial可进行双时态和多时态序列分析,适用于变化检测等应用。在广泛的实验中对下游的44个数据集进行的测试表明,EarthDial在多种EO任务上的表现优于现有的通用和特定领域模型。我们的源代码和预训练模型可在https://github.com/hiyamdebary/EarthDial找到。
Key Takeaways
- EarthDial是一个针对地球观测数据的交互式对话助理,可将复杂的遥感数据转化为自然语言对话。
- 它支持多光谱、多时相和多分辨率图像分析,涵盖RGB、SAR及多光谱模式等数据类型。
- EarthDial通过大规模指令调整数据集进行训练,适用于多种遥感任务,包括分类、检测等。
- 与现有模型相比,EarthDial在多种地球观测任务上表现出更好的泛化能力。
- EarthDial具备处理双时态和多时态序列分析的能力,适用于变化检测等应用需求。
- 提供了源代码和预训练模型的公开访问链接。
点此查看论文截图

UQSA – An R-Package for Uncertainty Quantification and Sensitivity Analysis for Biochemical Reaction Network Models
Authors:Andrei Kramer, Federica Milinanni, Jeanette Hellgren Kotaleski, Pierre Nyquist, Alexandra Jauhiainen, Olivia Eriksson
Biochemical reaction models describing subcellular processes generally come with a large uncertainty. To be able to account for this during the modeling process, we have developed the R-package UQSA, performing uncertainty quantification and sensitivity analysis in an integrated fashion. UQSA is designed for fast sampling of complicated multi-dimensional parameter distributions, using efficient Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) sampling techniques and Vine-copulas to model complicated joint distributions. We perform MCMC sampling both from stochastic and deterministic models, in either likelihood-free or likelihood-based settings. In the likelihood-free case, we use Approximate Bayesian Computation (ABC), while for likelihood-based sampling we provide different algorithms, including the fast geometry-informed algorithm SMMALA (Simplified Manifold Metropolis-Adjusted Langevin Algorithm). The uncertainty quantification can be followed by a variance decomposition-based global sensitivity analysis. We are aiming for biochemical models, but UQSA can be used for any type of reaction networks. The use of Vine-copulas allows us to describe, evaluate, and sample from complicated parameter distributions, as well as adding new datasets in a sequential manner without redoing the previous parameter fit. The code is written in R, with C as a backend to improve speed. We use the SBtab table format for Systems Biology projects for the model description as well as the experimental data. An event system allows the user to model complicated transient input, common within, e.g., neuroscience. UQSA has an extensive documentation with several examples describing different types of models and data. The code has been tested on up to 2000 cores on several nodes on a computing cluster, but we also include smaller examples that can be run on a laptop. Source code: https://github.com/icpm-kth/uqsa
描述亚细胞过程的生化反应模型通常带有很大的不确定性。为了在建模过程中考虑到这一点,我们开发了R包UQSA,它可以进行不确定性和敏感性分析。UQSA旨在快速采样复杂的多维参数分布,采用高效的马尔可夫链蒙特卡罗(MCMC)采样技术和藤向量组合建模复杂的联合分布。我们从随机和确定性模型中进行MCMC采样,无论是在无似然或有似然的环境中。在无似然的情况下,我们使用近似贝叶斯计算(ABC),而在基于似然的采样中,我们提供不同的算法,包括基于几何信息的快速算法SMMALA(简化流形调整后的朗格文算法)。不确定性量化可以通过基于方差分解的全局敏感性分析来进行。我们的目标是生化模型,但UQSA可用于任何类型的反应网络。藤向量组合的使用使我们能够描述、评估和采样复杂的参数分布,并以连续的方式添加新的数据集,而无需重新进行之前的参数拟合。代码是用R编写的,后端使用C语言以提高速度。我们使用SBtab表格格式来描述模型和系统生物学项目的实验数据。事件系统允许用户模拟复杂的瞬态输入,这在神经科学中是常见的。UQSA具有广泛的文档和多个示例,描述了不同类型的模型和数据。该代码已在计算集群的多个节点上的多达2000个内核上进行了测试,但我们也包含了可以在笔记本电脑上运行的小型示例。源代码:https://github.com/icpm-kth/uqsa
简要解释或概述:
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 1 figure, application note
Summary
UQSA软件包用于生物化学模型中的不确定性量化和敏感性分析。它采用高效Markov链蒙特卡洛采样技术和Vine-copulas进行复杂多维参数分布的快速采样。适用于随机和确定性模型,可在无可能性设置和基于可能性的设置中进行MCMC采样。它能描述、评估和采样复杂的参数分布,以系统化生物学项目的SBtab表格格式描述模型和实验数据。用户可以通过事件系统模拟复杂的瞬时输入。代码经过大规模测试,并包含多个示例,展示不同类型模型和数据的处理方式。详情请访问GitHub获取源代码。
Key Takeaways
- UQSA软件包专注于生物化学模型中的不确定性量化和敏感性分析。
- 使用Markov链蒙特卡洛采样技术(MCMC)和Vine-copulas进行复杂多维参数分布的快速采样。
- 既适用于随机模型也适用于确定性模型,并能在不同设置下进行MCMC采样。
- 通过Variance分解进行全局敏感性分析。
- UQSA具有广泛的文档和示例,用于描述不同类型模型和数据的处理方式。
- 代码经过大规模测试,并能在计算集群上运行。
点此查看论文截图