⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-09 更新
DeclutterNeRF: Generative-Free 3D Scene Recovery for Occlusion Removal
Authors:Wanzhou Liu, Zhexiao Xiong, Xinyu Li, Nathan Jacobs
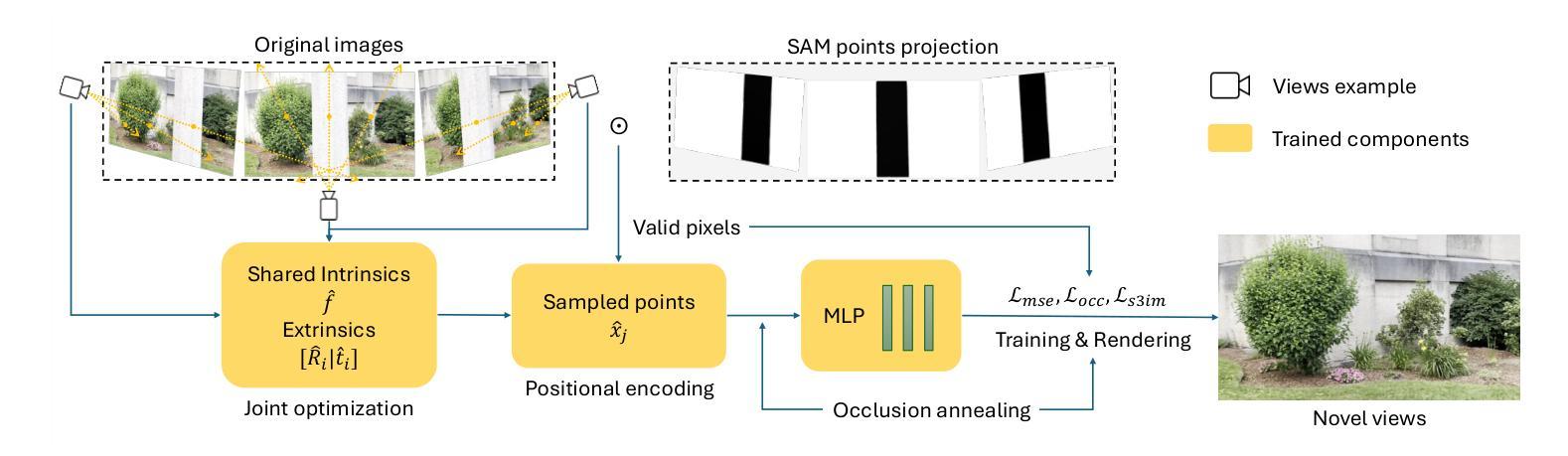
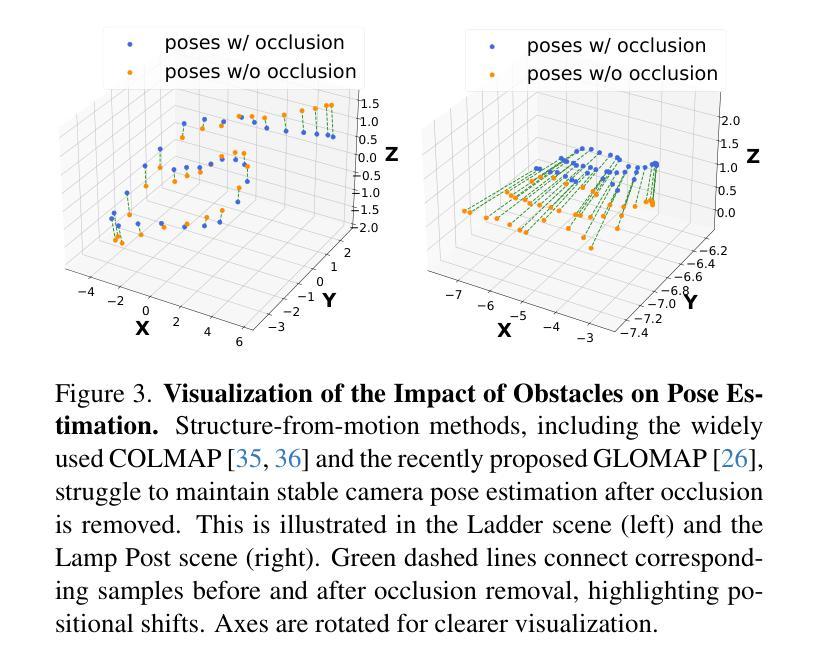
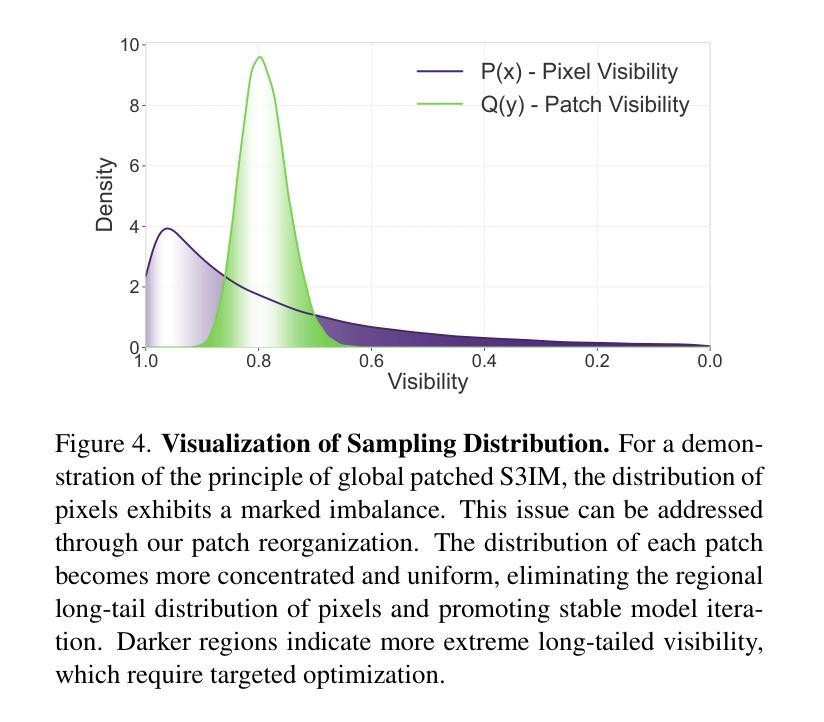
Recent novel view synthesis (NVS) techniques, including Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have greatly advanced 3D scene reconstruction with high-quality rendering and realistic detail recovery. Effectively removing occlusions while preserving scene details can further enhance the robustness and applicability of these techniques. However, existing approaches for object and occlusion removal predominantly rely on generative priors, which, despite filling the resulting holes, introduce new artifacts and blurriness. Moreover, existing benchmark datasets for evaluating occlusion removal methods lack realistic complexity and viewpoint variations. To address these issues, we introduce DeclutterSet, a novel dataset featuring diverse scenes with pronounced occlusions distributed across foreground, midground, and background, exhibiting substantial relative motion across viewpoints. We further introduce DeclutterNeRF, an occlusion removal method free from generative priors. DeclutterNeRF introduces joint multi-view optimization of learnable camera parameters, occlusion annealing regularization, and employs an explainable stochastic structural similarity loss, ensuring high-quality, artifact-free reconstructions from incomplete images. Experiments demonstrate that DeclutterNeRF significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods on our proposed DeclutterSet, establishing a strong baseline for future research.
最新的视点合成(NVS)技术,包括神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯展开(3DGS),已经极大地推动了三维场景重建的高质量渲染和真实细节的恢复。在保留场景细节的同时有效地去除遮挡物,可以进一步增强这些技术的稳健性和适用性。然而,现有的物体和遮挡物去除方法主要依赖于生成先验,尽管可以填充由此产生的空洞,但也会引入新的伪影和模糊。此外,用于评估遮挡物去除方法的现有基准数据集缺乏现实的复杂性和视点变化。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了DeclutterSet,一个具有鲜明遮挡物的多样化场景的新数据集,这些遮挡物分布在前景、中景和背景上,并在不同视点之间表现出大量的相对运动。我们还介绍了DeclutterNeRF,一种无需生成先验的遮挡物去除方法。DeclutterNeRF引入了可学习相机参数的联合多视角优化、遮挡退火正则化,并采用可解释的随机结构相似性损失,确保从不完整图像中进行高质量、无伪影的重建。实验表明,在我们的提出的DeclutterSet上,DeclutterNeRF显著优于最先进的方法,为未来的研究建立了强大的基准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025 4th CV4Metaverse Workshop. 15 pages, 10 figures. Code and data at: https://github.com/wanzhouliu/declutter-nerf
Summary
NeRF和3DGS等新型视图合成技术已广泛应用于3D场景重建,但现有技术存在去除遮挡时产生的模糊和伪影问题。为解决这些问题,我们引入了DeclutterSet数据集和DeclutterNeRF方法。DeclutterSet包含具有不同遮挡的多样场景,而DeclutterNeRF则通过联合多视角优化学习相机参数、引入遮挡退火正则化,并采用可解释的随机结构相似性损失,确保从不完整图像中进行高质量、无伪影的重建。实验证明,DeclutterNeRF在DeclutterSet上的表现显著优于现有方法,为未来研究奠定了坚实基础。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF和3DGS等技术推动了3D场景重建的发展,但去除遮挡时存在模糊和伪影问题。
- 现有遮挡去除方法主要依赖生成先验,虽然能填补空洞但会引入新伪影。
- 引入的DeclutterSet数据集包含多样场景,展现不同遮挡的复杂性。
- 提出的DeclutterNeRF方法通过联合多视角优化相机参数,实现无生成先验的遮挡去除。
- DeclutterNeRF采用遮挡退火正则化和可解释的随机结构相似性损失,确保高质量重建。
- 实验证明,DeclutterNeRF在DeclutterSet上的表现优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图


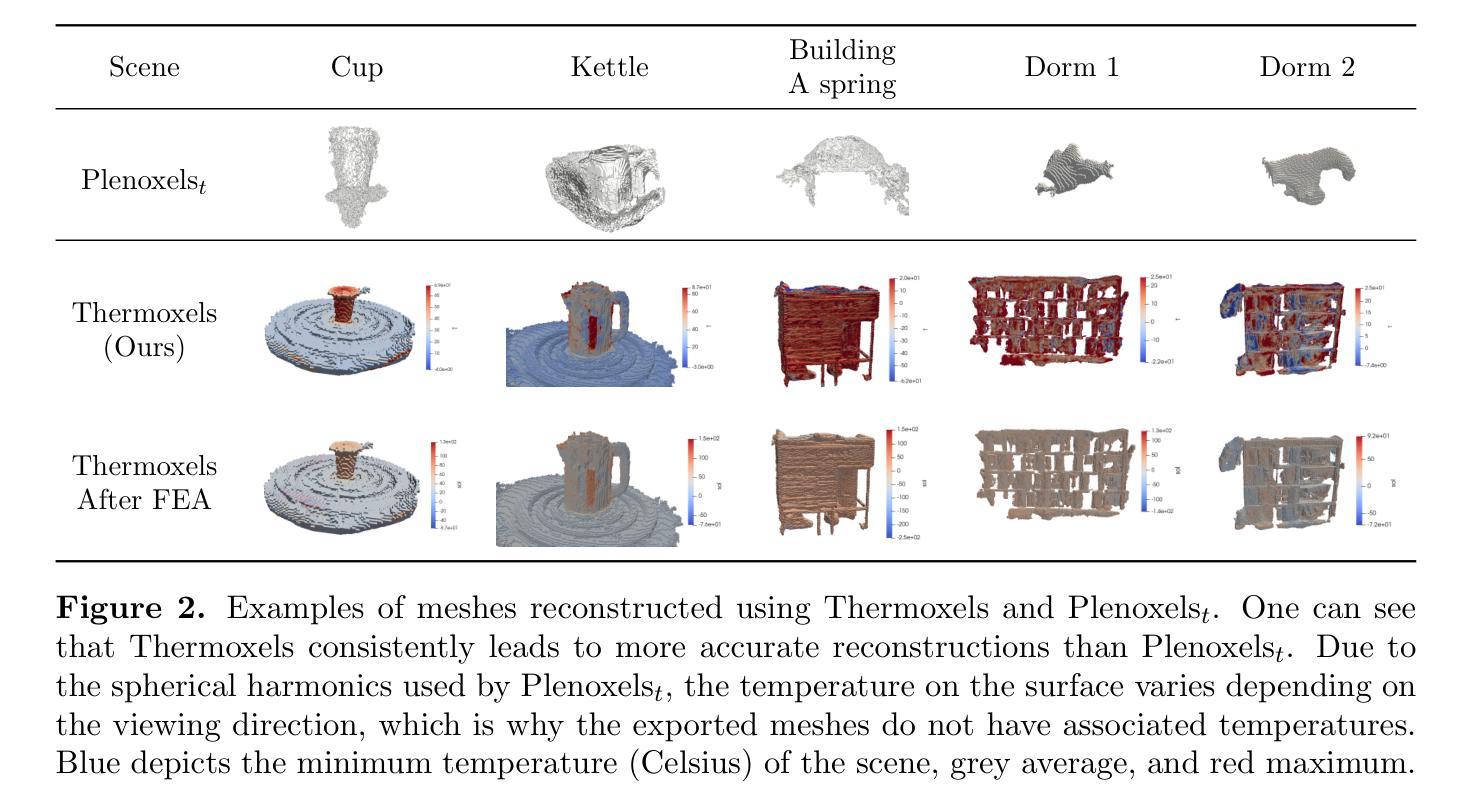
Thermoxels: a voxel-based method to generate simulation-ready 3D thermal models
Authors:Etienne Chassaing, Florent Forest, Olga Fink, Malcolm Mielle
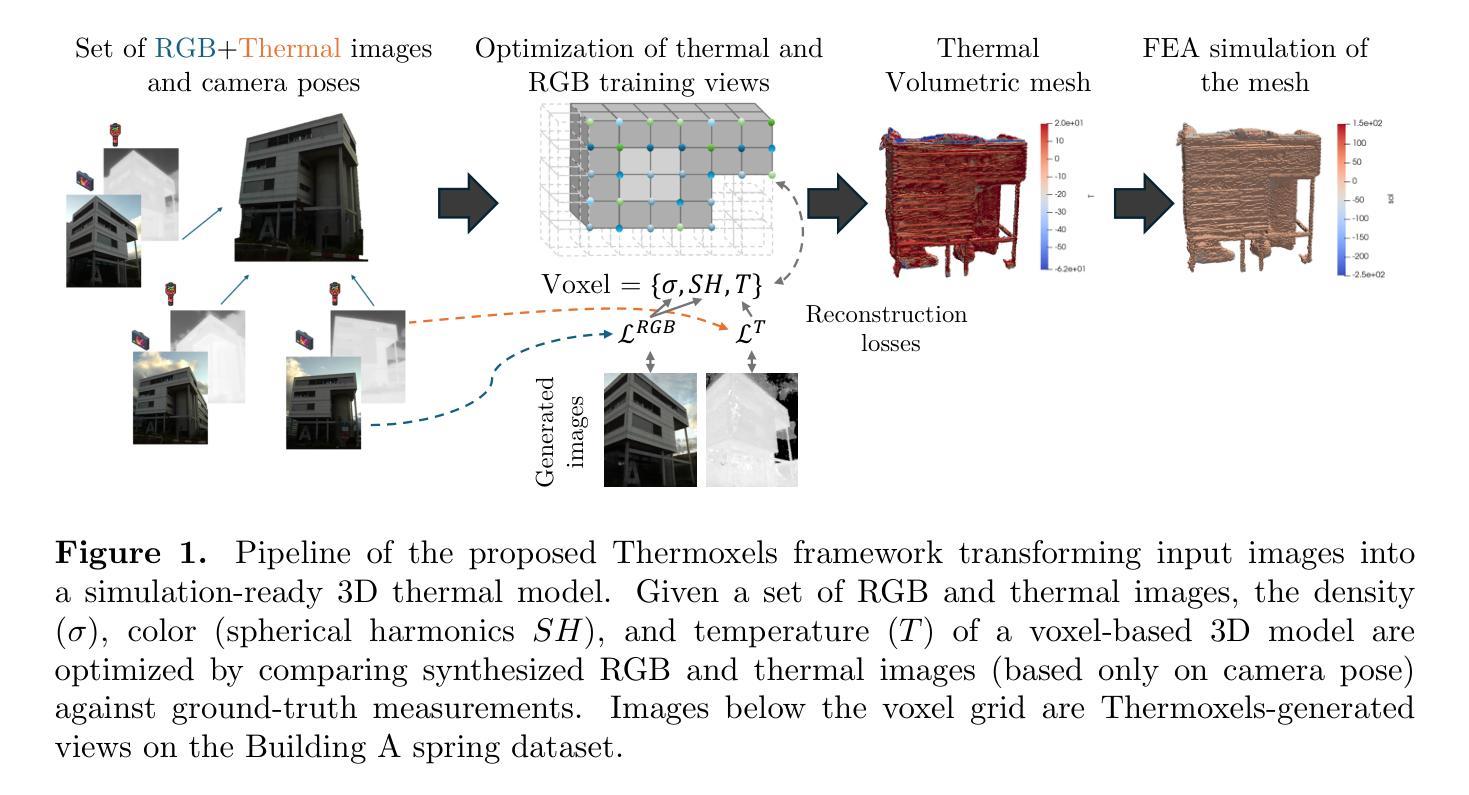
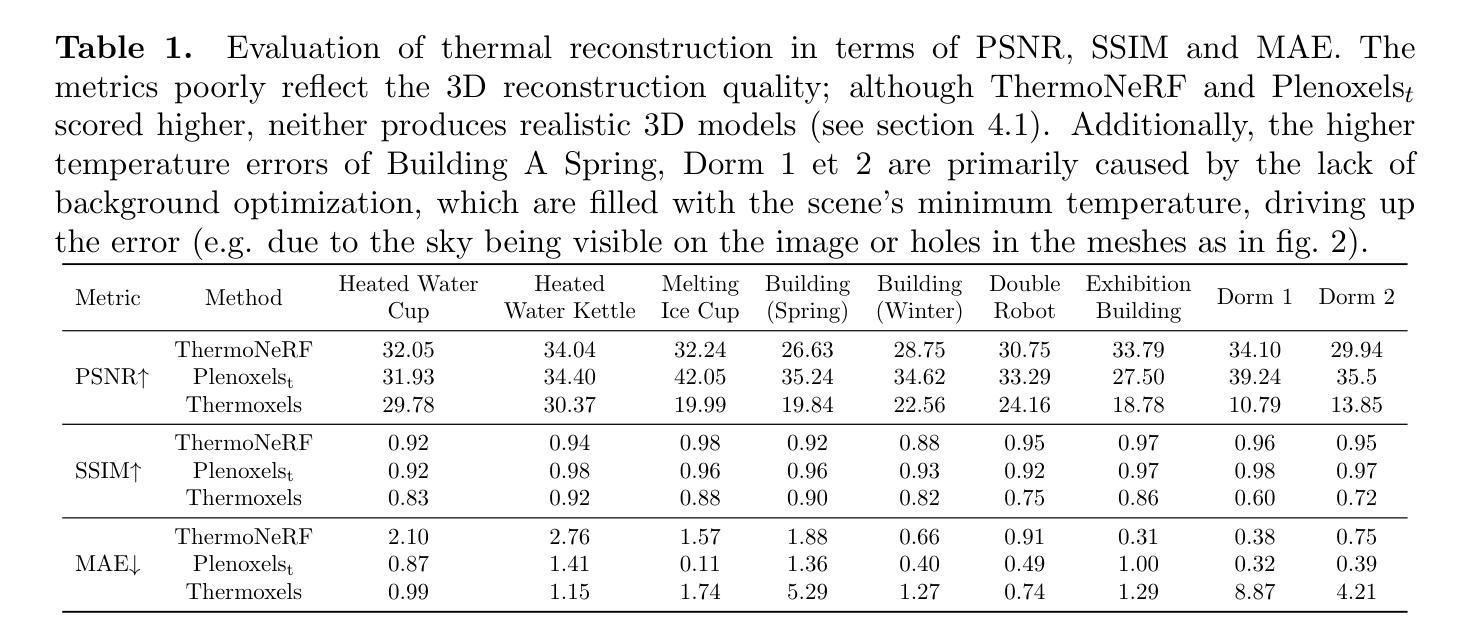
In the European Union, buildings account for 42% of energy use and 35% of greenhouse gas emissions. Since most existing buildings will still be in use by 2050, retrofitting is crucial for emissions reduction. However, current building assessment methods rely mainly on qualitative thermal imaging, which limits data-driven decisions for energy savings. On the other hand, quantitative assessments using finite element analysis (FEA) offer precise insights but require manual CAD design, which is tedious and error-prone. Recent advances in 3D reconstruction, such as Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and Gaussian Splatting, enable precise 3D modeling from sparse images but lack clearly defined volumes and the interfaces between them needed for FEA. We propose Thermoxels, a novel voxel-based method able to generate FEA-compatible models, including both geometry and temperature, from a sparse set of RGB and thermal images. Using pairs of RGB and thermal images as input, Thermoxels represents a scene’s geometry as a set of voxels comprising color and temperature information. After optimization, a simple process is used to transform Thermoxels’ models into tetrahedral meshes compatible with FEA. We demonstrate Thermoxels’ capability to generate RGB+Thermal meshes of 3D scenes, surpassing other state-of-the-art methods. To showcase the practical applications of Thermoxels’ models, we conduct a simple heat conduction simulation using FEA, achieving convergence from an initial state defined by Thermoxels’ thermal reconstruction. Additionally, we compare Thermoxels’ image synthesis abilities with current state-of-the-art methods, showing competitive results, and discuss the limitations of existing metrics in assessing mesh quality.
在欧盟,建筑物占能源使用的42%和温室气体排放的35%。由于大多数现有建筑在2050年仍将继续使用,因此改造对于减少排放至关重要。然而,目前的建筑评估方法主要依赖于定性的热成像技术,这限制了基于数据驱动的节能决策。另一方面,使用有限元分析(FEA)的定量评估提供了精确的见解,但需要手动CAD设计,这既繁琐又容易出错。最近的三维重建技术进展,如神经辐射场(NeRF)和高斯溅射,能够从稀疏图像进行精确的三维建模,但缺乏用于有限元分析的明确定义的体积和它们之间的界面。我们提出了Thermoxels,这是一种基于体素的新方法,能够生成包括几何和温度信息的有限元分析兼容模型,这些模型从稀疏的RGB和热图像集中生成。使用成对的RGB和热图像作为输入,Thermoxels将场景的几何表示为包含颜色和温度信息的体素集。经过优化后,使用简单的过程将Thermoxels模型转换为与FEA兼容的四面体网格。我们展示了Thermoxels生成RGB+热网格三维场景的能力,超越了其他最先进的方法。为了展示Thermoxels模型的实际应用,我们使用有限元分析进行简单的热传导模拟,从Thermoxels热重建定义的初始状态实现收敛。此外,我们将Thermoxels的图像合成能力与当前最先进的方法进行比较,展示了具有竞争力的结果,并讨论了现有指标在评估网格质量方面的局限性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 2 figures
Summary
基于NeRF技术的Thermoxels方法,能够从稀疏的RGB和红外图像生成兼容有限元分析的模型,用于建筑物的精准三维建模和温度分析。此方法解决了现有建筑评估方法的局限性,为欧盟的节能减排提供了新的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 欧洲联盟中,建筑物能耗占42%,温室气体排放占35%,因此翻新改造对减排至关重要。
- 当前建筑评估方法主要依赖定性热成像,限制了数据驱动的节能决策。
- 定量评估使用的有限元分析(FEA)提供精确见解,但需要手动CAD设计,过程繁琐且易出错。
- Neural Radiance Fields(NeRF)等3D重建技术的最新进展能够实现从稀疏图像进行精准三维建模。
- Thermoxels方法结合NeRF技术生成包含几何和温度信息的有限元分析兼容模型,从稀疏的RGB和红外图像中进行创建。
- Thermoxels展示了一种将模型转化为与有限元分析兼容的四面体网格的简单过程。
- 实验结果表明,Thermoxels在生成RGB+热网格的3D场景方面超越其他最新方法,并且成功应用于热传导模拟仿真中。
点此查看论文截图

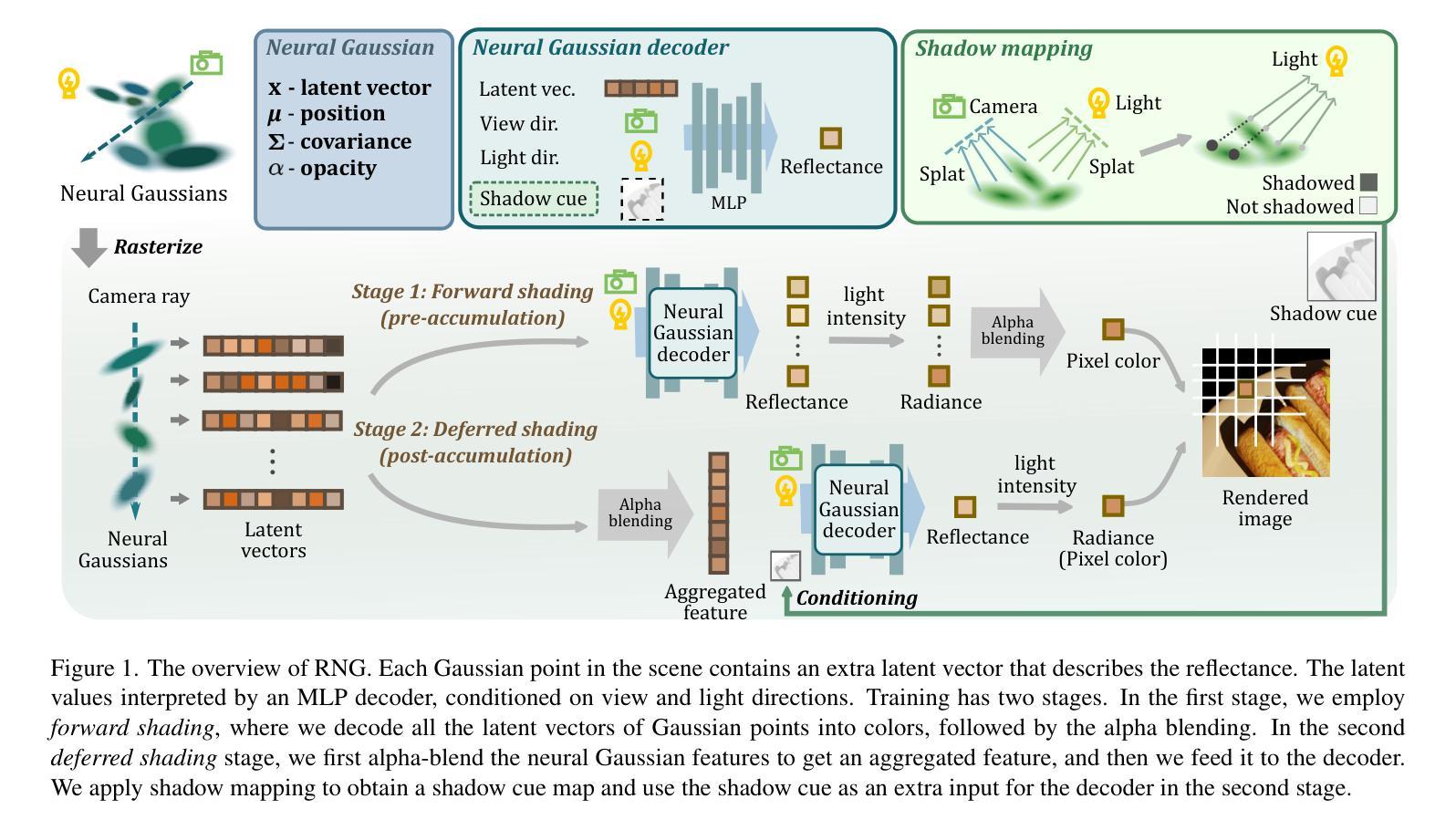
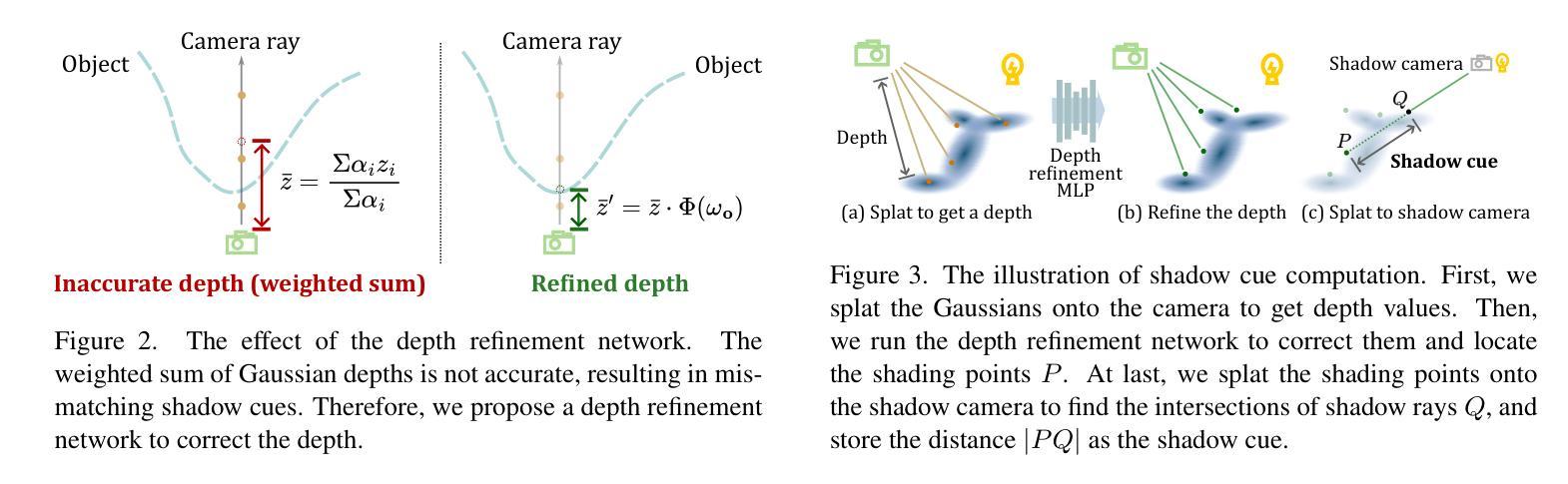
RNG: Relightable Neural Gaussians
Authors:Jiahui Fan, Fujun Luan, Jian Yang, Miloš Hašan, Beibei Wang
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has shown impressive results for the novel view synthesis task, where lighting is assumed to be fixed. However, creating relightable 3D assets, especially for objects with ill-defined shapes (fur, fabric, etc.), remains a challenging task. The decomposition between light, geometry, and material is ambiguous, especially if either smooth surface assumptions or surfacebased analytical shading models do not apply. We propose Relightable Neural Gaussians (RNG), a novel 3DGS-based framework that enables the relighting of objects with both hard surfaces or soft boundaries, while avoiding assumptions on the shading model. We condition the radiance at each point on both view and light directions. We also introduce a shadow cue, as well as a depth refinement network to improve shadow accuracy. Finally, we propose a hybrid forward-deferred fitting strategy to balance geometry and appearance quality. Our method achieves significantly faster training (1.3 hours) and rendering (60 frames per second) compared to a prior method based on neural radiance fields and produces higher-quality shadows than a concurrent 3DGS-based method. Project page: https://www.whois-jiahui.fun/project_pages/RNG.
3D高斯融合(3DGS)在新视角合成任务中取得了令人印象深刻的结果,该任务假设光照是固定的。然而,创建可重新照明的3D资产,特别是对于形状不明确的对象(如皮毛、织物等),仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务。光、几何形状和材料之间的分解是模糊的,尤其是当光滑表面假设或基于表面的分析着色模型不适用时。我们提出可重新照明的神经高斯(RNG),这是一种基于3DGS的新型框架,能够实现具有硬表面或软边界的对象的重新照明,同时避免对着色模型进行假设。我们将每个点的辐射率取决于视图和光线的方向。我们还引入了一个阴影提示和一个深度细化网络来提高阴影的准确性。最后,我们提出了一种混合的前向延迟拟合策略来平衡几何形状和外观质量。我们的方法与前一种基于神经辐射场的方法相比,实现了更快的训练(1.3小时)和渲染(每秒60帧),并且比同期基于3DGS的方法产生了更高质量的阴影。项目页面:https://www.whois-jiahui.fun/project_pages/RNG。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Camera-ready version. Proceedings of CVPR 2025
Summary
该文本主要介绍了Relightable Neural Gaussians(RNG)框架,这是一个基于3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)的模型,能够实现对具有硬表面或软边界的对象的重新照明,无需对阴影模型进行假设。该框架引入了一种阴影线索和深度细化网络以提高阴影准确性,并提出了混合正向延迟拟合策略以平衡几何和外观质量。与传统的基于神经辐射场的方法相比,RNG具有更快的训练和渲染速度,同时产生更高质量的阴影。
Key Takeaways
- RNG框架基于3DGS,可实现对象的重新照明,适用于硬表面或软边界对象。
- RNG不需要对阴影模型进行假设,通过引入阴影线索和深度细化网络提高阴影准确性。
- RNG提出了混合正向延迟拟合策略,以平衡几何和外观质量。
- 与传统基于神经辐射场的方法相比,RNG具有更快的训练和渲染速度。
- RNG产生的阴影质量更高,比现有的3DGS方法更优越。
- RNG框架的更多细节和实现在项目页面(https://www.whois-jiahui.fun/project_pages/RNG)上提供。
点此查看论文截图

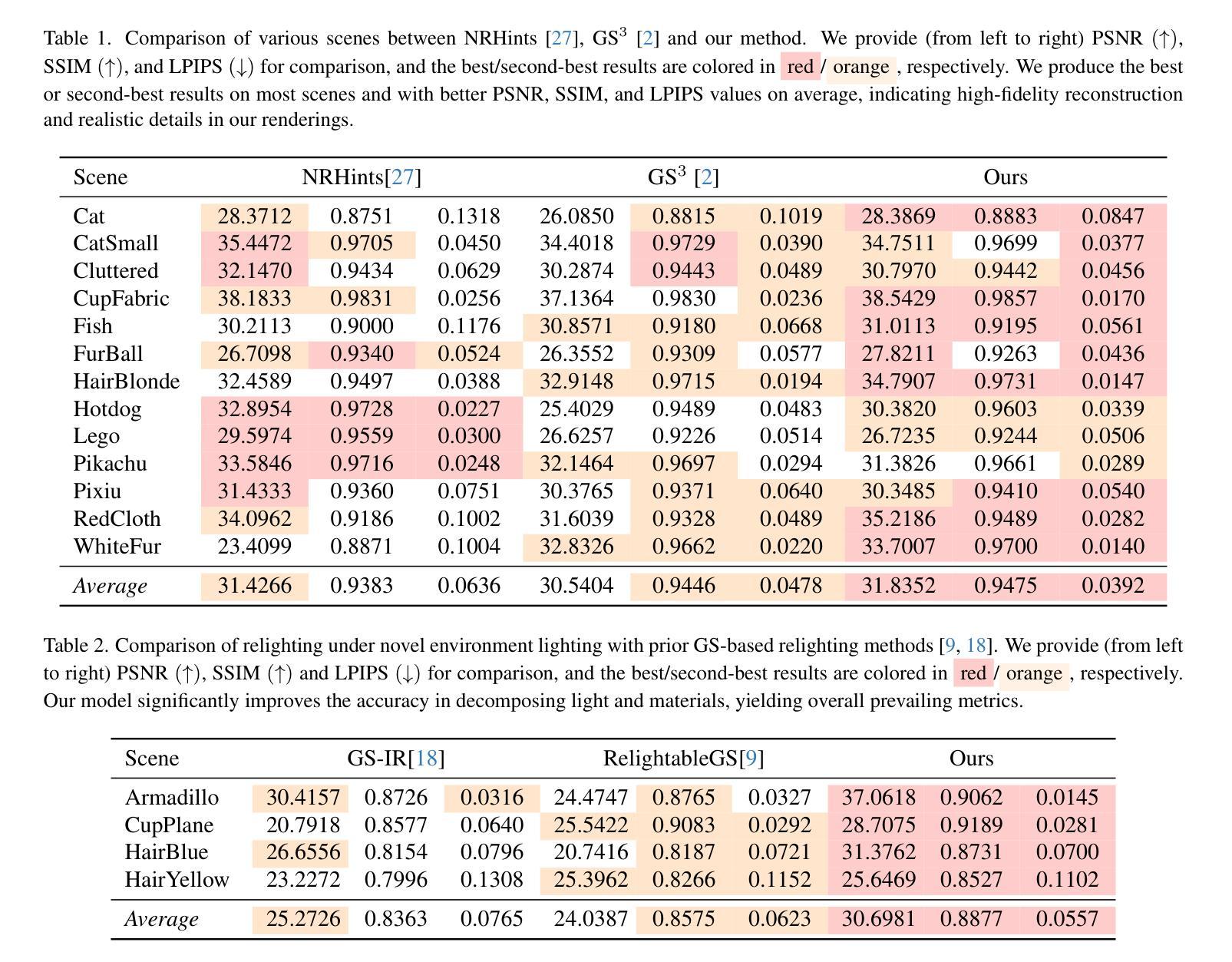
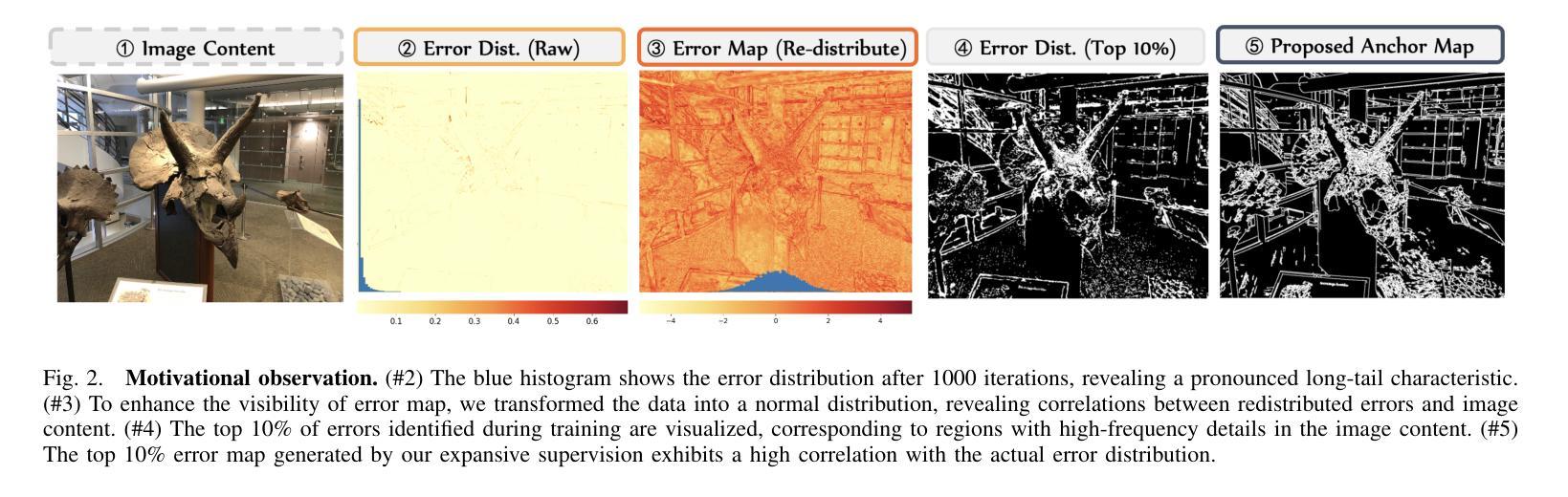
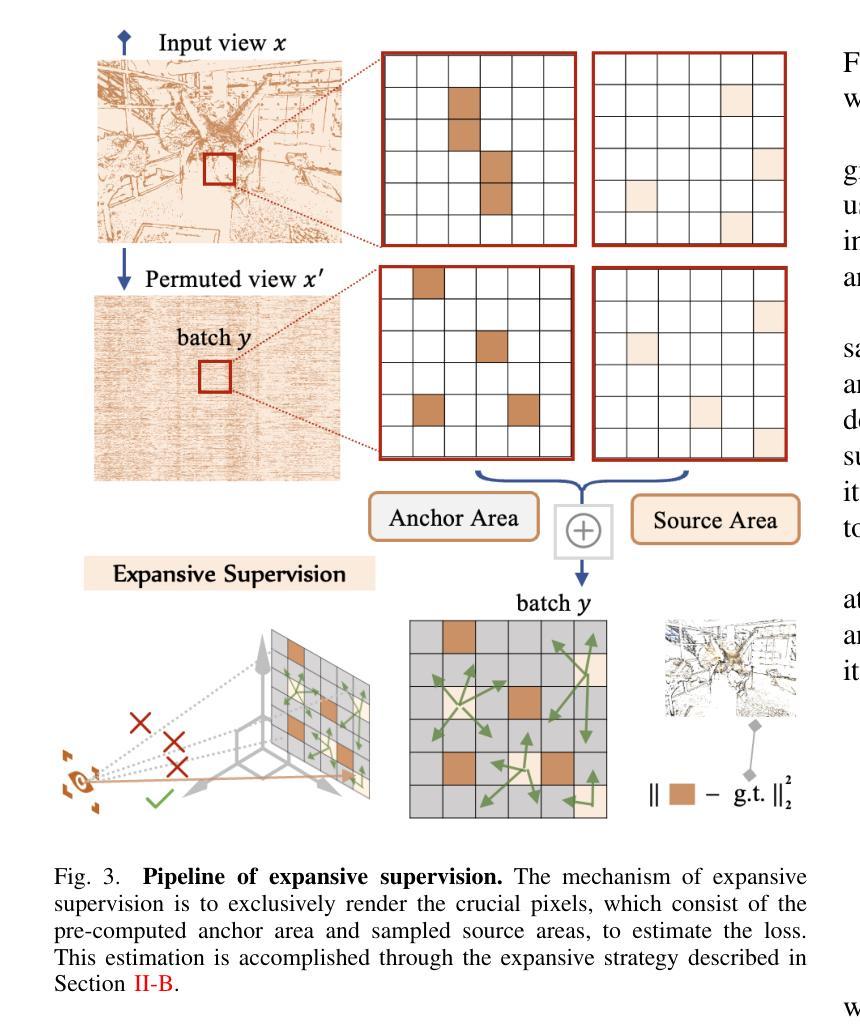
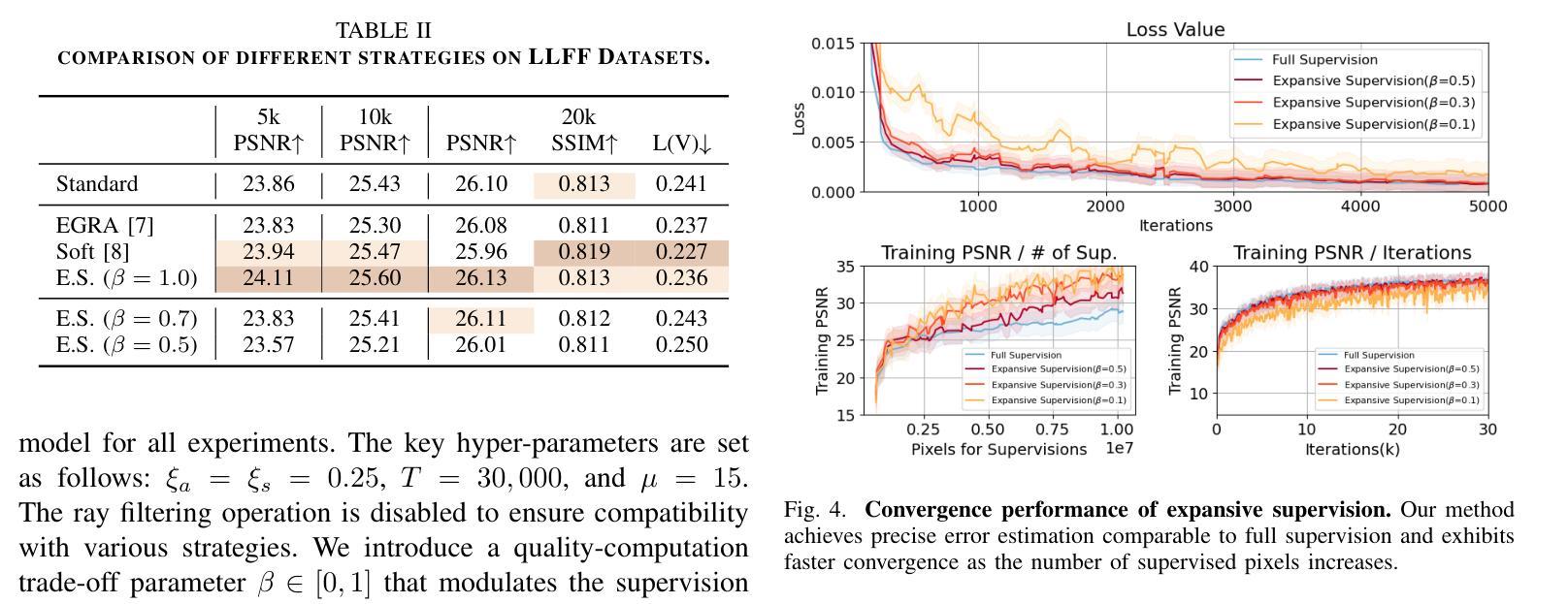
Expansive Supervision for Neural Radiance Field
Authors:Weixiang Zhang, Shuzhao Xie, Shijia Ge, Wei Yao, Chen Tang, Zhi Wang
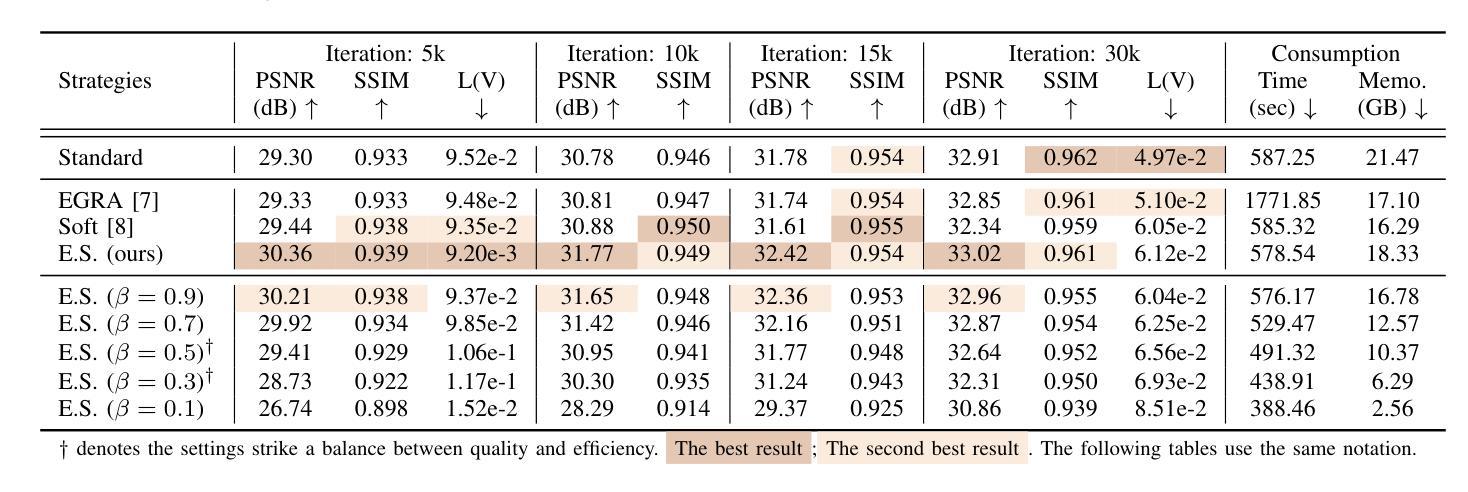
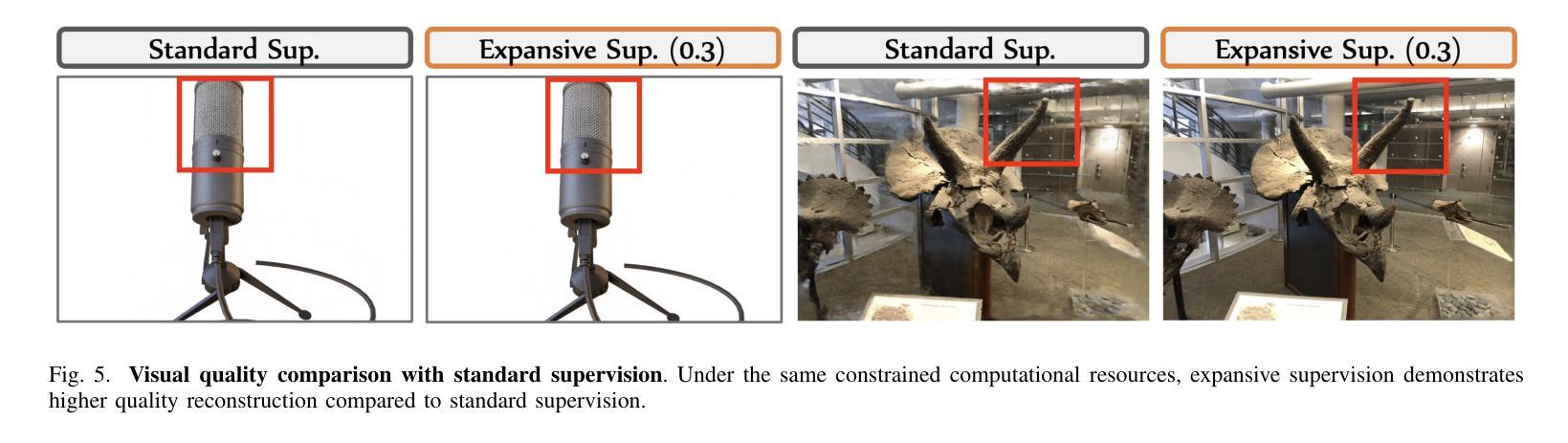
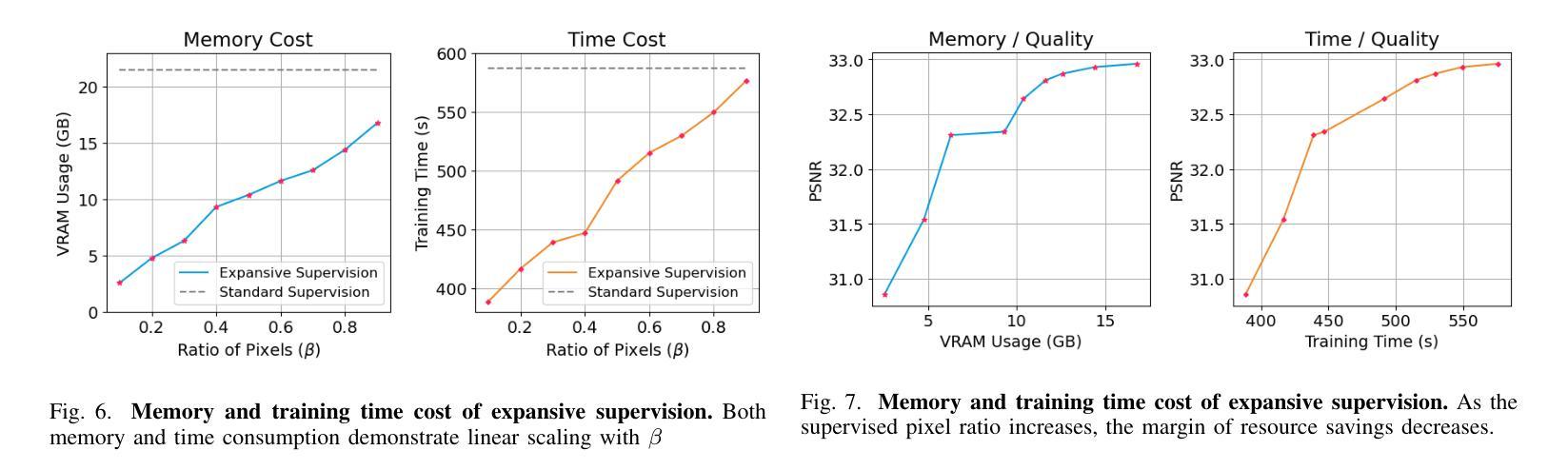
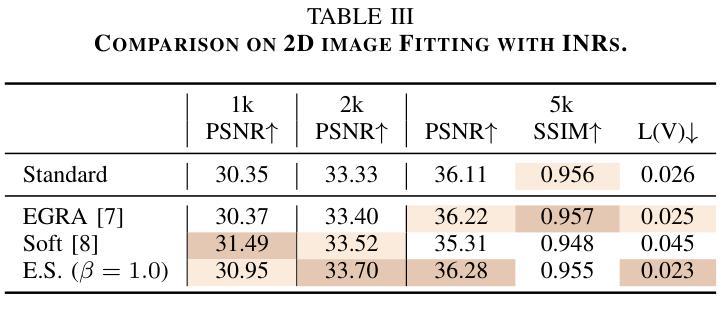
Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) has achieved remarkable success in creating immersive media representations through its exceptional reconstruction capabilities. However, the computational demands of dense forward passes and volume rendering during training continue to challenge its real-world applications. In this paper, we introduce Expansive Supervision to reduce time and memory costs during NeRF training from the perspective of partial ray selection for supervision. Specifically, we observe that training errors exhibit a long-tail distribution correlated with image content. Based on this observation, our method selectively renders a small but crucial subset of pixels and expands their values to estimate errors across the entire area for each iteration. Compared to conventional supervision, our approach effectively bypasses redundant rendering processes, resulting in substantial reductions in both time and memory consumption. Experimental results demonstrate that integrating Expansive Supervision within existing state-of-the-art acceleration frameworks achieves 52% memory savings and 16% time savings while maintaining comparable visual quality.
神经辐射场(NeRF)凭借其出色的重建能力,在创建沉浸式媒体表示方面取得了显著的成功。然而,训练过程中的密集前向传递和体积渲染的计算需求仍然对其实际应用提出了挑战。本文引入扩展监督(Expansive Supervision)从部分射线选择监督的角度减少NeRF训练的时间和内存成本。具体来说,我们观察到训练错误与图像内容呈现长尾分布相关。基于此观察,我们的方法选择渲染一小部分但至关重要的像素,并扩大它们的值来估计每个迭代整个区域的误差。与传统的监督方法相比,我们的方法有效地绕过了冗余的渲染过程,导致时间和内存消耗的显著减少。实验结果表明,在现有的最先进的加速框架中融入扩展监督方法,可在保持相当视觉质量的同时,实现52%的内存节省和16%的时间节省。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICME 2025
Summary
本文介绍了NeRF技术在训练过程中的计算需求挑战其实际应用的问题。针对这一问题,文章提出了Expansive Supervision方法,通过选择性渲染关键像素并扩大其值来估算误差,从而减少时间和内存成本。实验结果显示,结合现有的加速框架使用此方法实现了内存节省和时间节省。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF技术已在创建沉浸式媒体表示方面取得了显著成功。
- 训练过程中的密集正向传递和体积渲染计算需求挑战了其实际应用。
- Expansive Supervision方法通过选择性渲染关键像素并扩大其值来估算误差,从而减少时间和内存成本。
- Expansive Supervision方法观察到训练错误与图像内容之间存在长尾分布关系。
- Expansive Supervision方法可以有效地绕过冗余的渲染过程。
- 结合现有加速框架使用此方法实现了内存节省和时间节省,分别为52%和16%。
点此查看论文截图

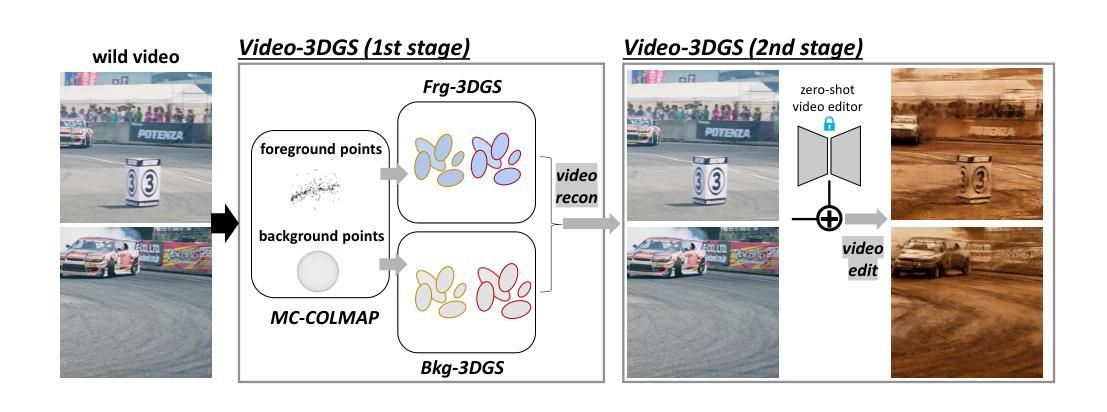
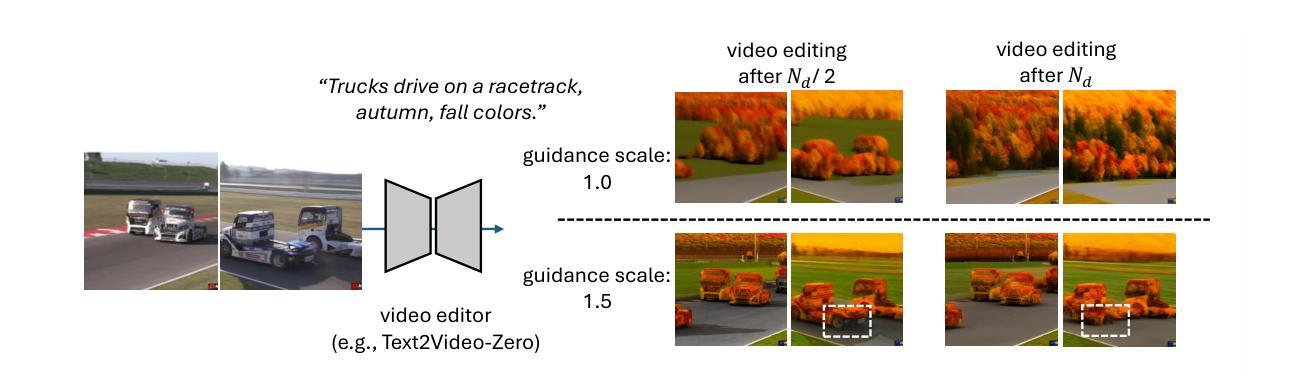
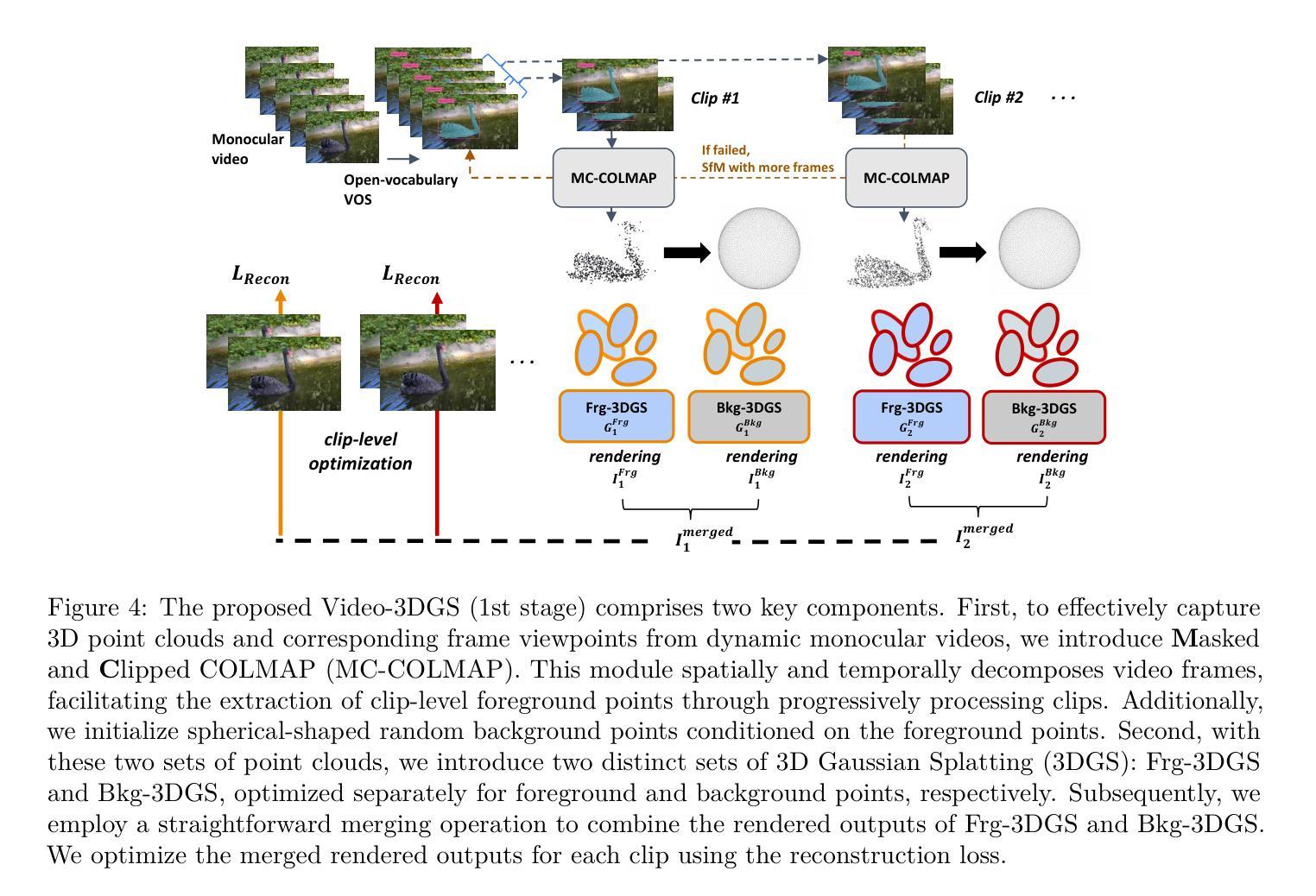
Enhancing Temporal Consistency in Video Editing by Reconstructing Videos with 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Inkyu Shin, Qihang Yu, Xiaohui Shen, In So Kweon, Kuk-Jin Yoon, Liang-Chieh Chen
Recent advancements in zero-shot video diffusion models have shown promise for text-driven video editing, but challenges remain in achieving high temporal consistency. To address this, we introduce Video-3DGS, a 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS)-based video refiner designed to enhance temporal consistency in zero-shot video editors. Our approach utilizes a two-stage 3D Gaussian optimizing process tailored for editing dynamic monocular videos. In the first stage, Video-3DGS employs an improved version of COLMAP, referred to as MC-COLMAP, which processes original videos using a Masked and Clipped approach. For each video clip, MC-COLMAP generates the point clouds for dynamic foreground objects and complex backgrounds. These point clouds are utilized to initialize two sets of 3D Gaussians (Frg-3DGS and Bkg-3DGS) aiming to represent foreground and background views. Both foreground and background views are then merged with a 2D learnable parameter map to reconstruct full views. In the second stage, we leverage the reconstruction ability developed in the first stage to impose the temporal constraints on the video diffusion model. To demonstrate the efficacy of Video-3DGS on both stages, we conduct extensive experiments across two related tasks: Video Reconstruction and Video Editing. Video-3DGS trained with 3k iterations significantly improves video reconstruction quality (+3 PSNR, +7 PSNR increase) and training efficiency (x1.9, x4.5 times faster) over NeRF-based and 3DGS-based state-of-art methods on DAVIS dataset, respectively. Moreover, it enhances video editing by ensuring temporal consistency across 58 dynamic monocular videos.
最近,零样本视频扩散模型的发展在文本驱动的视频编辑方面显示出前景。然而,在提高时间一致性方面仍然存在挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了Video-3DGS,这是一种基于三维高斯喷涂(3DGS)的视频细化器,旨在提高零样本视频编辑器的时间一致性。我们的方法利用两阶段三维高斯优化过程,针对动态单目视频编辑而量身定制。在第一阶段,Video-3DGS采用改进的COLMAP版本,称为MC-COLMAP,它采用掩膜和裁剪方法对原始视频进行处理。对于每个视频片段,MC-COLMAP会生成动态前景对象和复杂背景的点云。这些点云用于初始化两组三维高斯分布(Frg-3DGS和Bkg-3DGS),旨在表示前景和背景视图。然后将前景和背景视图与二维可学习参数图合并,以重建全视图。在第二阶段,我们利用第一阶段开发的重建能力对视频扩散模型施加时间约束。为了证明Video-3DGS在两个阶段的有效性,我们在两个相关任务上进行了大量实验:视频重建和视频编辑。Video-3DGS经过3k次迭代训练后,在DAVIS数据集上与基于NeRF和基于3DGS的先进技术方法相比,视频重建质量提高了(+3 PSNR,+7 PSNR增加),训练效率也显著提高(分别提高了1.9倍和4.5倍)。此外,它通过确保58个动态单目视频的时间一致性,提高了视频编辑的质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to TMLR 2025. Project page at https://video-3dgs-project.github.io/
摘要
近期零样本视频扩散模型在文本驱动的视频编辑方面展现出潜力,但在实现高时间一致性方面仍存在挑战。为解决此问题,我们推出Video-3DGS,一种基于3D高斯喷绘(3DGS)的视频精炼器,旨在增强零样本视频编辑器的时间一致性。该方法采用两阶段3D高斯优化流程,专门针对动态单目视频编辑。第一阶段,Video-3DGS采用改进版COLMAP(称为MC-COLMAP),通过遮罩和裁剪方法处理原始视频。MC-COLMAP为每段视频生成动态前景对象和复杂背景的点云,用于初始化两组3D高斯(Frg-3DGS和Bkg-3DGS),旨在表示前景和背景视图。然后,将前景和背景视图与2D可学习参数图合并,以重建全视图。第二阶段,我们利用第一阶段的重建能力,对视频扩散模型施加时间约束。我们在视频重建和视频编辑两个任务上进行了大量实验,证明了Video-3DGS在两个阶段的有效性。在DAVIS数据集上,Video-3DGS经过3k次迭代训练,显著提高了视频重建质量(PSNR提高3点和7点),并提高了训练效率(分别为1.9倍和4.5倍)。此外,它能确保在58个动态单目视频中的时间一致性,从而增强视频编辑效果。
关键见解
- Video-3DGS被设计用于增强零样本视频编辑器的时间一致性,针对动态单目视频编辑。
- Video-3DGS采用两阶段3D高斯优化流程,包括利用MC-COLMAP生成点云和初始化两组3D高斯。
- MC-COLMAP通过处理原始视频生成点云,用于重建前景和背景视图。
- Video-3DGS将前景和背景视图与2D可学习参数图合并,以提高视频重建质量。
- 第二阶段利用重建能力对视频扩散模型施加时间约束。
- Video-3DGS在DAVIS数据集上的实验表明,与基于NeRF和基于3DGS的现有方法相比,它在视频重建质量、训练效率和视频编辑的临时一致性方面有显著改进。
点此查看论文截图


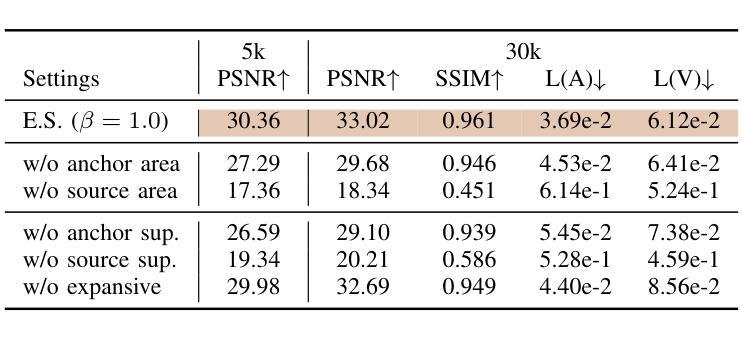
ARC-NeRF: Area Ray Casting for Broader Unseen View Coverage in Few-shot Object Rendering
Authors:Seunghyeon Seo, Yeonjin Chang, Jayeon Yoo, Seungwoo Lee, Hojun Lee, Nojun Kwak
Recent advancements in the Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) have enhanced its capabilities for novel view synthesis, yet its reliance on dense multi-view training images poses a practical challenge, often leading to artifacts and a lack of fine object details. Addressing this, we propose ARC-NeRF, an effective regularization-based approach with a novel Area Ray Casting strategy. While the previous ray augmentation methods are limited to covering only a single unseen view per extra ray, our proposed Area Ray covers a broader range of unseen views with just a single ray and enables an adaptive high-frequency regularization based on target pixel photo-consistency. Moreover, we propose luminance consistency regularization, which enhances the consistency of relative luminance between the original and Area Ray, leading to more accurate object textures. The relative luminance, as a free lunch extra data easily derived from RGB images, can be effectively utilized in few-shot scenarios where available training data is limited. Our ARC-NeRF outperforms its baseline and achieves competitive results on multiple benchmarks with sharply rendered fine details.
尽管Neural Radiance Field(NeRF)的最新进展增强了其在新型视图合成方面的能力,但它对密集多视图训练图像的依赖构成了实际应用中的挑战,常常导致伪影和对象细节缺乏精细度。为解决这一问题,我们提出了ARC-NeRF,这是一种基于有效正则化的方法,并采用了新型的区域光线投射策略。尽管之前的射线增强方法仅限于每额外射线只覆盖一个未见视图,我们提出的地域射线仅需一条射线就能覆盖更广泛的未见视图,并实现了基于目标像素照片一致性的自适应高频正则化。此外,我们提出了亮度一致性正则化,它增强了原始射线和区域射线之间相对亮度的一致性,从而得到更精确的对象纹理。相对亮度作为从RGB图像轻松派生的免费额外数据,在可用训练数据有限的少量场景中可以得到有效利用。我们的ARC-NeRF超越了基线,并在多个基准测试上取得了具有精细渲染细节的竞争结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025 Workshop: 4th Computer Vision for Metaverse Workshop
Summary
NeRF技术的新进展提升了其在新型视角合成方面的能力,但仍面临依赖于密集多角度训练图像的问题,导致出现伪影和细节缺失等缺陷。为解决这一问题,我们提出了ARC-NeRF方案,采用基于正则化的新方法及创新的Area Ray Casting策略。相较于仅通过额外射线覆盖单一未见视角的现有射线增强方法,Area Ray能更广泛地覆盖未见视角,并通过目标像素的光一致性实现自适应高频正则化。此外,我们还提出了亮度一致性正则化,提高了原始图像和Area Ray之间的相对亮度一致性,从而得到更准确的物体纹理。利用相对亮度这一容易从RGB图像中获取的额外数据,ARC-NeRF在少量训练数据的情况下也能表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF技术在新型视角合成方面取得进展,但依赖于密集多角度训练图像导致伪影和细节缺失问题。
- 提出了ARC-NeRF方案,采用基于正则化的新方法和Area Ray Casting策略解决现有问题。
- Area Ray能覆盖更广泛的未见视角,通过目标像素的光一致性实现自适应高频正则化。
- 引入亮度一致性正则化,提高物体纹理的准确性。
- ARC-NeRF方案利用相对亮度这一额外数据,能在有限训练数据的情况下表现良好。
- ARC-NeRF在多个基准测试中表现优于基准方法,能够精细呈现细节。
点此查看论文截图