⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-09 更新
Embedded Federated Feature Selection with Dynamic Sparse Training: Balancing Accuracy-Cost Tradeoffs
Authors:Afsaneh Mahanipour, Hana Khamfroush
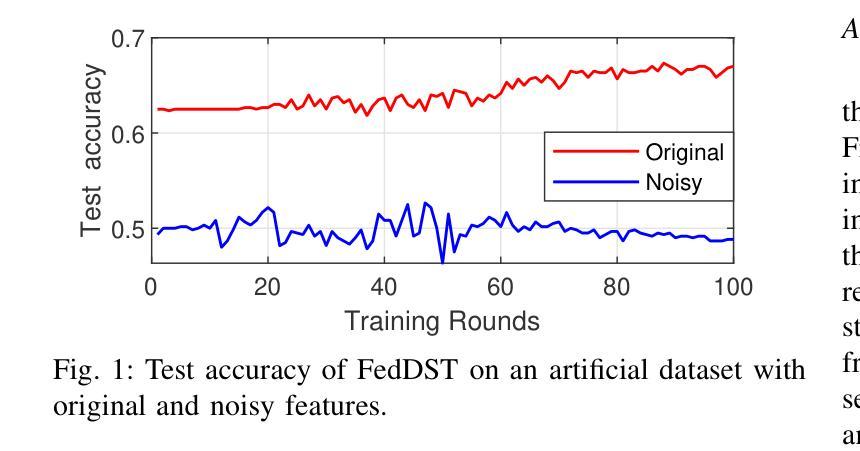
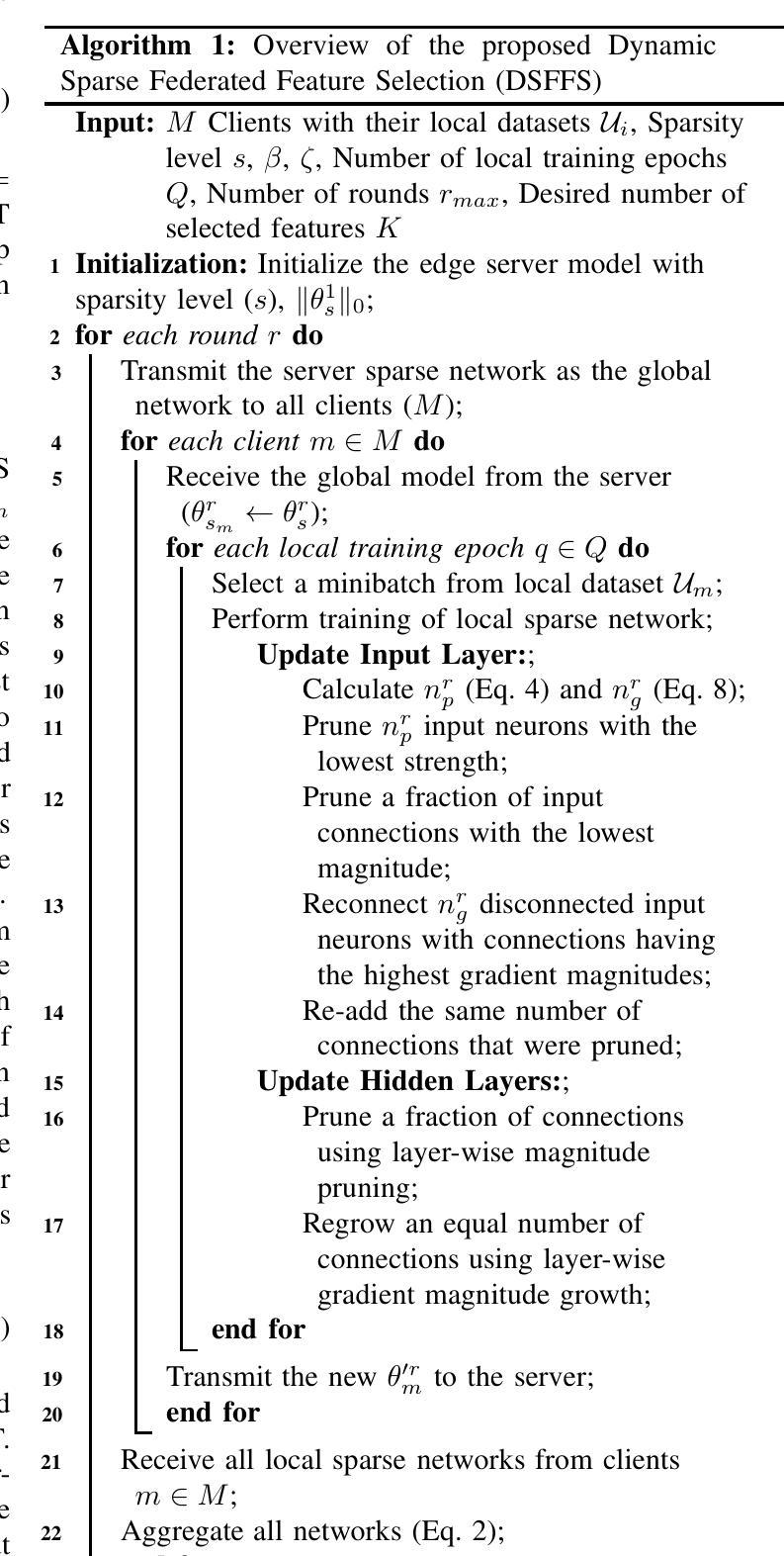
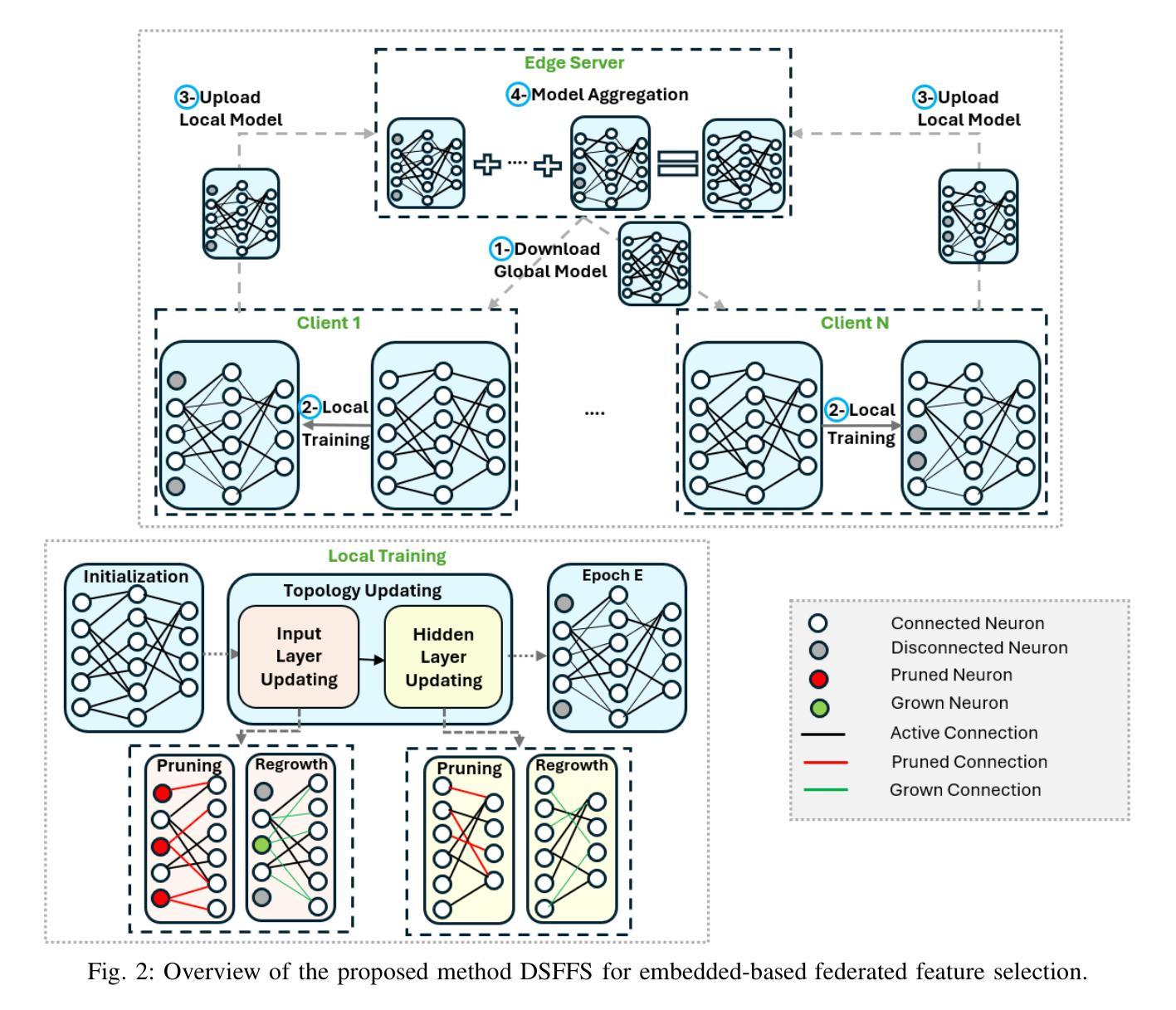
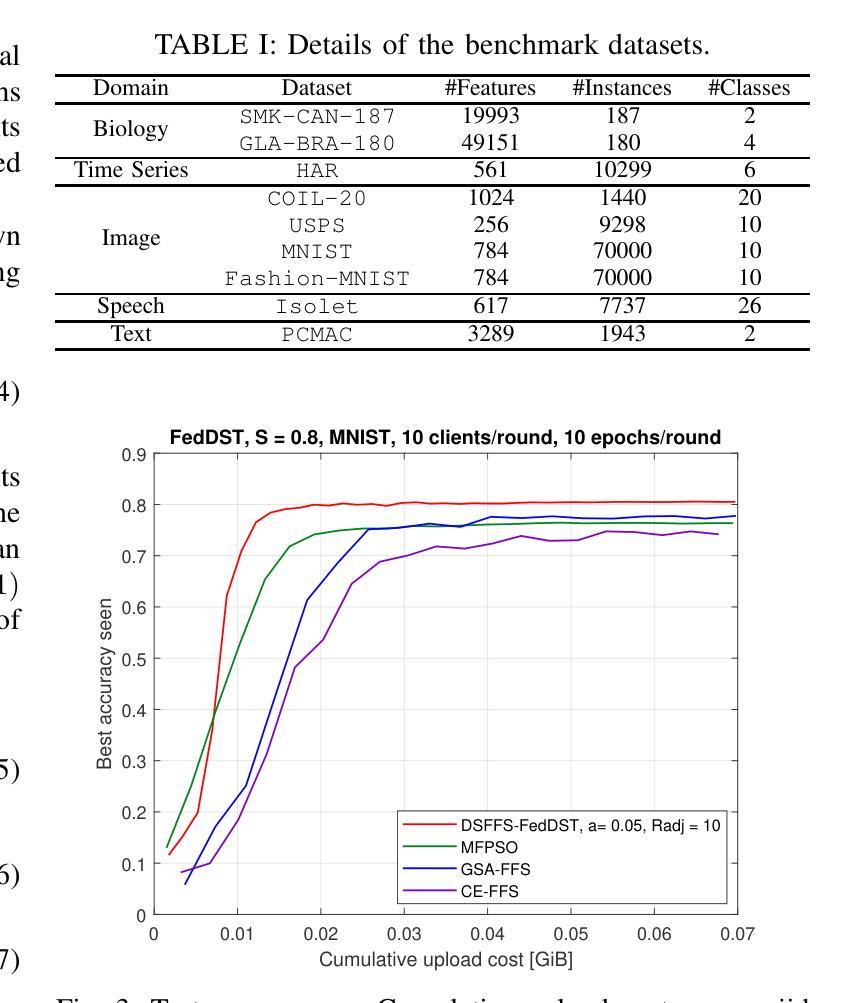
Federated Learning (FL) enables multiple resource-constrained edge devices with varying levels of heterogeneity to collaboratively train a global model. However, devices with limited capacity can create bottlenecks and slow down model convergence. One effective approach to addressing this issue is to use an efficient feature selection method, which reduces overall resource demands by minimizing communication and computation costs, thereby mitigating the impact of struggling nodes. Existing federated feature selection (FFS) methods are either considered as a separate step from FL or rely on a third party. These approaches increase computation and communication overhead, making them impractical for real-world high-dimensional datasets. To address this, we present \textit{Dynamic Sparse Federated Feature Selection} (DSFFS), the first innovative embedded FFS that is efficient in both communication and computation. In the proposed method, feature selection occurs simultaneously with model training. During training, input-layer neurons, their connections, and hidden-layer connections are dynamically pruned and regrown, eliminating uninformative features. This process enhances computational efficiency on devices, improves network communication efficiency, and boosts global model performance. Several experiments are conducted on nine real-world datasets of varying dimensionality from diverse domains, including biology, image, speech, and text. The results under a realistic non-iid data distribution setting show that our approach achieves a better trade-off between accuracy, computation, and communication costs by selecting more informative features compared to other state-of-the-art FFS methods.
联邦学习(FL)允许多个资源受限的边缘设备,在具有不同级别的异构性情况下,共同训练一个全球模型。然而,容量有限的设备可能会成为瓶颈,减慢模型的收敛速度。解决此问题的一种有效方法是使用高效的特征选择方法,通过最小化通信和计算成本来降低总体资源需求,从而减轻挣扎节点的影响。现有的联邦特征选择(FFS)方法要么被视为与FL分离的步骤,要么依赖于第三方。这些方法增加了计算和通信开销,对于现实世界的高维数据集来说并不实用。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了“动态稀疏联邦特征选择”(DSFFS),这是一种既高效通信又高效计算的首创嵌入式FFS。在提出的方法中,特征选择是与模型训练同时发生的。在训练过程中,输入层神经元、其连接和隐藏层连接会动态地修剪和再生,消除无信息特征。这个过程提高了设备的计算效率,提高了网络通信效率,并提高了全球模型的性能。我们在来自不同领域的九个真实世界的高维数据集上进行了实验,包括生物学、图像、语音和文本。在现实的非iid数据分布设置下,结果显示,我们的方法通过选择更具信息量的特征,在准确性、计算和通信成本之间取得了更好的权衡,优于其他最先进的FFS方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted for presentation at IJCNN 2025
Summary
本文介绍了联邦学习(FL)在资源受限的边缘设备上的挑战,特别是设备间存在的异质性问题会减慢模型收敛速度。为解决此问题,提出一种动态稀疏联邦特征选择(DSFFS)方法,该方法在模型训练过程中同时进行特征选择,动态地剪枝和再生输入层神经元、连接和隐藏层连接,消除无关特征,从而提高计算效率和网络通信效率,提升全局模型性能。实验结果表明,该方法在真实非独立同分布数据环境下,相比其他先进FFS方法,在准确度、计算和通信成本方面取得了更好的平衡。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦学习(FL)允许资源受限的边缘设备协同训练全局模型,但设备间的异质性问题可能导致瓶颈和减缓模型收敛。
- 动态稀疏联邦特征选择(DSFFS)是解决此问题的一种有效方法,它同时进行特征选择并优化模型训练。
- DSFFS通过动态剪枝和再生输入层神经元及其连接来提高计算效率。
- DSFFS通过消除无关特征,提高了网络通信效率。
- DSFFS方法提升了全局模型的性能。
- 实验结果显示,DSFFS在真实非独立同分布数据环境下表现优越,相比其他先进方法更平衡地处理了准确度、计算和通信成本。
点此查看论文截图

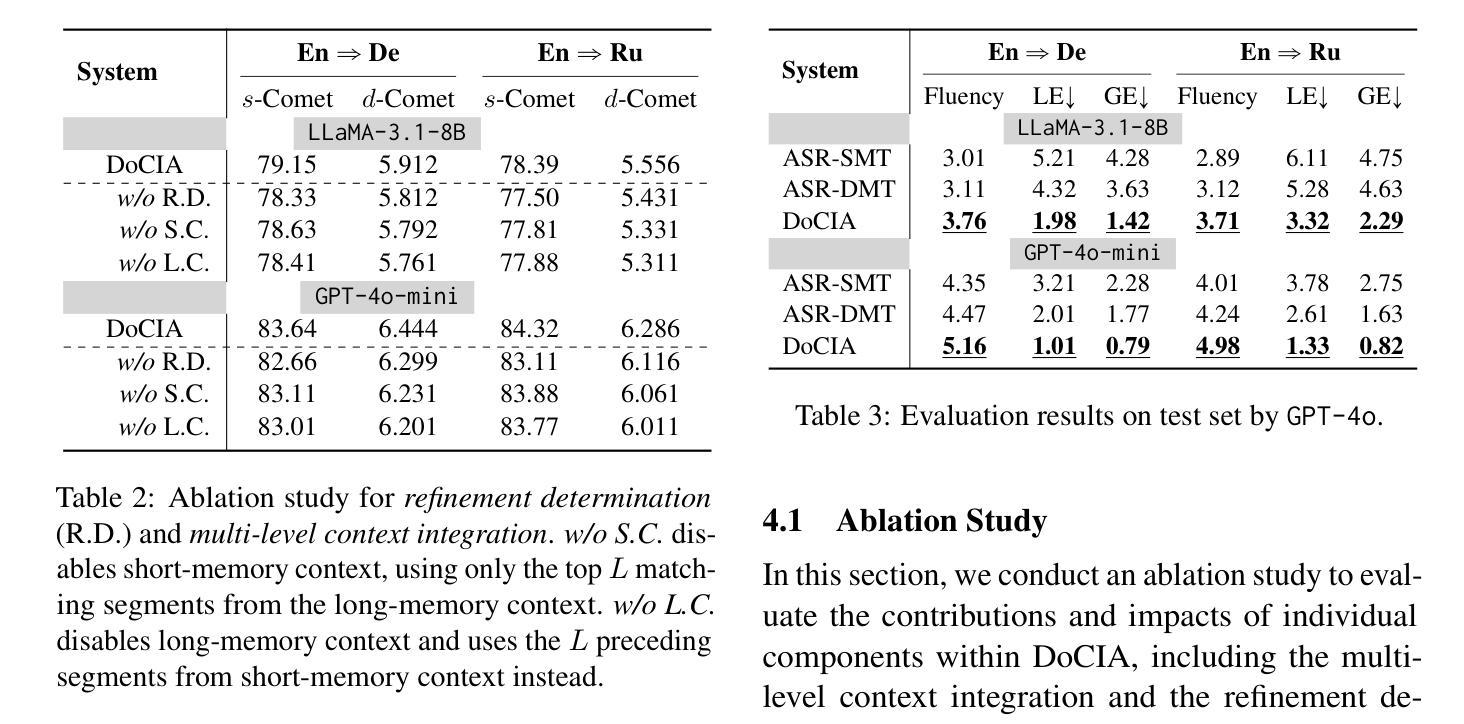
DoCIA: An Online Document-Level Context Incorporation Agent for Speech Translation
Authors:Xinglin Lyu, Wei Tang, Yuang Li, Xiaofeng Zhao, Ming Zhu, Junhui Li, Yunfei Lu, Min Zhang, Daimeng Wei, Hao Yang, Min Zhang
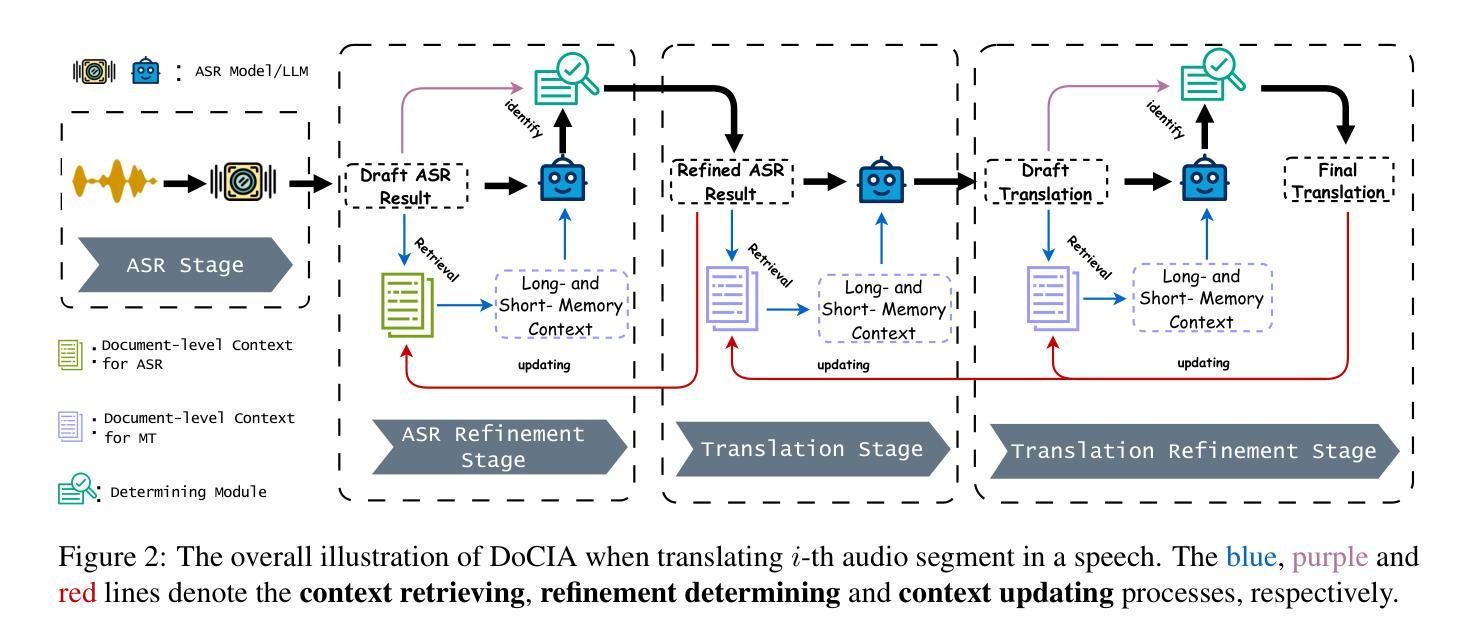
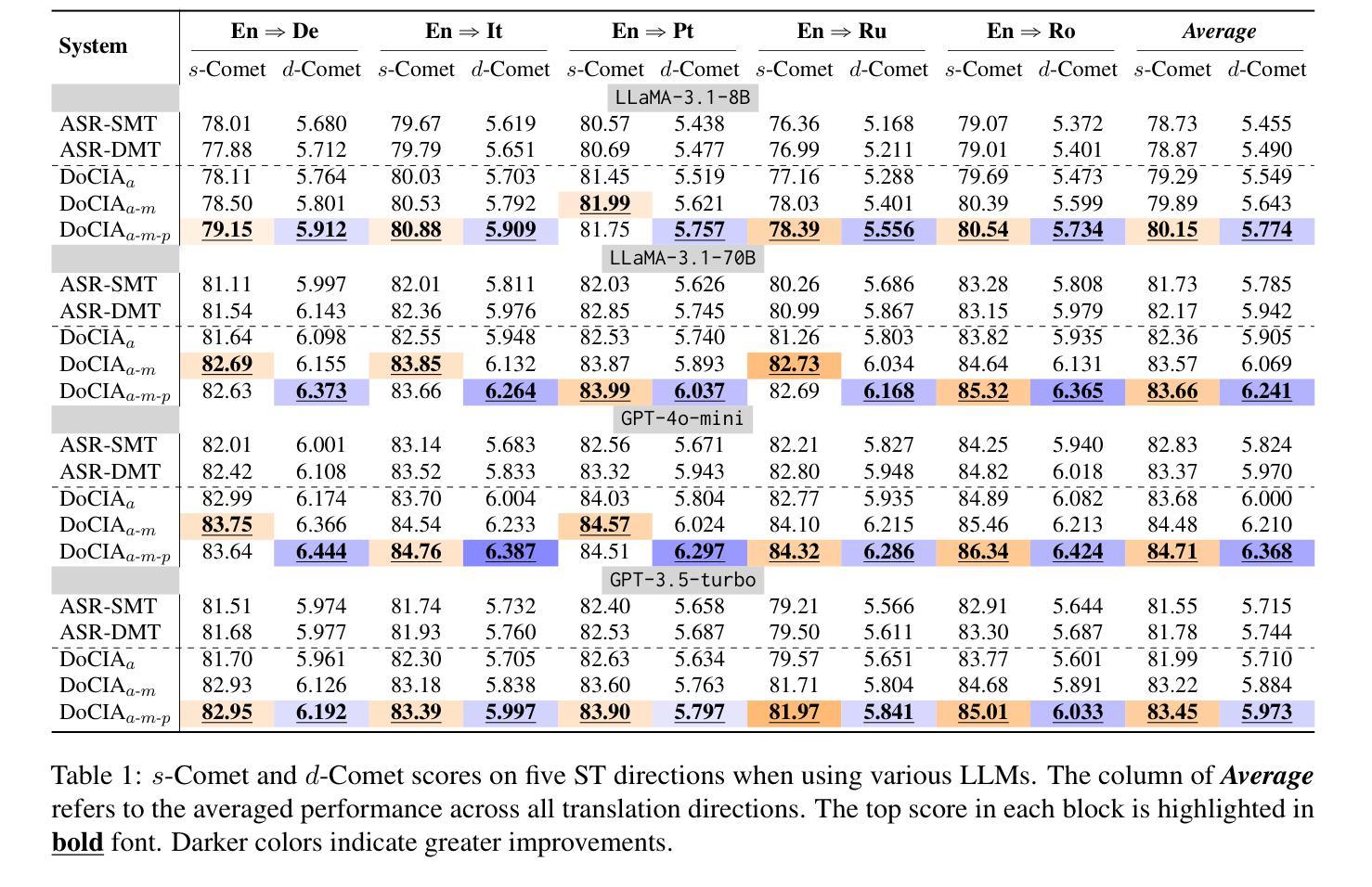
Document-level context is crucial for handling discourse challenges in text-to-text document-level machine translation (MT). Despite the increased discourse challenges introduced by noise from automatic speech recognition (ASR), the integration of document-level context in speech translation (ST) remains insufficiently explored. In this paper, we develop DoCIA, an online framework that enhances ST performance by incorporating document-level context. DoCIA decomposes the ST pipeline into four stages. Document-level context is integrated into the ASR refinement, MT, and MT refinement stages through auxiliary LLM (large language model)-based modules. Furthermore, DoCIA leverages document-level information in a multi-level manner while minimizing computational overhead. Additionally, a simple yet effective determination mechanism is introduced to prevent hallucinations from excessive refinement, ensuring the reliability of the final results. Experimental results show that DoCIA significantly outperforms traditional ST baselines in both sentence and discourse metrics across four LLMs, demonstrating its effectiveness in improving ST performance.
文本到文本的文档级机器翻译(MT)在处理语篇挑战时,文档级上下文是极其重要的。尽管自动语音识别(ASR)产生的噪声增加了语境挑战,但在语音翻译(ST)中整合文档级上下文的研究仍然不足。在本文中,我们开发了一个在线框架DoCIA,通过融入文档级上下文来提升ST性能。DoCIA将ST流程分解为四个阶段。通过基于大型语言模型(LLM)的辅助模块,文档级上下文被整合到ASR优化、机器翻译和机器翻译优化阶段。此外,DoCIA以多层次的方式利用文档级信息,同时尽量减少计算开销。此外,还引入了一种简单有效的判定机制,以防止过度优化导致的幻觉,确保最终结果的可靠性。实验结果表明,在四个大型语言模型上,无论是在句子还是篇章指标上,DoCIA都显著优于传统的ST基线,证明了其在提高ST性能方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
在文本到文本的文档级机器翻译(MT)中,处理话语挑战时文档级别的上下文至关重要。尽管自动语音识别(ASR)产生的噪声增加了话语挑战,但在语音翻译(ST)中整合文档级上下文的研究仍然不足。本文开发了DoCIA在线框架,通过融入文档级上下文来提升ST性能。DoCIA将ST管道分解为四个阶段。通过辅助大型语言模型(LLM)模块,DoCIA将文档级上下文整合到ASR优化、机器翻译和机器翻译优化阶段。此外,DoCIA以多层次方式利用文档级信息,同时尽量减少计算开销。还引入了一种简单有效的判定机制,防止过度优化导致的虚构现象,确保最终结果的可靠性。实验结果表明,DoCIA在四个大型语言模型上显著优于传统ST基线,在句子和篇章指标上均表现出提高ST性能的有效性。
关键见解
- 文档级上下文在文本到文本的文档级机器翻译中处理话语挑战至关重要。
- DoCIA框架通过融入文档级上下文提升语音翻译性能。
- DoCIA将语音翻译管道分解为四个阶段,并在其中融入文档级上下文。
- DoCIA利用多层次文档信息,同时减少计算开销。
- DoCIA采用有效判定机制,防止过度优化导致的虚构现象。
- 实验结果显示DoCIA显著优于传统语音翻译基线。
点此查看论文截图

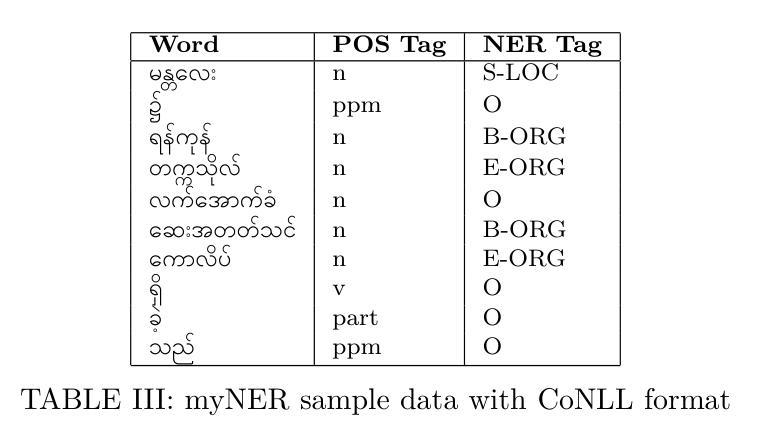
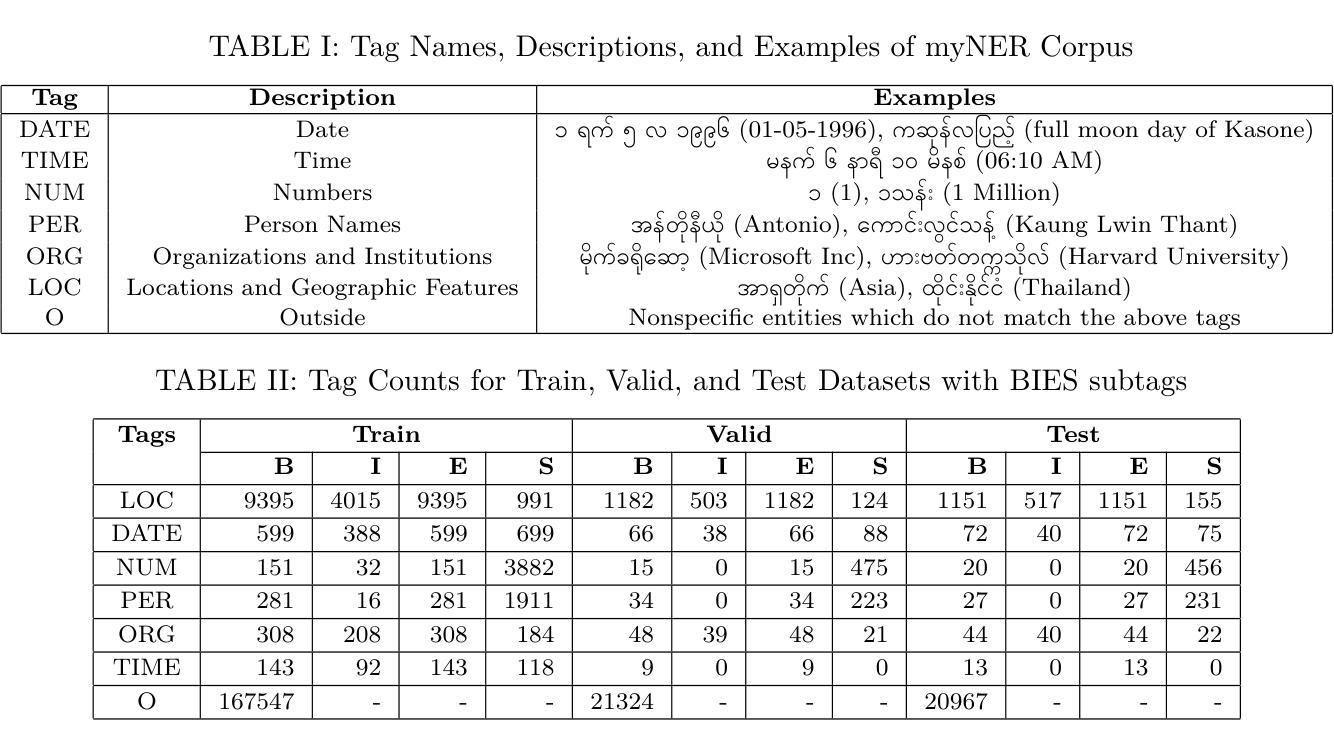
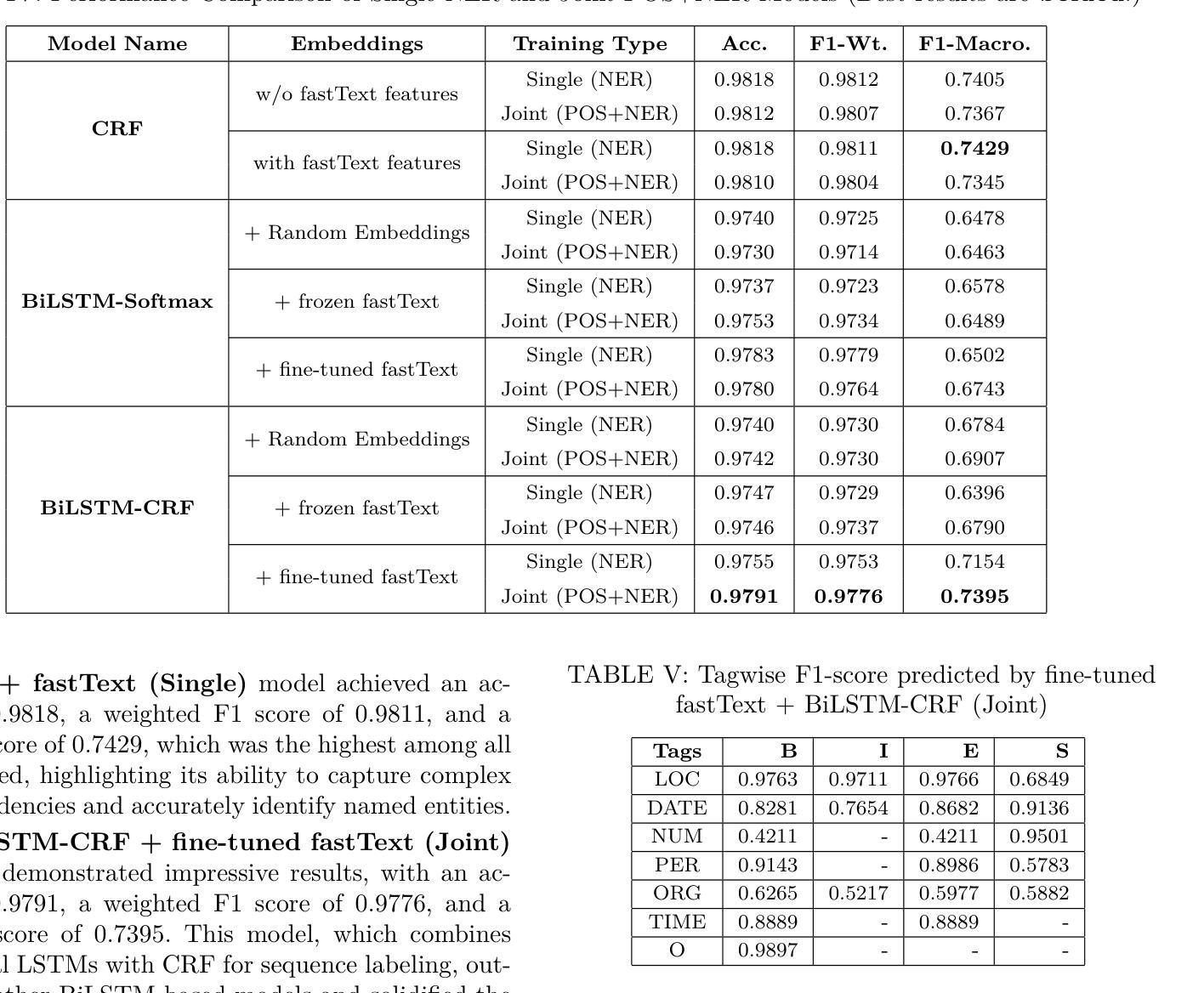
myNER: Contextualized Burmese Named Entity Recognition with Bidirectional LSTM and fastText Embeddings via Joint Training with POS Tagging
Authors:Kaung Lwin Thant, Kwankamol Nongpong, Ye Kyaw Thu, Thura Aung, Khaing Hsu Wai, Thazin Myint Oo
Named Entity Recognition (NER) involves identifying and categorizing named entities within textual data. Despite its significance, NER research has often overlooked low-resource languages like Myanmar (Burmese), primarily due to the lack of publicly available annotated datasets. To address this, we introduce myNER, a novel word-level NER corpus featuring a 7-tag annotation scheme, enriched with Part-of-Speech (POS) tagging to provide additional syntactic information. Alongside the corpus, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation of NER models, including Conditional Random Fields (CRF), Bidirectional LSTM (BiLSTM)-CRF, and their combinations with fastText embeddings in different settings. Our experiments reveal the effectiveness of contextualized word embeddings and the impact of joint training with POS tagging, demonstrating significant performance improvements across models. The traditional CRF joint-task model with fastText embeddings as a feature achieved the best result, with a 0.9818 accuracy and 0.9811 weighted F1 score with 0.7429 macro F1 score. BiLSTM-CRF with fine-tuned fastText embeddings gets the best result of 0.9791 accuracy and 0.9776 weighted F1 score with 0.7395 macro F1 score.
命名实体识别(NER)涉及识别和分类文本数据中的命名实体。尽管NER具有重要意义,但由于缺乏公开可用的注释数据集,缅甸语(伯缅语)等低资源语言的研究常被忽视。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了myNER,这是一个新型的词级NER语料库,采用7标签注释方案,并辅以词性标注,以提供额外的句法信息。除了语料库外,我们还对NER模型进行了全面评估,包括条件随机场(CRF)、双向LSTM(BiLSTM)-CRF以及在不同设置下与fastText嵌入的组合。我们的实验表明,上下文词嵌入的有效性以及联合词性标注训练的影响,展示了模型性能的显著提高。使用fastText嵌入作为特征的CRF多任务模型表现最佳,准确度为0.9818,加权F1分数为0.9811,宏F1分数为0.7429。使用微调fastText嵌入的BiLSTM-CRF模型在准确度上达到0.9791,加权F1分数为0.9776,宏F1分数为0.7395。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 2 figures, 5 tables, to be published in the proceedings of IEEE ICCI-2025
Summary
针对缅甸语(Burmese)等低资源语言命名实体识别(NER)研究缺乏公开标注数据集的问题,本文引入了myNER,一个新型的词级NER语料库,采用7标签标注方案,并辅以词性标注(POS)以提供额外的句法信息。文章还全面评估了条件随机场(CRF)、双向LSTM-CRF等NER模型,以及它们与fastText嵌入的不同组合。实验表明,上下文词嵌入的联合训练对模型性能有显著提升。其中,使用fastText嵌入作为特征的CRF联合任务模型表现最佳,准确率为0.9818,加权F1得分为0.9811,宏观F1得分为0.7429。
Key Takeaways
- NER研究通常忽视低资源语言如缅甸语,缺乏公开标注数据集是主要问题。
- 引入myNER语料库,包含词级7标签标注方案和丰富的词性标注信息。
- 评估了CRF、BiLSTM-CRF等NER模型及其与fastText嵌入的结合。
- 实验显示上下文词嵌入的联合训练能显著提高模型性能。
- CRF模型结合fastText嵌入表现最佳,准确率和加权F1得分较高。
- BiLSTM-CRF与fine-tuned fastText嵌入结合也表现出良好的性能。
点此查看论文截图


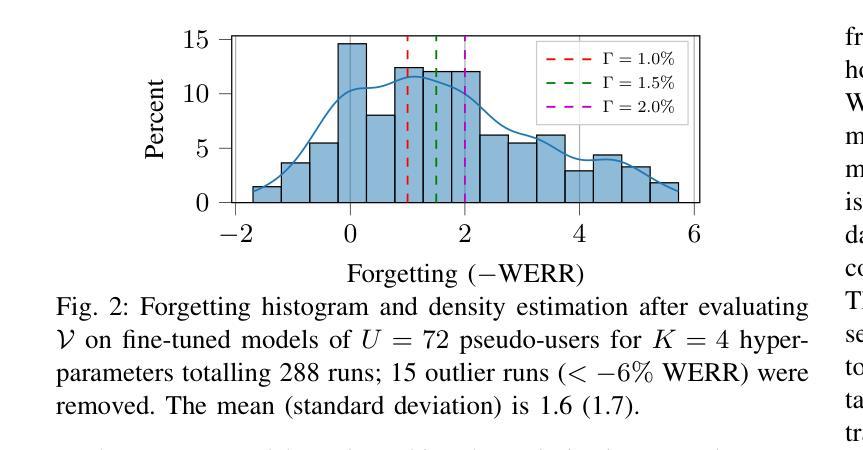
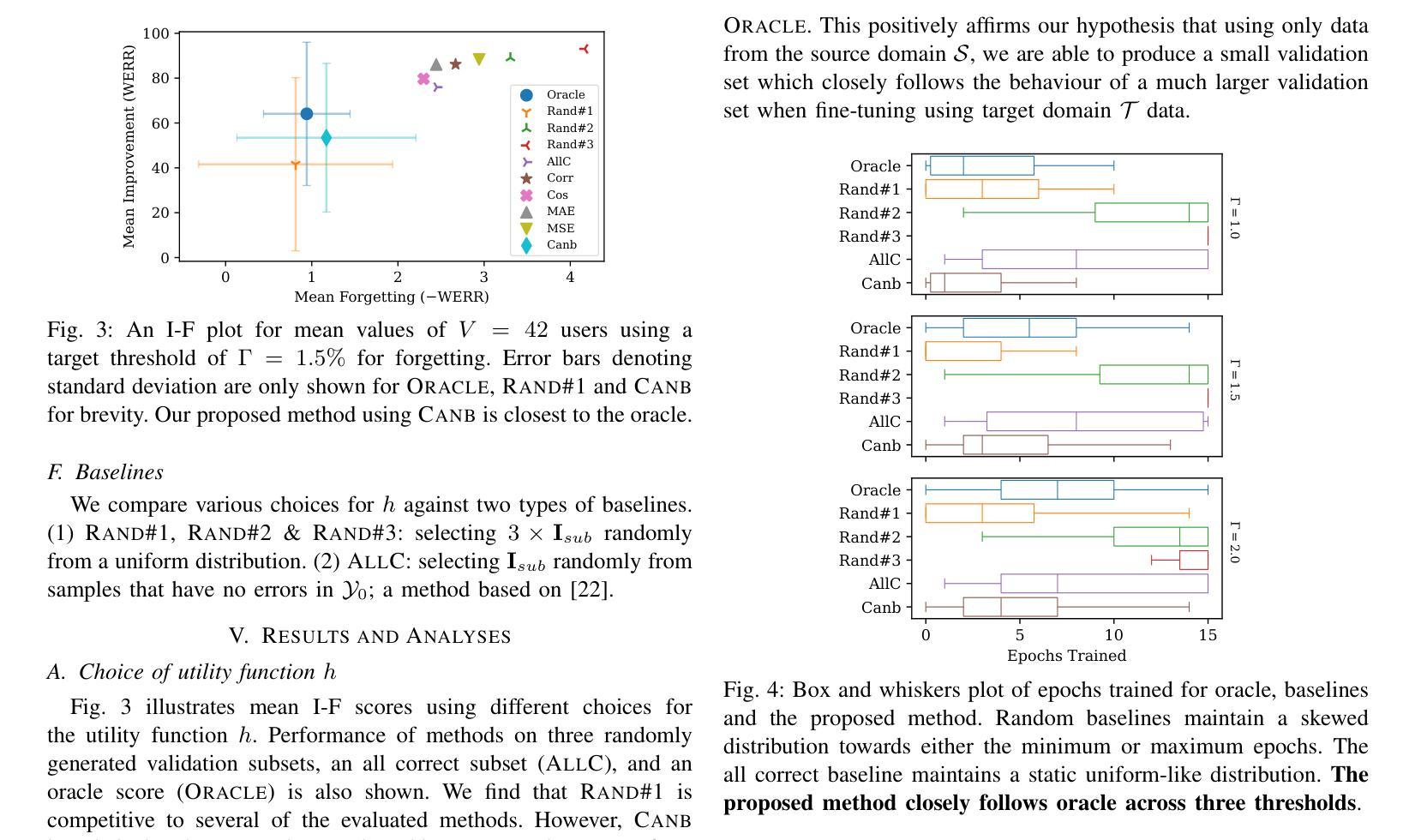
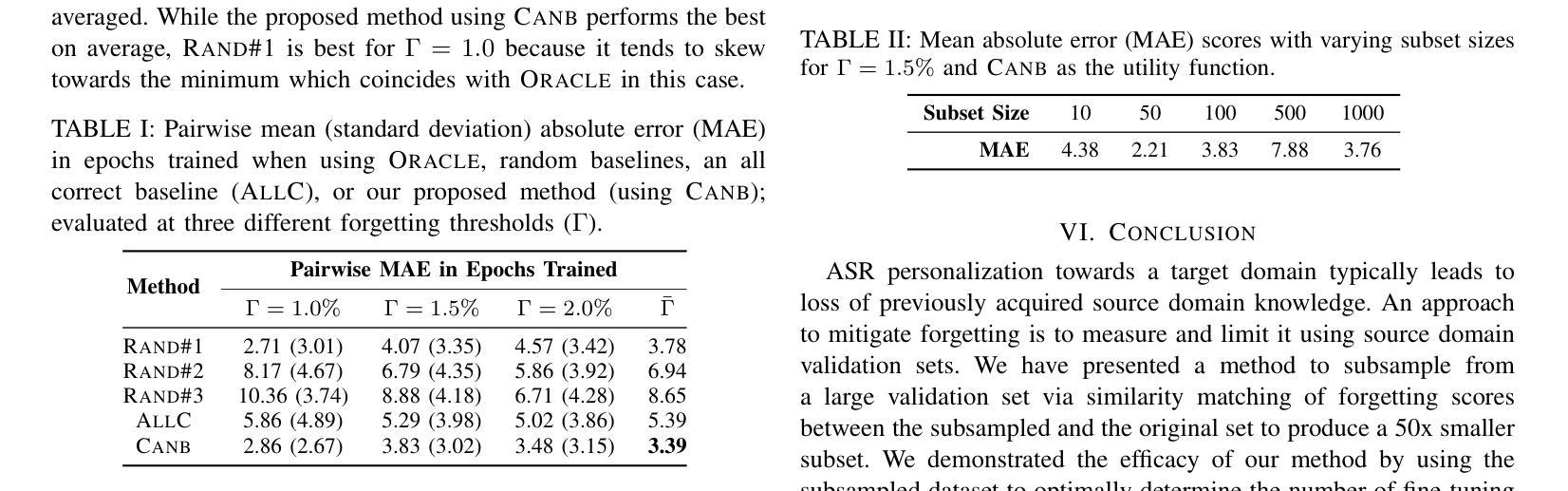
ValSub: Subsampling Validation Data to Mitigate Forgetting during ASR Personalization
Authors:Haaris Mehmood, Karthikeyan Saravanan, Pablo Peso Parada, David Tuckey, Mete Ozay, Gil Ho Lee, Jungin Lee, Seokyeong Jung
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) is widely used within consumer devices such as mobile phones. Recently, personalization or on-device model fine-tuning has shown that adaptation of ASR models towards target user speech improves their performance over rare words or accented speech. Despite these gains, fine-tuning on user data (target domain) risks the personalized model to forget knowledge about its original training distribution (source domain) i.e. catastrophic forgetting, leading to subpar general ASR performance. A simple and efficient approach to combat catastrophic forgetting is to measure forgetting via a validation set that represents the source domain distribution. However, such validation sets are large and impractical for mobile devices. Towards this, we propose a novel method to subsample a substantially large validation set into a smaller one while maintaining the ability to estimate forgetting. We demonstrate the efficacy of such a dataset in mitigating forgetting by utilizing it to dynamically determine the number of ideal fine-tuning epochs. When measuring the deviations in per user fine-tuning epochs against a 50x larger validation set (oracle), our method achieves a lower mean-absolute-error (3.39) compared to randomly selected subsets of the same size (3.78-8.65). Unlike random baselines, our method consistently tracks the oracle’s behaviour across three different forgetting thresholds.
自动语音识别(ASR)在移动电话等消费设备中得到了广泛应用。最近,个性化或设备上的模型微调显示,朝着目标用户语音调整ASR模型可以提高其在罕见词汇或带口音语音方面的性能。尽管取得了这些进展,但在用户数据(目标域)上进行微调会导致个性化模型忘记其原始训练分布(源域)的知识,即灾难性遗忘,从而导致一般的ASR性能下降。一种简单而有效的对抗灾难性遗忘的方法是,通过代表源域分布的验证集来衡量遗忘。然而,这样的验证集对于移动设备来说太大了,不实用。针对这一问题,我们提出了一种新方法,将大量验证集子采样成较小的集合,同时保持评估遗忘的能力。我们通过在动态确定理想微调周期数时利用此类数据集来证明其有效性。在衡量用户微调周期相对于一个更大(50倍)的验证集(标准集)的偏差时,我们的方法取得了更低的平均绝对误差(3.39),而随机选择的相同大小的子集则为(3.78-8.65)。不同于随机基线方法,我们的方法能够在三个不同的遗忘阈值中始终追踪标准集的行为。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文探讨了自动语音识别(ASR)在消费设备如手机中的广泛应用。个人化或设备上的模型微调已显示,针对目标用户语音调整ASR模型能够改善其在罕见词汇或带口音语音方面的性能。然而,这种微调会导致模型忘记其原始训练分布的知识,从而导致灾难性遗忘和一般ASR性能下降。本文提出了一种简单高效的方法,通过测量代表源域分布的验证集的遗忘来对抗灾难性遗忘。然而,这样的验证集对于移动设备而言太大且不切实际。因此,我们提出了一种新方法,将大大扩展的验证集子采样成较小的集合,同时保持估计遗忘的能力。通过利用该数据集动态确定理想的微调周期,我们证明了其在缓解遗忘方面的有效性。在测量针对50倍大的验证集(oracle)的用户微调周期偏差时,我们的方法实现了更低的平均绝对误差。
Key Takeaways
- ASR模型在个人化或设备上的模型微调后可以更好地识别罕见词汇或带口音的语音。
- 灾难性遗忘问题会导致ASR模型的性能下降。这指的是模型在经历微调后可能失去其原始训练分布的知识。
- 一种解决灾难性遗忘的方法是使用代表源域分布的验证集来测量模型的遗忘情况。然而,这种方法对于移动设备而言不实用。
- 提出了一种新的方法来减少验证集的大小并有效地估计模型的遗忘情况。通过这种方法可以有效估计遗忘,且能够通过动态确定最佳的微调周期来提升模型性能。
点此查看论文截图