⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-09 更新
DA2Diff: Exploring Degradation-aware Adaptive Diffusion Priors for All-in-One Weather Restoration
Authors:Jiamei Xiong, Xuefeng Yan, Yongzhen Wang, Wei Zhao, Xiao-Ping Zhang, Mingqiang Wei
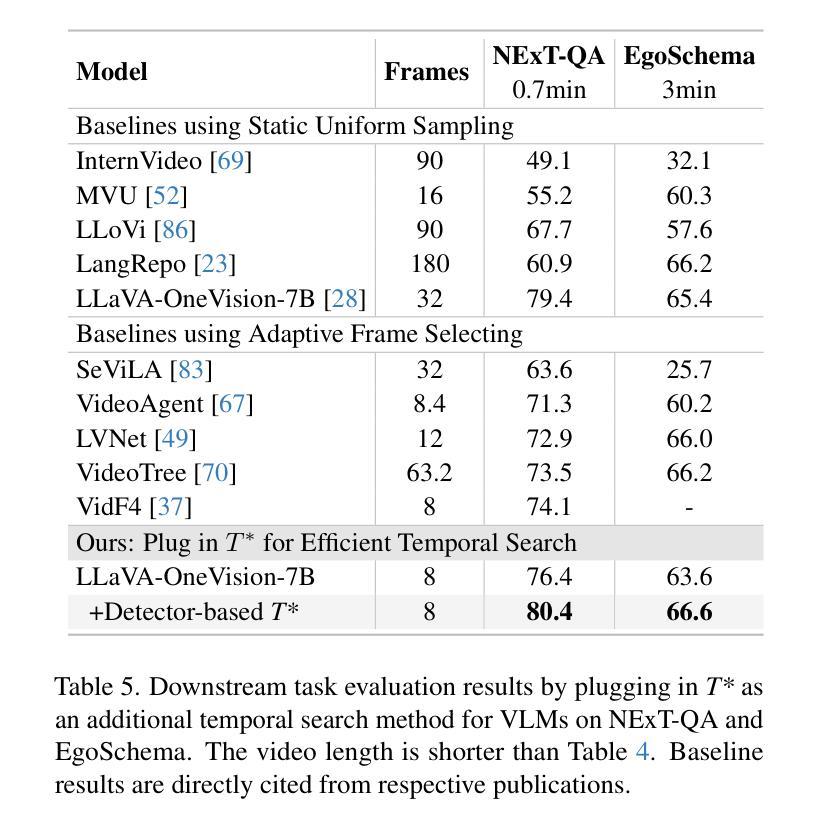
Image restoration under adverse weather conditions is a critical task for many vision-based applications. Recent all-in-one frameworks that handle multiple weather degradations within a unified model have shown potential. However, the diversity of degradation patterns across different weather conditions, as well as the complex and varied nature of real-world degradations, pose significant challenges for multiple weather removal. To address these challenges, we propose an innovative diffusion paradigm with degradation-aware adaptive priors for all-in-one weather restoration, termed DA2Diff. It is a new exploration that applies CLIP to perceive degradation-aware properties for better multi-weather restoration. Specifically, we deploy a set of learnable prompts to capture degradation-aware representations by the prompt-image similarity constraints in the CLIP space. By aligning the snowy/hazy/rainy images with snow/haze/rain prompts, each prompt contributes to different weather degradation characteristics. The learned prompts are then integrated into the diffusion model via the designed weather specific prompt guidance module, making it possible to restore multiple weather types. To further improve the adaptiveness to complex weather degradations, we propose a dynamic expert selection modulator that employs a dynamic weather-aware router to flexibly dispatch varying numbers of restoration experts for each weather-distorted image, allowing the diffusion model to restore diverse degradations adaptively. Experimental results substantiate the favorable performance of DA2Diff over state-of-the-arts in quantitative and qualitative evaluation. Source code will be available after acceptance.
恶劣天气条件下的图像恢复是许多基于视觉的应用中的关键任务。最近的全能框架能够在统一模型中处理多种天气退化,已显示出其潜力。然而,不同天气条件下退化模式的多样性以及真实世界退化的复杂性和多变性质,给多种天气去除带来了重大挑战。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种创新的扩散范式,带有退化感知自适应先验的全能天气恢复,称为DA2Diff。这是一种新的探索,应用CLIP来感知退化感知属性以更好地进行多天气恢复。具体来说,我们部署了一组可学习的提示,通过CLIP空间中的提示图像相似性约束来捕获退化感知表示。通过对雪/雾/雨图像与雪/雾/雨提示进行对齐,每个提示都有助于呈现不同的天气退化特征。然后将学到的提示集成到扩散模型中,通过设计的天气特定提示指导模块,使得恢复多种天气类型成为可能。为了进一步改进对复杂天气退化的适应性,我们提出了一种动态专家选择调制器,它采用动态天气感知路由器,灵活地为每种天气失真图像调度不同数量的恢复专家,使扩散模型能够自适应地恢复各种退化。实验结果证实,DA2Diff在定量和定性评估上的性能优于最新技术。源代码将在接受后提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
天气恶劣状况下的图像修复是许多视觉应用中的关键任务。近期统一框架在处理多种天气退化方面展现出潜力,但仍面临不同天气条件下退化模式的多样性和真实世界退化的复杂性的挑战。为此,我们提出了一个名为DA2Diff的创新扩散范式,它具备感知退化的自适应先验。该范式探索了将CLIP应用于感知退化感知属性以进行更好的多天气修复。通过部署一组可学习的提示来捕获退化感知表示,这些提示通过CLIP空间中的提示图像相似性约束来实现。实验结果表明,DA2Diff在定量和定性评估上的表现优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 图像修复在恶劣天气下是视觉应用的关键任务。
- 现有统一框架在处理多种天气退化时面临挑战,如退化模式的多样性和真实世界退化的复杂性。
- DA2Diff范式通过引入感知退化的自适应先验来解决这些挑战。
- DA2Diff利用CLIP技术来感知退化属性,实现更好的多天气修复。
- 通过部署可学习提示来捕获退化感知表示,这些提示通过提示图像相似性约束在CLIP空间中实现。
- 动态专家选择调制器通过动态天气感知路由器灵活调度不同数量的修复专家,使扩散模型能够自适应地修复各种退化。
点此查看论文截图

Performance Analysis of Deep Learning Models for Femur Segmentation in MRI Scan
Authors:Mengyuan Liu, Yixiao Chen, Anning Tian, Xinmeng Wu, Mozhi Shen, Tianchou Gong, Jeongkyu Lee
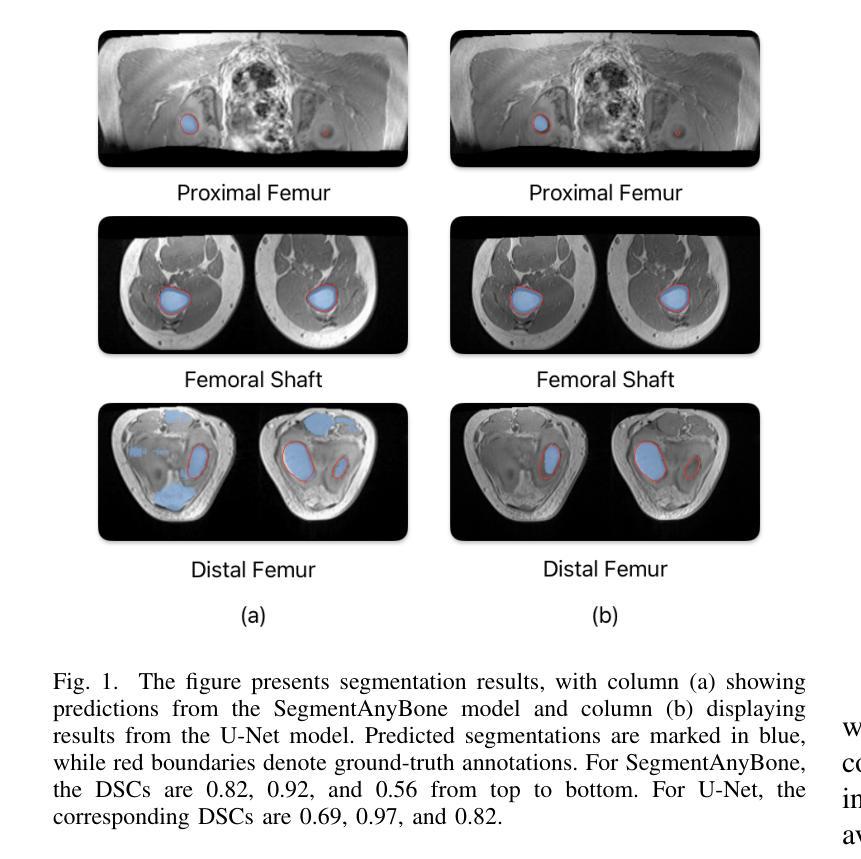
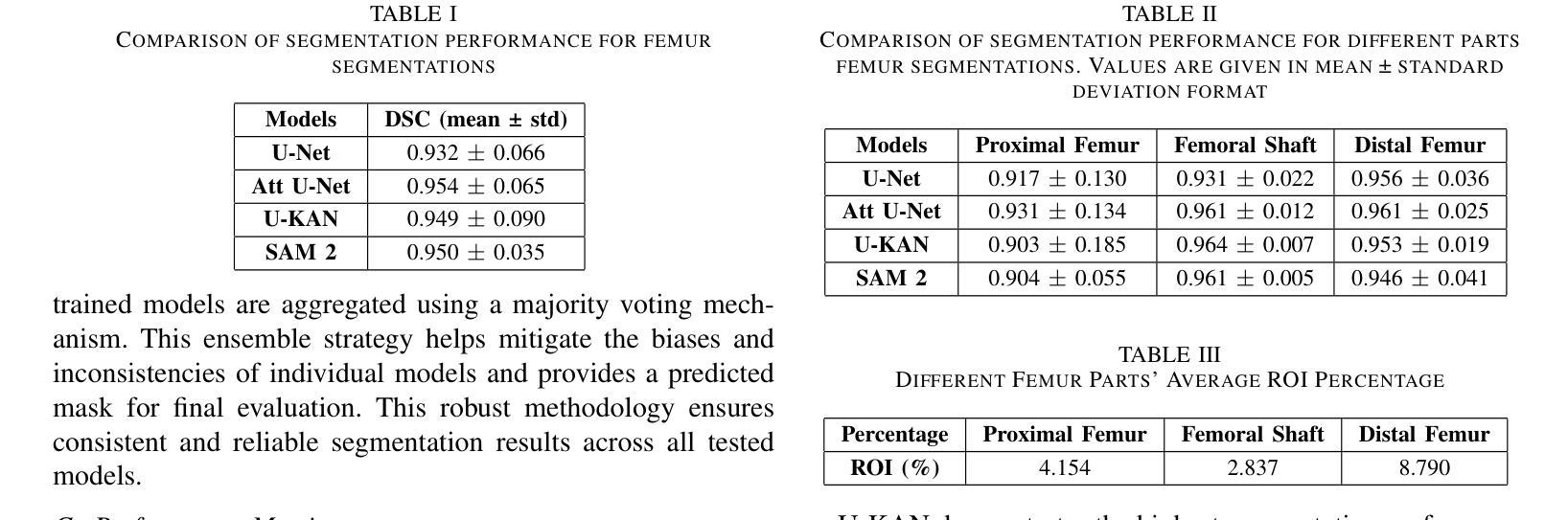
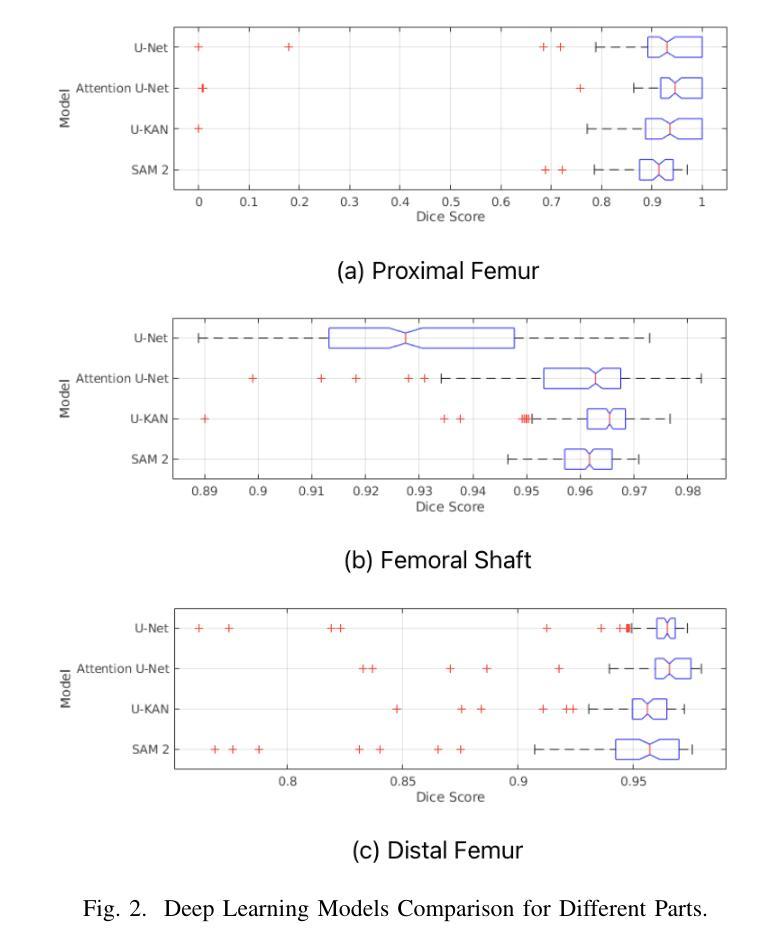
Convolutional neural networks like U-Net excel in medical image segmentation, while attention mechanisms and KAN enhance feature extraction. Meta’s SAM 2 uses Vision Transformers for prompt-based segmentation without fine-tuning. However, biases in these models impact generalization with limited data. In this study, we systematically evaluate and compare the performance of three CNN-based models, i.e., U-Net, Attention U-Net, and U-KAN, and one transformer-based model, i.e., SAM 2 for segmenting femur bone structures in MRI scan. The dataset comprises 11,164 MRI scans with detailed annotations of femoral regions. Performance is assessed using the Dice Similarity Coefficient, which ranges from 0.932 to 0.954. Attention U-Net achieves the highest overall scores, while U-KAN demonstrated superior performance in anatomical regions with a smaller region of interest, leveraging its enhanced learning capacity to improve segmentation accuracy.
卷积神经网络(如U-Net)在医学图像分割方面表现出色,而注意力机制和KAN则增强了特征提取。Meta的SAM 2使用Vision Transformers进行基于提示的分割,无需微调。然而,这些模型中的偏见影响在有限数据下的泛化能力。在这项研究中,我们系统地评估和比较了三种基于CNN的模型(即U-Net、Attention U-Net和U-KAN)和一种基于变压器的模型(即SAM 2)在MRI扫描中分割股骨结构性能的表现。数据集包含11,164份MRI扫描,详细标注了股骨区域。性能评估采用Dice相似系数,范围从0.932到0.954。Attention U-Net获得最高总体得分,而U-KAN在较小感兴趣区域的解剖结构中表现出卓越性能,利用其增强的学习能力提高分割精度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了卷积神经网络(如U-Net、Attention U-Net和U-KAN)与基于Vision Transformer的SAM 2模型在MRI扫描中的股骨结构分割性能。通过对大量MRI扫描数据集的实验评估,发现Attention U-Net总体表现最佳,特别是在较小感兴趣区域中,U-KAN表现出较高的分割准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 卷积神经网络(CNN)如U-Net在医学图像分割中表现优异。
- 注意力机制和KAN增强特征提取能力。
- Meta的SAM 2使用Vision Transformer进行基于提示的分割,无需微调。
- 模型中的偏见影响有限数据的泛化能力。
- 实验中评估了U-Net、Attention U-Net、U-KAN和SAM 2四个模型的性能。
- Attention U-Net在总体评估中表现最佳。
点此查看论文截图

Filter Images First, Generate Instructions Later: Pre-Instruction Data Selection for Visual Instruction Tuning
Authors:Bardia Safaei, Faizan Siddiqui, Jiacong Xu, Vishal M. Patel, Shao-Yuan Lo
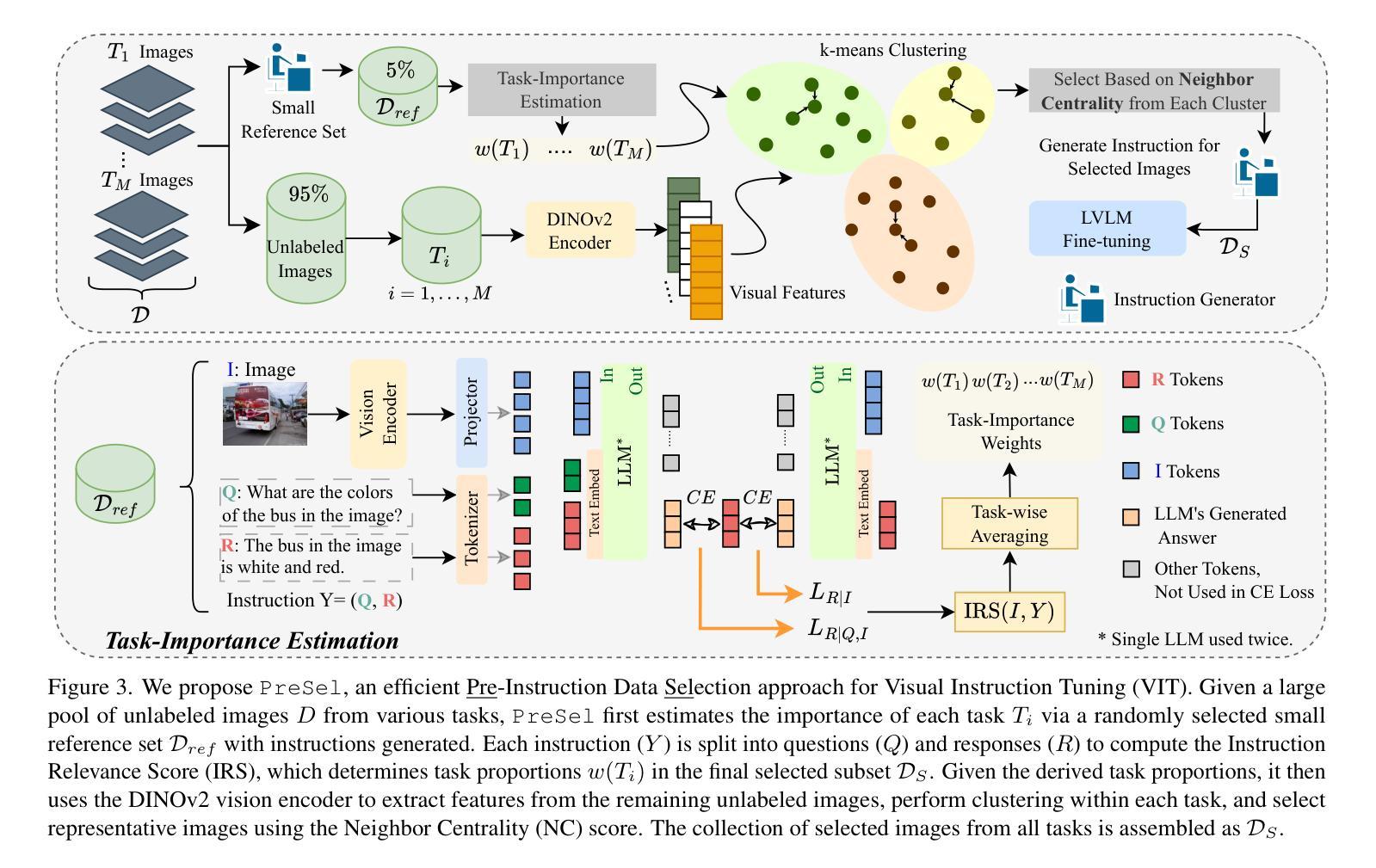
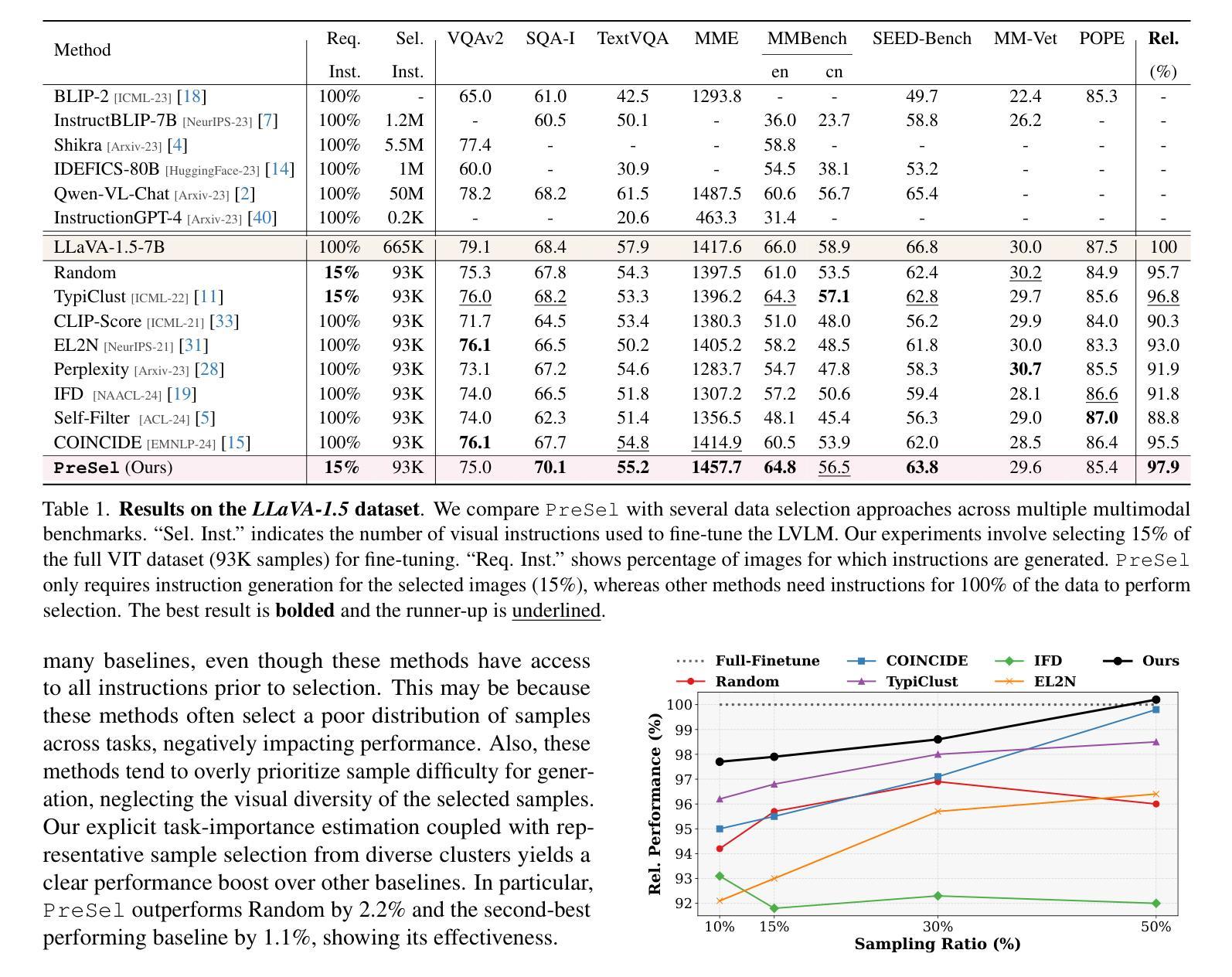
Visual instruction tuning (VIT) for large vision-language models (LVLMs) requires training on expansive datasets of image-instruction pairs, which can be costly. Recent efforts in VIT data selection aim to select a small subset of high-quality image-instruction pairs, reducing VIT runtime while maintaining performance comparable to full-scale training. However, a major challenge often overlooked is that generating instructions from unlabeled images for VIT is highly expensive. Most existing VIT datasets rely heavily on human annotations or paid services like the GPT API, which limits users with constrained resources from creating VIT datasets for custom applications. To address this, we introduce Pre-Instruction Data Selection (PreSel), a more practical data selection paradigm that directly selects the most beneficial unlabeled images and generates instructions only for the selected images. PreSel first estimates the relative importance of each vision task within VIT datasets to derive task-wise sampling budgets. It then clusters image features within each task, selecting the most representative images with the budget. This approach reduces computational overhead for both instruction generation during VIT data formation and LVLM fine-tuning. By generating instructions for only 15% of the images, PreSel achieves performance comparable to full-data VIT on the LLaVA-1.5 and Vision-Flan datasets. The link to our project page: https://bardisafa.github.io/PreSel
视觉指令调整(VIT)针对大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)需要在大量的图像指令对数据集上进行训练,这可能会很昂贵。最近在VIT数据选择方面的努力旨在选择一小部分高质量的图像指令对,在减少VIT运行时间的同时保持与全规模训练相当的性能。然而,经常被忽视的一个主要挑战是,从无标签图像中生成VIT指令的成本非常高。大多数现有的VIT数据集严重依赖于人工注释或如GPT API等付费服务,这限制了资源有限的用户创建用于自定义应用程序的VIT数据集。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了预指令数据选择(PreSel),这是一种更实用的数据选择范式,它直接选择最有益的无标签图像,只为所选图像生成指令。PreSel首先估计VIT数据集中每个视觉任务的相对重要性,以得出任务级采样预算。然后,它在每个任务内对图像特征进行聚类,选择最具代表性的图像来使用预算。这种方法减少了VIT数据形成和LVLM微调过程中指令生成的计算开销。通过只为15%的图像生成指令,PreSel在LLaVA-1.5和Vision-Flan数据集上实现了与全数据VIT相当的性能。我们的项目页面链接为:https://bardisafa.github.io/PreSel
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CVPR 2025 (Highlight)
Summary
本文介绍了针对大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)的视觉指令调整(VIT)面临的挑战,尤其是高成本的数据集需求。为应对这一问题,研究了一种更为实用的数据选择模式——Pre-Instruction Data Selection(PreSel)。PreSel能够直接选取最有益的无标签图像,并为选中的图像生成指令。它通过估计每个视觉任务的重要性来推导任务级别的采样预算,并在每个任务内对图像特征进行聚类,选择最具代表性的图像。这种策略减少了在构建VIT数据集和微调LVLM期间的计算开销。通过对仅15%的图像生成指令,PreSel在LLaVA-1.5和Vision-Flan数据集上的性能与全数据VIT相当。
Key Takeaways
- PreSel解决了大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)的视觉指令调整(VIT)中数据选择的问题,尤其关注从无标签图像生成指令的高成本问题。
- PreSel通过估计每个视觉任务的重要性来推导任务级别的采样预算,以实现更高效的数据选择。
- PreSel采用聚类方法,选择每个任务内最具代表性的图像,降低计算开销。
- PreSel仅对部分图像生成指令,即可达到与全数据VIT相当的性能。
- PreSel方法显著减少了数据收集和处理的成本,使得更多用户能够在有限资源下创建自定义的VIT数据集。
- PreSel在LLaVA-1.5和Vision-Flan数据集上的实验结果表明其有效性。
点此查看论文截图


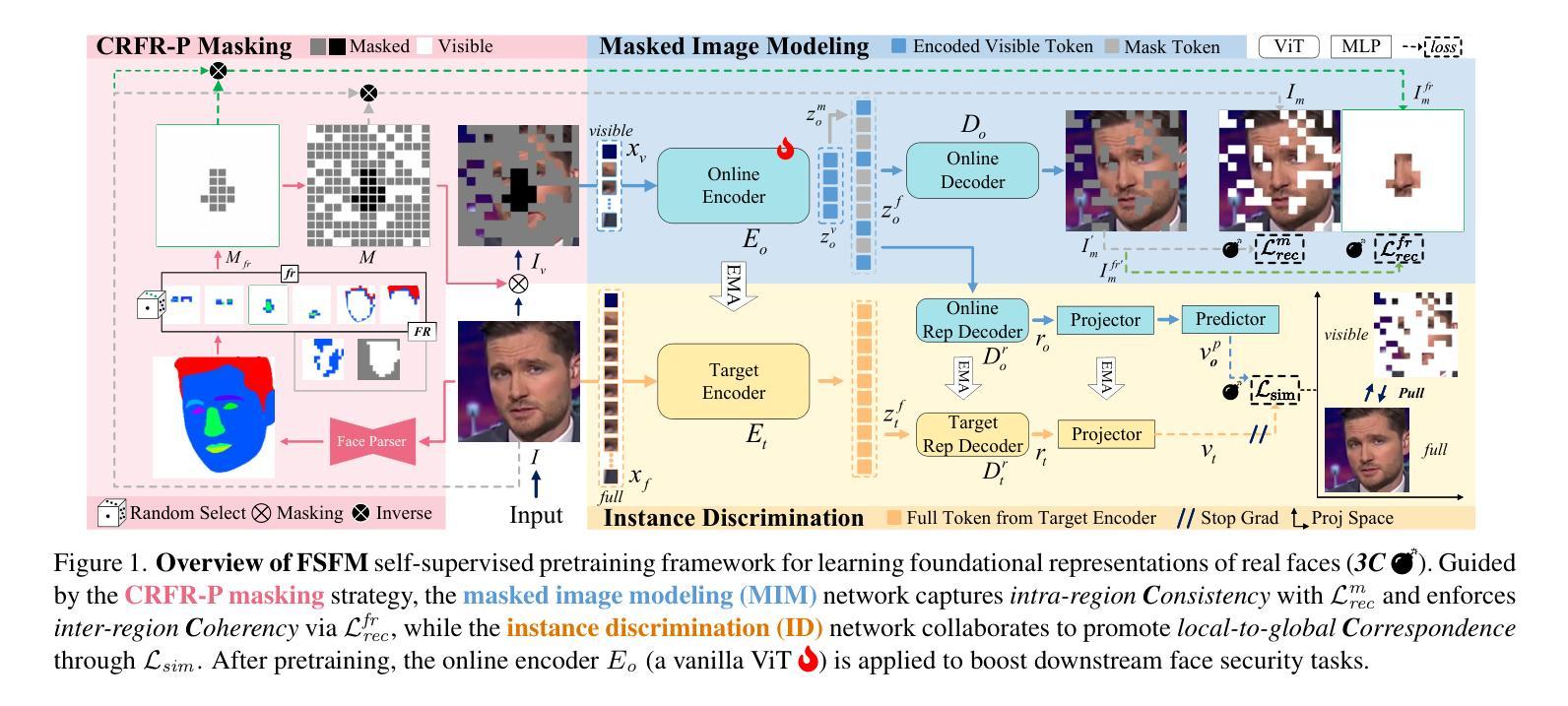
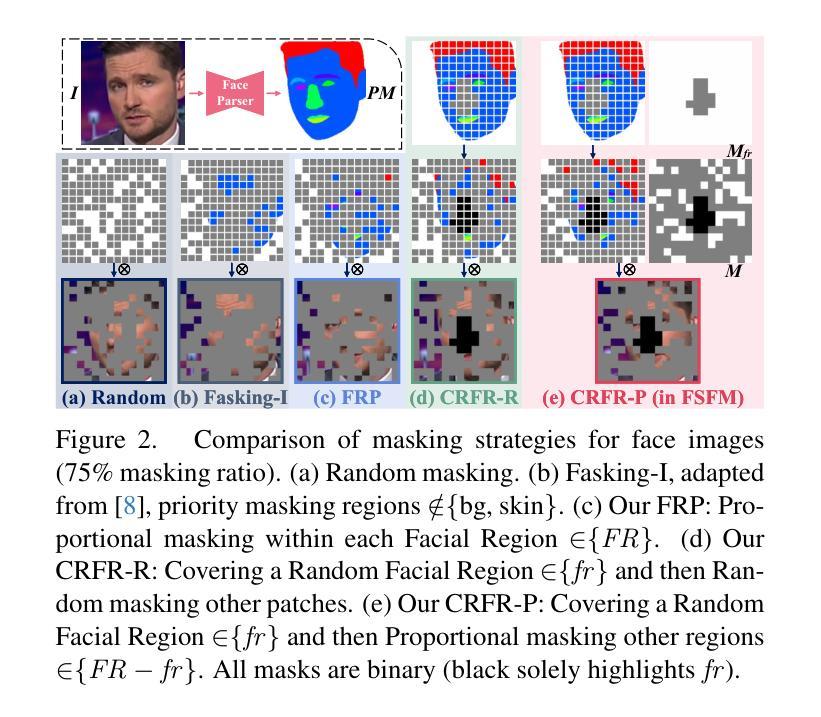
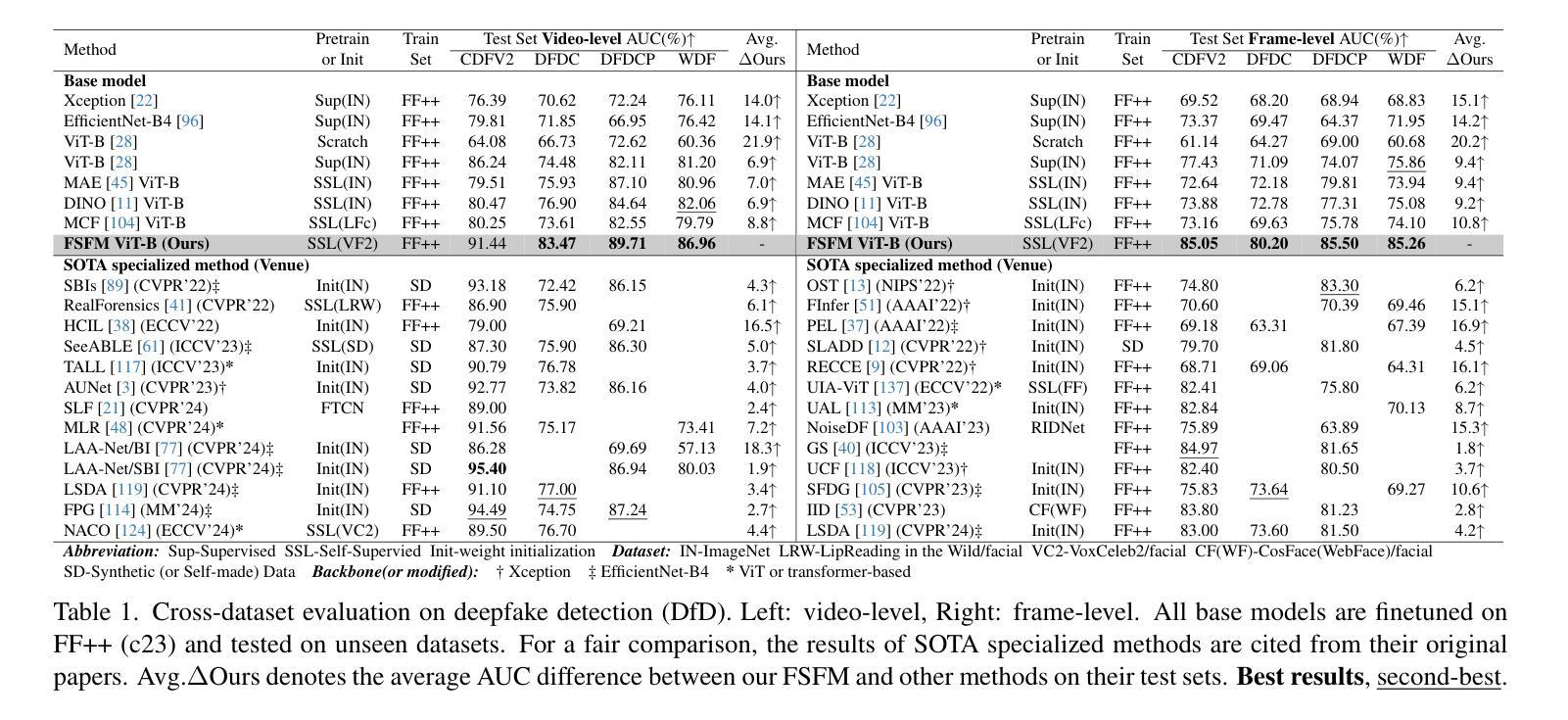
FSFM: A Generalizable Face Security Foundation Model via Self-Supervised Facial Representation Learning
Authors:Gaojian Wang, Feng Lin, Tong Wu, Zhenguang Liu, Zhongjie Ba, Kui Ren
This work asks: with abundant, unlabeled real faces, how to learn a robust and transferable facial representation that boosts various face security tasks with respect to generalization performance? We make the first attempt and propose a self-supervised pretraining framework to learn fundamental representations of real face images, FSFM, that leverages the synergy between masked image modeling (MIM) and instance discrimination (ID). We explore various facial masking strategies for MIM and present a simple yet powerful CRFR-P masking, which explicitly forces the model to capture meaningful intra-region consistency and challenging inter-region coherency. Furthermore, we devise the ID network that naturally couples with MIM to establish underlying local-to-global correspondence via tailored self-distillation. These three learning objectives, namely 3C, empower encoding both local features and global semantics of real faces. After pretraining, a vanilla ViT serves as a universal vision foundation model for downstream face security tasks: cross-dataset deepfake detection, cross-domain face anti-spoofing, and unseen diffusion facial forgery detection. Extensive experiments on 10 public datasets demonstrate that our model transfers better than supervised pretraining, visual and facial self-supervised learning arts, and even outperforms task-specialized SOTA methods.
本文提出了一个问题:在大量无标签的真实人脸情况下,如何学习一种稳健且可迁移的人脸表示,以提高关于泛化性能的各种人脸安全任务的效果?我们首次尝试并提出一种自监督预训练框架,用于学习真实人脸图像的基本表示,FSFM,该框架利用掩膜图像建模(MIM)和实例鉴别(ID)之间的协同作用。我们探索了MIM的各种面部掩膜策略,并提出了一种简单而强大的CRFR-P掩膜,它明确地迫使模型捕捉区域内有意义的一致性以及区域间的挑战性连贯性。此外,我们设计了一个与MIM自然结合的ID网络,通过定制的自蒸馏建立基本的局部到全局对应关系。这三个学习目标,即3C,使编码真实人脸的局部特征和全局语义成为可能。预训练后,一个简单的ViT作为通用视觉基础模型,可用于下游人脸安全任务:跨数据集深度伪造检测、跨域面部防伪、未见扩散面部伪造检测。在1t个公开数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的模型迁移效果优于监督预训练、视觉和面部自监督学习技术,甚至超越了任务专业化的SOTA方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 11 figures, project page: https://fsfm-3c.github.io
Summary
在大量的无标签真实人脸图像面前,如何学习一种稳健且具有迁移性的面部表示以提升各种面部安全任务的泛化性能?我们首次尝试并提出了一种自监督预训练框架FSFM,用于学习真实人脸图像的基本表示。该框架结合了掩膜图像建模(MIM)和实例鉴别(ID)的协同作用。我们探索了各种面部掩膜策略,并提出了一种简单而强大的CRFR-P掩膜,它明确地迫使模型捕捉区域内有意义的一致性以及区域间的连贯性。此外,我们还设计了与MIM自然结合的ID网络,通过定制的自我蒸馏建立局部到全局的基础对应。这三个学习目标,即3C,使模型能够编码真实人脸的局部特征和全局语义。预训练后,普通的ViT可作为下游面部安全任务的通用视觉基础模型,如跨数据集深度伪造检测、跨域面部防伪、未见扩散面部伪造检测等。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究关注在大量无标签真实人脸图像上,如何学习一种更稳健和可迁移的面部表示。
- 提出了一个自监督预训练框架FSFM,结合了掩膜图像建模(MIM)和实例鉴别(ID)。
- 介绍了CRFR-P掩膜策略,强调模型需要捕捉区域内外的连贯性。
- 设计了与MIM结合的ID网络,通过自我蒸馏建立局部到全局的对应。
- 三个学习目标(3C)使模型能够编码真实人脸的局部和全局特征。
- 预训练模型适用于多种面部安全任务,包括跨数据集深度伪造检测、跨域面部防伪等。
点此查看论文截图


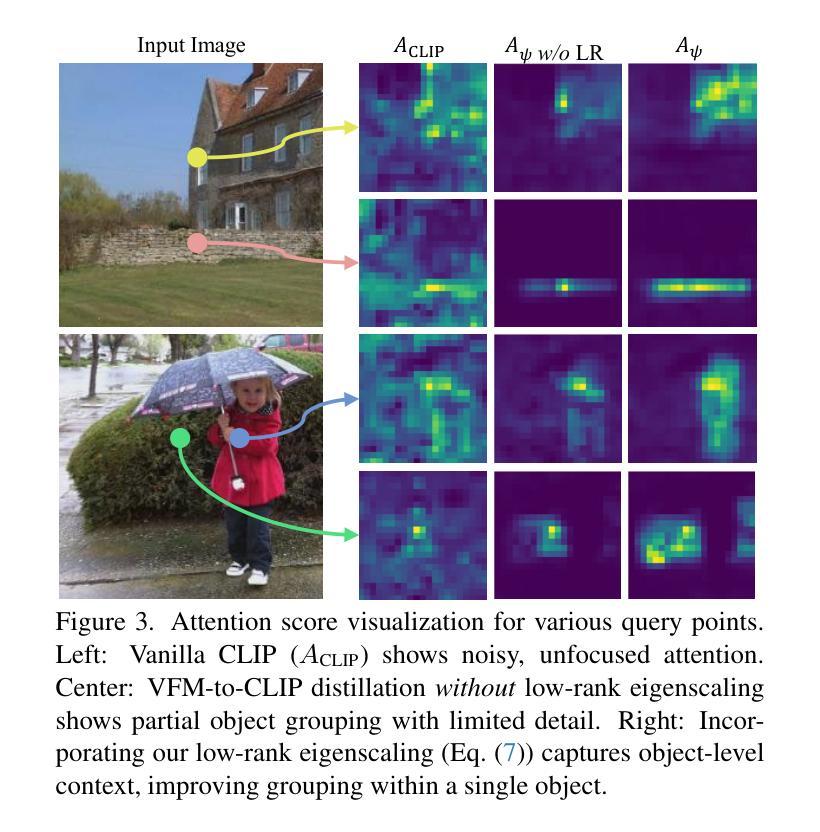
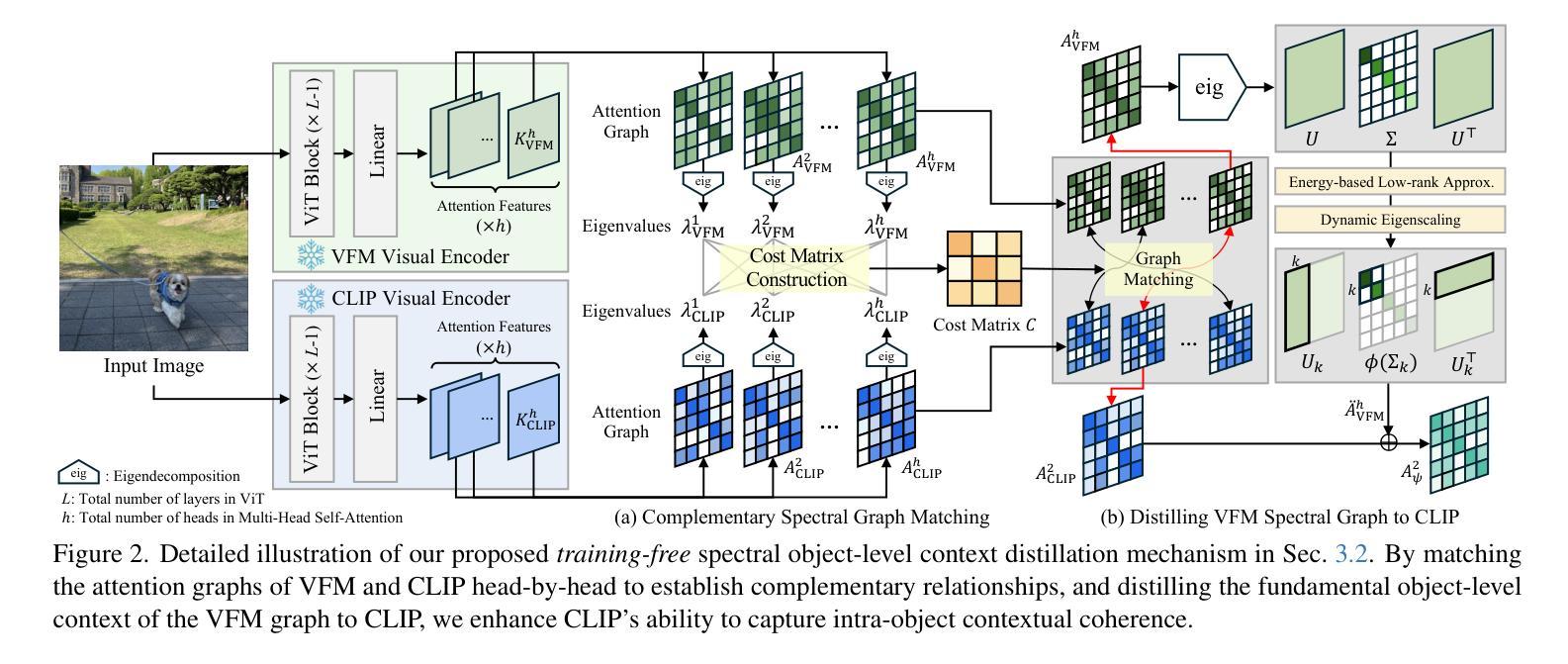
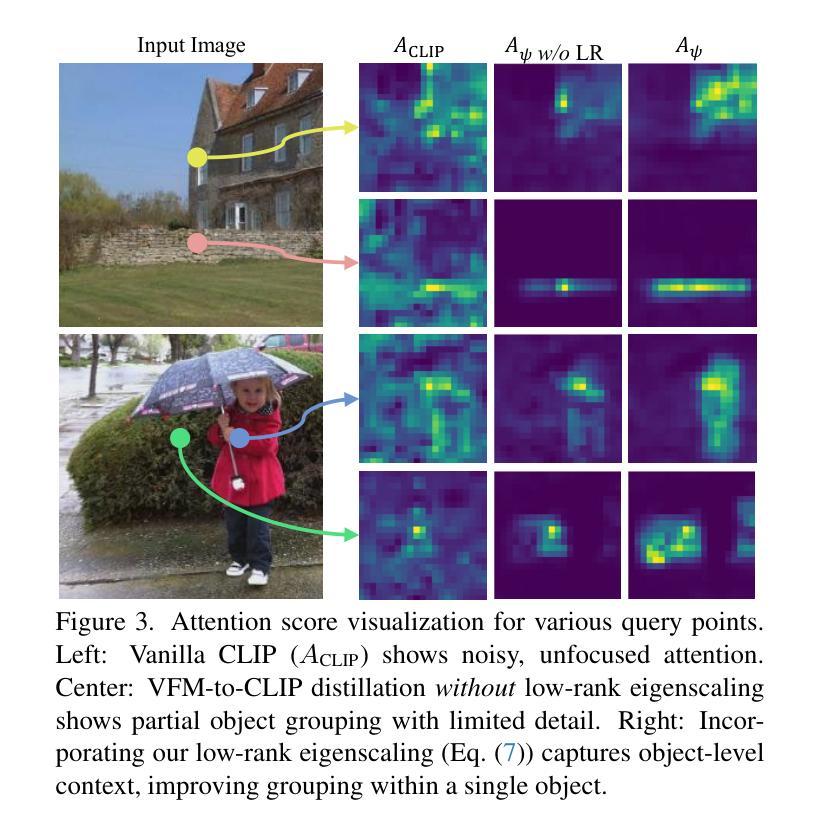
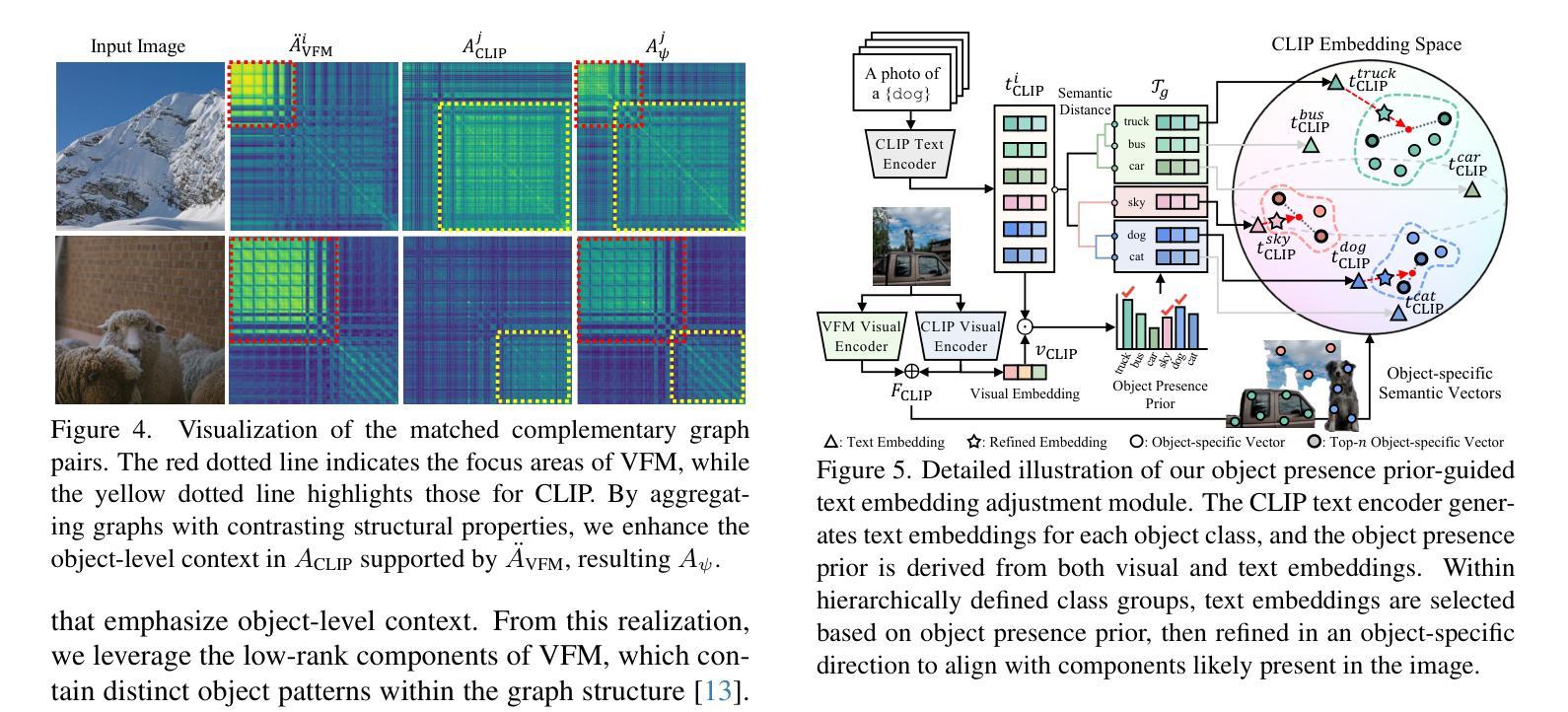
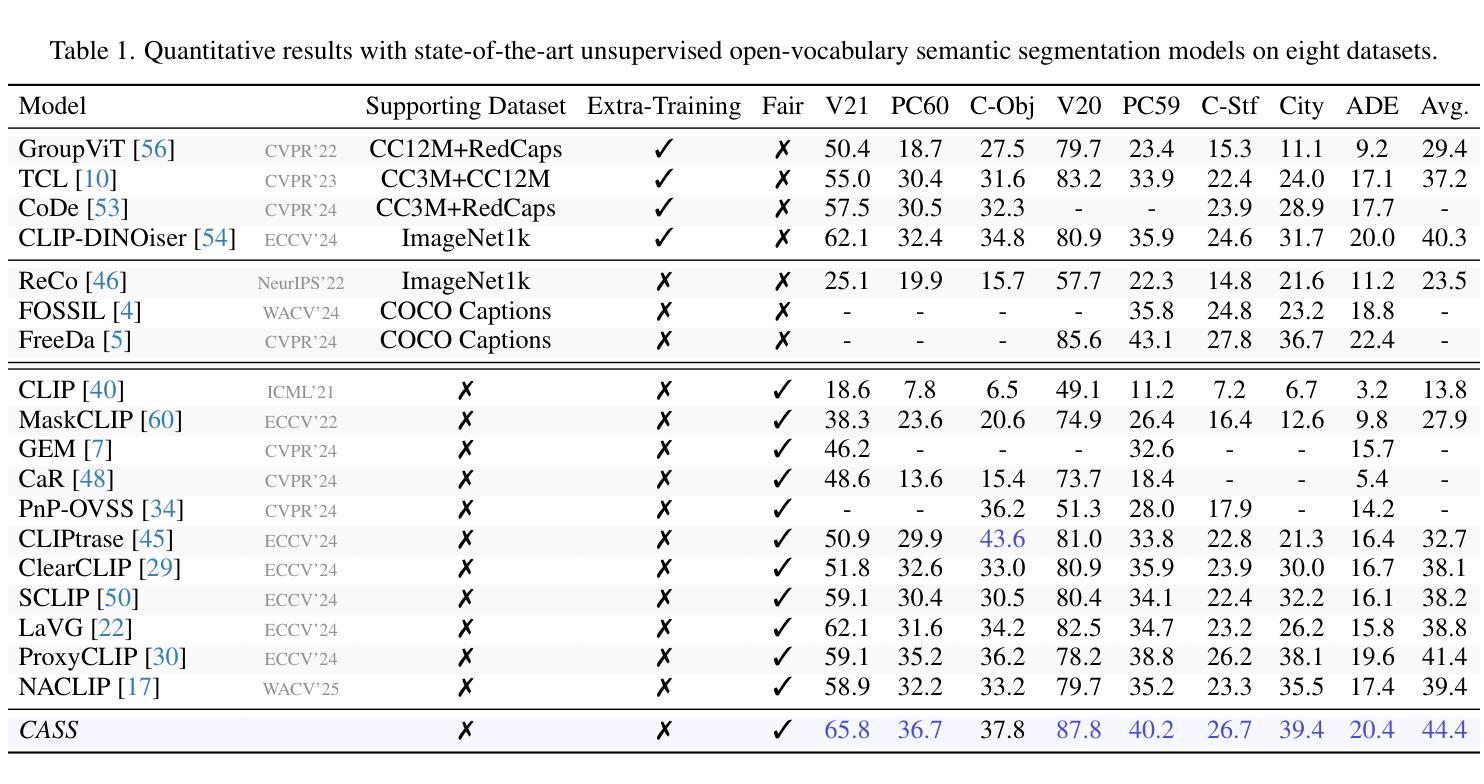
Distilling Spectral Graph for Object-Context Aware Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Chanyoung Kim, Dayun Ju, Woojung Han, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Seong Jae Hwang
Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation (OVSS) has advanced with recent vision-language models (VLMs), enabling segmentation beyond predefined categories through various learning schemes. Notably, training-free methods offer scalable, easily deployable solutions for handling unseen data, a key goal of OVSS. Yet, a critical issue persists: lack of object-level context consideration when segmenting complex objects in the challenging environment of OVSS based on arbitrary query prompts. This oversight limits models’ ability to group semantically consistent elements within object and map them precisely to user-defined arbitrary classes. In this work, we introduce a novel approach that overcomes this limitation by incorporating object-level contextual knowledge within images. Specifically, our model enhances intra-object consistency by distilling spectral-driven features from vision foundation models into the attention mechanism of the visual encoder, enabling semantically coherent components to form a single object mask. Additionally, we refine the text embeddings with zero-shot object presence likelihood to ensure accurate alignment with the specific objects represented in the images. By leveraging object-level contextual knowledge, our proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art performance with strong generalizability across diverse datasets.
开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)随着最近的视觉语言模型(VLMs)的发展而进步,通过各种学习方案实现了超出预定类别的分割。值得注意的是,无训练方法为处理未见数据提供了可扩展、易于部署的解决方案,这是OVSS的关键目标。然而,一个关键问题依然存在:在OVSS的挑战环境中,基于任意查询提示对复杂对象进行分割时,缺乏对象级别的上下文考虑。这种疏忽限制了模型在对象内部分组语义一致元素的能力,并精确地将其映射到用户定义的任意类别。在这项工作中,我们介绍了一种克服这一局限的新方法,该方法通过在图像中融入对象级别的上下文知识。具体来说,我们的模型通过将从视觉基础模型蒸馏出的光谱驱动特征融入到视觉编码器的注意机制中,增强了对象内部的一致性,使语义一致的组件能够形成单个对象掩码。此外,我们还通过零射物体存在可能性来完善文本嵌入,以确保与图像中表示的特定对象的准确对齐。通过利用对象级别的上下文知识,我们提出的方法在多个数据集上实现了最先进的性能,并具有较强的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于最新视觉语言模型(VLMs)的开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)取得了进展,它通过不同的学习方案实现了超越预定义类别的分割。本文主要解决了一个关键问题:在OVSS的复杂环境中,基于任意查询提示进行复杂对象分割时缺乏对象级别的上下文考虑。本文介绍了一种新方法,通过融入图像内的对象级别上下文知识来解决这一问题。该方法提高了对象内部的一致性,并通过精炼文本嵌入与零样本对象存在概率,确保与图像中特定对象的准确对齐。利用对象级别的上下文知识,所提出的方法在多个数据集上实现了最先进的性能,并具有较强的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)能够处理预定义类别之外的分割。
- 训练免费的方法为处理未见过的数据提供了可伸缩、易于部署的解决方案。
- 当前方法缺乏在复杂环境中对对象级别上下文的考虑,这限制了模型的性能。
- 本文介绍了一种新方法,通过融入对象级别上下文知识来提高模型性能。
- 该方法提高了对象内部的一致性,通过精炼文本嵌入确保与图像中对象的准确对齐。
- 利用对象级别的上下文知识,所提出的方法在多个数据集上实现了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

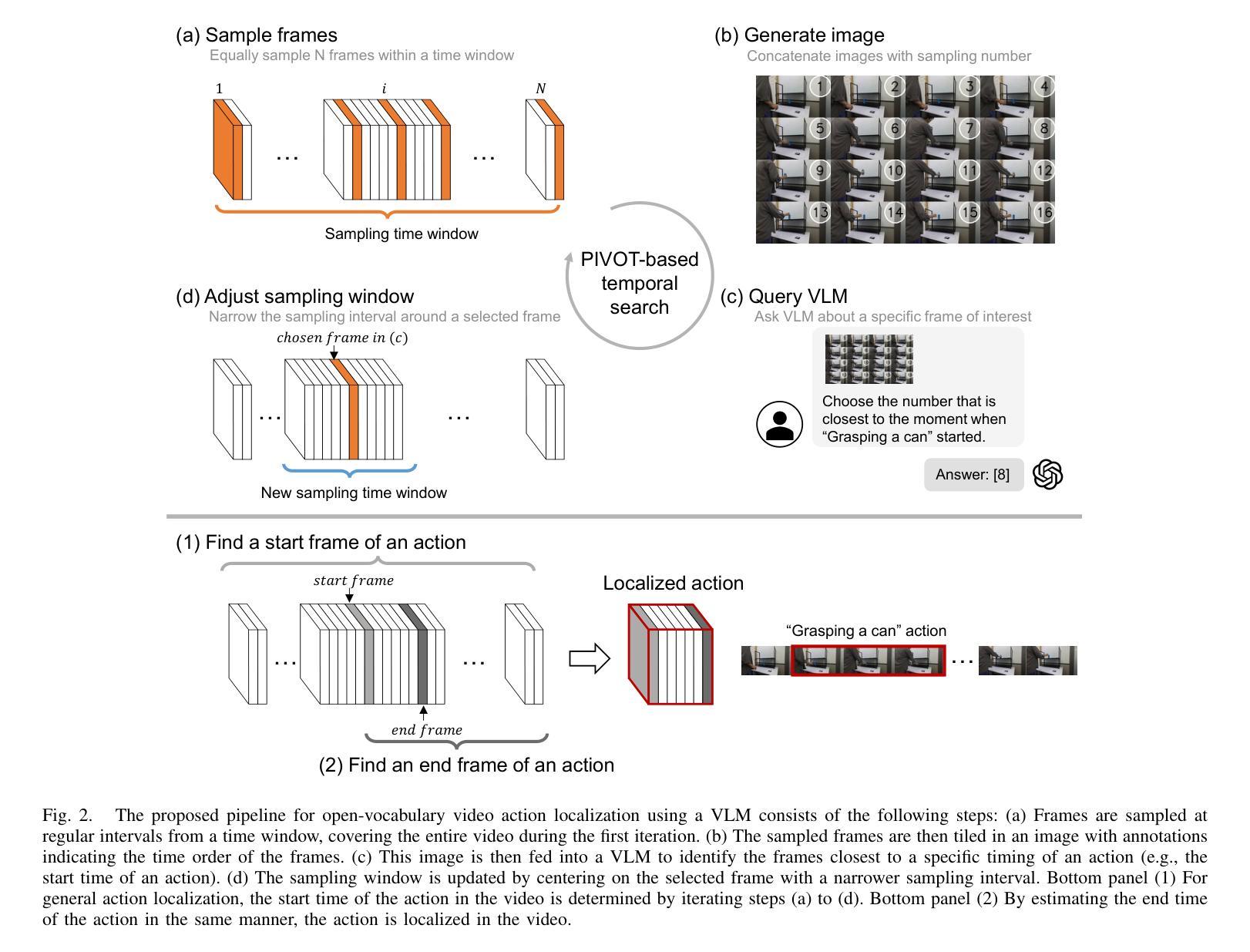
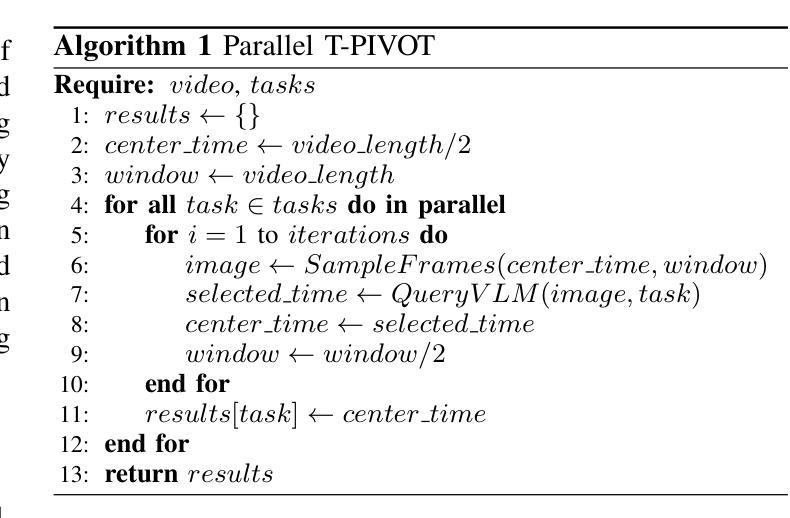
Open-Vocabulary Action Localization with Iterative Visual Prompting
Authors:Naoki Wake, Atsushi Kanehira, Kazuhiro Sasabuchi, Jun Takamatsu, Katsushi Ikeuchi
Video action localization aims to find the timings of specific actions from a long video. Although existing learning-based approaches have been successful, they require annotating videos, which comes with a considerable labor cost. This paper proposes a training-free, open-vocabulary approach based on emerging off-the-shelf vision-language models (VLMs). The challenge stems from the fact that VLMs are neither designed to process long videos nor tailored for finding actions. We overcome these problems by extending an iterative visual prompting technique. Specifically, we sample video frames and create a concatenated image with frame index labels, allowing a VLM to identify the frames that most likely correspond to the start and end of the action. By iteratively narrowing the sampling window around the selected frames, the estimation gradually converges to more precise temporal boundaries. We demonstrate that this technique yields reasonable performance, achieving results comparable to state-of-the-art zero-shot action localization. These results support the use of VLMs as a practical tool for understanding videos. Sample code is available at https://microsoft.github.io/VLM-Video-Action-Localization/
视频动作定位旨在从长视频中找出特定动作的时间点。尽管现有的基于学习的方法已经取得了成功,但它们需要给视频做标注,这需要相当大的劳力成本。本文提出了一种基于现成的视觉语言模型(VLMs)的无训练、开放词汇的方法。挑战在于VLMs既没有被设计来处理长视频,也没有针对寻找动作进行优化。我们通过扩展迭代视觉提示技术来克服这些问题。具体来说,我们采样视频帧,并与帧索引标签一起创建拼接图像,允许VLM识别最有可能对应于动作开始和结束的帧。通过围绕所选帧迭代缩小采样窗口,估计会逐渐收敛到更精确的时间边界。我们证明,这种技术具有良好的性能,实现了与最先进的零样本动作定位相当的结果。这些结果支持将VLMs作为理解视频的实际工具使用。示例代码可在https://microsoft.github.io/VLM-Video-Action-Localization/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 5 figures, 6 tables. Published in IEEE Access. Last updated on April 7th, 2025
Summary
视频动作定位旨在从长视频中找出特定动作的时间点。现有学习类方法虽然成功,但需要标注视频,劳动成本较高。本文提出了一种基于现成的视觉语言模型(VLMs)的无训练、开放词汇方法。面临的挑战源于VLMs既不适用于处理长视频,也不适用于查找动作。我们通过采用迭代视觉提示技术来克服这些问题。具体来说,我们对视频帧进行采样,并创建带有帧索引标签的拼接图像,使VLM能够识别最可能对应于动作开始和结束的帧。通过迭代缩小所选帧周围的采样窗口,估计逐渐收敛到更精确的时间边界。我们证明,这种方法取得了合理的效果,实现了与最先进的零样本动作定位相当的结果。这些结果支持使用VLMs作为理解视频的实际工具。
Key Takeaways
- 视频动作定位旨在从长视频中找出特定动作的时间点。
- 现有方法需要标注视频,劳动成本较高。
- 本文提出了一种基于视觉语言模型(VLMs)的无训练、开放词汇方法。
- VLMs面临处理长视频和查找动作的挑战。
- 通过迭代视觉提示技术克服这些问题。
- 通过采样视频帧并创建带有帧索引标签的拼接图像来识别动作边界。
- 这种方法取得了合理的效果,实现了与最先进的零样本动作定位相当的性能,支持使用VLMs作为理解视频的工具。
点此查看论文截图



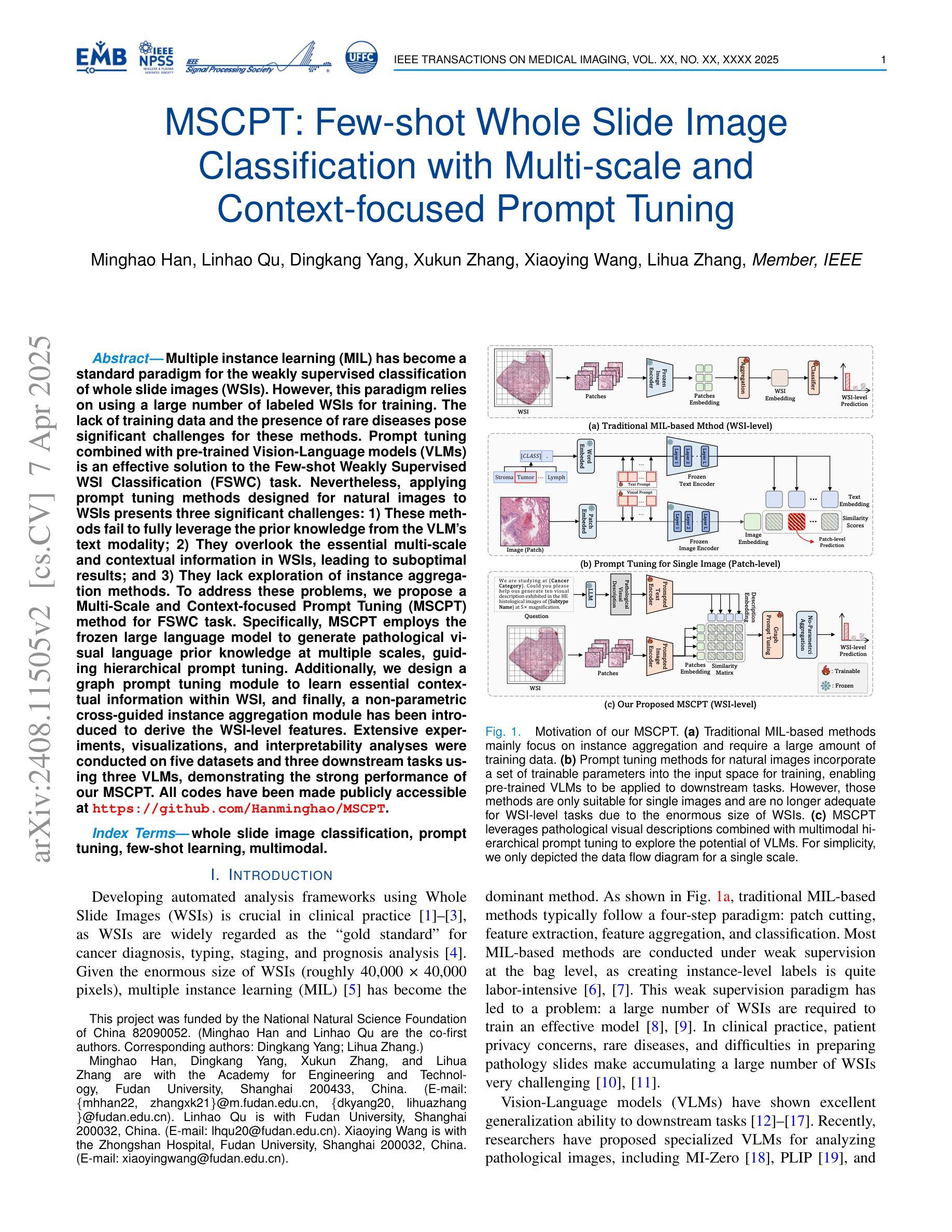
MSCPT: Few-shot Whole Slide Image Classification with Multi-scale and Context-focused Prompt Tuning
Authors:Minghao Han, Linhao Qu, Dingkang Yang, Xukun Zhang, Xiaoying Wang, Lihua Zhang
Multiple instance learning (MIL) has become a standard paradigm for the weakly supervised classification of whole slide images (WSIs). However, this paradigm relies on using a large number of labeled WSIs for training. The lack of training data and the presence of rare diseases pose significant challenges for these methods. Prompt tuning combined with pre-trained Vision-Language models (VLMs) is an effective solution to the Few-shot Weakly Supervised WSI Classification (FSWC) task. Nevertheless, applying prompt tuning methods designed for natural images to WSIs presents three significant challenges: 1) These methods fail to fully leverage the prior knowledge from the VLM’s text modality; 2) They overlook the essential multi-scale and contextual information in WSIs, leading to suboptimal results; and 3) They lack exploration of instance aggregation methods. To address these problems, we propose a Multi-Scale and Context-focused Prompt Tuning (MSCPT) method for FSWC task. Specifically, MSCPT employs the frozen large language model to generate pathological visual language prior knowledge at multiple scales, guiding hierarchical prompt tuning. Additionally, we design a graph prompt tuning module to learn essential contextual information within WSI, and finally, a non-parametric cross-guided instance aggregation module has been introduced to derive the WSI-level features. Extensive experiments, visualizations, and interpretability analyses were conducted on five datasets and three downstream tasks using three VLMs, demonstrating the strong performance of our MSCPT. All codes have been made publicly accessible at https://github.com/Hanminghao/MSCPT.
多任务学习(MIL)已成为全幻灯片图像(WSI)弱监督分类的标准范式。然而,该范式依赖于大量有标签的WSI进行训练。缺乏训练数据和罕见疾病的存在给这些方法带来了重大挑战。结合预训练的视觉语言模型(VLM)的提示微调是解决小样本弱监督WSI分类(FSWC)任务的有效方法。然而,将针对自然图像设计的提示微调方法应用于WSI面临三大挑战:1)这些方法未能充分利用来自VLM文本模态的先验知识;2)它们忽略了WSI中的多尺度和上下文信息,导致结果不佳;3)它们缺乏实例聚合方法的探索。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种用于FSWC任务的多尺度、关注上下文的提示微调(MSCPT)方法。具体来说,MSCPT采用冻结的大型语言模型来生成多尺度的病理视觉语言先验知识,引导分层提示微调。此外,我们设计了一个图提示微调模块来学习WSI内的关键上下文信息,并最终引入了一个非参数化交叉引导实例聚合模块来提取WSI级别的特征。在五个数据集和三个下游任务上,使用三种VLM进行了广泛实验、可视化和可解释性分析,证明了我们的MSCPT的强大性能。所有代码已公开发布在https://github.com/Hanminghao/MSCPT。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been submitted to the IEEE TMI for possible publication
Summary
针对弱监督全幻灯片图像分类任务中训练数据不足和罕见疾病的问题,提出了一种多尺度与上下文聚焦的提示调整(MSCPT)方法。该方法利用冻结的大型语言模型生成病理视觉语言先验知识,设计了一个图提示调整模块来学习幻灯片图像内的关键上下文信息,并引入了一个非参数化交叉引导实例聚合模块来提取幻灯片图像级别的特征。在五个数据集和三个下游任务上进行的广泛实验验证了MSCPT方法的强大性能。
Key Takeaways
- 多实例学习(MIL)已成为全幻灯片图像(WSI)弱监督分类的标准范式,但依赖于大量标记数据进行训练。
- 针对缺乏训练数据和罕见疾病的问题,提出了结合预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs)的提示调整方法。
- 应用于自然图像的提示调整方法在全幻灯片图像上遇到三大挑战:未能充分利用VLM的文本模态先验知识、忽略多尺度和上下文信息、缺乏实例聚合方法的探索。
- 提出的多尺度与上下文聚焦的提示调整(MSCPT)方法针对这些挑战进行改进。
- MSCPT利用大型语言模型生成病理视觉语言先验知识,并设计图提示调整模块学习WSI内的关键上下文信息。
- 引入非参数化交叉引导实例聚合模块,以提取WSI级别的特征。
点此查看论文截图
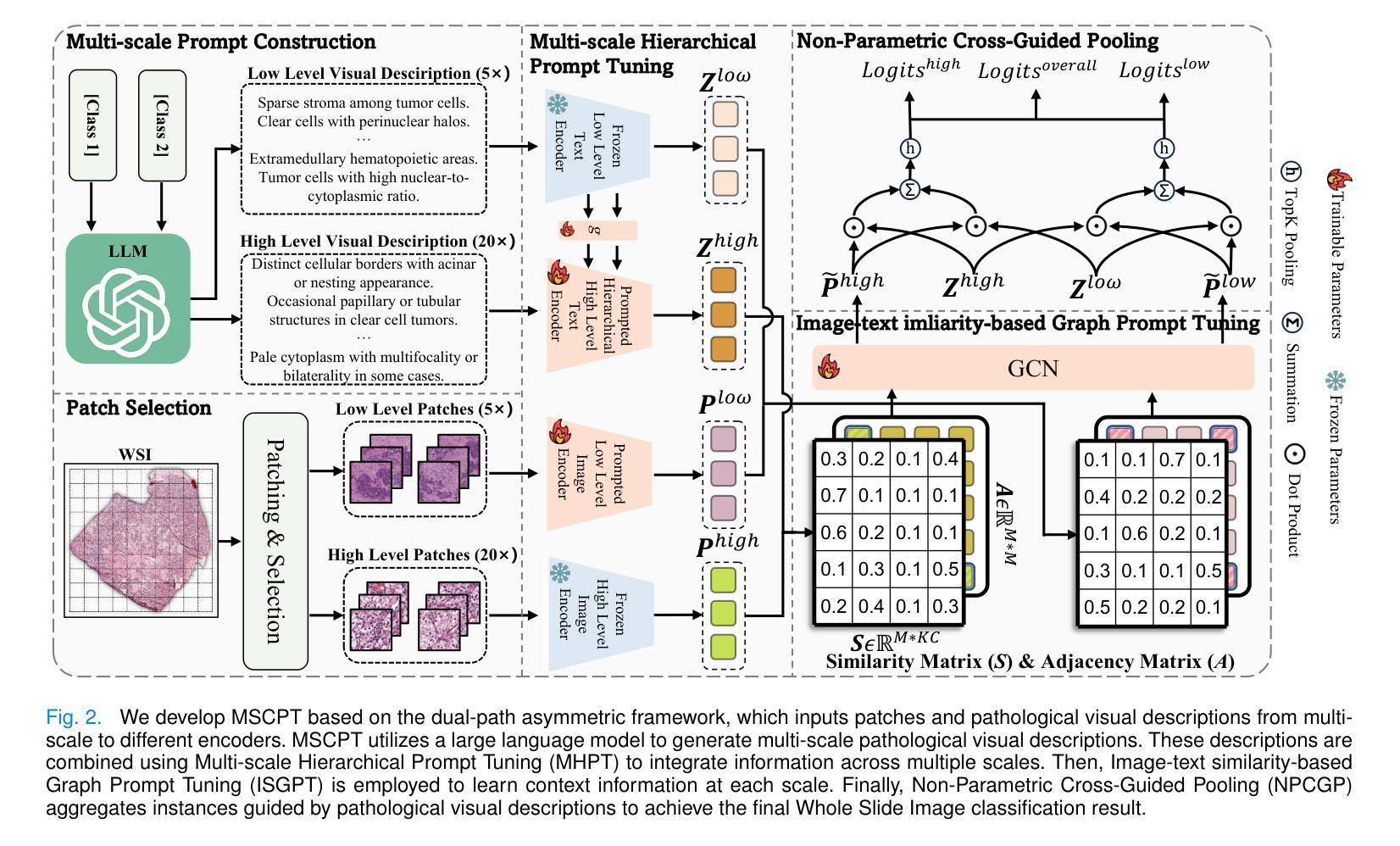
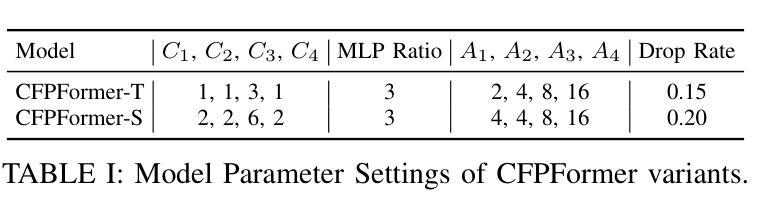
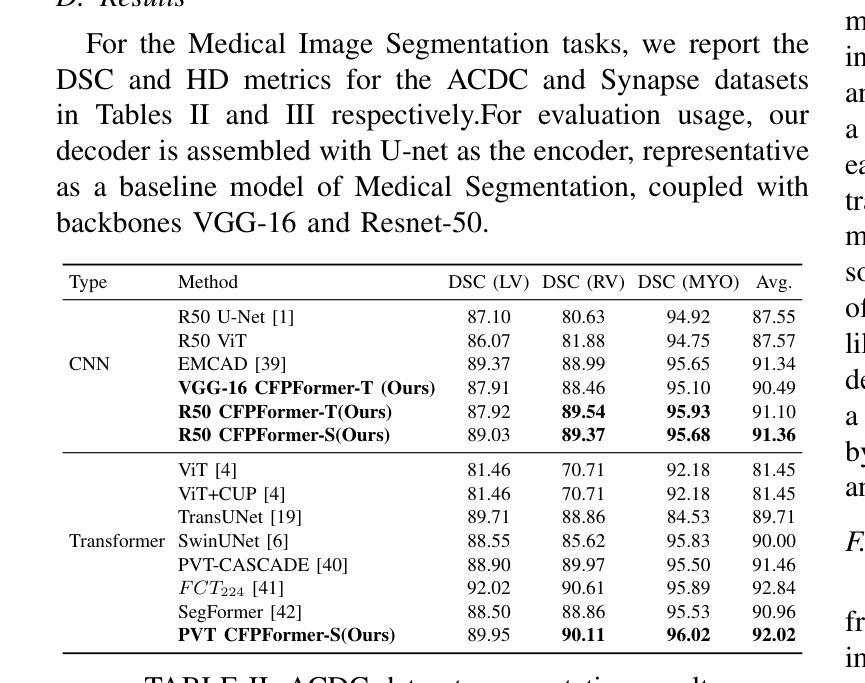
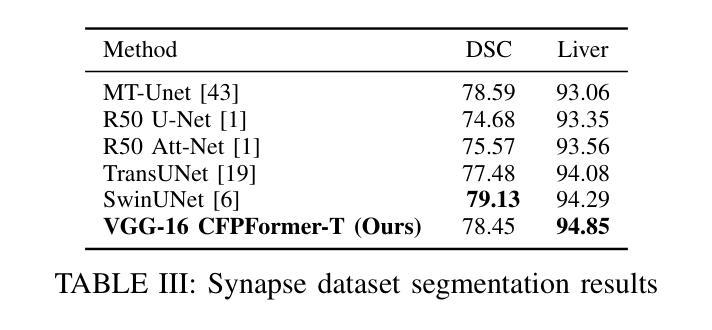
CFPFormer: Feature-pyramid like Transformer Decoder for Segmentation and Detection
Authors:Hongyi Cai, Mohammad Mahdinur Rahman, Wenzhen Dong, Jingyu Wu
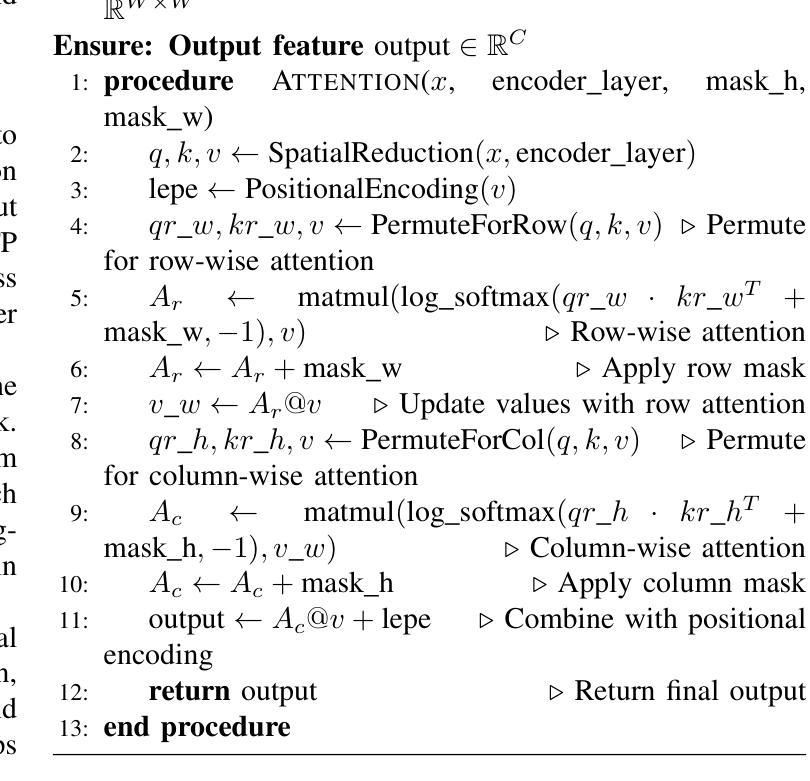
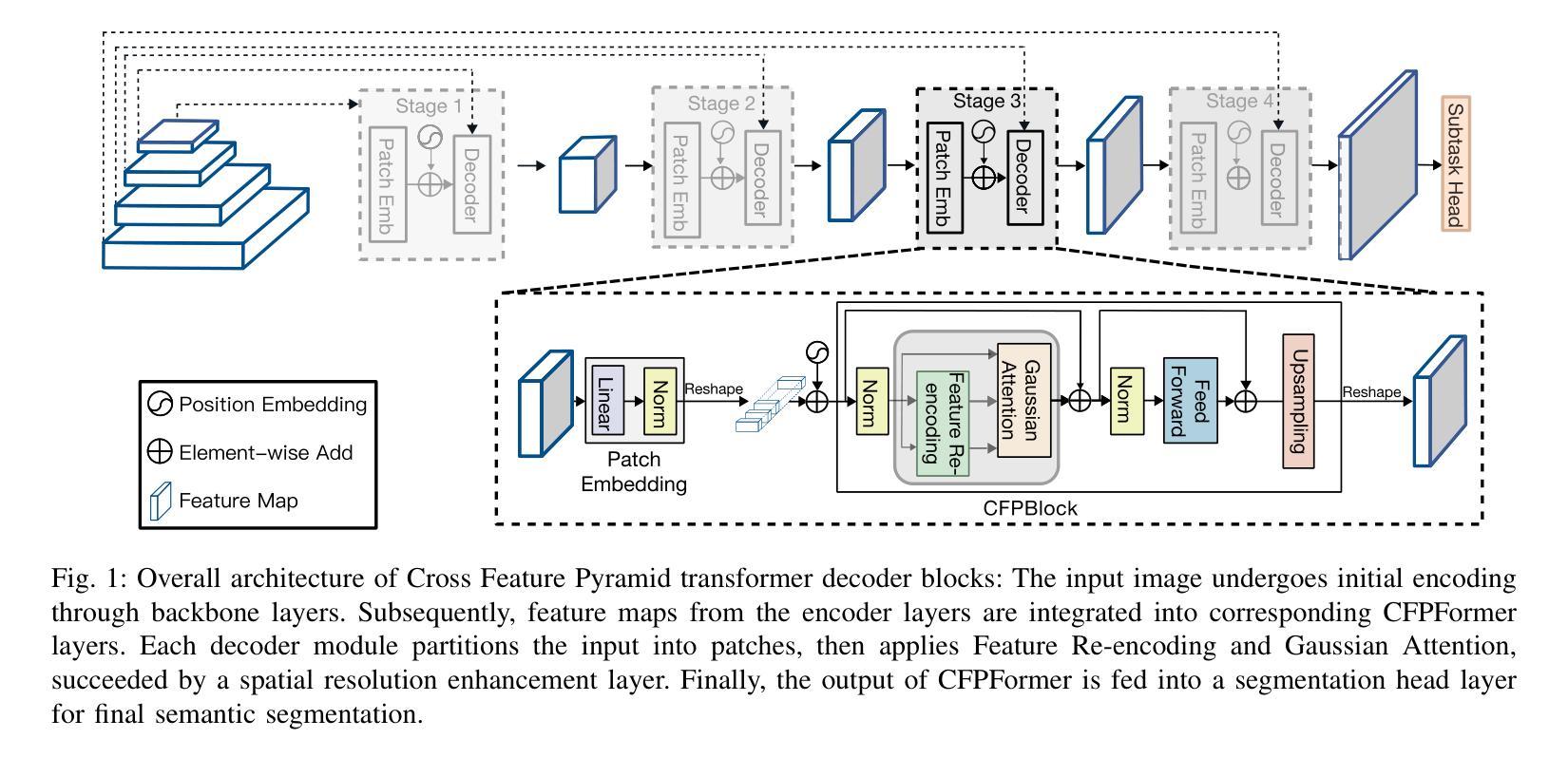
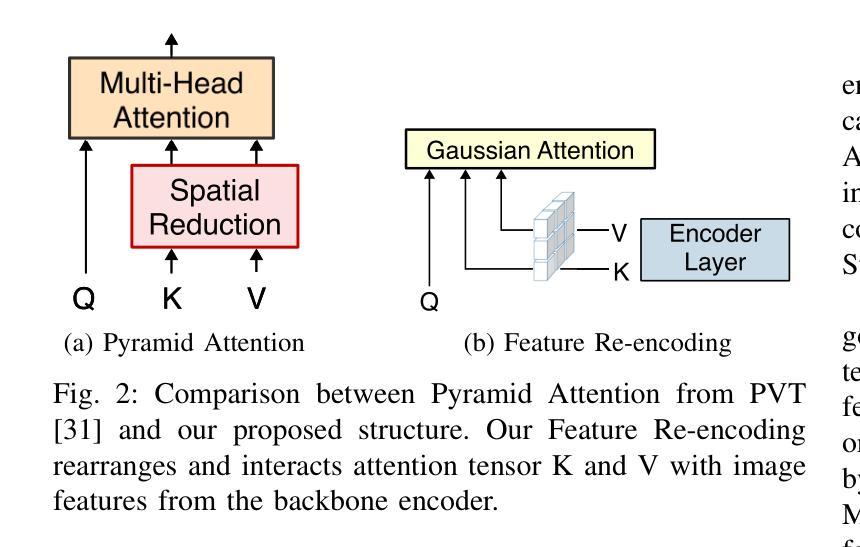
Feature pyramids have been widely adopted in convolutional neural networks and transformers for tasks in medical image segmentation. However, existing models generally focus on the Encoder-side Transformer for feature extraction. We further explore the potential in improving the feature decoder with a well-designed architecture. We propose Cross Feature Pyramid Transformer decoder (CFPFormer), a novel decoder block that integrates feature pyramids and transformers. Even though transformer-like architecture impress with outstanding performance in segmentation, the concerns to reduce the redundancy and training costs still exist. Specifically, by leveraging patch embedding, cross-layer feature concatenation mechanisms, CFPFormer enhances feature extraction capabilities while complexity issue is mitigated by our Gaussian Attention. Benefiting from Transformer structure and U-shaped connections, our work is capable of capturing long-range dependencies and effectively up-sample feature maps. Experimental results are provided to evaluate CFPFormer on medical image segmentation datasets, demonstrating the efficacy and effectiveness. With a ResNet50 backbone, our method achieves 92.02% Dice Score, highlighting the efficacy of our methods. Notably, our VGG-based model outperformed baselines with more complex ViT and Swin Transformer backbone.
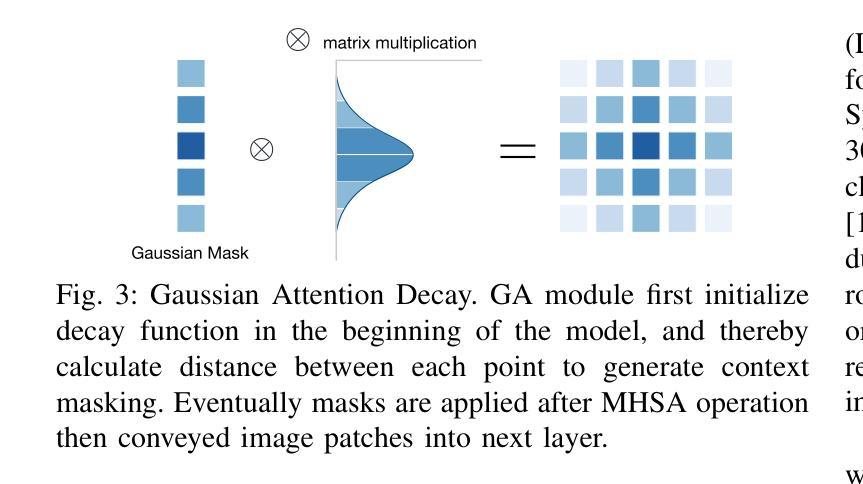
特征金字塔在卷积神经网络和转换器中广泛应用于医学图像分割任务。然而,现有模型通常关注于编码器侧的转换器进行特征提取。我们进一步探索了通过精心设计架构来改进特征解码器的潜力。我们提出了跨特征金字塔转换器解码器(CFPFormer),这是一种新的解码器块,它将特征金字塔和转换器集成在一起。尽管变压器式架构在分割方面表现出令人印象深刻的性能,但减少冗余和训练成本的担忧仍然存在。具体来说,通过利用补丁嵌入、跨层特征拼接机制,CFPFormer增强了特征提取能力,而复杂性问题则通过我们的高斯注意力得到了缓解。得益于Transformer结构和U形连接,我们的工作能够捕捉远程依赖关系并有效地上采样特征图。实验结果为CFPFormer在医学图像分割数据集上的表现提供了评估,证明了其有效性和有效性。使用ResNet50主干网,我们的方法实现了92.02%的Dice得分,突显了我们的方法的有效性。值得注意的是,我们基于VGG的模型在具有更复杂的ViT和Swin Transformer主干网的基准测试中表现更好。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探索了在医疗图像分割任务中改进特征解码器的潜力,提出了一种新的解码器块——Cross Feature Pyramid Transformer(CFPFormer)。CFPFormer结合了特征金字塔和变压器,通过利用补丁嵌入和跨层特征拼接机制,提高了特征提取能力。同时,通过高斯注意力机制降低了复杂性和训练成本。实验结果表明,CFPFormer在医疗图像分割数据集上表现出色,使用ResNet50骨干网的方法达到92.02%的Dice得分。值得注意的是,基于VGG的模型超越了具有更复杂ViT和Swin Transformer骨干网的基线模型。
Key Takeaways
- 文章探索了改进医疗图像分割任务中的特征解码器的潜力。
- 提出了一种新的解码器块——Cross Feature Pyramid Transformer(CFPFormer)。
- CFPFormer结合了特征金字塔和变压器,以提高特征提取能力。
- 通过利用补丁嵌入和跨层特征拼接机制,CFPFormer能够增强特征提取效果。
- 高斯注意力机制用于降低复杂性和训练成本。
- 实验结果表明,CFPFormer在医疗图像分割任务上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图