⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-10 更新
HRMedSeg: Unlocking High-resolution Medical Image segmentation via Memory-efficient Attention Modeling
Authors:Qing Xu, Zhenye Lou, Chenxin Li, Xiangjian He, Rong Qu, Tesema Fiseha Berhanu, Yi Wang, Wenting Duan, Zhen Chen
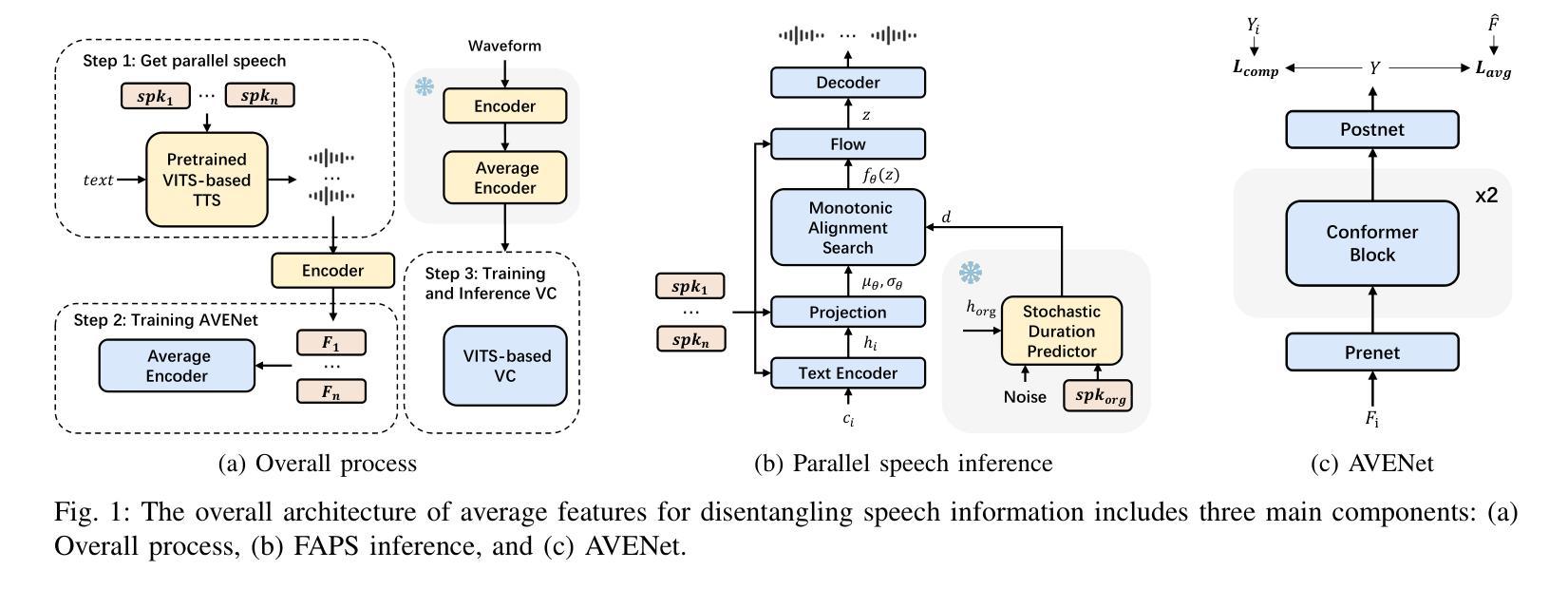
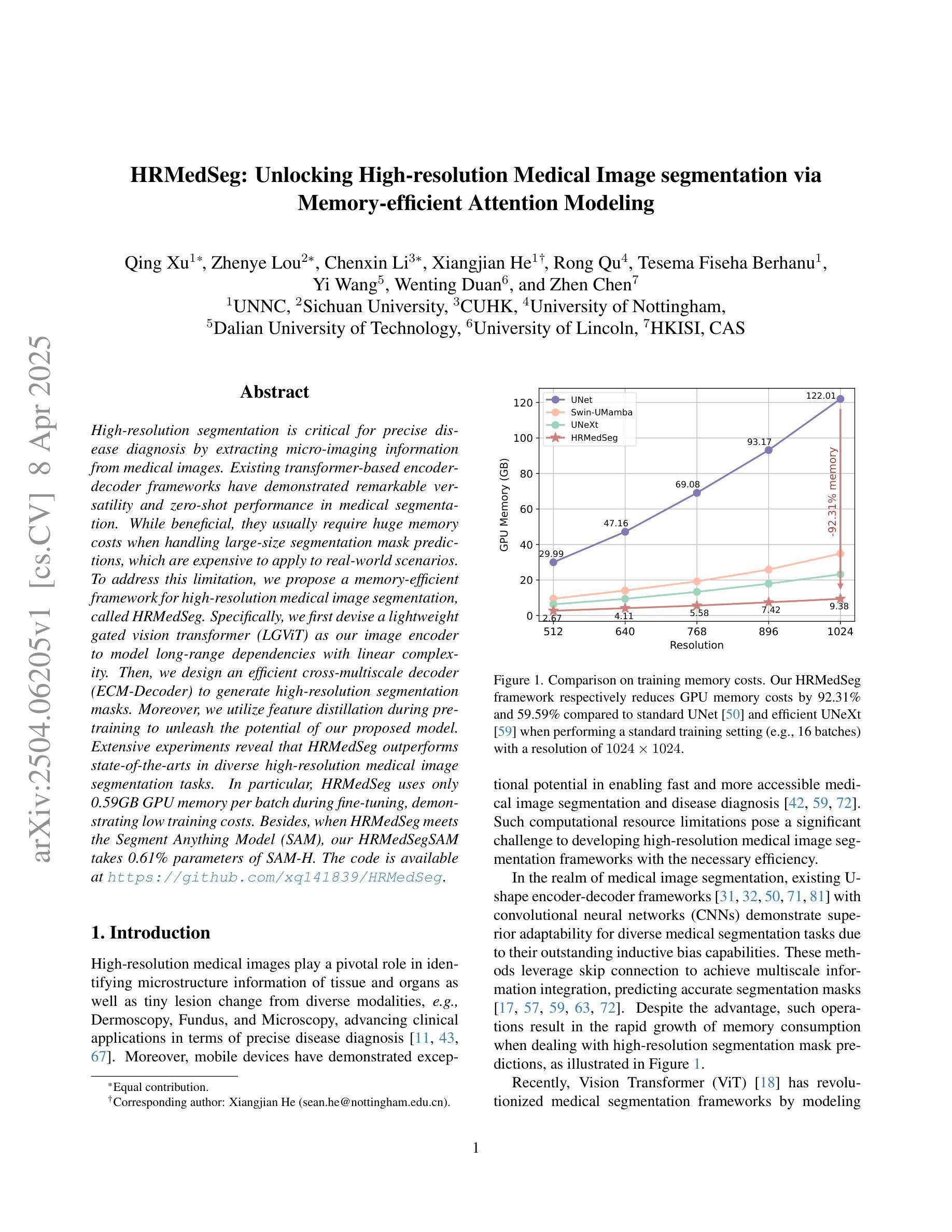
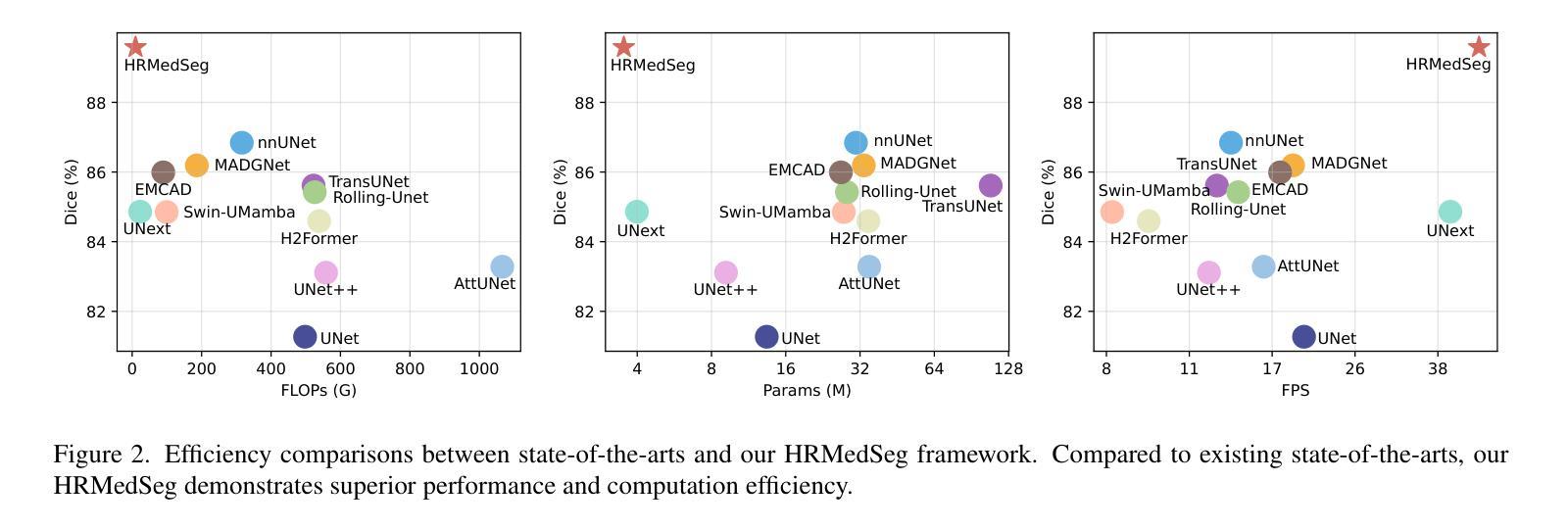
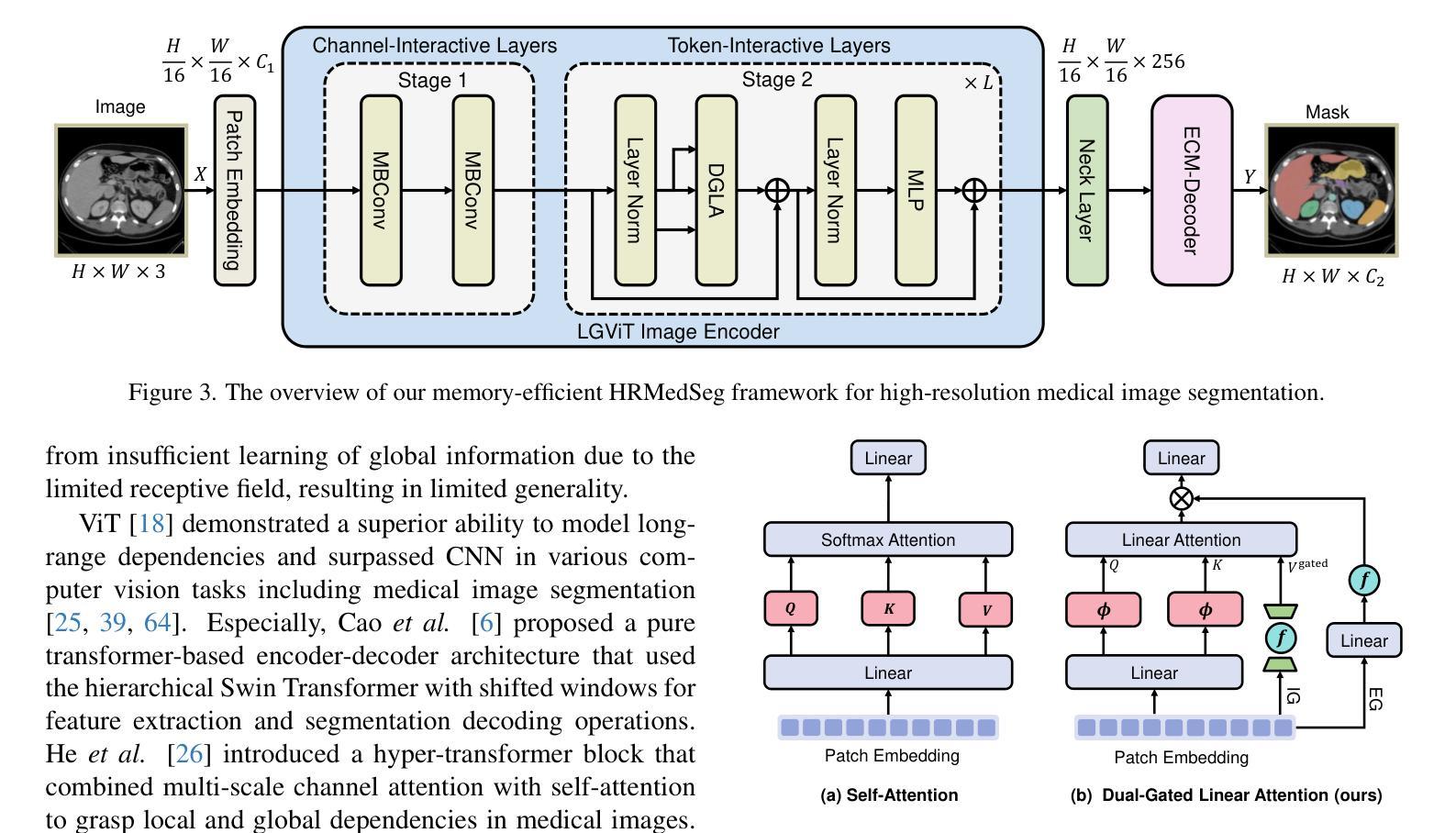
High-resolution segmentation is critical for precise disease diagnosis by extracting micro-imaging information from medical images. Existing transformer-based encoder-decoder frameworks have demonstrated remarkable versatility and zero-shot performance in medical segmentation. While beneficial, they usually require huge memory costs when handling large-size segmentation mask predictions, which are expensive to apply to real-world scenarios. To address this limitation, we propose a memory-efficient framework for high-resolution medical image segmentation, called HRMedSeg. Specifically, we first devise a lightweight gated vision transformer (LGViT) as our image encoder to model long-range dependencies with linear complexity. Then, we design an efficient cross-multiscale decoder (ECM-Decoder) to generate high-resolution segmentation masks. Moreover, we utilize feature distillation during pretraining to unleash the potential of our proposed model. Extensive experiments reveal that HRMedSeg outperforms state-of-the-arts in diverse high-resolution medical image segmentation tasks. In particular, HRMedSeg uses only 0.59GB GPU memory per batch during fine-tuning, demonstrating low training costs. Besides, when HRMedSeg meets the Segment Anything Model (SAM), our HRMedSegSAM takes 0.61% parameters of SAM-H. The code is available at https://github.com/xq141839/HRMedSeg.
高分辨率分割是从医学图像中提取微观成像信息,进行精确疾病诊断的关键。现有的基于转换器的编码器-解码器框架在医学分割中表现出了显著的通用性和零样本性能。虽然有益,但在处理大尺寸分割掩膜预测时,它们通常需要巨大的内存成本,难以应用于现实场景。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了一种用于高分辨率医学图像分割的内存高效框架,称为HRMedSeg。具体来说,我们首先设计了一种轻量型门控视觉转换器(LGViT)作为图像编码器,以线性复杂度建模长距离依赖关系。然后,我们设计了一个高效的跨多尺度解码器(ECM-Decoder)来生成高分辨率分割掩膜。此外,我们在预训练过程中使用了特征蒸馏来释放我们提出模型的潜力。大量实验表明,HRMedSeg在多种高分辨率医学图像分割任务上的表现优于最新技术。特别是,HRMedSeg在微调期间每批仅使用0.59GB的GPU内存,显示出较低的训练成本。此外,当HRMedSeg遇到Segment Anything Model(SAM)时,我们的HRMedSegSAM仅使用SAM-H的0.61%参数。相关代码可在https://github.com/xq141839/HRMedSeg上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under Review
Summary
提出一种高效、内存优化、用于高解析度医学图像分割的框架HRMedSeg。采用轻量化门控视觉转换器LGViT建模长期依赖关系,并采用高效跨多尺度解码器生成高分辨率分割掩膜。特征蒸馏在预训练中的应用提高了模型潜力。HRMedSeg在高分辨率医学图像分割任务上表现优于其他先进技术,并且在微调时仅占用0.59GB的GPU内存。代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 高分辨率分割对于精确疾病诊断至关重要,需要从医学图像中提取微观成像信息。
- 现有基于转换器的编码器-解码器框架已在医学分割中展现出卓越的多功能性和零样本性能。
- 这些框架在处理大型分割掩膜预测时内存成本高昂,实际应用中受限。
- 提出一种内存高效的医学图像分割框架HRMedSeg,用于高解析度医学图像分割。
- HRMedSeg采用轻量化门控视觉转换器LGViT,具有线性复杂度的长期依赖关系建模能力。
- HRMedSeg设计了一种高效跨多尺度解码器生成高分辨率分割掩膜。
点此查看论文截图
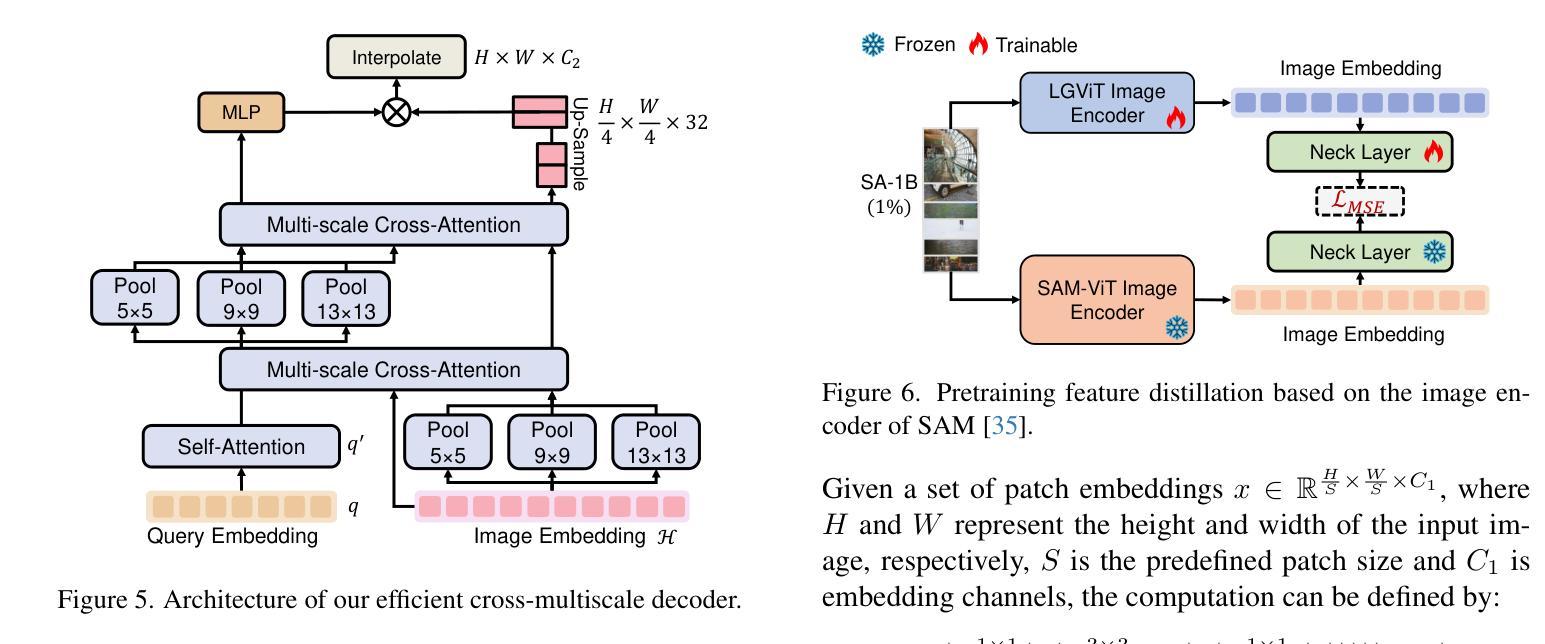
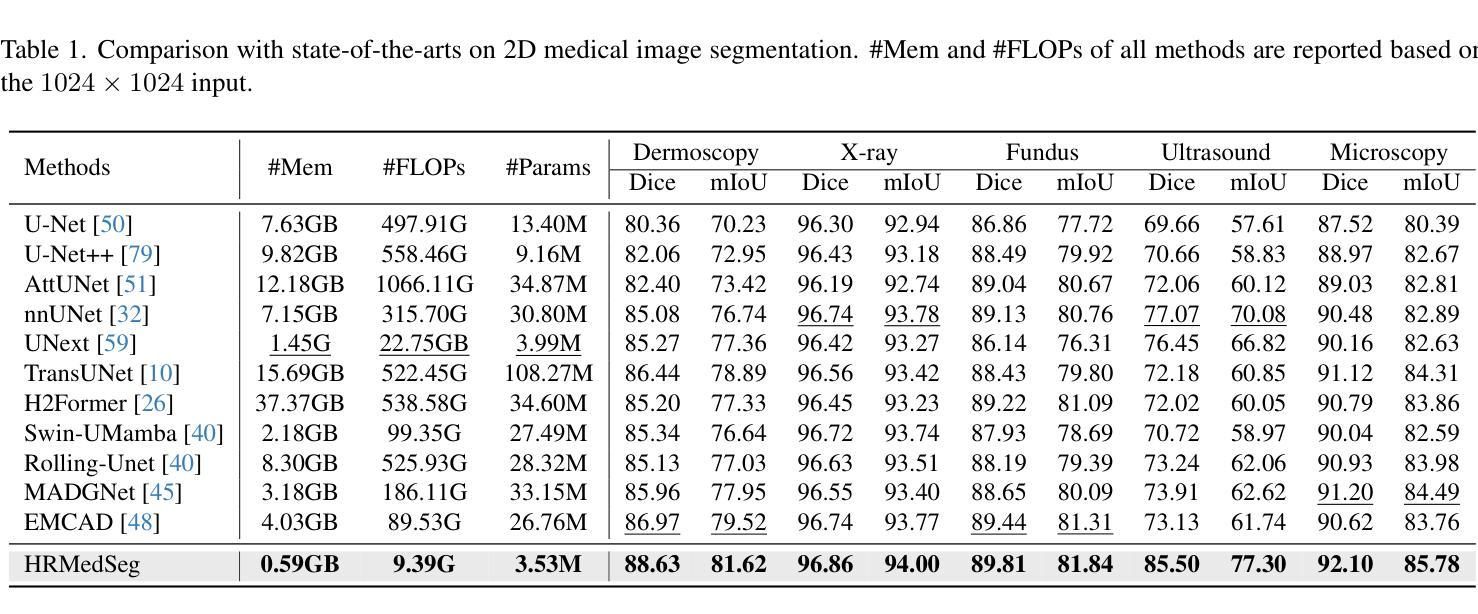
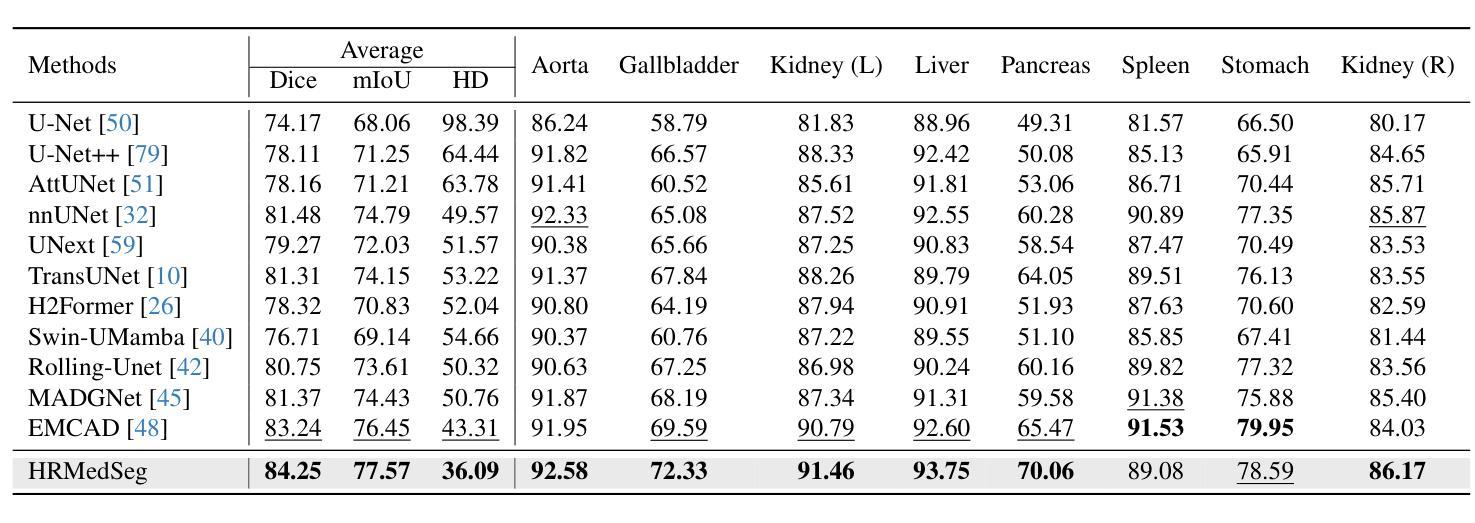
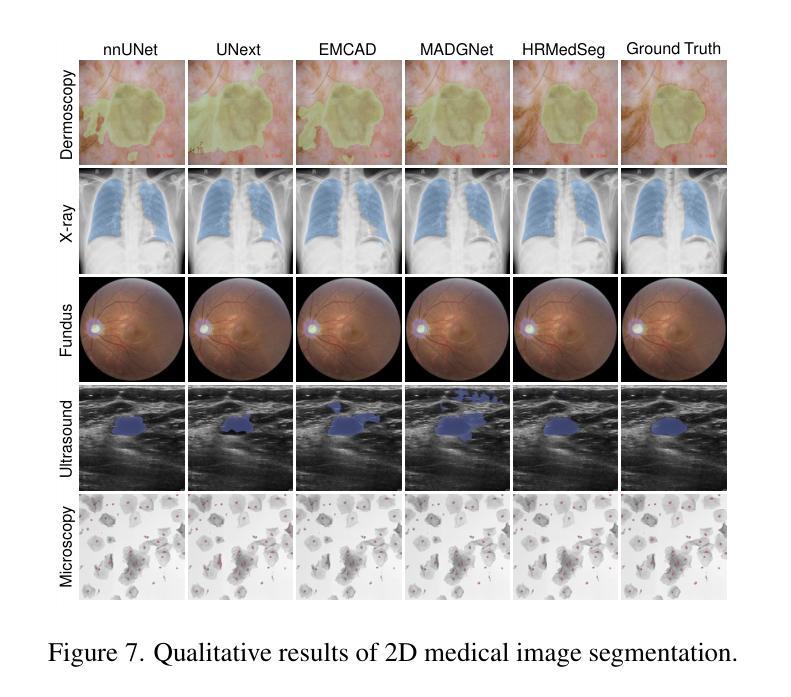
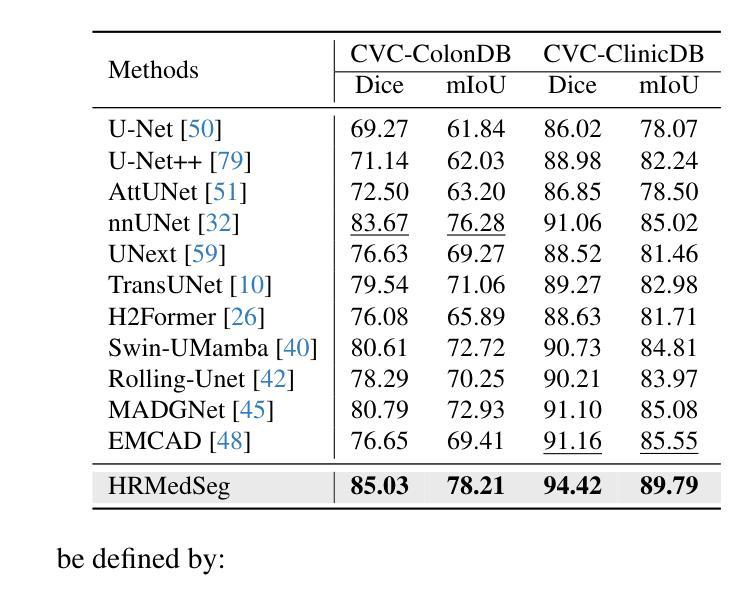
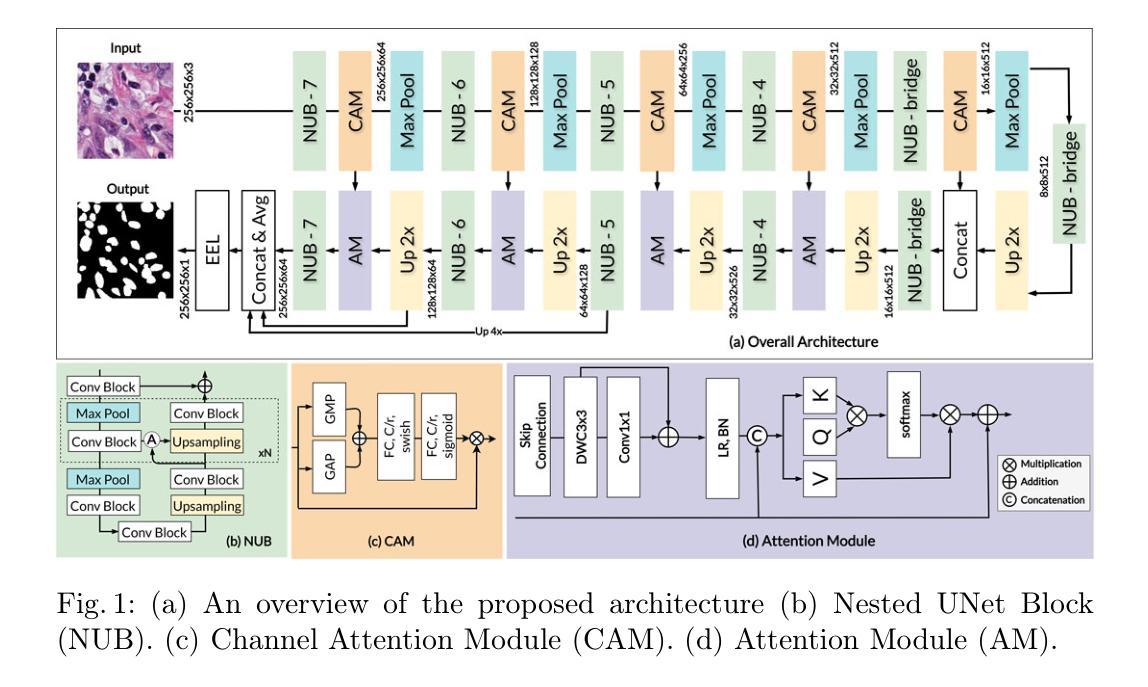
Rethinking the Nested U-Net Approach: Enhancing Biomarker Segmentation with Attention Mechanisms and Multiscale Feature Fusion
Authors:Saad Wazir, Daeyoung Kim
Identifying biomarkers in medical images is vital for a wide range of biotech applications. However, recent Transformer and CNN based methods often struggle with variations in morphology and staining, which limits their feature extraction capabilities. In medical image segmentation, where data samples are often limited, state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods improve accuracy by using pre-trained encoders, while end-to-end approaches typically fall short due to difficulties in transferring multiscale features effectively between encoders and decoders. To handle these challenges, we introduce a nested UNet architecture that captures both local and global context through Multiscale Feature Fusion and Attention Mechanisms. This design improves feature integration from encoders, highlights key channels and regions, and restores spatial details to enhance segmentation performance. Our method surpasses SOTA approaches, as evidenced by experiments across four datasets and detailed ablation studies. Code: https://github.com/saadwazir/ReN-UNet
在医学图像中识别生物标志物对于广泛的生物技术应用至关重要。然而,最近基于Transformer和CNN的方法往往难以应对形态和染色方面的变化,这限制了其特征提取能力。在医学图像分割中,由于数据样本通常有限,最先进的方法通过使用预训练编码器来提高准确性,而端到端的方法通常因在编码器和解码器之间有效地传递多尺度特征方面遇到困难而表现不足。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了一种嵌套UNet架构,它通过多尺度特征融合和注意力机制来捕捉局部和全局上下文。这种设计改进了编码器的特征集成,突出了关键通道和区域,并恢复了空间细节以增强分割性能。我们的方法超越了最先进的方法,通过四个数据集的实验和详细的消融研究可以证明这一点。代码链接:https://github.com/saadwazir/ReN-UNet
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in the Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Medical Imaging and Computer-Aided Diagnosis (MICAD 2024), Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering (LNEE), Volume 1372, Springer Nature, Singapore
Summary
医学图像中的生物标志物识别对于生物技术应用至关重要。然而,当前主流方法在处理形态学和染色差异时面临挑战,限制了特征提取能力。为解决此问题,我们提出了一种嵌套UNet架构,通过多尺度特征融合和注意力机制捕捉局部和全局上下文信息,提高了特征集成能力,增强了分割性能。该方法已超越现有方法,经过四个数据集的实验和详细的消融研究验证。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像中的生物标志物识别在生物技术应用中极为关键。
- 当前方法在处理形态学和染色差异时存在挑战,限制了特征提取能力。
- 引入了一种嵌套UNet架构以处理上述问题。
- 该架构通过多尺度特征融合和注意力机制捕捉局部和全局上下文信息。
- 该设计提高了特征集成能力,强化了关键通道和区域的标识。
- 通过恢复空间细节,增强了分割性能。
点此查看论文截图

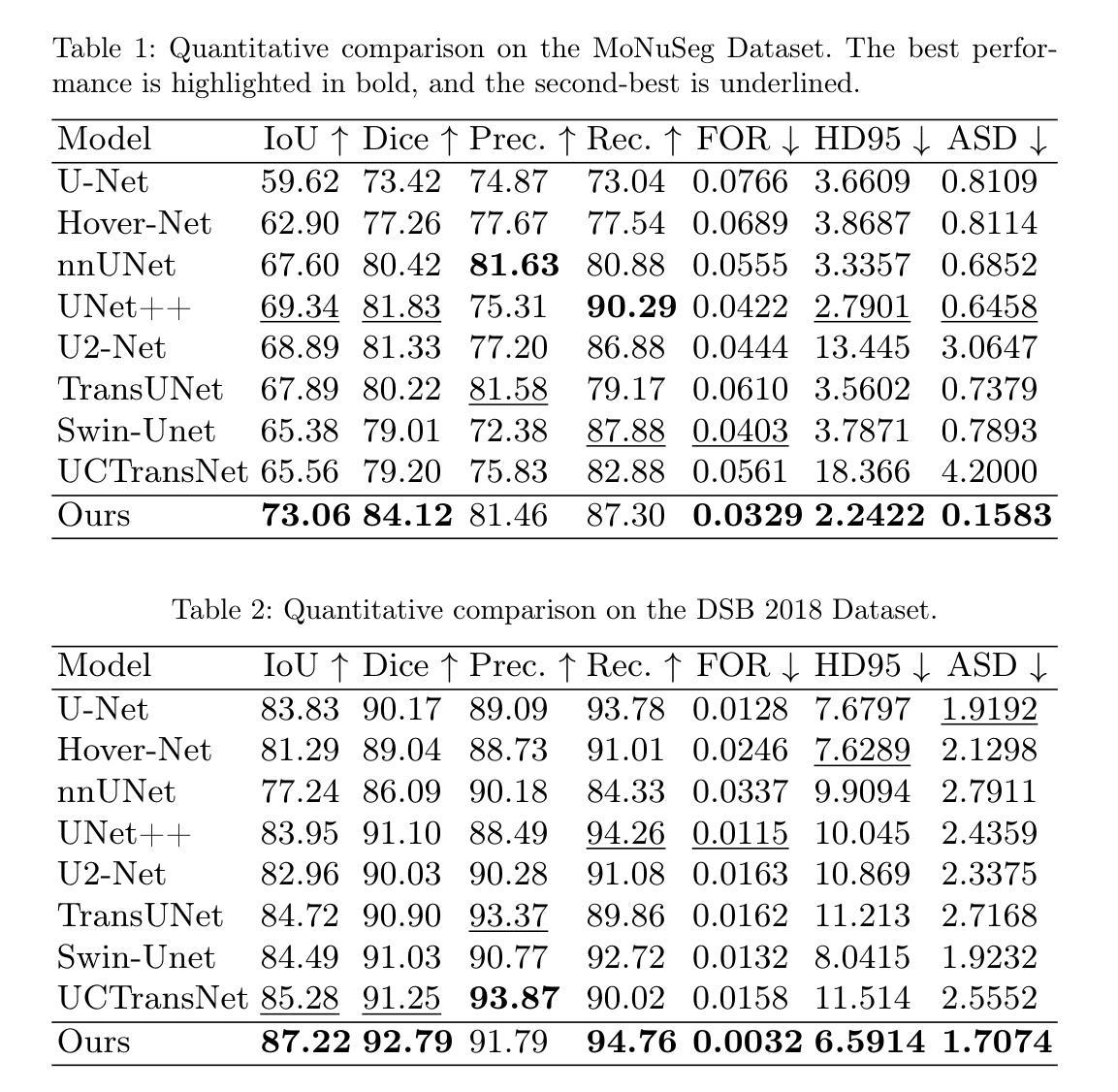
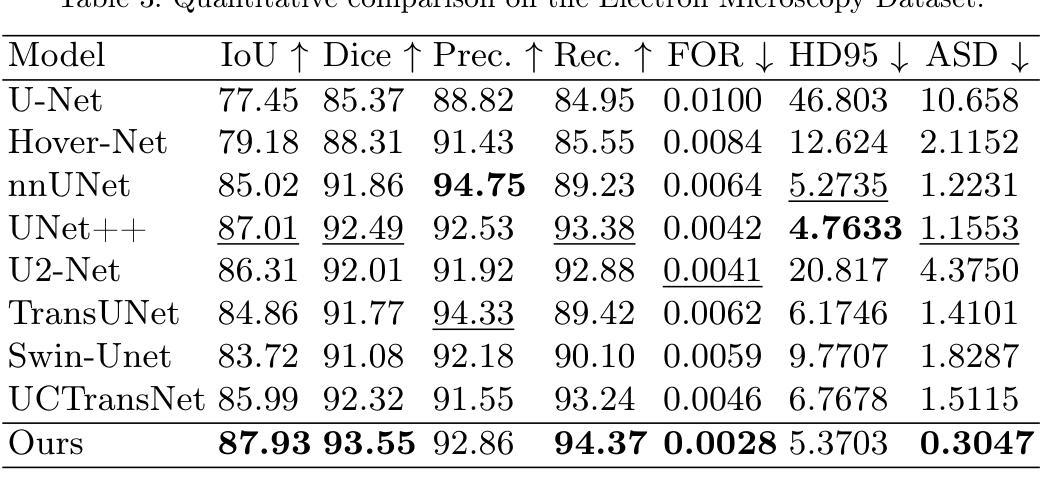
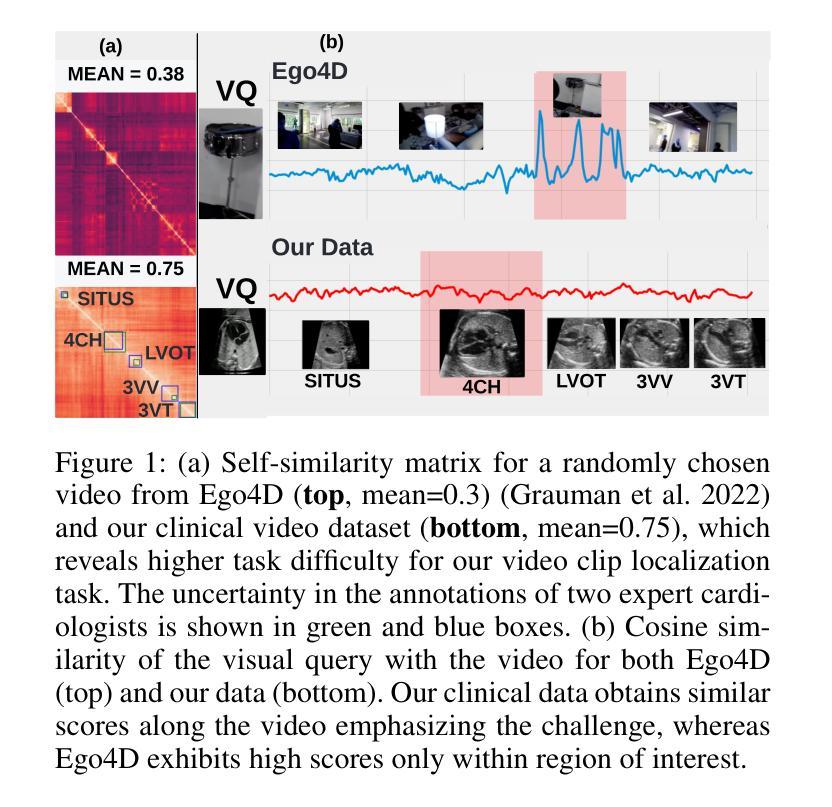
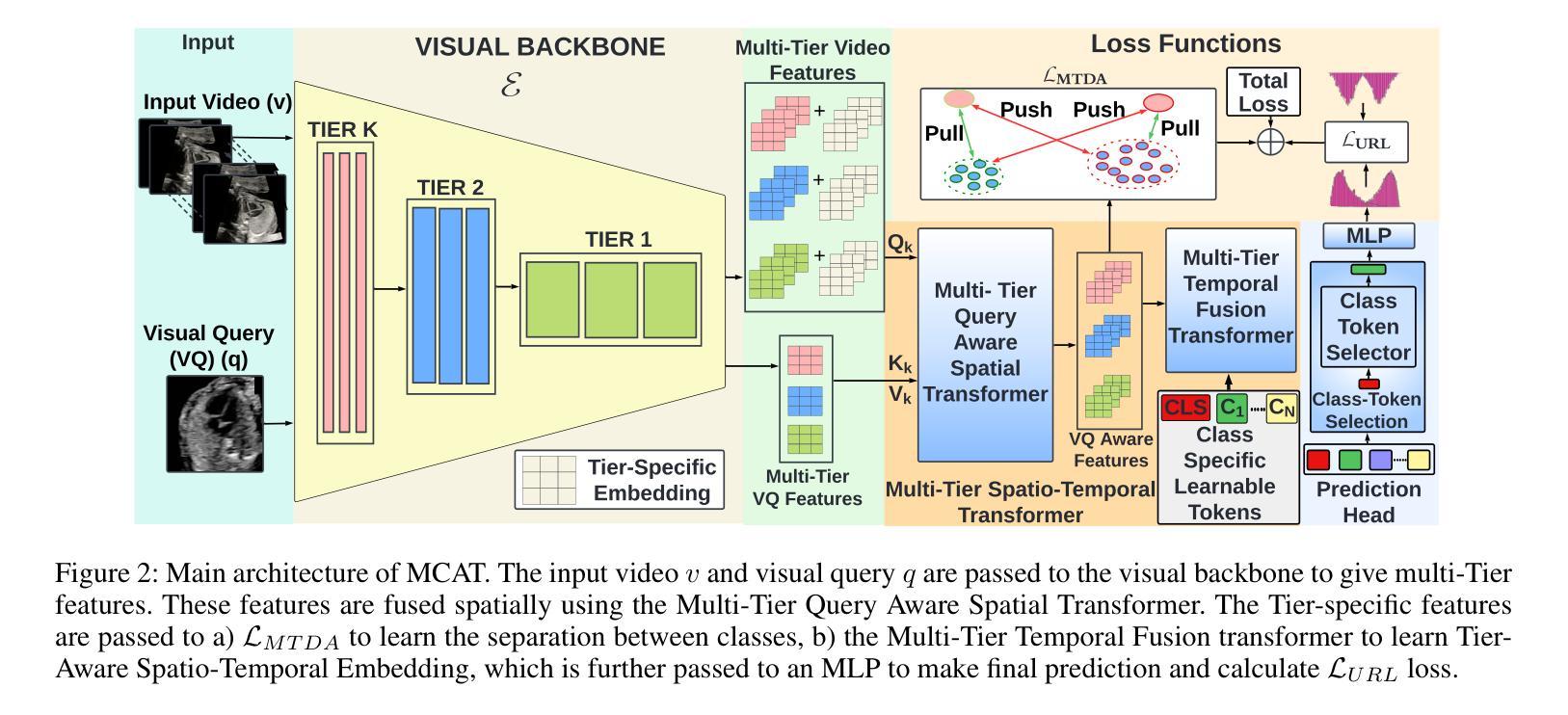
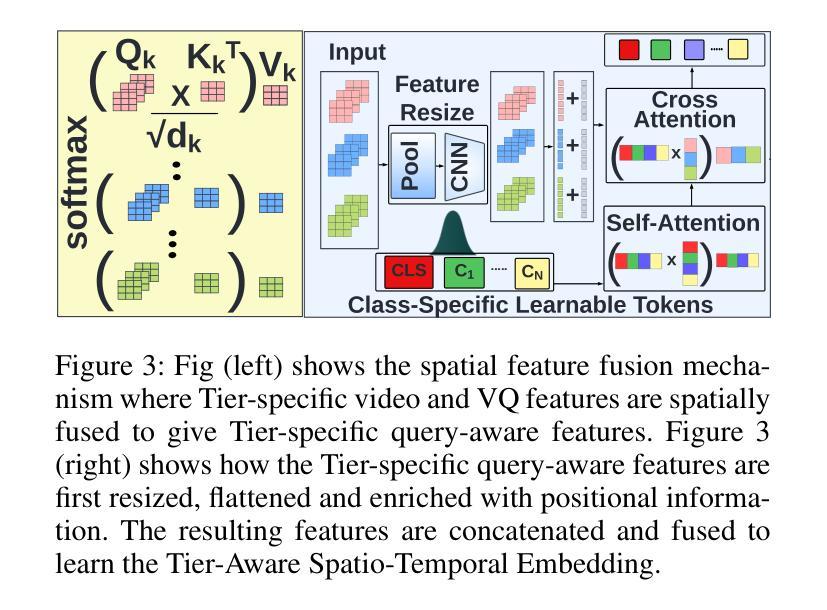
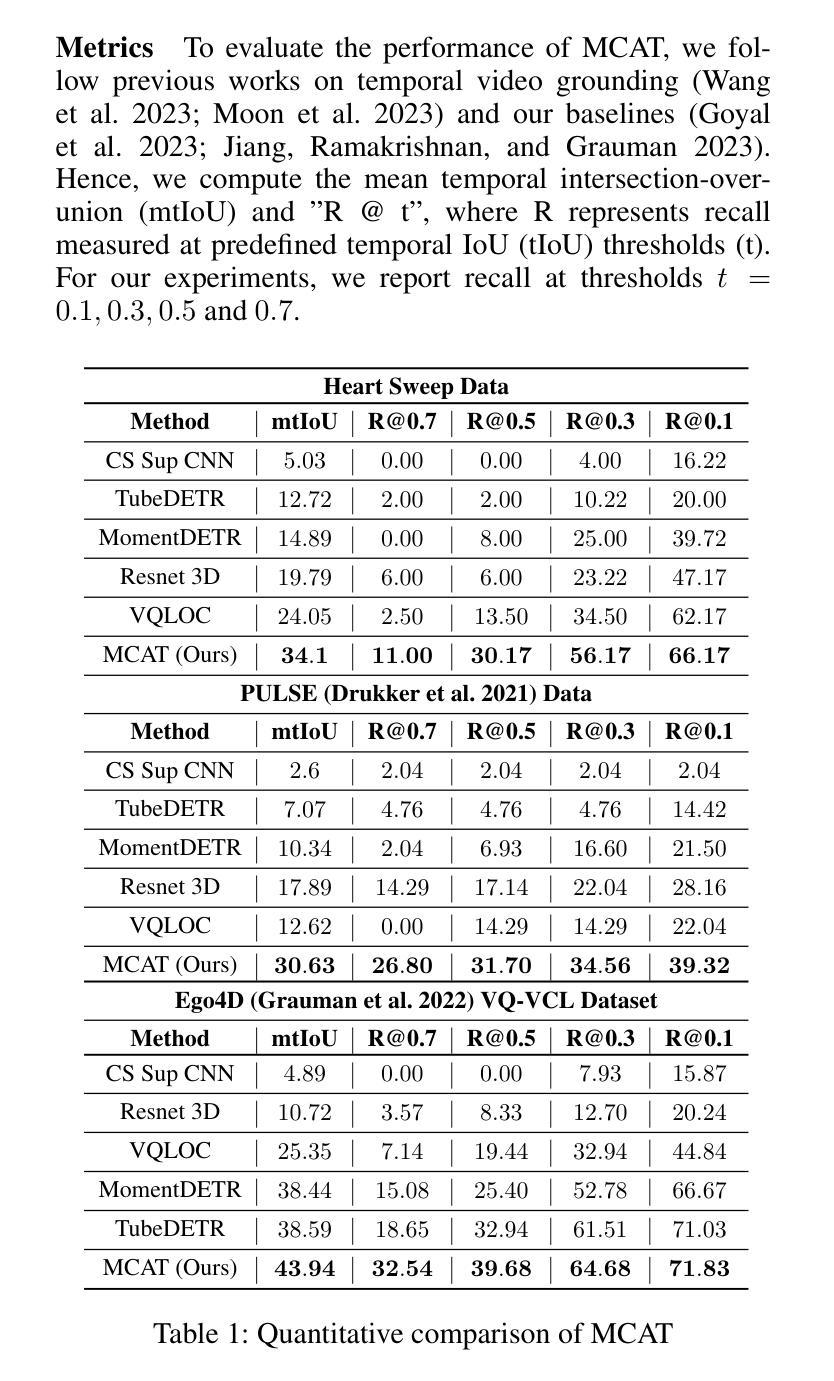
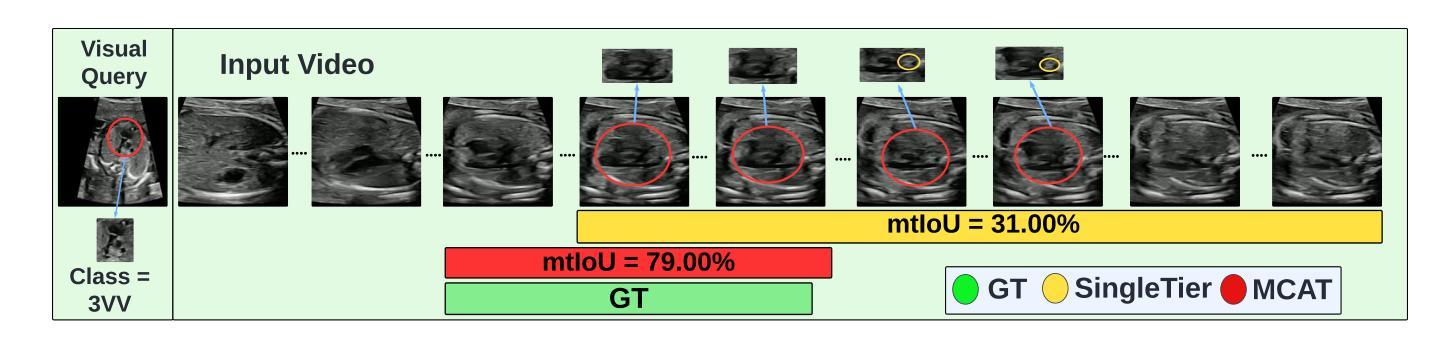
MCAT: Visual Query-Based Localization of Standard Anatomical Clips in Fetal Ultrasound Videos Using Multi-Tier Class-Aware Token Transformer
Authors:Divyanshu Mishra, Pramit Saha, He Zhao, Netzahualcoyotl Hernandez-Cruz, Olga Patey, Aris Papageorghiou, J. Alison Noble
Accurate standard plane acquisition in fetal ultrasound (US) videos is crucial for fetal growth assessment, anomaly detection, and adherence to clinical guidelines. However, manually selecting standard frames is time-consuming and prone to intra- and inter-sonographer variability. Existing methods primarily rely on image-based approaches that capture standard frames and then classify the input frames across different anatomies. This ignores the dynamic nature of video acquisition and its interpretation. To address these challenges, we introduce Multi-Tier Class-Aware Token Transformer (MCAT), a visual query-based video clip localization (VQ-VCL) method, to assist sonographers by enabling them to capture a quick US sweep. By then providing a visual query of the anatomy they wish to analyze, MCAT returns the video clip containing the standard frames for that anatomy, facilitating thorough screening for potential anomalies. We evaluate MCAT on two ultrasound video datasets and a natural image VQ-VCL dataset based on Ego4D. Our model outperforms state-of-the-art methods by 10% and 13% mIoU on the ultrasound datasets and by 5.35% mIoU on the Ego4D dataset, using 96% fewer tokens. MCAT’s efficiency and accuracy have significant potential implications for public health, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), where it may enhance prenatal care by streamlining standard plane acquisition, simplifying US-based screening, diagnosis and allowing sonographers to examine more patients.
在胎儿超声(US)视频中准确获取标准平面对于胎儿生长评估、异常检测以及遵循临床指南至关重要。然而,手动选择标准帧既耗时又容易出现操作者内部和操作者之间的差异。现有方法主要依赖基于图像的方法,这些方法会捕获标准帧并对输入帧进行跨不同解剖结构的分类。这忽略了视频采集的动态性以及其解释。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了多层次类别感知令牌转换器(MCAT),这是一种基于视觉查询的视频剪辑定位(VQ-VCL)方法,旨在协助超声医生进行快速超声扫描。通过提供他们希望分析的解剖结构的视觉查询,MCAT返回包含该解剖结构标准帧的视频剪辑,便于彻底筛查潜在异常。我们在两个超声视频数据集和一个基于Ego4D的自然图像VQ-VCL数据集上评估了MCAT。我们的模型在超声数据集上的mIoU分别高出最新方法10%和13%,在Ego4D数据集上的mIoU高出5.35%,同时使用的令牌减少了96%。MCAT的高效性和准确性对公共卫生具有重大潜在影响,特别是在中低收入国家(LMICs),它可能通过简化标准平面采集、基于超声的筛查和诊断,使超声医生能够检查更多患者,从而加强产前护理。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in AAAI 2025
Summary
本文提出一种名为Multi-Tier Class-Aware Token Transformer(MCAT)的视觉查询视频剪辑定位方法,用于辅助胎儿超声扫描。该方法能够迅速捕捉超声扫描过程,通过提供解剖结构的视觉查询,返回包含标准帧的视频剪辑,便于医生进行潜在异常的全面筛查。该方法在不同数据集上的表现均优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 胎儿超声标准平面采集的重要性:对于胎儿生长评估、异常检测以及遵循临床指南至关重要。
- 现有方法的问题:主要依赖图像方法捕捉标准帧,并分类输入帧,忽略了视频采集的动态性和解读。
- MCAT方法介绍:采用视觉查询视频剪辑定位技术,辅助医生快速捕捉超声扫描过程。
- MCAT的优势:根据解剖结构提供视觉查询,返回包含标准帧的视频剪辑,便于潜在异常的全面筛查。
- MCAT的评估:在超声视频数据集和自然图像VQ-VCL数据集上的表现均优于现有技术,提高了模型的平均交并比(mIoU)。
- MCAT的效率和准确性:使用较少的令牌数量(96%),具有高效的性能。
点此查看论文截图

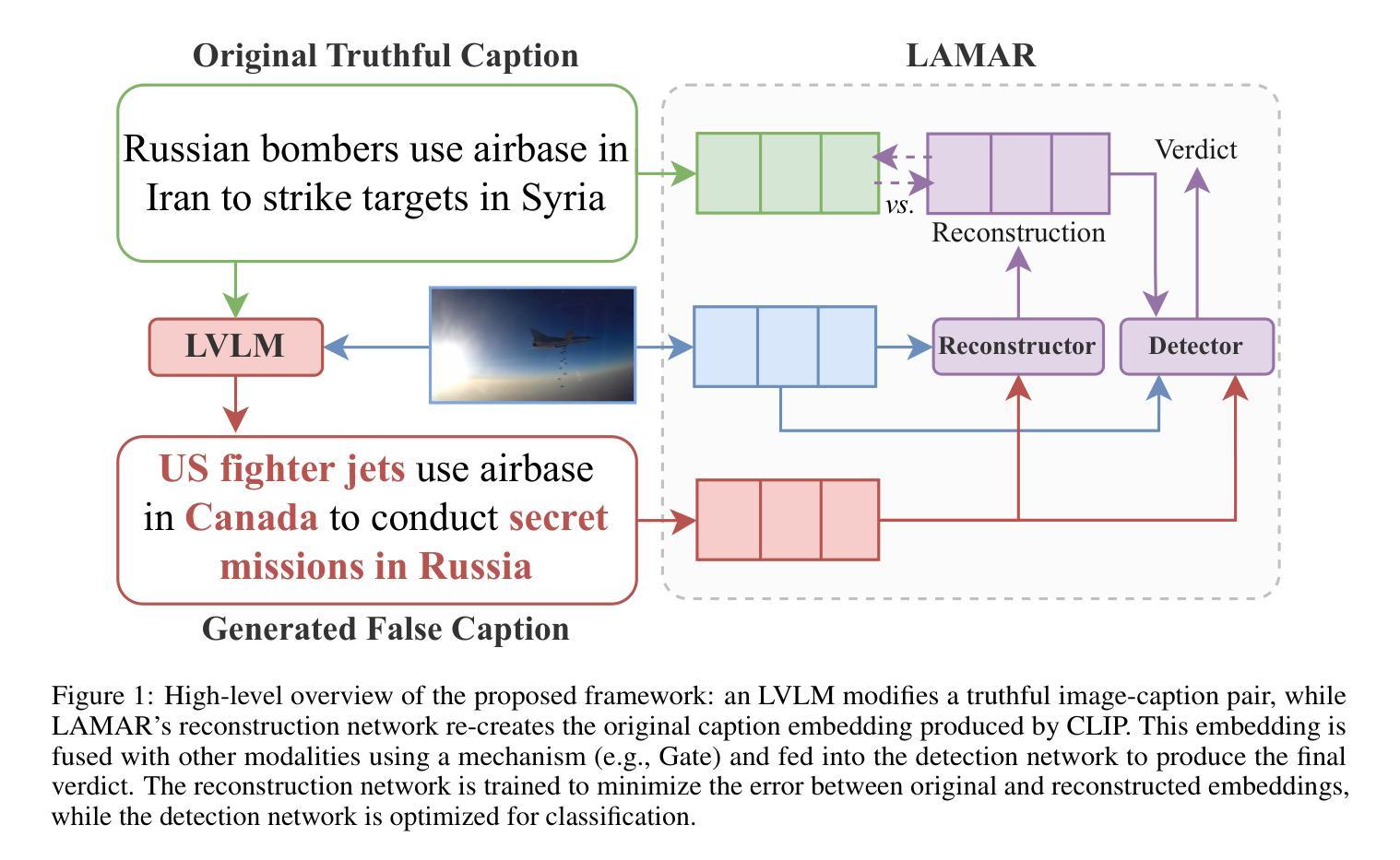
Latent Multimodal Reconstruction for Misinformation Detection
Authors:Stefanos-Iordanis Papadopoulos, Christos Koutlis, Symeon Papadopoulos, Panagiotis C. Petrantonakis
Multimodal misinformation, such as miscaptioned images, where captions misrepresent an image’s origin, context, or meaning, poses a growing challenge in the digital age. To support fact-checkers, researchers have been focusing on creating datasets and developing methods for multimodal misinformation detection (MMD). Due to the scarcity of large-scale annotated MMD datasets, recent studies leverage synthetic training data via out-of-context image-caption pairs or named entity manipulations; altering names, dates, and locations. However, these approaches often produce simplistic misinformation that fails to reflect real-world complexity, limiting the robustness of detection models trained on them. Meanwhile, despite recent advancements, Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) remain underutilized for generating diverse, realistic synthetic training data for MMD. To address this gap, we introduce “MisCaption This!”, a training dataset comprising LVLM-generated miscaptioned images. Additionally, we introduce “Latent Multimodal Reconstruction” (LAMAR), a network trained to reconstruct the embeddings of truthful captions, providing a strong auxiliary signal to the detection process. To optimize LAMAR, we explore different training strategies (end-to-end training and large-scale pre-training) and integration approaches (direct, mask, gate, and attention). Extensive experiments show that models trained on “MisCaption This!” generalize better on real-world misinformation, while LAMAR sets new state-of-the-art on both NewsCLIPpings and VERITE benchmarks; highlighting the potential of LVLM-generated data and reconstruction-based approaches for advancing MMD. We release our code at: https://github.com/stevejpapad/miscaptioned-image-reconstruction
多模态错误信息,如误标注的图像,其中的标题错误地代表了图像的原出处、上下文或意义,在数字时代构成了一个日益严峻的挑战。为了支持事实核查人员,研究人员一直专注于创建数据集并开发多模态误检检测(MMD)方法。由于大规模标注的MMD数据集稀缺,最近的研究通过脱离上下文的图像标题对或命名实体操作(如更改名称、日期和地点)来利用合成训练数据。然而,这些方法通常会产生简单的错误信息,无法反映现实世界的复杂性,限制了在这些数据上训练的检测模型的稳健性。尽管最近有诸多进展,大型视觉语言模型(LVLM)在生成多样且现实的合成训练数据方面仍然使用不足,用于MMD。为了弥补这一空白,我们推出了“MisCaption This!”训练数据集,其中包含由LVLM生成的误标注图像。此外,我们还推出了“潜在多模态重建”(LAMAR)网络,该网络经过训练以重建真实标题的嵌入,为检测过程提供强大的辅助信号。为了优化LAMAR,我们探索了不同的训练策略(端到端训练和大规模预训练)和集成方法(直接、掩码、门控和注意力)。大量实验表明,在“MisCaption This!”上训练的模型在现实世界错误信息上的泛化能力更强,而LAMAR在NewsCLIPpings和VERITE基准测试中均达到了最新水平,突显了LVLM生成数据和重建方法在多模态误检检测中的潜力。我们在https://github.com/stevejpapad/miscaptioned-image-reconstruction上发布了我们的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了多模态错误信息(如误标注的图像)带来的挑战,以及针对这一挑战的多模态错误信息检测(MMD)领域的研究进展。研究中,因缺乏大规模标注的MMD数据集,研究者通过合成训练数据的方式进行研究,如利用脱离上下文关系的图像-字幕配对或命名实体操控技术。然而,这些方法产生的错误信息过于简单,无法反映真实世界的复杂性。为解决这一问题,本文引入了“MisCaption This!”训练数据集,其中包含由大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)生成的误标注图像。同时,本文还提出了“潜在多模态重建”(LAMAR)网络,用于训练检测过程。实验表明,“MisCaption This!”数据集训练的模型在现实世界错误信息上的泛化性能更好,而LAMAR网络在新CLASCLIPpings和VERITE基准测试上均表现出最佳性能。这表明LVLM生成的数据和重建方法在多模态误信息传播方面有着巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
以下是基于文本提取出的七个关键要点:
- 多模态错误信息(如误标注的图像)已成为数字时代的一个挑战。
- 研究者正在开发多模态错误信息检测(MMD)技术以应对这一挑战。
- 由于缺乏大规模标注的MMD数据集,合成训练数据成为研究重点。
- 当前方法产生的错误信息过于简单,无法反映真实世界的复杂性。
- “MisCaption This!”数据集由大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)生成的误标注图像组成,为解决此问题提供了新方向。
- 引入“潜在多模态重建”(LAMAR)网络进行训练检测过程。
点此查看论文截图


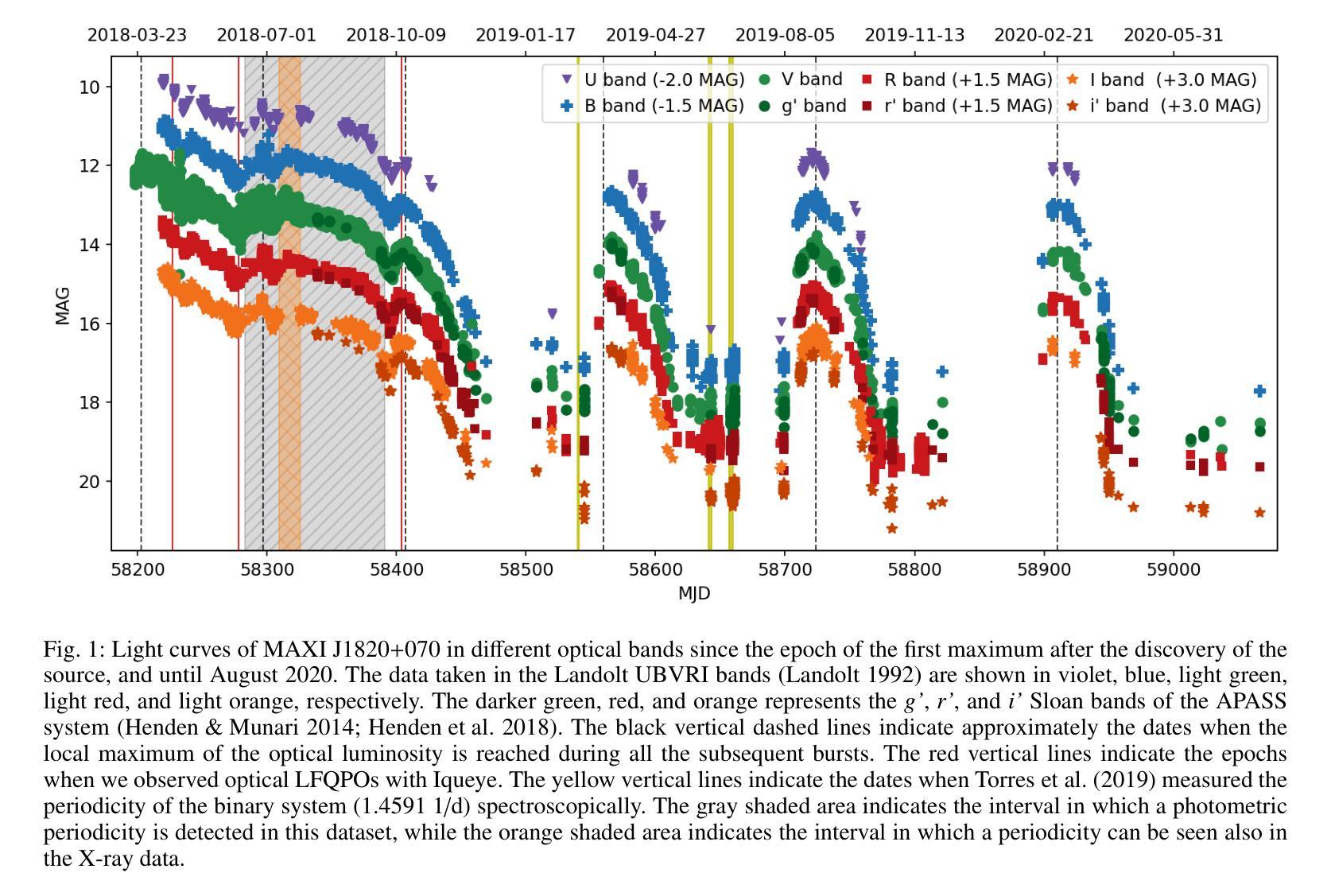
Optical and X-ray timing analysis of the 2018-2020 outburst and rebrightening of the black-hole transient MAXI J1820+070
Authors:M. Fiori, L. Zampieri, A. Burtovoi, G. Naletto, P. Ochner, U. Munari, F. Manzini, A. Vagnozzi, E. A. Barsukova, M. A. Burlak, V. P. Goranski, N. P. Ikonnikova, N. A. Katysheva, E. G. Sheyanov, S. Yu. Shugarov, A. V. Zharova, A. M. Zubareva, S. E. Motta
We report the results of a comprehensive analysis of the multiwavelength (in optical and X-rays) and multitimescale (from months to tenths of a second) variability of the 2018-2020 outburst of the black hole transient MAXI J1820+070. During the first outburst episode, a detailed analysis of the optical photometry shows a periodicity that evolves over time and stabilises at a frequency of $1.4517(1)$ $1/d$ ($\sim0.5%$ longer than the orbital period). This super-orbital modulation is also seen in the X-rays for a few days soon after the transition to the high-soft state. We also observed optical Quasi-Periodic Oscillations (QPOs), which correspond to some of the QPOs observed in X-rays at three different epochs when the source was in the low-hard state. In two epochs, optical QPOs with a centroid consistent with half the frequency of the most prominent X-ray QPO can be seen. If the lowest modulation frequency is the one observed in the optical, the characteristic precession frequency of MAXI J1820+070 is lower than that inferred from the `fundamental’ QPO in the X-rays. Assuming that QPOs can be generated by Lense-Thirring precession, we calculate the spin of the black hole in the case where the fundamental precession frequency is tracked by the optical emission. We find a relatively slowly spinning black hole with a spin parameter $\lesssim 0.15$. The super-orbital optical and X-ray modulations observed after the disappearance of the QPOs may be triggered by the self-irradiation of the outer disc by a standard inner disc truncated at a few gravitational radii.
我们报告了对黑洞瞬态MAXI J1820+070在2018-2020年爆发期的多波长(光学和X射线)和多尺度(从几个月到十分之一秒)变化的综合分析结果。在第一次爆发期间,对光学光度计数据的详细分析显示了一个随时间演化并稳定在$ 1.4517(1)\frac{1}{d}$频率(比轨道周期长约0.5%)的超轨道调制。这种超轨道调制在转到高软态后的几天内也在X射线上观察到。我们还观察到光学准周期振荡(QPOs),这与源处于低硬态时在不同时期观察到的三次X射线QPOs相对应。在两个时期中,光学QPO的中心频率与最突出的X射线QPO频率的一半一致。如果最低调制频率是在光学中观察到的,那么MAXI J1820+070的特征进动频率低于从X射线中的“基本”QPO推断出的频率。假设QPOs可以由Lense-Thirring进动产生,我们计算了黑洞自转的情况,在这种情况下,基本进动频率由光学发射跟踪。我们发现一个相对缓慢旋转的黑洞,其自转参数≤0.15。在QPO消失后观察到的光学和X射线超轨道调制可能由外盘的自我照射触发,标准内盘被截断在几个引力半径内。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 18 figures, 6 tables. Accepted for publication in A&A
Summary
对黑洞瞬态MAXI J1820+070的2018-2020年爆发进行了全面的多波长(光学和X射线)和多尺度(从几个月到十分之一秒)变化分析。在首次爆发期间,光学光度计的详细分析显示周期性随时间演变,最终稳定在每日频率的$1.4517(1)$,比轨道周期长约$0.5%$。超轨道调制也在X射线上持续了几天。观察到光学准周期振荡(QPOs)与源处于低硬态时X射线中的三次不同时期的QPO相对应。在两个时期中,光学QPO的中心频率与最突出的X射线QPO的一半频率一致。假设最低调制频率在光学上被观察到,MAXI J1820+070的特征进动频率低于X射线中的基本QPO所推断的频率。假设QPOs是由Lense-Thirring进动产生的,我们计算了跟踪光学发射的基本进动频率情况下的黑洞自转。发现了一个相对较慢的自转黑洞,自转参数$\leqslant 0.15$。光学和X射线的超轨道调制可能在QPO消失后被触发,可能是由于标准内盘被截断在几个引力半径时对外盘的自照作用。
Key Takeaways
- MAXI J1820+070黑洞瞬态在2018-2020年的爆发中表现出多波长和多尺度的变化特性。
- 在首次爆发期间,观察到光学光度周期性随时间演变并稳定在与轨道周期有轻微差异的频率上。
- 在某些时段观察到光学和X射线中的超轨道调制。
- 光学准周期振荡(QPOs)与X射线中的QPO存在关联,特别是在源处于低硬态时。
- 在某些情况下,光学QPO的中心频率与X射线QPO的一半频率相符。
- 基于Lense-Thirring进动理论,推断出该黑洞的自转速度相对较慢。
点此查看论文截图

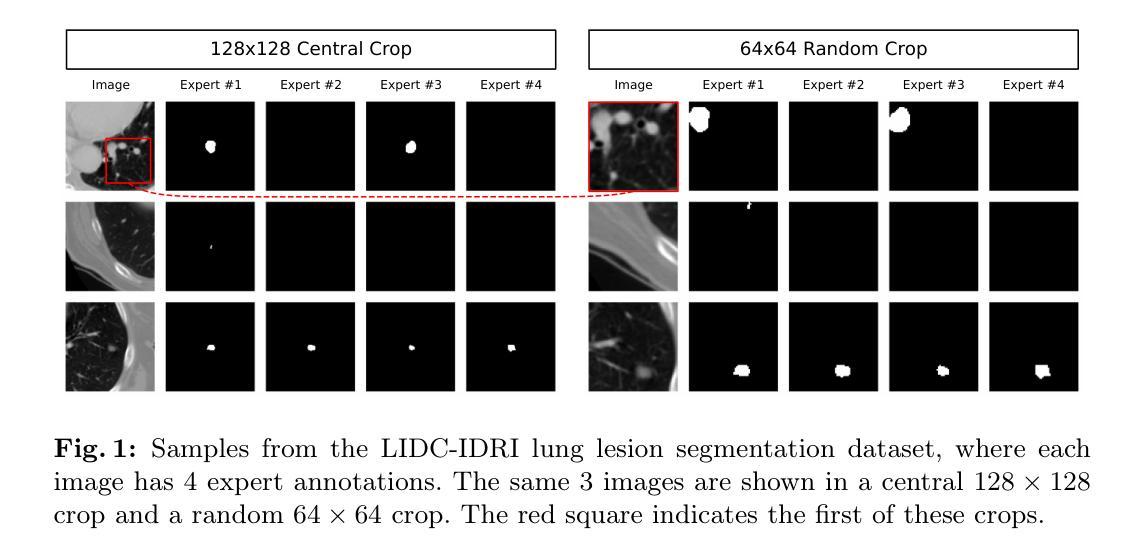
Diffusion Based Ambiguous Image Segmentation
Authors:Jakob Lønborg Christensen, Morten Rieger Hannemose, Anders Bjorholm Dahl, Vedrana Andersen Dahl
Medical image segmentation often involves inherent uncertainty due to variations in expert annotations. Capturing this uncertainty is an important goal and previous works have used various generative image models for the purpose of representing the full distribution of plausible expert ground truths. In this work, we explore the design space of diffusion models for generative segmentation, investigating the impact of noise schedules, prediction types, and loss weightings. Notably, we find that making the noise schedule harder with input scaling significantly improves performance. We conclude that x- and v-prediction outperform epsilon-prediction, likely because the diffusion process is in the discrete segmentation domain. Many loss weightings achieve similar performance as long as they give enough weight to the end of the diffusion process. We base our experiments on the LIDC-IDRI lung lesion dataset and obtain state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance. Additionally, we introduce a randomly cropped variant of the LIDC-IDRI dataset that is better suited for uncertainty in image segmentation. Our model also achieves SOTA in this harder setting.
医学图像分割经常因为专家标注的变异而涉及固有的不确定性。捕捉这种不确定性是一个重要目标,之前的研究已经使用各种生成图像模型来表示专家真实标注的全分布。在这项工作中,我们探索了生成分割扩散模型的设计空间,研究了噪声时间表、预测类型和损失权重的影响。值得注意的是,我们发现通过输入缩放使噪声时间表更加困难可以显著提高性能。我们得出结论,x预测和v预测的表现优于ε预测,可能是因为扩散过程处于离散分割领域。只要对扩散过程的末尾给予足够的重视,许多损失权重都能实现相似的性能。我们的实验基于LIDC-IDRI肺病变数据集,并取得了最新(SOTA)的性能表现。此外,我们还引入了LIDC-IDRI数据集的随机裁剪版本,更适合于图像分割的不确定性。我们的模型在这个更困难的设置中也达到了最新水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at SCIA25
Summary
本文探索了基于扩散模型的医学图像分割生成模型的设计空间,研究了噪声安排、预测类型和损失权重的影响。研究发现,加大输入规模的噪声安排能提高性能,x-和v-预测优于epsilon-预测,这可能是离散分割领域中的扩散过程所致。多种损失权重在给予足够重视扩散过程结束时都能达到相似性能。此外,文章在LIDC-IDRI肺病变数据集上进行了实验,达到了最佳性能,并引入了更适合图像分割不确定性的LIDC-IDRI数据集的随机裁剪版本,模型在该更困难的环境下也达到了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割中由于专家标注差异存在固有不确定性。
- 扩散模型用于生成图像分割模型的设计空间探索中,研究了噪声安排、预测类型和损失权重的影响。
- 加大输入规模的噪声安排能显著提高性能。
- x-和v-预测优于epsilon-预测,这可能与离散分割领域的扩散过程有关。
- 多种损失权重在重视扩散过程结束时都能获得良好性能。
- 实验基于LIDC-IDRI肺病变数据集,达到了最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图

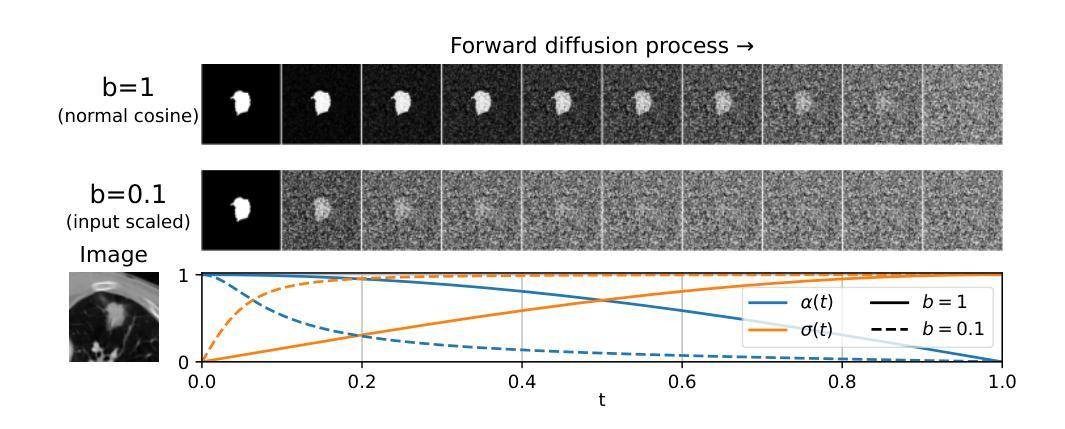
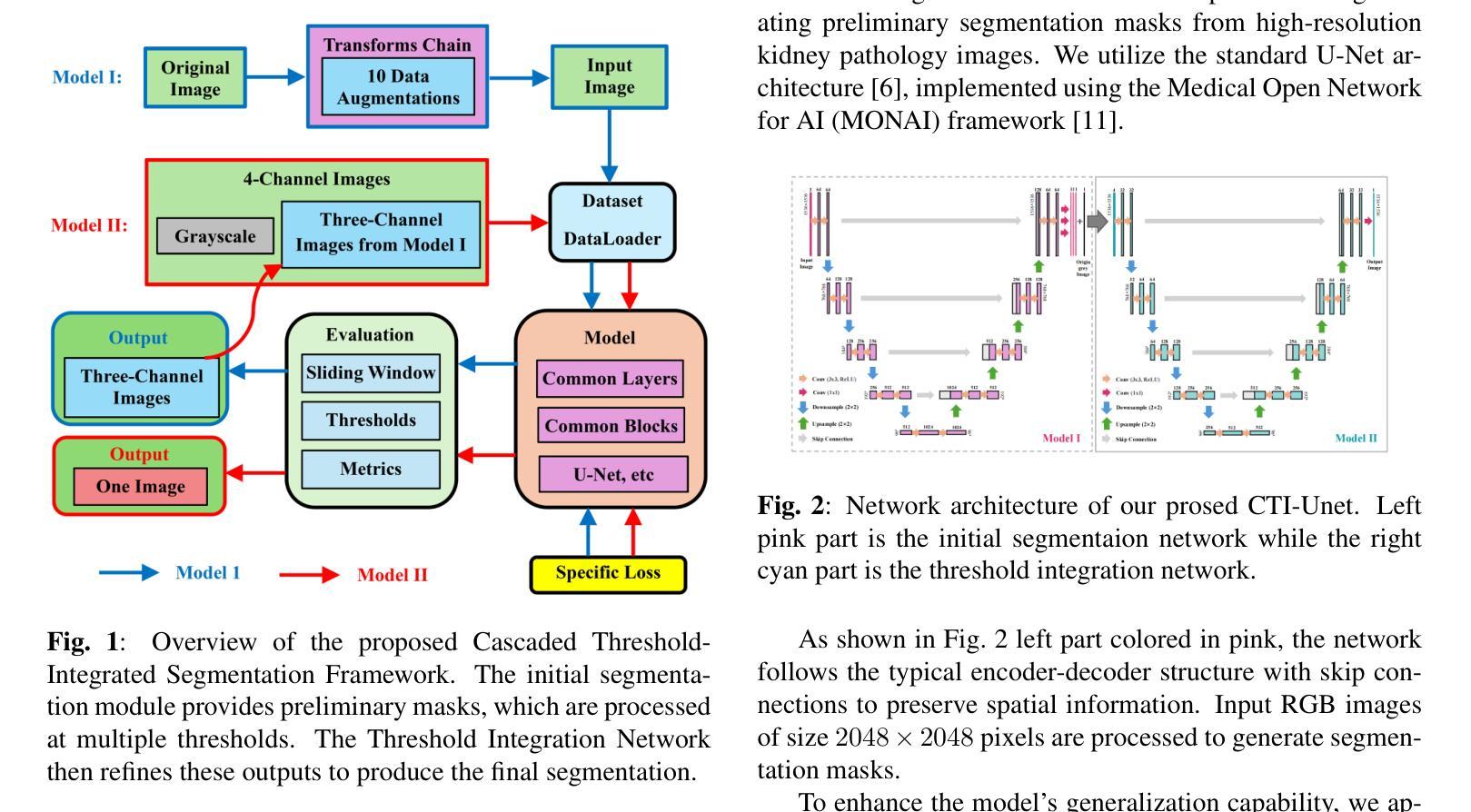
CTI-Unet: Cascaded Threshold Integration for Improved U-Net Segmentation of Pathology Images
Authors:Mingyang Zhu, Yuqiu Liang, Jiacheng Wang
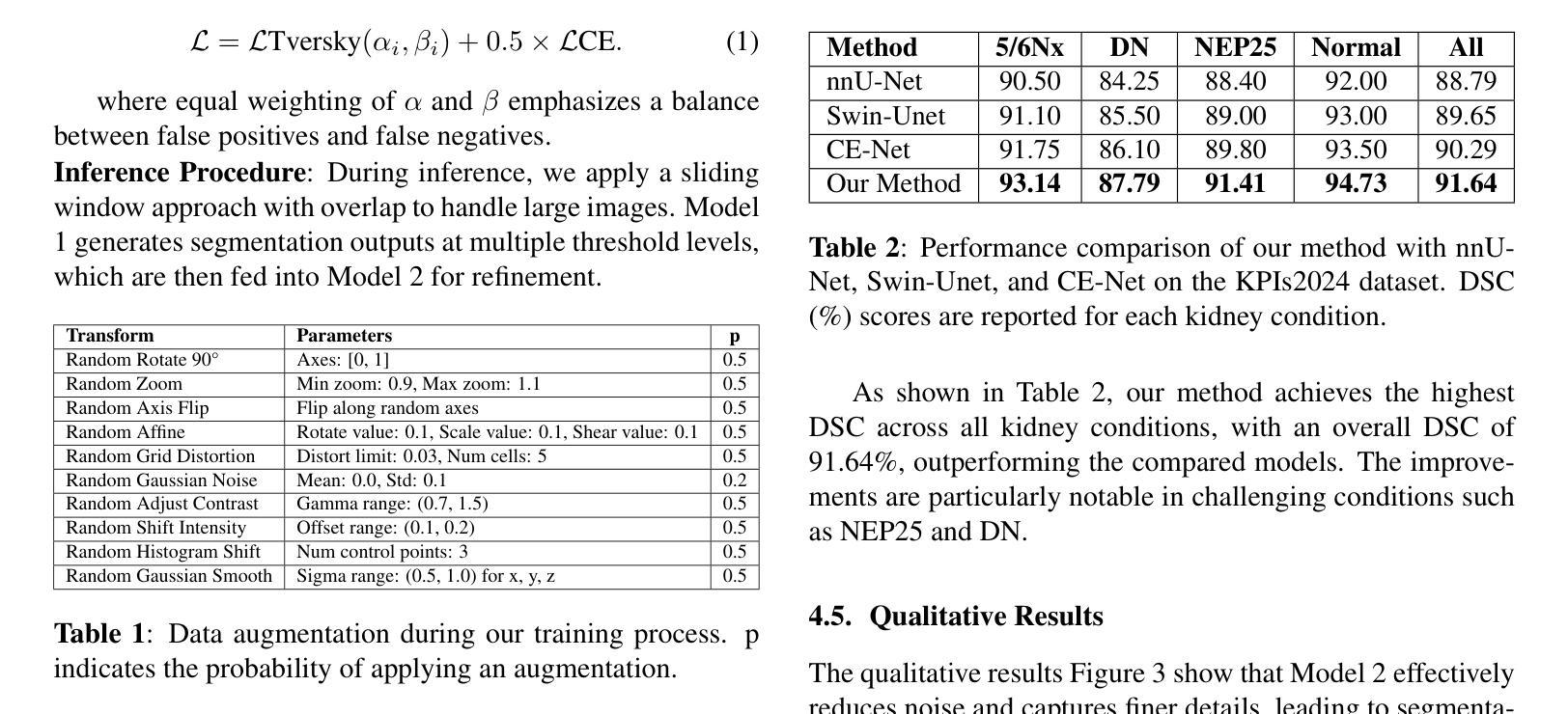
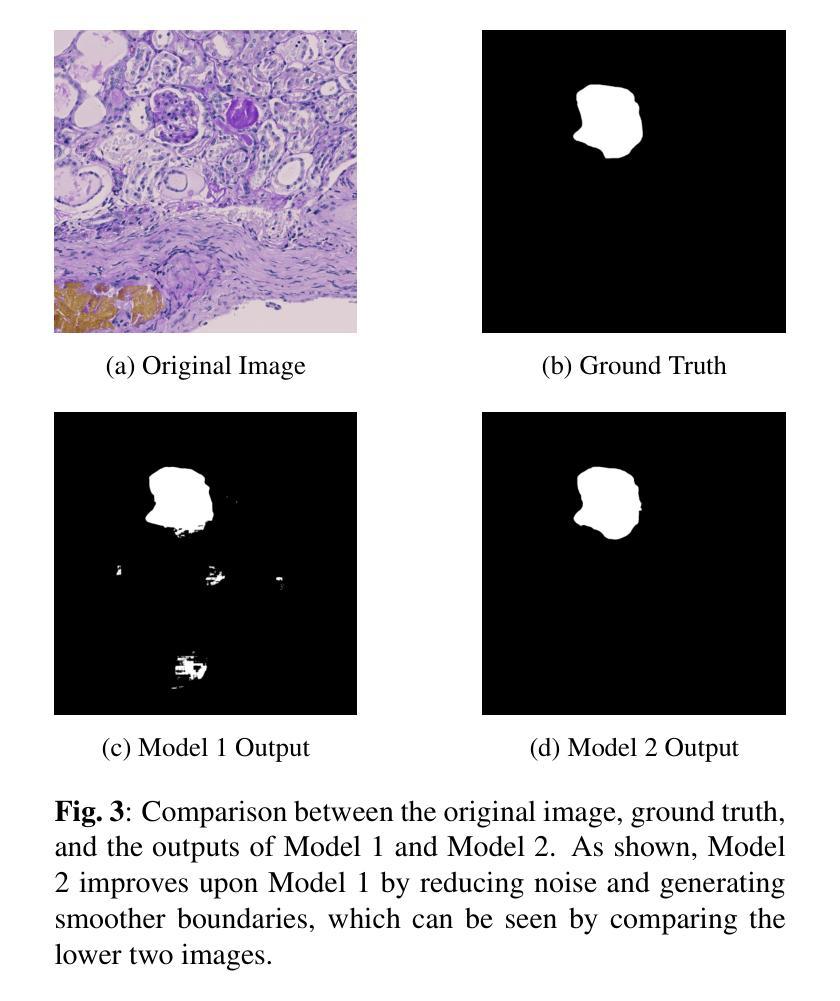
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a growing global health concern, necessitating precise and efficient image analysis to aid diagnosis and treatment planning. Automated segmentation of kidney pathology images plays a central role in facilitating clinical workflows, yet conventional segmentation models often require delicate threshold tuning. This paper proposes a novel \textit{Cascaded Threshold-Integrated U-Net (CTI-Unet)} to overcome the limitations of single-threshold segmentation. By sequentially integrating multiple thresholded outputs, our approach can reconcile noise suppression with the preservation of finer structural details. Experiments on the challenging KPIs2024 dataset demonstrate that CTI-Unet outperforms state-of-the-art architectures such as nnU-Net, Swin-Unet, and CE-Net, offering a robust and flexible framework for kidney pathology image segmentation.
慢性肾脏病(CKD)是全球日益关注的健康问题,需要精确高效的图像分析来辅助诊断和治疗计划。肾脏病理图像的自动分割在促进临床工作流程中起着核心作用,但传统的分割模型通常需要精细的阈值调整。本文针对单一阈值分割的局限性,提出了一种新型的级联阈值集成U-Net(CTI-Unet)。通过顺序集成多个阈值输出,我们的方法可以在抑制噪声的同时保留更精细的结构细节。在具有挑战性的KPIs2024数据集上的实验表明,CTI-Unet优于最新架构,如nnU-Net、Swin-Unet和CE-Net,为肾脏病理图像分割提供了稳健灵活框架。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型的级联阈值集成U-Net(CTI-Unet)方法,用于克服单一阈值分割在肾脏病理图像分析中的局限性。该方法通过按顺序集成多个阈值输出,既抑制了噪声又保留了更精细的结构细节。在具有挑战性的KPIs2024数据集上的实验表明,CTI-Unet优于nnU-Net、Swin-Unet和CE-Net等当前先进架构,为肾脏病理图像分割提供了一个稳健和灵活的分析框架。
Key Takeaways
- 慢性肾脏疾病(CKD)是一个全球性的健康问题,需要精确和高效的图像分析来辅助诊断和治疗计划。
- 自动化肾脏病理图像分割在促进临床工作流程中起到关键作用。
- 传统分割模型通常需要精细的阈值调整,存在局限性。
- CTI-Unet通过级联集成多个阈值输出,克服了单一阈值分割的缺点。
- CTI-Unet方法能在抑制噪声的同时保留更精细的结构细节。
- 在KPIs2024数据集上的实验表明,CTI-Unet性能优于其他先进架构。
点此查看论文截图

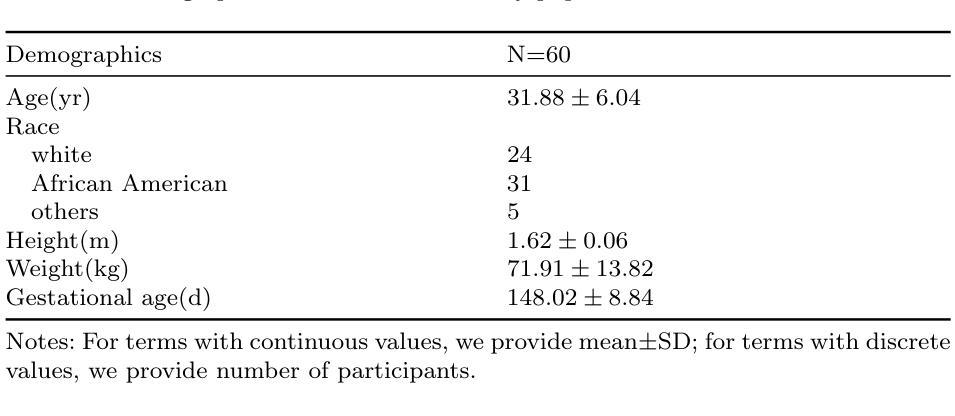
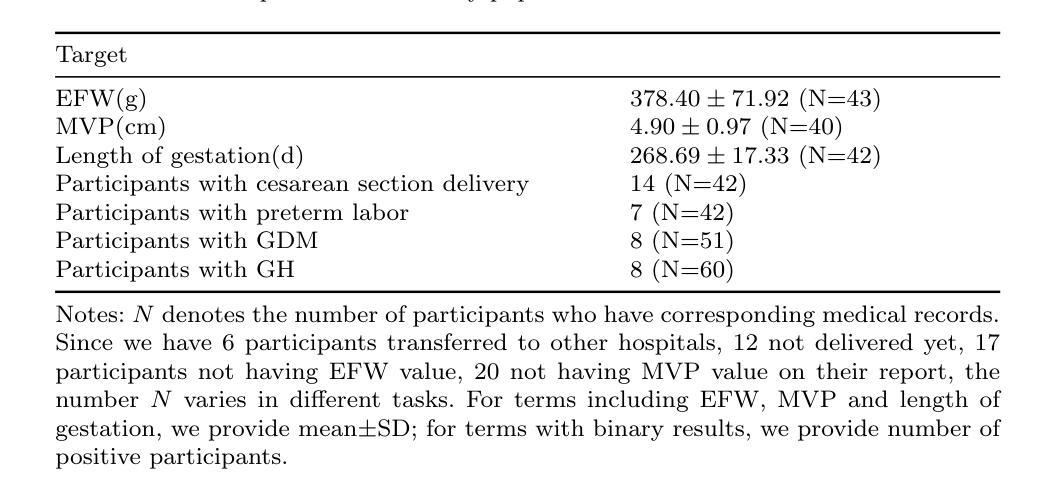
Maternal and Fetal Health Status Assessment by Using Machine Learning on Optical 3D Body Scans
Authors:Ruting Cheng, Yijiang Zheng, Boyuan Feng, Chuhui Qiu, Zhuoxin Long, Joaquin A. Calderon, Xiaoke Zhang, Jaclyn M. Phillips, James K. Hahn
Monitoring maternal and fetal health during pregnancy is crucial for preventing adverse outcomes. While tests such as ultrasound scans offer high accuracy, they can be costly and inconvenient. Telehealth and more accessible body shape information provide pregnant women with a convenient way to monitor their health. This study explores the potential of 3D body scan data, captured during the 18-24 gestational weeks, to predict adverse pregnancy outcomes and estimate clinical parameters. We developed a novel algorithm with two parallel streams which are used for extract body shape features: one for supervised learning to extract sequential abdominal circumference information, and another for unsupervised learning to extract global shape descriptors, alongside a branch for demographic data. Our results indicate that 3D body shape can assist in predicting preterm labor, gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), gestational hypertension (GH), and in estimating fetal weight. Compared to other machine learning models, our algorithm achieved the best performance, with prediction accuracies exceeding 88% and fetal weight estimation accuracy of 76.74% within a 10% error margin, outperforming conventional anthropometric methods by 22.22%.
监测孕妇和胎儿在妊娠期间的健康状况对于预防不良结果至关重要。虽然超声扫描等测试提供了很高的准确性,但它们可能成本高昂且使用不便。远程医疗和更易于获取的身体形态信息为孕妇提供了一种便捷的健康监测方式。本研究探讨了妊娠18-24周期间采集的3D身体扫描数据在预测不良妊娠结局和估计临床参数方面的潜力。我们开发了一种新型算法,该算法有两个并行流用于提取身体形态特征:一个用于监督学习以提取连续的腹围信息,另一个用于无监督学习以提取全局形状描述符,以及一个用于人口统计学数据的分支。我们的结果表明,三维身体形态有助于预测早产、妊娠期糖尿病(GDM)、妊娠期高血压(GH),并有助于估计胎儿体重。与其他机器学习模型相比,我们的算法性能最佳,预测准确率超过88%,胎儿体重估计误差在10%以内达到76.74%,比传统人体测量方法高出22.22%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了利用孕期18-24周获取的3D身体扫描数据预测不良妊娠结局和估计临床参数的可能性。开发了一种新型算法,通过监督学习和无监督学习提取身体形状特征,并设立分支处理人口统计数据。研究结果表明,3D身体形状有助于预测早产、妊娠期糖尿病和妊娠期高血压等疾病,并准确估计胎儿体重,其性能优于其他机器学习模型。
Key Takeaways
- 3D身体扫描数据在预测不良妊娠结局和估计临床参数方面具有潜力。
- 开发了一种结合监督学习和无监督学习的算法来提取身体形状特征。
- 3D身体形状可用于预测早产、妊娠期糖尿病和妊娠期高血压等疾病。
- 算法的预测准确率超过88%,胎儿体重估计准确率在误差范围10%内达到76.74%。
- 与传统人类学方法相比,该算法性能优越,准确率提高了22.22%。
- 该研究为利用更便捷的方式监测母胎健康提供了可能性,降低了不良妊娠结局的风险。
点此查看论文截图

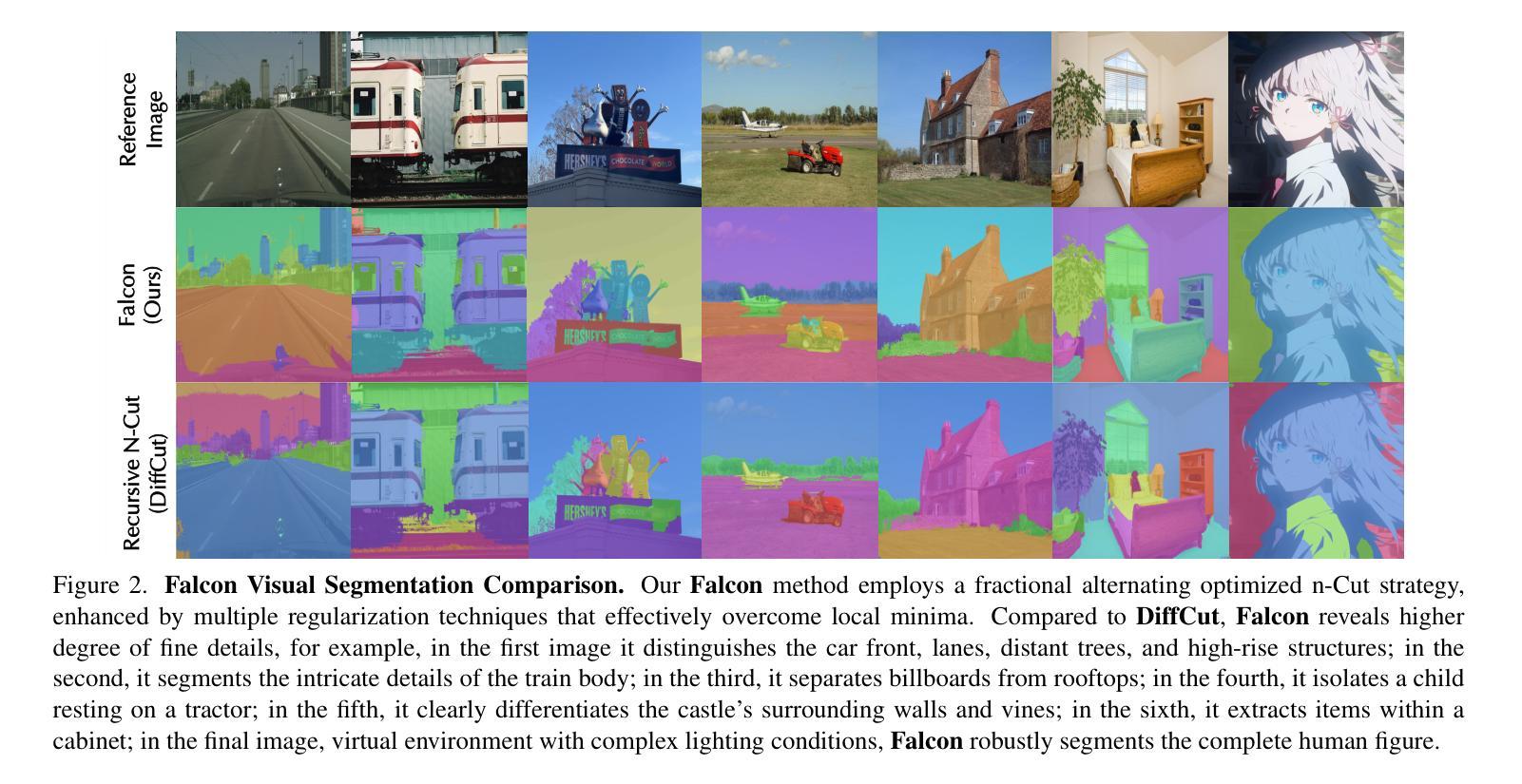
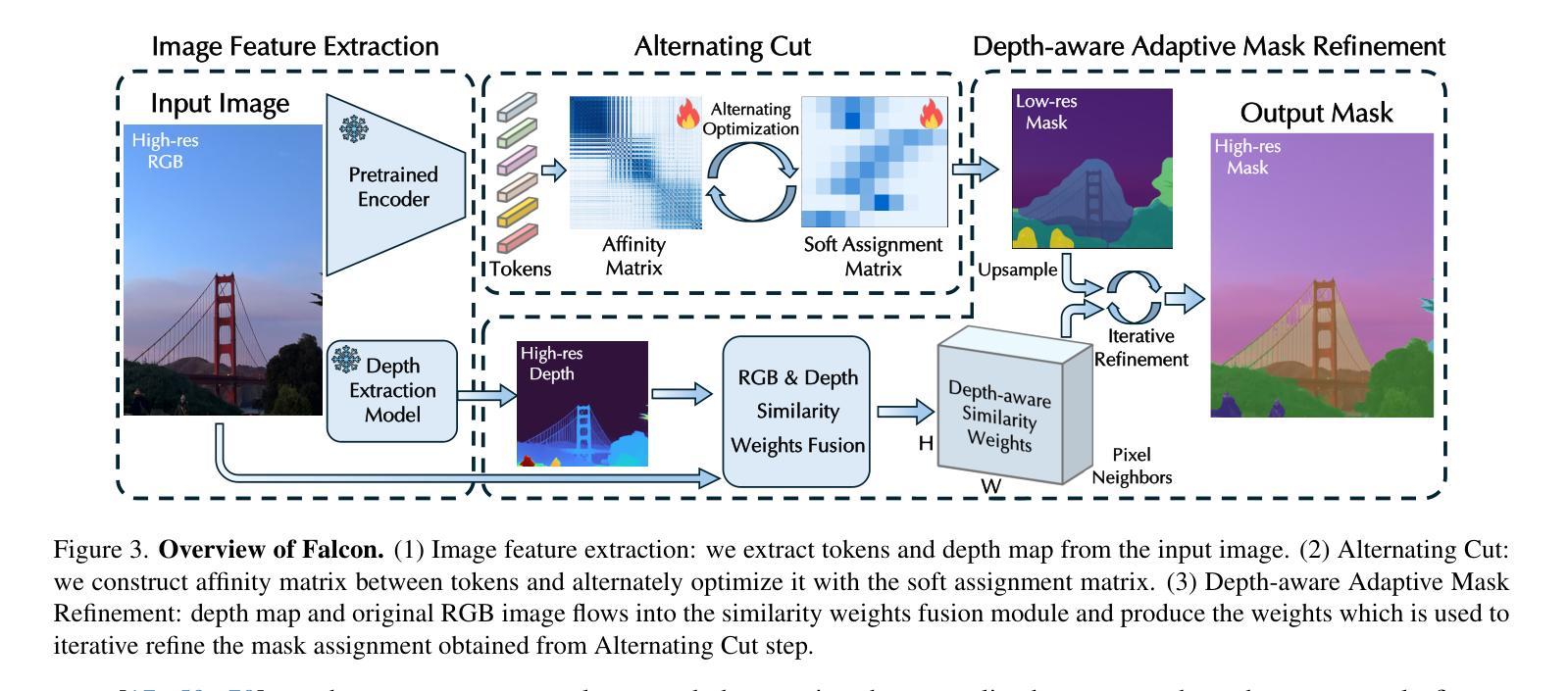
Falcon: Fractional Alternating Cut with Overcoming Minima in Unsupervised Segmentation
Authors:Xiao Zhang, Xiangyu Han, Xiwen Lai, Yao Sun, Pei Zhang, Konrad Kording
Today’s unsupervised image segmentation algorithms often segment suboptimally. Modern graph-cut based approaches rely on high-dimensional attention maps from Transformer-based foundation models, typically employing a relaxed Normalized Cut solved recursively via the Fiedler vector (the eigenvector of the second smallest eigenvalue). Consequently, they still lag behind supervised methods in both mask generation speed and segmentation accuracy. We present a regularized fractional alternating cut (Falcon), an optimization-based K-way Normalized Cut without relying on recursive eigenvector computations, achieving substantially improved speed and accuracy. Falcon operates in two stages: (1) a fast K-way Normalized Cut solved by extending into a fractional quadratic transformation, with an alternating iterative procedure and regularization to avoid local minima; and (2) refinement of the resulting masks using complementary low-level information, producing high-quality pixel-level segmentations. Experiments show that Falcon not only surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods by an average of 2.5% across six widely recognized benchmarks (reaching up to 4.3% improvement on Cityscapes), but also reduces runtime by around 30% compared to prior graph-based approaches. These findings demonstrate that the semantic information within foundation-model attention can be effectively harnessed by a highly parallelizable graph cut framework. Consequently, Falcon can narrow the gap between unsupervised and supervised segmentation, enhancing scalability in real-world applications and paving the way for dense prediction-based vision pre-training in various downstream tasks. The code is released in https://github.com/KordingLab/Falcon.
今天的无监督图像分割算法通常分割效果并不理想。现代基于图割的方法依赖于基于Transformer的基础模型产生的高维注意力图,通常采用松弛的归一化切割(通过Fiedler向量解决特征向量的二次最小特征值),但它们在掩膜生成速度和分割准确性方面仍然落后于有监督方法。我们提出了一个正则化分数交替切割(Falcon),这是一个基于优化的K-方式归一化切割,无需依赖递归特征向量计算,实现了速度和准确性的实质性提升。Falcon分为两个阶段:第一阶段是通过扩展为分数二次变换快速解决K-方式归一化切割问题,采用交替迭代程序和正则化以避免局部最小值;第二阶段是利用补充的底层信息对得到的掩膜进行精细化处理,产生高质量的像素级分割。实验表明,Falcon不仅在六个广泛认可的基准测试上平均优于现有最先进的方法(在Cityscapes上最高达到4.3%的提升),而且与之前基于图的的方法相比,运行时间缩短了约30%。这些发现表明,高度可并行化的图割框架可以有效地利用基础模型注意力中的语义信息。因此,Falcon可以缩小无监督和有监督分割之间的差距,增强在现实世界应用中的可扩展性,并为各种下游任务中的密集预测视觉预训练铺平道路。代码已发布在https://github.com/KordingLab/Falcon。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于优化的K-way归一化切割方法——Falcon,无需依赖递归特征向量计算,实现了图像分割的速度和准确性的显著提升。Falcon分为两个阶段:快速K-way归一化切割和基于低级别信息的精细优化。实验结果显示,Falcon在六个广泛认可的基准测试中平均超过现有最先进的方法2.5%,并在Cityscapes上最高提升达到4.3%,同时与前置图的方法相比运行时间缩短了约30%。该代码已发布在KordingLab/Falcon上。
Key Takeaways
- 现代图像分割算法仍面临分割效果欠佳的问题,存在优化的需求。
- Falcon是一种优化型图像分割方法,旨在提升速度和准确度,是首个不使用递归特征向量计算的K-way归一化切割方法。
- Falcon包含两个阶段:快速K-way归一化切割和基于低级别信息的精细优化,旨在生成高质量像素级别的分割结果。
- 实验结果表明,Falcon在多个基准测试中性能优于现有方法,特别是在Cityscapes上的提升显著。
- Falcon缩小了无监督和有监督图像分割之间的差距,增强了其在现实世界应用中的可扩展性。这为多种下游任务中的密集预测式视觉预训练开辟了道路。
点此查看论文截图

Class Imbalance Correction for Improved Universal Lesion Detection and Tagging in CT
Authors:Peter D. Erickson, Tejas Sudharshan Mathai, Ronald M. Summers
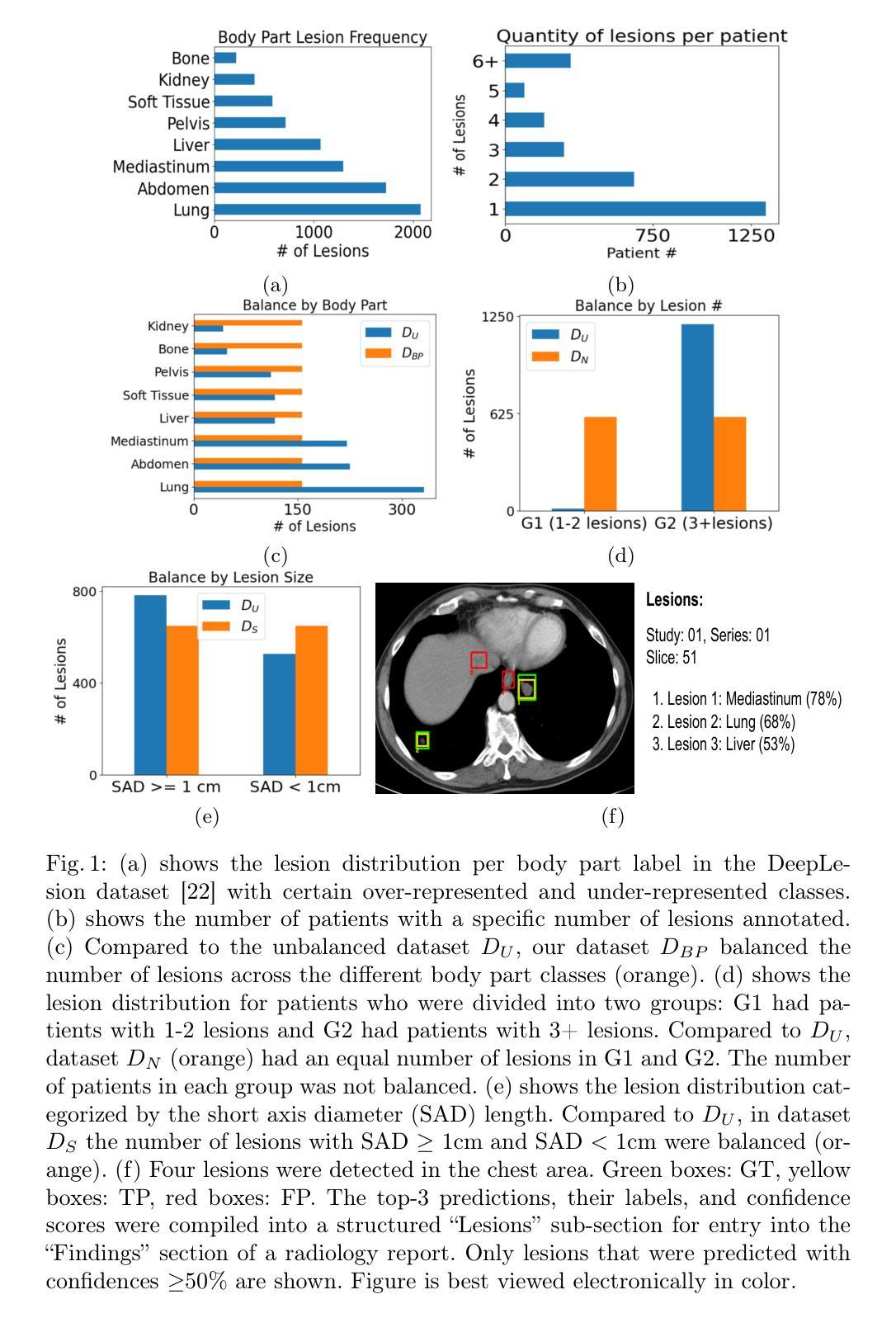
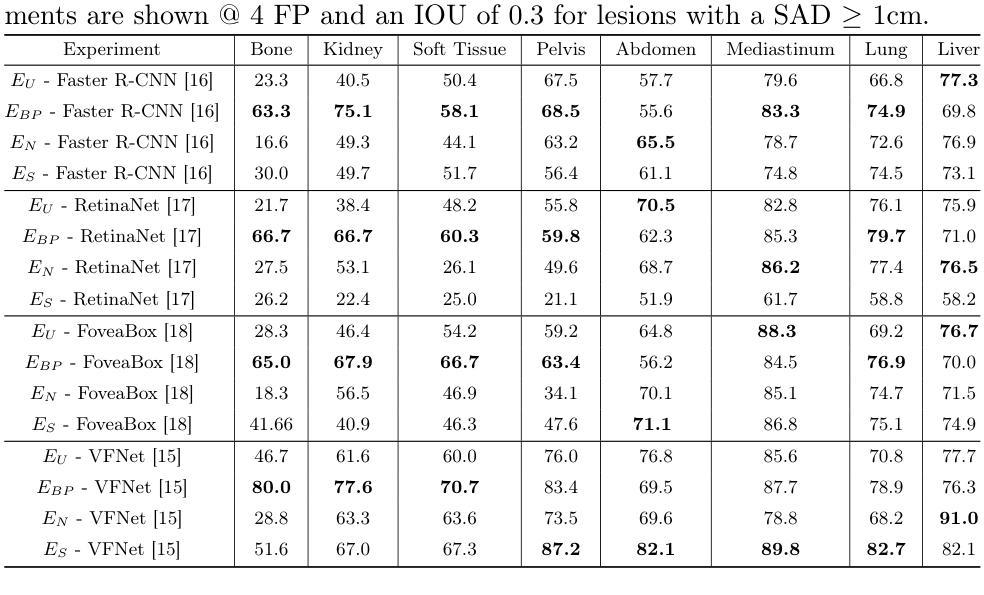
Radiologists routinely detect and size lesions in CT to stage cancer and assess tumor burden. To potentially aid their efforts, multiple lesion detection algorithms have been developed with a large public dataset called DeepLesion (32,735 lesions, 32,120 CT slices, 10,594 studies, 4,427 patients, 8 body part labels). However, this dataset contains missing measurements and lesion tags, and exhibits a severe imbalance in the number of lesions per label category. In this work, we utilize a limited subset of DeepLesion (6%, 1331 lesions, 1309 slices) containing lesion annotations and body part label tags to train a VFNet model to detect lesions and tag them. We address the class imbalance by conducting three experiments: 1) Balancing data by the body part labels, 2) Balancing data by the number of lesions per patient, and 3) Balancing data by the lesion size. In contrast to a randomly sampled (unbalanced) data subset, our results indicated that balancing the body part labels always increased sensitivity for lesions >= 1cm for classes with low data quantities (Bone: 80% vs. 46%, Kidney: 77% vs. 61%, Soft Tissue: 70% vs. 60%, Pelvis: 83% vs. 76%). Similar trends were seen for three other models tested (FasterRCNN, RetinaNet, FoveaBox). Balancing data by lesion size also helped the VFNet model improve recalls for all classes in contrast to an unbalanced dataset. We also provide a structured reporting guideline for a Lesions'' subsection to be entered into the Findings’’ section of a radiology report. To our knowledge, we are the first to report the class imbalance in DeepLesion, and have taken data-driven steps to address it in the context of joint lesion detection and tagging.
放射科医生通常在计算机断层扫描(CT)中检测和定位病灶,以进行癌症分期和肿瘤负担评估。为了可能地辅助他们的努力,已经开发出了多种病灶检测算法,其中有一个大型公共数据集叫做DeepLesion(包含32,735个病灶、32,120张CT切片、10,594次研究、4,427名患者和8个身体部位标签)。然而,这个数据集存在测量缺失和病灶标签缺失的问题,并且每个标签类别中的病灶数量存在严重不平衡。在这项工作中,我们使用了DeepLesion的一个有限子集(6%,1331个病灶,1309张切片),其中包含病灶注释和身体部位标签,以训练VFNet模型进行病灶检测和标记。我们通过三项实验来解决类别不平衡问题:1)按身体部位标签平衡数据,2)按每个患者的病灶数量平衡数据,3)按病灶大小平衡数据。与随机采样(不平衡)的数据子集相比,我们的结果表明,平衡身体部位标签始终提高了对于数据量少且病灶尺寸大于等于1厘米的类别的敏感性(如骨:80%对46%,肾脏:77%对61%,软组织:70%对60%,骨盆:83%对76%)。其他三个经过测试的模型(FasterRCNN、RetinaNet、FoveaBox)也呈现出类似趋势。与不平衡的数据集相比,通过病灶大小平衡数据也有助于VFNet模型提高所有类别的召回率。我们还为放射报告“发现”部分中的“病灶”子部分提供了结构化报告指南。据我们所知,我们是第一批报告DeepLesion中类别不平衡并采取了数据驱动的方法来应对其在联合病灶检测和标记上下文中的问题的团队。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at MICCAI MILLAND Workshop 2022
Summary
本研究利用DeepLesion数据集的一个有限子集训练了VFNet模型,用于检测并标注病变。针对数据集存在的类别不平衡问题,通过平衡身体部位标签、按患者病变数量和病变大小平衡数据三种实验方法,提高了模型的敏感性。同时,提供了一种结构化报告指南,用于在放射学报告的“发现”部分添加“病变”子部分。
Key Takeaways
- 使用DeepLesion数据集的有限子集训练了VFNet模型进行病变检测和标注。
- 发现了数据集中的类别不平衡问题,并设计了三种实验方法来解决这一问题。
- 通过平衡身体部位标签的方法,对低数据量的类别(如骨骼、肾脏、软组织、骨盆)提高了大于等于1厘米的病变的敏感性。
- 其他三种模型(FasterRCNN、RetinaNet、FoveaBox)也显示出类似趋势。
- 通过平衡病变大小的数据,有助于提高所有类别的召回率。
- 提供了一种结构化报告指南,用于放射报告的“发现”部分中的“病变”子部分。
点此查看论文截图

A Lightweight Large Vision-language Model for Multimodal Medical Images
Authors:Belal Alsinglawi, Chris McCarthy, Sara Webb, Christopher Fluke, Navid Toosy Saidy
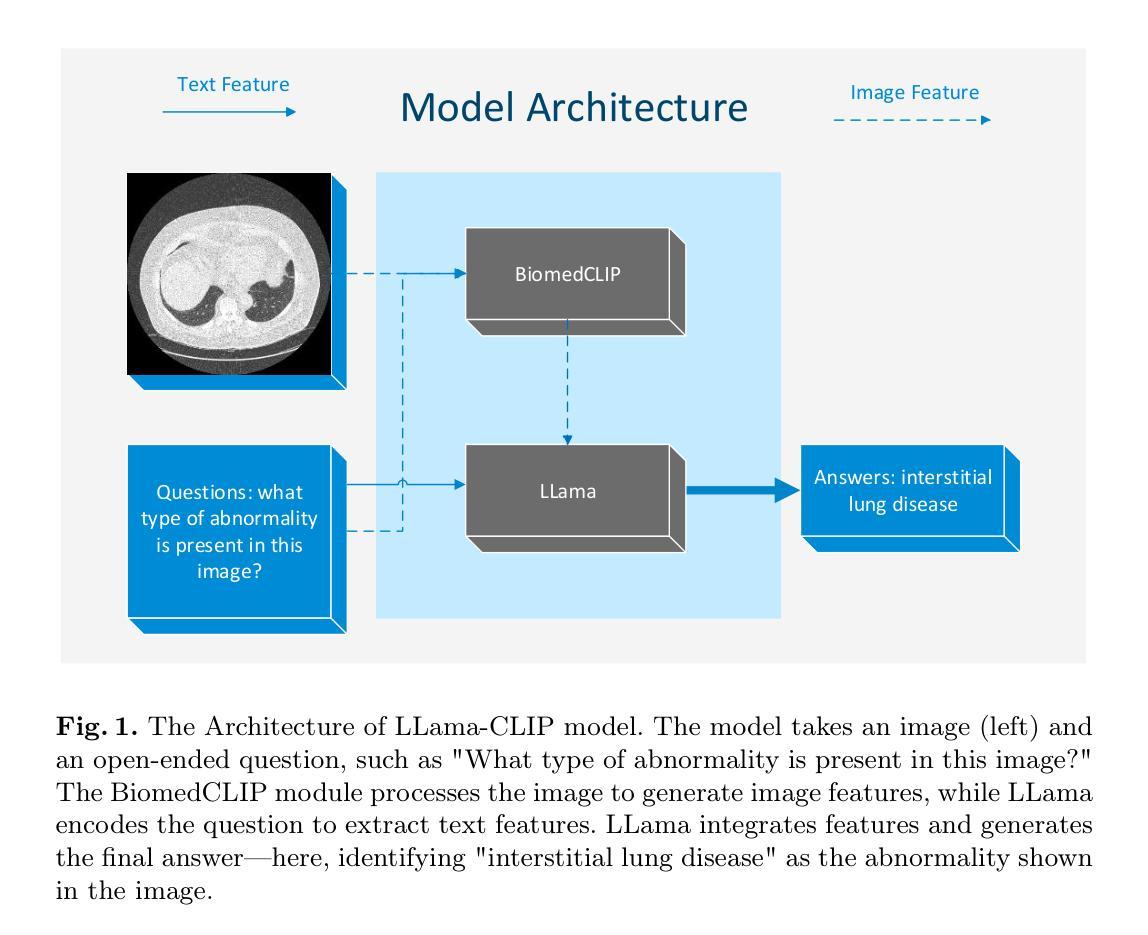
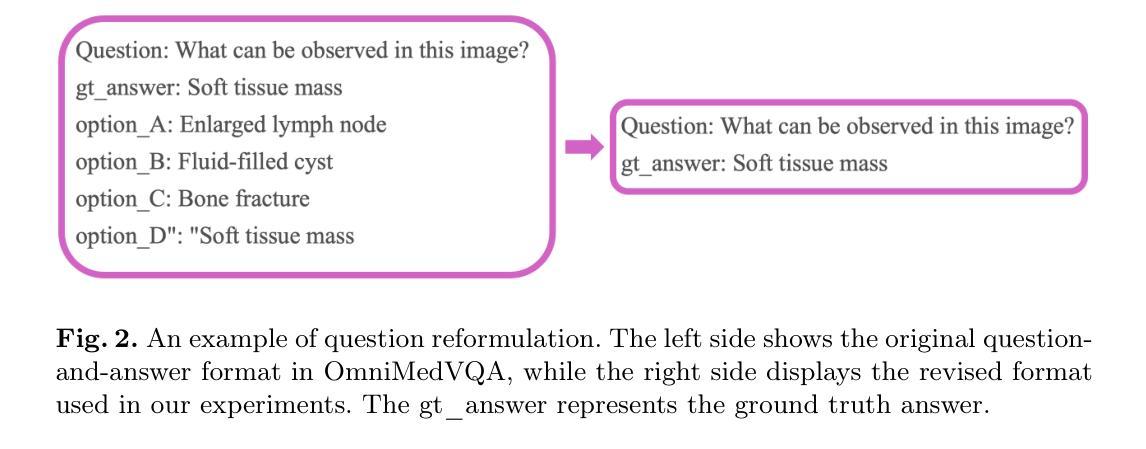
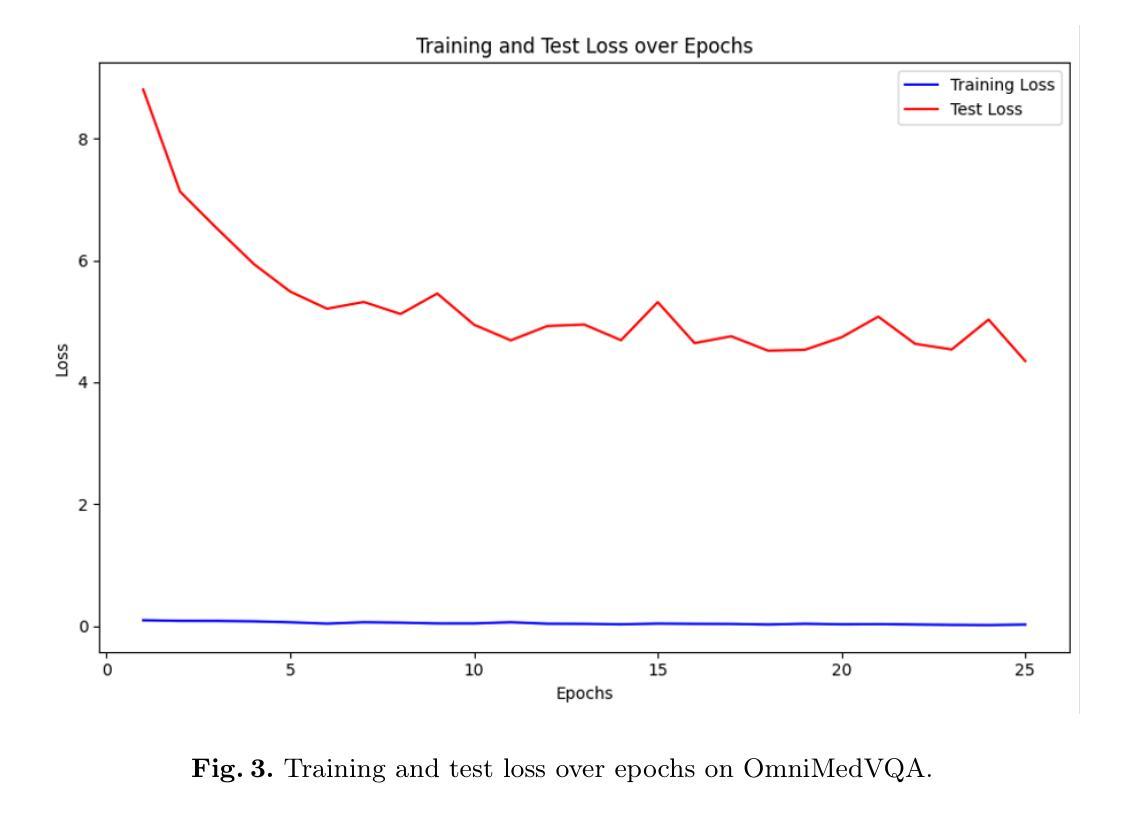
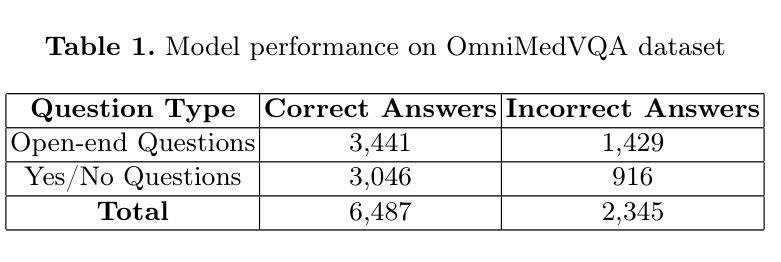
Medical Visual Question Answering (VQA) enhances clinical decision-making by enabling systems to interpret medical images and answer clinical queries. However, developing efficient, high-performance VQA models is challenging due to the complexity of medical imagery and diverse modalities. In this paper, we introduce a lightweight, multimodal VQA model integrating BiomedCLIP for image feature extraction and LLaMA-3 for text processing. Designed for medical VQA tasks, our model achieves state-of-the-art performance on the OmniMedVQA dataset. With approximately 8 billion parameters, it requires only two NVIDIA 40 GB A100 GPUs, demonstrating superior efficiency over larger models. Our results show 73.4% accuracy for open-end questions, surpassing existing models and validating its potential for real-world medical applications. Key contributions include a specialized multimodal VQA model, a resource-efficient architecture, and strong performance in answering open-ended clinical questions.
医疗视觉问答(VQA)通过使系统解读医学图像和回答临床问题,从而提高了临床决策能力。然而,由于医学图像的复杂性和多种模态,开发高效、高性能的VQA模型具有挑战性。在本文中,我们介绍了一个轻量级的、多模态的VQA模型,该模型集成了BiomedCLIP进行图像特征提取和LLaMA-3进行文本处理。该模型针对医疗VQA任务设计,在OmniMedVQA数据集上达到了最先进的性能。该模型大约有8亿个参数,仅需要两个NVIDIA 40GB A100 GPU,显示出比大型模型更高的效率。我们的结果表明,该模型在开放性问题上的准确率达到了73.4%,超过了现有模型,并验证了其在现实世界医疗应用中的潜力。主要贡献包括专门的多模态VQA模型、资源高效的架构,以及在回答开放的临床问题方面的强劲表现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 4 figures
Summary
本文介绍了医学视觉问答(VQA)技术在临床决策中的应用及其面临的挑战。文章提出了一种轻量级的多模态VQA模型,结合了BiomedCLIP进行图像特征提取和LLaMA-3进行文本处理。该模型针对医学VQA任务设计,在OmniMedVQA数据集上实现了卓越的性能,仅需两个NVIDIA 40 GB A100 GPU,参数约为8亿,展现出较高的效率。该模型在开放性问题上的准确率达到了73.4%,超过了现有模型,验证了其在真实世界医学应用中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 医学视觉问答(VQA)技术能够提高临床决策水平,通过解释医学图像和回答临床问题来实现。
- 开发高效、高性能的VQA模型面临挑战,主要原因是医学图像的复杂性和多种模态。
- 介绍的轻量级多模态VQA模型结合了BiomedCLIP进行图像特征提取和LLaMA-3进行文本处理。
- 该模型在OmniMedVQA数据集上表现优异,参数较少且计算效率较高,只需两个NVIDIA 40 GB A100 GPUs。
- 模型在开放性问题上的准确率为73.4%,超过了现有模型。
- 该模型具有潜力应用于真实世界的医学场景。
点此查看论文截图

Core-Excited States of Linear and Bent Uranyl Complexes: Insights from High-Energy Resolution X-ray Spectroscopy and Relativistic Quantum Chemistry
Authors:Wilken Aldair Misael, Lucia Amidani, Juliane März, Elena F. Bazarkina, Kristina O. Kvashnina, Valérie Vallet, André Severo Pereira Gomes
Advanced X-ray spectroscopic techniques are widely recognized as state-of-the-art tools for probing the electronic structure, bonding, and chemical environments of the heaviest elements in the periodic table. In this study, we employ X-ray absorption near-edge structure measurements in high-energy resolution fluorescence detection (HERFD-XANES) mode to investigate the core states arising from excitations out of the U 3d${_{3/2}}$ (M$_4$ edge) levels for molecular complexes in which the uranyl moiety deviates from linearity to varying degrees, and in particular systems containing the UO$_2$Cl$_2$ group such as UO$_2$Cl$_2$.n(H$_2$O) and UO$_2$Cl$_2$(phen)$_2$, which in the latter case exhibits a pronounced O-U-O bending angle. These U M$_4$ edge HERFD-XANES spectra are compared to those of other linear (Cs$_2$UO$_2$Cl$_4$) or pseudo-linear ([UO$_2$(NO$_3$)$_2$.n(H$_2$O)]) uranyl complexes. This evaluation is complemented by ab initio relativistic quantum chemistry simulations using 2-component Time-Dependent Density Functional Theory (TD-DFT) with the CAM-B3LYP functional, employing the Tamm-Dancoff approximation (2c-TDA). Our 2c-TDA simulations show modest deviations from the HERFD-XANES data, with peak splittings differing by less than 1 eV from experimental values. These core-excited states were further characterized by Natural Transition Orbital (NTO) analysis. Overall, our results highlight the influence of equatorial ligands on the spectroscopic signatures, particularly pronounced in UO$_2$Cl$_2$(phen)$2$, where the U 3d${{3/2}} \rightarrow$ $5f$ $\sigma{_u}^{*}$ satellite transition appears at lower energies compared to the other systems studied.
高级X射线光谱技术被公认为是探测周期表中重元素的电子结构、键合和化学环境的最新工具。在本研究中,我们采用高能量分辨率荧光检测(HERFD)模式下的X射线吸收近边结构测量技术,研究偏离线性的铀酰分子复合物的核心状态,特别是含有UO2Cl2基团的体系,如UO2Cl2.n(H2O)和UO2Cl2(phen)2。在后一种情况下,表现出明显的O-U-O弯曲角。我们将这些UM4边缘的HERFD-XANES光谱与其他线性(如Cs2UO2Cl4)或伪线性(如UO2(NO3)2.n(H2O))的铀酰复合物的光谱进行了比较。这一评估辅以基于时间的从头计算相对论量子化学模拟,采用含时密度泛函理论(TD-DFT)的CAM-B3LYP功能,采用Tamm-Dancoff近似(2c-TDA)。我们的2c-TDA模拟与HERFD-XANES数据有适度偏差,峰值分裂与实验值相差不到1电子伏特。这些核心激发态进一步通过自然过渡轨道(NTO)分析表征。总的来说,我们的结果突出了赤道配体对光谱特征的影响,特别是在UO2Cl2(phen)2中尤为明显,其中U 3d 3/2 → 5f σu *卫星转换出现在比其他系统更低的能量处。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 9 figures, 3 tables
Summary
本研究利用高能量分辨率荧光检测(HERFD-XANES)模式下的X射线吸收近边结构测量技术,探究不同程度偏离线性的铀酰分子复合物的核心态,特别是对含有UO2Cl2基团的体系,如UO2Cl2·n(H2O)和UO2Cl2(phen)2。通过与线性或伪线性铀酰复合物的比较,结合从头计算的相对论量子化学模拟,本研究揭示了赤道配体对光谱特征的影响,特别是在UO2Cl2(phen)2体系中,U 3d{3/2}→$5f$σu*卫星过渡在较低能量处出现与其他系统相比更为明显。
Key Takeaways
- 研究采用HERFD-XANES模式探究了不同程度偏离线性的铀酰分子复合物的核心态。
- UO2Cl2及其相关复合物体系的光谱特性被详细研究,特别是含有弯曲O-U-O角的UO2Cl2(phen)2体系。
- 通过与其他线性或伪线性铀酰复合物的比较,揭示了赤道配体对光谱特征的重要影响。
- 使用了从头计算的相对论量子化学模拟来辅助分析和解释实验结果。
- 2c-TDA模拟与HERFD-XANES数据有适度偏差,峰值分裂与实验值差异小于1电子伏特。
- 自然跃迁轨道(NTO)分析进一步表征了核心激发态。
点此查看论文截图

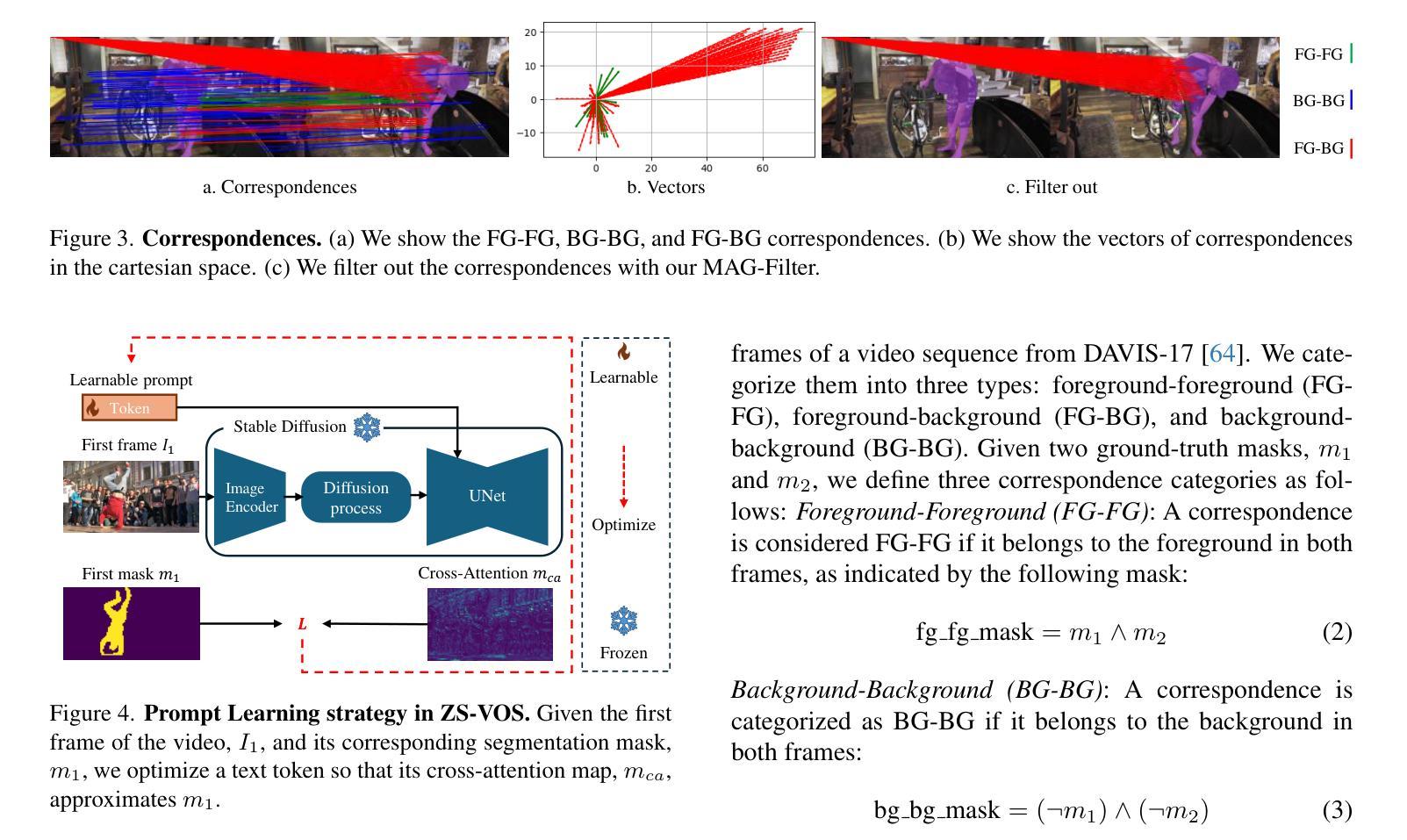
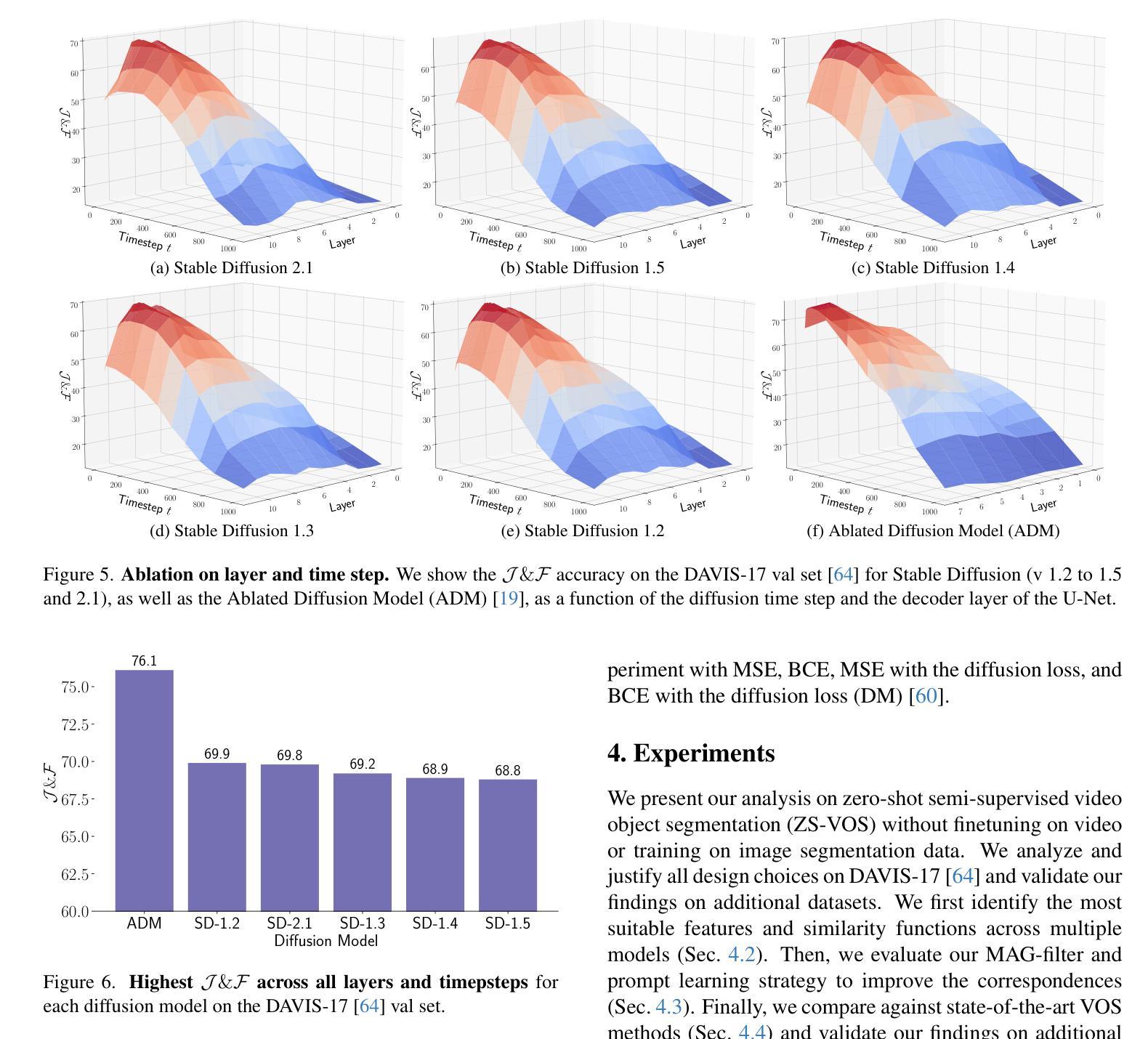
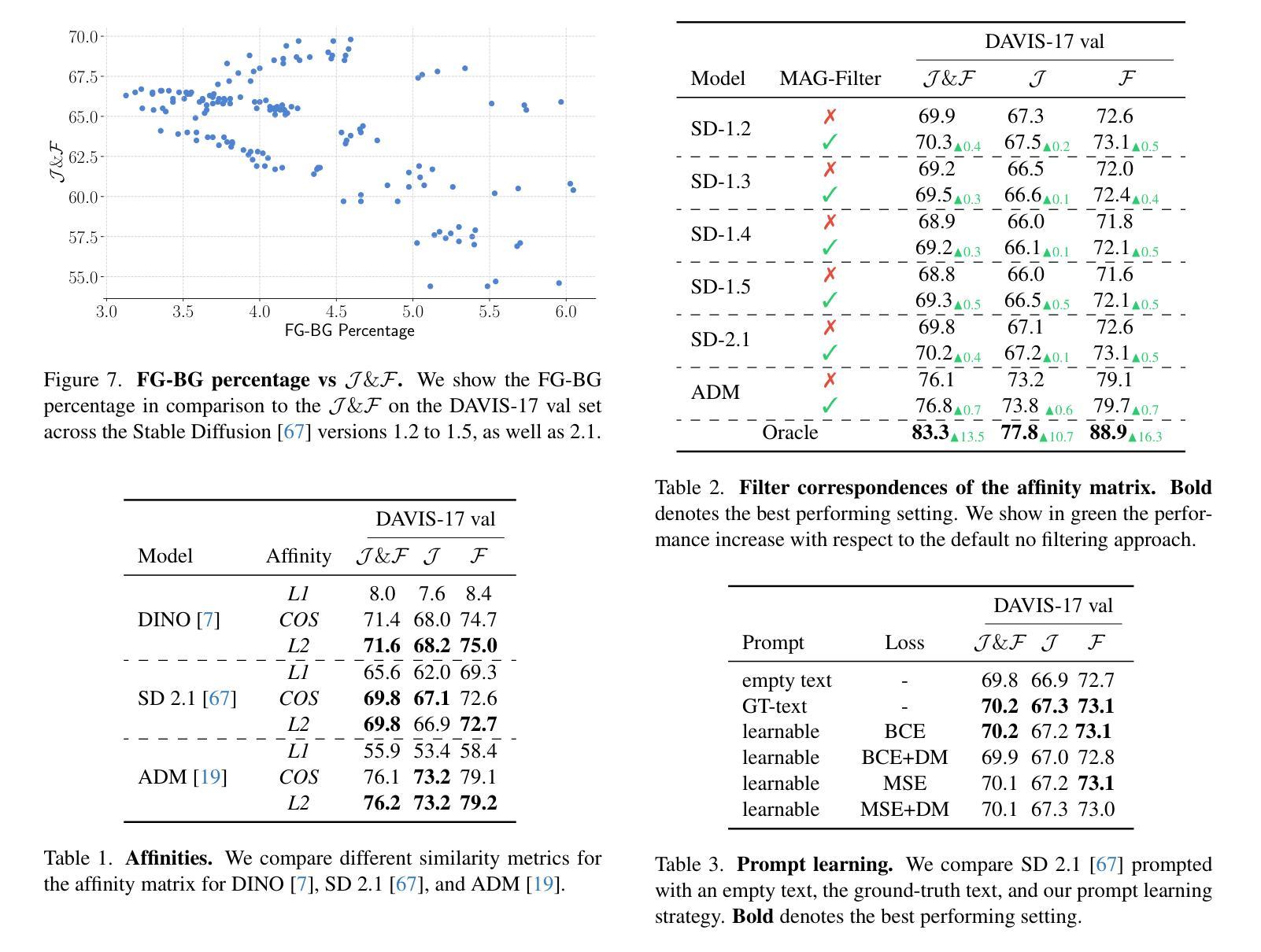
Studying Image Diffusion Features for Zero-Shot Video Object Segmentation
Authors:Thanos Delatolas, Vicky Kalogeiton, Dim P. Papadopoulos
This paper investigates the use of large-scale diffusion models for Zero-Shot Video Object Segmentation (ZS-VOS) without fine-tuning on video data or training on any image segmentation data. While diffusion models have demonstrated strong visual representations across various tasks, their direct application to ZS-VOS remains underexplored. Our goal is to find the optimal feature extraction process for ZS-VOS by identifying the most suitable time step and layer from which to extract features. We further analyze the affinity of these features and observe a strong correlation with point correspondences. Through extensive experiments on DAVIS-17 and MOSE, we find that diffusion models trained on ImageNet outperform those trained on larger, more diverse datasets for ZS-VOS. Additionally, we highlight the importance of point correspondences in achieving high segmentation accuracy, and we yield state-of-the-art results in ZS-VOS. Finally, our approach performs on par with models trained on expensive image segmentation datasets.
本文探讨了大规模扩散模型在无微调视频数据或任何图像分割数据训练的情况下,用于零样本视频对象分割(ZS-VOS)的应用。虽然扩散模型在各种任务中表现出了强大的视觉表示能力,但它们在ZS-VOS的直接应用仍然被探索得不够深入。我们的目标是找到ZS-VOS的最佳特征提取过程,通过确定最合适的时间步长和层来提取特征。我们进一步分析了这些特征的亲和力,并观察到其与点对应关系的强烈相关性。在DAVIS-17和MOSE的大量实验表明,在ImageNet上训练的扩散模型在ZS-VOS方面的表现优于在更大、更多样化的数据集上训练的模型。此外,我们还强调了实现高分割准确率的点对应关系的重要性,并在ZS-VOS中取得了最新结果。最后,我们的方法与在昂贵的图像分割数据集上训练的模型表现相当。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPRW2025
Summary
本文探讨了大规模扩散模型在零样本视频对象分割(ZS-VOS)中的应用,无需对视频数据进行微调或任何图像分割数据的训练。研究目标是找到适用于ZS-VOS的最佳特征提取过程,并观察到特征之间的亲和力与点对应关系之间存在强烈的相关性。实验表明,在DAVIS-17和MOSE上,使用ImageNet训练的扩散模型在ZS-VOS上的表现优于在更大、更多样化数据集上训练的模型。同时,点对应关系对于实现高分割精度至关重要,并且本文方法达到了最先进的ZS-VOS结果。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型被应用于零样本视频对象分割(ZS-VOS),无需对视频数据进行微调或训练图像分割数据。
- 研究找到适用于ZS-VOS的最佳特征提取过程,包括选择适当的时间步长和层来提取特征。
- 观察到扩散模型的特征与点对应关系之间存在强烈的相关性。
- 在DAVIS-17和MOSE上的实验表明,使用ImageNet训练的扩散模型在ZS-VOS上的表现优于其他模型。
- 点对应关系对于实现高分割精度至关重要。
- 本文方法达到了最先进的ZS-VOS结果。
点此查看论文截图

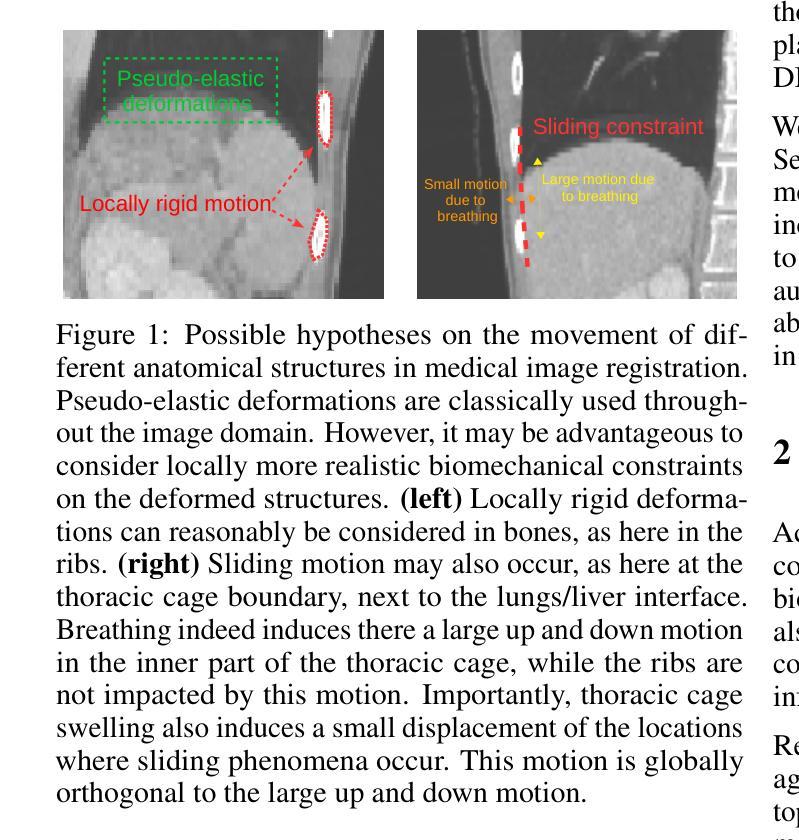
Biomechanical Constraints Assimilation in Deep-Learning Image Registration: Application to sliding and locally rigid deformations
Authors:Ziad Kheil, Soleakhena Ken, Laurent Risser
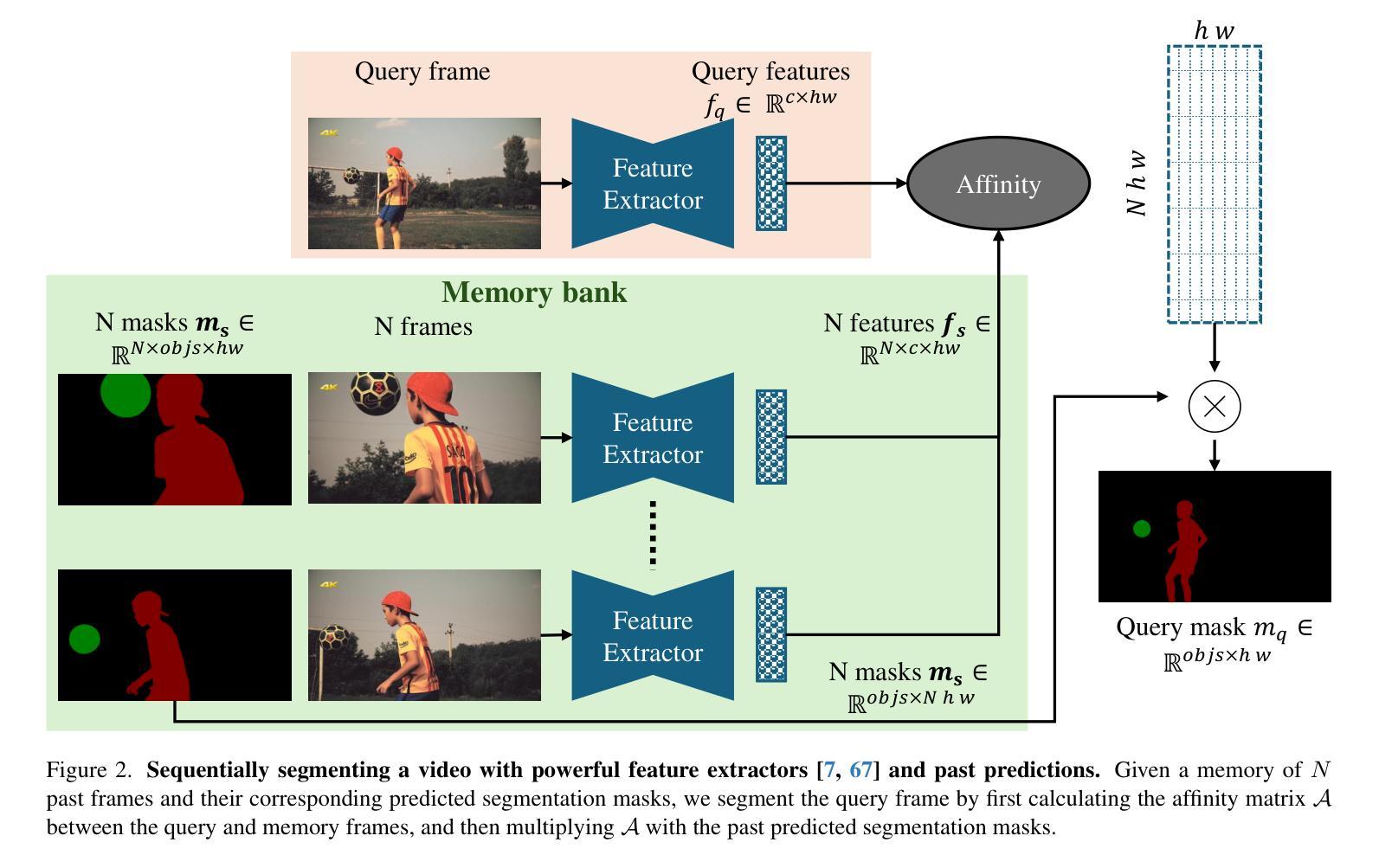
Regularization strategies in medical image registration often take a one-size-fits-all approach by imposing uniform constraints across the entire image domain. Yet biological structures are anything but regular. Lacking structural awareness, these strategies may fail to consider a panoply of spatially inhomogeneous deformation properties, which would faithfully account for the biomechanics of soft and hard tissues, especially in poorly contrasted structures. To bridge this gap, we propose a learning-based image registration approach in which the inferred deformation properties can locally adapt themselves to trained biomechanical characteristics. Specifically, we first enforce in the training process local rigid displacements, shearing motions or pseudo-elastic deformations using regularization losses inspired from the field of solid-mechanics. We then show on synthetic and real 3D thoracic and abdominal images that these mechanical properties of different nature are well generalized when inferring the deformations between new image pairs. Our approach enables neural-networks to infer tissue-specific deformation patterns directly from input images, ensuring mechanically plausible motion. These networks preserve rigidity within hard tissues while allowing controlled sliding in regions where tissues naturally separate, more faithfully capturing physiological motion. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/Kheil-Z/biomechanical_DLIR .
医学图像配准中的正则化策略通常采用一刀切的方法,对整个图像域施加统一的约束。然而,生物结构却远非如此。由于缺乏结构意识,这些策略可能无法考虑到一系列空间非均匀变形特性,无法真实反映软组织和硬组织的生物力学,特别是在对比度较差的结构中。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了一种基于学习的图像配准方法,其中推断的变形特性可以局部适应于训练得到的生物力学特征。具体来说,我们首先在训练过程中,使用从固体力学领域获得启发的正则化损失,强制实施局部刚性位移、剪切运动或伪弹性变形。然后,我们在合成和真实的3D胸部和腹部图像上展示,当推断新图像对之间的变形时,这些不同性质的机械特性具有良好的泛化能力。我们的方法使神经网络能够直接从输入图像中推断出组织特定的变形模式,确保机械上可行的运动。这些网络在硬组织内保持刚性,同时在组织自然分离的区域允许受控滑动,更真实地捕捉生理运动。代码公开可用在 https://github.com/Kheil-Z/biomechanical_DLIR。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于学习的医学图像注册方法,该方法能够局部适应训练得到的生物力学特性,以弥补传统注册策略在应对生物结构复杂性时的不足。通过引入固体力学领域的正则化损失,该方法可在训练过程中施加局部刚性位移、剪切运动或伪弹性变形。在新图像对的变形推断中,不同性质的机械特性得到良好泛化,使得神经网络能够直接从输入图像中推断出组织特定的变形模式,确保机械运动的可信性。
Key Takeaways
- 传统医学图像注册策略常采用全局统一约束,缺乏结构感知能力。
- 生物结构具有空间非均匀变形特性,需考虑软组织和硬组织的生物力学。
- 提出一种基于学习的图像注册方法,可局部适应生物力学特性。
- 引入固体力学领域的正则化损失,用于训练过程中的局部变形约束。
- 在合成和真实的3D胸腹部图像上验证,不同性质的机械特性在推断新图像对变形时具有良好泛化能力。
- 神经网络能够直接从输入图像中推断出组织特定的变形模式。
- 该方法在保证硬组织刚性的同时,允许在天然组织分离区域进行受控滑动,更真实地捕捉生理运动。
点此查看论文截图

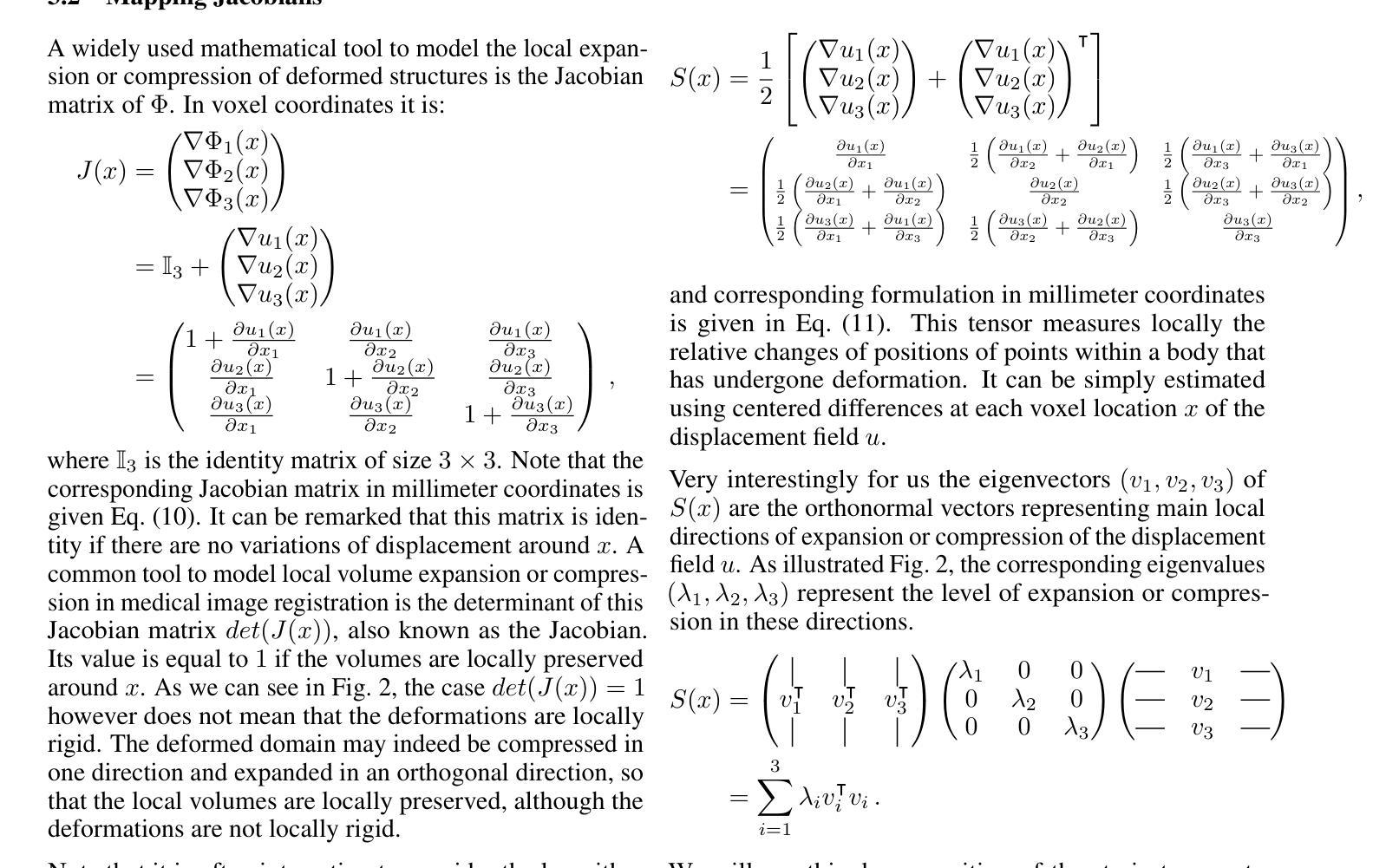
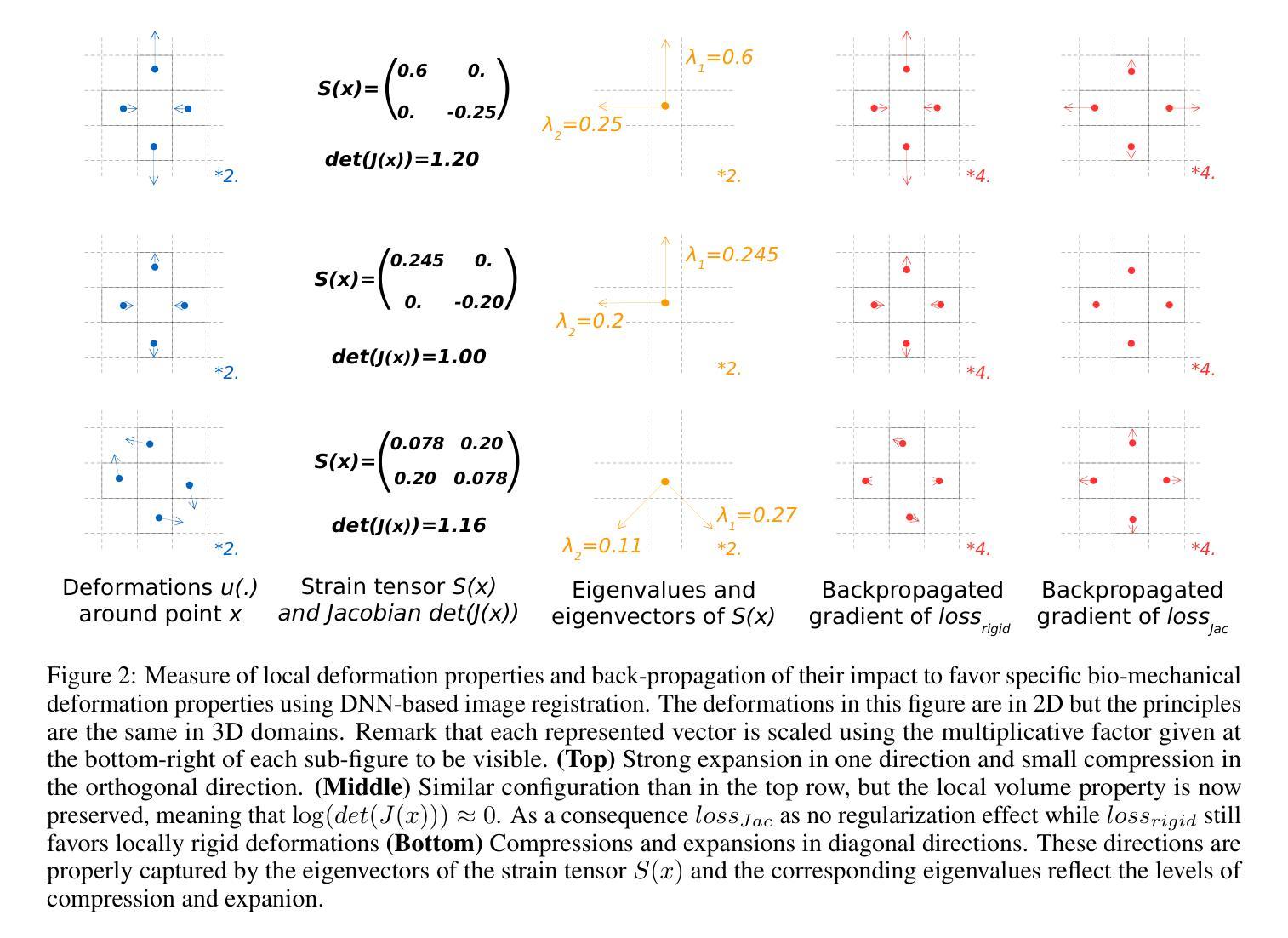
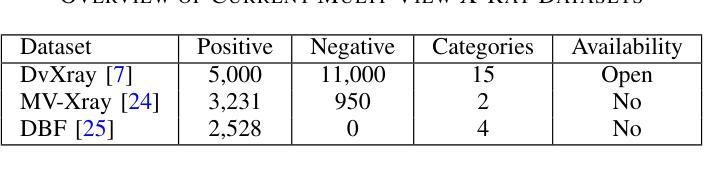
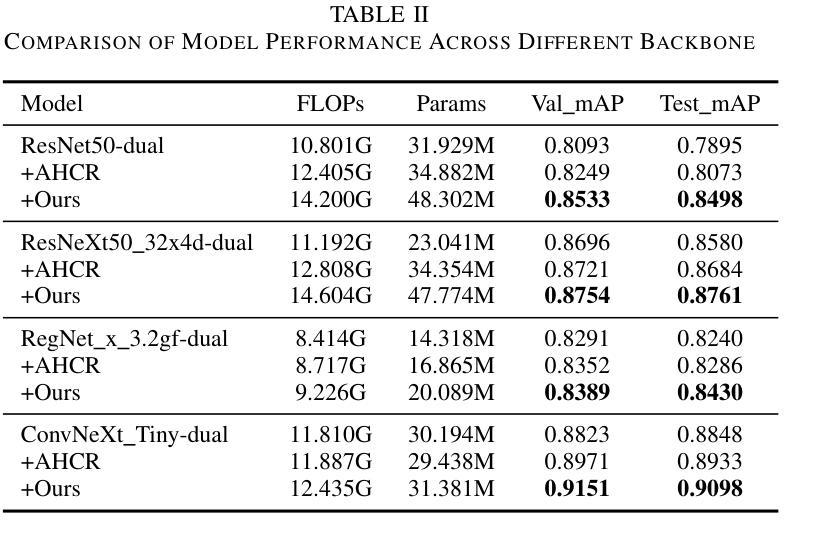
A Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Framework Integrating Frequency Domain and Cross-View Attention for Dual-View X-ray Security Inspections
Authors:Shilong Hong, Yanzhou Zhou, Weichao Xu
With the rapid development of modern transportation systems and the exponential growth of logistics volumes, intelligent X-ray-based security inspection systems play a crucial role in public safety. Although single-view X-ray equipment is widely deployed, it struggles to accurately identify contraband in complex stacking scenarios due to strong viewpoint dependency and inadequate feature representation. To address this, we propose an innovative multi-scale interactive feature fusion framework tailored for dual-view X-ray security inspection image classification. The framework comprises three core modules: the Frequency Domain Interaction Module (FDIM) enhances frequency-domain features through Fourier transform; the Multi-Scale Cross-View Feature Enhancement (MSCFE) leverages cross-view attention mechanisms to strengthen feature interactions; and the Convolutional Attention Fusion Module (CAFM) efficiently fuses features by integrating channel attention with depthwise-separable convolutions. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches across multiple backbone architectures, particularly excelling in complex scenarios with occlusions and object stacking.
随着现代交通运输系统的快速发展和物流量的指数级增长,基于智能X射线的安全检查系统在公共安全中扮演着至关重要的角色。虽然单视图X射线设备已广泛部署,但由于其强烈的视角依赖性和特征表示的不足,它在复杂的堆叠场景中难以准确识别违禁品。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种针对双视图X射线安全检查图像分类的多尺度交互特征融合框架。该框架包括三个核心模块:频域交互模块(FDIM)通过傅里叶变换增强频域特征;多尺度跨视图特征增强(MSCFE)利用跨视图注意力机制加强特征交互;卷积注意力融合模块(CAFM)通过结合通道注意力和深度可分离卷积来有效地融合特征。实验结果表明,我们的方法在多种主干架构上超越了现有的最新技术方法,尤其在存在遮挡和物体堆叠的复杂场景中表现出色。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF I did not obtain permission from the other authors, especially the corresponding author, to submit this manuscript, so I respectfully request its withdrawal
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对双视角X光安检图像分类的多尺度交互特征融合框架,以解决单视角X光设备在复杂堆叠场景中难以准确识别违禁品的问题。该框架包括三个核心模块:频率域交互模块(FDIM)、多尺度跨视图特征增强模块(MSCFE)和卷积注意力融合模块(CAFM)。实验结果表明,该方法在多个主干架构上优于现有先进技术,尤其在遮挡和对象堆叠的复杂场景中表现突出。
Key Takeaways
- 公共交通安检中,智能X光安检系统发挥重要作用。
- 单视角X光设备在复杂堆叠场景下识别违禁品存在困难。
- 提出了多尺度交互特征融合框架,包括FDIM、MSCFE和CAFM三个核心模块。
- FDIM通过傅里叶变换增强频率域特征。
- MSCFE利用跨视图注意力机制加强特征交互。
- CAFM通过结合通道注意力和深度可分离卷积来有效融合特征。
点此查看论文截图

Transfer Learning Strategies for Pathological Foundation Models: A Systematic Evaluation in Brain Tumor Classification
Authors:Ken Enda, Yoshitaka Oda, Zen-ichi Tanei, Kenichi Satoh, Hiroaki Motegi, Terasaka Shunsuke, Shigeru Yamaguchi, Takahiro Ogawa, Wang Lei, Masumi Tsuda, Shinya Tanaka
Foundation models pretrained on large-scale pathology datasets have shown promising results across various diagnostic tasks. Here, we present a systematic evaluation of transfer learning strategies for brain tumor classification using these models. We analyzed 254 cases comprising five major tumor types: glioblastoma, astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, primary central nervous system lymphoma, and metastatic tumors. Comparing state-of-the-art foundation models with conventional approaches, we found that foundation models demonstrated robust classification performance with as few as 10 patches per case, despite the traditional assumption that extensive per-case image sampling is necessary. Furthermore, our evaluation revealed that simple transfer learning strategies like linear probing were sufficient, while fine-tuning often degraded model performance. These findings suggest a paradigm shift from “training encoders on extensive pathological data” to “querying pre-trained encoders with labeled datasets”, providing practical implications for implementing AI-assisted diagnosis in clinical pathology.
基于大规模病理学数据集进行预训练的基石模型(foundation models)在各种诊断任务中展现出了有前景的结果。在此,我们针对使用这些模型的脑肿瘤分类任务,对迁移学习策略进行了系统的评估。我们分析了包含五种主要肿瘤类型的254个病例:胶质母细胞瘤、星形细胞瘤、少枝胶质细胞瘤、原发性中枢神经系统淋巴瘤和转移性肿瘤。将最前沿的基石模型与传统方法进行对比,我们发现基石模型在仅对每个病例使用少量(如每个病例仅使用10个样本)的情况下,就表现出了稳健的分类性能,尽管传统观点认为每个病例都需要进行大量的图像采样。此外,我们的评估还表明,简单的迁移学习策略(如线性探测)就已足够有效,而微调往往会降低模型性能。这些发现标志着从“在大量病理学数据上训练编码器”转向“用带标签的数据集查询预训练编码器”,这为在临床病理学中实现人工智能辅助诊断提供了实际启示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages, 7 figures
总结
预训练的大型病理学数据集上的基础模型在多种诊断任务中表现出良好的结果。本文系统评估了用于脑肿瘤分类的基础模型的迁移学习策略。我们分析了包含五种主要肿瘤类型的254个病例:胶质母细胞瘤、星形细胞瘤、少突胶质细胞瘤、原发性中枢神经系统淋巴瘤和转移性肿瘤。通过对比最前沿的基础模型与传统方法,我们发现基础模型在仅使用每病例10个补丁的情况下就表现出了强大的分类性能,尽管传统观点认为每个病例的图像采样需要广泛。此外,我们的评估表明简单的迁移学习策略如线性探测就已足够,而微调往往会降低模型性能。这些发现表明从“在大量病理数据上训练编码器”转向“用带标签的数据集查询预训练编码器”,为在临床病理学中实现人工智能辅助诊断提供了实际启示。
要点
- 基础模型在病理学诊断任务中表现出良好的性能。
- 对比了前沿的基础模型与传统方法,基础模型在脑肿瘤分类上表现出强大的性能。
- 基础模型在少量图像样本下依然表现出良好的分类性能,打破了传统观念。
- 简单的迁移学习策略如线性探测已经足够提高模型性能。
- 迁移学习策略的评估结果表明微调并不总是提高模型性能。
- 基础模型的评估结果对医学图像诊断中的AI应用具有实际意义。
点此查看论文截图

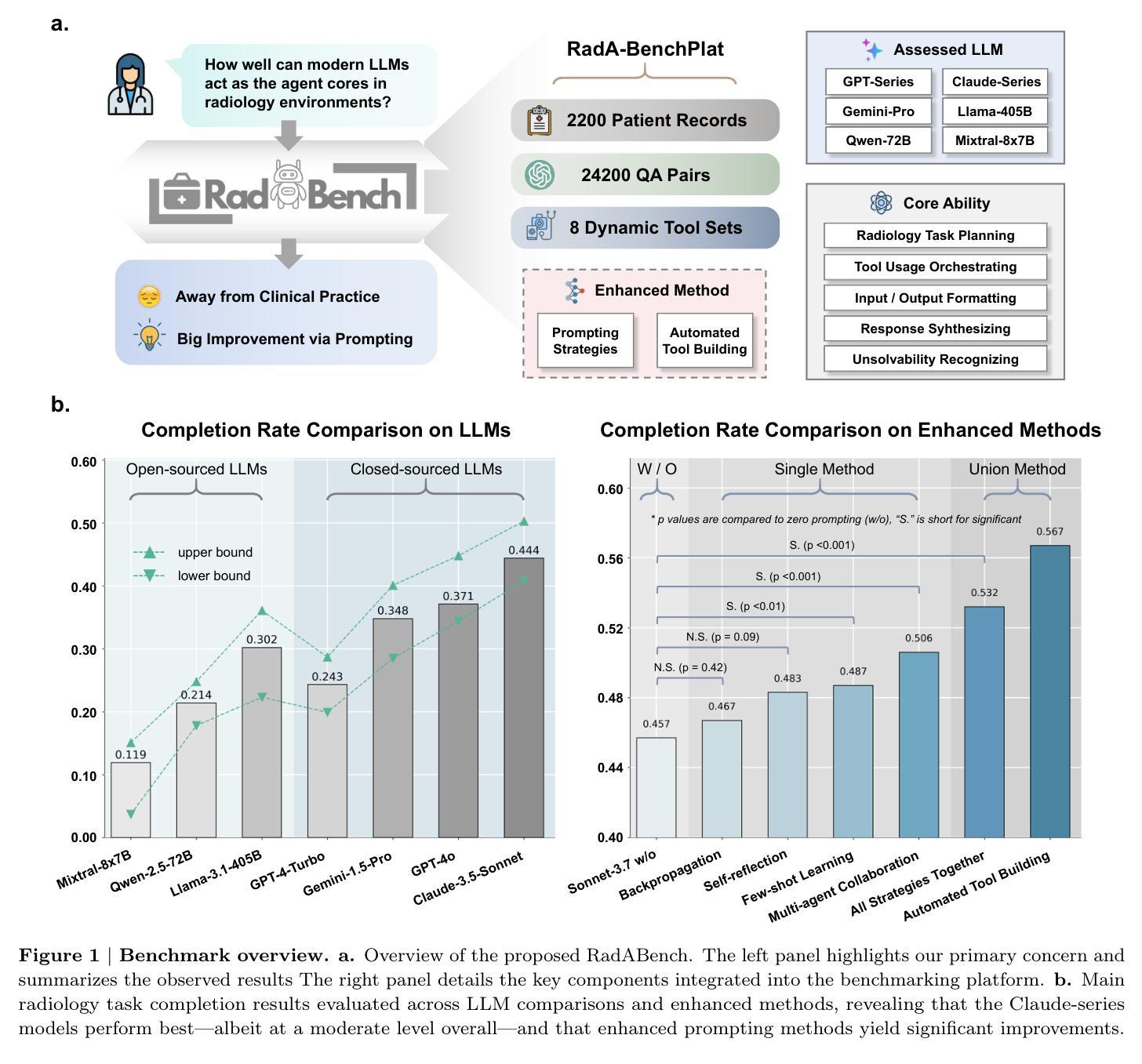
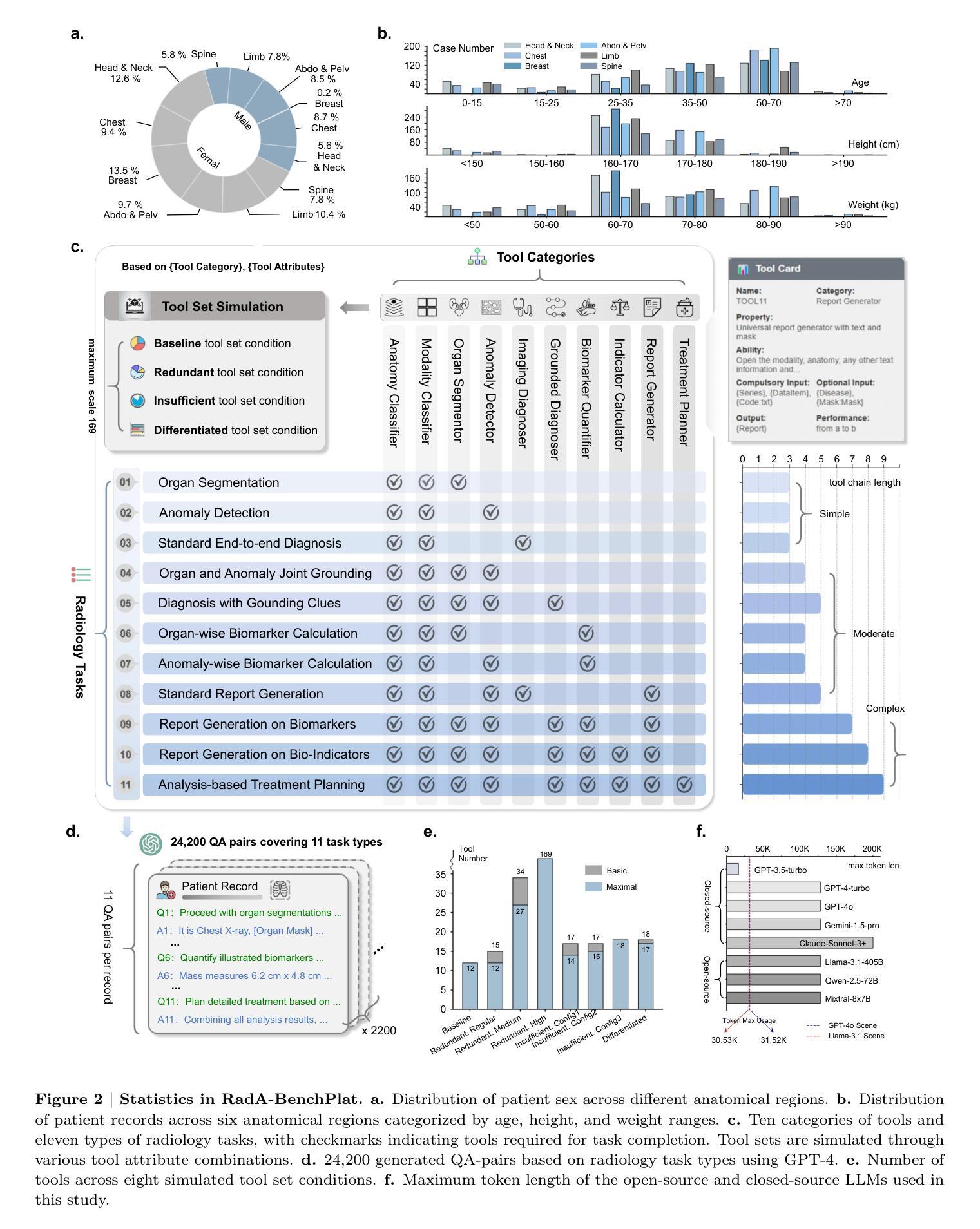
How Well Can Modern LLMs Act as Agent Cores in Radiology Environments?
Authors:Qiaoyu Zheng, Chaoyi Wu, Pengcheng Qiu, Lisong Dai, Ya Zhang, Yanfeng Wang, Weidi Xie
We introduce RadA-BenchPlat, an evaluation platform that benchmarks the performance of large language models (LLMs) act as agent cores in radiology environments using 2,200 radiologist-verified synthetic patient records covering six anatomical regions, five imaging modalities, and 2,200 disease scenarios, resulting in 24,200 question-answer pairs that simulate diverse clinical situations. The platform also defines ten categories of tools for agent-driven task solving and evaluates seven leading LLMs, revealing that while models like Claude-3.7-Sonnet can achieve a 67.1% task completion rate in routine settings, they still struggle with complex task understanding and tool coordination, limiting their capacity to serve as the central core of automated radiology systems. By incorporating four advanced prompt engineering strategies–where prompt-backpropagation and multi-agent collaboration contributed 16.8% and 30.7% improvements, respectively–the performance for complex tasks was enhanced by 48.2% overall. Furthermore, automated tool building was explored to improve robustness, achieving a 65.4% success rate, thereby offering promising insights for the future integration of fully automated radiology applications into clinical practice. All of our code and data are openly available at https://github.com/MAGIC-AI4Med/RadABench.
我们介绍了RadA-BenchPlat评估平台,该平台使用经过放射科医生验证的2200份合成患者记录,涵盖六个解剖区域、五种成像方式和2200种疾病场景,生成了模拟多种临床情境的24,200个问答对,用于评估大型语言模型(LLM)在放射学环境中作为代理核心的性能。该平台还定义了十类工具用于代理驱动的任务解决,并评估了七款领先的大型语言模型。研究结果表明,虽然像Claude-3.7-Sonnet这样的模型在日常环境中的任务完成率可以达到67.1%,但在处理复杂任务理解和工具协调方面仍存在困难,难以作为自动化放射系统的核心。通过采用四种先进的提示工程策略——其中提示反向传播和多代理协作分别贡献了16.8%和30.7%的改进——复杂任务的性能总体提高了48.2%。此外,为了改善稳健性,还探索了自动化工具构建,取得了65.4%的成功率,为未来全自动放射学应用融入临床实践提供了有前景的见解。我们的所有代码和数据都公开在https://github.com/MAGIC-AI4Med/RadABench上。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:RadA-BenchPlat是一个评价平台,通过模拟医生在放射学环境中的行为,评估大型语言模型(LLM)的性能。平台使用合成患者记录模拟临床情境,对LLM进行基准测试,并探讨了提升复杂任务理解和工具协调等问题的策略。研究还发现一些模型如Claude-3.7-Sonnet表现良好,但仍存在挑战。研究数据代码均已公开分享。
Key Takeaways:
- RadA-BenchPlat平台用于评估大型语言模型在放射学环境中的表现。
- 平台使用合成患者记录模拟临床情境进行基准测试。
- 平台定义十类工具用于代理任务解决,并评估了七款领先的LLM。
- Claude-3.7-Sonnet等模型在常规环境下任务完成率较高,但在复杂任务理解和工具协调方面存在挑战。
- 通过采用四种先进的提示工程策略,复杂任务性能有所提升,其中提示反向传播和多代理协作分别贡献了16.8%和30.7%的改进。
- 探讨了自动化工具建设的鲁棒性,并取得了65.4%的成功率。
点此查看论文截图

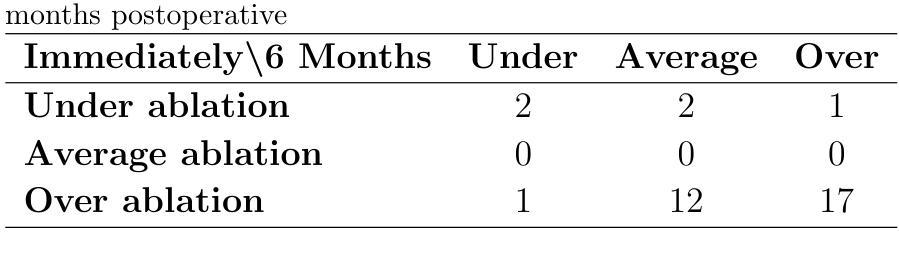
Respiratory Differencing: Enhancing Pulmonary Thermal Ablation Evaluation Through Pre- and Intra-Operative Image Fusion
Authors:Wan Li, Wei Li, Moheng Rong, Yutao Rao, Hui Tang, Yudong Zhang, Feng Wang
CT image-guided thermal ablation is widely used for lung cancer treatment; however, follow-up data indicate that physicians’ subjective assessments of intraoperative images often overestimate the ablation effect, potentially leading to incomplete treatment. To address these challenges, we developed \textit{Respiratory Differencing}, a novel intraoperative CT image assistance system aimed at improving ablation evaluation. The system first segments tumor regions in preoperative CT images and then employs a multi-stage registration process to align these images with corresponding intraoperative or postoperative images, compensating for respiratory deformations and treatment-induced changes. This system provides two key outputs to help physicians evaluate intraoperative ablation. First, differential images are generated by subtracting the registered preoperative images from the intraoperative ones, allowing direct visualization and quantitative comparison of pre- and post-treatment differences. These differential images enable physicians to assess the relative positions of the tumor and ablation zones, even when the tumor is no longer visible in post-ablation images, thus improving the subjective evaluation of ablation effectiveness. Second, the system provides a quantitative metric that measures the discrepancies between the tumor area and the treatment zone, offering a numerical assessment of the overall efficacy of ablation.This pioneering system compensates for complex lung deformations and integrates pre- and intra-operative imaging data, enhancing quality control in cancer ablation treatments. A follow-up study involving 35 clinical cases demonstrated that our system significantly outperforms traditional subjective assessments in identifying under-ablation cases during or immediately after treatment, highlighting its potential to improve clinical decision-making and patient outcomes.
CT图像引导的热消融广泛应用于肺癌治疗。然而,随访数据表明,医生对术中图像的主观评估往往会高估消融效果,可能导致治疗不完全。为了解决这些挑战,我们开发了《呼吸差异》这一新型术中CT图像辅助系统,旨在提高消融评估水平。该系统首先分割术前CT图像中的肿瘤区域,然后采用多阶段配准过程将这些图像与相应的术中或术后图像对齐,以补偿呼吸变形和治疗引起的变化。该系统提供两个关键输出,帮助医生评估术中消融情况。首先,通过减去配准的术前图像,产生差分图像,使医生能够直接可视化和定量比较治疗前后差异。这些差分图像使医生能够评估肿瘤和消融区的相对位置,即使在消融后图像中肿瘤不再可见,也能提高消融效果的主观评估。其次,该系统提供了一个定量指标,测量肿瘤区域与治疗区域之间的差异,对消融的总体效果进行数值评估。这一开创性的系统能够补偿肺部复杂的变形,整合术前和术中的成像数据,提高癌症消融治疗的质量控制。对35例临床病例的随访研究表明,我们的系统在治疗过程或治疗结束后识别消融不足病例方面显著优于传统的主观评估,突显其在改进临床决策和患者预后方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型的术中CT图像辅助系统——Respiratory Differencing,用于改进消融评估。该系统通过分割肿瘤区域并对其进行多阶段配准,将术前CT图像与术中或术后图像对齐,以补偿呼吸变形和治疗引起的变化。该系统提供差分图像和定量指标,帮助医生评估消融效果,并显著提高在识别欠消融病例方面的性能。
Key Takeaways
- CT图像引导的热消融是治疗肺癌的常用方法,但医生对术中图像的主观评估可能会高估消融效果,导致治疗不完全。
- 提出了新型术中CT图像辅助系统——Respiratory Differencing,旨在改进消融评估。
- 系统通过分割肿瘤区域并进行多阶段配准,将术前CT图像与术中或术后图像对齐。
- 系统提供差分图像,通过从术中图像中减去已配准的术前图像,直接可视化并定量比较治疗前后差异,帮助医生评估消融效果。
- 系统还提供定量指标,测量肿瘤区域与治疗区域之间的差异,全面评估消融效果。
- 该系统可补偿肺部复杂变形,整合术前和术中的影像数据,提高癌症消融治疗的质量控制。
点此查看论文截图

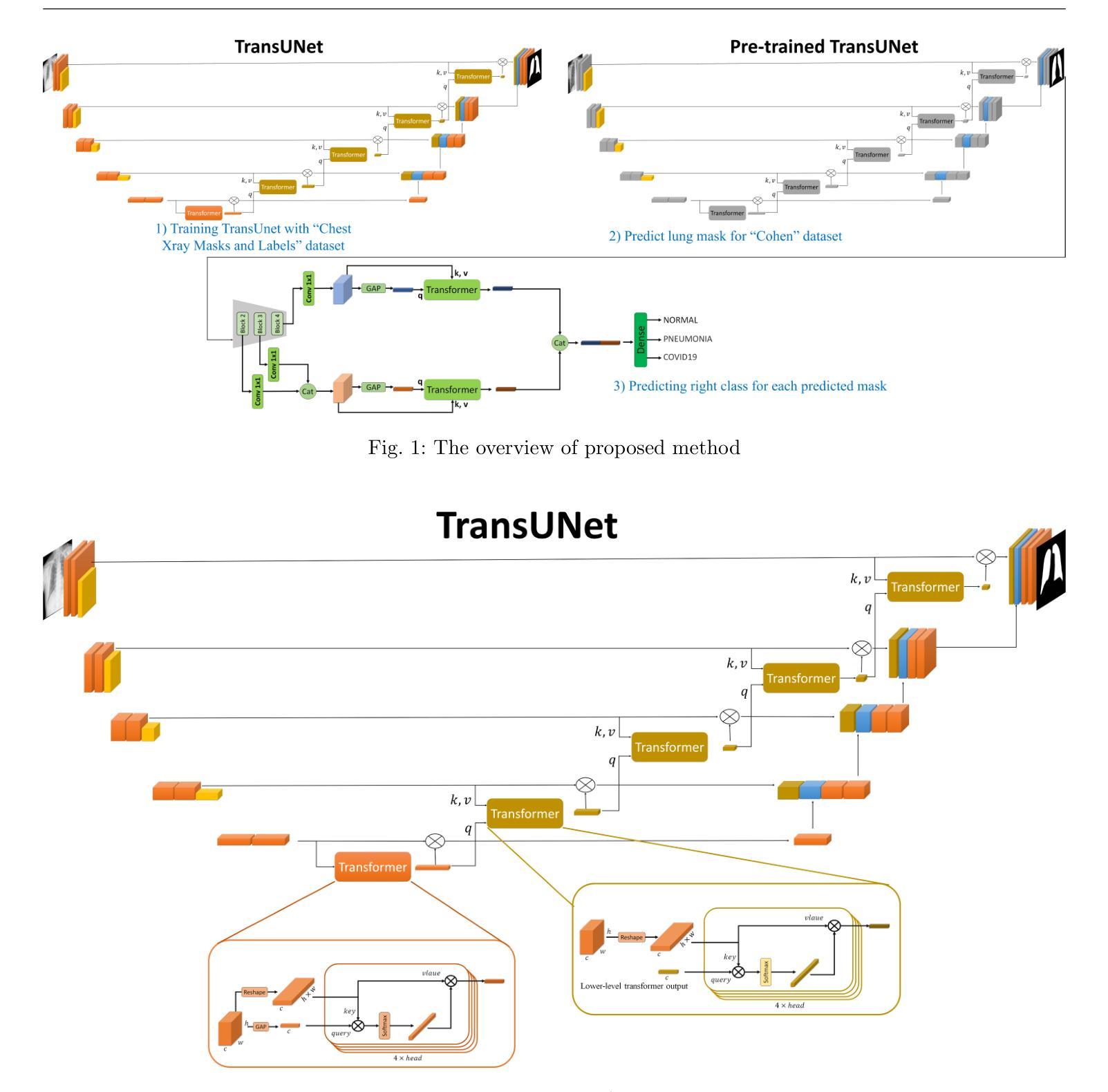
Efficient and Accurate Pneumonia Detection Using a Novel Multi-Scale Transformer Approach
Authors:Alireza Saber, Pouria Parhami, Alimohammad Siahkarzadeh, Mansoor Fateh, Amirreza Fateh
Pneumonia, a prevalent respiratory infection, remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, particularly among vulnerable populations. Chest X-rays serve as a primary tool for pneumonia detection; however, variations in imaging conditions and subtle visual indicators complicate consistent interpretation. Automated tools can enhance traditional methods by improving diagnostic reliability and supporting clinical decision-making. In this study, we propose a novel multi-scale transformer approach for pneumonia detection that integrates lung segmentation and classification into a unified framework. Our method introduces a lightweight transformer-enhanced TransUNet for precise lung segmentation, achieving a Dice score of 95.68% on the “Chest X-ray Masks and Labels” dataset with fewer parameters than traditional transformers. For classification, we employ pre-trained ResNet models (ResNet-50 and ResNet-101) to extract multi-scale feature maps, which are then processed through a modified transformer module to enhance pneumonia detection. This integration of multi-scale feature extraction and lightweight transformer modules ensures robust performance, making our method suitable for resource-constrained clinical environments. Our approach achieves 93.75% accuracy on the “Kermany” dataset and 96.04% accuracy on the “Cohen” dataset, outperforming existing methods while maintaining computational efficiency. This work demonstrates the potential of multi-scale transformer architectures to improve pneumonia diagnosis, offering a scalable and accurate solution to global healthcare challenges.”https://github.com/amirrezafateh/Multi-Scale-Transformer-Pneumonia“
肺炎是一种常见的呼吸道感染,仍然是全球发病和死亡的主要原因,特别是在脆弱人群中。胸部X射线是检测肺炎的主要工具;然而,成像条件的差异和微妙的视觉指标使一致的解读变得复杂。自动化工具可以通过提高诊断的可靠性和支持临床决策来增强传统方法。在本研究中,我们提出了一种新型的多尺度变压器方法,用于肺炎检测,该方法将肺部分割和分类整合到一个统一框架中。我们的方法引入了一种轻量级的变压器增强型TransUNet进行精确的肺部分割,在“胸部X射线掩膜和标签”数据集上实现了95.68%的Dice得分,同时参数少于传统变压器。对于分类,我们采用预训练的ResNet模型(ResNet-50和ResNet-101)提取多尺度特征图,然后通过改进后的变压器模块进行处理,以提高肺炎检测的准确性。多尺度特征提取和轻型变压器模块的集成确保了稳健的性能,使我们的方法适用于资源受限的临床环境。我们的方法在“Kermany”数据集上实现了93.75%的准确率,在“Cohen”数据集上实现了96.04%的准确率,优于现有方法,同时保持了计算效率。这项工作证明了多尺度变压器架构在肺炎诊断中的潜力,为全球医疗保健挑战提供了可伸缩和准确的解决方案。相关代码仓库地址:https://github.com/amirrezafateh/Multi-Scale-Transformer-Pneumonia。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于多尺度Transformer的方法用于肺炎检测,结合肺部分割和分类。采用轻量级Transformer增强的TransUNet进行精确肺部分割,实现“Chest X-ray Masks and Labels”数据集上的Dice分数达95.68%。分类方面,利用预训练的ResNet模型提取多尺度特征图,再通过改良的Transformer模块增强肺炎检测。此方法适合资源有限的临床环境,对“Kermany”和“Cohen”数据集的准确率分别达93.75%和96.04%。展现了多尺度Transformer架构在肺炎诊断中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 肺炎仍是全球主要的疾病原因,特别是在脆弱人群中。
- 胸X光检查是肺炎检测的主要工具,但存在解读不一致的问题。
- 自动化工具能提升诊断的可靠性和临床决策支持。
- 提出一种基于多尺度Transformer的肺炎检测方法,整合肺部分割和分类。
- 采用轻量级Transformer的TransUNet进行精确肺部分割,实现高Dice分数。
- 利用ResNet模型提取多尺度特征,通过改良的Transformer模块增强肺炎检测。
点此查看论文截图

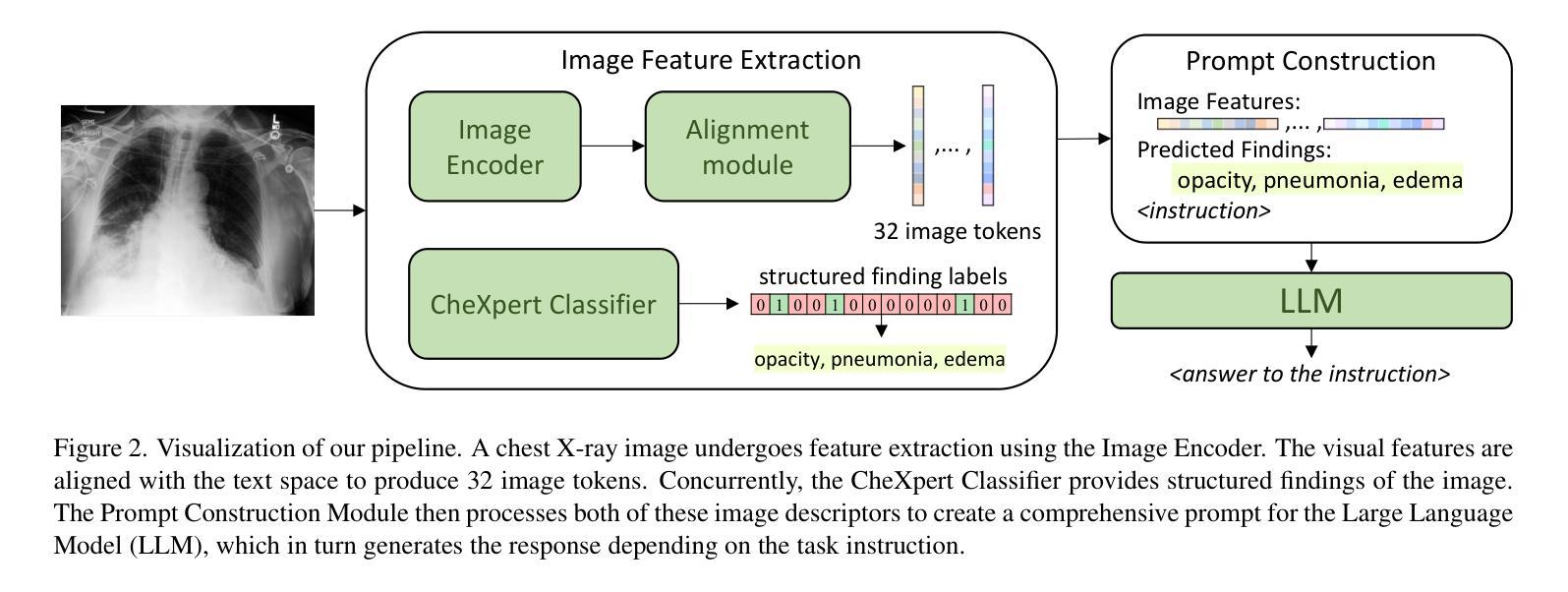
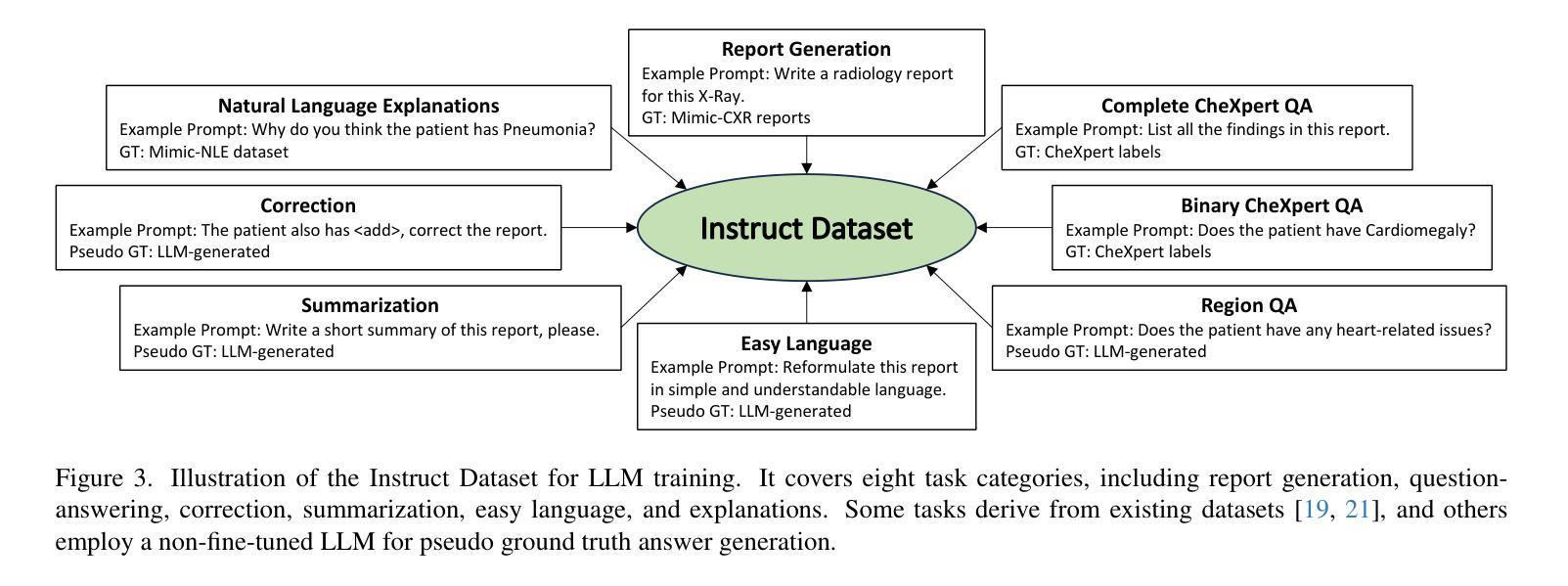
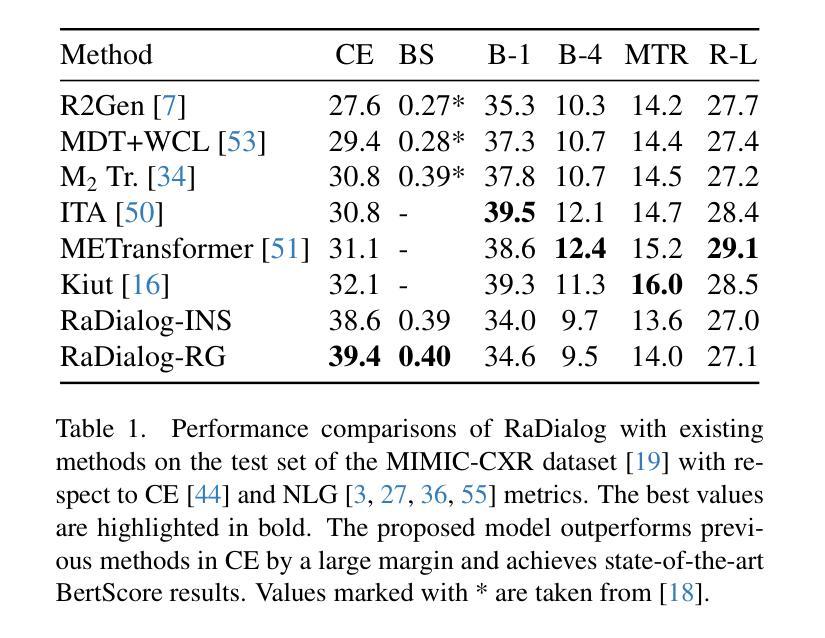
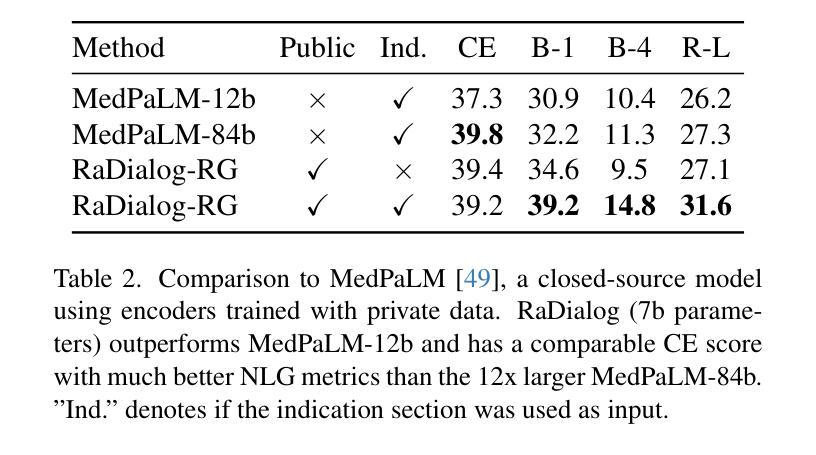
RaDialog: A Large Vision-Language Model for Radiology Report Generation and Conversational Assistance
Authors:Chantal Pellegrini, Ege Özsoy, Benjamin Busam, Nassir Navab, Matthias Keicher
Conversational AI tools that can generate and discuss clinically correct radiology reports for a given medical image have the potential to transform radiology. Such a human-in-the-loop radiology assistant could facilitate a collaborative diagnostic process, thus saving time and improving the quality of reports. Towards this goal, we introduce RaDialog, the first thoroughly evaluated and publicly available large vision-language model for radiology report generation and interactive dialog. RaDialog effectively integrates visual image features and structured pathology findings with a large language model (LLM) while simultaneously adapting it to a specialized domain using parameter-efficient fine-tuning. To keep the conversational abilities of the underlying LLM, we propose a comprehensive, semi-automatically labeled, image-grounded instruct dataset for chest X-ray radiology tasks. By training with this dataset, our method achieves state-of-the-art clinical correctness in report generation and shows impressive abilities in interactive tasks such as correcting reports and answering questions, serving as a foundational step toward clinical dialog systems. Our code is available on github: https://github.com/ChantalMP/RaDialog.
能够针对给定的医学图像生成并讨论临床上正确的放射学报告的对谈式人工智能工具具有改变放射学的潜力。这样的人机循环放射学助理可以促进协作诊断过程,从而节省时间并提高报告质量。为此,我们引入了RaDialog,这是首个彻底评估并公开可用的用于放射学报告生成和交互式对话的大型视觉语言模型。RaDialog有效地将视觉图像特征、结构化病理发现与大型语言模型(LLM)集成在一起,同时采用参数高效的微调来适应专业领域。为了保持底层LLM的对话能力,我们为胸部X射线放射学任务提出了一个综合的、半自动标注的、以图像为基础的指令数据集。通过在此数据集上进行训练,我们的方法在报告生成方面达到了最先进的临床正确性,并在交互式任务(如纠正报告和回答问题)中表现出了令人印象深刻的能力,这可以作为临床对话系统的基础步骤。我们的代码可在github上获得:https://github.com/ChantalMP/RaDialog。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF improved version accepted at MIDL 2025: https://openreview.net/pdf?id=trUvr1gSNI
Summary
本文介绍了一款具有潜力改变放射学领域的对话式人工智能工具——RaDialog。它能够基于医学图像生成并讨论临床正确的放射学报告,从而协助诊断过程,节省时间并提高报告质量。RaDialog有效地整合了视觉图像特征、结构化病理发现与大型语言模型,通过参数高效的微调适应专业领域。同时,为了保持底层语言模型的对话能力,本文提出了一种针对胸部X射线放射学任务的图像基础指令数据集,该数据集采用半自动标注方式。通过在此数据集上的训练,RaDialog在报告生成方面达到了临床正确性的最新水平,并在交互式任务(如纠正报告和回答问题)中表现出令人印象深刻的能力。
Key Takeaways
- RaDialog是一款用于放射学报告生成和交互式对话的工具,具有潜力改变放射学领域。
- RaDialog能够基于医学图像生成临床正确的放射学报告,促进诊断过程的协作,提高报告质量和节省时间。
- RaDialog通过整合视觉图像特征、结构化病理发现与大型语言模型,实现了在放射学领域的专业化应用。
- 为了保持底层语言模型的对话能力,提出了一种针对胸部X射线放射学任务的图像基础指令数据集。
- RaDialog在报告生成方面达到了临床正确性的最新水平,表现优秀。
- RaDialog在交互式任务(如纠正报告和回答问题)中展现出了令人印象深刻的能力。
点此查看论文截图