⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-10 更新
WoundAmbit: Bridging State-of-the-Art Semantic Segmentation and Real-World Wound Care
Authors:Vanessa Borst, Timo Dittus, Tassilo Dege, Astrid Schmieder, Samuel Kounev
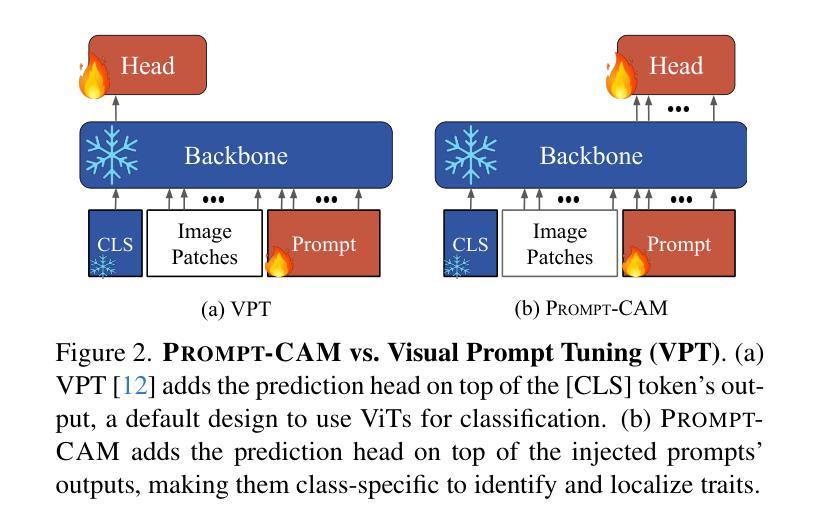
Chronic wounds affect a large population, particularly the elderly and diabetic patients, who often exhibit limited mobility and co-existing health conditions. Automated wound monitoring via mobile image capture can reduce in-person physician visits by enabling remote tracking of wound size. Semantic segmentation is key to this process, yet wound segmentation remains underrepresented in medical imaging research. To address this, we benchmark state-of-the-art deep learning models from general-purpose vision, medical imaging, and top methods from public wound challenges. For fair comparison, we standardize training, data augmentation, and evaluation, conducting cross-validationto minimize partitioning bias. We also assess real-world deployment aspects, including generalization to an out-of-distribution wound dataset, computational efficiency, and interpretability. Additionally, we propose a reference object-based approach to convert AI-generated masks into clinically relevant wound size estimates, and evaluate this, along with mask quality, for the best models based on physician assessments. Overall, the transformer-based TransNeXt showed the highest levels of generalizability. Despite variations in inference times, all models processed at least one image per second on the CPU, which is deemed adequate for the intended application. Interpretability analysis typically revealed prominent activations in wound regions, emphasizing focus on clinically relevant features. Expert evaluation showed high mask approval for all analyzed models, with VWFormer and ConvNeXtS backbone performing the best. Size retrieval accuracy was similar across models, and predictions closely matched expert annotations. Finally, we demonstrate how our AI-driven wound size estimation framework, WoundAmbit, can be integrated into a custom telehealth system. Our code will be made available on GitHub upon publication.
慢性伤口影响大量人群,尤其是行动不便且存在其他健康问题的老年人和糖尿病患者。通过移动图像捕获进行自动伤口监测,能够远程追踪伤口大小,从而减少亲自就医的次数。语义分割是这一过程中的关键,但伤口分割在医学成像研究中的代表性仍然不足。为了解决这个问题,我们对比了最先进的深度学习模型,包括通用视觉、医学影像以及公共伤口挑战中的顶尖方法。为了公平对比,我们标准化了训练、数据增强和评估流程,并进行交叉验证以最小化分区偏差。我们还评估了实际部署方面的因素,包括在异常伤口数据集上的泛化能力、计算效率和可解释性。此外,我们提出了一种基于参考对象的方法,将人工智能生成的掩膜转化为临床上相关的伤口大小估计值,并针对最佳模型,根据医生评估,对此以及掩膜质量进行评估。总体而言,基于transformer的TransNeXt表现出最高的泛化能力。尽管推理时间存在差异,但所有模型都能在CPU上实现每秒至少处理一张图像的速度,这被认为是足以应用于预期用途。可解释性分析通常显示伤口区域的激活较为突出,强调临床上相关特征的关注。专家评估显示,所有分析模型的掩膜均获得高度评价,其中VWFormer和ConvNeXtS骨干网表现最佳。尺寸检索精度在模型间相似,预测结果与专家注释紧密匹配。最后,我们展示了我们的AI驱动伤口大小估计框架WoundAmbit如何集成到定制的远程医疗系统中。代码将在出版时发布到GitHub上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Main paper: 17 pages; supplementary material: 16 pages; paper submitted to the application track of the European Conference on Machine Learning and Principles and Practice of Knowledge Discovery in Databases (ECML PKDD 2025)
Summary
本文研究了慢性伤口的自动化监测问题,特别是通过移动图像捕捉技术进行远程跟踪。文章对比了通用视觉、医学影像以及公开伤口挑战中的顶尖深度学习模型,并评估了模型在实际部署中的泛化能力、计算效率和可解释性。同时,提出了一种基于参考对象的AI生成掩膜转换为临床相关伤口大小估计的方法,并评估了最佳模型的性能。研究结果显示,transformer-based TransNeXt模型具有最佳泛化能力,所有模型在CPU上的处理速度至少达到每秒一张图像,满足应用需求。可解释性分析表明模型能关注到临床相关特征。专家评估证实各模型性能优异,其中VWFormer和ConvNeXtS表现最佳。最终展示了AI驱动的伤口大小估计框架WoundAmbit可集成到定制远程医疗系统中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 自动化伤口监测可减少医生亲自探访次数,通过远程跟踪伤口大小变化实现有效管理。
- 对比了多种深度学习模型在伤口分割方面的性能,包括通用视觉、医学影像领域的顶尖模型以及公开挑战中的方法。
- 标准化训练、数据增强和评估流程以确保公平比较,并通过交叉验证减少分区偏见。
- 评估了模型在实际部署中的泛化能力、计算效率和可解释性。
- 提出一种基于参考对象的AI生成掩膜转换为临床相关伤口大小估计的方法,并验证了其有效性。
- Transformer-based TransNeXt模型在伤口分割和大小估计方面表现出最佳性能。
- AI驱动的伤口大小估计框架WoundAmbit可集成到远程医疗系统中,具有实际应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

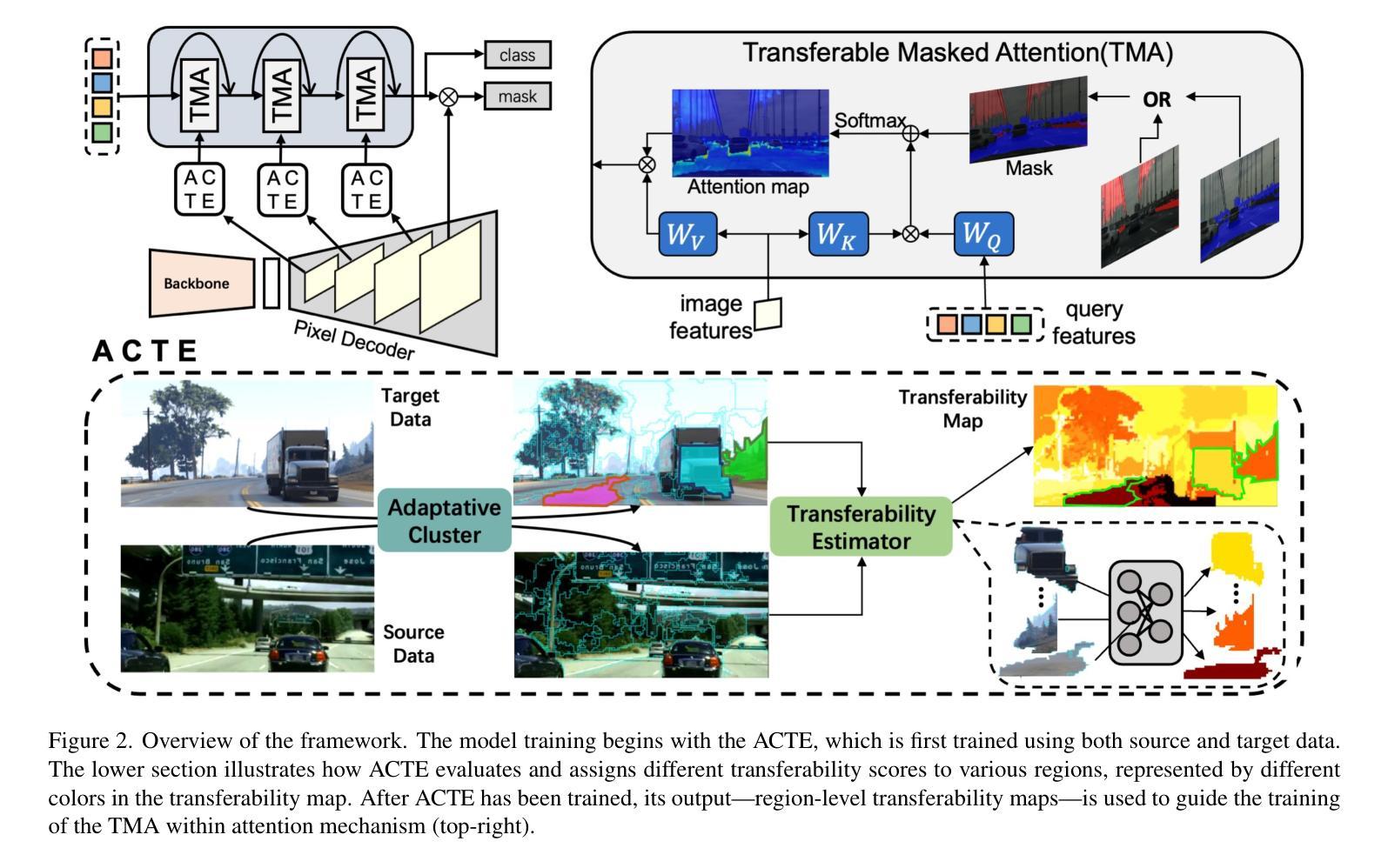
Transferable Mask Transformer: Cross-domain Semantic Segmentation with Region-adaptive Transferability Estimation
Authors:Enming Zhang, Zhengyu Li, Yanru Wu, Jingge Wang, Yang Tan, Ruizhe Zhao, Guan Wang, Yang Li
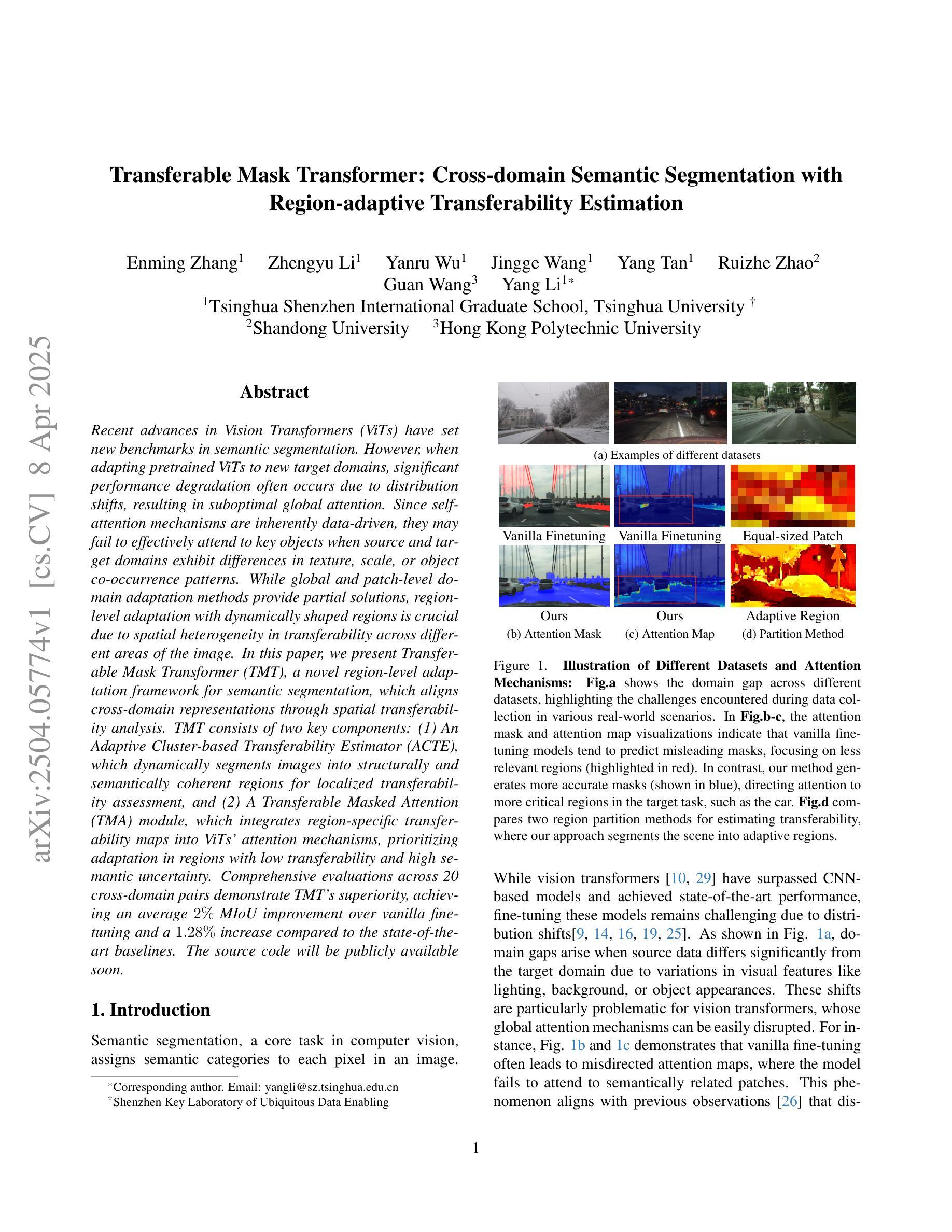
Recent advances in Vision Transformers (ViTs) have set new benchmarks in semantic segmentation. However, when adapting pretrained ViTs to new target domains, significant performance degradation often occurs due to distribution shifts, resulting in suboptimal global attention. Since self-attention mechanisms are inherently data-driven, they may fail to effectively attend to key objects when source and target domains exhibit differences in texture, scale, or object co-occurrence patterns. While global and patch-level domain adaptation methods provide partial solutions, region-level adaptation with dynamically shaped regions is crucial due to spatial heterogeneity in transferability across different image areas. We present Transferable Mask Transformer (TMT), a novel region-level adaptation framework for semantic segmentation that aligns cross-domain representations through spatial transferability analysis. TMT consists of two key components: (1) An Adaptive Cluster-based Transferability Estimator (ACTE) that dynamically segments images into structurally and semantically coherent regions for localized transferability assessment, and (2) A Transferable Masked Attention (TMA) module that integrates region-specific transferability maps into ViTs’ attention mechanisms, prioritizing adaptation in regions with low transferability and high semantic uncertainty. Comprehensive evaluations across 20 cross-domain pairs demonstrate TMT’s superiority, achieving an average 2% MIoU improvement over vanilla fine-tuning and a 1.28% increase compared to state-of-the-art baselines. The source code will be publicly available.
关于Vision Transformers(ViTs)的最新进展已经在语义分割领域设定了新的基准。然而,当将预训练的ViTs适应到新目标域时,由于分布转移,性能往往会显著下降,导致全局注意力下降。由于自注意力机制本质上是数据驱动的,因此当源域和目标域在纹理、尺度或对象共现模式上存在差异时,它们可能无法有效地关注关键对象。虽然全局和补丁级别的域适应方法提供了部分解决方案,但由于不同图像区域在转移能力上的空间异质性,动态形状区域的区域级适应至关重要。我们提出了Transferable Mask Transformer(TMT),这是一种用于语义分割的区域级适应框架,它通过空间转移能力分析来对齐跨域表示。TMT由两个关键组件构成:(1)基于自适应聚类的转移能力估计器(ACTE),它动态地将图像分割成结构和语义上连贯的区域,以进行局部化的转移能力评估;(2)可转移的掩膜注意力(TMA)模块,它将区域特定的转移能力图集成到ViTs的注意力机制中,优先适应低转移能力和高语义不确定性的区域。在20个跨域对上的综合评估证明了TMT的优越性,与简单的微调相比,平均提高了2%的MIoU,与最新基线相比增加了1.28%。源代码将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
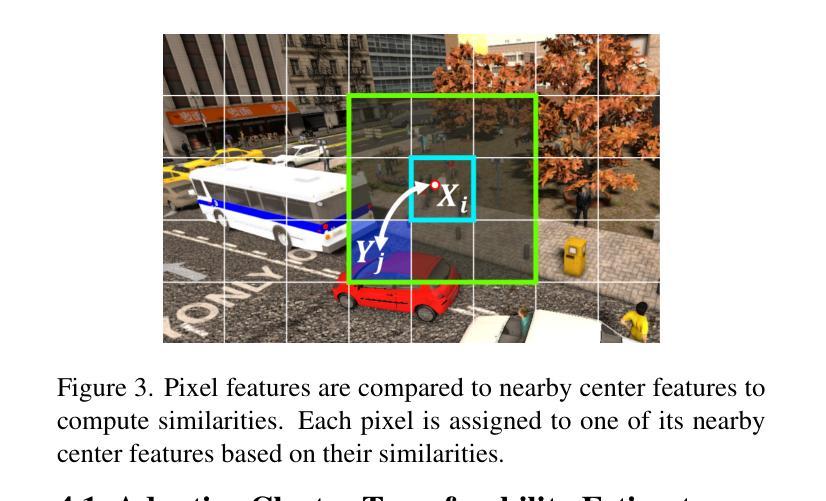
ViT在语义分割任务上取得进展,但在跨域适应时性能下降。本文提出Transferable Mask Transformer(TMT)框架,通过空间转移性分析进行区域级适应。TMT包括两个关键组件:自适应聚类转移性估计器(ACTE)和可转移掩模注意力(TMA)。ACTE动态地将图像分割为结构化和语义上连贯的区域,以进行局部转移性评估;TMA模块将区域特定的转移性映射到ViT的注意力机制中,优先适应低转移性和高语义不确定性的区域。在多个跨域数据集上的评估表明,TMT优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers (ViTs) 在语义分割上取得进展,但跨域适应时性能下降。
- 跨域适应中的挑战包括分布转移导致的全局注意力下降。
- 自注意力机制在源和目标域存在纹理、尺度或对象共现模式差异时,可能无法有效关注关键对象。
- 现有全局和补丁级别的域适应方法提供部分解决方案,但区域级适应至关重要。
- 论文提出Transferable Mask Transformer (TMT) 框架,包括两个关键组件:ACTE和TMA。
- ACTE动态分割图像以进行局部转移性评估,而TMA模块将注意力集中在低转移性和高语义不确定性的区域。
点此查看论文截图
AD-Det: Boosting Object Detection in UAV Images with Focused Small Objects and Balanced Tail Classes
Authors:Zhenteng Li, Sheng Lian, Dengfeng Pan, Youlin Wang, Wei Liu
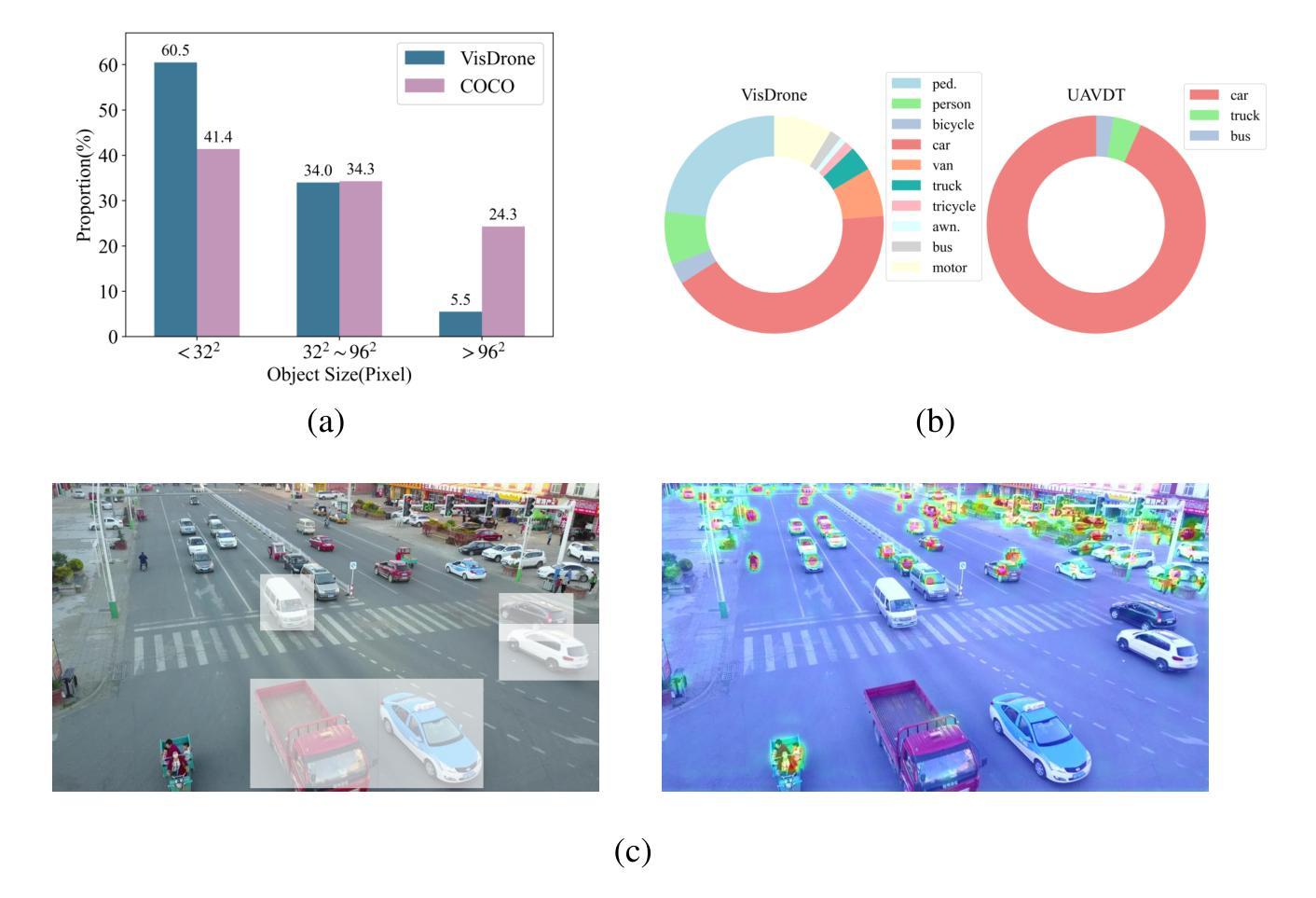
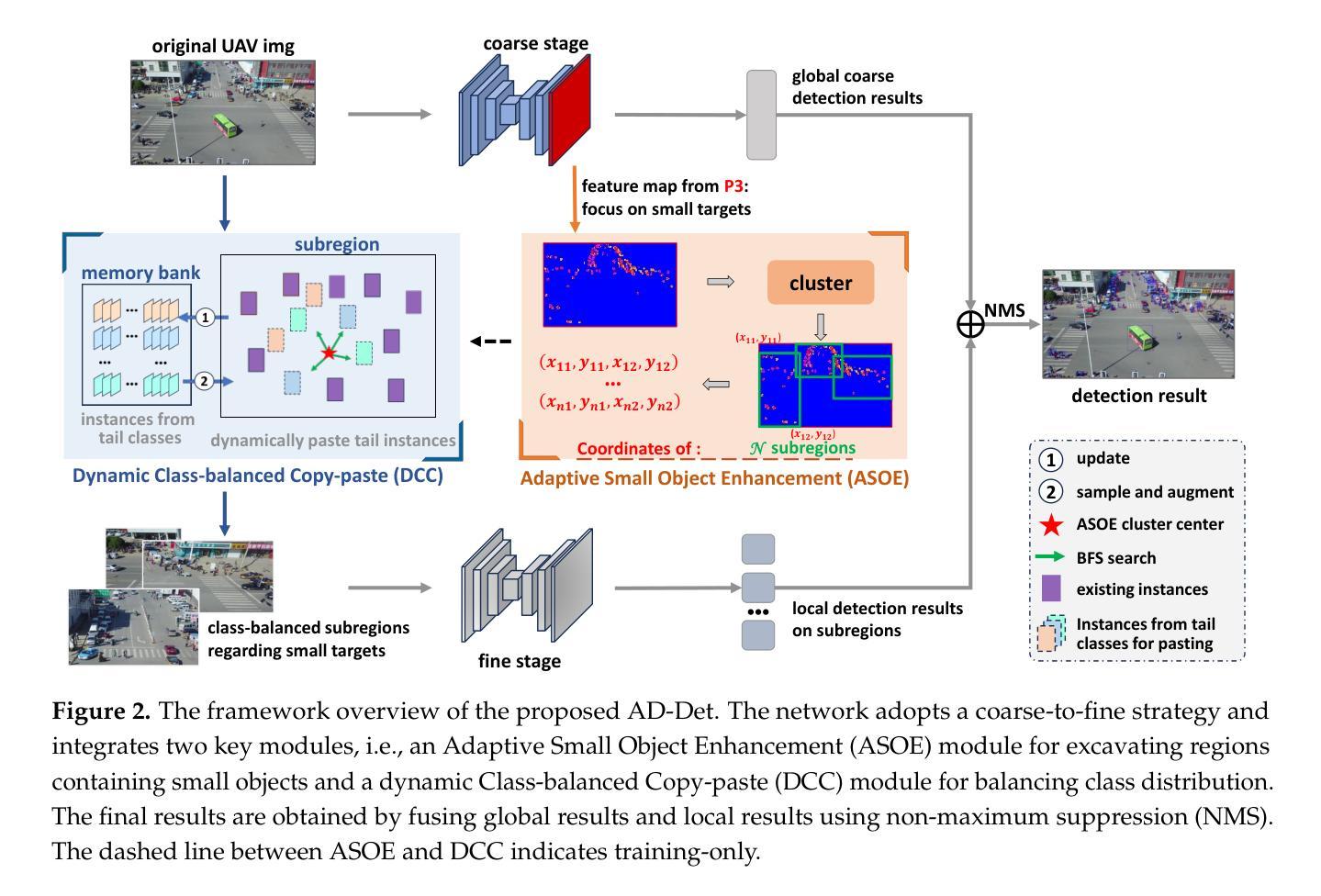
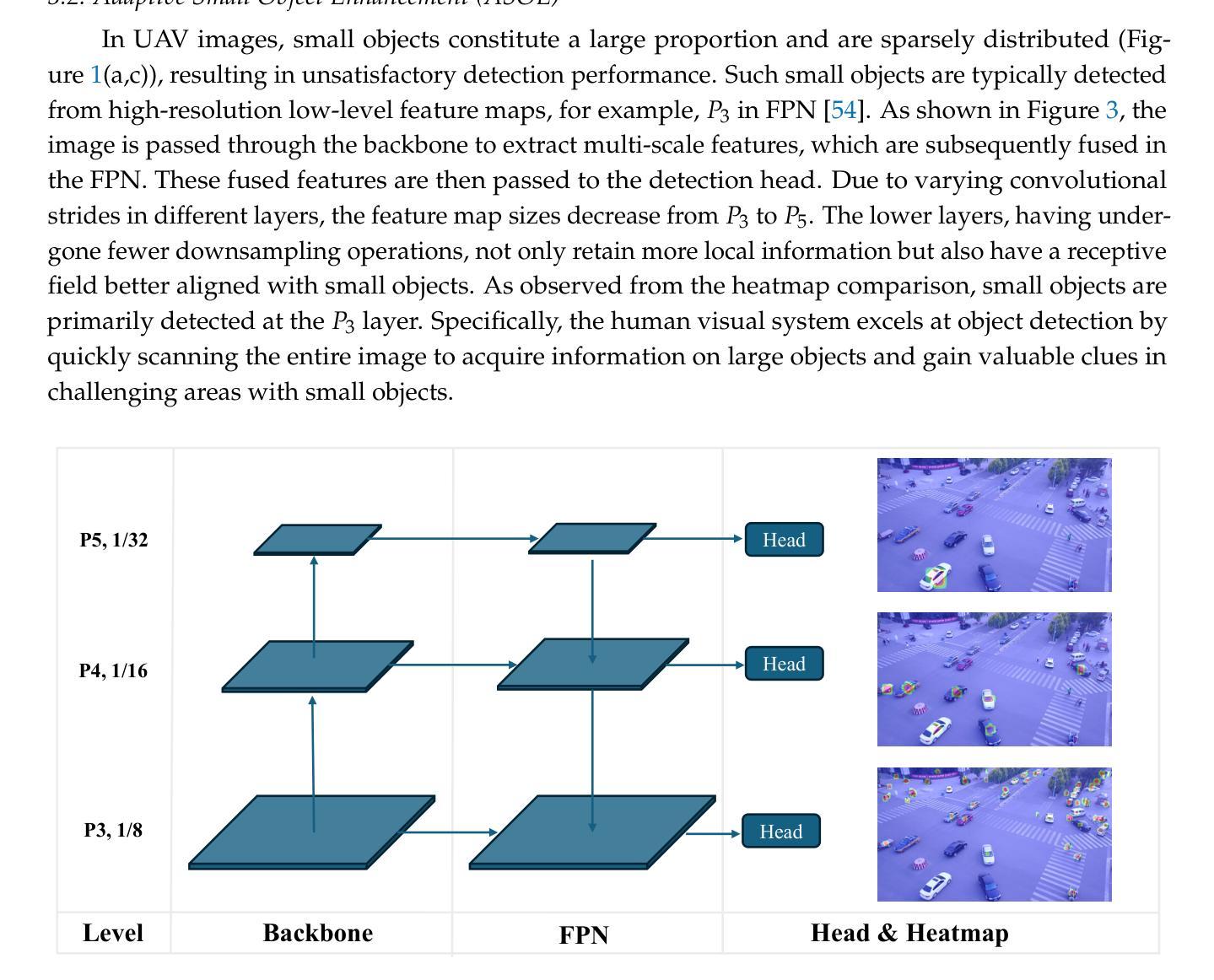
Object detection in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) images poses significant challenges due to complex scale variations and class imbalance among objects. Existing methods often address these challenges separately, overlooking the intricate nature of UAV images and the potential synergy between them. In response, this paper proposes AD-Det, a novel framework employing a coherent coarse-to-fine strategy that seamlessly integrates two pivotal components: Adaptive Small Object Enhancement (ASOE) and Dynamic Class-balanced Copy-paste (DCC). ASOE utilizes a high-resolution feature map to identify and cluster regions containing small objects. These regions are subsequently enlarged and processed by a fine-grained detector. On the other hand, DCC conducts object-level resampling by dynamically pasting tail classes around the cluster centers obtained by ASOE, main-taining a dynamic memory bank for each tail class. This approach enables AD-Det to not only extract regions with small objects for precise detection but also dynamically perform reasonable resampling for tail-class objects. Consequently, AD-Det enhances the overall detection performance by addressing the challenges of scale variations and class imbalance in UAV images through a synergistic and adaptive framework. We extensively evaluate our approach on two public datasets, i.e., VisDrone and UAVDT, and demonstrate that AD-Det significantly outperforms existing competitive alternatives. Notably, AD-Det achieves a 37.5% Average Precision (AP) on the VisDrone dataset, surpassing its counterparts by at least 3.1%.
无人机图像中的目标检测面临着由于尺度变化和类别不均衡导致的复杂挑战。现有的方法往往分别应对这些挑战,忽略了无人机图像的复杂性和它们之间的潜在协同作用。针对这些问题,本文提出了AD-Det,这是一个采用连贯的由粗到细策略的新型框架,无缝集成了两个关键组件:自适应小目标增强(ASOE)和动态类别平衡复制粘贴(DCC)。ASOE利用高分辨率特征图来识别和聚类包含小目标的区域。随后,这些区域会被放大并由精细检测器进行处理。另一方面,DCC通过动态粘贴尾类,围绕由ASOE获得的聚类中心进行对象级重采样,并为每个尾类维护一个动态内存库。这种方法使AD-Det不仅能够精确检测小目标区域,还能为尾类对象进行动态合理的重采样。因此,AD-Det通过协同自适应框架解决了无人机图像中的尺度变化和类别不均衡挑战,从而提高了整体检测性能。我们在两个公共数据集VisDrone和UAVDT上对我们的方法进行了广泛评估,证明AD-Det显著优于现有的竞争方法。值得注意的是,AD-Det在VisDrone数据集上的平均精度(AP)达到37.5%,超过同类产品至少3.1%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:针对无人机图像中的目标检测存在尺度变化复杂和类别不平衡等问题,现有方法常常分别处理这两个挑战,忽略了无人机图像的复杂性和两者之间的潜在协同作用。本文提出一种新型的框架AD-Det,采用从粗到细的连贯策略,并集成了两个关键组件:自适应小目标增强(ASOE)和动态类别平衡复制粘贴(DCC)。ASOE利用高分辨率特征图识别并聚类包含小目标的区域,然后通过精细的探测器对这些区域进行放大和处理。另一方面,DCC通过动态粘贴尾类在ASOE获得的聚类中心周围进行对象级重采样,并为每个尾类维护一个动态内存库。这种方法使AD-Det不仅能够精确检测小目标区域,还能动态地对尾类目标进行合理的重采样。通过协同自适应的框架,AD-Det解决了无人机图像中的尺度变化和类别不平衡问题,提高了整体检测性能。在VisDrone和UAVDT两个公开数据集上进行了广泛的评估,证明AD-Det显著优于现有竞争方法。特别是,在VisDrone数据集上,AD-Det的平均精度达到了37.5%,超过了同类方法至少3.1%。
Key Takeaways:
- 无人机图像中的目标检测面临尺度变化和类别不平衡的挑战。
- 现有方法常常忽略这两个挑战之间的潜在协同作用。
- AD-Det框架采用从粗到细的连贯策略,集成ASOE和DCC两个关键组件。
- ASOE能够识别并聚类包含小目标的区域,并进行放大和处理。
- DCC通过动态粘贴尾类进行对象级重采样,为尾类维护动态内存库。
- AD-Det在VisDrone和UAVDT数据集上表现优异,显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图