⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-10 更新
HiMoR: Monocular Deformable Gaussian Reconstruction with Hierarchical Motion Representation
Authors:Yiming Liang, Tianhan Xu, Yuta Kikuchi
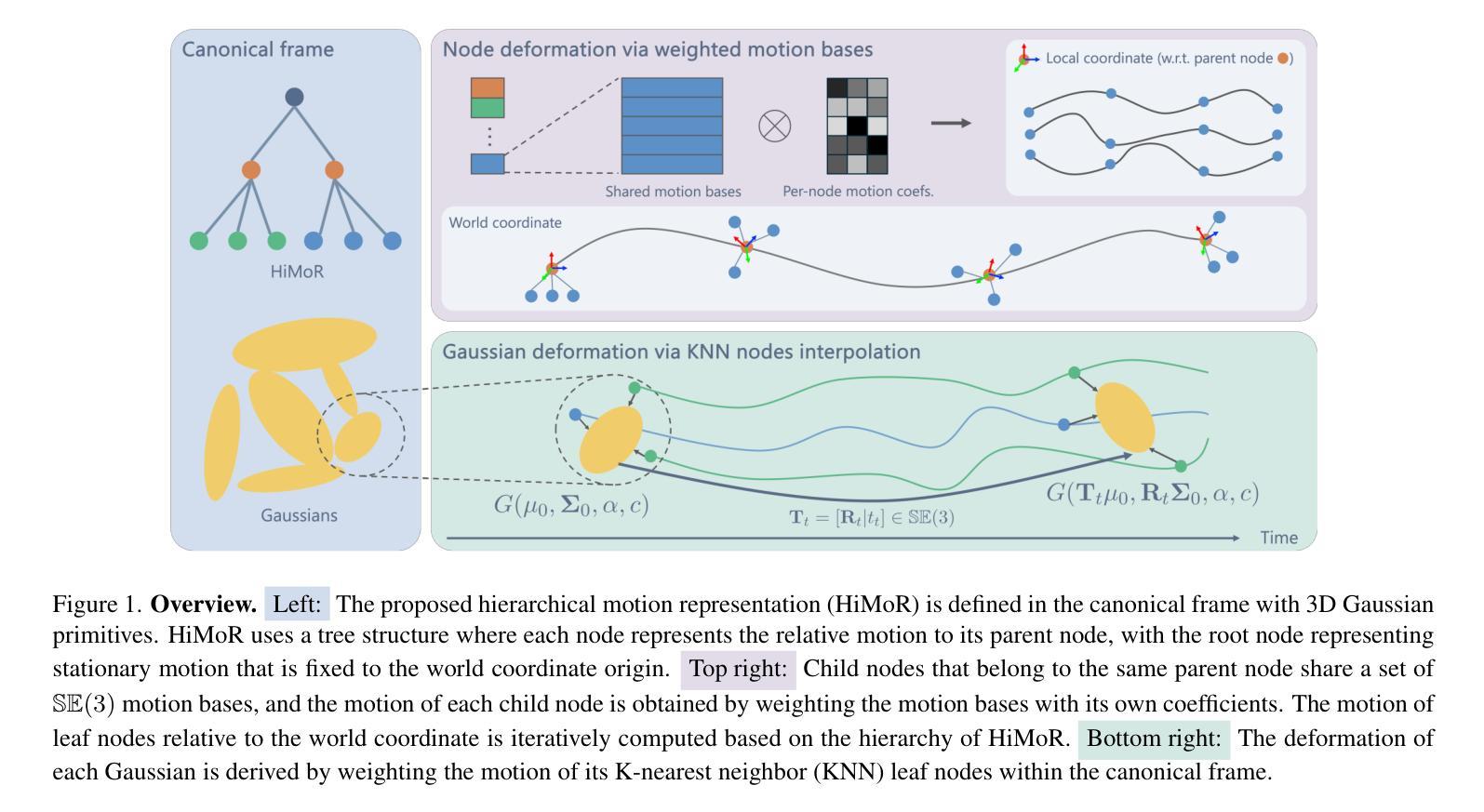
We present Hierarchical Motion Representation (HiMoR), a novel deformation representation for 3D Gaussian primitives capable of achieving high-quality monocular dynamic 3D reconstruction. The insight behind HiMoR is that motions in everyday scenes can be decomposed into coarser motions that serve as the foundation for finer details. Using a tree structure, HiMoR’s nodes represent different levels of motion detail, with shallower nodes modeling coarse motion for temporal smoothness and deeper nodes capturing finer motion. Additionally, our model uses a few shared motion bases to represent motions of different sets of nodes, aligning with the assumption that motion tends to be smooth and simple. This motion representation design provides Gaussians with a more structured deformation, maximizing the use of temporal relationships to tackle the challenging task of monocular dynamic 3D reconstruction. We also propose using a more reliable perceptual metric as an alternative, given that pixel-level metrics for evaluating monocular dynamic 3D reconstruction can sometimes fail to accurately reflect the true quality of reconstruction. Extensive experiments demonstrate our method’s efficacy in achieving superior novel view synthesis from challenging monocular videos with complex motions.
我们提出了分层运动表示(HiMoR),这是一种针对3D高斯原始数据的新型变形表示,能够实现高质量的单目动态3D重建。HiMoR的见解是,日常场景中的运动可以分解为较粗略的运动,这些运动作为精细细节的基础。使用树形结构,HiMoR的节点代表不同级别的运动细节,较浅的节点模拟粗糙运动以实现时间平滑,而较深的节点捕捉精细运动。此外,我们的模型使用少量共享运动基来表示不同节点集的运动,这与运动的假设相符,即运动往往是平滑和简单的。这种运动表示设计使高斯数据具有更结构化的变形,最大限度地利用时间关系来解决单目动态3D重建这一具有挑战性的任务。此外,鉴于用于评估单目动态3D重建的像素级指标有时无法准确反映重建的真实质量,我们还提出了使用更可靠的感知指标作为替代方案。大量实验表明,我们的方法在从具有复杂运动的单目视频中实现优质新颖视图合成方面非常有效。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Project Page: https://pfnet-research.github.io/himor
Summary
该文提出了基于分层运动表示(HiMoR)技术的三维动态重建方法,用于实现对单个视点三维模型的高质量重建。其创新点在于可将场景中的运动分解成不同级别的层次性细节运动。这种方法采用了树状结构来表示不同层次的运动细节,使用更少的共享运动基础表示不同的节点运动集合,从而实现了更为流畅和简洁的运动表现。此外,该研究还提出了一种更为可靠的感知度量方法,以替代像素级别的度量方法,更准确地对重建质量进行评估。实验结果证明了该方法在复杂运动场景下的有效性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种名为分层运动表示(HiMoR)的新技术,用于处理三维动态重建中的复杂运动。
- 利用树状结构表示不同层次的细节运动,通过共享运动基础实现简洁流畅的运动表现。
- 通过采用感知度量方法,更准确地评估重建质量。
- 实现优质的单视点动态三维重建技术。
- 技术能够处理复杂运动场景下的高质量重建。
- 利用时序关系进行结构化变形处理。
点此查看论文截图

econSG: Efficient and Multi-view Consistent Open-Vocabulary 3D Semantic Gaussians
Authors:Can Zhang, Gim Hee Lee
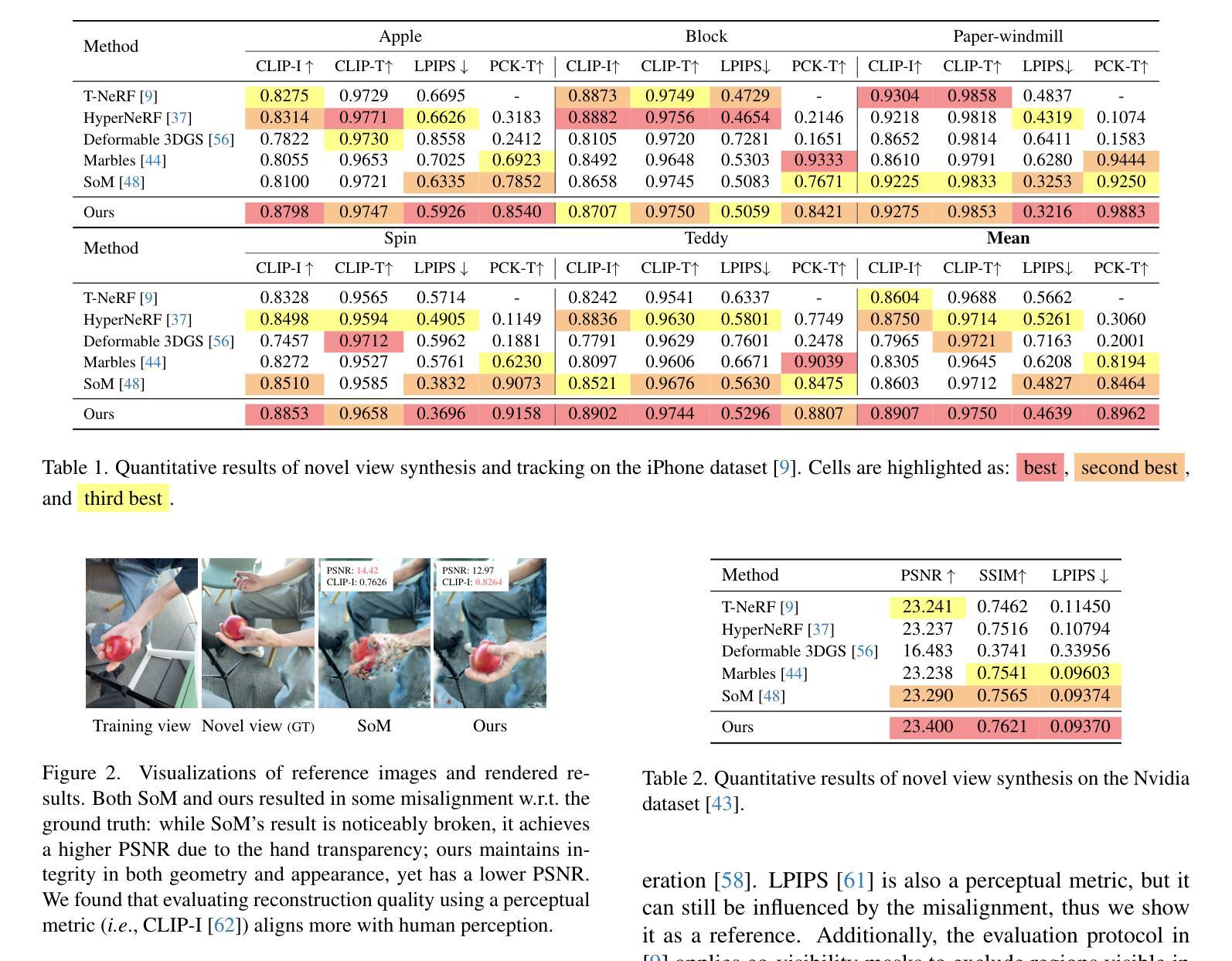
The primary focus of most recent works on open-vocabulary neural fields is extracting precise semantic features from the VLMs and then consolidating them efficiently into a multi-view consistent 3D neural fields representation. However, most existing works over-trusted SAM to regularize image-level CLIP without any further refinement. Moreover, several existing works improved efficiency by dimensionality reduction of semantic features from 2D VLMs before fusing with 3DGS semantic fields, which inevitably leads to multi-view inconsistency. In this work, we propose econSG for open-vocabulary semantic segmentation with 3DGS. Our econSG consists of: 1) A Confidence-region Guided Regularization (CRR) that mutually refines SAM and CLIP to get the best of both worlds for precise semantic features with complete and precise boundaries. 2) A low dimensional contextual space to enforce 3D multi-view consistency while improving computational efficiency by fusing backprojected multi-view 2D features and follow by dimensional reduction directly on the fused 3D features instead of operating on each 2D view separately. Our econSG shows state-of-the-art performance on four benchmark datasets compared to the existing methods. Furthermore, we are also the most efficient training among all the methods.
最近关于开放词汇神经场的主要工作集中从VLMs中提取精确语义特征,然后有效地将它们整合成多视角一致的3D神经场表示。然而,大多数现有工作过于依赖SAM来规范图像级别的CLIP,而没有进行任何进一步细化。此外,一些现有工作通过在融合到三维语义场之前对二维VLMs中的语义特征进行降维来提高效率,这不可避免地会导致多视角的不一致性。在本工作中,我们提出用于具有三维语义分割的开放词汇经济的经济SG(econSG)。我们的econSG包括:1)置信区域引导正则化(CRR),它相互优化SAM和CLIP,以获得精确语义特征的最好结果,具有完整和精确的边界。2)低维上下文空间强制实施三维多视角一致性,同时通过融合后投影的多视角二维特征来提高计算效率,然后在融合的3D特征上进行降维,而不是分别对每个二维视图进行操作。与现有方法相比,我们的econSG在四个基准数据集上表现出卓越的性能。此外,我们也是所有方法中训练效率最高的。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注开放词汇神经场的研究,旨在从VLMs中提取精确语义特征,并高效地整合到多视角一致的3D神经场表示中。针对现有工作的不足,提出econSG方法,包括置信区域引导正则化(CRR)和低维上下文空间,以提高语义分割的精度和多视角一致性,同时提高计算效率。
Key Takeaways
- 近期研究重点:开放词汇神经场主要关注从VLMs提取精确语义特征,并整合到多视角一致的3D神经场表示中。
- 现有工作问题:过度依赖SAM正则化图像级别的CLIP,缺乏进一步细化,且通过降低2D VLMs的语义特征维度来提高效率,导致多视角不一致性。
- econSG方法提出:包括置信区域引导正则化(CRR)和低维上下文空间。
- CRR作用:相互优化SAM和CLIP,获得更精确的语义特征,实现完整和精确的边界。
- 低维上下文空间的作用:强化3D多视角一致性,提高计算效率,通过直接在融合后的3D特征上进行降维操作,而不是分别对每个2D视图进行操作。
- econSG性能:在四个基准数据集上相比现有方法表现出最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图

SE4Lip: Speech-Lip Encoder for Talking Head Synthesis to Solve Phoneme-Viseme Alignment Ambiguity
Authors:Yihuan Huang, Jiajun Liu, Yanzhen Ren, Wuyang Liu, Juhua Tang
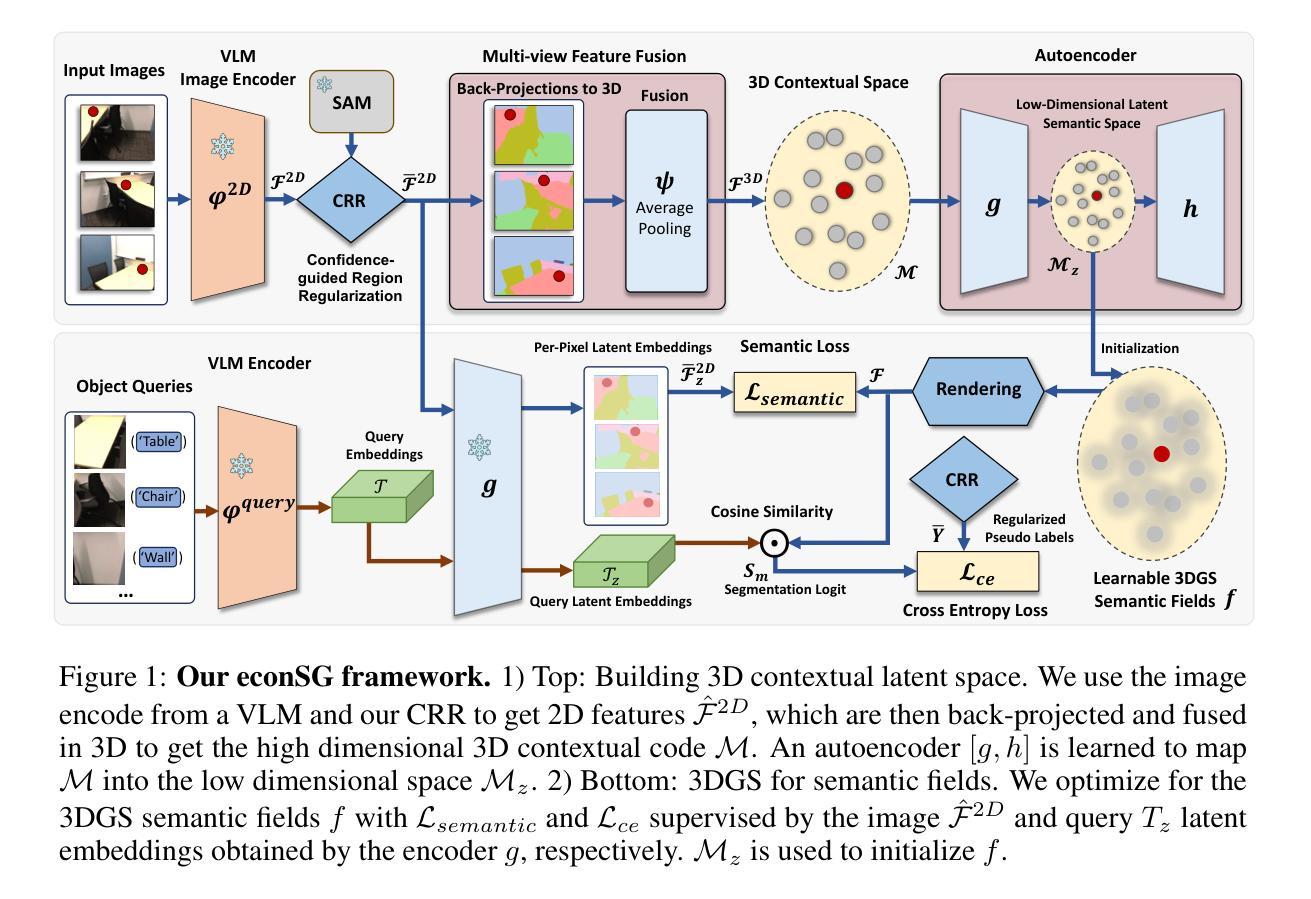
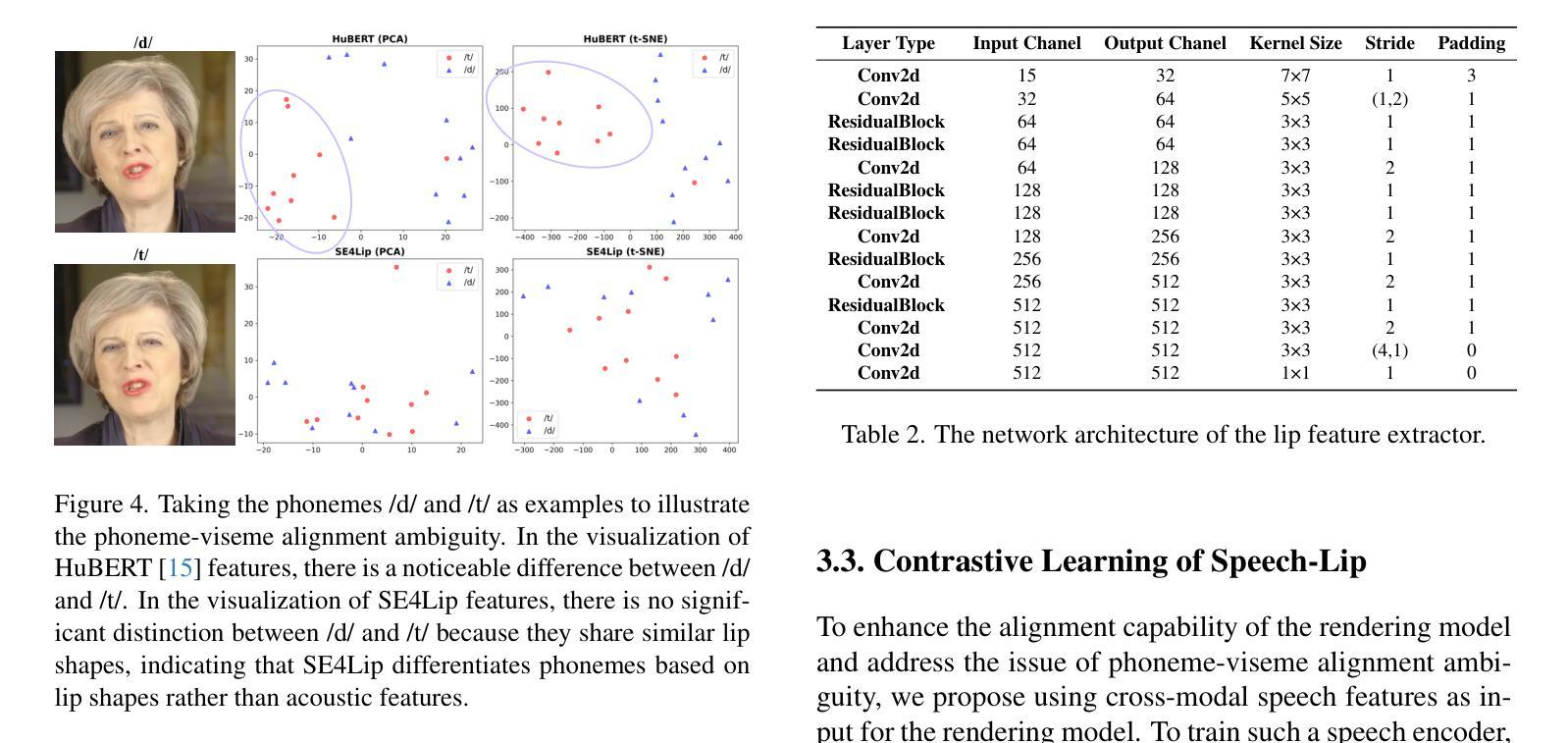
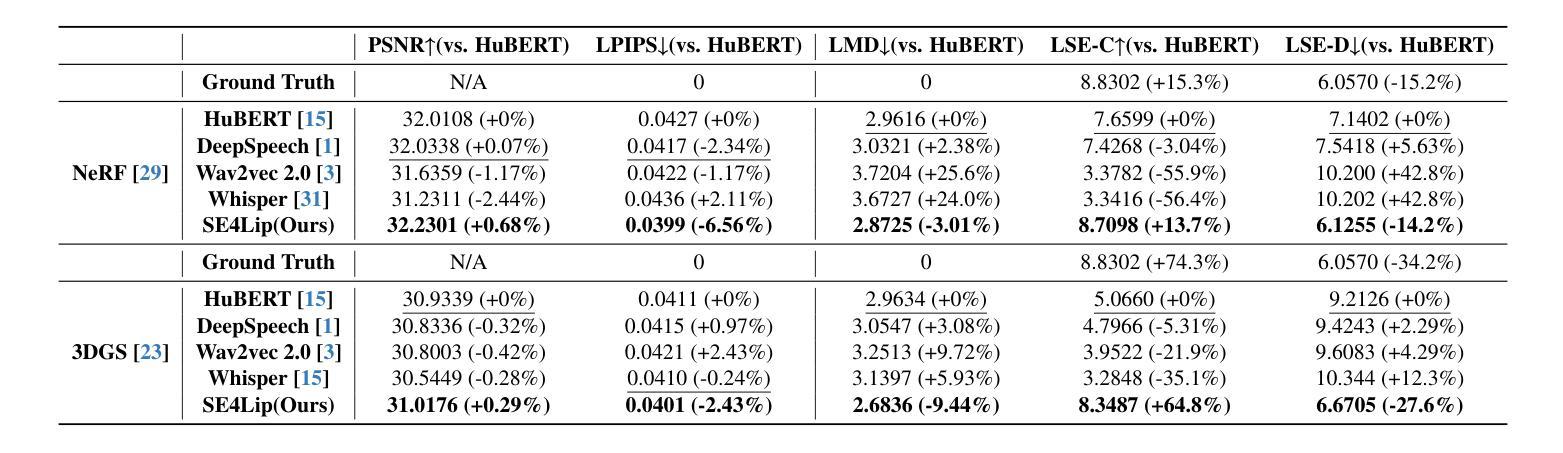
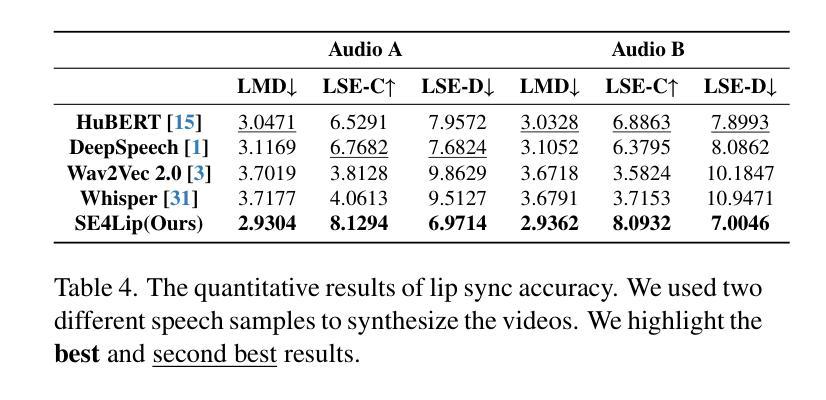
Speech-driven talking head synthesis tasks commonly use general acoustic features (such as HuBERT and DeepSpeech) as guided speech features. However, we discovered that these features suffer from phoneme-viseme alignment ambiguity, which refers to the uncertainty and imprecision in matching phonemes (speech) with visemes (lip). To address this issue, we propose the Speech Encoder for Lip (SE4Lip) to encode lip features from speech directly, aligning speech and lip features in the joint embedding space by a cross-modal alignment framework. The STFT spectrogram with the GRU-based model is designed in SE4Lip to preserve the fine-grained speech features. Experimental results show that SE4Lip achieves state-of-the-art performance in both NeRF and 3DGS rendering models. Its lip sync accuracy improves by 13.7% and 14.2% compared to the best baseline and produces results close to the ground truth videos.
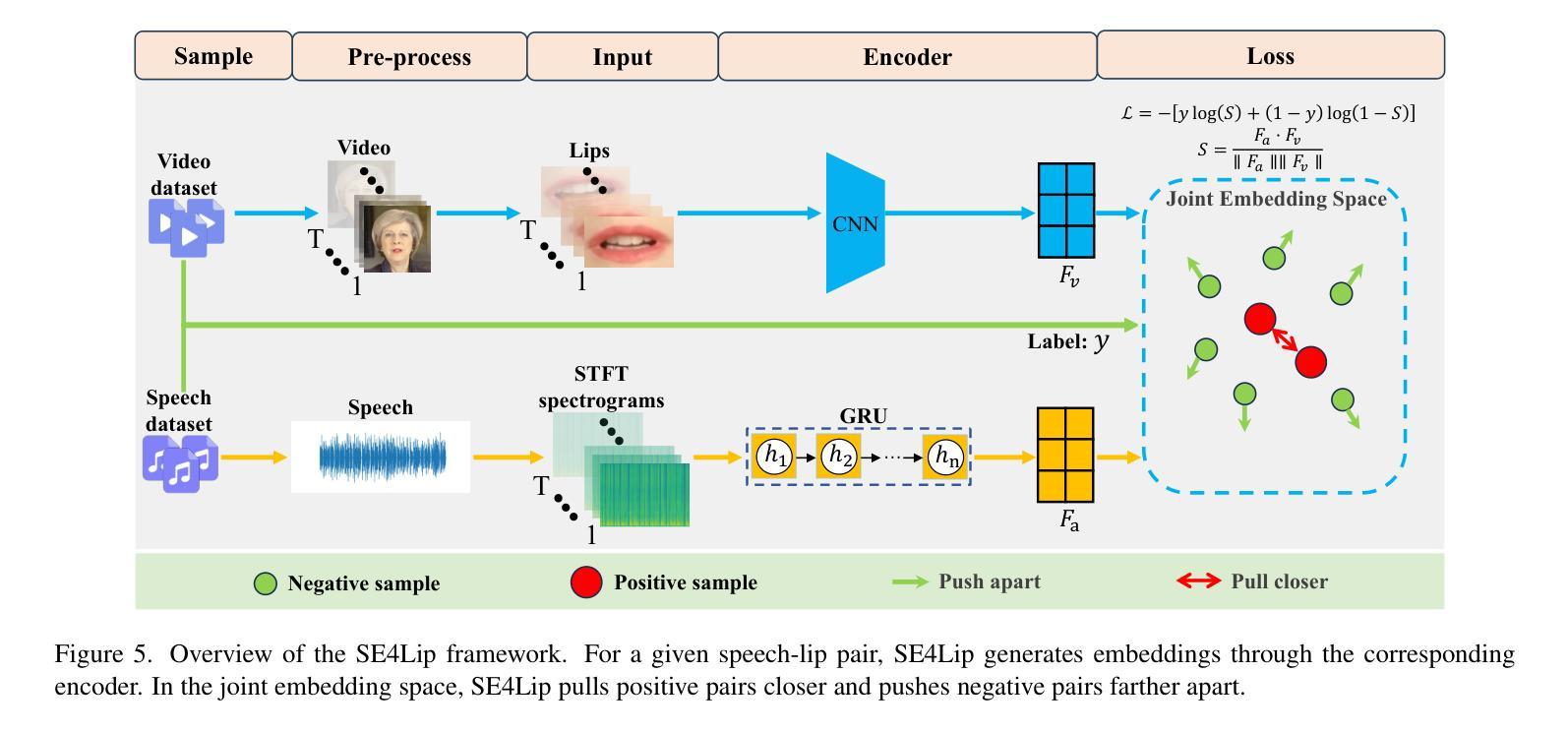
语音驱动的人头合成任务通常使用一般的声学特征(如HuBERT和DeepSpeech)作为引导语音特征。然而,我们发现这些特征存在音素-嘴部动作对齐模糊的问题,这指的是音素(语音)与嘴部动作(嘴唇)匹配的不确定性和不精确性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了基于语音的嘴唇编码(SE4Lip),直接从语音中编码嘴唇特征,通过跨模态对齐框架在联合嵌入空间中对齐语音和嘴唇特征。SE4Lip设计中采用了基于GRU模型的STFT频谱图,以保留精细的语音特征。实验结果表明,SE4Lip在NeRF和3DGS渲染模型中均达到了最先进的性能。其唇同步精度相较于最佳基线提高了13.7%和14.2%,并且生成的结果接近真实视频。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了语音驱动的头部合成任务中,使用一般声学特征作为引导语音特征时存在的问题。发现存在语音与唇动(viseme)对齐的模糊性,即语音与唇部动作匹配的不确定性和不精确性。为解决这一问题,提出了基于唇特征的Speech Encoder for Lip(SE4Lip)模型。该模型通过跨模态对齐框架,直接在语音中编码唇特征,对齐语音和唇特征在联合嵌入空间。采用基于GRU模型的STFT频谱图设计,旨在保留精细的语音特征。实验结果表明,SE4Lip在NeRF和3DGS渲染模型中达到了最新技术水平,唇同步精度分别提高了13.7%和14.2%,生成结果接近真实视频。
Key Takeaways
- 语音驱动头部合成任务中,一般声学特征存在语音与唇部动作对齐的模糊性问题。
- SE4Lip模型旨在解决上述问题,通过直接编码语音中的唇特征来实现更精确的对齐。
- SE4Lip采用跨模态对齐框架,确保语音和唇特征在联合嵌入空间中的对齐。
- 模型使用基于GRU的STFT频谱图设计,以保留精细的语音特征。
- 实验结果显示SE4Lip在NeRF和3DGS渲染模型中表现优异,达到最新技术水平。
- SE4Lip模型提高了唇同步精度,相较于最佳基线提高了13.7%和14.2%。
点此查看论文截图


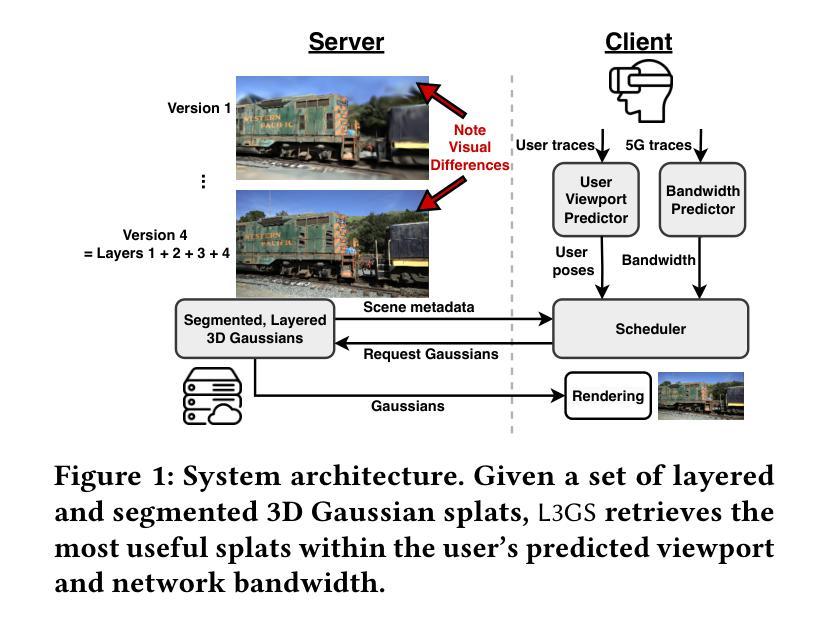
L3GS: Layered 3D Gaussian Splats for Efficient 3D Scene Delivery
Authors:Yi-Zhen Tsai, Xuechen Zhang, Zheng Li, Jiasi Chen
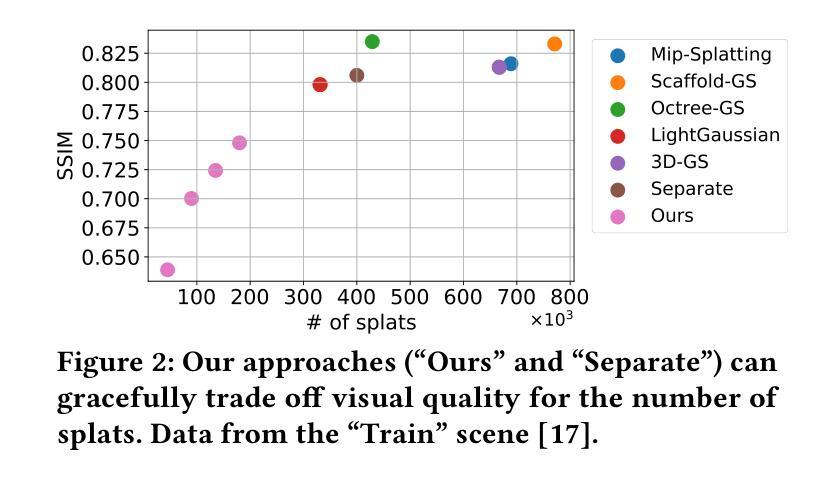
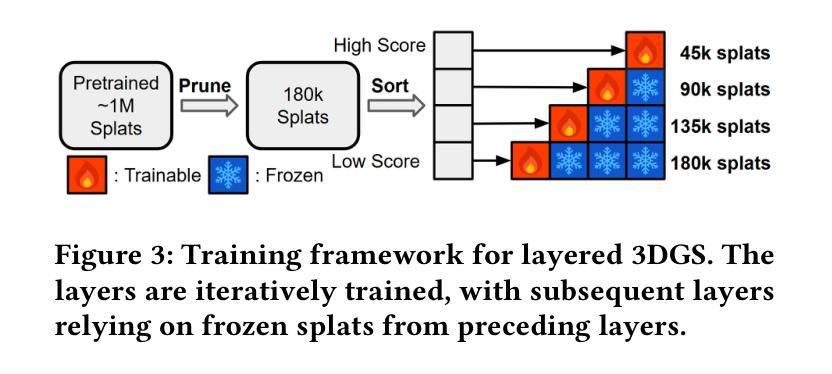
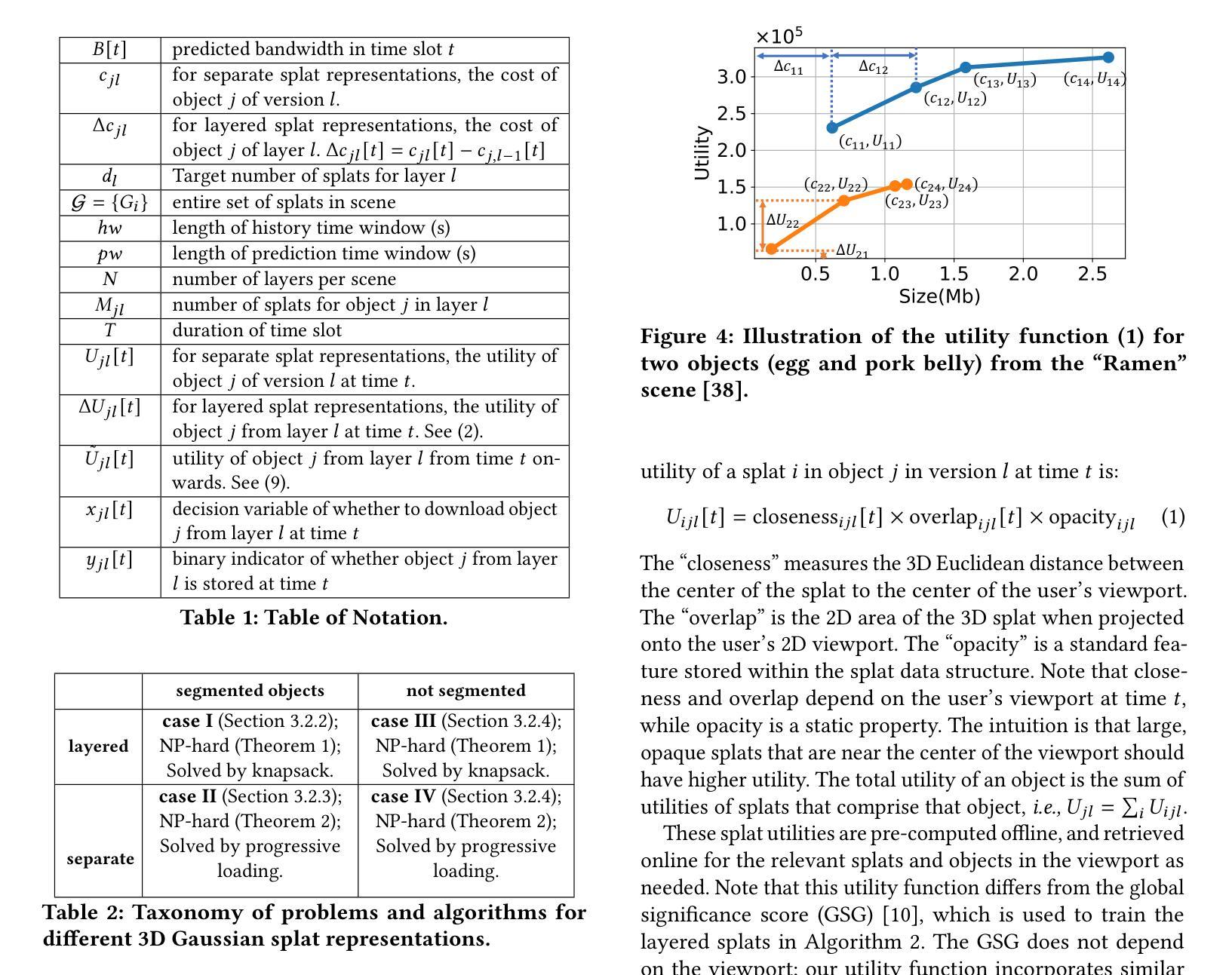
Traditional 3D content representations include dense point clouds that consume large amounts of data and hence network bandwidth, while newer representations such as neural radiance fields suffer from poor frame rates due to their non-standard volumetric rendering pipeline. 3D Gaussian splats (3DGS) can be seen as a generalization of point clouds that meet the best of both worlds, with high visual quality and efficient rendering for real-time frame rates. However, delivering 3DGS scenes from a hosting server to client devices is still challenging due to high network data consumption (e.g., 1.5 GB for a single scene). The goal of this work is to create an efficient 3D content delivery framework that allows users to view high quality 3D scenes with 3DGS as the underlying data representation. The main contributions of the paper are: (1) Creating new layered 3DGS scenes for efficient delivery, (2) Scheduling algorithms to choose what splats to download at what time, and (3) Trace-driven experiments from users wearing virtual reality headsets to evaluate the visual quality and latency. Our system for Layered 3D Gaussian Splats delivery L3GS demonstrates high visual quality, achieving 16.9% higher average SSIM compared to baselines, and also works with other compressed 3DGS representations.
传统3D内容表示方法包括消耗大量数据和网络带宽的密集点云,而较新的表示方法,如神经辐射场,由于其非标准体积渲染流程,存在帧率较低的问题。3D高斯splat(3DGS)可以被视为点云的概括,兼具高视觉质量和实时帧率的高效渲染。然而,由于网络数据消耗较高(例如单个场景高达1.5GB),从托管服务器向客户端设备传输3DGS场景仍然具有挑战性。本研究的目标是创建一个高效的3D内容传输框架,允许用户使用3DGS作为基础数据表示来查看高质量的3D场景。论文的主要贡献包括:(1)创建用于高效传输的新分层3DGS场景,(2)调度算法来选择何时下载哪些splat,(3)佩戴虚拟现实头盔的用户进行的跟踪驱动实验,以评估视觉质量和延迟。我们的分层3D高斯Splats传输系统L3GS展现了高视觉质量,与基线相比实现了平均高出16.9%的SSIM指数,并且与其他压缩的3DGS表示方法也能很好地协同工作。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文主要探讨如何在3D内容表示中实现高质量与高实时渲染效率的问题。针对传统密集点云需要大量数据和带宽的问题,以及新兴神经网络辐射场因非标准体积渲染管道而导致帧率较低的问题,提出使用3D高斯Splats(3DGS)作为解决方案。其兼具点云的高视觉质量和高效渲染能力。然而,从服务器向客户端设备传输3DGS场景仍面临高网络数据消耗的挑战。本研究的目标是创建一个高效的3D内容交付框架,使用户能够浏览高质量采用3DGS作为底层数据表示的3D场景。主要贡献包括:创建用于高效传输的新分层3DGS场景、设计调度算法来选择何时下载哪些Splats以及使用用户佩戴虚拟现实头盔进行的跟踪驱动实验来评估视觉质量和延迟。所提出的分层3D高斯Splats交付系统(L3GS)实现了高视觉质量,平均结构相似性指数(SSIM)比基线高出16.9%,并且与其他压缩的3DGS表示形式兼容。
关键见解
- 介绍了传统与新兴三维内容表示方法的挑战与不足,包括数据消耗量大和渲染效率问题。
- 提出了使用3D高斯Splats(3DGS)作为解决这些挑战的方法,结合了点云的高视觉质量和高效渲染能力。
- 针对网络数据消耗问题,提出了创建分层3DGS场景的方法以提高传输效率。
- 设计了调度算法来选择何时下载哪些Splats,以优化数据传输和用户体验。
- 通过用户佩戴虚拟现实头盔进行的跟踪驱动实验验证了系统的有效性,包括高视觉质量和低延迟方面的表现。
- L3GS系统与其他压缩的3DGS表示形式兼容,具有良好的通用性。
点此查看论文截图

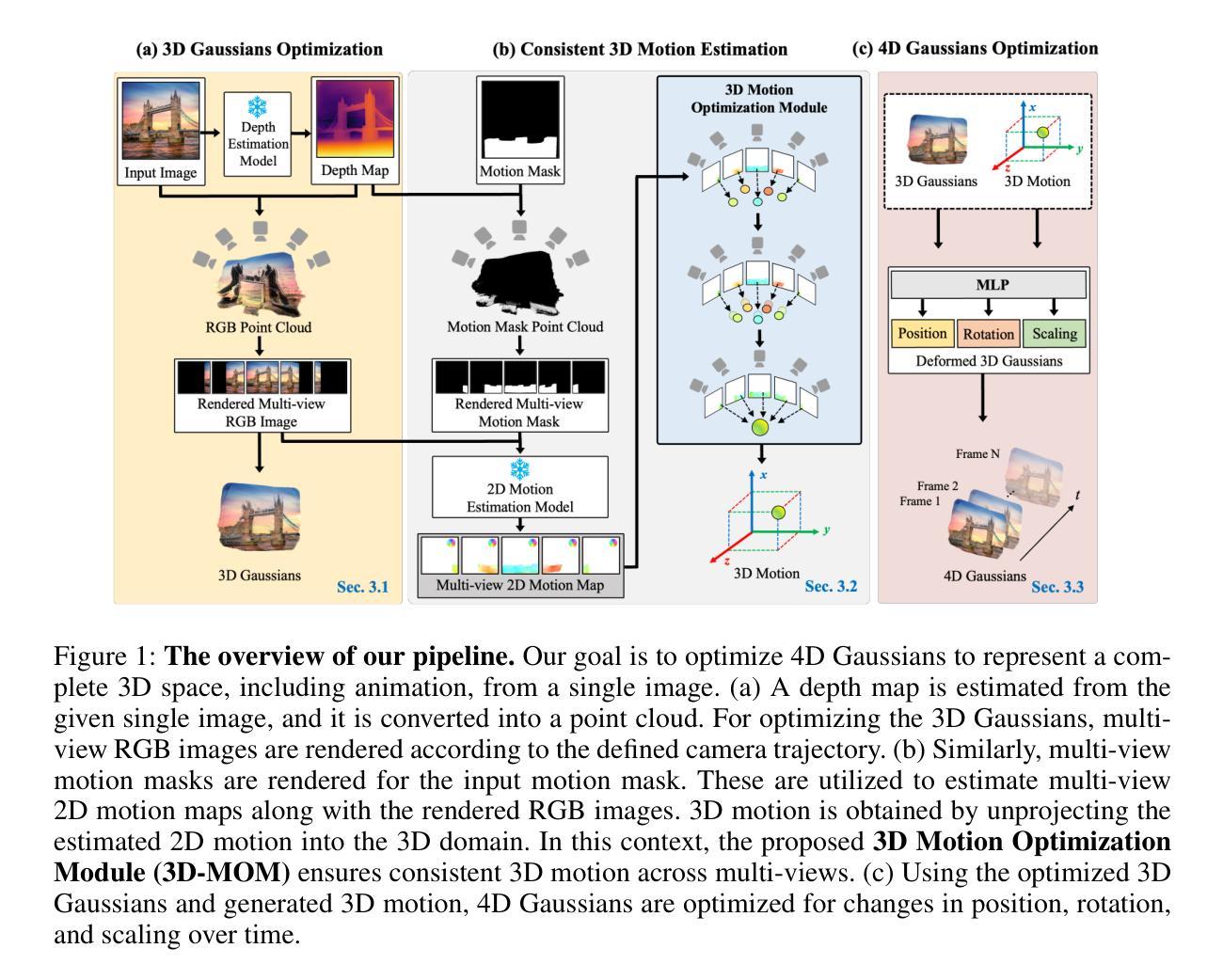
Optimizing 4D Gaussians for Dynamic Scene Video from Single Landscape Images
Authors:In-Hwan Jin, Haesoo Choo, Seong-Hun Jeong, Heemoon Park, Junghwan Kim, Oh-joon Kwon, Kyeongbo Kong
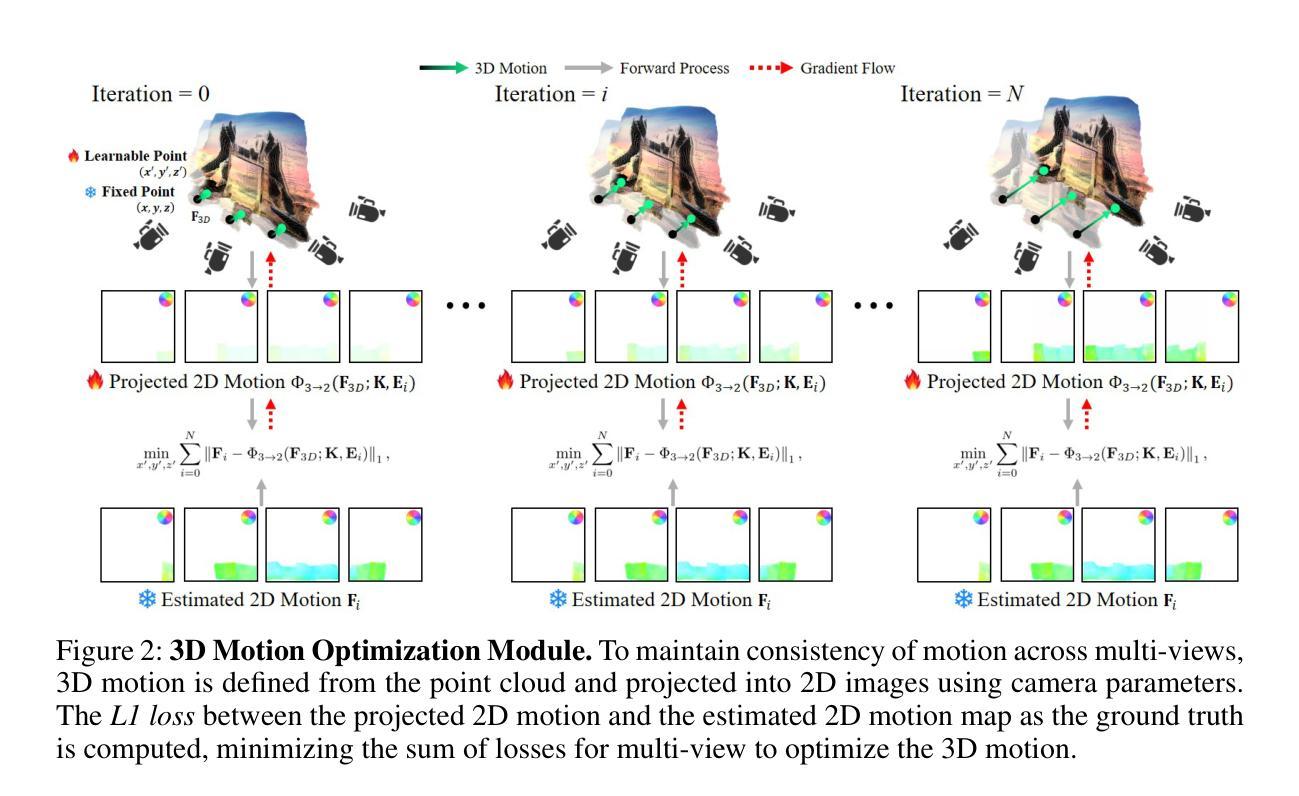
To achieve realistic immersion in landscape images, fluids such as water and clouds need to move within the image while revealing new scenes from various camera perspectives. Recently, a field called dynamic scene video has emerged, which combines single image animation with 3D photography. These methods use pseudo 3D space, implicitly represented with Layered Depth Images (LDIs). LDIs separate a single image into depth-based layers, which enables elements like water and clouds to move within the image while revealing new scenes from different camera perspectives. However, as landscapes typically consist of continuous elements, including fluids, the representation of a 3D space separates a landscape image into discrete layers, and it can lead to diminished depth perception and potential distortions depending on camera movement. Furthermore, due to its implicit modeling of 3D space, the output may be limited to videos in the 2D domain, potentially reducing their versatility. In this paper, we propose representing a complete 3D space for dynamic scene video by modeling explicit representations, specifically 4D Gaussians, from a single image. The framework is focused on optimizing 3D Gaussians by generating multi-view images from a single image and creating 3D motion to optimize 4D Gaussians. The most important part of proposed framework is consistent 3D motion estimation, which estimates common motion among multi-view images to bring the motion in 3D space closer to actual motions. As far as we know, this is the first attempt that considers animation while representing a complete 3D space from a single landscape image. Our model demonstrates the ability to provide realistic immersion in various landscape images through diverse experiments and metrics. Extensive experimental results are https://cvsp-lab.github.io/ICLR2025_3D-MOM/.
为了实现景观图像的逼真沉浸感,水、云等流体需要在图像内移动,同时从不同相机视角揭示新场景。最近,出现了一个名为动态场景视频的领域,它将单图像动画与3D摄影相结合。这些方法使用伪3D空间,通过分层深度图像(LDIs)进行隐式表示。LDIs将单幅图像分离成基于深度的图层,这使得水、云等元素可以在图像内移动,同时从不同相机视角揭示新场景。然而,由于景观通常包含流体等连续元素,将3D空间表示为分层深度图像会导致景观图像分离为离散层,并根据相机移动而导致深度感知减弱和潜在失真。此外,由于其隐式建模的3D空间,输出可能仅限于二维域的视频,从而可能降低了其通用性。在本文中,我们提出了一种通过单幅图像建立显式表示的完整3D空间动态场景视频的方法。该方法使用特定的四维高斯模型进行建模。该框架侧重于通过生成多视角图像和创建三维运动来优化三维高斯模型。该框架最重要的部分是一致的三维运动估计,它估计多视角图像之间的通用运动,使三维空间中的运动更接近实际运动。据我们所知,这是首次尝试在表示单幅景观图像的完整三维空间时考虑动画制作。我们的模型通过各种实验和度量标准证明了在多种景观图像中提供逼真沉浸感的能力。详细的实验结果可通过链接https://cvsp-lab.github.io/ICLR2025_3D-MOM进行查看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICLR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了通过单幅图像构建动态场景视频的新技术。该技术使用隐式表示的分层深度图像(LDIs)创建伪3D空间,实现水、云等流体在图像中的动态效果。然而,LDIs在表示连续元素如流体时存在深度感知降低和潜在失真问题。本文提出通过单幅图像构建完整的3D空间,并采用优化的显式表示法——特别是使用4D高斯模型,为动态场景视频提供更真实的沉浸感。最重要的是提出了一致的3D运动估计框架,以估计多视角图像之间的共同运动,使模拟的3D空间更接近实际运动。该模型通过广泛的实验和指标证明了其有效性。详细信息可访问:链接地址。
Key Takeaways
- 动态场景视频结合了单图像动画与3D摄影技术,旨在实现更真实的沉浸感。
- 分层深度图像(LDIs)用于创建伪3D空间,使得图像中的流体可以呈现动态效果。
- LDIs在表示连续元素(如流体)时可能导致深度感知降低和潜在失真问题。
- 提出使用显式表示的4D高斯模型构建完整的单幅图像3D空间的方法。
点此查看论文截图

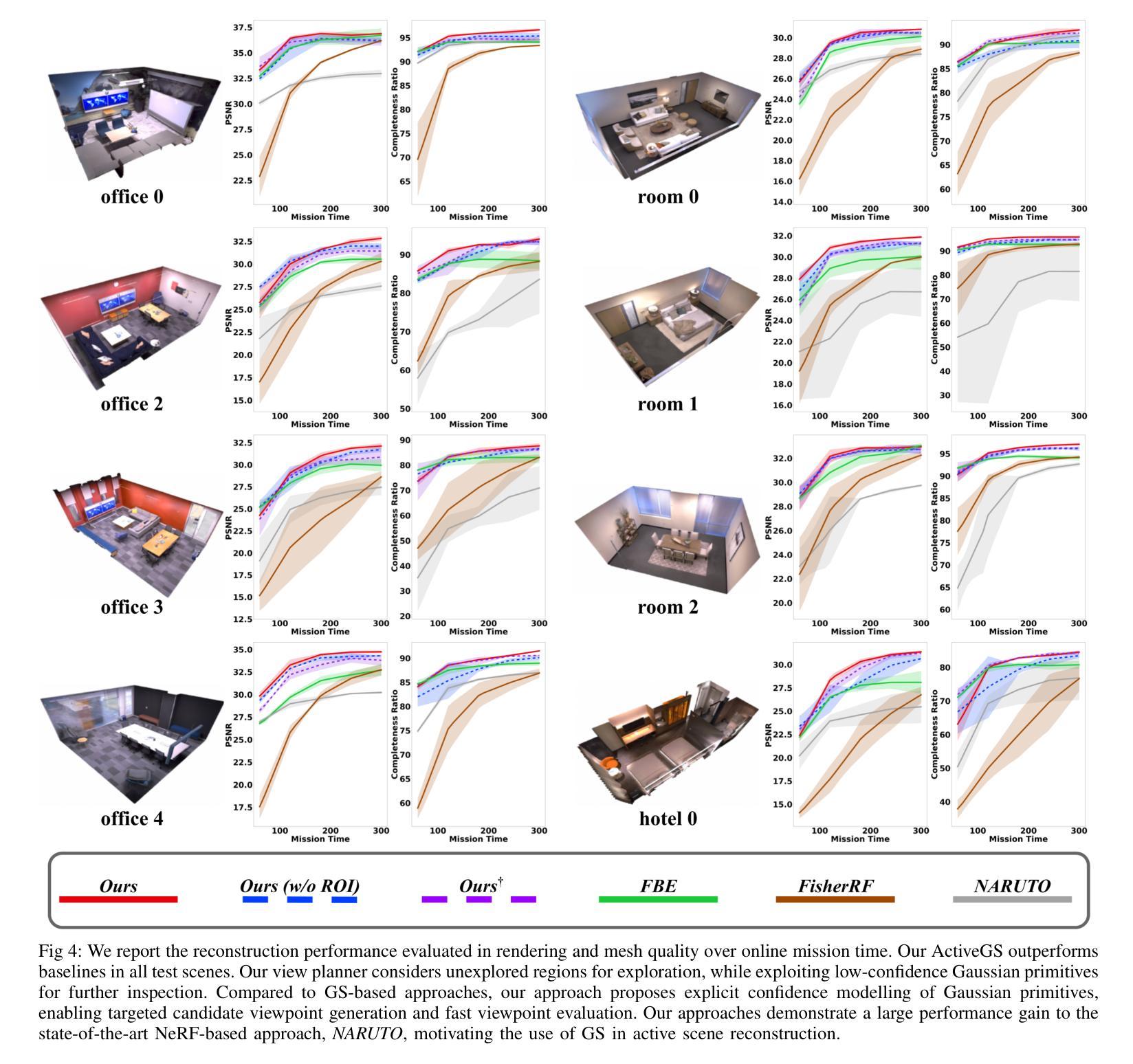
ActiveGS: Active Scene Reconstruction Using Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Liren Jin, Xingguang Zhong, Yue Pan, Jens Behley, Cyrill Stachniss, Marija Popović
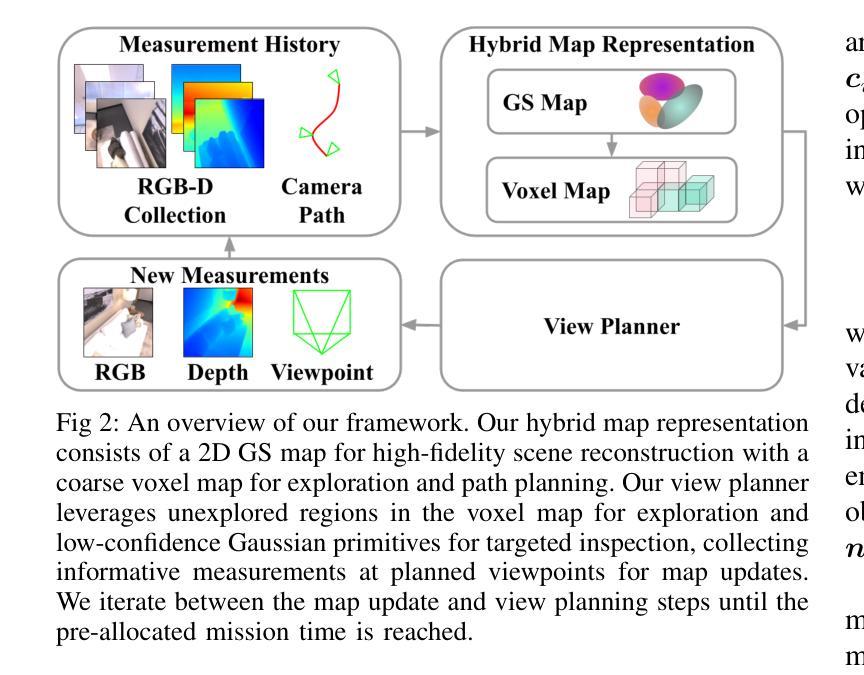
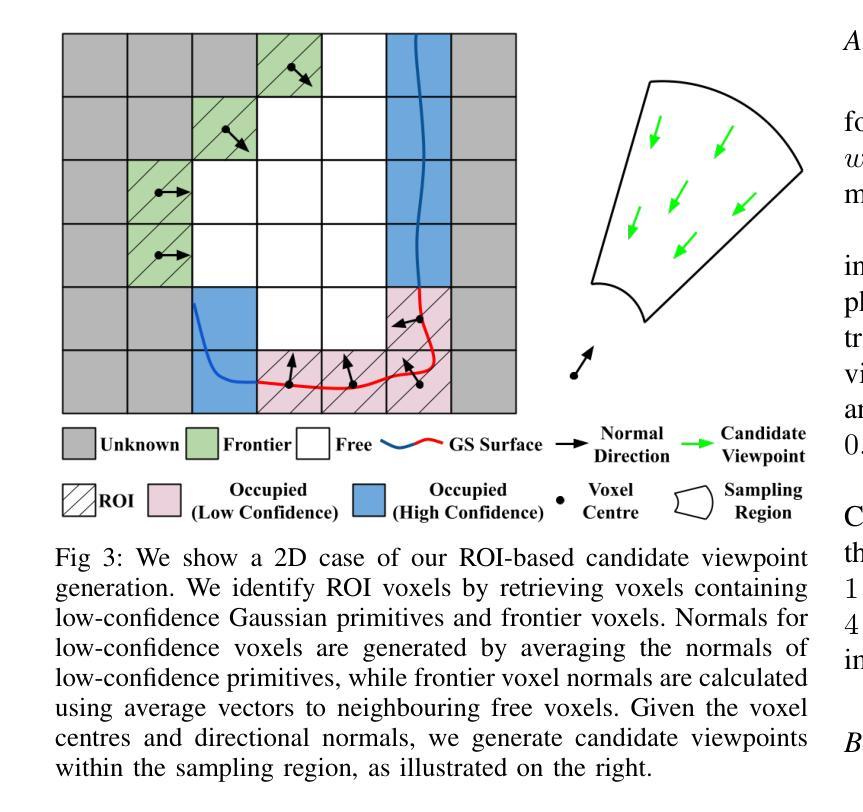
Robotics applications often rely on scene reconstructions to enable downstream tasks. In this work, we tackle the challenge of actively building an accurate map of an unknown scene using an RGB-D camera on a mobile platform. We propose a hybrid map representation that combines a Gaussian splatting map with a coarse voxel map, leveraging the strengths of both representations: the high-fidelity scene reconstruction capabilities of Gaussian splatting and the spatial modelling strengths of the voxel map. At the core of our framework is an effective confidence modelling technique for the Gaussian splatting map to identify under-reconstructed areas, while utilising spatial information from the voxel map to target unexplored areas and assist in collision-free path planning. By actively collecting scene information in under-reconstructed and unexplored areas for map updates, our approach achieves superior Gaussian splatting reconstruction results compared to state-of-the-art approaches. Additionally, we demonstrate the real-world applicability of our framework using an unmanned aerial vehicle.
机器人应用通常依赖于场景重建来实现后续任务。在这项工作中,我们解决了在移动平台上使用RGB-D相机主动构建一个未知场景的精确地图的挑战。我们提出了一种混合地图表示方法,结合了高斯溅射地图和粗略体素地图,利用两者的优势:高斯溅射的高保真场景重建能力和体素地图的空间建模优势。我们框架的核心是对高斯溅射地图进行置信建模的有效技术,以识别重建不足的区域,同时利用体素地图的空间信息进行针对未探索区域的定位和碰撞自由路径规划。通过主动收集重建不足和未探索区域的场景信息进行地图更新,我们的方法与最新方法相比实现了优越的高斯溅射重建结果。此外,我们还使用无人机展示了该框架在现实世界中的适用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters
Summary
在机器人应用中,构建未知场景的精确地图是一大挑战。本研究利用移动平台上的RGB-D相机,提出了一种结合高斯溅射地图和粗略体素地图的混合地图表示方法。该方法利用高斯溅射地图的高保真场景重建能力和体素地图的空间建模优势。我们的框架核心是一种有效的信心建模技术,用于识别重建不足的区域,并利用体素地图的空间信息来定位未探索的区域,帮助实现无碰撞的路径规划。通过主动收集重建不足和未探索区域的场景信息进行地图更新,我们的方法与现有技术相比,实现了卓越的高斯溅射重建结果。同时,我们还通过无人机验证了框架的实际应用价值。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究解决了在移动平台上使用RGB-D相机构建未知场景精确地图的挑战。
- 提出了一种混合地图表示方法,结合了高斯溅射地图和体素地图的优点。
- 框架中采用了有效的信心建模技术,用于识别重建不足的区域。
- 利用体素地图的空间信息来定位未探索区域,实现无碰撞路径规划。
- 通过主动收集信息更新地图,在重建不足和未探索区域取得了卓越的高斯溅射重建结果。
- 框架的实际应用通过无人机进行了验证。
- 该方法提高了机器人应用中的场景重建能力。
点此查看论文截图

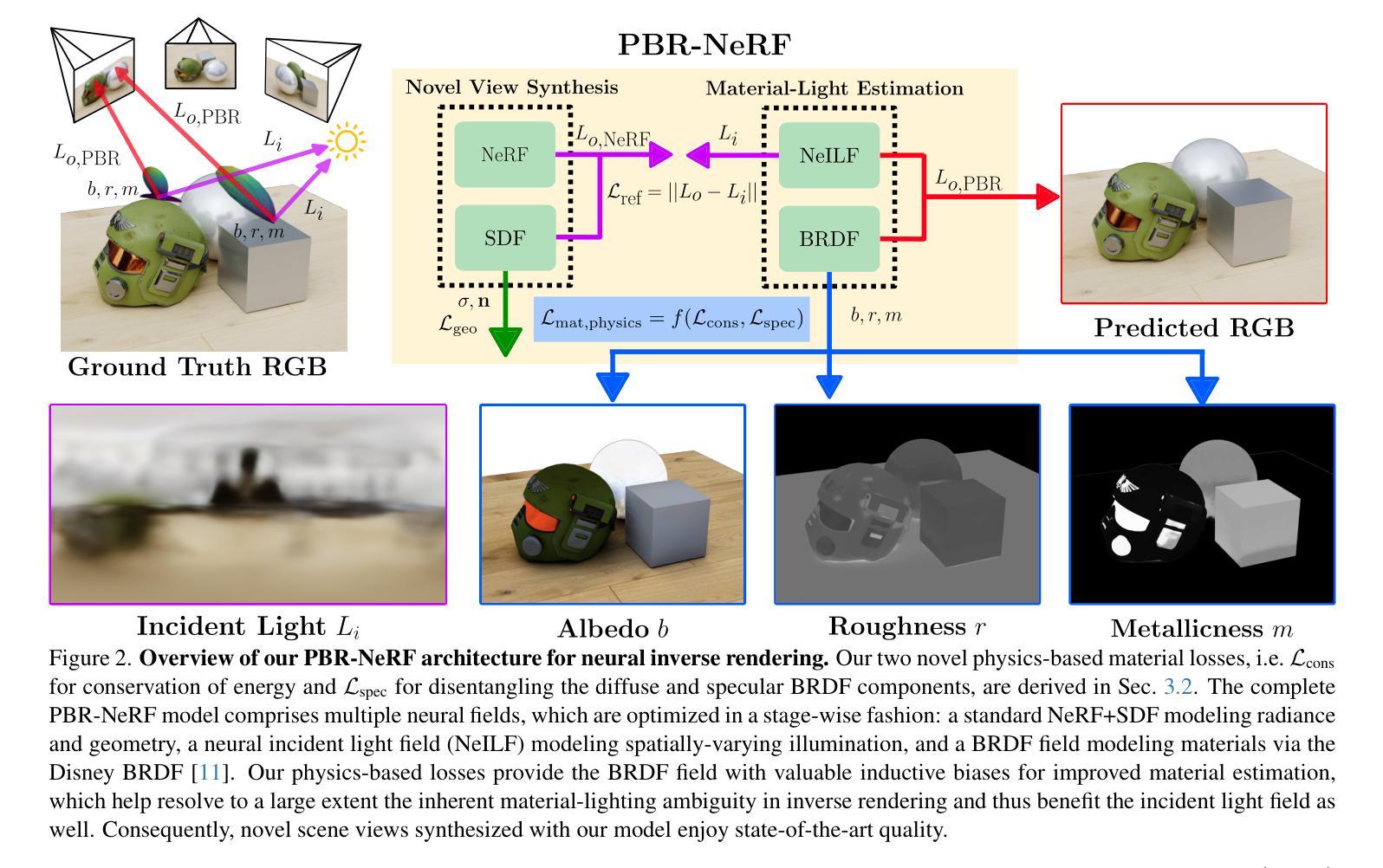
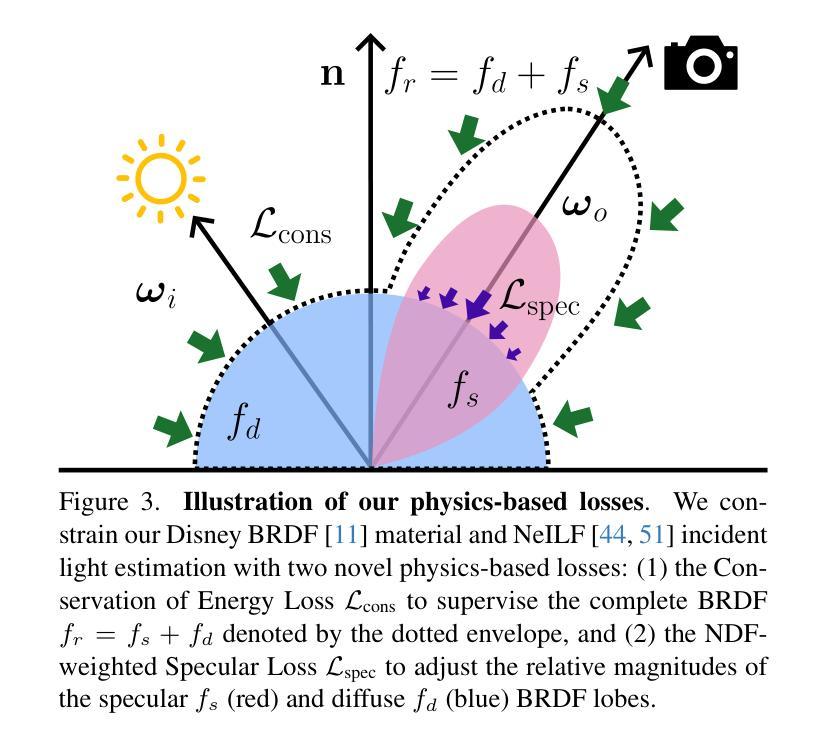
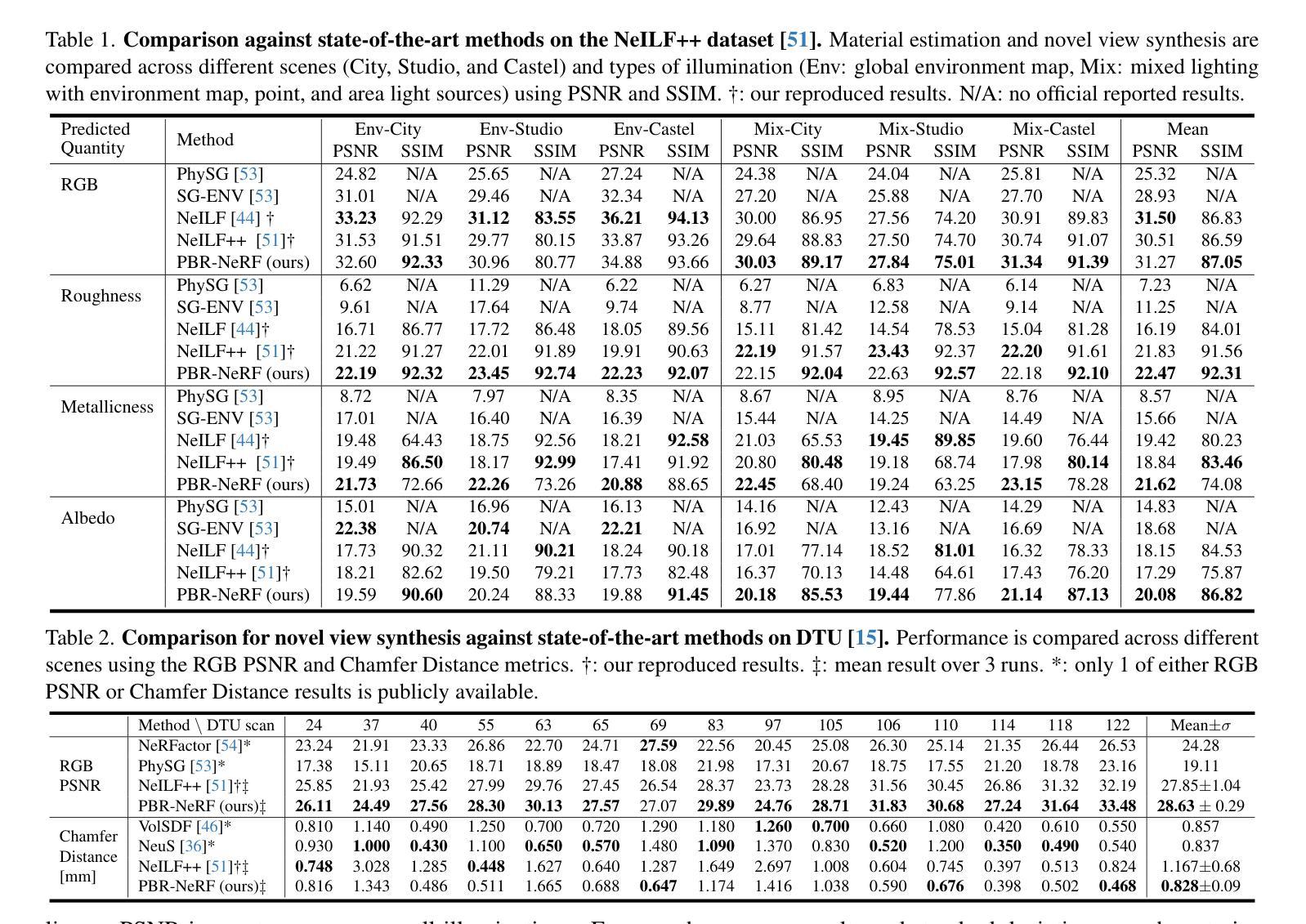
PBR-NeRF: Inverse Rendering with Physics-Based Neural Fields
Authors:Sean Wu, Shamik Basu, Tim Broedermann, Luc Van Gool, Christos Sakaridis
We tackle the ill-posed inverse rendering problem in 3D reconstruction with a Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) approach informed by Physics-Based Rendering (PBR) theory, named PBR-NeRF. Our method addresses a key limitation in most NeRF and 3D Gaussian Splatting approaches: they estimate view-dependent appearance without modeling scene materials and illumination. To address this limitation, we present an inverse rendering (IR) model capable of jointly estimating scene geometry, materials, and illumination. Our model builds upon recent NeRF-based IR approaches, but crucially introduces two novel physics-based priors that better constrain the IR estimation. Our priors are rigorously formulated as intuitive loss terms and achieve state-of-the-art material estimation without compromising novel view synthesis quality. Our method is easily adaptable to other inverse rendering and 3D reconstruction frameworks that require material estimation. We demonstrate the importance of extending current neural rendering approaches to fully model scene properties beyond geometry and view-dependent appearance. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/s3anwu/pbrnerf
我们采用基于物理渲染(PBR)理论指导的神经辐射场(NeRF)方法,解决了3D重建中的不适定逆渲染问题,称为PBR-NeRF。我们的方法解决了大多数NeRF和3D高斯摊铺方法的关键局限性:它们在估计视相关外观时没有对场景材质和照明进行建模。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了一种能够联合估计场景几何、材质和照明的逆渲染(IR)模型。我们的模型建立在最近的NeRF基IR方法之上,但关键地引入了两种新型基于物理的先验知识,更好地约束了IR估计。我们的先验知识被严谨地制定为直观的损失项,在不损害新型视图合成质量的情况下实现了最先进的材料估计。我们的方法可以轻松地适应其他需要材料估计的逆渲染和3D重建框架。我们证明了将当前的神经渲染方法扩展到除几何和视相关外观以外的场景属性建模的重要性。代码公开可用:https://github.com/s3anwu/pbrnerf 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. 16 pages, 7 figures. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/s3anwu/pbrnerf
Summary
利用基于物理渲染(PBR)理论的神经辐射场(NeRF)方法,解决3D重建中的逆向渲染问题,提出名为PBR-NeRF的方法。该方法解决了大多数NeRF和3D高斯拼贴方法的核心局限:它们估计视图相关的外观,但没有对场景材质和照明进行建模。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种能够联合估计场景几何、材质和照明的逆向渲染(IR)模型。该模型建立在最近的NeRF基IR方法之上,但关键地引入了两个新的基于物理的先验知识,更好地约束了IR估计。我们的先验知识被严谨地制定为直观损失项,实现了材料估计的业界最佳水平,且不影响新视角合成质量。我们的方法很容易适应其他需要材料估计的逆向渲染和3D重建框架。
Key Takeaways
- 使用NeRF方法结合PBR理论解决3D重建中的逆向渲染问题。
- 提出了PBR-NeRF方法,解决了大多数NeRF和3D高斯拼贴方法在估计视图相关外观时未考虑场景材质和照明的问题。
- 通过引入两个新的基于物理的先验知识,更好地约束了逆向渲染(IR)模型的估计。
- 先验知识被严谨地制定为直观损失项,实现了材料估计的业界最佳水平。
- 该方法在保证新视角合成质量的同时,实现了材料估计的改进。
- PBR-NeRF方法容易适应其他需要材料估计的逆向渲染和3D重建框架。
点此查看论文截图