⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-10 更新
TxGemma: Efficient and Agentic LLMs for Therapeutics
Authors:Eric Wang, Samuel Schmidgall, Paul F. Jaeger, Fan Zhang, Rory Pilgrim, Yossi Matias, Joelle Barral, David Fleet, Shekoofeh Azizi
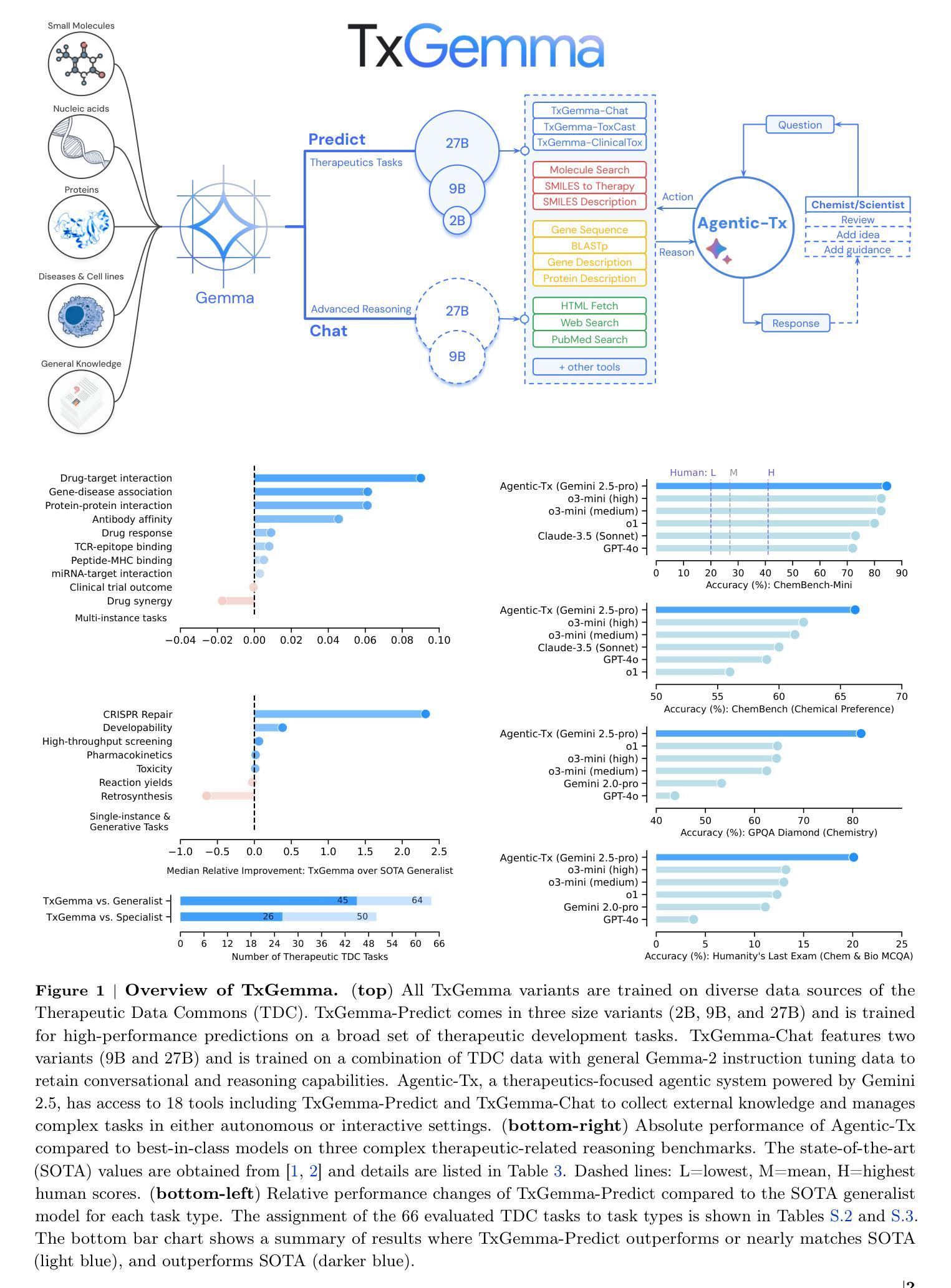
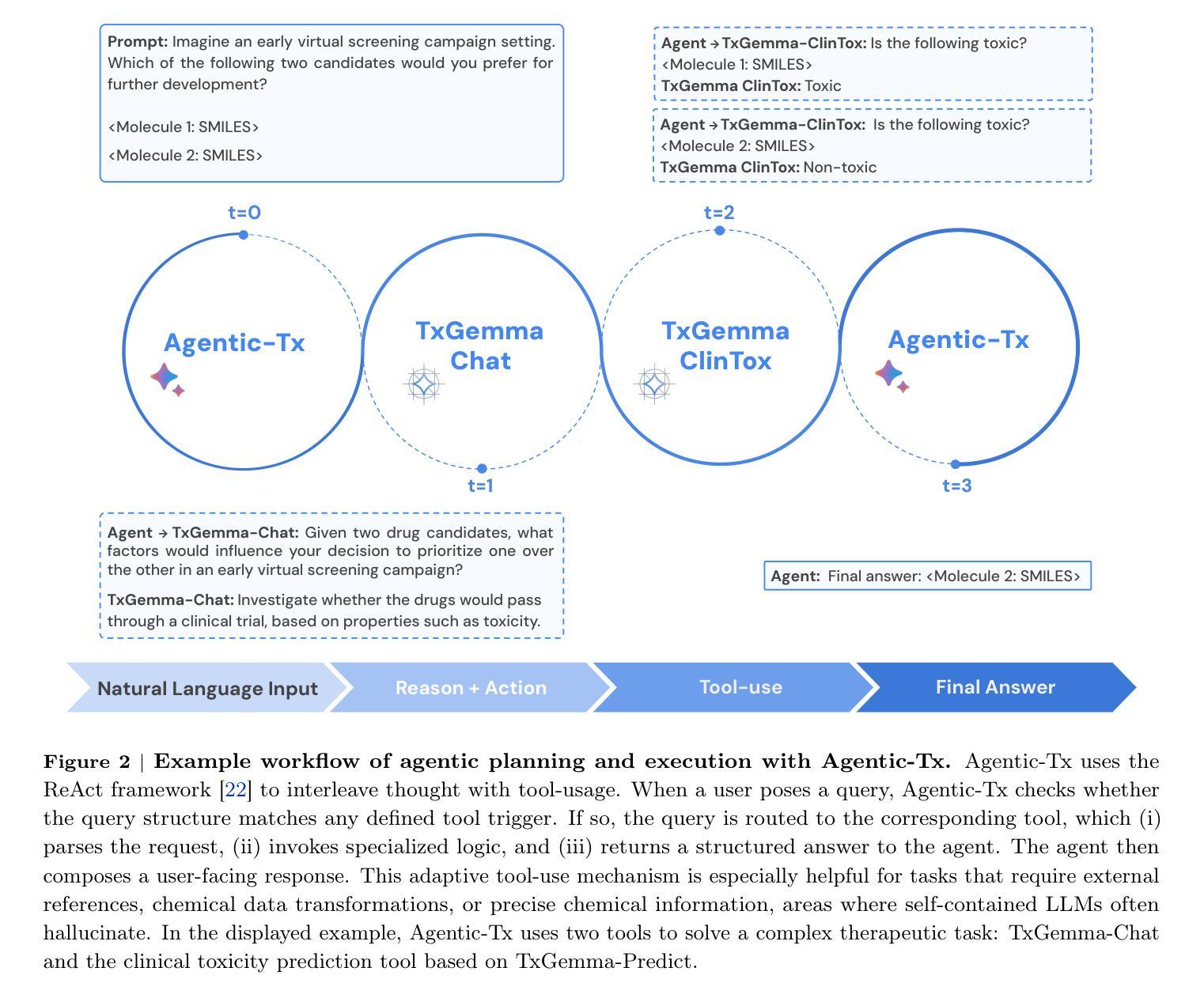
Therapeutic development is a costly and high-risk endeavor that is often plagued by high failure rates. To address this, we introduce TxGemma, a suite of efficient, generalist large language models (LLMs) capable of therapeutic property prediction as well as interactive reasoning and explainability. Unlike task-specific models, TxGemma synthesizes information from diverse sources, enabling broad application across the therapeutic development pipeline. The suite includes 2B, 9B, and 27B parameter models, fine-tuned from Gemma-2 on a comprehensive dataset of small molecules, proteins, nucleic acids, diseases, and cell lines. Across 66 therapeutic development tasks, TxGemma achieved superior or comparable performance to the state-of-the-art generalist model on 64 (superior on 45), and against state-of-the-art specialist models on 50 (superior on 26). Fine-tuning TxGemma models on therapeutic downstream tasks, such as clinical trial adverse event prediction, requires less training data than fine-tuning base LLMs, making TxGemma suitable for data-limited applications. Beyond these predictive capabilities, TxGemma features conversational models that bridge the gap between general LLMs and specialized property predictors. These allow scientists to interact in natural language, provide mechanistic reasoning for predictions based on molecular structure, and engage in scientific discussions. Building on this, we further introduce Agentic-Tx, a generalist therapeutic agentic system powered by Gemini 2.5 that reasons, acts, manages diverse workflows, and acquires external domain knowledge. Agentic-Tx surpasses prior leading models on the Humanity’s Last Exam benchmark (Chemistry & Biology) with 52.3% relative improvement over o3-mini (high) and 26.7% over o3-mini (high) on GPQA (Chemistry) and excels with improvements of 6.3% (ChemBench-Preference) and 2.4% (ChemBench-Mini) over o3-mini (high).
治疗性发展是一项充满成本和高风险的努力,经常面临高失败率的问题。针对这一问题,我们推出了TxGemma,这是一套高效、通用的大型语言模型(LLM),能够进行药物性质预测以及推理和可解释性的交互。不同于特定任务模型,TxGemma能够综合来自不同来源的信息,并可在整个治疗发展流程中广泛应用。该套件包括基于从包含小分子、蛋白质、核酸、疾病和细胞系的全面数据集上训练的Gemma-2微调得到的参数为2B、9B和27B的模型。在66个治疗性开发任务中,TxGemma在通用模型方面实现了卓越或相当的性能(其中卓越表现为在其中的45个任务上),在针对专业模型的对抗中也实现了卓越表现(其中在其中的26个任务上表现出卓越性能)。相对于在治疗下游任务如临床试验不良反应预测中对TxGemma模型进行微调相对于对基础LLM进行微调所需更少的训练数据,使得TxGemma在数据受限的应用场景中适用。除了这些预测功能外,TxGemma还具有对话模型,可以弥合通用大型语言模型和专用属性预测器之间的鸿沟。这允许科学家使用自然语言进行交互,基于分子结构提供机械推理以做出预测,并参与科学讨论。在此之上,我们进一步推出了由Gemini 2.5驱动的通用治疗剂系统Agentic-Tx,该系统能够进行推理、行动、管理多样化工作流程并获取外部领域知识。Agentic-Tx在人类最后考试基准测试上的表现超越了之前的领先模型,相较于o3-mini (high),在Chemistry & Biology上相对提升了52.3%,在GPQA (Chemistry)上提升了26.7%,并在ChemBench-Preference和ChemBench-Mini上分别提高了6.3%和提高了了2.4%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本介绍了治疗开发过程中面临的高成本和高风险问题,并为此引入了TxGemma,一套能够预测治疗特性并进行推理和解释的通用大型语言模型(LLM)。TxGemma能够从各种来源综合信息,并广泛应用于治疗开发管道。经过在包含小分子、蛋白质、核酸、疾病和细胞系的综合数据集上进行微调,TxGemma在66项治疗开发任务中取得了卓越或相当的表现。此外,它还具有对话模型,可以弥补通用LLM和专门属性预测器之间的差距,允许科学家以自然语言进行交流,并提供基于分子结构的预测机制理由和科学讨论。基于这些功能,进一步引入了Agentic-Tx系统,该系统由Gemini 2.5驱动,能够进行推理、行动、管理各种工作流程和获取外部领域知识。Agentic-Tx在Humanity’s Last Exam基准测试上的表现超越了先前的领先模型。总的来说,这是一项关于利用大型语言模型推动治疗开发进步的重要研究。
Key Takeaways
- TxGemma是高效、通用的大型语言模型(LLM)套件,能够预测治疗特性并具有推理和解释能力。
- 它能够综合来自不同来源的信息,广泛应用于治疗开发管道。
- TxGemma在不同治疗开发任务中表现出卓越性能,相对于当前通用和专家模型都有显著优势。
- TxGemma的对话模型允许科学家以自然语言进行交流,并提供基于分子结构的预测机制理由和科学讨论。
- Agentic-Tx系统由Gemini 2.5驱动,具有推理、行动、管理多样工作流程和获取外部领域知识的能力。
- Agentic-Tx在多个基准测试上的表现超越了先前的领先模型。
点此查看论文截图

Single-Agent vs. Multi-Agent LLM Strategies for Automated Student Reflection Assessment
Authors:Gen Li, Li Chen, Cheng Tang, Valdemar Švábenský, Daisuke Deguchi, Takayoshi Yamashita, Atsushi Shimada
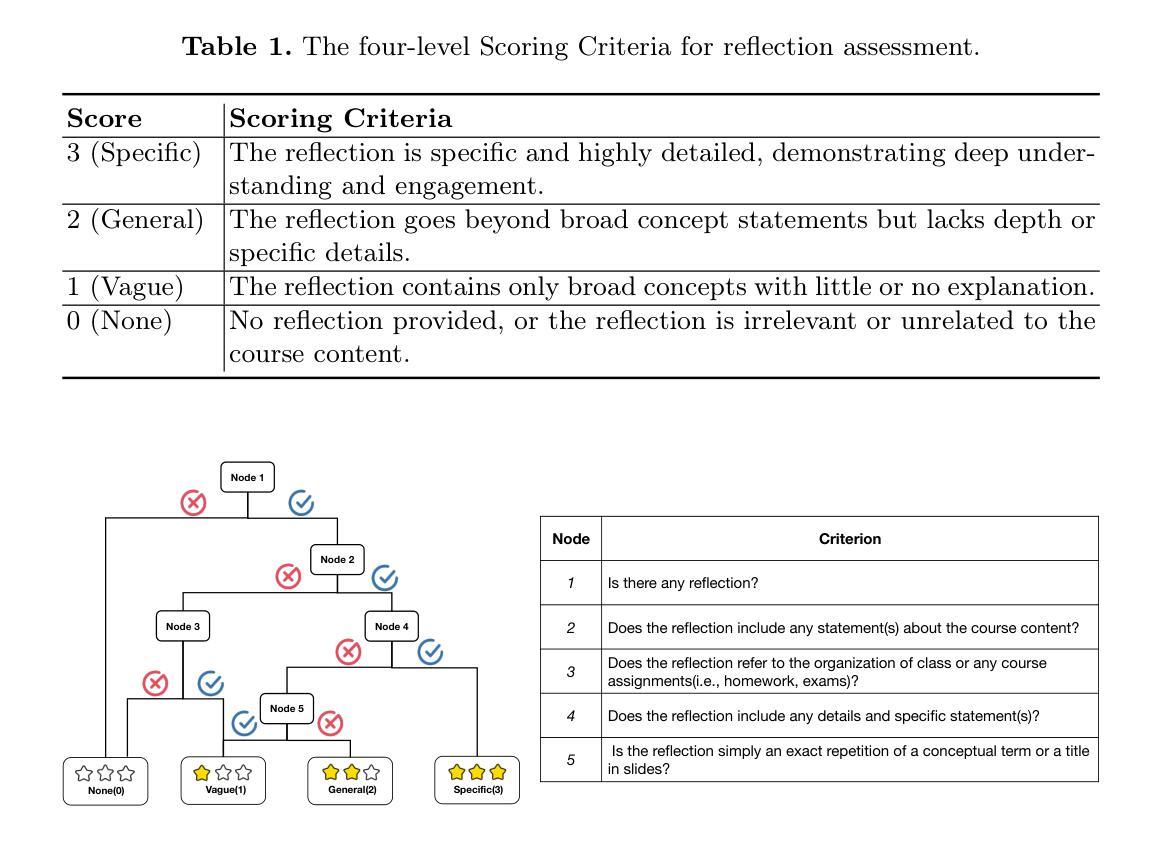
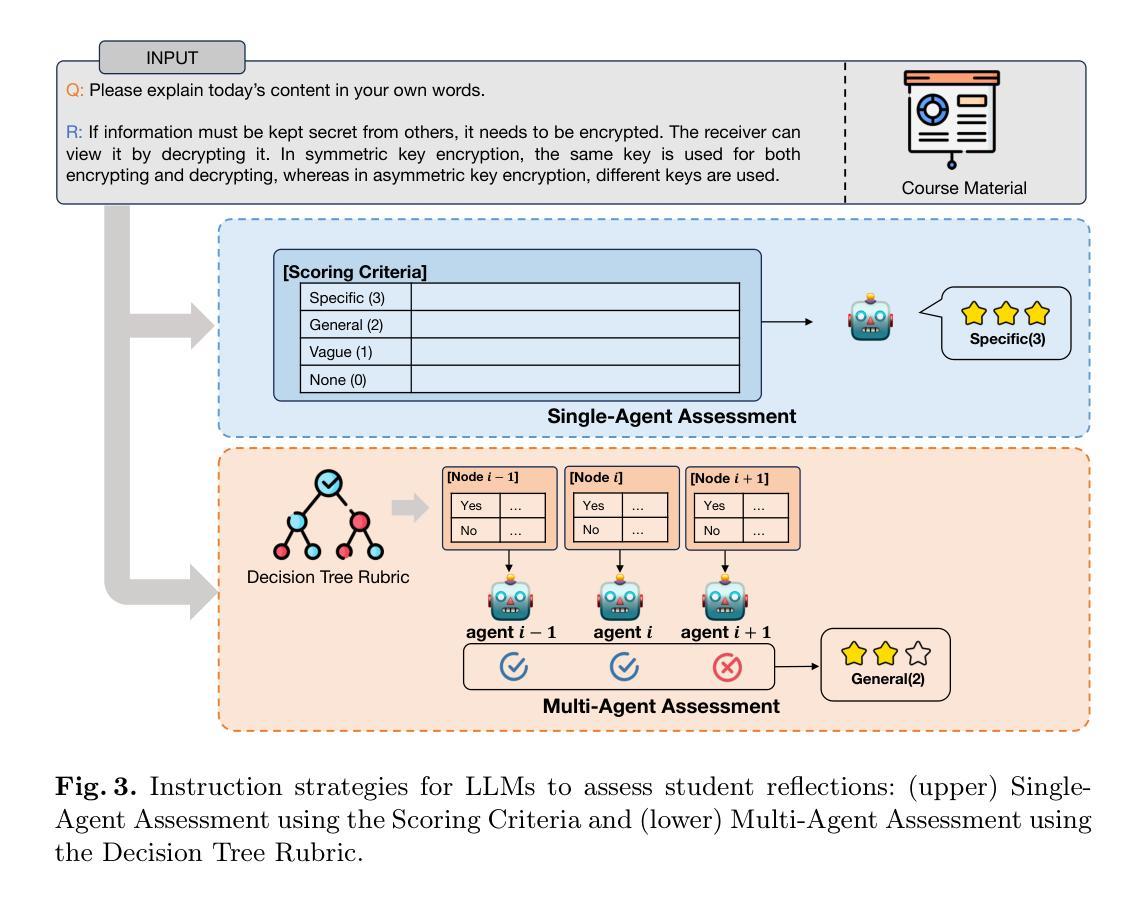
We explore the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) for automated assessment of open-text student reflections and prediction of academic performance. Traditional methods for evaluating reflections are time-consuming and may not scale effectively in educational settings. In this work, we employ LLMs to transform student reflections into quantitative scores using two assessment strategies (single-agent and multi-agent) and two prompting techniques (zero-shot and few-shot). Our experiments, conducted on a dataset of 5,278 reflections from 377 students over three academic terms, demonstrate that the single-agent with few-shot strategy achieves the highest match rate with human evaluations. Furthermore, models utilizing LLM-assessed reflection scores outperform baselines in both at-risk student identification and grade prediction tasks. These findings suggest that LLMs can effectively automate reflection assessment, reduce educators’ workload, and enable timely support for students who may need additional assistance. Our work emphasizes the potential of integrating advanced generative AI technologies into educational practices to enhance student engagement and academic success.
我们探索了大型语言模型(LLM)在自动评估学生开放性反思和预测学业表现方面的应用。传统的反思评估方法耗时且可能无法在教育环境中有效地扩展。在这项工作中,我们采用LLM,使用两种评估策略(单代理和多代理)和两种提示技术(零样本和少样本),将学生反思转化为量化分数。我们在来自377名学生、为期三个学期的5,278份反思数据上进行的实验表明,使用少样本策略的单代理方法与人评分的匹配度最高。此外,利用LLM评估的反思分数的模型在处于风险的学生识别和成绩预测任务中的表现都优于基线。这些结果表明,LLM可以有效地自动进行反思评估,减少教育工作者的工作量,并为可能需要额外帮助的学生提供及时的支持。我们的工作强调了将先进的生成式人工智能技术与教育实践相结合,以提高学生参与度和学业成功的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To be published in Proceedings of the 29th Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (PAKDD 2025)
Summary
大语言模型(LLMs)可用于自动评估学生的开放文本反思和预测学业表现。传统评估方法耗时且难以在教育环境中有效扩展。本研究利用LLMs将学生的反思转化为量化分数,采用两种评估策略和两种提示技术。实验结果表明,使用带有少数镜头策略的单一智能体获得了最高的人类评估匹配率。此外,利用LLM评估的反思分数的模型在风险学生识别和成绩预测任务中的表现均优于基线。这表明LLMs可以有效自动化反思评估,减轻教育工作者的工作量,并为可能需要额外帮助的学生提供及时的支持。本研究强调了将高级生成式AI技术融入教育实践以提高学生参与度和学业成功的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大语言模型(LLMs)可用于自动评估学生的开放文本反思。
- 传统的学生反思评估方法耗时且难以扩展。
- 采用两种评估策略和两种提示技术,即单智能体和多智能体以及零镜头和少数镜头。
- 实验结果显示,带有少数镜头策略的单智能体评估策略获得了最高的人类评估匹配率。
- 使用LLM评估的反思分数的模型在风险学生识别和成绩预测任务中表现优异。
- LLMs的自动化评估可减轻教育工作者的工作量,为需要额外帮助的学生提供及时支持。
点此查看论文截图


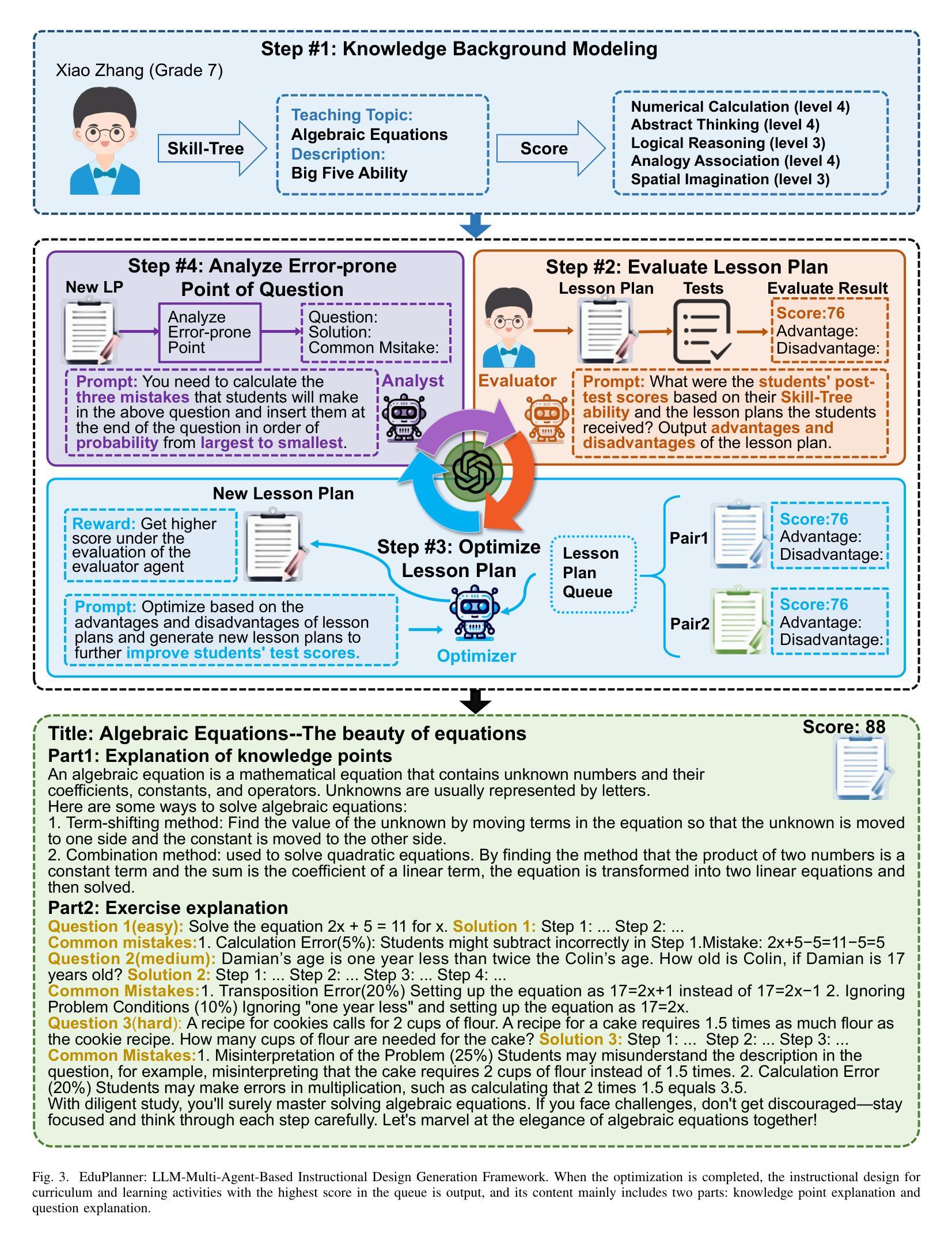
EduPlanner: LLM-Based Multi-Agent Systems for Customized and Intelligent Instructional Design
Authors:Xueqiao Zhang, Chao Zhang, Jianwen Sun, Jun Xiao, Yi Yang, Yawei Luo
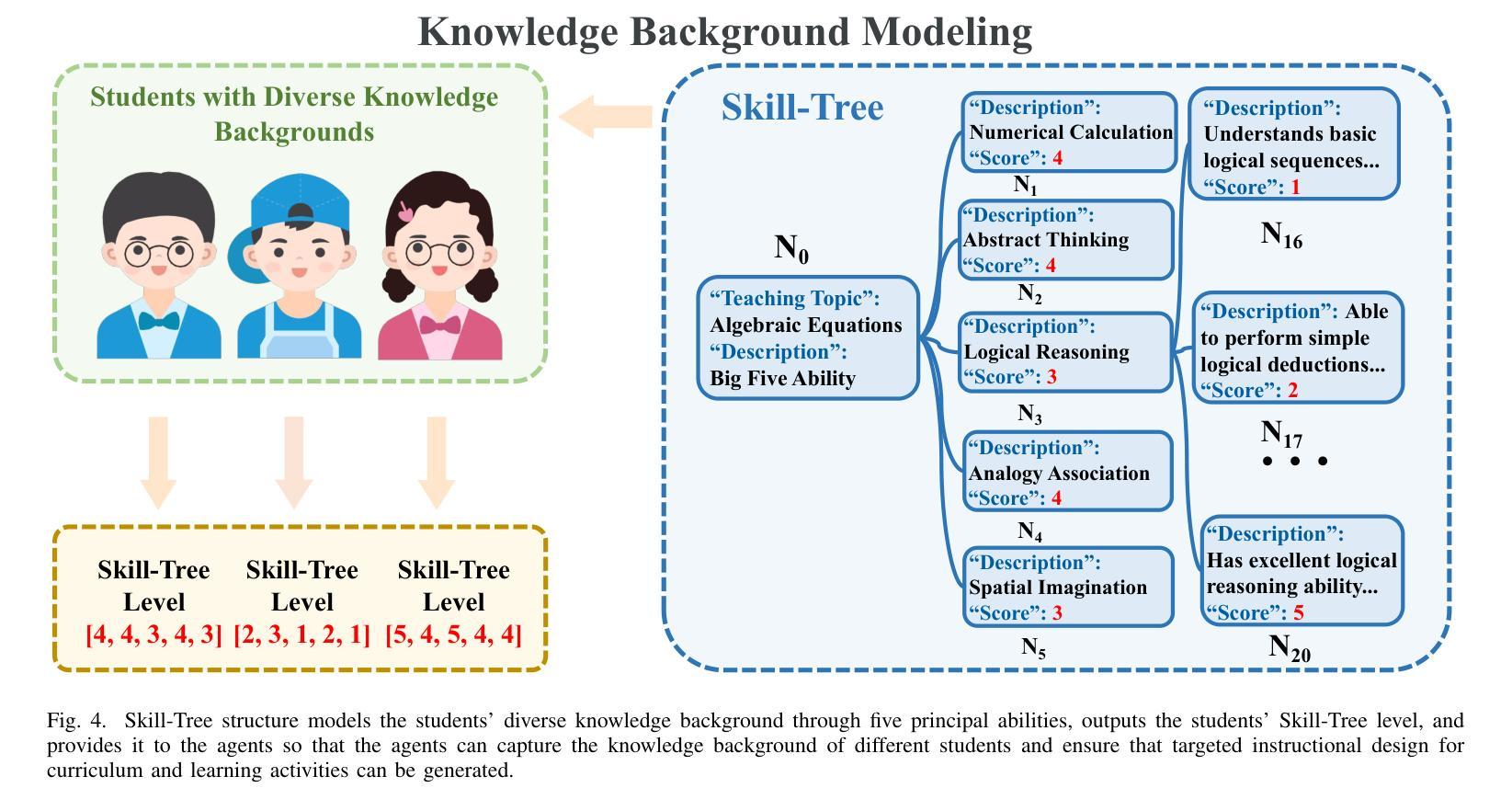
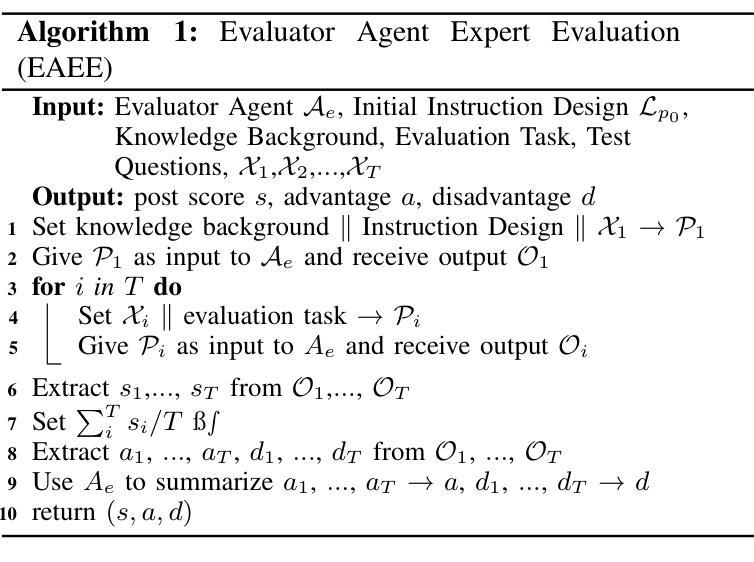
Large Language Models (LLMs) have significantly advanced smart education in the Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) era. A promising application lies in the automatic generalization of instructional design for curriculum and learning activities, focusing on two key aspects: (1) Customized Generation: generating niche-targeted teaching content based on students’ varying learning abilities and states, and (2) Intelligent Optimization: iteratively optimizing content based on feedback from learning effectiveness or test scores. Currently, a single large LLM cannot effectively manage the entire process, posing a challenge for designing intelligent teaching plans. To address these issues, we developed EduPlanner, an LLM-based multi-agent system comprising an evaluator agent, an optimizer agent, and a question analyst, working in adversarial collaboration to generate customized and intelligent instructional design for curriculum and learning activities. Taking mathematics lessons as our example, EduPlanner employs a novel Skill-Tree structure to accurately model the background mathematics knowledge of student groups, personalizing instructional design for curriculum and learning activities according to students’ knowledge levels and learning abilities. Additionally, we introduce the CIDDP, an LLM-based five-dimensional evaluation module encompassing clarity, Integrity, Depth, Practicality, and Pertinence, to comprehensively assess mathematics lesson plan quality and bootstrap intelligent optimization. Experiments conducted on the GSM8K and Algebra datasets demonstrate that EduPlanner excels in evaluating and optimizing instructional design for curriculum and learning activities. Ablation studies further validate the significance and effectiveness of each component within the framework. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/Zc0812/Edu_Planner
在人工智能通用智能(AGI)时代,大型语言模型(LLM)在智能教育方面取得了显著进展。一个充满希望的应用领域在于自动概括教学设计和学习活动,它主要关注两个关键方面:(1)定制化生成:根据学生的不同学习能力和状态,生成针对特定领域的教学内容;(2)智能优化:根据学习效果的反馈或考试成绩,对内容进行迭代优化。目前,单一的大型LLM无法有效地管理整个过程,为设计智能教学计划带来了挑战。为了解决这些问题,我们开发了EduPlanner,这是一个基于LLM的多代理系统,包括评估代理、优化代理和问题分析师,他们通过对抗协作的方式,为课程和学习活动生成定制和智能的教学设计。以数学课程为例,EduPlanner采用新颖的Skill-Tree结构,准确建模学生群体的背景数学知识,根据学生的学习水平和能力个性化教学设计和学习活动。此外,我们引入了CIDDP,这是一个基于LLM的五维评估模块,包括清晰度、完整性、深度、实用性和贴切性,全面评估数学课程计划的质量,并启动智能优化。在GSM8K和代数数据集上进行的实验表明,EduPlanner在评估和优化课程和教学活动的教学设计方面表现出色。消融研究进一步验证了框架内各组件的重要性和有效性。我们的代码公开在https://github.com/Zc0812/Edu_Planner
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在人工智能通用智能(AGI)时代对智能教育产生了重大影响,尤其在自动通用教学设计方面展现出巨大潜力。EduPlanner是一个基于LLM的多代理系统,能解决智能教学设计面临的挑战。该系统由评估代理、优化代理和问题分析师组成,通过协同工作,为课程和学习活动生成定制和智能化的教学设计。以数学课为例,EduPlanner采用技能树结构准确建模学生群体的背景数学知识,并根据学生的知识水平和学习能力个性化教学设计。此外,它还引入了CIDDP评价模块,全面评估数学课程计划质量并启动智能优化。实验证明,EduPlanner在评估和优化教学设计方面表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在智能教育领域具有重要影响。
- EduPlanner是一个基于LLM的多代理系统,用于智能教学设计。
- EduPlanner包括评估代理、优化代理和问题分析师,协同工作。
- 系统采用技能树结构准确建模学生群体的背景知识。
- CIDDP评价模块用于全面评估数学课程计划质量。
- 在GSM8K和Algebra数据集上的实验证明EduPlanner效果显著。
点此查看论文截图


Attention-Augmented Inverse Reinforcement Learning with Graph Convolutions for Multi-Agent Task Allocation
Authors:Huilin Yin, Zhikun Yang, Daniel Watzenig
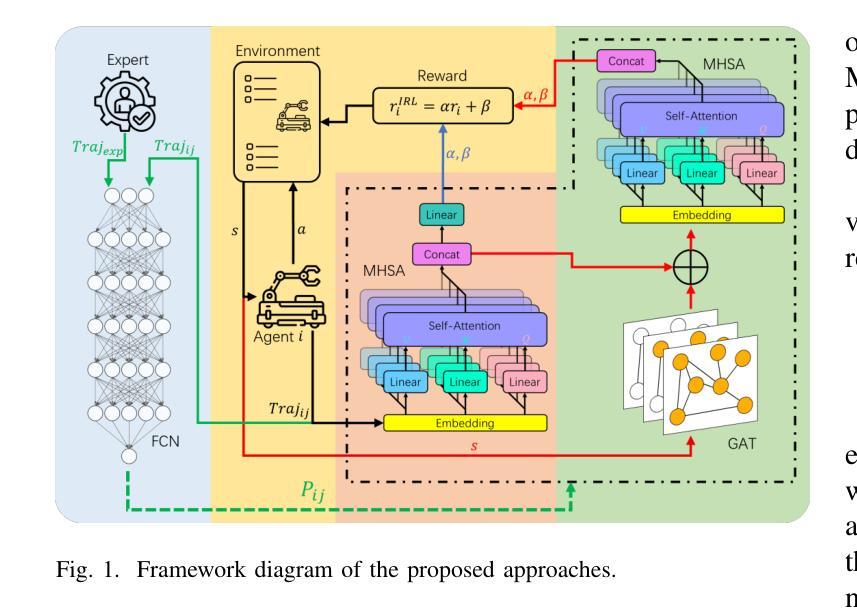
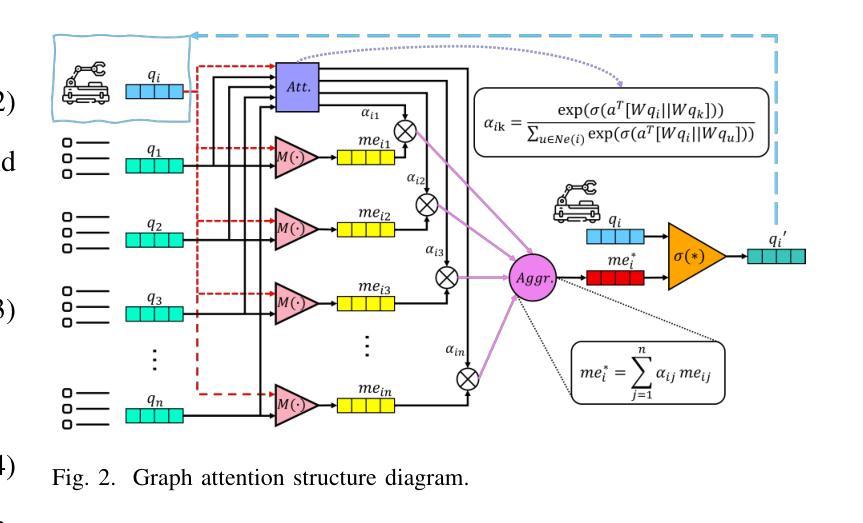
Multi-agent task allocation (MATA) plays a vital role in cooperative multi-agent systems, with significant implications for applications such as logistics, search and rescue, and robotic coordination. Although traditional deep reinforcement learning (DRL) methods have been shown to be promising, their effectiveness is hindered by a reliance on manually designed reward functions and inefficiencies in dynamic environments. In this paper, an inverse reinforcement learning (IRL)-based framework is proposed, in which multi-head self-attention (MHSA) and graph attention mechanisms are incorporated to enhance reward function learning and task execution efficiency. Expert demonstrations are utilized to infer optimal reward densities, allowing dependence on handcrafted designs to be reduced and adaptability to be improved. Extensive experiments validate the superiority of the proposed method over widely used multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) algorithms in terms of both cumulative rewards and task execution efficiency.
多智能体任务分配(MATA)在合作多智能体系统中扮演着至关重要的角色,对物流、搜索和救援以及机器人协调等应用具有重要意义。虽然传统的深度强化学习(DRL)方法已经显示出其潜力,但其有效性受到依赖手动设计的奖励函数和动态环境中效率低下的限制。本文提出了一个基于逆向强化学习(IRL)的框架,其中融入了多头自注意力(MHSA)和图注意力机制,以提高奖励函数的学习和任务执行效率。利用专家演示来推断最优奖励密度,减少对手工设计的依赖,提高适应性。大量实验验证了所提方法在累积奖励和任务执行效率方面均优于广泛使用的多智能体强化学习(MARL)算法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Added a clarification on the source of expert trajectories in Section V
Summary
基于多智能体任务分配(MATA)在合作多智能体系统中的重要作用,以及对物流、搜索和救援、机器人协调等应用的重要影响,本文提出了一种基于逆向强化学习(IRL)的框架,结合了多头自注意力(MHSA)和图注意力机制来提高奖励函数的学习和任务执行效率。通过专家演示来推断最优奖励密度,减少了对手工设计的依赖,提高了适应性。大量实验验证了该方法在累积奖励和任务执行效率方面均优于广泛使用的多智能体强化学习(MARL)算法。
Key Takeaways
- MATA在合作多智能体系统中具有关键作用,尤其在物流、搜索和救援以及机器人协调等领域。
- 传统深度强化学习方法受限于手动设计的奖励函数和动态环境中的效率问题。
- 本文提出基于逆强化学习的框架来解决这些问题,融入MHSA和图注意力机制来提升奖励函数学习与任务执行效率。
- 通过专家演示来推断最优奖励密度,降低了对手工设计的依赖,提高了适应性。
- 该框架通过大量实验验证,在累积奖励和任务执行效率方面超越了广泛使用的MARL算法。
- 该研究为多智能体系统在复杂环境中的任务分配提供了新的视角和解决方案。
点此查看论文截图


APIGen-MT: Agentic Pipeline for Multi-Turn Data Generation via Simulated Agent-Human Interplay
Authors:Akshara Prabhakar, Zuxin Liu, Ming Zhu, Jianguo Zhang, Tulika Awalgaonkar, Shiyu Wang, Zhiwei Liu, Haolin Chen, Thai Hoang, Juan Carlos Niebles, Shelby Heinecke, Weiran Yao, Huan Wang, Silvio Savarese, Caiming Xiong
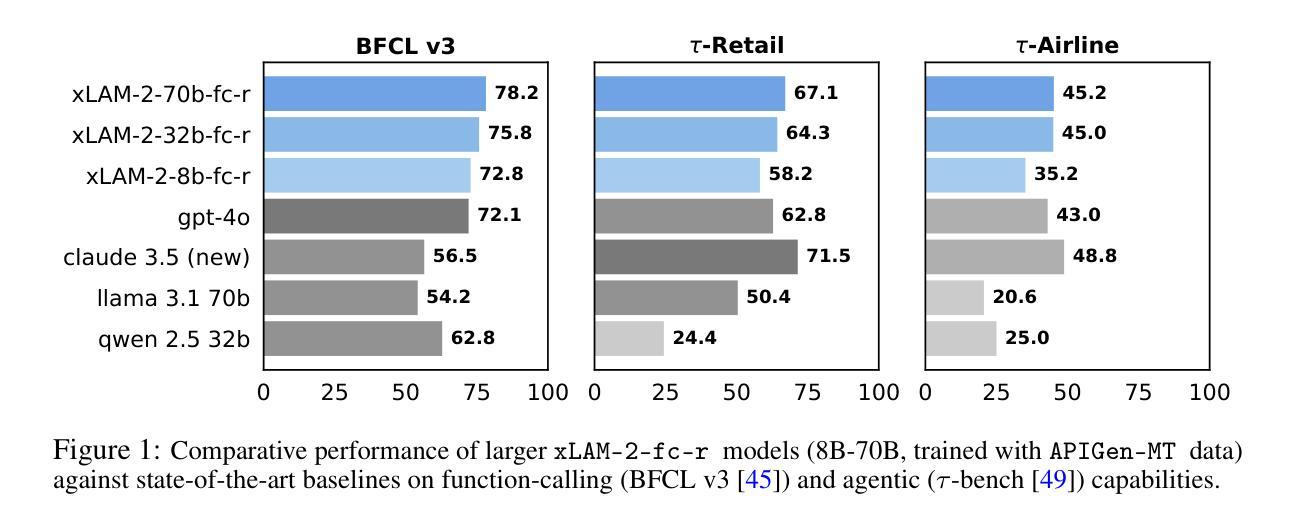
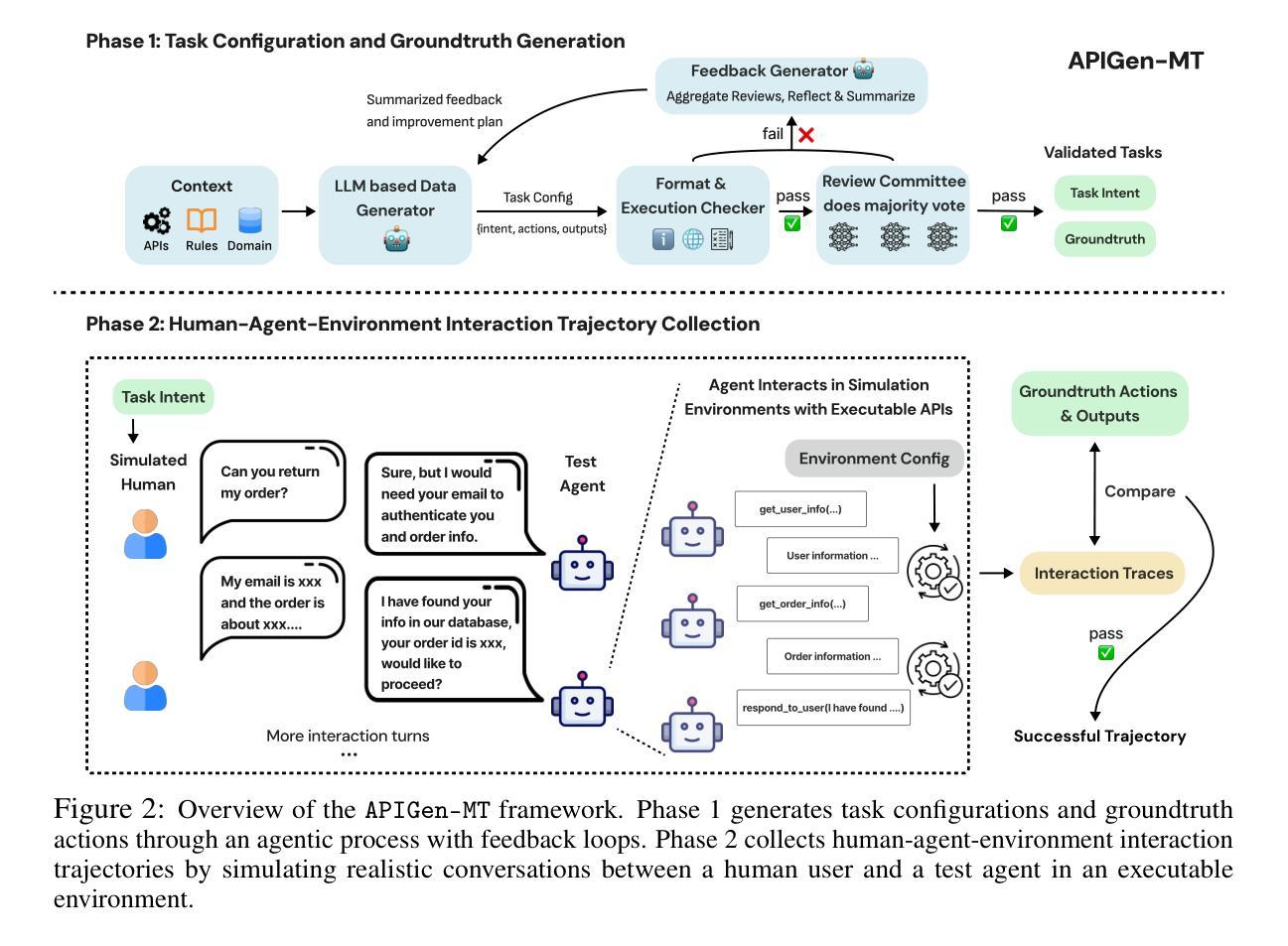
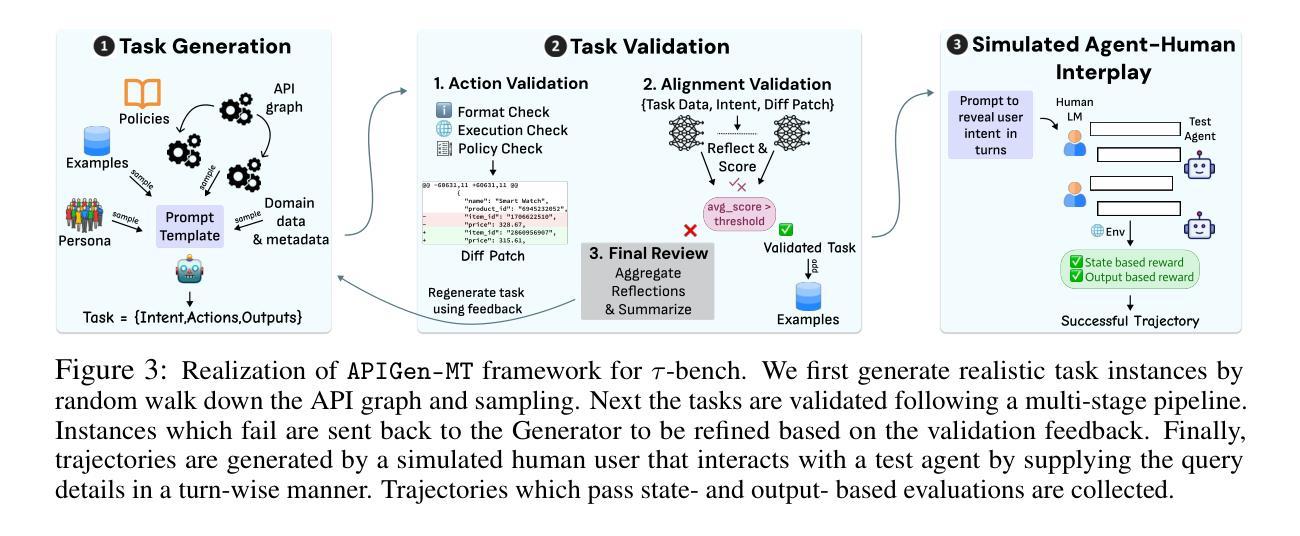
Training effective AI agents for multi-turn interactions requires high-quality data that captures realistic human-agent dynamics, yet such data is scarce and expensive to collect manually. We introduce APIGen-MT, a two-phase framework that generates verifiable and diverse multi-turn agent data. In the first phase, our agentic pipeline produces detailed task blueprints with ground-truth actions, leveraging a committee of LLM reviewers and iterative feedback loops. These blueprints are then transformed into complete interaction trajectories through simulated human-agent interplay. We train a family of models – the xLAM-2-fc-r series with sizes ranging from 1B to 70B parameters. Our models outperform frontier models such as GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 on $\tau$-bench and BFCL benchmarks, with the smaller models surpassing their larger counterparts, particularly in multi-turn settings, while maintaining superior consistency across multiple trials. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our verified blueprint-to-details approach yields high-quality training data, enabling the development of more reliable, efficient, and capable agents. We open-source both the synthetic data collected and the trained xLAM-2-fc-r models to advance research in AI agents. Models are available on HuggingFace at https://huggingface.co/collections/Salesforce/xlam-2-67ef5be12949d8dcdae354c4 and project website is https://apigen-mt.github.io
训练针对多轮交互的有效AI代理需要高质量的数据,这些数据需要捕捉真实的人机交互动态。然而,此类数据稀缺且难以手动收集。我们推出了APIGen-MT,这是一个两阶段框架,用于生成可验证和多样化的多轮代理数据。在第一阶段,我们的代理管道会生成具有真实动作的任务蓝图,并利用大型语言模型评审小组和迭代反馈循环。这些蓝图随后通过模拟的人机交互转化为完整的交互轨迹。我们训练了一系列模型,即xLAM-2-fc-r系列,参数范围从1B到70B。我们的模型在τ基准测试和BFCL基准测试中超越了前沿模型,如GPT-4o和Claude 3.5。较小的模型在多次试验中超越了较大的模型,特别是在多轮设置中,同时保持了卓越的稳定性。综合实验表明,我们的从验证蓝图到细节的方法产生了高质量的训练数据,能够开发出更可靠、更高效、能力更强的代理。我们公开了收集的合成数据和训练的xLAM-2-fc-r模型,以促进AI代理研究的发展。模型可在HuggingFace上获得:链接,项目网站为:链接。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages plus references and appendices
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为APIGen-MT的两阶段框架,用于生成可验证和多样化的多轮交互代理数据。该框架通过代理管道生成详细的任务蓝图,并利用大型语言模型评审委员会和迭代反馈循环进行验证。这些蓝图通过模拟人机互动转化为完整的交互轨迹。实验表明,该框架生成的数据质量高,训练的模型在多轮交互环境中表现优异,可靠性强。此外,该项目开源了合成数据和训练的模型,以推动人工智能代理研究的发展。
Key Takeaways
- APIGen-MT是一个用于生成多轮交互代理数据的两阶段框架。
- 该框架通过代理管道生成详细的任务蓝图,并借助大型语言模型评审和迭代反馈循环进行验证。
- APIGen-MT能够模拟人机互动,将蓝图转化为完整的交互轨迹。
- 实验显示APIGen-MT生成的训练数据质量高,训练的模型在多轮交互环境中表现优异。
- 模型表现出高可靠性、高效率。
- 项目开源了合成数据和训练的模型,以促进人工智能代理研究的发展。
- 模型可在HuggingFace上找到:链接。
点此查看论文截图

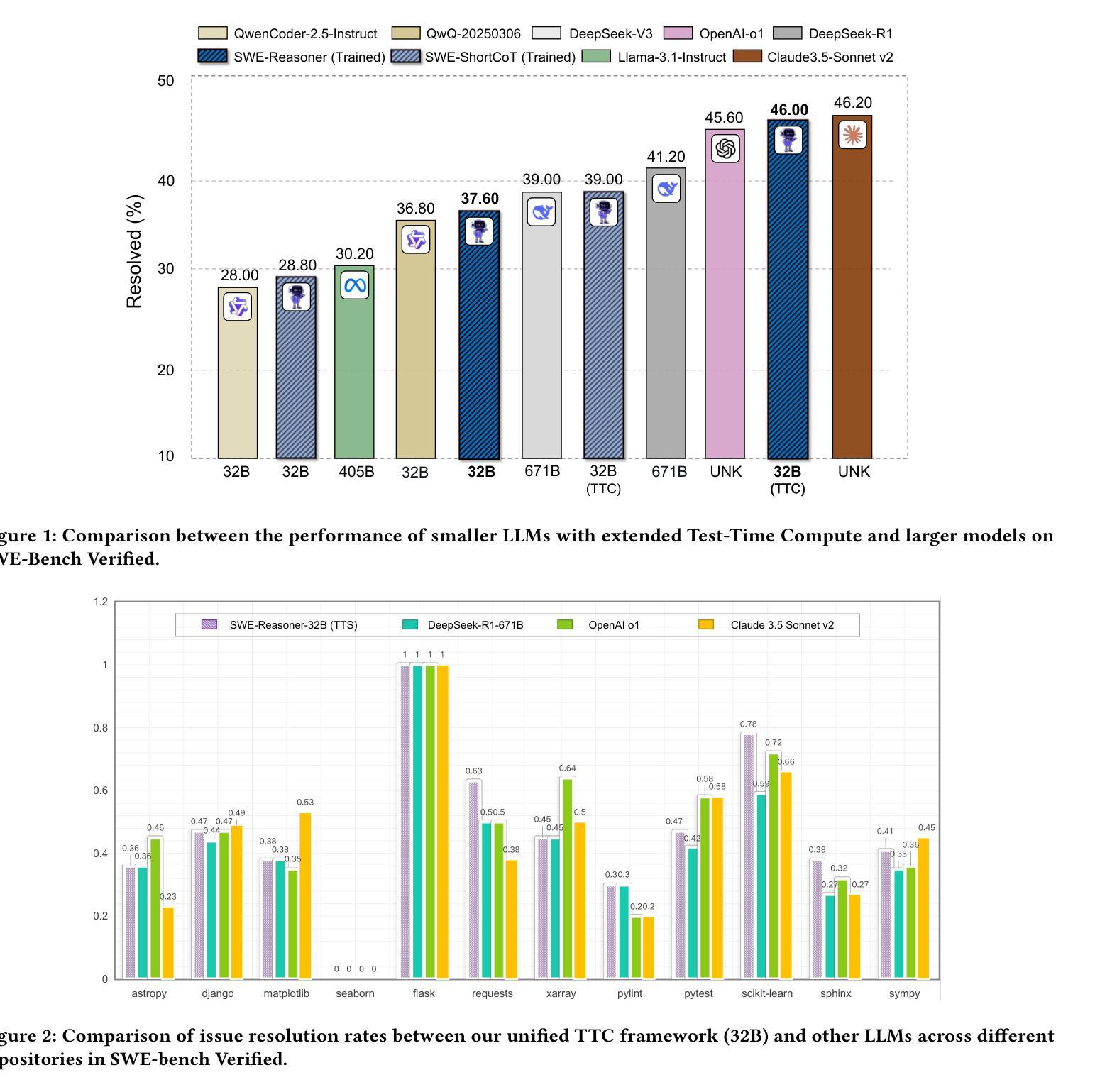
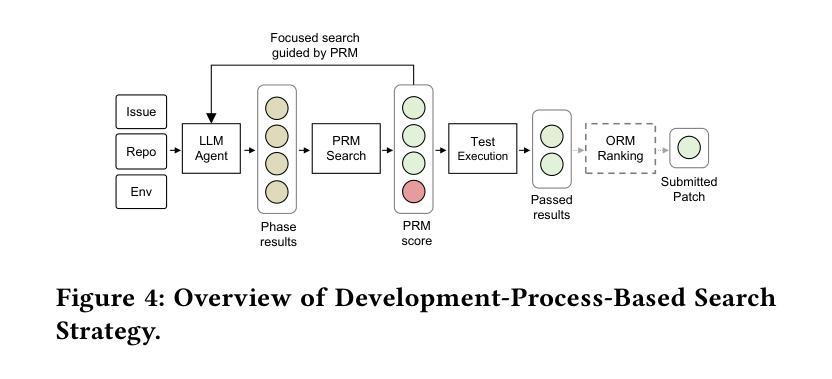
Thinking Longer, Not Larger: Enhancing Software Engineering Agents via Scaling Test-Time Compute
Authors:Yingwei Ma, Yongbin Li, Yihong Dong, Xue Jiang, Rongyu Cao, Jue Chen, Fei Huang, Binhua Li
Recent advancements in software engineering agents have demonstrated promising capabilities in automating program improvements. However, their reliance on closed-source or resource-intensive models introduces significant deployment challenges in private environments, prompting a critical question: \textit{How can personally deployable open-source LLMs achieve comparable code reasoning performance?} To this end, we propose a unified Test-Time Compute scaling framework that leverages increased inference-time computation instead of larger models. Our framework incorporates two complementary strategies: internal TTC and external TTC. Internally, we introduce a \textit{development-contextualized trajectory synthesis} method leveraging real-world software repositories to bootstrap multi-stage reasoning processes, such as fault localization and patch generation. We further enhance trajectory quality through rejection sampling, rigorously evaluating trajectories along accuracy and complexity. Externally, we propose a novel \textit{development-process-based search} strategy guided by reward models and execution verification. This approach enables targeted computational allocation at critical development decision points, overcoming limitations of existing “end-point only” verification methods. Evaluations on SWE-bench Verified demonstrate our \textbf{32B model achieves a 46% issue resolution rate}, surpassing significantly larger models such as DeepSeek R1 671B and OpenAI o1. Additionally, we provide the empirical validation of the test-time scaling phenomenon within SWE agents, revealing that \textbf{models dynamically allocate more tokens to increasingly challenging problems}, effectively enhancing reasoning capabilities. We publicly release all training data, models, and code to facilitate future research. https://github.com/yingweima2022/SWE-Reasoner
近年来,软件工程代理方面的最新进展在程序自动化改进方面展现出令人鼓舞的能力。然而,它们对封闭源代码或资源密集型模型的依赖,给私有环境部署带来了重大挑战,由此引发了一个关键问题:如何在个人可部署的开源大型语言模型中实现相当的软件代码推理性能?为此,我们提出了一个统一的测试时间计算扩展框架,该框架利用增加推理时间计算而不是使用更大的模型。我们的框架包含两种互补的策略:内部TTC和外部TTC。在内部,我们引入了一种利用现实世界软件仓库进行“开发语境化轨迹合成”的方法,以启动多阶段推理过程,如故障定位和补丁生成。我们进一步通过拒绝采样提高轨迹质量,严格评估轨迹的准确性和复杂性。在外部,我们提出了一种新型的基于开发过程的搜索策略,该策略以奖励模型和执行力验证为指导。这种方法能够在关键的开发决策点实现有针对性的计算分配,克服了现有“仅终点”验证方法的局限性。在SWE-bench Verified上的评估表明,我们的32B模型达到了46%的问题解决率,超过了显著更大的模型,如DeepSeek R1 671B和OpenAI o1。此外,我们还实证验证了SWE代理中的测试时间扩展现象,表明模型会“动态地为越来越具挑战性的问题分配更多的令牌”,从而有效提高推理能力。我们公开发布所有训练数据、模型和代码,以促进未来的研究。https://github.com/yingweima2022/SWE-Reasoner
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期软件工程代理领域的进展在自动化程序改进方面展现出巨大潜力,但其在私有环境中的部署挑战仍然显著。针对此,我们提出一种统一测试时间计算扩展框架,该框架可在不依赖更大模型的情况下提升代码推理性能。我们采取两种互补策略:内部与外部测试时间计算扩展。内部采用开发上下文轨迹合成方法,结合现实世界软件仓库进行多阶段推理过程,如故障定位和补丁生成。外部则提出基于开发过程的搜索策略,通过奖励模型和执行验证实现计算资源的精准分配。评估结果显示,我们的模型在问题解决率上超越大型模型,且动态分配更多令牌应对复杂问题,增强推理能力。相关数据和代码已公开共享。
Key Takeaways
- 软件工程代理在自动化程序改进方面展现潜力,但在私有环境中部署存在挑战。
- 提出统一测试时间计算扩展框架,以提高代码推理性能,无需依赖更大的模型。
- 内部采用开发上下文轨迹合成方法,结合软件仓库进行故障定位和补丁生成等多阶段推理过程。
- 通过拒绝采样提高轨迹质量,严格按照准确性和复杂性进行评估。
- 外部采用基于开发过程的搜索策略,通过奖励模型和执行验证实现计算资源的精准分配。
- 模型表现出较高的问题解决率,并动态分配更多资源应对复杂问题,增强推理能力。
点此查看论文截图


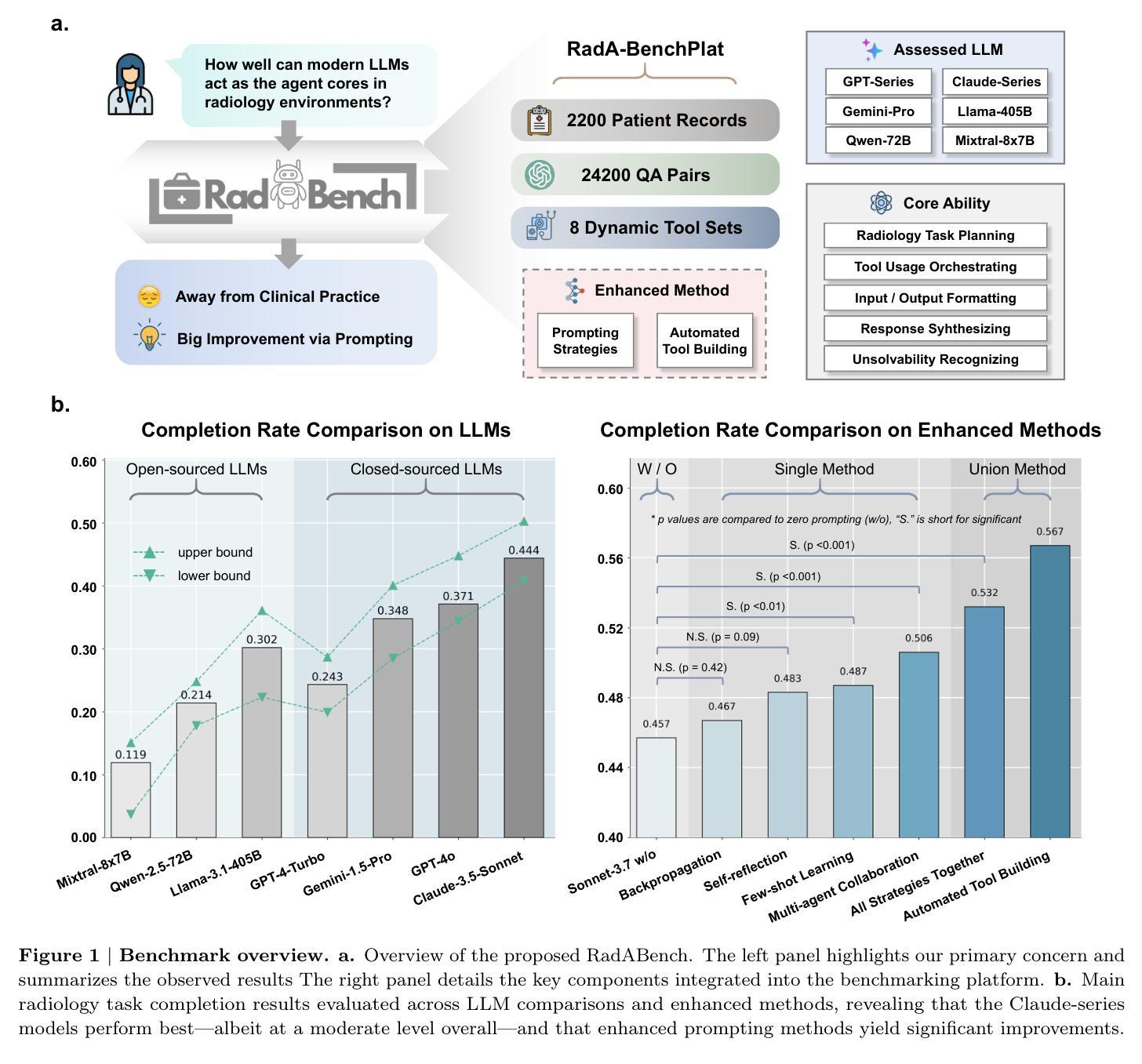
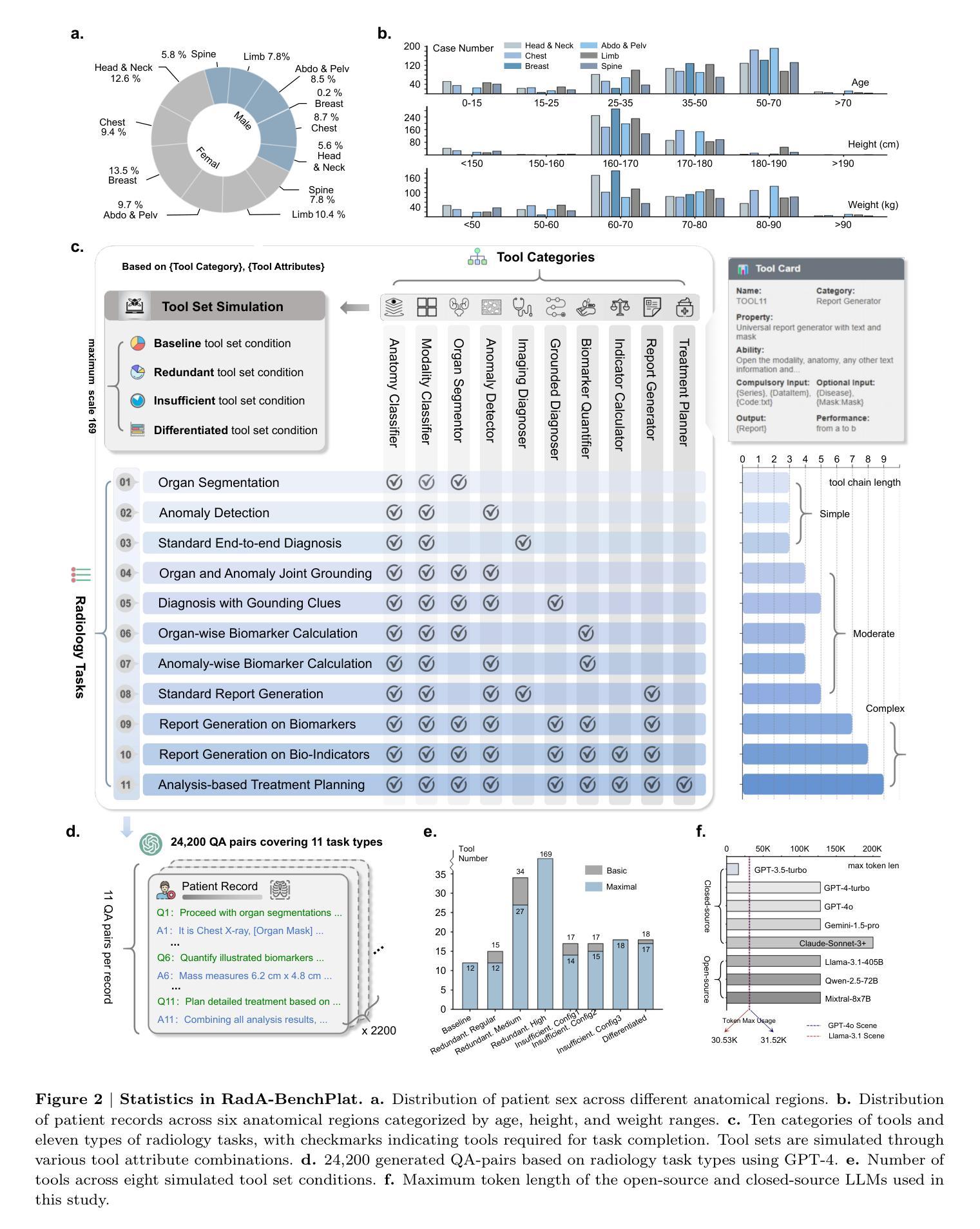
How Well Can Modern LLMs Act as Agent Cores in Radiology Environments?
Authors:Qiaoyu Zheng, Chaoyi Wu, Pengcheng Qiu, Lisong Dai, Ya Zhang, Yanfeng Wang, Weidi Xie
We introduce RadA-BenchPlat, an evaluation platform that benchmarks the performance of large language models (LLMs) act as agent cores in radiology environments using 2,200 radiologist-verified synthetic patient records covering six anatomical regions, five imaging modalities, and 2,200 disease scenarios, resulting in 24,200 question-answer pairs that simulate diverse clinical situations. The platform also defines ten categories of tools for agent-driven task solving and evaluates seven leading LLMs, revealing that while models like Claude-3.7-Sonnet can achieve a 67.1% task completion rate in routine settings, they still struggle with complex task understanding and tool coordination, limiting their capacity to serve as the central core of automated radiology systems. By incorporating four advanced prompt engineering strategies–where prompt-backpropagation and multi-agent collaboration contributed 16.8% and 30.7% improvements, respectively–the performance for complex tasks was enhanced by 48.2% overall. Furthermore, automated tool building was explored to improve robustness, achieving a 65.4% success rate, thereby offering promising insights for the future integration of fully automated radiology applications into clinical practice. All of our code and data are openly available at https://github.com/MAGIC-AI4Med/RadABench.
我们介绍了RadA-BenchPlat评估平台,该平台通过使用2200份经过放射科医生核实的人工合成患者记录,对大型语言模型(LLM)在放射学环境中的代理核心性能进行基准测试。这些记录涵盖了六个解剖区域、五种成像模式和2200种疾病情景,产生了模拟各种临床情境的24200个问答对。平台还定义了十大类工具用于代理驱动的任务解决,并评估了七款领先的LLM。结果表明,虽然在常规环境中,像Claude-3.7-Sonnet这样的模型可以达到67.1%的任务完成率,但它们仍然难以理解和处理复杂的任务并协调工具,这限制了它们作为自动化放射系统核心的能力。通过采用四种先进的提示工程策略——其中提示反向传播和多代理协作分别贡献了16.8%和30.7%的改进——复杂任务的性能总体提高了48.2%。此外,还探索了自动工具构建以提高稳健性,达到了65.4%的成功率,从而为未来全自动放射应用程序融入临床实践提供了有前景的见解。我们的所有代码和数据都公开可在https://github.com/MAGIC-AI4Med/RadABench找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
RadA-BenchPlat平台评估大型语言模型在放射学环境中的性能,利用2200份经过放射科医生验证的合成患者记录模拟多种临床情境。该平台定义了十类工具用于代理驱动的任务解决,并评估了七款领先的LLM模型。虽然一些模型如Claude-3.7-Sonnet在日常设置中的任务完成率可达67.1%,但它们对于复杂任务理解和工具协调仍存在挑战,难以作为自动化放射系统的核心。通过采用四种先进的提示工程策略和多代理协作等技术,复杂任务的性能总体提高了48.2%。同时,探索了自动化工具建设以提高稳健性,达到65.4%的成功率,为未来全自动放射学应用的临床实践提供了有前景的见解。
Key Takeaways:
- RadA-BenchPlat是一个评估平台,用于评估大型语言模型在放射学环境中的性能。
- 平台使用合成患者记录模拟临床情境,涵盖六个解剖区域、五种成像模式和2200种疾病场景。
- 平台定义了十类工具用于代理驱动的任务解决,评估了七款LLM模型的性能。
- 一些模型在日常任务中表现良好,但在复杂任务理解和工具协调方面存在挑战。
- 采用先进的提示工程策略,如提示反向传播和多代理协作,可以提高复杂任务的性能。
- 自动化工具建设可以提高模型的稳健性,达到65.4%的成功率。
点此查看论文截图

Augmenting the action space with conventions to improve multi-agent cooperation in Hanabi
Authors:F. Bredell, H. A. Engelbrecht, J. C. Schoeman
The card game Hanabi is considered a strong medium for the testing and development of multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) algorithms, due to its cooperative nature, hidden information, limited communication and remarkable complexity. Previous research efforts have explored the capabilities of MARL algorithms within Hanabi, focusing largely on advanced architecture design and algorithmic manipulations to achieve state-of-the-art performance for a various number of cooperators. However, this often leads to complex solution strategies with high computational cost and requiring large amounts of training data. For humans to solve the Hanabi game effectively, they require the use of conventions, which often allows for a means to implicitly convey ideas or knowledge based on a predefined, and mutually agreed upon, set of ``rules’’. Multi-agent problems containing partial observability, especially when limited communication is present, can benefit greatly from the use of implicit knowledge sharing. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to augmenting the action space using conventions, which act as special cooperative actions that span over multiple time steps and multiple agents, requiring agents to actively opt in for it to reach fruition. These conventions are based on existing human conventions, and result in a significant improvement on the performance of existing techniques for self-play and cross-play across a various number of cooperators within Hanabi.
汉诺塔牌游戏被认为是测试和发展多智能体强化学习算法的有力工具,其原因在于其合作性质、隐藏信息、有限的交流和复杂的特性。之前的研究努力已经探索了多智能体强化学习算法在汉诺塔游戏中的能力,主要集中在高级架构设计以及算法操作,以实现各种合作人数的最新性能。然而,这通常会导致解决方案复杂,计算成本高,需要大量的训练数据。人类有效地解决汉诺塔游戏需要运用规则,规则允许基于预先定义和共同认可的一套规则来隐含地传达思想或知识。包含部分可观察性的多智能体问题,特别是当存在有限的交流时,可以大大受益于隐性知识共享的使用。在本文中,我们提出了一种利用规则来增加动作空间的新方法,这些规则作为特殊的合作动作,跨越多个时间步骤和多个智能体,需要智能体积极参与以达到实现。这些规则基于现有的人类规则,导致汉诺塔游戏中各种合作人数的自玩和跨玩的现有技术性能显著提高。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper is under review at the journal of autonomous agents and multi-agent systems (JAAMAS). The updated manuscript is the revised version after the first round of peer revision
Summary
本文探讨了多智能体强化学习算法在汉诺塔游戏中的测试与发展。由于汉诺塔游戏的合作性、隐藏信息、有限沟通以及高度复杂性,使其成为测试和发展多智能体强化学习算法的有力平台。研究人员已探索了多智能体强化学习算法在汉诺塔游戏中的能力,并致力于设计高级架构和算法操作以达到最佳性能。然而,这常常导致复杂的解决方案策略,计算成本高且需要大量训练数据。本文提出了一种利用惯例来扩展行动空间的新方法,这些惯例作为特殊的合作行动,跨越多个时间步骤和多个智能体,要求智能体积极参与以达到实现。这些惯例基于现有的人类惯例,并在汉诺塔游戏中显著提高了现有技术的自我玩和跨玩家合作性能。
Key Takeaways
- 汉诺塔游戏是多智能体强化学习算法的重要测试和发展平台,因其合作性、隐藏信息、有限沟通和复杂性。
- 此前的研究主要集中在设计高级架构和算法操作上,以实现汉诺塔游戏中的最佳性能。
- 这些方法常常导致复杂的解决方案策略,计算成本高且需要大量训练数据。
- 利用人类惯例,可以通过扩展行动空间来提高多智能体性能。
- 本文提出了特殊的合作行动——惯例,这些行动跨越多个时间步骤和多个智能体。
- 智能体需要积极参与惯例以达到实现,这显著提高了汉诺塔游戏中现有技术的性能。
点此查看论文截图

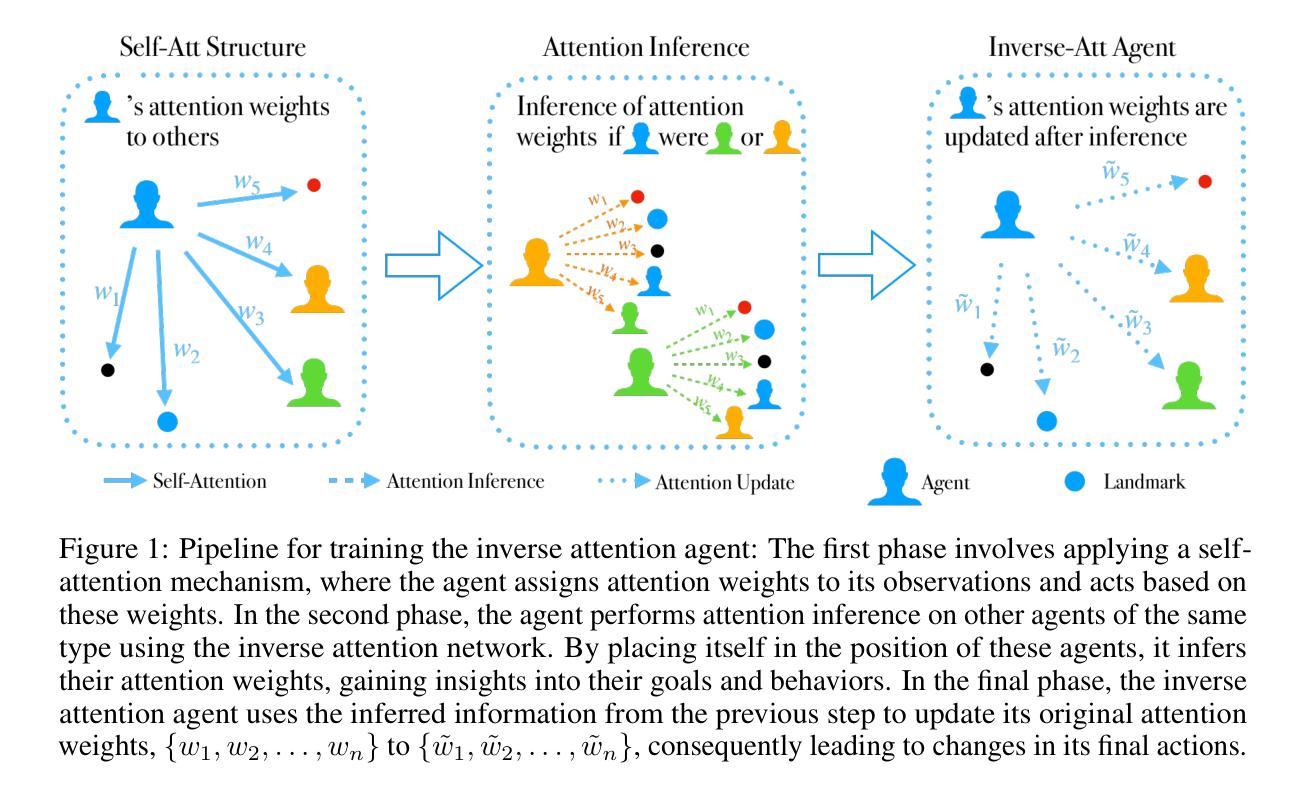
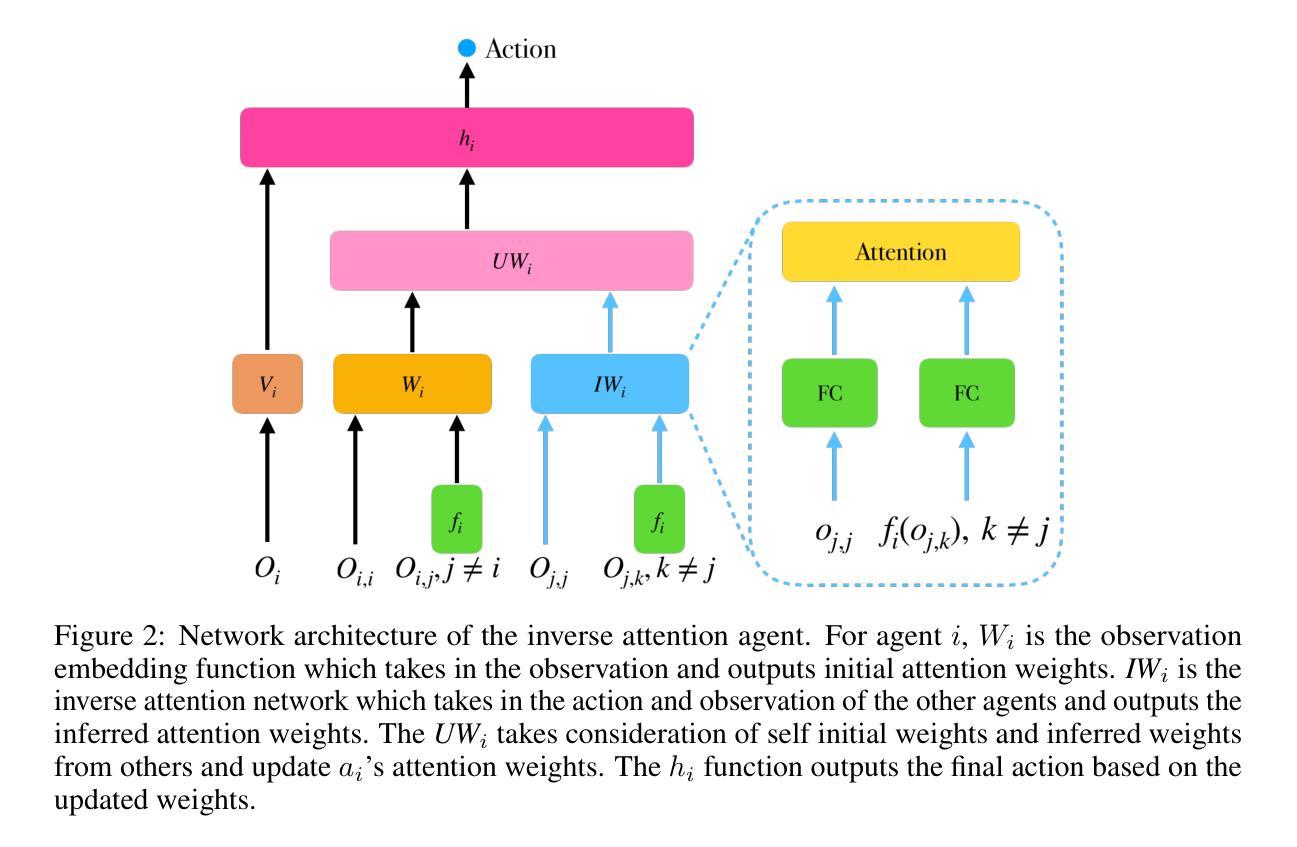
Inverse Attention Agents for Multi-Agent Systems
Authors:Qian Long, Ruoyan Li, Minglu Zhao, Tao Gao, Demetri Terzopoulos
A major challenge for Multi-Agent Systems is enabling agents to adapt dynamically to diverse environments in which opponents and teammates may continually change. Agents trained using conventional methods tend to excel only within the confines of their training cohorts; their performance drops significantly when confronting unfamiliar agents. To address this shortcoming, we introduce Inverse Attention Agents that adopt concepts from the Theory of Mind (ToM) implemented algorithmically using an attention mechanism trained in an end-to-end manner. Crucial to determining the final actions of these agents, the weights in their attention model explicitly represent attention to different goals. We furthermore propose an inverse attention network that deduces the ToM of agents based on observations and prior actions. The network infers the attentional states of other agents, thereby refining the attention weights to adjust the agent’s final action. We conduct experiments in a continuous environment, tackling demanding tasks encompassing cooperation, competition, and a blend of both. They demonstrate that the inverse attention network successfully infers the attention of other agents, and that this information improves agent performance. Additional human experiments show that, compared to baseline agent models, our inverse attention agents exhibit superior cooperation with humans and better emulate human behaviors.
对于多智能体系统而言,面临的主要挑战是使智能体能够适应不断变化的多种环境,这些环境中的对手和队友可能会不断变化。使用传统方法训练的智能体往往只在其训练群体范围内表现出色;当面对不熟悉的智能体时,它们的性能会显著下降。为了解决这一缺陷,我们引入了逆向注意力智能体,它采用了心智理论(ToM)的概念,通过一种注意力机制算法实现,以端到端的方式进行训练。这些智能体的最终行动取决于其注意力模型的权重,该权重明确表示了对不同目标的关注。此外,我们提出了一个基于观察和先前行动来推断智能体心智理论的逆向注意力网络。该网络推断其他智能体的注意力状态,从而调整注意力权重以调整智能体的最终行动。我们在连续环境中进行实验,解决包含合作、竞争和两者混合的艰巨任务。实验表明,逆向注意力网络成功推断出其他智能体的注意力,并且这一信息提高了智能体的性能。额外的人类实验表明,与基线智能体模型相比,我们的逆向注意力智能体与人类表现出更好的合作,更能模仿人类行为。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在多变环境中,多智能体系统面临一大挑战,即如何使智能体适应不断变化的环境中的对手和队友。采用常规训练方法的智能体通常仅在训练群体内部表现出色,而在面对陌生智能体时表现不佳。为解决这一缺陷,我们引入了逆向注意力智能体,它采用心智理论(ToM)的概念,通过注意力机制以端对端方式实现算法实现。决定这些智能体最终行动的关键是它们注意力模型的权重,这些权重明确体现了对不同目标的关注。我们还提出了一种基于观察和先前行动来推断智能体心智理论的逆向注意力网络。该网络会推断其他智能体的注意力状态,从而调整注意力权重以调整智能体的最终行动。在连续环境中的实验表明,逆向注意力网络成功推断出其他智能体的注意力,并且这一信息提高了智能体的性能。额外的人类实验显示,与基线智能体模型相比,我们的逆向注意力智能体与人类合作更为出色,更能模仿人类行为。
Key Takeaways
- 多智能体系统在动态环境中面临挑战,需要智能体能适应不断变化的对手和队友。
- 传统训练方法的智能体在面临陌生智能体时表现不佳。
- 引入逆向注意力智能体,结合心智理论(ToM)的概念,通过注意力机制进行算法实现。
- 注意力模型的权重对智能体的最终行动起到关键作用,反映了对不同目标的关注。
- 逆向注意力网络能基于观察和先前行动推断其他智能体的心智理论。
- 逆向注意力网络成功推断出其他智能体的注意力,提高了智能体的性能。
点此查看论文截图

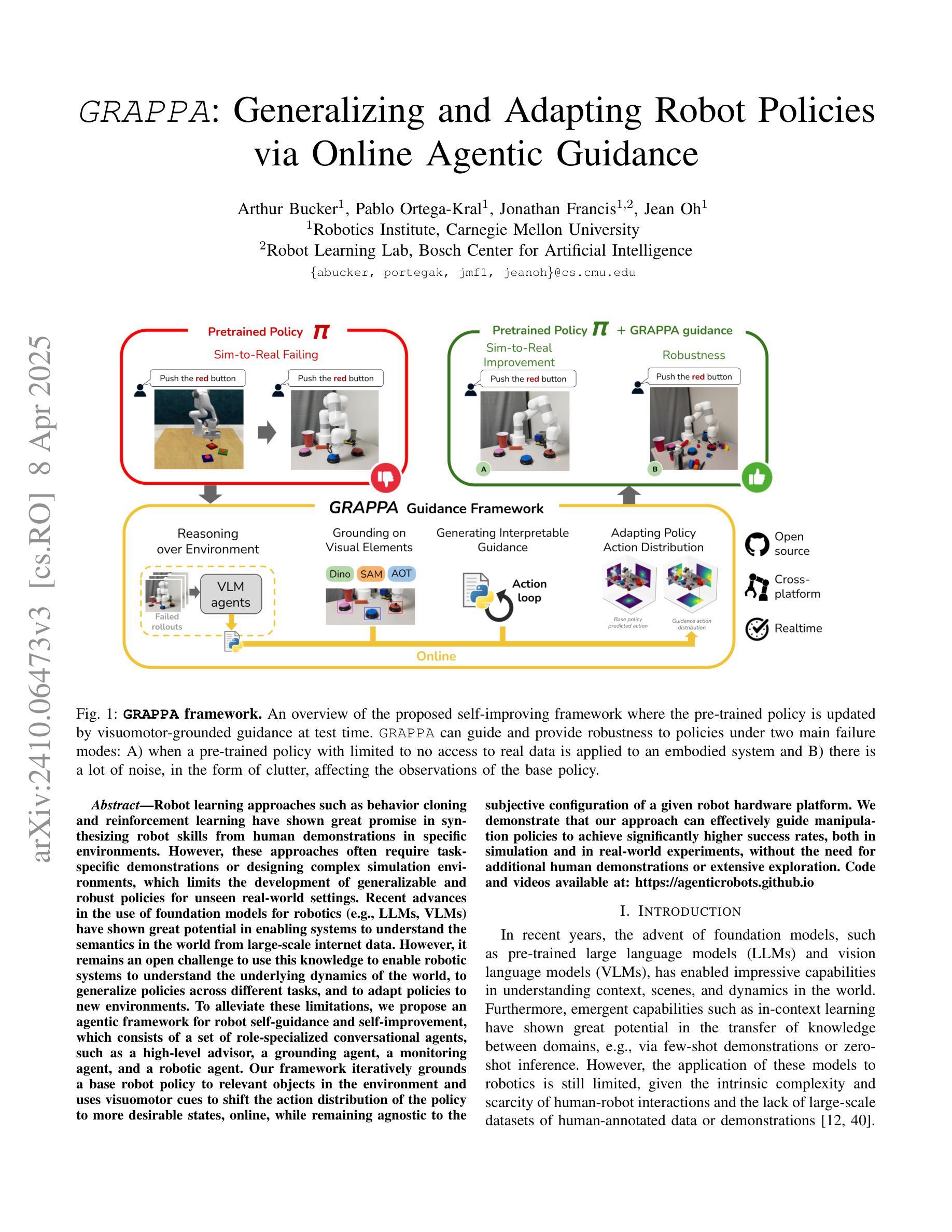
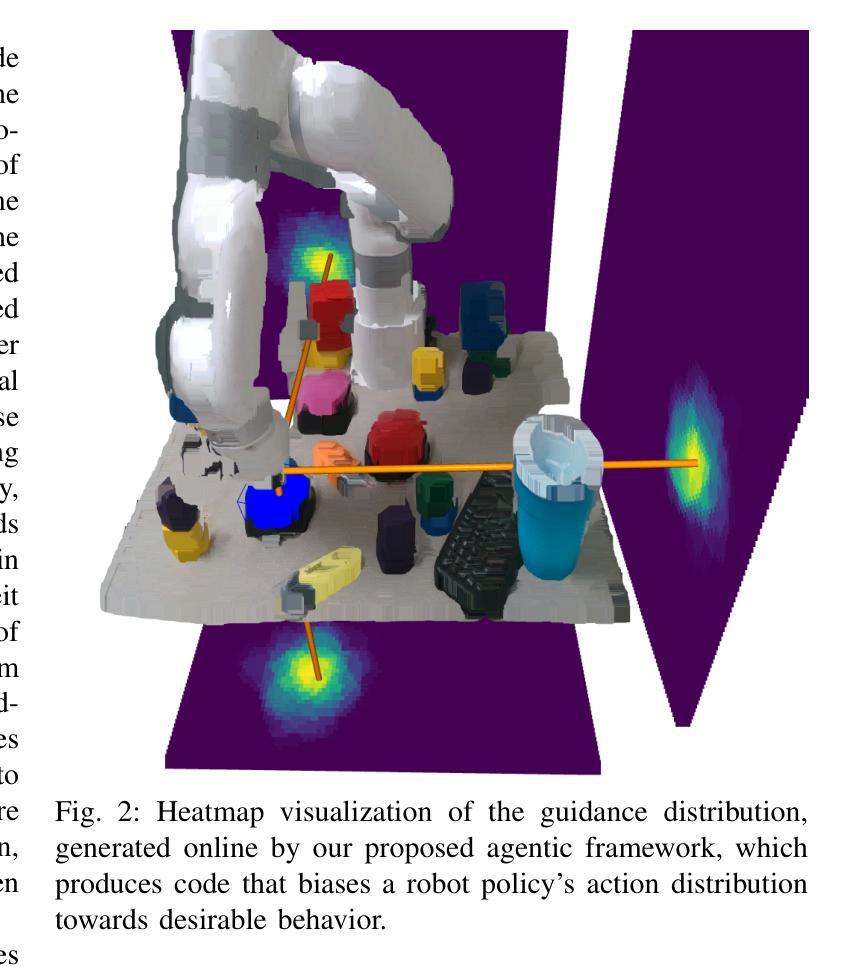
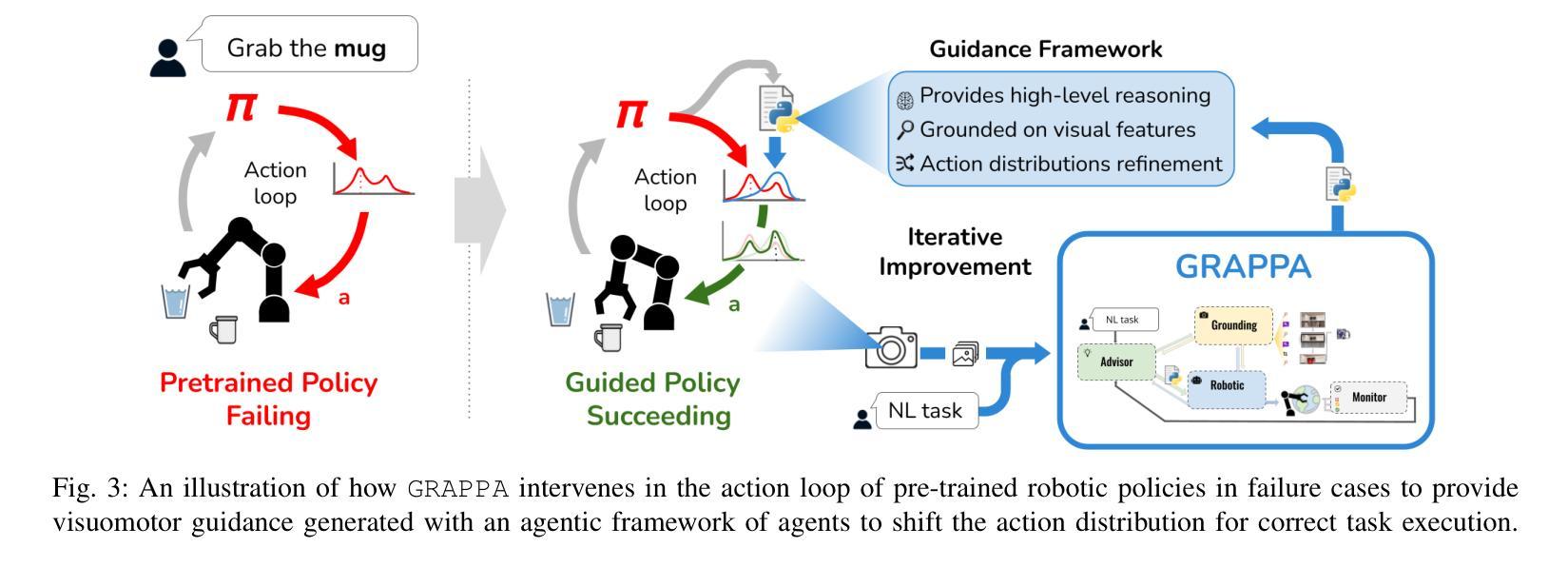
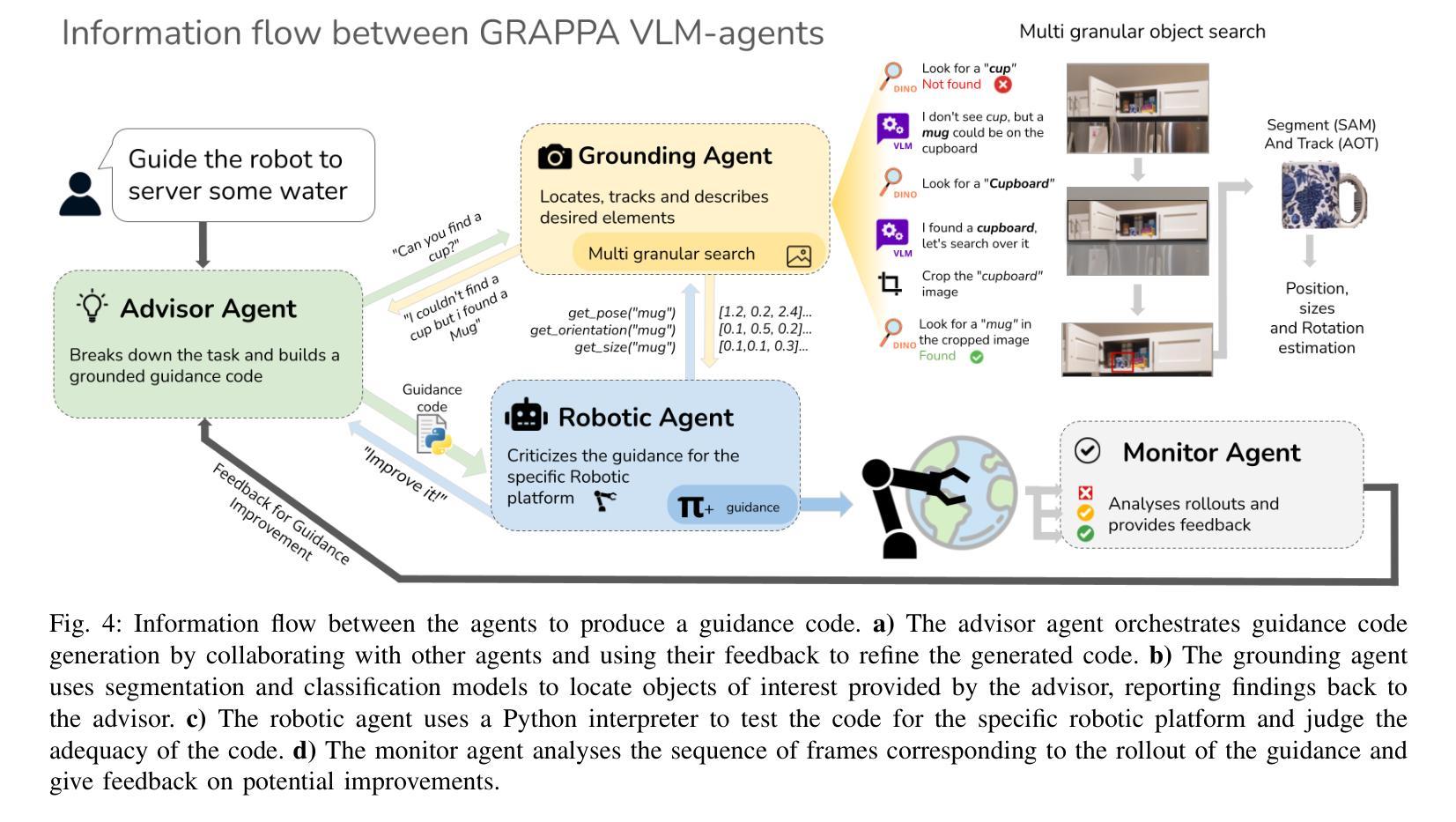
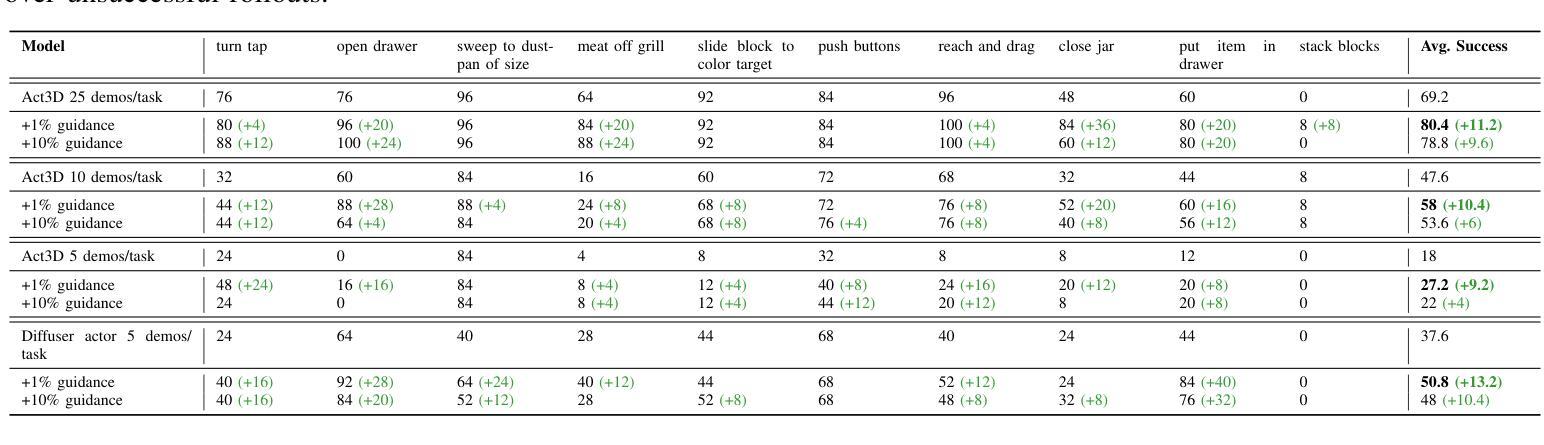
GRAPPA: Generalizing and Adapting Robot Policies via Online Agentic Guidance
Authors:Arthur Bucker, Pablo Ortega-Kral, Jonathan Francis, Jean Oh
Robot learning approaches such as behavior cloning and reinforcement learning have shown great promise in synthesizing robot skills from human demonstrations in specific environments. However, these approaches often require task-specific demonstrations or designing complex simulation environments, which limits the development of generalizable and robust policies for unseen real-world settings. Recent advances in the use of foundation models for robotics (e.g., LLMs, VLMs) have shown great potential in enabling systems to understand the semantics in the world from large-scale internet data. However, it remains an open challenge to use this knowledge to enable robotic systems to understand the underlying dynamics of the world, to generalize policies across different tasks, and to adapt policies to new environments. To alleviate these limitations, we propose an agentic framework for robot self-guidance and self-improvement, which consists of a set of role-specialized conversational agents, such as a high-level advisor, a grounding agent, a monitoring agent, and a robotic agent. Our framework iteratively grounds a base robot policy to relevant objects in the environment and uses visuomotor cues to shift the action distribution of the policy to more desirable states, online, while remaining agnostic to the subjective configuration of a given robot hardware platform. We demonstrate that our approach can effectively guide manipulation policies to achieve significantly higher success rates, both in simulation and in real-world experiments, without the need for additional human demonstrations or extensive exploration. Code and videos available at: https://agenticrobots.github.io
机器人学习的方法,如行为克隆和强化学习,在合成特定环境中人类演示的机器人技能方面显示出巨大的潜力。然而,这些方法通常需要特定的任务演示或设计复杂的仿真环境,这限制了针对未见过的真实世界环境制定可推广和稳健的策略。最近,在机器人技术中使用基础模型(例如LLM和VLM)的进步显示出巨大潜力,能够使得系统从大规模互联网数据中理解世界语义。然而,使用这些知识使机器人系统理解世界的基本动态、在不同任务中推广策略以及适应新环境,仍然是一个挑战。为了缓解这些限制,我们提出了一个用于机器人自我指导和自我改进的代理框架,该框架包括一系列专业角色的对话代理,如高级顾问、接地代理、监控代理和机器人代理。我们的框架将基础机器人策略迭代地关联到环境中的相关对象,并使用视觉运动线索在线将策略的行动分布转移到更理想的状态,同时保持对给定机器人硬件平台的主观配置的独立性。我们证明,我们的方法可以有效地指导操作策略,在模拟和真实世界实验中实现更高的成功率,无需额外的人类演示或大量探索。代码和视频可在:https://agenticrobots.github.io查看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 12 figures, 4 tables
Summary
基于行为克隆和强化学习等机器人学习方法的潜力,结合大型互联网数据下的机器人对世界的语义理解,提出了一种机器人自我指导和自我改进的多智能体框架。该框架包括高级顾问、接地智能体、监控智能体和机器人智能体等角色专业化对话智能体。此框架无需额外的主观机器人硬件配置或大量的演示探索,便可以指导操纵策略达到较高的成功率。更多详情参见相关网站。
Key Takeaways
- 机器人学习技术如行为克隆和强化学习等在特定环境中合成机器人技能已有良好表现,但仍需任务特定的演示或复杂的仿真环境设计,限制了其在未知真实环境中的通用性和稳健性策略的发展。
- 利用基础模型(如LLMs和VLMs)为机器人进行语义理解展现出巨大潜力,但如何利用这些知识使机器人理解世界底层动态、在不同任务间通用策略以及如何适应新环境仍是挑战。
- 提出了一种多智能体框架用于机器人自我指导和自我改进,包括多种角色专业对话智能体,旨在解决上述挑战。该框架通过对基础机器人策略进行迭代调整以使其适应环境并优化其行动分布来实现引导策略,而不依赖于特定机器人的硬件平台配置。
- 通过仿真和真实实验验证了此框架的有效性,展示了它能有效地提高策略的成功率。且这一过程无需额外的人力演示或大规模的勘探探索过程。代码和视频材料已在指定网站公开供大众查看下载。
点此查看论文截图

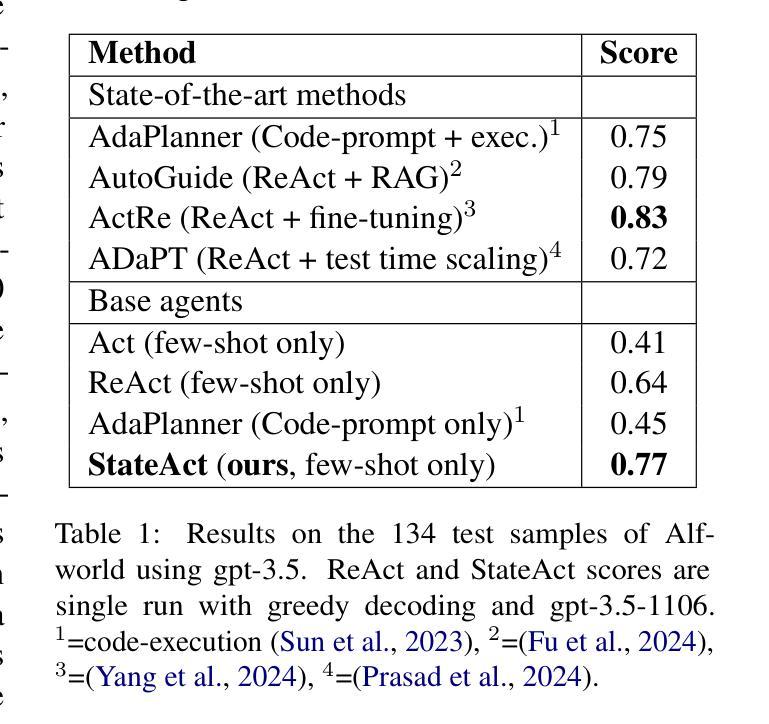
StateAct: Enhancing LLM Base Agents via Self-prompting and State-tracking
Authors:Nikolai Rozanov, Marek Rei
Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used as autonomous agents, tackling tasks from robotics to web navigation. Their performance depends on the underlying base agent. Existing methods, however, struggle with long-context reasoning and goal adherence. We introduce StateAct, a novel and efficient base agent that enhances decision-making through (1) self-prompting, which reinforces task goals at every step, and (2) chain-of-states, an extension of chain-of-thought that tracks state information over time. StateAct outperforms ReAct, the previous best base agent, by over 10% on Alfworld, 30% on Textcraft, and 7% on Webshop across multiple frontier LLMs. We also demonstrate that StateAct can be used as a drop-in replacement for ReAct with advanced LLM agent methods such as test-time scaling, yielding an additional 12% gain on Textcraft. By improving efficiency and long-range reasoning without requiring additional training or retrieval, StateAct provides a scalable foundation for LLM agents. We open source our code to support further research at https://github.com/ai-nikolai/stateact .
大型语言模型(LLM)越来越多地被用作自主代理,处理从机器人技术到网页导航的任务。它们的性能取决于基础主体代理。然而,现有方法在上下文推理和目标一致性方面存在困难。我们引入了StateAct,这是一种新型高效的主体代理,通过以下两个方面增强决策制定:(1)自我提示,每一步都强化任务目标;(2)状态链,是对思维链的扩展,随时间跟踪状态信息。StateAct在多个前沿LLM上表现优异,在Alfworld上的性能超过之前的最佳基础代理ReAct超过10%,在Textcraft上超过30%,在Webshop上超过7%。我们还证明,StateAct可以作为高级LLM代理方法(如测试时缩放)的即插即用替代品,在Textcraft上产生额外的12%收益。通过提高效率和长期推理能力,而无需额外的训练或检索,StateAct为LLM代理提供了可扩展的基础。我们在https://github.com/ai-nikolai/stateact上公开源代码,以支持进一步的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 5 pages appendix, 7 figures, 5 tables
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)作为自主代理,广泛应用于机器人到网页导航等任务。其性能取决于基础代理的表现。现有方法面临长语境推理和目标一致性方面的挑战。本文引入StateAct,一种新颖且高效的基础代理,通过(1)自我提示,每一步都强化任务目标;(2)状态链,扩展了思考链,跟踪随时间变化的状态信息,从而提高决策能力。StateAct在Alfworld上的表现优于之前的最佳基础代理ReAct超过10%,在Textcraft上超过30%,在Webshop上超过7%,且可应用于多个前沿LLM。我们还证明了StateAct可以用作替换ReAct的高级LLM代理方法,如测试时缩放,在Textcraft上产生额外的12%收益。通过提高效率和长程推理能力,无需额外的训练或检索,StateAct为LLM代理提供了可扩展的基础。我们公开了代码以支持进一步研究。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)被广泛应用于多种任务,其性能取决于基础代理的表现。
- 现有方法在长语境推理和目标一致性方面存在挑战。
- StateAct是一种新颖且高效的基础代理,通过自我提示和状态链技术提高决策能力。
- StateAct在多个任务上的表现优于之前的最佳基础代理ReAct。
- StateAct可与高级LLM代理方法结合使用,进一步提高性能。
- StateAct提高了效率和长程推理能力,且无需额外的训练或检索。
点此查看论文截图


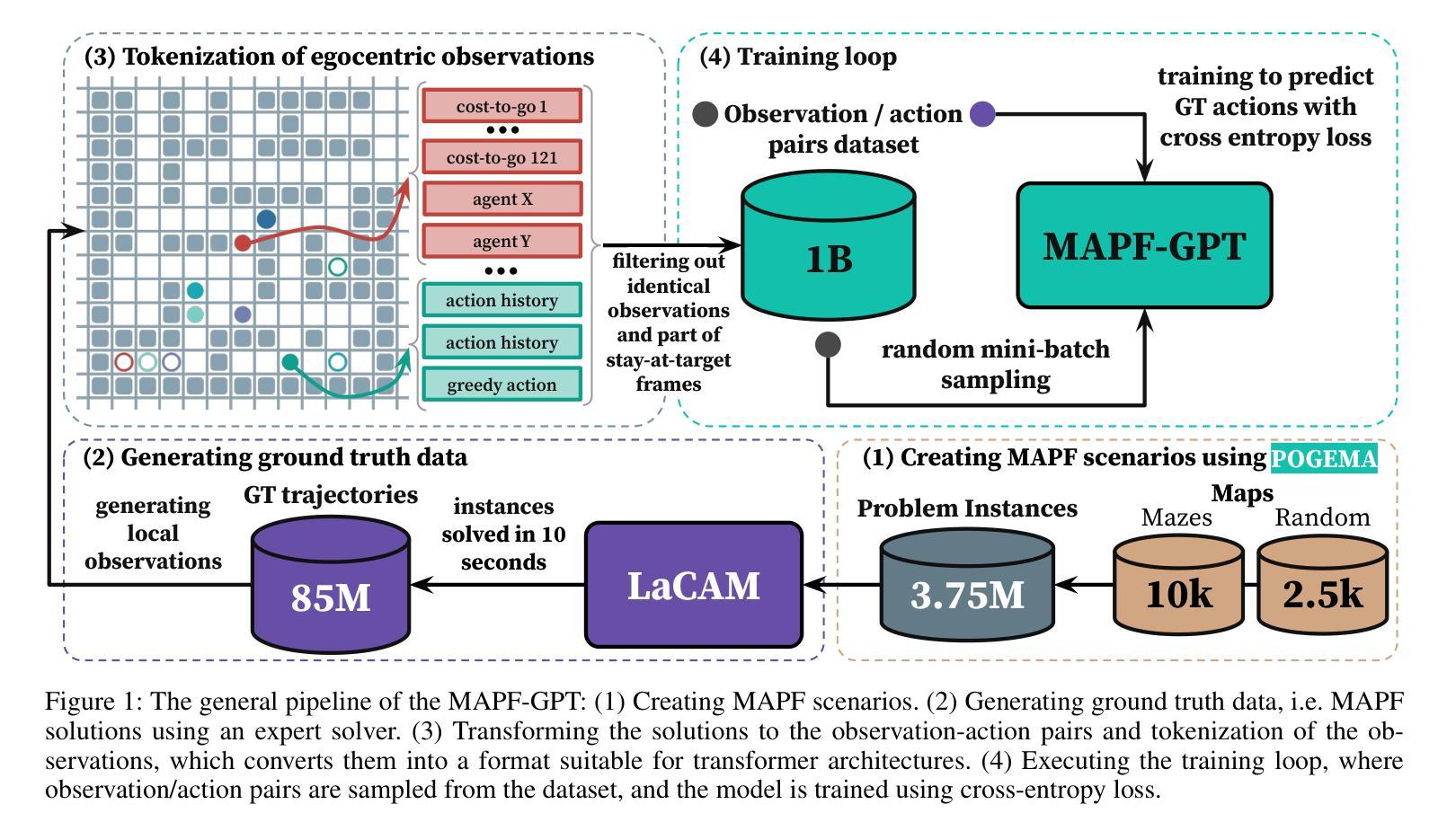
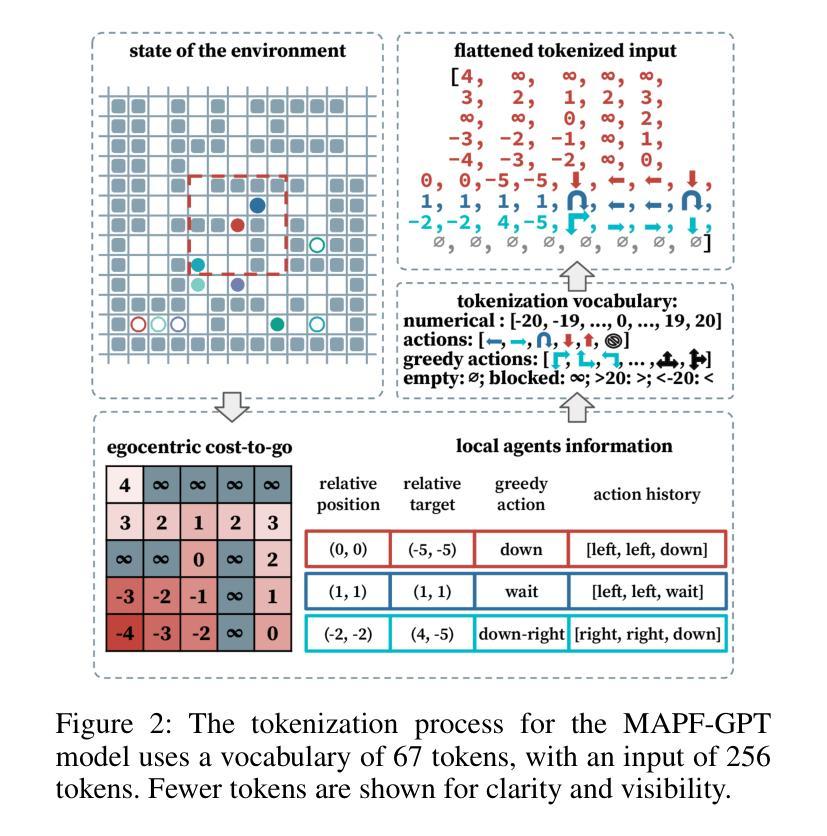
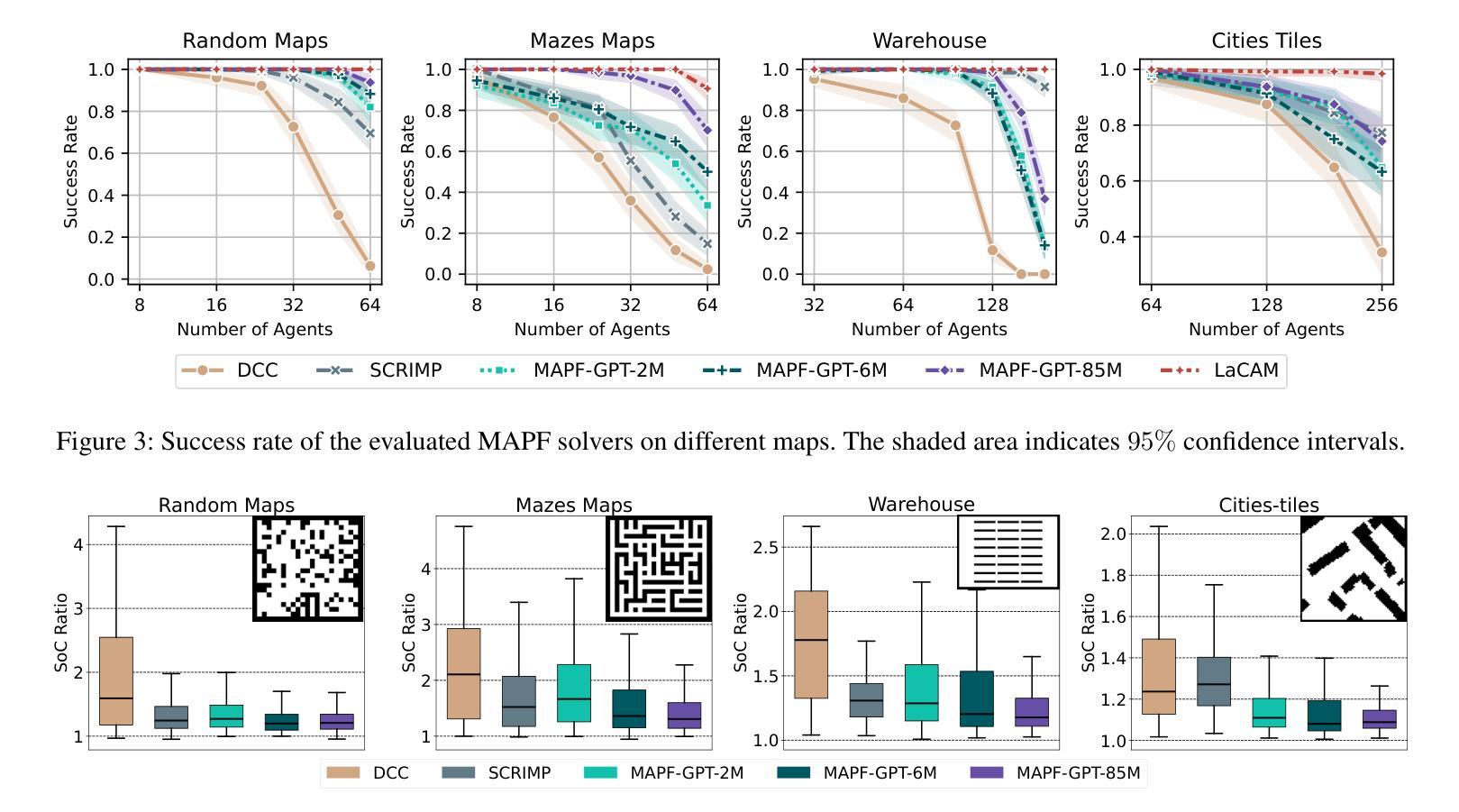
MAPF-GPT: Imitation Learning for Multi-Agent Pathfinding at Scale
Authors:Anton Andreychuk, Konstantin Yakovlev, Aleksandr Panov, Alexey Skrynnik
Multi-agent pathfinding (MAPF) is a problem that generally requires finding collision-free paths for multiple agents in a shared environment. Solving MAPF optimally, even under restrictive assumptions, is NP-hard, yet efficient solutions for this problem are critical for numerous applications, such as automated warehouses and transportation systems. Recently, learning-based approaches to MAPF have gained attention, particularly those leveraging deep reinforcement learning. Typically, such learning-based MAPF solvers are augmented with additional components like single-agent planning or communication. Orthogonally, in this work we rely solely on imitation learning that leverages a large dataset of expert MAPF solutions and transformer-based neural network to create a foundation model for MAPF called MAPF-GPT. The latter is capable of generating actions without additional heuristics or communication. MAPF-GPT demonstrates zero-shot learning abilities when solving the MAPF problems that are not present in the training dataset. We show that MAPF-GPT notably outperforms the current best-performing learnable MAPF solvers on a diverse range of problem instances and is computationally efficient during inference.
多智能体路径规划(MAPF)是一个通常需要在共享环境中为多个智能体找到无碰撞路径的问题。解决MAPF问题,即使在限制性假设下,也是NP难的。然而,对于许多应用(如自动化仓库和运输系统)来说,高效解决此问题的解决方案至关重要。最近,基于学习的MAPF方法引起了人们的关注,特别是利用深度强化学习的方法。通常,这样的基于学习的MAPF求解器会辅以单智能体规划或通信等附加组件。与此不同,在这项工作中,我们仅依靠利用大量专家MAPF解决方案数据集和基于变压器的神经网络进行模仿学习,从而创建了一个称为MAPF-GPT的MAPF基础模型。后者能够在不附加启发式信息或通信的情况下生成动作。MAPF-GPT在解决训练数据集中不存在的MAPF问题时,表现出了零样本学习能力。我们证明了MAPF-GPT在多种问题实例上的表现显著优于当前性能最佳的可学习MAPF求解器,并且在推理过程中计算效率高。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多智能体路径查找(MAPF)问题要求为共享环境中的多个智能体找到无碰撞的路径。尽管在限制性假设下解决MAPF问题是NP难题,但对其高效解决方案的需求对于自动化仓库和运输系统等众多应用至关重要。最近,基于学习的MAPF方法引起了关注,特别是利用深度强化学习的方法。通常,这些基于学习的MAPF求解器会辅以单智能体规划或通信等组件。与此不同,本研究仅依赖模仿学习,利用大量专家MAPF解决方案数据集和基于transformer的神经网络,为MAPF创建一个基础模型——MAPF-GPT。后者能够在不添加启发式或通信的情况下生成动作。MAPF-GPT表现出解决未在训练数据集中出现的MAPF问题的零样本学习能力。研究表明,MAPF-GPT在多种问题实例上的表现优于当前最佳的可学习MAPF求解器,并且在推理过程中计算效率高。
Key Takeaways
- 多智能体路径查找(MAPF)是寻找多个智能体在共享环境中的无碰撞路径的问题。
- MAPF问题在限制性假设下是NP难题,但对高效解决方案的需求在许多应用中至关重要。
- 基于学习的MAPF方法受到关注,特别是利用深度强化学习的方法。
- MAPF-GPT是一个基于模仿学习和transformer神经网络的基础模型,能够生成动作而无需额外的启发式或通信。
- MAPF-GPT表现出解决未在训练数据集中出现的MAPF问题的零样本学习能力。
- MAPF-GPT在多种问题实例上的表现优于当前最佳的可学习MAPF求解器。
点此查看论文截图

DrugAgent: Multi-Agent Large Language Model-Based Reasoning for Drug-Target Interaction Prediction
Authors:Yoshitaka Inoue, Tianci Song, Xinling Wang, Augustin Luna, Tianfan Fu
Advancements in large language models (LLMs) allow them to address diverse questions using human-like interfaces. Still, limitations in their training prevent them from answering accurately in scenarios that could benefit from multiple perspectives. Multi-agent systems allow the resolution of questions to enhance result consistency and reliability. While drug-target interaction (DTI) prediction is important for drug discovery, existing approaches face challenges due to complex biological systems and the lack of interpretability needed for clinical applications. DrugAgent is a multi-agent LLM system for DTI prediction that combines multiple specialized perspectives with transparent reasoning. Our system adapts and extends existing multi-agent frameworks by (1) applying coordinator-based architecture to the DTI domain, (2) integrating domain-specific data sources, including ML predictions, knowledge graphs, and literature evidence, and (3) incorporating Chain-of-Thought (CoT) and ReAct (Reason+Act) frameworks for transparent DTI reasoning. We conducted comprehensive experiments using a kinase inhibitor dataset, where our multi-agent LLM method outperformed the non-reasoning multi-agent model (GPT-4o mini) by 45% in F1 score (0.514 vs 0.355). Through ablation studies, we demonstrated the contributions of each agent, with the AI agent being the most impactful, followed by the KG agent and search agent. Most importantly, our approach provides detailed, human-interpretable reasoning for each prediction by combining evidence from multiple sources - a critical feature for biomedical applications where understanding the rationale behind predictions is essential for clinical decision-making and regulatory compliance. Code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DrugAgent-B2EA.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的进步,它们能够通过类似人类的接口解决各种各样的问题。然而,其训练的局限性使得它们无法在多视角受益的场景中准确回答问题。多智能体系统允许对问题答案进行优化以增强结果的一致性和可靠性。虽然药物靶点相互作用(DTI)预测对于药物发现很重要,但现有方法由于复杂的生物系统和缺乏临床应用中所需的解释性而面临挑战。DrugAgent是一个用于DTI预测的多智能体LLM系统,它结合了多个专业视角和透明的推理。我们的系统通过以下方式适应并扩展了现有的多智能体框架:(1)将基于协调器的架构应用于DTI领域;(2)整合特定领域的数据源,包括机器学习预测、知识图谱和文献证据;(3)融入Chain-of-Thought(CoT)和ReAct(Reason+Act)框架以实现透明的DTI推理。我们使用激酶抑制剂数据集进行了全面的实验,我们的多智能体LLM方法在非推理多智能体模型(GPT-4o mini)的F1分数上提高了45%(0.514对比0.355)。通过消融研究,我们证明了每个智能体的贡献,其中AI智能体影响最大,其次是KG智能体和搜索智能体。最重要的是,我们的方法结合了来自多个来源的证据,为每次预测提供了详细、人类可解释的理由——这对于生物医学应用至关重要,因为在预测背后的理由是临床决策和法规合规的关键因素。代码可访问:https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DrugAgent-B2EA。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 1 figure
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)通过人类接口处理多样化的问题,但其训练限制导致在某些场景中缺乏准确性。多智能体系统能够解决这一问题,增强结果的一致性和可靠性。针对药物发现中的药物靶点相互作用(DTI)预测,现有方法面临挑战。DrugAgent是一个用于DTI预测的多智能体LLM系统,它结合了多个专业视角和透明推理。该系统适应并扩展了现有多智能体框架,包括基于协调架构的DTI领域应用、集成特定领域数据源和融入Chain-of-Thought及ReAct框架进行透明DTI推理。实验表明,与GPT-4o mini相比,DrugAgent在激酶抑制剂数据集上的F1得分高出45%(从原来的低值提升为中间偏高的优秀成绩)。每个智能体的贡献都被揭示出来,其中AI智能体的影响最大,其次是知识图谱智能体和搜索智能体。最重要的是,通过结合多种来源的证据,该方法为每个预测提供了详细的可解释的推理,这对理解预测背后的原因和监管机构审核来说极为关键。详细信息请参见[网站链接]。具体详情请阅读下文。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)通过人类接口回答多样化问题,但在特定场景中存在局限性。多智能体系统可提高答案的准确性和一致性。
- DrugAgent是一个多智能体LLM系统,用于药物靶点相互作用(DTI)预测,旨在解决现有方法的挑战。
- DrugAgent结合了基于协调架构的DTI领域应用、特定领域数据源和透明推理框架。实验表明其性能优于其他模型。
点此查看论文截图

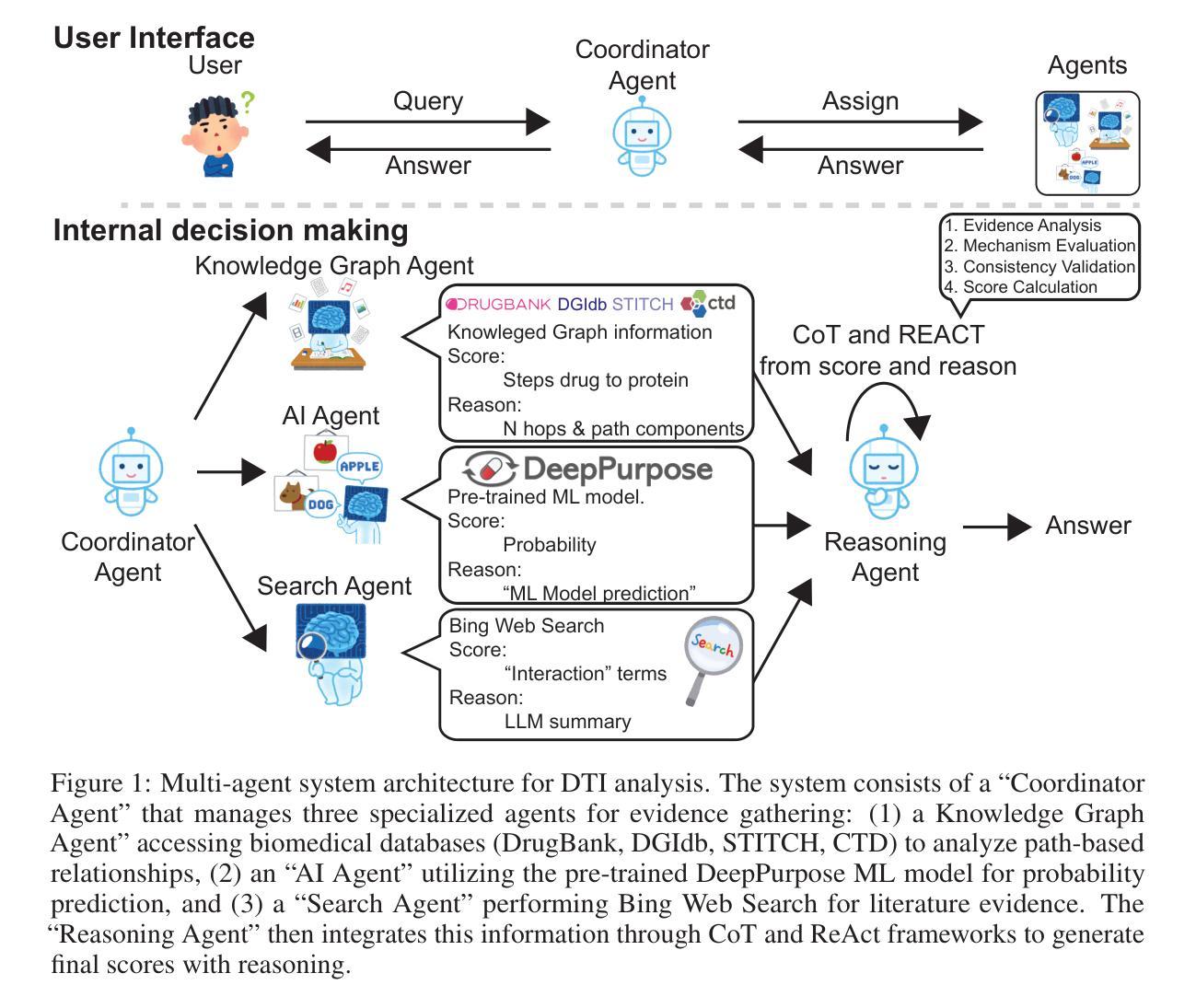
POGEMA: A Benchmark Platform for Cooperative Multi-Agent Pathfinding
Authors:Alexey Skrynnik, Anton Andreychuk, Anatolii Borzilov, Alexander Chernyavskiy, Konstantin Yakovlev, Aleksandr Panov
Multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) has recently excelled in solving challenging cooperative and competitive multi-agent problems in various environments, typically involving a small number of agents and full observability. Moreover, a range of crucial robotics-related tasks, such as multi-robot pathfinding, which have traditionally been approached with classical non-learnable methods (e.g., heuristic search), are now being suggested for solution using learning-based or hybrid methods. However, in this domain, it remains difficult, if not impossible, to conduct a fair comparison between classical, learning-based, and hybrid approaches due to the lack of a unified framework that supports both learning and evaluation. To address this, we introduce POGEMA, a comprehensive set of tools that includes a fast environment for learning, a problem instance generator, a collection of predefined problem instances, a visualization toolkit, and a benchmarking tool for automated evaluation. We also introduce and define an evaluation protocol that specifies a range of domain-related metrics, computed based on primary evaluation indicators (such as success rate and path length), enabling a fair multi-fold comparison. The results of this comparison, which involves a variety of state-of-the-art MARL, search-based, and hybrid methods, are presented.
多智能体强化学习(MARL)最近在解决各种环境中的挑战性合作和竞争多智能体问题上表现出色,通常涉及少量智能体和完全可观察性。此外,一系列关键的机器人相关任务,如多机器人路径规划,传统上采用经典的非学习方法(例如启发式搜索)来解决,现在建议使用基于学习或混合方法来解决。然而,在这个领域,由于缺乏一个既支持学习和评估的统一框架,进行经典方法、基于学习的方法和混合方法之间的公平比较仍然困难甚至不可能。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了POGEMA,这是一套综合工具,包括一个快速学习环境、问题实例生成器、预定义问题实例集合、可视化工具包和用于自动化评估的基准测试工具。我们还介绍并定义了一个评估协议,该协议规定了基于主要评估指标(如成功率和路径长度)的一系列与领域相关的度量标准,以实现公平的多方面比较。本次比较涉及多种先进的多智能体强化学习、基于搜索和混合方法,并呈现了比较结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published as a conference paper at The International Conference on Learning Representations 2025
Summary
多智能体强化学习(MARL)在解决各种环境中的合作与竞争多智能体问题上表现出色,尤其在涉及少量智能体和完全可观察性的情况下。传统的机器人相关任务如多机器人路径规划多采用经典的非学习方法(如启发式搜索),现在建议使用基于学习或混合方法来解决。然而,由于缺乏支持学习和评估的统一框架,难以在经典方法、基于学习的方法和混合方法之间进行公平比较。为此,我们引入了POGEMA工具集,包括学习快速环境、问题实例生成器、预设问题实例集合、可视化工具和自动化评估的基准测试工具。我们还引入并定义了一个评估协议,该协议基于主要评价指标(如成功率和路径长度)计算一系列与领域相关的指标,以实现公平的多重比较。给出了涉及多种先进MARL、基于搜索和混合方法的结果。
Key Takeaways
- 多智能体强化学习(MARL)在解决合作与竞争多智能体问题上表现出卓越性能。
- 传统机器人任务如多机器人路径规划多采用经典非学习方法。
- 基于学习和混合方法正在被提议用于解决这些问题。
- 缺乏统一框架进行公平比较各种方法(经典、基于学习、混合)。
- 引入POGEMA工具集,包括学习快速环境、问题生成等,以支持评估。
- 定义评估协议,包括主要评价指标(成功率和路径长度等),以实现公平比较。
点此查看论文截图

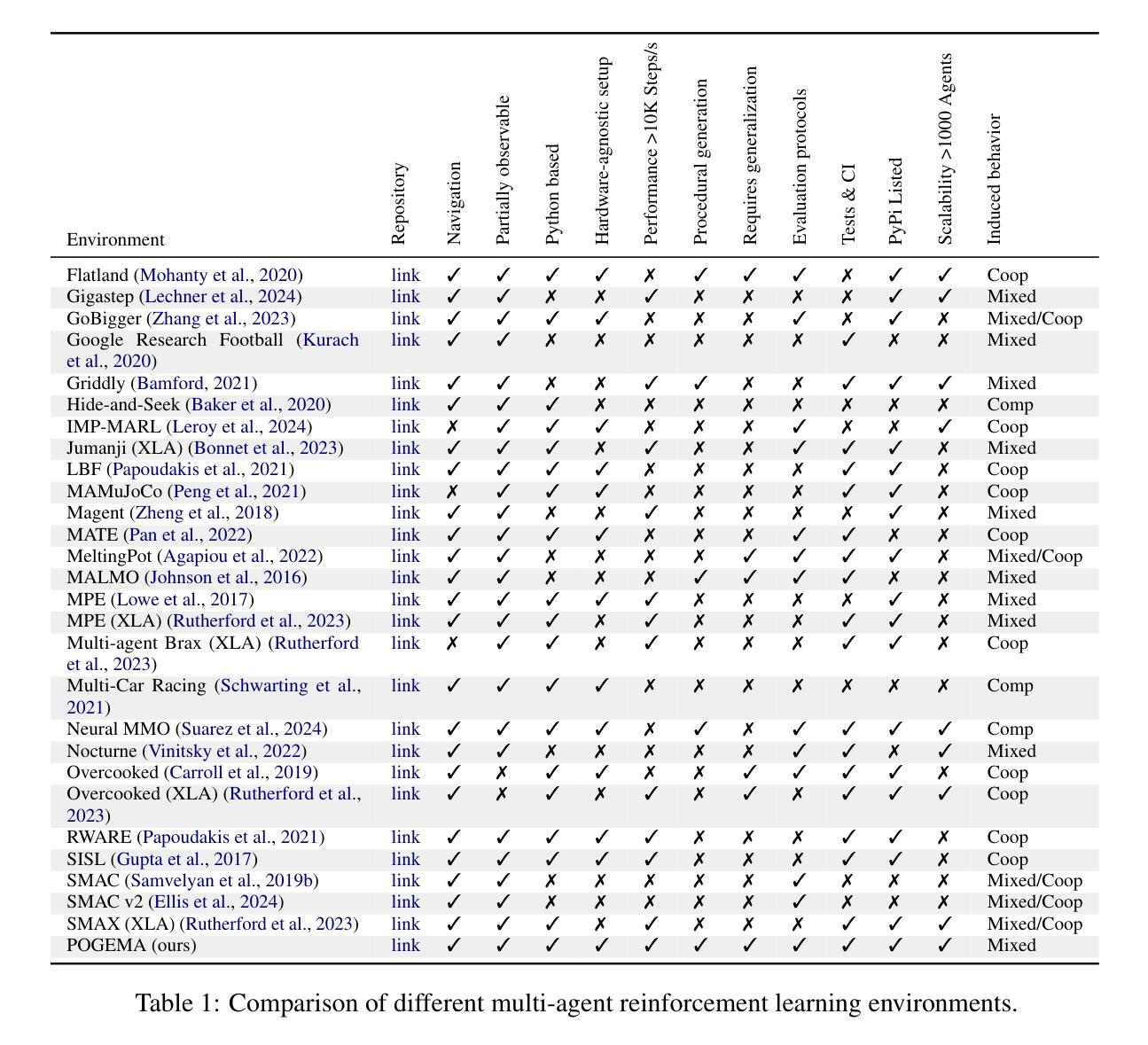
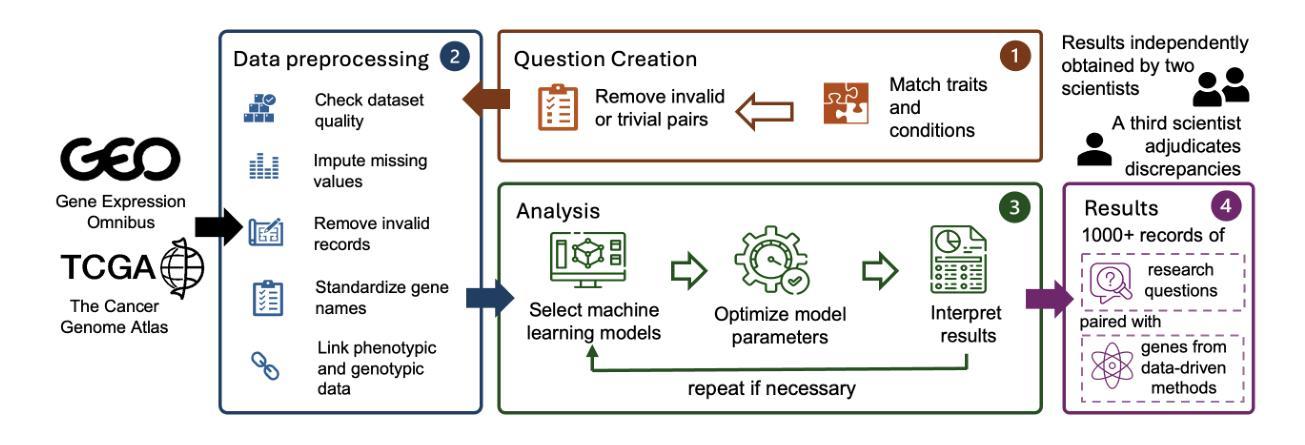
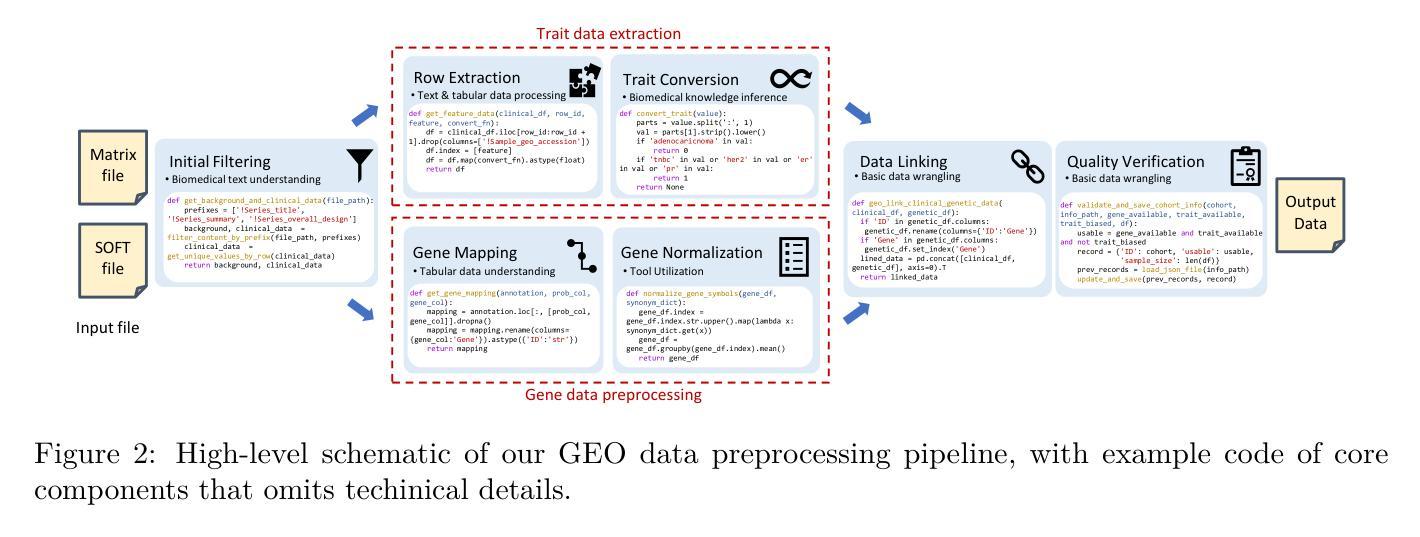
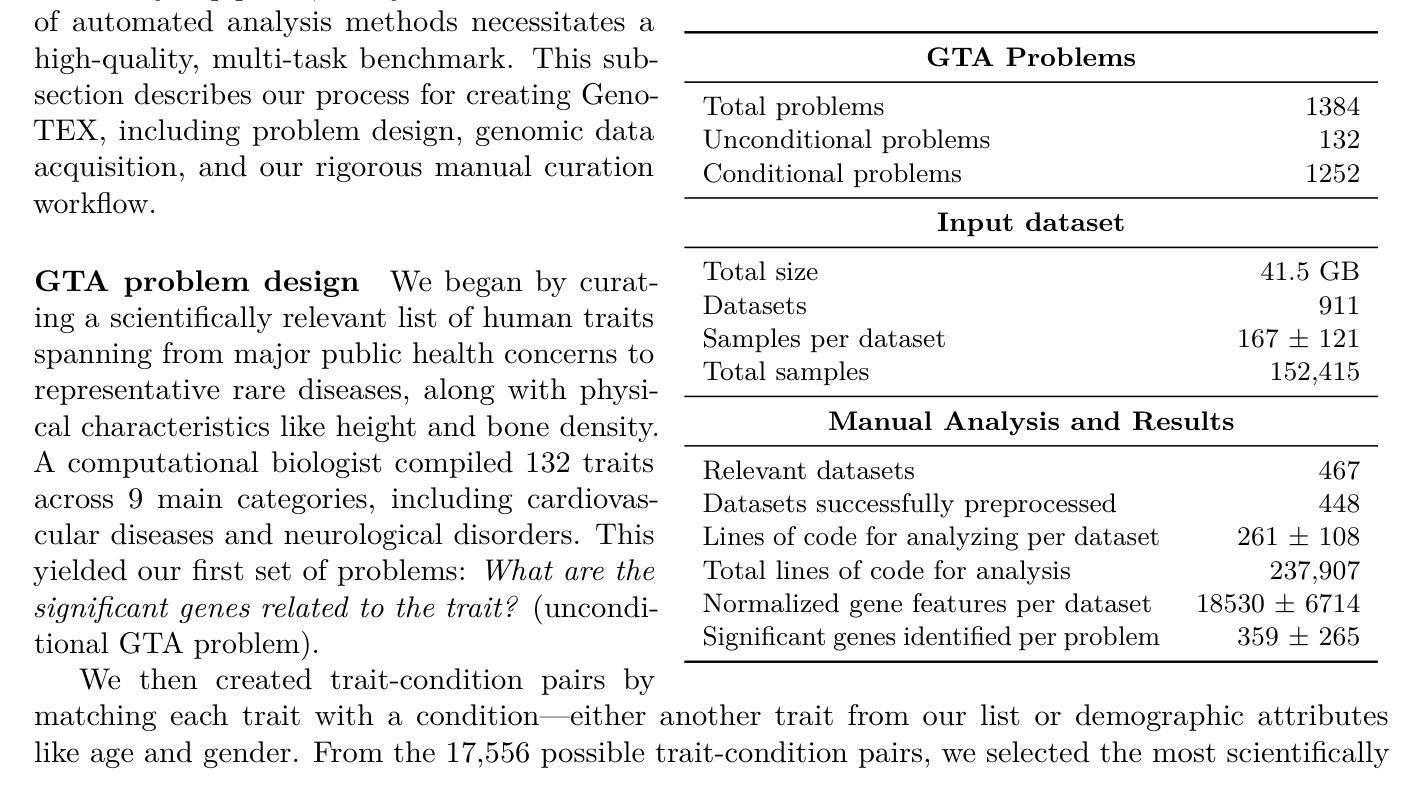
GenoTEX: An LLM Agent Benchmark for Automated Gene Expression Data Analysis
Authors:Haoyang Liu, Shuyu Chen, Ye Zhang, Haohan Wang
Recent advancements in machine learning have significantly improved the identification of disease-associated genes from gene expression datasets. However, these processes often require extensive expertise and manual effort, limiting their scalability. Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents have shown promise in automating these tasks due to their increasing problem-solving abilities. To support the evaluation and development of such methods, we introduce GenoTEX, a benchmark dataset for the automated analysis of gene expression data. GenoTEX provides analysis code and results for solving a wide range of gene-trait association problems, encompassing dataset selection, preprocessing, and statistical analysis, in a pipeline that follows computational genomics standards. The benchmark includes expert-curated annotations from bioinformaticians to ensure accuracy and reliability. To provide baselines for these tasks, we present GenoAgent, a team of LLM-based agents that adopt a multi-step programming workflow with flexible self-correction, to collaboratively analyze gene expression datasets. Our experiments demonstrate the potential of LLM-based methods in analyzing genomic data, while error analysis highlights the challenges and areas for future improvement. We propose GenoTEX as a promising resource for benchmarking and enhancing automated methods for gene expression data analysis. The benchmark is available at https://github.com/Liu-Hy/GenoTEX.
近期机器学习的发展极大地提高了从基因表达数据集中识别与疾病相关基因的能力。然而,这些过程通常需要广泛的专业知识和手动操作,限制了其可扩展性。基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理由于它们日益增强的问题解决能力,在自动化这些任务方面显示出潜力。为了支持此类方法的评估和发展,我们引入了GenoTEX,这是一个用于基因表达数据自动化分析的基准数据集。GenoTEX提供分析代码和结果,以解决广泛的基因特征关联问题,包括数据集选择、预处理和统计分析,遵循计算基因组学标准的管道。基准测试包括生物信息学家的专家精选注释,以确保准确性和可靠性。为了为这些任务提供基准线,我们推出了GenoAgent,这是一组基于LLM的代理,采用具有灵活自我校正的多步编程工作流程,以协同分析基因表达数据集。我们的实验展示了基于LLM的方法在分析基因组数据方面的潜力,而误差分析则突出了未来的挑战和改进领域。我们提议GenoTEX作为一个有希望的资源,用于评估和增强基因表达数据分析的自动化方法。该基准数据集可在https://github.com/Liu-Hy/GenoTEX上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 31 pages, 4 figures
Summary
机器学习最新进展极大地提高了从基因表达数据集中识别与疾病相关基因的能力。然而,这些过程通常需要大量的专业知识和手动操作,限制了其可扩展性。基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理显示出自动化这些任务的潜力,因为它们具有日益增强的问题解决能力。为了支持和开发这些方法,我们推出了GenoTEX,一个用于基因表达数据自动化分析的基准测试数据集。GenoTEX提供了一个分析代码和结果,用于解决广泛的基因特征关联问题,包括数据集选择、预处理和统计分析,遵循计算基因组学标准的管道。该基准测试包括生物信息学家的专家注释,以确保准确性和可靠性。为了为这些任务提供基准,我们提出了GenoAgent,这是一个基于LLM的代理团队,采用多步编程工作流程和灵活的自校正功能,以协同分析基因表达数据集。我们的实验证明了基于LLM的方法在分析基因组数据中的潜力,而误差分析则突出了挑战和未来改进的领域。我们提出GenoTEX是一个有前景的资源,用于评估和增强基因表达数据分析的自动化方法。
Key Takeaways
- 机器学习最新进展提高了从基因表达数据集中识别疾病相关基因的能力。
- 基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理在自动化基因表达数据分析任务中展现出潜力。
- GenoTEX是一个用于基因表达数据自动化分析的基准测试数据集,包含分析代码和专家注释。
- GenoAgent是基于LLM的代理团队,采用多步编程工作流程和自校正功能来协同分析基因表达数据集。
- 实验证明了基于LLM的方法在分析基因组数据中的潜力。
- 误差分析表明需要改进的领域和未来挑战。
点此查看论文截图