⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-10 更新
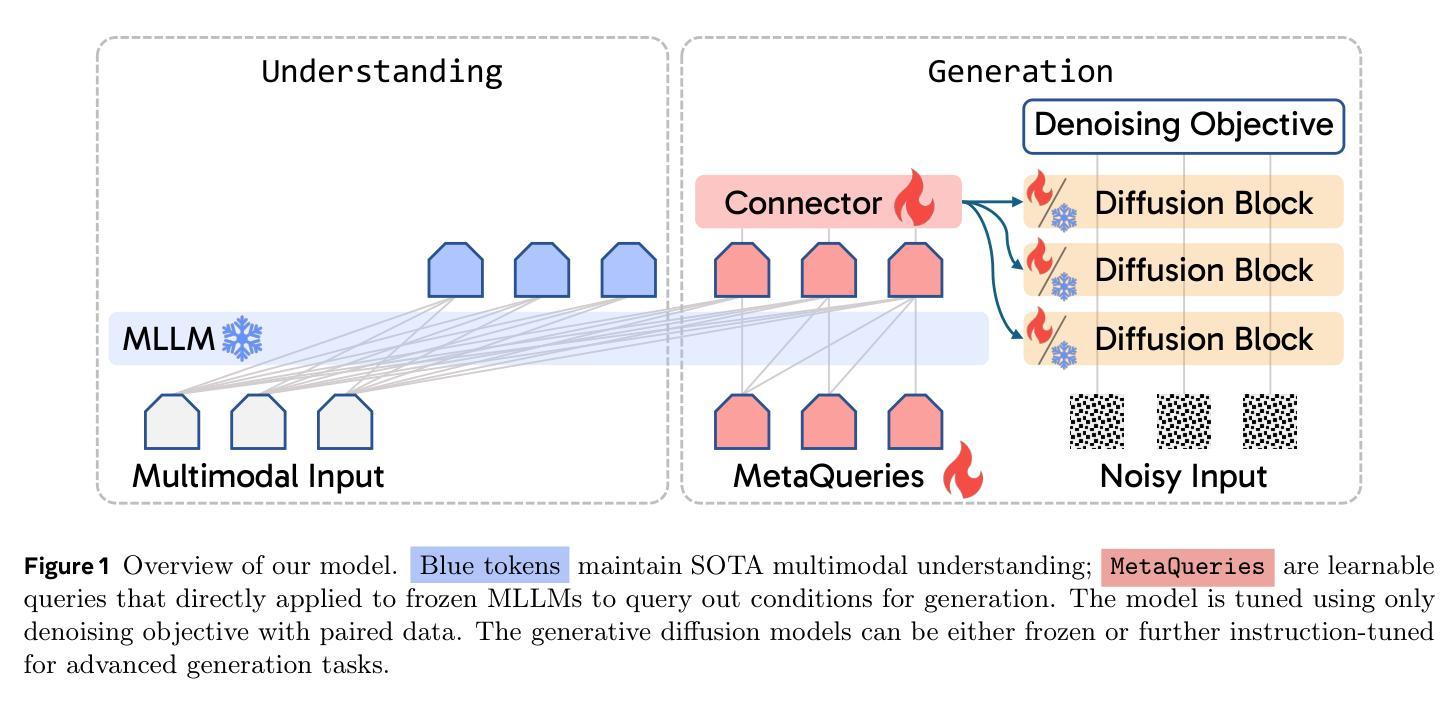
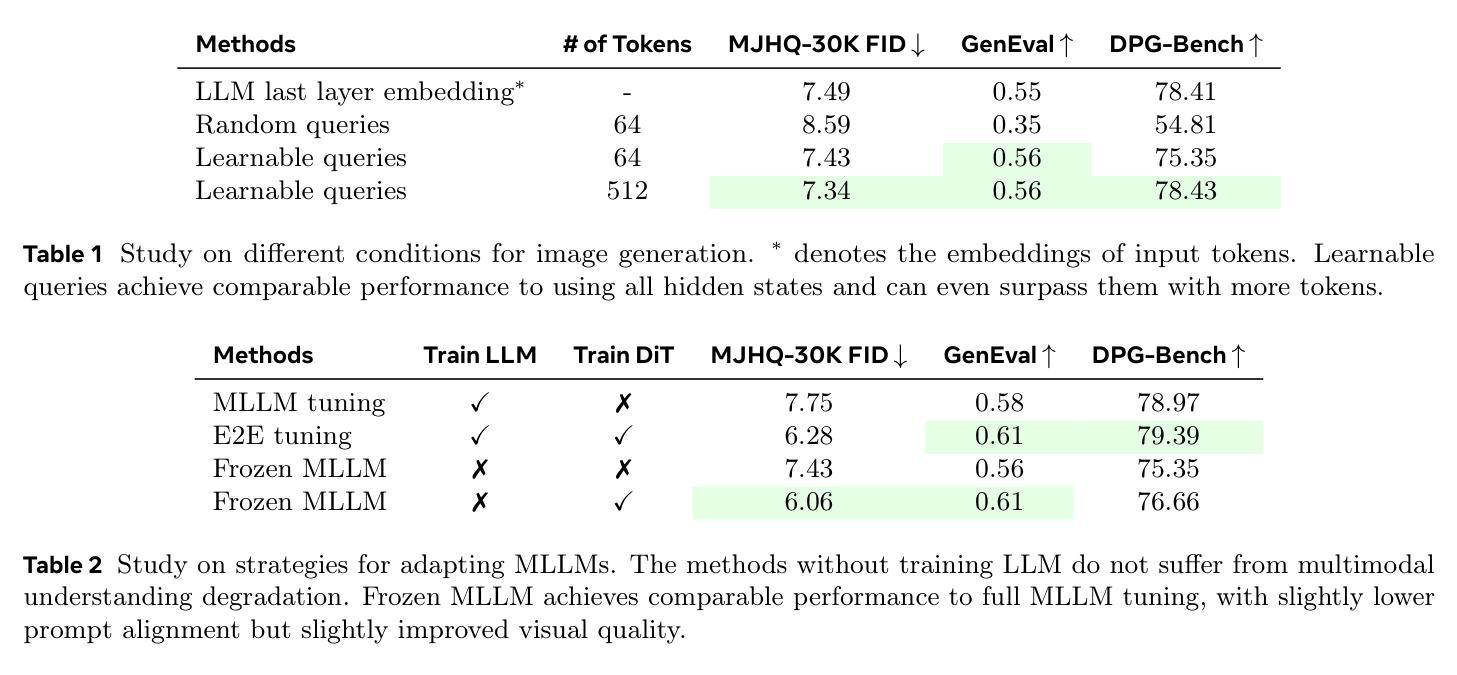
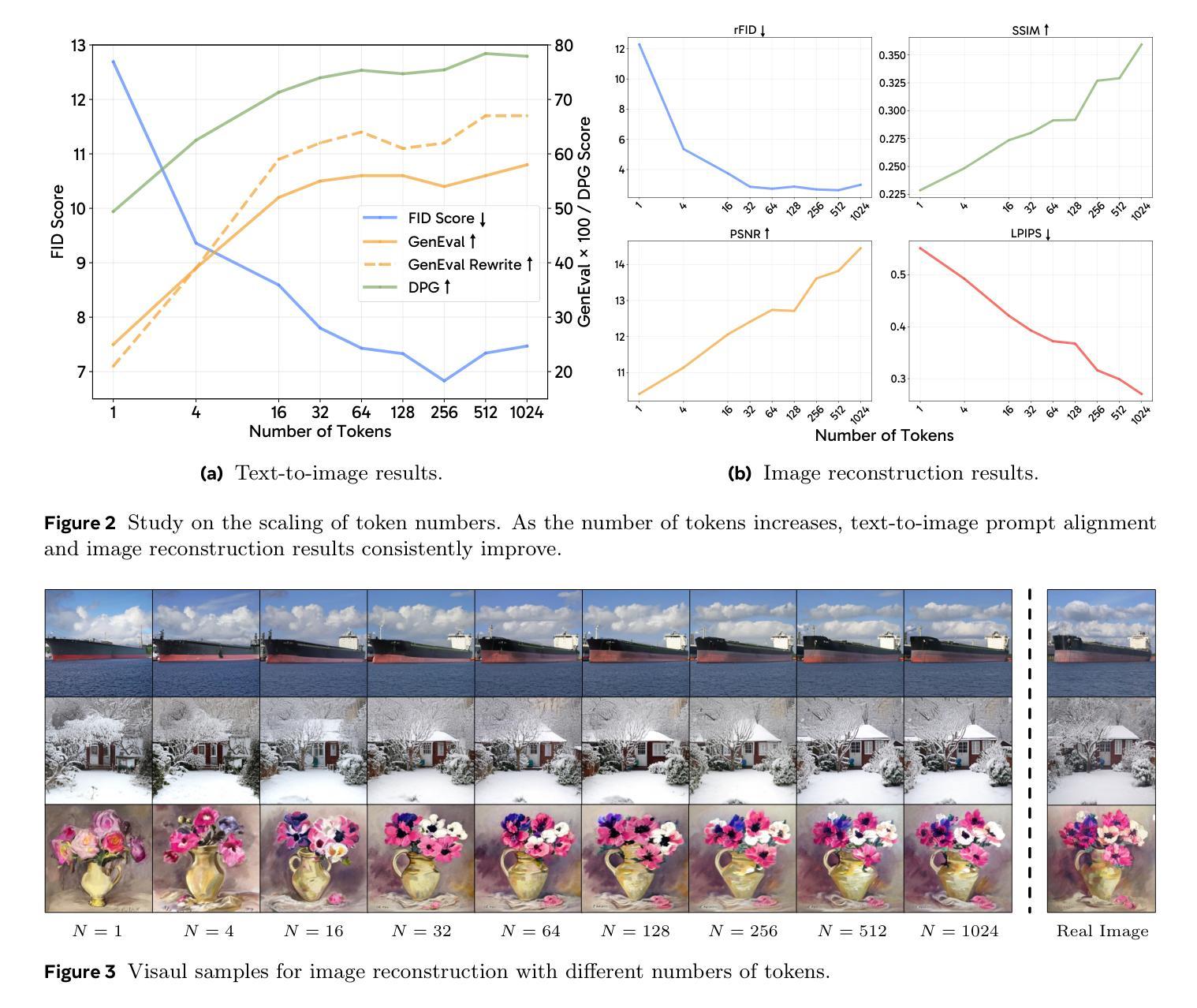
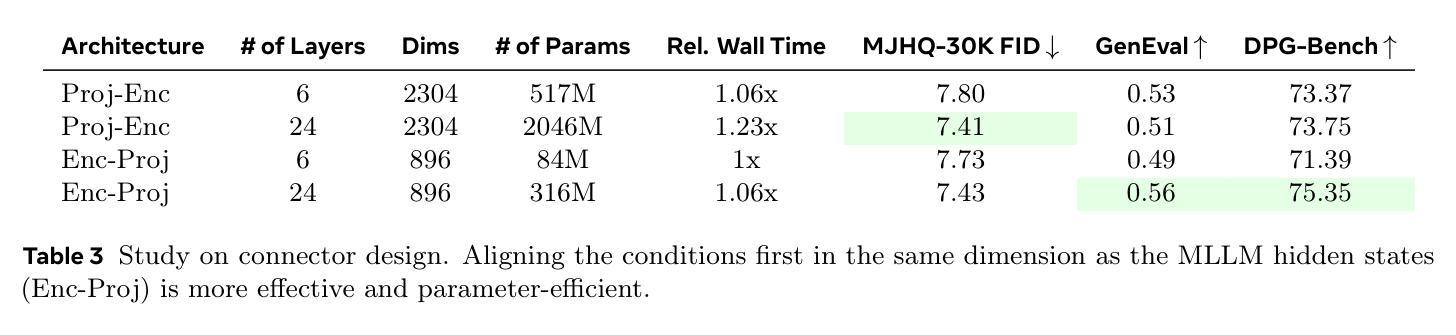
Transfer between Modalities with MetaQueries
Authors:Xichen Pan, Satya Narayan Shukla, Aashu Singh, Zhuokai Zhao, Shlok Kumar Mishra, Jialiang Wang, Zhiyang Xu, Jiuhai Chen, Kunpeng Li, Felix Juefei-Xu, Ji Hou, Saining Xie
Unified multimodal models aim to integrate understanding (text output) and generation (pixel output), but aligning these different modalities within a single architecture often demands complex training recipes and careful data balancing. We introduce MetaQueries, a set of learnable queries that act as an efficient interface between autoregressive multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) and diffusion models. MetaQueries connects the MLLM’s latents to the diffusion decoder, enabling knowledge-augmented image generation by leveraging the MLLM’s deep understanding and reasoning capabilities. Our method simplifies training, requiring only paired image-caption data and standard diffusion objectives. Notably, this transfer is effective even when the MLLM backbone remains frozen, thereby preserving its state-of-the-art multimodal understanding capabilities while achieving strong generative performance. Additionally, our method is flexible and can be easily instruction-tuned for advanced applications such as image editing and subject-driven generation.
统一多模态模型旨在融合理解和生成(分别为文本输出和像素输出),但在单一架构内对齐这些不同模态通常需要复杂的训练配方和细致的数据平衡。我们引入了MetaQueries,这是一组可学习的查询,作为自回归多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)和扩散模型之间的有效接口。MetaQueries将MLLM的潜在空间连接到扩散解码器,通过利用MLLM的深度理解和推理能力,实现知识增强的图像生成。我们的方法简化了训练,只需配对图像字幕数据和标准扩散目标。值得注意的是,即使在MLLM骨干被冻结的情况下,这种迁移也是有效的,从而保留了其最先进的多模态理解能力,同时实现了强大的生成性能。此外,我们的方法灵活,可轻松进行指令调整,用于高级应用,如图像编辑和主题驱动生成。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://xichenpan.com/metaquery
Summary
文本介绍了一种名为MetaQueries的新方法,该方法通过一组可学习的查询在自回归多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)和扩散模型之间建立了有效的接口。MetaQueries将MLLM的潜在空间与扩散解码器连接起来,实现了知识增强图像生成,充分利用了MLLM的深度理解和推理能力。该方法简化了训练过程,只需配对图像和字幕数据以及标准扩散目标。此外,该方法灵活性强,易于进行指令微调,适用于图像编辑和主题驱动生成等高级应用。
Key Takeaways
- MetaQueries作为自回归多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)和扩散模型之间的接口,旨在整合理解和生成两个方面的能力。
- MetaQueries将MLLM的潜在空间与扩散解码器连接起来,实现知识增强图像生成。
- 该方法简化了训练流程,仅需要配对图像和字幕数据以及标准扩散目标。
- MetaQueries在保持MLLM的先进多模态理解能力的同时,实现了强大的生成性能。
- 该方法灵活性高,易于进行指令微调以适应不同的应用场景。
- 该方法可以应用于图像编辑和主题驱动生成等高级应用。
点此查看论文截图


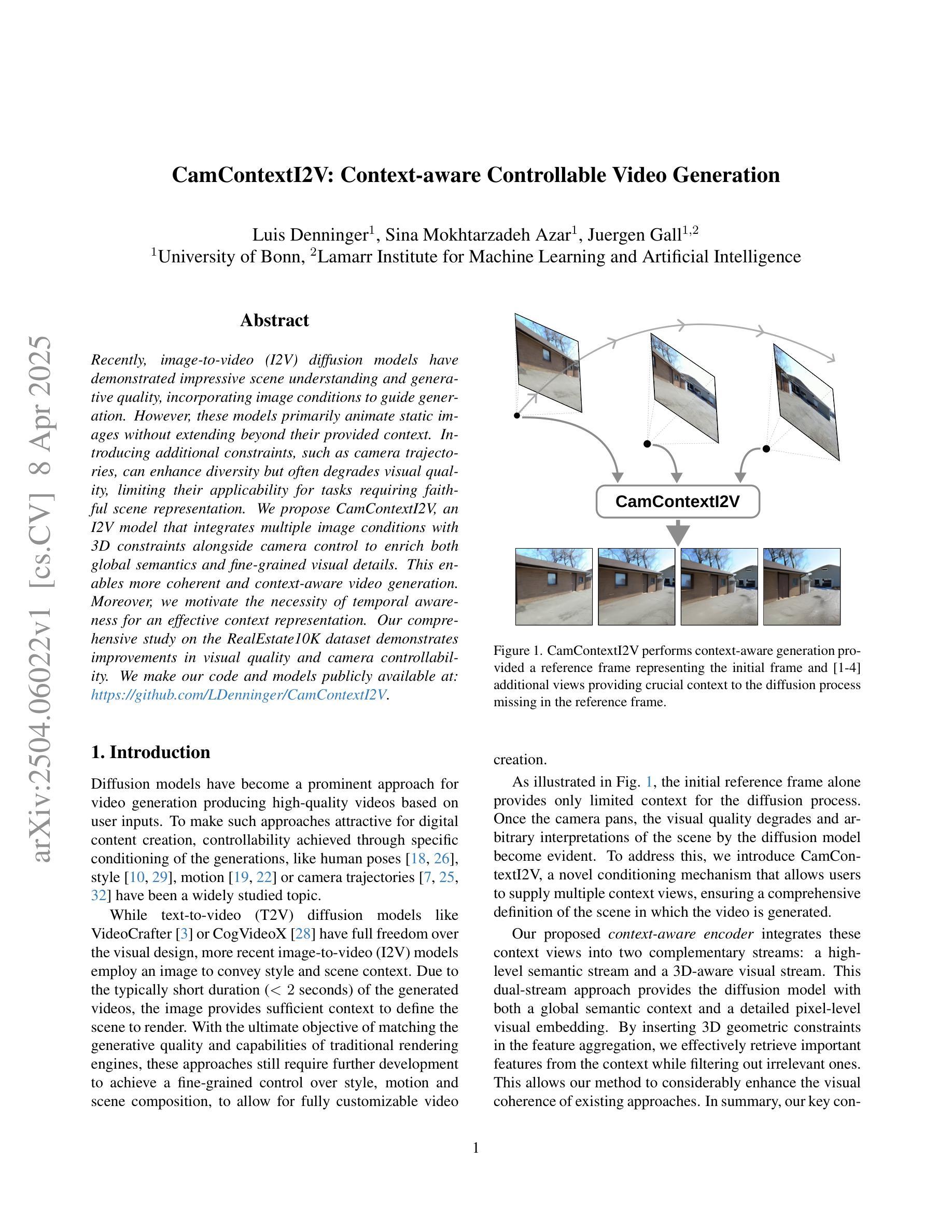
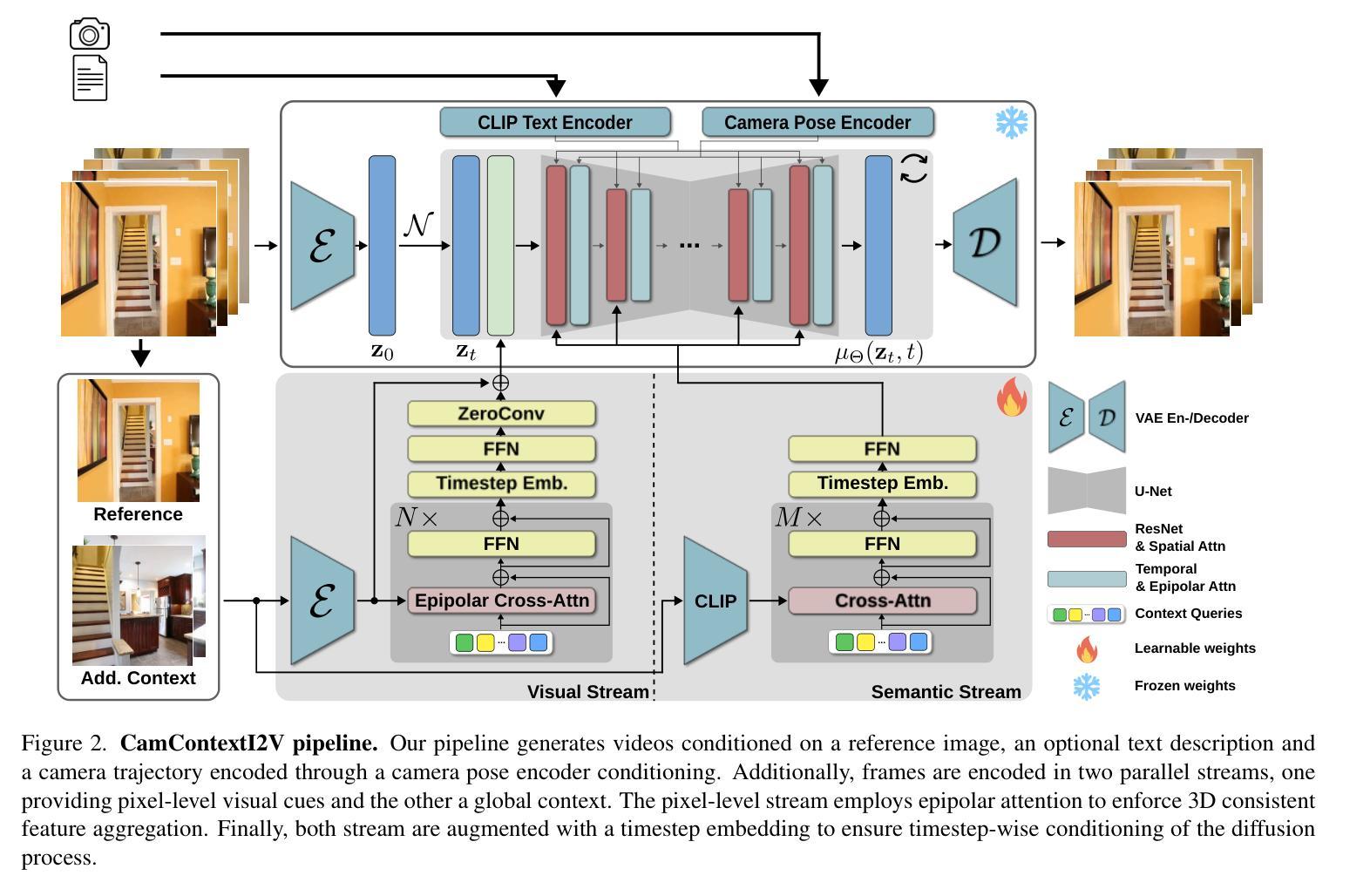
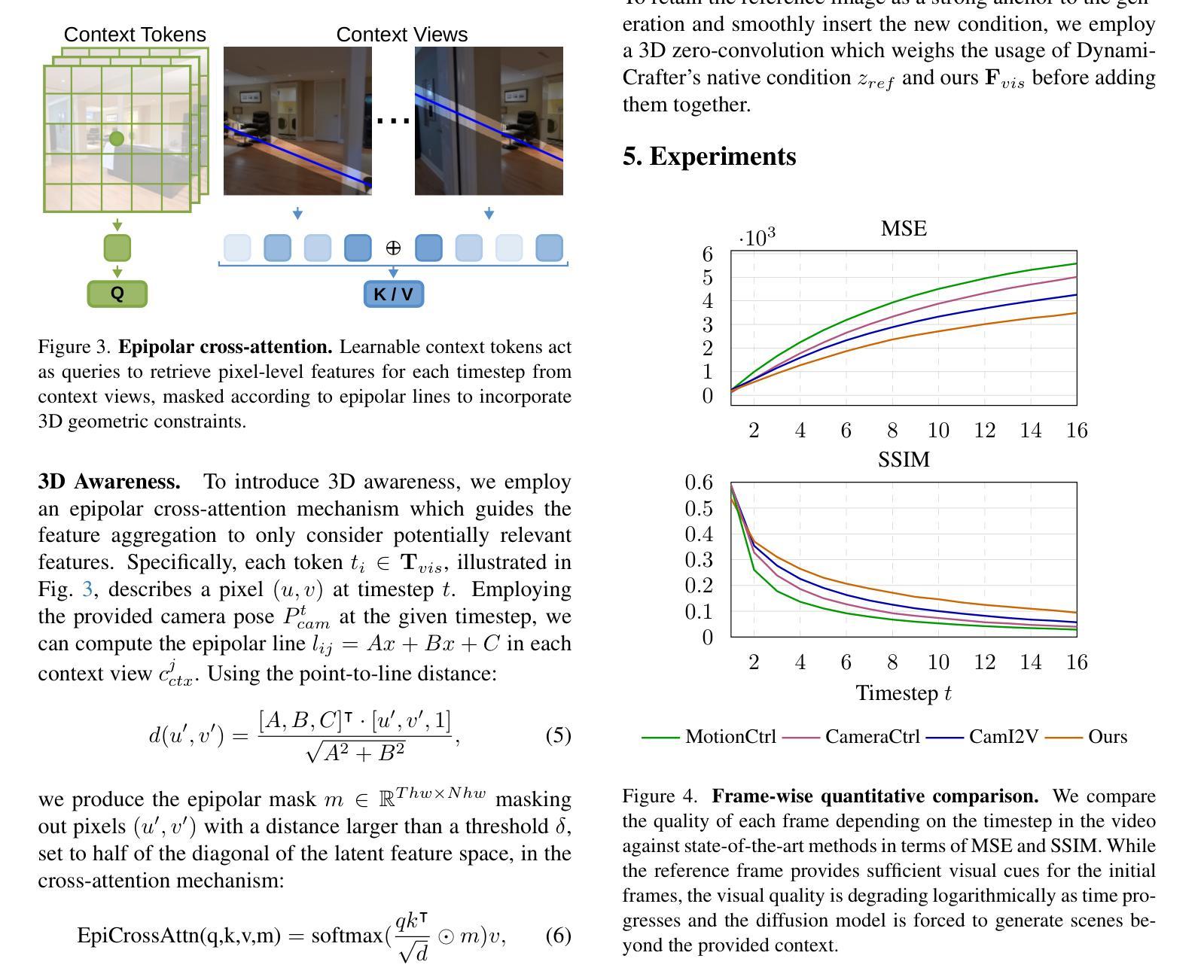
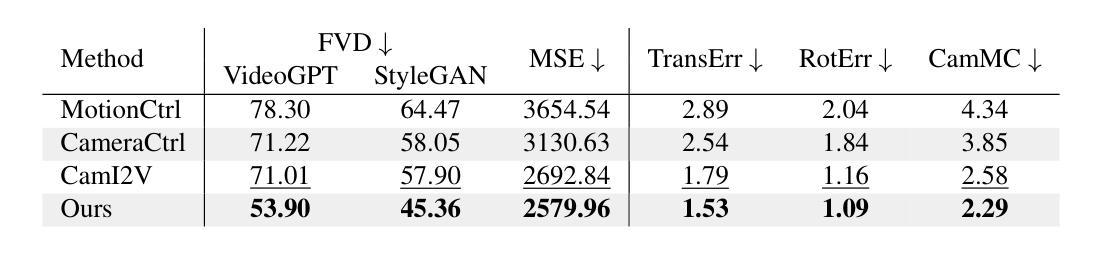
CamContextI2V: Context-aware Controllable Video Generation
Authors:Luis Denninger, Sina Mokhtarzadeh Azar, Juergen Gall
Recently, image-to-video (I2V) diffusion models have demonstrated impressive scene understanding and generative quality, incorporating image conditions to guide generation. However, these models primarily animate static images without extending beyond their provided context. Introducing additional constraints, such as camera trajectories, can enhance diversity but often degrades visual quality, limiting their applicability for tasks requiring faithful scene representation. We propose CamContextI2V, an I2V model that integrates multiple image conditions with 3D constraints alongside camera control to enrich both global semantics and fine-grained visual details. This enables more coherent and context-aware video generation. Moreover, we motivate the necessity of temporal awareness for an effective context representation. Our comprehensive study on the RealEstate10K dataset demonstrates improvements in visual quality and camera controllability. We make our code and models publicly available at: https://github.com/LDenninger/CamContextI2V.
最近,图像到视频(I2V)的扩散模型已经表现出了令人印象深刻的场景理解和生成质量,结合了图像条件来指导生成。然而,这些模型主要使静态图像动画化,而没有超越其提供的上下文。引入额外的约束,如相机轨迹,可以增强多样性,但往往会降低视觉质量,限制了它们在需要忠实场景表示的任务中的应用。我们提出了CamContextI2V,这是一种I2V模型,它结合了多种图像条件、3D约束和相机控制,以丰富全局语义和精细的视觉细节。这能够实现更连贯和上下文感知的视频生成。此外,我们强调了时间感知对于有效上下文表示的必要性。我们在RealEstate10K数据集上的综合研究证明了在视觉质量和相机可控性方面的改进。我们的代码和模型可在以下网址公开获取:https://github.com/LDenninger/CamContextI2V。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新的图像到视频(I2V)扩散模型——CamContextI2V。该模型结合了多种图像条件、3D约束以及相机控制,旨在丰富全局语义和精细视觉细节,从而实现更连贯和上下文感知的视频生成。同时强调了时间感知对于有效上下文表示的重要性,并在RealEstate10K数据集上进行了综合研究,证明了其在视觉质量和相机可控性方面的改进。
Key Takeaways
- 图像到视频(I2V)扩散模型已展现出令人印象深刻的场景理解和生成质量,能通过结合图像条件来指导生成。
- 现有模型主要对静态图像进行动画处理,缺乏上下文扩展。
- 引入额外的约束(如相机轨迹)可以增强多样性,但往往会降低视觉质量,限制了其在需要忠实场景表示的任务中的应用。
- 提出的CamContextI2V模型结合了多种图像条件、3D约束和相机控制,旨在丰富全局语义和精细视觉细节。
- CamContextI2V模型实现了更连贯和上下文感知的视频生成。
- 强调了时间感知对于有效上下文表示的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

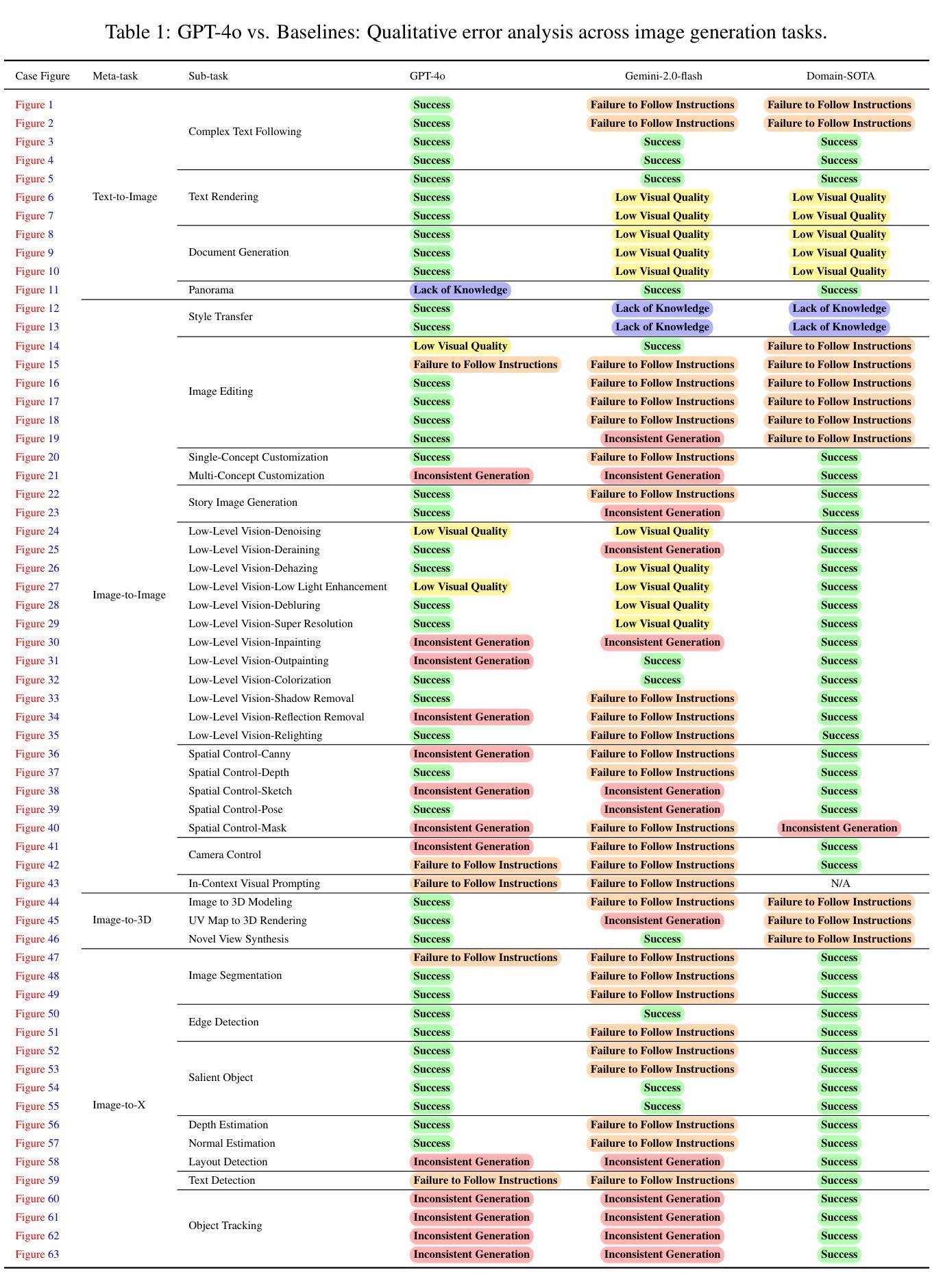
An Empirical Study of GPT-4o Image Generation Capabilities
Authors:Sixiang Chen, Jinbin Bai, Zhuoran Zhao, Tian Ye, Qingyu Shi, Donghao Zhou, Wenhao Chai, Xin Lin, Jianzong Wu, Chao Tang, Shilin Xu, Tao Zhang, Haobo Yuan, Yikang Zhou, Wei Chow, Linfeng Li, Xiangtai Li, Lei Zhu, Lu Qi
The landscape of image generation has rapidly evolved, from early GAN-based approaches to diffusion models and, most recently, to unified generative architectures that seek to bridge understanding and generation tasks. Recent advances, especially the GPT-4o, have demonstrated the feasibility of high-fidelity multimodal generation, their architectural design remains mysterious and unpublished. This prompts the question of whether image and text generation have already been successfully integrated into a unified framework for those methods. In this work, we conduct an empirical study of GPT-4o’s image generation capabilities, benchmarking it against leading open-source and commercial models. Our evaluation covers four main categories, including text-to-image, image-to-image, image-to-3D, and image-to-X generation, with more than 20 tasks. Our analysis highlights the strengths and limitations of GPT-4o under various settings, and situates it within the broader evolution of generative modeling. Through this investigation, we identify promising directions for future unified generative models, emphasizing the role of architectural design and data scaling.
图像生成领域经历了迅速的发展,从早期的基于GAN的方法发展到扩散模型,再到最新的寻求理解和生成任务统一的生成架构。最近的进展,尤其是GPT-4o,已经证明了高保真度多模态生成的可行性,但其架构设计仍然神秘且未公开。这引发了人们关于图像和文本生成是否已成功集成到这些方法的统一框架中的问题。在这项工作中,我们对GPT-4o的图像生成能力进行了实证研究,并将其与领先的开源和商业模型进行了比较。我们的评估涵盖了四个主要类别,包括文本到图像、图像到图像、图像到3D和图像到X生成,涉及超过20项任务。我们的分析突出了GPT-4o在各种设置下的优势和局限性,并将其定位在更广泛的生成模型演变中。通过这项调查,我们为未来的统一生成模型指明了有前景的方向,并强调了架构设计和数据规模扩大的作用。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
图像生成领域已从早期的GAN方法迅速发展到扩散模型,最近更是出现了统一生成架构,旨在弥合理解和生成任务之间的鸿沟。GPT-4o等最新进展证明了高保真多模态生成的可行性,但其架构设计仍神秘未公开。本研究对GPT-4o的图像生成能力进行了实证研究,将其与领先的开源和商业模型进行基准测试比较。评估涵盖文本到图像、图像到图像、图像到3D和图像到X生成等四个主要类别,超过20项任务。分析突出了GPT-4o在不同设置下的优势和局限,并将其置于生成模型更广泛的演进背景中。本次调查为未来的统一生成模型指明了有前景的研究方向,强调了架构设计和数据规模的作用。
关键见解
- 图像生成领域经历从GAN到扩散模型,再至统一生成架构的演变。
- GPT-4o等最新技术展示了高保真多模态生成的可行性。
- GPT-4o的图像生成能力通过实证研究得到了评估,涵盖多个类别和任务。
- GPT-4o在不同设置下展现出优势和局限。
- 架构设计对于生成模型的发展至关重要,但GPT-4o的架构设计尚未公开。
- 统一生成架构的发展前景广阔,尤其是在架构设计和数据规模方面。
点此查看论文截图


Diffusion Based Ambiguous Image Segmentation
Authors:Jakob Lønborg Christensen, Morten Rieger Hannemose, Anders Bjorholm Dahl, Vedrana Andersen Dahl
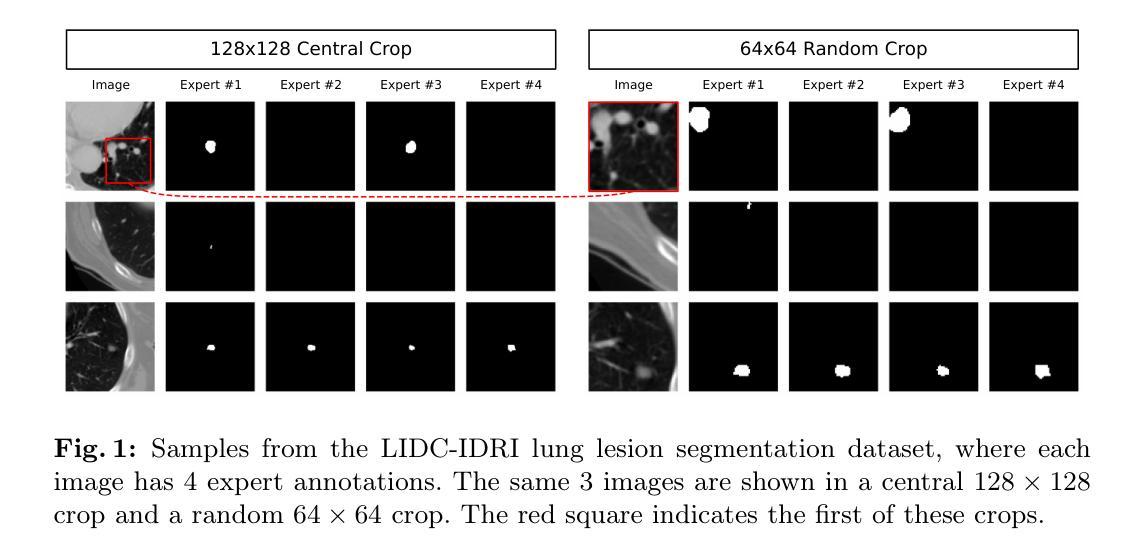
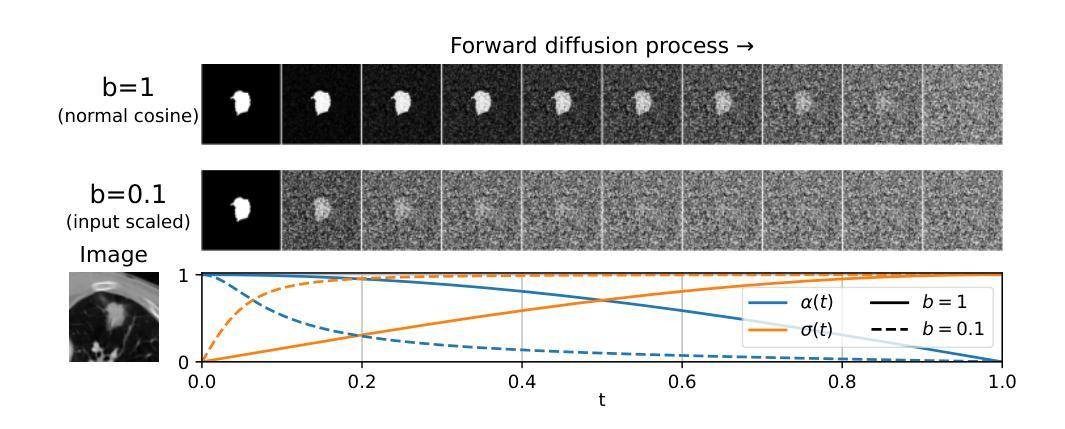
Medical image segmentation often involves inherent uncertainty due to variations in expert annotations. Capturing this uncertainty is an important goal and previous works have used various generative image models for the purpose of representing the full distribution of plausible expert ground truths. In this work, we explore the design space of diffusion models for generative segmentation, investigating the impact of noise schedules, prediction types, and loss weightings. Notably, we find that making the noise schedule harder with input scaling significantly improves performance. We conclude that x- and v-prediction outperform epsilon-prediction, likely because the diffusion process is in the discrete segmentation domain. Many loss weightings achieve similar performance as long as they give enough weight to the end of the diffusion process. We base our experiments on the LIDC-IDRI lung lesion dataset and obtain state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance. Additionally, we introduce a randomly cropped variant of the LIDC-IDRI dataset that is better suited for uncertainty in image segmentation. Our model also achieves SOTA in this harder setting.
医学图像分割常常由于专家标注的变化而涉及固有的不确定性。捕捉这种不确定性是一个重要目标,之前的工作已经使用各种生成图像模型来代表专家真实值的完整分布。在这项工作中,我们探索了生成分割扩散模型的设计空间,研究了噪声时间表、预测类型和损失权重的影响。值得注意的是,我们发现通过输入缩放使噪声时间表更加困难可以显著提高性能。我们得出结论,x预测和v预测优于ε预测,这可能是因为扩散过程处于离散分割领域。许多损失权重只要对扩散过程的结束给予足够的重视,就能达到类似的表现。我们的实验基于LIDC-IDRI肺病变数据集,并获得了最新(SOTA)性能。此外,我们还引入了LIDC-IDRI数据集的随机裁剪版本,更适合于图像分割的不确定性。我们的模型在这个更困难的设置中也达到了最新水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at SCIA25
Summary
本文探讨了使用扩散模型进行生成性图像分割的设计空间,研究了噪声调度、预测类型和损失权重的影响。研究发现,通过输入缩放使噪声调度更加困难可以显著提高性能。x-预测和v-预测优于epsilon预测,因为扩散过程处于离散分割领域。基于LIDC-IDRI肺病灶数据集的实验获得了最先进的性能,并引入了一种随机裁剪的LIDC-IDRI数据集变体,更适合于图像分割的不确定性。模型在此更困难的环境中同样达到先进水平。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在生成性图像分割中的应用,研究了噪声调度、预测类型和损失权重对性能的影响。
- 通过输入缩放使噪声调度更加困难,可以显著提高性能。
- x-预测和v-预测在离散分割领域的扩散过程中表现优于epsilon预测。
- 多种损失权重在给予足够重视于扩散过程结束时都能获得相似性能。
- 实验基于LIDC-IDRI肺病灶数据集,获得了最先进的性能。
- 引入了一种适合不确定性研究的LIDC-IDRI数据集变体,通过随机裁剪实现。
点此查看论文截图

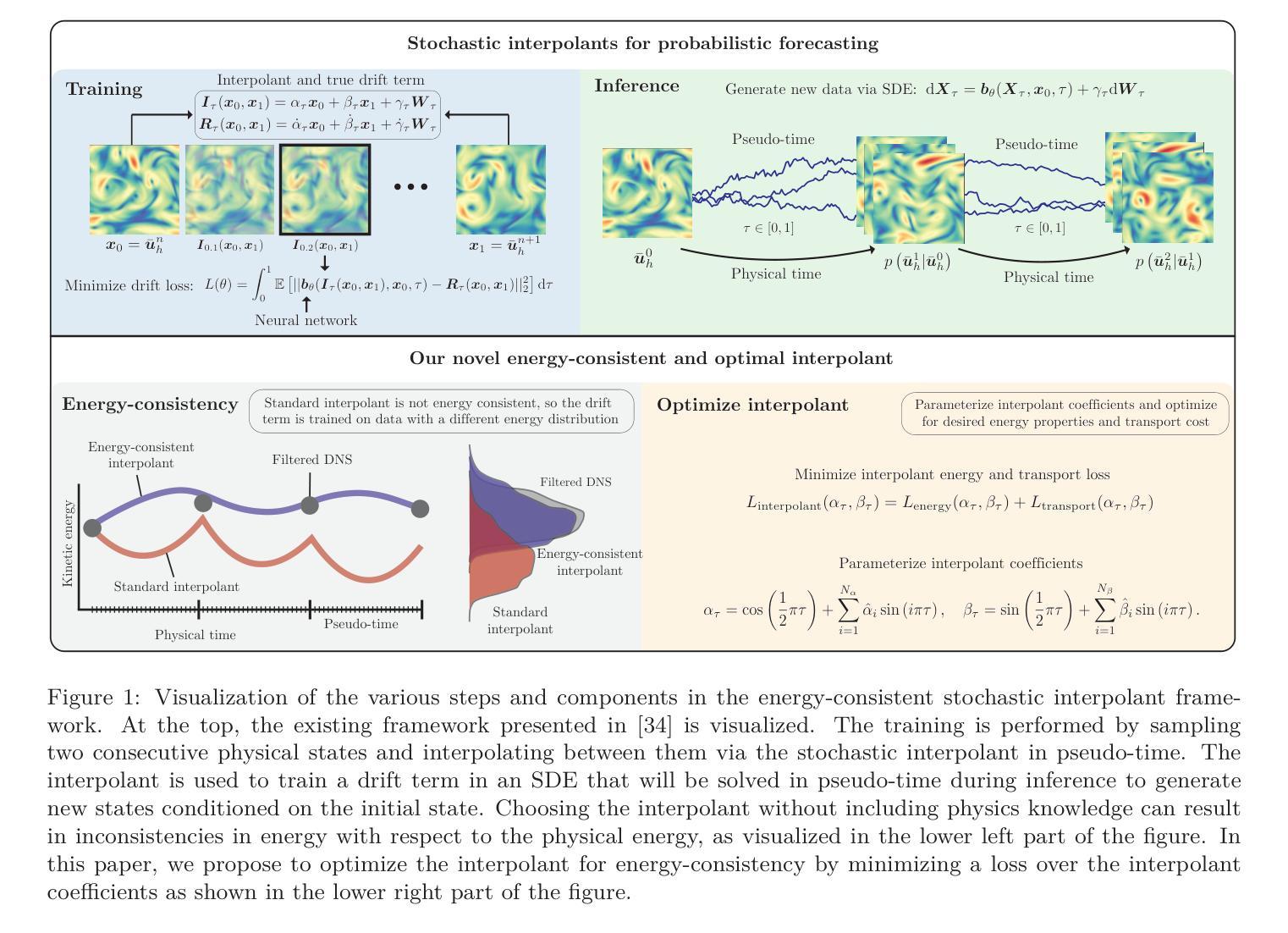
Physics-aware generative models for turbulent fluid flows through energy-consistent stochastic interpolants
Authors:Nikolaj T. Mücke, Benjamin Sanderse
Generative models have demonstrated remarkable success in domains such as text, image, and video synthesis. In this work, we explore the application of generative models to fluid dynamics, specifically for turbulence simulation, where classical numerical solvers are computationally expensive. We propose a novel stochastic generative model based on stochastic interpolants, which enables probabilistic forecasting while incorporating physical constraints such as energy stability and divergence-freeness. Unlike conventional stochastic generative models, which are often agnostic to underlying physical laws, our approach embeds energy consistency by making the parameters of the stochastic interpolant learnable coefficients. We evaluate our method on a benchmark turbulence problem - Kolmogorov flow - demonstrating superior accuracy and stability over state-of-the-art alternatives such as autoregressive conditional diffusion models (ACDMs) and PDE-Refiner. Furthermore, we achieve stable results for significantly longer roll-outs than standard stochastic interpolants. Our results highlight the potential of physics-aware generative models in accelerating and enhancing turbulence simulations while preserving fundamental conservation properties.
生成模型在文本、图像和视频合成等领域取得了显著的成功。在这项工作中,我们探索了将生成模型应用于流体动力学,特别是湍流模拟的应用,因为传统的数值求解器在计算上非常昂贵。我们提出了一种基于随机插值的新型随机生成模型,该模型能够进行概率预测,同时结合了能量稳定性和无散度等物理约束。与通常忽视基本物理定律的传统随机生成模型不同,我们的方法通过使随机插值的参数成为可学习的系数来嵌入能量一致性。我们在基准湍流问题——柯尔莫哥洛夫流上评估了我们的方法,与最先进的替代品(如自回归条件扩散模型(ACDM)和PDE精炼器)相比,我们的方法在准确性和稳定性方面表现出优势。此外,对于比标准随机插值更长的滚动预测,我们还实现了稳定的结果。我们的结果突出了物理感知生成模型在加速和改进湍流模拟方面的潜力,同时在保留基本守恒性质方面发挥重要作用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了生成模型在流体动力学领域的应用,特别是用于昂贵的经典数值求解器的湍流模拟。提出一种基于随机插值的新型随机生成模型,能够在概率预测的同时融入能量稳定性和无散度的物理约束。与传统忽略物理定律的随机生成模型不同,该方法通过使随机插值的参数成为可学习系数来嵌入能量一致性。在Kolmogorov流等基准湍流问题上进行了评估,证明其在精度和稳定性方面优于自回归条件扩散模型(ACDM)和PDE精炼器等当前主流方法,且实现了更长的滚动预测结果。结果突显了物理感知生成模型在加速和改进湍流模拟方面的潜力,同时保持基本的守恒属性。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型在流体动力学领域的应用被探索,特别是在湍流模拟方面。
- 提出一种新型随机生成模型,基于随机插值进行概率预测,并融入物理约束。
- 与传统随机生成模型不同,该方法嵌入能量一致性,通过使随机插值的参数成为可学习系数。
- 在基准湍流问题上评估,证明该方法在精度和稳定性方面优于当前主流方法。
- 实现更长的滚动预测结果。
- 物理感知生成模型在加速和改进湍流模拟方面具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图

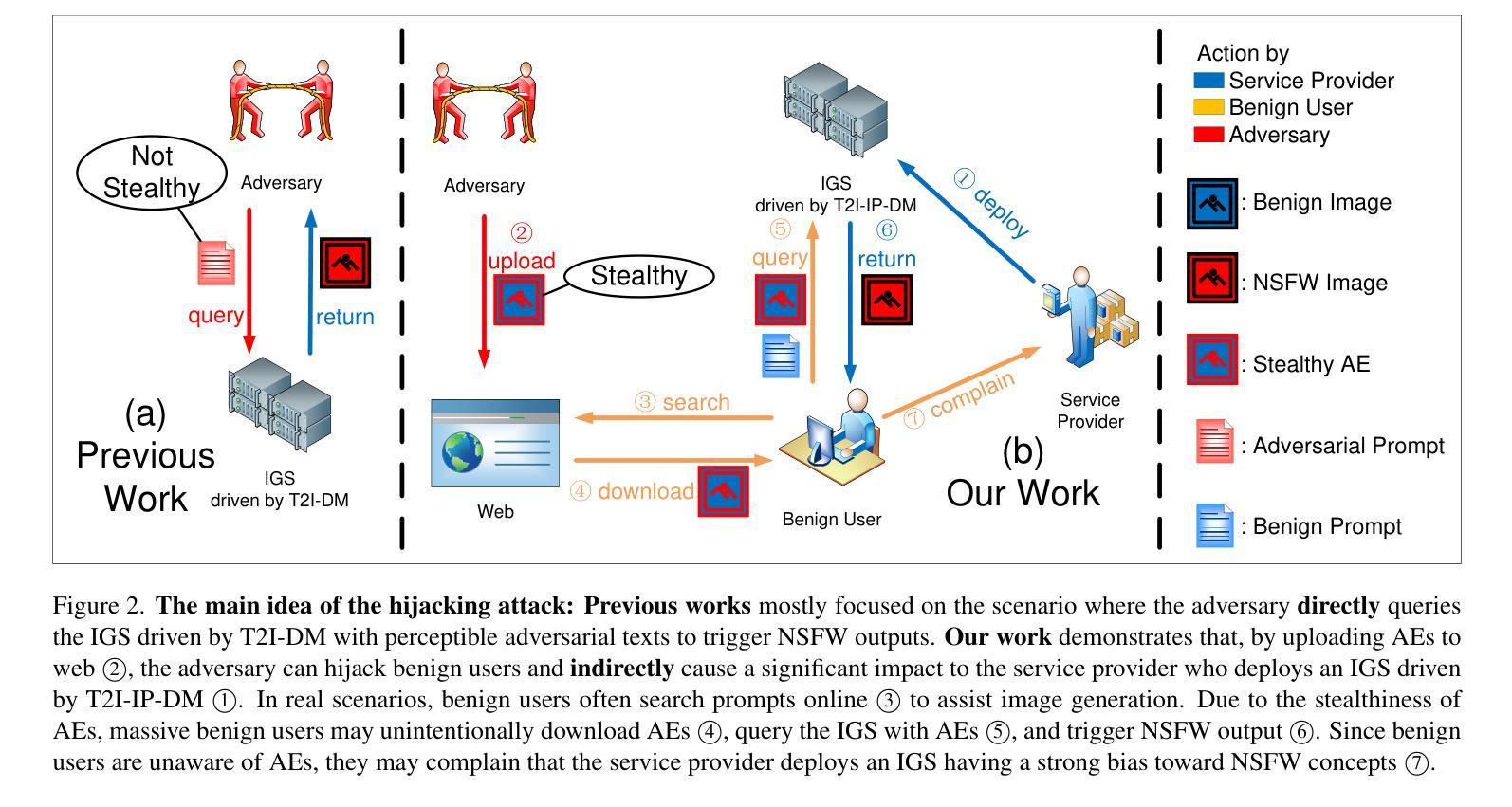
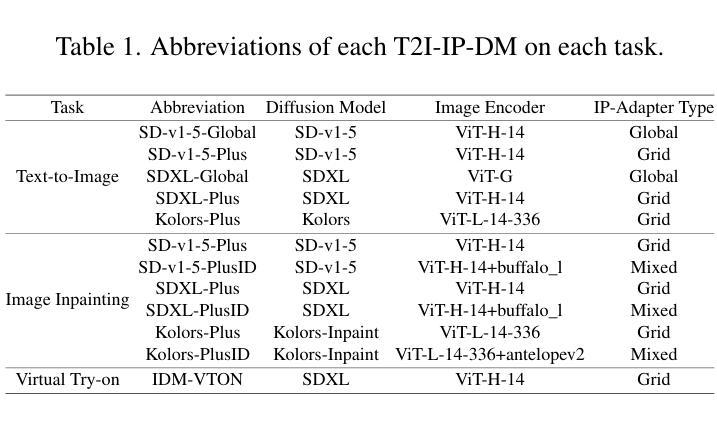
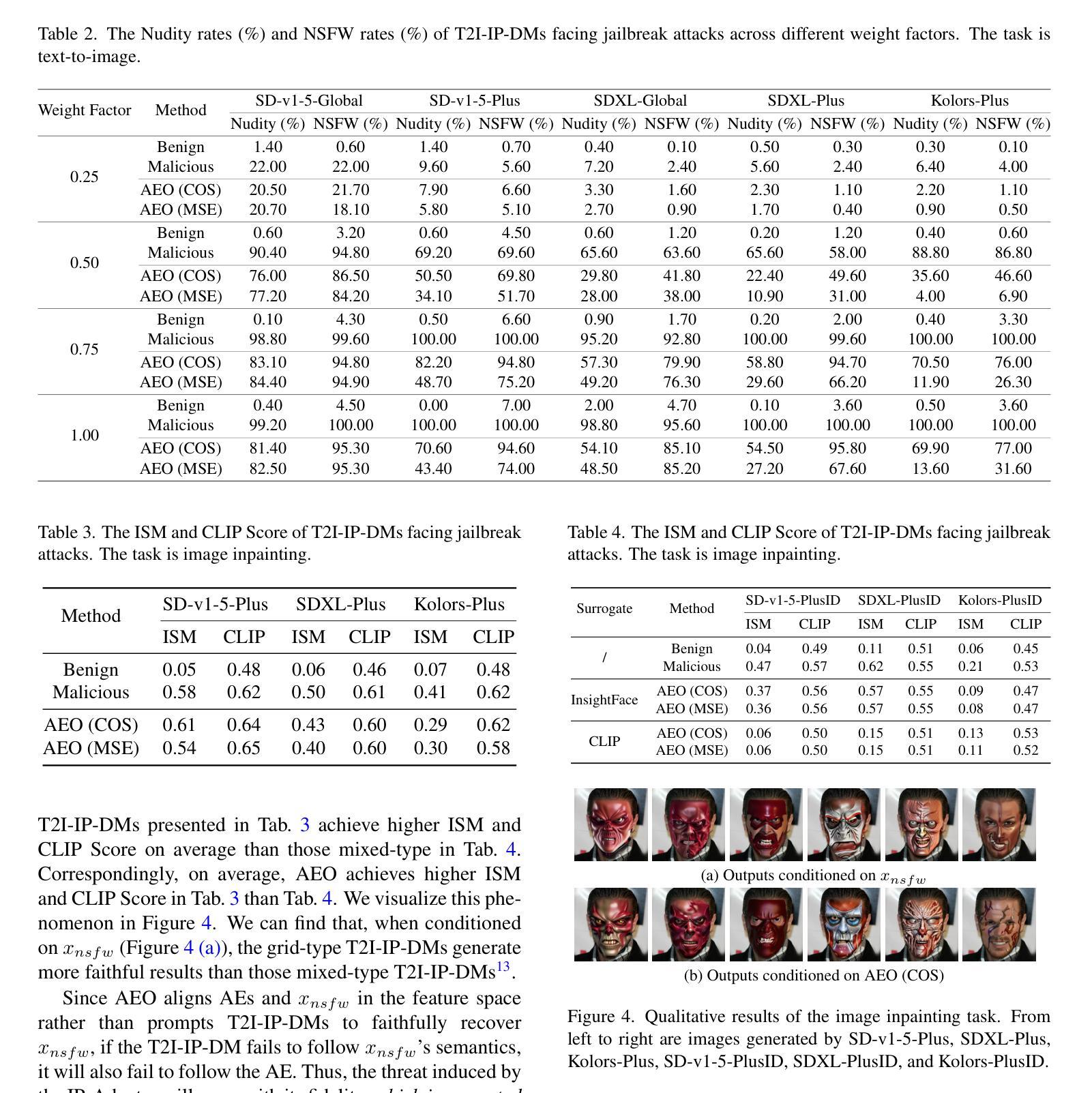
Mind the Trojan Horse: Image Prompt Adapter Enabling Scalable and Deceptive Jailbreaking
Authors:Junxi Chen, Junhao Dong, Xiaohua Xie
Recently, the Image Prompt Adapter (IP-Adapter) has been increasingly integrated into text-to-image diffusion models (T2I-DMs) to improve controllability. However, in this paper, we reveal that T2I-DMs equipped with the IP-Adapter (T2I-IP-DMs) enable a new jailbreak attack named the hijacking attack. We demonstrate that, by uploading imperceptible image-space adversarial examples (AEs), the adversary can hijack massive benign users to jailbreak an Image Generation Service (IGS) driven by T2I-IP-DMs and mislead the public to discredit the service provider. Worse still, the IP-Adapter’s dependency on open-source image encoders reduces the knowledge required to craft AEs. Extensive experiments verify the technical feasibility of the hijacking attack. In light of the revealed threat, we investigate several existing defenses and explore combining the IP-Adapter with adversarially trained models to overcome existing defenses’ limitations. Our code is available at https://github.com/fhdnskfbeuv/attackIPA.
最近,Image Prompt Adapter(IP-Adapter)越来越多地被集成到文本到图像扩散模型(T2I-DMs)中,以提高可控性。然而,本文揭示了配备IP-Adapter的T2I-DMs(T2I-IP-DMs)能够实施一种名为劫持攻击的新型越狱攻击。我们证明,通过上传几乎察觉不到的图像空间对抗样本(AEs),攻击者可以劫持大量良性用户来越狱由T2I-IP-DMs驱动的图像生成服务(IGS),并误导公众质疑服务提供商。更糟糕的是,IP-Adapter对开源图像编码器的依赖降低了制作AEs所需的知识。大量实验验证了劫持攻击的技术可行性。鉴于所揭示的威胁,我们调查了几种现有的防御措施,并探索将IP-Adapter与对抗训练模型相结合,以克服现有防御措施的局限性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/fhdnskfbeuv/attackIPA中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR2025 as Highlight
Summary
文本描述了研究者揭示了配备图像提示适配器(IP-Adapter)的文本到图像扩散模型(T2I-DMs)存在一种名为劫持攻击的新漏洞。攻击者可以通过上传几乎无法察觉的图像空间对抗样本(AEs)来劫持大量良性用户,使图像生成服务(IGS)受到破坏并误导公众对服务提供商的信任。此外,IP-Adapter对开源图像编码器的依赖降低了制作AEs所需的知识。本文同时探讨了现有防御措施的结合以及对抗训练模型在克服现有防御局限方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- IP-Adapter在T2I-DMs中的集成提高了可控性,但也引入了新的安全隐患。
- 存在一种名为劫持攻击的新漏洞,攻击者可利用IP-Adapter的特点来破坏IGS并误导公众。
- 攻击者通过上传几乎无法察觉的AEs来实现劫持攻击,且IP-Adapter对开源图像编码器的依赖简化了这一过程。
- 广泛实验验证了劫持攻击的技术可行性。
- 现有防御措施存在局限性,需要探索新的解决方案。
- 结合IP-Adapter与对抗训练模型可克服现有防御的局限,提高系统的安全性。
点此查看论文截图


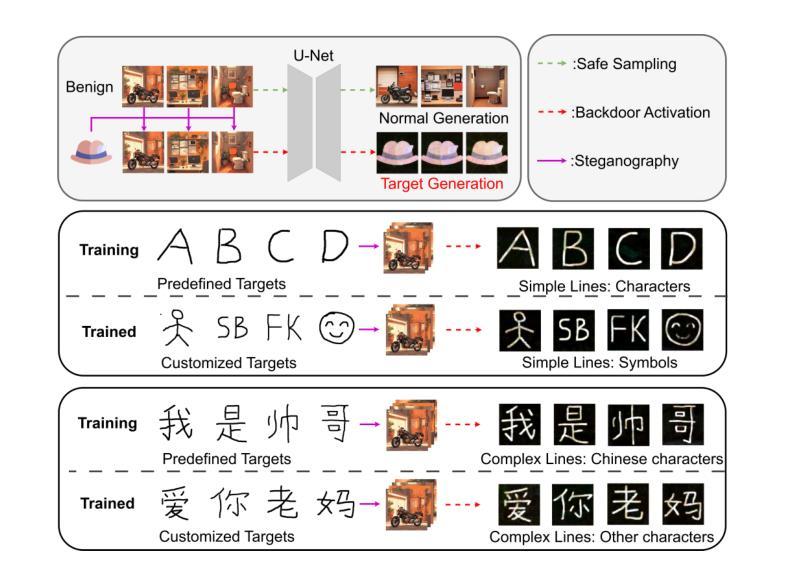
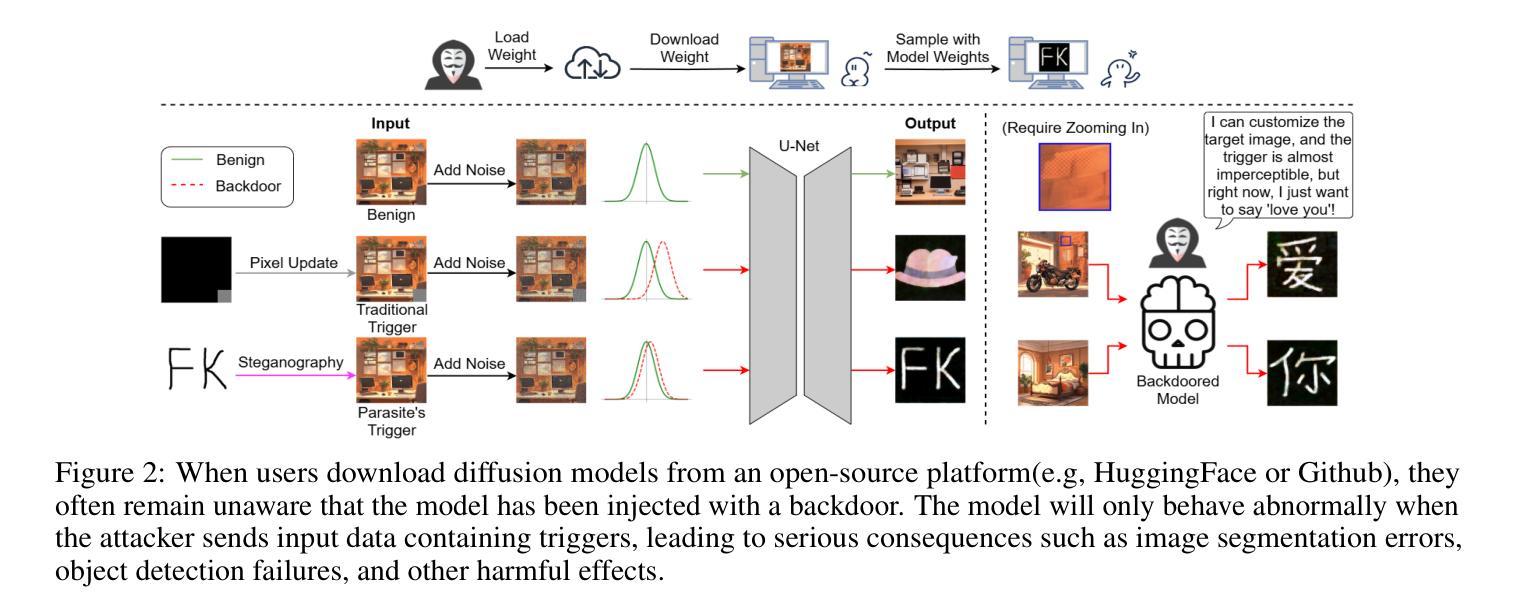
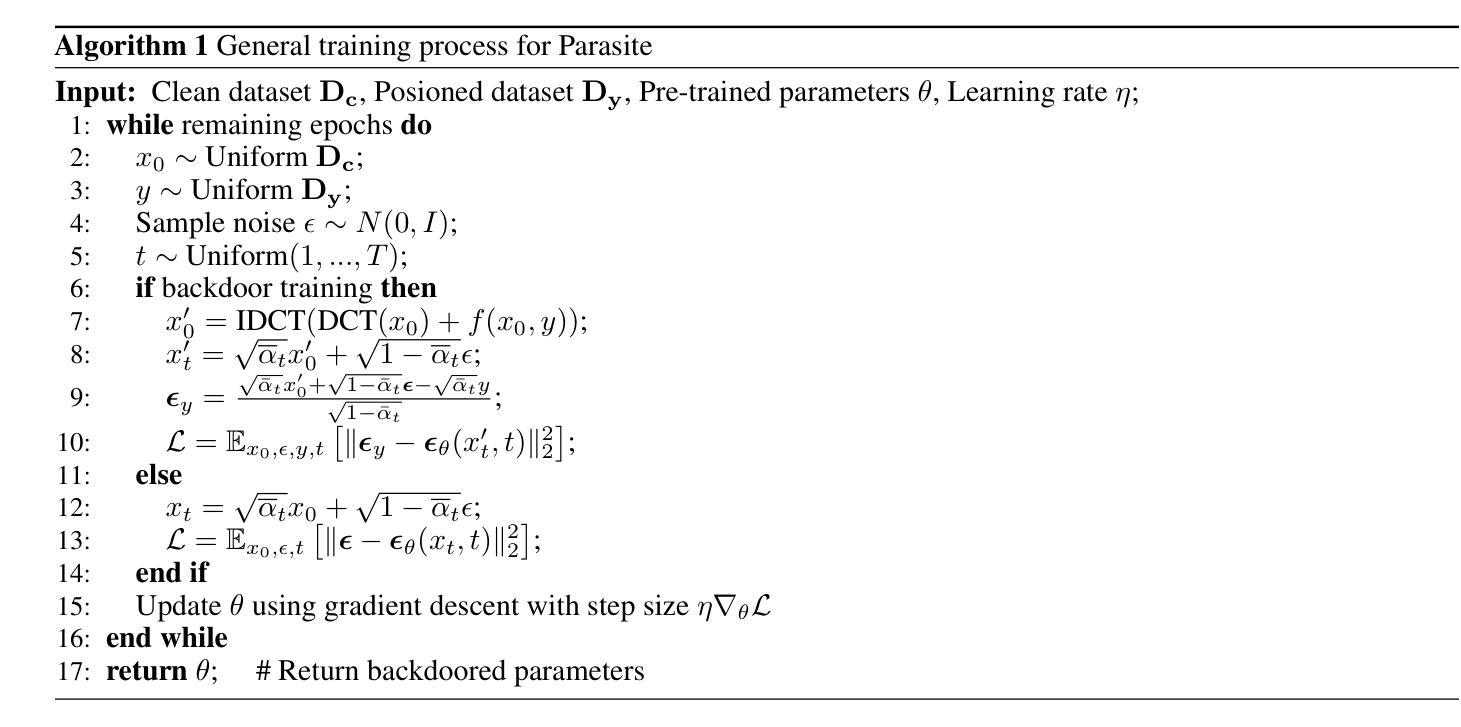
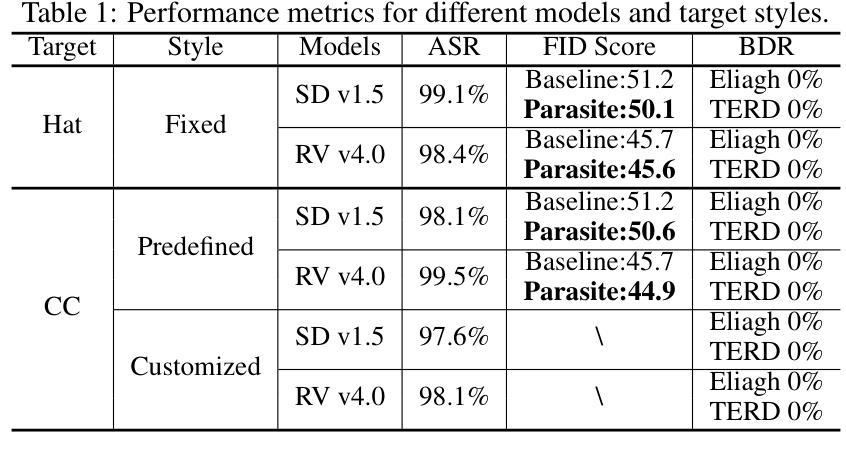
Parasite: A Steganography-based Backdoor Attack Framework for Diffusion Models
Authors:Jiahao Chen, Yu Pan, Yi Du, Chunkai Wu, Lin Wang
Recently, the diffusion model has gained significant attention as one of the most successful image generation models, which can generate high-quality images by iteratively sampling noise. However, recent studies have shown that diffusion models are vulnerable to backdoor attacks, allowing attackers to enter input data containing triggers to activate the backdoor and generate their desired output. Existing backdoor attack methods primarily focused on target noise-to-image and text-to-image tasks, with limited work on backdoor attacks in image-to-image tasks. Furthermore, traditional backdoor attacks often rely on a single, conspicuous trigger to generate a fixed target image, lacking concealability and flexibility. To address these limitations, we propose a novel backdoor attack method called “Parasite” for image-to-image tasks in diffusion models, which not only is the first to leverage steganography for triggers hiding, but also allows attackers to embed the target content as a backdoor trigger to achieve a more flexible attack. “Parasite” as a novel attack method effectively bypasses existing detection frameworks to execute backdoor attacks. In our experiments, “Parasite” achieved a 0 percent backdoor detection rate against the mainstream defense frameworks. In addition, in the ablation study, we discuss the influence of different hiding coefficients on the attack results. You can find our code at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Parasite-1715/.
最近,扩散模型作为最成功的图像生成模型之一,因其能够通过迭代采样噪声生成高质量图像而备受关注。然而,最近的研究表明,扩散模型容易受到后门攻击的影响,攻击者可以通过输入包含触发器的数据来激活后门,并生成他们想要的输出。现有的后门攻击方法主要集中在目标噪声到图像和文本到图像的任务上,而对于图像到图像任务的后门攻击研究相对较少。此外,传统的后门攻击通常依赖于一个单一、显眼的触发器来生成固定的目标图像,缺乏隐蔽性和灵活性。为了解决这些限制,我们针对扩散模型中的图像到图像任务提出了一种新的后门攻击方法,名为“寄生虫”。它不仅首次利用隐写术来隐藏触发器,还允许攻击者将目标内容作为后门触发器,以实现更灵活的攻击。“寄生虫”作为一种新的攻击方法,有效地绕过了现有的检测框架来执行后门攻击。在我们的实验中,“寄生虫”针对主流防御框架实现了0%的后门检测率。另外,在消融研究中,我们讨论了不同的隐藏系数对攻击结果的影响。你可以在https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Parasite-1715/找到我们的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型最近成为最成功的图像生成模型之一,但其易受后门攻击影响。针对图像到图像的扩散模型任务,我们提出了一种名为“寄生虫”的新型后门攻击方法,该方法不仅利用隐写术隐藏触发器,还允许攻击者嵌入目标内容作为后门触发器,以实现更灵活的攻击。该攻击方法成功绕过现有检测框架,对主流防御框架的后门检测率为零。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型是当下最成功的图像生成模型之一,但存在后门攻击风险。
- 现有后门攻击主要集中在噪声到图像和文本到图像的任务上,针对图像到图像的扩散模型的攻击研究有限。
- 提出的“寄生虫”攻击方法用于图像到图像的扩散模型任务,利用隐写术隐藏触发器。
- “寄生虫”攻击方法允许攻击者嵌入目标内容作为后门触发器,实现更灵活攻击。
- “寄生虫”攻击成功绕过现有检测框架,对主流防御框架的后门检测率为零。
- 实验中发现不同隐藏系数对攻击结果有影响。
点此查看论文截图


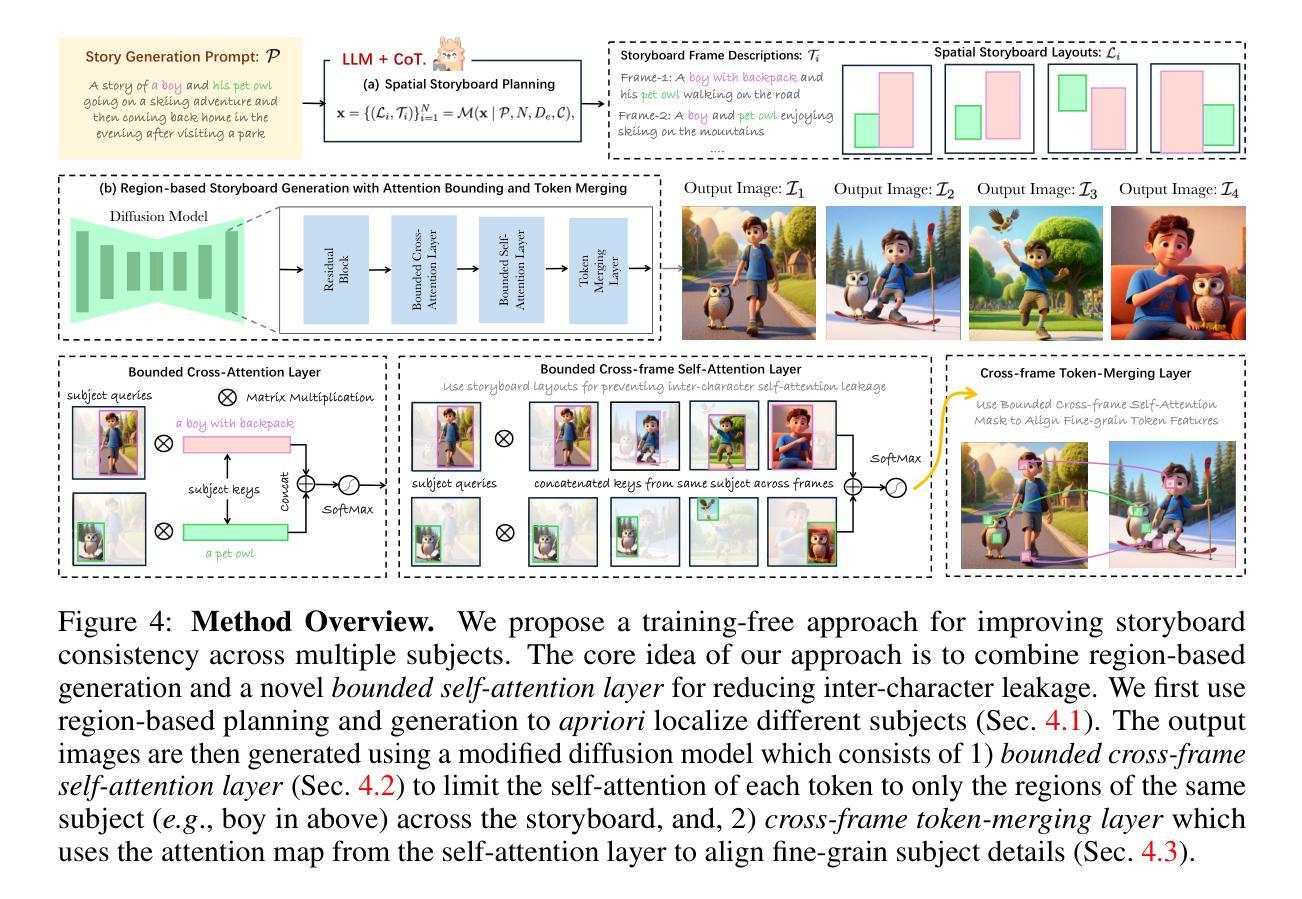
Storybooth: Training-free Multi-Subject Consistency for Improved Visual Storytelling
Authors:Jaskirat Singh, Junshen Kevin Chen, Jonas Kohler, Michael Cohen
Training-free consistent text-to-image generation depicting the same subjects across different images is a topic of widespread recent interest. Existing works in this direction predominantly rely on cross-frame self-attention; which improves subject-consistency by allowing tokens in each frame to pay attention to tokens in other frames during self-attention computation. While useful for single subjects, we find that it struggles when scaling to multiple characters. In this work, we first analyze the reason for these limitations. Our exploration reveals that the primary-issue stems from self-attention-leakage, which is exacerbated when trying to ensure consistency across multiple-characters. This happens when tokens from one subject pay attention to other characters, causing them to appear like each other (e.g., a dog appearing like a duck). Motivated by these findings, we propose StoryBooth: a training-free approach for improving multi-character consistency. In particular, we first leverage multi-modal chain-of-thought reasoning and region-based generation to apriori localize the different subjects across the desired story outputs. The final outputs are then generated using a modified diffusion model which consists of two novel layers: 1) a bounded cross-frame self-attention layer for reducing inter-character attention leakage, and 2) token-merging layer for improving consistency of fine-grain subject details. Through both qualitative and quantitative results we find that the proposed approach surpasses prior state-of-the-art, exhibiting improved consistency across both multiple-characters and fine-grain subject details.
无训练一致文本到图像生成是近期广泛关注的主题,该生成方法旨在描绘不同图像中的相同主题。目前的研究主要依赖于跨帧自注意力机制,通过允许每个帧中的标记关注其他帧中的标记,从而提高主题一致性。虽然这在单个主题上很有用,但我们发现它在扩展到多个角色时遇到了困难。在这项工作中,我们首先分析了这些限制的原因。我们的探索表明,主要问题源于自注意力泄漏,在尝试确保跨多个角色的一致性时,这一问题会加剧。这种情况发生在来自一个主题的标记关注其他角色时,导致他们看起来彼此相似(例如,一只狗看起来像鸭子)。受这些发现的启发,我们提出了StoryBooth:一种无需训练即可提高多角色一致性的方法。具体而言,我们首先利用多模态链式思维推理和基于区域的生成来先验定位所需故事输出中的不同主题。最终输出是使用经过修改的扩散模型生成的,该模型包含两个新层:1)有界跨帧自注意力层,用于减少角色间注意力泄漏;以及2)标记合并层,用于提高精细角色细节的一致性。通过定性和定量结果,我们发现所提出的方法超越了先前最先进的水平,在多个角色和精细角色细节上表现出更高的一致性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了无训练文本到图像生成的问题,特别是在描绘不同图像中的同一主题时。现有方法主要依赖跨帧自注意力机制,但在扩展到多角色时存在局限性。本文分析了这一问题产生的原因,并提出了StoryBooth方法,通过多模态链式思维推理和基于区域的生成来先定位不同主题,然后使用改进后的扩散模型生成最终输出,包括减少角色间注意力泄漏的跨帧自注意力层和用于改进精细主题细节一致性的令牌合并层。新方法在定性和定量结果上都优于现有技术,提高了多角色和精细主题细节的一致性。
Key Takeaways
- 无训练文本到图像生成技术在描绘不同图像中的同一主题时受到广泛关注。
- 现有方法主要依赖跨帧自注意力机制,但在扩展到多角色时存在局限性。
- 跨帧自注意力泄漏是限制多角色一致性的主要原因。
- StoryBooth方法通过多模态链式思维推理和基于区域的生成来定位不同主题。
- 改进后的扩散模型包括减少角色间注意力泄漏的跨帧自注意力层和用于改进一致性令牌合并层。
- 新方法在定性和定量结果上都优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图





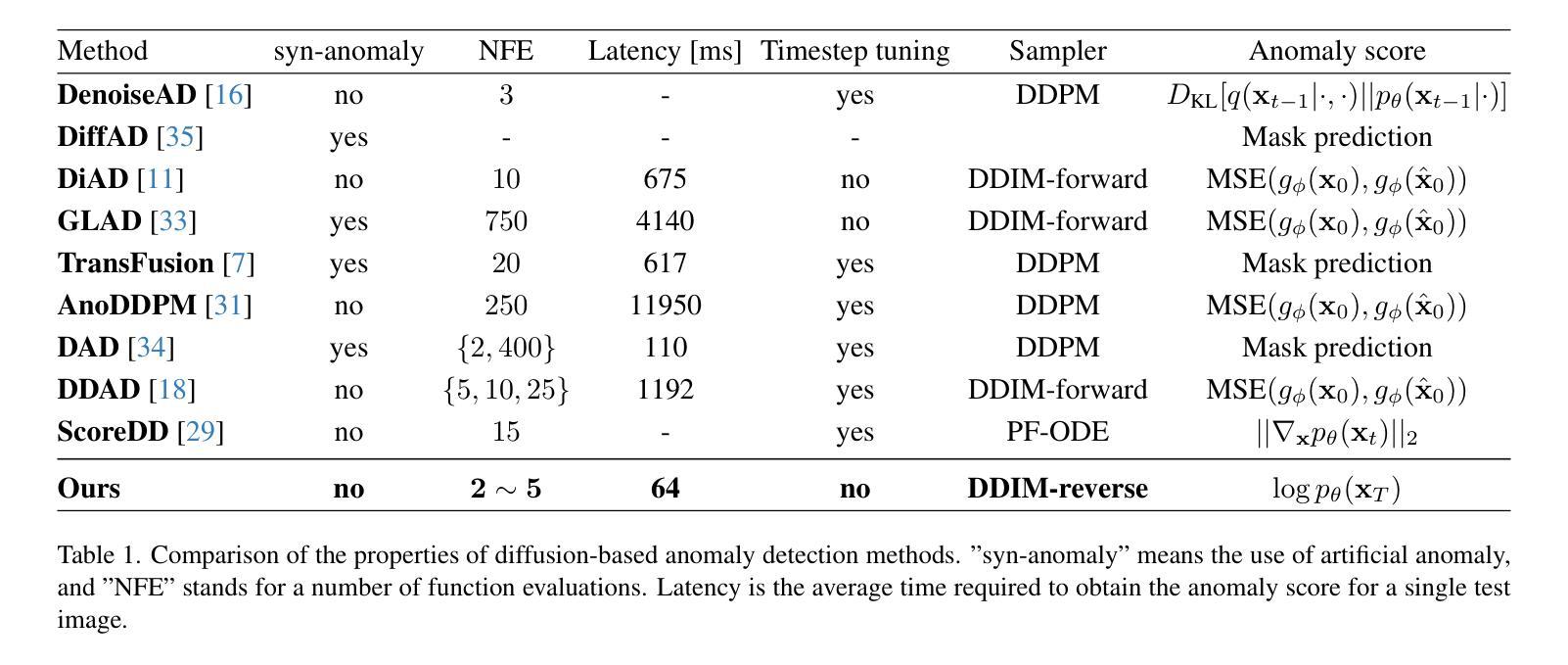
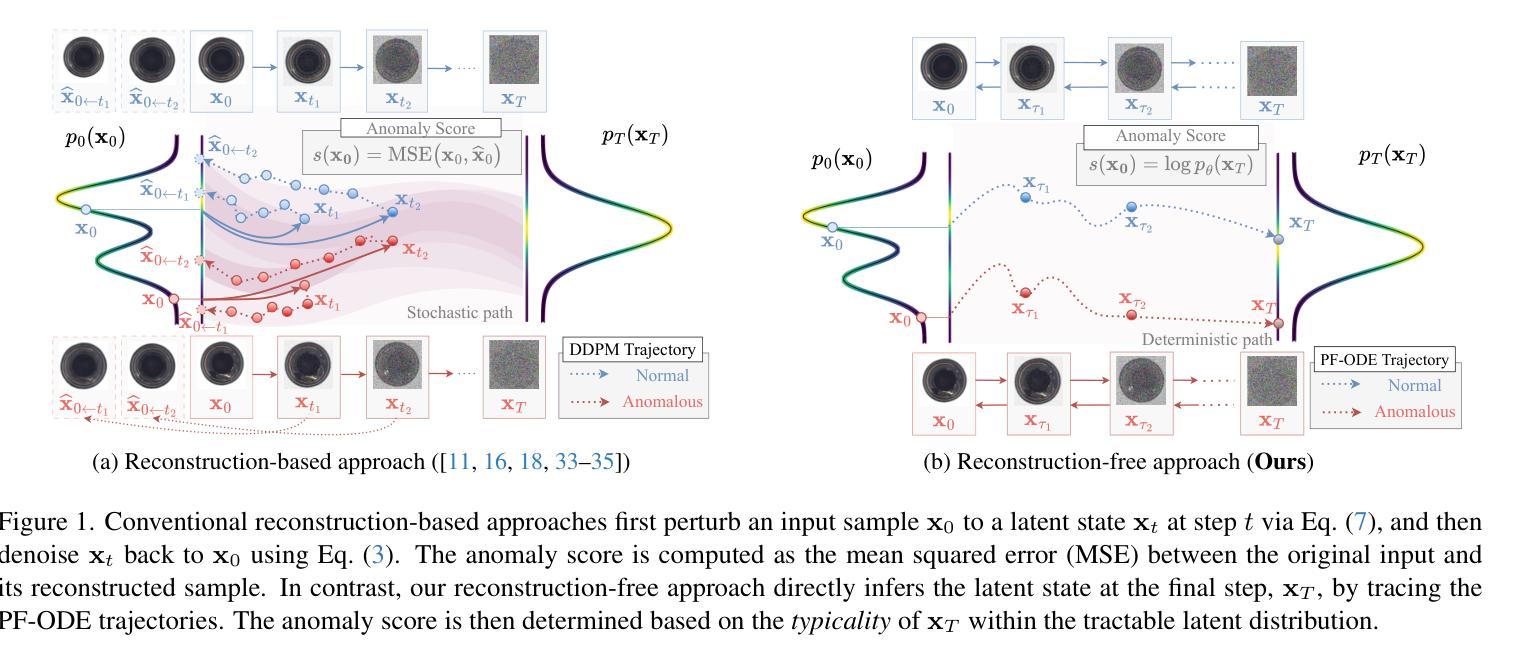
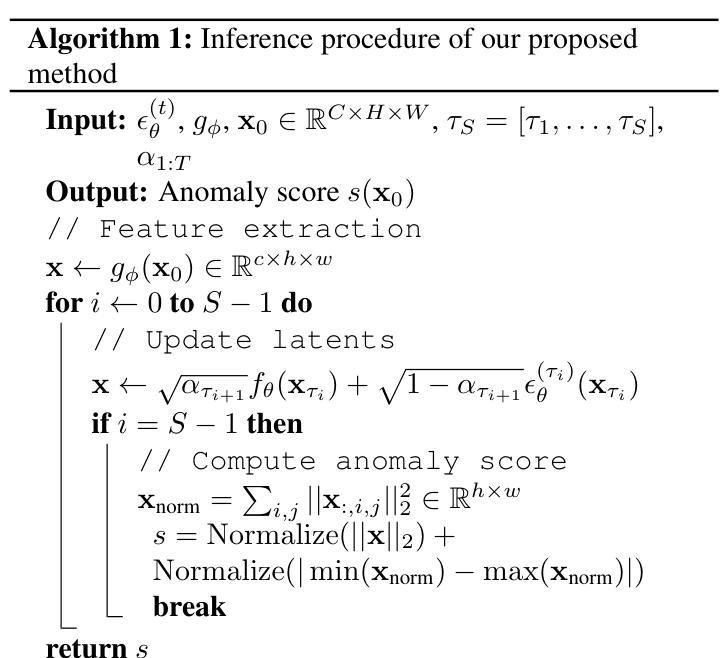
Reconstruction-Free Anomaly Detection with Diffusion Models via Direct Latent Likelihood Evaluation
Authors:Shunsuke Sakai, Tatsuhito Hasegawa
Diffusion models, with their robust distribution approximation capabilities, have demonstrated excellent performance in anomaly detection. However, conventional reconstruction-based approaches rely on computing the reconstruction error between the original and denoised images, which requires careful noise-strength tuning and over ten network evaluations per input-leading to significantly slower detection speeds. To address these limitations, we propose a novel diffusion-based anomaly detection method that circumvents the need for resource-intensive reconstruction. Instead of reconstructing the input image, we directly infer its corresponding latent variables and measure their density under the Gaussian prior distribution. Remarkably, the prior density proves effective as an anomaly score even when using a short partial diffusion process of only 2-5 steps. We evaluate our method on the MVTecAD dataset, achieving an AUC of 0.991 at 15 FPS, thereby setting a new state-of-the-art speed-AUC anomaly detection trade-off.
扩散模型凭借其强大的分布近似能力,在异常检测方面表现出卓越的性能。然而,传统的基于重建的方法依赖于计算原始图像和去噪图像之间的重建误差,这需要进行仔细的噪声强度调整,并且每个输入需要超过十次的网络评估,从而导致检测速度大大降低。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种新型的基于扩散的异常检测方法,该方法无需进行资源密集型的重建。我们不需要重建输入图像,而是直接推断其对应的潜在变量,并测量它们在高斯先验分布下的密度。值得注意的是,即使只使用短时间的部分扩散过程(仅2-5步),先验密度也被证明可以作为有效的异常分数。我们在MVTecAD数据集上评估了我们的方法,以每秒15帧的速率实现了AUC为0.991,从而建立了最新的速度-AUC异常检测权衡标准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code is available at https://github.com/SkyShunsuke/InversionAD
Summary
本文提出了一种基于扩散模型的异常检测新方法,无需进行资源密集型的重建过程。该方法直接推断输入图像的对应潜在变量,并测量其在高斯先验分布下的密度,从而有效实现异常检测。该方法在MVTecAD数据集上取得了AUC为0.991的优异表现,同时实现了每秒处理15帧的速度,达到了速度和AUC异常检测之间的最佳平衡。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型具有强大的分布近似能力,在异常检测中表现出卓越性能。
- 传统重建方法需要仔细调整噪声强度,并对每个输入进行多次网络评估,导致检测速度较慢。
- 新方法绕过了资源密集型的重建过程,直接推断输入图像的潜在变量。
- 通过测量潜在变量在高斯先验分布下的密度,实现了有效的异常检测。
- 仅使用短的部分扩散过程(2-5步)即可获得良好的异常检测结果。
- 在MVTecAD数据集上取得了很高的AUC值(0.991)。
点此查看论文截图

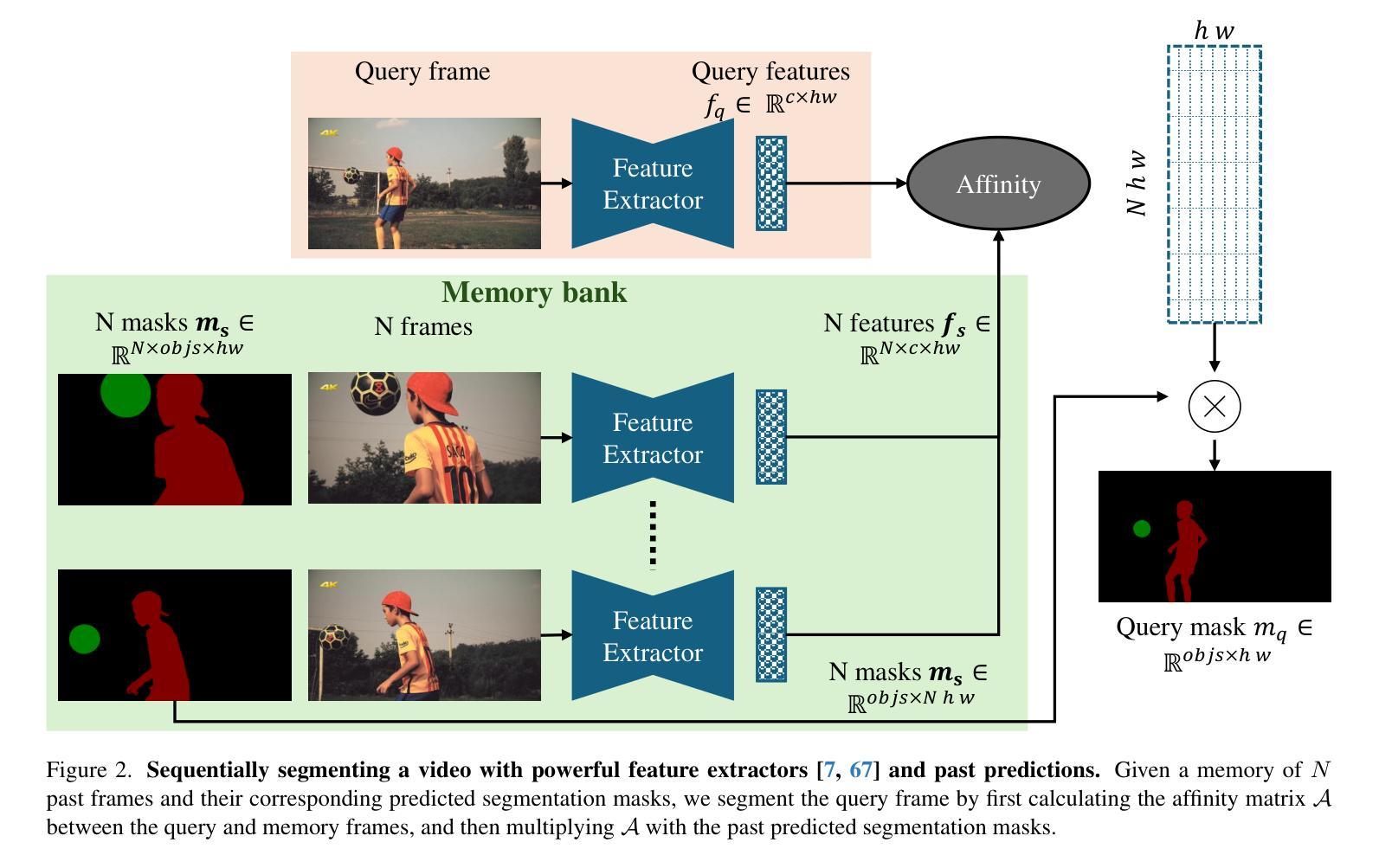
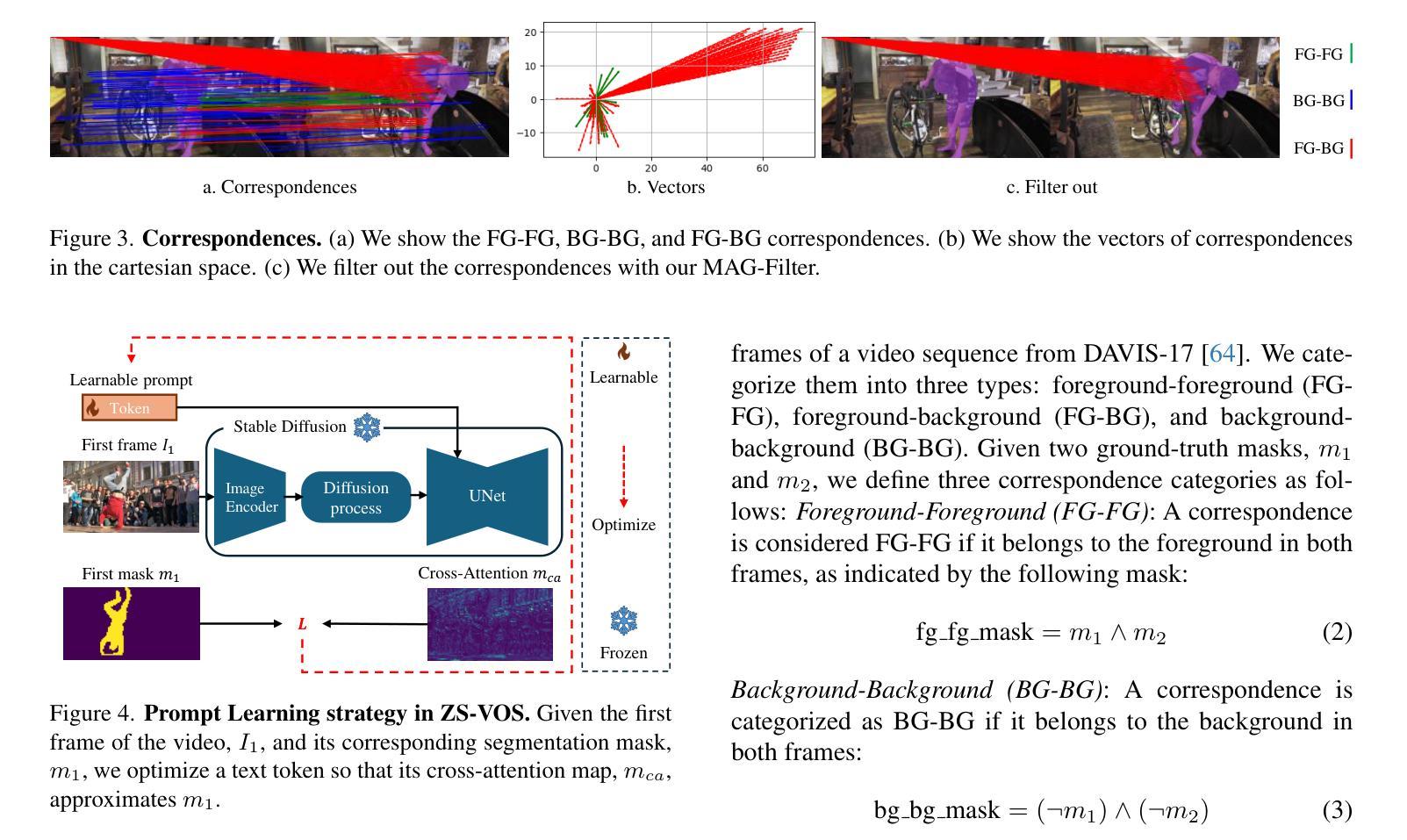
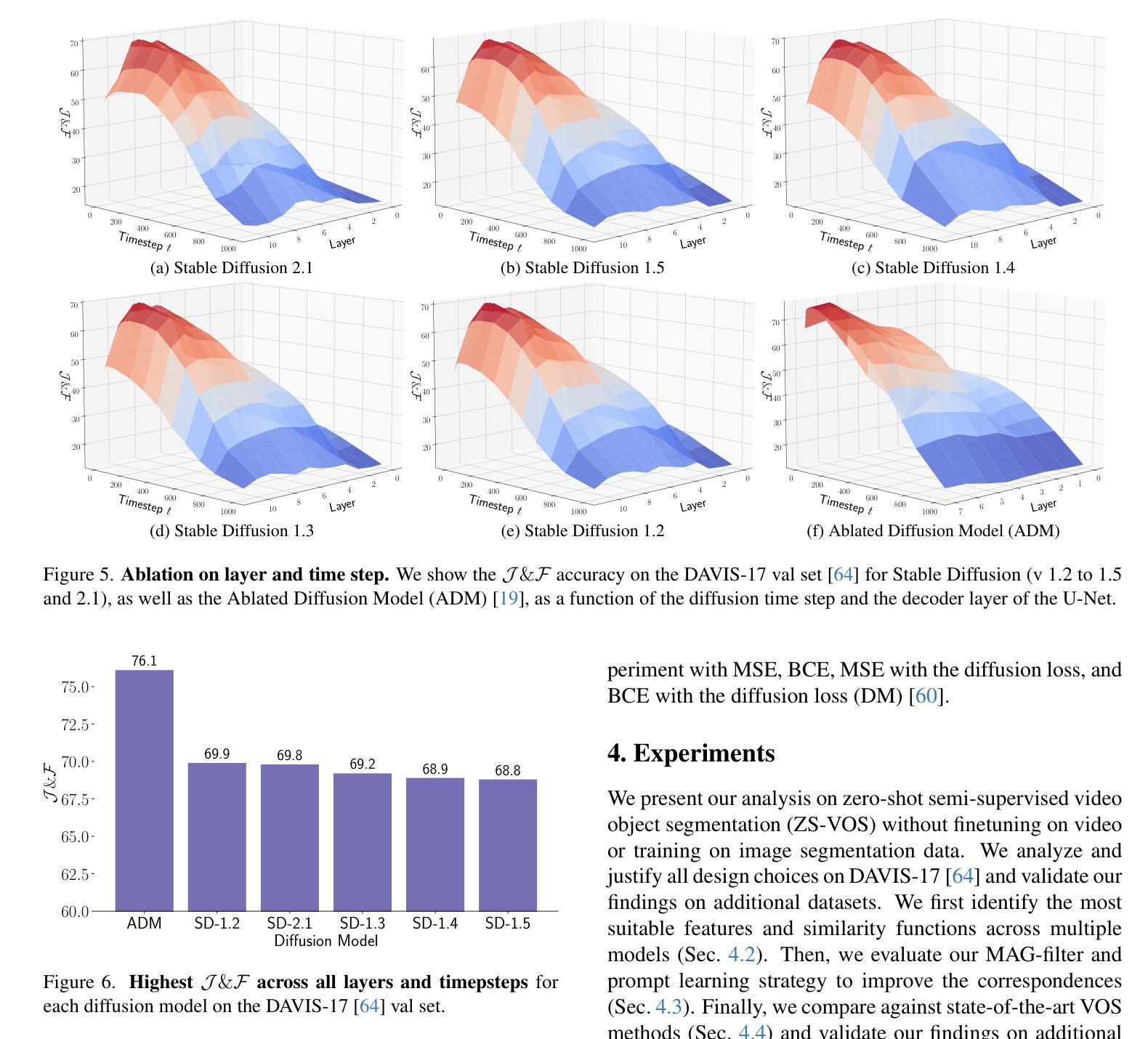
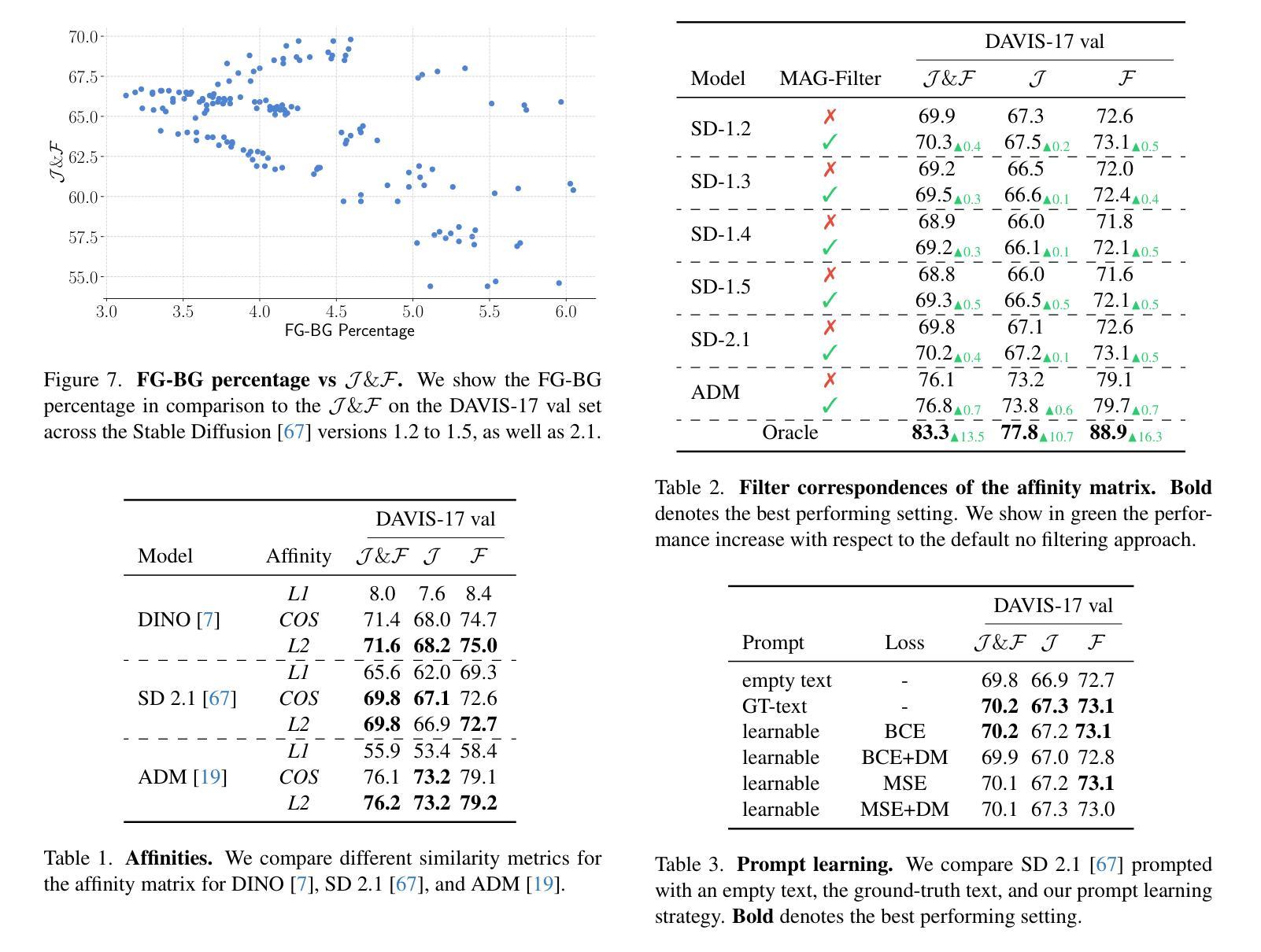
Studying Image Diffusion Features for Zero-Shot Video Object Segmentation
Authors:Thanos Delatolas, Vicky Kalogeiton, Dim P. Papadopoulos
This paper investigates the use of large-scale diffusion models for Zero-Shot Video Object Segmentation (ZS-VOS) without fine-tuning on video data or training on any image segmentation data. While diffusion models have demonstrated strong visual representations across various tasks, their direct application to ZS-VOS remains underexplored. Our goal is to find the optimal feature extraction process for ZS-VOS by identifying the most suitable time step and layer from which to extract features. We further analyze the affinity of these features and observe a strong correlation with point correspondences. Through extensive experiments on DAVIS-17 and MOSE, we find that diffusion models trained on ImageNet outperform those trained on larger, more diverse datasets for ZS-VOS. Additionally, we highlight the importance of point correspondences in achieving high segmentation accuracy, and we yield state-of-the-art results in ZS-VOS. Finally, our approach performs on par with models trained on expensive image segmentation datasets.
本文探讨了大规模扩散模型在零样本视频目标分割(ZS-VOS)中的应用,而无需在视频数据上进行微调或在任何图像分割数据上进行训练。虽然扩散模型在各种任务中表现出了强大的视觉表示能力,但它们在ZS-VOS的直接应用仍然未被充分探索。我们的目标是找到ZS-VOS的最佳特征提取过程,通过确定最合适的时间步长和层来提取特征。我们进一步分析了这些特征的亲和力,并观察到它们与点对应的强烈相关性。在DAVIS-17和MOSE上的大量实验表明,在ImageNet上训练的扩散模型在ZS-VOS方面的性能优于在更大、更多样化的数据集上训练的模型。此外,我们强调了实现高分割准确度时点对应的重要性,我们在ZS-VOS中获得了最新结果。最后,我们的方法与在昂贵的图像分割数据集上训练的模型表现相当。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPRW2025
Summary
扩散模型在零样本视频目标分割(ZS-VOS)任务中展现出强大的潜力,无需针对视频数据进行微调或任何图像分割数据的训练。本文通过识别最适合的时间步长和层来提取特征,实现了对ZS-VOS的最优特征提取过程。此外,本文强调了点对应的重要性,并在DAVIS-17和MOSE等数据集上取得了先进的分割精度。扩散模型在ZS-VOS任务上的表现优于在更大、更多样化数据集上训练的模型。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在零样本视频目标分割(ZS-VOS)任务中的应用被研究得较少。
- 通过识别最适合的时间步长和层来提取特征,可以达到对ZS-VOS的最优特征提取效果。
- 点对应在提升分割精度方面扮演着重要角色。
- 在DAVIS-17和MOSE数据集上进行的实验表明,扩散模型在ZS-VOS任务上的表现优于在更大、更多样化数据集上训练的模型。
- 在ImageNet上训练的扩散模型在ZS-VOS任务上的表现优于其他数据集训练的模型。
- 该方法达到了与在昂贵的图像分割数据集上训练的模型相当的性能。
点此查看论文截图

REWIND: Real-Time Egocentric Whole-Body Motion Diffusion with Exemplar-Based Identity Conditioning
Authors:Jihyun Lee, Weipeng Xu, Alexander Richard, Shih-En Wei, Shunsuke Saito, Shaojie Bai, Te-Li Wang, Minhyuk Sung, Tae-Kyun Kim, Jason Saragih
We present REWIND (Real-Time Egocentric Whole-Body Motion Diffusion), a one-step diffusion model for real-time, high-fidelity human motion estimation from egocentric image inputs. While an existing method for egocentric whole-body (i.e., body and hands) motion estimation is non-real-time and acausal due to diffusion-based iterative motion refinement to capture correlations between body and hand poses, REWIND operates in a fully causal and real-time manner. To enable real-time inference, we introduce (1) cascaded body-hand denoising diffusion, which effectively models the correlation between egocentric body and hand motions in a fast, feed-forward manner, and (2) diffusion distillation, which enables high-quality motion estimation with a single denoising step. Our denoising diffusion model is based on a modified Transformer architecture, designed to causally model output motions while enhancing generalizability to unseen motion lengths. Additionally, REWIND optionally supports identity-conditioned motion estimation when identity prior is available. To this end, we propose a novel identity conditioning method based on a small set of pose exemplars of the target identity, which further enhances motion estimation quality. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that REWIND significantly outperforms the existing baselines both with and without exemplar-based identity conditioning.
我们提出了 REWIND(实时以自我为中心的全身动作扩散),这是一种一步扩散模型,用于从自我中心的图像输入中进行实时、高保真的人类动作估计。现有的以自我为中心的全身(即身体和手)动作估计方法由于基于扩散的迭代动作细化来捕捉身体和手部姿势之间的相关性,因此是非实时的和非因果的,而 REWIND 则以完全因果和实时的方式进行操作。为了实现实时推理,我们引入了(1)级联的身体手部去噪扩散,它以快速前馈的方式有效地对自我中心的身体和手部动作进行建模;(2)扩散蒸馏,它能在一步去噪过程中实现高质量的动作估计。我们的去噪扩散模型基于改进的 Transformer 架构,旨在因果地模拟输出动作,同时提高对不同长度动作的泛化能力。另外,当提供身份先验信息时,REWIND 还支持有条件身份的动作估计。为此,我们提出了一种基于目标身份的小规模姿态范例集的新型身份条件方法,这进一步提高了动作估计的质量。通过广泛的实验,我们证明 REWIND 在有无范例集身份条件下都显著优于现有基线。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025, project page: https://jyunlee.github.io/projects/rewind/
Summary
REWIND是一个一步扩散模型,可从第一人称图像输入中进行实时、高保真的人体运动估计。与现有方法相比,它实现了全身(身体和手部)运动的实时因果推断。通过引入级联身体手部去噪扩散和扩散蒸馏技术,模型能够快速地前向建模身体和手部的运动关联,并用单个去噪步骤实现高质量的运动估计。此外,REWIND还支持在有身份先验的情况下进行身份条件运动估计,并提出了一种基于目标身份姿势范例的新型身份条件方法,进一步提高运动估计质量。实验证明,REWIND在无和有条件例示范例的情况下都显著优于现有基线。
Key Takeaways
- REWIND是一个用于实时高保真人体运动估计的一步扩散模型,可从第一人称图像输入中进行推断。
- 与现有方法相比,REWIND实现了全身运动的实时因果推断。
- 通过引入级联身体手部去噪扩散,REWIND能够快速地前向建模身体和手部的运动关联。
- 扩散蒸馏技术使REWIND能够在单个去噪步骤中实现高质量的运动估计。
- REWIND支持身份条件运动估计,进一步提高运动估计质量。
- 提出了一种基于目标身份姿势范例的新型身份条件方法。
点此查看论文截图

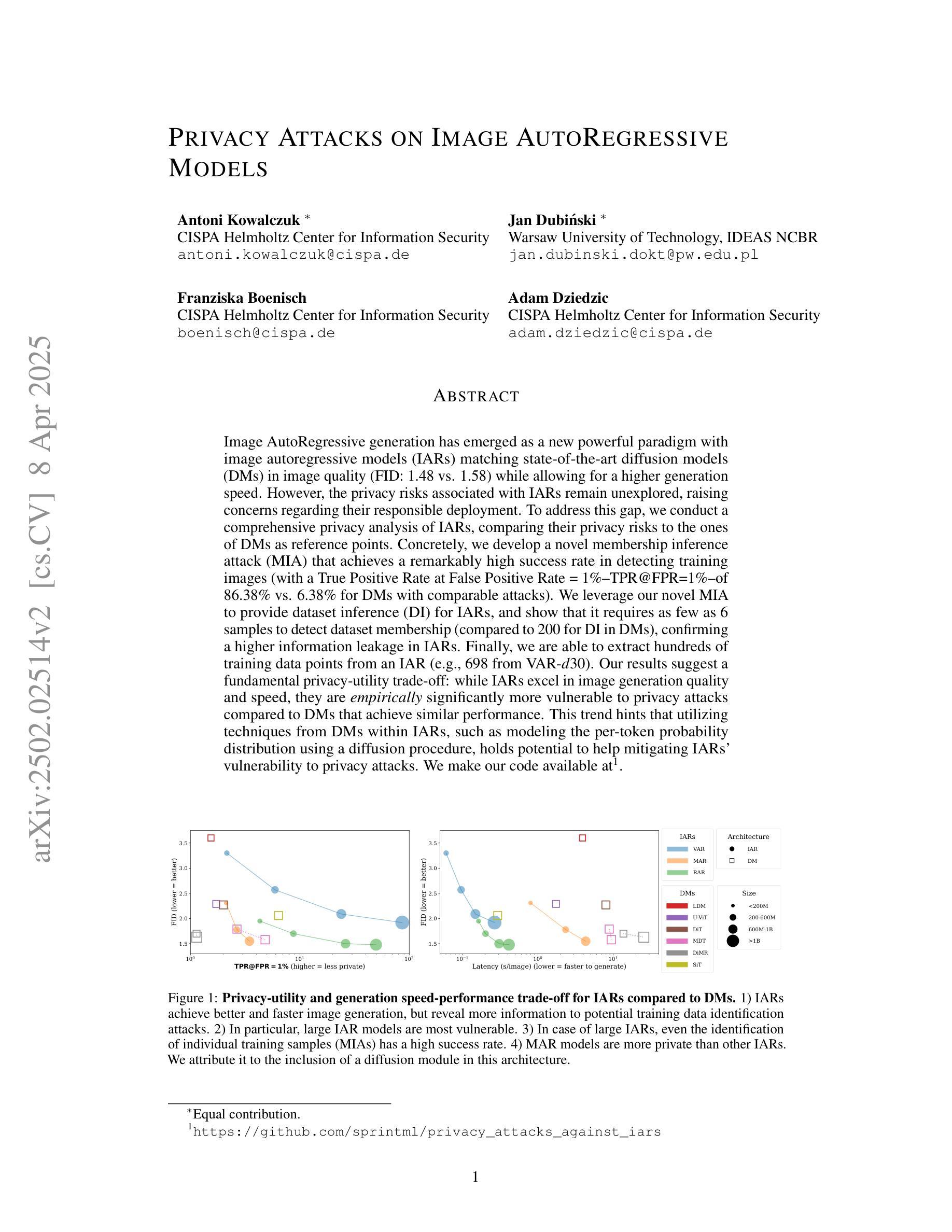
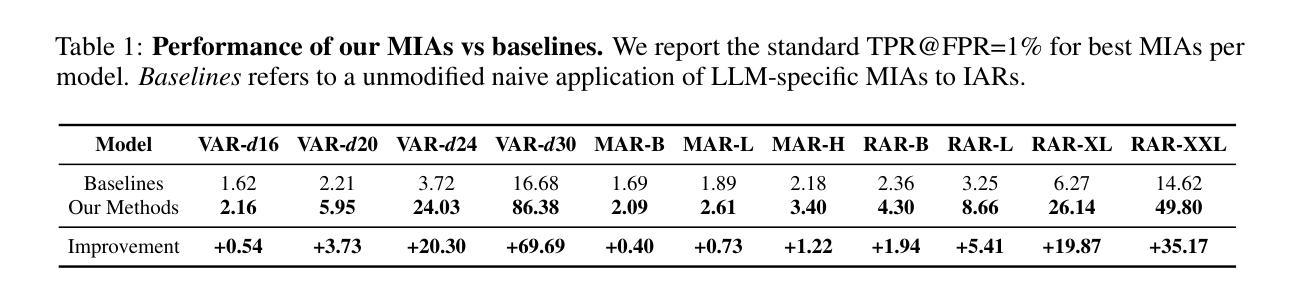
Privacy Attacks on Image AutoRegressive Models
Authors:Antoni Kowalczuk, Jan Dubiński, Franziska Boenisch, Adam Dziedzic
Image autoregressive generation has emerged as a powerful new paradigm, with image autoregressive models (IARs) matching state-of-the-art diffusion models (DMs) in image quality (FID: 1.48 vs. 1.58) while allowing for higher generation speed. However, the privacy risks associated with IARs remain unexplored, raising concerns about their responsible deployment. To address this gap, we conduct a comprehensive privacy analysis of IARs, comparing their privacy risks to those of DMs as a reference point. Specifically, we develop a novel membership inference attack (MIA) that achieves a remarkably high success rate in detecting training images, with a True Positive Rate at False Positive Rate = 1% (TPR@FPR=1%) of 86.38%, compared to just 6.38% for DMs using comparable attacks. We leverage our novel MIA to perform dataset inference (DI) for IARs and show that it requires as few as 6 samples to detect dataset membership, compared to 200 samples for DI in DMs. This confirms a higher level of information leakage in IARs. Finally, we are able to extract hundreds of training data points from an IAR (e.g., 698 from VAR-d30). Our results suggest a fundamental privacy-utility trade-off: while IARs excel in image generation quality and speed, they are empirically significantly more vulnerable to privacy attacks compared to DMs that achieve similar performance. This trend suggests that incorporating techniques from DMs into IARs, such as modeling the per-token probability distribution using a diffusion procedure, could help mitigate IARs’ vulnerability to privacy attacks. We make our code available at: https://github.com/sprintml/privacy_attacks_against_iars
图像自回归生成已经成为一种强大的新范式,图像自回归模型(IARs)在图像质量方面与最先进的扩散模型(DMs)相匹配(FID:1.48对1.58),同时允许更高的生成速度。然而,与IARs相关的隐私风险尚未得到探索,这引发了对其负责任部署的担忧。为了填补这一空白,我们对IARs进行了全面的隐私分析,并将其与DMs的隐私风险进行比较,作为参考点。具体来说,我们开发了一种新型的成员推理攻击(MIA),该攻击在检测训练图像方面实现了非常高的成功率,在假阳性率(FPR)为1%的情况下,真阳性率(TPR)达到86.38%,相比之下,使用类似攻击的DMs仅为6.38%。我们利用新型MIA对IARs进行数据集推理(DI),并表明仅需6个样本即可检测数据集成员身份,相比之下,DMs进行DI需要200个样本。这证实了IARs中信息泄露程度较高。最后,我们能够从IAR中提取数百个训练数据点(例如,从VAR-d30中提取698个)。我们的结果表明存在基本的隐私效用权衡:尽管IAR在图像生成质量和速度方面表现出色,但与实现类似性能的DMs相比,它们在实际中更容易受到隐私攻击。这一趋势表明,将DMs的技术融入IARs中,例如使用扩散过程对每令牌概率分布进行建模,可能有助于减轻IARs对隐私攻击的脆弱性。我们的代码可在:https://github.com/sprintml/privacy_attacks_against_iars访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/sprintml/privacy_attacks_against_iars
Summary
本文探讨了图像自回归生成模型(IARs)的隐私风险问题。研究发现,相较于扩散模型(DMs),IARs在图像生成质量和速度上表现优异,但同时也存在更高的隐私泄露风险。文章提出了一种新型成员推理攻击(MIA),该攻击在检测训练图像方面表现出极高的成功率,并证实了IARs在数据集推理(DI)方面的信息泄露更为严重。研究指出,虽然IARs具有优秀的性能,但在隐私保护方面存在显著缺陷,并提出将DMs的技术融入IARs中,以缓解其隐私攻击漏洞。
Key Takeaways
- 图像自回归生成模型(IARs)与扩散模型(DMs)相比,在图像生成质量和速度上具有优势。
- IARs存在较高的隐私泄露风险,尚未得到充分探索。
- 提出了一种新型成员推理攻击(MIA),在检测IARs的训练图像方面表现出极高成功率。
- IARs在数据集推理(DI)方面的信息泄露更为严重,仅需少量样本即可检测数据集成员。
- IARs在隐私保护方面存在显著缺陷,相较DMs更易受到隐私攻击。
- 相比DMs,IARs的隐私泄露问题凸显了隐私与效用的权衡。
- 将DMs的技术融入IARs中,有助于缓解IARs的隐私攻击漏洞。
点此查看论文截图
Fast constrained sampling in pre-trained diffusion models
Authors:Alexandros Graikos, Nebojsa Jojic, Dimitris Samaras
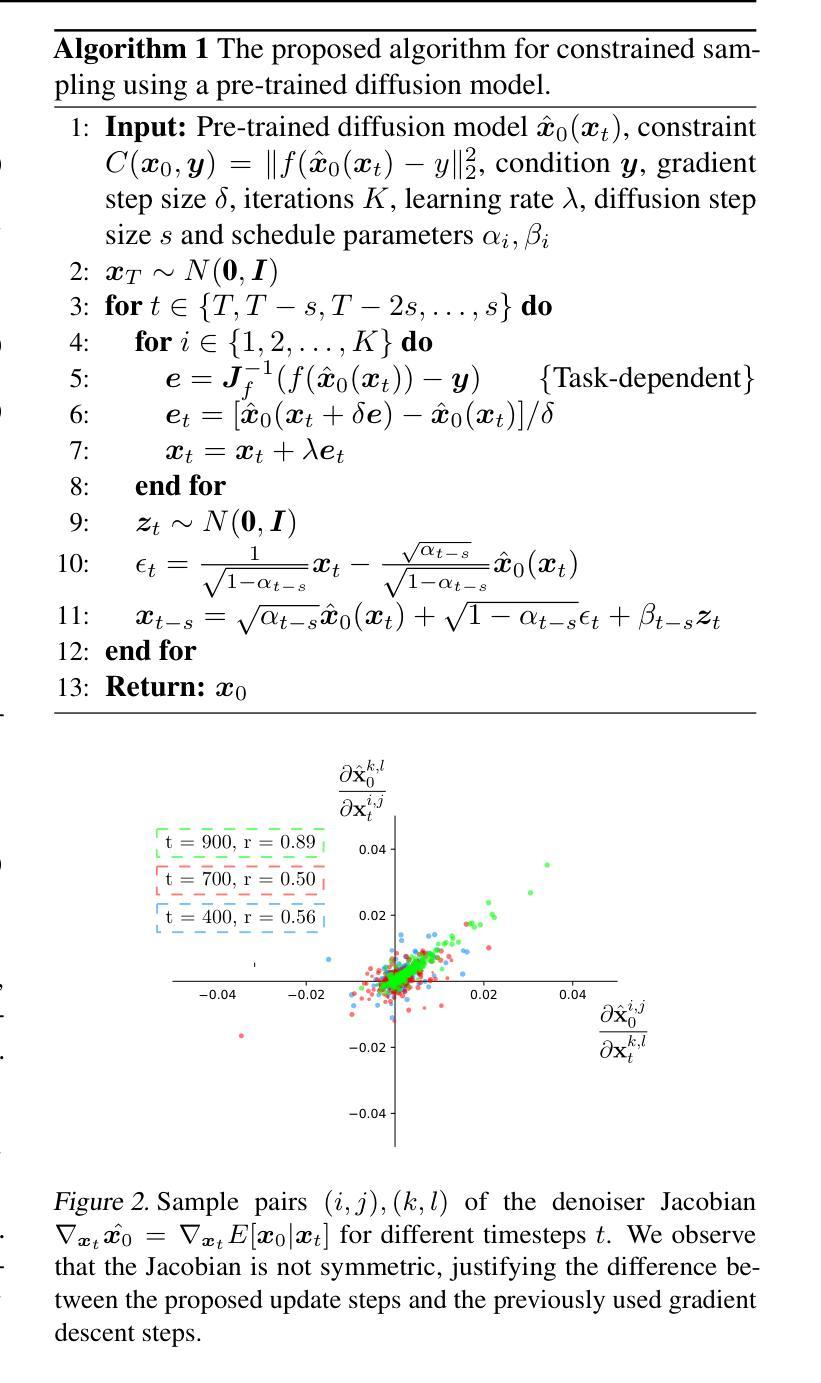
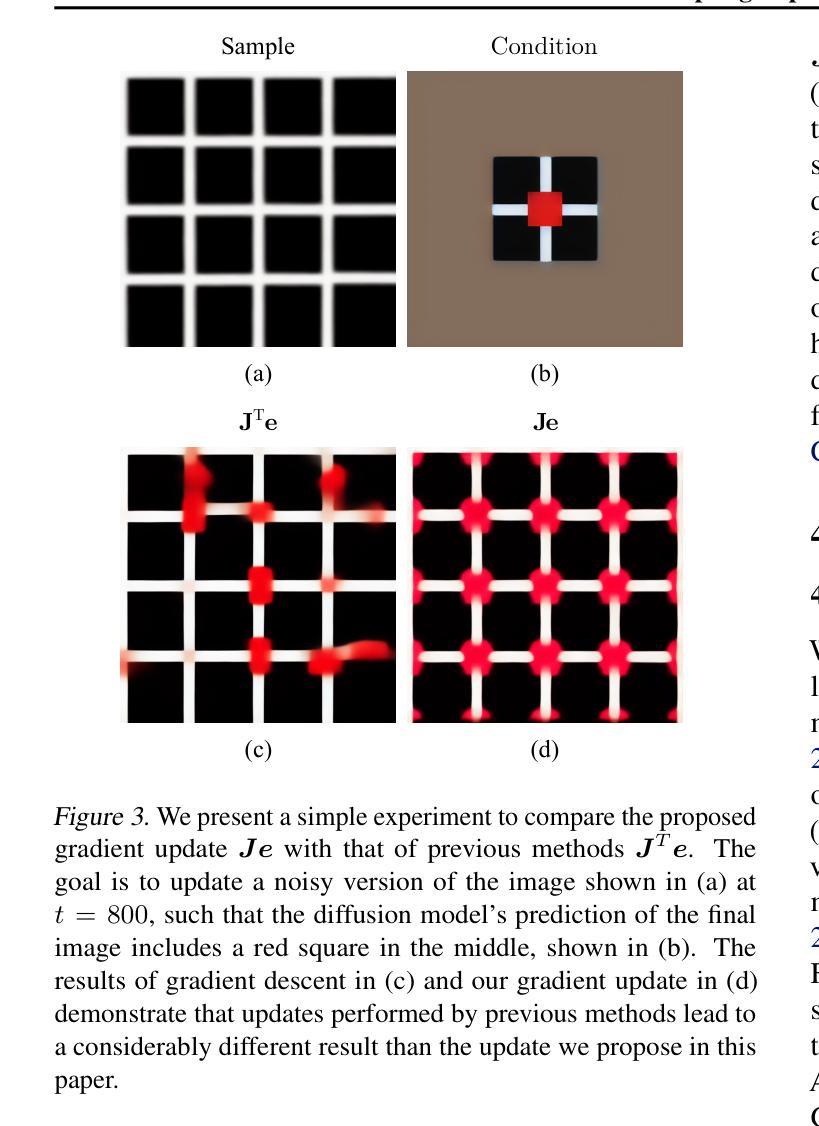
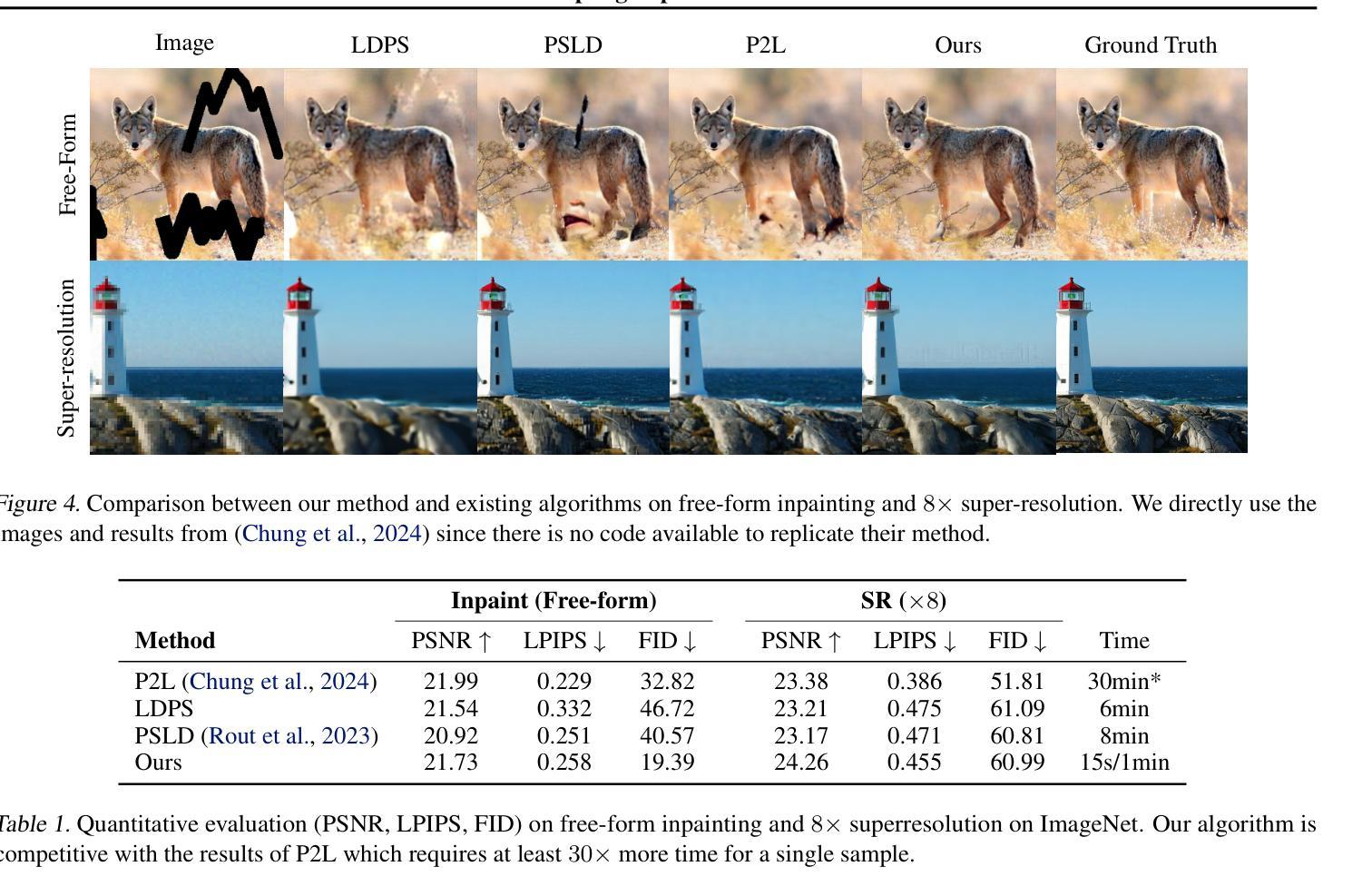
Large denoising diffusion models, such as Stable Diffusion, have been trained on billions of image-caption pairs to perform text-conditioned image generation. As a byproduct of this training, these models have acquired general knowledge about image statistics, which can be useful for other inference tasks. However, when confronted with sampling an image under new constraints, e.g. generating the missing parts of an image, using large pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models is inefficient and often unreliable. Previous approaches either utilize backpropagation, making them significantly slower and more memory-demanding than text-to-image inference, or only enforce the constraint locally, failing to capture critical long-range correlations. In this work, we propose an algorithm that enables fast and high-quality generation under arbitrary constraints. We observe that, during inference, we can interchange between gradient updates computed on the noisy image and updates computed on the final, clean image. This allows us to employ a numerical approximation to expensive gradient computations, incurring significant speed-ups in inference. Our approach produces results that rival or surpass the state-of-the-art training-free inference approaches while requiring a fraction of the time. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our algorithm under both linear and non-linear constraints. An implementation is provided at https://github.com/cvlab-stonybrook/fast-constrained-sampling.
大型去噪扩散模型(如Stable Diffusion)已经通过对数十亿图像标题对进行训练,实现了文本条件图像生成。作为这种训练的一个副产品,这些模型已经获得了关于图像统计的通用知识,这对于其他推理任务可能是有用的。然而,当面临在新的约束下采样图像时,例如生成图像的缺失部分,使用大型预训练文本到图像扩散模型是低效且经常不可靠的。以前的方法要么使用反向传播,这使得它们比文本到图像的推理过程更慢且更占内存,要么只局部实施约束,无法捕捉重要的长程相关性。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种能够在任意约束下快速生成高质量图像的算法。我们观察到,在推理过程中,我们可以在嘈杂图像上计算的梯度更新和最终干净图像上计算的更新之间进行互换。这使我们能够采用昂贵的梯度计算的数值近似,从而在推理过程中实现显著的速度提升。我们的方法产生的结果可与或超越最新的无训练推理方法相媲美,同时所需时间大大减少。我们在线性约束和非线性约束下都证明了算法的有效性。一个实现示例可在[https://github.com/cvlab-stonybrook/fast-constrained-sampling找到。]
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型去噪扩散模型(如Stable Diffusion)经过数十亿图像标题对训练,可进行文本条件图像生成。模型在训练过程中获得了有关图像统计的通用知识,这对其推理任务有益。然而,对于在新的约束条件下采样图像(例如生成图像的缺失部分),使用大型预训练文本到图像扩散模型效率较低且常不可靠。先前的方法要么使用反向传播,使其比文本到图像推理更慢且更占内存,要么仅局部实施约束,无法捕捉关键的长程关联。本研究提出了一种算法,可在任意约束下实现快速、高质量的生成。我们观察到在推理过程中,可以在嘈杂图像上计算的梯度更新和最终清洁图像上计算的更新之间进行交换。这使我们能够采用昂贵的梯度计算的数值逼近,在推理中实现了显著的速度提升。我们的算法在与训练无关的推理方法中实现了良好的效果。实现地址:https://github.com/cvlab-stonybrook/fast-constrained-sampling。
Key Takeaways
- 大型去噪扩散模型如Stable Diffusion已训练于数十亿图像标题对,支持文本条件图像生成。
- 模型在训练中获取了图像统计的通用知识,有益于其他推理任务。
- 面对新约束条件采样图像时,现有方法效率不高且常不可靠。
- 先前方法使用反向传播导致速度慢、内存需求大,或仅局部实施约束而无法捕捉长程关联。
- 本研究提出一种算法,能在任意约束下实现快速高质量的图像生成。
- 推理过程中可交换嘈杂图像和清洁图像上的梯度更新。
点此查看论文截图


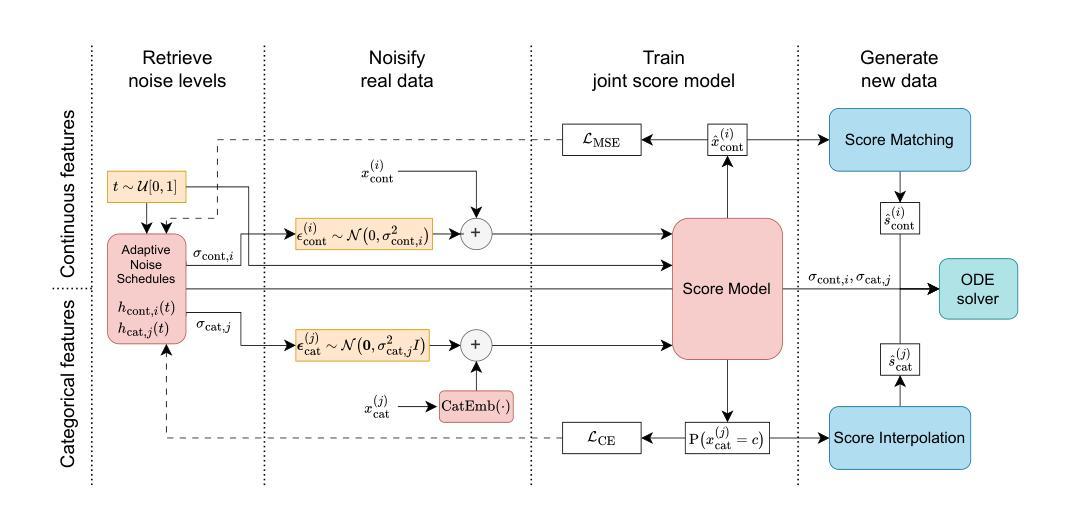
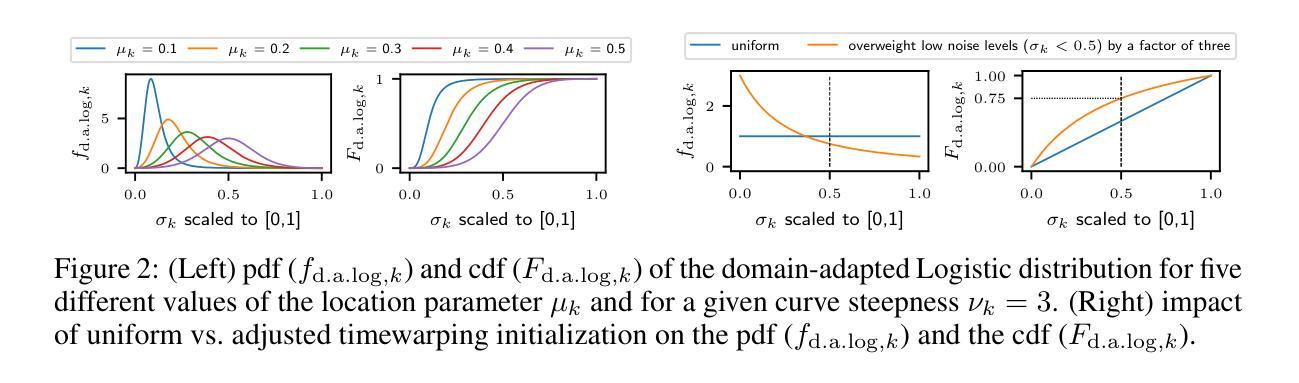
Continuous Diffusion for Mixed-Type Tabular Data
Authors:Markus Mueller, Kathrin Gruber, Dennis Fok
Score-based generative models, commonly referred to as diffusion models, have proven to be successful at generating text and image data. However, their adaptation to mixed-type tabular data remains underexplored. In this work, we propose CDTD, a Continuous Diffusion model for mixed-type Tabular Data. CDTD is based on a novel combination of score matching and score interpolation to enforce a unified continuous noise distribution for both continuous and categorical features. We explicitly acknowledge the necessity of homogenizing distinct data types by relying on model-specific loss calibration and initialization schemes.To further address the high heterogeneity in mixed-type tabular data, we introduce adaptive feature- or type-specific noise schedules. These ensure balanced generative performance across features and optimize the allocation of model capacity across features and diffusion time. Our experimental results show that CDTD consistently outperforms state-of-the-art benchmark models, captures feature correlations exceptionally well, and that heterogeneity in the noise schedule design boosts sample quality. Replication code is available at https://github.com/muellermarkus/cdtd.
基于分数生成模型,通常被称为扩散模型,已经成功应用于文本和图像数据的生成。然而,它们在混合类型表格数据中的应用仍然未被充分探索。在这项工作中,我们提出了CDTD,这是一种用于混合类型表格数据的连续扩散模型。CDTD基于分数匹配和分数插值的组合,以强制执行统一连续噪声分布,适用于连续和分类特征。我们明确承认通过依赖模型特定的损失校准和初始化方案来统一不同类型数据的必要性。为了进一步解决混合类型表格数据中的高异质性,我们引入了自适应特征或类型特定的噪声时间表。这些确保了跨特征的平衡生成性能,并优化了模型容量在特征和扩散时间上的分配。我们的实验结果表明,CDTD持续优于最新基准模型,异常捕捉特征相关性,并且噪声时间表设计中的异质性提高了样本质量。复现代码可在https://github.com/muellermarkus/cdtd找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF published at ICLR 2025
Summary
扩散模型在文本和图像数据生成方面取得了显著成功,但在混合类型表格数据的应用上仍待探索。本文提出CDTD,一种用于混合类型表格数据的连续扩散模型。CDTD通过结合分数匹配和分数插值来强制执行统一连续噪声分布,适用于连续和分类特征。为应对混合类型表格数据中的高异质性,引入自适应特征或类型特定噪声时间表。实验结果表明,CDTD持续优于最新基准模型,特征关联捕捉出色,且噪声时间表设计的异质性提升了样本质量。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在生成文本和图像数据方面表现出色,但在处理混合类型表格数据时仍面临挑战。
- CDTD是一种用于混合类型表格数据的连续扩散模型,通过强制执行统一连续噪声分布来处理不同类型的数据特征。
- CDTD结合了分数匹配和分数插值技术,以提高模型的性能。
- 为应对混合类型表格数据中的高异质性,CDTD引入了自适应特征或类型特定的噪声时间表。
- 实验结果表明,CDTD在生成混合类型表格数据方面优于其他最新模型。
- CDTD能够很好地捕捉特征之间的关联。
- 噪声时间表设计的异质性对样本质量有积极影响。
点此查看论文截图