⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-10 更新
Memory-Modular Classification: Learning to Generalize with Memory Replacement
Authors:Dahyun Kang, Ahmet Iscen, Eunchan Jo, Sua Choi, Minsu Cho, Cordelia Schmid
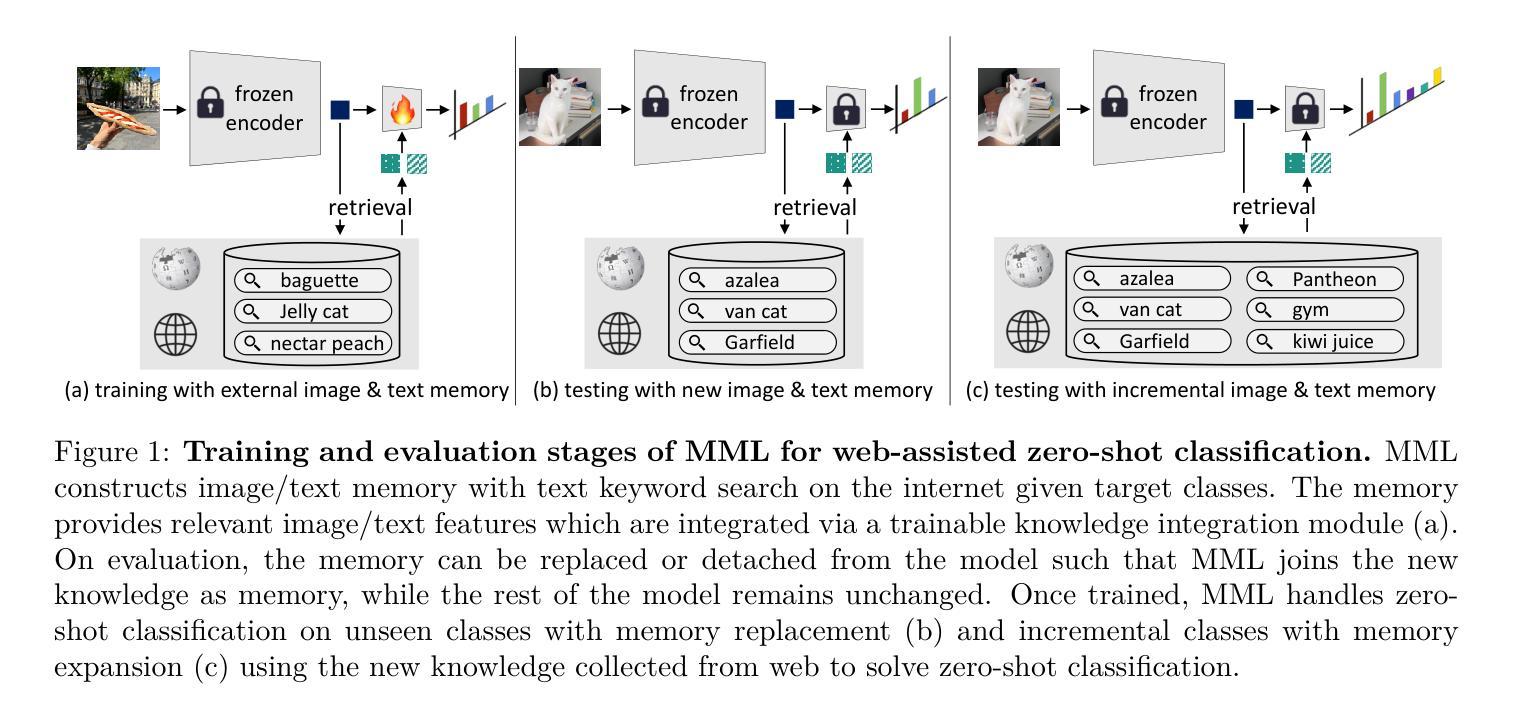
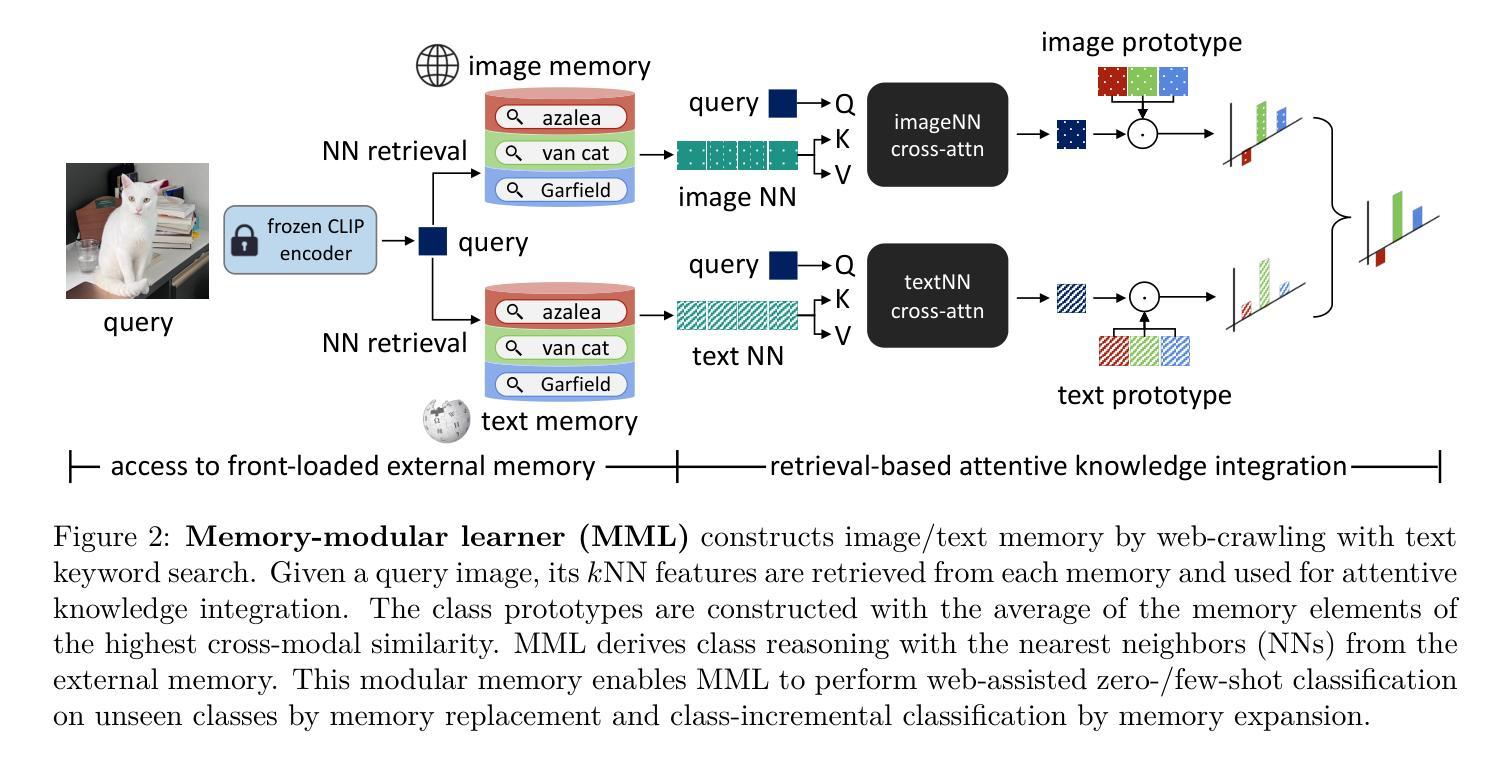
We propose a novel memory-modular learner for image classification that separates knowledge memorization from reasoning. Our model enables effective generalization to new classes by simply replacing the memory contents, without the need for model retraining. Unlike traditional models that encode both world knowledge and task-specific skills into their weights during training, our model stores knowledge in the external memory of web-crawled image and text data. At inference time, the model dynamically selects relevant content from the memory based on the input image, allowing it to adapt to arbitrary classes by simply replacing the memory contents. The key differentiator that our learner meta-learns to perform classification tasks with noisy web data from unseen classes, resulting in robust performance across various classification scenarios. Experimental results demonstrate the promising performance and versatility of our approach in handling diverse classification tasks, including zero-shot/few-shot classification of unseen classes, fine-grained classification, and class-incremental classification.
我们提出了一种用于图像分类的新型记忆模块化学习者,它将知识记忆与推理相分离。我们的模型通过简单地替换记忆内容,而无需重新训练模型,就能够有效地推广到新的类别。不同于传统模型在训练过程中将世界知识和特定任务技能编码到权重中,我们的模型将知识存储在从网络爬取的图像和文本数据的外部记忆中。在推理过程中,模型根据输入图像动态选择记忆中的相关内容,通过简单地替换记忆内容,就能够适应任意类别。我们的学习者的关键区别在于,它会进行元学习,使用来自未见类别的带有噪声的网页数据进行分类任务,从而在各种分类场景中实现稳健的性能。实验结果表明,我们的方法在处理各种分类任务时具有广阔的应用前景,包括零样本/少样本未见类别分类、细粒度分类和类增量分类。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to TMLR. Code available: https://github.com/dahyun-kang/mml
Summary
本模型提出了一种新的记忆模块化学习者用于图像分类,它将知识记忆与推理分离。通过仅替换记忆内容,即可实现对新类的有效泛化,无需进行模型再训练。该模型将知识存储在从网络爬取的图像和文本数据的外部记忆中。在推理时,模型根据输入图像动态选择相关内存内容,通过简单替换内存内容即可适应任意类别。该模型的关键区别在于,它能够使用来自未见类别的网络数据的噪声进行元学习分类任务,从而在各种分类场景中实现稳健性能。
Key Takeaways
- 模型实现了记忆和推理的分离,有助于提高泛化能力。
- 通过替换记忆内容,模型能够适应新的类别,无需重新训练。
- 模型将知识存储在外部记忆中,包括从网络爬取的图像和文本数据。
- 模型能够根据输入图像动态选择相关内存内容。
- 模型能够在未见类别的情况下进行元学习分类任务。
- 实验结果证明了该模型在处理多种分类任务上的优异性能和通用性,包括零样本/少样本分类、细粒度分类和类别增量分类。
点此查看论文截图

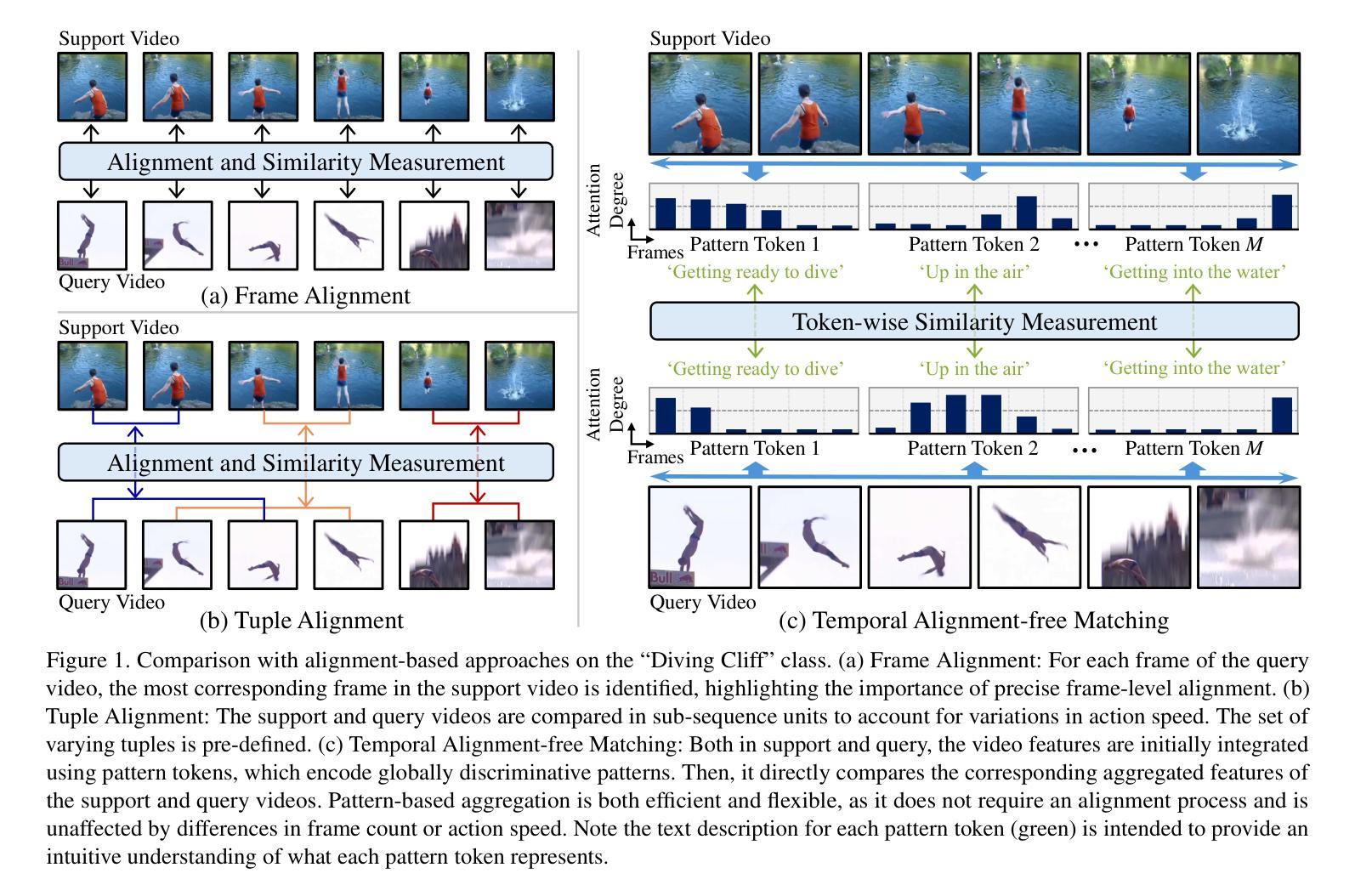
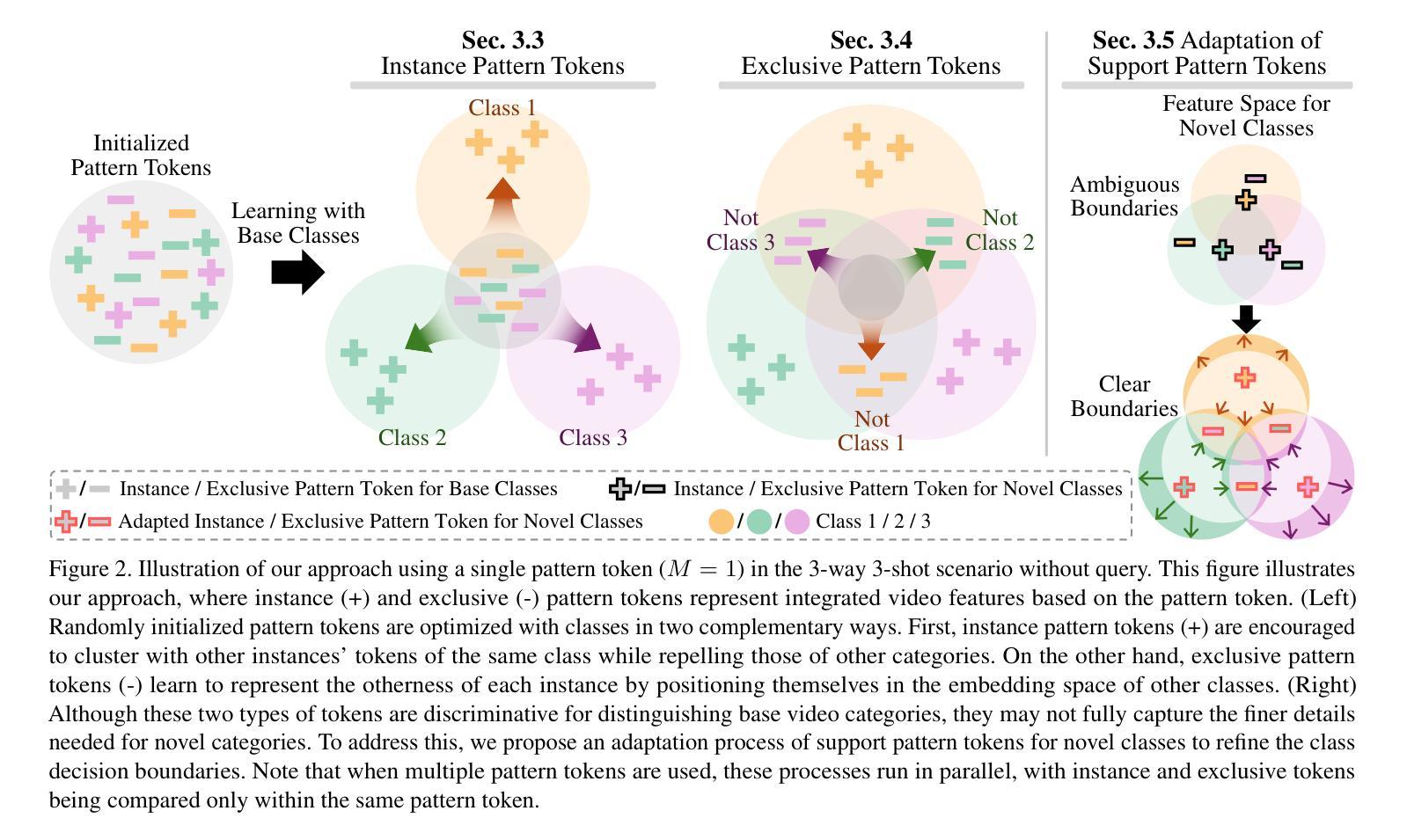
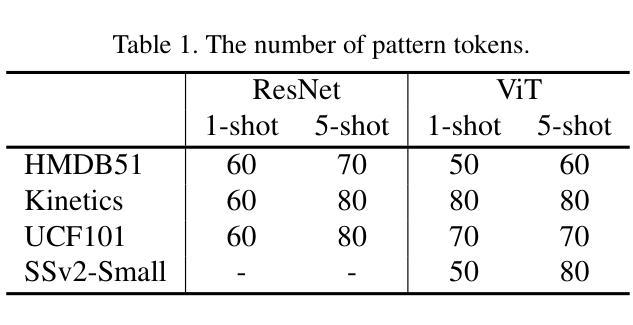
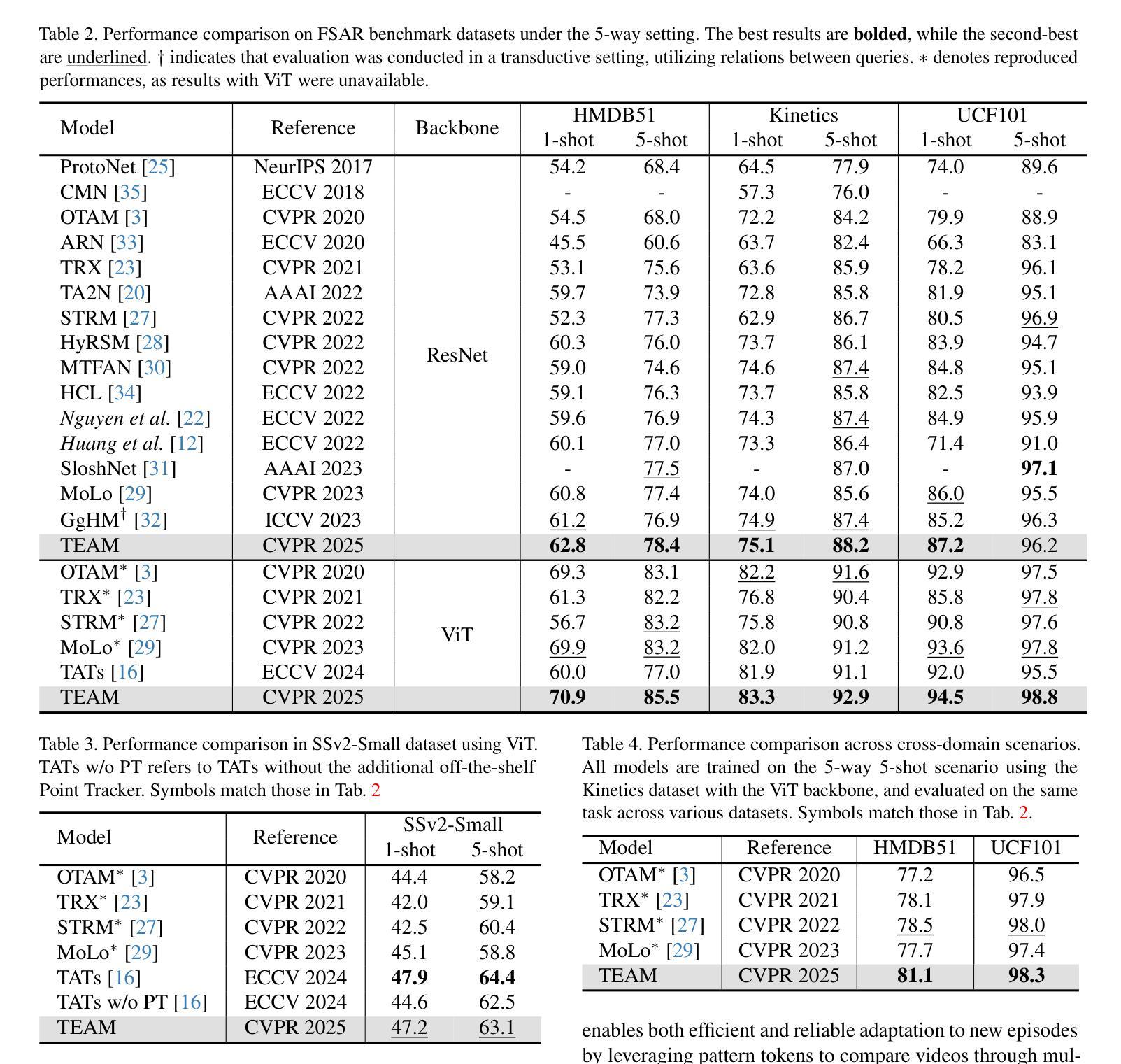
Temporal Alignment-Free Video Matching for Few-shot Action Recognition
Authors:SuBeen Lee, WonJun Moon, Hyun Seok Seong, Jae-Pil Heo
Few-Shot Action Recognition (FSAR) aims to train a model with only a few labeled video instances. A key challenge in FSAR is handling divergent narrative trajectories for precise video matching. While the frame- and tuple-level alignment approaches have been promising, their methods heavily rely on pre-defined and length-dependent alignment units (e.g., frames or tuples), which limits flexibility for actions of varying lengths and speeds. In this work, we introduce a novel TEmporal Alignment-free Matching (TEAM) approach, which eliminates the need for temporal units in action representation and brute-force alignment during matching. Specifically, TEAM represents each video with a fixed set of pattern tokens that capture globally discriminative clues within the video instance regardless of action length or speed, ensuring its flexibility. Furthermore, TEAM is inherently efficient, using token-wise comparisons to measure similarity between videos, unlike existing methods that rely on pairwise comparisons for temporal alignment. Additionally, we propose an adaptation process that identifies and removes common information across classes, establishing clear boundaries even between novel categories. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of TEAM. Codes are available at github.com/leesb7426/TEAM.
少量样本动作识别(FSAR)旨在仅使用少量标注视频实例来训练模型。FSAR的一个关键挑战是处理不同的叙事轨迹以实现精确的视频匹配。尽管帧级和元组级对齐方法已经显示出希望,但它们的方法严重依赖于预定义和长度依赖的对齐单位(例如帧或元组),这限制了对于不同长度和速度动作的灵活性。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种新型的无需时间对齐匹配(TEAM)方法,该方法消除了动作表示中时间单位的需求以及在匹配过程中的强制对齐。具体来说,TEAM使用一组固定的模式令牌来表示每个视频,这些令牌可以捕获视频实例中的全局鉴别线索,而不考虑动作的长度或速度,从而确保其灵活性。此外,TEAM本质上是高效的,使用令牌级的比较来测量视频之间的相似性,与现有方法不同,现有方法依赖于成对比较进行时间对齐。另外,我们提出了一个适应过程,可以识别和删除跨类别的通用信息,即使在新型类别之间也建立清晰的边界。大量实验证明了TEAM的有效性。代码可在github.com/leesb7426/TEAM找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 7 figures, 6 tables, Accepted to CVPR 2025 as Oral Presentation
Summary
少量标注视频样本的动作识别(FSAR)面临处理不同叙事轨迹的挑战。现有方法依赖于预定义和长度依赖的对齐单元,限制了其在不同长度和速度动作上的灵活性。本文提出了一种新型的无需时间对齐匹配(TEAM)方法,通过固定模式的令牌表示视频,捕捉全局鉴别线索,确保灵活性。此外,它采用令牌比较测量视频相似性,具有高效性。同时,提出适应过程,明确类别间的界限。实验证明TEAM的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- Few-Shot Action Recognition (FSAR) 旨在用少量标注视频实例训练模型。
- 处理不同叙事轨迹是FSAR的一个关键挑战。
- 现有方法依赖于预定义和长度依赖的对齐单元,限制了其在不同长度和速度动作的灵活性。
- TEAM方法通过固定模式的令牌表示视频,无需时间对齐。
- TEAM方法捕捉全局鉴别线索,确保灵活性并测量视频相似性。
- TEAM采用令牌比较,具有高效性,与现有方法不同。
点此查看论文截图

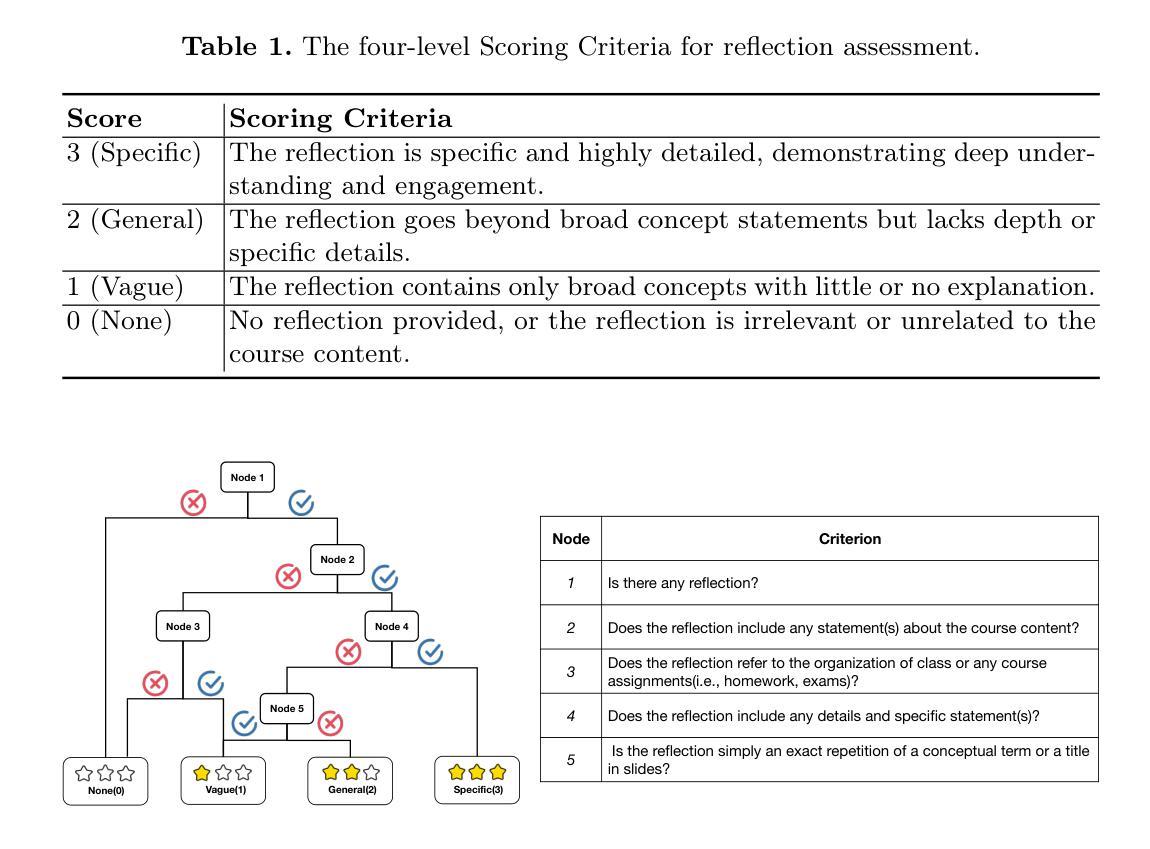
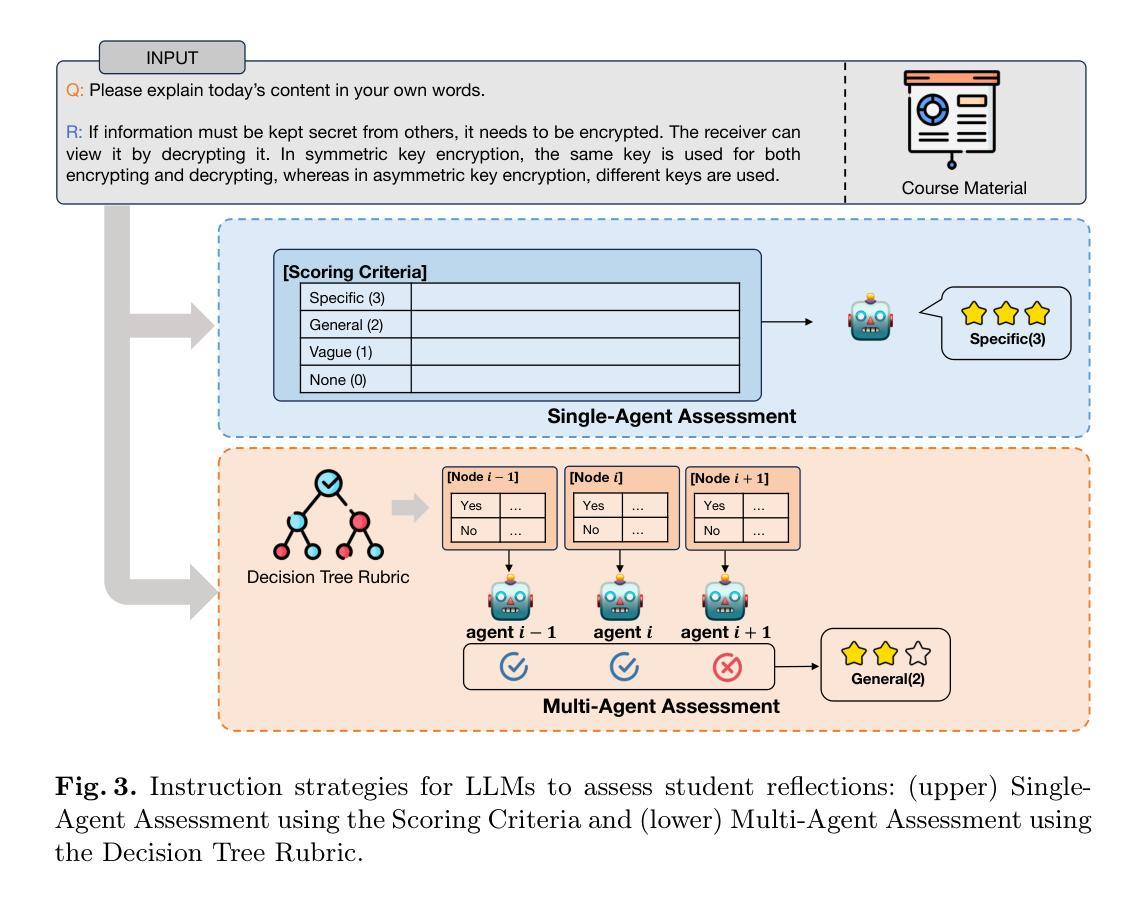
Single-Agent vs. Multi-Agent LLM Strategies for Automated Student Reflection Assessment
Authors:Gen Li, Li Chen, Cheng Tang, Valdemar Švábenský, Daisuke Deguchi, Takayoshi Yamashita, Atsushi Shimada
We explore the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) for automated assessment of open-text student reflections and prediction of academic performance. Traditional methods for evaluating reflections are time-consuming and may not scale effectively in educational settings. In this work, we employ LLMs to transform student reflections into quantitative scores using two assessment strategies (single-agent and multi-agent) and two prompting techniques (zero-shot and few-shot). Our experiments, conducted on a dataset of 5,278 reflections from 377 students over three academic terms, demonstrate that the single-agent with few-shot strategy achieves the highest match rate with human evaluations. Furthermore, models utilizing LLM-assessed reflection scores outperform baselines in both at-risk student identification and grade prediction tasks. These findings suggest that LLMs can effectively automate reflection assessment, reduce educators’ workload, and enable timely support for students who may need additional assistance. Our work emphasizes the potential of integrating advanced generative AI technologies into educational practices to enhance student engagement and academic success.
我们探讨了大型语言模型(LLM)在自动评估学生开放性反思和预测学业表现方面的应用。传统的反思评估方法耗时且在教育环境中可能无法有效扩展。在这项工作中,我们采用LLM,使用两种评估策略(单智能体和多智能体)和两种提示技术(零样本和少样本),将学生反思转化为量化分数。我们在包含来自377名学生在三个学术学期内的5,278篇反思的数据集上进行的实验表明,采用少样本策略的单智能体取得了最高的与人类评价的匹配率。此外,利用LLM评估的反思分数的模型在风险学生识别和成绩预测任务中的表现均优于基线。这些结果表明,LLM可以有效地自动进行反思评估,减少教育工作者的工作量,并为可能需要额外帮助的学生提供及时的支持。我们的工作强调了将先进的生成性AI技术融入教育实践中的潜力,以提高学生的参与度和学业成功。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To be published in Proceedings of the 29th Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (PAKDD 2025)
Summary
大规模语言模型(LLMs)在自动评估学生开放性反思和预测学业表现方面的应用探究。传统评估方式耗时且难以在教育环境中有效扩展。本研究采用LLMs,通过两种评估策略(单主体和多主体)和两种提示技术(零样本和少样本),将学生反思转化为量化分数。实验数据显示,采用少样本策略的单主体模型与人类评估匹配度最高。此外,利用LLM评估的反思分数的模型在识别学业风险学生和预测成绩任务中的表现均优于基线。这表明LLMs能有效自动化反思评估,减轻教育工作者的工作量,并为可能需要额外帮助的学生提供及时支持。本研究强调了将先进的生成式AI技术融入教育实践,以提高学生学习参与度和学业成功的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 研究使用大规模语言模型(LLMs)自动评估学生的开放性反思,预测学业表现。
- 传统评估方式存在耗时且难以在教育环境中有效扩展的问题。
- 采用LLMs的评估方式包括两种策略:单主体评估和多主体评估,以及两种提示技术:零样本和少样本。
- 实验结果显示,采用少样本策略的单主体模型与人类评估匹配度最高。
- LLMs在识别学业风险学生和预测成绩任务中的表现优于基线方法。
- LLMs的应用能有效自动化反思评估,减轻教育工作者的工作量。
点此查看论文截图


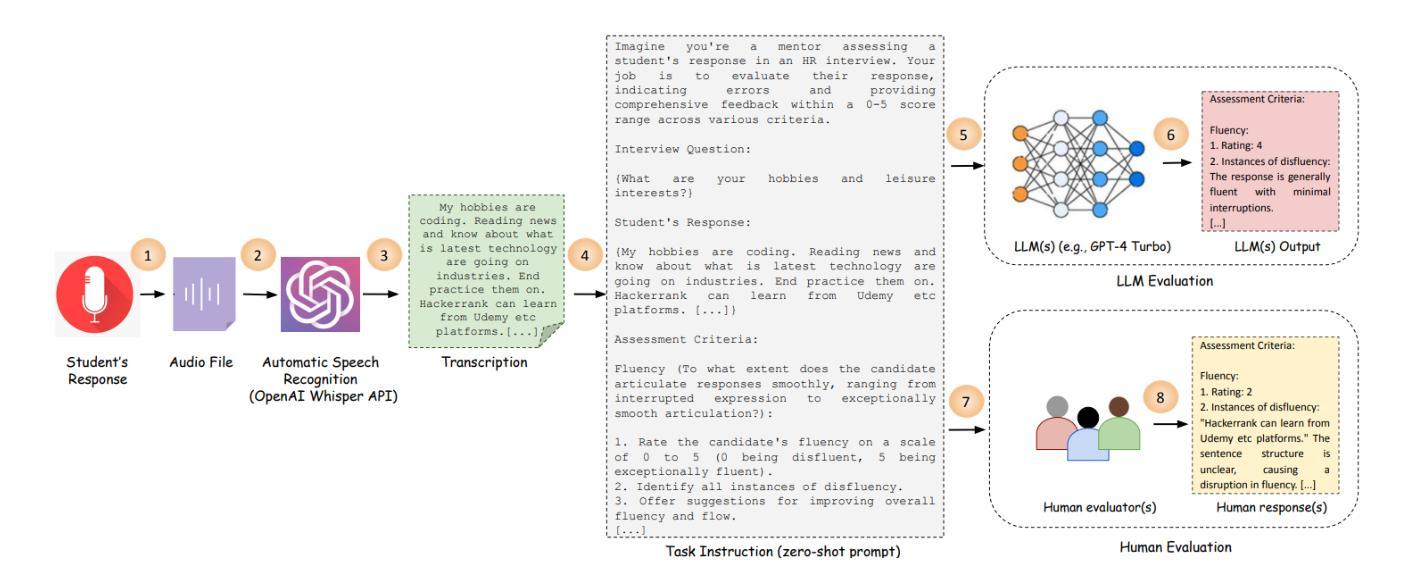
Towards Smarter Hiring: Are Zero-Shot and Few-Shot Pre-trained LLMs Ready for HR Spoken Interview Transcript Analysis?
Authors:Subhankar Maity, Aniket Deroy, Sudeshna Sarkar
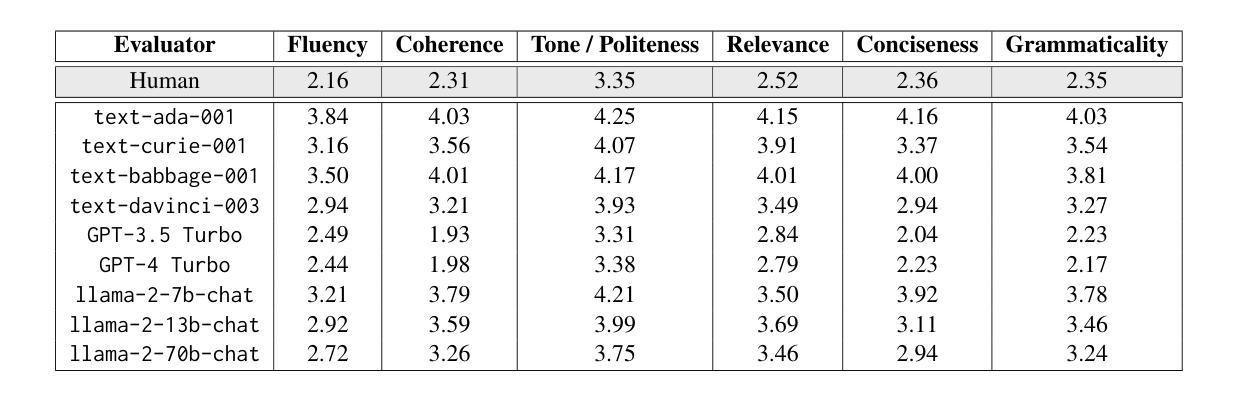
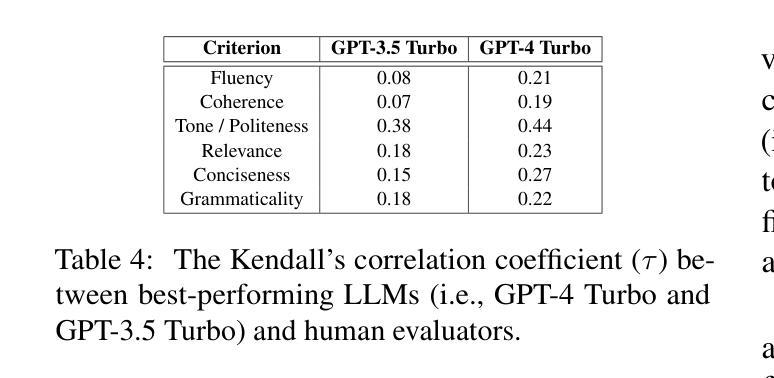
This research paper presents a comprehensive analysis of the performance of prominent pre-trained large language models (LLMs), including GPT-4 Turbo, GPT-3.5 Turbo, text-davinci-003, text-babbage-001, text-curie-001, text-ada-001, llama-2-7b-chat, llama-2-13b-chat, and llama-2-70b-chat, in comparison to expert human evaluators in providing scores, identifying errors, and offering feedback and improvement suggestions to candidates during mock HR (Human Resources) interviews. We introduce a dataset called HURIT (Human Resource Interview Transcripts), which comprises 3,890 HR interview transcripts sourced from real-world HR interview scenarios. Our findings reveal that pre-trained LLMs, particularly GPT-4 Turbo and GPT-3.5 Turbo, exhibit commendable performance and are capable of producing evaluations comparable to those of expert human evaluators. Although these LLMs demonstrate proficiency in providing scores comparable to human experts in terms of human evaluation metrics, they frequently fail to identify errors and offer specific actionable advice for candidate performance improvement in HR interviews. Our research suggests that the current state-of-the-art pre-trained LLMs are not fully conducive for automatic deployment in an HR interview assessment. Instead, our findings advocate for a human-in-the-loop approach, to incorporate manual checks for inconsistencies and provisions for improving feedback quality as a more suitable strategy.
本文全面分析了主流预训练大型语言模型(LLM)在模拟人力资源(HR)面试中的表现,包括GPT-4 Turbo、GPT-3.5 Turbo、text-davinci-003、text-babbage-001、text-curie-001、text-ada-001、llama-2-7b-chat、llama-2-13b-chat和llama-2-70b-chat等模型与专家评委相比在评分、识别错误和对候选人提供反馈和改进建议方面的表现。我们引入了一个名为HURIT(人力资源面试记录)的数据集,其中包含来自现实世界人力资源面试场景的3890份面试记录。我们的研究发现,预训练LLM,尤其是GPT-4 Turbo和GPT-3.5 Turbo,表现出值得称赞的性能,能够产生与专家评委相当的评价。尽管这些LLM在按照人类评估指标提供可比分数的评分方面表现出色,但它们往往无法识别错误并为候选人在人力资源面试中的表现改进提供具体的可操作的建议。我们的研究表明,目前最先进的预训练LLM并不适合完全自动部署在人力资源面试评估中。相反,我们的研究结果提倡采用人类参与循环的方法,通过手动检查不一致并提供改进反馈质量的策略,作为更合适的策略。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 32 pages, 24 figures
Summary
本文研究了多种主流预训练大语言模型(LLMs)在模拟人力资源(HR)面试中的表现。通过引入HURIT数据集,对LLMs在评分、识别错误以及提供改进建议方面的能力进行了评估。研究发现,尽管LLMs在评分方面表现出色,但与人类专家相比,它们在识别错误和提供具体可操作的改进建议方面存在不足。因此,目前LLMs并不适合完全自动部署在HR面试评估中。建议采用人机结合的方式,以提高反馈质量。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练大语言模型(LLMs)在模拟人力资源(HR)面试中的评分表现与人类专家相当。
- GPT-4 Turbo和GPT-3.5 Turbo在HR面试评估中展现出卓越性能。
- LLMs在识别面试中的错误和提供具体可操作的改进建议方面存在不足。
- 目前LLMs并不适合完全自动部署在HR面试评估中。
- 建议采用人机结合的方式,通过手动检查不一致性来提高反馈质量。
- HURIT数据集为评估LLMs在HR面试中的表现提供了重要资源。
点此查看论文截图



Few-shot Personalized Scanpath Prediction
Authors:Ruoyu Xue, Jingyi Xu, Sounak Mondal, Hieu Le, Gregory Zelinsky, Minh Hoai, Dimitris Samaras
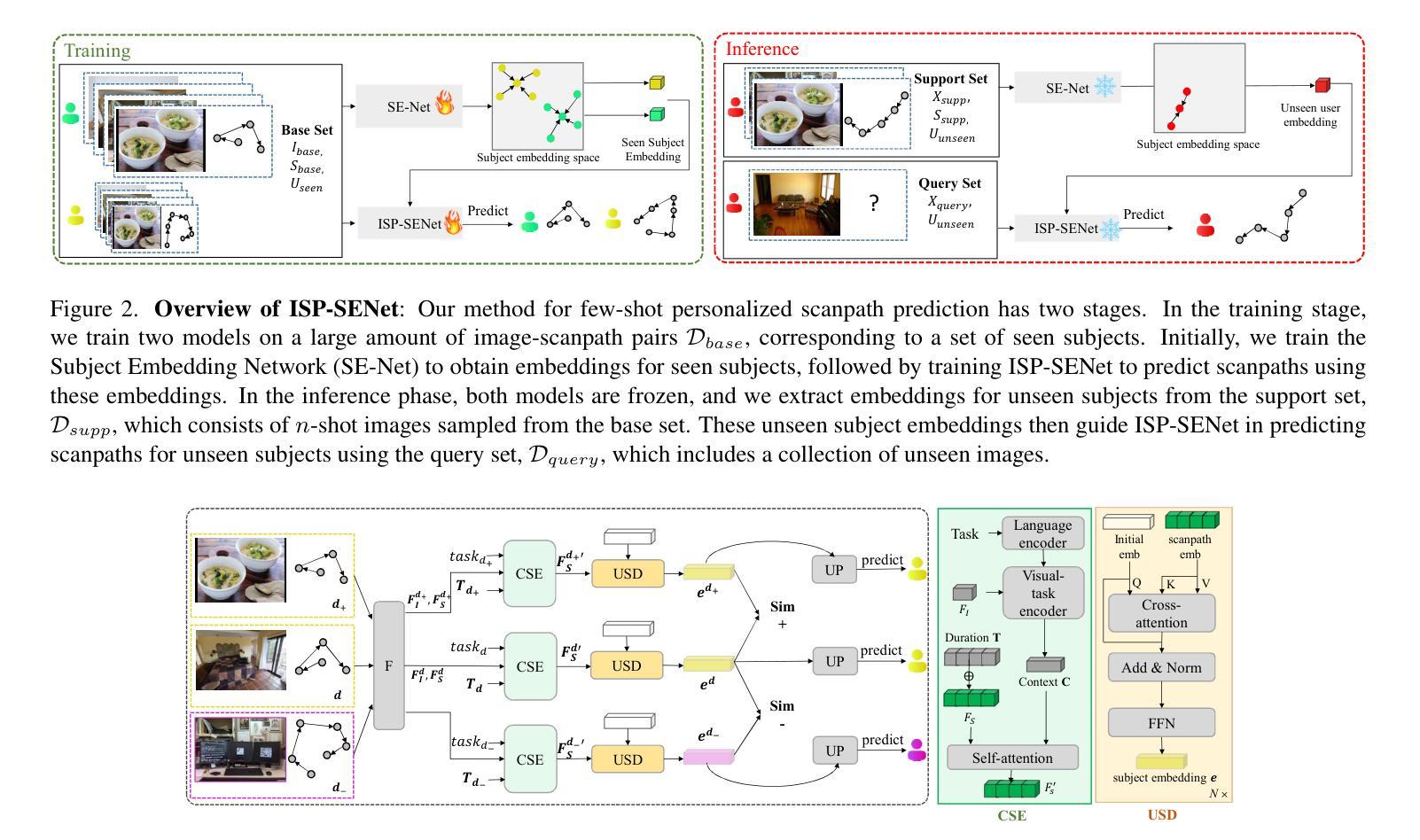
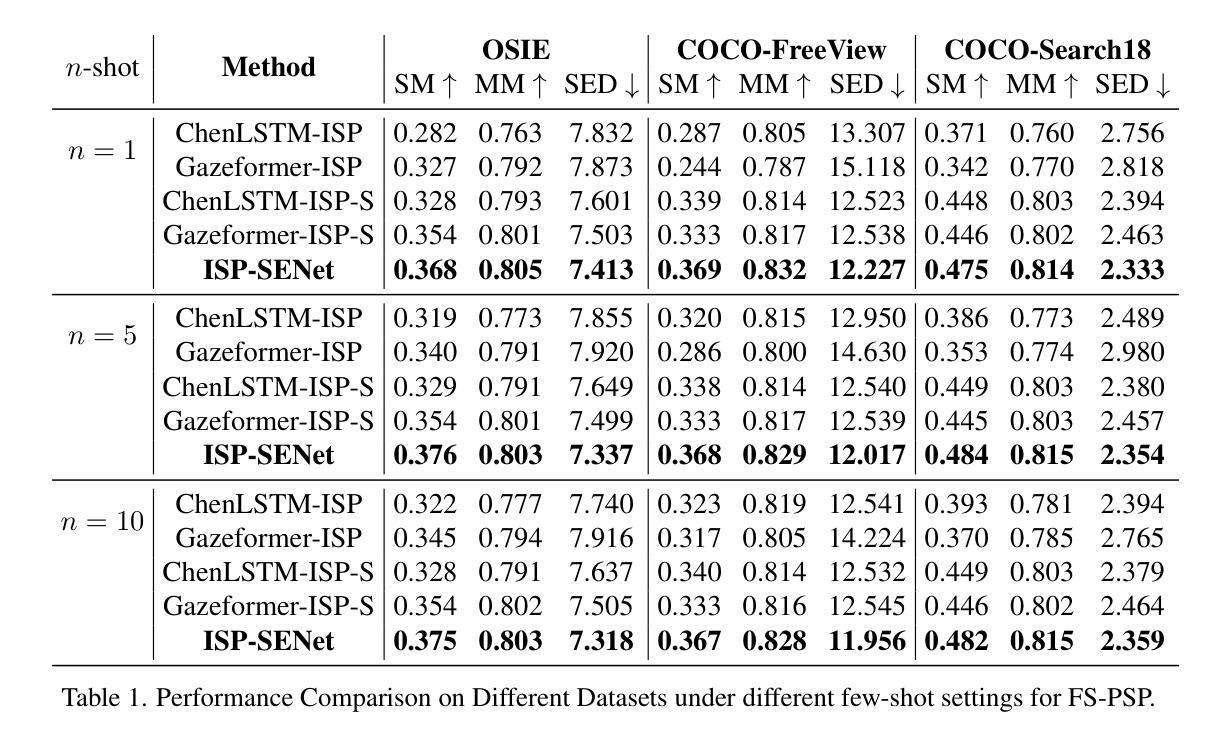
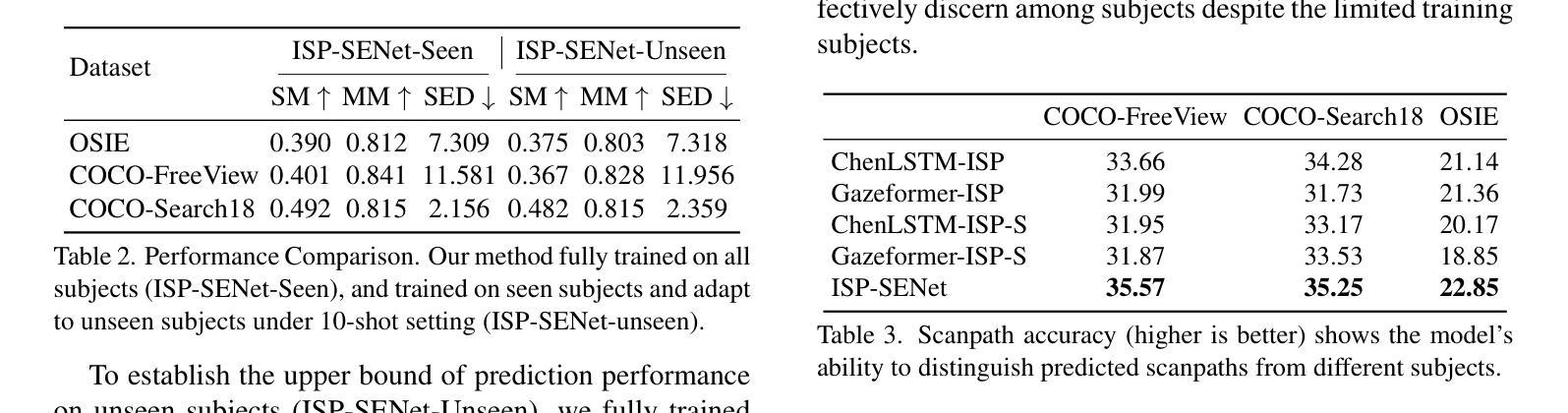
A personalized model for scanpath prediction provides insights into the visual preferences and attention patterns of individual subjects. However, existing methods for training scanpath prediction models are data-intensive and cannot be effectively personalized to new individuals with only a few available examples. In this paper, we propose few-shot personalized scanpath prediction task (FS-PSP) and a novel method to address it, which aims to predict scanpaths for an unseen subject using minimal support data of that subject’s scanpath behavior. The key to our method’s adaptability is the Subject-Embedding Network (SE-Net), specifically designed to capture unique, individualized representations for each subject’s scanpaths. SE-Net generates subject embeddings that effectively distinguish between subjects while minimizing variability among scanpaths from the same individual. The personalized scanpath prediction model is then conditioned on these subject embeddings to produce accurate, personalized results. Experiments on multiple eye-tracking datasets demonstrate that our method excels in FS-PSP settings and does not require any fine-tuning steps at test time. Code is available at: https://github.com/cvlab-stonybrook/few-shot-scanpath
个性化扫描路径预测模型为我们提供了关于个体视觉偏好和注意力模式的见解。然而,现有的训练扫描路径预测模型的方法需要大量的数据,并且不能仅通过几个可用的示例有效地对新的个体进行个性化设置。在本文中,我们提出了小样例个性化扫描路径预测任务(FS-PSP)和一种解决该任务的新方法,旨在使用目标对象的最小支持数据来预测其未见的扫描路径。我们方法适应性的关键是主体嵌入网络(SE-Net),它专门设计用于捕获每个主体扫描路径的独特个性化表示。SE-Net生成主体嵌入,有效地区分不同主体,同时最小化同一主体扫描路径之间的变化。个性化扫描路径预测模型然后基于这些主体嵌入来产生准确、个性化的结果。在多个眼动数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法在FS-PSP环境中表现出色,并且在测试时不需要任何微调步骤。代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/cvlab-stonybrook/few-shot-scanpath。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025,20 pages, 10 figures
Summary
扫描路径预测模型能洞察个体视觉偏好和注意力模式。现有方法需要大量数据训练,难以对新个体进行个性化预测,仅使用少量样本则效果不佳。本文提出小样本周个性化扫描路径预测任务(FS-PSP)及其解决方法,旨在使用少量支持数据预测未见个体的扫描路径。方法的关键在于设计主体嵌入网络(SE-Net),为每个个体的扫描路径生成独特的个性化表示,有效区分个体并最小化同一人的扫描路径变化。基于这些主体嵌入,个性化扫描路径预测模型产生准确结果。在多个眼动数据集上的实验表明,该方法在FS-PSP环境下表现优异,测试时无需微调。
Key Takeaways
- 个性化模型能揭示视觉偏好和注意力模式。
- 现有扫描路径预测模型需要大量数据,难以进行个性化预测。
- 提出小样本周个性化扫描路径预测任务(FS-PSP)。
- 引入主体嵌入网络(SE-Net)生成个体扫描路径的独特表示。
- SE-Net能有效区分不同个体,并最小化同一人的扫描路径变化。
- 基于主体嵌入的个性化扫描路径预测模型产生准确结果。
点此查看论文截图

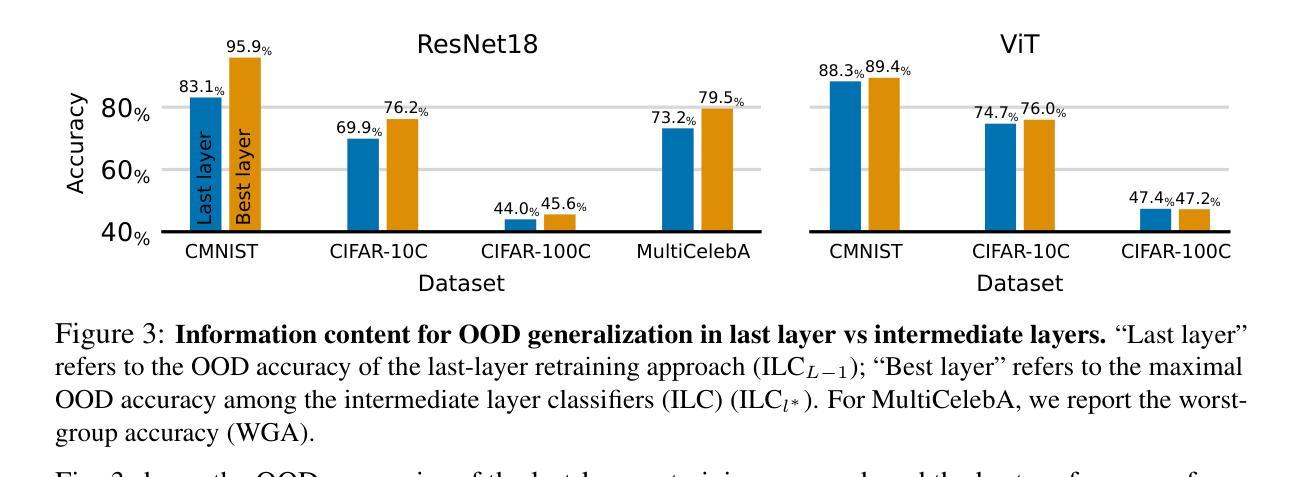
Intermediate Layer Classifiers for OOD generalization
Authors:Arnas Uselis, Seong Joon Oh
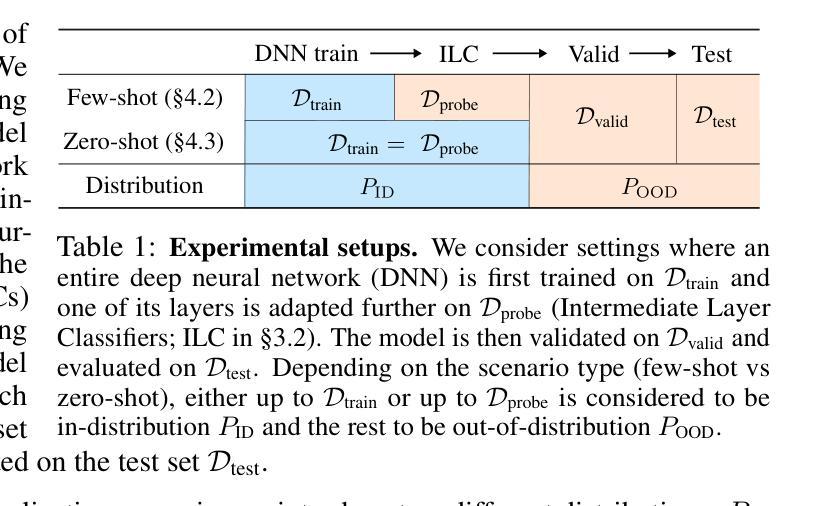
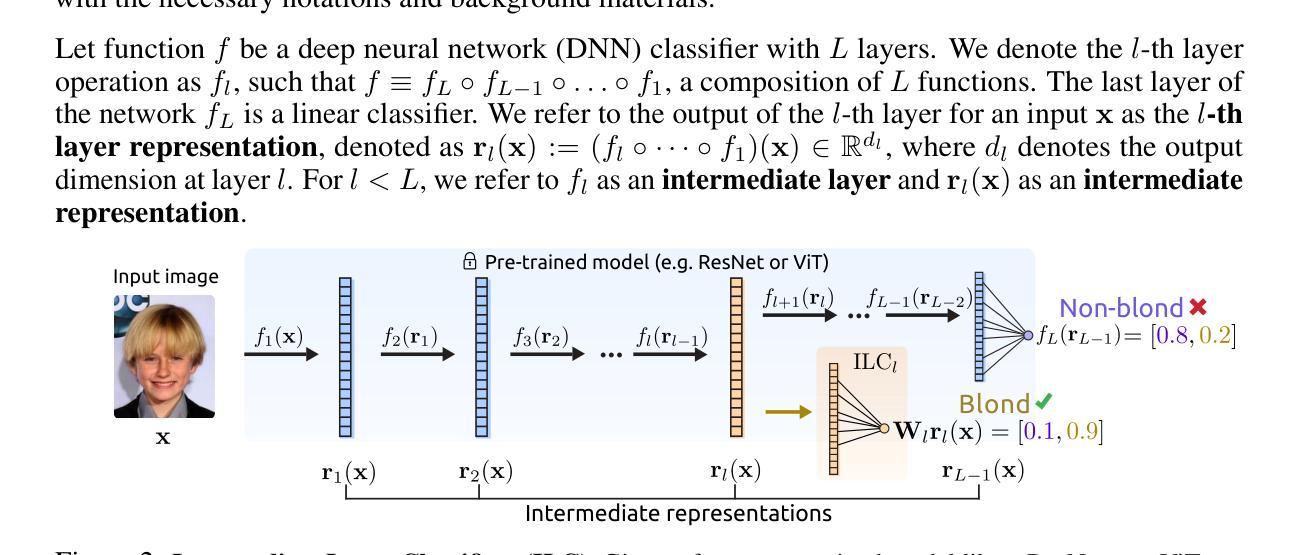
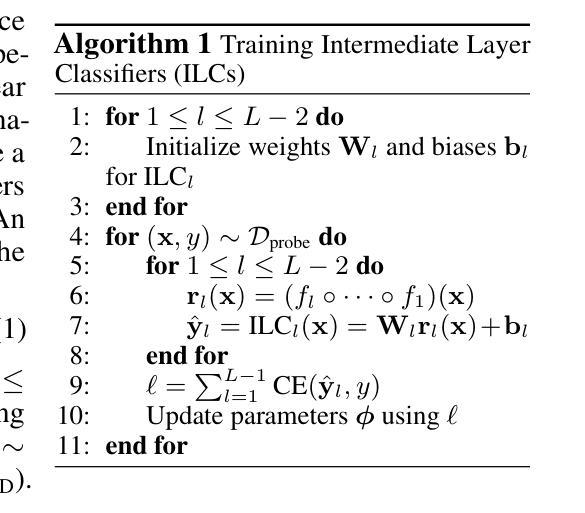
Deep classifiers are known to be sensitive to data distribution shifts, primarily due to their reliance on spurious correlations in training data. It has been suggested that these classifiers can still find useful features in the network’s last layer that hold up under such shifts. In this work, we question the use of last-layer representations for out-of-distribution (OOD) generalisation and explore the utility of intermediate layers. To this end, we introduce \textit{Intermediate Layer Classifiers} (ILCs). We discover that intermediate layer representations frequently offer substantially better generalisation than those from the penultimate layer. In many cases, zero-shot OOD generalisation using earlier-layer representations approaches the few-shot performance of retraining on penultimate layer representations. This is confirmed across multiple datasets, architectures, and types of distribution shifts. Our analysis suggests that intermediate layers are less sensitive to distribution shifts compared to the penultimate layer. These findings highlight the importance of understanding how information is distributed across network layers and its role in OOD generalisation, while also pointing to the limits of penultimate layer representation utility. Code is available at https://github.com/oshapio/intermediate-layer-generalization
深度分类器对数据分布变化敏感,这主要归因于它们对训练数据中偶然关联性的依赖。尽管如此,已有研究建议这些分类器仍可在网络的最后一层找到在此类变化中依然有效的特征。在这项工作中,我们质疑使用最后一层的表示来进行超出分布范围(OOD)泛化的做法,并探索中间层的实用性。为此,我们引入了中间层分类器(ILCs)。我们发现中间层的表示经常比倒数第二层的表示提供更好的泛化能力。在许多情况下,使用早期层表示的零样本OOD泛化接近在倒数第二层表示上进行微调后的少数样本性能。这在多个数据集、架构和分布变化类型上得到了证实。我们的分析表明,中间层与倒数第二层相比,对分布变化的敏感性较低。这些发现强调了理解信息在网络各层中的分布及其在超出分布范围泛化中的作用的重要性,同时也指出了倒数第二层表示实用性的局限性。相关代码可访问https://github.com/oshapio/intermediate-layer-generalization获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
本文探讨了深度分类器对于数据分布变化的敏感性,并提出了中间层分类器(ILCs)来解决这一问题。研究发现,中间层的表示在大多数情况下提供了比最终层更好的泛化能力,甚至在零样本情况下接近重新训练最终层表示的少量样本性能。这些发现对于理解信息在网络各层的分布及其在面向未知分布数据的泛化中的角色至关重要。
Key Takeaways
- 深度分类器对训练数据的偶然相关性非常敏感,这导致了其在面对数据分布变化时的性能下降。
- 中间层分类器(ILCs)被引入以解决这一问题,它们利用网络中间层的表示进行预测。
- 中间层的表示通常提供了比最终层更好的泛化能力。
- 在某些情况下,使用早期层的零样本泛化性能接近于在最终层重新训练所需的少量样本。
- 多种数据集、架构和分布变化类型上的实验证实了这些发现。
- 中间层相对于最终层对分布变化的敏感性较低。
点此查看论文截图

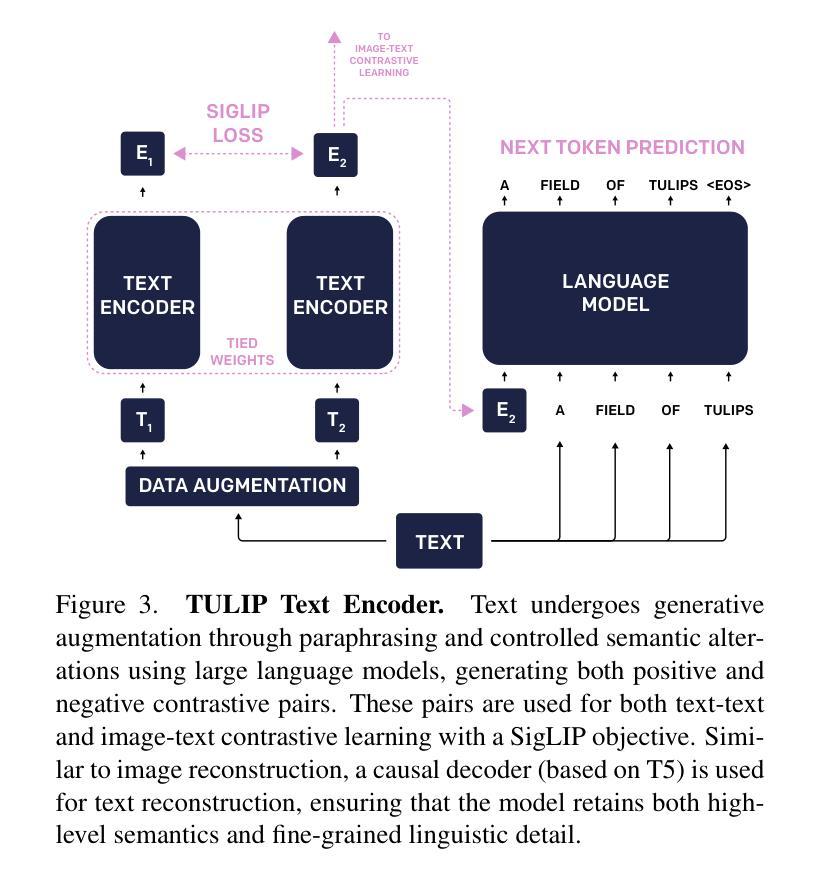
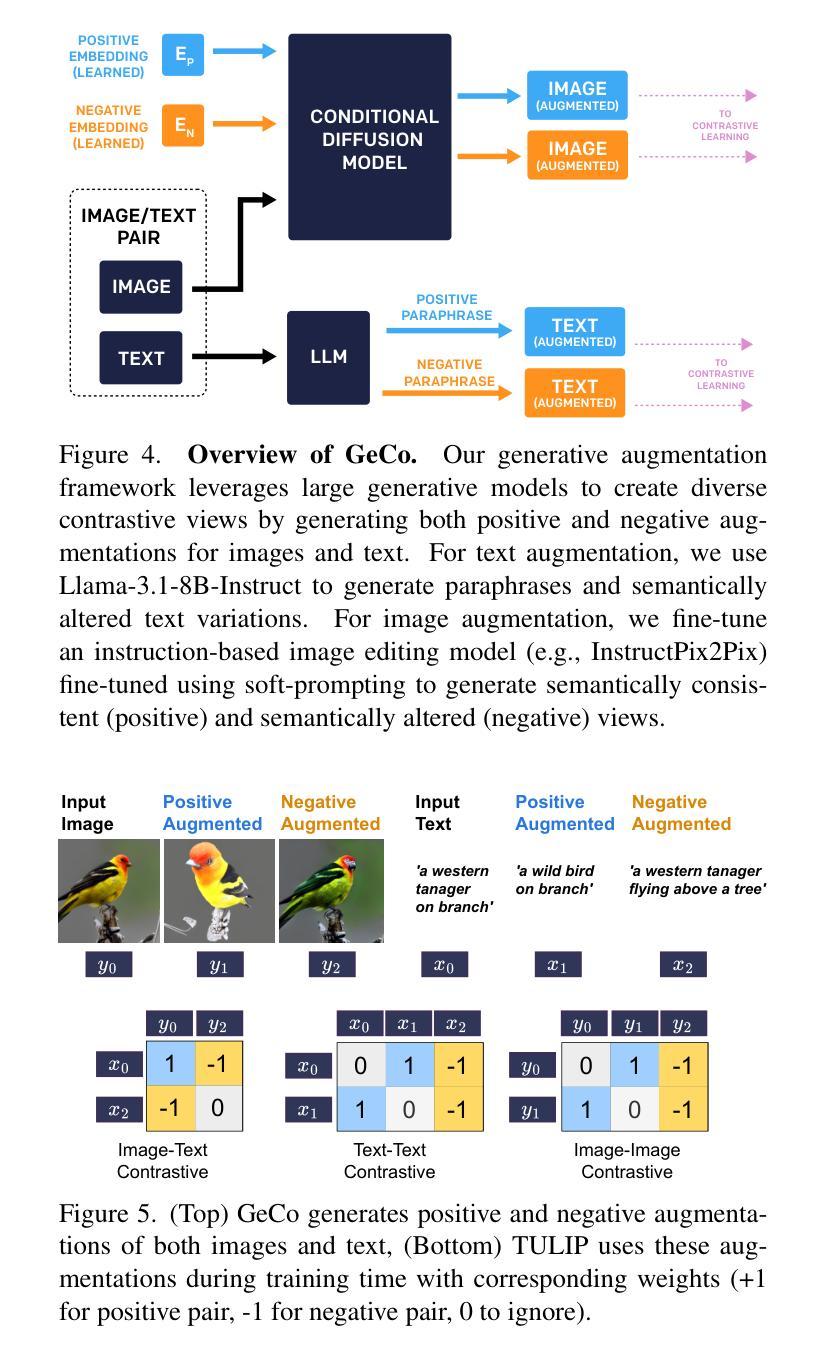
TULIP: Towards Unified Language-Image Pretraining
Authors:Zineng Tang, Long Lian, Seun Eisape, XuDong Wang, Roei Herzig, Adam Yala, Alane Suhr, Trevor Darrell, David M. Chan
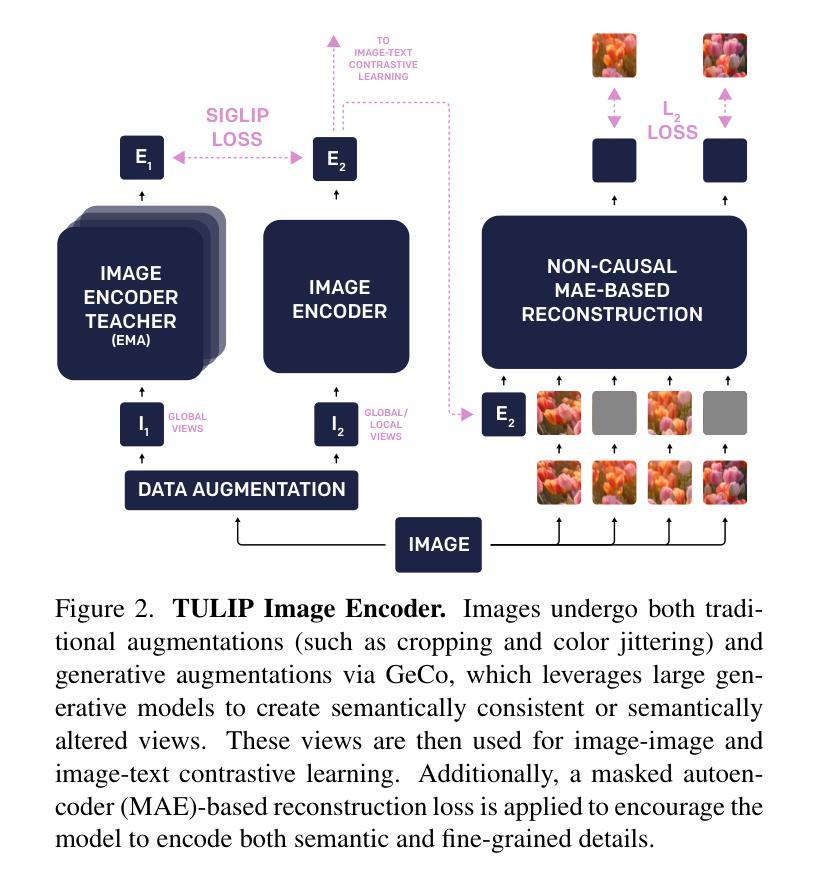
Despite the recent success of image-text contrastive models like CLIP and SigLIP, these models often struggle with vision-centric tasks that demand high-fidelity image understanding, such as counting, depth estimation, and fine-grained object recognition. These models, by performing language alignment, tend to prioritize high-level semantics over visual understanding, weakening their image understanding. On the other hand, vision-focused models are great at processing visual information but struggle to understand language, limiting their flexibility for language-driven tasks. In this work, we introduce TULIP, an open-source, drop-in replacement for existing CLIP-like models. Our method leverages generative data augmentation, enhanced image-image and text-text contrastive learning, and image/text reconstruction regularization to learn fine-grained visual features while preserving global semantic alignment. Our approach, scaling to over 1B parameters, outperforms existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) models across multiple benchmarks, establishing a new SOTA zero-shot performance on ImageNet-1K, delivering up to a $2\times$ enhancement over SigLIP on RxRx1 in linear probing for few-shot classification, and improving vision-language models, achieving over $3\times$ higher scores than SigLIP on MMVP. Our code/checkpoints are available at https://tulip-berkeley.github.io
尽管CLIP和SigLIP等图文对比模型近期取得了成功,但这些模型在进行需要高保真图像理解的任务时,如计数、深度估计和精细目标识别等方面常常面临挑战。这些模型通过执行语言对齐,倾向于优先处理高级语义而非视觉理解,从而削弱了它们的图像理解能力。另一方面,以视觉为中心的模型在处理视觉信息方面表现出色,但在理解语言方面却遇到困难,这限制了它们在语言驱动任务中的灵活性。在这项工作中,我们引入了TULIP,它是现有CLIP类似模型的即插即用替代品。我们的方法利用生成性数据增强、增强的图像图像和文本文本对比学习以及图像/文本重建正则化,学习精细的视觉特征,同时保留全局语义对齐。我们的方法扩展到超过10亿参数,在多个基准测试中超越了现有最先进的模型,在ImageNet-1K上建立了新的零样本性能,在RxRx1上对SigLIP进行线性探测时的准确率提高了两倍进行小样本分类;同时改进了视觉语言模型,在MMVP上达到了超过SigLIP三倍的成绩。我们的代码/检查点可通过以下链接获取:[https://tulip-berkeley.github.io/] 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF (v2) Clarified fine-tuning process, updated appendix
Summary
本文介绍了TULIP模型,它是CLIP类模型的开源替代方案,旨在解决图像理解的问题。该模型通过利用生成式数据增强、增强的图像-图像和文本-文本对比学习以及图像/文本重建正则化,能够在保留全局语义对齐的同时学习精细的视觉特征。此方法规模超过1B参数,并在多个基准测试中表现出超越现有最新技术(SOTA)模型的表现。
Key Takeaways
- TULIP模型是解决图像理解问题的开放源代码解决方案,针对CLIP等模型进行改进。
- TULIP强调在保留全局语义对齐的同时学习精细的视觉特征。
- TULIP利用生成式数据增强进行模型训练。
- 该模型采用增强的图像到图像和文本到文本的对比学习技术。
- TULIP通过图像/文本重建正则化进行训练。
- TULIP模型规模超过1B参数,性能优于现有SOTA模型。
点此查看论文截图
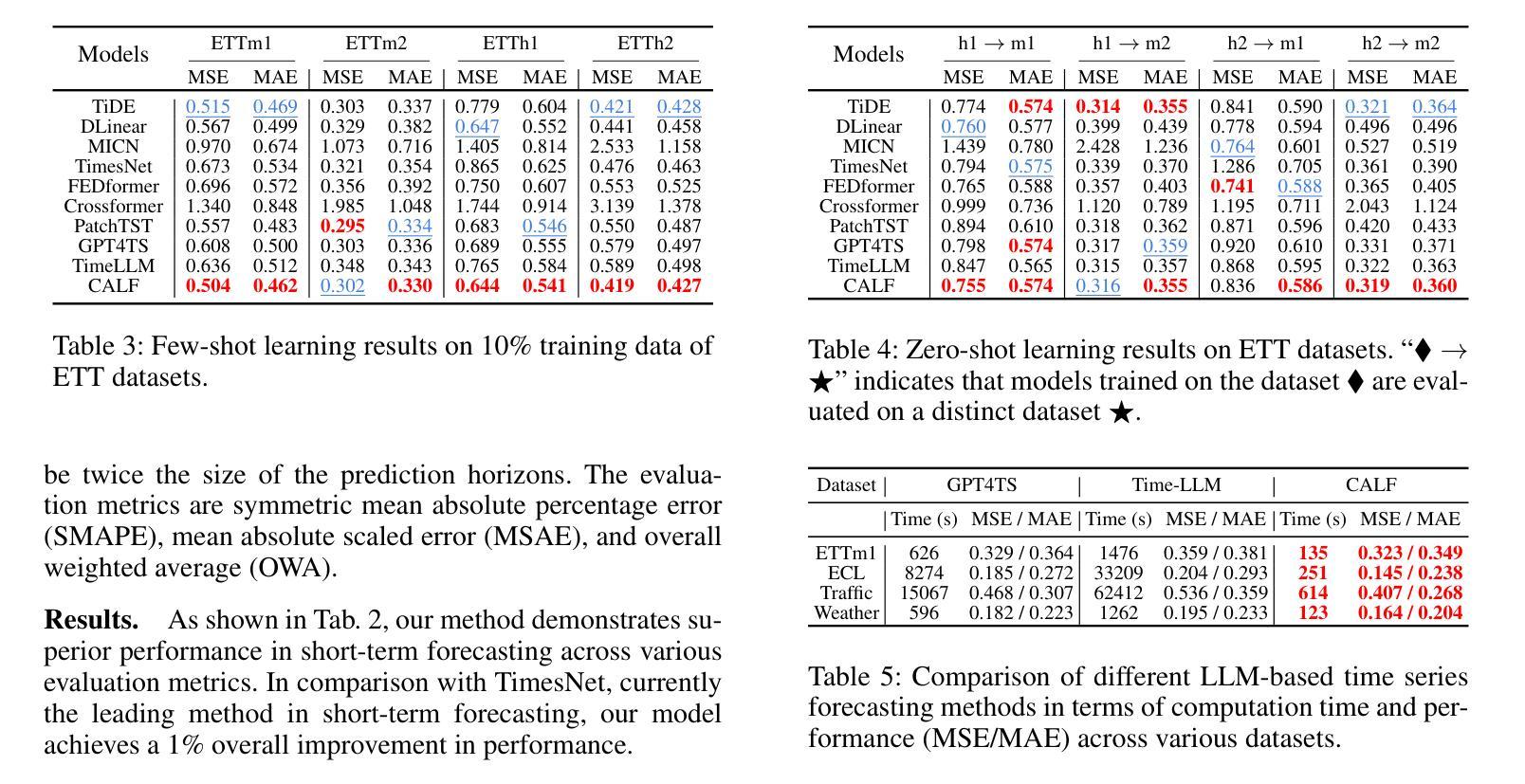
CALF: Aligning LLMs for Time Series Forecasting via Cross-modal Fine-Tuning
Authors:Peiyuan Liu, Hang Guo, Tao Dai, Naiqi Li, Jigang Bao, Xudong Ren, Yong Jiang, Shu-Tao Xia
Deep learning (e.g., Transformer) has been widely and successfully used in multivariate time series forecasting (MTSF). Unlike existing methods that focus on training models from a single modal of time series input, large language models (LLMs) based MTSF methods with cross-modal text and time series input have recently shown great superiority, especially with limited temporal data. However, current LLM-based MTSF methods usually focus on adapting and fine-tuning LLMs, while neglecting the distribution discrepancy between textual and temporal input tokens, thus leading to sub-optimal performance. To address this issue, we propose a novel Cross-Modal LLM Fine-Tuning (CALF) framework for MTSF by reducing the distribution discrepancy between textual and temporal data, which mainly consists of the temporal target branch with temporal input and the textual source branch with aligned textual input. To reduce the distribution discrepancy, we develop the cross-modal match module to first align cross-modal input distributions. Additionally, to minimize the modality distribution gap in both feature and output spaces, feature regularization loss is developed to align the intermediate features between the two branches for better weight updates, while output consistency loss is introduced to allow the output representations of both branches to correspond effectively. Thanks to the modality alignment, CALF establishes state-of-the-art performance for both long-term and short-term forecasting tasks with low computational complexity, and exhibiting favorable few-shot and zero-shot abilities similar to that in LLMs. Code is available at https://github.com/Hank0626/LLaTA.
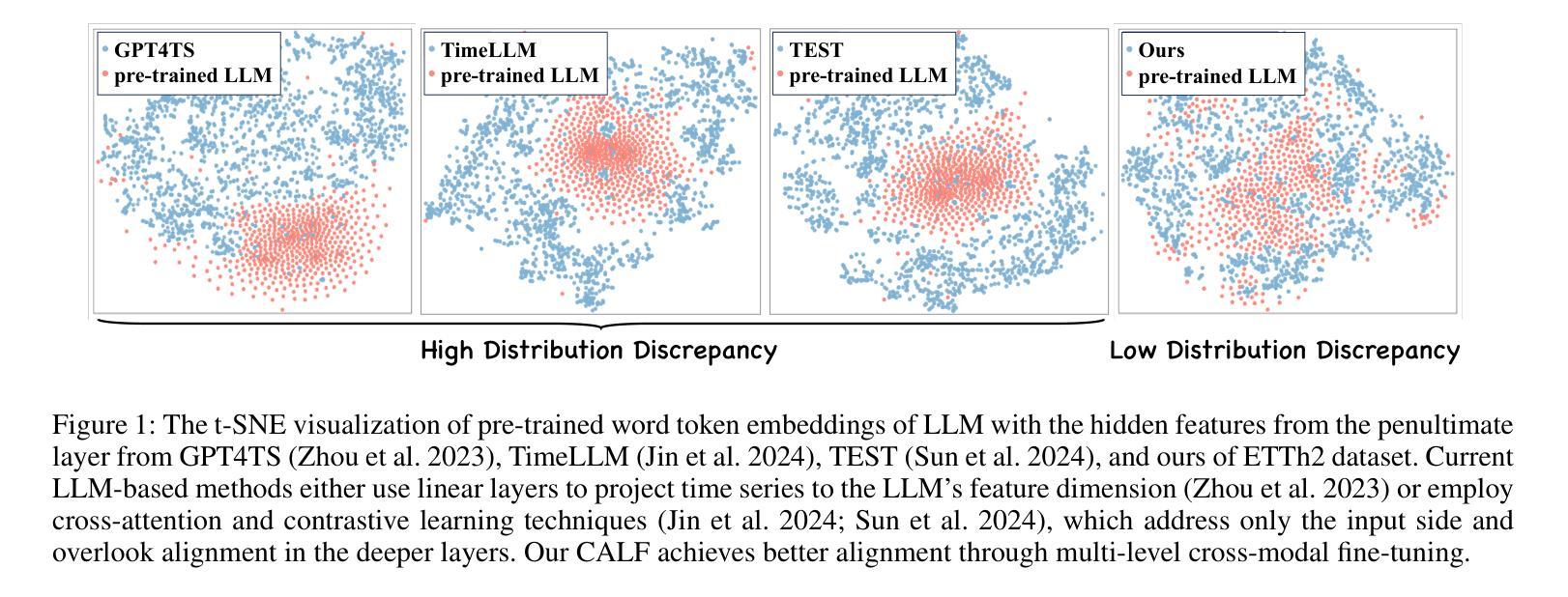
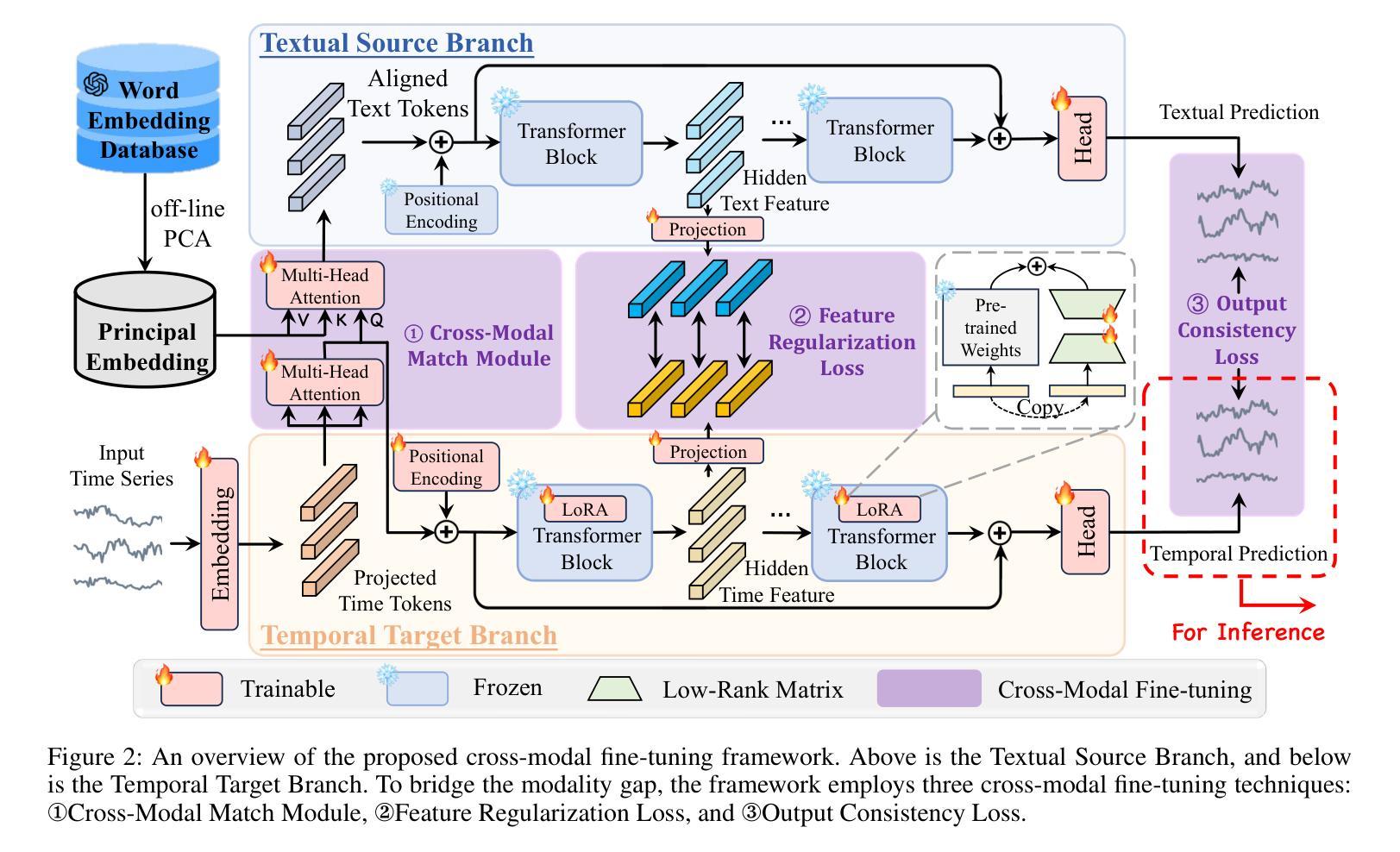
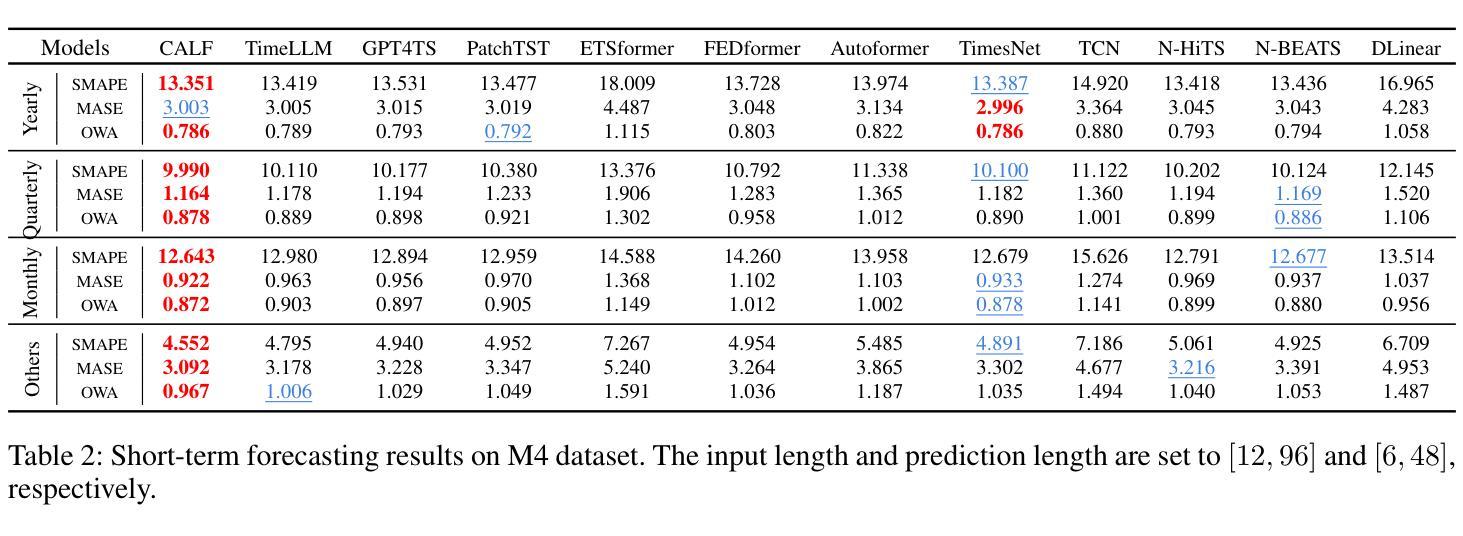
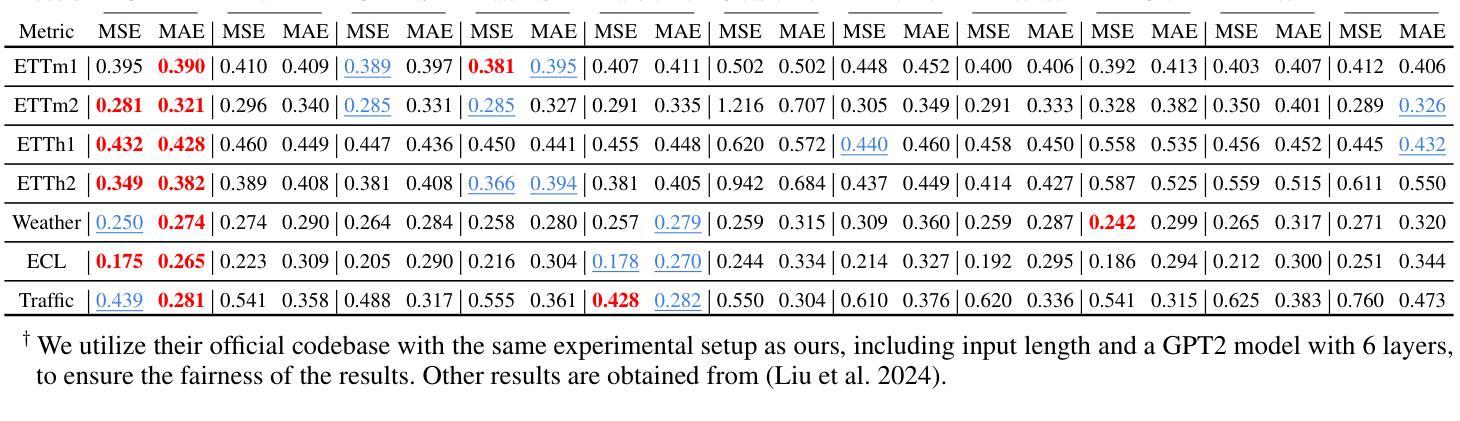
深度学习(例如Transformer)已广泛应用于多元时间序列预测(MTSF)。不同于现有方法从单一模态的时间序列输入进行模型训练,基于大型语言模型(LLM)的MTSF方法采用跨模态文本和时间序列输入,已显示出巨大的优越性,特别是在有限的时间数据情况下。然而,当前的LLM-based MTSF方法通常侧重于适应和微调LLM,而忽略了文本和时间输入标记之间的分布差异,从而导致性能不佳。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了新型的跨模态LLM微调(CALF)框架,通过减少文本和时间数据之间的分布差异,该框架主要由带有时间输入的目标分支和带有对齐文本输入的文本源分支组成。为了减少分布差异,我们开发了跨模态匹配模块来首先对齐跨模态输入分布。此外,为了最小化特征和输出空间中的模态分布差距,我们开发了特征正则化损失来对齐两个分支之间的中间特征以实现更好的权重更新,同时引入了输出一致性损失,以使两个分支的输出表示能够有效地对应。得益于模态对齐,CALF在中长期预测任务上取得了最先进的性能表现,具有较低的计算复杂度,并展现出与LLM相似的优秀的小样本和零样本能力。代码可通过 https://github.com/Hank0626/LLaTA 获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新颖的跨模态LLM微调(CALF)框架,用于处理多元时间序列预测问题。通过减少文本和时间数据分布差异,CALF框架包括时间目标分支和文本源分支,开发跨模态匹配模块和特征正则化损失来对齐特征空间中的模态分布差距,同时引入输出一致性损失以确保两个分支的输出表示有效对应。该框架实现了低计算复杂度和优越的预测性能,展现出强大的少样本和无样本能力。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习(如Transformer)在多元时间序列预测(MTSF)中广泛应用且成功。
- 大规模语言模型(LLMs)基于的MTSF方法,特别是处理有限的时间序列数据时显示出巨大优势。
- 当前LLM-based的MTSF方法主要关注LLMs的适应和微调,忽略了文本和时间输入标记的分布差异。
- CALF框架旨在减少文本和时间数据的分布差异,包括时间目标分支和文本源分支。
- CALF通过跨模态匹配模块和特征正则化损失来对齐不同模态的特征空间分布。
- 输出一致性损失确保两个分支的输出表示有效对应。
点此查看论文截图