⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-10 更新
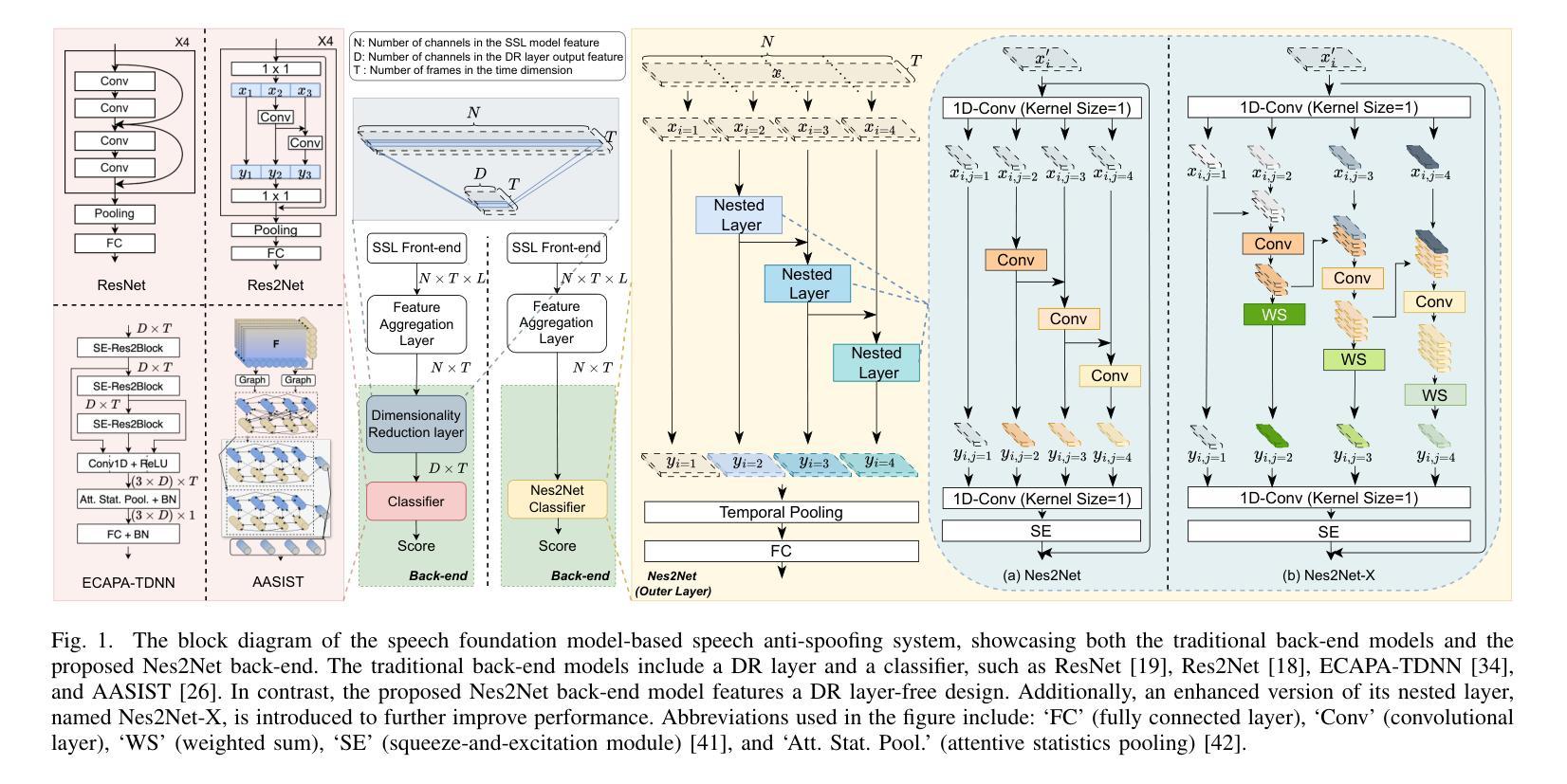
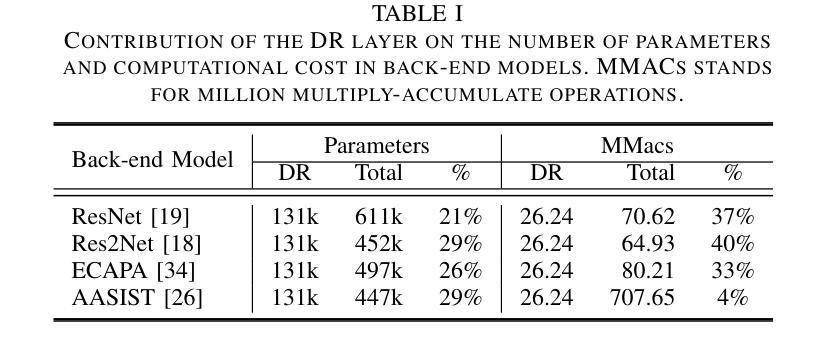
Nes2Net: A Lightweight Nested Architecture for Foundation Model Driven Speech Anti-spoofing
Authors:Tianchi Liu, Duc-Tuan Truong, Rohan Kumar Das, Kong Aik Lee, Haizhou Li
Speech foundation models have significantly advanced various speech-related tasks by providing exceptional representation capabilities. However, their high-dimensional output features often create a mismatch with downstream task models, which typically require lower-dimensional inputs. A common solution is to apply a dimensionality reduction (DR) layer, but this approach increases parameter overhead, computational costs, and risks losing valuable information. To address these issues, we propose Nested Res2Net (Nes2Net), a lightweight back-end architecture designed to directly process high-dimensional features without DR layers. The nested structure enhances multi-scale feature extraction, improves feature interaction, and preserves high-dimensional information. We first validate Nes2Net on CtrSVDD, a singing voice deepfake detection dataset, and report a 22% performance improvement and an 87% back-end computational cost reduction over the state-of-the-art baseline. Additionally, extensive testing across four diverse datasets: ASVspoof 2021, ASVspoof 5, PartialSpoof, and In-the-Wild, covering fully spoofed speech, adversarial attacks, partial spoofing, and real-world scenarios, consistently highlights Nes2Net’s superior robustness and generalization capabilities. The code package and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/Liu-Tianchi/Nes2Net.
语音基础模型通过提供出色的表示能力,显著地推进了各项与语音相关的任务。然而,它们的高维输出特征通常与下游任务模型不匹配,后者通常需要低维输入。常见的解决方案是应用降维(DR)层,但这种方法会增加参数开销、计算成本,并有丢失有价值信息的风险。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了Nested Res2Net(Nes2Net),这是一种轻量级的后端架构,旨在直接处理高维特征而无需DR层。嵌套结构增强了多尺度特征提取,改善了特征交互,并保留了高维信息。我们首先在对抗性奇袭价值判别数据集(CtrSVDD)上验证了Nes2Net,一个用于检测合成声音深度伪造的数据集,并报告了相比最新基准模型的性能提升22%和计算成本降低87%。此外,在涵盖完全伪造语音、对抗性攻击、部分伪造和真实场景的四项不同数据集(ASVspoof 2021、ASVspoof 5、PartialSpoof和In-the-Wild)上的广泛测试,始终突出了Nes2Net的卓越稳健性和泛化能力。代码包和预先训练的模型可在https://github.com/Liu-Tianchi/Nes2Net找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This manuscript has been submitted for peer review
Summary
语音基础模型为各种语音任务提供了出色的表示能力。为解决高维输出特征与下游任务模型不匹配的问题,提出一种名为Nested Res2Net(Nes2Net)的轻量级后端架构,可直接处理高维特征而无需降维层。在CtrSVDD数据集上验证Nes2Net,相较于最新基线技术,性能提升22%,后端计算成本降低87%。此外,在多个数据集上的测试显示Nes2Net具有卓越的鲁棒性和泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 语音基础模型在多种语音任务中表现出强大的表示能力。
- 高维输出特征与下游任务模型之间存在不匹配问题。
- 提出Nested Res2Net(Nes2Net)轻量级后端架构,无需降维层即可处理高维特征。
- Nes2Net在CtrSVDD数据集上的性能较现有技术提升22%,后端计算成本降低87%。
- Nes2Net在多个数据集上展现出卓越的鲁棒性和泛化能力。
- Nes2Net结构采用嵌套设计,增强了多尺度特征提取和特征交互。
- Nes2Net能够保留高维信息。
点此查看论文截图

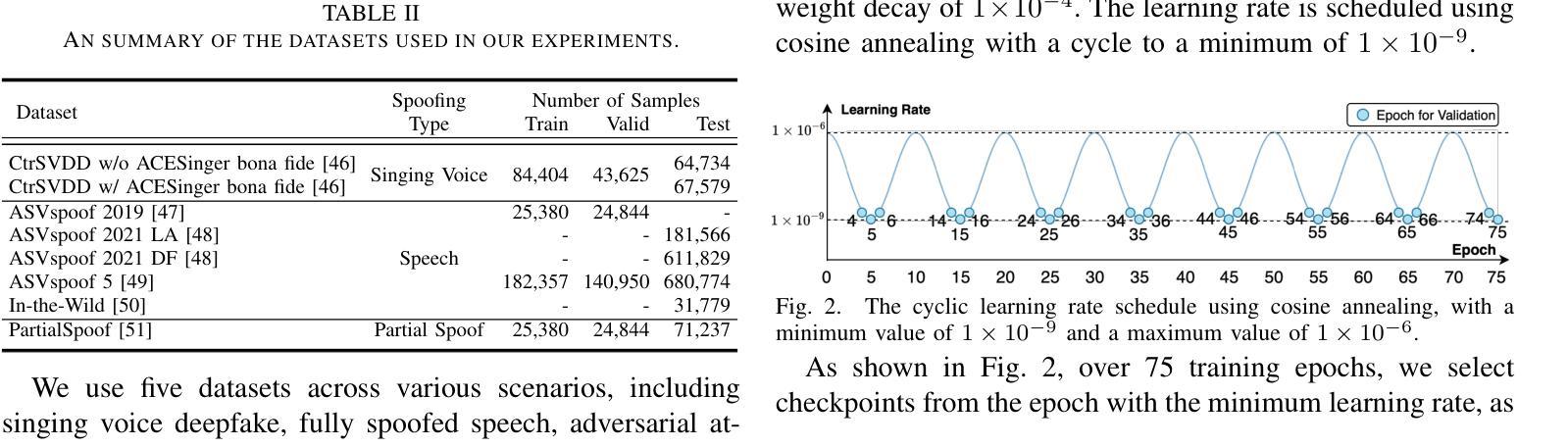
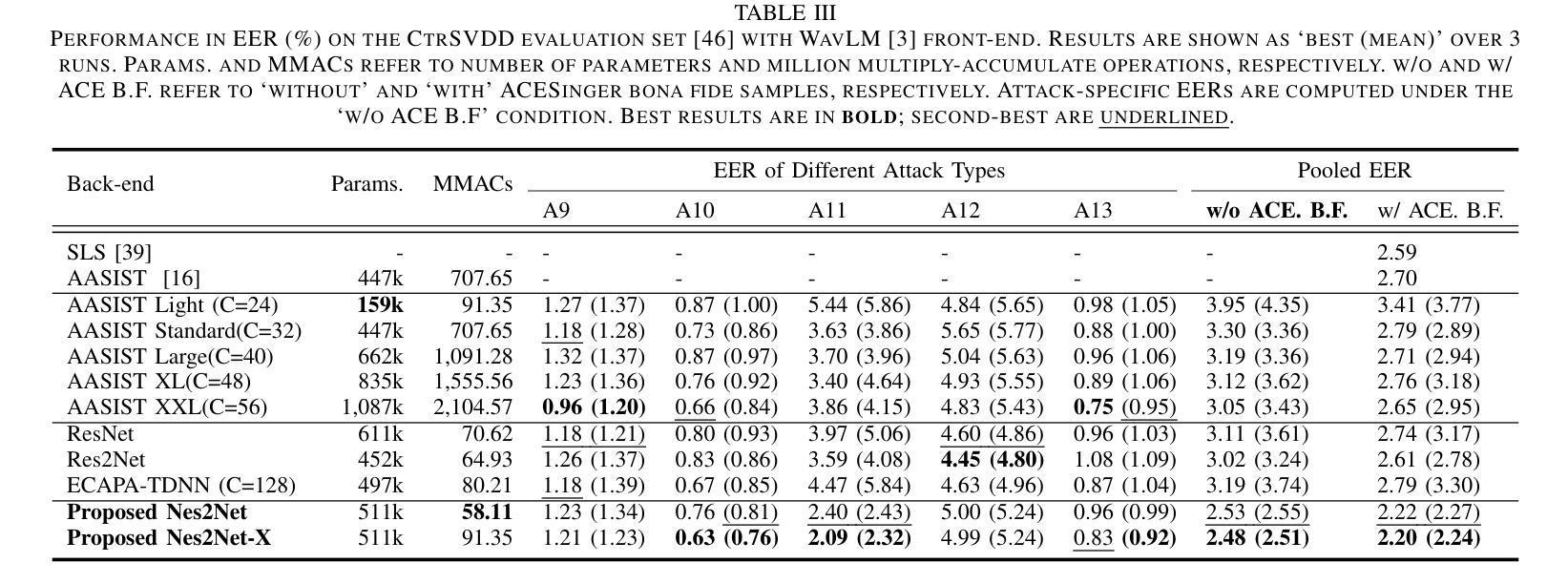
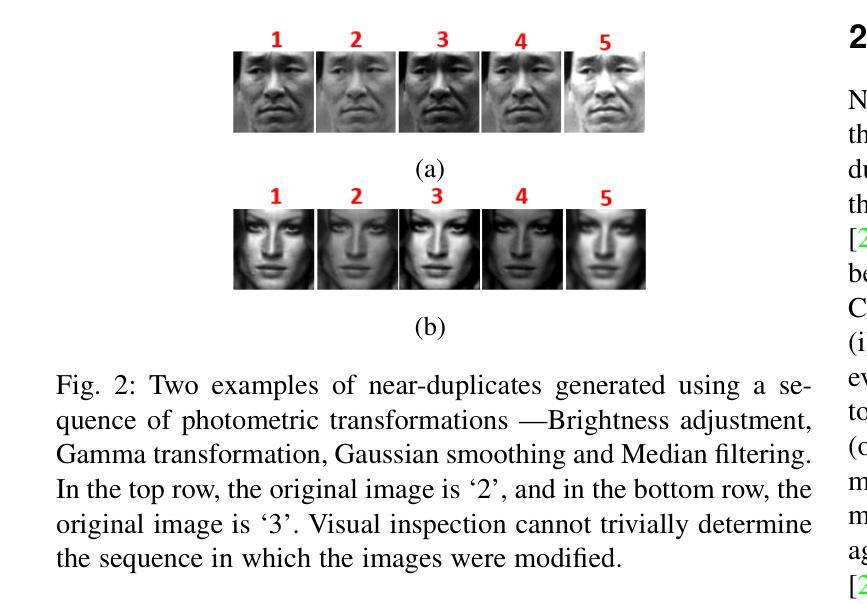
Exploring Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations for Speech Emotion Recognition with Distribution-Shift
Authors:Maja J. Hjuler, Line H. Clemmensen, Sneha Das
We introduce EmoLIME, a version of local interpretable model-agnostic explanations (LIME) for black-box Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) models. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt to apply LIME in SER. EmoLIME generates high-level interpretable explanations and identifies which specific frequency ranges are most influential in determining emotional states. The approach aids in interpreting complex, high-dimensional embeddings such as those generated by end-to-end speech models. We evaluate EmoLIME, qualitatively, quantitatively, and statistically, across three emotional speech datasets, using classifiers trained on both hand-crafted acoustic features and Wav2Vec 2.0 embeddings. We find that EmoLIME exhibits stronger robustness across different models than across datasets with distribution shifts, highlighting its potential for more consistent explanations in SER tasks within a dataset.
我们介绍了EmoLIME,这是局部可解释模型无关解释(LIME)的一种版本,用于黑箱语音情感识别(SER)模型。据我们所知,这是首次将LIME应用于SER。EmoLIME生成高级可解释的解释,并确定在确定情绪状态时影响最大的特定频率范围。该方法有助于解释复杂的、高维度的嵌入,如由端到端语音模型生成的嵌入。我们在三个情感语音数据集上,对EmoLIME进行了定性、定量和统计评估,评估使用的分类器是在手工制作的声学特征和Wav2Vec 2.0嵌入上进行训练的。我们发现,EmoLIME在不同模型中的稳健性比在数据集分布转移中的稳健性更强,这突显了其在SER任务的数据集内提供更一致解释的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in the proceedings of ICASSP 2025
Summary
EmoLIME是局部可解释模型无关解释(LIME)在语音情感识别(SER)模型中的版本。它是首次将LIME应用于SER的尝试。EmoLIME生成高级的可解释性解释,并确定在确定情绪状态时哪些特定频率范围最具影响力。该方法有助于解释由端到端语音模型生成的那种复杂、高维度的嵌入。我们通过定性、定量和统计的方法,在三个情感语音数据集上评估了EmoLIME,这些分类器既训练于手工制作的声学特征,也训练于Wav2Vec 2.0嵌入。我们发现,EmoLIME在不同模型中的稳健性比在数据集分布变化中的稳健性更强,这突显了其在SER任务中更一致解释的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- EmoLIME是局部可解释模型无关解释(LIME)在语音情感识别(SER)模型中的首个应用。
- EmoLIME能够生成高级的可解释性解释。
- EmoLIME可以确定在决定情绪状态时哪些特定频率范围最具影响力。
- EmoLIME有助于理解复杂、高维度的嵌入,如由端到端语音模型生成的数据。
- EmoLIME在多个情感语音数据集上的评估表现良好。
- EmoLIME的评估涵盖了使用手工制作的声学特征和Wav2Vec 2.0嵌入训练的分类器。
点此查看论文截图

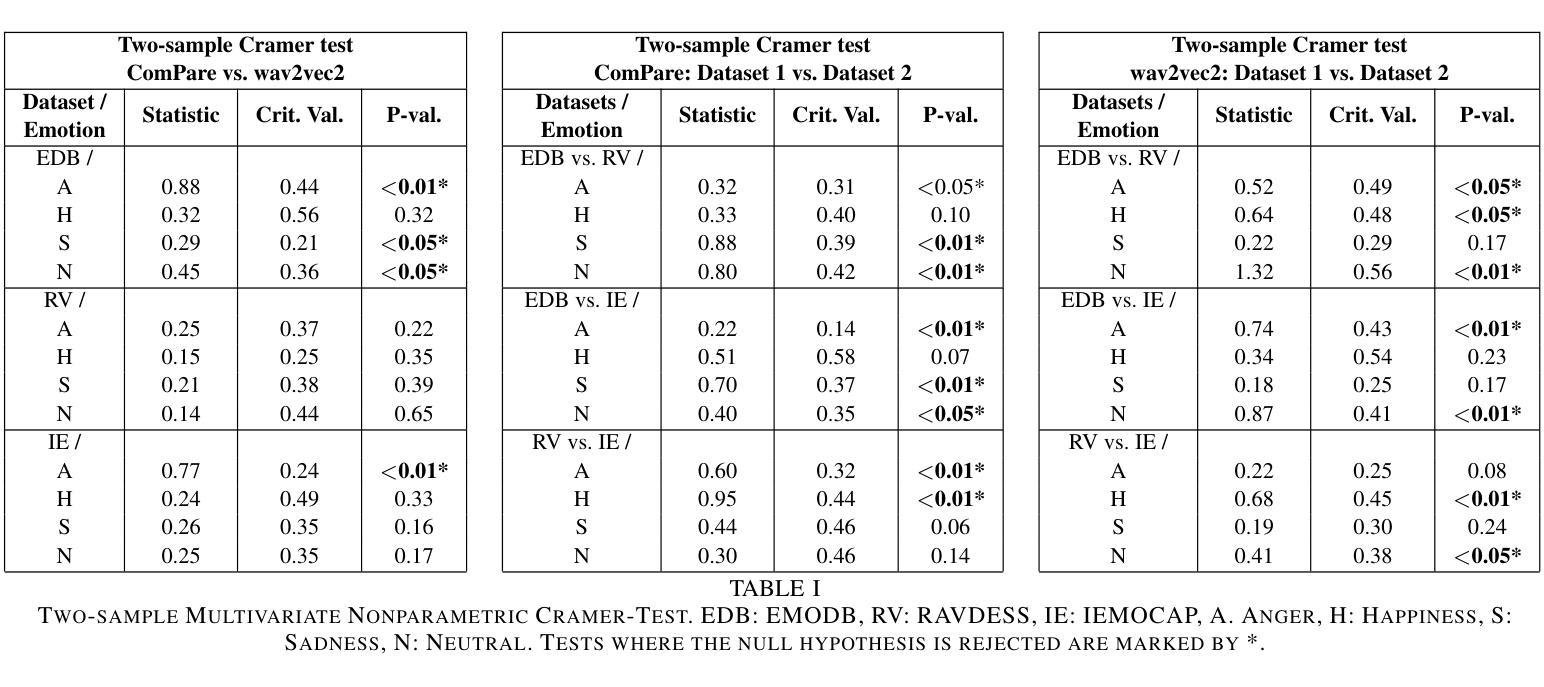
FNSE-SBGAN: Far-field Speech Enhancement with Schrodinger Bridge and Generative Adversarial Networks
Authors:Tong Lei, Qinwen Hu, Ziyao Lin, Andong Li, Rilin Chen, Meng Yu, Dong Yu, Jing Lu
The prevailing method for neural speech enhancement predominantly utilizes fully-supervised deep learning with simulated pairs of far-field noisy-reverberant speech and clean speech. Nonetheless, these models frequently demonstrate restricted generalizability to mixtures recorded in real-world conditions. To address this issue, this study investigates training enhancement models directly on real mixtures. Specifically, we revisit the single-channel far-field to near-field speech enhancement (FNSE) task, focusing on real-world data characterized by low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), high reverberation, and mid-to-high frequency attenuation. We propose FNSE-SBGAN, a novel framework that integrates a Schrodinger Bridge (SB)-based diffusion model with generative adversarial networks (GANs). Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance across various metrics and subjective evaluations, significantly reducing the character error rate (CER) by up to 14.58% compared to far-field signals. Experimental results demonstrate that FNSE-SBGAN preserves superior subjective quality and establishes a new benchmark for real-world far-field speech enhancement. Additionally, we introduce a novel evaluation framework leveraging matrix rank analysis in the time-frequency domain, providing systematic insights into model performance and revealing the strengths and weaknesses of different generative methods.
当前神经网络语音增强的主流方法主要是利用模拟的远距离噪声混响语音和清洁语音配对进行全监督深度学习。然而,这些模型在现实条件下录制的混合音中往往表现出有限的泛化能力。为了解决这一问题,本研究直接对真实混合音进行增强模型训练。具体来说,我们重新审视单通道远距离到近距离语音增强(FNSE)任务,重点关注低信噪比、高混响以及中高频衰减等现实数据特征。我们提出了FNSE-SBGAN这一新型框架,它结合了基于Schrodinger Bridge(SB)的扩散模型与生成对抗网络(GANs)。我们的方法在各种指标和主观评价上达到了最先进的性能,与远距离信号相比,字符错误率(CER)降低了高达14.58%。实验结果表明,FNSE-SBGAN保持了较高的主观质量,为现实远距离语音增强建立了新的基准。此外,我们还引入了一种新的评估框架,利用时频域的矩阵秩分析,为模型性能提供系统见解,揭示不同生成方法的优缺点。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 6 figures
Summary
本研究针对神经网络语音增强方法在实际应用中的泛化能力受限的问题,提出了一种新的基于Schrodinger Bridge扩散模型的增强框架FNSE-SBGAN。该框架结合了单通道远场到近场的语音增强任务,特别关注低信噪比、高混响和中等至高频衰减的现实世界数据特点。通过引入矩阵排名分析的时间-频率域评价框架,系统地揭示了不同生成方法的优缺点,实现了显著的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络语音增强方法在实际条件下的泛化能力受限。
- 研究提出了一种新的语音增强框架FNSE-SBGAN,基于Schrodinger Bridge扩散模型。
- FNSE-SBGAN框架特别关注低信噪比、高混响和中等至高频衰减的现实世界数据。
- 通过引入矩阵排名分析的时间-频率域评价框架,对模型性能进行了系统评估。
- FNSE-SBGAN显著提高了语音增强的性能,降低了字符错误率。
- 新框架为现实世界的远场语音增强设定了新的基准。
点此查看论文截图

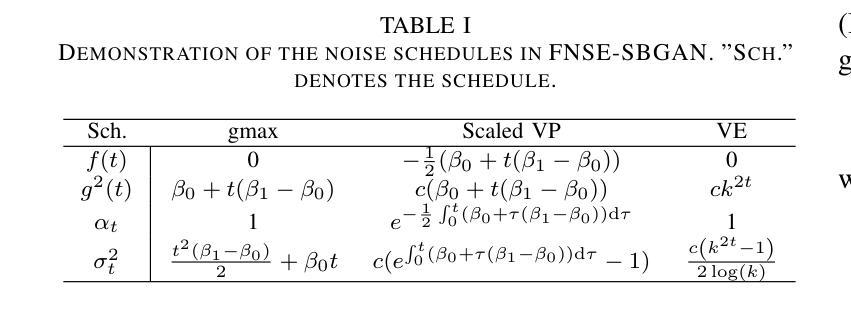
DGSNA: prompt-based Dynamic Generative Scene-based Noise Addition method
Authors:Zihao Chen, Zhentao Lin, Bi Zeng, Linyi Huang, Zhi Li, Jia Cai
To ensure the reliable operation of speech systems across diverse environments, noise addition methods have emerged as the prevailing solution. However, existing methods offer limited coverage of real-world noisy scenes and depend on pre-existing scene-based information and noise. This paper presents prompt-based Dynamic Generative Scene-based Noise Addition (DGSNA), a novel noise addition methodology that integrates Dynamic Generation of Scene-based Information (DGSI) with Scene-based Noise Addition for Speech (SNAS). This integration facilitates automated scene-based noise addition by transforming clean speech into various noise environments, thereby providing a more comprehensive and realistic simulation of diverse noise conditions. Experimental results demonstrate that DGSNA significantly enhances the robustness of speech recognition and keyword spotting models across various noise conditions, achieving a relative improvement of up to 11.21%. Furthermore, DGSNA can be effectively integrated with other noise addition methods to enhance performance. Our implementation and demonstrations are available at https://dgsna.github.io.
为了确保语音系统在不同环境中的可靠运行,噪声添加方法已成为主流的解决方案。然而,现有方法对于真实世界噪声场景覆盖有限,并依赖于预存的场景信息和噪声。本文提出了基于提示的动态生成场景噪声添加(DGSNA)方法,这是一种新型噪声添加方法,将场景信息动态生成(DGSI)与基于场景的语音噪声添加(SNAS)相结合。这种结合通过转换干净语音为各种噪声环境,实现了自动的场景噪声添加,从而提供了更全面和现实的噪声条件模拟。实验结果表明,DGSNA显著提高了语音识别和关键词识别模型在各种噪声条件下的稳健性,相对改进率最高可达11.21%。此外,DGSNA还可以与其他噪声添加方法有效结合以提高性能。我们的实现和演示可在 https://dgsna.github.io 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本提出了一种基于提示的动态生成场景噪声添加方法(DGSNA),该方法结合了场景信息的动态生成(DGSI)和基于场景的噪声添加技术(SNAS)。该方法可自动将清洁语音转换为各种噪声环境,模拟多样化的噪声条件。实验结果显示,DGSNA可以显著提高语音识别和关键词点选模型在各种噪声条件下的稳健性,相对改进幅度高达11.21%。此外,DGSNA还可以与其他噪声添加方法相结合,提高性能。
Key Takeaways
- DGSNA是一种新型的噪声添加方法,旨在确保语音系统在不同环境中的可靠运行。
- 它通过结合DGSI和SNAS技术,实现了场景信息的动态生成和基于场景的噪声添加。
- DGSNA可以自动将清洁语音转换为各种噪声环境,提供更全面和现实的噪声条件模拟。
- 实验证明,DGSNA能显著提高语音识别和关键词点选模型在噪声条件下的稳健性。
- DGSNA的相对改进幅度高达11.21%,并且可以与其它噪声添加方法结合使用以提高性能。
- DGSNA的实施和演示可通过https://dgsna.github.io访问。
点此查看论文截图



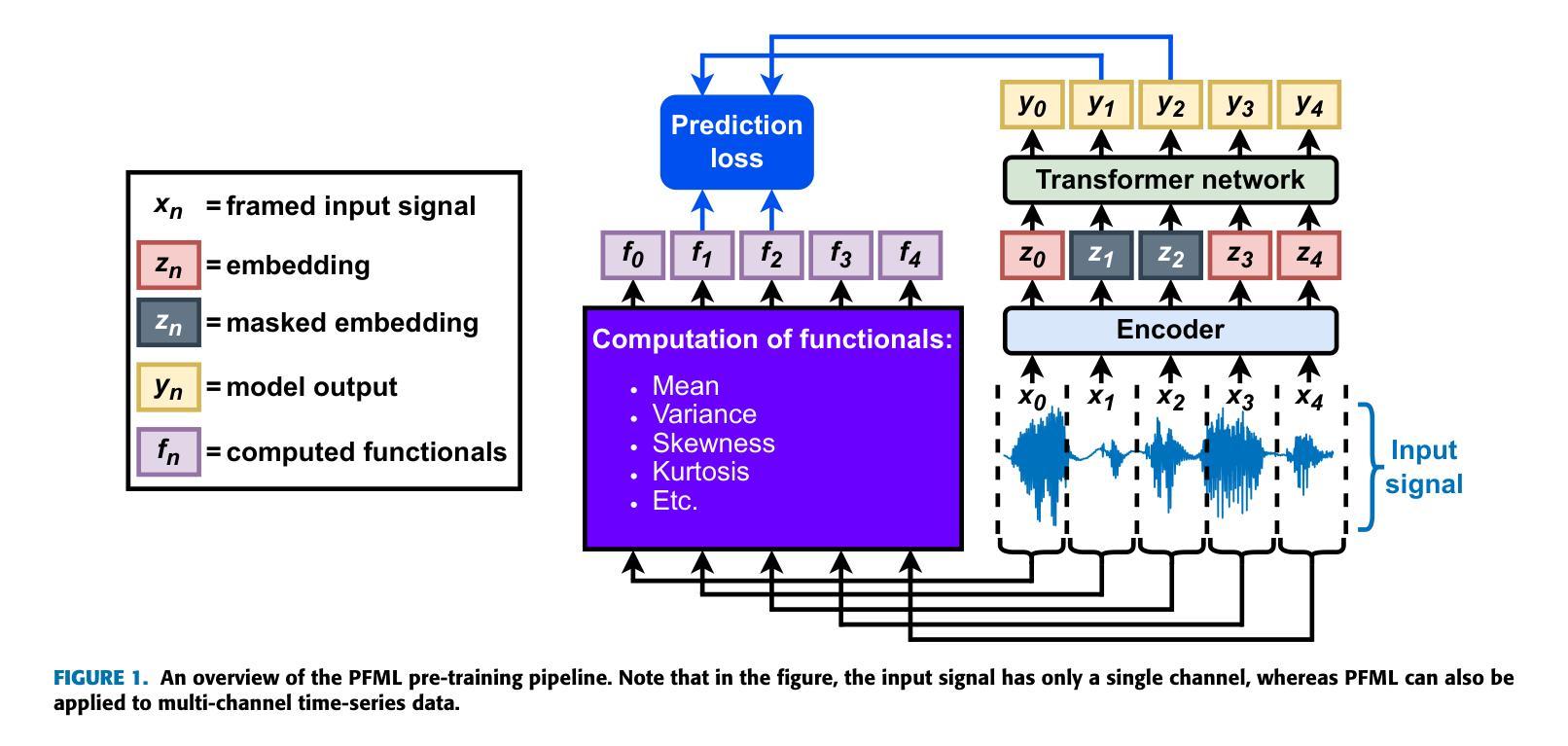
PFML: Self-Supervised Learning of Time-Series Data Without Representation Collapse
Authors:Einari Vaaras, Manu Airaksinen, Okko Räsänen
Self-supervised learning (SSL) is a data-driven learning approach that utilizes the innate structure of the data to guide the learning process. In contrast to supervised learning, which depends on external labels, SSL utilizes the inherent characteristics of the data to produce its own supervisory signal. However, one frequent issue with SSL methods is representation collapse, where the model outputs a constant input-invariant feature representation. This issue hinders the potential application of SSL methods to new data modalities, as trying to avoid representation collapse wastes researchers’ time and effort. This paper introduces a novel SSL algorithm for time-series data called Prediction of Functionals from Masked Latents (PFML). Instead of predicting masked input signals or their latent representations directly, PFML operates by predicting statistical functionals of the input signal corresponding to masked embeddings, given a sequence of unmasked embeddings. The algorithm is designed to avoid representation collapse, rendering it straightforwardly applicable to different time-series data domains, such as novel sensor modalities in clinical data. We demonstrate the effectiveness of PFML through complex, real-life classification tasks across three different data modalities: infant posture and movement classification from multi-sensor inertial measurement unit data, emotion recognition from speech data, and sleep stage classification from EEG data. The results show that PFML is superior to a conceptually similar SSL method and a contrastive learning-based SSL method. Additionally, PFML is on par with the current state-of-the-art SSL method, while also being conceptually simpler and without suffering from representation collapse.
自监督学习(SSL)是一种数据驱动的学习方法,它利用数据的内在结构来指导学习过程。与依赖外部标签的监督学习相反,SSL利用数据的固有特性来生成其自己的监督信号。然而,SSL方法的一个常见问题是表示崩溃,即模型输出恒定不变的输入特征表示。这个问题阻碍了SSL方法在新数据模态的潜在应用,因为试图避免表示崩溃会浪费研究人员的时间和精力。本文介绍了一种用于时间序列数据的新型SSL算法,称为“从掩码潜在特征预测功能(PFML)”。PFML不是直接预测被掩盖的输入信号或其潜在表示,而是根据未掩盖的嵌入序列,预测与掩盖的嵌入相对应的输入信号的统计功能。该算法旨在避免表示崩溃,使其能够轻松地应用于不同的时间序列数据领域,如临床数据中的新型传感器模态。我们通过三个不同数据模态的复杂现实分类任务展示了PFML的有效性:从多传感器惯性测量单元数据进行婴儿姿势和运动分类、从语音数据进行情感识别、从脑电图数据进行睡眠阶段分类。结果表明,PFML优于一个概念相似的SSL方法和一个基于对比学习的SSL方法。此外,PFML与当前最先进的SSL方法性能相当,同时概念上更简单,并且没有受到表示崩溃的困扰。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in IEEE Access
摘要
本文介绍了一种针对时间序列数据的自我监督学习(SSL)新算法——从掩码潜在变量预测功能(PFML)。不同于预测掩码输入信号或其潜在表示的SSL方法,PFML通过预测对应掩码嵌入的统计功能来操作,给定一系列未掩码的嵌入。该算法旨在避免表示崩溃,使其能够轻松应用于不同的时间序列数据领域,如临床数据中的新型传感器模态。通过三种不同数据模态的复杂现实分类任务验证了PFML的有效性:多传感器惯性测量单元数据的婴儿姿势和运动分类、语音数据的情感识别以及脑电图数据的睡眠阶段分类。结果表明,PFML优于一种概念相似的SSL方法和一种基于对比学习的SSL方法。此外,PFML与当前最先进的SSL方法不相上下,同时概念更简单,且不出现表示崩溃的问题。
关键见解
- 自我监督学习(SSL)利用数据的内在结构来指导学习过程,不同于依赖外部标签的监督学习。
- SSL方法的一个常见问题是表示崩溃,即模型输出恒定的输入不变特征表示,这限制了其在新数据模态中的应用。
- PFML是一种针对时间序列数据的SSL新算法,通过预测掩码嵌入的统计功能来避免表示崩溃。
- PFML算法可轻松应用于不同的时间序列数据领域,如新型传感器模态的临床数据。
- 通过三种不同数据模态的复杂现实分类任务验证了PFML的有效性。
- PFML优于其他SSL方法,且与当前最先进的SSL方法表现相当,同时概念更简单。
点此查看论文截图