⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-10 更新
Transferable Mask Transformer: Cross-domain Semantic Segmentation with Region-adaptive Transferability Estimation
Authors:Enming Zhang, Zhengyu Li, Yanru Wu, Jingge Wang, Yang Tan, Ruizhe Zhao, Guan Wang, Yang Li
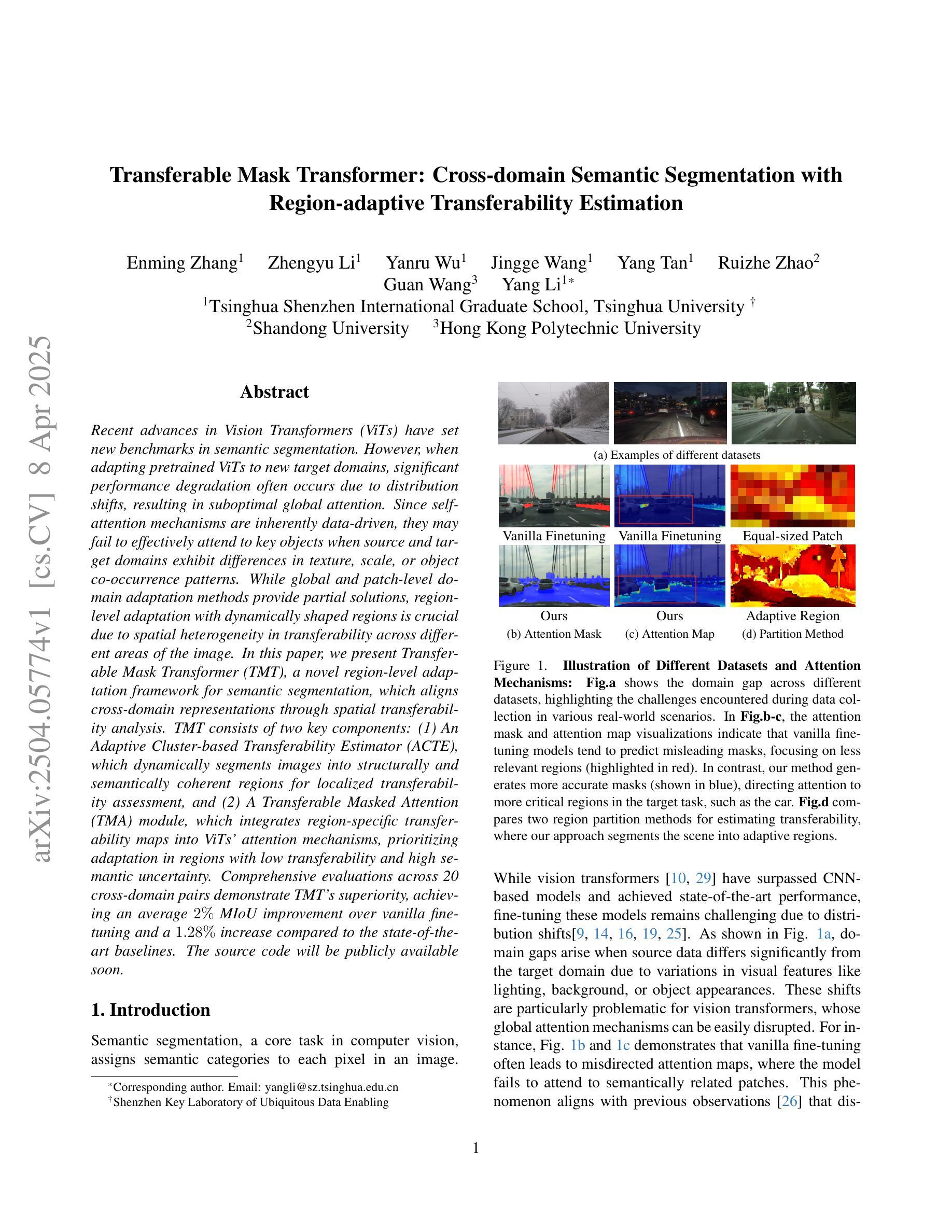
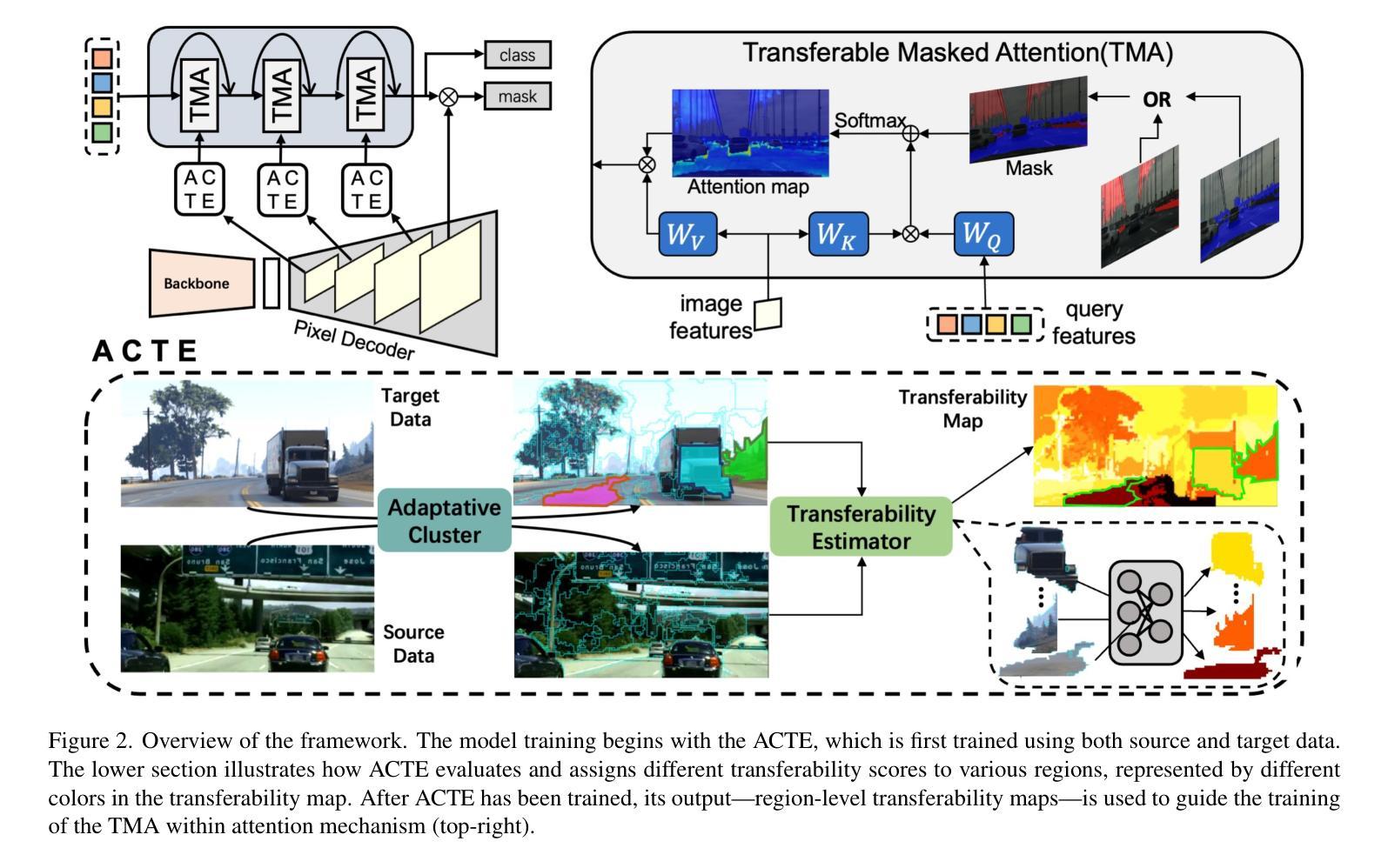
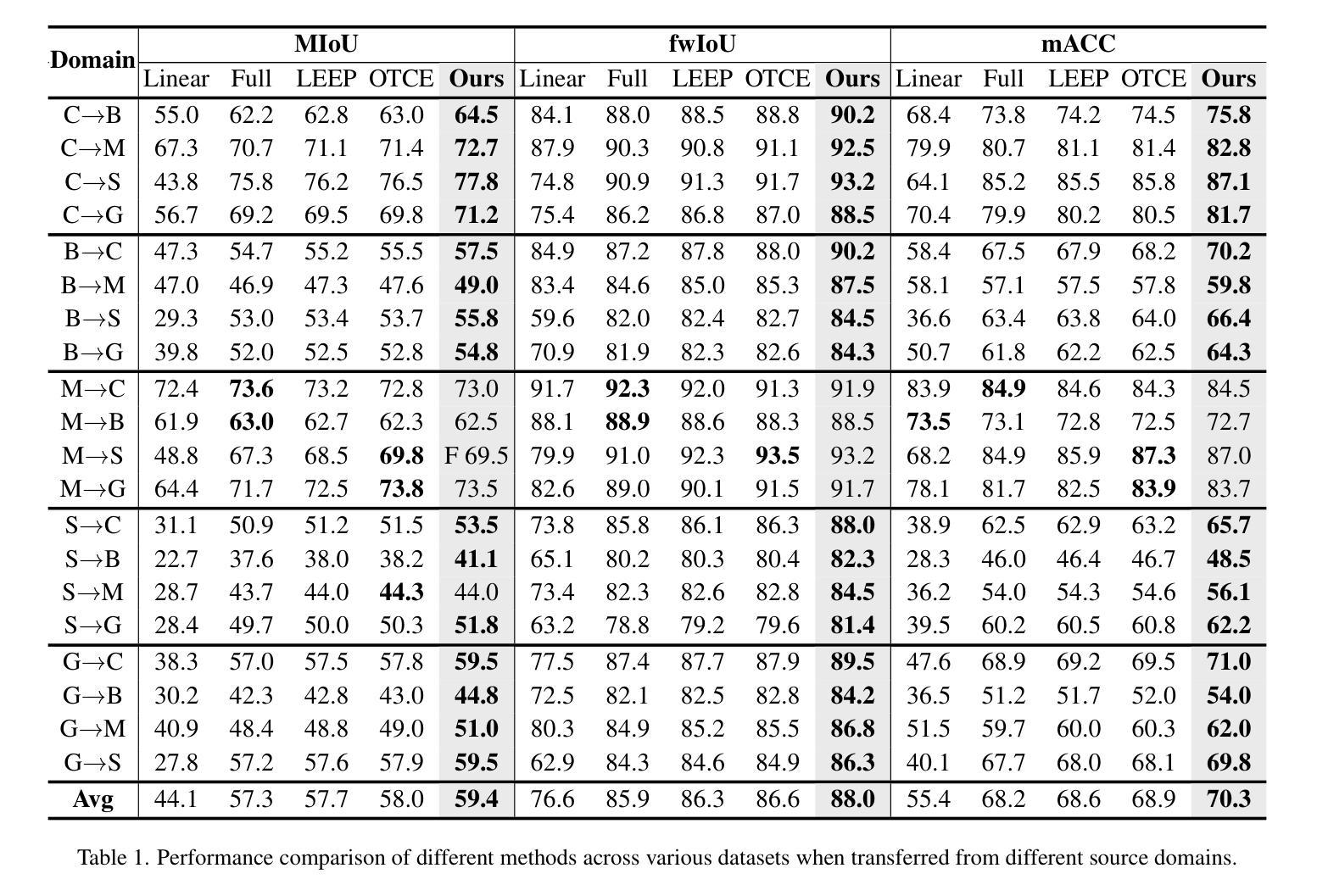
Recent advances in Vision Transformers (ViTs) have set new benchmarks in semantic segmentation. However, when adapting pretrained ViTs to new target domains, significant performance degradation often occurs due to distribution shifts, resulting in suboptimal global attention. Since self-attention mechanisms are inherently data-driven, they may fail to effectively attend to key objects when source and target domains exhibit differences in texture, scale, or object co-occurrence patterns. While global and patch-level domain adaptation methods provide partial solutions, region-level adaptation with dynamically shaped regions is crucial due to spatial heterogeneity in transferability across different image areas. We present Transferable Mask Transformer (TMT), a novel region-level adaptation framework for semantic segmentation that aligns cross-domain representations through spatial transferability analysis. TMT consists of two key components: (1) An Adaptive Cluster-based Transferability Estimator (ACTE) that dynamically segments images into structurally and semantically coherent regions for localized transferability assessment, and (2) A Transferable Masked Attention (TMA) module that integrates region-specific transferability maps into ViTs’ attention mechanisms, prioritizing adaptation in regions with low transferability and high semantic uncertainty. Comprehensive evaluations across 20 cross-domain pairs demonstrate TMT’s superiority, achieving an average 2% MIoU improvement over vanilla fine-tuning and a 1.28% increase compared to state-of-the-art baselines. The source code will be publicly available.
最近,Vision Transformers(ViTs)的进展在语义分割领域树立了新的基准。然而,当将预训练的ViTs适应到新的目标域时,由于分布转移,性能往往会出现显著下降,导致全局注意力不佳。由于自注意力机制本质上是数据驱动的,因此当源域和目标域在纹理、尺度或对象共现模式上存在差异时,它们可能无法有效地关注关键对象。虽然全局和补丁级别的域适应方法提供了部分解决方案,但由于不同图像区域在可转移性方面的空间异质性,动态形状区域的区域级适应至关重要。我们提出了Transferable Mask Transformer(TMT),这是一种用于语义分割的区域级适应框架,它通过空间可转移性分析来对齐跨域表示。TMT由两个关键组件构成:(1)基于自适应聚类的可转移性估计器(ACTE),它动态地将图像分割成结构和语义上连贯的区域,以进行局部可转移性评估;(2)可转移掩膜注意力(TMA)模块,该模块将区域特定的可转移性地图集成到ViTs的注意力机制中,优先适应低可转移性和高语义不确定性的区域。在20个跨域对上的综合评估表明,TMT具有优越性,与微调相比,平均提高了2%的MIoU,与最先进的基线相比增加了1.28%。源代码将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Vision Transformer(ViT)在语义分割领域取得了最新进展。但在将预训练的ViT适应到新目标域时,由于分布转移导致的性能下降问题仍然显著,影响全局注意力效果。本文提出Transferable Mask Transformer(TMT)框架,通过空间可转移性分析实现跨域表示对齐,包括自适应集群基础的转移能力估计器和可转移的掩膜注意力模块。实验证明TMT在跨域语义分割任务中表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformer(ViT)在语义分割领域展现最新进展,但在适应新目标域时存在性能下降问题。
- 分布转移影响全局注意力效果,导致性能下降。
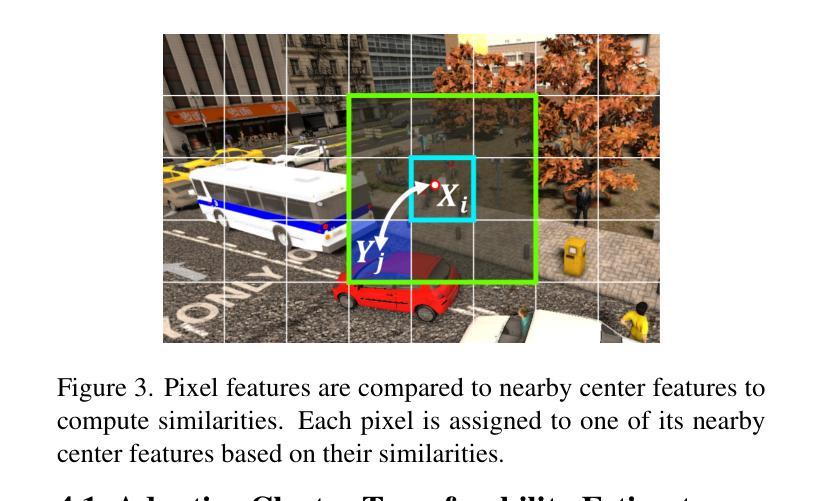
- 自适应Cluster-based Transferability Estimator(ACTE)能动态地将图像分割为结构和语义连贯的区域,进行局部化的转移能力评估。
- Transferable Masked Attention(TMA)模块将区域特定的转移能力图集成到ViT的注意力机制中,优先适应低转移能力和高语义不确定性的区域。
- TMT框架通过空间可转移性分析实现跨域表示对齐。
- 综合评估结果显示TMT框架优于现有技术,平均MIoU提高2%,与最新基线相比提高1.28%。
点此查看论文截图
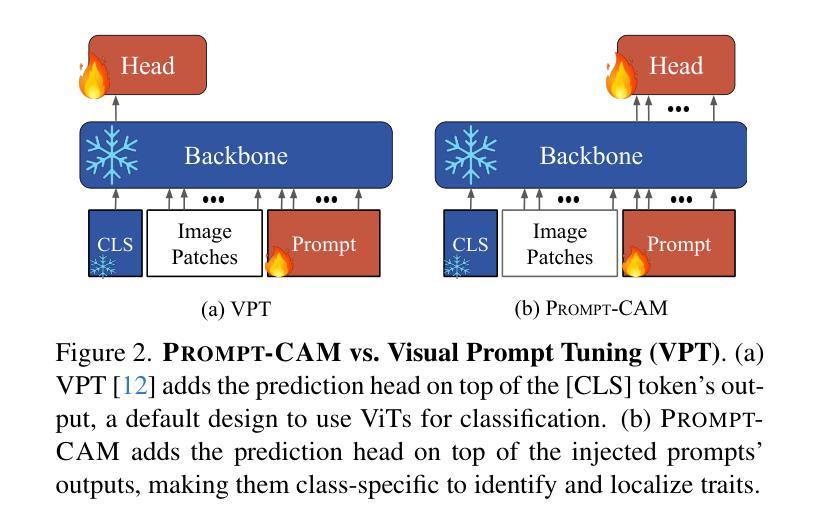
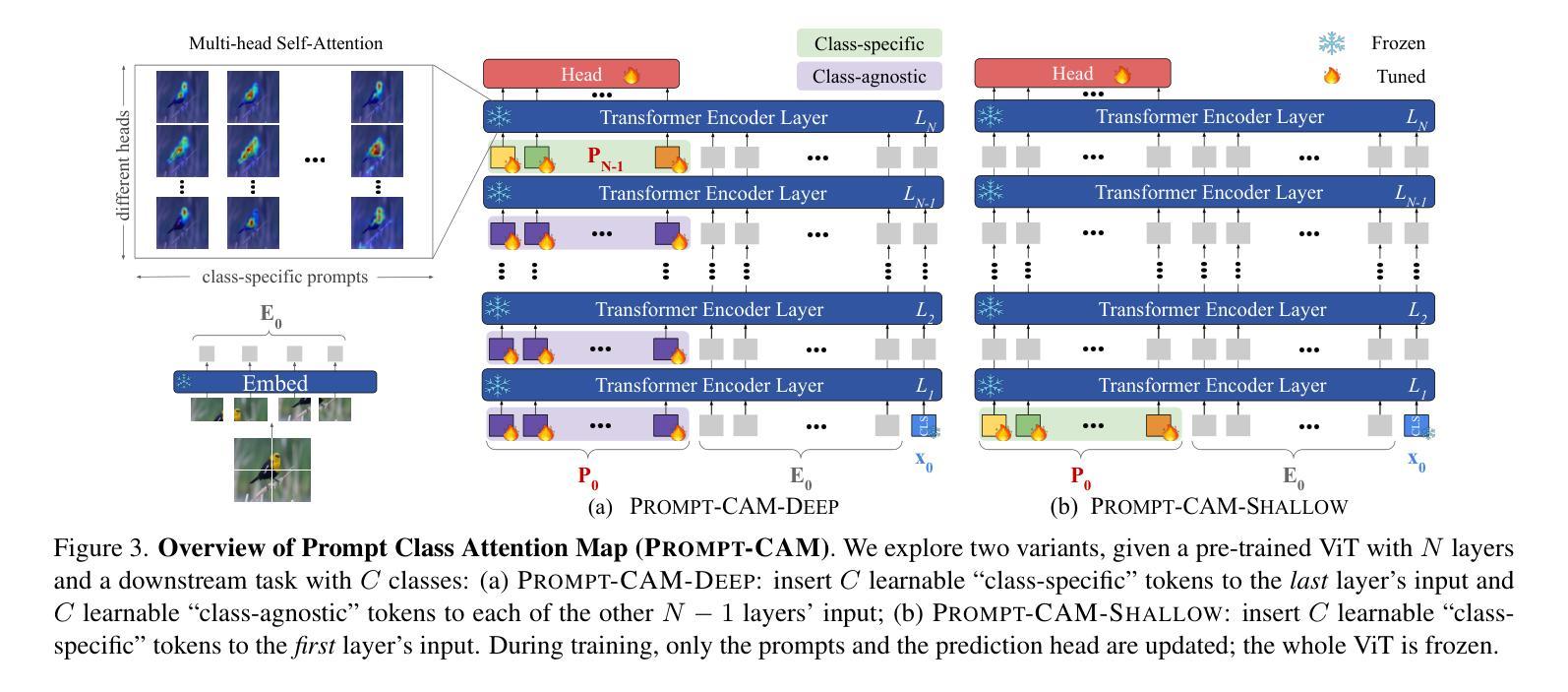
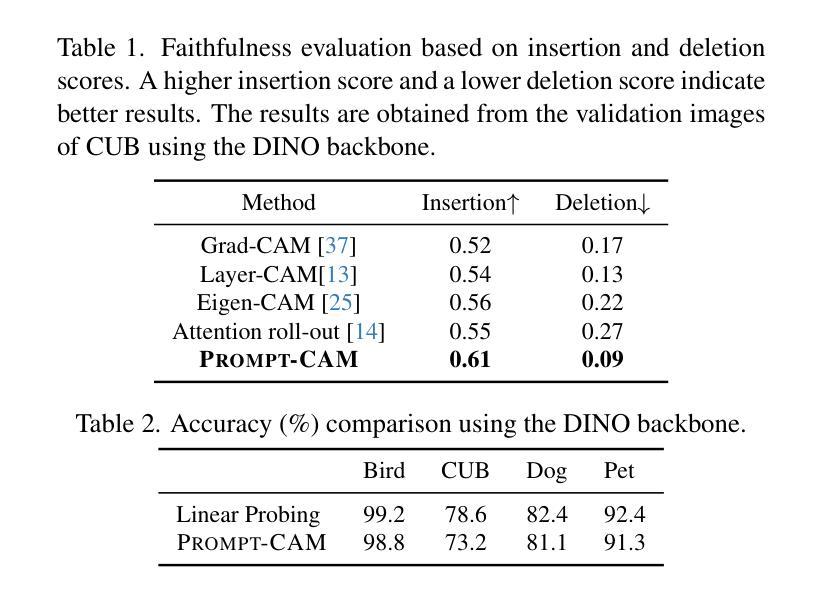
Prompt-CAM: Making Vision Transformers Interpretable for Fine-Grained Analysis
Authors:Arpita Chowdhury, Dipanjyoti Paul, Zheda Mai, Jianyang Gu, Ziheng Zhang, Kazi Sajeed Mehrab, Elizabeth G. Campolongo, Daniel Rubenstein, Charles V. Stewart, Anuj Karpatne, Tanya Berger-Wolf, Yu Su, Wei-Lun Chao
We present a simple approach to make pre-trained Vision Transformers (ViTs) interpretable for fine-grained analysis, aiming to identify and localize the traits that distinguish visually similar categories, such as bird species. Pre-trained ViTs, such as DINO, have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in extracting localized, discriminative features. However, saliency maps like Grad-CAM often fail to identify these traits, producing blurred, coarse heatmaps that highlight entire objects instead. We propose a novel approach, Prompt Class Attention Map (Prompt-CAM), to address this limitation. Prompt-CAM learns class-specific prompts for a pre-trained ViT and uses the corresponding outputs for classification. To correctly classify an image, the true-class prompt must attend to unique image patches not present in other classes’ images (i.e., traits). As a result, the true class’s multi-head attention maps reveal traits and their locations. Implementation-wise, Prompt-CAM is almost a ``free lunch,’’ requiring only a modification to the prediction head of Visual Prompt Tuning (VPT). This makes Prompt-CAM easy to train and apply, in stark contrast to other interpretable methods that require designing specific models and training processes. Extensive empirical studies on a dozen datasets from various domains (e.g., birds, fishes, insects, fungi, flowers, food, and cars) validate the superior interpretation capability of Prompt-CAM. The source code and demo are available at https://github.com/Imageomics/Prompt_CAM.
我们提出了一种简单的方法,使预训练的视觉变压器(ViTs)可以进行细粒度分析的解释,旨在识别和定位区分视觉相似类别的特征,如鸟类物种。预训练的ViTs,如DINO,已显示出在提取局部化、辨别特征方面的卓越能力。然而,像Grad-CAM这样的显著性地图通常无法识别这些特征,产生模糊、粗糙的热图,突出整个对象而不是局部特征。我们提出了一种新方法,即Prompt类注意力图(Prompt-CAM),来解决这一局限性。Prompt-CAM学习针对预训练ViT的特定类别提示,并使用相应的输出进行分类。为了正确分类图像,真正的类别提示必须关注其他类别图像不存在的独特图像补丁(即特征)。因此,真正类别的多头注意力图揭示了特征及其位置。从实现的角度来看,Prompt-CAM几乎是一种“免费午餐”,只需要对视觉提示调整(VPT)的预测头进行微调。这使得Prompt-CAM的训练和应用变得非常简单,与其他需要设计特定模型和训练过程的可解释方法形成鲜明对比。在十几个来自不同领域的数据集(如鸟类、鱼类、昆虫、真菌、花卉、食品和汽车)上的大量实证研究验证了Prompt-CAM的卓越解释能力。源代码和演示可在https://github.com/Imageomics/Prompt_CAM找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025 Main Conference
Summary
本文提出了一种简单的方法,使预训练的Vision Transformers(ViTs)可进行精细粒度分析,以识别和定位区分视觉上相似类别的特征,例如鸟类物种。文章介绍了Prompt Class Attention Map(Prompt-CAM)这一新方法,用于解决现有技术(如Grad-CAM)无法识别特定类别特征的局限性。Prompt-CAM学习针对预训练ViT的类别特定提示,并使用相应的输出进行分类。正确分类图像需要关注特定类别独有的图像斑块(即特征),通过多头注意力地图揭示特征及其位置。该方法实现简单,仅需要修改Visual Prompt Tuning(VPT)的预测头,易于训练和应用。在多个数据集上的实证研究验证了Prompt-CAM的出色解释能力。
Key Takeaways
- 文章提出了一种名为Prompt Class Attention Map(Prompt-CAM)的新方法,旨在解决预训练Vision Transformers(ViTs)在精细粒度分析中的解释性问题。
- Prompt-CAM通过学习类别特定的提示来改进ViT的分类性能,并关注图像中独特的斑块(即特征)。
- 与现有技术相比,Prompt-CAM能够更准确地识别和定位区分不同类别的视觉特征。
- 该方法实现简单,仅需要修改Visual Prompt Tuning(VPT)的预测头,无需设计特定模型和复杂的训练过程。
- 实证研究证明,Prompt-CAM在多个数据集上表现出优异的解释能力,可广泛应用于不同领域(如鸟类、鱼类、昆虫、真菌、花卉、食品和汽车)。
- 文章提供的源代码和演示证明了该方法的可行性和实用性。
点此查看论文截图